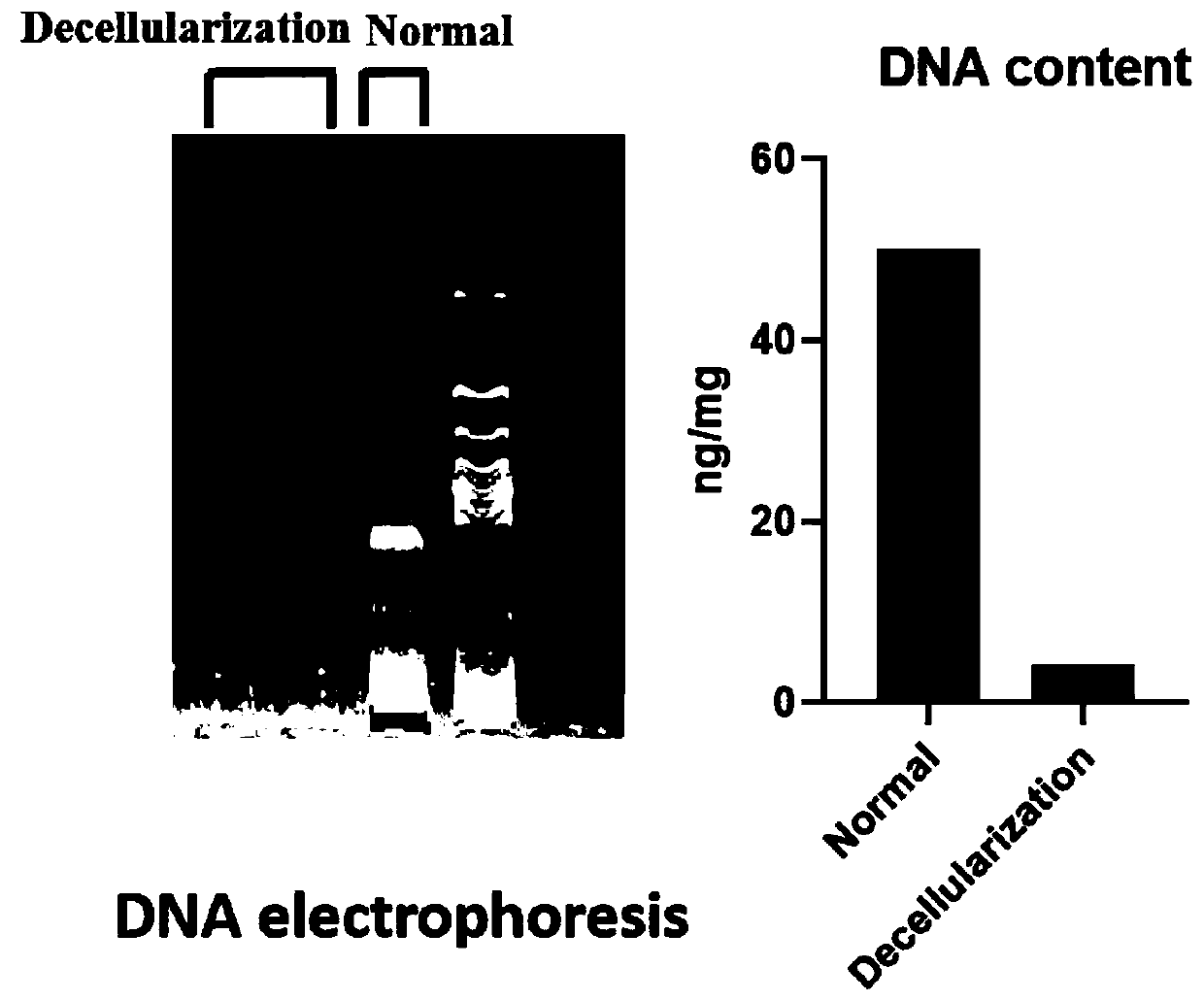
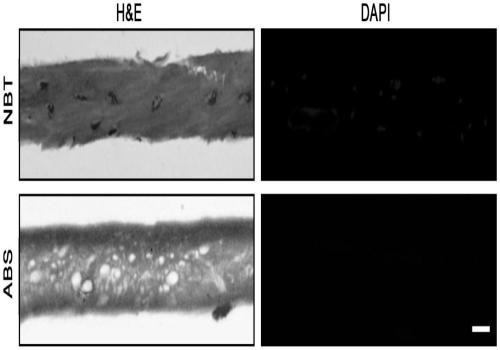
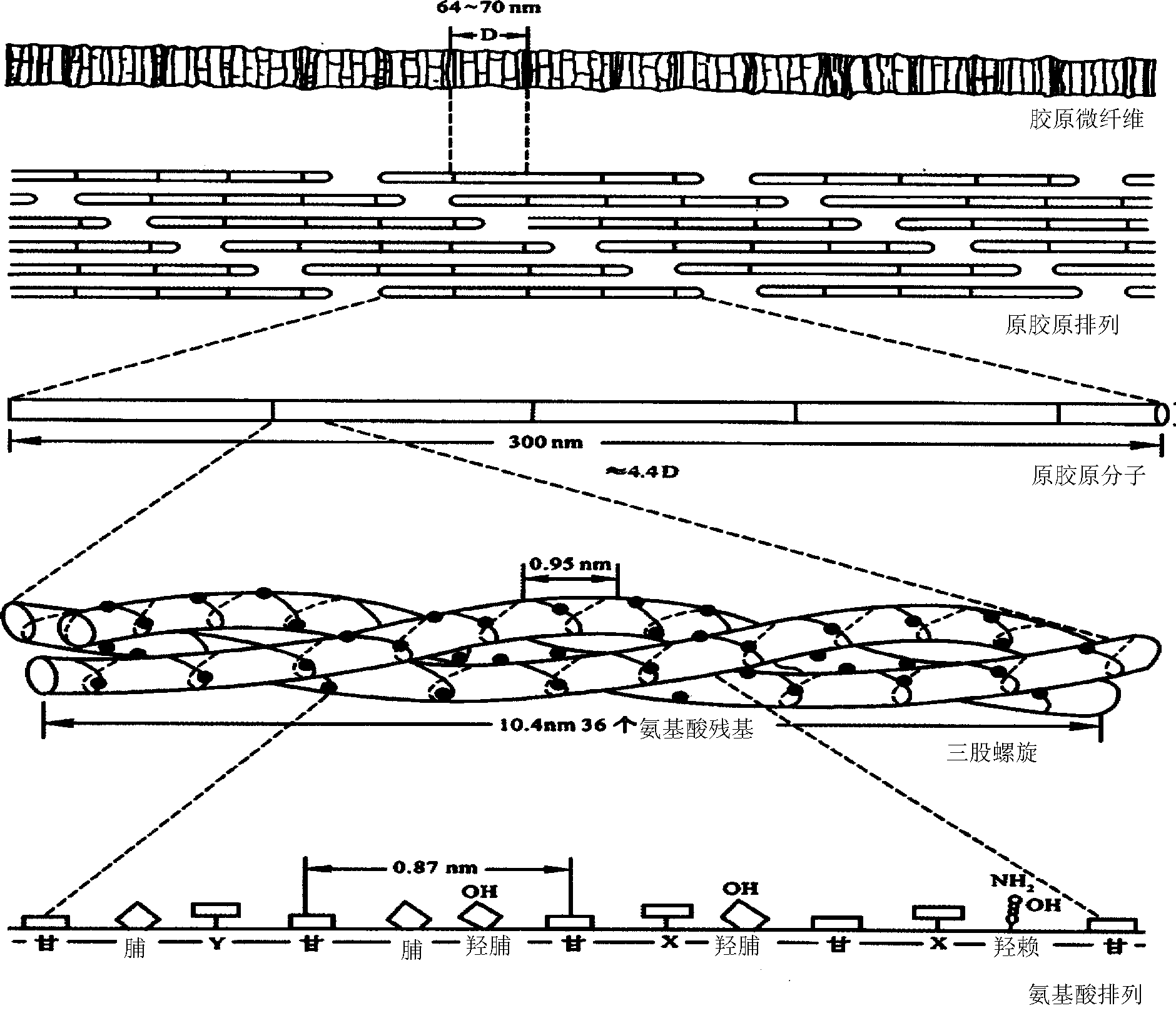
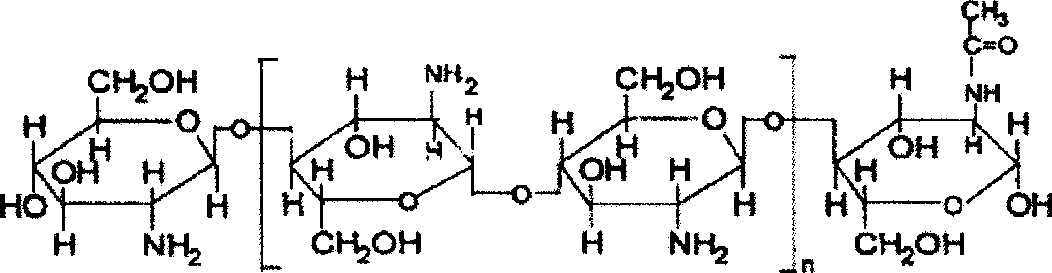
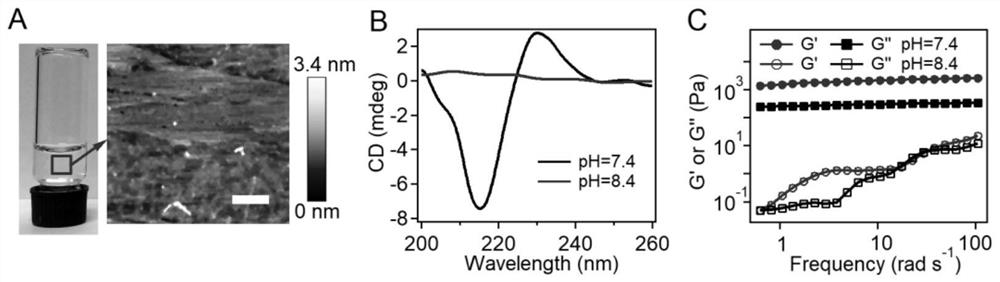
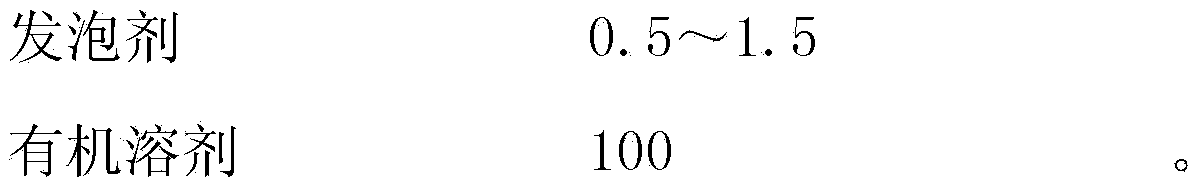Patents
Literature
49 results about "Biomedical tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biomedical tissue is biological tissue used for organ transplantation and medical research, particularly cancer research. When it is used for research it is a biological specimen. Such tissues and organs may be referred to as implant tissue, allograft, xenograft, skin graft tissue, human transplant tissue, or implant bone. Tissue is stored in tissue establishments or tissue banks under cryogenic conditions. Fluids such as blood, blood products and urine are stored in fluid banks under similar conditions.
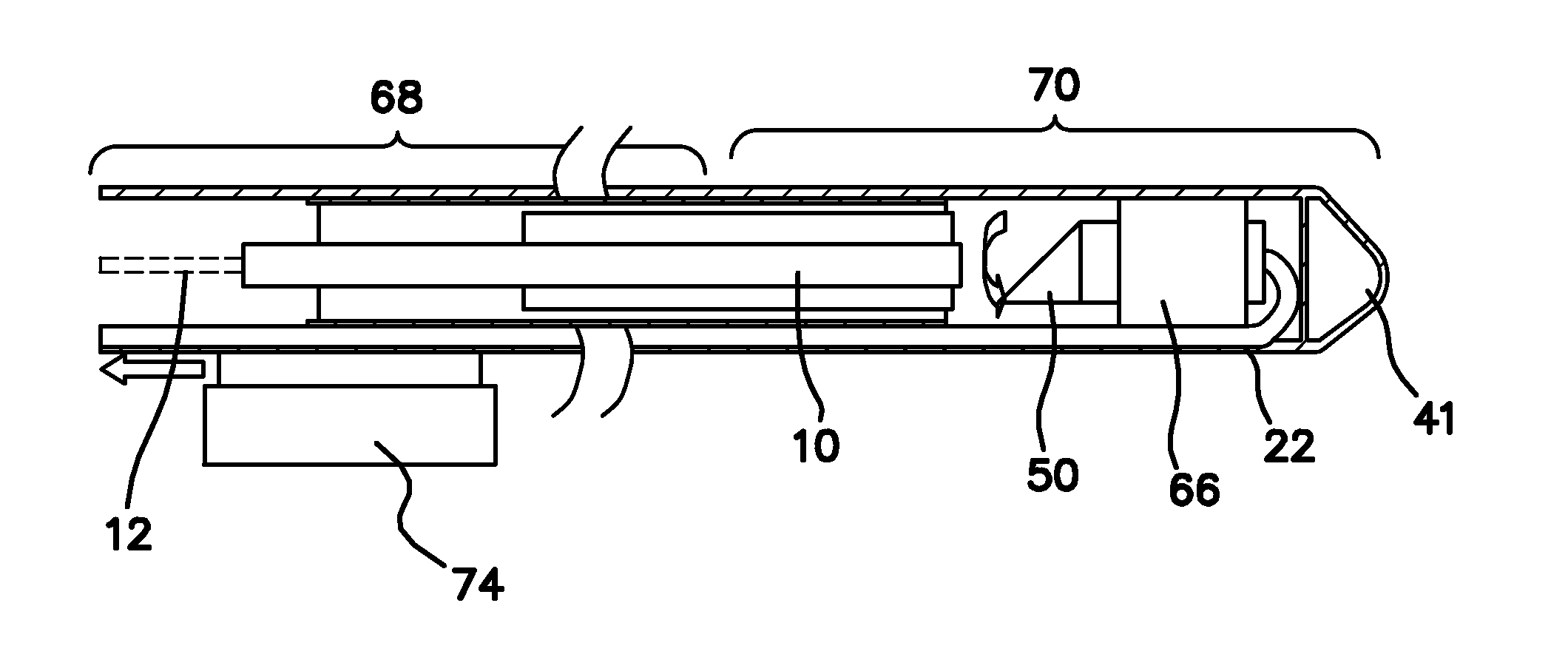
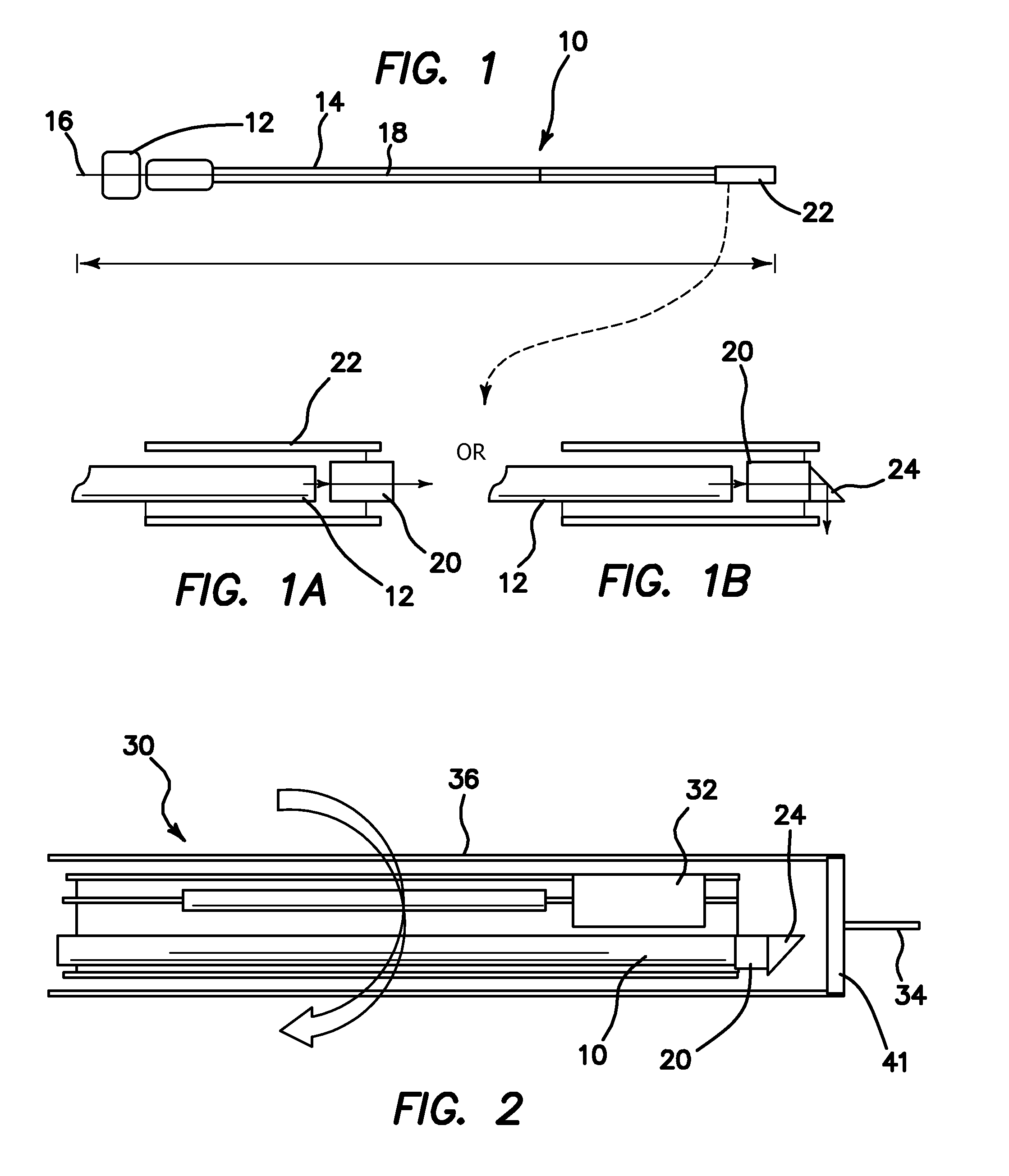
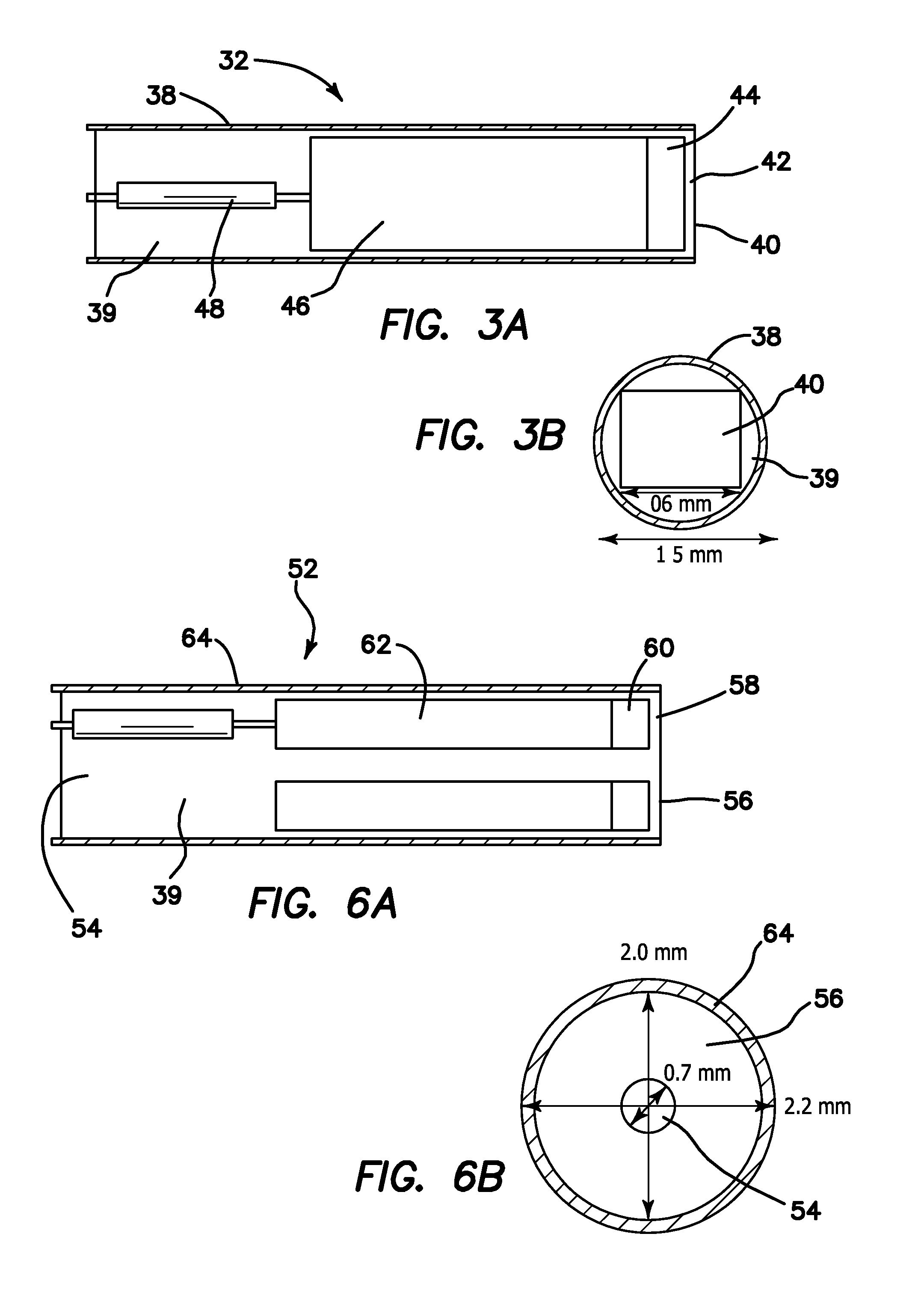
Ultrasound guided optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic probe for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS20110098572A1High resolution imagingEasy accessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHigh resolution imaging
An imaging probe for a biological sample includes an OCT probe and an ultrasound probe combined with the OCT probe in an integral probe package capable of providing by a single scanning operation images from the OCT probe and ultrasound probe to simultaneously provide integrated optical coherence tomography (OCT) and ultrasound imaging of the same biological sample. A method to provide high resolution imaging of biomedical tissue includes the steps of finding an area of interest using the guidance of ultrasound imaging, and obtaining an OCT image and once the area of interest is identified where the combination of the two imaging modalities yields high resolution OCT and deep penetration depth ultrasound imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
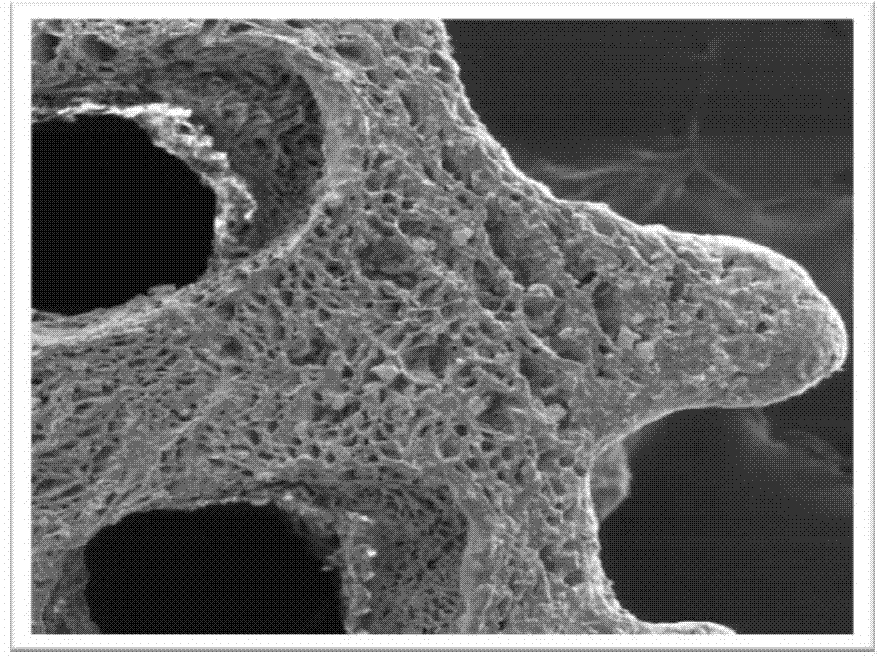
Preparation method of polyporous material for biological medicine tissue engineering scaffold
InactiveCN101455862ACause extrusion stressCause mechanical stressStentsSurgeryPorosityMetallic materials
The invention relates to the technical field of biomaterials, is particularly suitable for the field of preparation of biomedical tissue engineering support materials, in particular to a method for preparing porous materials used by a tissue engineering support. The method is to adopt mechanical processing technology to prepare the porous materials, to use the porous materials in the tissue engineering support, and to provide a three-dimensional space for adhesion, growth and so on of cells. The mechanical processing method comprises laser processing technology and digital control drilling processing technology. The porous materials prepared by the mechanical processing method have a permeable porous structure, wherein the porosity is between 5 and 99 percent, and the aperture is between 50 and 900 mu m. The method can prepare various metallic materials, wherein the laser drilling technology can also prepare porous polymer materials, ceramic materials, composite materials and so on and have wide application scope.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
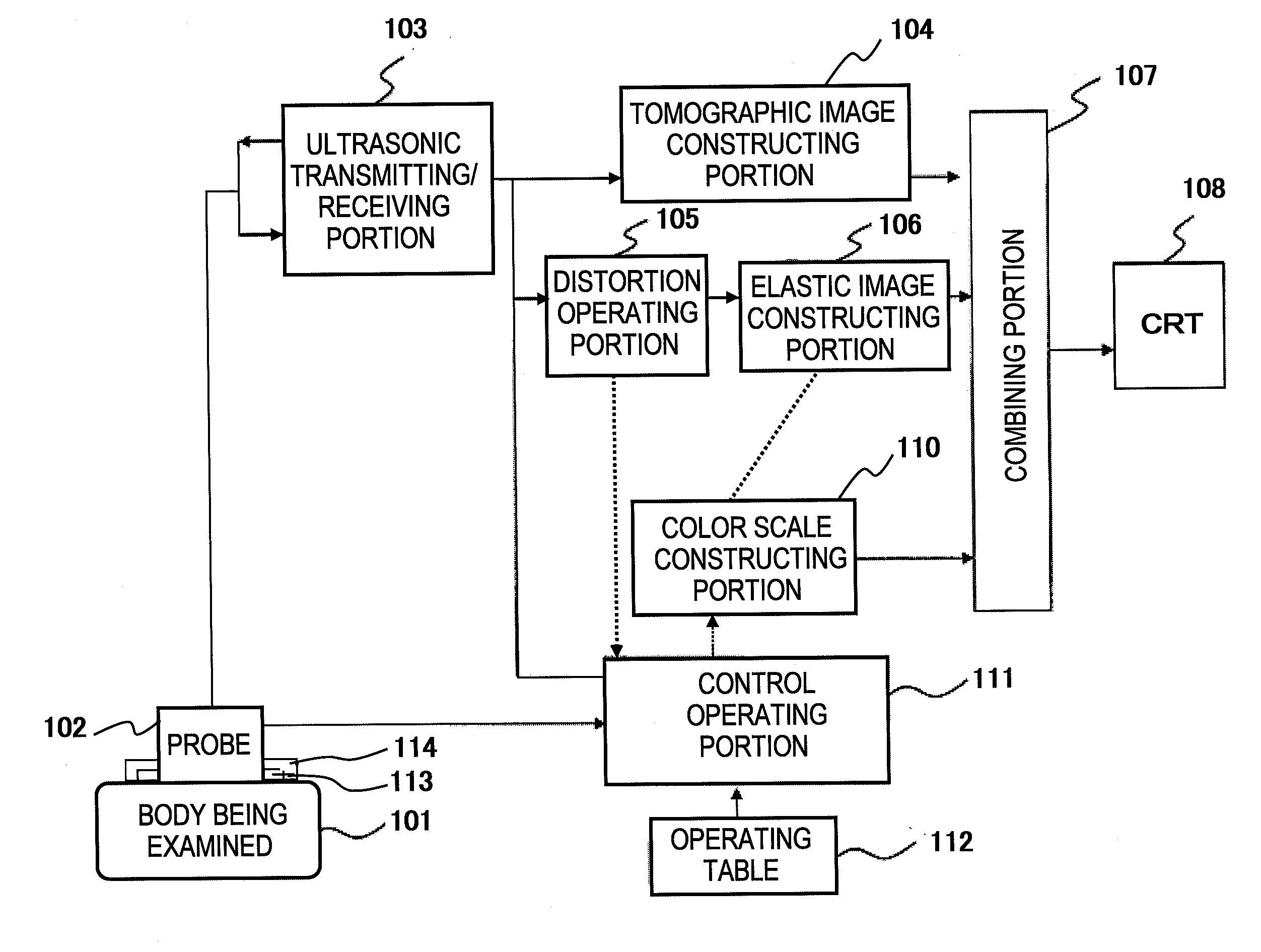
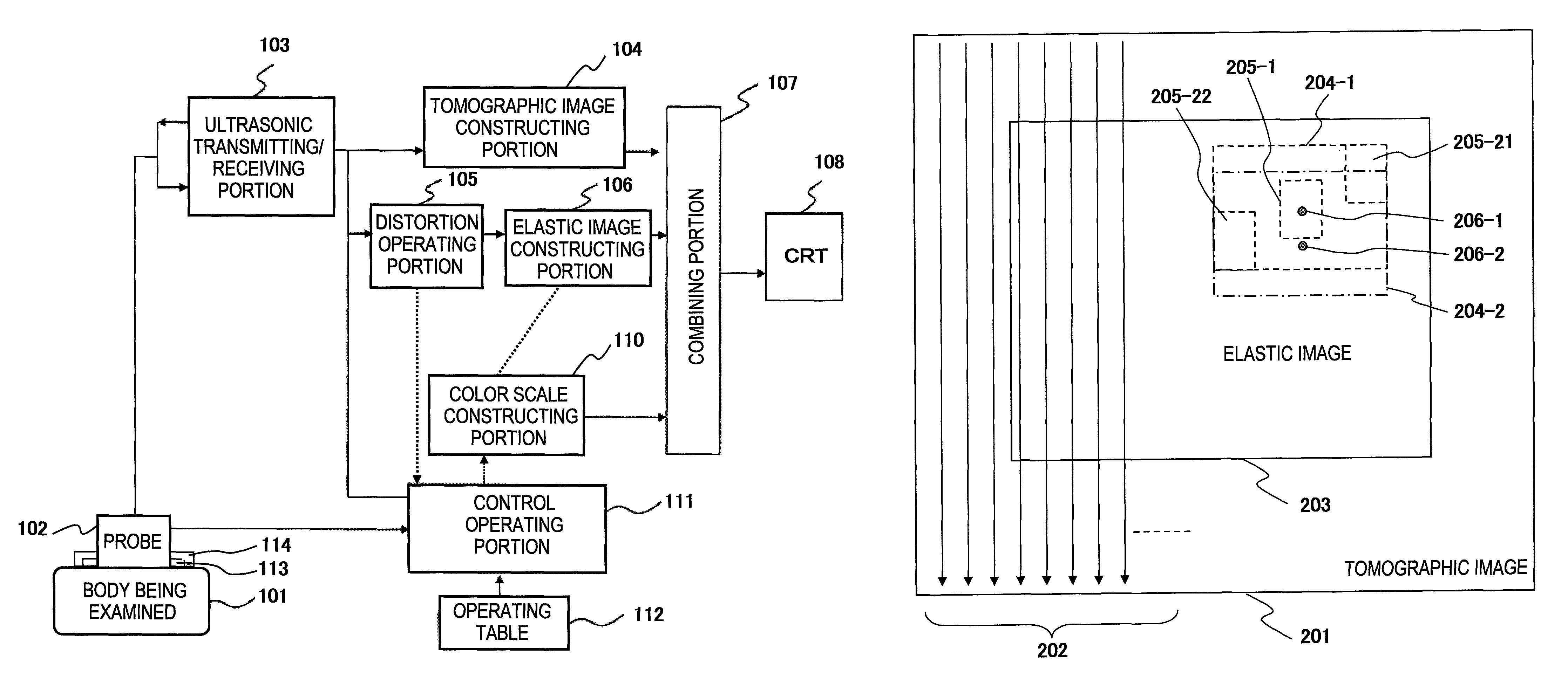
Ultrasonic Diagnostic Apparatus
InactiveUS20080188743A1Shorten diagnostic timeNone is suitable for purposeWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationTissue elasticity
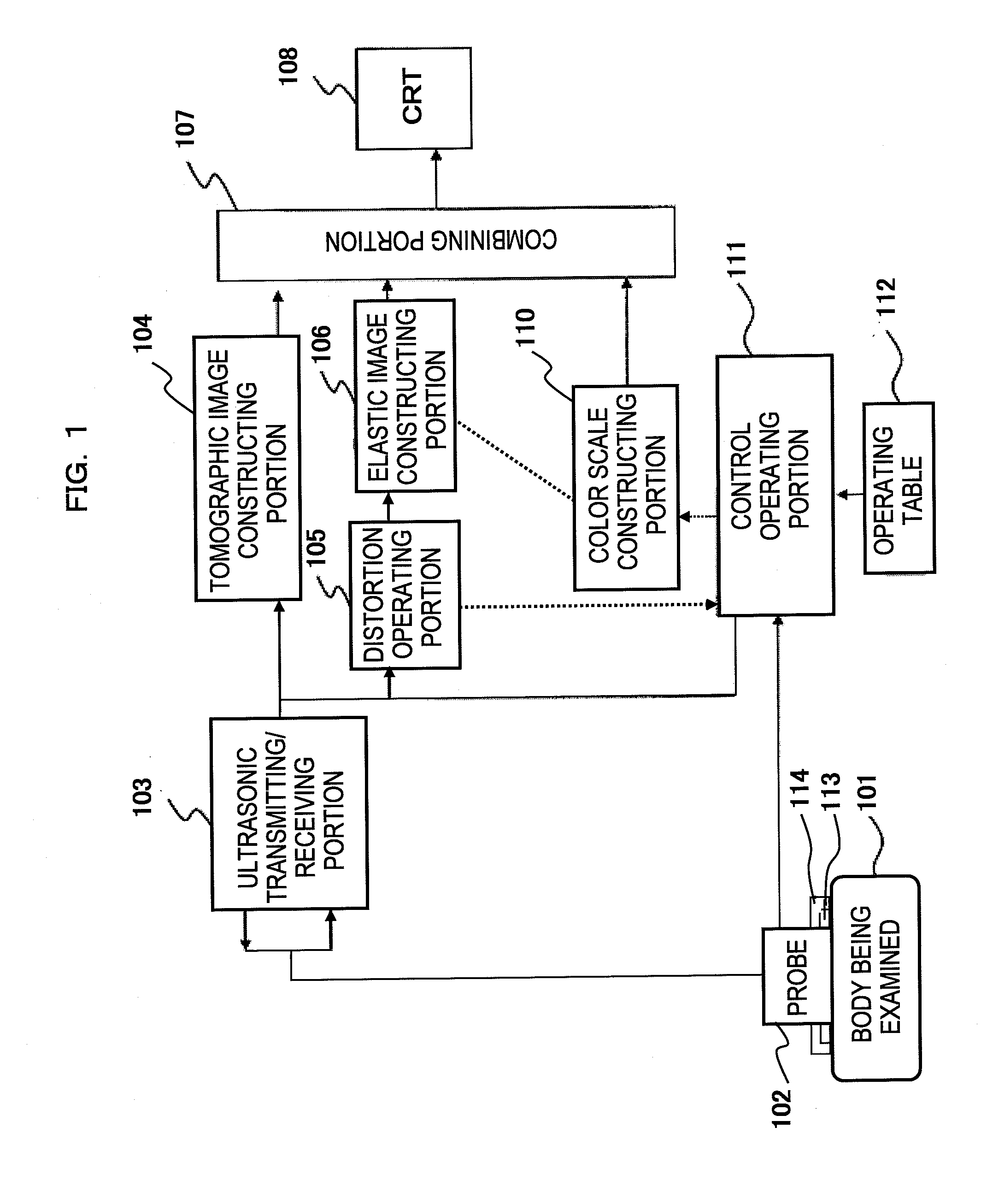
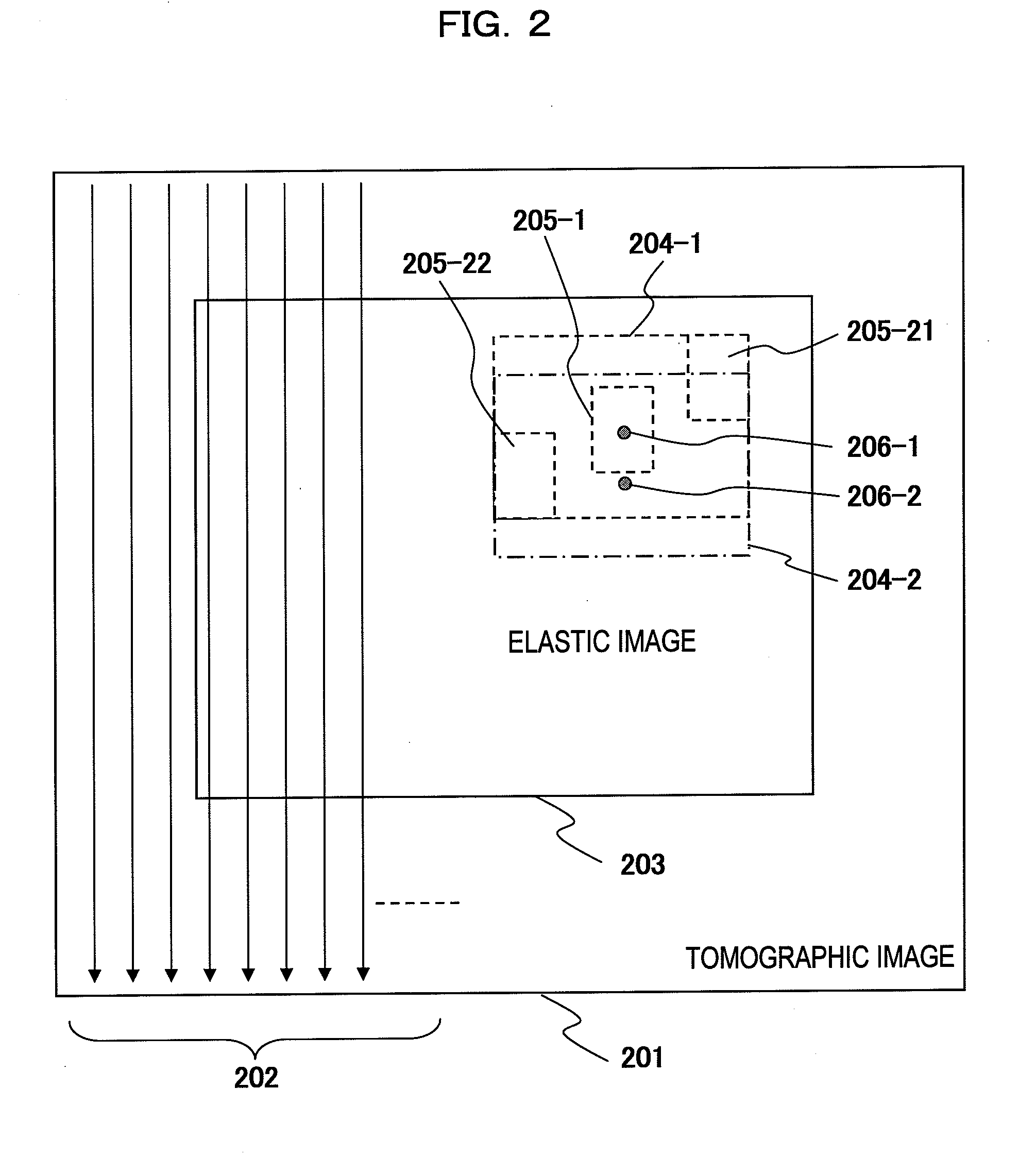
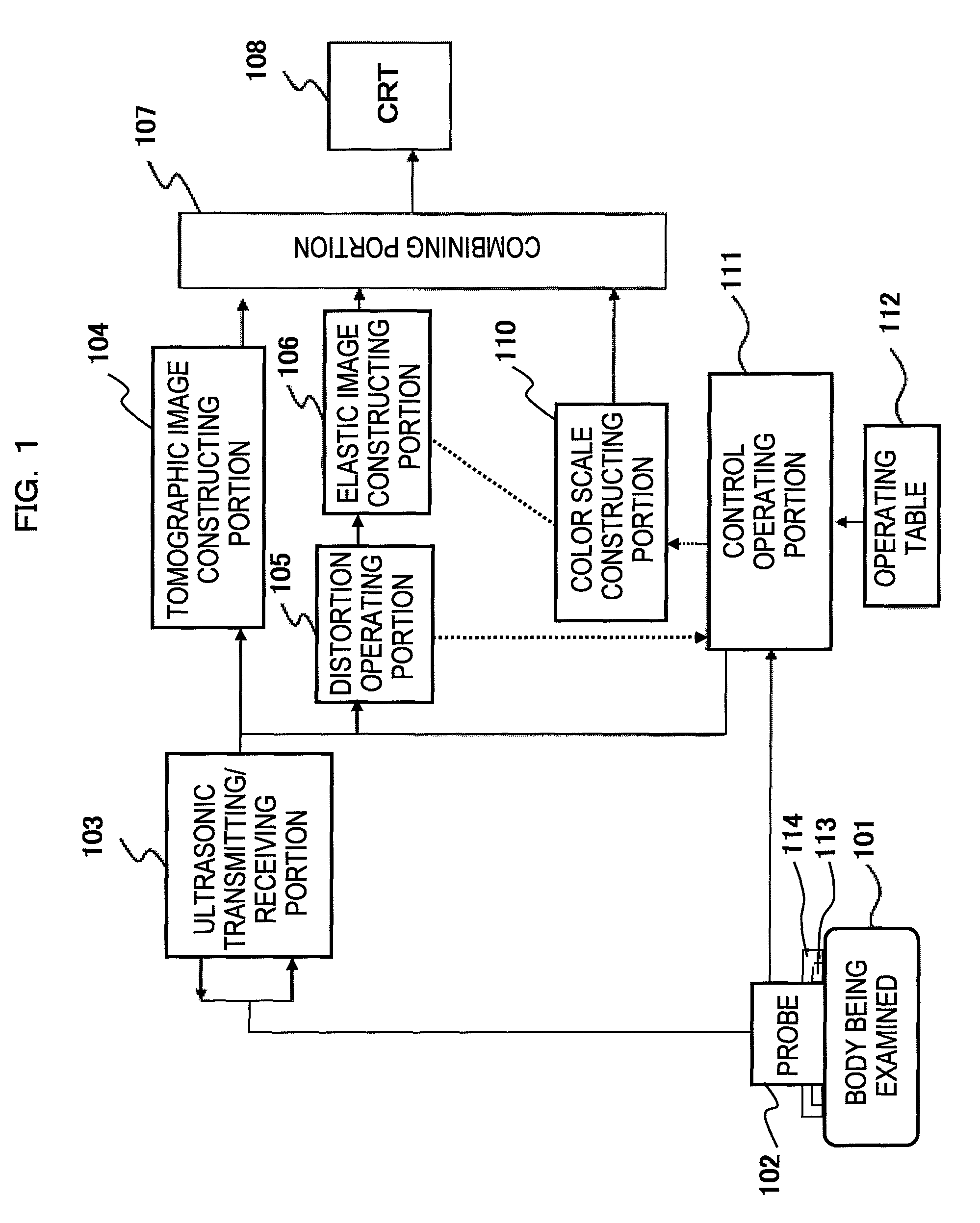
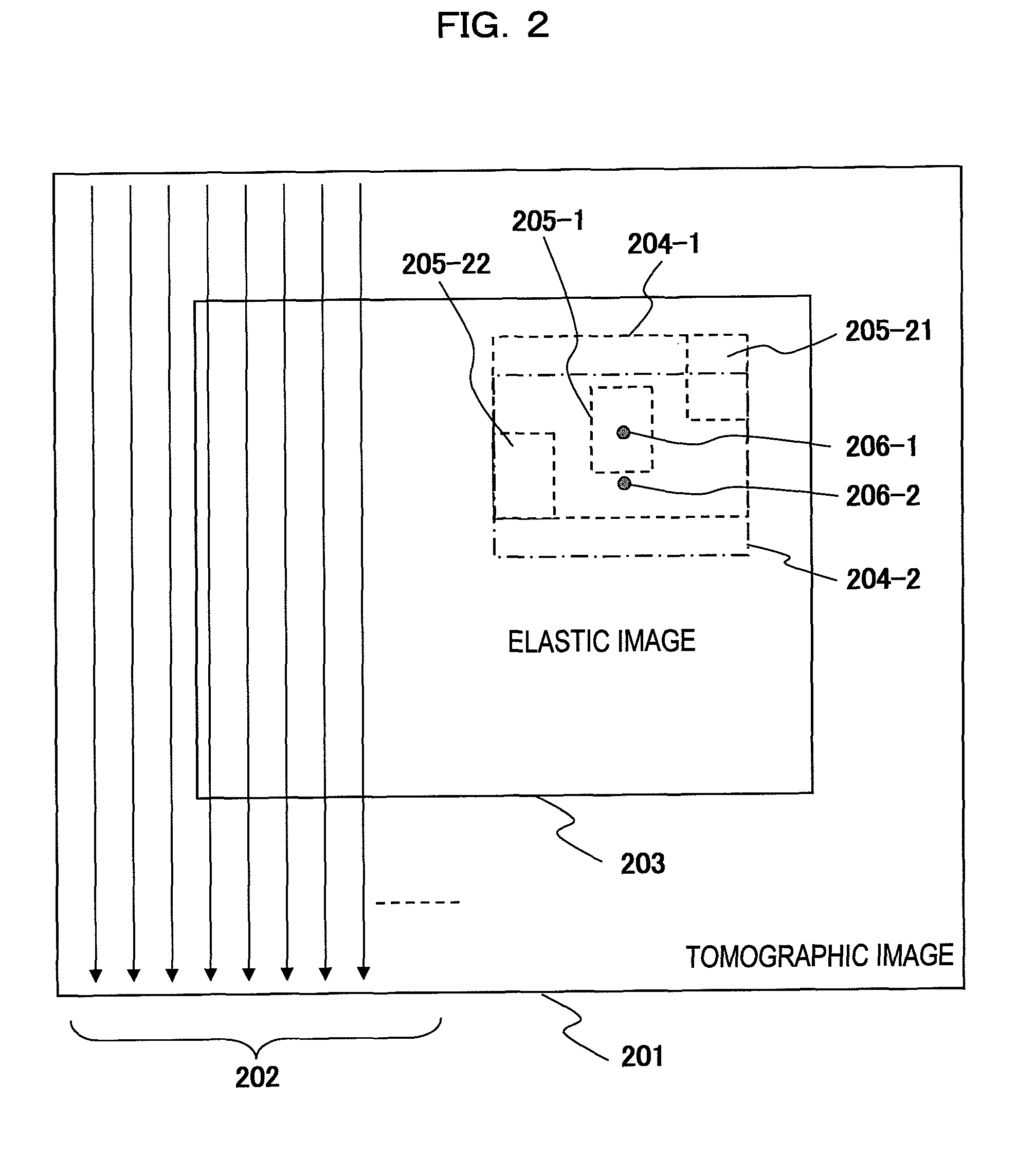
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus having a function of obtaining a tomographic image and an elastic image is adaptable to not only a close examination mode, but also a screening mode, and obtains an elastic image suitable for each examination purpose. Accordingly, the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus of the present invention comprises tomographic image acquisition means for transmitting an ultrasonic wave from a probe to a body being examined, and receiving a reflection echo signal corresponding to the transmission of the ultrasonic wave to obtain a tomographic image, elastic image acquisition means having a first acquisition mode for determining a tissue elasticity amount of a biomedical tissue of the body being examined on the basis of the reflection echo signal to obtain an elastic image, and display means for displaying at least the elastic image. The elastic image acquisition means has a second acquisition mode different from the first acquisition mode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
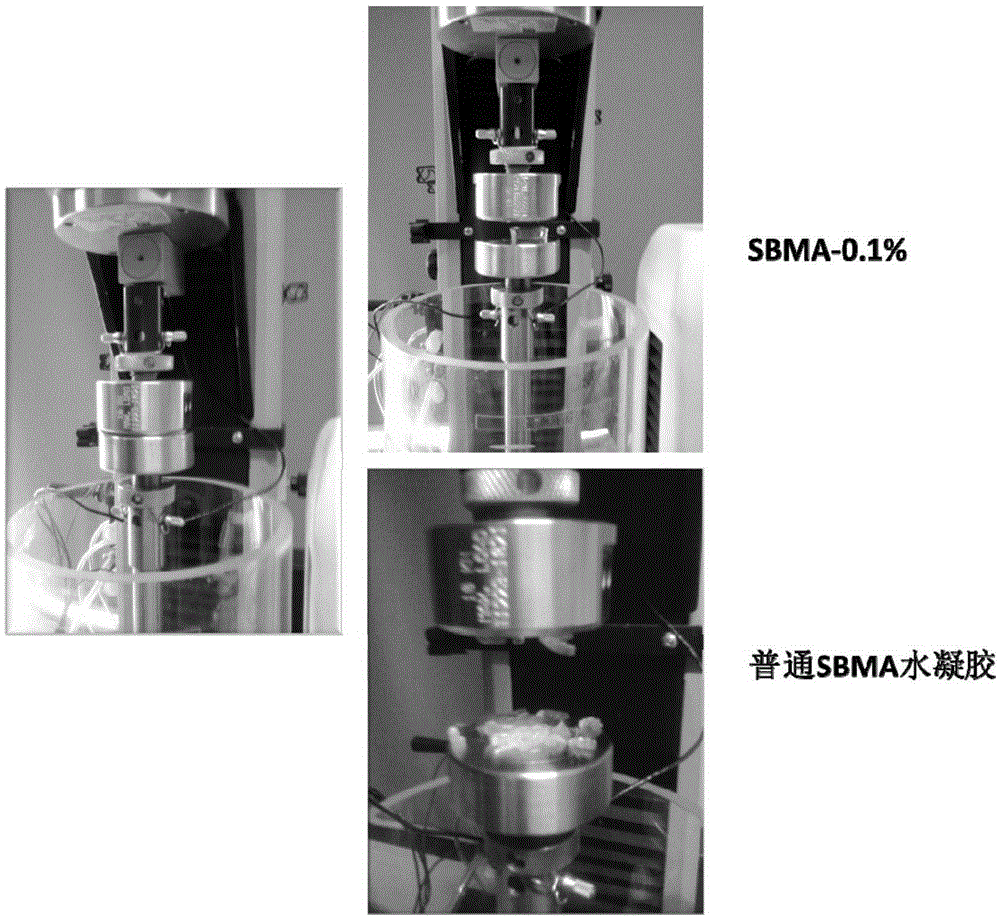
Preparation method of high-flexibility amphoteric ionic hydrogel
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-flexibility amphoteric ionic hydrogel. By changing the concentration of [2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl) ammonium hydroxide monomers, cross-linking agents and initiators, the high-flexibility amphoteric ionic SBMA hydrogel is obtained. The SBMA hydrogel prepared through the method has good mechanical property, protein adsorption resistance and cell adsorption performance through interaction of a large number of positive and negative charges of SB units, and meanwhile thermosensitivity and saline ion responding performance and self-restoration performance are achieved. Application of hydrogel based on amphoteric ions in the field of biomedical tissue engineering can be further expanded, and particularly in the fields, where certain mechanical strength is needed, such as artificial joints, blood vessels and the like. At the same time, the preparation method avoids the situation that traditionally, an amphoteric ionic SBMA main chain is modified through grafting, operation is easier, and industrialization of the whole process is easy.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Epsilon-polylysine-DOHA in-situ gel adhesive material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103223190AMechanical Strength AdjustmentMild preparation conditionsSurgical adhesivesBiocompatibilityBiological materials
The invention discloses an epsilon-polylysine-3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid (DOHA) in-situ gel adhesive material and a preparation method thereof. The in-situ gel adhesive material is composed of glucan aldehyde, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid modified polylysine, and water. The preparation method comprises the steps that: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid modified epsilon-polylysine is synthesized; with PBS as a solvent, an epsilon-polylysine-3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid solution is prepared; with PBS as a solvent, a glucan aldehyde solution is prepared; and the two solutions are uniformly mixed under a physiological pH condition, such that the in-situ gel is formed. The in-situ gel adhesive material and the method provided by the invention have the advantages that: natural biological materials are adopted; the cost is low; the process is simple; the reaction is fast and controllable; and the prepared material has good adhesion performance, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. As a biomedical tissue adhesive, the material has good application prospect in the fields of tissue adhesion, nerve anastomosis reparation, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ultrasound guided optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic probe for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS8764666B2High resolution imageEasy accessOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHigh resolution imaging
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
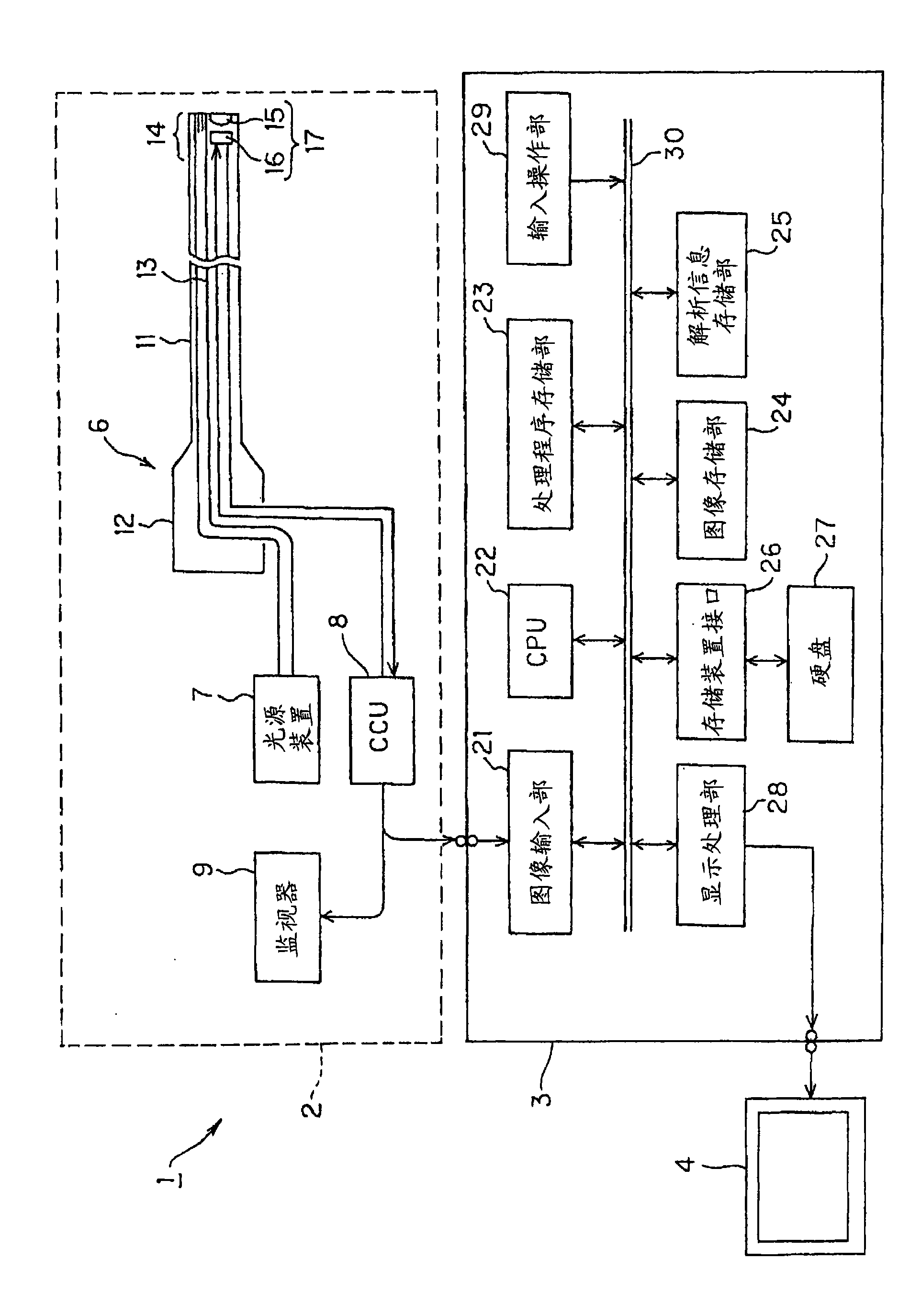
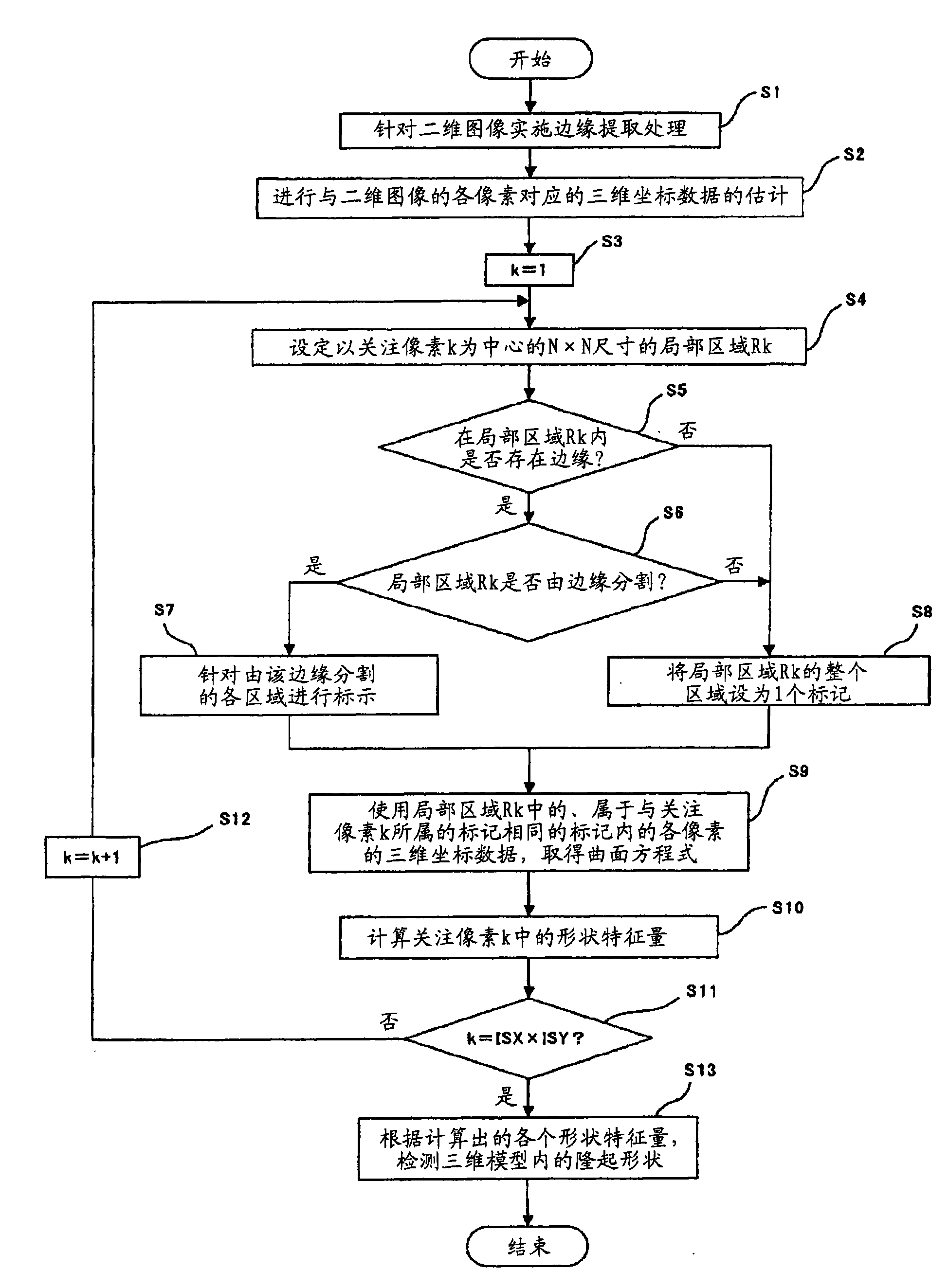
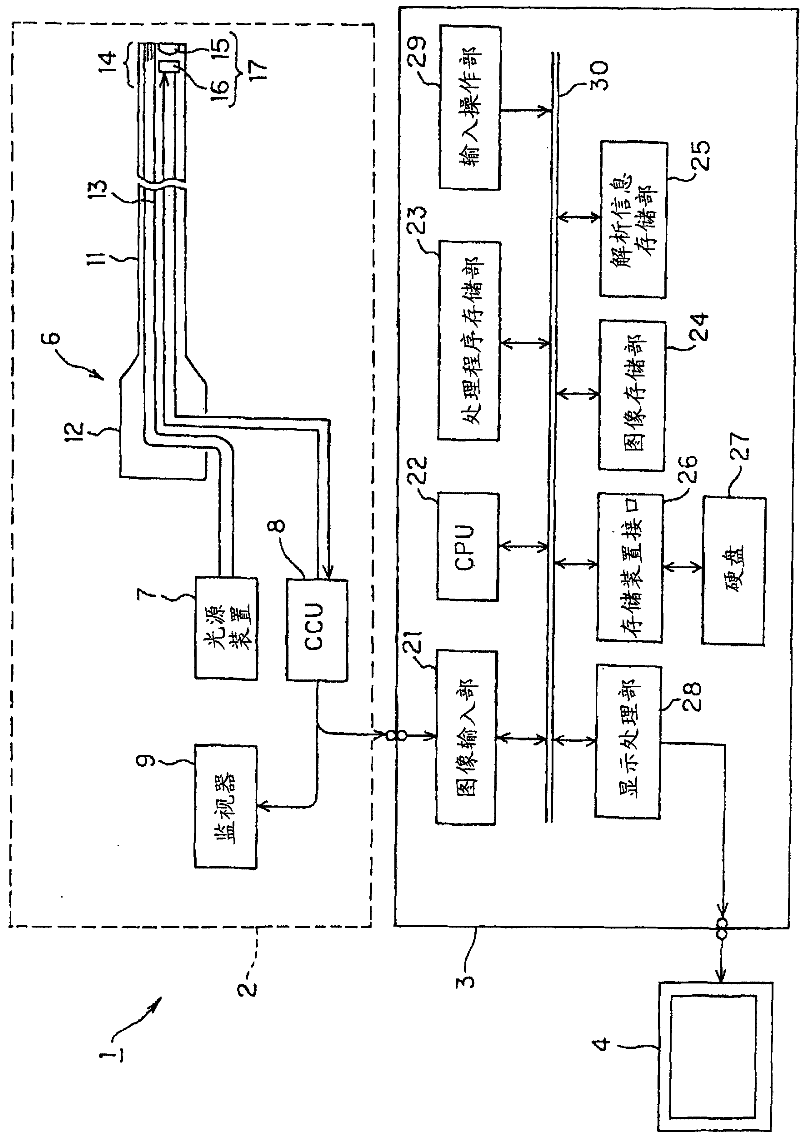
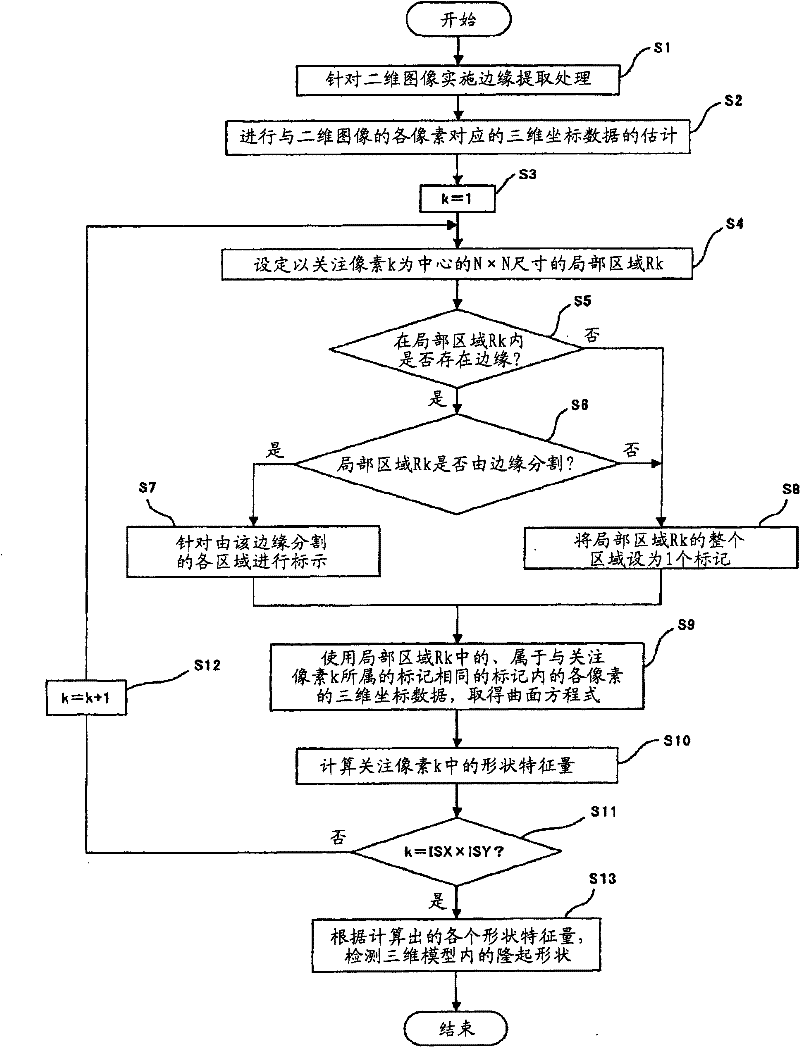
Medical image processing device and medical image processing method
ActiveCN101594817AImprove detection efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMedical treatment
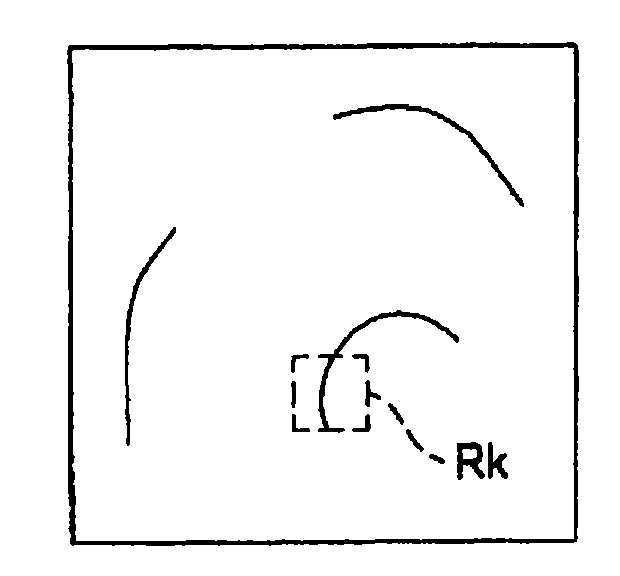
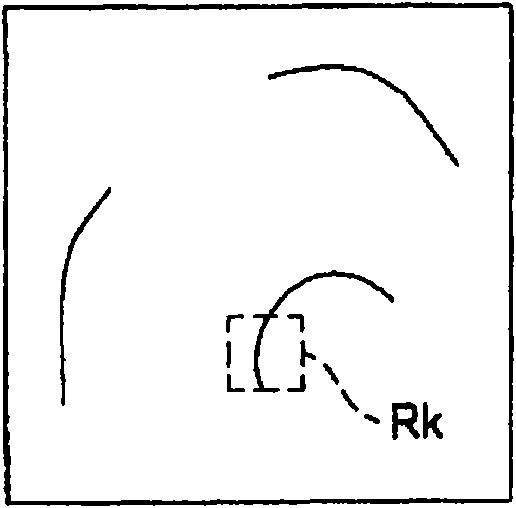
A medical image processing device is characterized in comprising an edge extracting unit for extracting a two-dimensional image of a biomedical tissue input from a medical image picking-up device; a three-dimensional model estimating unit for estimating a three-dimensional image of the biomedical tissue; a local region setting unit for setting a local region where a pixel of interest is treated as the center in the two-dimensional image; a judging unit for judging whether or not the local region is divided by at least a part of the edge extracted in the extracting unit; a shape characteristic calculating unit for calculating a shape characteristic amount of the pixel of interest while using three-dimensional data of regions that are not divided by the edge in the edge extracting unit out of the local region based on a judging result of the judging unit and that correspond to a region where the pixel of interest exists; and a projecting shape detecting unit for detecting a projecting shape based on a calculation result of the shape characteristic amount calculating unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
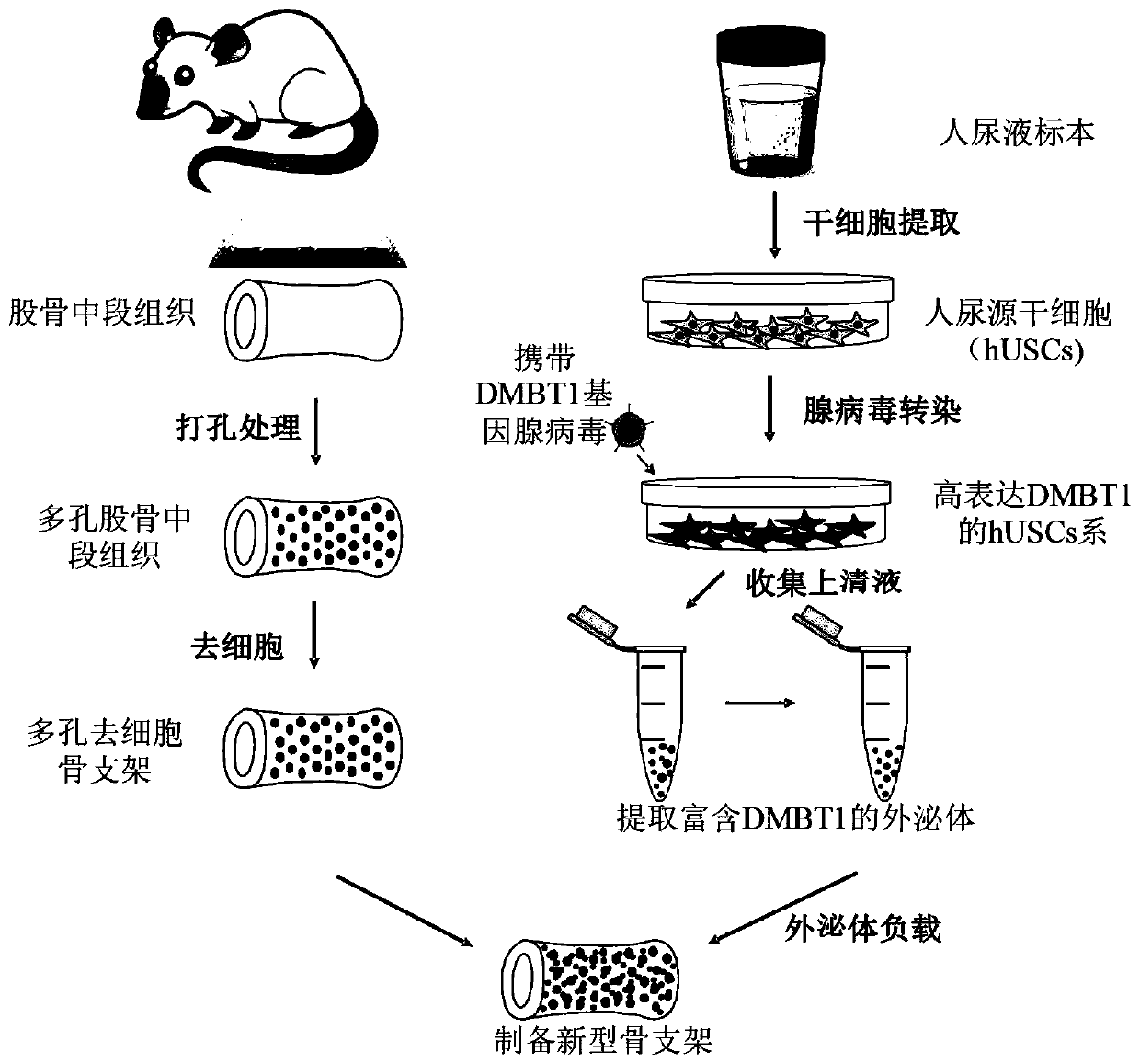
Novel bone tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical tissue engineering, in particular to a novel bone tissue engineering scaffold and a preparation method thereof. The bone scaffold comprises abone material and an exosome-loaded fibrin gel compound, the bone material is provided with holes, and the gel compound is distributed in the holes. The invention researches a bone material which ishighly similar to a natural bone matrix and has osteogenesis and vascularization activities. The porous decellularized tissue engineering scaffold is closer to a normal bone, has good biomechanical properties, is suitable for bone defect repair of a load bearing area, and maximally retains inherent components of the scaffold. According to the method, cell components with most antigens in tissues can be effectively removed, the immunological rejection reaction of grafts is reduced, the approximate morphological structure of the tissues can be maintained, and most tissue matrix components and bioactive factors are retained.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Degradable skin tissue engineering bracket material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a material in the field of biomedical tissue engineering, in particular a method for preparing a skin tissue engineering bracket by adopting polysaccharide substances in nature and utilizing a blending method. The method comprises the following steps that: a glycerol solution of II-type collagen and a protonation solution of chitosan are first prepared respectively, evenly blended, added with quantitative konjak glucomannan fine powder and continually stirred to be sol; a gel sample is put into a vacuum foam-removing device for foam removal, taken out, kept to stand and poured into a die; and a film is formed, dried at a constant temperature and then taken off. The material is a polymer material applied to skin or nerve repair, and the prepared film is ideal in mechanical properties, degradation performance, water absorption and steam transmission coefficient. The invention relates to a degradable skin tissue engineering bracket material and a preparation method thereof.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel human-like collagen haemostatic dressing
ActiveCN105536043AGood biocompatibilityGrowth promotionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBandagesChelated calciumFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a novel human-like collagen haemostatic dressing which has good biocompatibility, can be absorbed and is rich in calcium, zinc, copper and iron, and discloses a preparation method of the novel human-like collagen haemostatic dressing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking modified protein obtained by chelating humanized human-like collagen prepared by high-density fermentation with calcium, zinc, copper and iron ions respectively as a raw material as well as taking lysyloxidase existing in mammals as a cross-linking agent, carrying out low-temperature cross-linking reaction and freeze-drying processes to obtain the novel collagen haemostatic dressing which can be used for hemostasis of wounds and postoperative hemostasis. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are easy to obtain, the cost is low, the synthetic process is simple and easy to realize, process amplification is easy, and the reproducibility is good; and the human-like collagen haemostatic dressing prepared by the preparation method does not have animal-derived virus hidden danger, has an obvious haemostatic effect, can be used for hemostasis of various wounds and postoperative hemostasis, and can be used for basic research and application of related fields, such as biomedical tissue engineering.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Preparation method of oriented shish-kebab fiber
InactiveCN105463848AEasy to fixImprove hydrophilicityFibre typesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberBone tissue
The invention relates to a preparation method of an oriented shish-kebab fiber and belongs to the technical field of biomedical tissue engineering. The preparation method includes the following steps that oriented nanofibers are obtained through an electrostatic spinning method, grafted copolymer is obtained through a graft copolymerization method, and finally the oriented shish-kebab fiber is obtained through the method that the nanofibers obtained through an electrostatic spinning method induce the grafted copolymer to conduct crystallization. Through the special structure, performance of different polymers can be combined to improve the hydrophilia and the cytocompatibility of electrostatic spinning fibers, and the purpose of stimulating a bone tissue structure on the microscopic scale can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Tissue- engineered cartilage graftimplant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103495208AImprove adhesionPromote vascularizationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisCartilage cellsBiomechanics
The invention relates to a tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of induced differentiation carried out on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) by utilizing a bioactive inducing factor to form a cartilage cell chondroblast composite scaffold material and so as to construct a tissue tissue-engineered cartilage by utilizing a biological activity inducing factor in biomedicine tissue engineering. The tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant is prepared by adopting the method comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a Nano-HA / PLLA (hyaluronic aciddroxyapatite / poly left L-lactic acid) cartilage scaffold material; (2) carrying out coculture on BMSCs and the Nano-HA / PLLA cartilage scaffold material, and carrying out induced differentiation on BMSCs to form cartilage cells by adopting a cartilage formation inducing solution, so that the tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant is obtained. The tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant improves flexibility and biodegradability of the cartilage scaffold material, improves biomechanical property and is more beneficial to adhesion, growth and vascularization of bone cells; an animal experiment proves that the tissue tissue-engineered cartilage graftimplant has a good cartilage defect repairing function.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
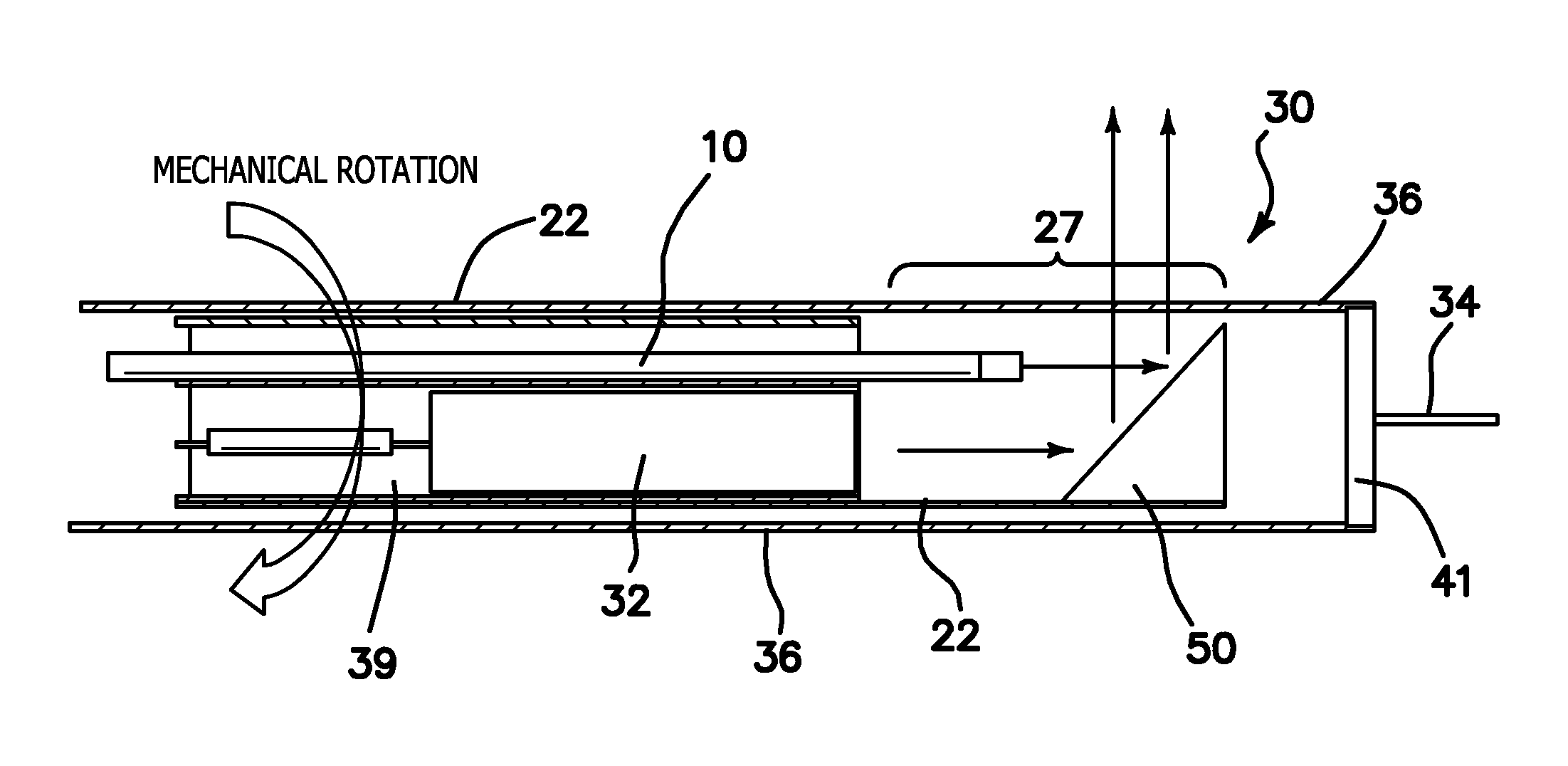
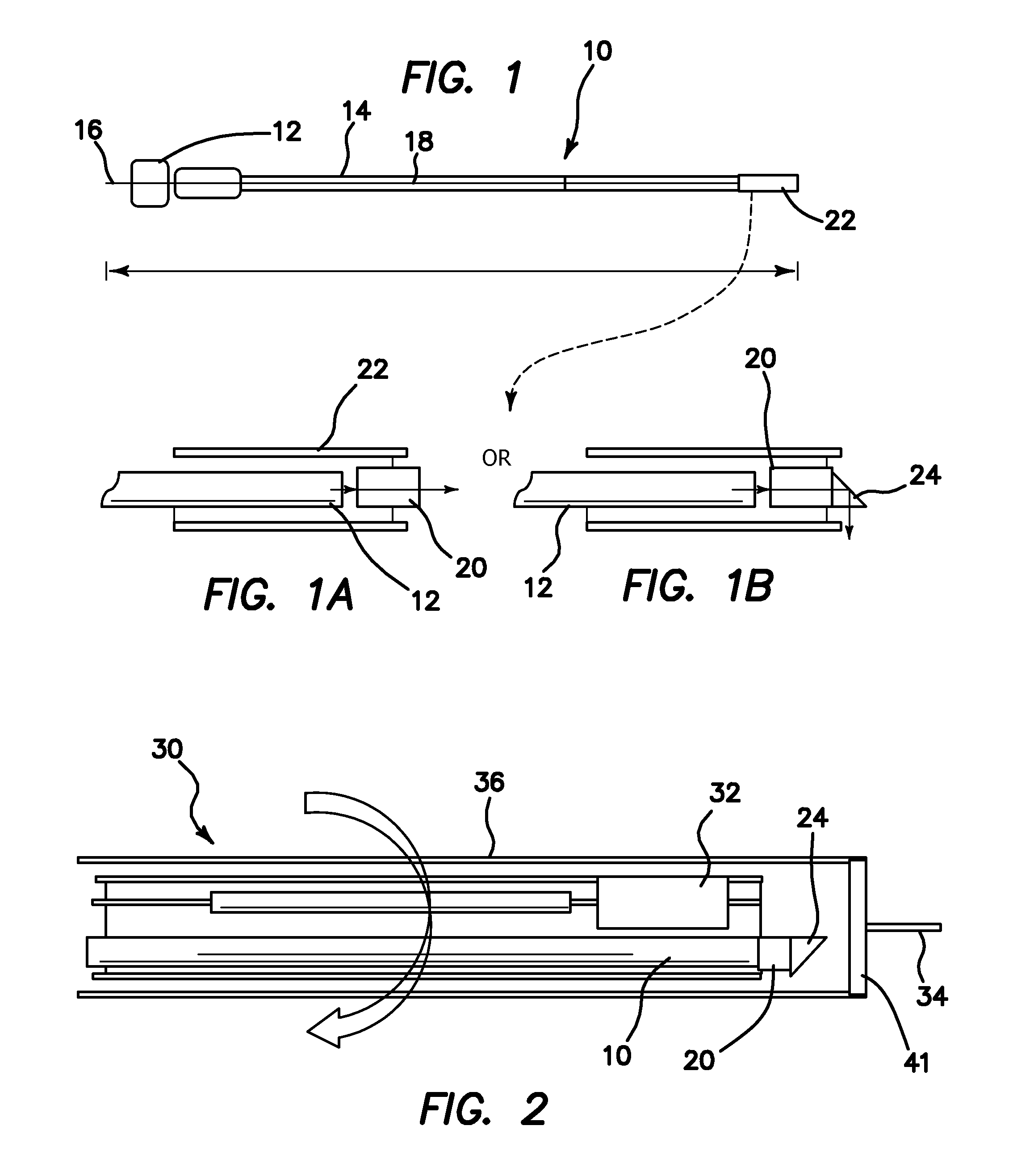
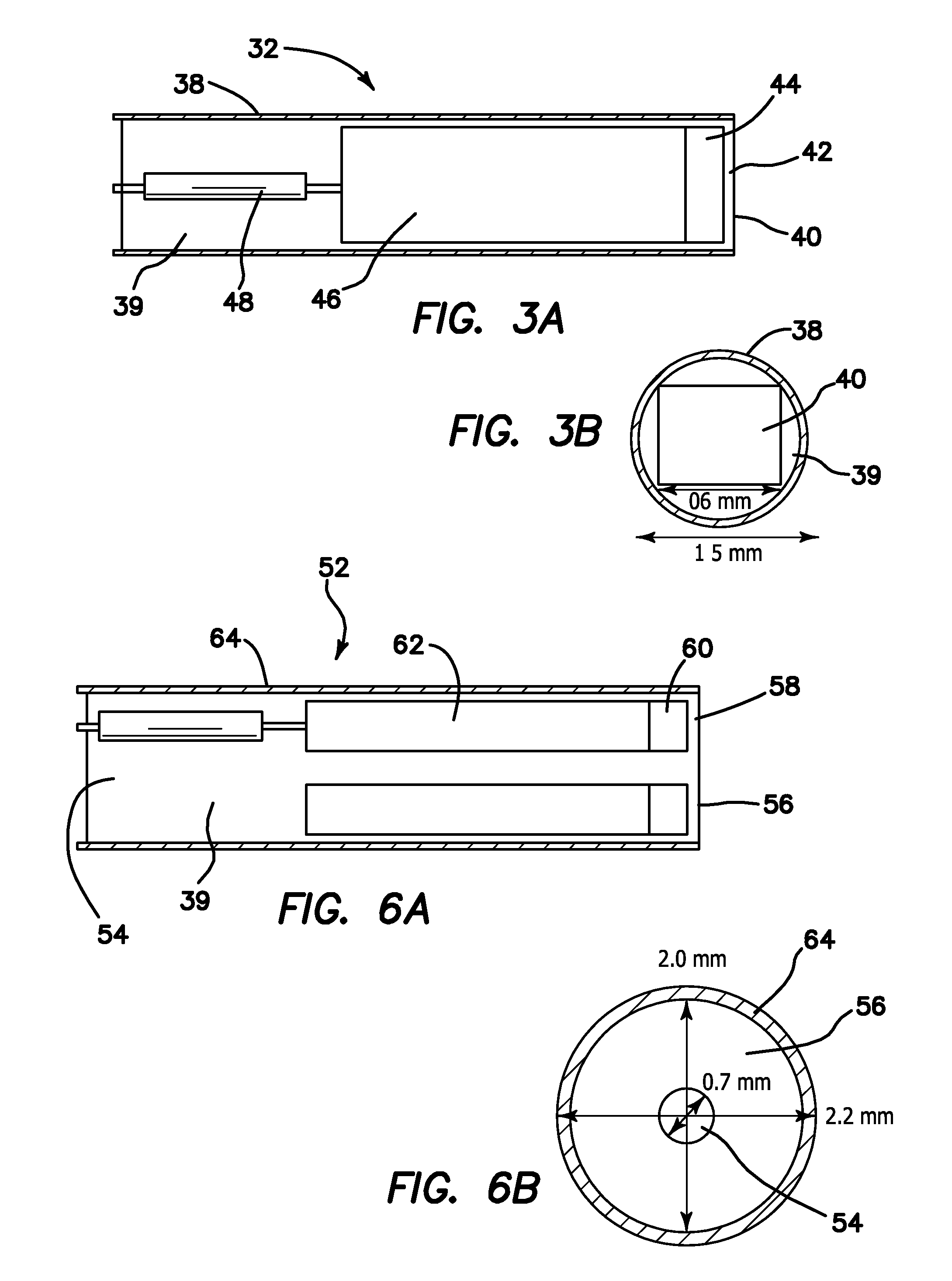
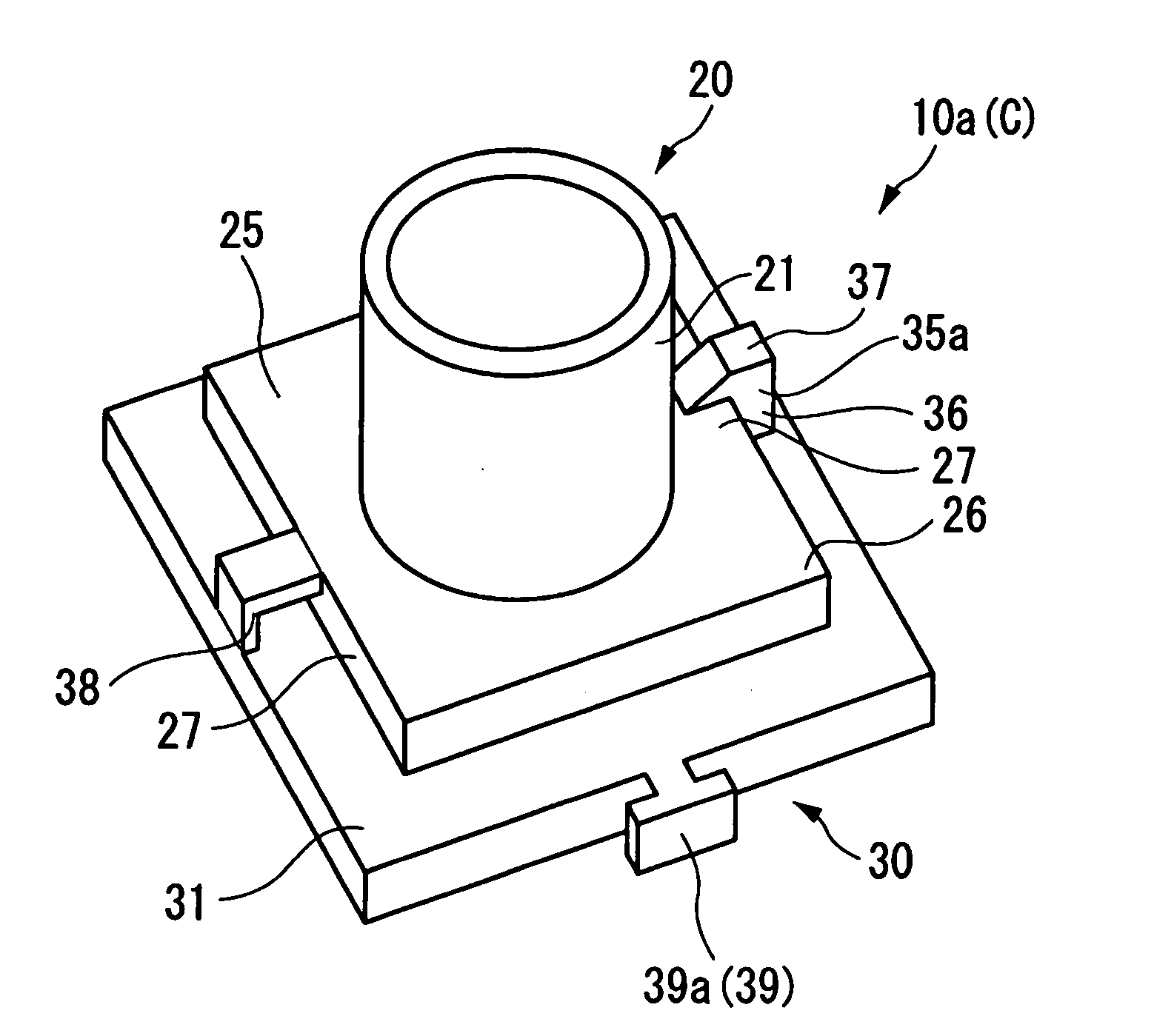
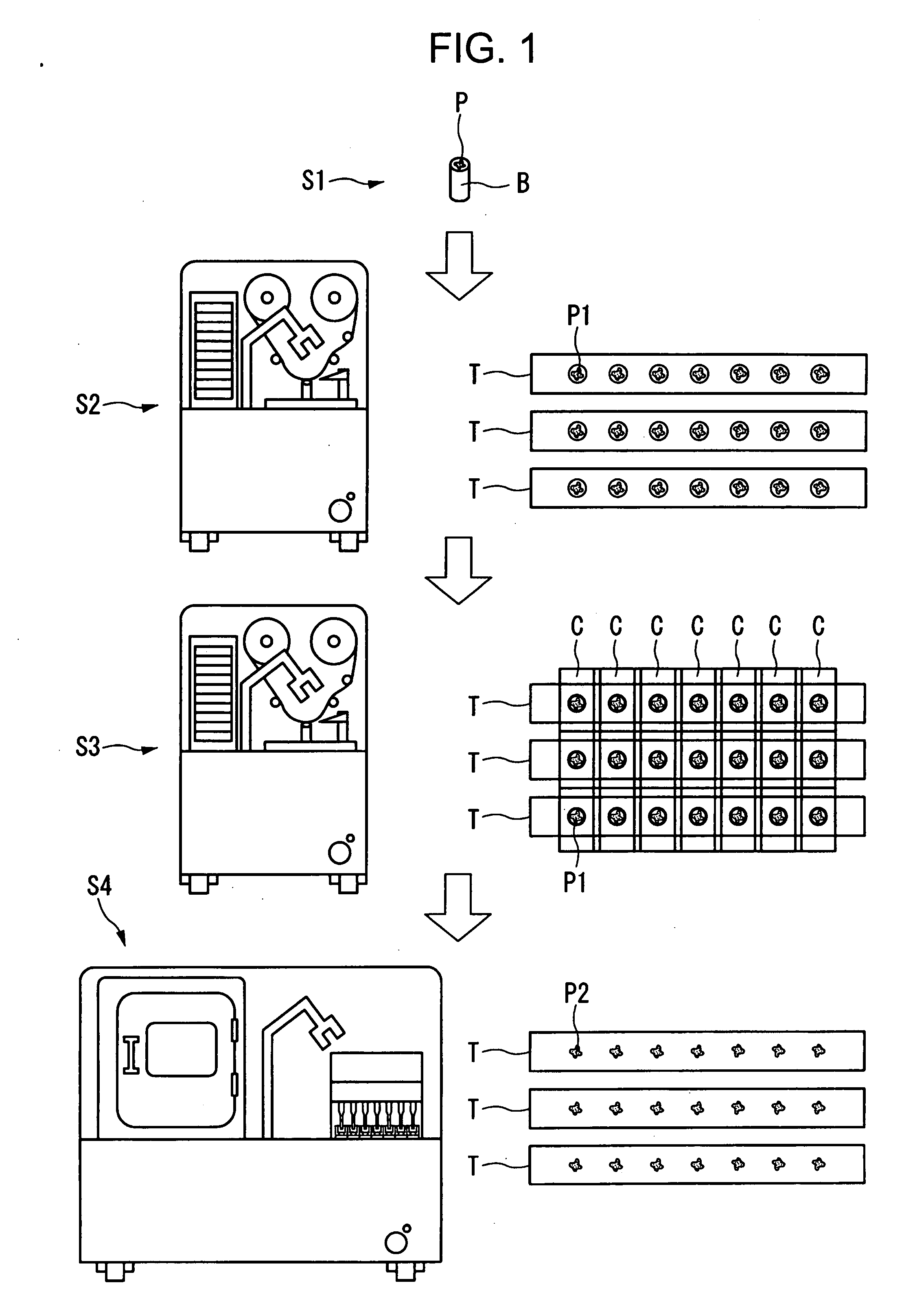
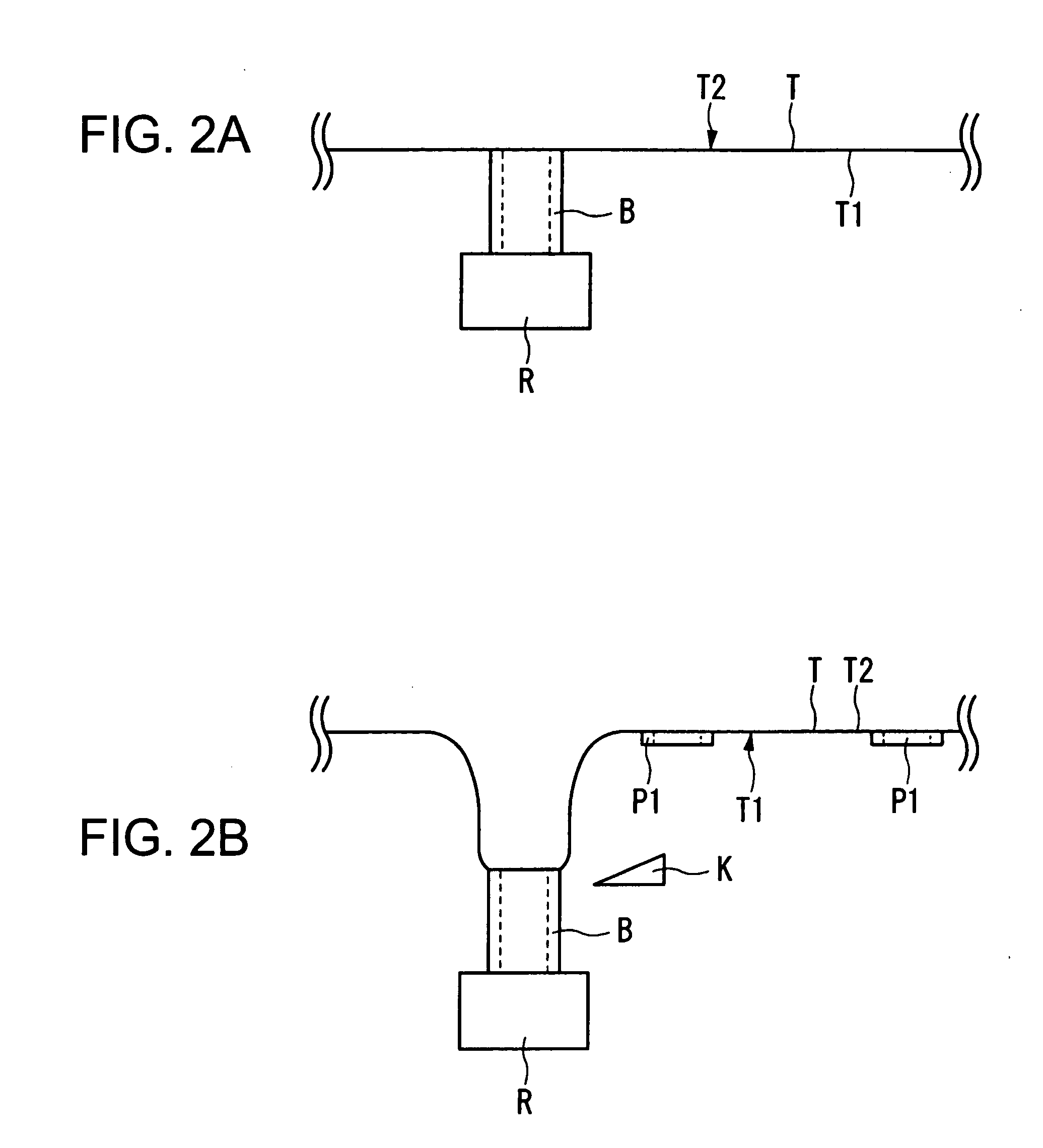
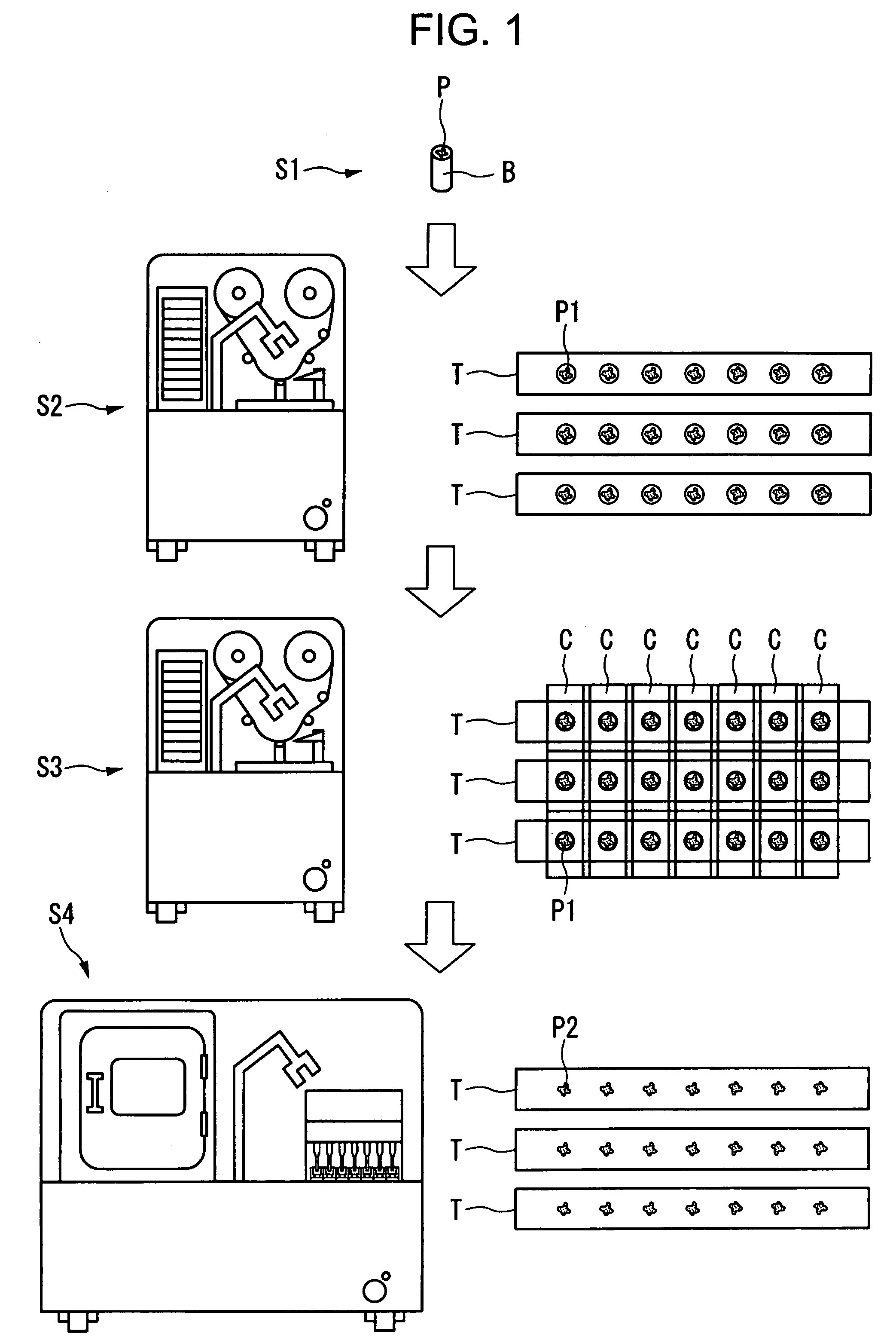
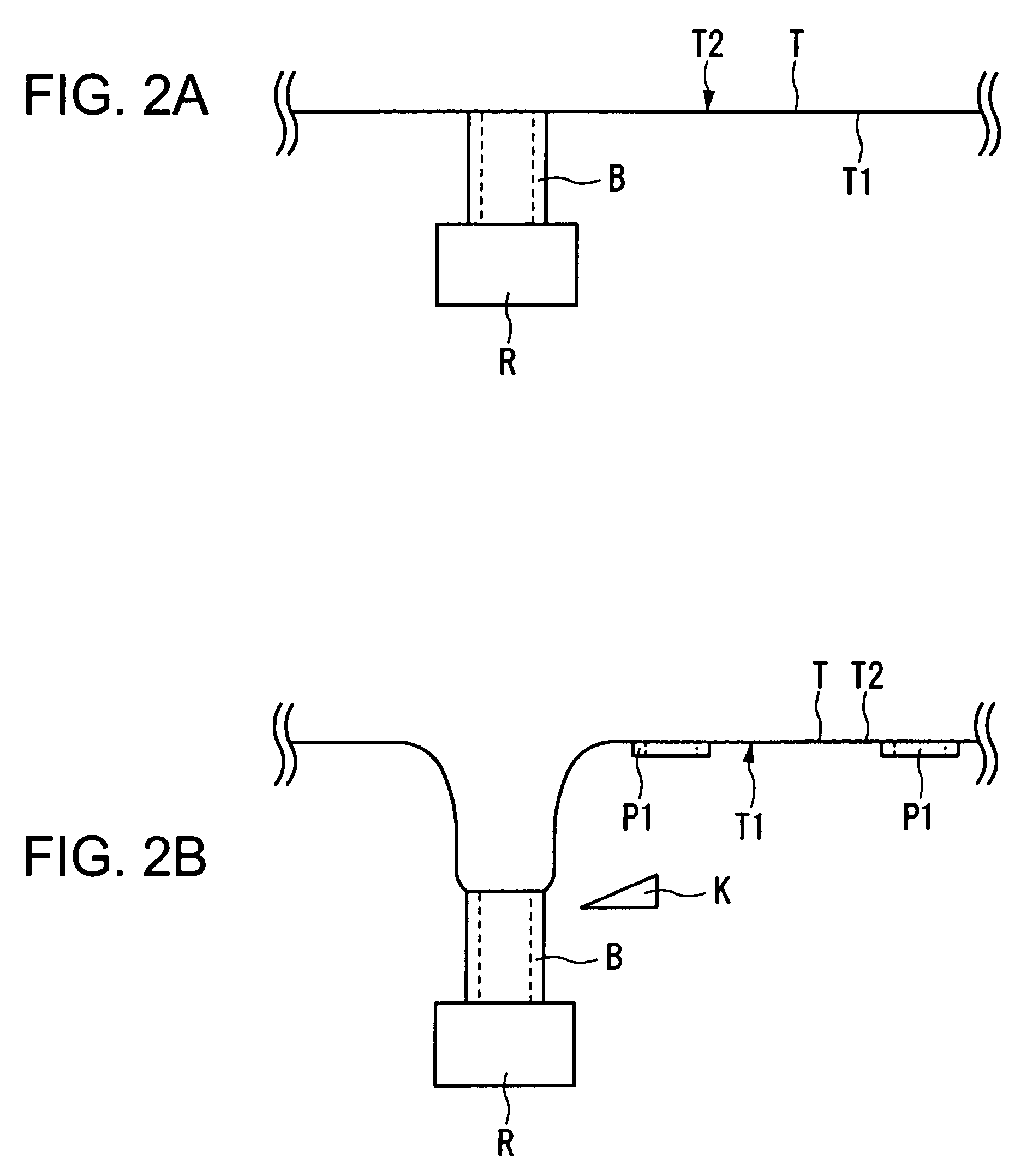
Container for Processing Section Samples, Processing Method for Section Samples, and Processing Apparatus for Section Samples
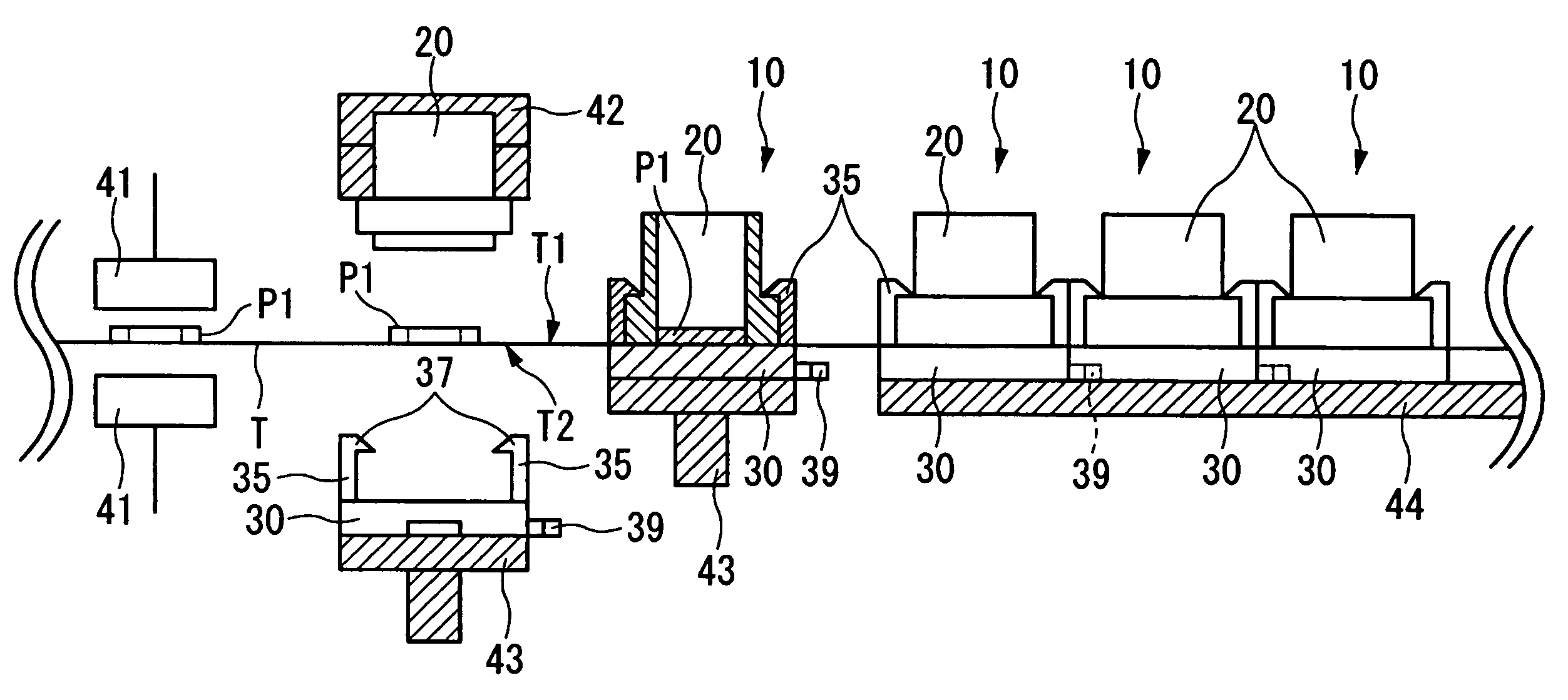
InactiveUS20080088834A1Precise positioningEasy to handleImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound (substance)Thin section
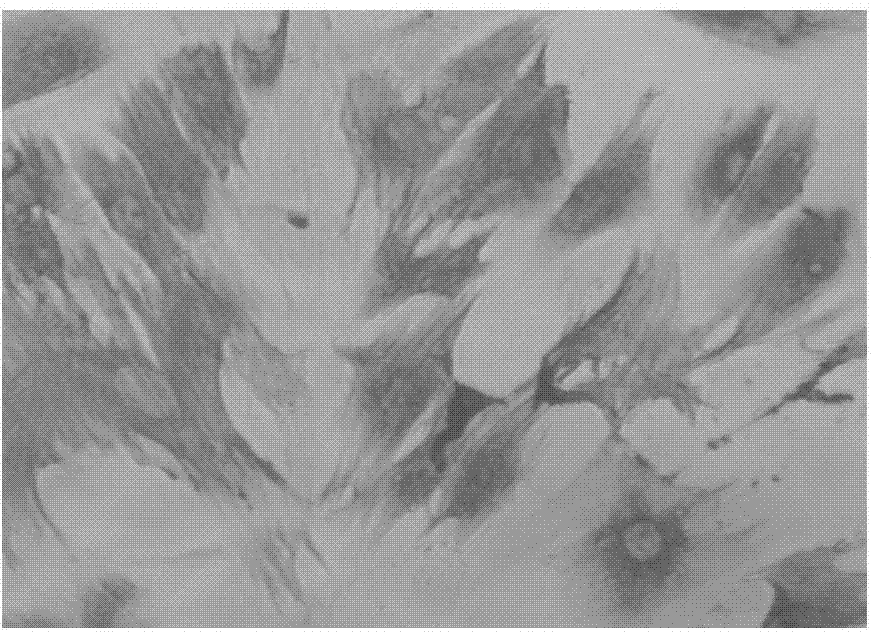
The container comprises a cylindrical member 20 which constitutes the side wall member, a bottom member 30 which is in contact with the bottom plane of the cylindrical member 20 and which constitutes the bottom part, and an engaged fixing part 35 for engaging the cylindrical member 20 with the bottom member 30; the cylindrical member 20 and the bottom member 30 sandwiches the carrier tape T from one side T1 of the carrier tape T and from the other side T2 of the carrier tape T, respectively, such that one of the plural thin section samples P1 may be disposed inside the cylindrical member 20. Accordingly, without cutting a sequence of tapes carrying thereon the thin section samples of biomedical tissues, each of the thin section samples of the biomedical tissues can be individually processed with different chemicals depending on the required observation for various types of biomedical tissues.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
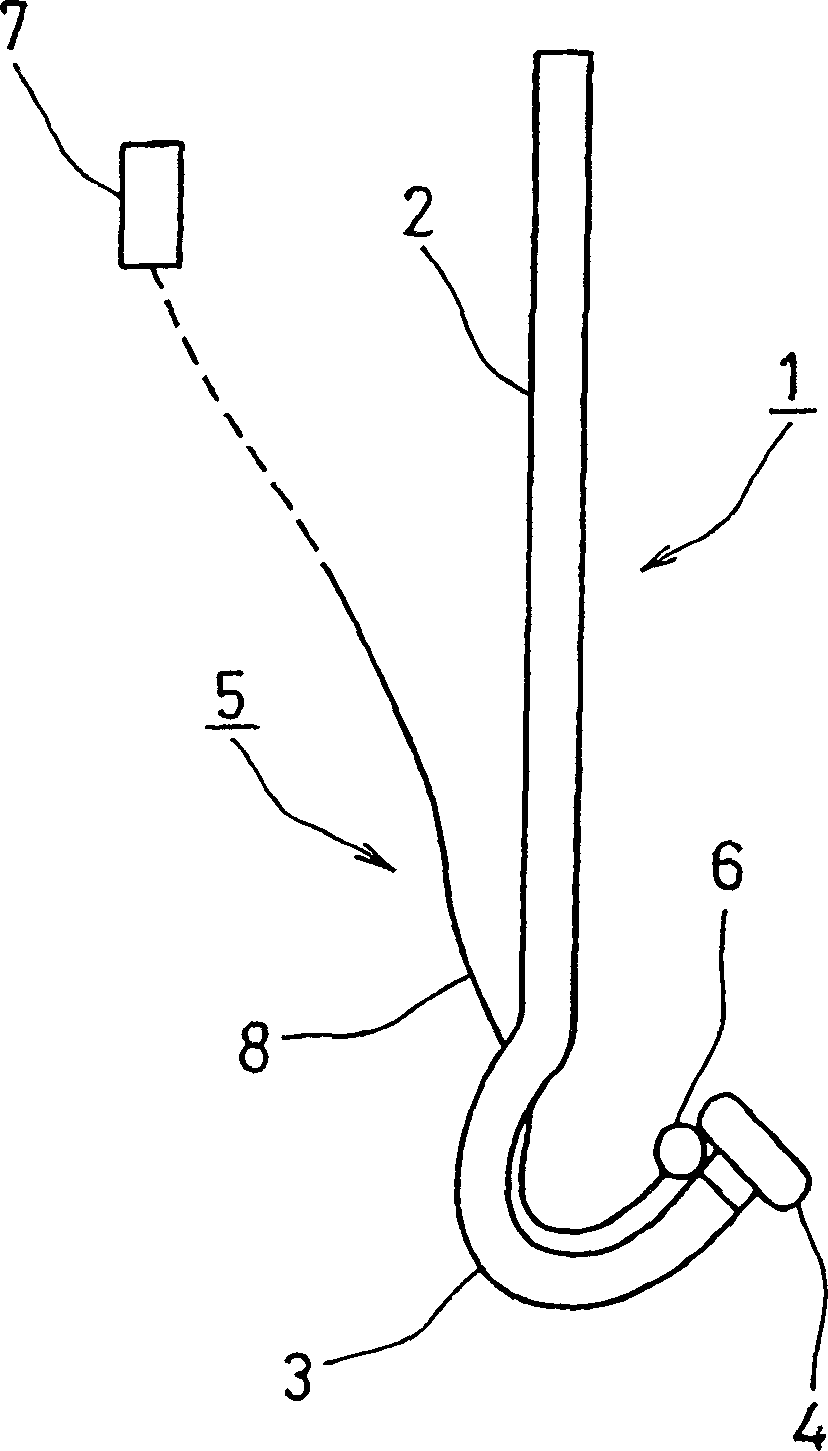
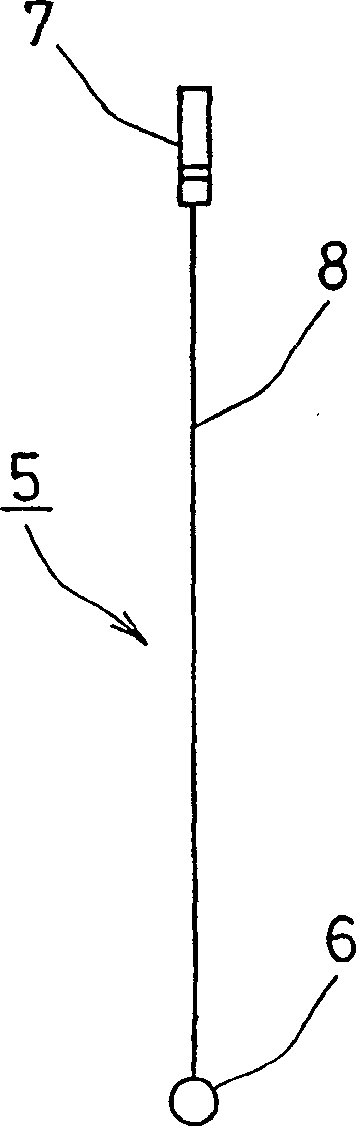
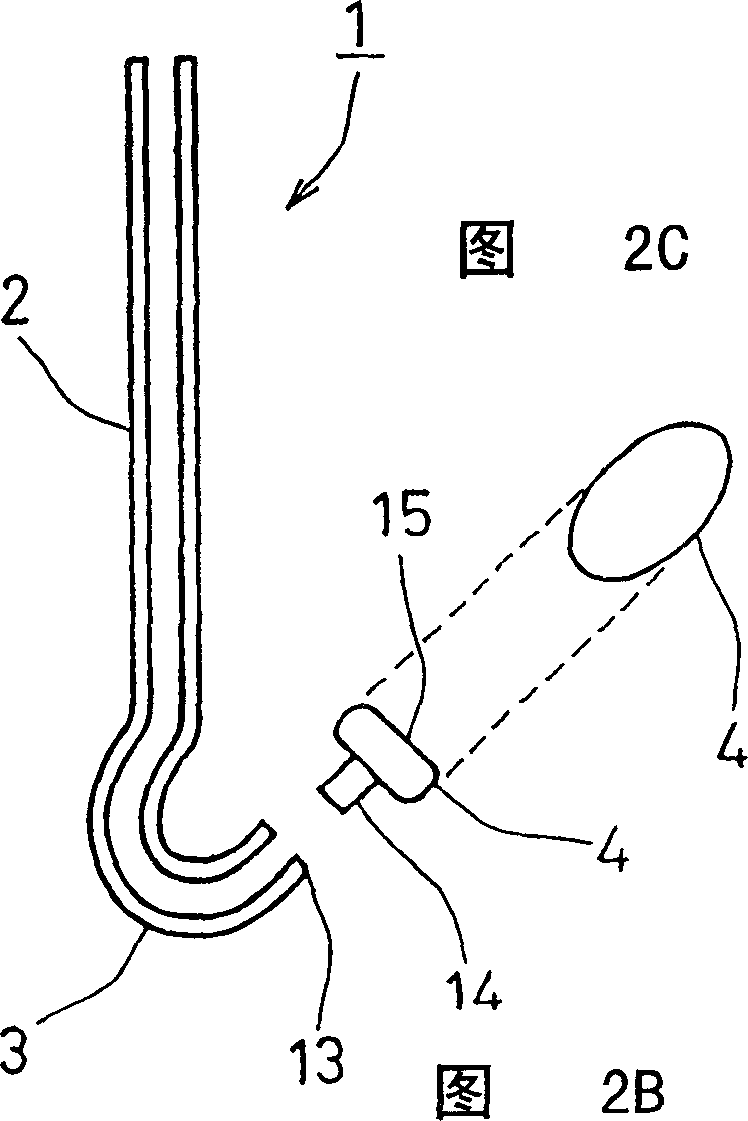
Tissue supporting device for medical treatment
The invention provides a biomedical tissue support device for supporting, during valve repair, an unhealthy part to be excised, and performing the surgical procedure swiftly and accurately. The device includes a substantially straight rod portion (2), a curved hook portion (3) that is linked to a front end of the rod portion, and a support prop (4) connected to the hook portion's front end. The support prop has a shape that is more expanded than a connection portion to the front end of the hook portion.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
Sample preparation method and sample preparation device for maldi
ActiveUS20160035553A1High detection sensitivitySaves preparation laborSamples introduction/extractionPretreated surfacesGas phaseSolvent
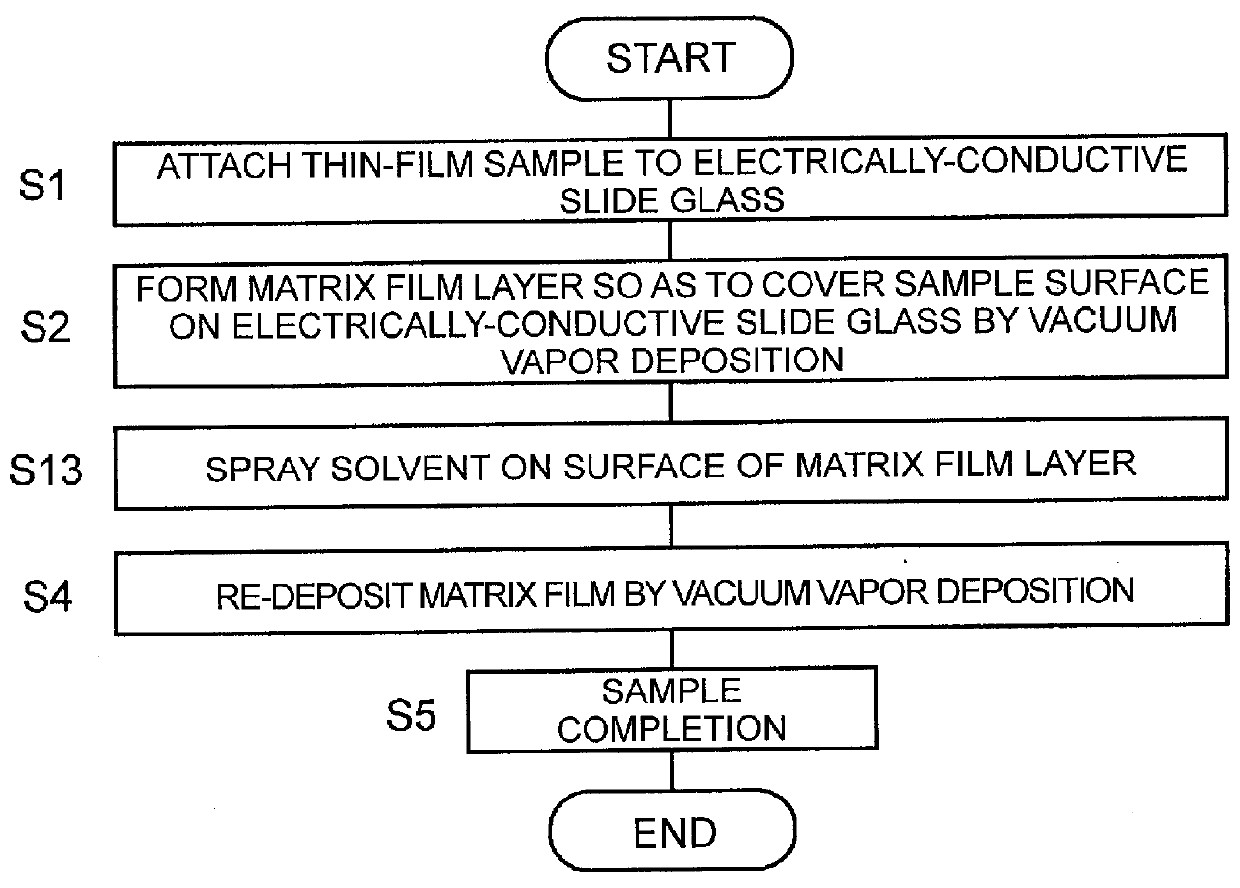
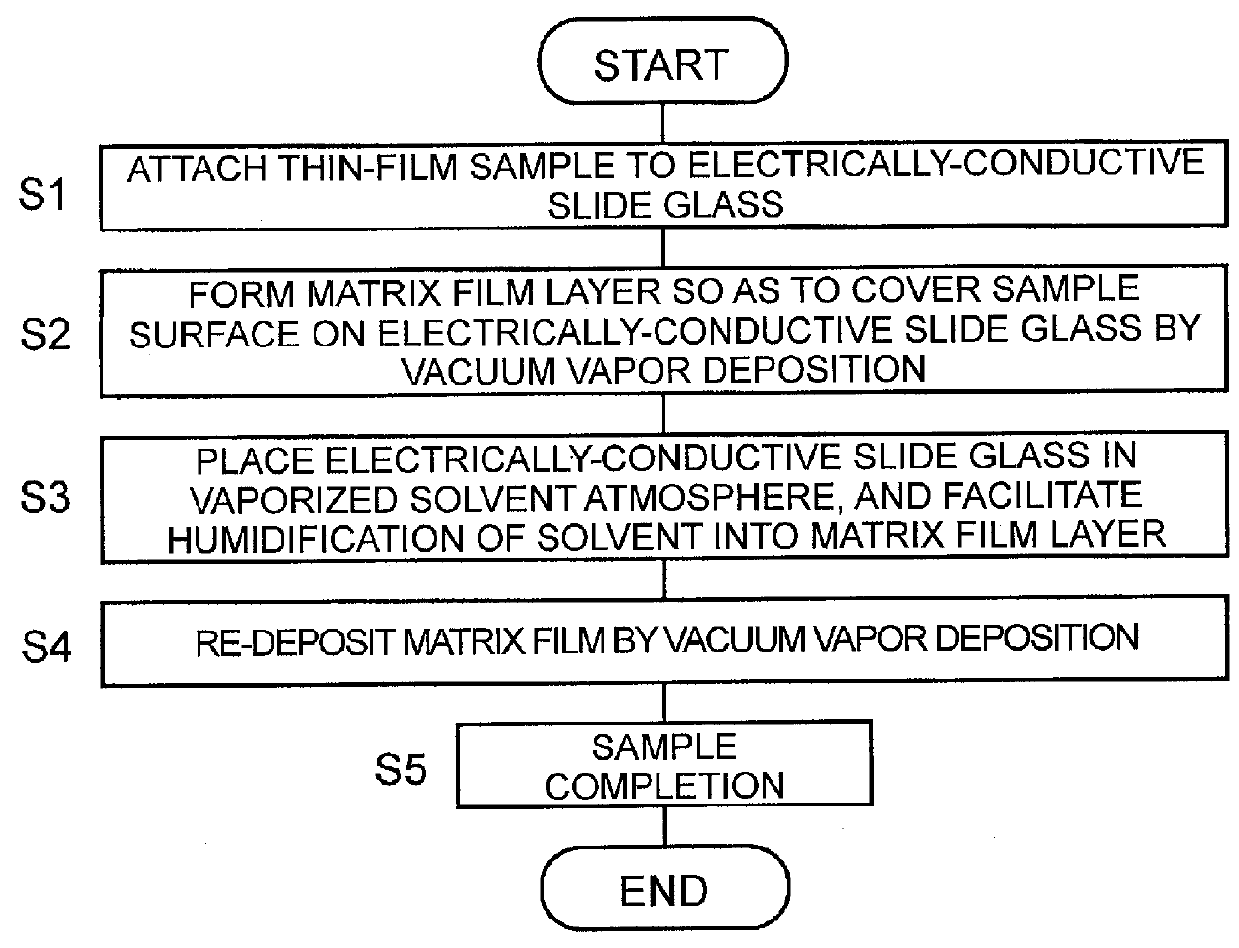
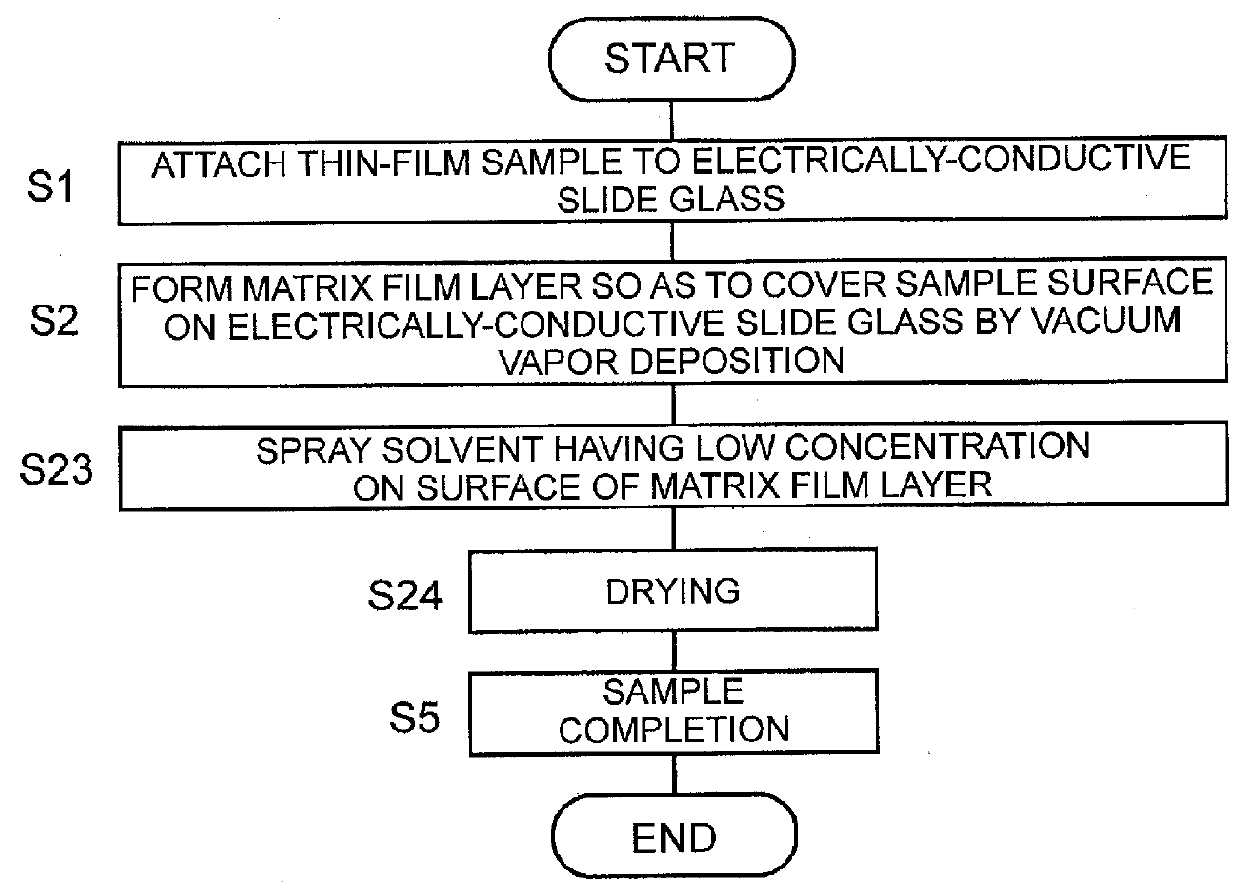
After a sample such as a biomedical tissue section is attached to an electrically-conductive slide glass (S1), the film layer of a matrix substance is appropriately formed by vapor deposition so as to cover the sample (S2). The crystal of the matrix substance in the film layer is very fine and uniform. Subsequently, the slide glass on which the matrix film layer is formed is placed in a vaporized solvent atmosphere, and the solvent infiltrates into the matrix film layer (S3). When the solvent sufficiently infiltrated is vaporized, a substance to be measured in the sample takes in the matrix and re-crystallized. Furthermore, the matrix film layer is formed again on the surface by the vapor deposition (S4). The added matrix film layer absorbs excessive energy of a laser beam during MALDI, which suppresses the denaturation of the substance to be measured and the like, so that high detection sensitivity can be achieved while high spatial resolution is maintained.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Conductive shower-shaped microcellular foaming functional film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a conductive shower-shaped microcellular foaming functional film and a preparation method thereof. The film comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.010-0.030 parts of multi-wall carbon nano tube, 9.0-29.0 parts of polymer, 0.5-1.5 parts of foaming agent and 100 parts of organic solvent. The conductive shower-shaped microcellular foaming functional film provided by the invention is prepared from the multi-wall carbon nano tube and a polymer through blending and foaming in the organic solvent by using the foaming agent. The microcellular foaming functional film is prepared by using the foaming agent in manners of forming bubbles and molding, and does not need a template, so that the conductive shower-shaped microcellular foaming functional film has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost and short production period; the product can be applied to the fields of a series of electrochemical energy conversion and storage equipment (for example, batteries and super capacitors), medical membrane separation and biomedical tissue engineering scaffolds and the like, and especially can be widely applied to the fields such as communication, medical treatment, bioscience, environment detection and the like as a miniature apparatus.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Process for synthesizing lactic acid-serine copolymer by catalyzing and carrying out ring-opening copolymerization on acetate bicyclo guanidine
ActiveCN102443166AGood compatibilityHigh biosecuritySuture equipmentsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLactideMorpholine
The invention relates to a process for synthesizing a lactic acid-serine copolymer (mol content of serine is 1-5%) by catalyzing and carrying out ring-opening copolymerization on acetate bicyclo guanidine. According to the invention, acetate bicyclo guanidine is taken as a catalyst, lactide and serine morpholine diketone are taken as monomer, the bulk is subjected to ring-opening polymerization reaction and O-benzyl removal reaction and synthesized to obtain the lactic acid-serine copolymer. The invention is characterized in that the catalyst acetate bicyclo guanidine is bionic organic guanidine salt with the characteristics of high efficient, nontoxic and metal free. The conversion rate of the copolymerization monomer is high (greater than or equal to 95%), and the yield is high (greaterthan or equal to 93%); the product contains no metal and other toxic residue, and has great biological safety; the number-average molecular weight can be adjusted in the scope of 1.5-3.0*104 and the molecular weight distribution is narrow (PDI is less than or equal to 1.30); the mol content of serine in the copolymer can be adjusted in the scope of 1-5%. The synthesized lactic acid-serine copolymer is amphiphilic functionalized biodegradation polymer, suitable for targeted and controlled release medicine carrier, and can be used for other aspects in biomedical tissue engineering field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS7871380B2Shorten diagnostic timeNone is suitable for purposeWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationTissue elasticity
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus having a function of obtaining a tomographic image and an elastic image is adaptable to not only a close examination mode, but also a screening mode, and obtains an elastic image suitable for each examination purpose. Accordingly, the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus of the present invention comprises tomographic image acquisition means for transmitting an ultrasonic wave from a probe to a body being examined, and receiving a reflection echo signal corresponding to the transmission of the ultrasonic wave to obtain a tomographic image, elastic image acquisition means having a first acquisition mode for determining a tissue elasticity amount of a biomedical tissue of the body being examined on the basis of the reflection echo signal to obtain an elastic image, and display means for displaying at least the elastic image. The elastic image acquisition means has a second acquisition mode different from the first acquisition mode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Polypeptide molecular derivative with mineralizing function for biomedicine tissue engineering and application thereof
ActiveCN110172081ACan induce mineralization regeneration repairInduced oriented growthCell culture supports/coatingTissue regenerationBone tissueBone tissue engineering
The invention provides a polypeptide molecular derivative with a mineralizing function for biomedicine tissue engineering and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials. The polypeptide molecular derivative has a molecular structure general formula of X-X-Cys-Cys-Cys-Cys-Y-Y-Z-W-NH2; wherein X is Asn or glucoylated asparagine; Y is Arg or Lys; Z is Glu or Asp;and W is phosphorylated serine or phosphorylated threonine. The polypeptide molecular derivative provided by the invention can induce the oriented growth of apatite crystals to form a biological material with a structure similar to an organism sclerous tissues microstructure; can be automatically assembled to form 3D (three-dimensional) nanometer hydrogel under the induction of calcium chloride, so as to be applied to a scaffold material for bone tissue engineering or to 3D in-situ cultivation of cells; can be compounded with collagenous fiber to induce the mineralization of the collagenous fiber, so as to be applied to study on bone tissue regeneration, as well as to induce the mineralizing regeneration and repair of cementum and dentin.
Owner:NANJING JIUZHENWEI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
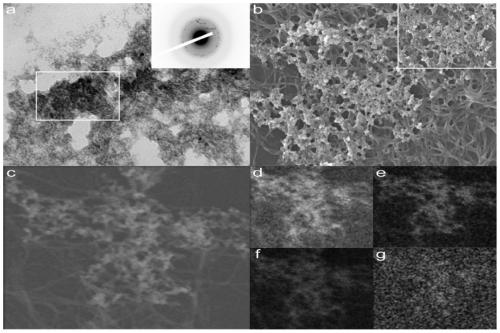
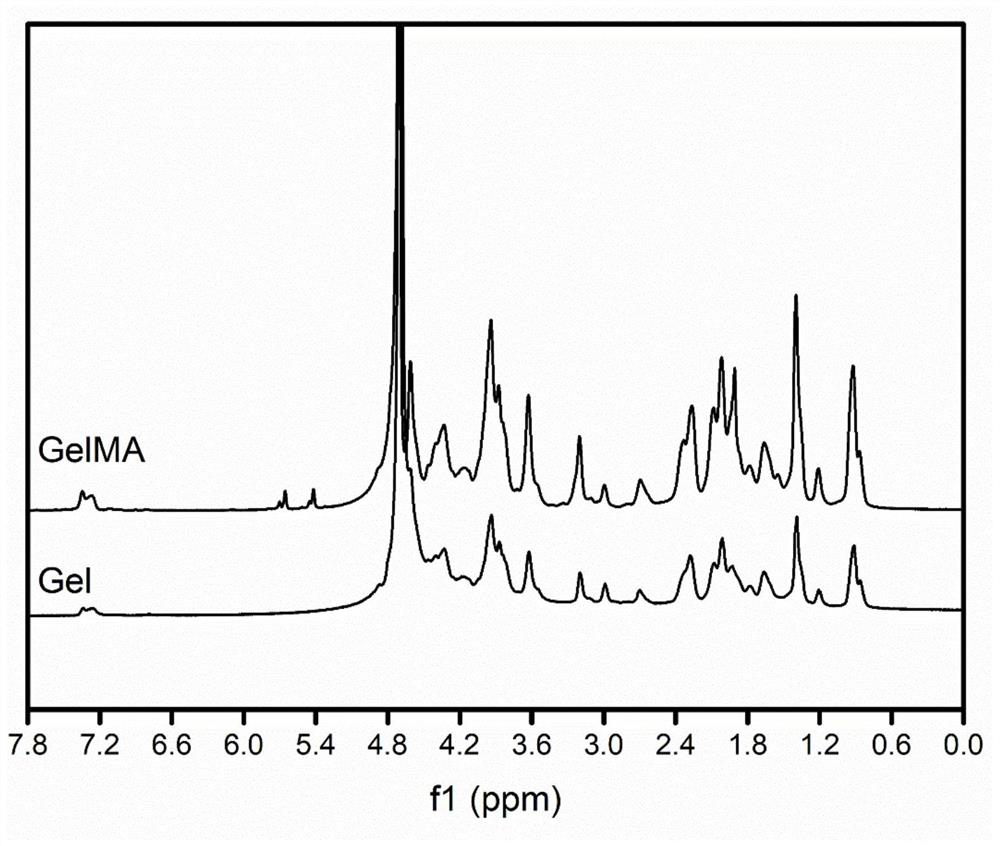
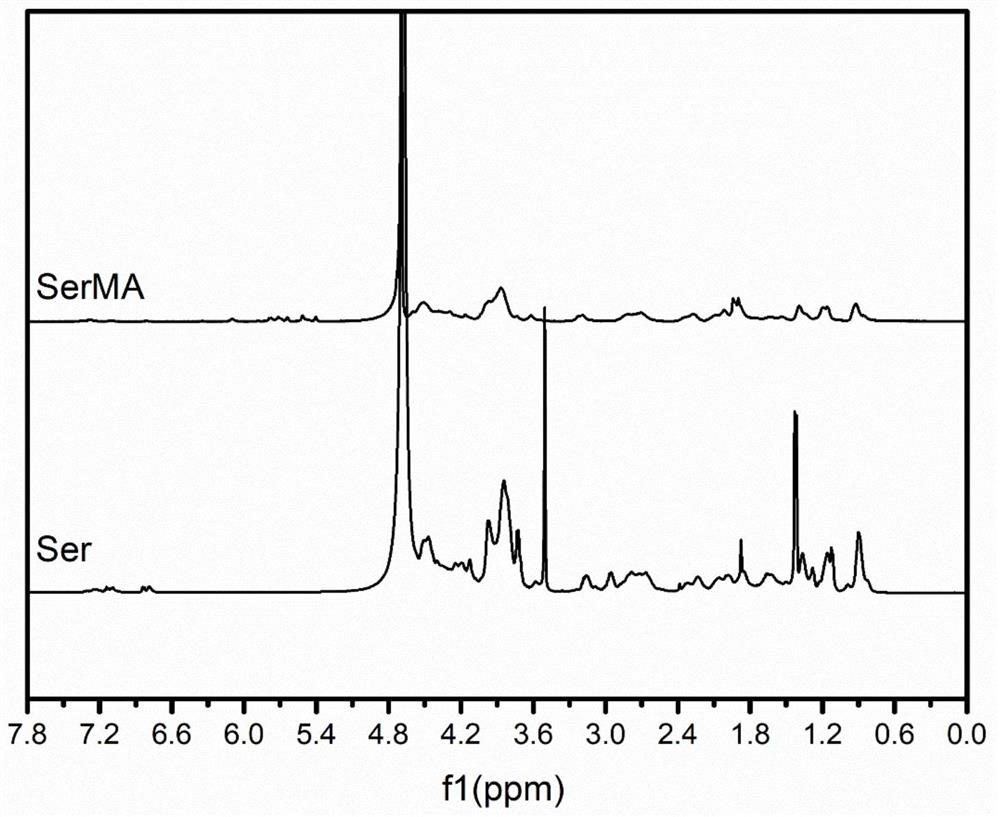
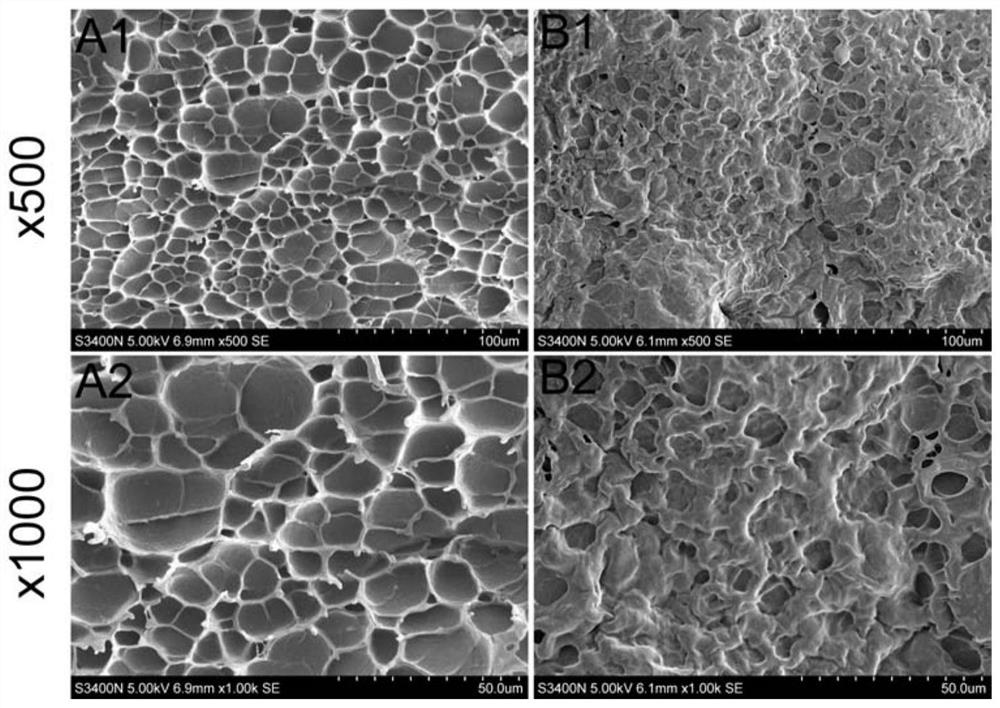
Preparation method of double-protein hydrogel
The invention provides a preparation method of double-protein hydrogel, and belongs to the technical field of medical biological materials. Methacrylated gelatin, methacrylated sericin and a blue light initiator are dissolved in water, then blue light is used for irradiation, and the double-protein hydrogel is obtained. The structure, mechanical properties, hydrogel properties and degradability ofthe obtained double-protein hydrogel can be adjusted by adjusting the concentrations and proportions of the methacrylated gelatin and the methacrylated sericin in the reaction solution, and the obtained double-protein hydrogel has good biocompatibility, can support stem cell adhesion, and has high cell encapsulation rate and cell release capacity when used for loading cells. The released cells can maintain high biological activity, and in-vitro release of stem cells can last for more than 7 days. The double-protein hydrogel is suitable for the fields of biomedicine, tissue engineering and thelike.
Owner:广州达康基因技术有限公司
Preparation method of self-repairing bionic hydrogel with toughness and adhesion
The invention discloses a preparation method of a self-repairing bionic hydrogel with both toughness and adhesion. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving agar powder in water, and heating and stirring the mixture to highly swell the mixture to obtain a uniform agar sol solution; dissolving a dopamine hydrochloride monomer into the solution, performing ultrasonic uniform dispersing; and dropwise adding a buffer solution to control the pH value of the solution so as to make the dopamine hydrochloride monomer polymerized into a short-chain network; after performing treatment, mixing an obtained product with an N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide monomer, and meanwhile, adding a photoinitiator to obtain a pre-gel solution; and putting the pre-gel solution into a mold, and carrying out an ultraviolet irradiation reaction. The multifunctional bionic double-network hydrogel prepared by the preparation method of the invention has the advantages of high mechanical strength, strong adhesion, strong self-healing capability, low cost, mild reaction and good biocompatibility, and has potential application value in the fields of biomedicine and tissue engineering and drug delivery systems.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Coating layer material suitable for adhesion and survival of neurons and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109554343AHigh densityThere is no detachment from the surface of the composite filmNervous system cellsCell culture supports/coatingNeuron adhesionColloid
The invention relates to a coating layer material suitable for adhesion and survival of neurons and a preparation method thereof. Generally speaking, the invention relates to a method for a graphene-based drug-loaded composite coating layer, wherein the method comprises the steps: the characteristics of a graphene-based material which has tissue inductivity and can be applied in the field of biomedical tissue engineering are used, a graphene oxide colloid is prepared by an improved Hummers method, then a diluted graphene oxide solution is evenly mixed with a cytosine arabinoside solution, andfinally, the graphene-based drug-loaded composite coating layer is prepared by vacuum drying treatment. The product prepared by the method can significantly promote the adhesion and survival of the neuron cells. The method provided by the invention is simple and easy to operate, low in cost, good in consistency and easy to transform. A prepared graphene-based film has broad application prospects and practical value in the field of tissue engineering.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Photocuring 3D printing preparation method of degradable meniscus scaffold
ActiveCN112220969AGood biocompatibilityMatching biomechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationPolymer scienceComputer printing
The invention relates to a photocuring 3D printing preparation method of a degradable meniscus scaffold, and belongs to preparation of biomedical tissue engineering scaffold materials. The photosensitive resin for printing the meniscus scaffold is prepared from the following raw material components in parts by weight of 10-80 parts of urethane acrylate, 20-80 parts of acrylate monomer, 0.5-3.0 parts of free radical type photoinitiator and 0.001-0.5 part of defoaming agent. The method comprises the following steps of adding photosensitive resin into a resin tank of a 3D printer, carrying out equipment printing according to set printing parameters to obtain a meniscus scaffold blank, cleaning with ethanol, carrying out ultraviolet curing, and carrying out oven curing to obtain a meniscus scaffold sample piece. The meniscus scaffold provided by the invention is good in biocompatibility and has mechanical properties similar to those of a natural meniscus, and photocuring printing has the characteristics of high precision, high speed and capability of accurately controlling a three-dimensional structure and a porous structure of the scaffold.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Bionic cell-containing large bone cartilage biological scaffold and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114129775APromote reconstructionAvoid necrosisAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOsteochondral scaffoldBiology
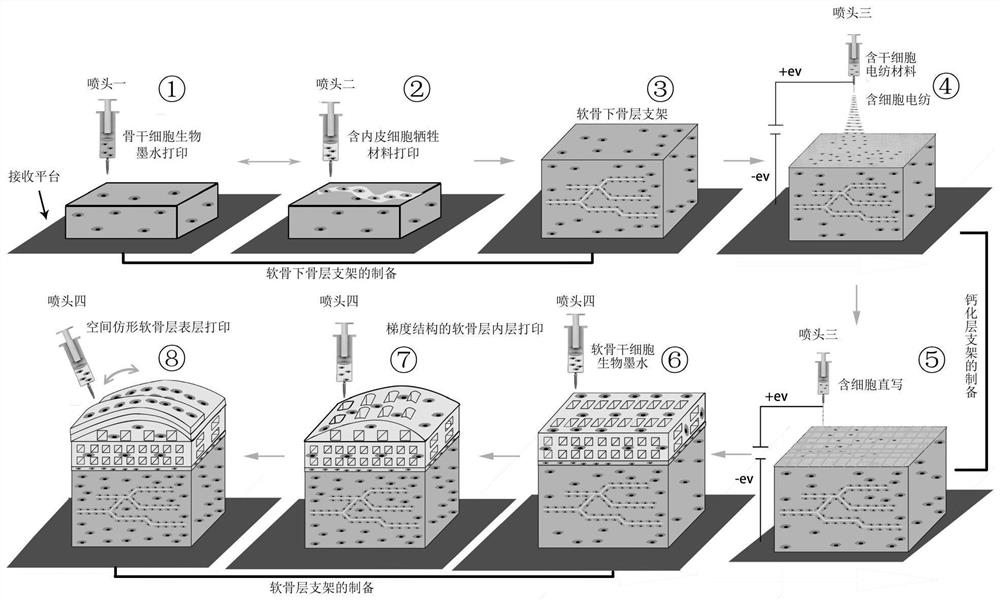
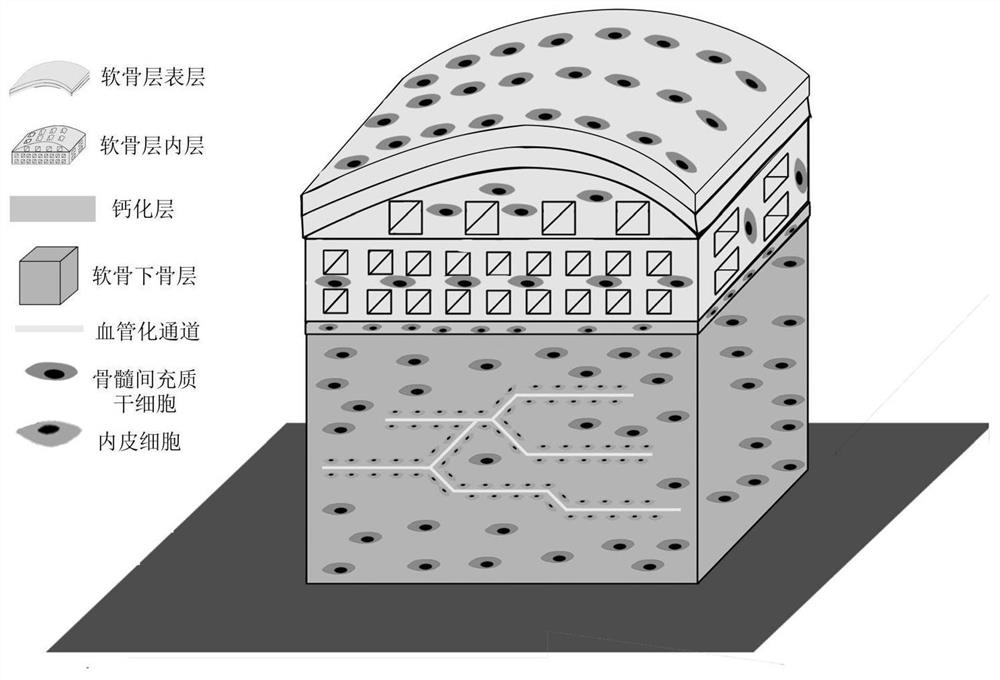
The invention provides a bionic cell-containing large bone cartilage biological scaffold and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedical tissue engineering. According to the invention, a composite process including a cell extrusion 3D printing technology, a cell electrostatic spinning technology, a cell electrohydrodynamic direct writing technology and a sacrificial material method is adopted, so that not only can the formation of an integrated osteochondral scaffold with a bionic human osteochondral tissue structure be realized, but also the preparation of a cell-containing osteochondral scaffold can be realized; a solution is provided for construction of a large osteochondral biological scaffold, and integrated repair and reconstruction of osteochondral tissues are promoted.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Container for processing section samples, processing method for section samples, and processing apparatus for section samples
InactiveUS7616302B2Precise positioningEasy to handleImmobilised enzymesCombination devicesThin sectionBiomedical tissue
The container comprises a cylindrical member 20 which constitutes the side wall member, a bottom member 30 which is in contact with the bottom plane of the cylindrical member 20 and which constitutes the bottom part, and an engaged fixing part 35 for engaging the cylindrical member 20 with the bottom member 30; the cylindrical member 20 and the bottom member 30 sandwiches the carrier tape T from one side T1 of the carrier tape T and from the other side T2 of the carrier tape T, respectively, such that one of the plural thing section samples P1 may be disposed inside the cylindrical member 20. Accordingly, without cutting a sequence of tapes carrying thereon the thin section samples of biomedical tissues, each of the thin section samples of the biomedical tissues can be individually processed with different chemicals depending on the required observation for various types of biomedical tissues.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
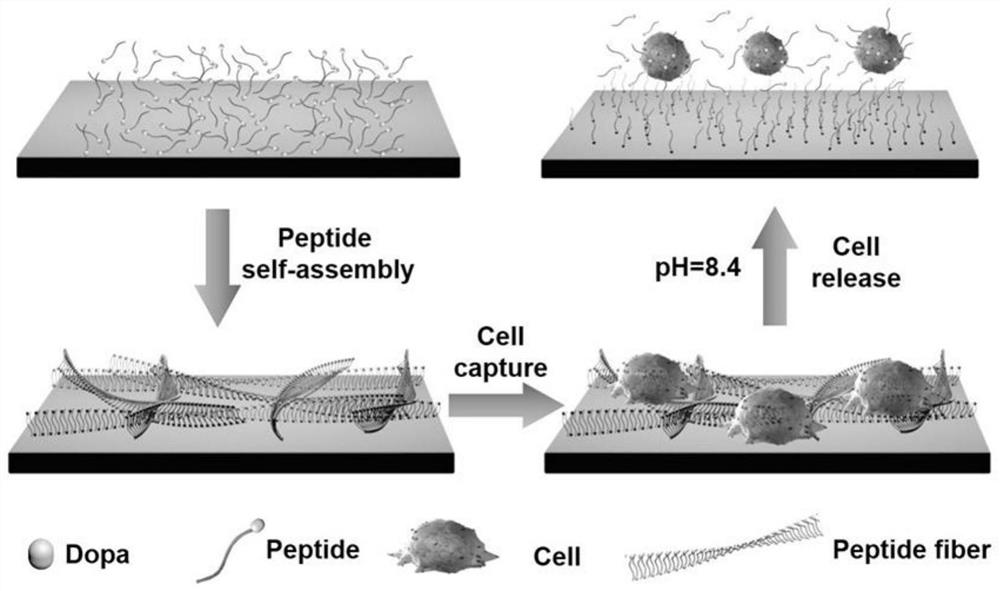
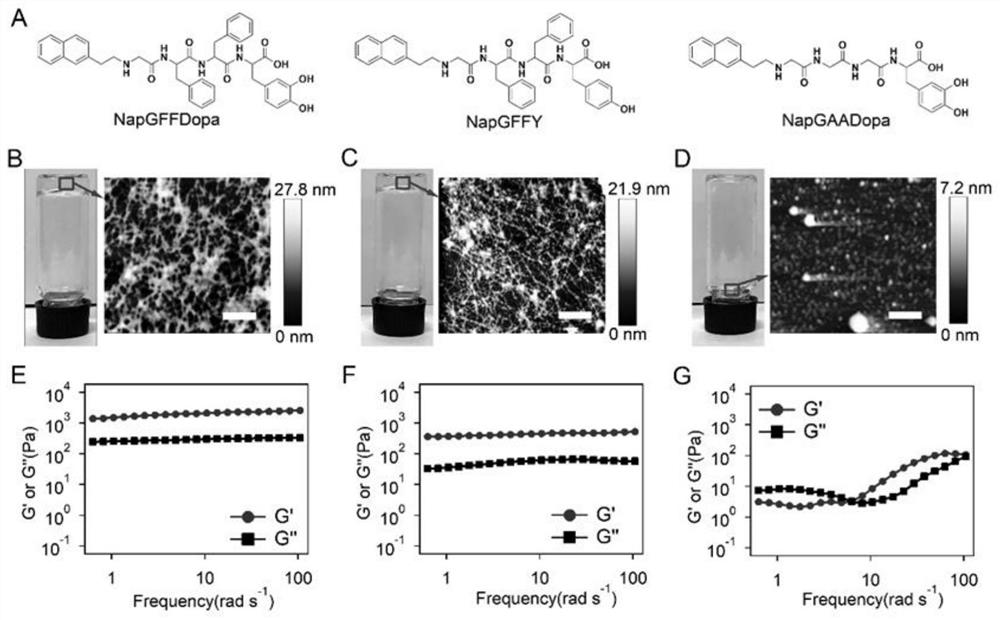
Novel bionic adhesive material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112126405AGood biocompatibilityImprove the environmentNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesProtein adhesivesBiologyBiomedicine
The invention relates to a novel bionic adhesive material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The intelligent adhesive material is formed by self-assembly of dopa-containing polypeptidenanofibers; and the dopa-containing intelligent polypeptide nanofiber material has very excellent biological adhesion performance, can be widely applied to the fields of biomedicine, tissue engineering, intelligent soft materials and the like, and is suitable for capturing and releasing various biological cells so as to carry out research work of research and development of various biological materials and medicines.
Owner:南京大学深圳研究院
A preparation method of hydrogel composite biological patch for repairing abdominal wall defect
ActiveCN110038163BHelps growGood biocompatibilityTissue regenerationProsthesisVascularizesCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical tissue engineering, and discloses a method for preparing a hydrogel composite biological patch for repairing abdominal wall defects. In the preparation method, pig dermis de-extracellular matrix powder and gelatin are used as biomaterials, and a composite hydrogel biopatch is prepared by mold casting and enzymatic cross-linking forming techniques. The present invention mixes the biomaterial porcine dermis de-extracellular matrix powder with gelatin to prepare the patch, not only the hydrogel patch exhibits excellent biocompatibility, but also enhances the biomechanical properties of the hydrogel patch, solving the problem There are deficiencies with single material patches. At the same time, the preparation process is simple and the required materials are easy to obtain. The composite biological patch scaffold prepared by the present invention contains pre-vascularized channels, which is helpful for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients and the discharge of metabolic waste, and accelerates the vascularization of tissues; in addition, the through-channel structure helps cells and tissues in the scaffold The ingrowth can accelerate the reconstruction of abdominal wall tissue, help to solve the existing technical bottleneck of biological mesh, and effectively improve the therapeutic effect of abdominal wall defect repair.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Medical image processing device and medical image processing method
ActiveCN101594817BImprove detection efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
A medical image processing device is characterized in comprising an edge extracting unit for extracting a two-dimensional image of a biomedical tissue input from a medical image picking-up device; a three-dimensional model estimating unit for estimating a three-dimensional image of the biomedical tissue; a local region setting unit for setting a local region where a pixel of interest is treated as the center in the two-dimensional image; a judging unit for judging whether or not the local region is divided by at least a part of the edge extracted in the extracting unit; a shape characteristiccalculating unit for calculating a shape characteristic amount of the pixel of interest while using three-dimensional data of regions that are not divided by the edge in the edge extracting unit out of the local region based on a judging result of the judging unit and that correspond to a region where the pixel of interest exists; and a projecting shape detecting unit for detecting a projecting shape based on a calculation result of the shape characteristic amount calculating unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
A kind of photocrosslinkable hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to photo-crosslinkable hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. A matrix of the hydrogel comprises keratin; the keratin contains a plurality of free sulfhydryl groups. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the keratin into a buffering solution, and adding a photoinitiator; after sufficiently dissolving, illuminating under an ultraviolet lamp to form the photo-crosslinkable hydrogel. According to the hydrogel provided by the invention, the gelling time of materials is short, and the mechanical strength is high; the photo-crosslinkable hydrogel can be used for in-vivo injection and gelling, and has wide application value in the aspects of biomedicines, tissue engineering, medicine delivery and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method for tissue engineering corium
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical tissue engineering, and relates to a tissue engineering dermis and a preparation method thereof. The characteristics of the method include the acquisition and expanded culture of skin fibroblasts, the preparation of extracellular matrix complexes, the preparation of biological scaffold materials, the preparation of medium, the preparation of tissue engineered dermis and three-dimensional culture. The prepared tissue engineered dermis is constructed by compounding skin fibroblasts on the surface of biological scaffold materials. The tissue engineered dermis prepared by the invention not only has certain elasticity and toughness, but also has short culture time and no obvious immune rejection reaction, which is similar to the structure of natural dermis. It will play a multi-faceted role in clinical treatment.
Owner:陕西艾尔肤组织工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com