Application of ascorbic acid to improvement of plant photosynthesis efficiency
A technology of ascorbic acid and photosynthetic efficiency, applied in the fields of application, plant growth regulator, plant growth regulator, etc., can solve the problem of reducing crop leaf transpiration rate, stomatal conductance concentration net photosynthetic rate, affecting soybean water and nutrient absorption, affecting Plant growth, crop yield and other issues, to achieve the effect of increasing net photosynthetic rate, increasing growth and yield, and reducing H2O2 accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: The cultivation and processing of SB, RB plants, concrete steps are as follows:
[0020] 1. The experimental materials are SB and RB seedlings
[0021] After selecting plump SB and RB seeds to sterilize and accelerate germination, accelerate germination in the dark at 25°C, and transfer to 0.5mmol / L CaCl when the root grows 2cm 2 Equilibrate in the solution for one day, then transfer to 1 / 4 Hoagland's culture medium for one week, transfer to Hoagland's culture medium after growing two leaves, and use it for this experiment when the seedlings grow to four pairs of leaves.
[0022] 2. Prepare AsA treatment solutions with different concentrations (0.1, 0.5, 2, 5, 10 mmol / L) and AlCl with different concentrations (0, 50, 100, 200, 400 μmol / L) 3 treatment fluid.
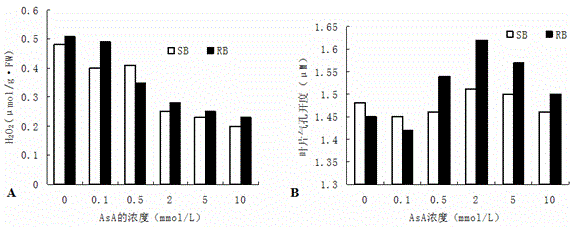
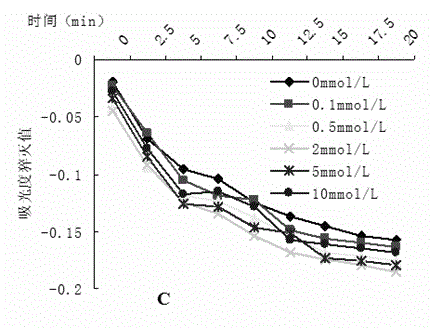
[0023] 3. Treat SB and RB seedlings with the above-mentioned AsA gradient concentration for 24 hours, and take samples for H 2 o 2 Content, stomatal opening, cytoplasmic membrane H + - Determina...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Adopt the SB, RB blade after the 3rd step process in embodiment 1 to carry out H 2 o 2 content, leaf stomatal opening and plasma membrane H + - Pump activity assay
[0026] 1.H 2 o 2 Content determination: xylenol orange method. Weigh fresh plant leaves, add according to the ratio of 1g of material to 1mL of pre-cooled acetone extractant, add a little quartz sand to grind into a homogenate, transfer to a centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 12000g at 4°C for 20min, discard the residue, and the supernatant is Sample extract; respectively with ddH 2 O Prepare reagent A (containing 3.3 mmol / L FeSO 4 , 3.3 mmol / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 412.5 mmol / L H 2 SO4 ) and reagent B (containing 165 μmol / L xylenol orange, 165 mmol / L sorbitol), before use, reagent A and reagent B are mixed in a ratio of 1:10 (v / v) to form a working reagent; this working reagent with H 2 o 2 The solution to be tested was mixed in a ratio of 2:1 (v / v), developed in a water bath at 30°C f...
Embodiment 3
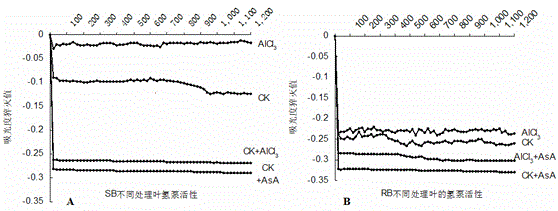
[0035] Example 3: According to the above SB, RB leaf cell H 2 o 2 Content, stomatal opening, cytoplasmic membrane H + - As a result of the determination of the pump activity content, 2 mmol / L was selected as the optimal treatment concentration of AsA. In order to verify that under the stress of different aluminum concentrations (0, 100 μmol / L), 2 mmol / L AsA has a greater promotion effect on the photosynthetic characteristic parameters of different varieties of soybeans, the optimal concentration of 2 mmol / L AsA treatment solution was used for the examples 1 For the treatment in the third step, the SB and RB seedlings were respectively treated with AsA concentration of 0 as a control, and the plasma membrane H of the plant leaves was measured for 24 hours + - pump activity ( image 3 A, 3B).
[0036] from image 3 It can be seen that after treatment with 2 mmol / L AsA, the H of soybean leaves + -Pump increased in different degrees compared with soybean plants under the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com