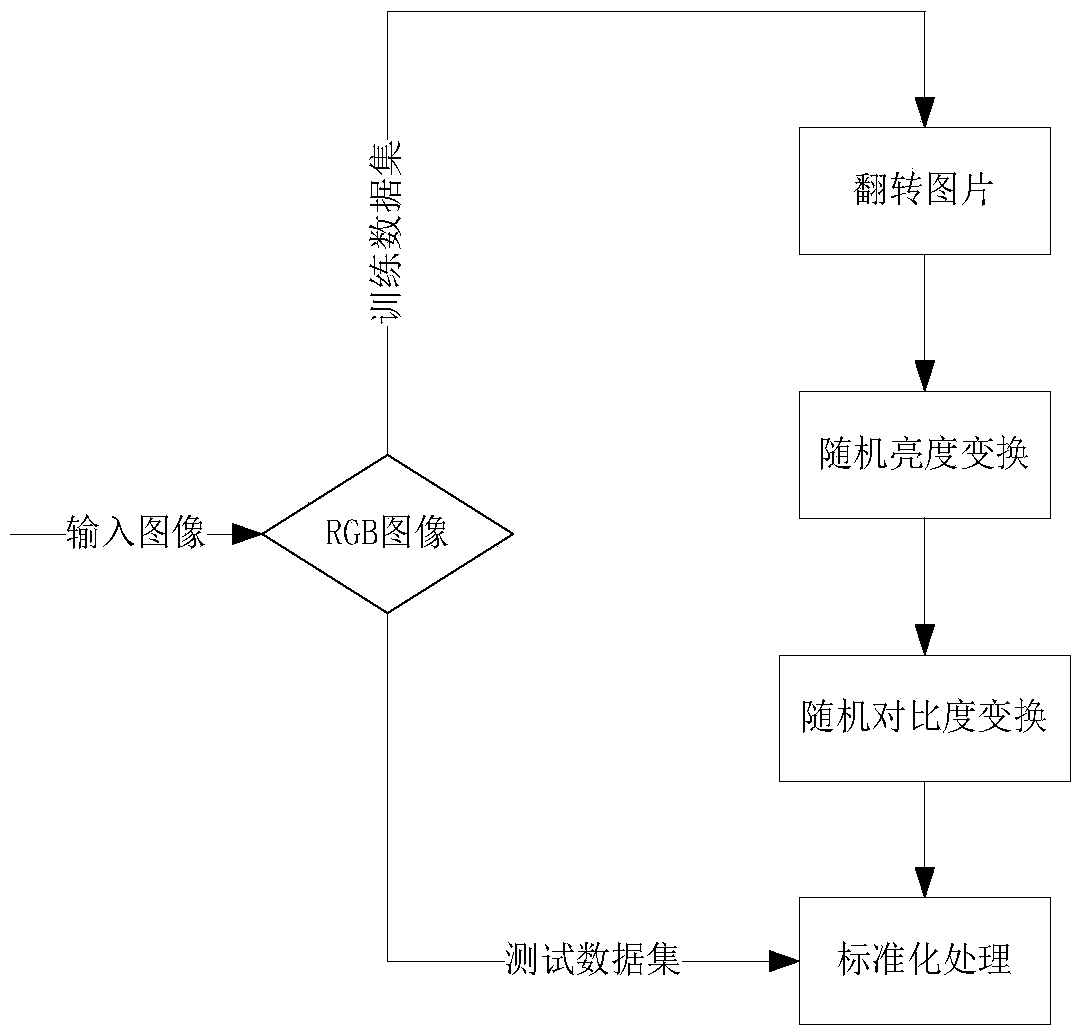
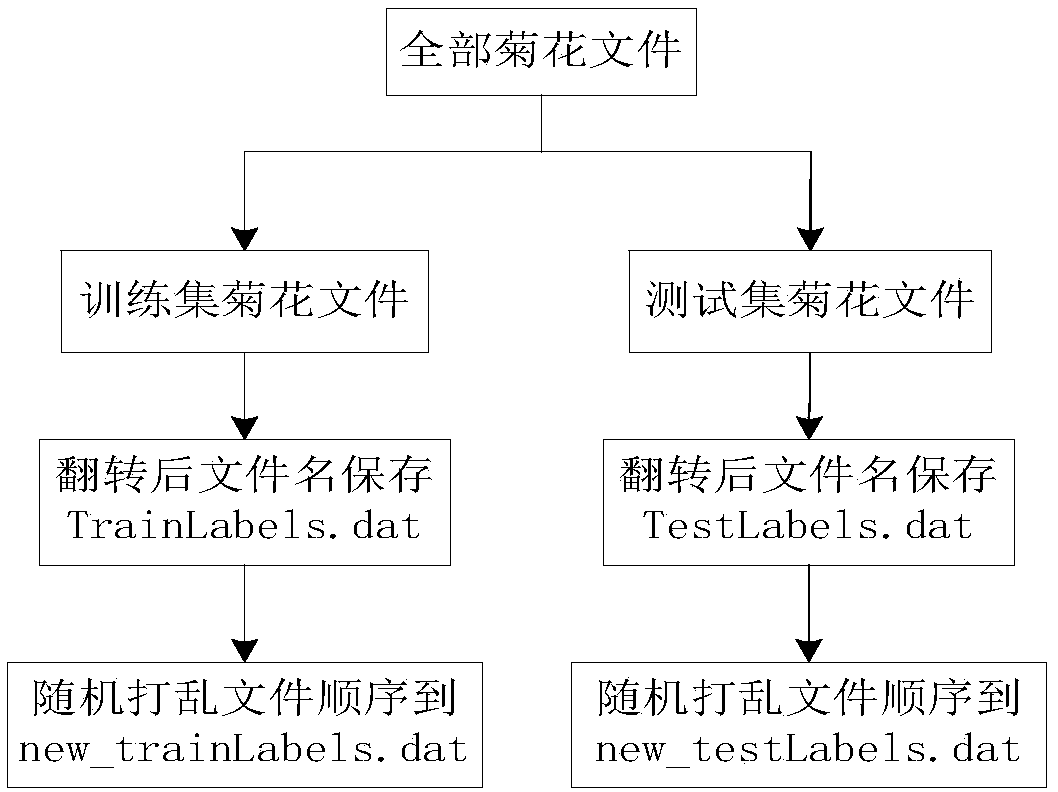
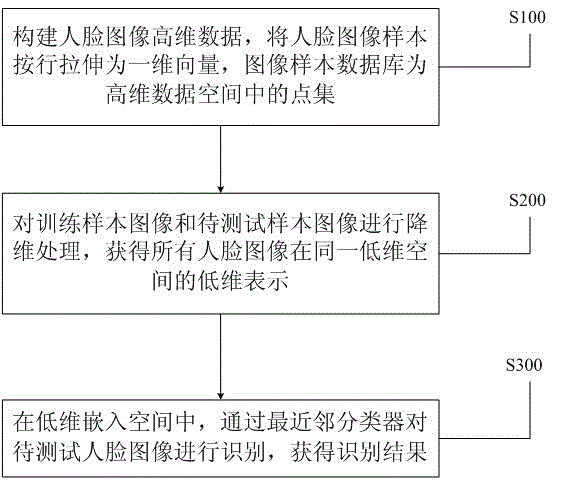
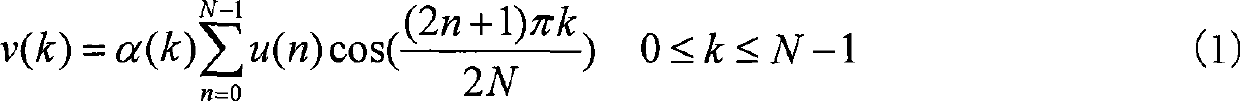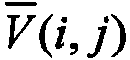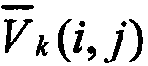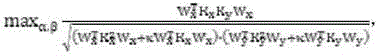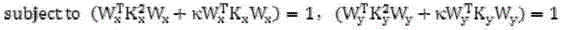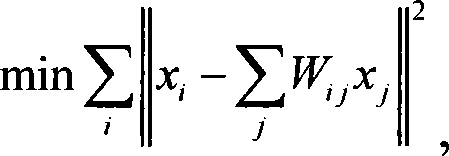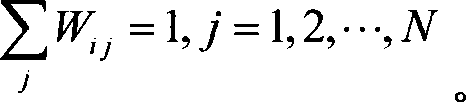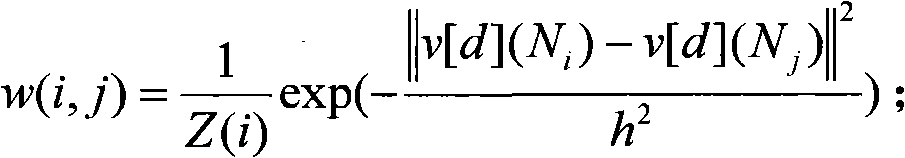Patents
Literature
401 results about "Lower dimensional space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Monocular tracking of 3D human motion with a coordinated mixture of factor analyzers
ActiveUS7450736B2Efficiently and accurately trackingSmall sizeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOffline learningMultiple hypothesis tracking
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Monocular tracking of 3D human motion with a coordinated mixture of factor analyzers
ActiveUS20070104351A1Efficiently and accurately trackingSmall sizeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOffline learningMultiple hypothesis tracking
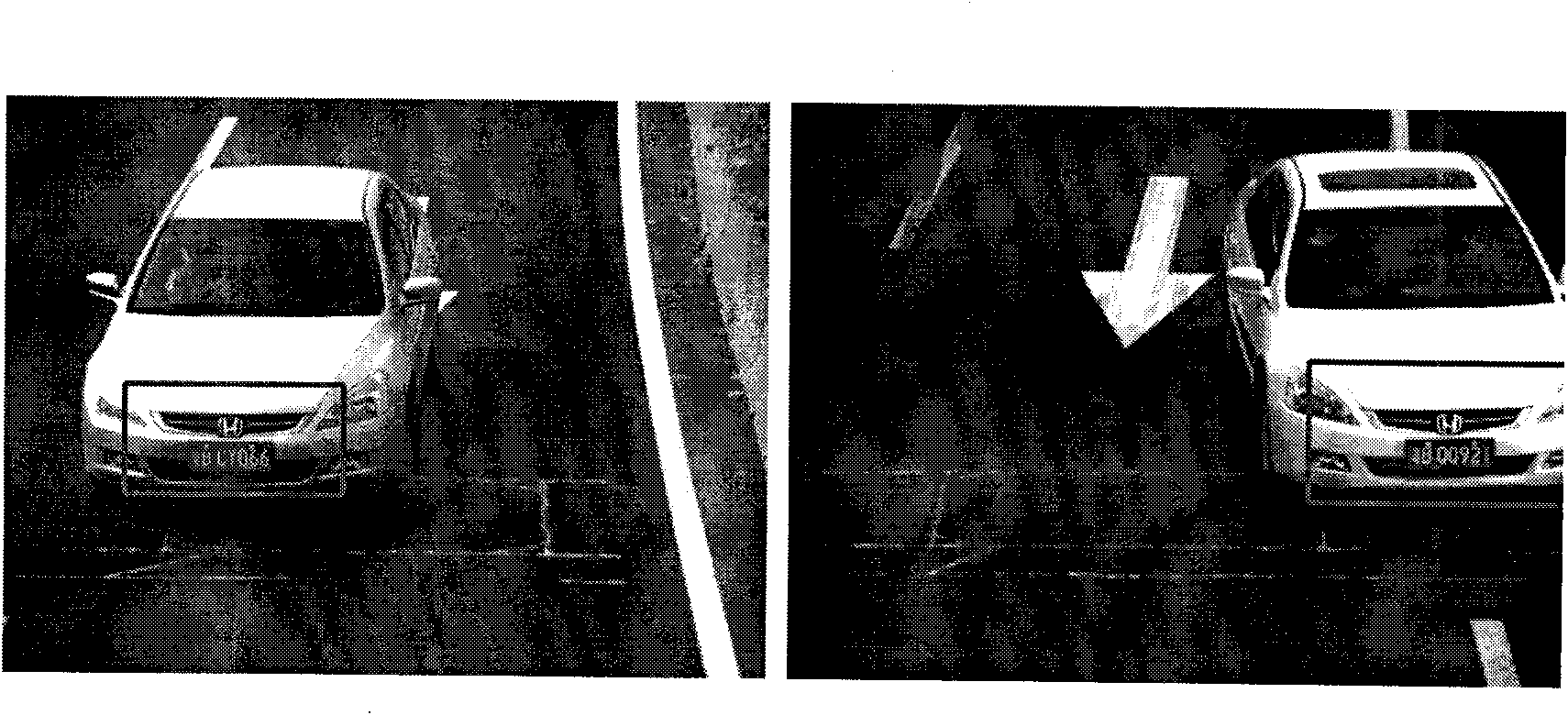
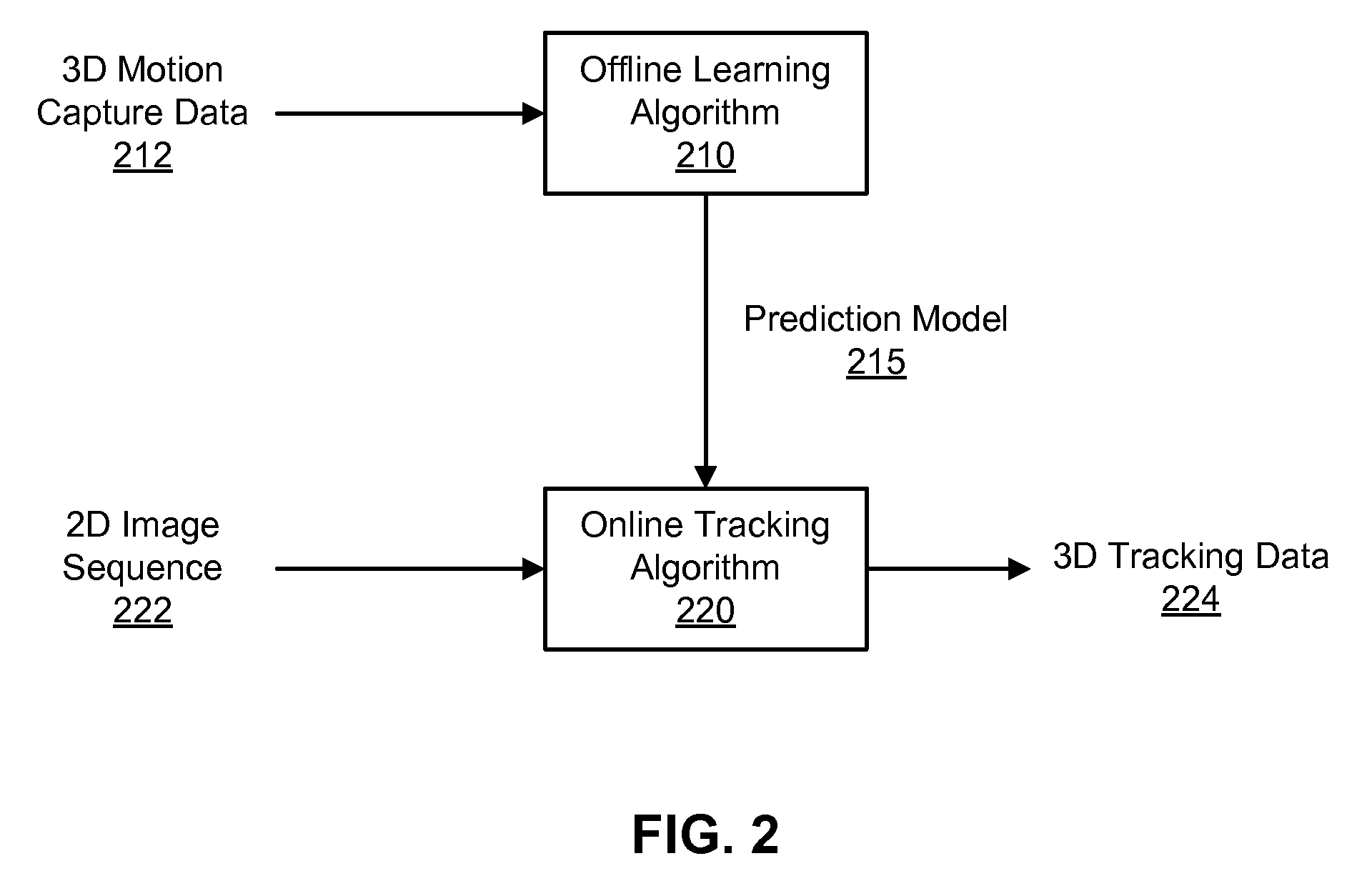
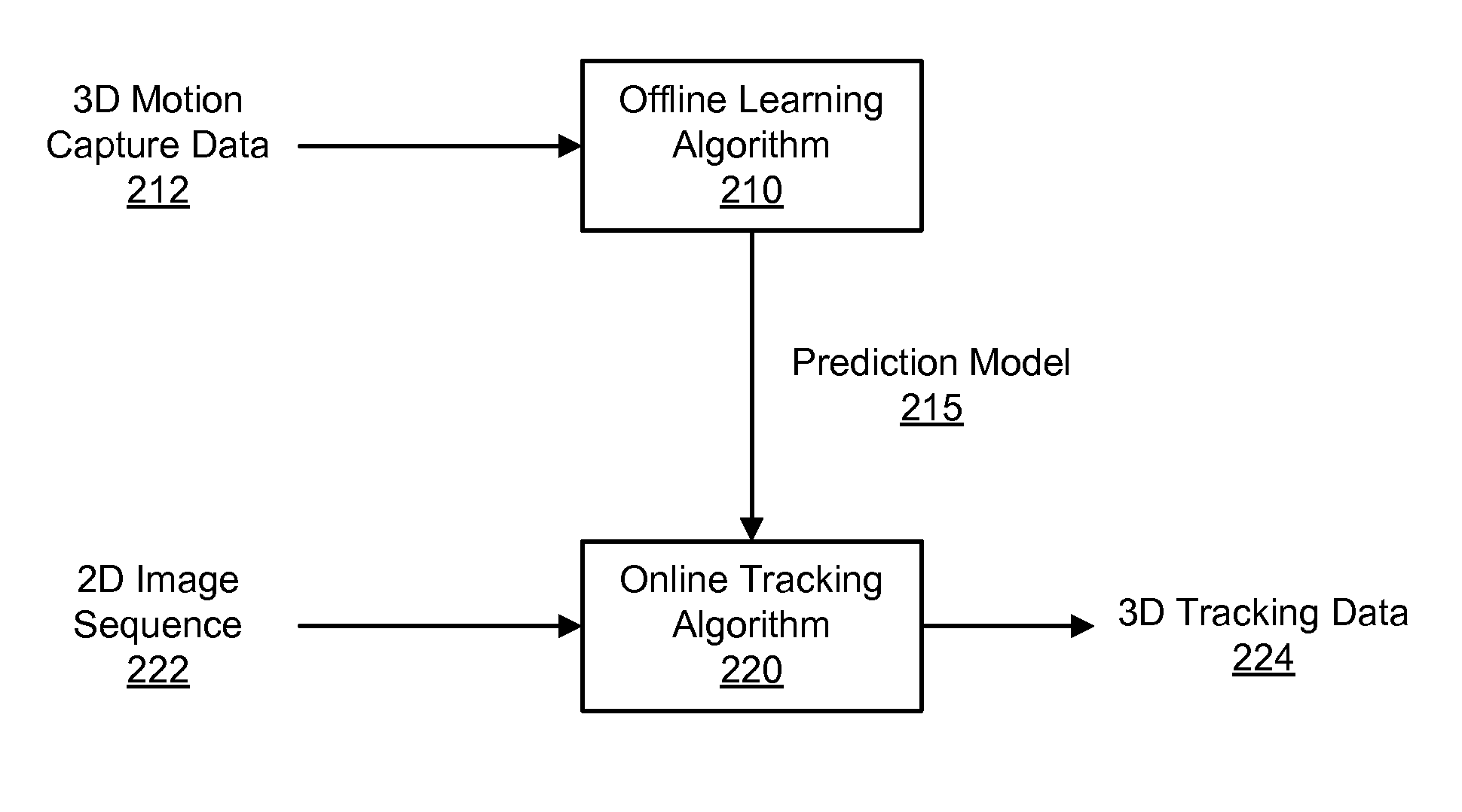
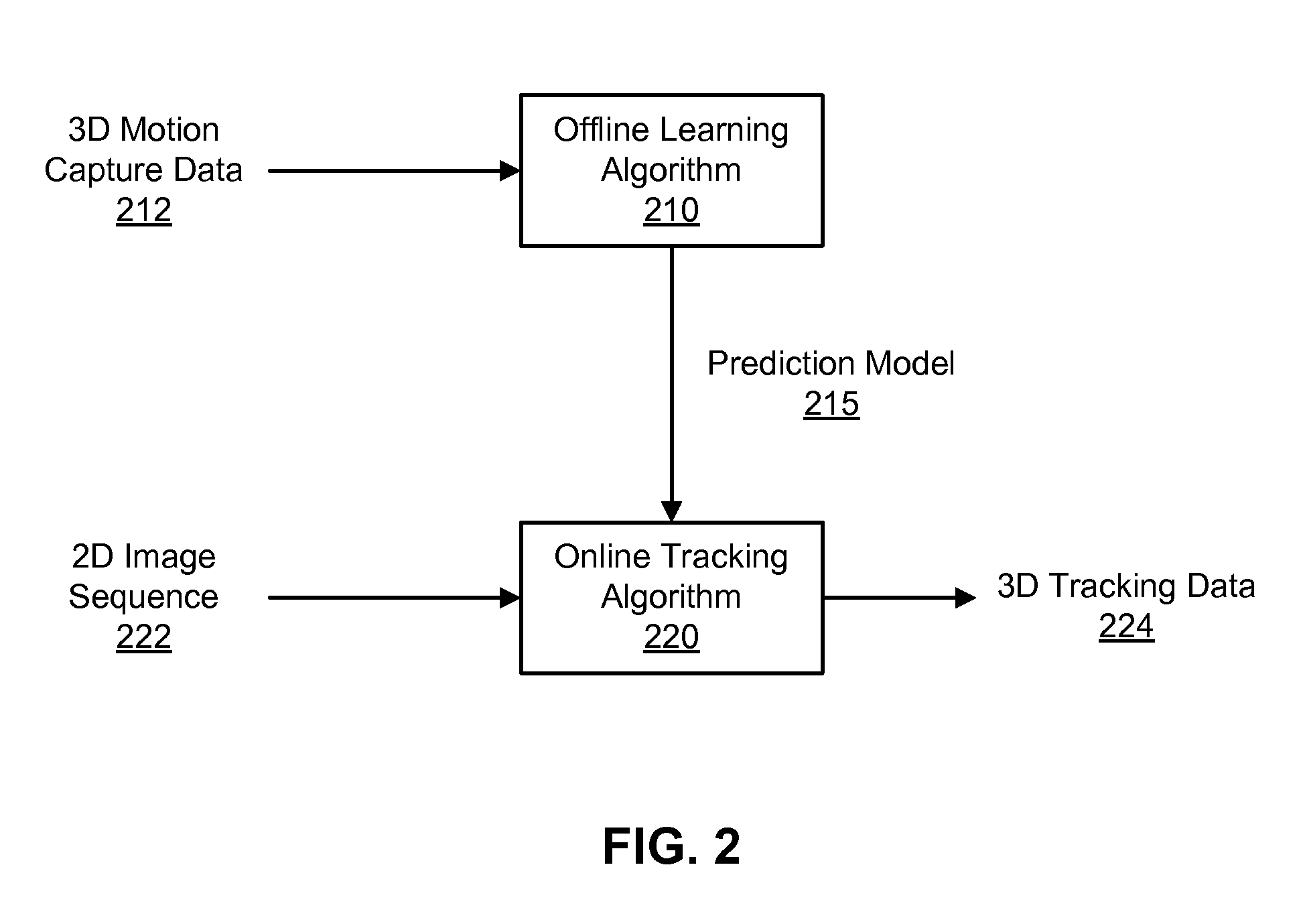
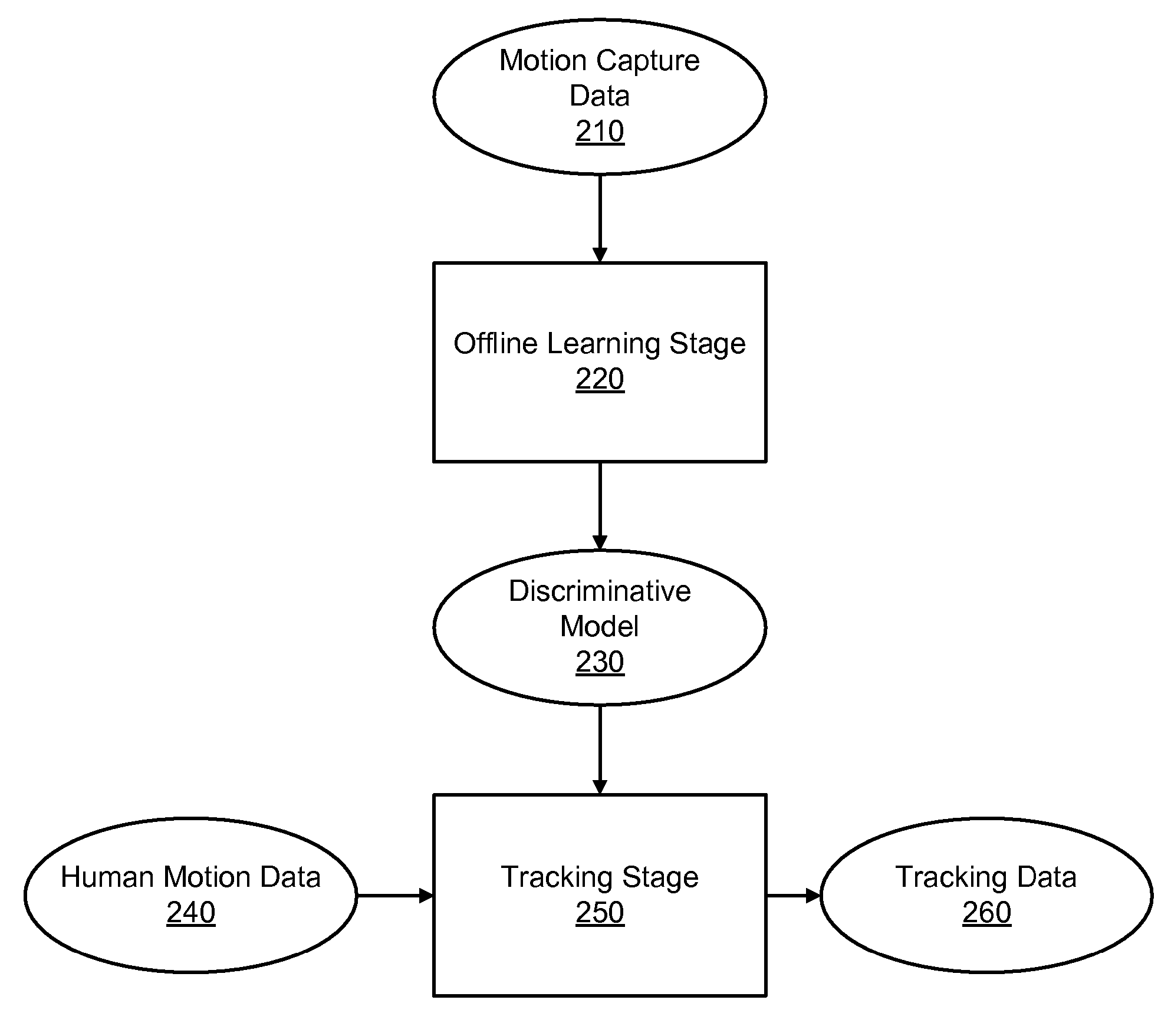
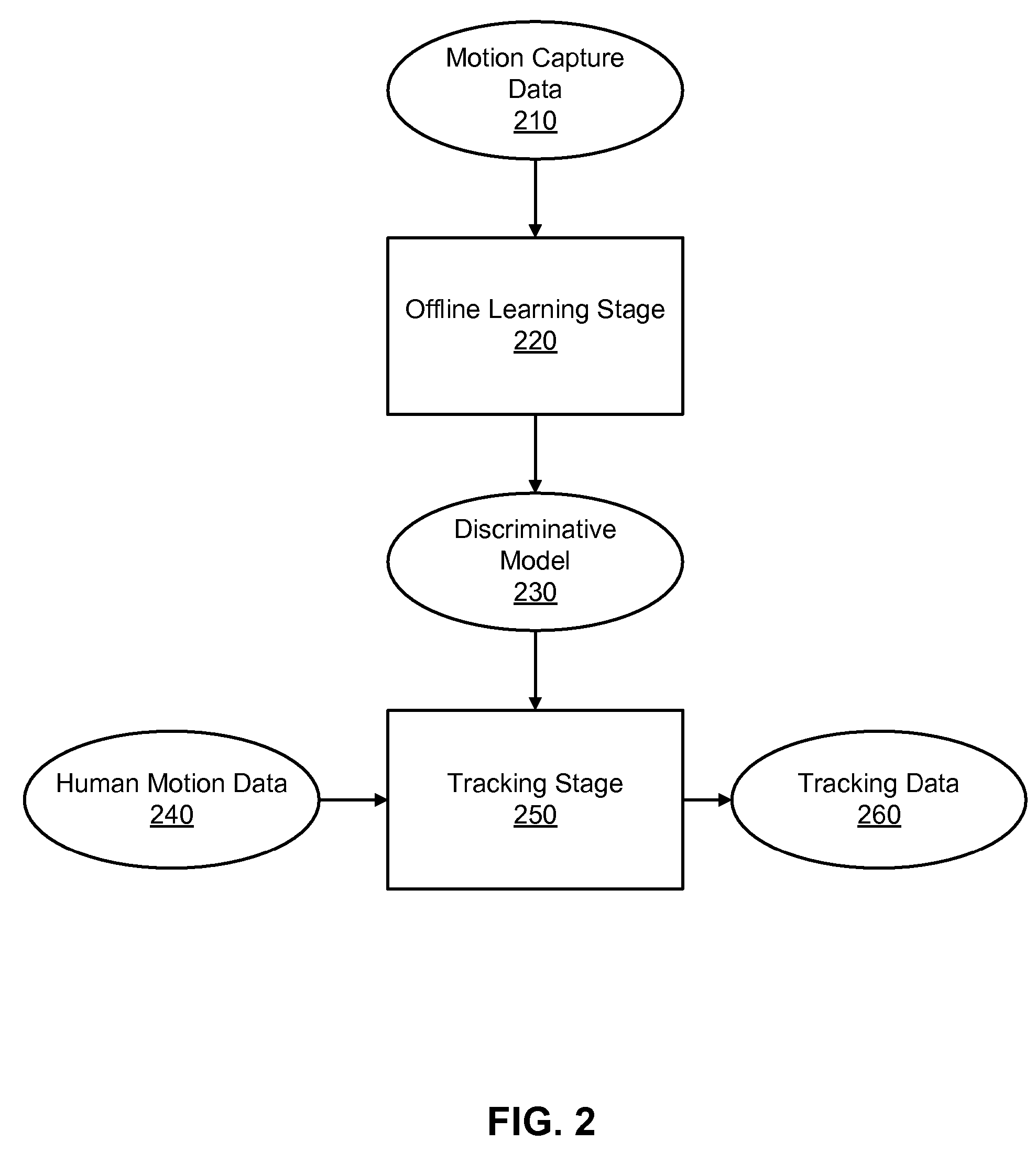
Disclosed is a method and system for efficiently and accurately tracking three-dimensional (3D) human motion from a two-dimensional (2D) video sequence, even when self-occlusion, motion blur and large limb movements occur. In an offline learning stage, 3D motion capture data is acquired and a prediction model is generated based on the learned motions. A mixture of factor analyzers acts as local dimensionality reducers. Clusters of factor analyzers formed within a globally coordinated low-dimensional space makes it possible to perform multiple hypothesis tracking based on the distribution modes. In the online tracking stage, 3D tracking is performed without requiring any special equipment, clothing, or markers. Instead, motion is tracked in the dimensionality reduced state based on a monocular video sequence.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Optimized human face recognition method and apparatus
InactiveCN101329724AReduce dimensionalityImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisCharacteristic space
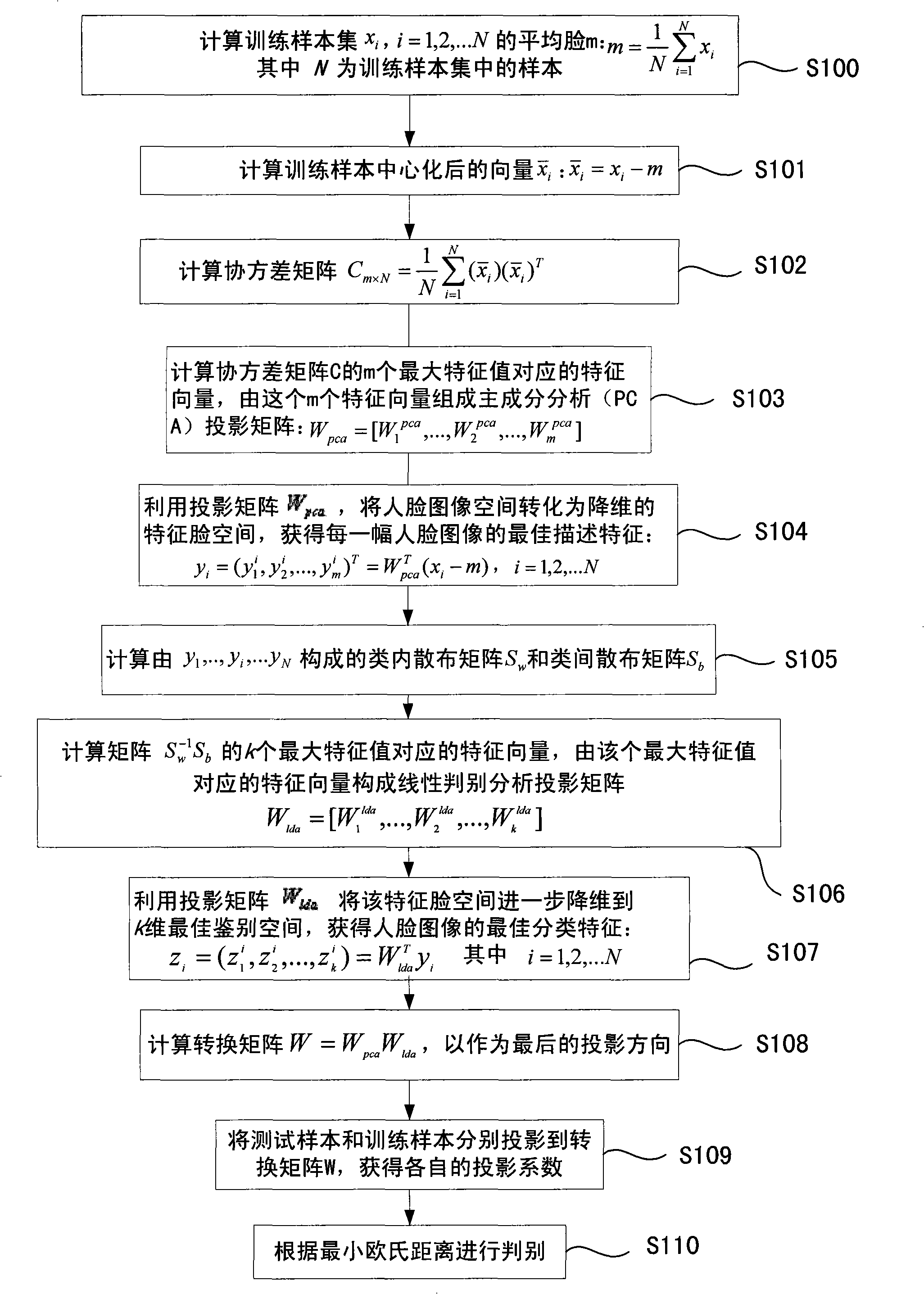
The invention discloses an optimized face recognition method and a device thereof, which improve the rate of facial image recognition. The technical proposal is that: the method and the device combine principal component analysis and linear discriminant analysis to solve the recognition problem; namely, the principal component analysis is carried out first before the conduction of the linear discriminant analysis so as to obtain relatively low dimensional space, then the space is utilized to carry out the linear discriminant analysis, and therefore, an intra-class dispersion matrix can not be caused and the process of the linear discrimination is effective. The invention firstly adopts the principal component analysis to obtain the best feature description, based on which, optimum identifying features are obtained by adopting the linear discriminant analysis, thereby greatly reducing the space dimension of facial features; finally, a minimum distance method is adopted to carry out classification and identification and therefore the rate of recognizing human faces is evidently increased. The method and the device of the invention are applied to face recognition.
Owner:上海天冠卫视技术研究所 +1
Human face identification method based on independent characteristic fusion
ActiveCN101388075ARemove redundant featuresReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorGlobal information
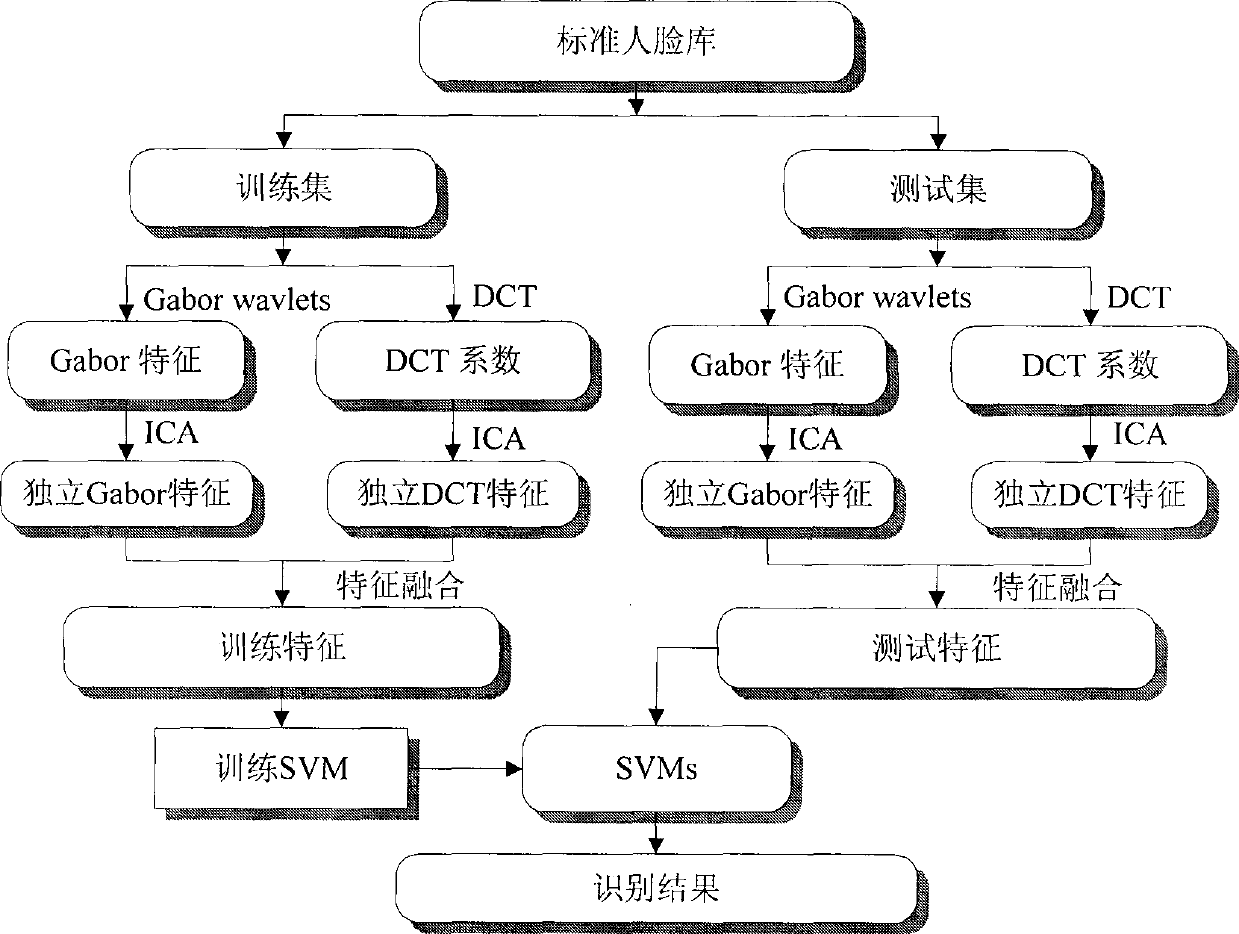
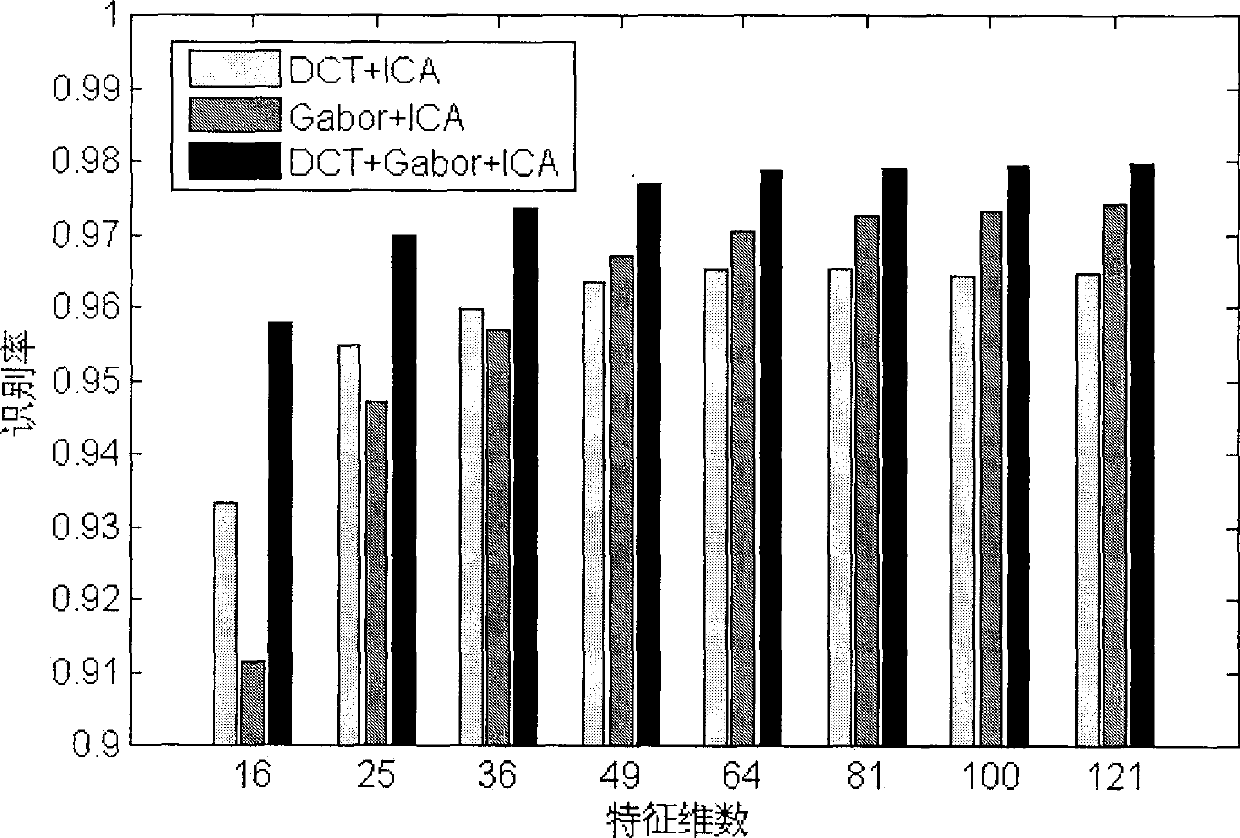
The invention discloses a face identification method which blends a global feature and a local feature based on an ICA. As a DCT can efficiently transit a high-dimensional face image into a low-dimensional space and reserves most of identifiable information of the image, the DCT is suitable for extracting the global feature of the image, while a Gabor wavelet transformation is suitable for extracting the local feature and the classification feature of the image, and the two features are widely applied to the face identification. Based on the two methods, we bring in the ICA technology to extract the independent Gabor feature and the independent DCT feature of the image, then efficiently blends the independent Gabor feature and the independent DCT feature to obtain a novel independent feature, enables the novel independent feature to have the local information of the Gabor feature and the global information of the DCT feature, efficiently reduces the dimension of a feature vector, and removes superfluous features. Finally, the blended independent feature is used for the SVM to realize the face classification identification.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Object Recognition with 3D Models
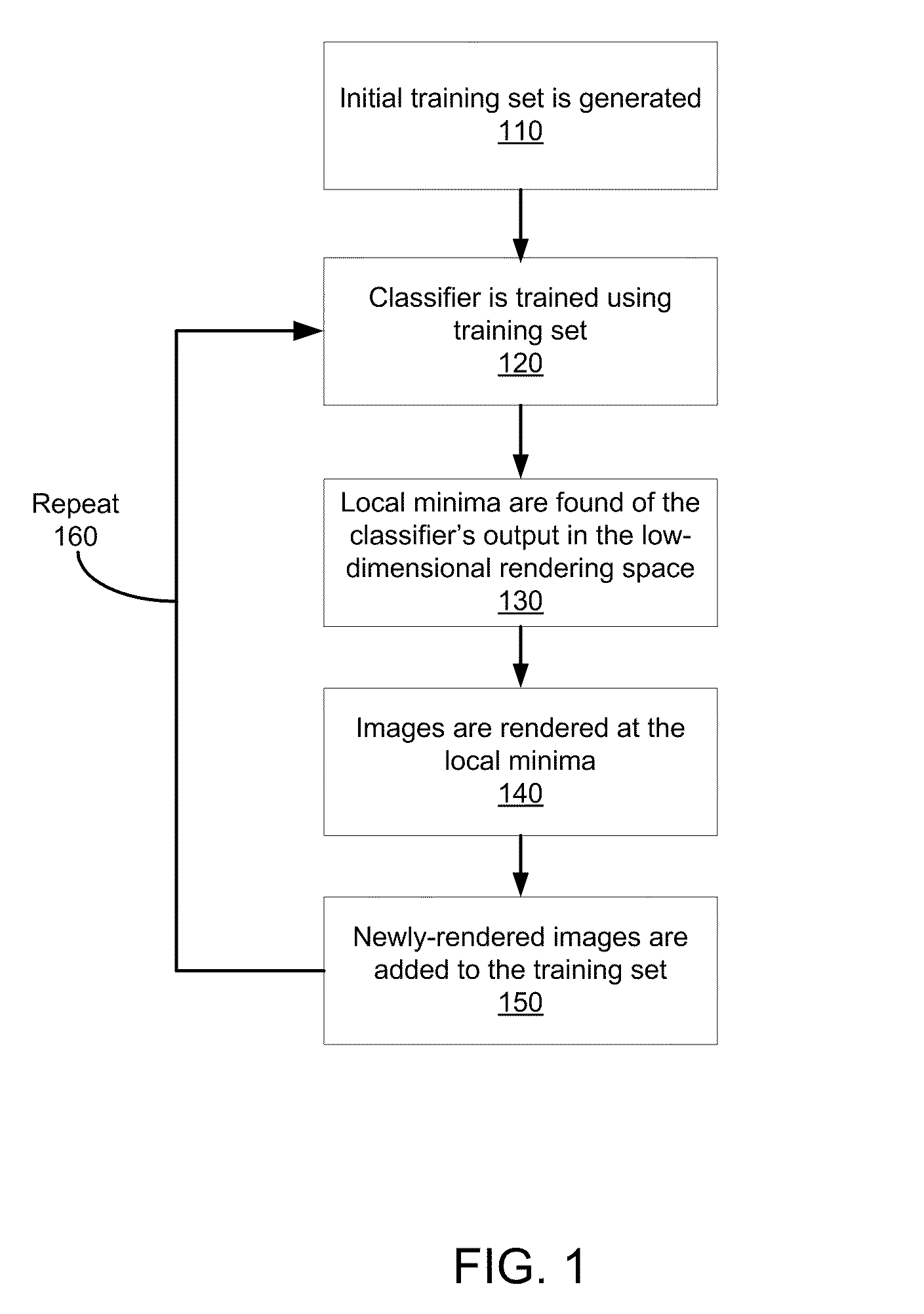
An “active learning” method trains a compact classifier for view-based object recognition. The method actively generates its own training data. Specifically, the generation of synthetic training images is controlled within an iterative training process. Valuable and / or informative object views are found in a low-dimensional rendering space and then added iteratively to the training set. In each iteration, new views are generated. A sparse training set is iteratively generated by searching for local minima of a classifier's output in a low-dimensional space of rendering parameters. An initial training set is generated. The classifier is trained using the training set. Local minima are found of the classifier's output in the low-dimensional rendering space. Images are rendered at the local minima. The newly-rendered images are added to the training set. The procedure is repeated so that the classifier is retrained using the modified training set.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Blog map for searching and/or navigating the blogosphere
ActiveUS20060284873A1Easy searchEasy to navigateDigital data information retrievalDrawing from basic elementsFeature vectorBlogosphere
A blog map for searching and / or navigating the blogosphere is provided. In accordance with one method for generating a blog map, a number of blog posts within the blogosphere are accessed. Each of the blog posts is converted to a feature vector, which represents the position of the blog post in a high-dimensional space. The dimensionality of the feature vectors is reduced from the high-dimensional space to a low-dimensions space, such that each blog post is represented in the low-dimensional space. A map is then generated based on the position of the blog posts in the low-dimensional space.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
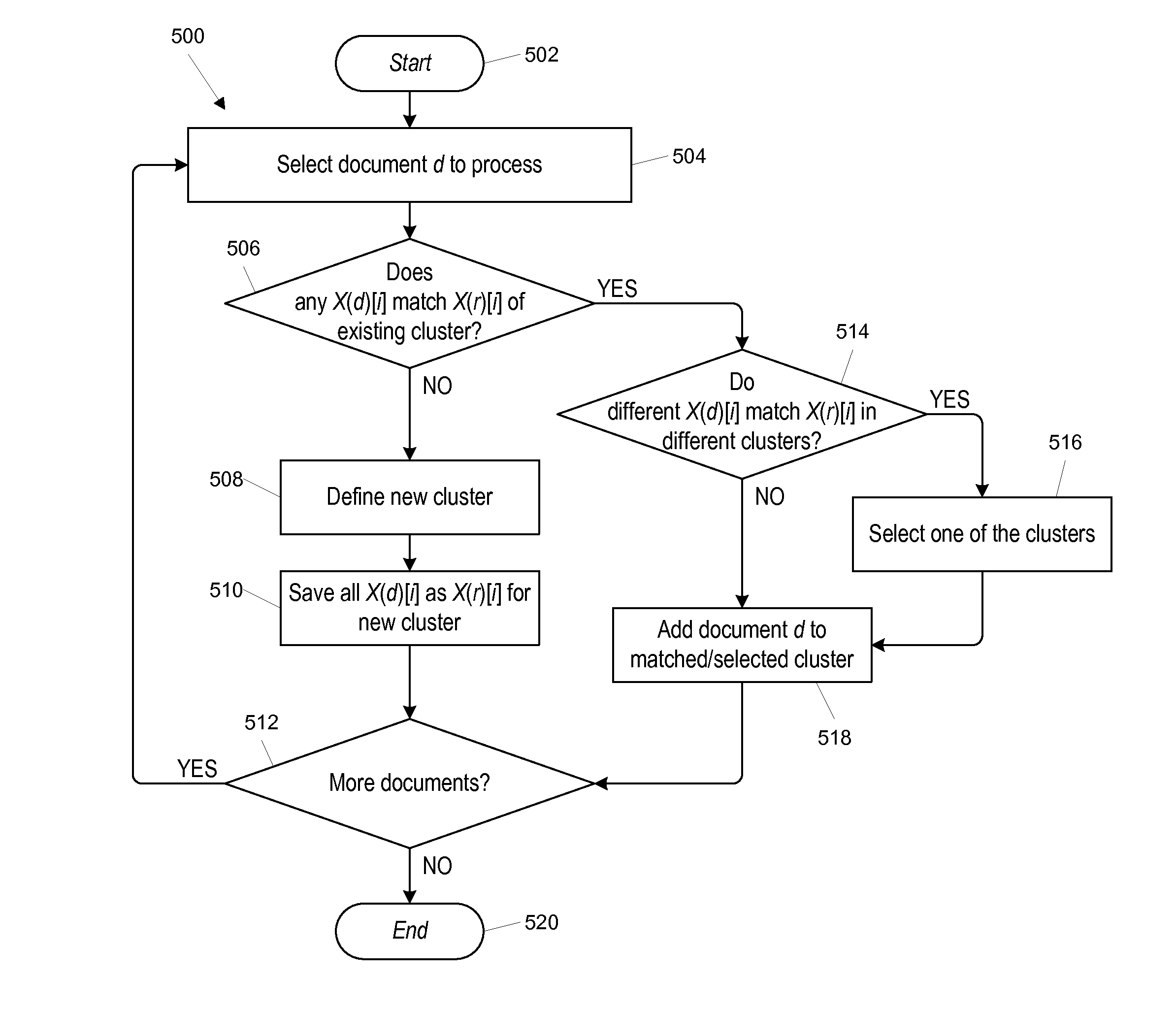
Clustering of near-duplicate documents
InactiveUS20110087668A1Increase maximum edit distanceEliminate needDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsDocument preparationCluster based
Documents likely to be near-duplicates are clustered based on document vectors that represent word-occurrence patterns in a relatively low-dimensional space. Edit distance between documents is defined based on comparing their document vectors. In one process, initial clusters are formed by applying a first edit-distance constraint relative to a root document of each cluster. The initial clusters can be merged subject to a second edit-distance constraint that limits the maximum edit distance between any two documents in the cluster. The second edit-distance constraint can be defined such that whether it is satisfied can be determined by comparing cluster structures rather than individual documents.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Real time intelligent control method based on natural video frequency
InactiveCN101311947ASave human effortReduce mistakesCharacter and pattern recognitionSerial sectionSmart surveillance
The invention discloses a real-time intelligent monitoring method based on natural video. The method uses the knowledge of computer image processing and artificial intelligence and realizes unmanned intelligent monitoring and alarm to the action of pedestrian in public places and important sensitive places. Firstly, video frame serial sections which need to be studied are extracted, movable historical images are obtained, which reflect the movement process of the people; on this base, the user-defined method for extracting the eigenvector is used, vector representation of the specific movement series is obtained, and the vector sample is stored in the sample database; as for the video frame serial which need to be monitored, the eigenvector and sample data are mapped in the low dimensional space, the corresponding classification by the optimized method is obtained and alarm is carried out. Owing to the sample study mechanism and the classification mechanism of the designed actions in the text, the method of the invention improves the accuracy of identification and strengthens the expansibility of identification; by designing the eigenvector representation and extraction method of movement serial of the people, the completeness and accuracy of action representation are strengthened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Discriminative motion modeling for human motion tracking
InactiveUS7728839B2Efficiently recognize and trackAccurate and Efficient TrackingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMotion dynamicsHuman motion
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Video retrieval method based on multi-core canonical correlation analysis
ActiveCN103559196AEfficient retrievalHigh precisionImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsVideo retrievalFeature vector
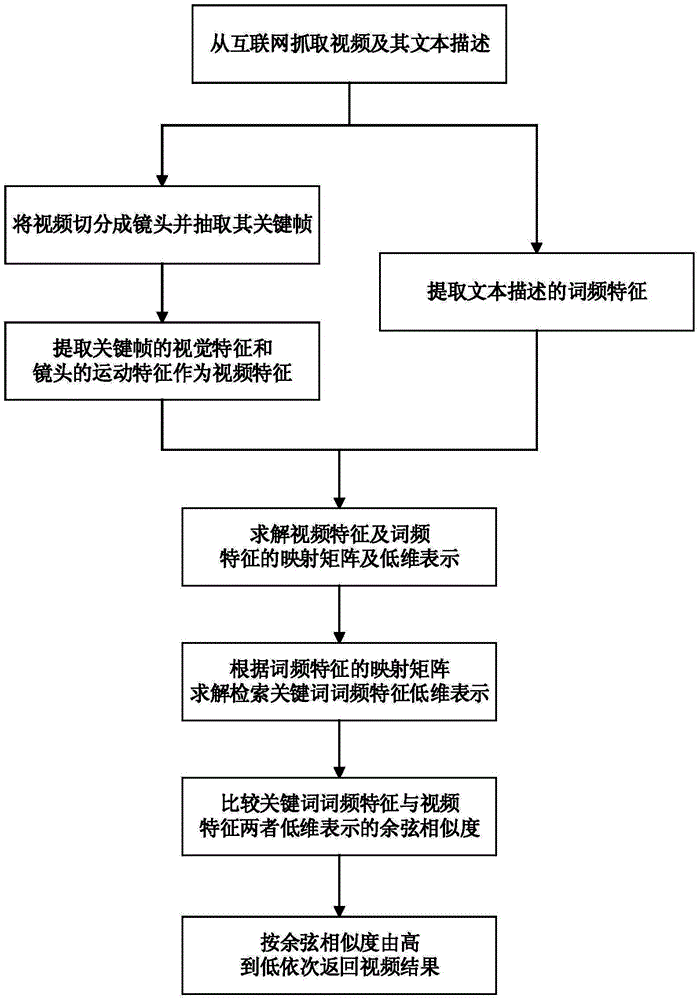
Disclosed is a video retrieval method based on multi-core canonical correlation analysis. The method includes grasping text descriptions corresponding to the video on internet, and then operating on the video: firstly dividing the video according to whether a shot is mutated or not, extracting key frames, extracting vision features of the key frames and moving features of the shot to form video feature vectors, and extracting word-frequency features from the text descriptions of each video; then utilizing the method of the multi-core canonical correlation analysis to obtain mapping matrixes and low-dimensional representation of the video features and the word-frequency features, and allowing the mapping matrixes and the low-dimensional representation to have the maximum correlation in low-dimensional space; finally, when a user inputs key words to perform video retrieval, acquiring the low-dimensional representation of the word-frequency features of the key words according to the mapping matrixes of the word-frequency features, and returning video retrieval results sequentially from large to small of the degrees of cosine similarity with the low-dimensional representation of the video features. The method has the advantages that the correlation of video content and the retrieval key words is enhanced, and the accuracy of retrieval by the user is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
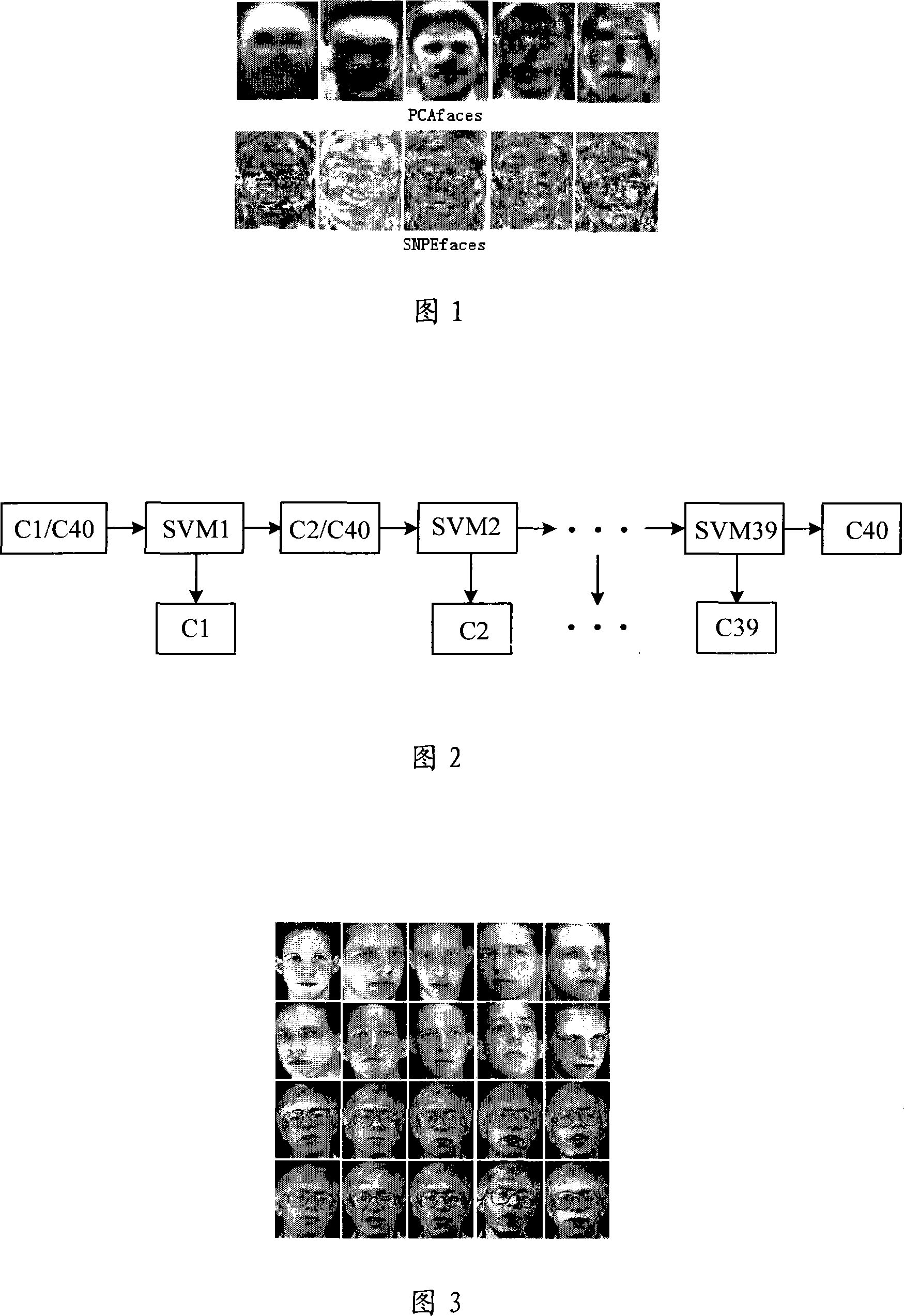
Face recognition method based on supervisory neighbour keeping inlaying and supporting vector machine
InactiveCN101187986AReduce running timeDimensionality reductionCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine
The invention discloses a facial recognition method based on supervised neighborhood preserving embedding (SNPE) and a support vector machine (SVM). The method comprises a training process and a test process, and includes specifically the following procedures: a, a weight matrix for a given data sample group is constructed; b, according to the weight matrix obtained in the procedure a, a generalized characteristic vector problem about the data samples is solved and an embedding matrix projecting the data samples into a low-dimensional data space is searched; c, characteristic extraction is performed on the data samples with the embedding matrix to acquire characteristic data of the low-dimensional space; d, mode classification of the acquired characteristic data in the procedure c is conducted with the SVM to realize the type recognition of the data samples. The facial recognition method provided by the invention can solve the problems in the prior that the linear dimensionality reduction method cannot maintain well inter- and intra-type sample structures; the non-linear dimensionality reduction method has large computational amount; and the common classifier has over-learning and under-learning problems.
Owner:HISENSE
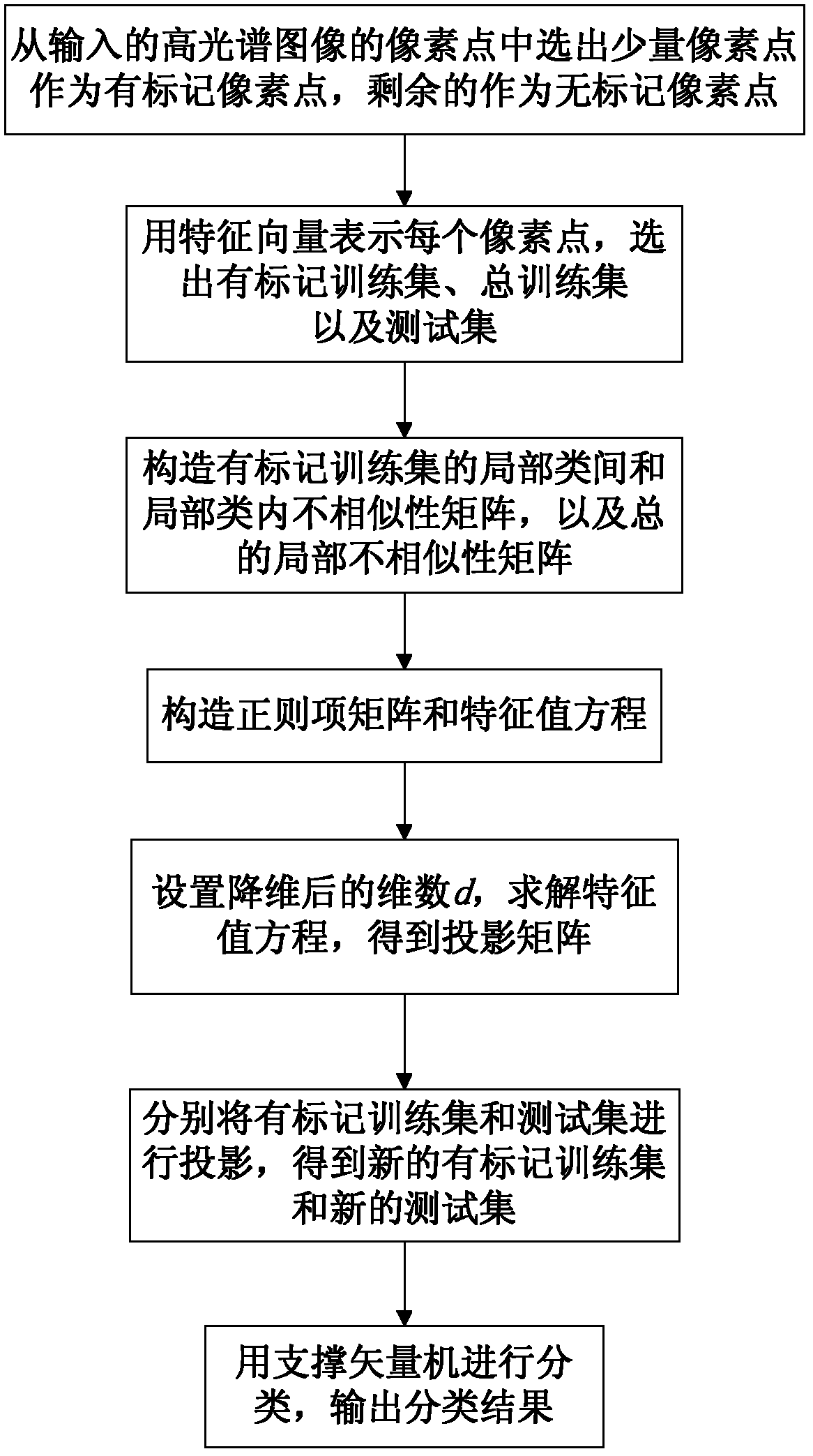
Semi-supervised dimension reduction-based hyper-spectral image classification method
InactiveCN102208034ASmall amount of calculationFast classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixFeature vector
The invention discloses a semi-supervised dimension reduction-based hyper-spectral image classification method for mainly solving the problems of high calculation quantity caused by over high hyper-spectral image data dimensions and low classification accuracy of the conventional method. The method comprises the following steps of: expressing each pixel point of a hyper-spectral image by using a feature vector, and selecting a marked training set, a test set and a total training set; constructing local inter-class and local intra-class dissimilarity matrixes of the marked training set respectively to obtain a total local dissimilarity matrix; constructing and solving a feature value equation to obtain a projection matrix; projecting the marked training set and the test set to a low-dimensional space respectively to obtain a new marked training set and a new test set; and inputting the new marked training set and the new test set to a support vector machine, and performing classification to obtain class information of the test set. By adopting the thought of semi-supervision, higher classification accuracy can be acquired; and the method can be applied to the fields of map design, vegetation survey and military intelligence acquisition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
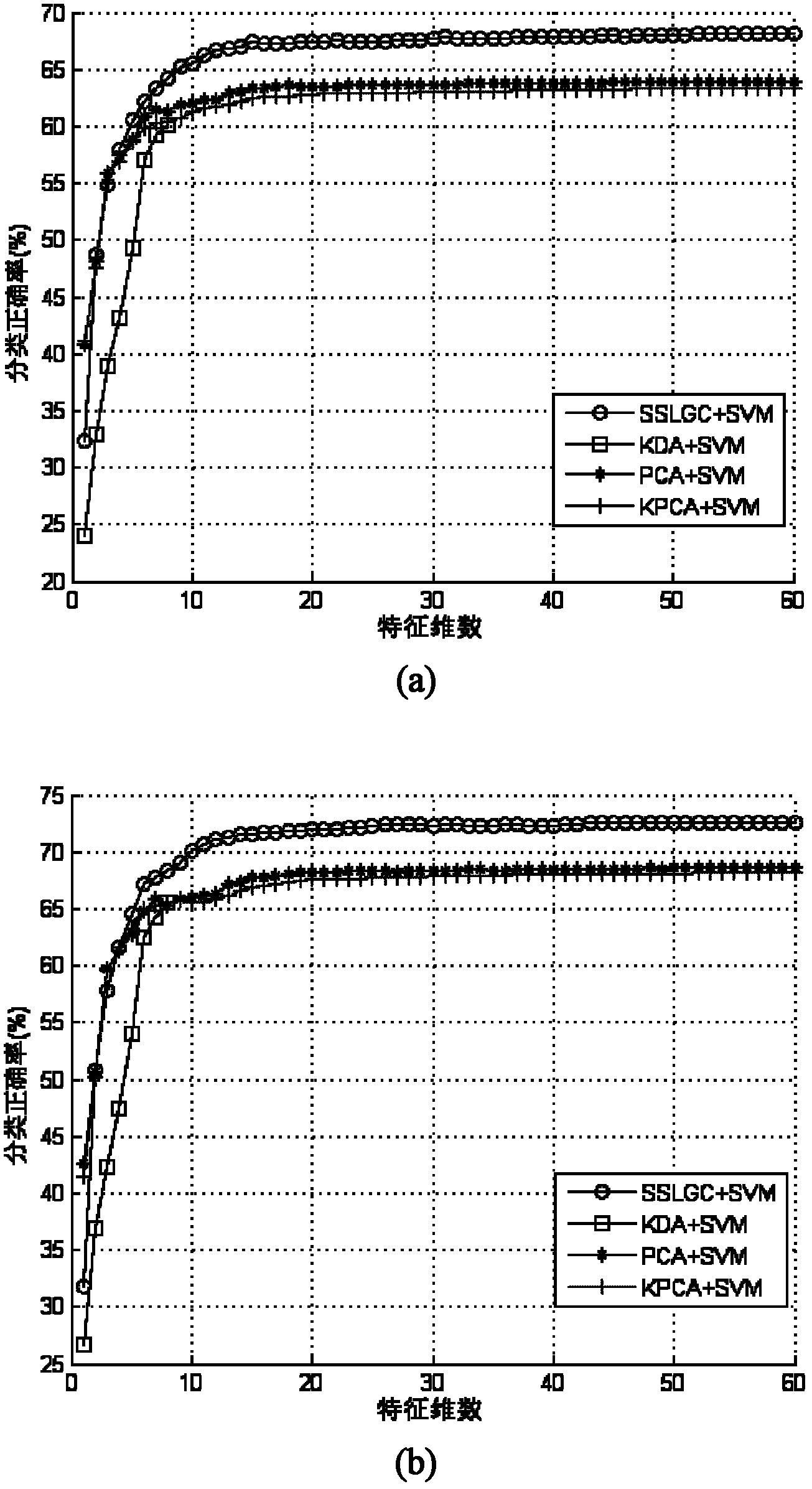
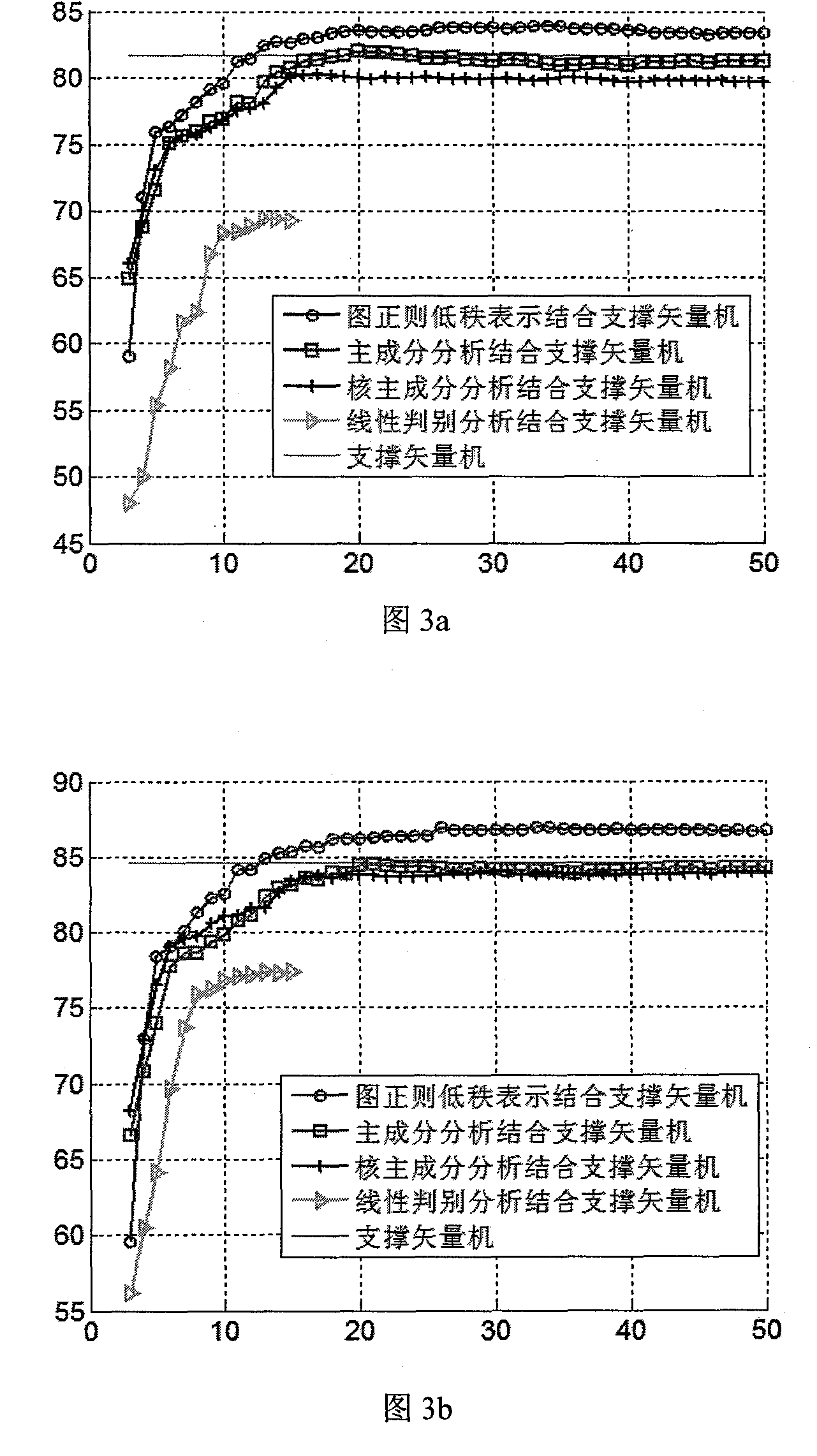
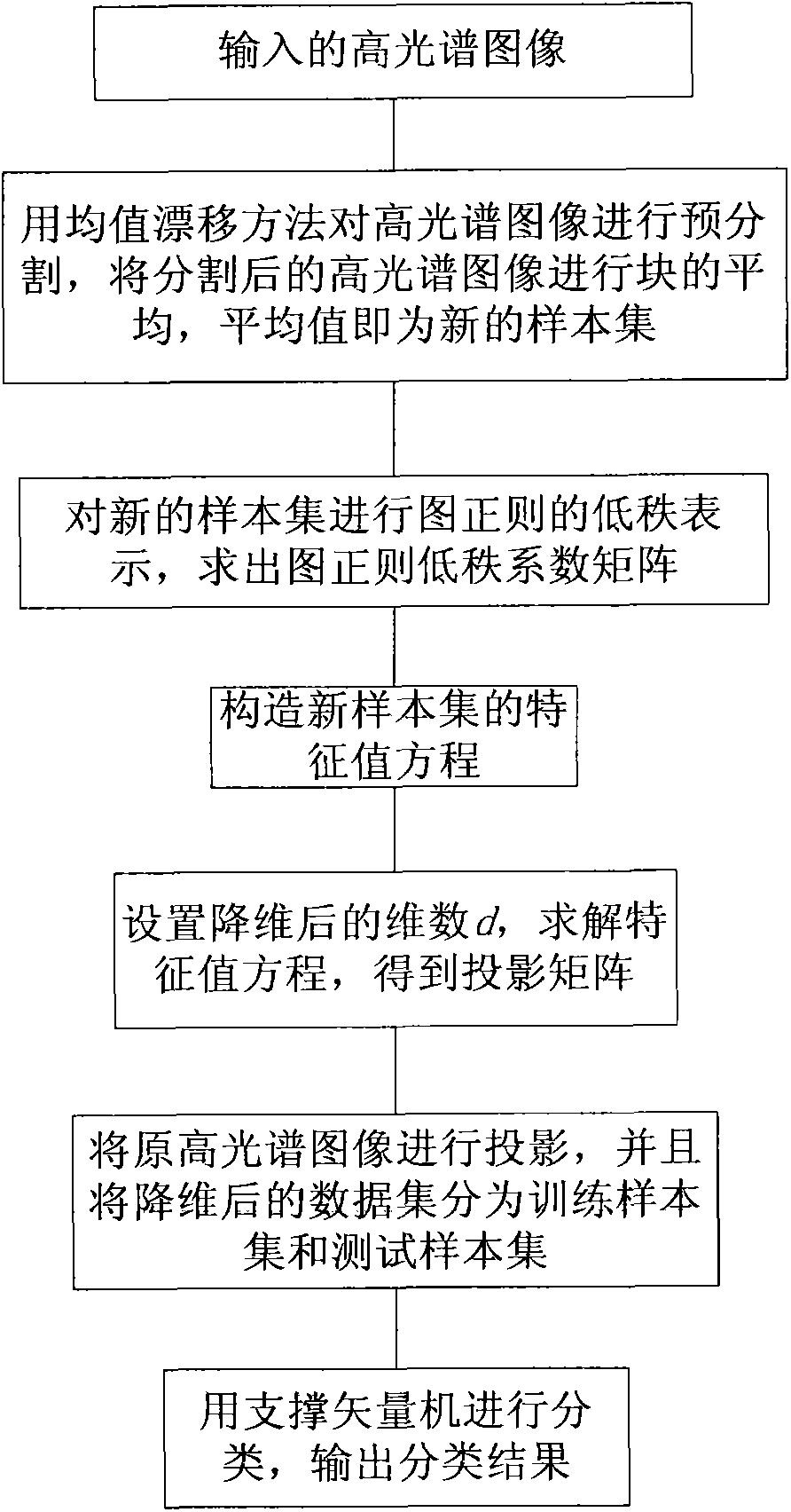
Hyperspectral image classification method based on image regular low-rank expression dimensionality reduction
ActiveCN103413151AHigh similarityRegionally consistentClimate change adaptationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityGoal recognition
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on image regular low-rank expression dimensionality reduction. The method includes the steps that a mean shift technology is used for conducting pre-segmentation on a hyperspectral image first, image regular low-rank coefficient expression is conduced on the hyperspectral image after pre-segmentation to obtain an image regular low-rank coefficient matrix, a characteristic value equation is constructed, a mapping matrix of the dimensionality reduction is studied, and original high dimensional data are transformed to low-dimensional space to be further classified. According to the hyperspectral image classification method, a hyperspectral image local manifold structure is excavated, the spatial distribution character of an original image is kept, effective dimensionality reduction space is studied, the classification accuracy of hyperspectral images is improved, computation complexity is lowered, the problems that the dimensionality of the hyperspectral image is too high so that the calculation amount can be large, and an existing method is low in classification accuracy are mainly solved, and the hyperspectral image classification method can be used for important fields such as precision agriculture, object identification and environment monitor.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Nonnegative matrix factorization-based dimensionality reducing method used for clustering
InactiveCN101853239ADigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData compressionNonnegative matrix factorisation
The invention belongs to the technical field of statistical model identification and machine learning, and in particular discloses a nonnegative matrix factorization-based dimensionality reducing method used for clustering. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting a KL distance; adding a data normalization constraint; directly discovering the internal relation among data dimensionalities by minimizing an object error function between data compression and reconstruction; obtaining a mapping matrix; and projecting high-dimensional data to a low-dimensional subspace by using the mapping matrix so as to perform effective data analysis such as clustering and the like. A simpler iterative formula compared with an original factorization method is obtained by the method; and normalization can be maintained naturally in each iterative updating. The normalization makes a final mapping matrix have higher sparsity compared with the original factorization method. In the obtained low-dimensional space, a clustering result shows that a more effective low-dimensional data characteristic can be obtained by the method; and an algorithm is simple and effective.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
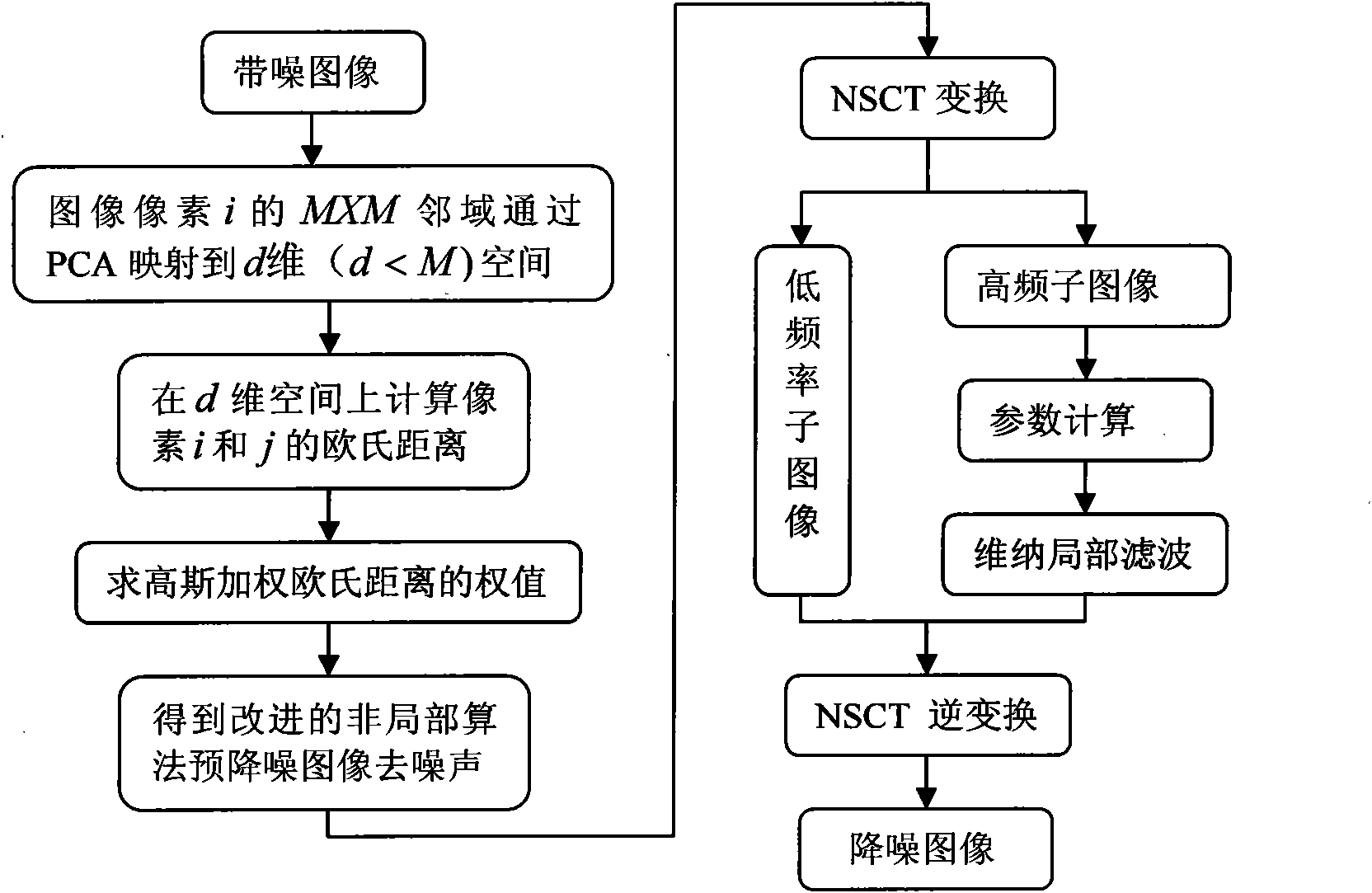
Image denoising method based on non-local means and multi-level directional images
ActiveCN101847257AQuality improvementAccurate targetImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisDecomposition
The invention relates to an image denoising method based on non-local means and multi-level directional images, comprising the steps of: firstly, carrying out preprocessing on an image with noise in an empty space by utilizing a non-local mean arithmetic of a small window and the similarity of the local structure of the image, and mapping the local window to a low-dimensional space to improve the speed of the arithmetic by utilizing principal component analysis (PCA); then carrying out multi-scale multi-direction sparse decomposition on the preprocessed image through NSCT (Non-subsampled Contourlet); eliminating low-frequency noise by adopting Wiener filtering in an NSCT transform domain by utilizing the neighborhood statistical property of the coefficient; and obtaining the denoised image through NSCT inverse transformation. The method improves the quality of the denoised image, provides more comprehensive and accurate targets and background information, and achieves relatively ideal denoising effect. The invention has wide application prospect in systems in the military field and the non-military field such as optical imaging, target detection, safety monitoring, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER +1
Elevator fault diagnosis method and device
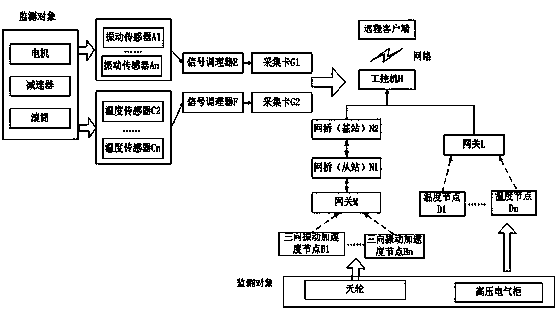
InactiveCN103359572AGuaranteed real-timeGuaranteed stabilityElevatorsWireless sensor networkingMechanical equipment
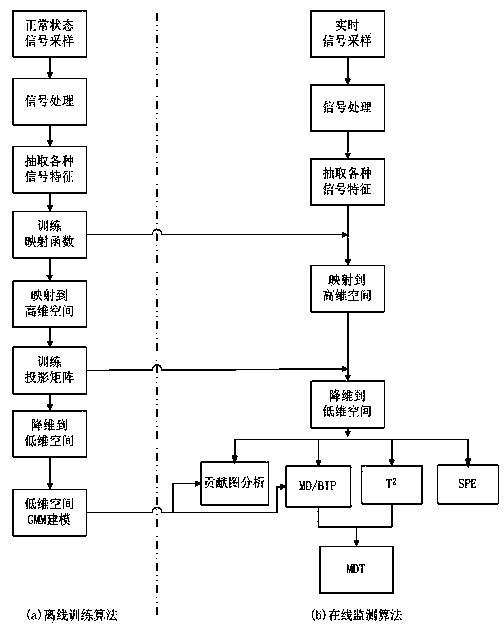
The invention discloses an elevator fault diagnosis method and a device, and relates to the field of mechanical equipment fault diagnosis and wireless sensor networks. (1) A multi-core fault monitoring method of global maintenance and partial identification comprises the steps of off-line training and on-line fault monitoring, wherein the off-line training is conducted on a projection matrix W with a maintained structure; a high-dimensional data sample is projected to a low-dimensional space; then a GMM (Gaussian Mixture Model) is trained; T<2>, SPE, BIP and MD monitoring statistical magnitude is computed; and fault detection and diagnosis are conducted by combining a contribution pattern. (2) The elevator fault diagnosis device acquires and transmits a signal in wired and wireless manners, and is suitable for remote monitoring of equipment in a complex environment. An application effect indicates that signal acquisition and transmission are reliable; the monitoring accuracy is high; the cost is moderate; and the method and the device have promotion values.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Content retrieval method for chrysanthemum image based on deep hash learning
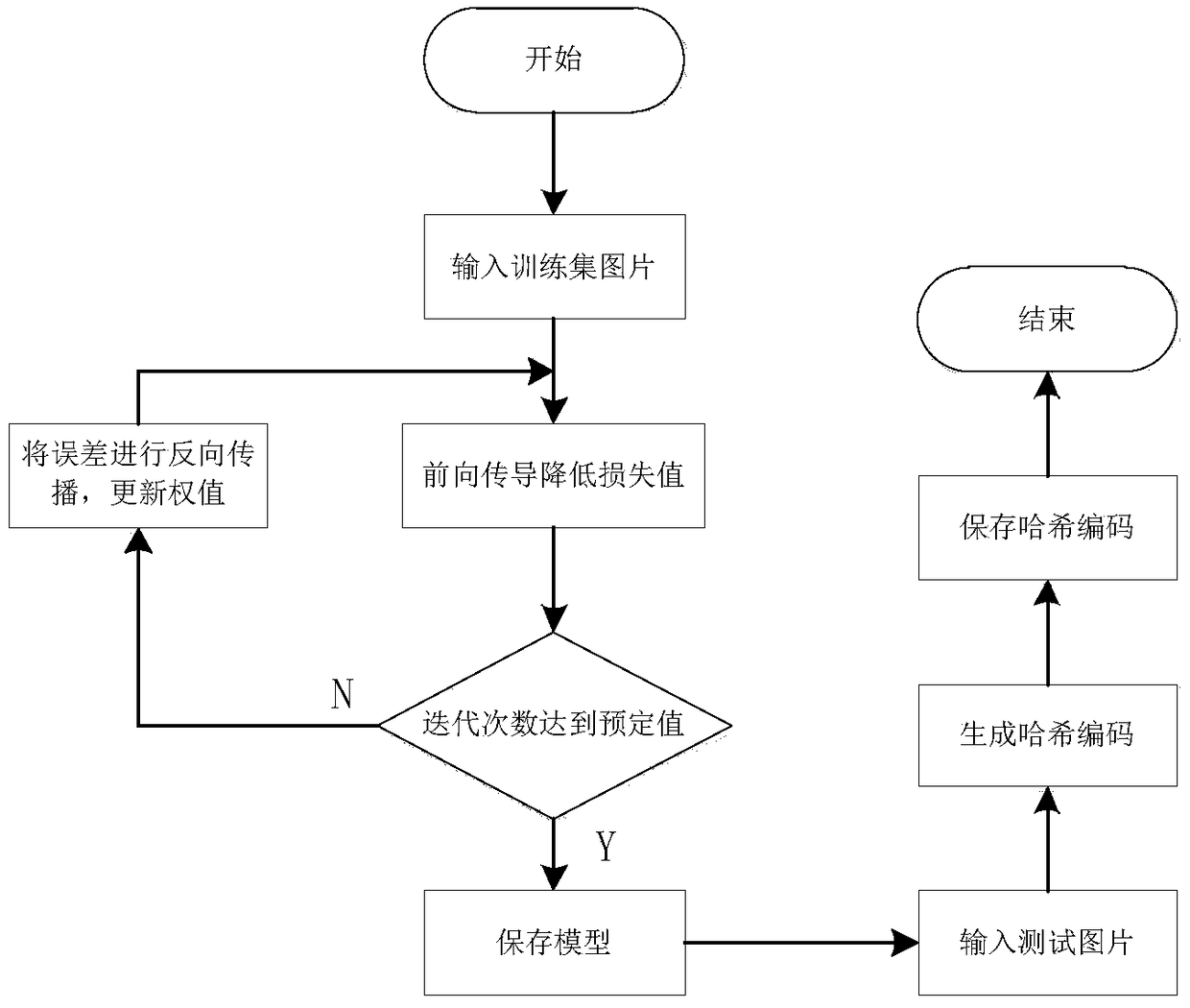
InactiveCN108932314AImprove generalization abilityImprove accuracyNeural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsData setContent retrieval
The invention discloses a content retrieval method for a chrysanthemum image based on deep hash learning. A deep neural network algorithm and Hash coding are used to recognize and retrieve images. Themethod comprises: firstly, establishing a training set and a test set to perform pre-data-processing on a to-be-identified image, to enhance generalization ability and recognition degree of the image; secondly, establishing a chrysanthemum image feature extraction model through a convolution neural network, and realizing query calculation by hash coding in a hash layer of the convolution neural network. The method is based on the deep hash learning, so that when high-dimensional data is mapped to a low-dimensional space, similarity of the data in high-dimensional space can be maintained in aHamming space, a coding balance criterion is maintained when the high-dimensional data is mapped to the low-dimensional space. The method processes a chrysanthemum data set, enhances the data set to enhance model generalization ability, and improves image retrieval quality and retrieval efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Human face identification method based on manifold learning
InactiveCN103336960AImprove recognition accuracyReduce operational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingNearest neighbour classifiers
The invention discloses a human face identification method based on manifold learning, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method solves the problem of excessive resource consumption of the traditional method for directly processing high-dimension images. The method is combined with two kinds of methods including the nearest characteristic sub space classifier method and the local linear embedding method for realizing the dimension reducing processing on human face images, then, the nearest classifier is adopted for identifying the data subjected to dimension reduction, firstly, the human face image high-dimension data is firstly built, and the human face image samples are stretched into one-dimension vectors in lines; then, the built human face image high-dimension data is subjected to dimension reduction processing, and the low-dimension expression of all obtained human face images is obtained; and finally, the data is embedded into the space at the low dimension. Through the training on the images, the images to be tested are collected in real time, the human face identification is carried out, the method is more reasonable than a local linear embedding method based on Euclidean distance, the identification accuracy is higher, the method has lower operation complexity than a method of directly adopting high-dimension data for identification, and the method is simpler and more convenient.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
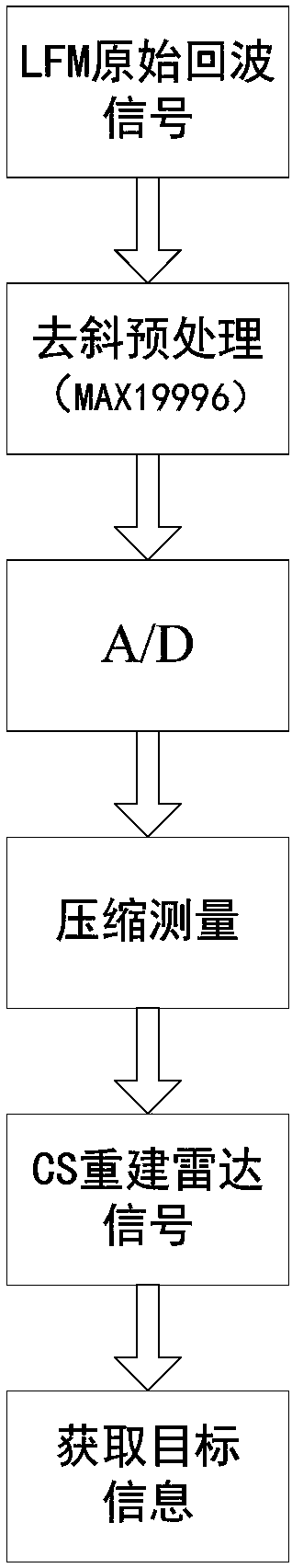
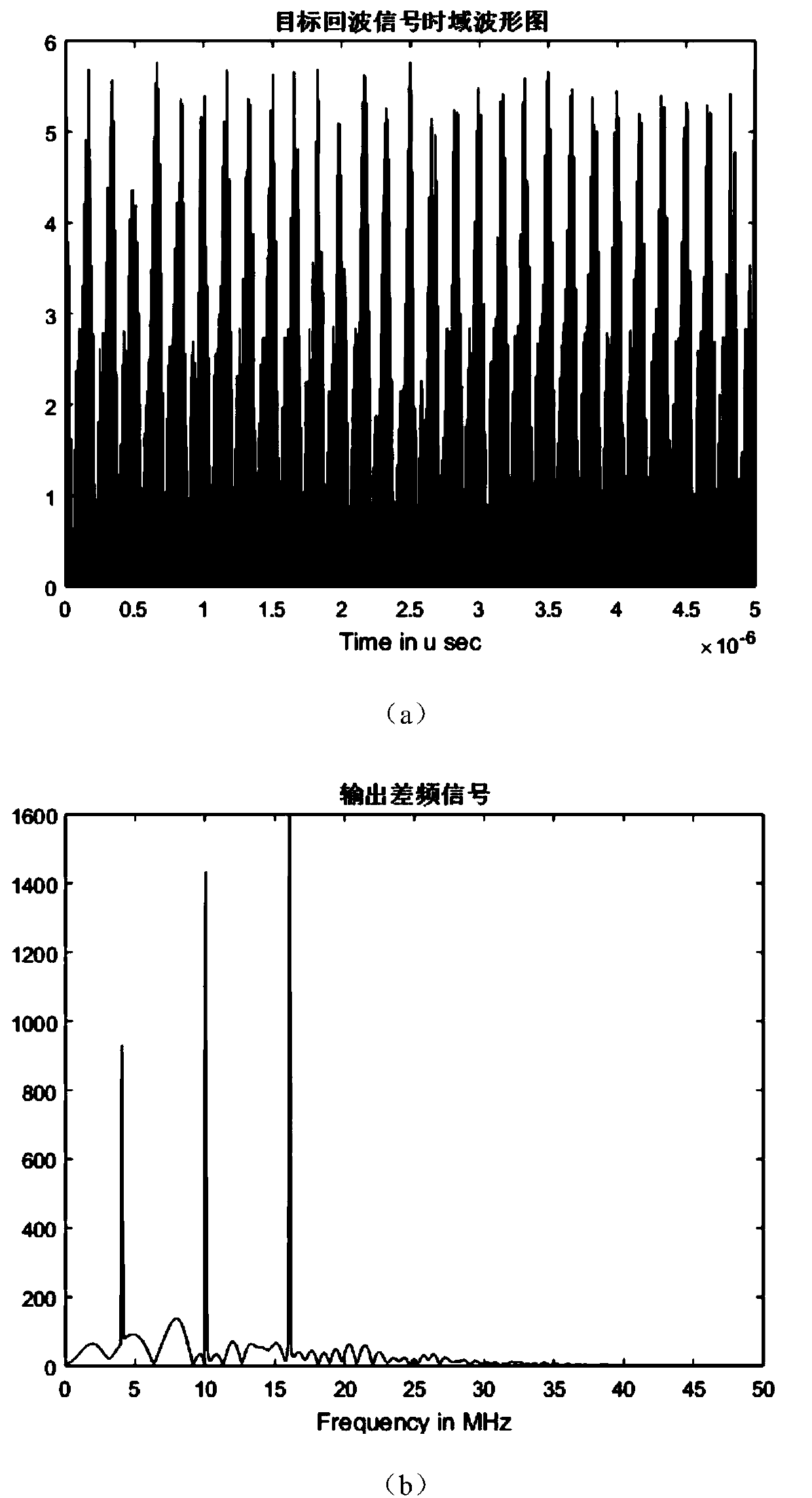
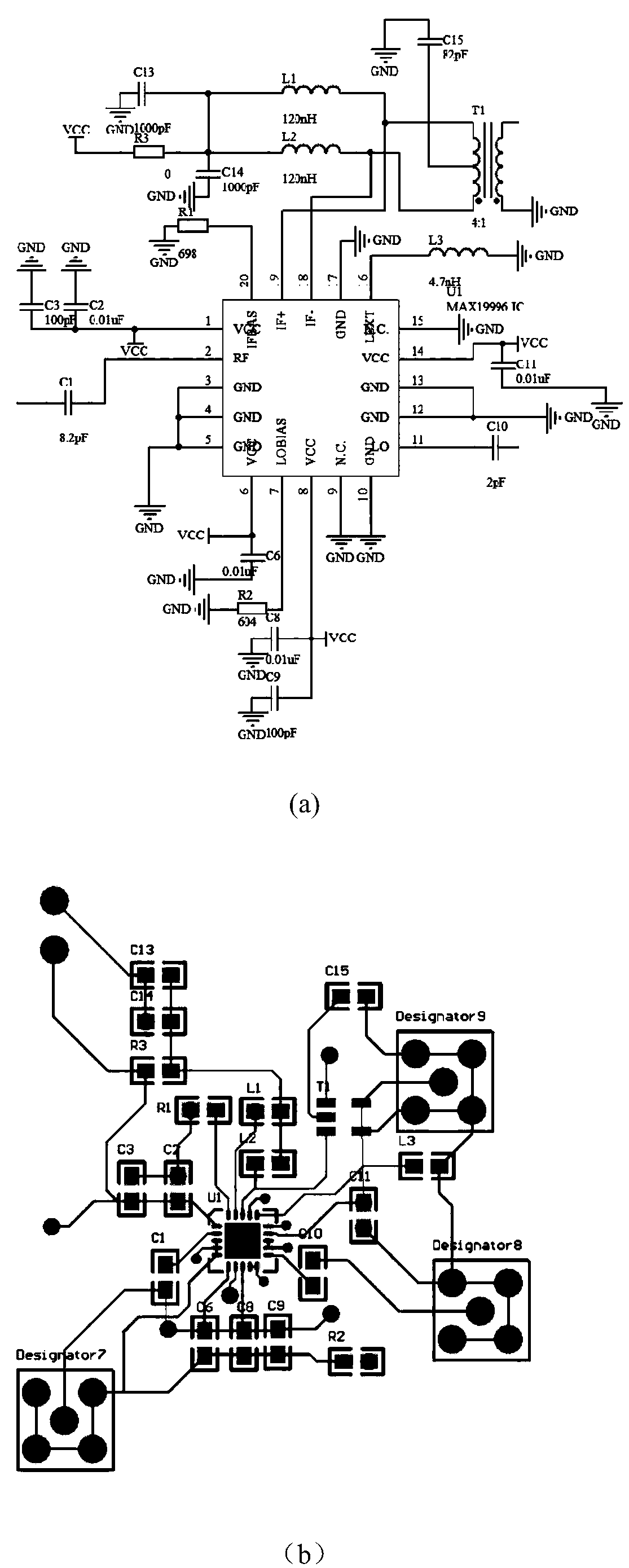
Linear frequency modulation radar signal processing method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107064883AEfficient acquisitionAchieve compressionWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar observations
The invention discloses a linear frequency modulation radar signal processing method based on compressed sensing. The method comprises the steps of (1) emitting a linear frequency modulation signal to a radar and preprocessing an echo signal, which means that the deramping processing of the echo signal is carried out, a difference frequency signal is outputted, and a signal model of deramping processing is established in a time domain, (2) according to the sparsity of the difference frequency signal in a frequency domain, constructing a sparse conversion matrix, and establishing a sparse representation model of the radar echo signal, (3) constructing a measurement matrix, and realizing the projection transformation of a difference frequency sparse signal to a low dimensional space, and (4) using an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm, reconstructing a radar difference frequency signal, and efficiently obtaining target information. Accoding to the method, the compression of radar echo signal data can be fundamentally realized, the change of a sparse model according to a radar observation distance is not needed, finally the target information is obtained, and the method is suitable for the echo signal processing of an actual radar.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
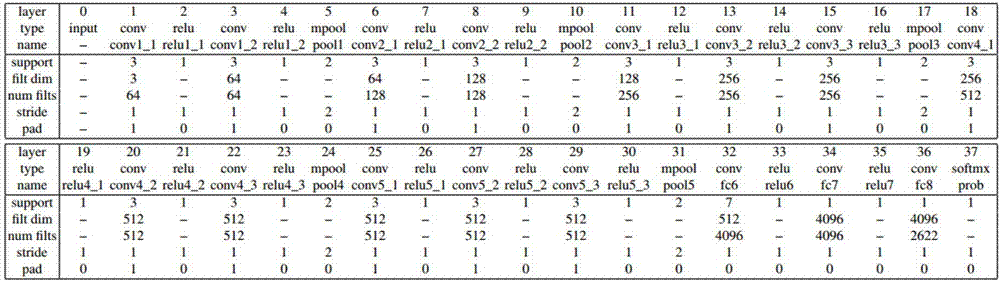
Face identification method based on deep convolutional neural network
InactiveCN107330383AAvoid dependenceReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHat matrixFeature vector
The present invention discloses a face identification method based on a deep convolutional neural network. The method comprises: respectively feeding each image in a face identification database into three constructed deep convolutional neural network for feature extraction; performing normalization of output features, performing affine projection of the features to a low-dimensional space, obtaining a projection matrix, training a projection matrix through minimization of a ternary loss function, and obtaining feature vectors of each image; searching the weight value of each filter in the deep convolutional neural network through a gradient descending method, performing training test, and selecting a deep convolutional neural network having the highest average identification precision; and applying the selected deep convolutional neural network to a standard face identification database, performing Euclidean distance calculation of feature vectors of face images to be detected and each image, and if the feature vectors are smaller than a threshold value, determining that the images show the same person. Few images are used in the training, and the employed convolutional neural network is simple in structure so as to improve the face identification precision and reduce the training complexity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
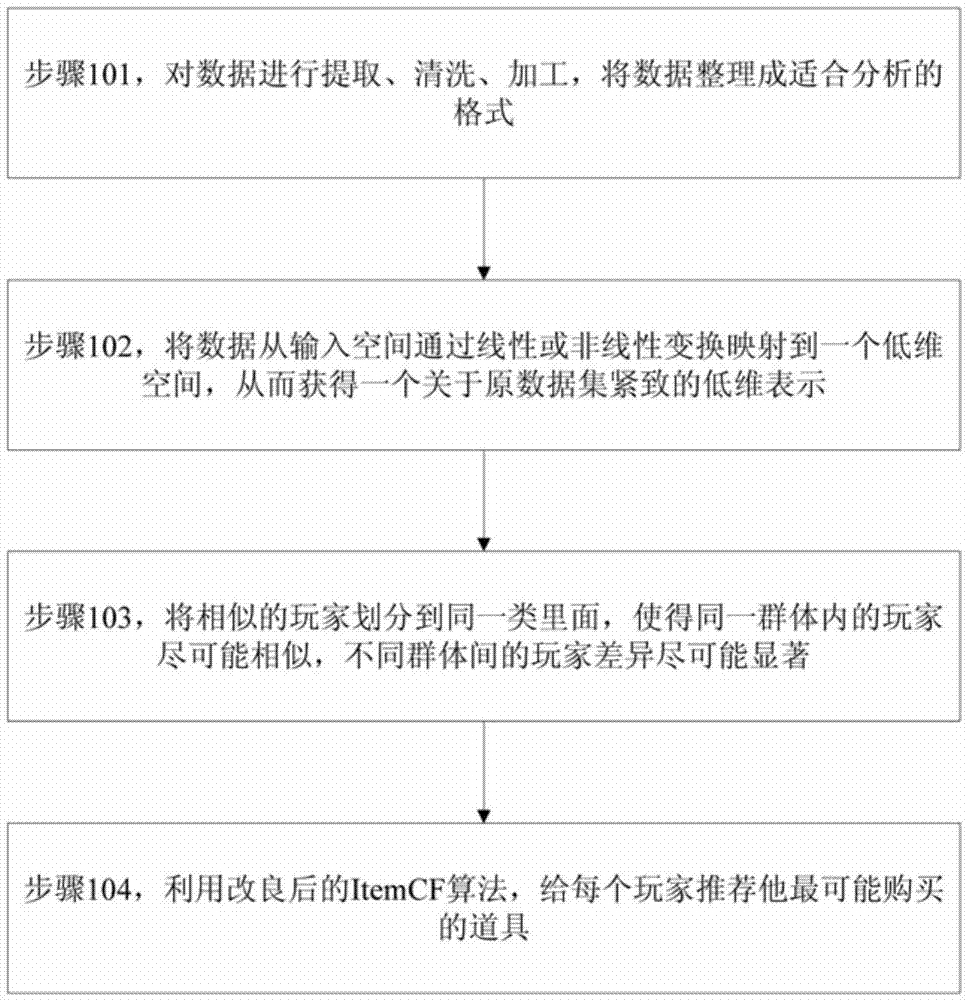
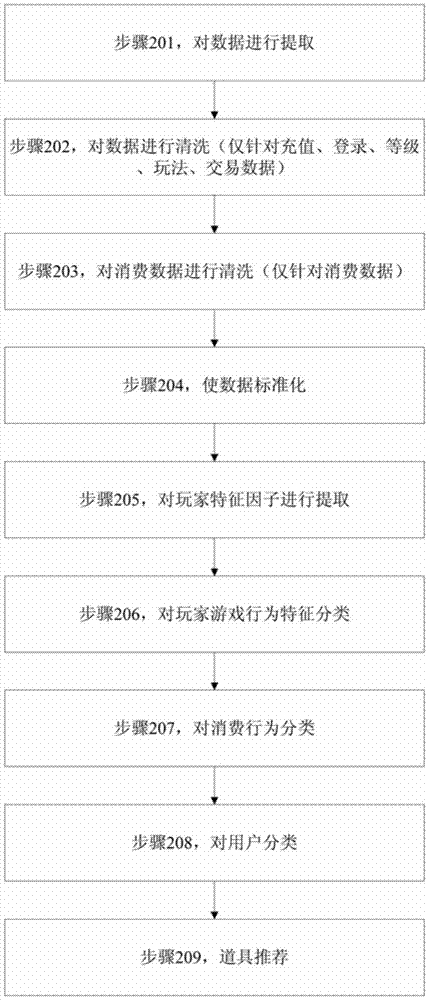
Game prop personalized recommendation method
InactiveCN105447126AImprove accuracySmall amount of calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationComputer science
The present invention relates to a game prop personalized recommendation method, comprising: carrying out extraction, cleaning and processing on data; mapping the data into a low-dimensional space from an input space; classifying the data to partition players into different categories; and recommending props which are most possibly bought by each player for the player. According to the game prop personalized recommendation method disclosed by the present invention, a calculated amount of a recommendation algorithm is greatly reduced, prop recommendation accuracy is significantly improved, and a user experience effect of a network game is promoted.
Owner:SNAIL GAMES
Classification method for hyperspectral remote sensing image based on full convolutional network
InactiveCN108171122AFully extractedThe classification result is accurateGeometric image transformationScene recognitionClassification methodsNetwork model
The invention discloses a classification method for a hyperspectral remote sensing image based on a full convolutional network. The method comprises the following three steps of data preprocessing, feature extraction and classification; the hyperspectral remote sensing image is input into the full convolutional network to be processed, the characteristics of the full convolutional network are usedfor extracting and classifying the features of the hyperspectral remote sensing image. firstly, the hyperspectral remote sensing data is lowered to low-dimensional space, then, a low-dimensional hyperspectral image is input into the full convolutional network model to be processed, and a convolutional layer obtained in a processing process is taken as features; then, the obtained feature image isclassified into a training set and a testing set, and a sparse representation dictionary is trained; and finally, the testing set is subjected to sparse reconstruction, and a classification result isobtained. The spectrum and the spatial features of the hyperspectral data can be fully combined, the advantage that the full convolutional network does not restrict input sizes is used to fully extract feature information from the hyperspectral remote sensing image data of different sizes and different sample distribution situations, and an accurate classification result is obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
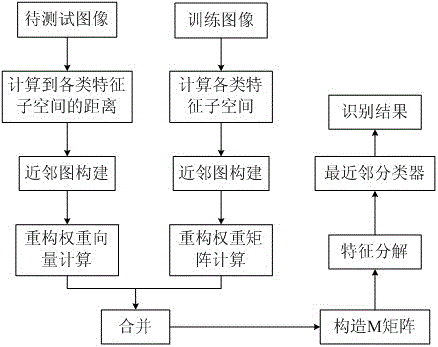
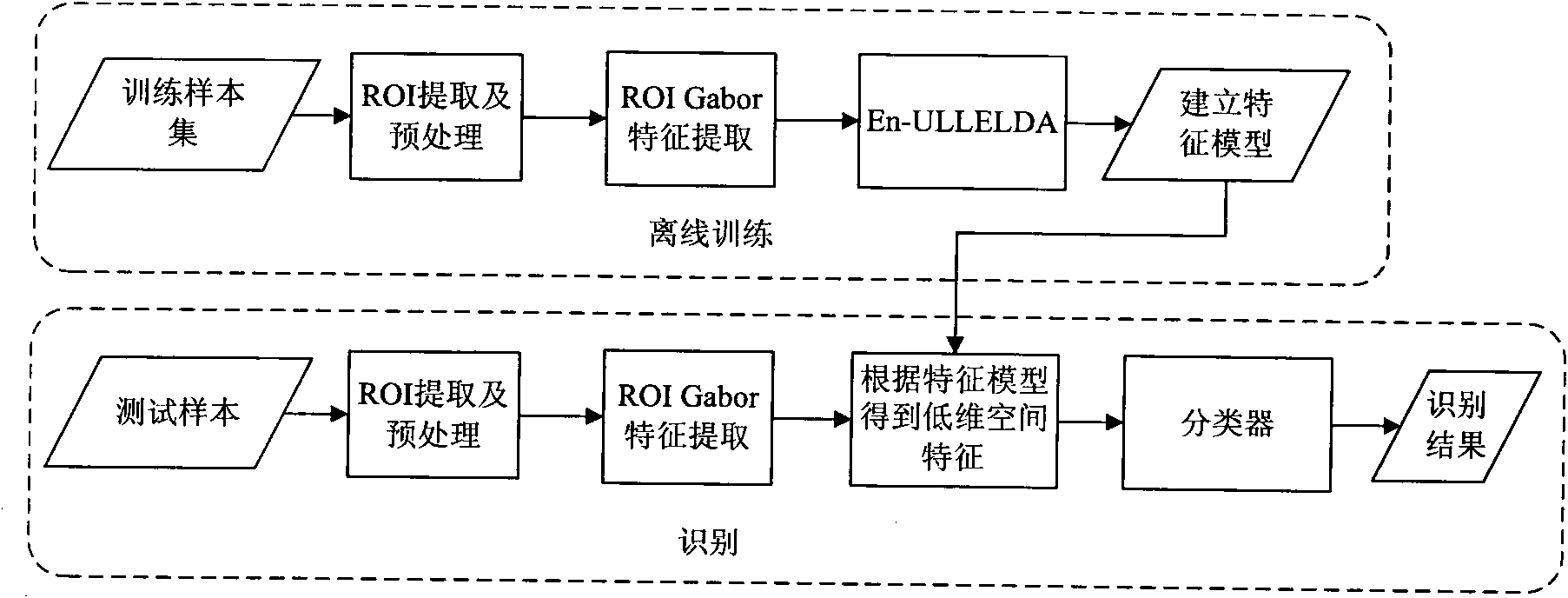
En-ULLELDA-based method of multi-view model recognition
InactiveCN101635027AImprove recognition rateCharacter and pattern recognitionGabor wavelet transformTest sample
The invention provides an En-ULLELDA-based (ensemble-unified locally linear embedding and linear discriminant analysis) method of multi-view model recognition. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting a vehicle ROI (region of interest); secondly, extracting the high-level information that can reflect the model as features through Gabor wavelet transform; then, carrying out the dimension reduction of features on the basis of a novel manifold learning algorithm En-ULLELDA, so as to transform the features to a low-dimensional space; and obtaining the corresponding models from the features of a test sample by a classifier during the recognition. According to test results, the invention can effectively handle the problem of multi-view model recognition on urban roads; and the invention can eliminate the effects of parameter variation on the recognition results by employing the integration technology, so that the invention has higher robustness.
Owner:深圳市麟静科技有限公司
Behavior recognition method based on action subspace and weight behavior recognition model
InactiveCN102938070AImprove joint accuracyAccurate identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman behaviorUtilization behavior
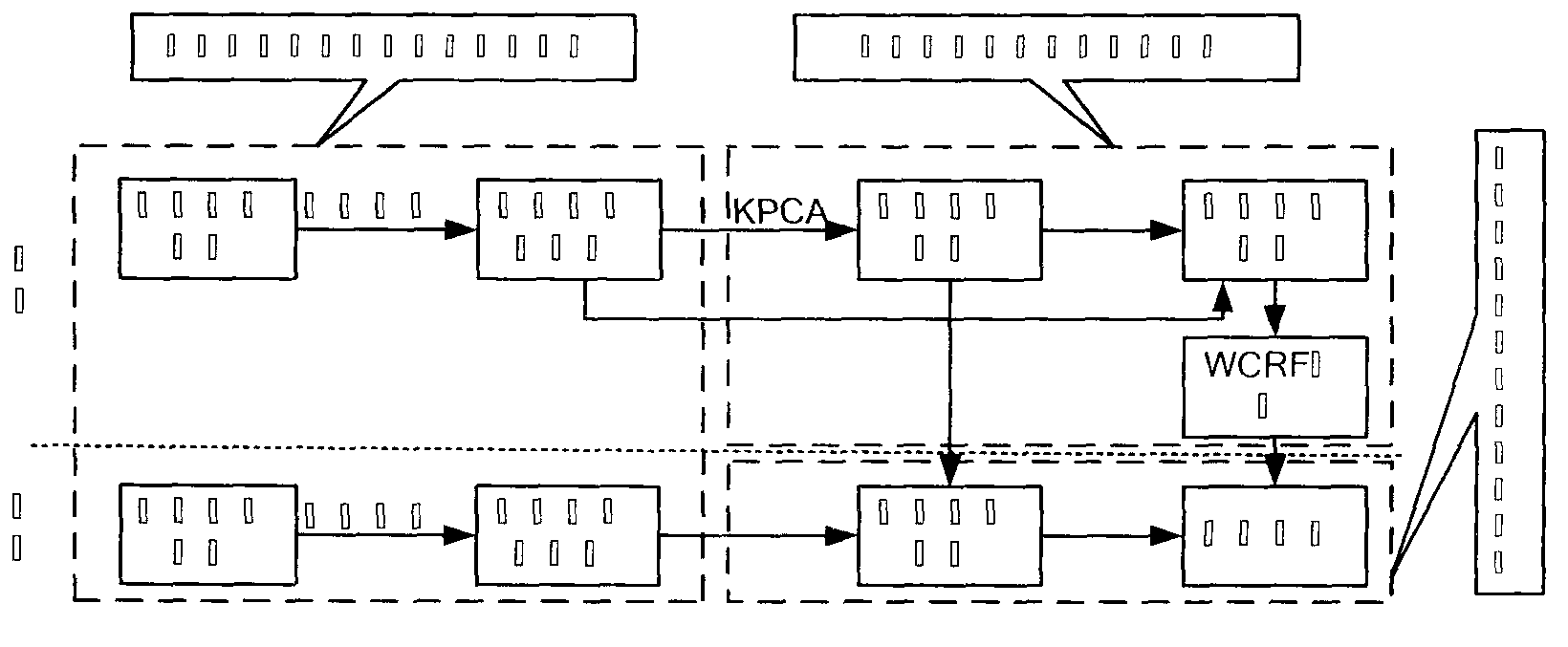
The invention discloses a behavior recognition method based on an action subspace and weight behavior recognition model. The behavior recognition method includes the following steps: A1, inputting a behavior video sequence to be tested, using a dynamic background detection method or a static background detection method for detecting background images, and using a background reduction method for obtaining foreground images; A2, extracting an outline of a moving object, and expressing outline characteristics correspondingly; A3, using a kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) algorithm for achieving nonlinear dimensionality reduction on high-dimensional characteristics in kernel guide subspace, and mapping behavior track in a low-dimensional space; and A4, using the behavior recognition model namely a world cancer research fund (WCRF) module for performing behavior recognition. An experimental result shows that a provided framework can recognize human behavior of personnel changes inside and outside an area along the time accurately and is strong in robustness of noise and other influencing factors.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
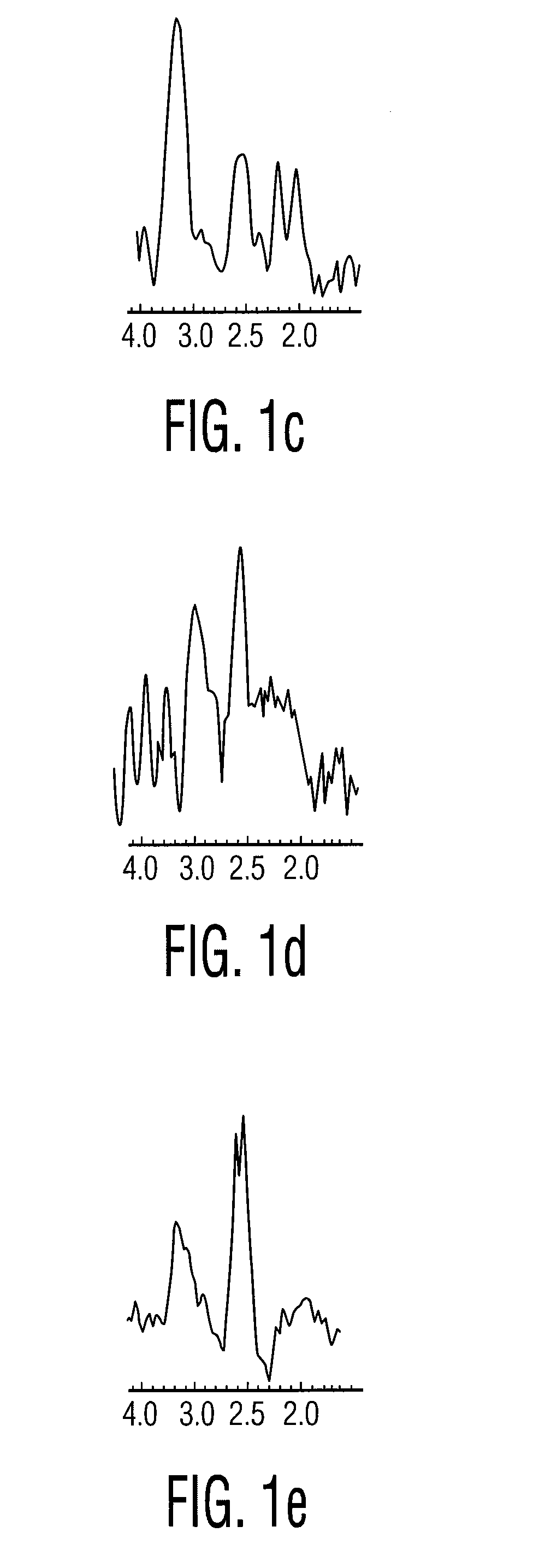
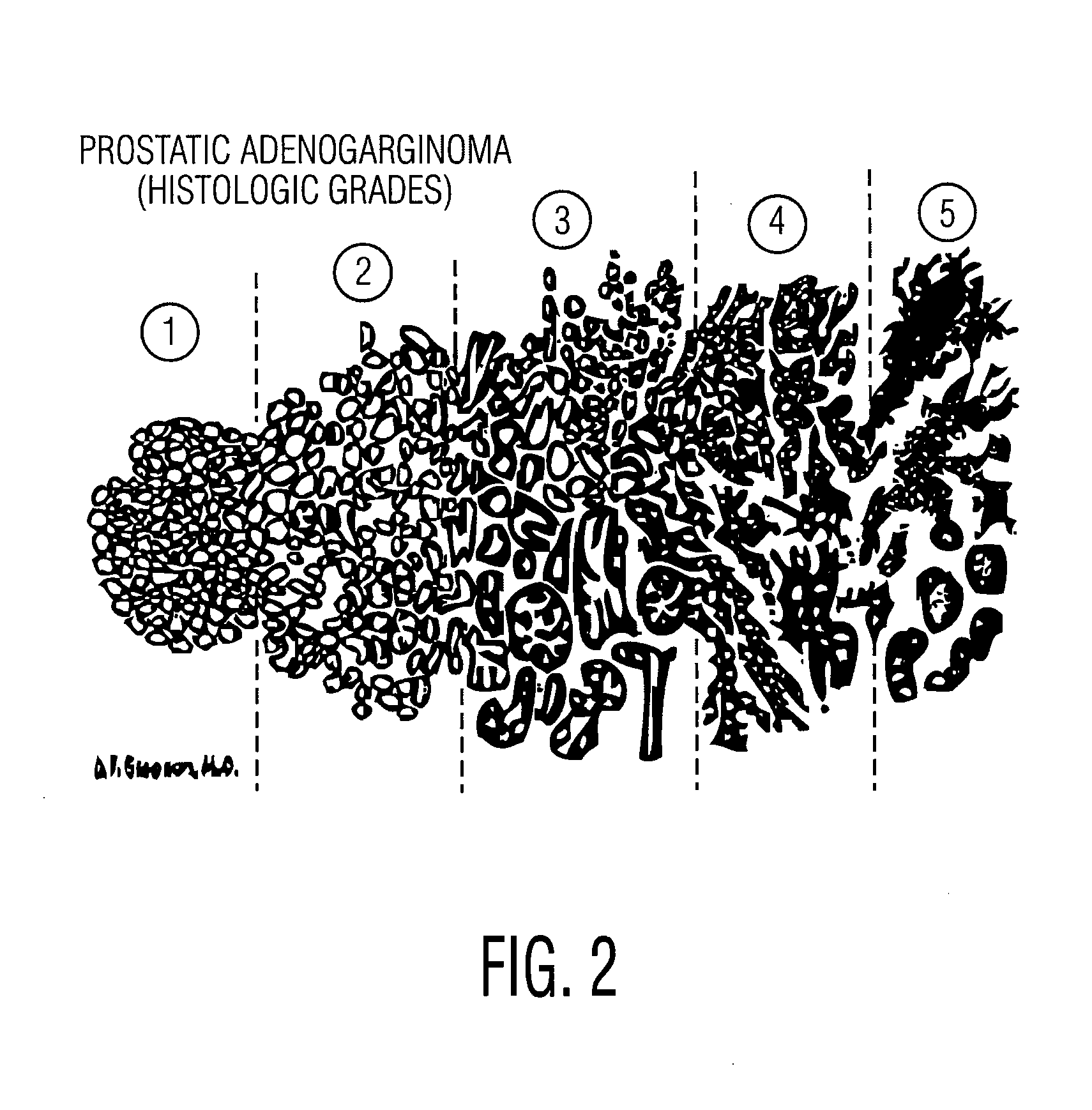
Defining quantitative signatures for different gleason grades of prostate cancer using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20100169024A1Image enhancementImage analysisMagnetic resonance spectroscopicPattern recognition
A method for classifying a possible cancer from a magnetic resonance spectrographic (MRS) dataset includes extracting at least one feature from the MRS dataset as being identified with the possible cancer and embedding the extracted feature into a low dimensional space to form an embedded space. The method then clusters the embedded space into clusters representing a plurality of predetermined classes and spectrally decomposing the clusters to identify substantially significant independent metabolic signatures. The method then classifies the possible cancer as belong to one of at least two cancer classes based on the identified independent metabolic signatures.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Methods of multivariate data cluster separation and visualization
InactiveUS20100198900A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningTransformation matrix
A method separates multivariate data points in lower dimensional space, where each data point has been classified into one of a plurality of data clusters including at least a first data cluster and a second data cluster. The method includes the step of acquiring an ND-to-3D transformation matrix for transforming the plurality of multivariate data points to a plurality of three-dimensional data points. The method preferably includes the sub-step of performing a center of mass (COM) separation of the clusters to acquire a COM transformation matrix, where the COM transformation matrix is the ND-to-3D transformation matrix. The method also includes the step of performing a receiver-operator characteristic curve (ROC) separation to acquire an ROC transformation matrix for transforming the plurality of three-dimensional data points to a plurality of data points in a dimension lower than 3D and preferably a re-optimized COM transformation matrix.
Owner:GIFFORD SEAN
Network abnormity flow monitoring system based on density peak value cluster
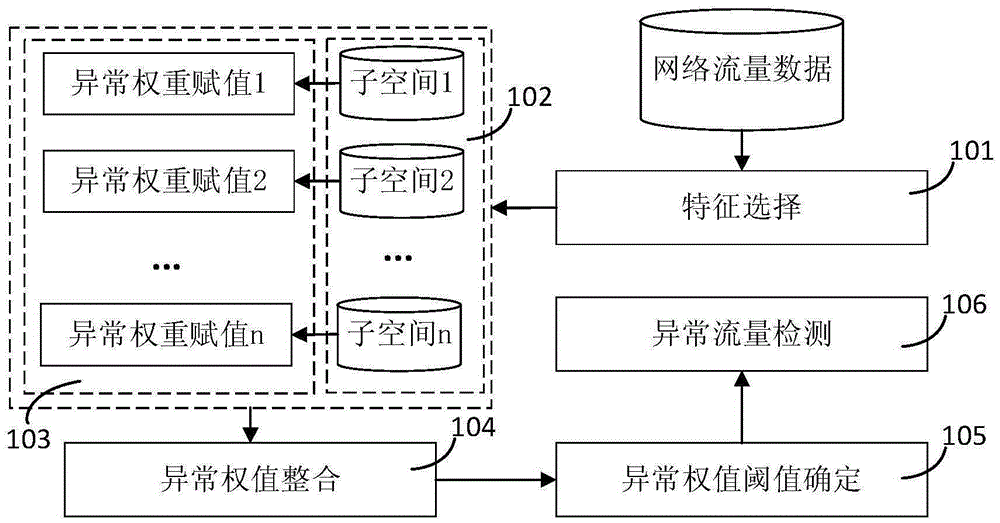
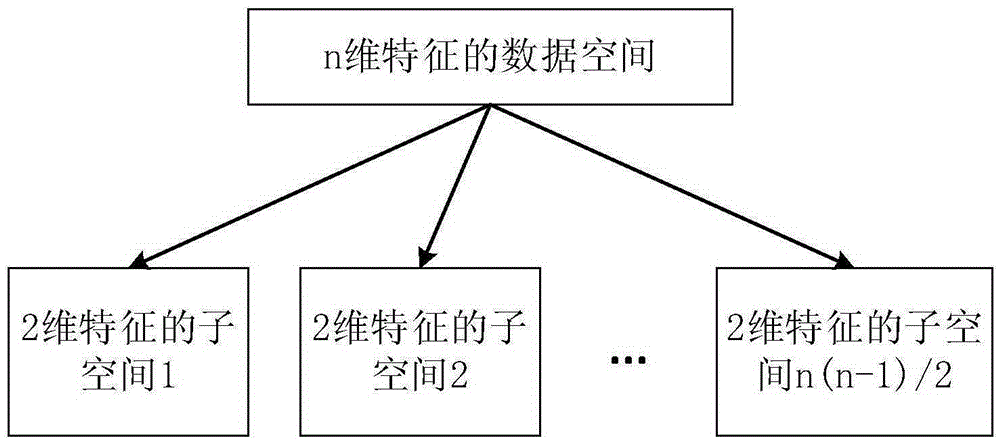
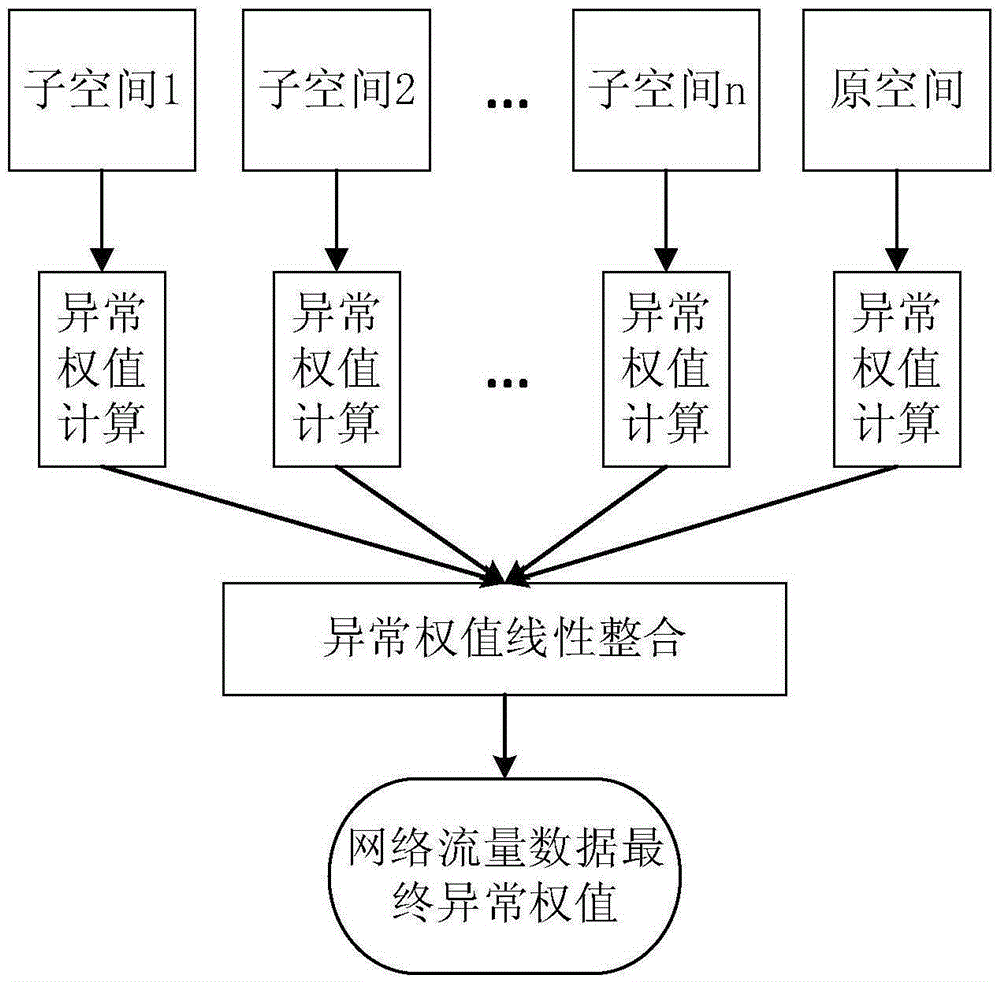
ActiveCN105376260AFully excavatedAvoid disadvantages such as large information biasTransmissionIp addressDensity based
The invention discloses a network abnormal flow monitoring system based on a density peak value cluster, comprising a characteristic selection module, a subspace mapping module, an abnormal weight assignment module, an abnormal weight value integration module, an abnormal weight value threshold determination module, and an abnormal flow detection module. The characteristic selection module chooses a new characteristic space module through a key character source IP address collected in a unit time of one minute; the subspace mapping module maps a high dimension characteristic space to a plurality of low dimension spaces to form a plurality of new characteristic space data; the abnormal weight assignment module calculates the abnormal weight of each data point in each subspace on the basis of distance weight assignment method of the density and the distance; the abnormal weight value integration module calculates the abnormal weight values in the subspace to perform integration to obtain the ultimate abnormal weight of the original space data point; the abnormal weight threshold determination module takes the gradient abrupt change position as a detection threshold after sorting the ultimate abnormal weights according to the reverse order; and the network flow, the abnormal weight of which is greater than the threshold, is abnormal flow, and otherwise, the network flow is the normal flow. The network abnormity flow monitoring system based on the density peak value cluster is applicable to various network environments and can improve the accuracy of the detection precision.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Image super resolution (SR) reconstruction method based on subspace projection and neighborhood embedding
InactiveCN102629374AFeature validReduce dimensionalityImage enhancementOriginal dataWeight coefficient
The invention discloses an image super resolution (SR) reconstruction method based on subspace projection and neighborhood embedding. The method is characterized by: using first and secondary subspace projection methods to project original high-dimensional data to a low-dimensional space, using dimension reduction feature vectors to show a feature of a low-resolution image block so that global structure information and local structure information of original data can be maintained; comparing a Euclidean distance between the dimension reduction feature vectors in the low-dimensional space, finding a neighborhood block which is most matched with the low-resolution image block to be reconstructed, using a similarity and a scale factor between the feature vectors to construct an accurate embedded weight coefficient so that a searching speed and matching precision can be increased; then constructing the similarity and the scale factor between the feature vectors, calculating the accurate weight coefficient and acquiring more high frequency information from a training database; finally, according to the weight coefficient and the neighborhood block, estimating the high-resolution image block with high precision, reconstructing the image which has the high similarity with a real object, which is good for later-stage real object identification processing.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
DWT- and Parametric t-SNE-based characteristic extracting method of motor imagery EEG(Electroencephalogram) signals
ActiveCN105809124AImprove classification accuracySolving generalization learning problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmWigner ville
The invention provides a DWT- and Parametric t-SNE-based characteristic extracting method of motor imagery EEG(Electroencephalogram) signals. First, effective time and frequency ranges of EEG characteristics are determined by using a Wigner-Ville distribution and power spectrum; the EEG signals in a specific time and frequency segment is subjected to three-layer discrete wavelet decomposition and statistical characteristic quantity including the average value, the energy average value, the mean square error and the like are calculated and are taken as the time frequency characteristic of the EEG signals; at the same time, a parameterization t-SNE algorithm is utilized for performing non-linear characteristic mapping on said wavelet coefficients and embedded coordinates corresponding to a low-dimensional space are taken as the non-linear characteristic; the two characteristics are standardized and a characteristic vector including both the time frequency information and the non-linear information of the EEG signals in the specific time frequency segment is obtained. According to the invention, EEG characteristics of compactness and completeness are obtained and a method for solving a problem of poor generalization performance of a traditional manifold learning algorithm in pattern classification application through fitting a multilayer forward propagation neural network to nonlinear mapping is proposed, so that accuracy of pattern classification of MI-EEG signals is improved further.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Valve inner leakage defect type recognition and inner leakage rate calculation method
InactiveCN103488906AReduce lossReduce dependenceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmAcoustic emission
The invention provides a valve inner leakage defect type recognition and inner leakage rate calculation method. The method comprises the step one of carrying out valve inner leakage detection experiments based on the acoustic emission technology and obtaining experimental data; the step two of extracting the data of valve features, process parameters, acoustic emission signal features and the like and constructing high-dimensional feature space; the step three of carrying out locality preserving projection and dimension reduction on the data of the high-dimensional feature space and extracting the low-dimensional space features; the step four of setting up a valve inner leakage defect type recognition model based on classification of support vectors, selecting the RBF kernel function, determining the optimal parameters of the model according to the particle group algorithm, and inputting the low-dimensional space flag data for carrying out training; the step five of marking no-label data samples influencing the model largely based on the active-learning method, and setting up a valve inner leakage rate calculation model of the regressive support vectors; the step six of utilizing the model to forecast the inner leakage defect types and the inner rates of a valve to be tested. According to the method, dependence on the number of the data samples is lowered, and the problem of difficulty of valve inner leakage quantitative detection can be solved effectively.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com