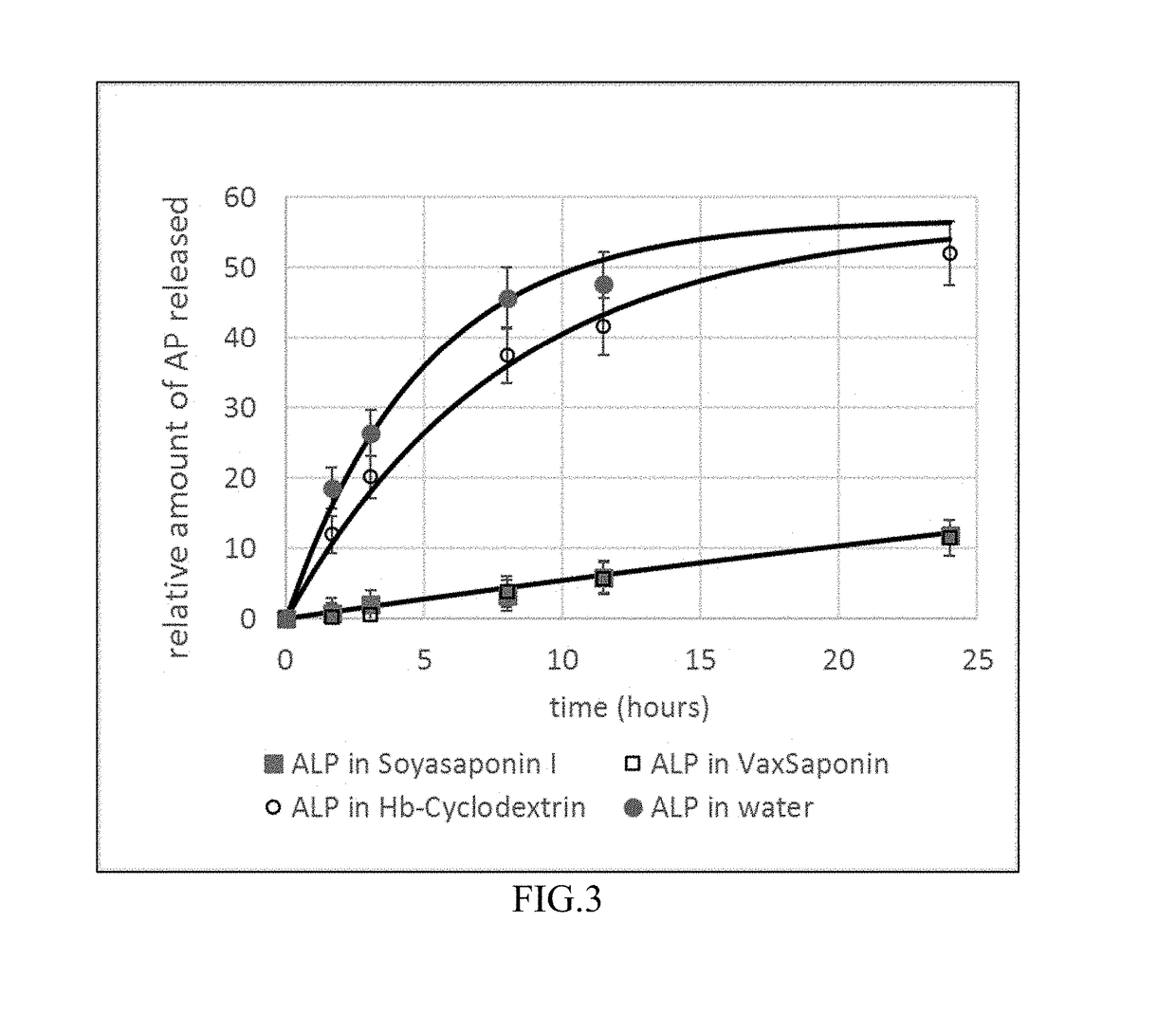
Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Detection is slight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
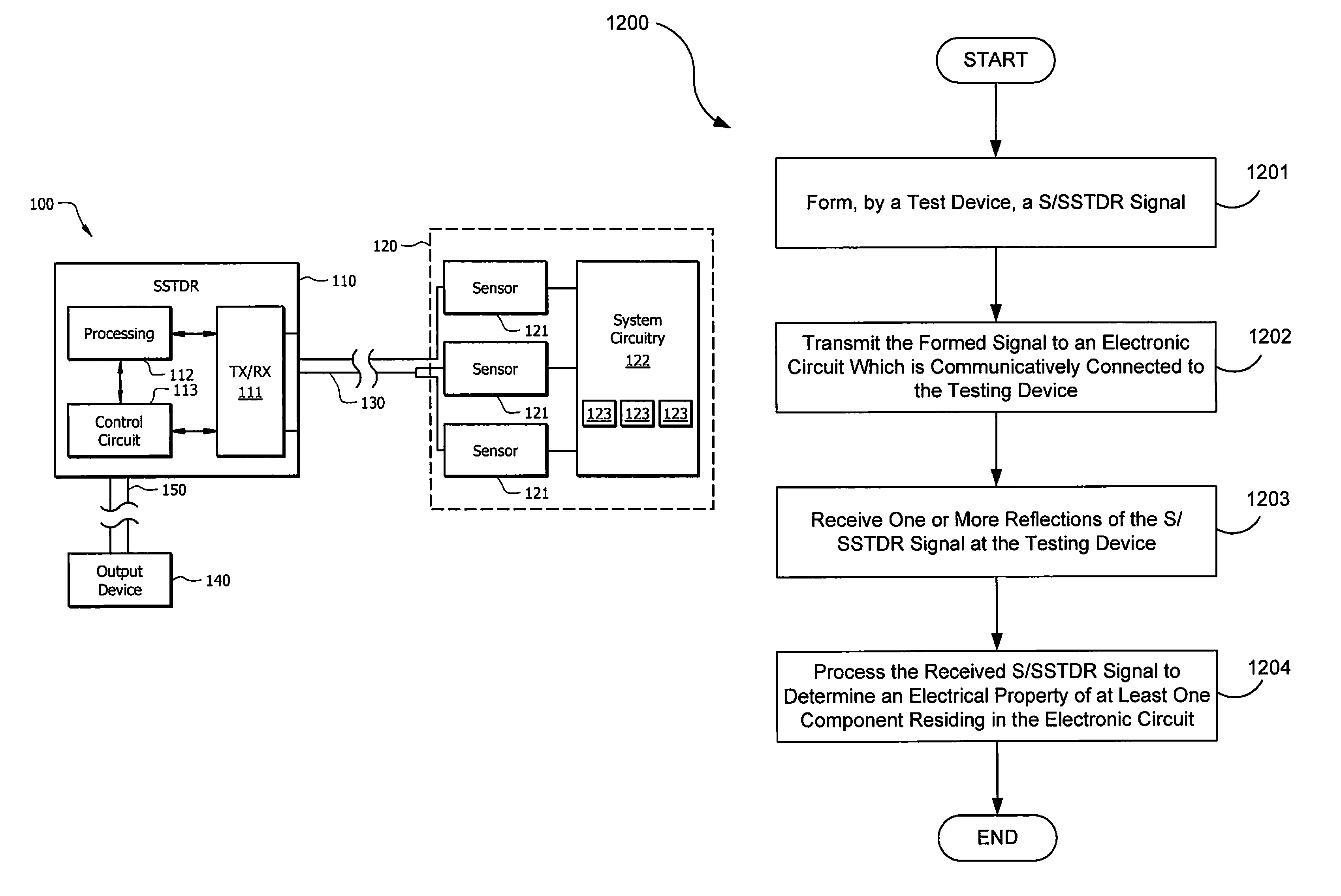
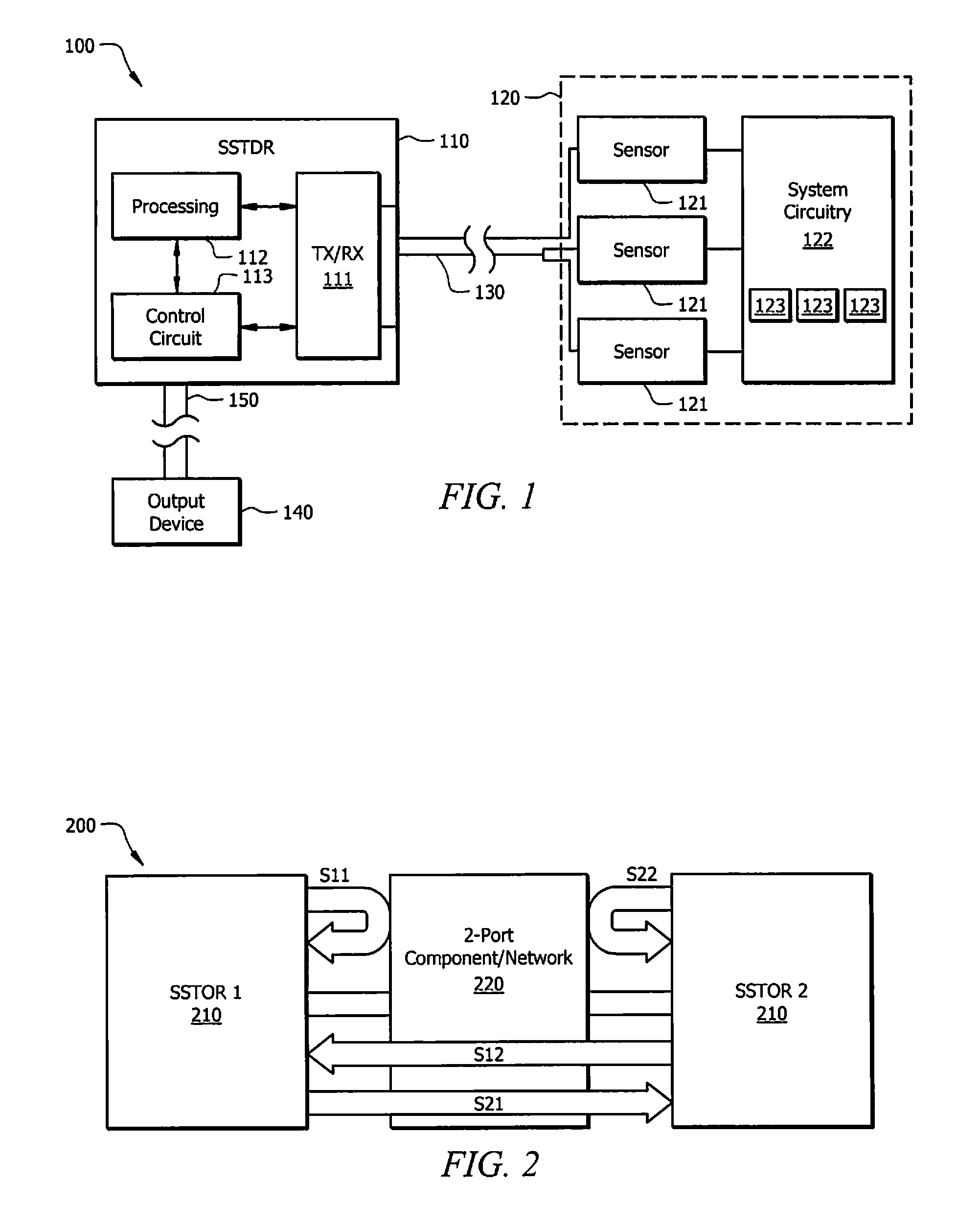
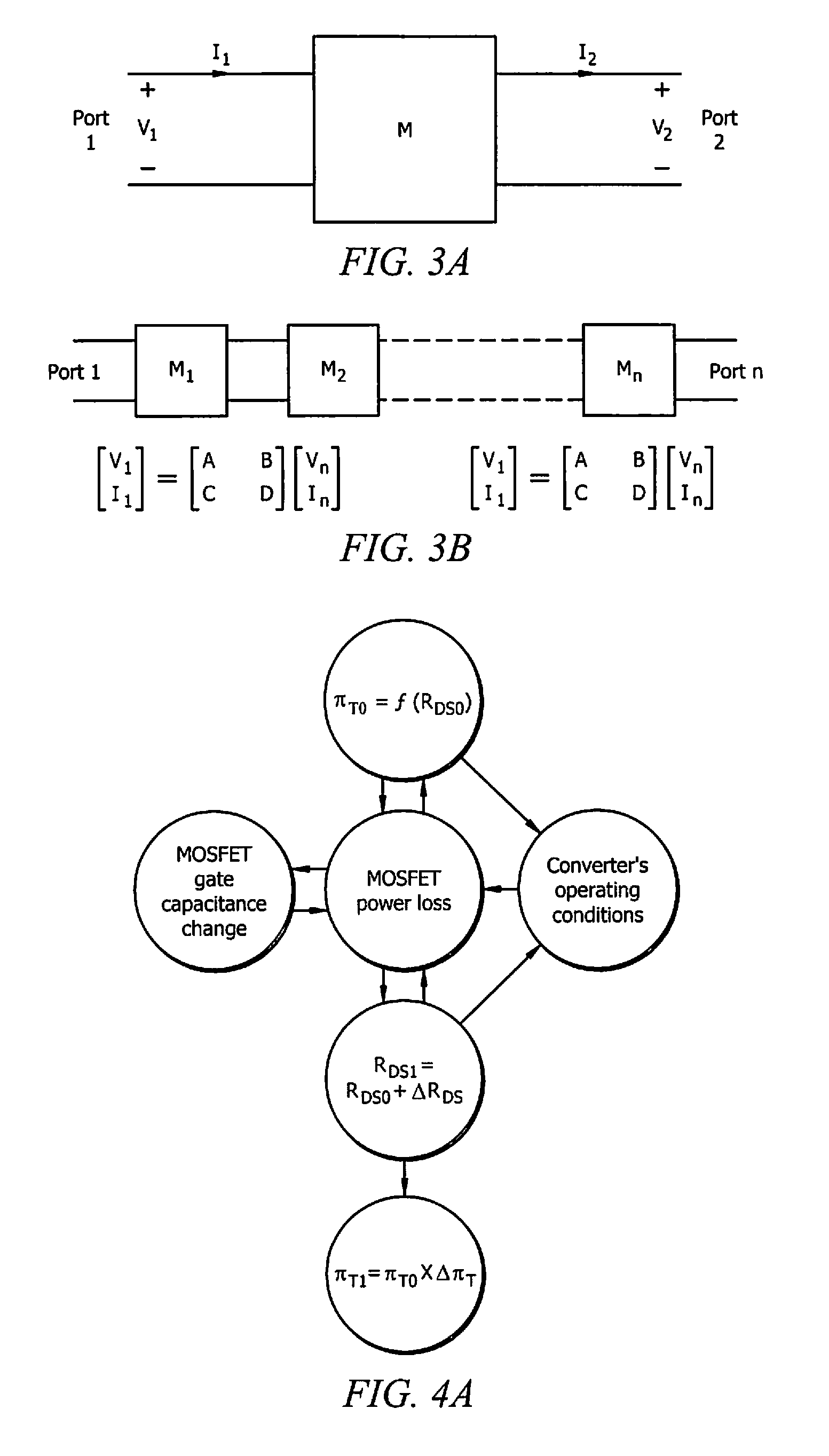
Systems and methods for implementing S/SSTDR measurements
ActiveUS9244117B2Shorten the timeAccurate measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingCircuit under testSpread spectrum
Systems and methods which utilize spread spectrum sensing on live circuits to obtain information regarding a circuit under test are provided. In some embodiments S / SSTDR testing may be utilized to obtain R, L, C and Z measurements from circuit components. In yet further embodiments, these measurements may be utilized to monitor the output of sensors on a circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
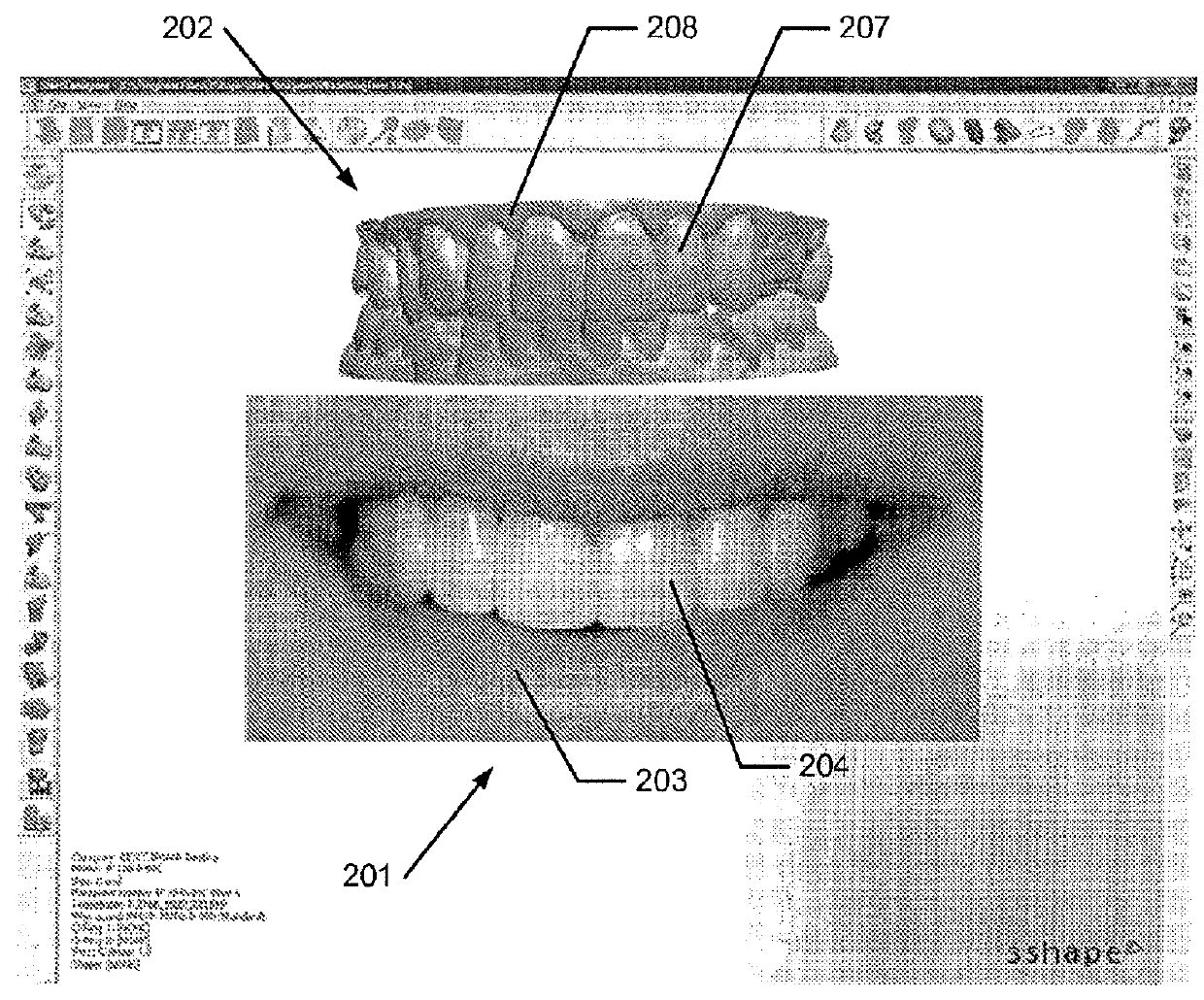
2D image arrangement
ActiveUS9336336B2Accurate modelingGood for comparisonImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed is a method of designing a dental restoration for a patient, wherein the method includes providing one or more 2D images, where at least one 2D image includes at least one facial feature; providing a 3D virtual model of at least part of the patient's oral cavity; arranging at least one of the one or more 2D images relative to the 3D virtual model in a virtual 3D space such that the 2D image and the 3D virtual model are aligned when viewed from a viewpoint, whereby the 3D virtual model and the 2D image are both visualized in the 3D space; and modeling a restoration on the 3D virtual model, where the restoration is designed to fit the facial feature of the at least one 2D image.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
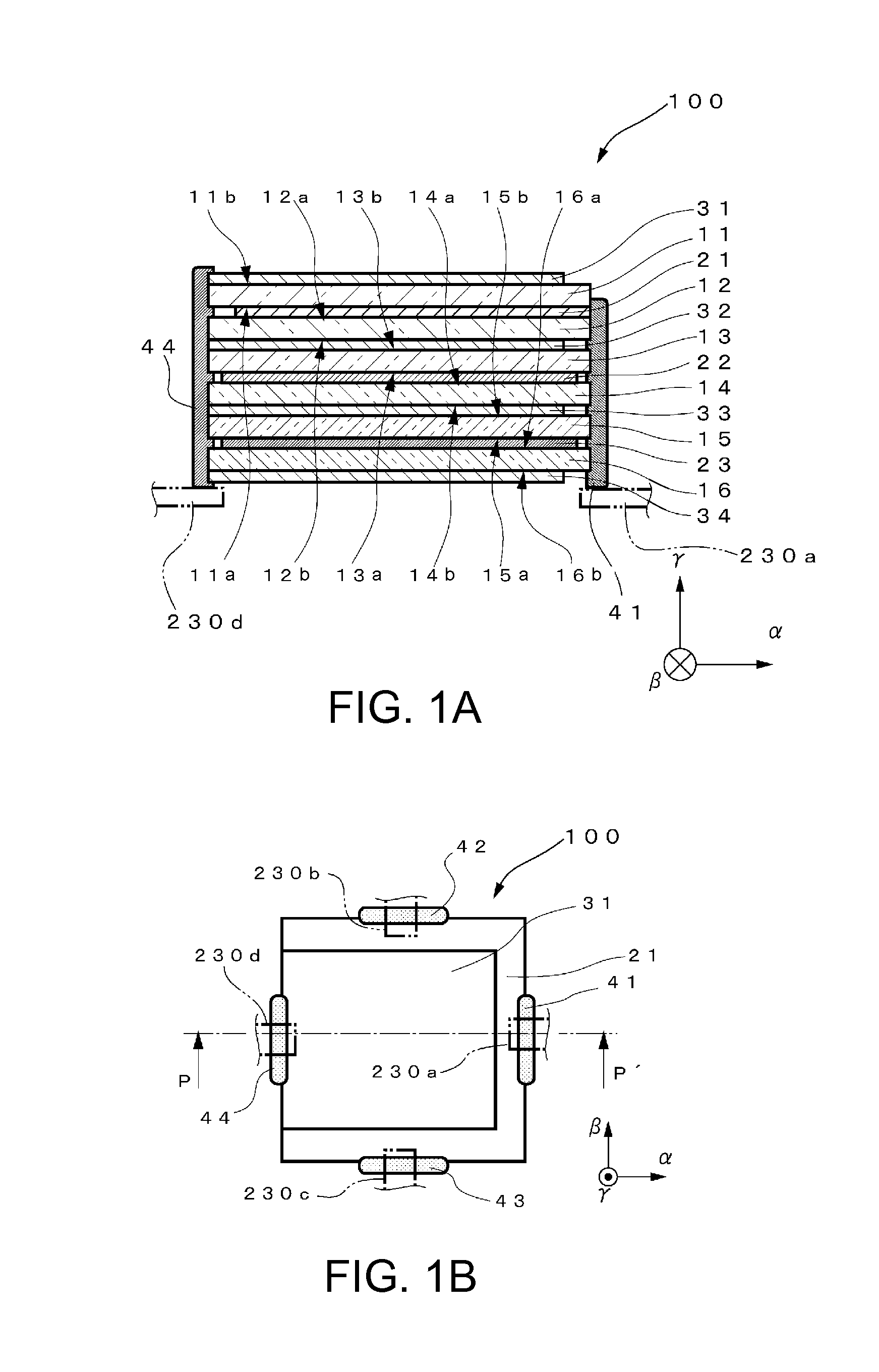
Sensor element, force detecting device, and robot
ActiveUS20130112010A1Improve reliabilityImprove securityForce measurementTension measurementElectrical conductorPhysics
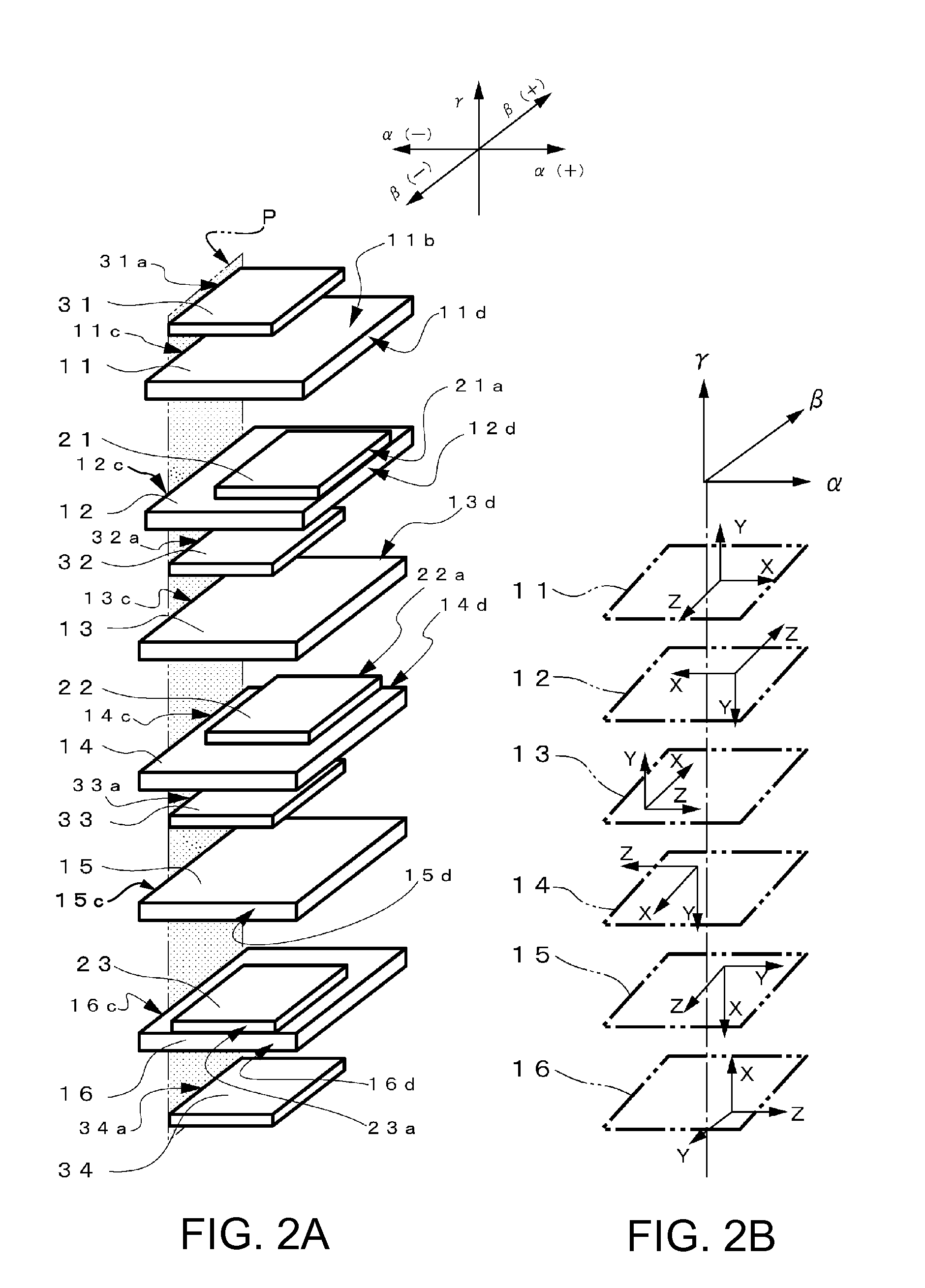
A sensor element is formed by, when an α axis, a β axis orthogonal to the α axis, and a γ axis orthogonal to the α axis and the β axis are set, laminating piezoelectric substrates and electrodes in the γ axis direction. The sensor element includes connecting sections arranged such that a part of external sections of the electrodes aligns with a part of external sections of the piezoelectric substrates. The connecting sections are arranged not to align with one another in a direction of the γ axis. Conductors that electrically connect the connecting sections and external connecting sections are formed along outer peripheral sections of the piezoelectric substrates.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
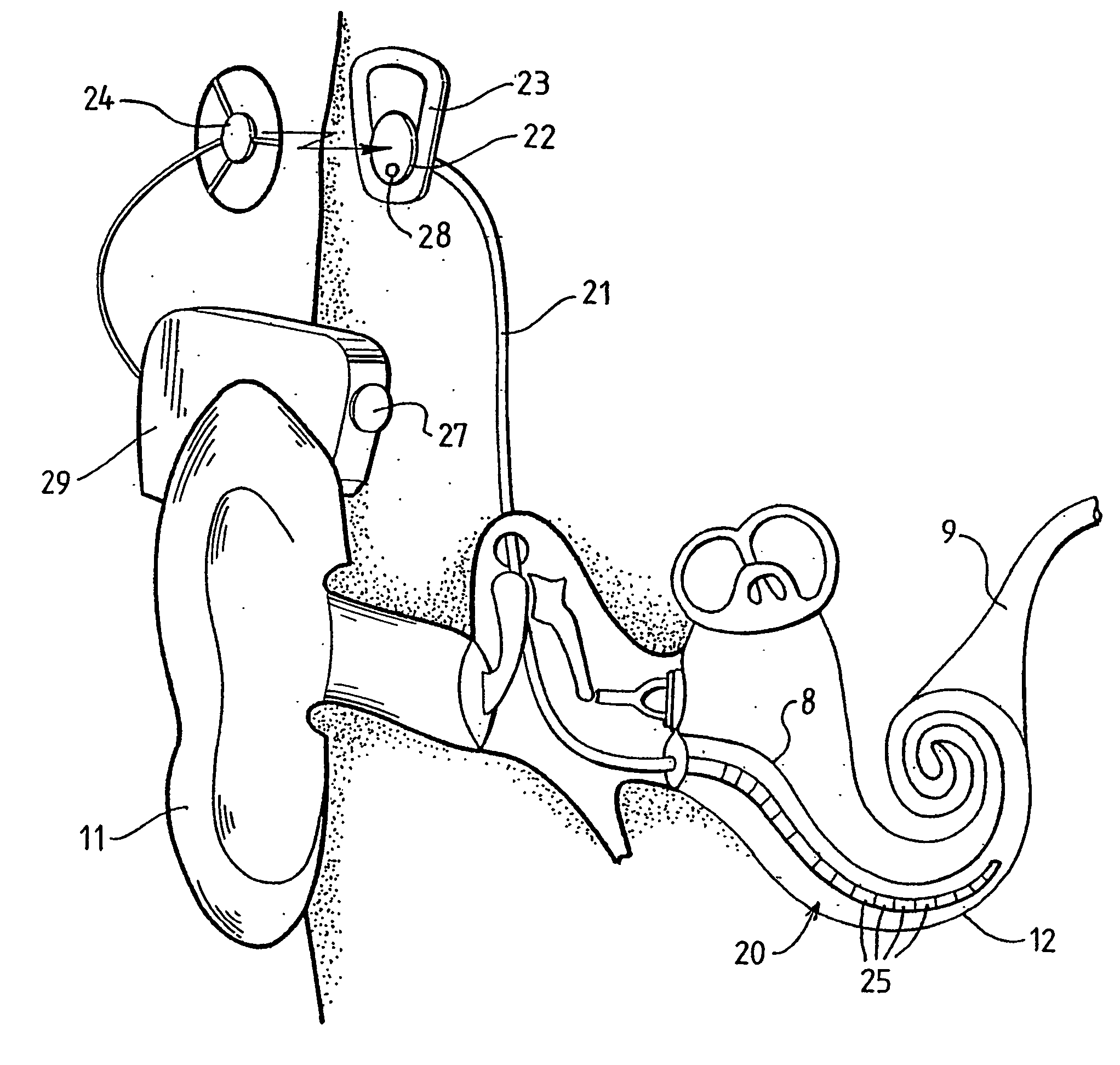
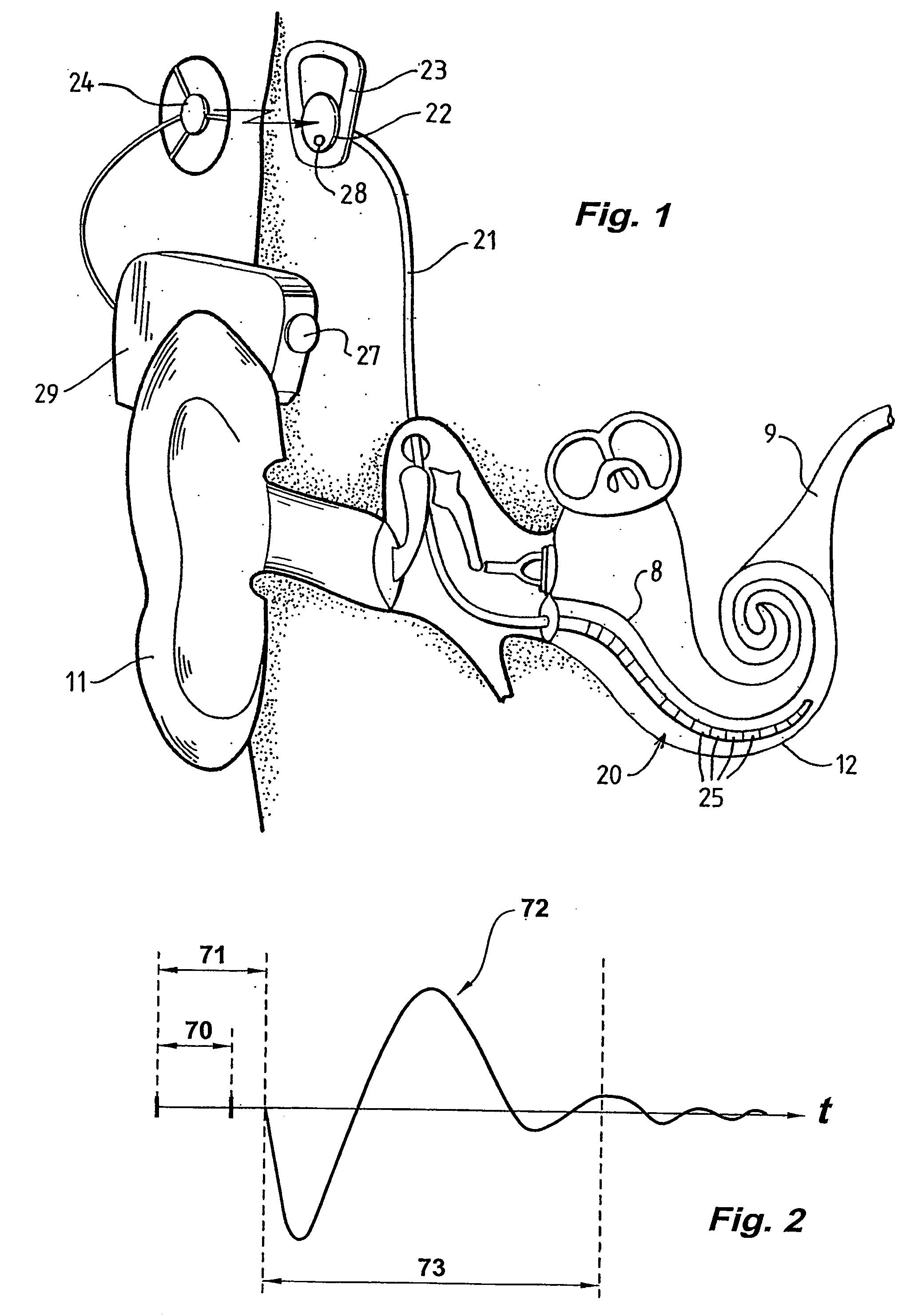
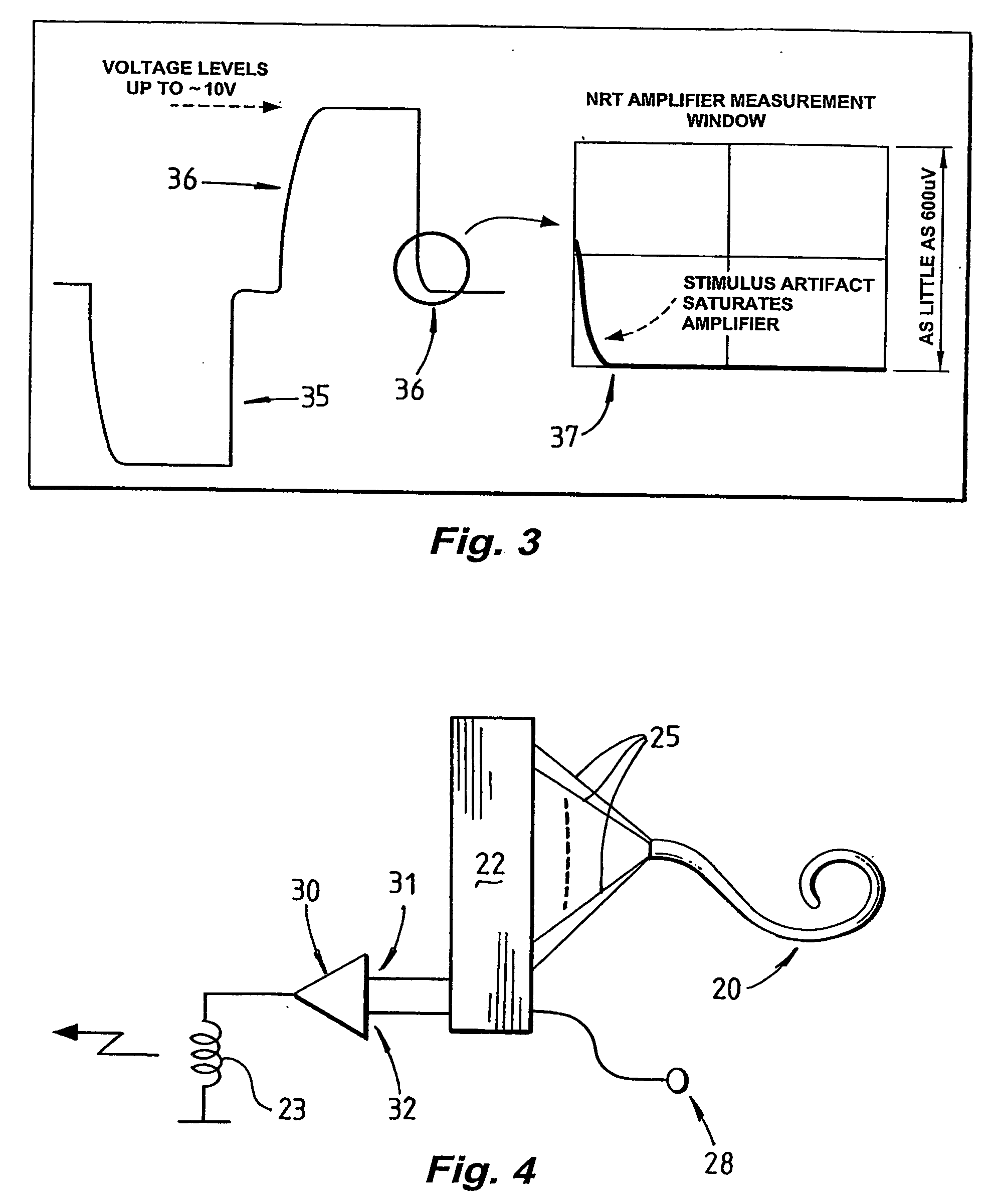
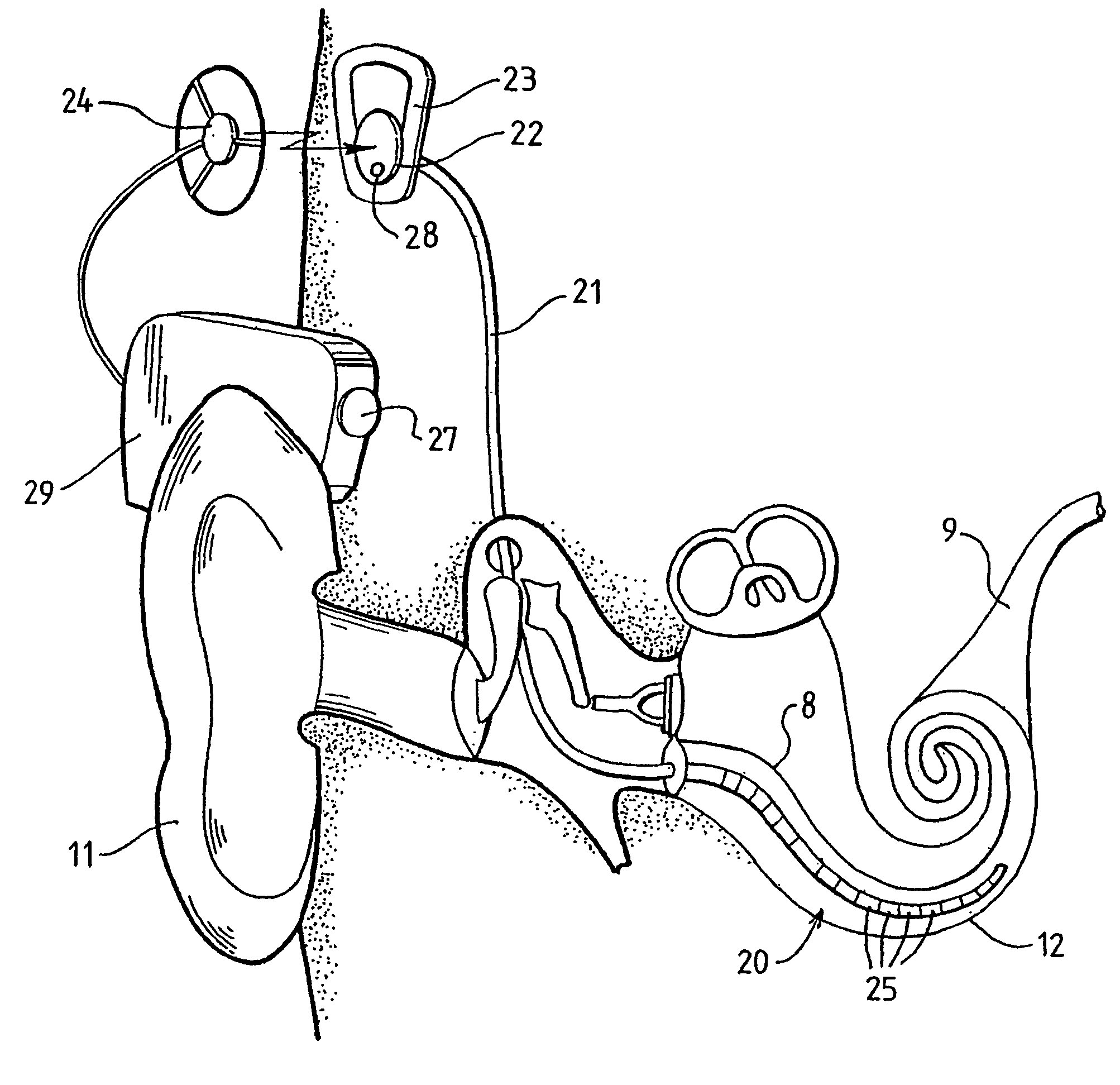
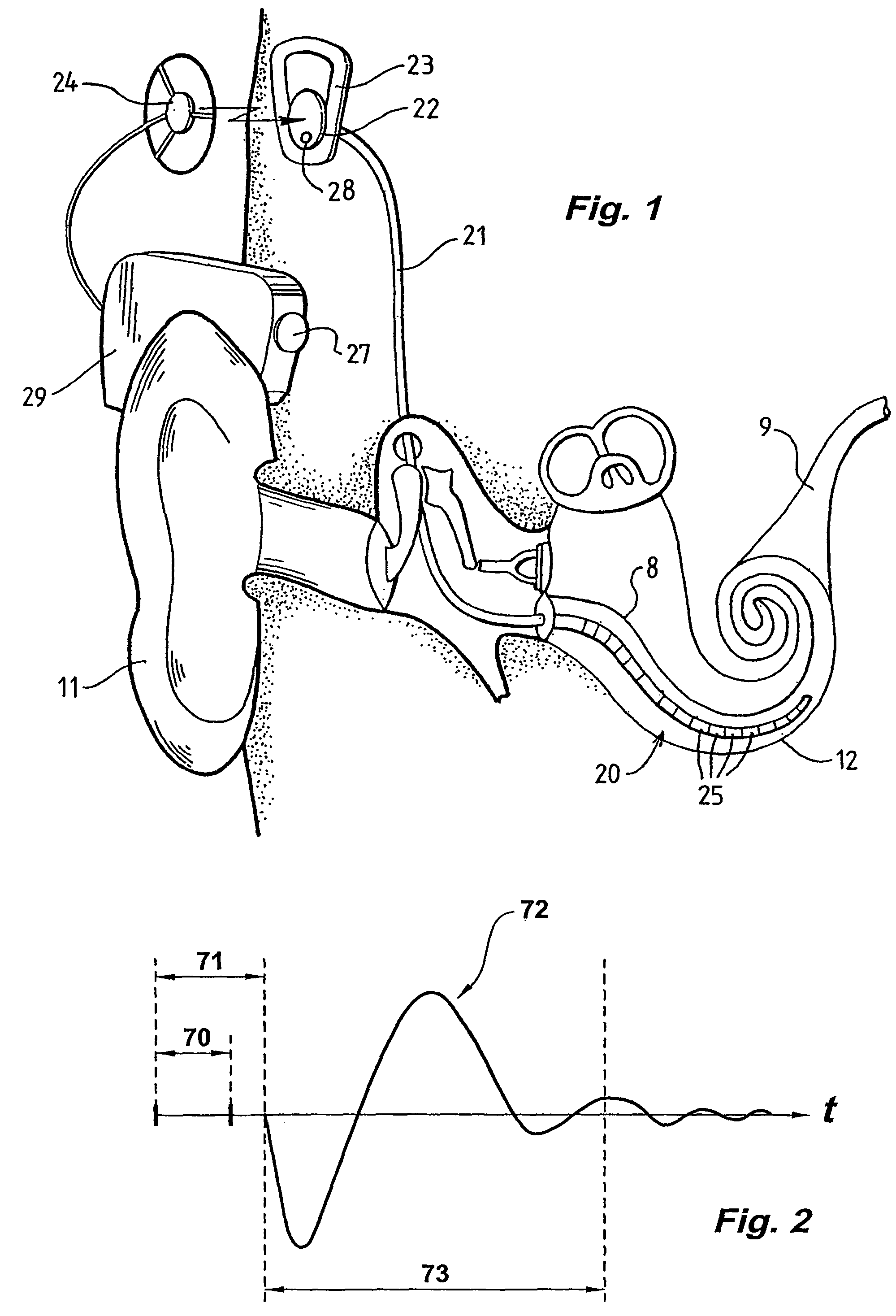
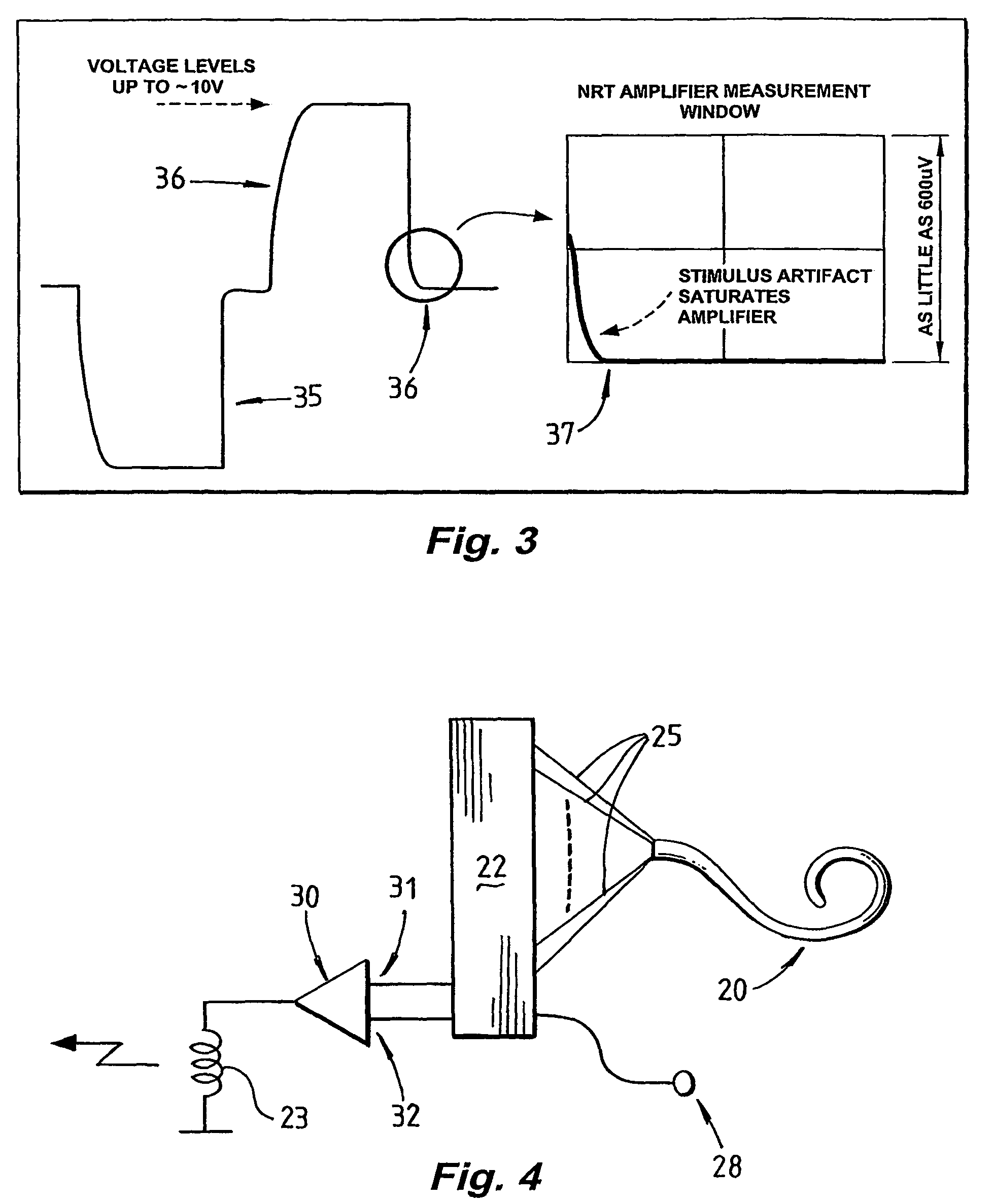
Method and apparatus for measurement of evoked neural response
InactiveUS20060089561A1Reduce impact of noiseAvoid effectElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyVoltage referenceEngineering
A method and device for measuring an evoked neural response comprising a sensor (25) for obtaining a sensed signal representing the evoked neural response, a high gain amplifier (30) having a signal input (31) for receiving the sensed signal and having a reference input (32), and means for altering or setting a reference voltage at the reference input (32) to prevent the amplifier (30) saturating with variations of the sensed signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Throttle Twist Grip
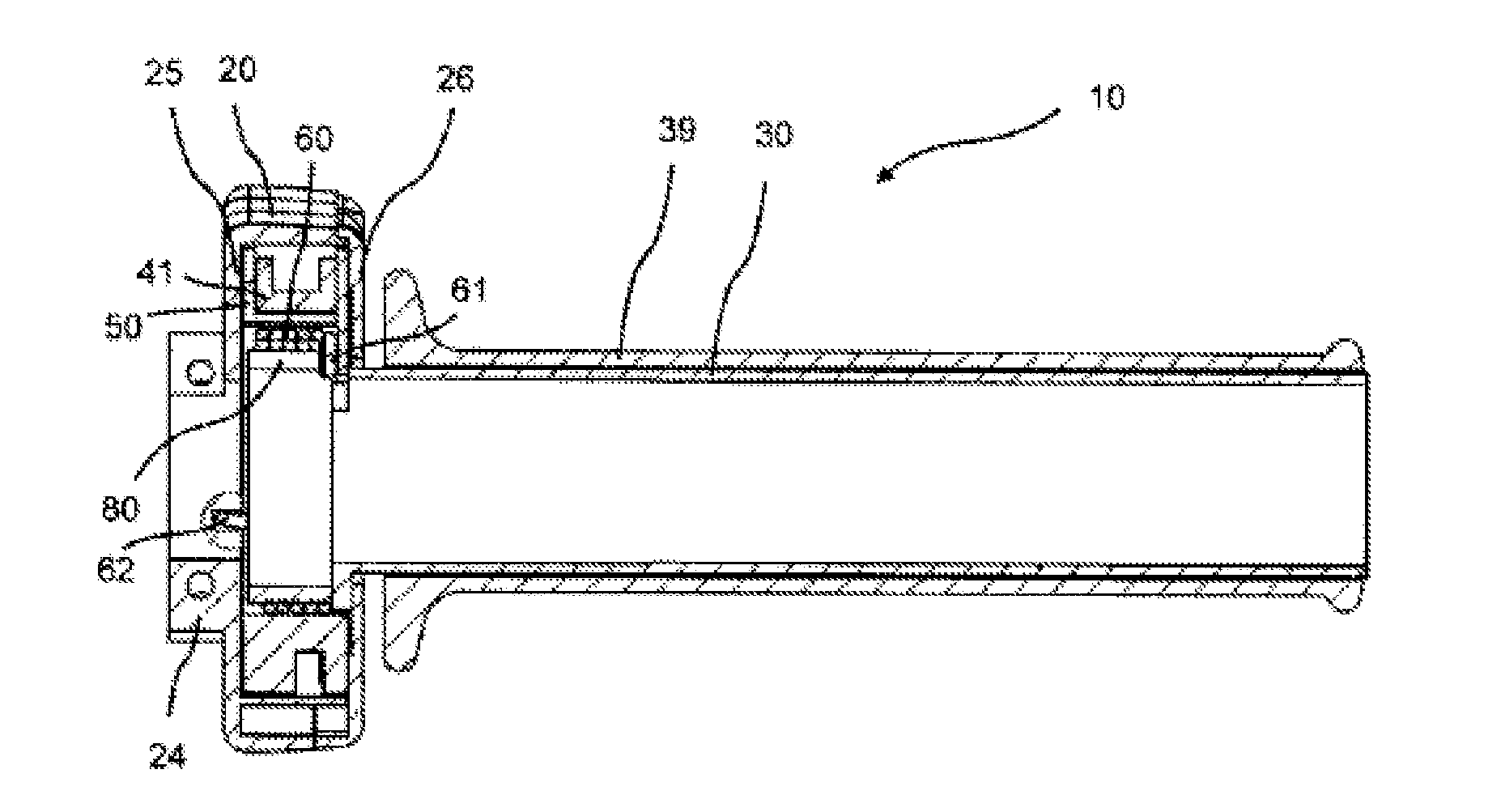
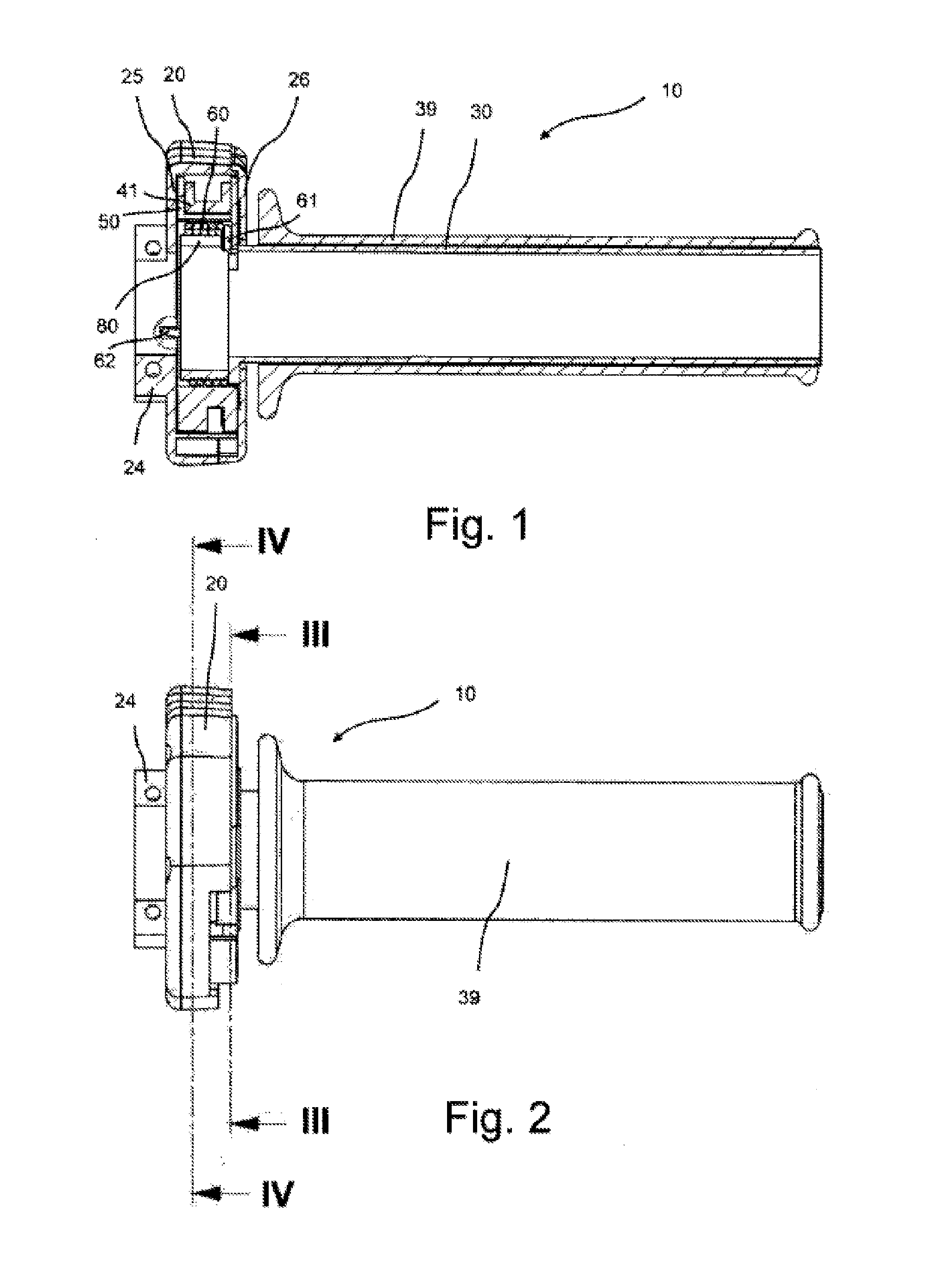
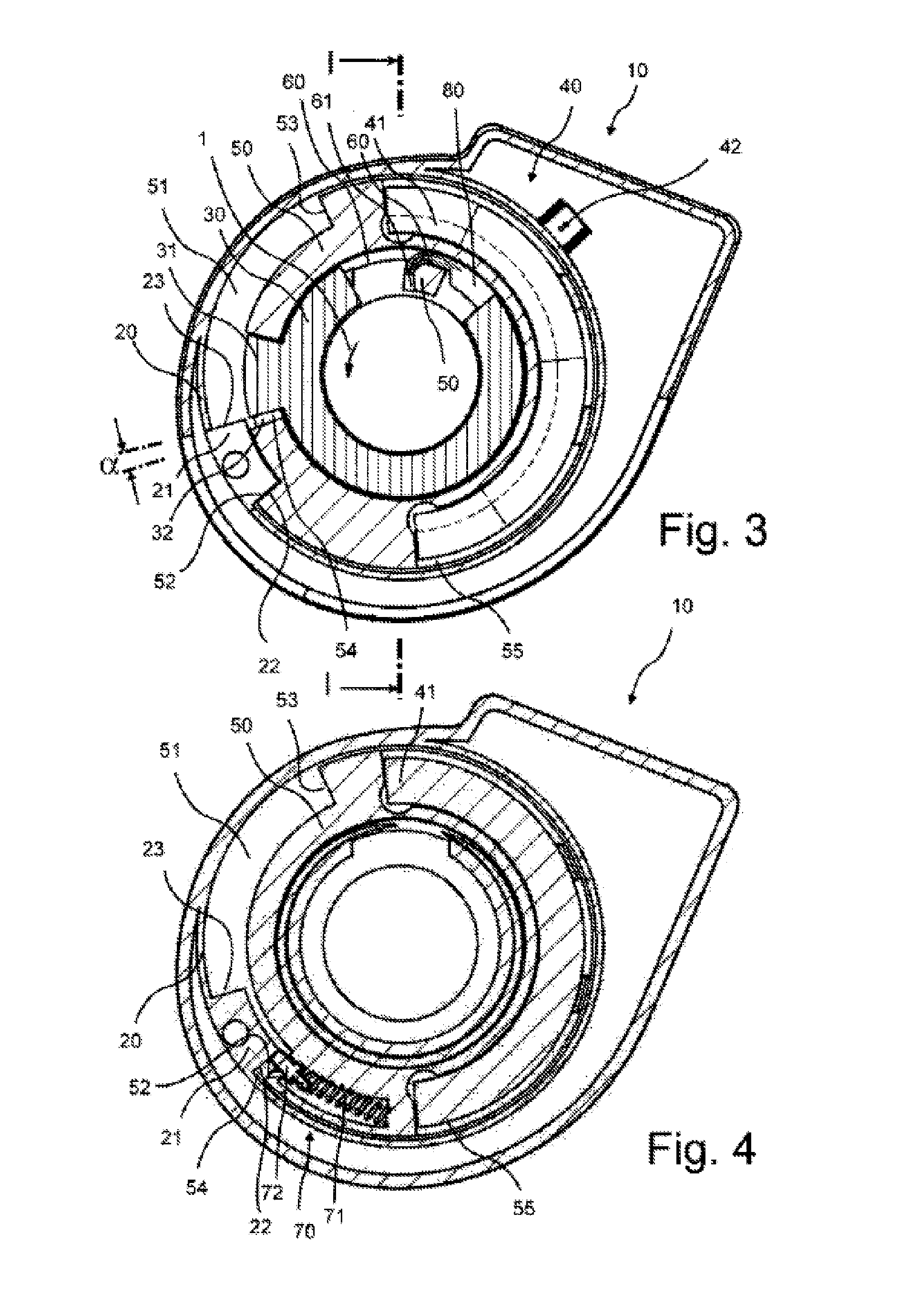
InactiveUS20130111983A1Easily connectReduce stepsEngine testingCycle control systemsEngineeringThrottle
A throttle twist grip includes a housing, a grip tube rotatable about an axis of rotation relative to the housing, a position detector having a position indicator and a sensor operable to detect relative position of the grip tube relative to the housing, a holder shaped to receive part of the position detector, and at least one of the holder being mounted rotatably about the axis in relation to the grip tube, the grip tube having a catch operable to carry along the holder upon actuation, the holder being rotatable about the axis in relation to the grip tube by an angle corresponding to idling play, a cruise control switch-off device, an angle of rotation limiting device disposed substantially in an axial plane of the holder, and a friction device operable to have a greater frictional resistance in an actuating direction than counter to the actuating direction upon actuation.
Owner:GUSTAV MAGENWIRTH
Dual-axis acceleration detection element
InactiveUS20110179870A1High sensitivityGood linear relationshipAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsCapacitanceClassical mechanics
A dual-axis acceleration detection element comprises a first detection element, a second detection element and a stationary unit. The first detection element is movable relative to the second detection element. The second detection element is movable relative to the stationary unit. The relative movements take place on different axes to detect acceleration on two different axes. The first detection element and the second detection element are interposed by corresponding detection electrodes, and the second detection element and the stationary unit also are interposed by other corresponding detection electrodes. Hence when the relative movements occur among the first and second detection elements and the stationary unit, overlapped areas of the detection electrodes change to generate and output a capacitance difference, thereby acceleration alteration can be detected.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
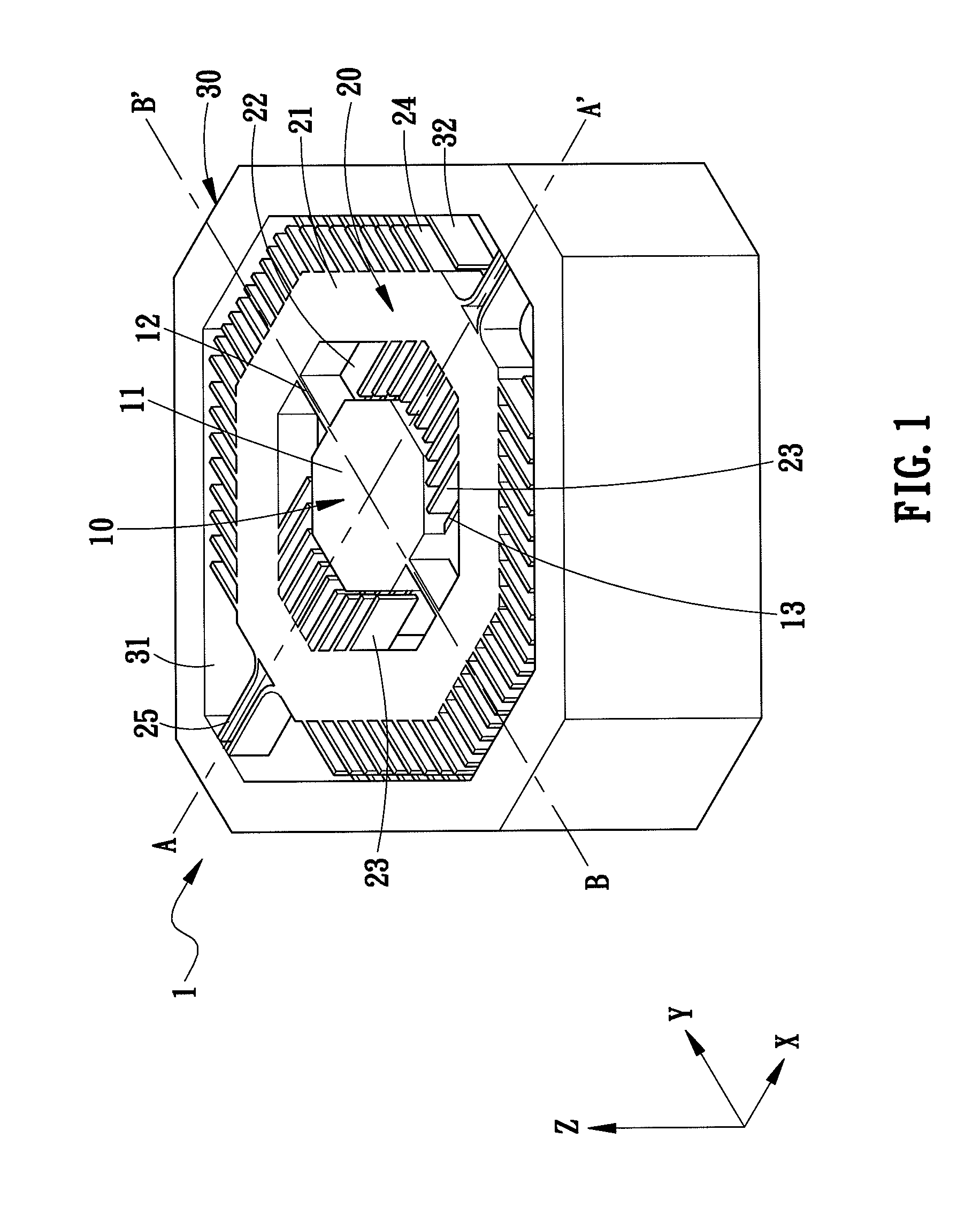
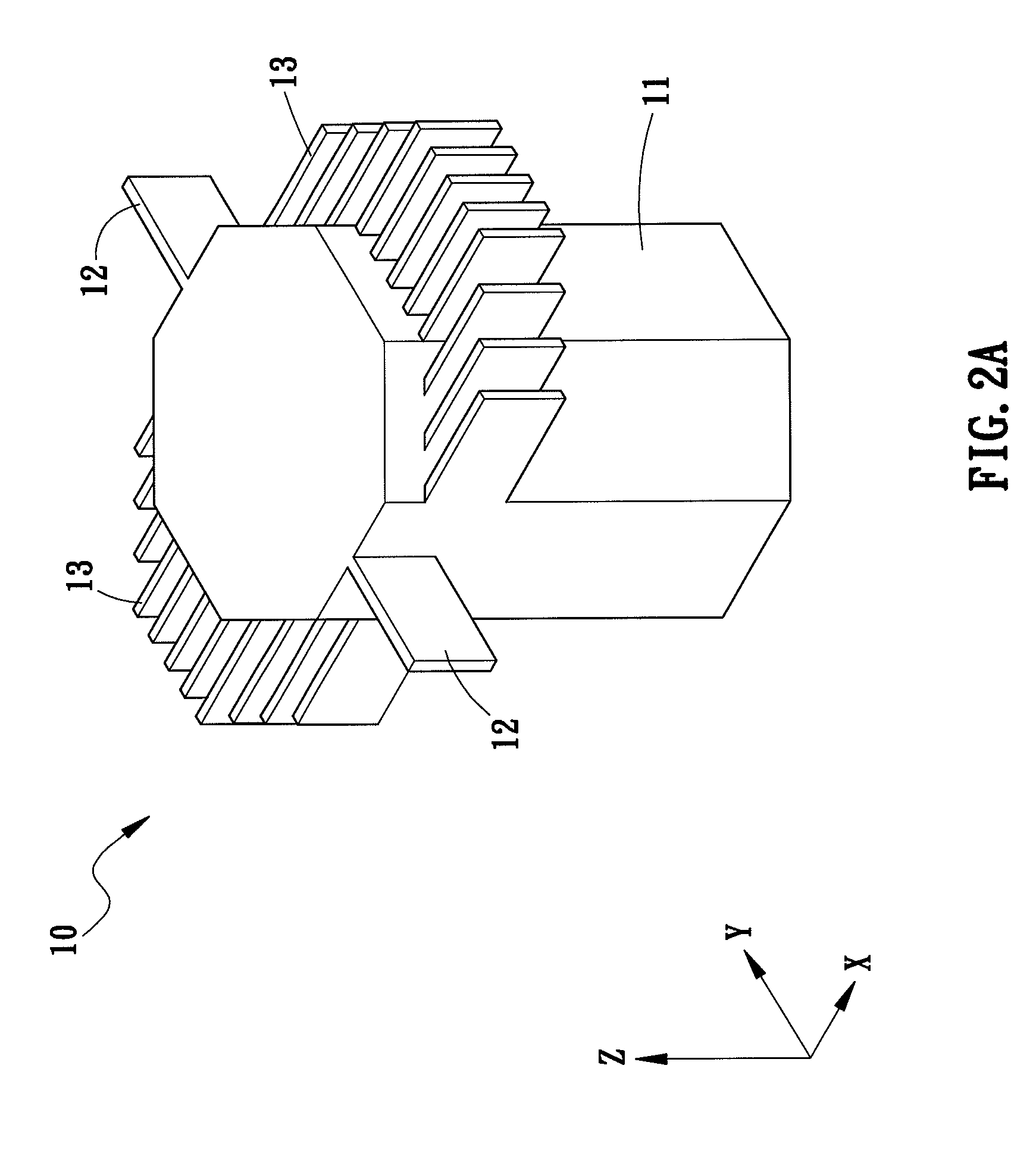
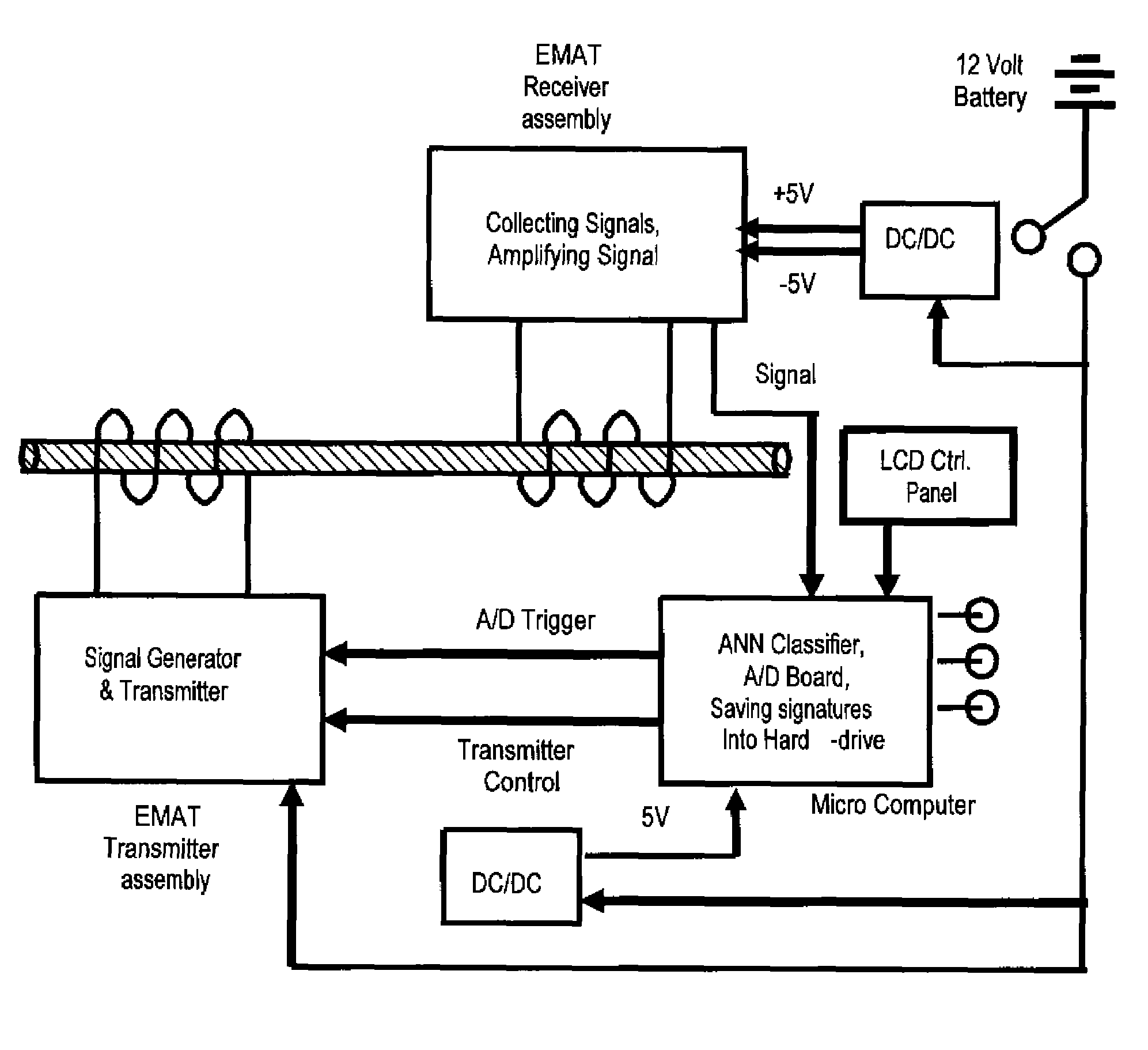
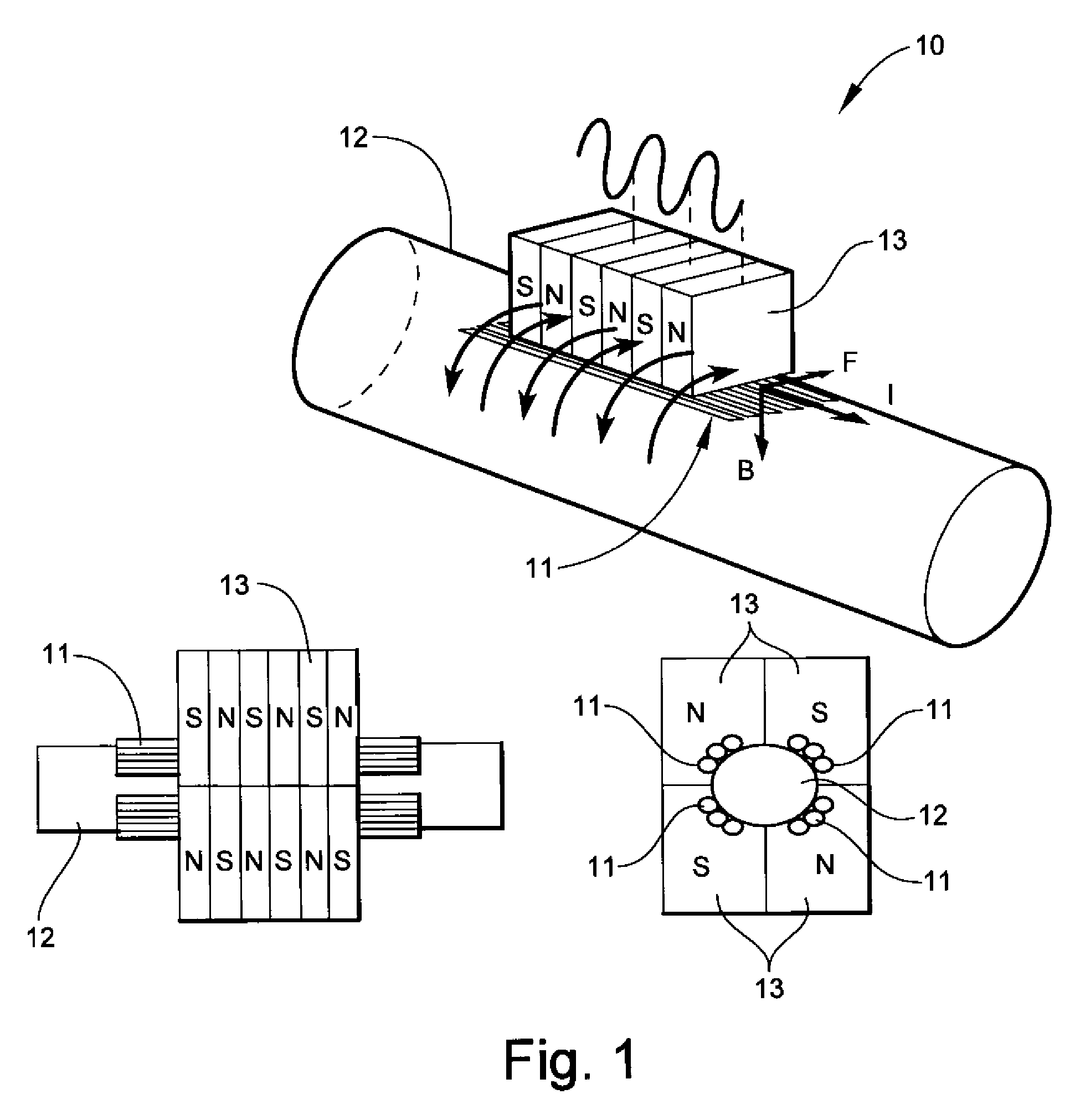
Self-contained apparatus for inspection of electric conductors
ActiveUS7437934B2Detected quickly and efficientlyDetection is slightAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFault location by pulse reflection methodsElectrical conductorTransmitter
A self-contained apparatus for inspecting energized and de-energized conductors. The apparatus includes a housing, at least one transmitter contained within the housing for generating and impinging pulses onto an electrical conductor, such that the pulses travel through and are reflected by the electrical conductor, and at least one receiver contained within the housing for receiving reflected pulses from the electrical conductor. The apparatus further including a controller for determining a condition of the electrical conductor based on an evaluation of the reflected pulses, and at least one indicator for displaying the condition of the electrical conductor determined by the controller.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DENVER
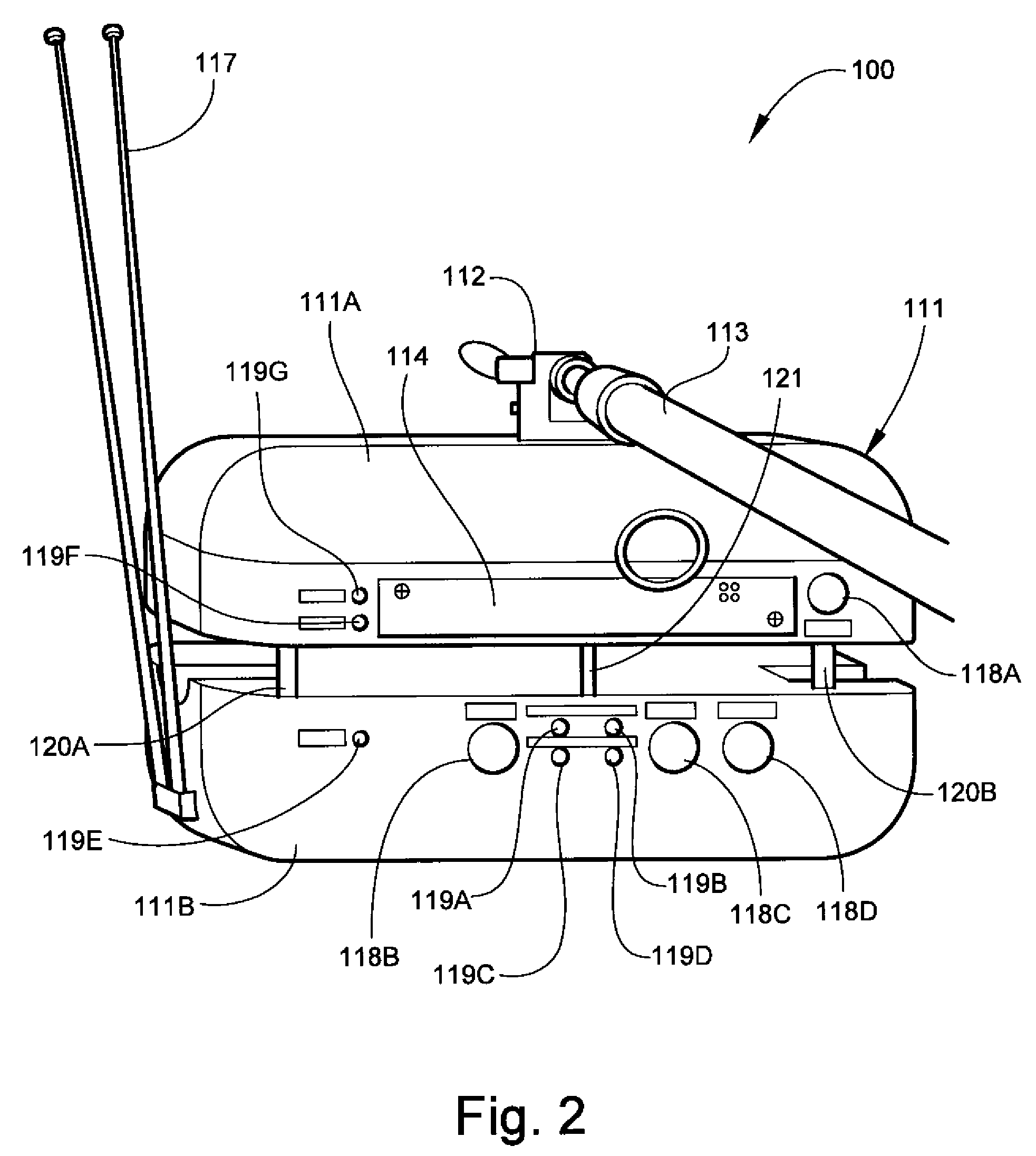
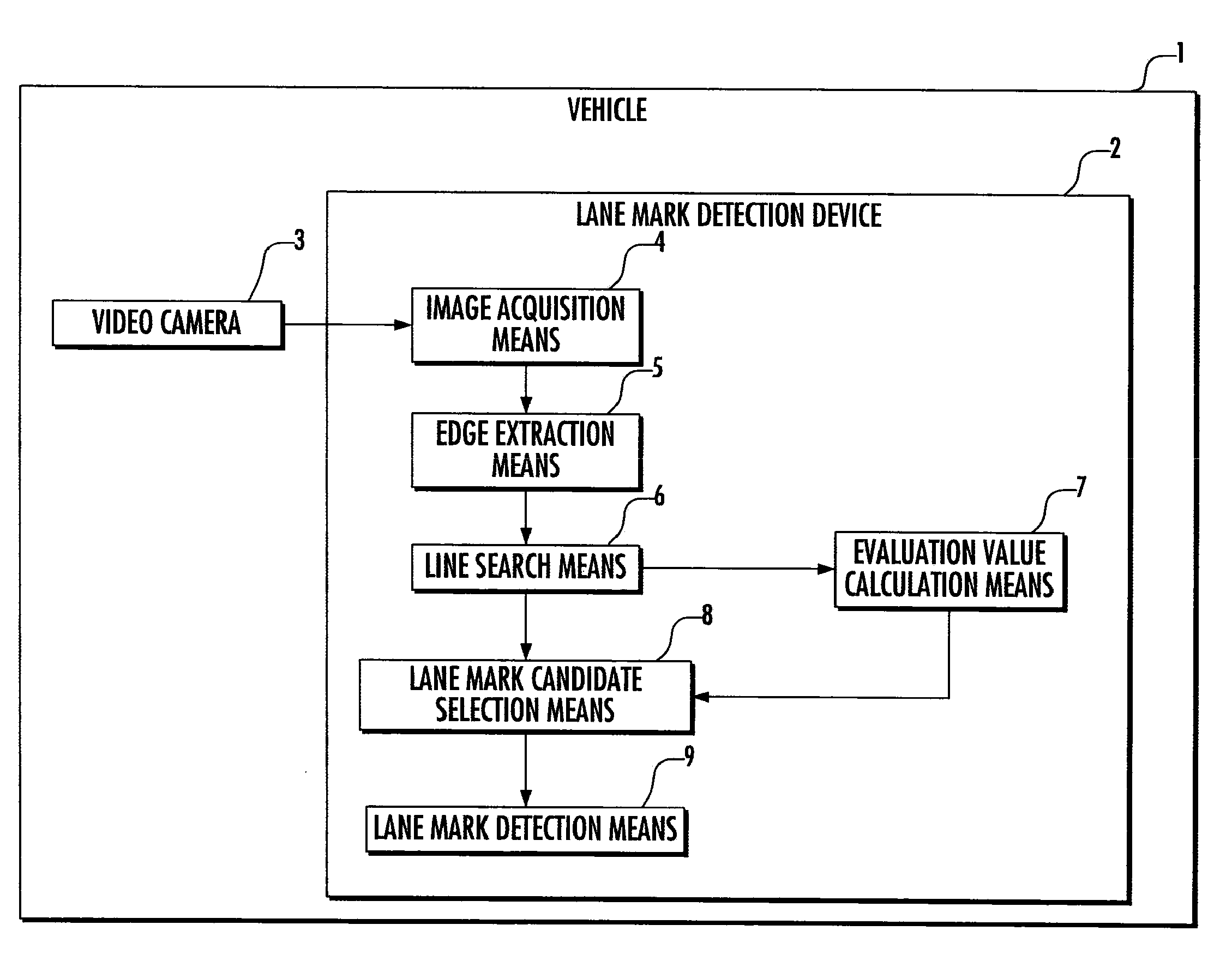
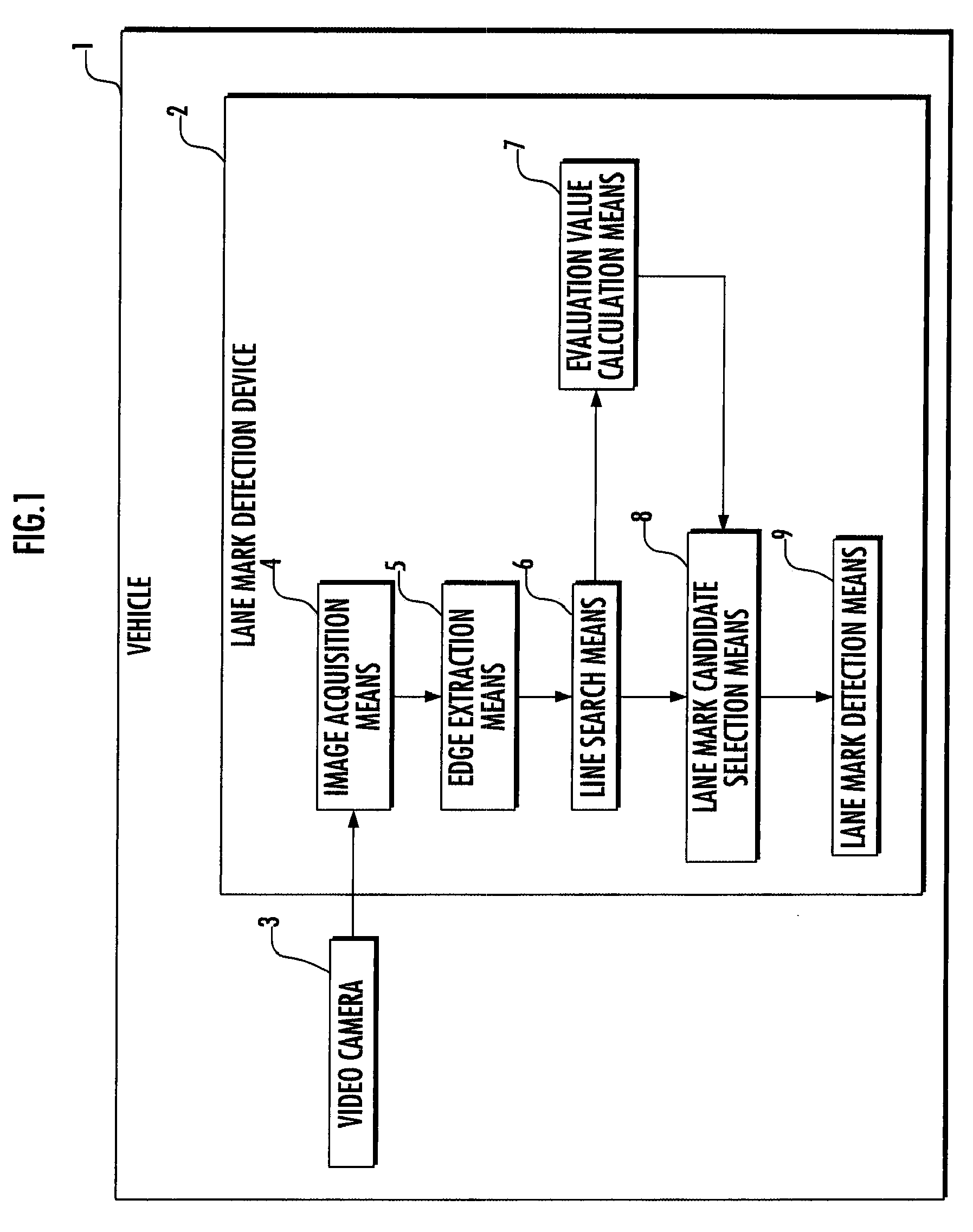
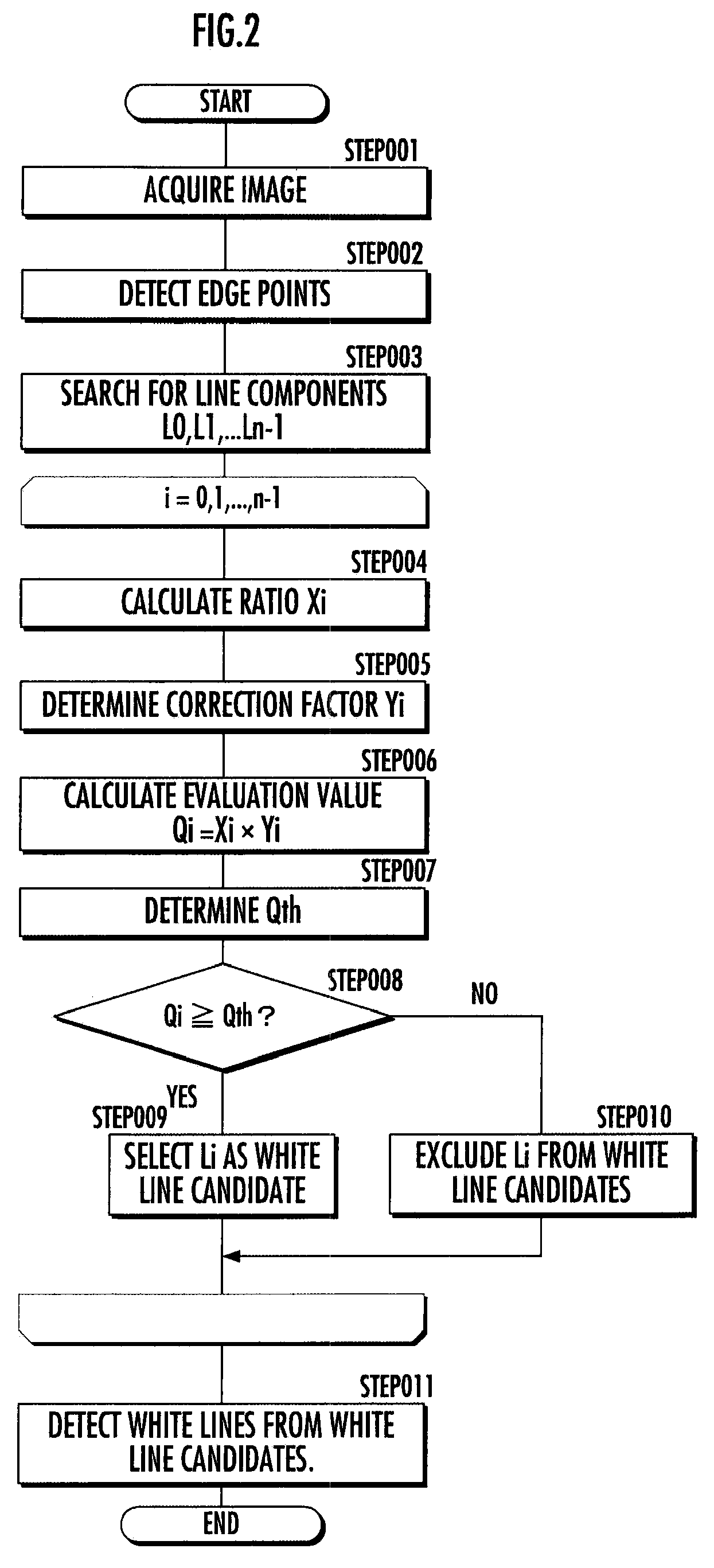
Vehicle and lane mark detection device
InactiveUS8208021B2Improve detection accuracyReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Line search
A vehicle includes: an image acquisition means (4) which acquires a road image via an imaging means (3); an edge extraction means (5) which extracts edge points from the acquired image; a line search means (6) which searches the extracted edge points for line components; an evaluation value calculation means (7) which calculates an evaluation value indicating the degree that each line component approximates a linear lane mark on the road for the line components searched for; a lane mark candidate selection means (8) which selects line components each having an evaluation value greater than a predetermined threshold value as candidates for a line component corresponding to the lane mark from the line components searched for; and a lane mark detection means (9) which detects the lane mark by determining the line component corresponding to the lane mark from the selected candidates for the line component. This allows the detection accuracy to be increased by preventing an object other than a lane mark on the road from being incorrectly detected as a linear lane mark such as a white line when detecting a linear lane mark such as a white line from the road image.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
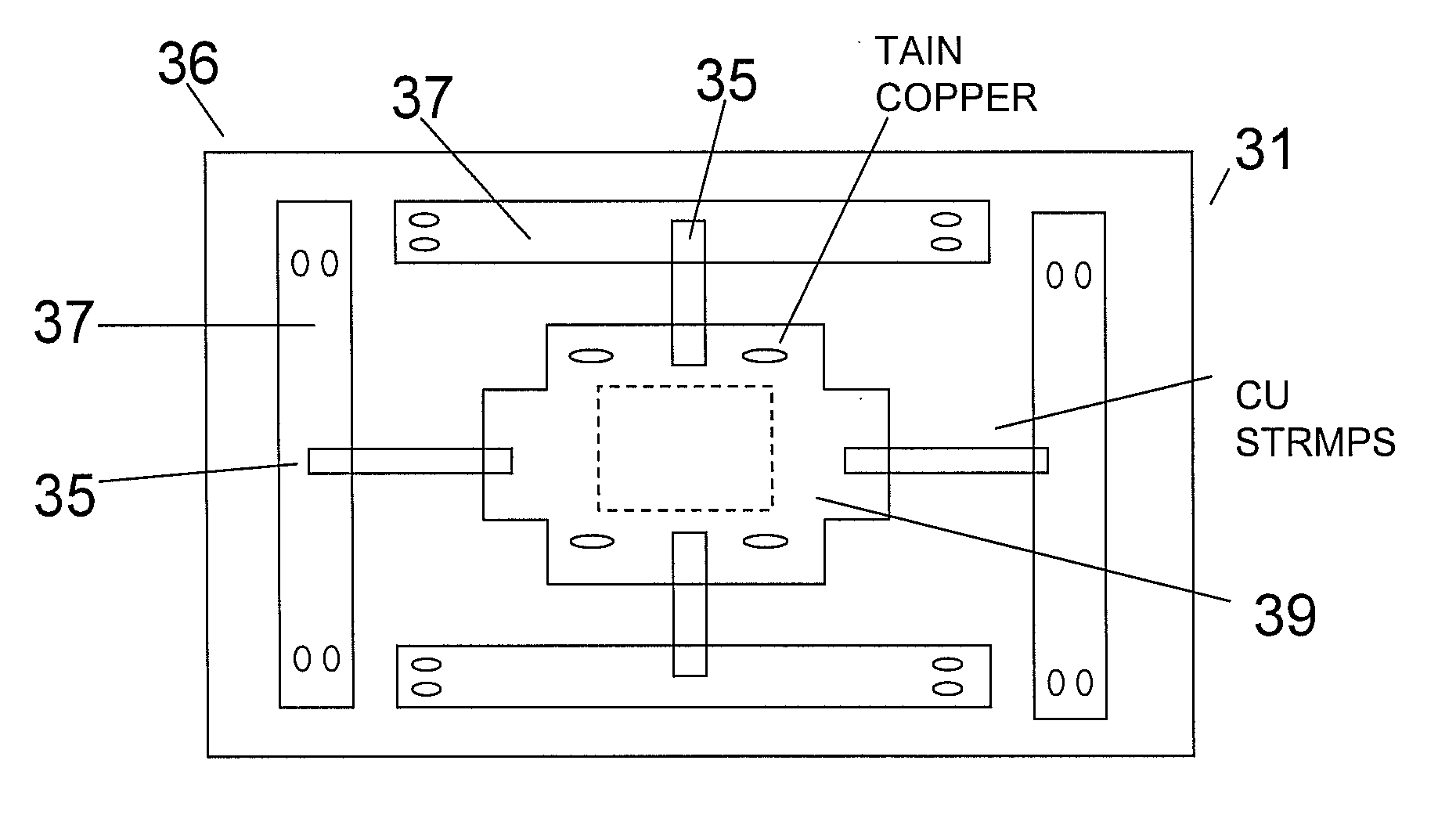
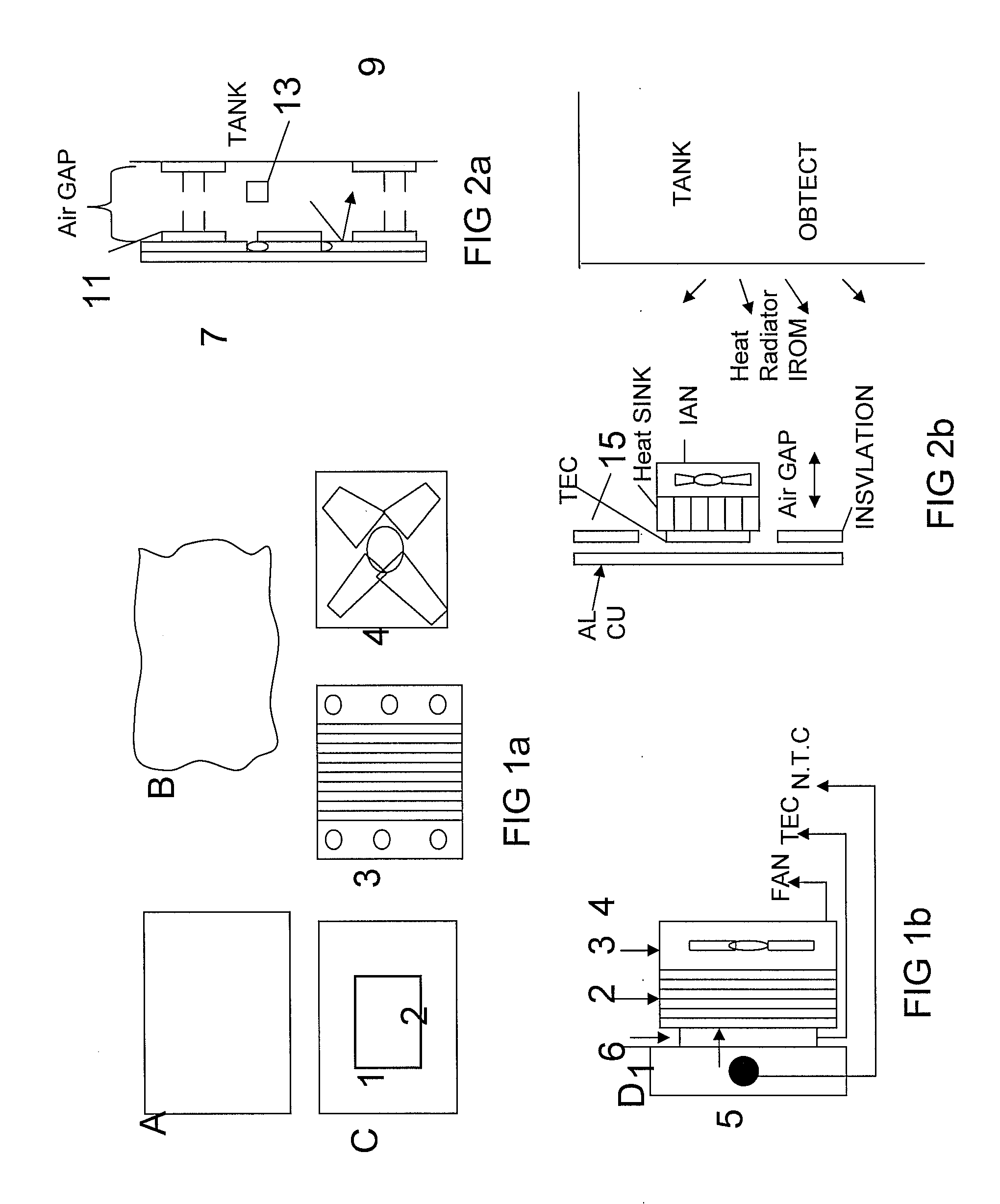
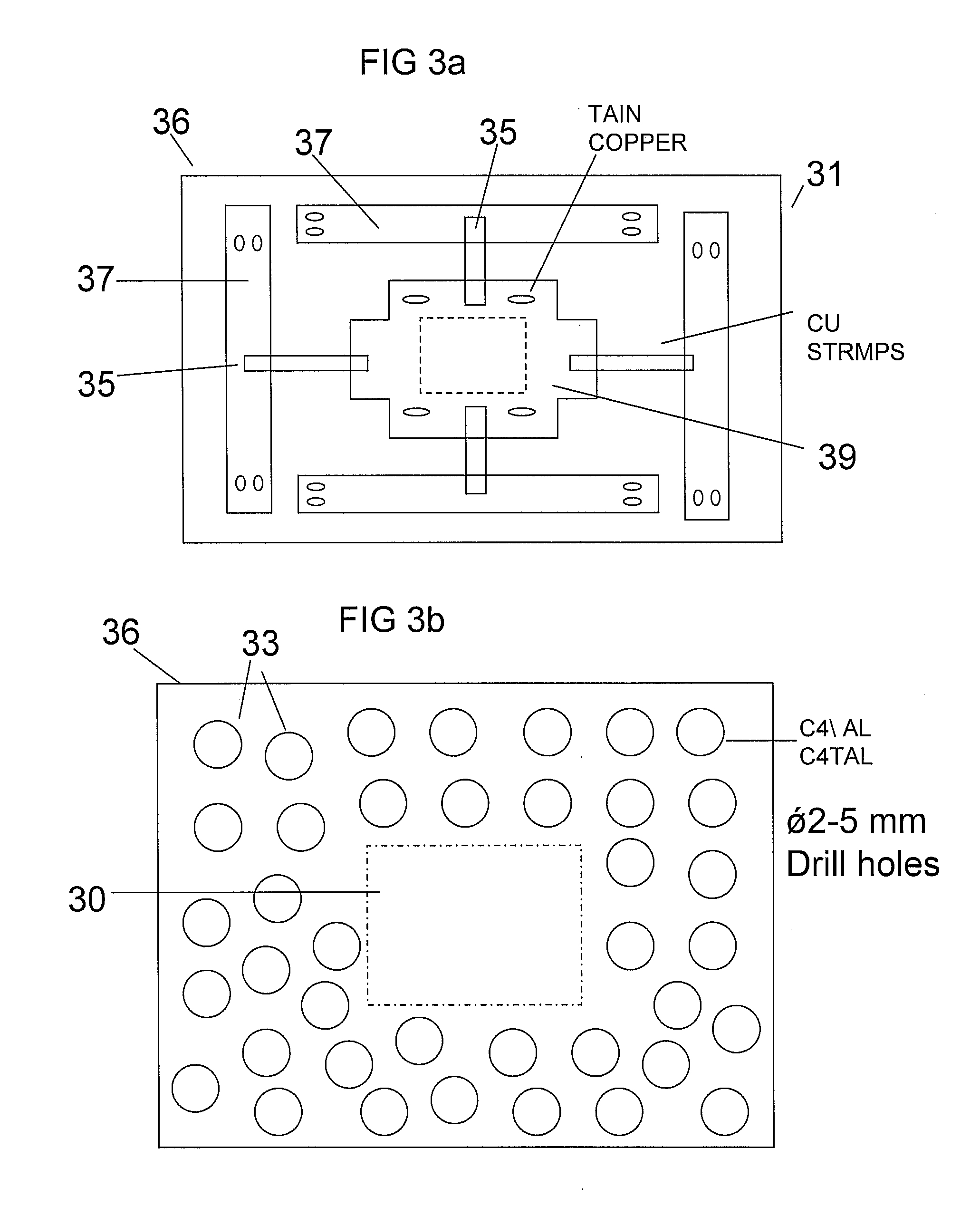
Active adaptive thermal stealth system
ActiveUS20130342701A1Accurate comparisonAccuracy of correspondenceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNight visionThermoelectric cooling
The present invention relates to a thermal vision countermeasure system to enable concealment of objects from identification by thermal imaging night vision systems, including a screen made of thermoelectric modules, disposed between the target object and an IR detector. The screen, formed of at least one thermoelectric unit, is coupled to the target object, and the thermoelectric unit includes a Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) module coupled to a plate formed of a material selected from aluminum, copper, or aluminum with copper, the plate being substantially larger than the TEC module.
Owner:ELTICS LTD
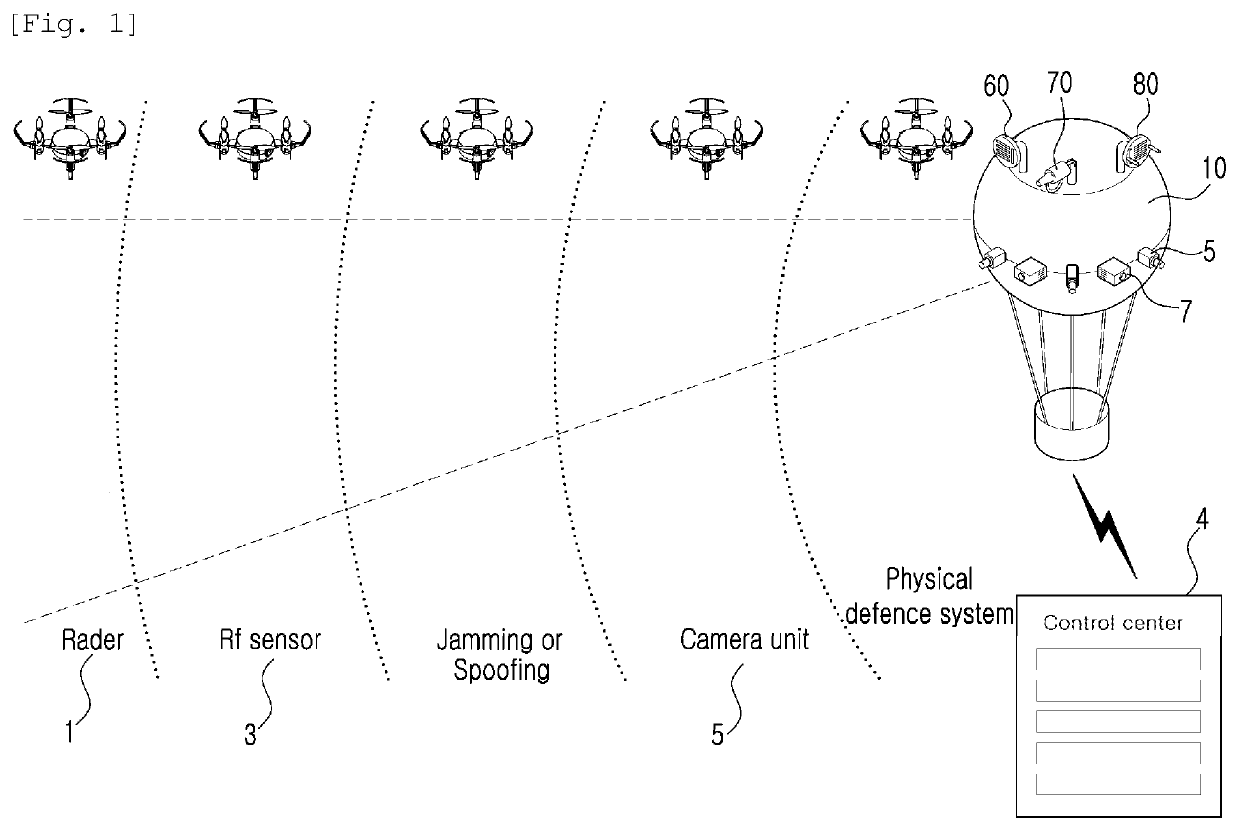
Low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle surveillance system
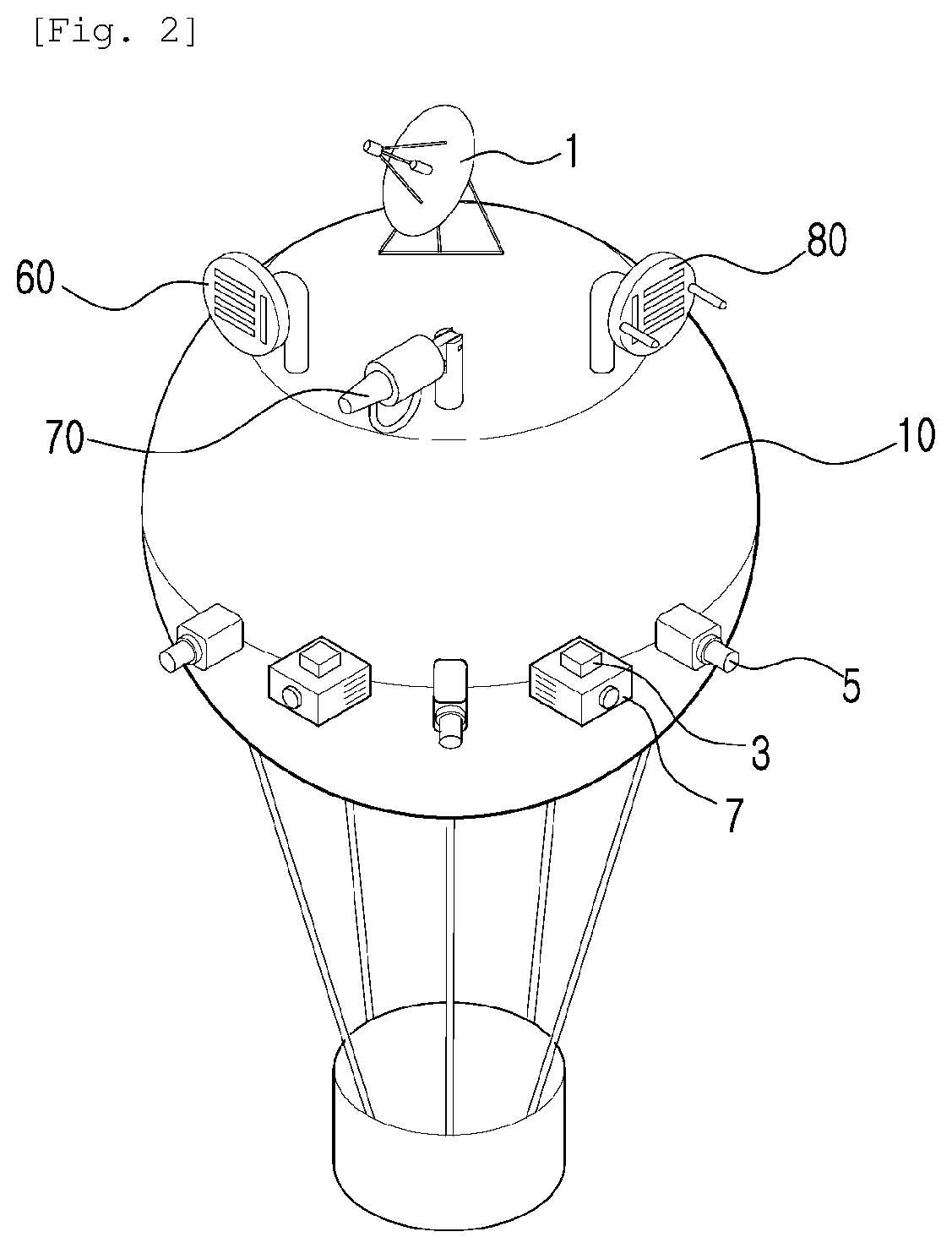
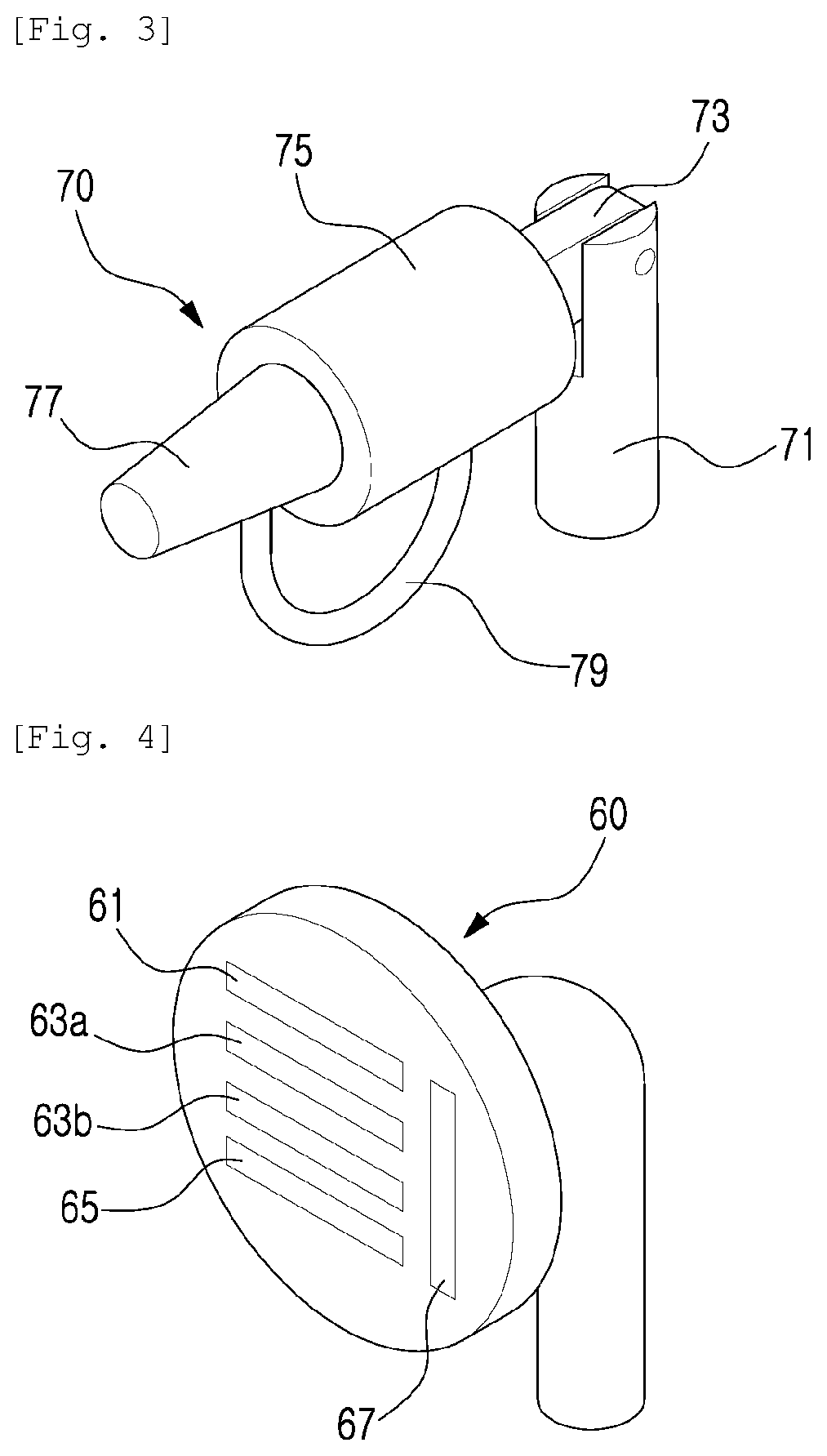
ActiveUS20200062392A1Lower the altitudeDetection is slightAircraft componentsUnmanned aerial vehiclesRadarMonitoring system
Disclosed is a low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle surveillance system. According to an embodiment, monitoring is performed using a balloon main body filled with gas and staying in the air; radar; camera units being provided outside the balloon main body, and including a camera taking an image of a subject; radio frequency detectors; and sound detectors and correspondingly, interceptor means is included. As interceptor means, a jammer, a jamming gun, and a spoofing device corresponding to jamming are disclosed.
Owner:CHOI SEUNG HEE +1
Neurosteroid compositions and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20180050107A1Detection is slightExtended circulation timeOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPerinatal DepressionPharmacology
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Afferent pupil tester
A new device, called Afferent Pupil Tester, designed for close up and magnified examination of both pupils at the same time, superimposed, as they react to direct and consensual light, comprises of high plus lenses, measuring grid, bright LED lights controlled with momentary switches, UV lights controlled by momentary switches, batteries, built-in camera and / or external camera, detachable facemask, and a sturdy casing.
Owner:KAMKAR BABAK
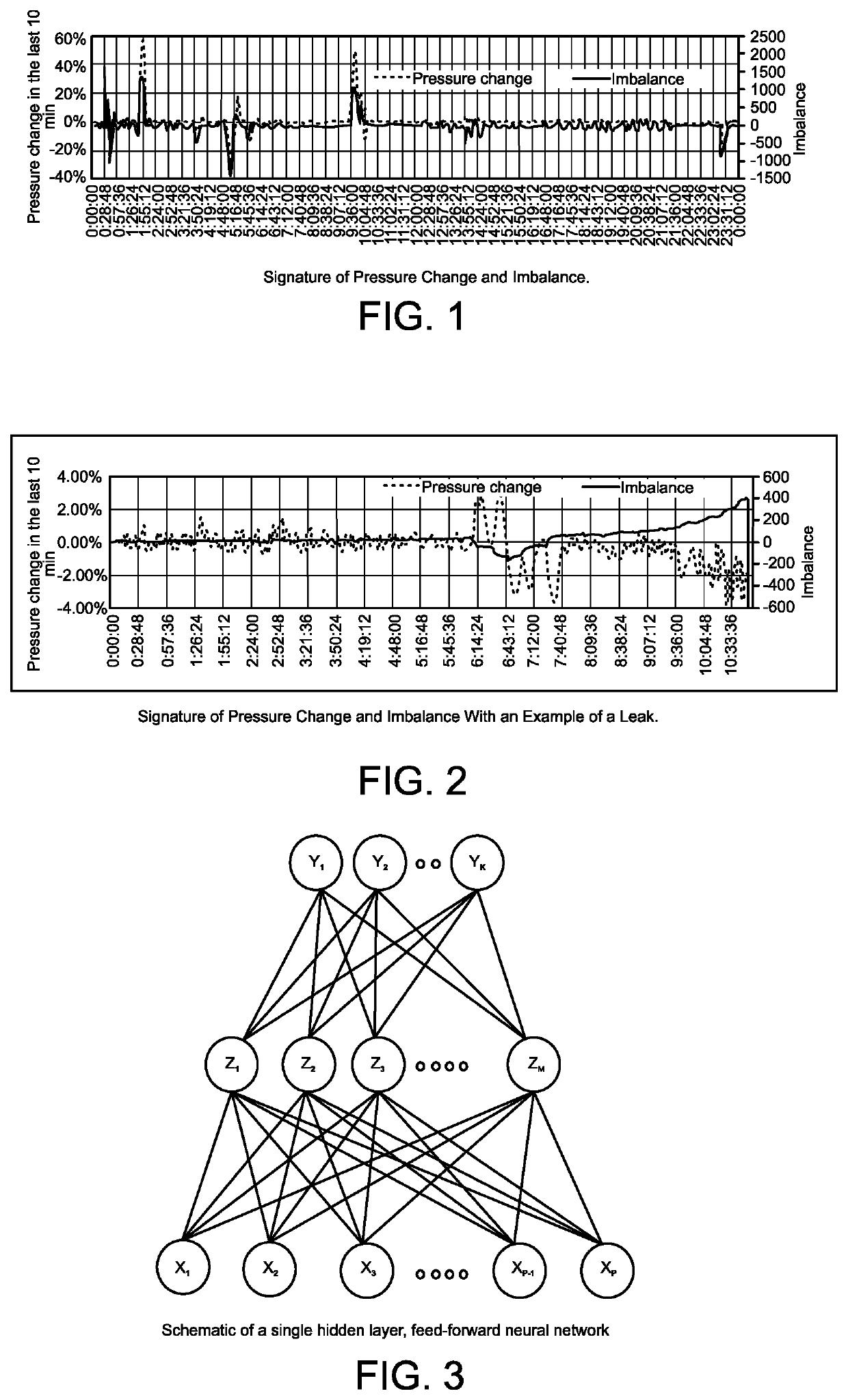
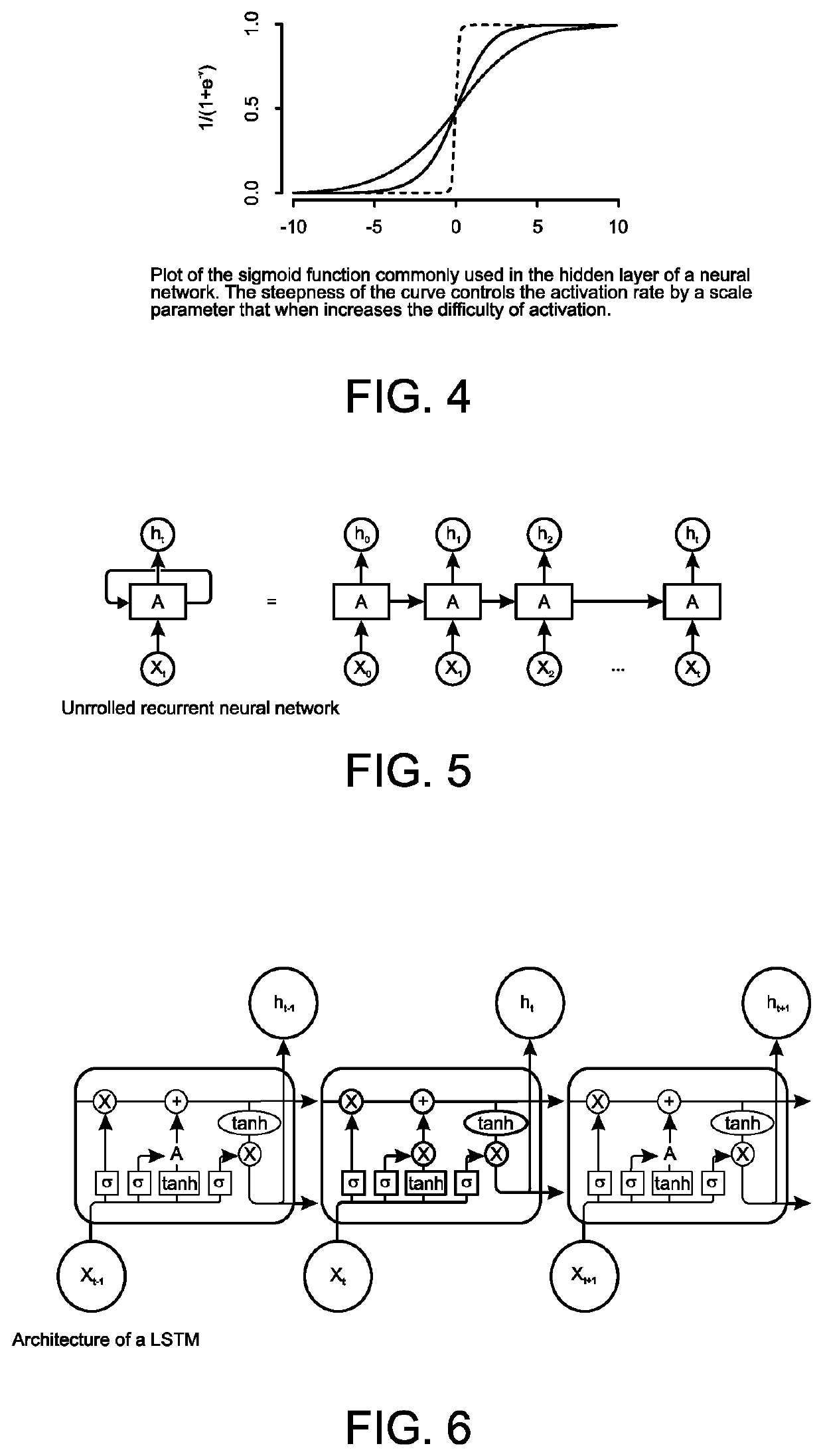
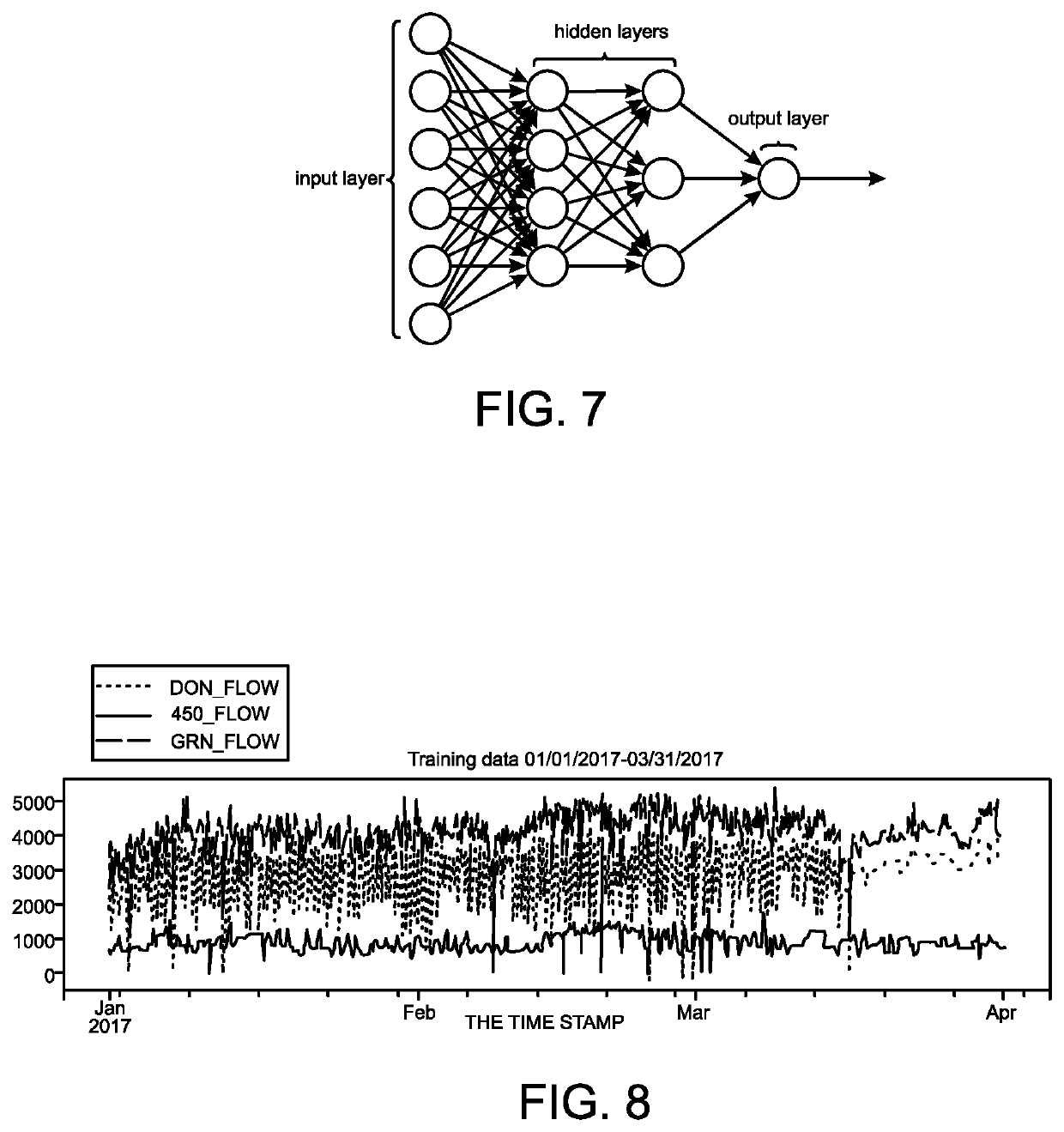
Leak detection with artificial intelligence
PendingUS20210216852A1Quick and easy implementationLess timeData processing applicationsFluid-tightness measurementAlgorithmEngineering
Computer-implemented methods, systems, and software of detecting leaks, for example, in a pipeline that conveys a liquid or gas. Embodiments include inputting into a computer system a first set of data acquired (e.g., from the pipeline) during (e.g., normal) operation (e.g., of the pipeline), acquiring a second set of data (e.g., from the pipeline) while simulating leaks (e.g., from the pipeline) by releasing quantities of the liquid or gas (e.g., from the pipeline) from multiple locations (e.g., along the pipeline), inputting into the computer system the second set of data, and training the computer system to detect the leaks (e.g., from the pipeline) including communicating to the computer system that no leaks existed while the first set of data was acquired and communicating to the computer system that leaks existed while the second set of data was acquired.
Owner:FLOWSTATE TECH LLC
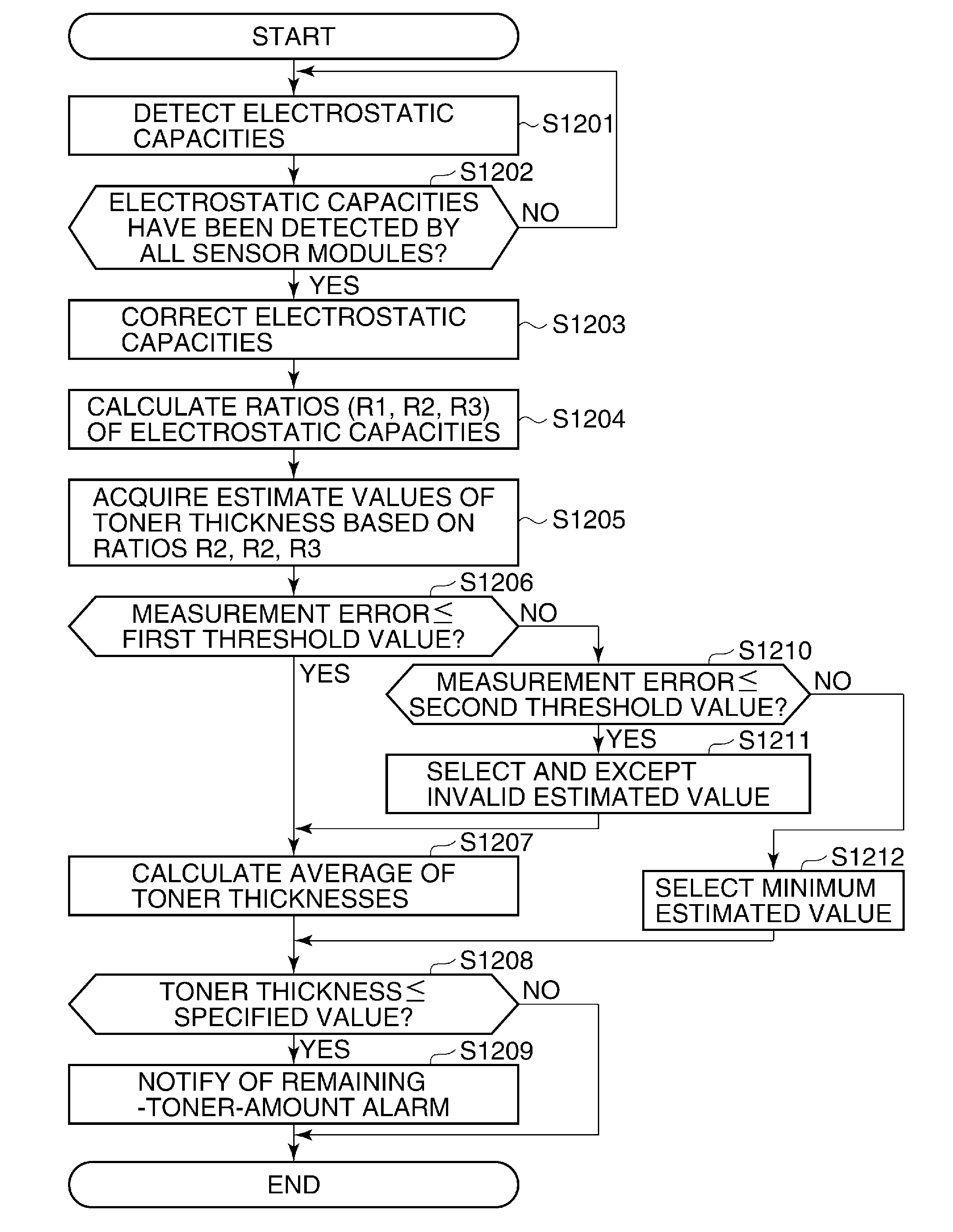
Image forming apparatus, control method therefor, and storage medium storing control program therefor
InactiveUS20130266329A1Effect of variationDetection is slightElectrographic process apparatusCapacitanceComputer module
An image forming apparatus that is capable of reducing an effect of variation of specific inductive capacity of toner due to environmental variation with a small detection error when the remaining toner amount is detected. The image forming apparatus forms an image with an electrophotographic system. A container unit stores toner. A toner detection unit has sensor modules that are arranged at positions where the toner is stagnated in the container unit, and that show different electrostatic capacities with respect to the same toner thickness. An electrostatic capacity detection unit detects the electrostatic capacities of the sensor modules. A determination unit determines a remaining toner amount in the container unit based on the electrostatic capacities of the sensor modules that are detected by the electrostatic capacity detection unit.
Owner:CANON KK
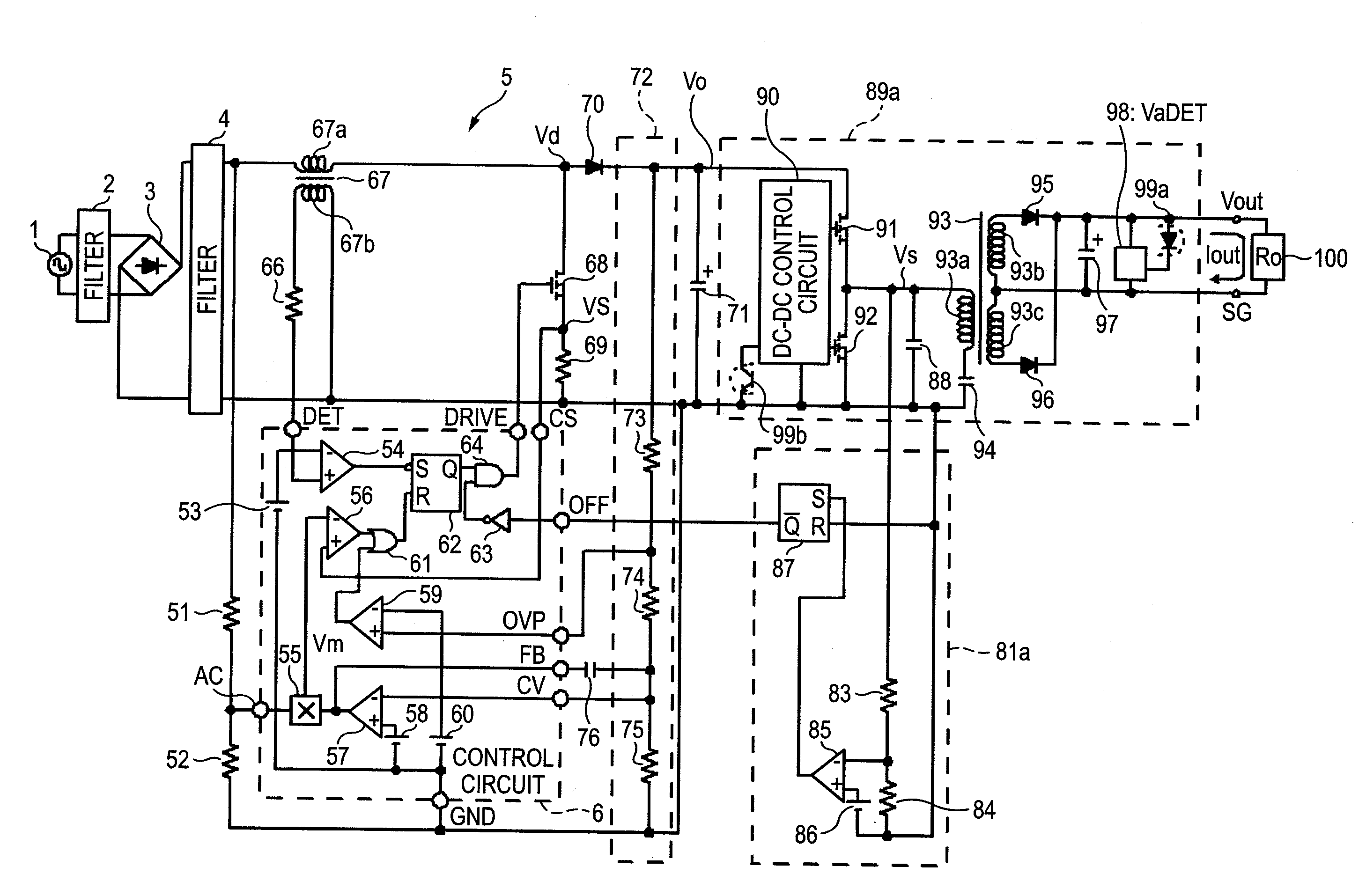
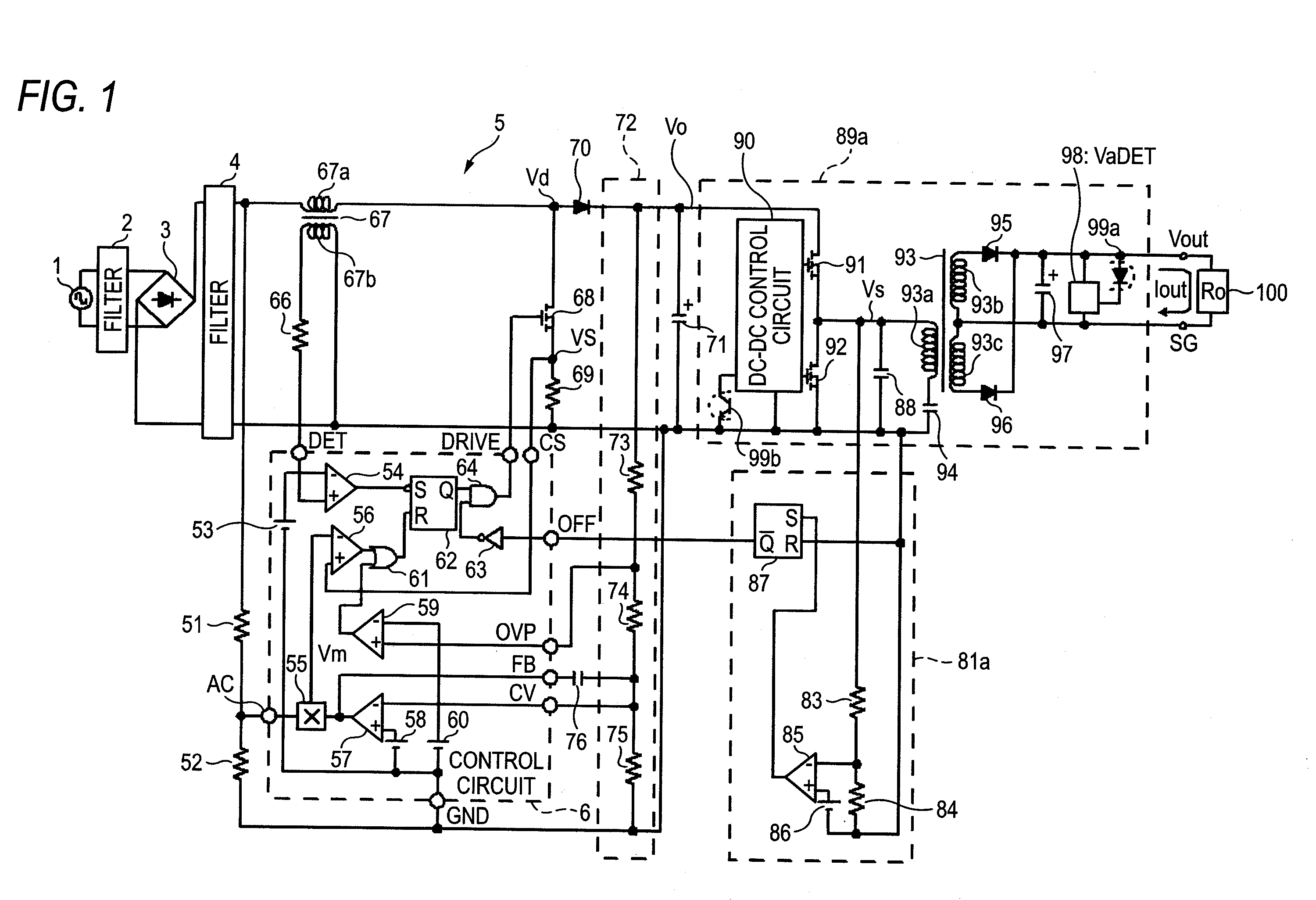
Power factor improvement circuit
InactiveUS20110051462A1Increase freedomDegradation in power with timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterPower factor
An over-voltage protection circuit of the invention is connected with a DC-DC converter having a structure in which a plurality of switching elements is serially connected to a direct current output voltage terminal of a power factor improvement circuit. An output over-voltage detection resistance of a latch-type output over-voltage detection circuit is connected to a connection point at which the plurality of switching elements is connected.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
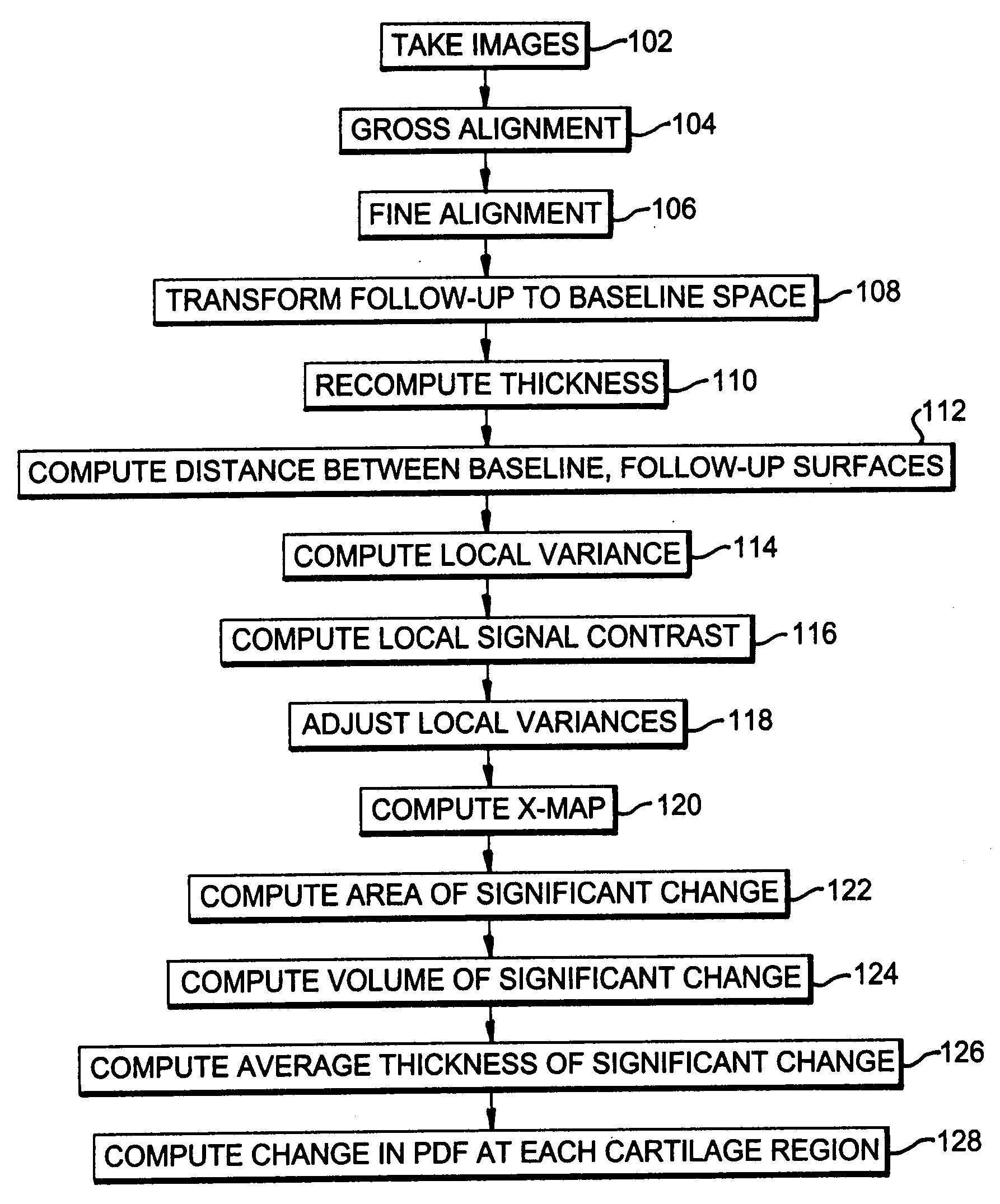
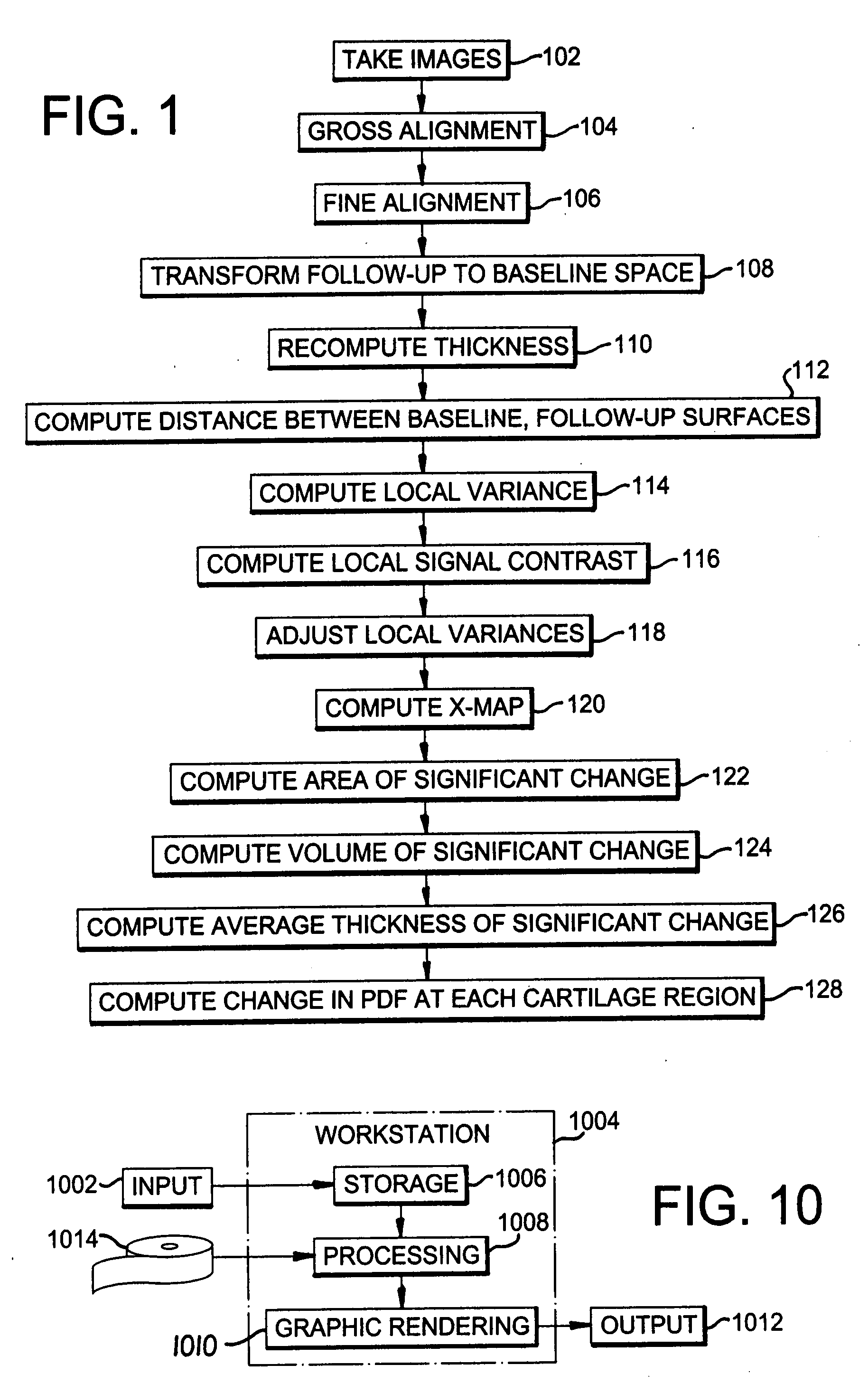
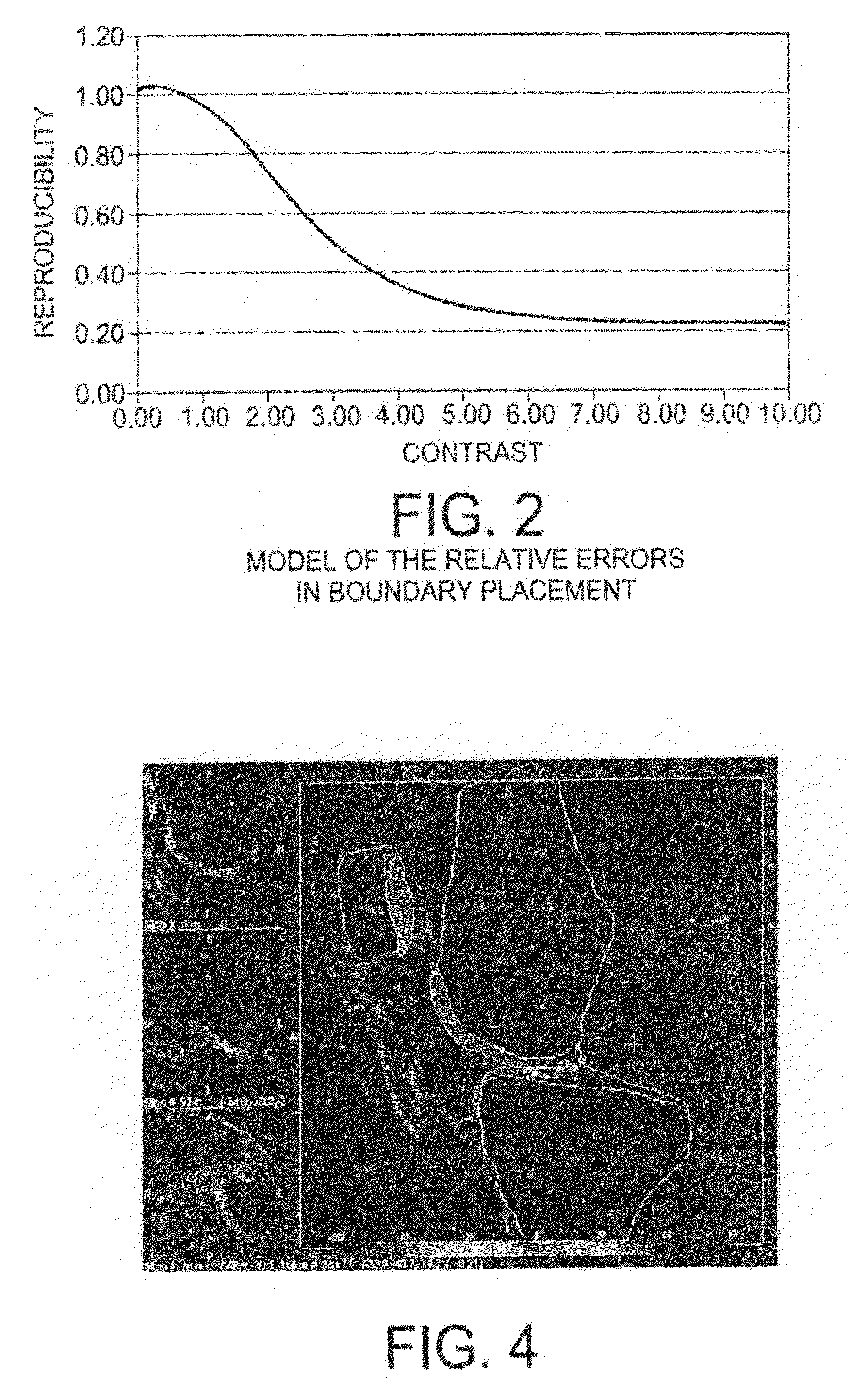
Structural quantification of cartilage changes using statistical parametric mapping
InactiveUS20080200840A1Reduce errorsImprove abilitiesImage enhancementImage analysisStatistical parametric mappingBiomedical engineering
The analysis of the focal changes in the morphology of a tissue such as cartilage is completed through statistical parametric mapping by first detecting the amount of thickness changes; followed by the point by point estimation of the variance in the thickness delta estimation. Once the change and the variance are estimated, the z-map is computed. The z-map is used to compute single change parameters. i.e: volume significant change, area of significant change, average thickness of the significant changes, and D values from the probability distributions. That can be used for treatment decisions.
Owner:VIRTUALSCOPICS
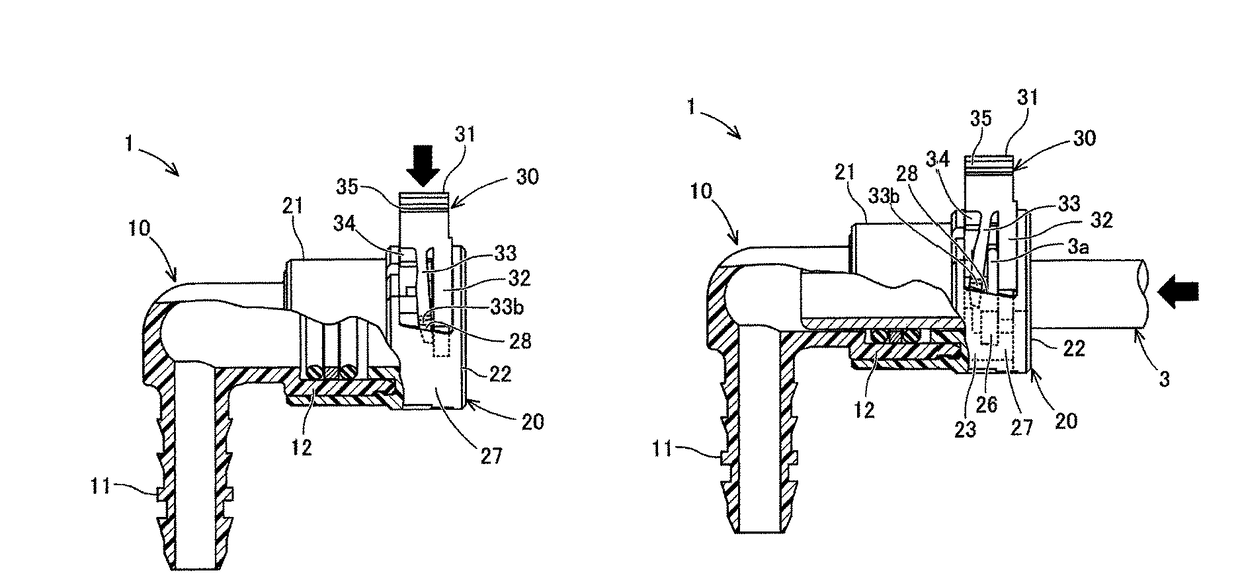
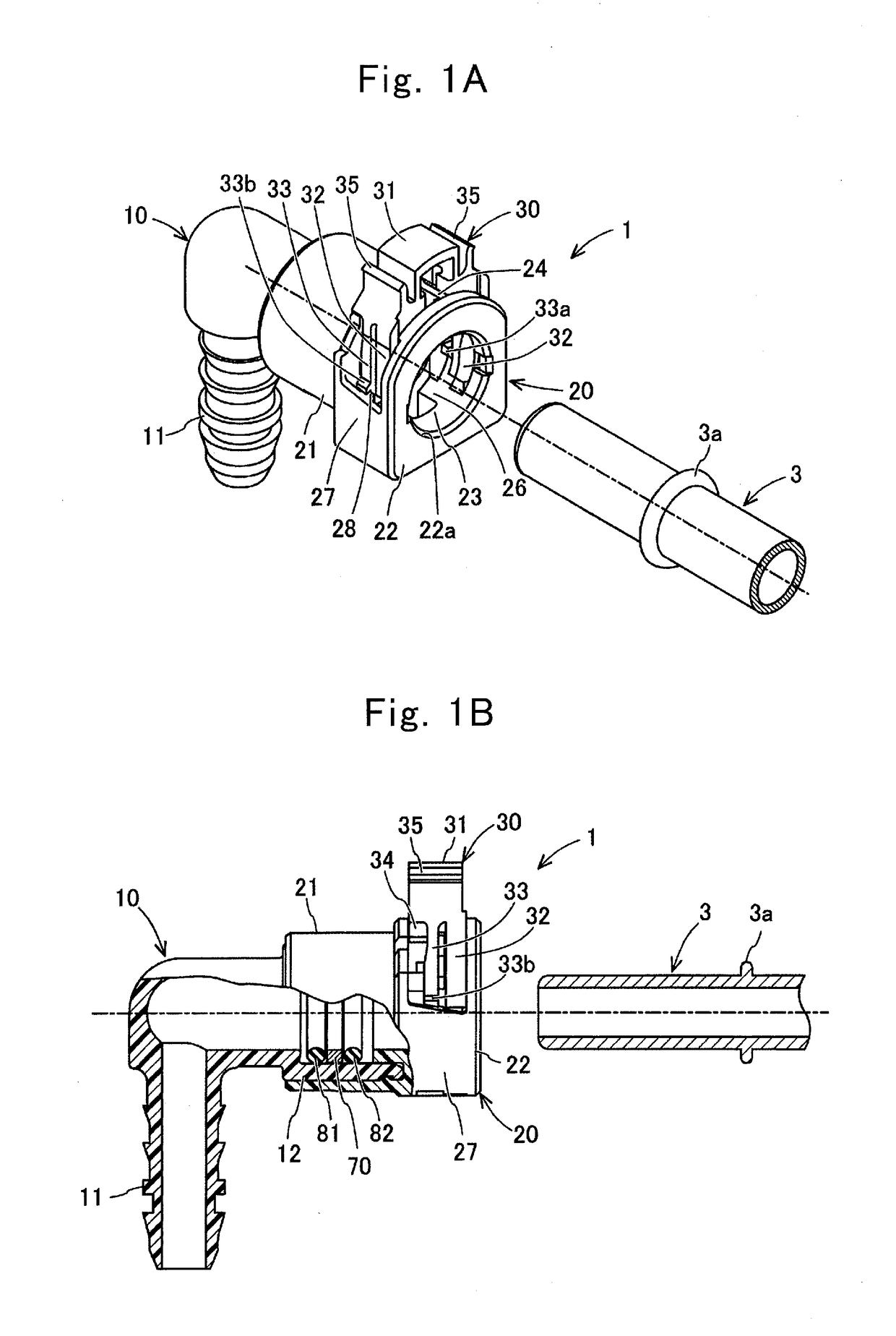
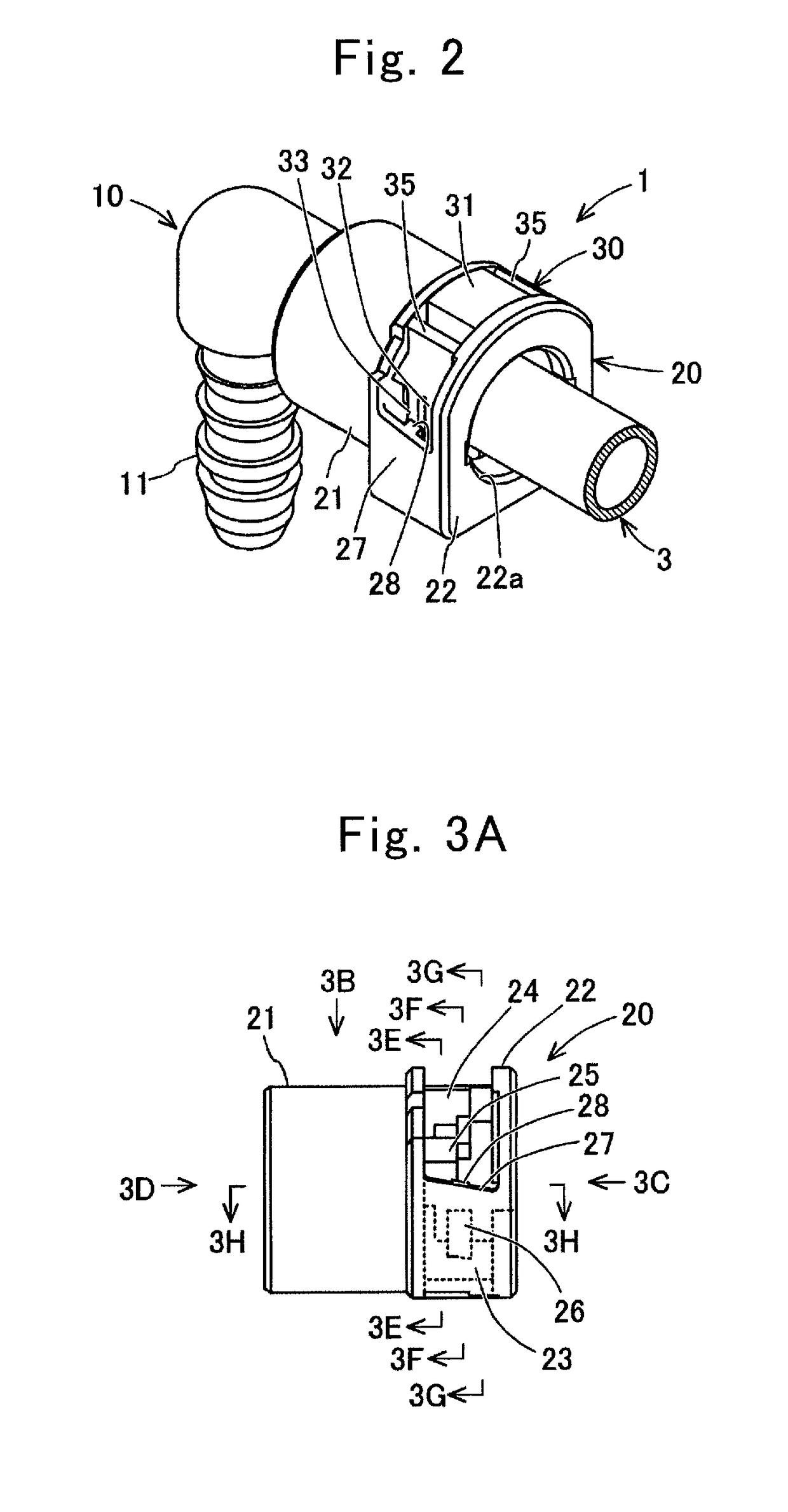
Quick connector
ActiveUS9915388B2Shorten the lengthShift amount of the push-in inhibition portion is smallPipe couplingsCouplingsEngineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
Concentrated Solution of 17-Hydroxydocosahexaenoic Acid
InactiveUS20180050005A1Detection is slightExtended circulation timeIon-exchange process apparatusOrganic active ingredientsSelf-assemblyPost-pregnancy depression
A method of treating a mother having postpartum depression, comprising administering to the mother a composition comprising a plurality of mixed self-assemblies comprising:i) at least 50 wt % of a soyasaponin, andii) allopregnanolone.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Biochemical assay detection in a liquid receptacle using a fiber optic exciter
InactiveUS7218810B2No loss of intensityEasy to useWithdrawing sample devicesColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberCuvette
Biochemical assays that are performed in cuvettes and in the wells of multi-well plates and that utilize excitation and light emission as labels for detection are enhanced by an illumination and detection system that supplies excitation light through an optical fiber that transmits excitation light from an excitation light source to the cuvette or well. Emission light produced by the excitation is then collected by a collimating lens and converted to a signal that is compiled by conventional software for analysis. The optical fiber and collimating lens can either be on the same side of the receptacle (generally the open side) or on opposite sides, i.e., one above and the other below. When the optical fiber and the collimating lens are both on the open side of the receptacle, they are arranged such that the direction of travel of the excitation light and the direction along which the emission light is collected are not coaxial, and preferably both are at an acute angle to the axis normal to the mouth of the receptacle. Illumination systems are also disclosed in which a ultraviolet, visible, or near-infrared light source is optically coupled to an optical fiber.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
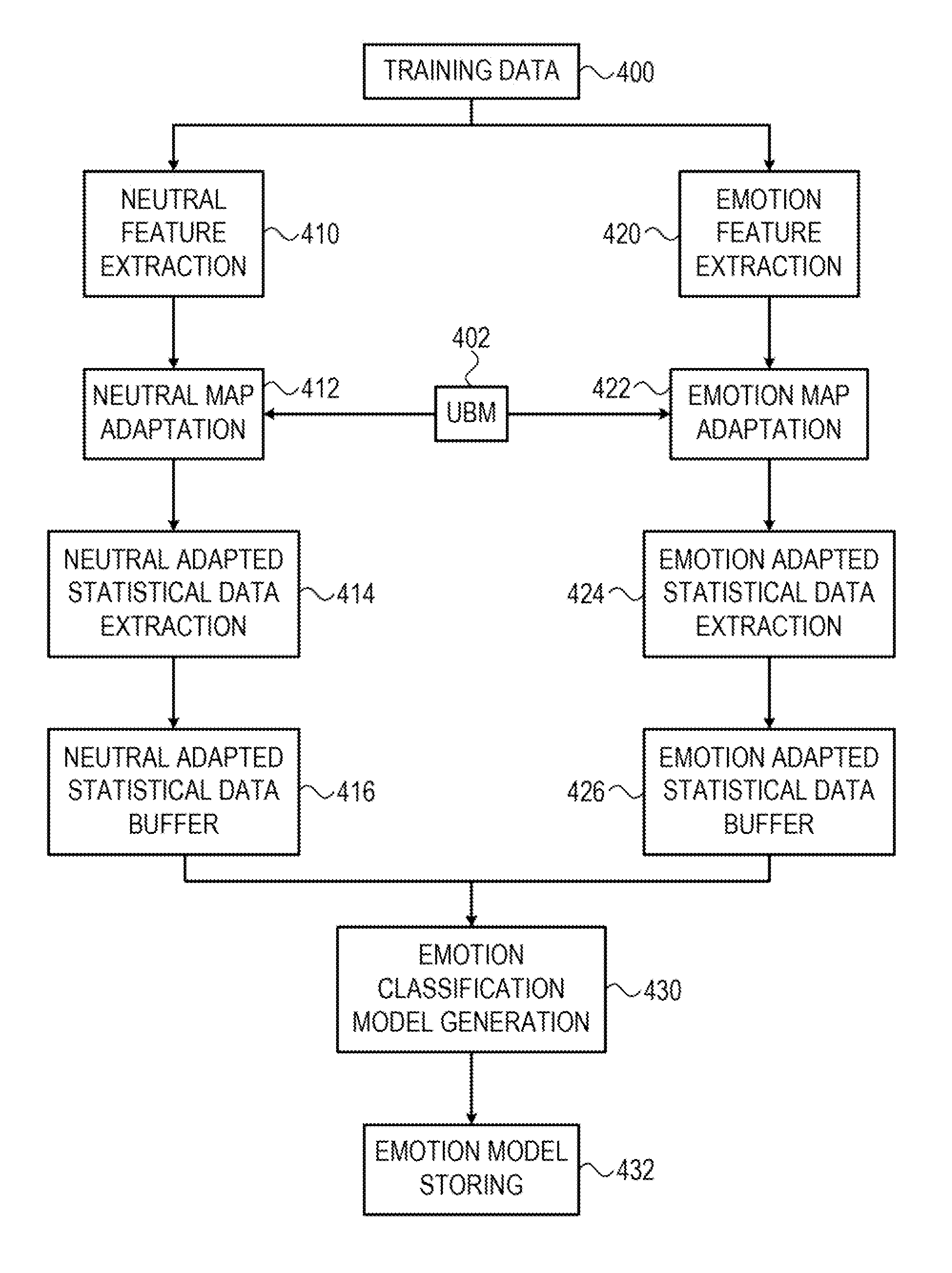
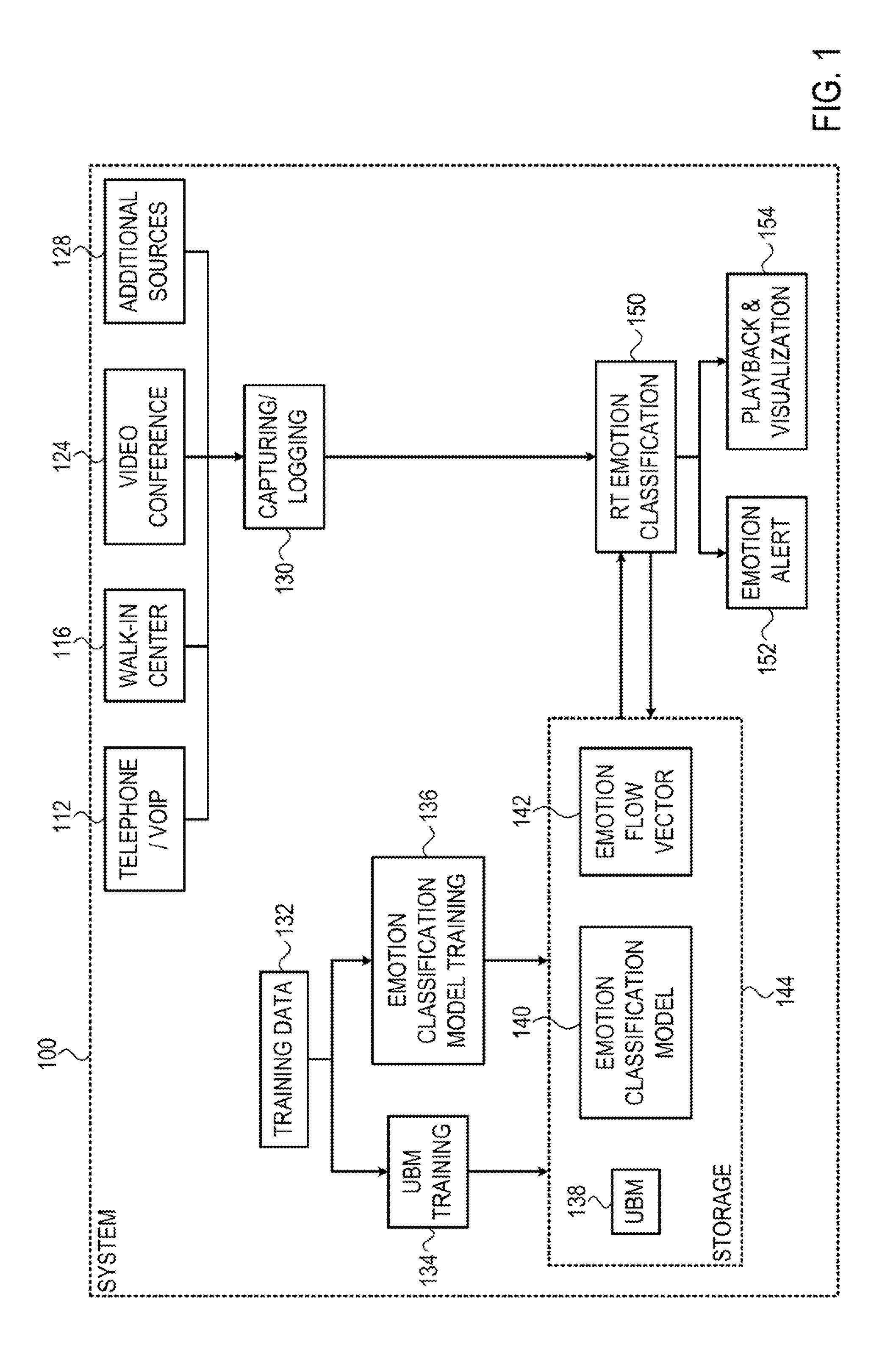
Method and apparatus for real time emotion detection in audio interactions
The subject matter discloses a computerized method for real time emotion detection in audio interactions comprising: receiving at a computer server a portion of an audio interaction between a customer and an organization representative, the portion of the audio interaction comprises a speech signal; extracting feature vectors from the speech signal; obtaining a statistical model; producing adapted statistical data by adapting the statistical model according to the speech signal using the feature vectors extracted from the speech signal; obtaining an emotion classification model; and producing an emotion score based on the adapted statistical data and the emotion classification model, said emotion score represents the probability that the speaker that produced the speech signal is in an emotional state.
Owner:NICE LTD
Extracorporeal blood treatment machine comprising leakage detection and method of detecting leakages in dialysis fluid systems
ActiveUS20150196701A1Accurate and reliable workImprove ventilationSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionBlood treatmentsControl manner
The invention relates to an extracorporeal blood treatment machine, such as a dialysis machine, comprising leakage detection as well as to a method of detecting leakages in the dialysis fluid circuit of a dialysis machine, wherein at least part of the dialysis fluid system to be monitored in terms of leakage is accommodated in a hermetically sealed housing and the housing is or can be ventilated in a controlled manner, and wherein a parameter, such as the air humidity of the air flowing into the housing is compared to a corresponding parameter, preferably air humidity of the air flowing out of the housing.
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
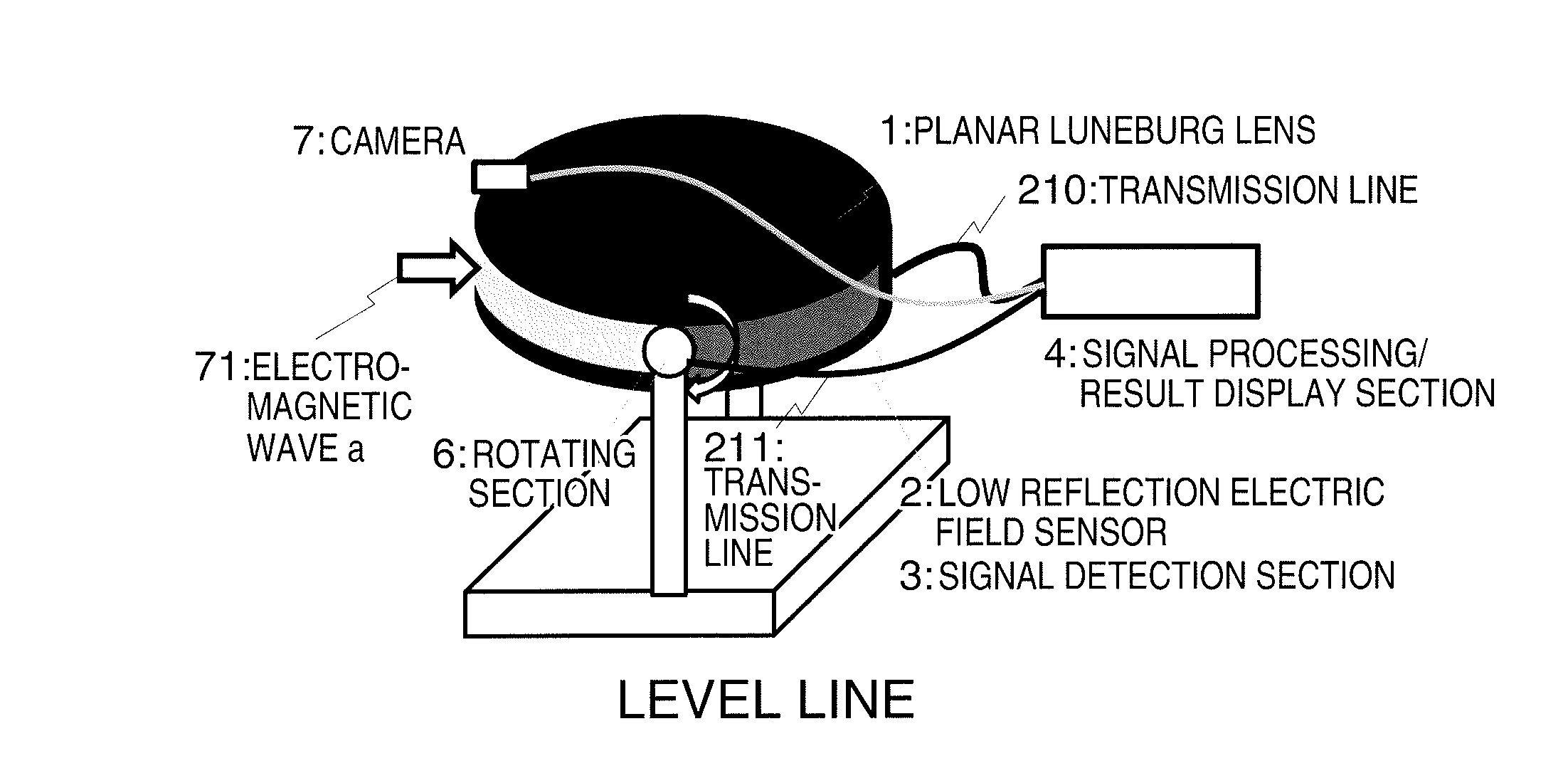
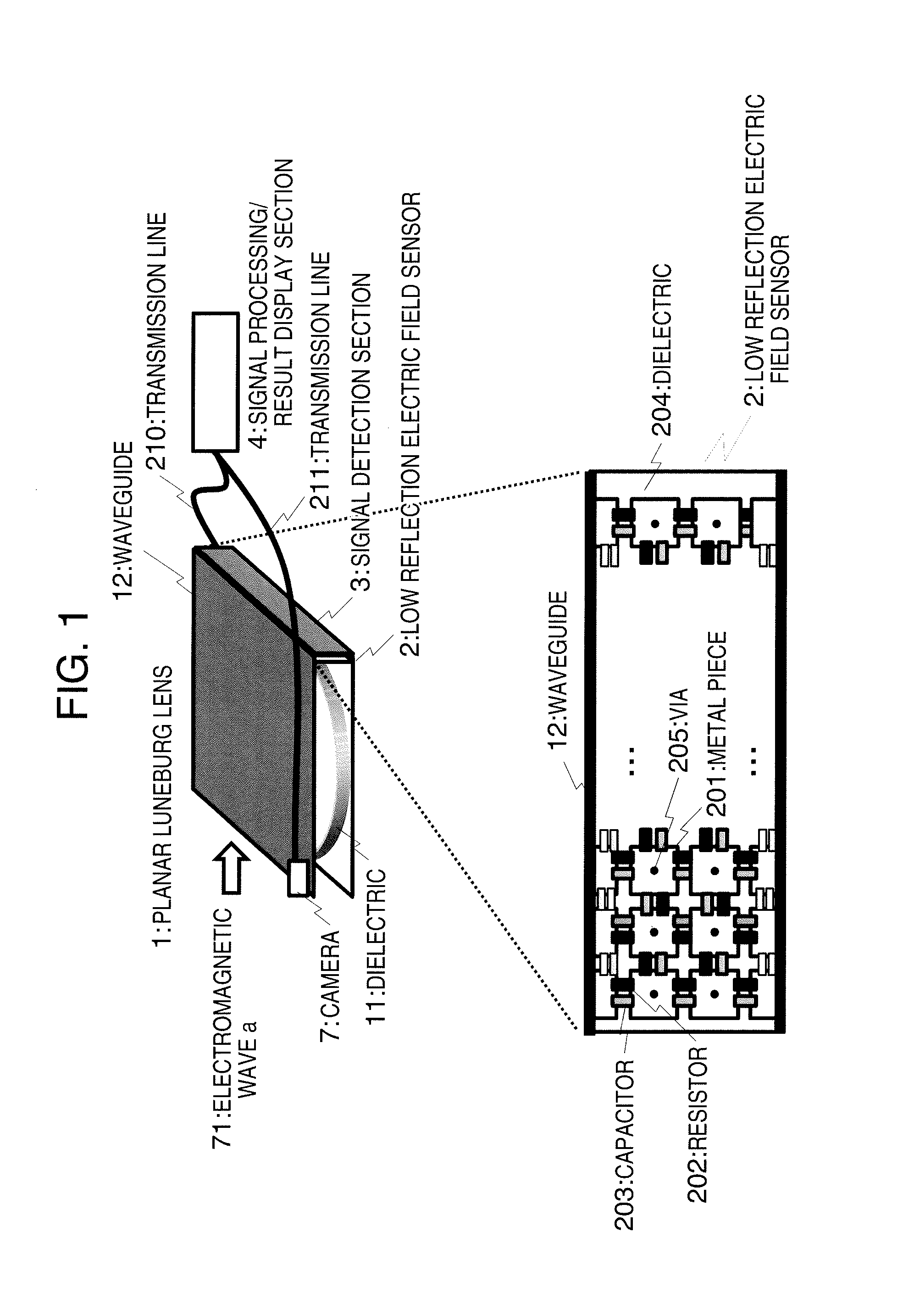
Electromagnetic Wave Detection Apparatus
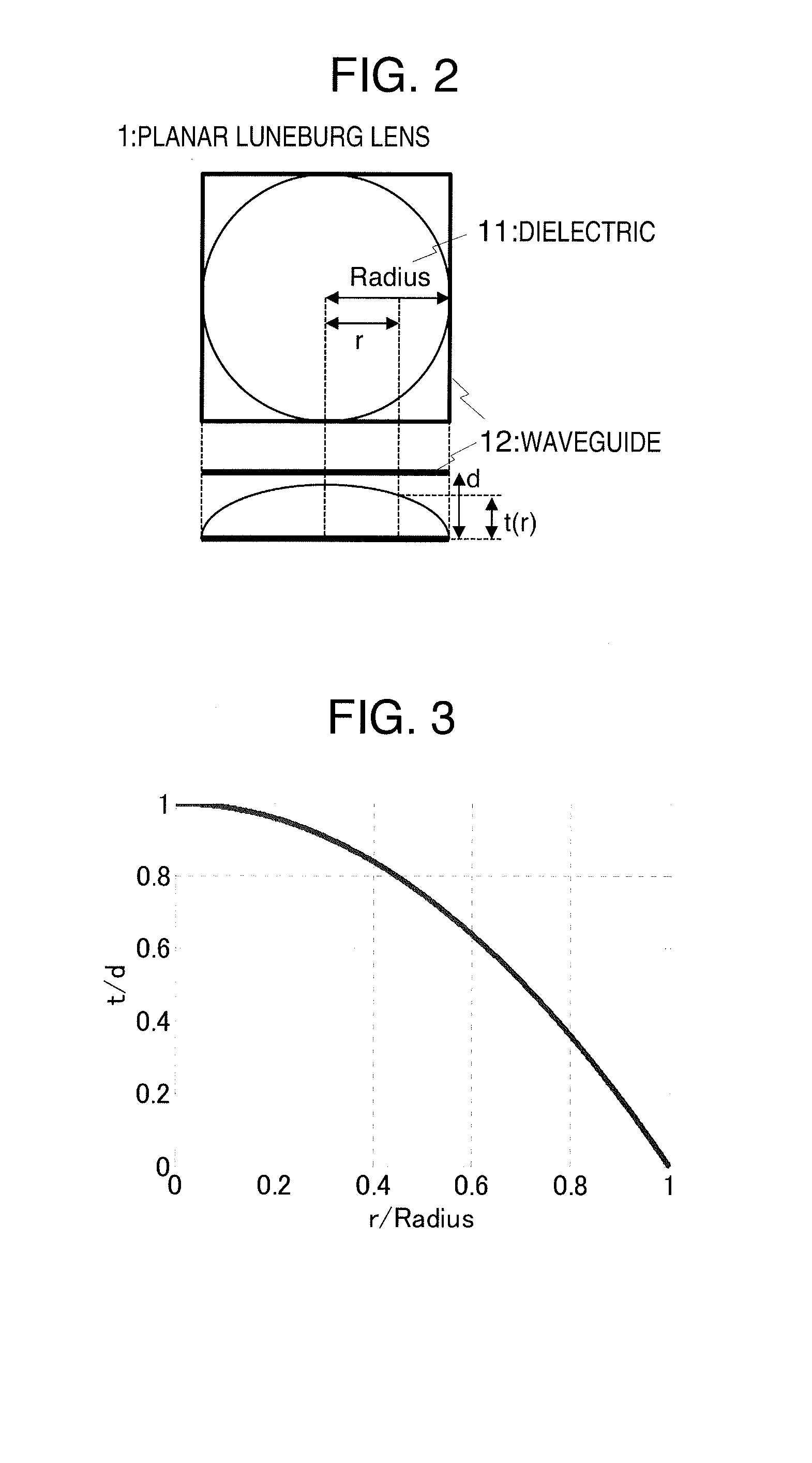
ActiveUS20160334451A1Detection is slightElectromagentic field characteristicsElectricityElectric field sensor
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a small electromagnetic wave detection apparatus. This electromagnetic wave detection apparatus has: a planar Luneburg lens, which is covered with metal plates facing each other, and which changes the output direction of electromagnetic waves corresponding to the input direction of the electromagnetic waves; and an electric field sensor electrically connected to the metal plates. The electric field sensor detects the electromagnetic waves outputted from the Luneburg lens, and outputs a detection signal having an intensity corresponding to the direction in which the electromagnetic waves have traveled thereto, and the level of the energy of the electromagnetic waves thus detected.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Steering column monitoring system and sensor
ActiveUS20200232858A1Simple structureLow costWork measurementUsing electrical meansSteering columnMagneto elastic
A sensor for at least detecting steering torque of a steel steering column comprises: a magnetic field generating element, configured to generate a magnetic field, the magnetic field penetrating the steering column so as to magnetize a steel material thereof; a magnetic field detection element, configured to detect a magnetic field change caused by a magnetoelastic effect of the magnetized steel material of the steering column when the steering column is subjected to torque stress, wherein an output signal of the magnetic field detection element characterizes steering torque; and a base plate, bearing the magnetic field generating element and the magnetic field detection element.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
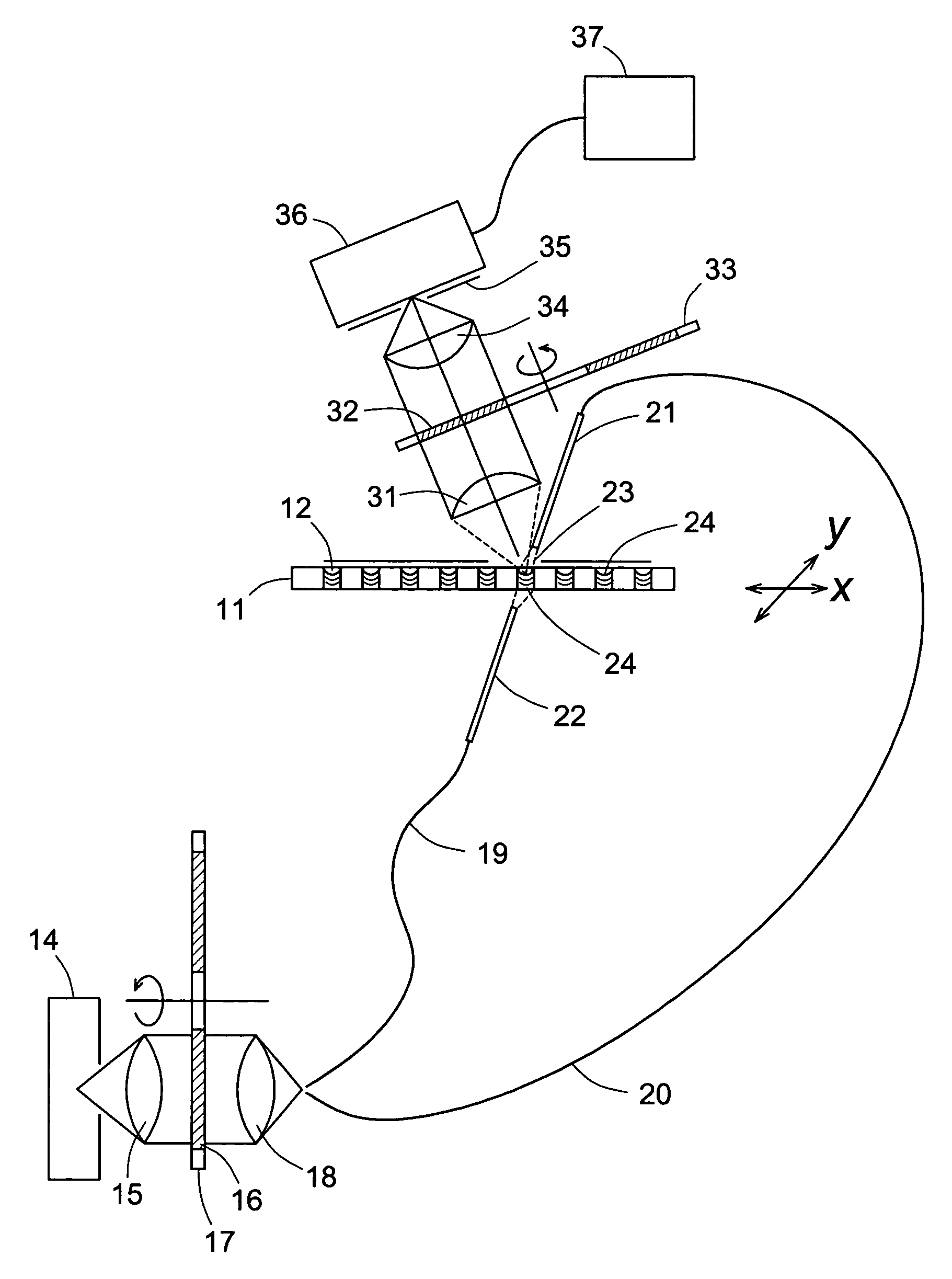
Optical scanner device
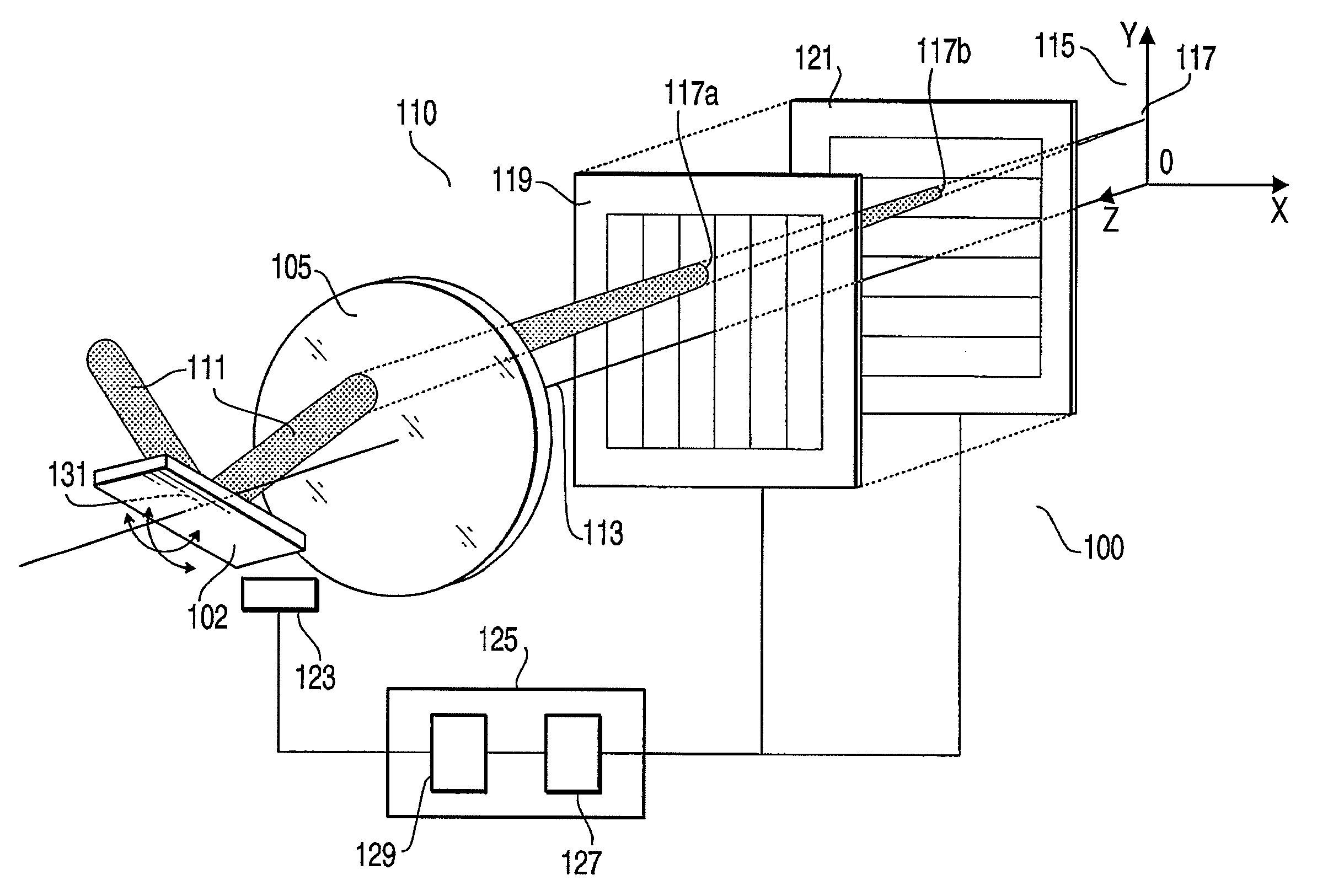
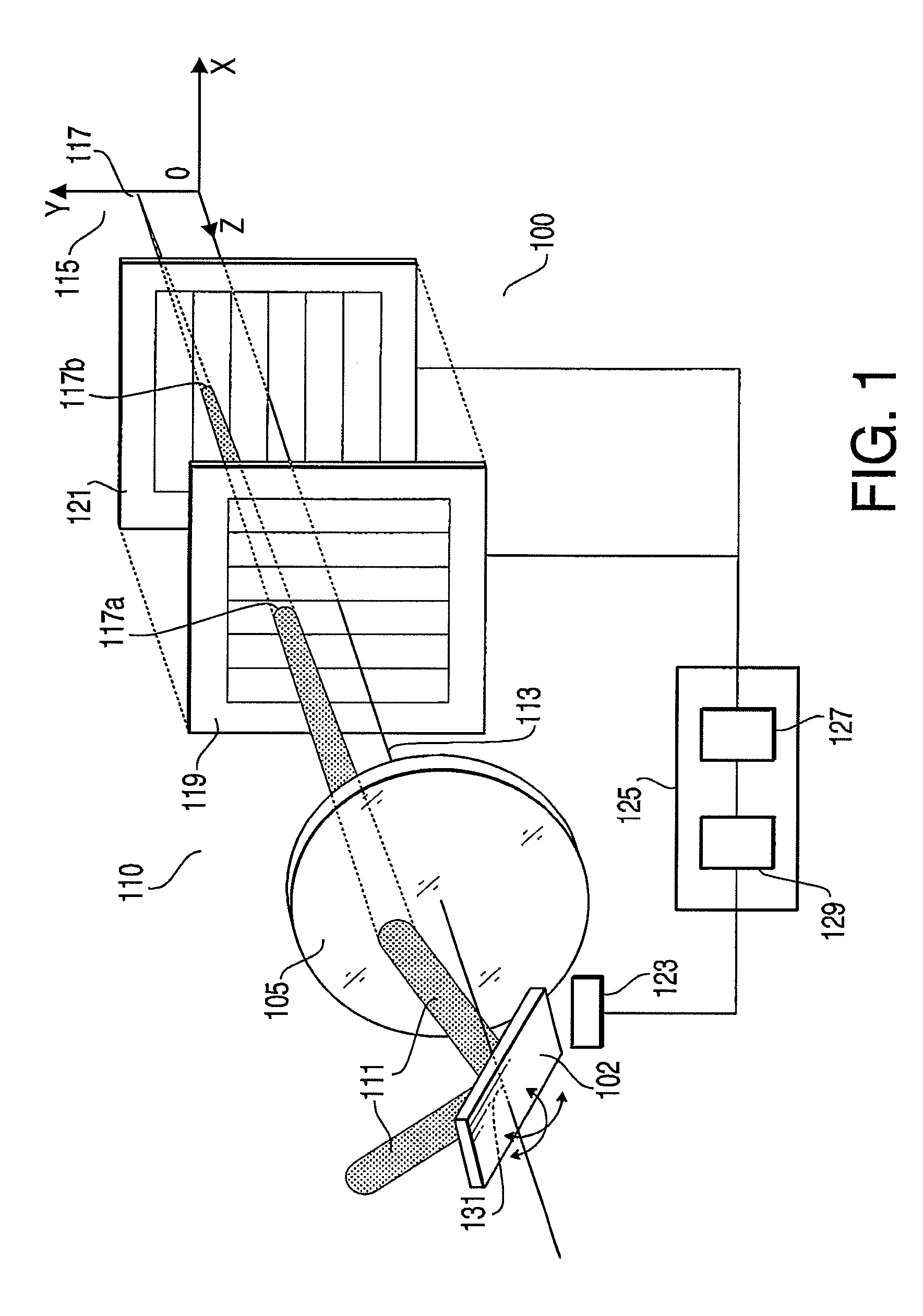
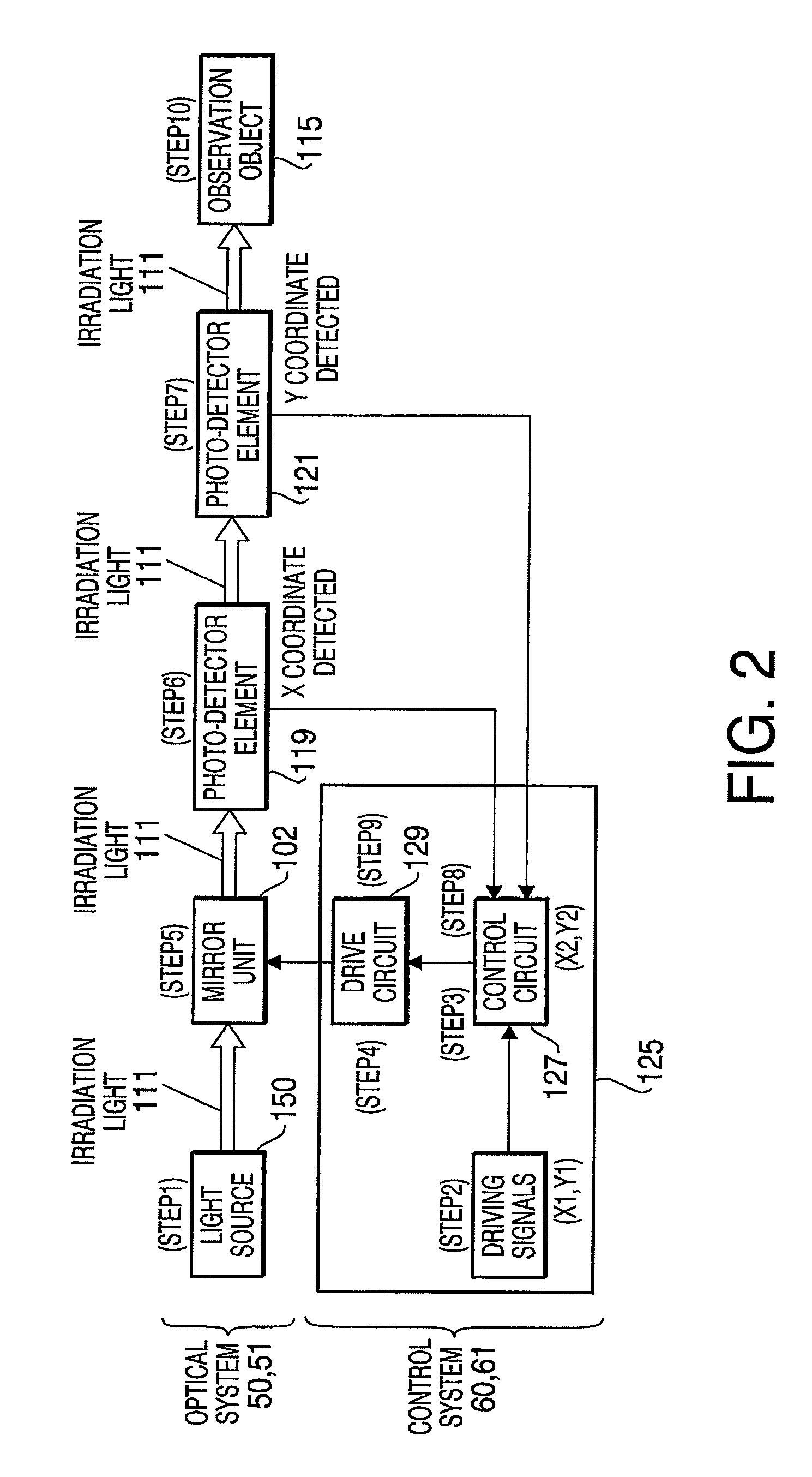
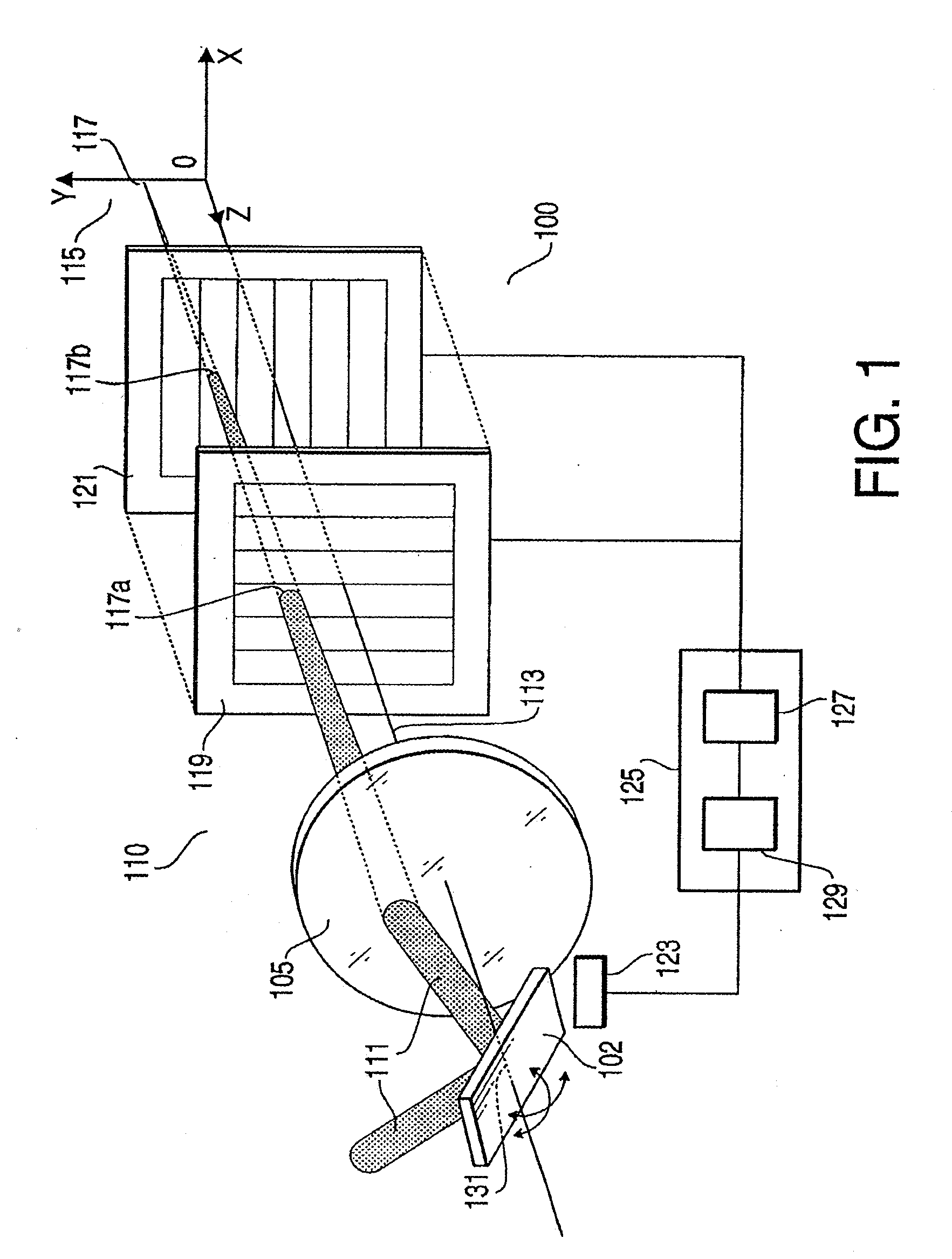
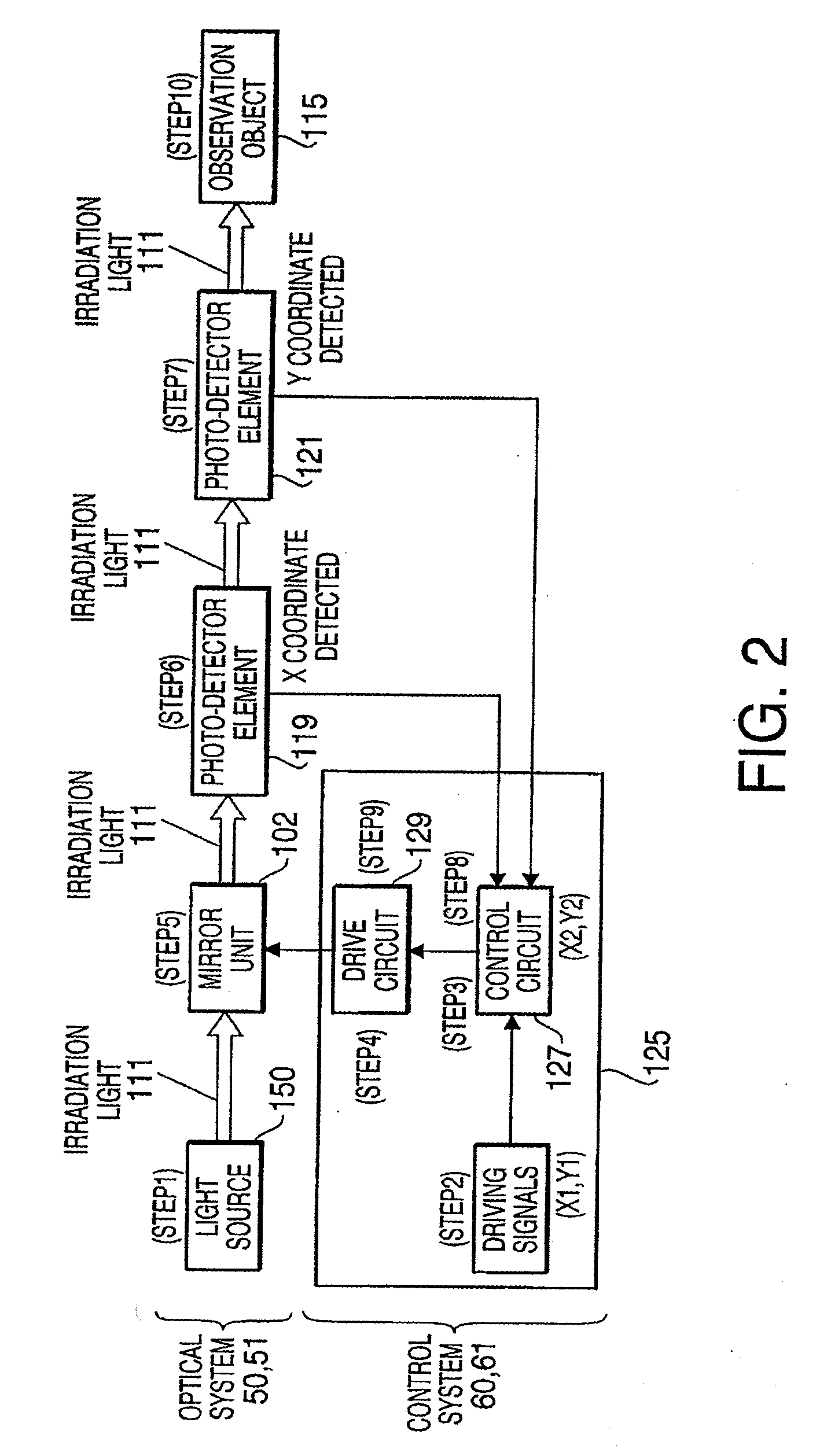
InactiveUS7479626B2Improve accuracyDetection is slightBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight spotOptical axis
An optical scanner device, comprising a scanning unit, which casts irradiation light emitted from a light source in an arbitrary direction to scan an observation object, an objective lens system, which converges the irradiation light on the observation object, and a photo-detector unit, which is disposed on an optical axis of the objective lens system to have the irradiation light transmit therethrough, is provided. A position of the irradiation light converged on the observation object is detected based on a position of a light spot of the irradiation light transmitting through the photo-detector unit.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Bio-sensor with hard-direction field
InactiveUS8334147B2Detection is slightDetection errorRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetizationOrthogonal array
A magnetic sensor for identifying small magnetic particles bound to a substrate includes a regular, planar orthogonal array of MTJ cells formed within or beneath that substrate. Each MTJ cell has a high aspect ratio and positions of stable magnetic equilibrium along an easy magnetic axis and positions of unstable magnetic equilibrium along a hard magnetic axis. By initializing the magnetizations of each MTJ cell in its unstable hard-axis position, the presence of even a small magnetic particle can exert a sufficient perturbative strayfield to tip the magnetization to its stable position. The magnetization change in an MTJ cell can be measured after each of two successive opposite polarity magnetizations of a bound particle and the presence of the particle thereby detected.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Immobilized protein system for rapid and enhanced multiplexed diagnostics
ActiveUS9547014B2Small sizeEnhanced signalMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAssayBiology
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Input device, terminal equipped with the same, and inputting method
ActiveUS8730159B2Improve portabilitySmall sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHuman bodyData transformation
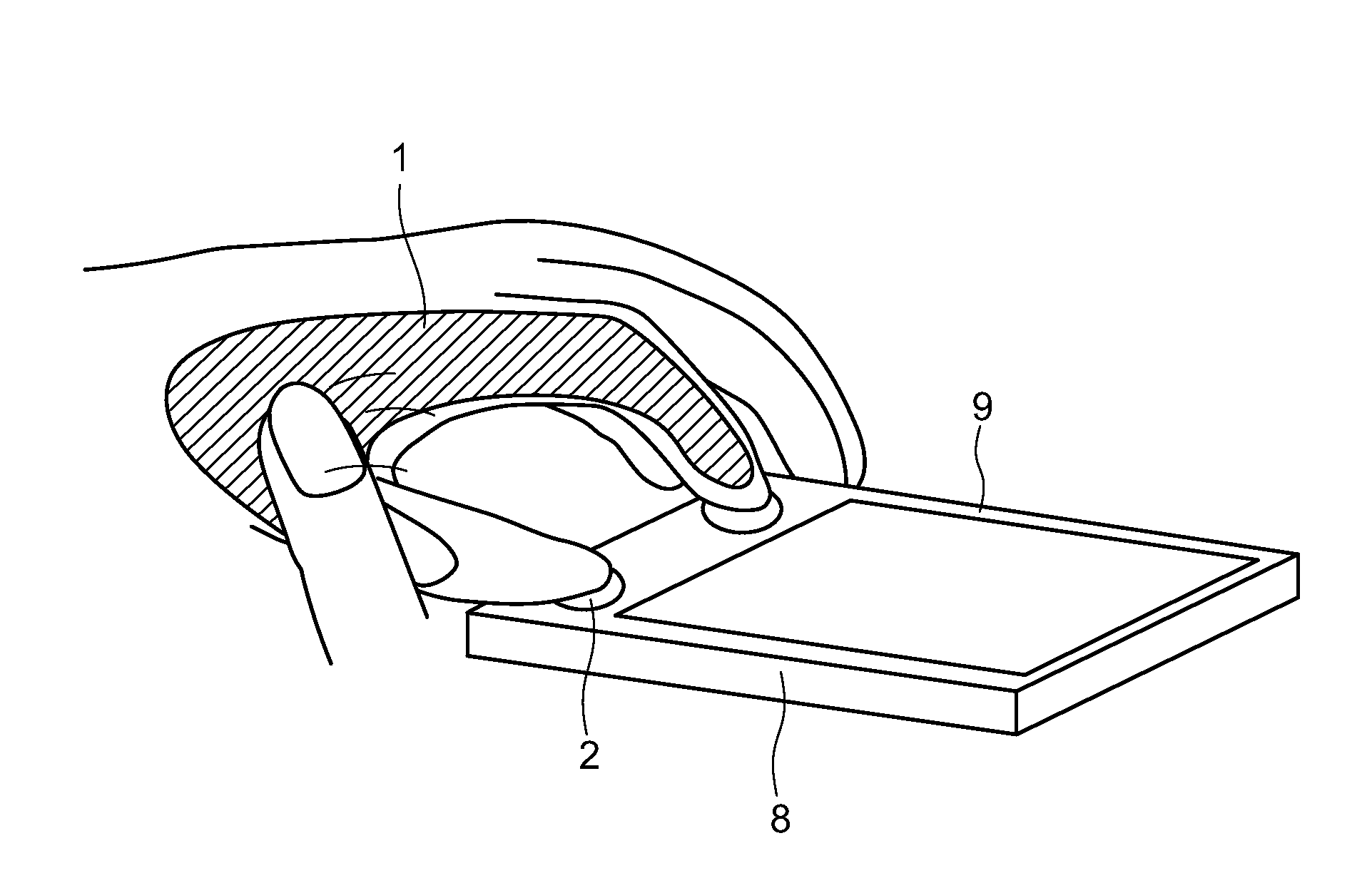
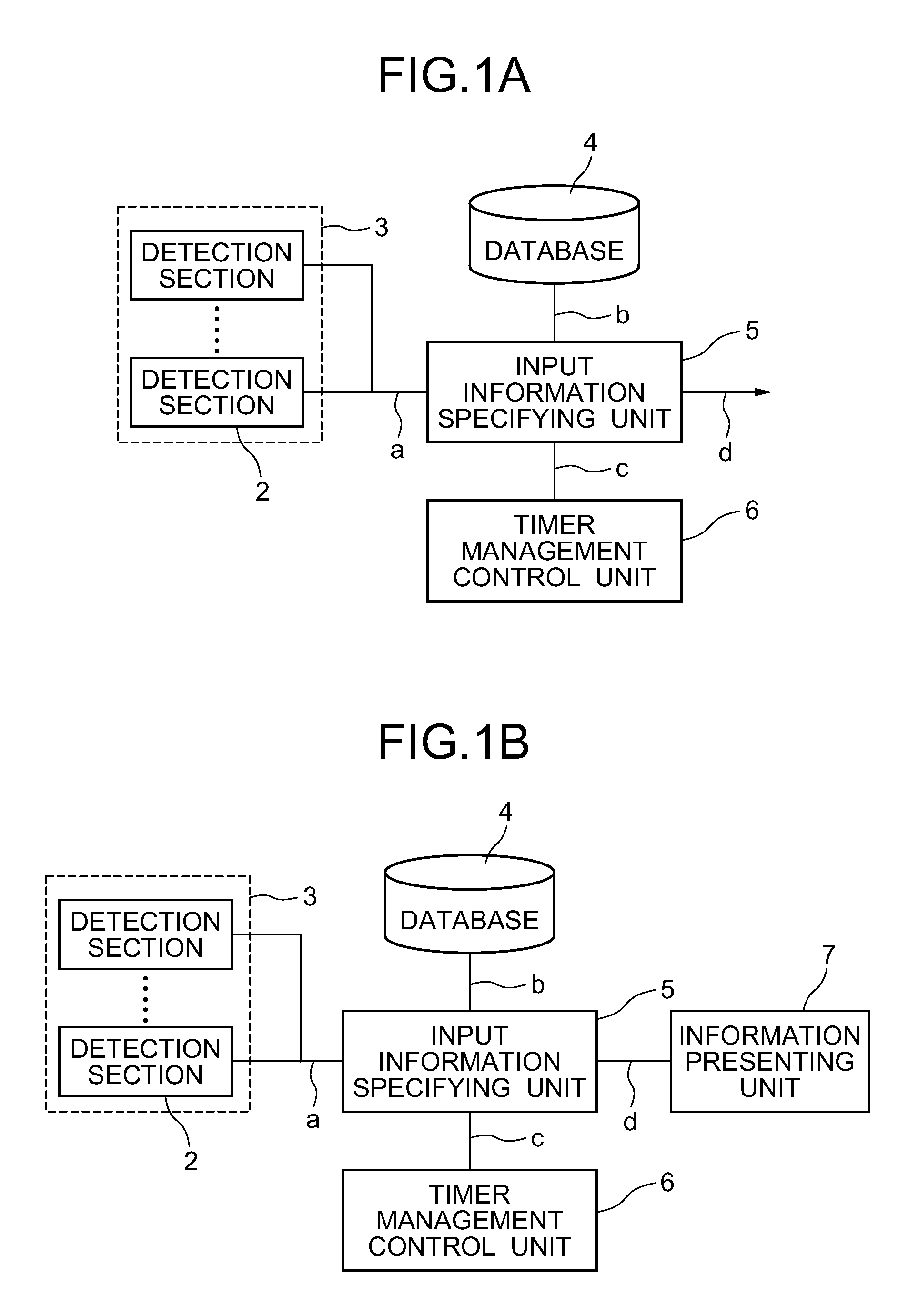
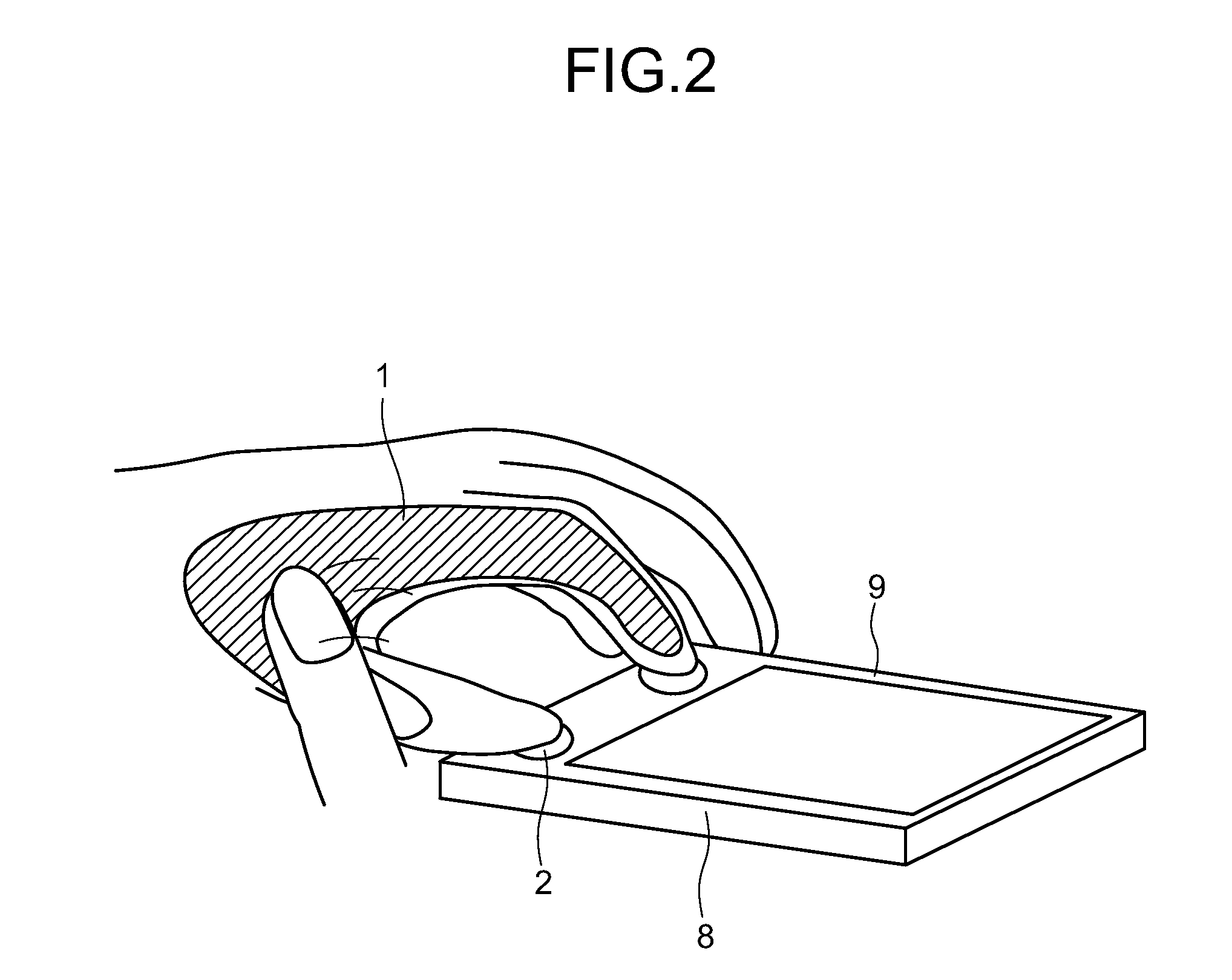
An input device includes an input section having a detection section which detects a force transmitted via a human body when a trailing operation is performed on a part of the body contacting the input device, and outputs the force as detection data “a”; a timer management control unit which generates a timing for converting the detection data “a” into time-series data and outputs the timing as timing data “c”; an input information specifying unit which converts the detection data “a” into time-series data based on the timing data “c”, compares the time-series data with stored data “b” in a database which has been set beforehand, to thereby specify an input operation and output the input operation as input information specifying data “d”; and an information presenting unit which, upon receiving the input information specifying data “d”, displays a function assigned to the input operation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Measurement of evoked neural response
InactiveUS7809445B2Detection is slightEasy to rebuildElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method and device for measuring an evoked neural response comprising a sensor (25) for obtaining a sensed signal representing the evoked neural response, a high gain amplifier (30) having a signal input (31) for receiving the sensed signal and having a reference input (32), and means for altering or setting a reference voltage at the reference input (32) to prevent the amplifier (30) saturating with variations of the sensed signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Optical scanner device
InactiveUS20090101801A1Improve accuracyDetection is slightBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight spotOptical axis
An optical scanner device, comprising a scanning unit, which casts irradiation light emitted from a light source in an arbitrary direction to scan an observation object, an objective lens system, which converges the irradiation light on the observation object, and a photo-detector unit, which is disposed on an optical axis of the objective lens system to have the irradiation light transmit therethrough, is provided. A position of the irradiation light converged on the observation object is detected based on a position of a light spot of the irradiation light transmitting through the photo-detector unit.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Power transmission device and power reception device
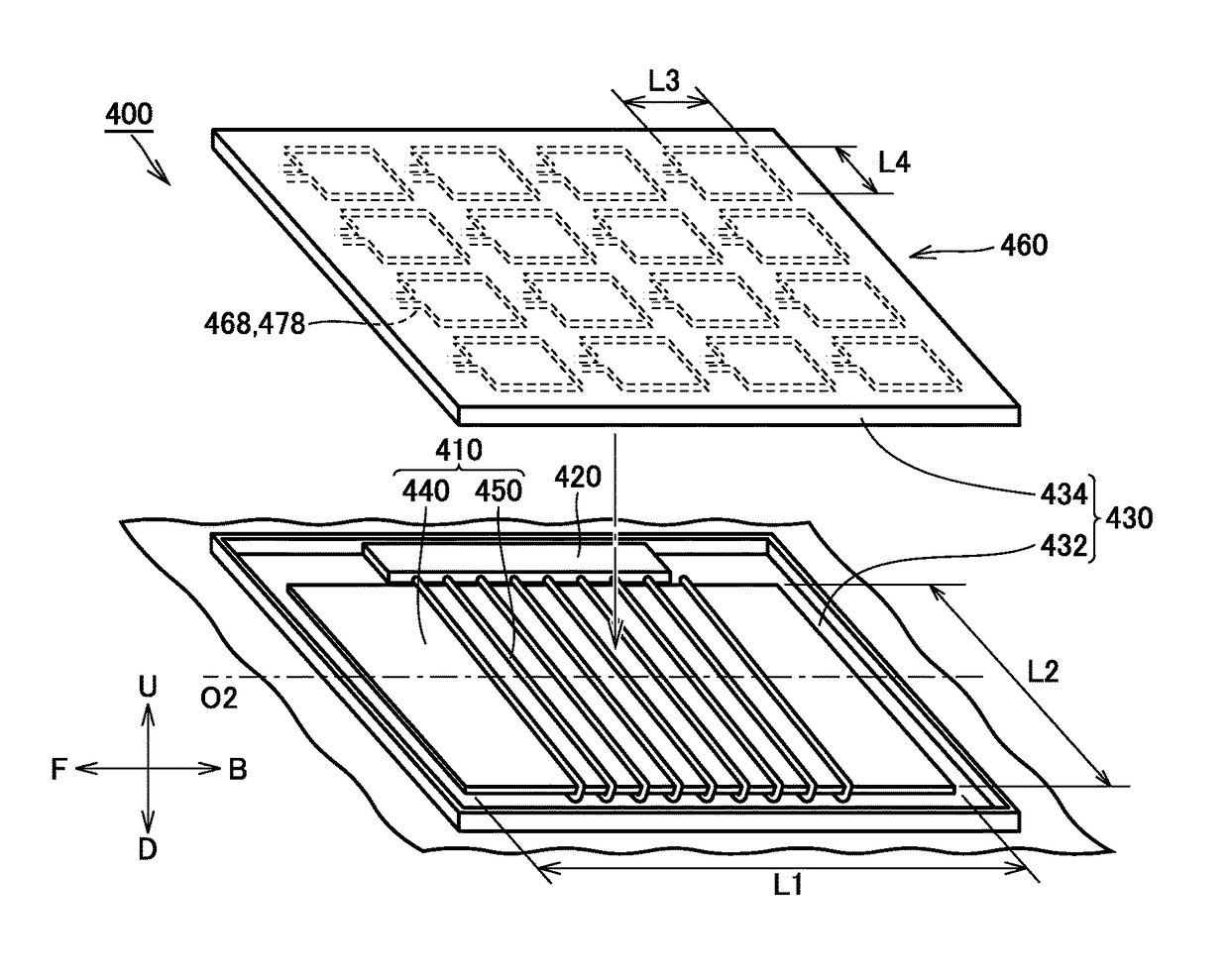
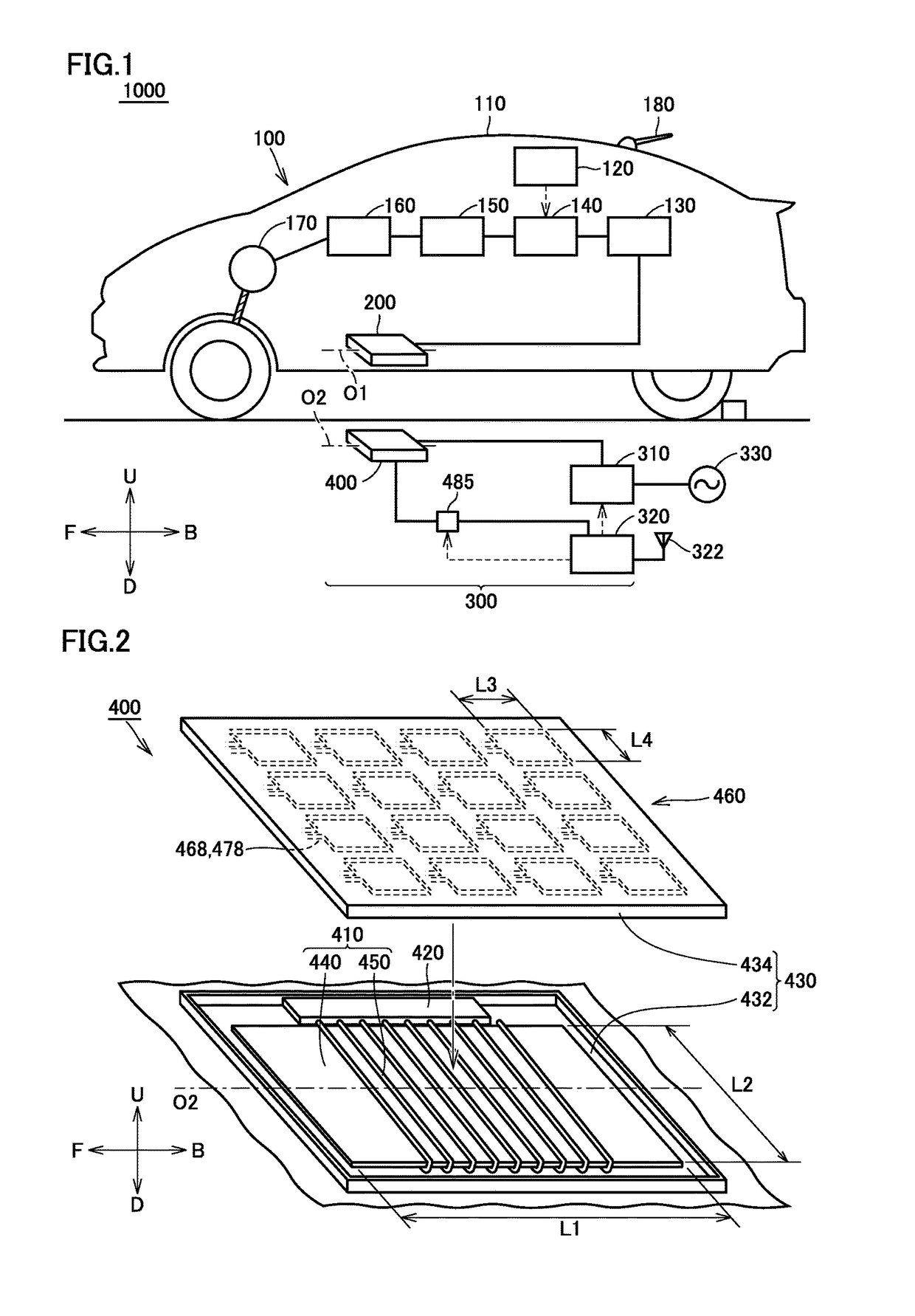
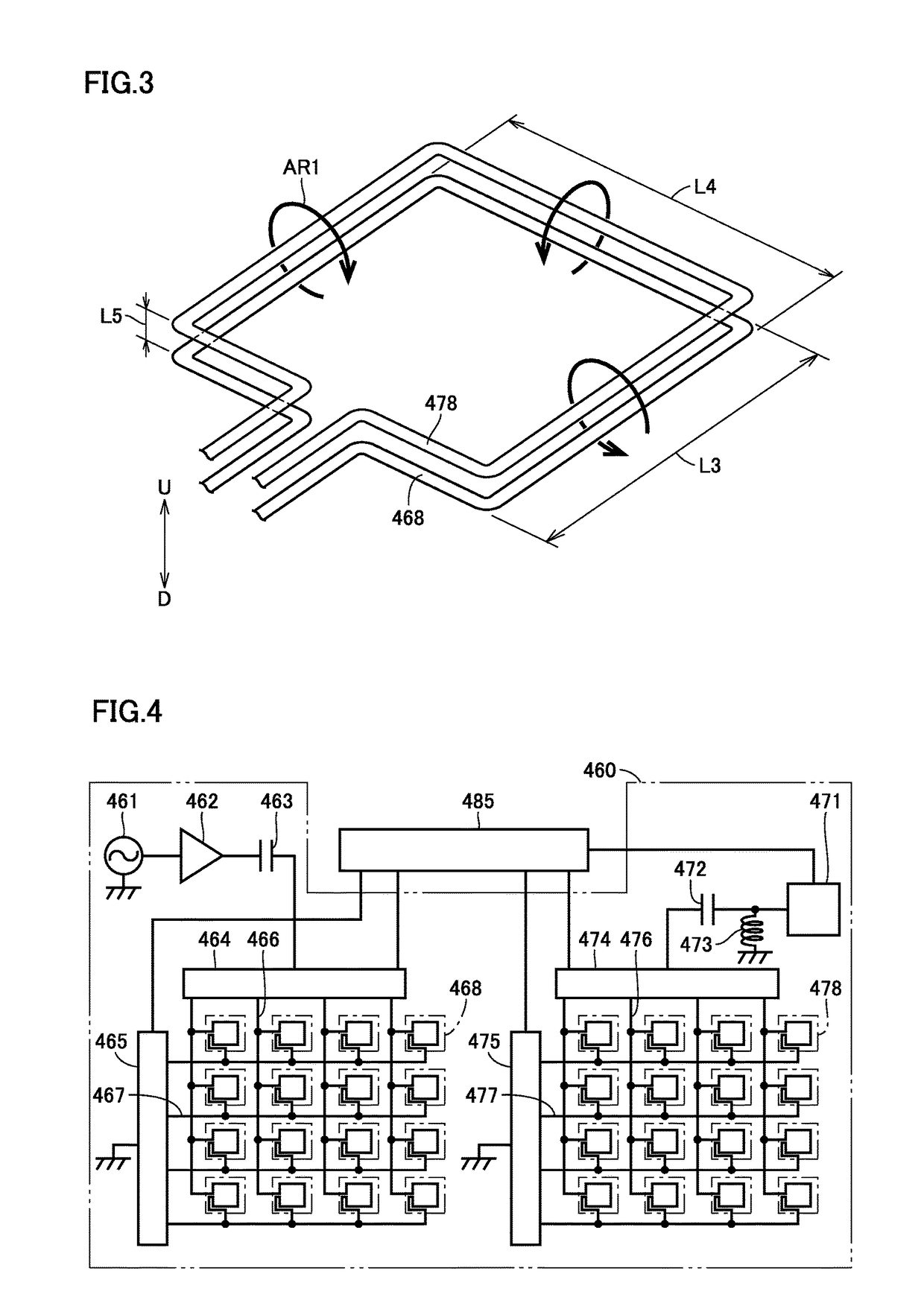
ActiveUS9981564B2Reduce distanceSmall sizeCharging stationsTransformersEngineeringPower transmission
A foreign object detector includes a plurality of first coils and a plurality of second coils. The plurality of first coils are arranged along an upper surface of a power transmission coil. The plurality of second coils are provided to correspond to the plurality of first coils, with the second coils each being arranged to face a corresponding one of the first coils. An outer shape of each of the plurality of first coils and each of the plurality of second coils is smaller than an outer shape of the power transmission coil when the power transmission coil is viewed two-dimensionally from above the power transmission coil.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com