Patents
Literature
75results about How to "Minimize adhesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
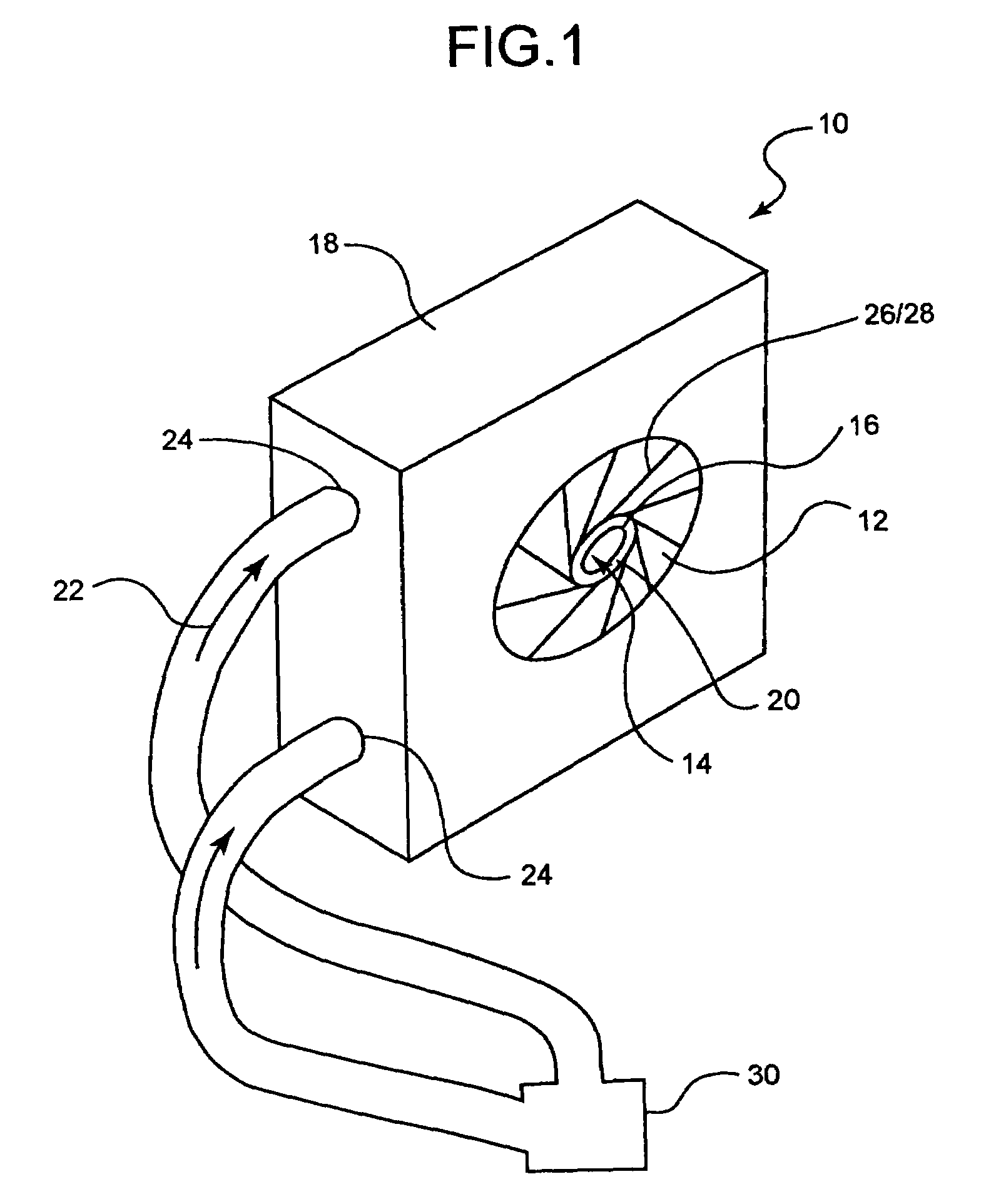
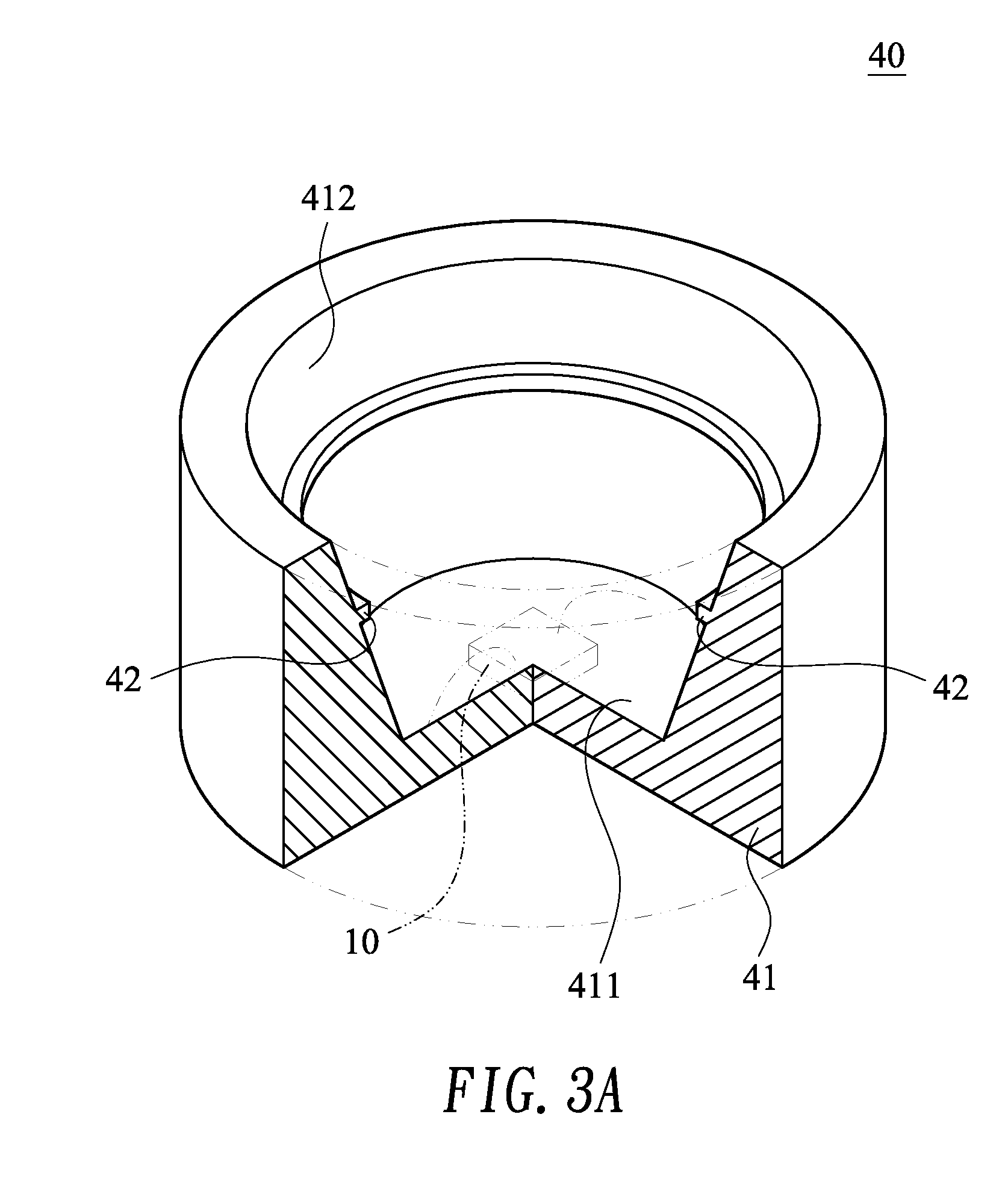
Multi-lumen vascular catheter and method for manufacturing the same
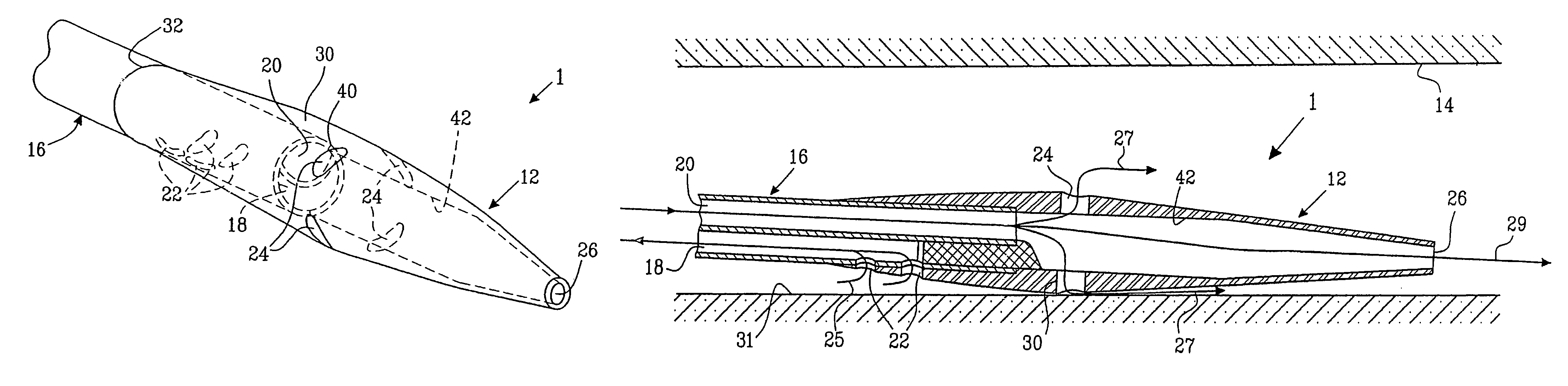
ActiveUS20050288623A1Avoid recyclingMinimize adhesionMulti-lumen catheterMedical syringesVeinVenous blood
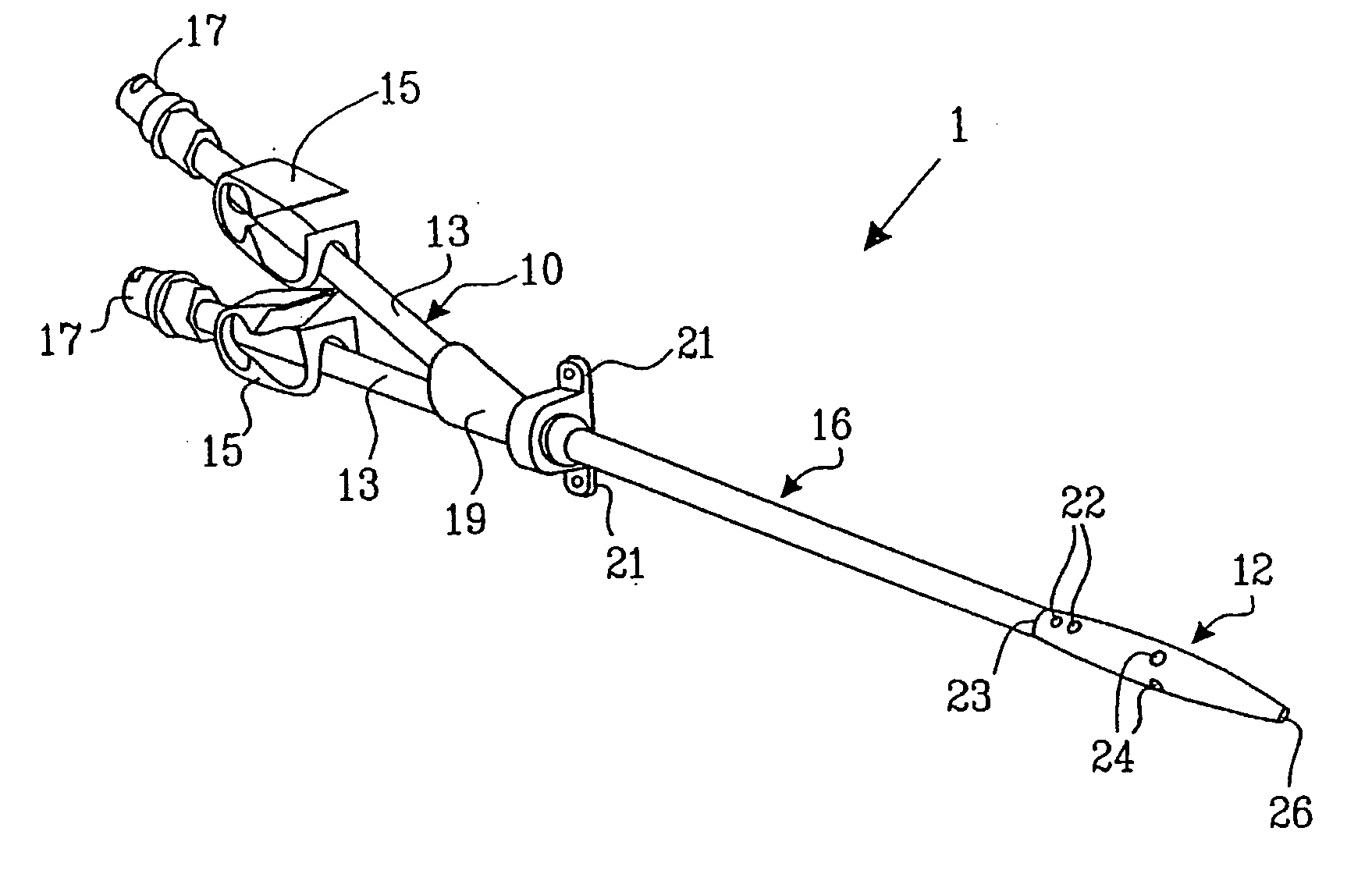
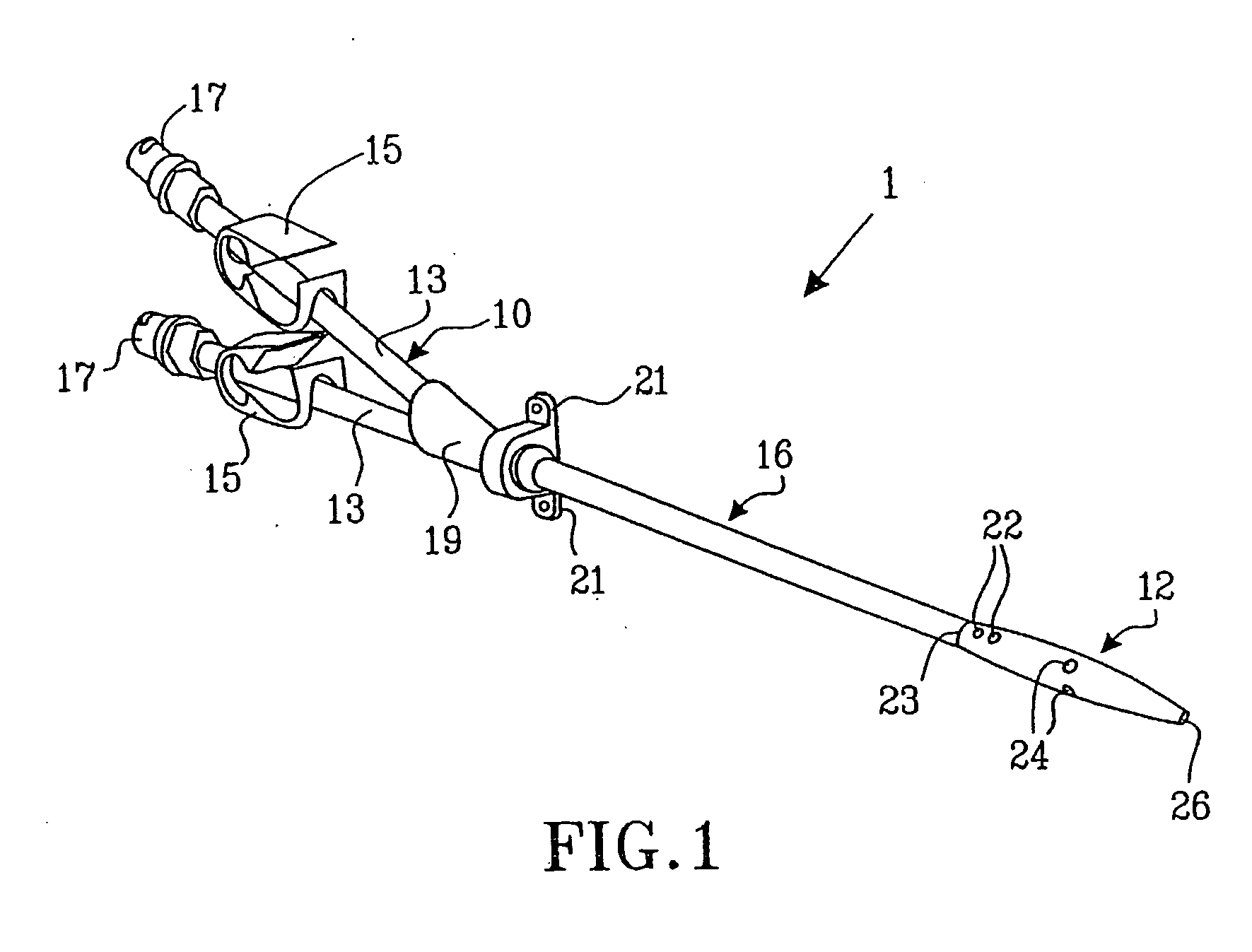
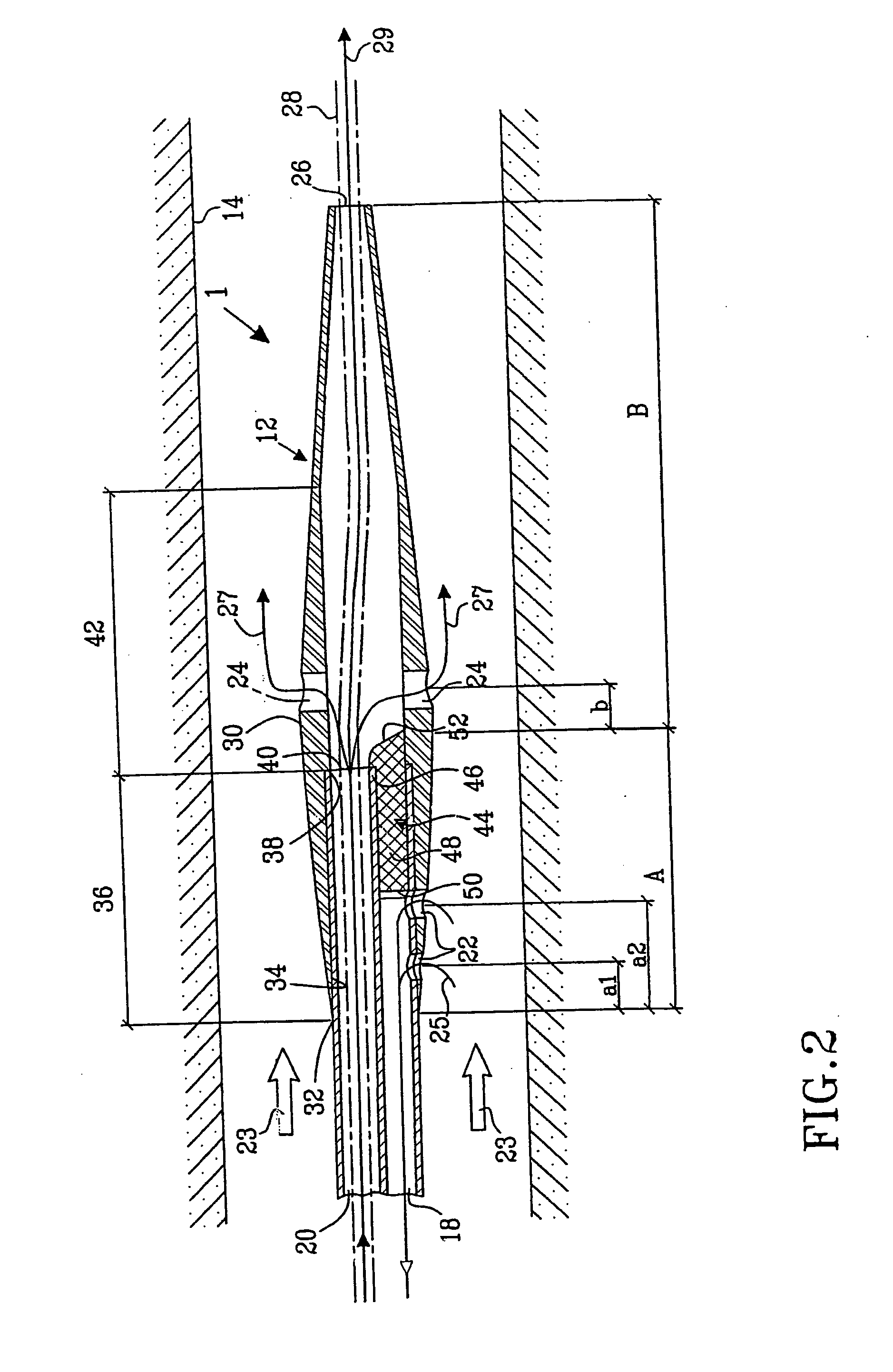
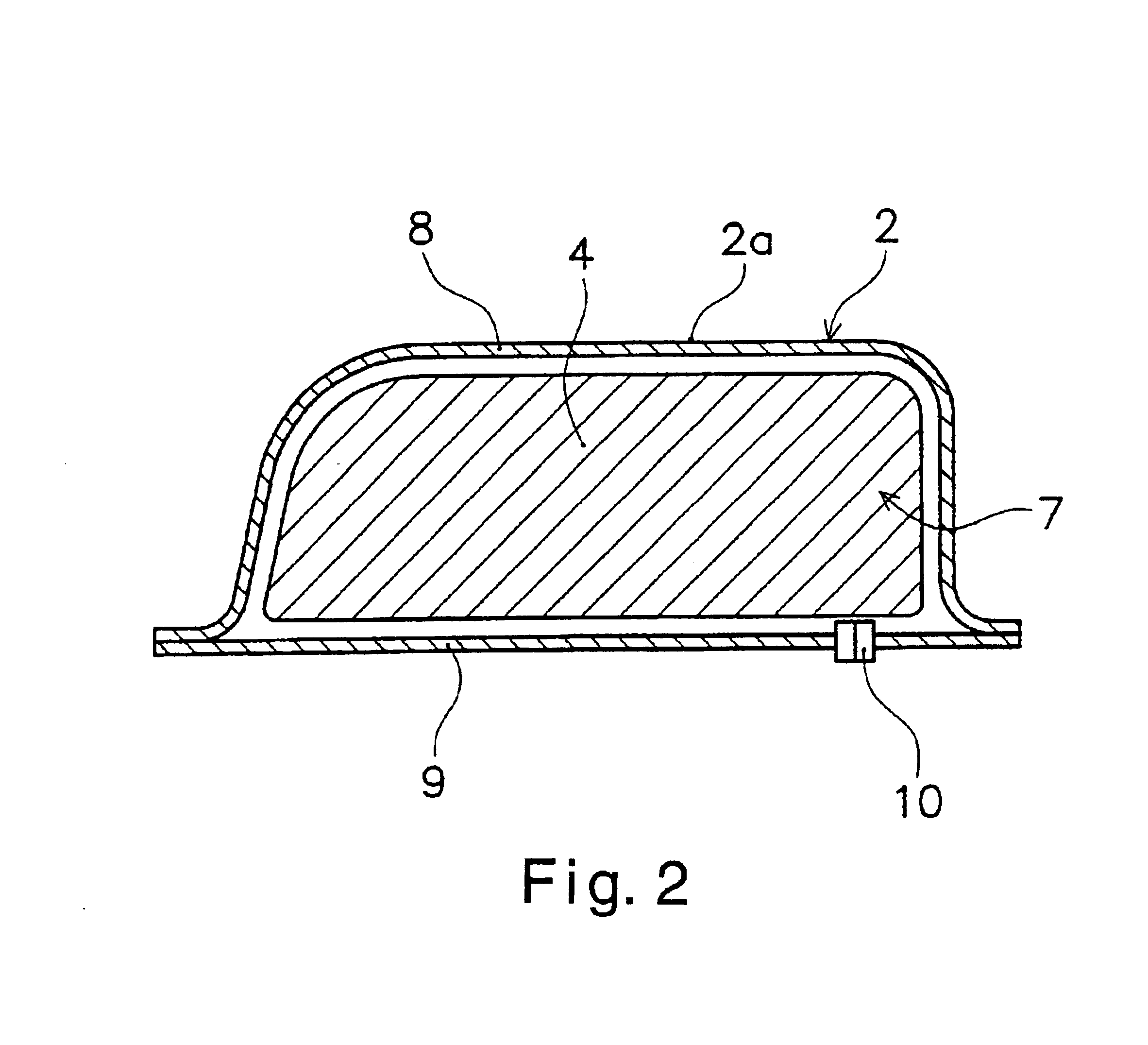
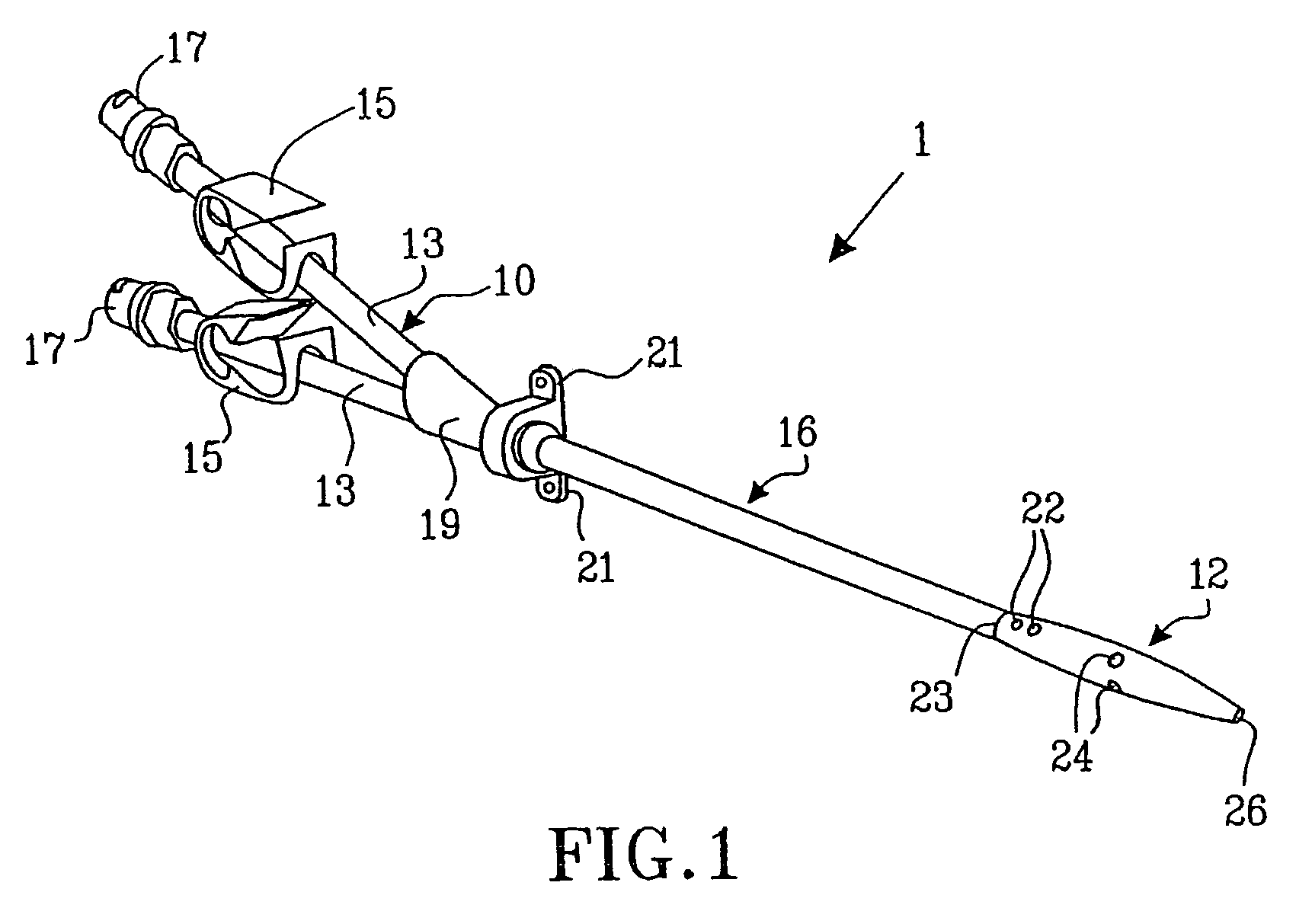
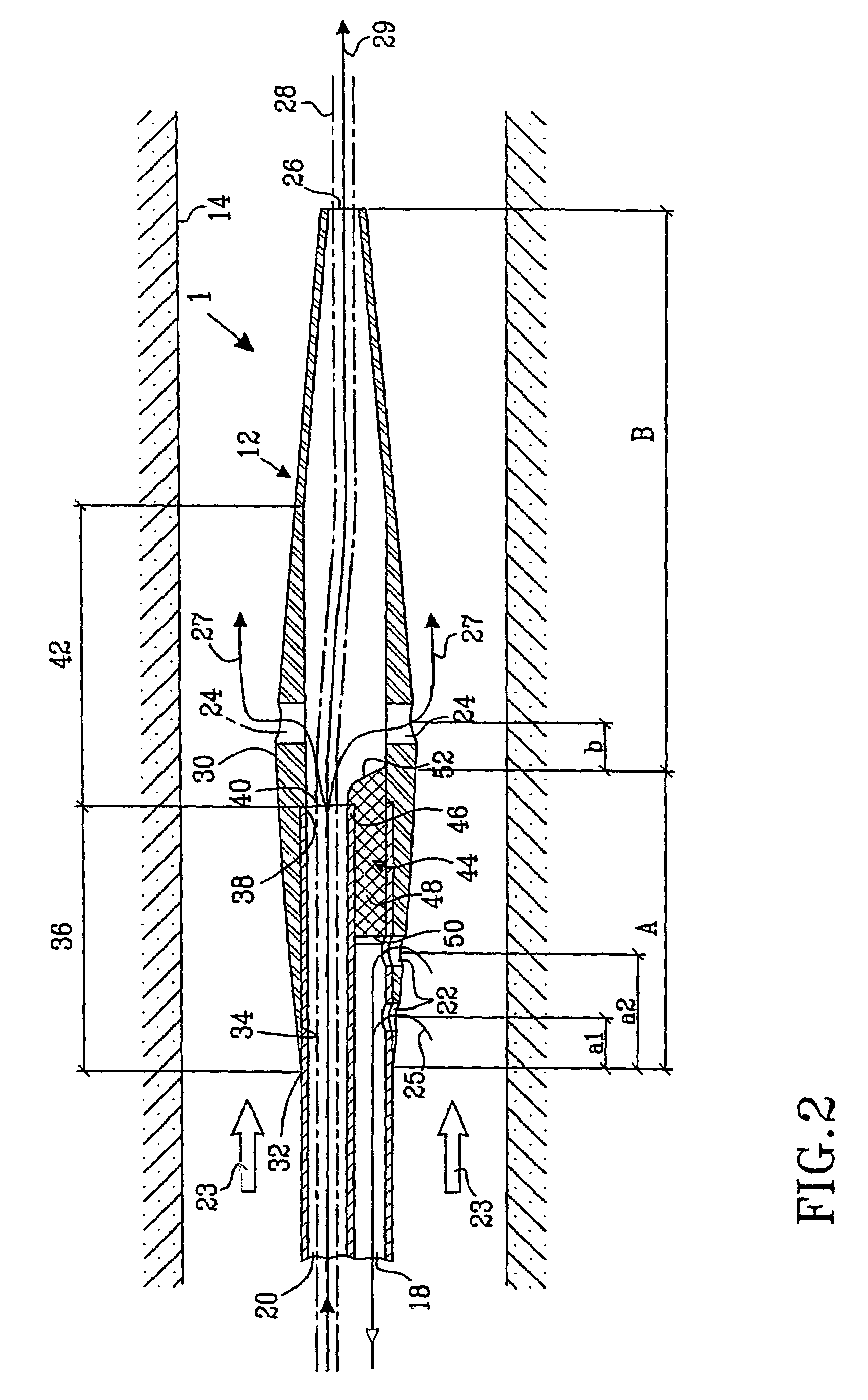
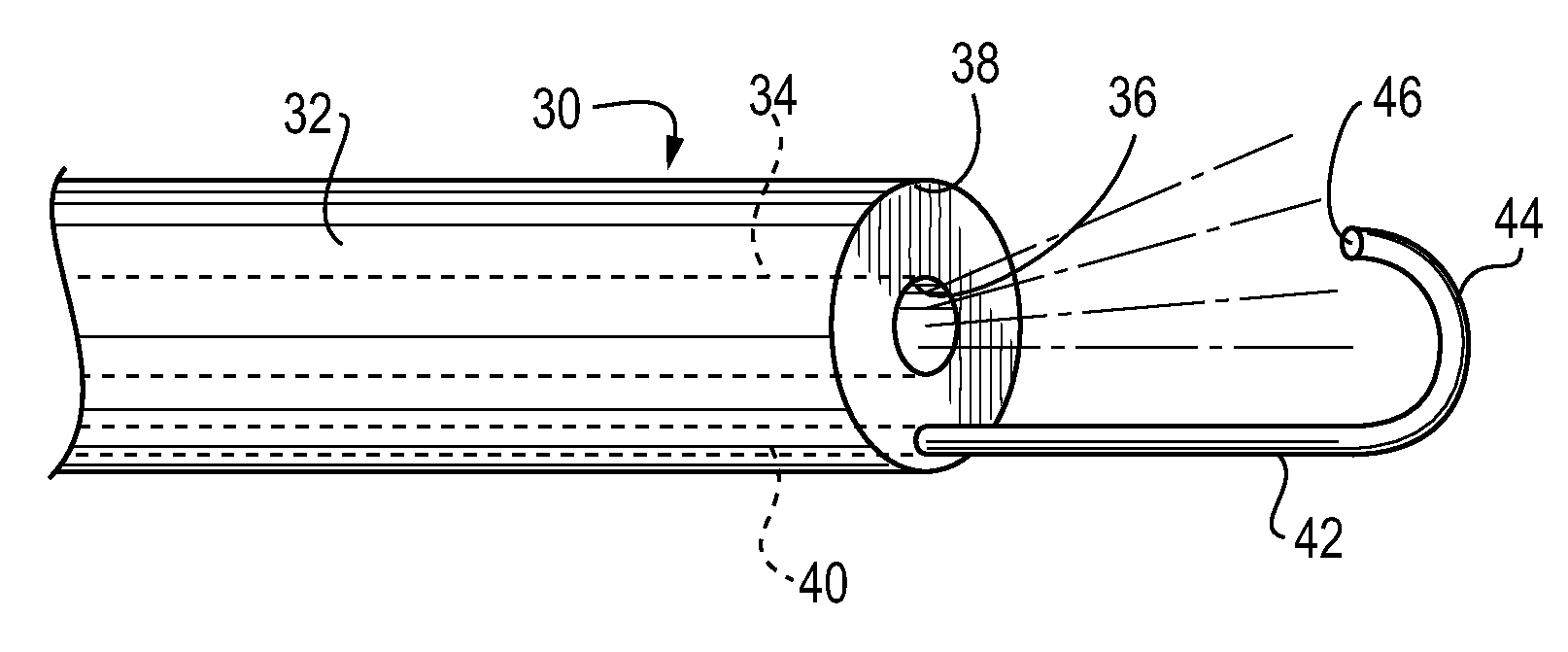
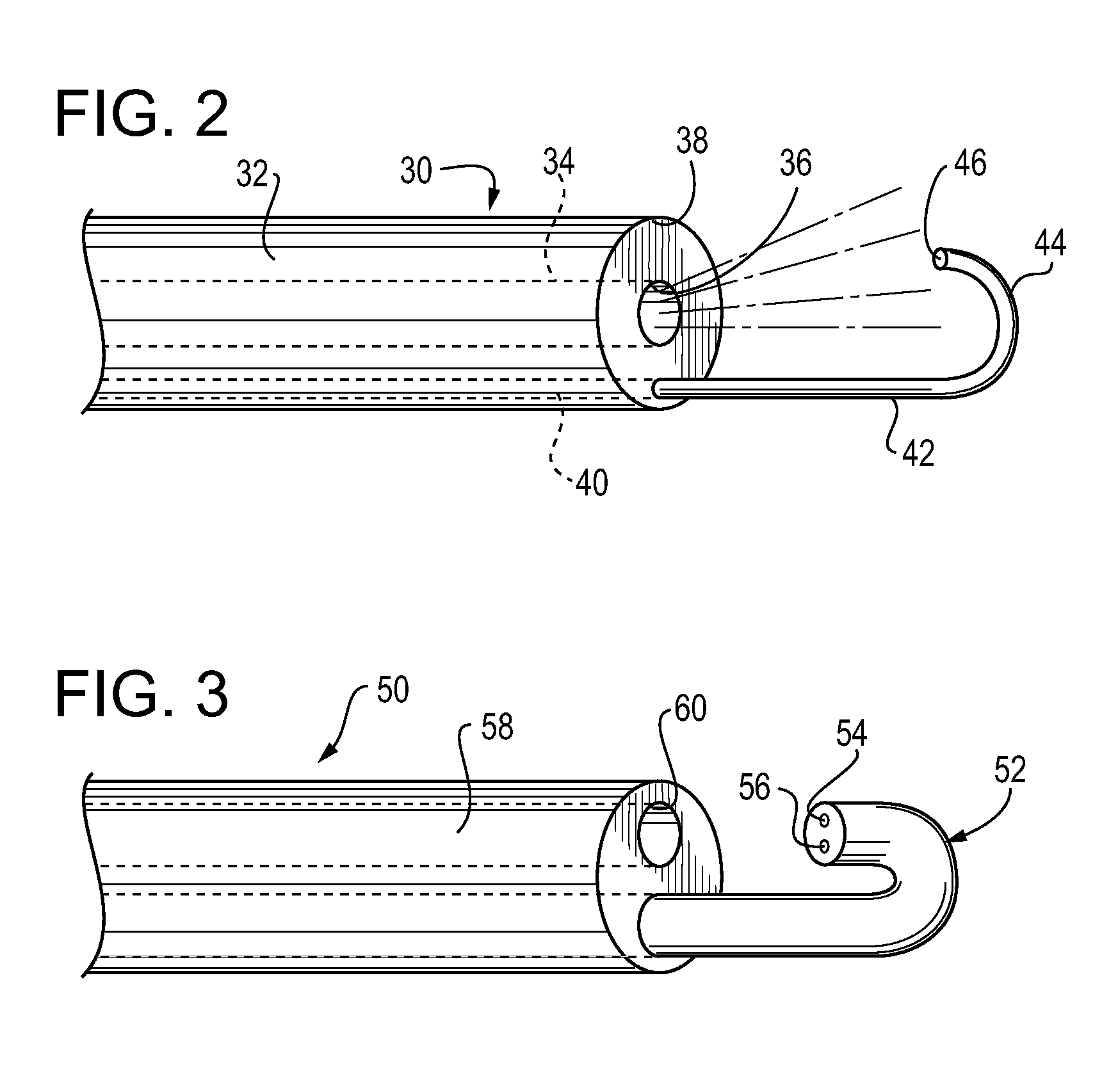
A multilumen vascular catheter (1) for treatment of patients by insertion of the vascular catheter in a venous blood vessel (14) by means of a guide-wire (28), the vascular catheter having a proximal connection point (10), a distal end-portion (12) which is terminated within a guide-wire opening (26), and a flexible catheter tube (16) arranged between the proximal connection portion (10) and the distal end-portion (12). The catheter tube (16) has a first lumen (18) for extraction of fluid such as untreated blood from the vessel (1) and a second lumen (20) for introducing fluid such as treated blood to the blood vessel (14). One or more suction openings (22) communicate with the first lumen (18) and are located upstream of one or more outlet openings (24), which in turn communicate with the second lumen (20), the suction openings (22) and the outlet openings (24) being located at the distal end-portion (12). The distal end-portion (12) is permanently bulbous and has a first, widening section (A) starting from the catheter tube (16) with a gradually increasing external cross-section in the direction toward the guide-wire opening (26). The first section (A) transits downstream via a shoulder (30) with a maximum external diameter into a second, narrowing section (B) having a gradually decreasing external cross-section in the direction toward the guide-wire opening (26). One or more of the suction openings (22) are located in the first, widening section (A) of the distal end-portion (12) while one or more of the outlet openings (24) are located in the second, narrowing section (B).
Owner:NORDIC MED COM
Exhaust emission control device with additive injector
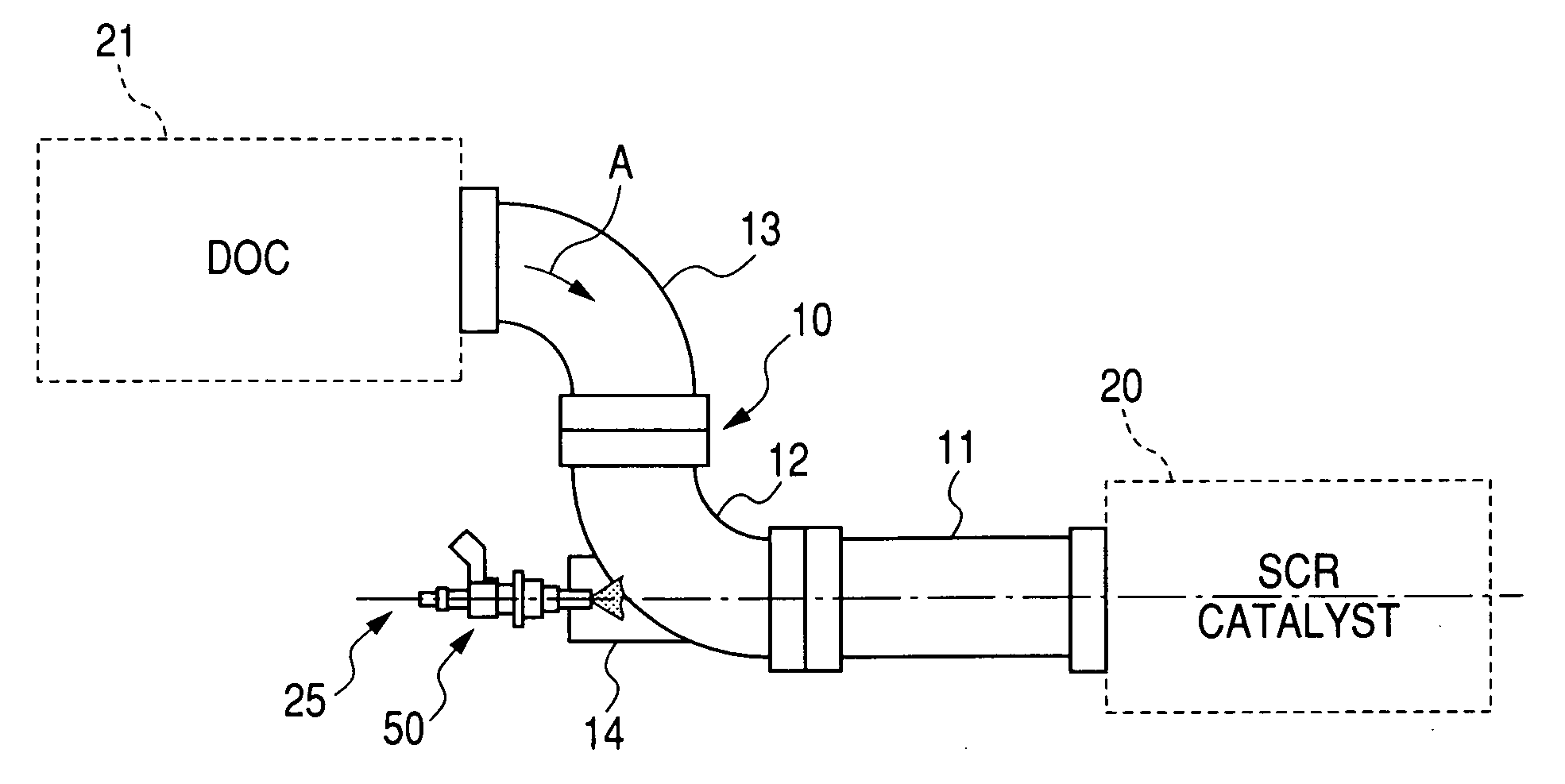
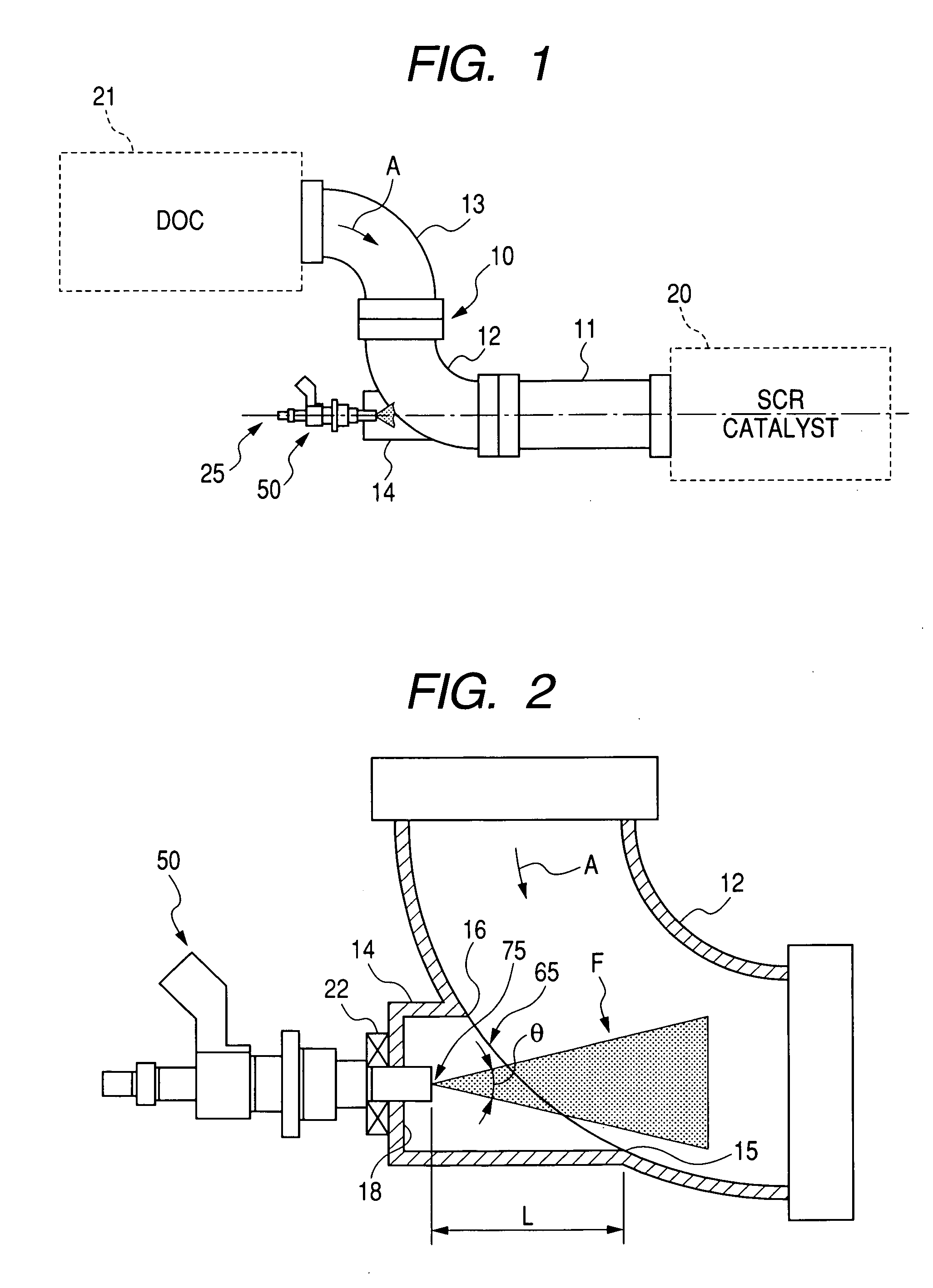
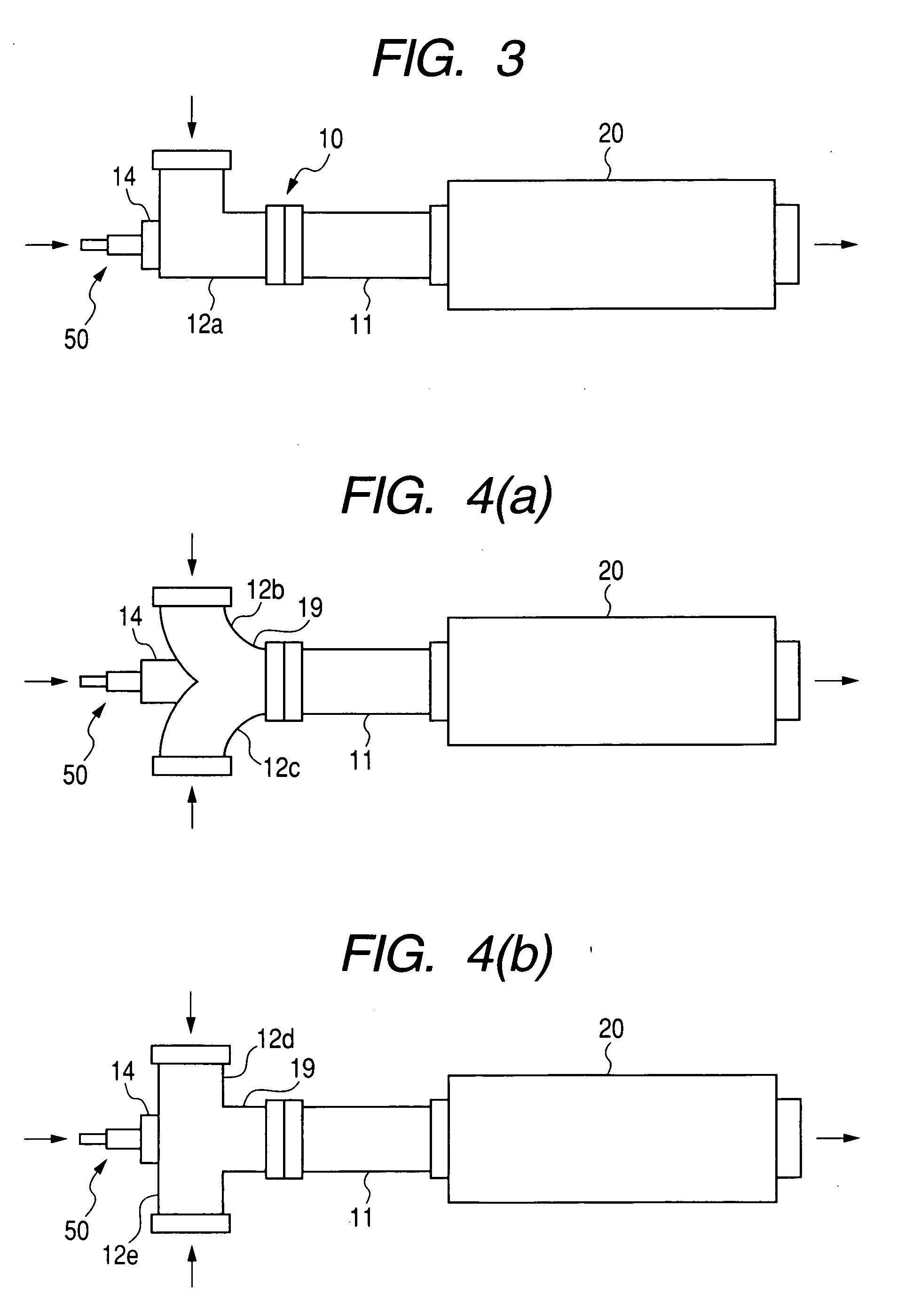
InactiveUS20080155973A1Minimize transmissionMinimize adhesionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesAqueous solution
An exhaust emission control apparatus is provided which is equipped with an additive injector to inject additive such as a urea aqueous solution into an exhaust pipe through which exhaust emissions flow. The exhaust pipe includes a straight section and a bent section. A catalyst such as a SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst is disposed downstream of the straight section. A hollow protrusion is formed on an outer peripheral wall of the bent section substantially in parallel to a longitudinal center line of the straight section. The protrusion has an opening formed in one of opposed ends thereof which communicates with inside the bent section. The additive injector is designed to produce a cone-shaped spray of additive and installed on the other end of the protrusion to inject the cone-shaped spray of additive into the exhaust pipe without interfering with at least a downstream edge of the opening.
Owner:DENSO CORP
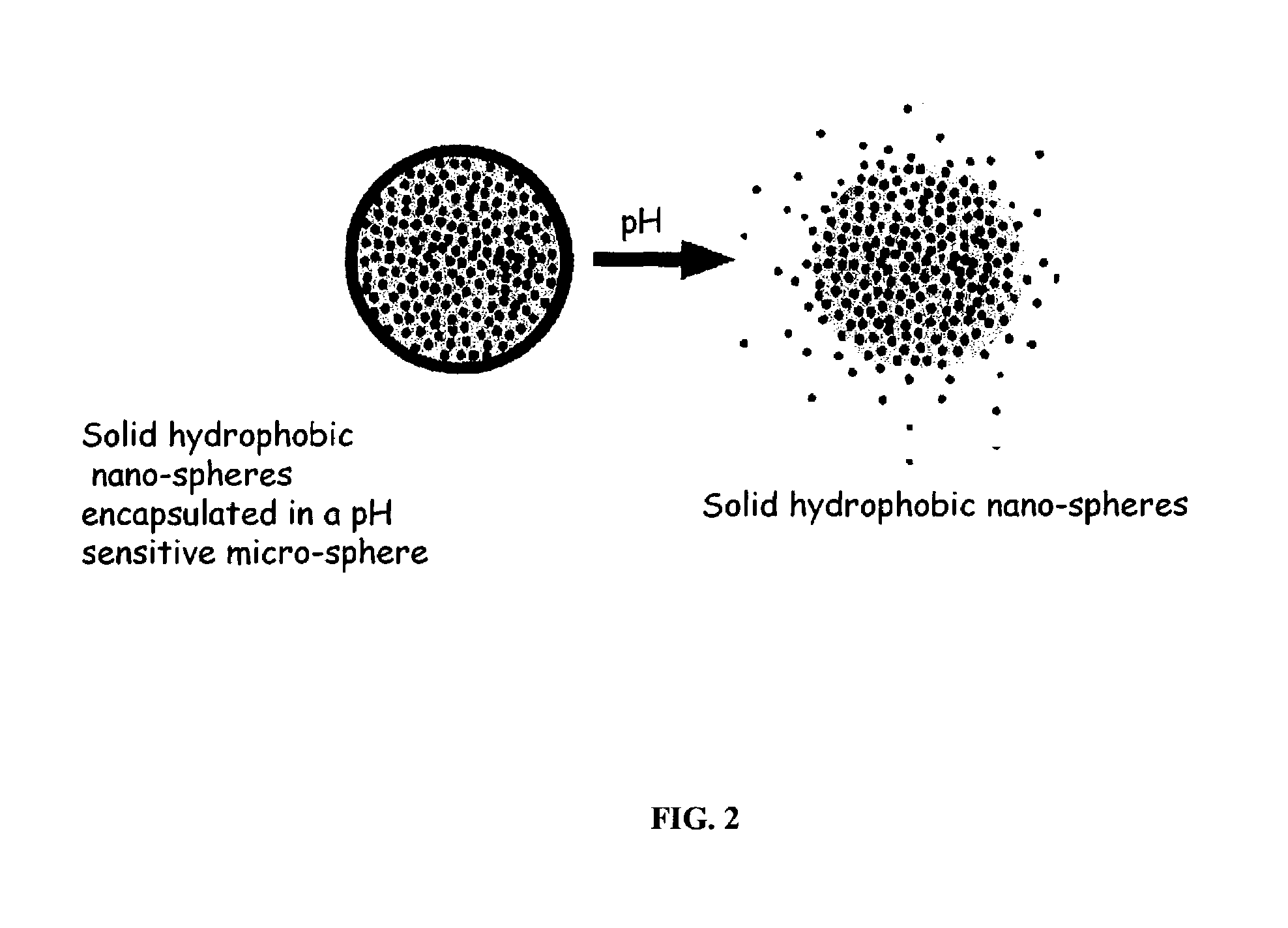
pH triggered targeted controlled release systems for the delivery of pharmaceutical active ingredients
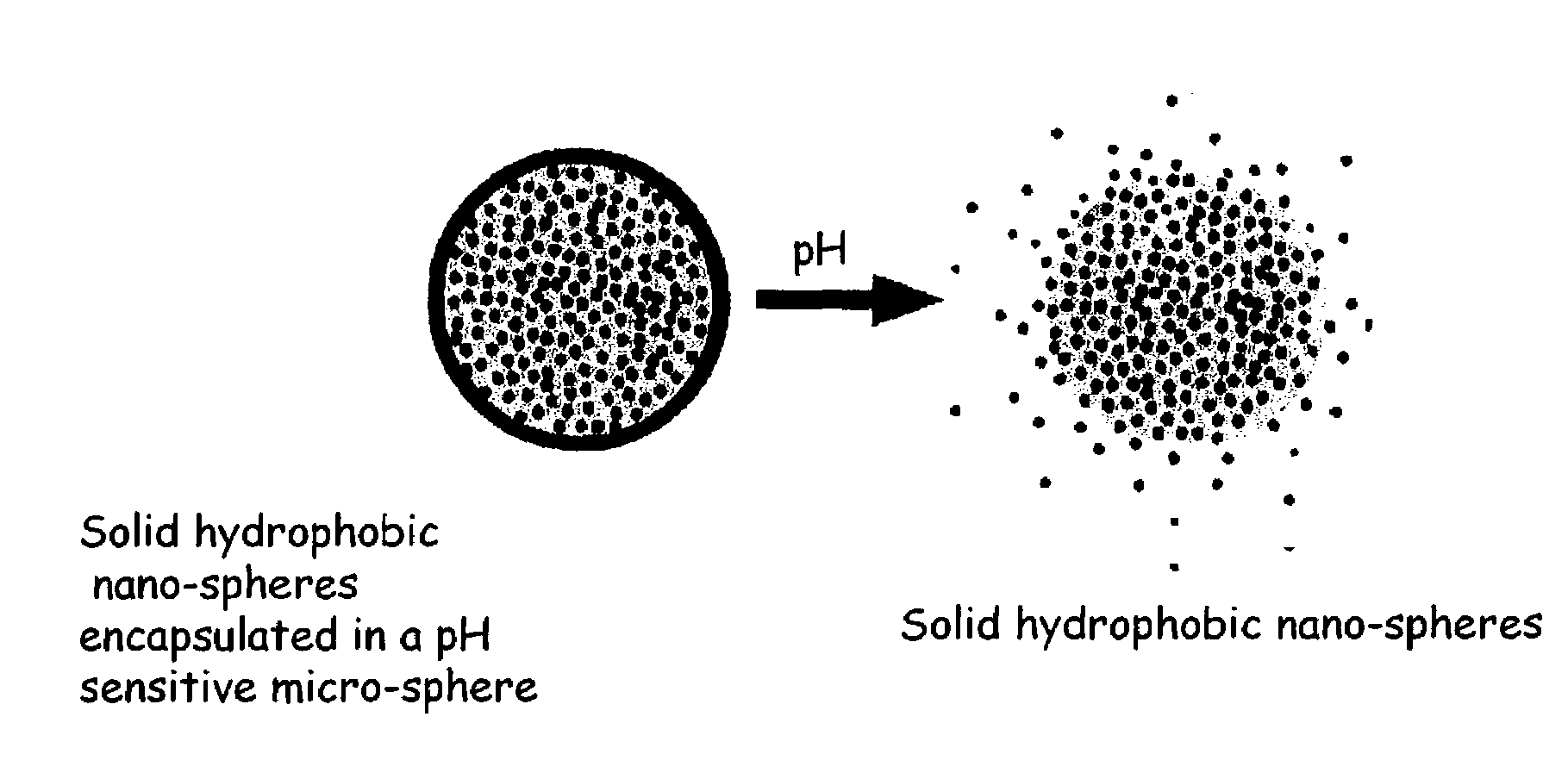
InactiveUS7670627B2Improve bioavailabilityRelease effective levelPowder deliveryNanomedicineControlled releaseTarget control
The present invention relates to a novel pH triggered, targeted controlled release system. The controlled delivery system of the present invention is substantially a free-flowing powder formed of solid hydrophobic nano-spheres comprising pharmaceutical active ingredients that are encapsulated in a pH sensitive micro-spheres. The invention also relates to the processes for preparing the compositions and processes for using same. The controlled release system can be used to target and control the release of pharmaceutical active ingredients onto certain regions of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and the small intestine. The invention further pertains to pharmaceutical products comprising the controlled release system of the present invention.
Owner:SALVONA
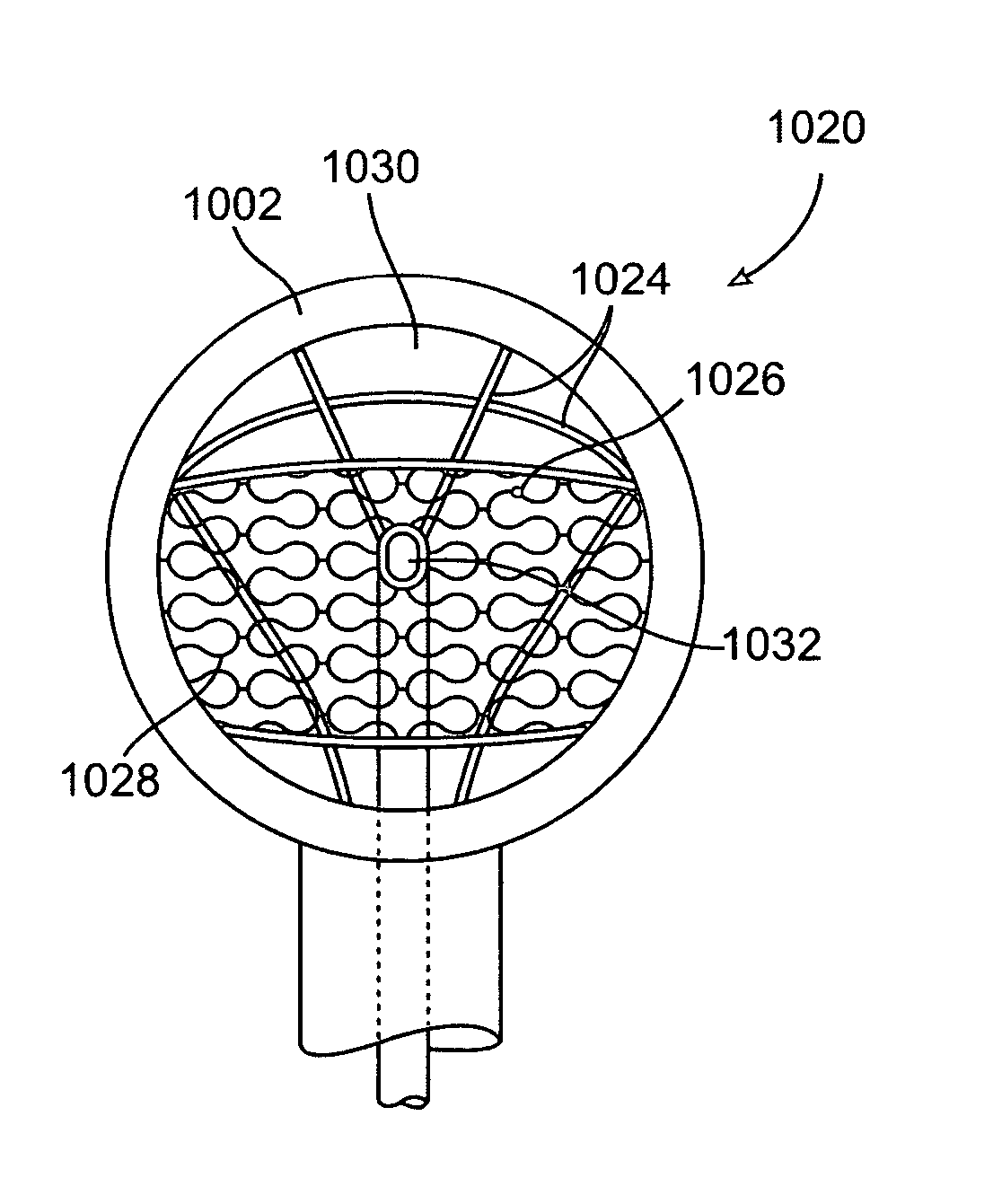
Methods and electrode apparatus to achieve a closure of a layered tissue defect
ActiveUS20060271040A1Increase engagementSubstantial sealElectrotherapyBalloon catheterTissue defectPatent foramen ovale
Methods for treating anatomic tissue defects such as a patent foramen ovale generally involve positioning a distal end of a catheter device at the site of the defect, exposing a housing and energy transmission member from the distal end of the catheter, engaging the housing with tissues at the site of the defect, applying suction or other approximating tool to the tissue via the housing to bring the tissue together, and applying energy to the tissue with the energy transmission member or to deliver a clip or fixation device to substantially close the defect. Apparatus generally include a catheter body, a housing extending from a distal end of the catheter body for engaging tissue at the site of the defect, and further adapted to house a fusing or fixation device such as an energy transmission member adjacent a distal end of the housing, or a clip or fixation delivery element.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Biological component comprising artificial membrane
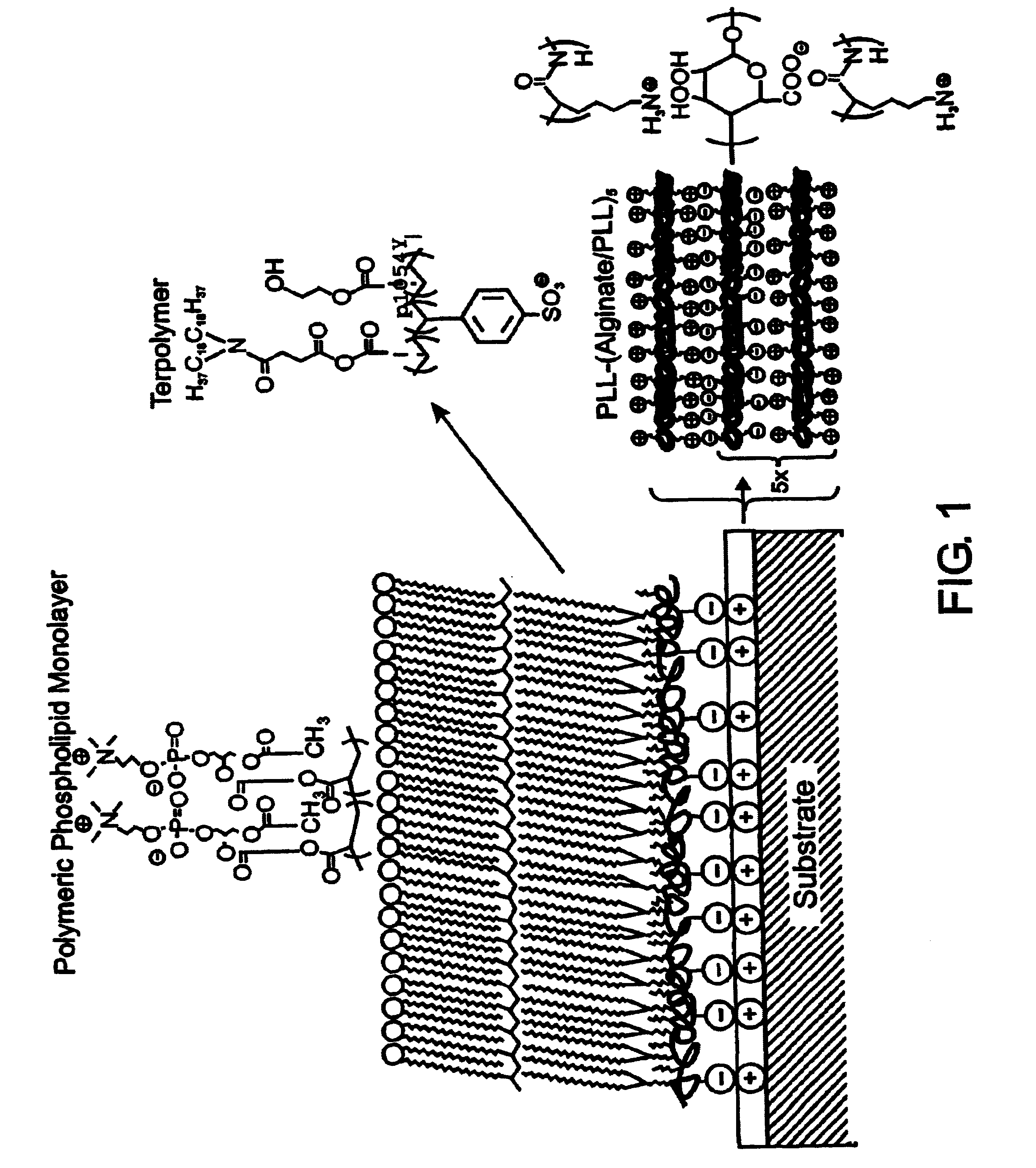
InactiveUS7713544B2Improved performance characteristicsMinimize adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyMicroorganismsAmount of substanceMembrane mimetic
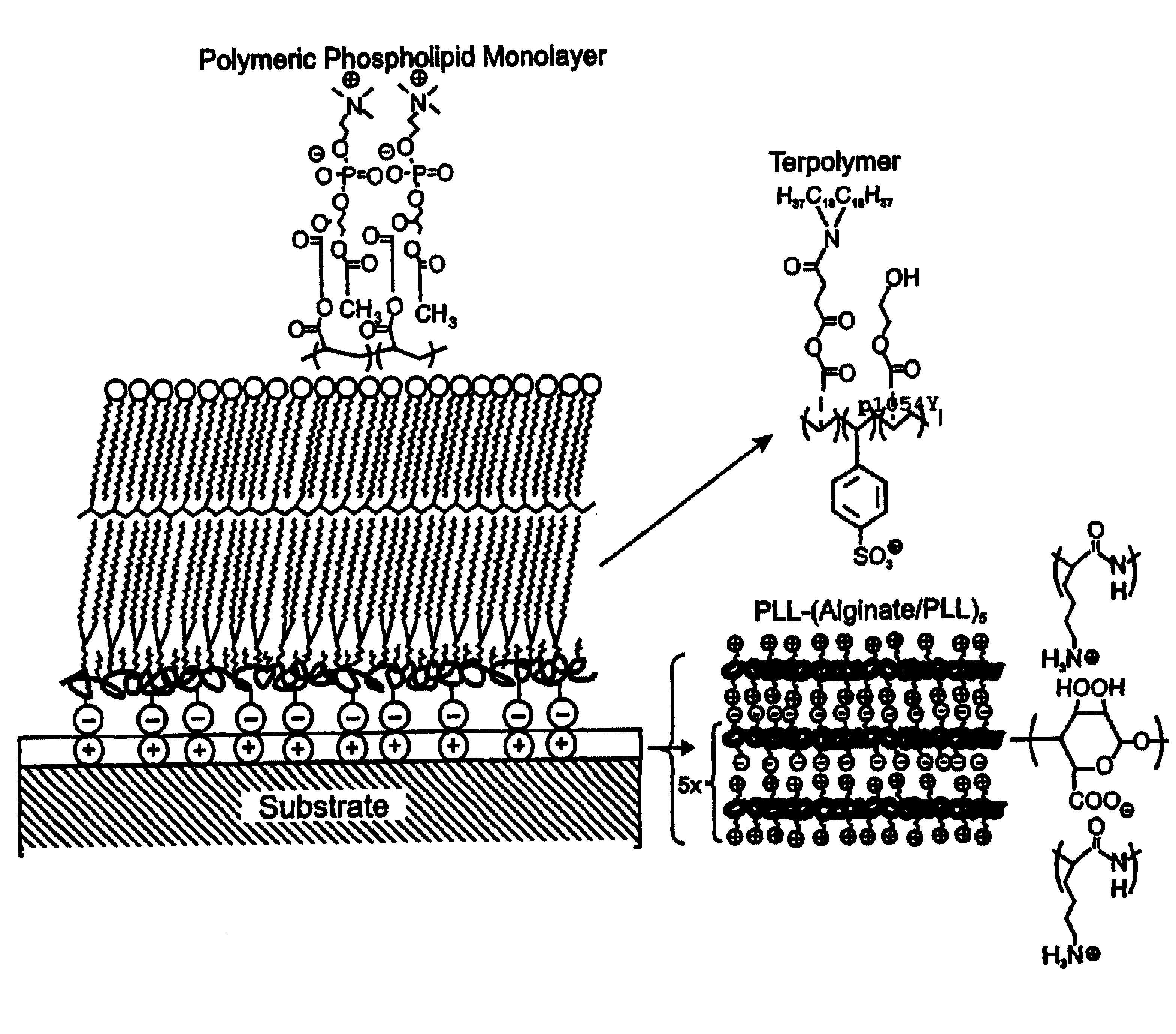
A biocompatible biological component is provided comprising a membrane-mimetic surface film covering a substrate. Suitable substrates include hydrated substrates, e.g. hydrogels which may contain drugs for delivery to a patient through the membrane-mimetic film, or may be made up of cells, such as islet cells, for transplantation. The surface may present exposed bioactive molecules or moieties for binding to target molecules in vivo, for modulating host response when implanted into a patient (e.g. the surface may be antithrombogenic or antiinflammatory) and the surface may have pores of selected sizes to facilitate transport of substances therethrough. An optional hydrophilic cushion or spacer between the substrate and the membrane-mimetic surface allows transmembrane proteins to extend from the surface through the hydrophilic cushion, mimicking the structure of naturally-occurring cells. An alkylated layer directly beneath the membrane-mimetic surface facilates bonding of the surface to the remainder of the biological component. Alkyl chains may extend entirely through the hydrophilic cushion when present. To facilitate binding, the substrate may optionally be treated with a polyelectrolyte or alternating layers of oppositely-charged polyelectrolytes to facilitate charged binding of the membrane-mimetic film or alkylated layer beneath the membrane-mimetic film to the substrate. The membrane-mimetic film is preferably made by in situ polymerization of phospholipid vesicles.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Stent reducing system and device
ActiveUS7284401B2Reduce frictionMinimize adhesionShaping toolsStentsFluid bearing% diameter reduction
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
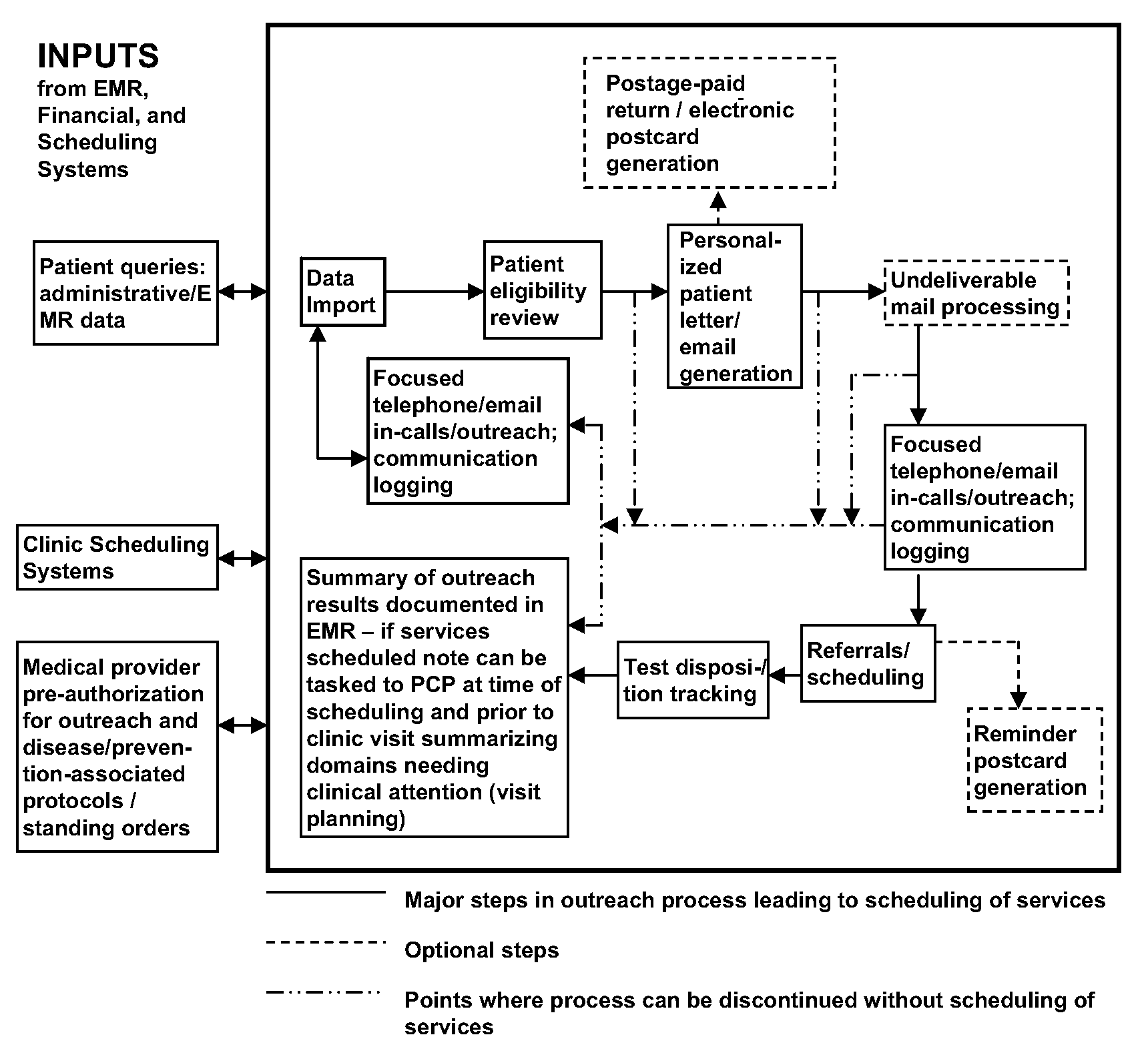
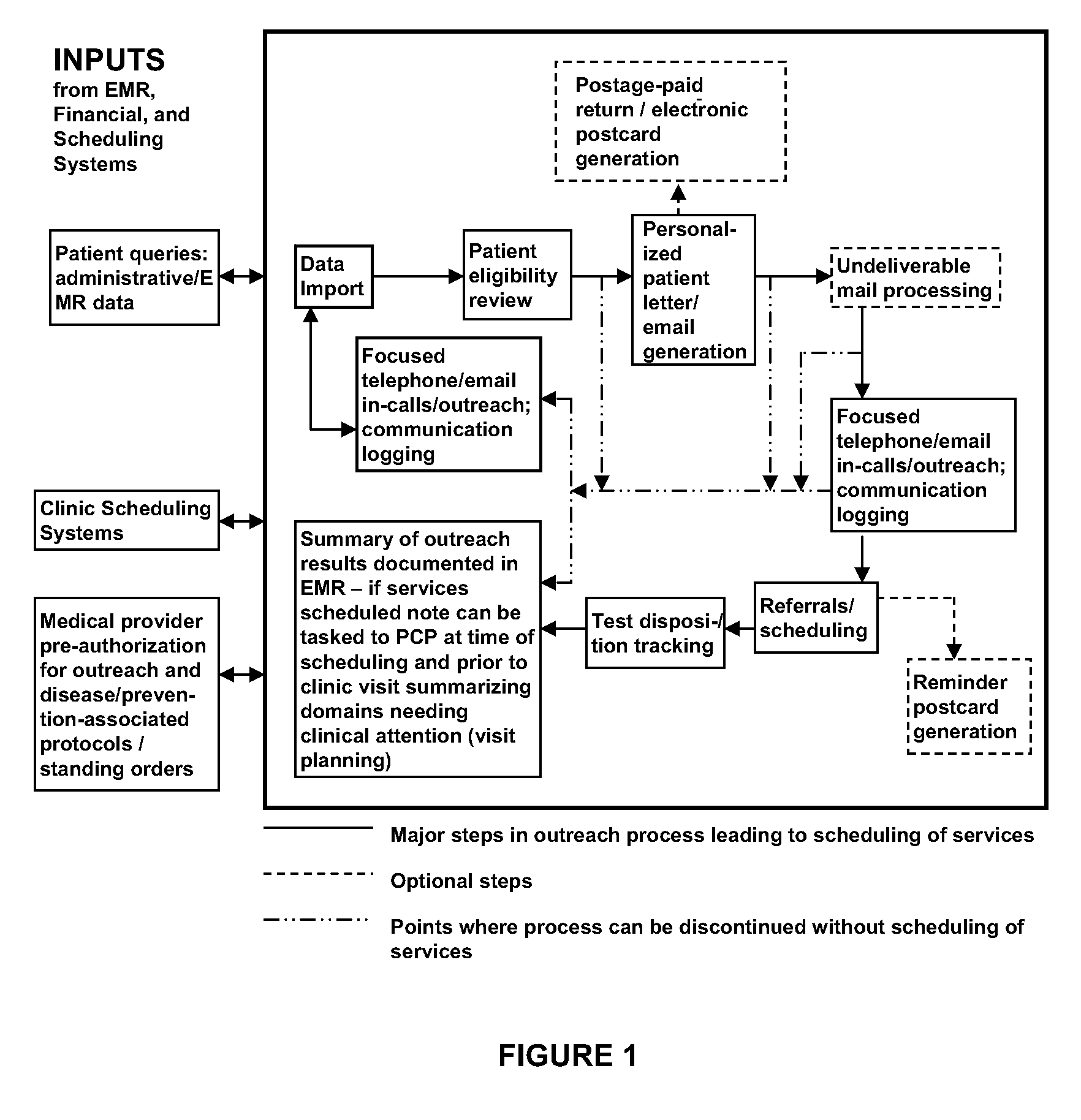
Health Promotion Outreach System
InactiveUS20090138285A1Easy accessReduce deliveryFinanceDigital data processing detailsDiseaseClinical information
Patient receipt of recommended preventive and chronic disease care is suboptimal, partly because of poorly organized clinical information and time-limited and sporadic appointments with medical providers. To overcome these problems, we provide a Health Promotion Outreach System (HPOS) based on electronic data queries, active patient-centered outreach, and minimizing patient barriers to adherence. HPOS has many advantages over traditional preventive care delivery systems and chronic disease management programs, and helps promote the type of clinical practice change contemplated by the chronic care model.
Owner:DENBERG THOMAS D
Container for housing a mask blank, method of housing a mask blank, and a mask blank package
ActiveUS8496133B2Improve cleanlinessMinimize adhesionCapsLarge containersEngineeringMechanical engineering
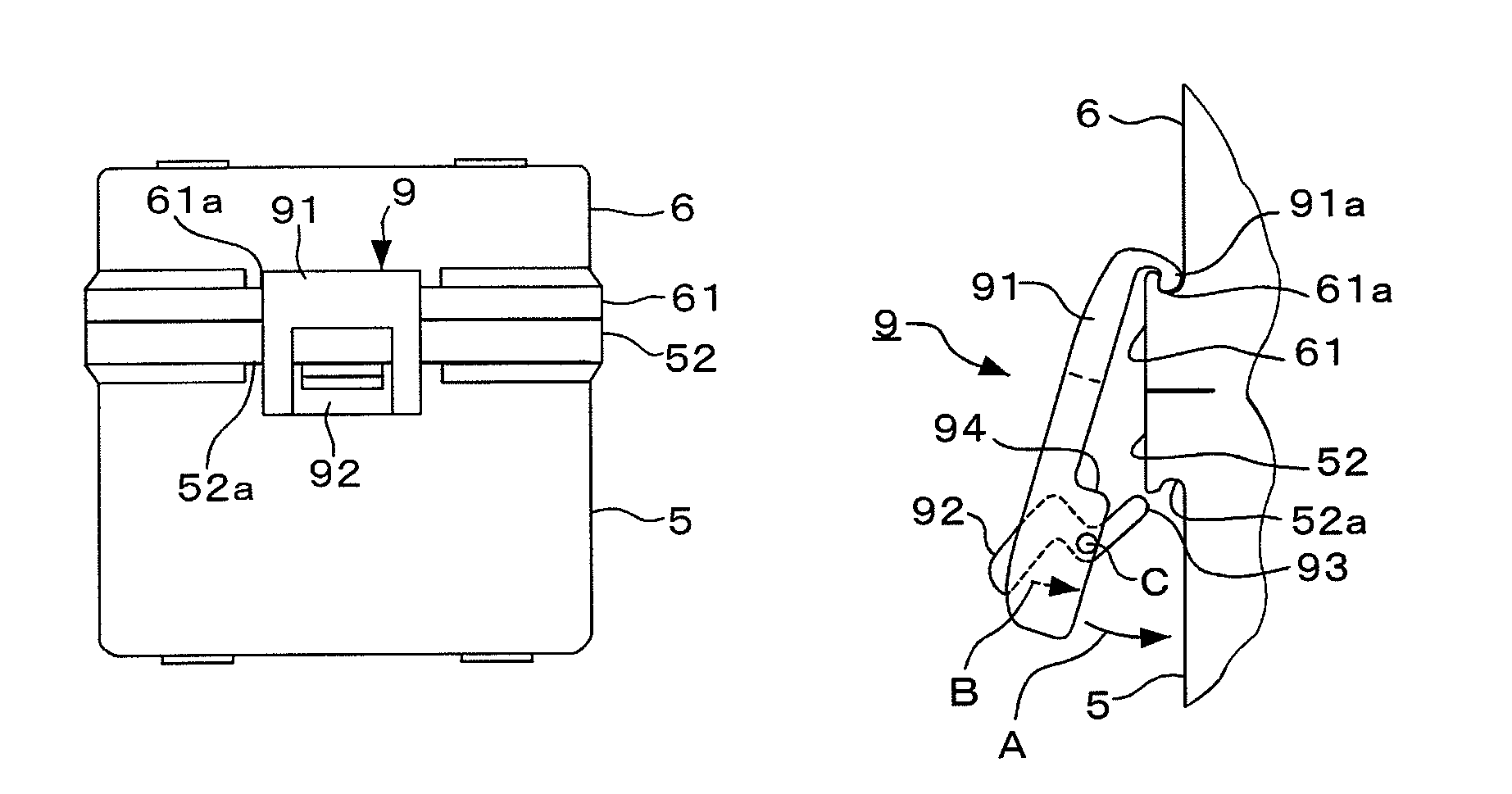
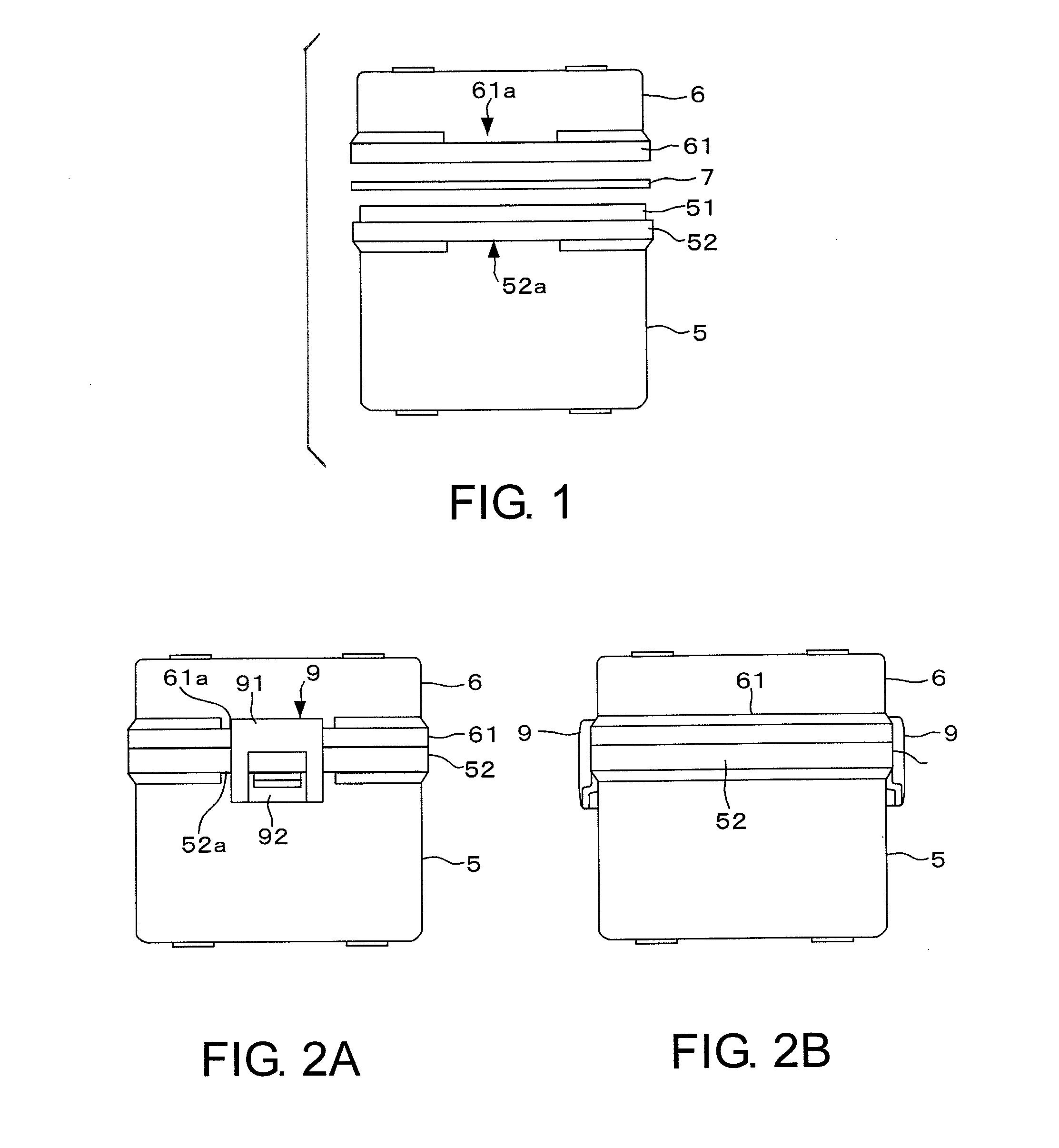
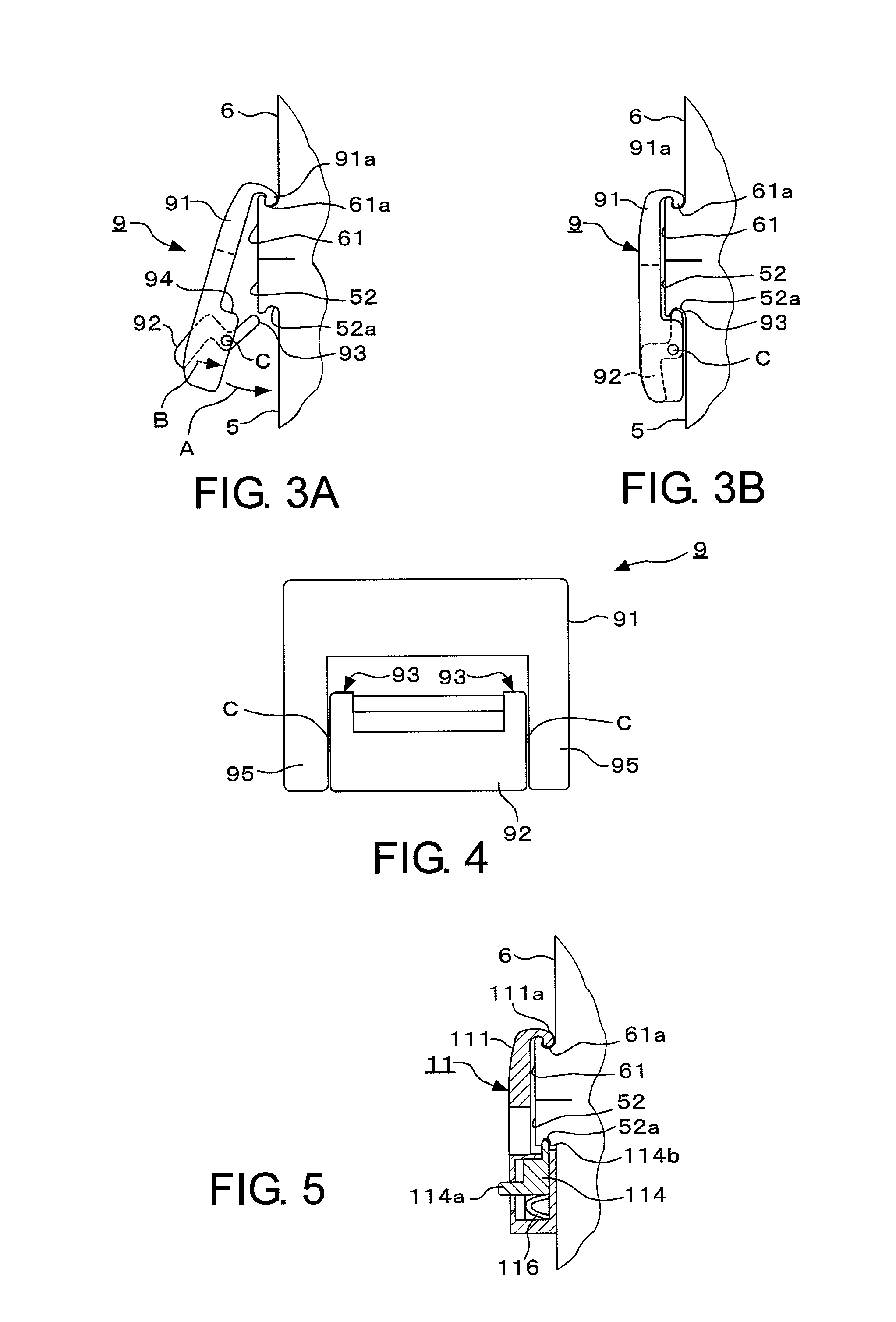
A mask blank container adapted to house a mask blank with a resist film. The container comprises a container body 5 for receiving the mask blank; a cap member 6 to be put on the container body; and a fixing member 9 adapted to fix the container body and the cap member to each other when the cap member is put on the container body. The container body and the cap member have fitting portions 51 and 61 made of a resin material and fitted to each other, respectively. The fixing member comprises a first member 91 having an engaging portion 91 a to be engaged with the fitting portion of the cap member, and a second member 92 having an engaging portion 93 to be engaged with the fitting portion of the container body. A distance between the engaging portions of the first and the second members is desired to be variable.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Multilayer PTC thermistor
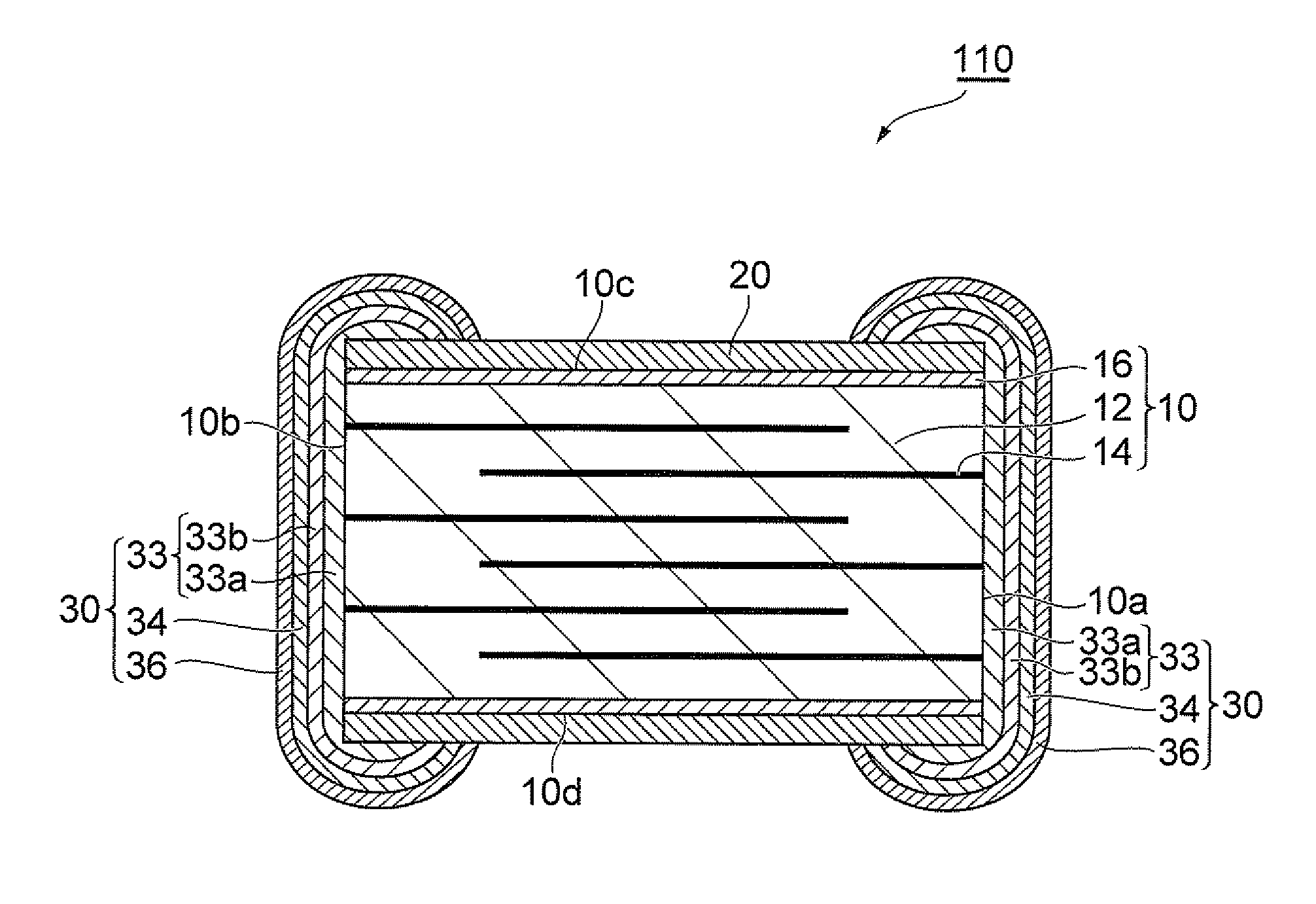
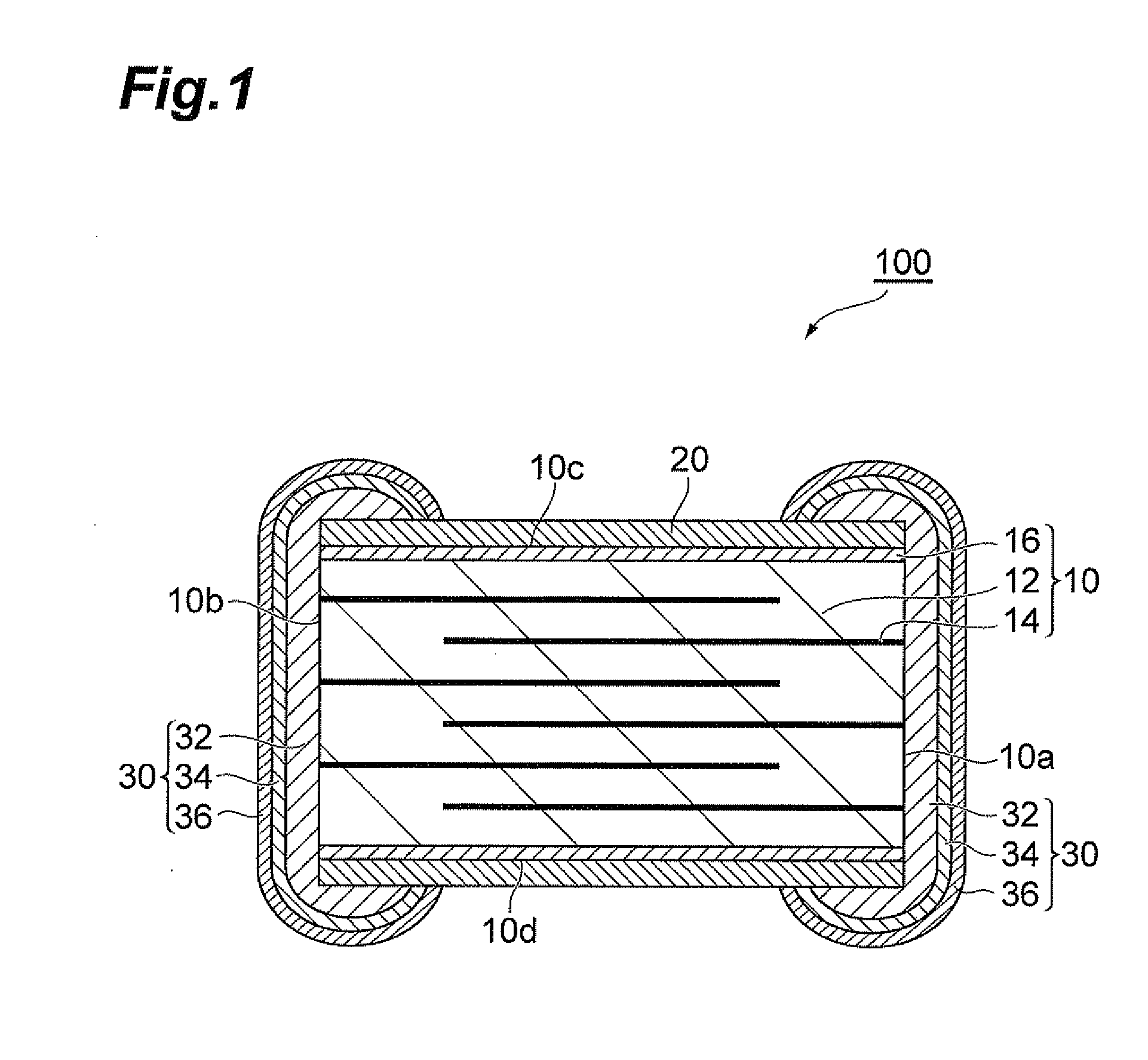
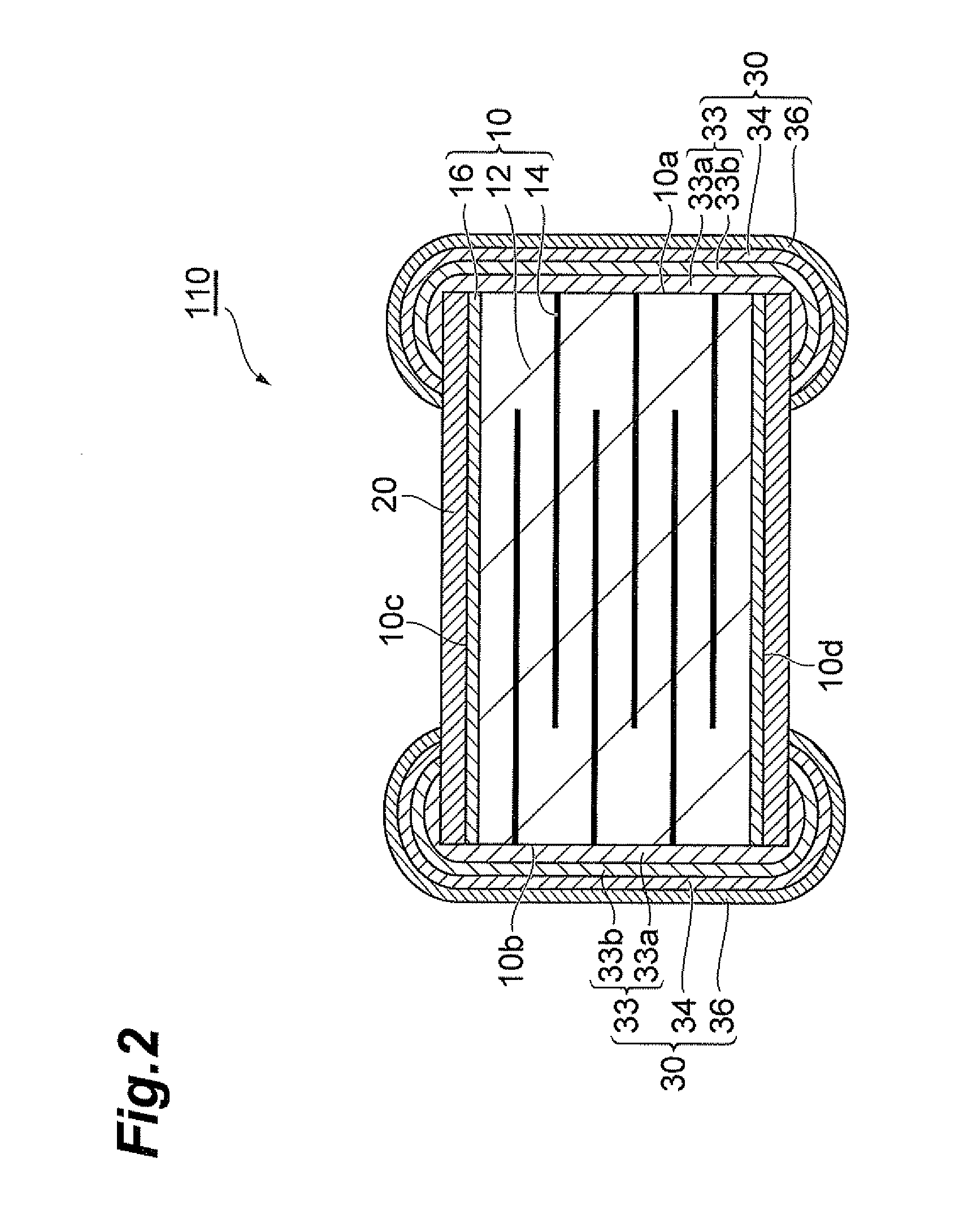
ActiveUS20120056709A1Altering PTC characteristicExcellent PTC characteristicTantalum compoundsCurrent responsive resistorsBismuthThermistor
A multilayer PTC thermistor 100 includes a ceramic body 10 having a plurality of ceramic layers 12 and internal electrodes 14 between adjacent ceramic layers 12, external electrodes 30 on the end faces 10a, 10b of the ceramic body 10, and a glass layer 20 on the surfaces 10c, 10d of the ceramic body 10, the glass layer 20 containing an oxide of at least one element selected from the group consisting of zinc and bismuth as the major component, wherein the alkali oxide content of the glass layer is no greater than 0.8 mass %.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method for use of hyaluronic acid in wound management
InactiveUS20030021834A1Minimize tissue damageReduce drynessBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWound healingSurgical site
A method for decreasing or shortening the length of time required to complete a surgical procedure by the application of hyaluronic acid to the surgical site, and for wound management by topical application of hyaluronic acid to a wound by syringe through a thin film dressing. The method of wound management results in accelerated wound healing time. The solution of hyaluronic acid may include an effective amount of a polysulfated glycosaminoglycan for stimulating macrophage activity at the surgical wound site.
Owner:PETITO GEORGE D
Pre-treatment to eliminate the defects formed during electrochemical plating
InactiveUS20070080067A1Reduce formationPromote wettingVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh ratePre treatment
Embodiments of the invention provide methods for reducing formation of void-type defects on the surface of a substrate during electrochemical plating. Embodiments of the invention provide methods to improve the wetting of a substrate surface prior to immersion and thereby minimize adhesion of bubbles to the substrate surface during immersion. A thin uniform metal oxide is formed on a metal layer on the substrate immediately prior to substrate immersion. In one aspect, exposing the substrate to an oxygen-containing gas, e.g. air, forms the metal oxide. The oxygen-containing gas may be flowed over the substrate or the substrate may be rotated at a high rate in the presence of an oxygen-containing gas. In another aspect, non-uniform metal oxides are first removed from the substrate in an anneal process and a thin uniform metal oxide is subsequently re-formed. An optimized substrate immersion method may also be used to further reduce void defects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor manufacturing device and its heating unit
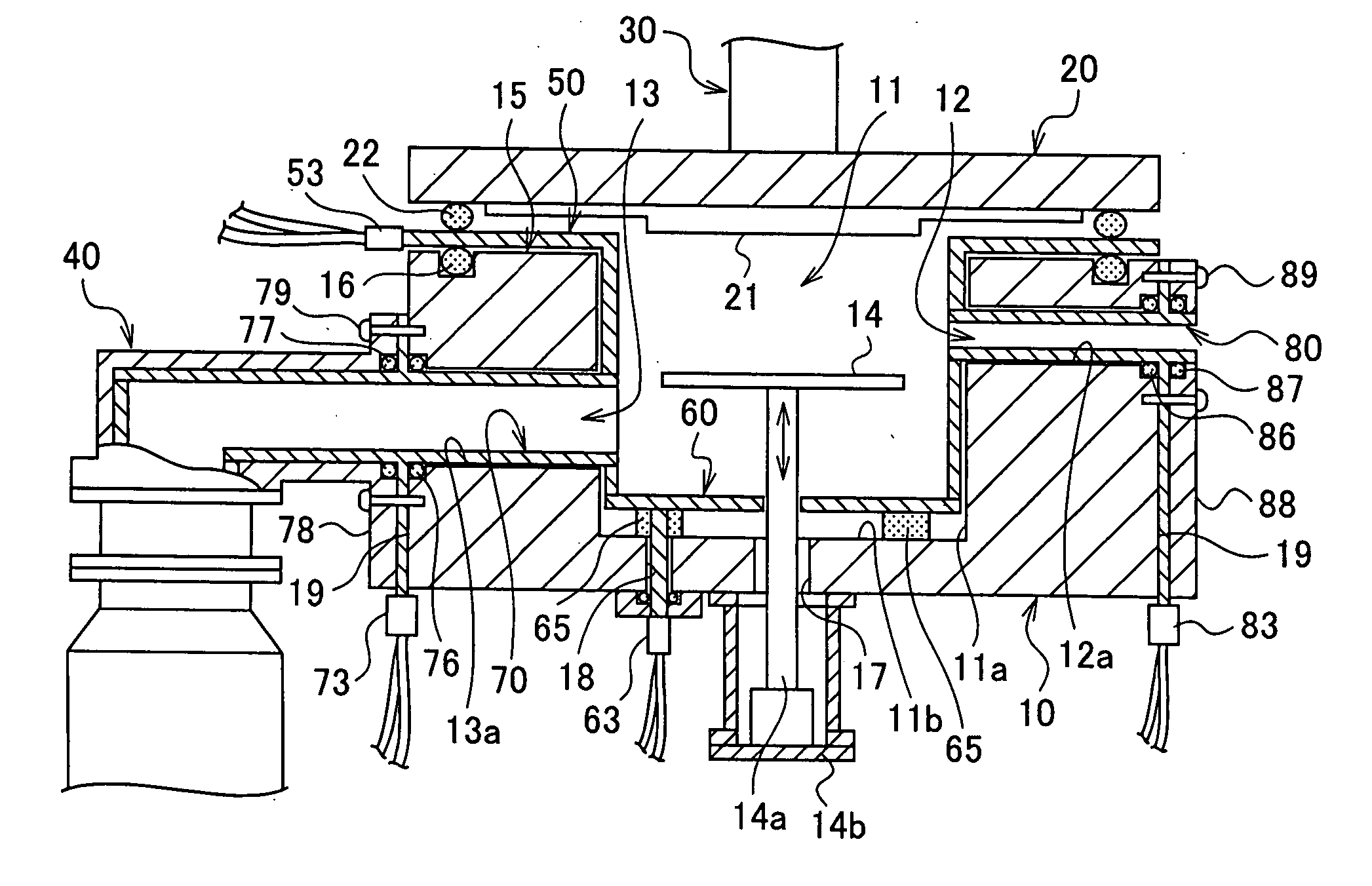
InactiveUS20070034159A1Easy to processIncrease resistancePipe heating/coolingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringHeating efficiency
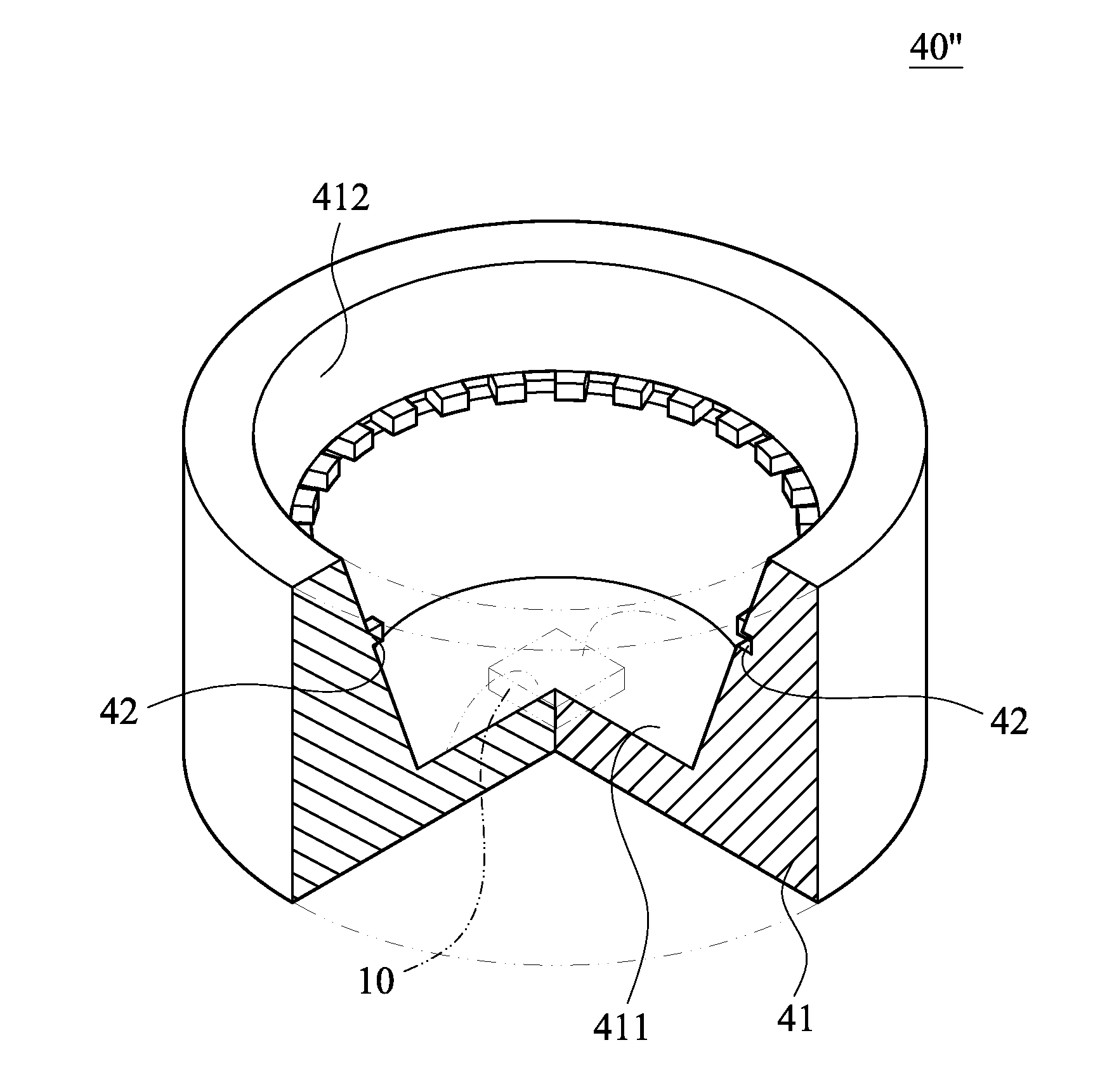
A semiconductor manufacturing device according to the present invention includes a processing chamber (11), a transferring passage (12) through which a wafer is put in and taken out of the processing chamber (11), an exhaust passage (13) and exhaust lines (40 and 40′) through which a processing gas inside the processing chamber (11) is exhausted, and so on, and in order to heat the inner wall faces (11a, 11b, 12a, 13a, 410a, and 420a) of the processing chamber (11), the transferring passage (12), the exhaust passage (13) and the exhaust pipes (410 and 420), further includes sheet-like heating units (50, 60, 70, 80, 170, and 270) that sandwich and cover a thin plate-shaped resistive heating element by a pair of metal plates and cover the inner wall faces from the inner side. Thereby, the heating efficiency on the wall faces to be exposed to the processing gas increases, adhesion of by-products can be prevented, and deterioration of the resistive heating element can also be prevented.
Owner:EAGLE INDS +1
Miniaturized contact spring
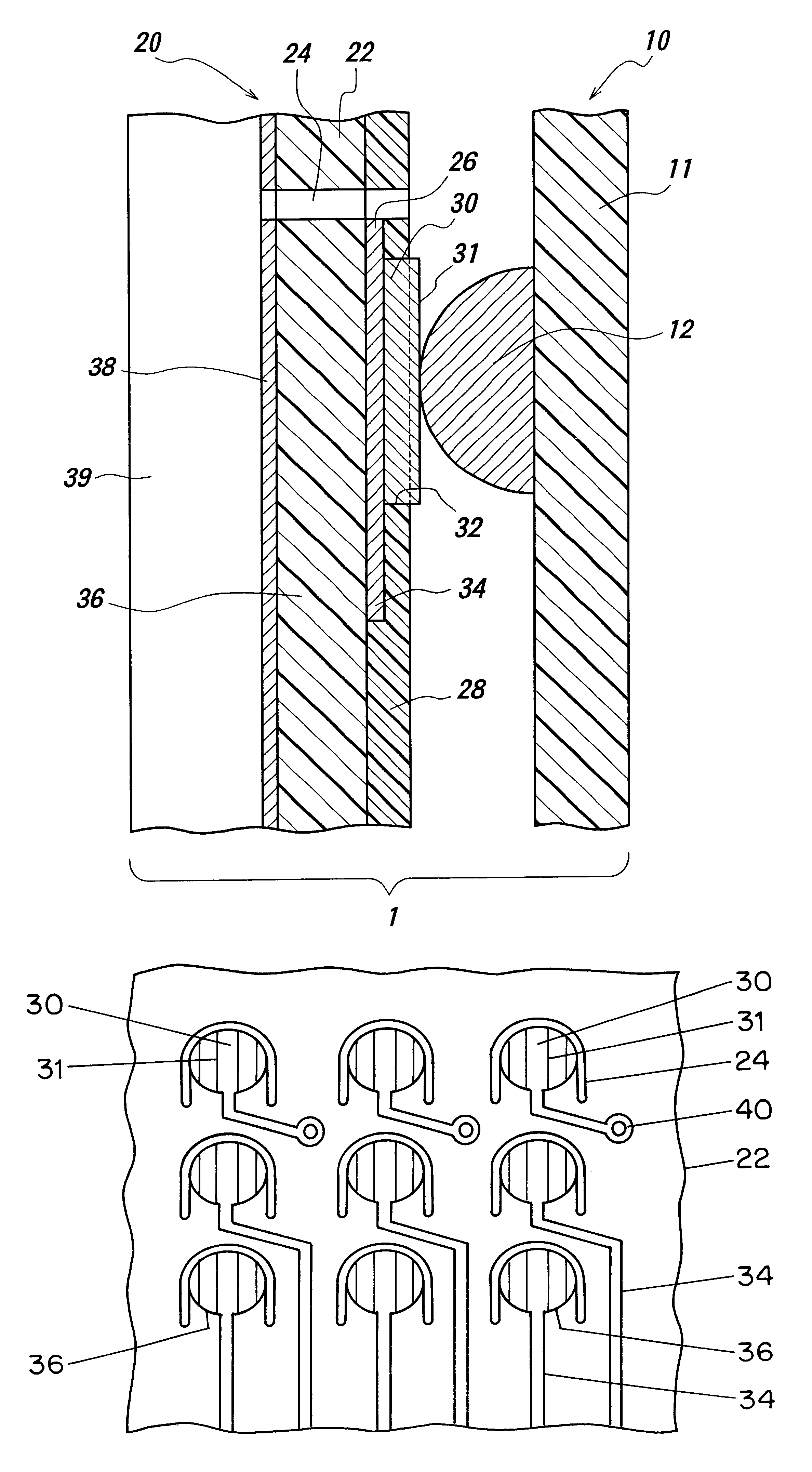
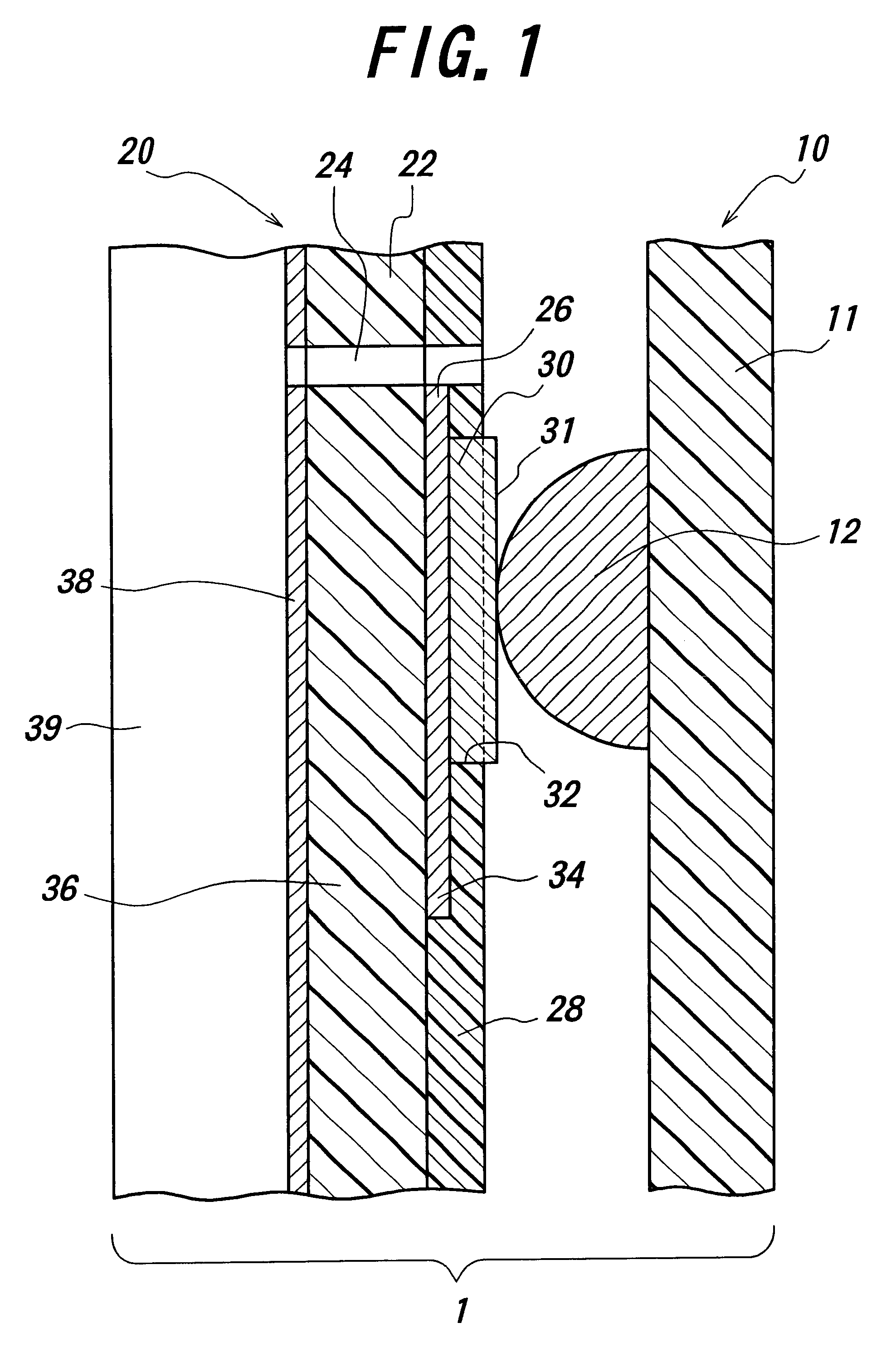
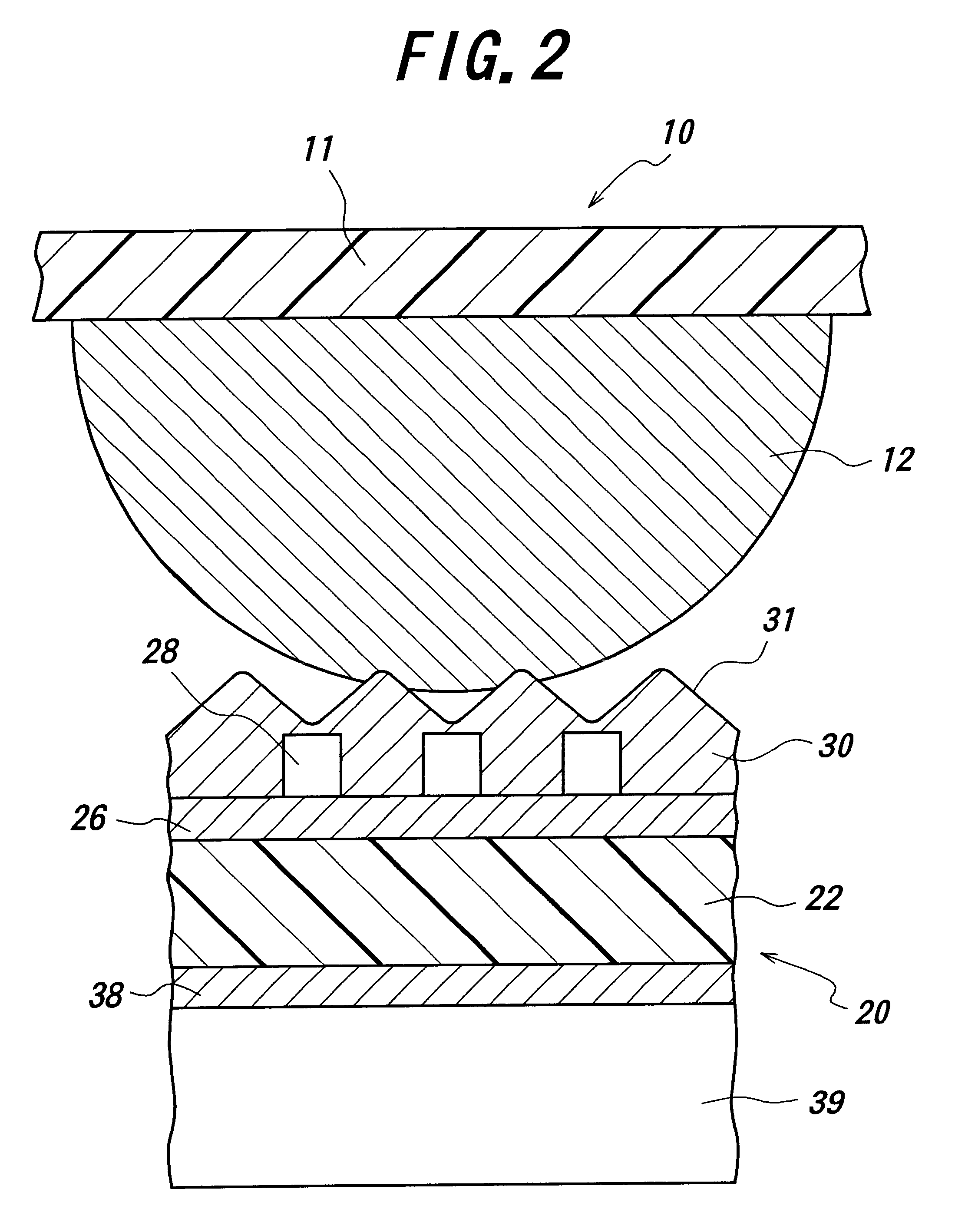
InactiveUS7126220B2Increase yield strength and fatigue strengthReliably fabricateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padLife time
This invention provides a solution to increase the yield strength and fatigue strength of miniaturized springs, which can be fabricated in arrays with ultra-small pitches. It also discloses a solution to minimize adhesion of the contact pad materials to the spring tips upon repeated contacts without affecting the reliability of the miniaturized springs. In addition, the invention also presents a method to fabricate the springs that allow passage of relatively higher current without significantly degrading their lifetime.
Owner:ADVANTEST SINGAPORE PTE LTD
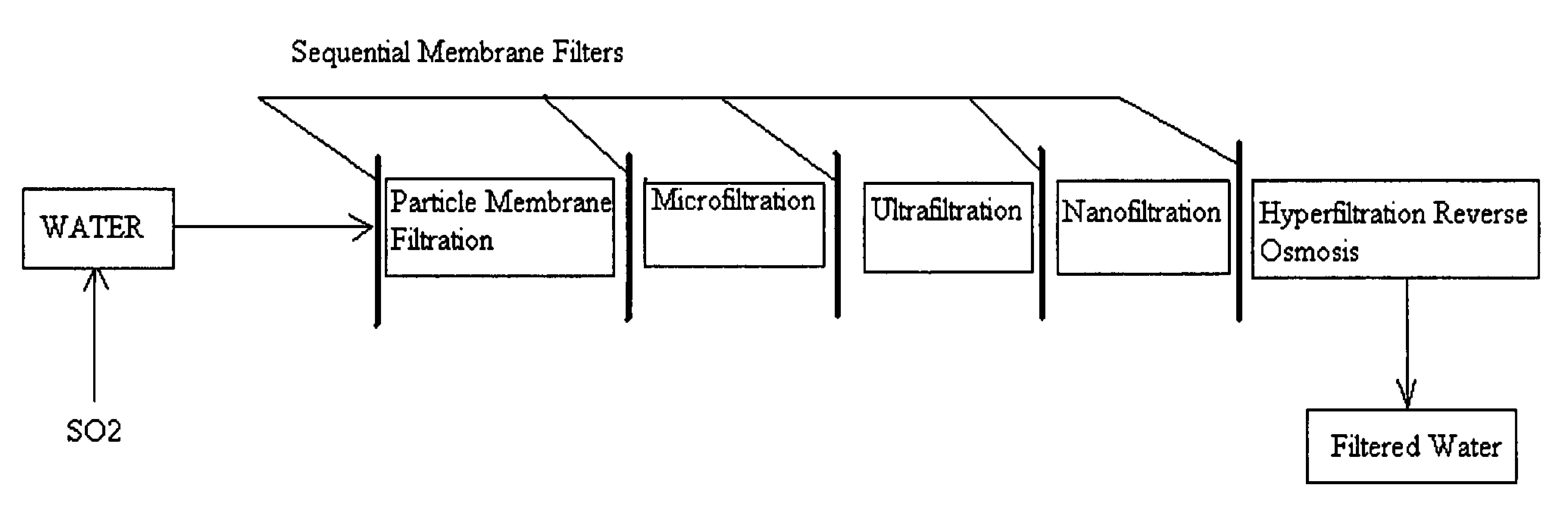
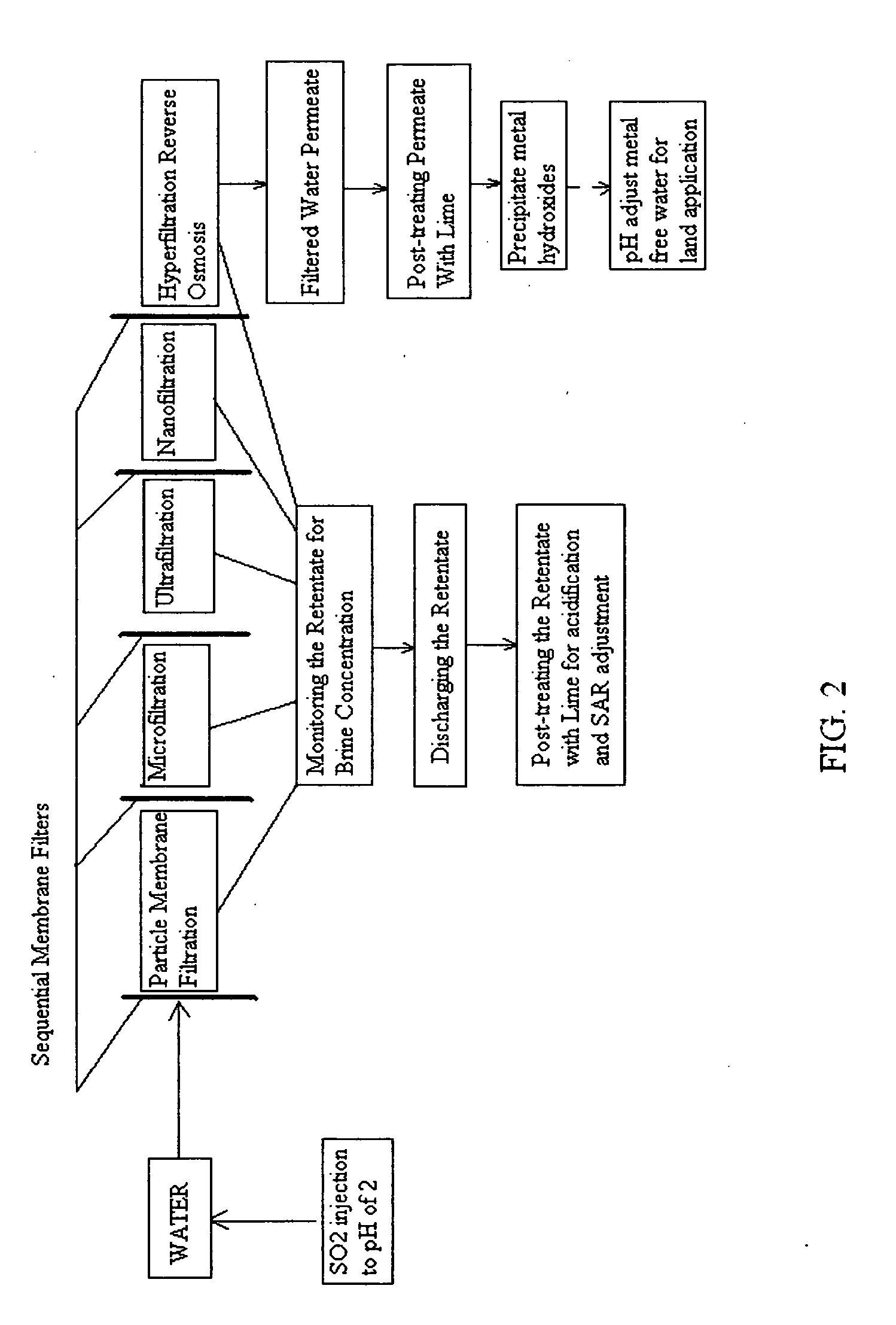
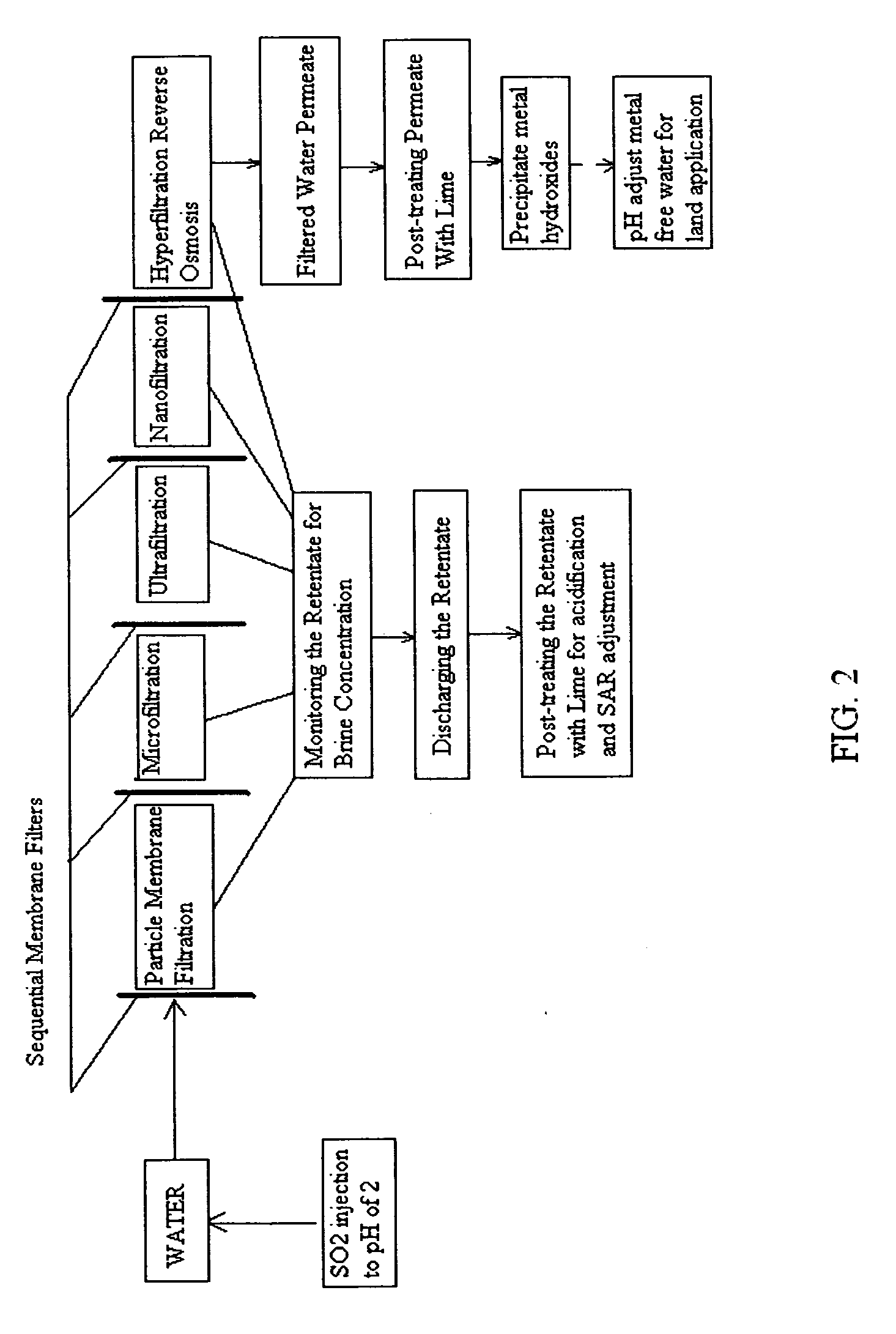
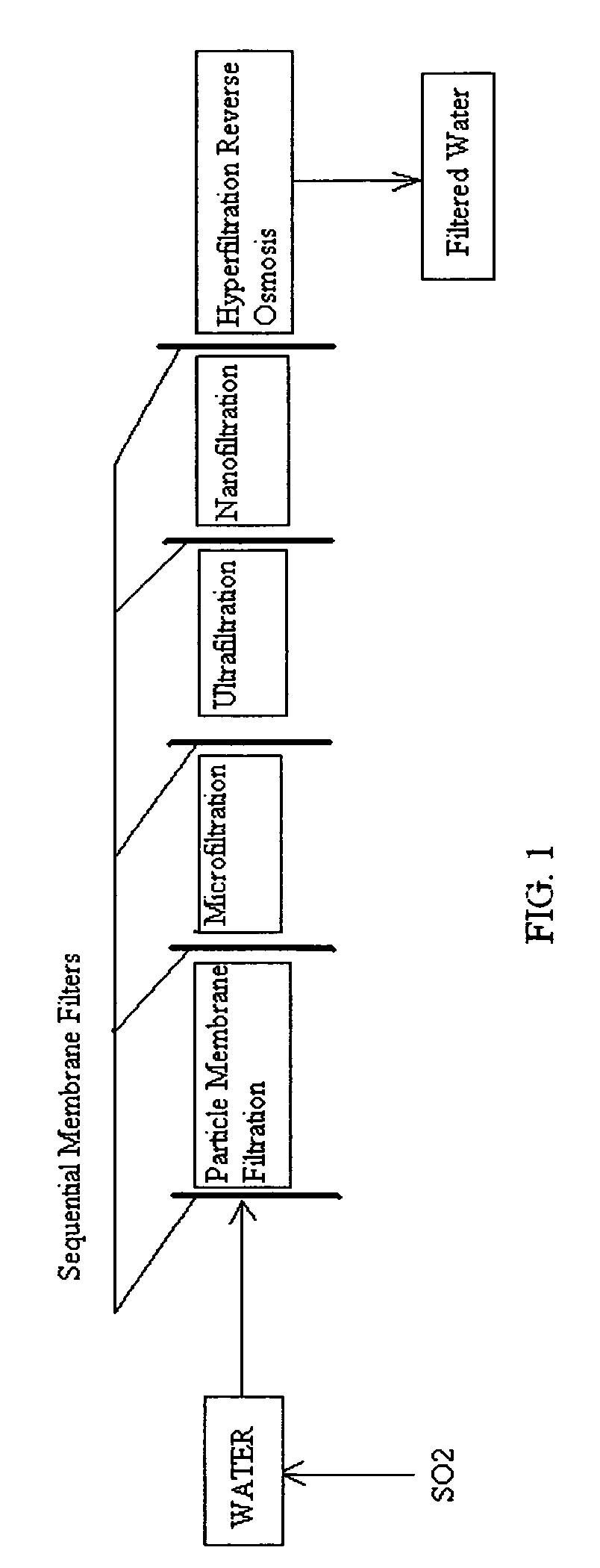
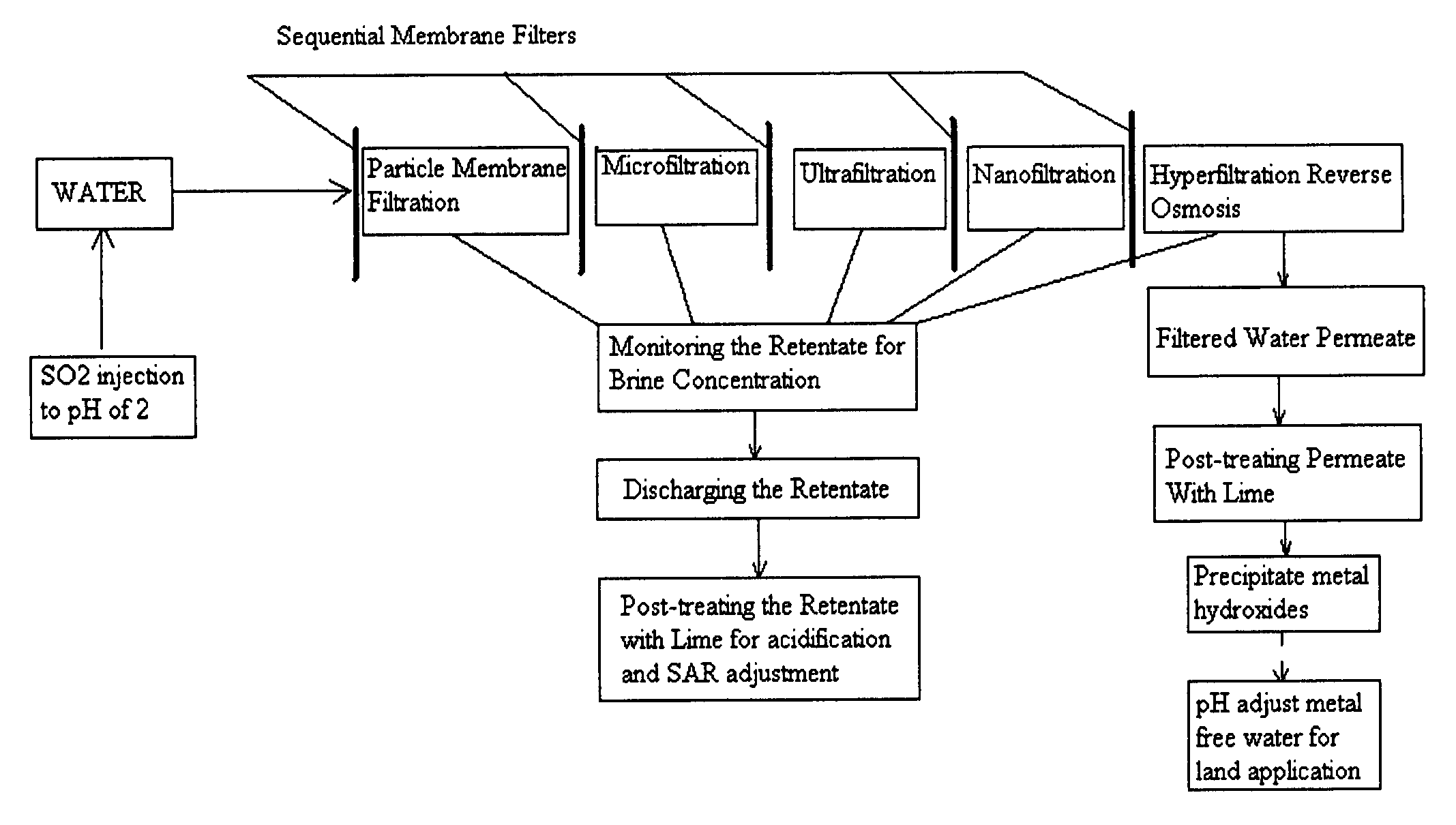
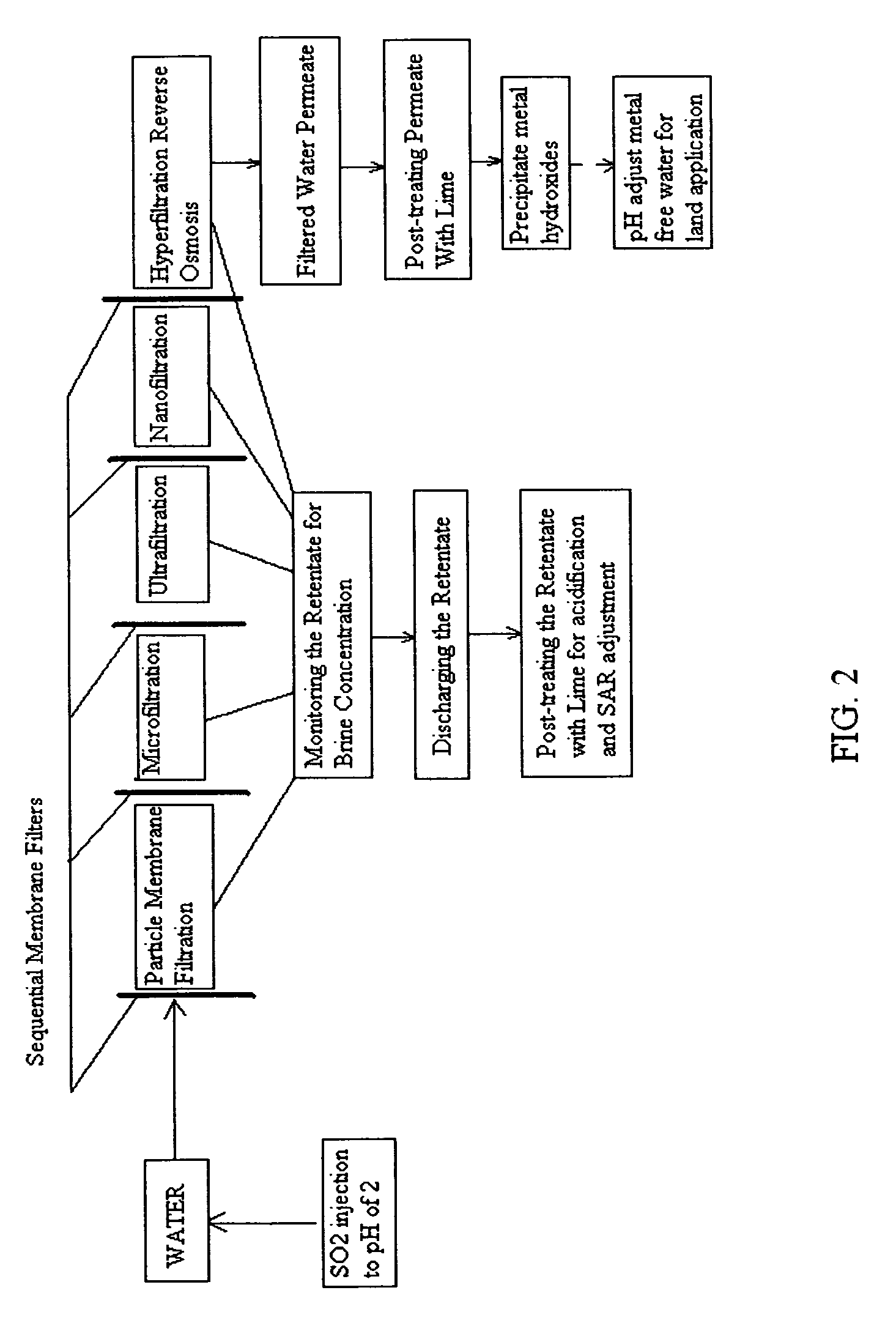
Pre-treatment reverse osmosis water recovery method for brine retentate metals removal
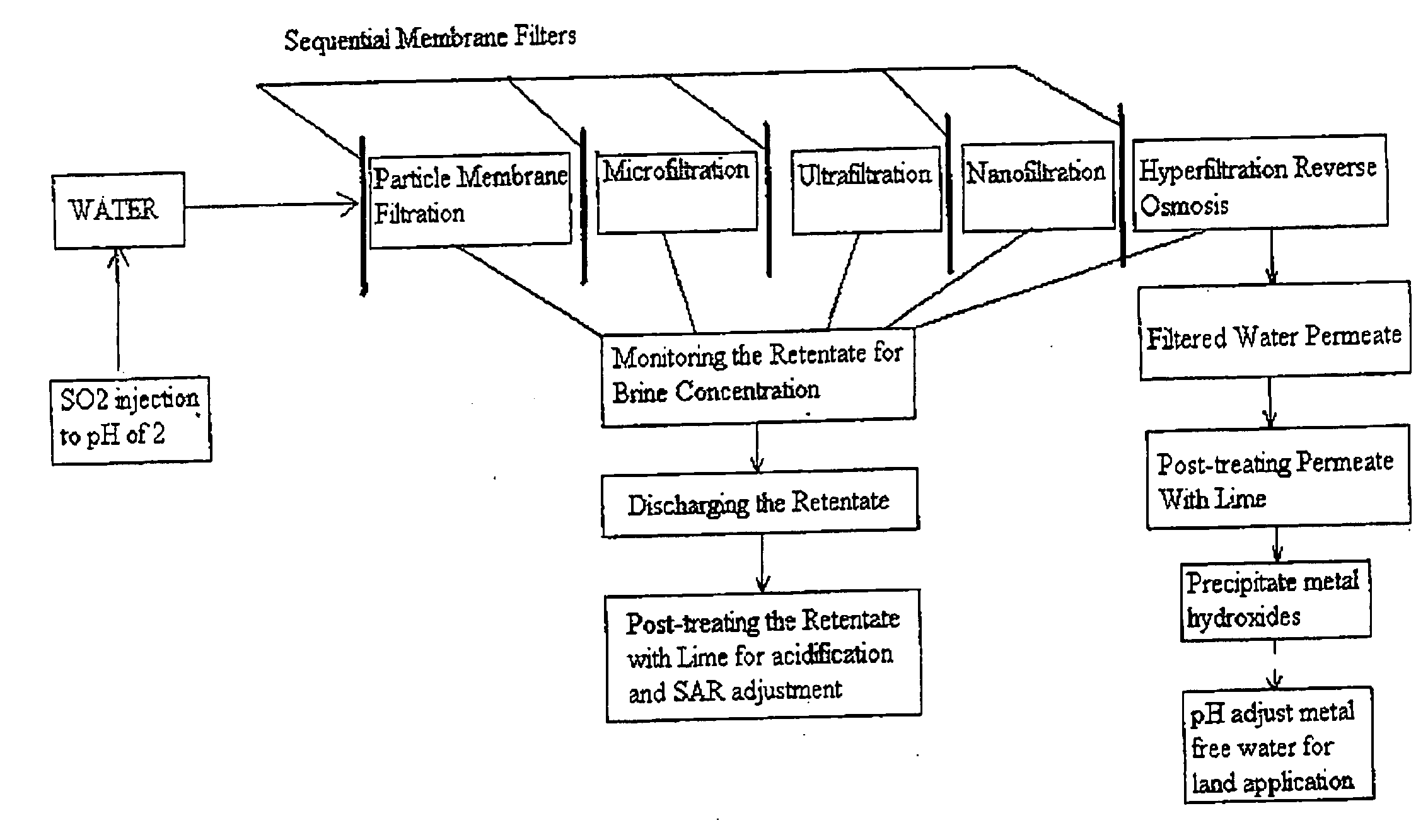
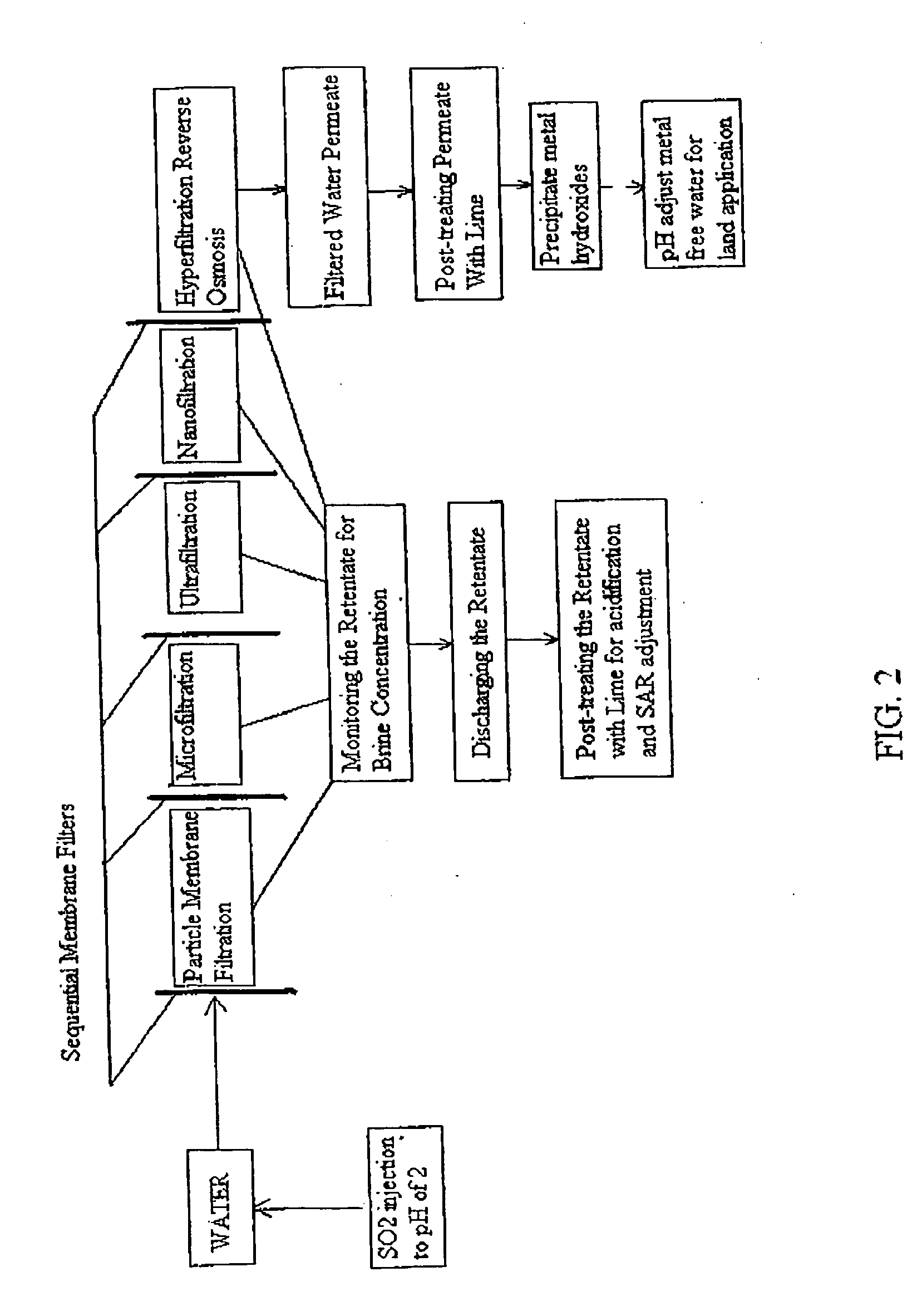
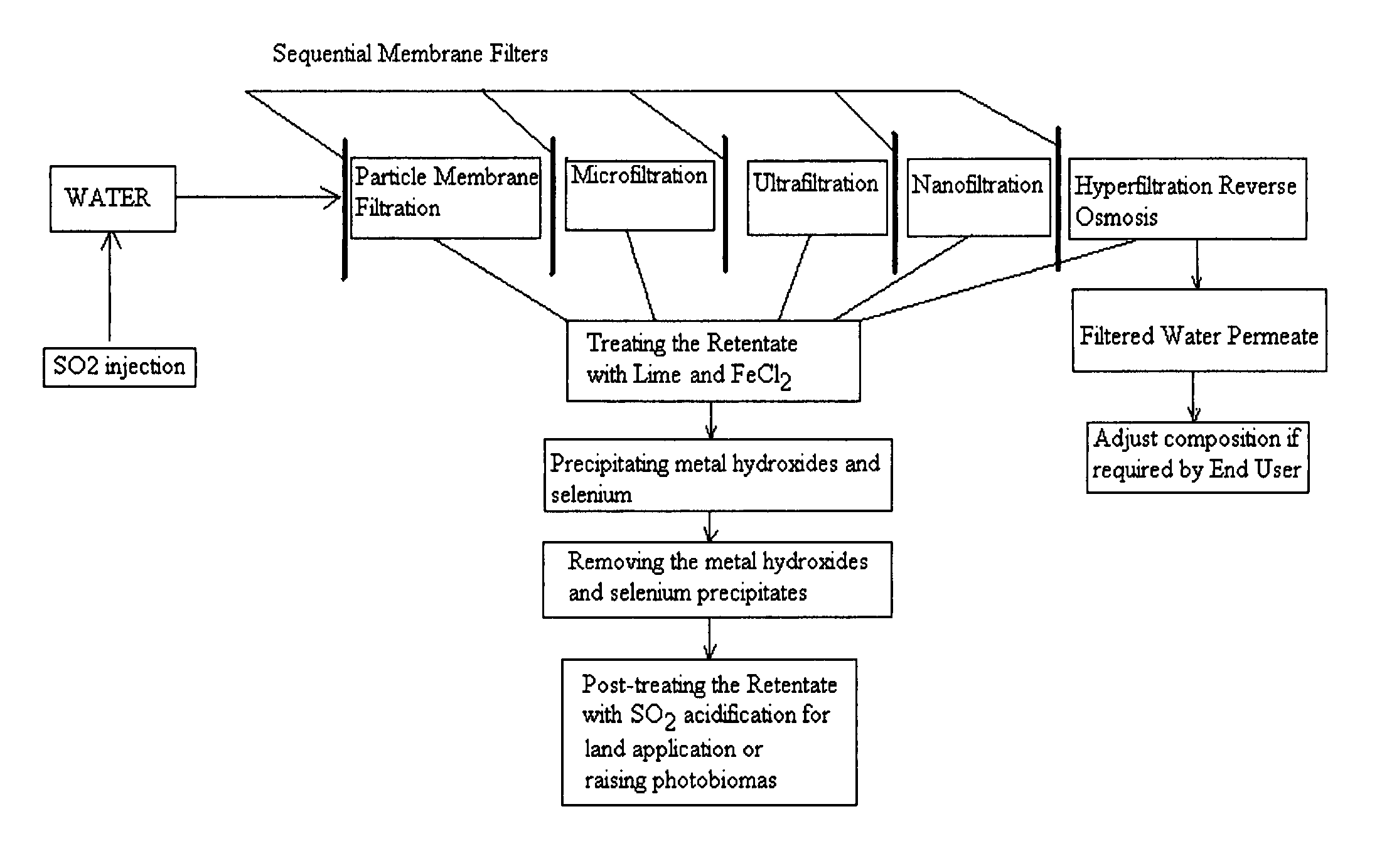
ActiveUS20100193436A1Minimize adhesionPrevent bacterial growthMembranesOther chemical processesRecovery methodPretreatment method
A pre-treatment method for cleaning and maintaining reverse osmosis membrane filters by injecting sulfurous acid into waters with suspended solids in a liquid fraction to be filtered to form sulfurous acid (H2SO3) to acid leach heavy metals into the liquid fraction, reduce alkalinity and mineral scaling, add sufficient SO2 as a biocide to attack bacteria and other micro organisms to prevent membrane fouling, reduce iron to prevent iron deposit build-up, scavenge and remove dissolved oxygen prior to filtration to prevent membrane oxidation, and then sequentially filtering the acidified water through membrane filters to create a metal free permeate and a brine retentate, which can be pH adjusted to remove the heavy metals as metal hydroxide precipitates.
Owner:EARTH RENAISSANCE TECH
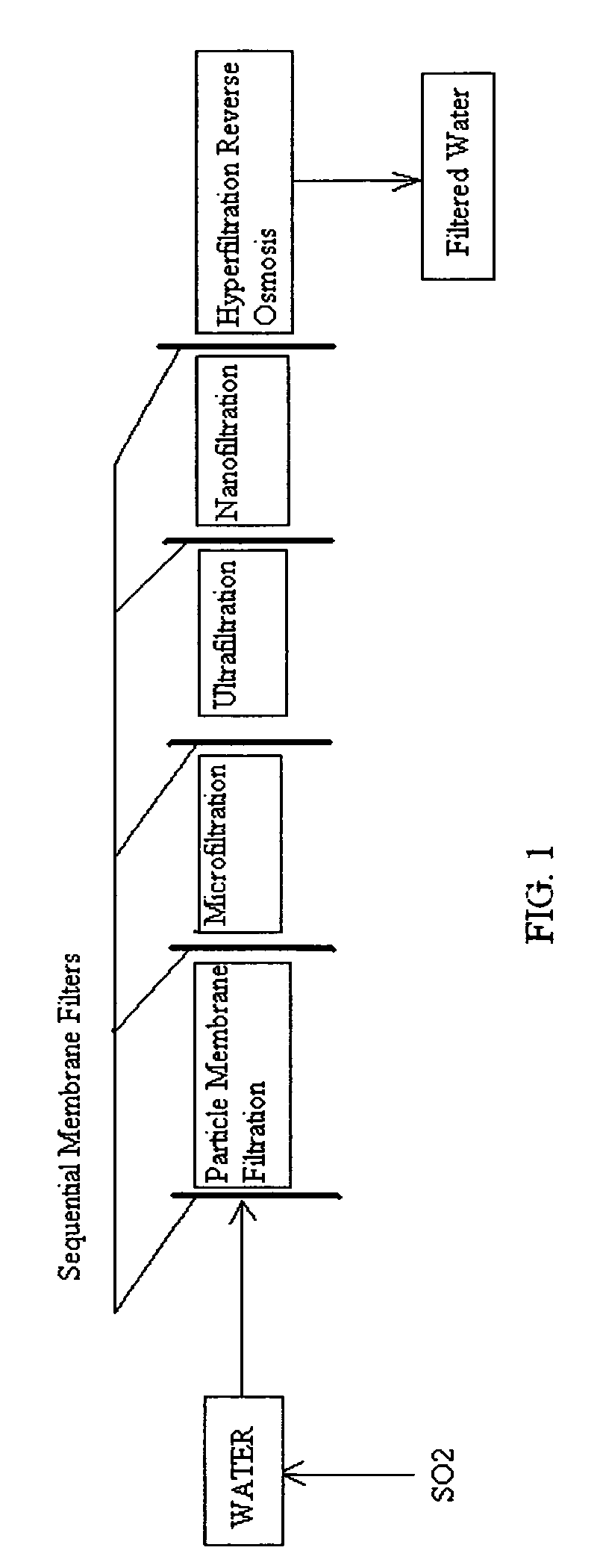
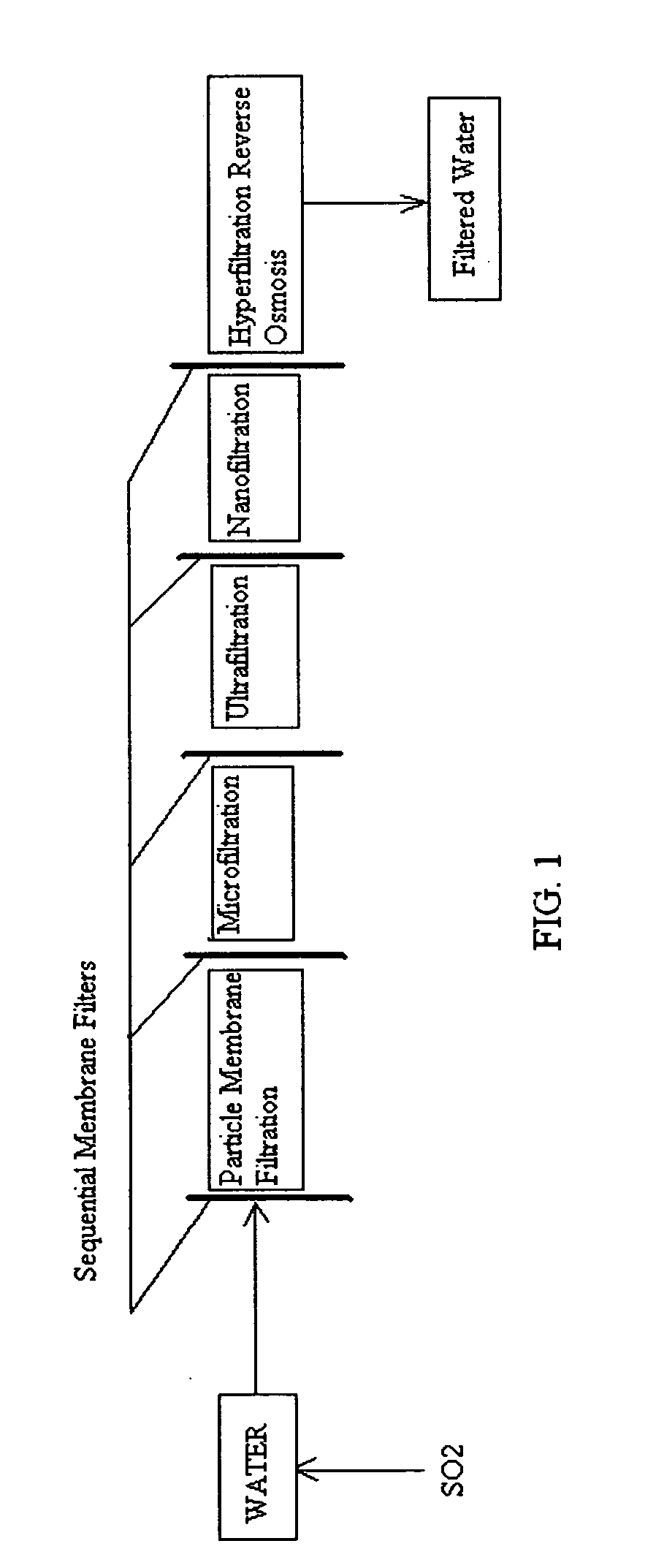
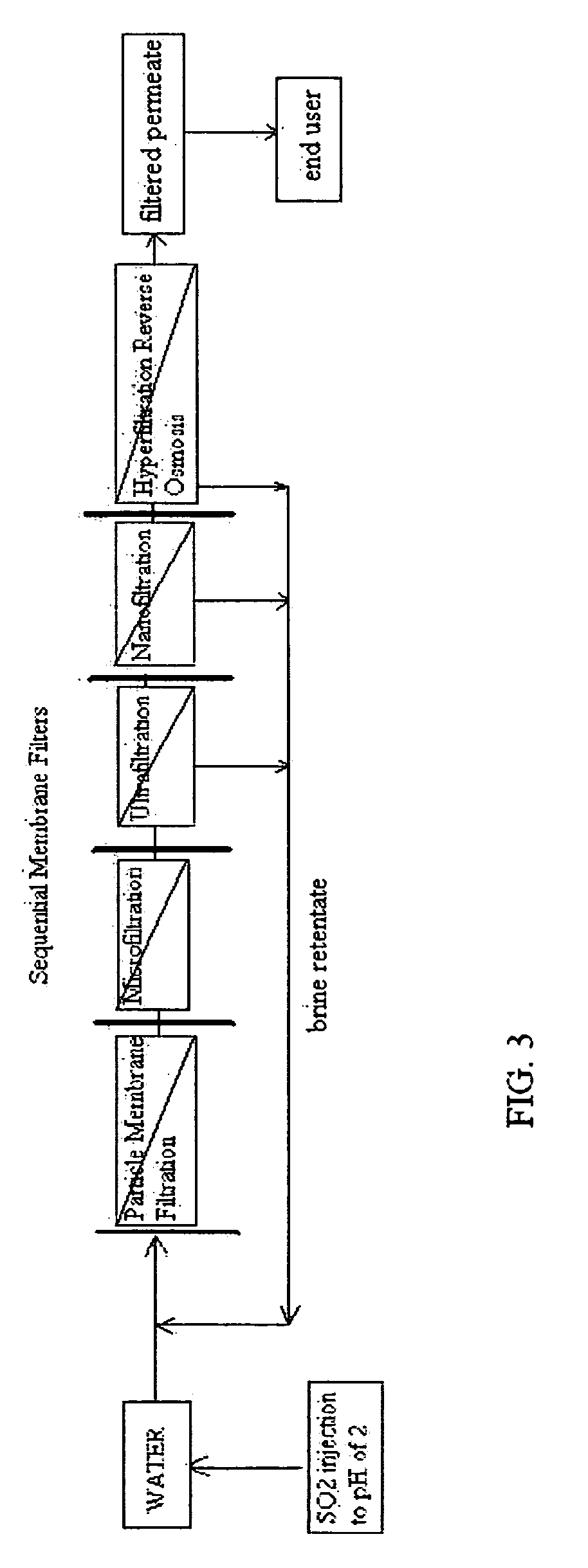
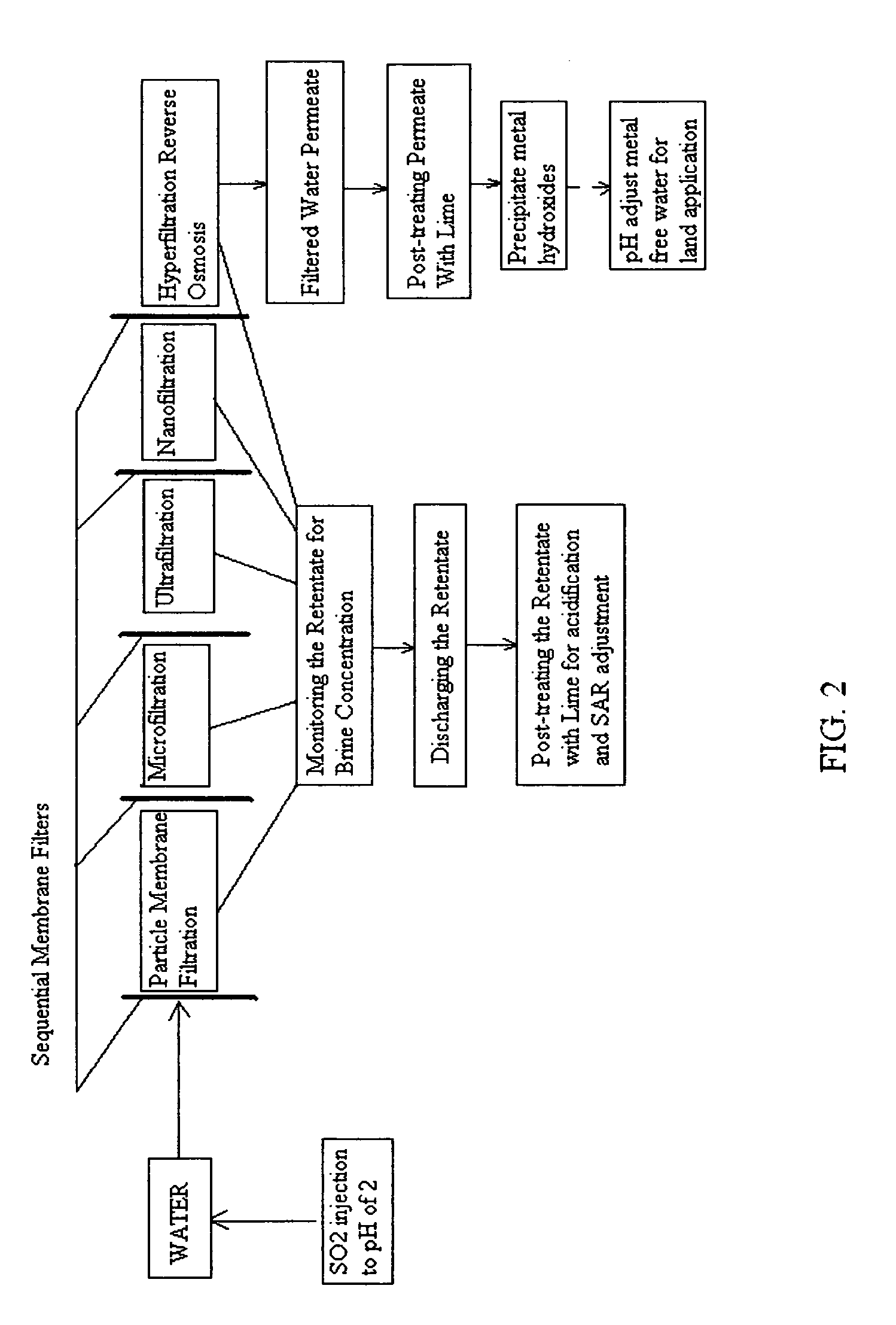
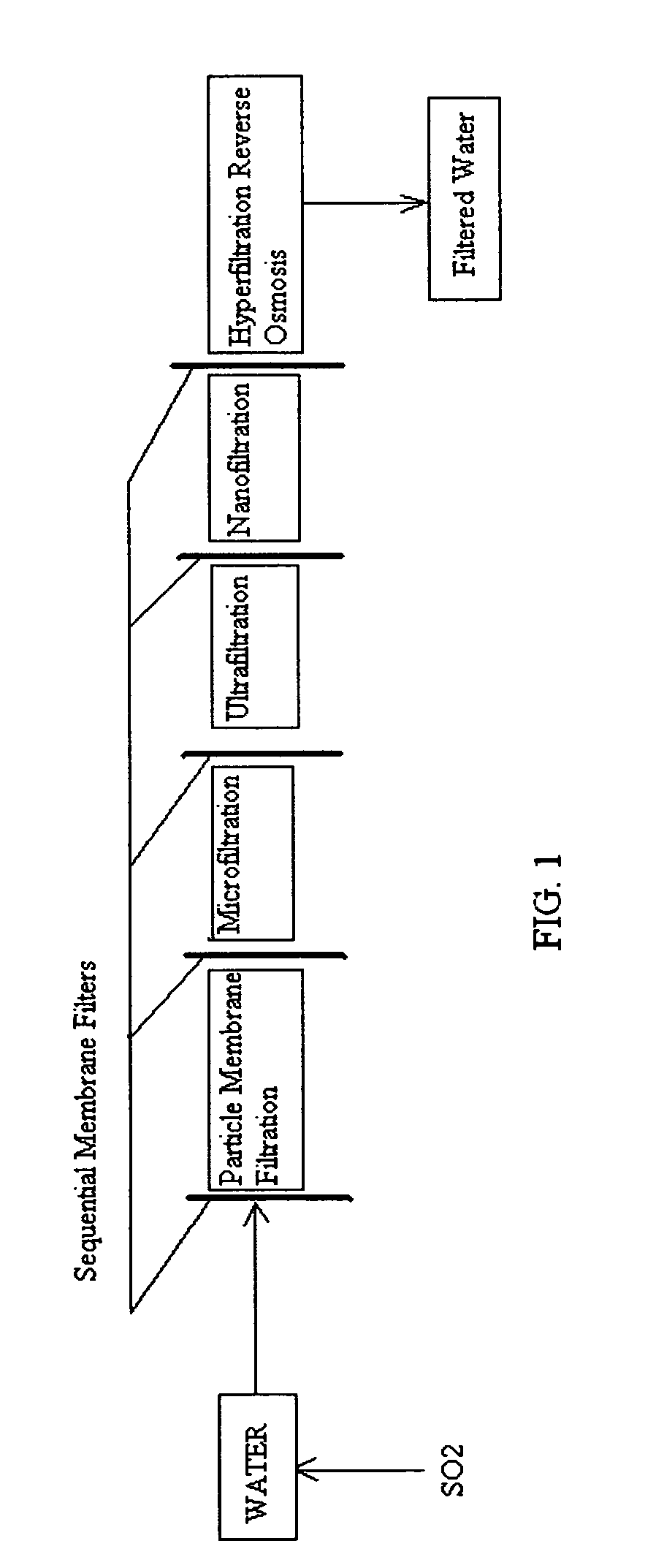
Reverse osmosis water recover method
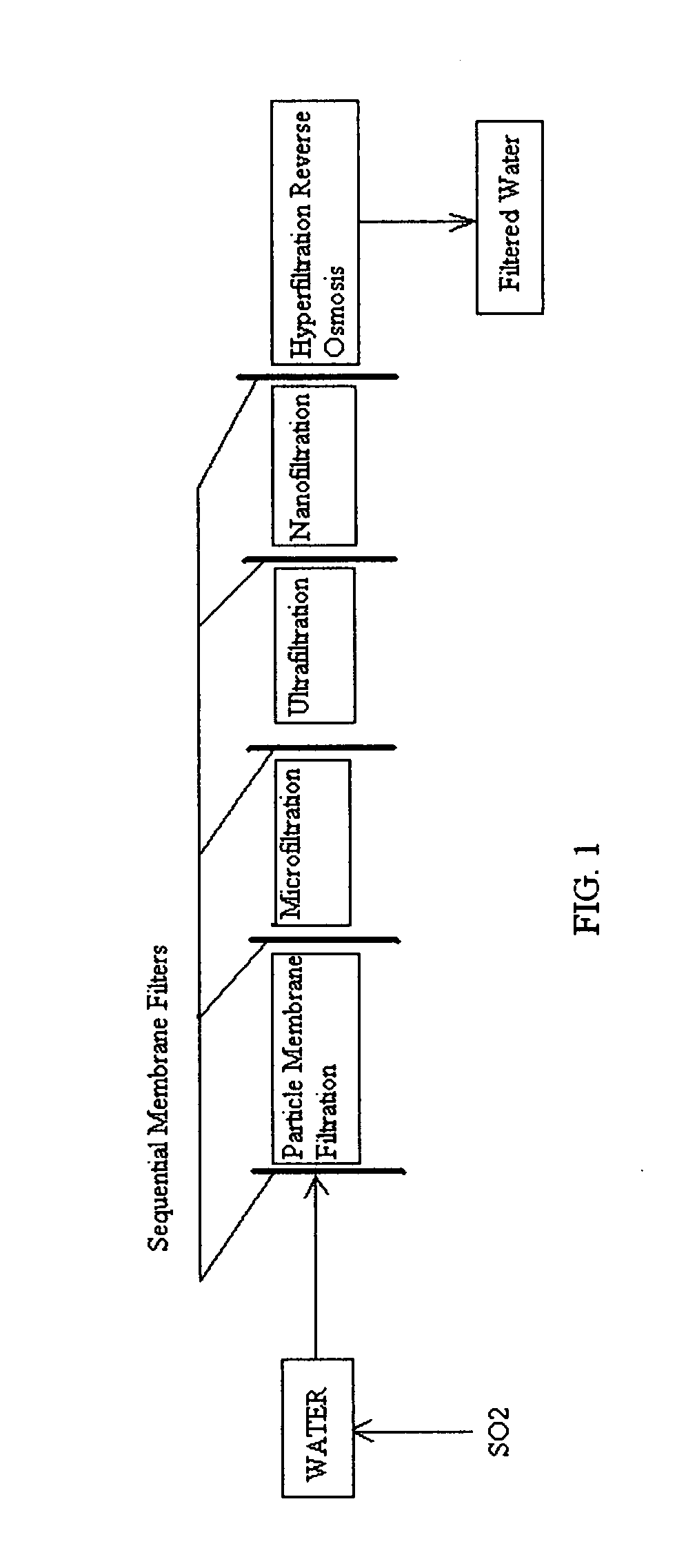
ActiveUS20100018921A1Avoid applicationPrevent water infiltrationMembranesSedimentation separationMicroorganismFiltration
A method for cleaning and maintaining reverse osmosis membrane filters by injecting sulfurous acid into water to form sulfurous acid (H2SO3), and then sequentially filtering the acidified water through membrane filters to reduce alkalinity and mineral scaling, add sufficient SO2 as a biocide to attack bacteria and other micro organisms to prevent membrane fouling, reduce iron to prevent iron deposit build-up, scavenge and remove dissolved oxygen prior to filtration to prevent membrane oxidation, and prevent concentrated salts within the retentate from precipitating out of solution during transport for land application.
Owner:EARTH RENAISSSANCE TECH
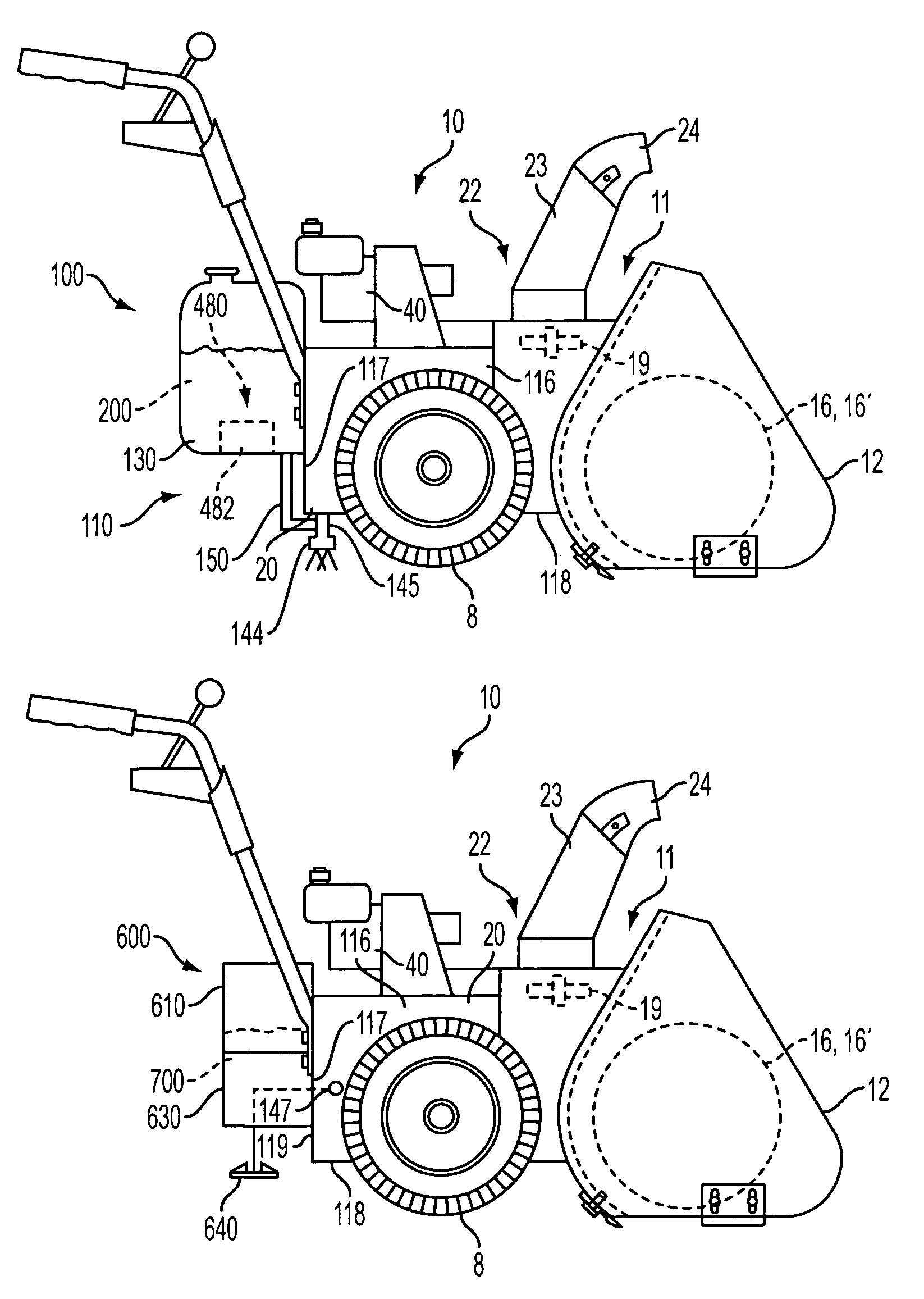
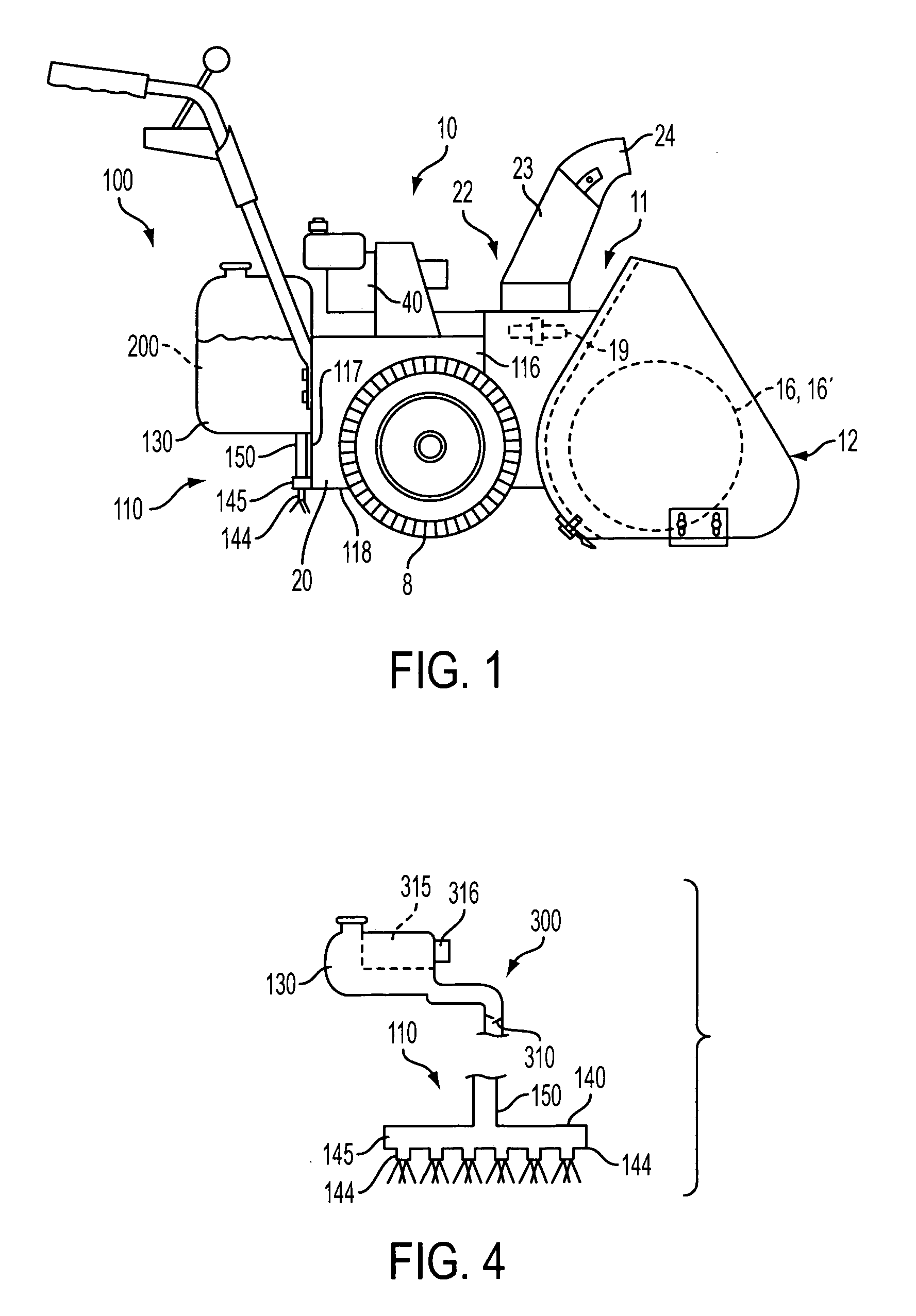
Snow removal machine with system for applying a surface treatment material
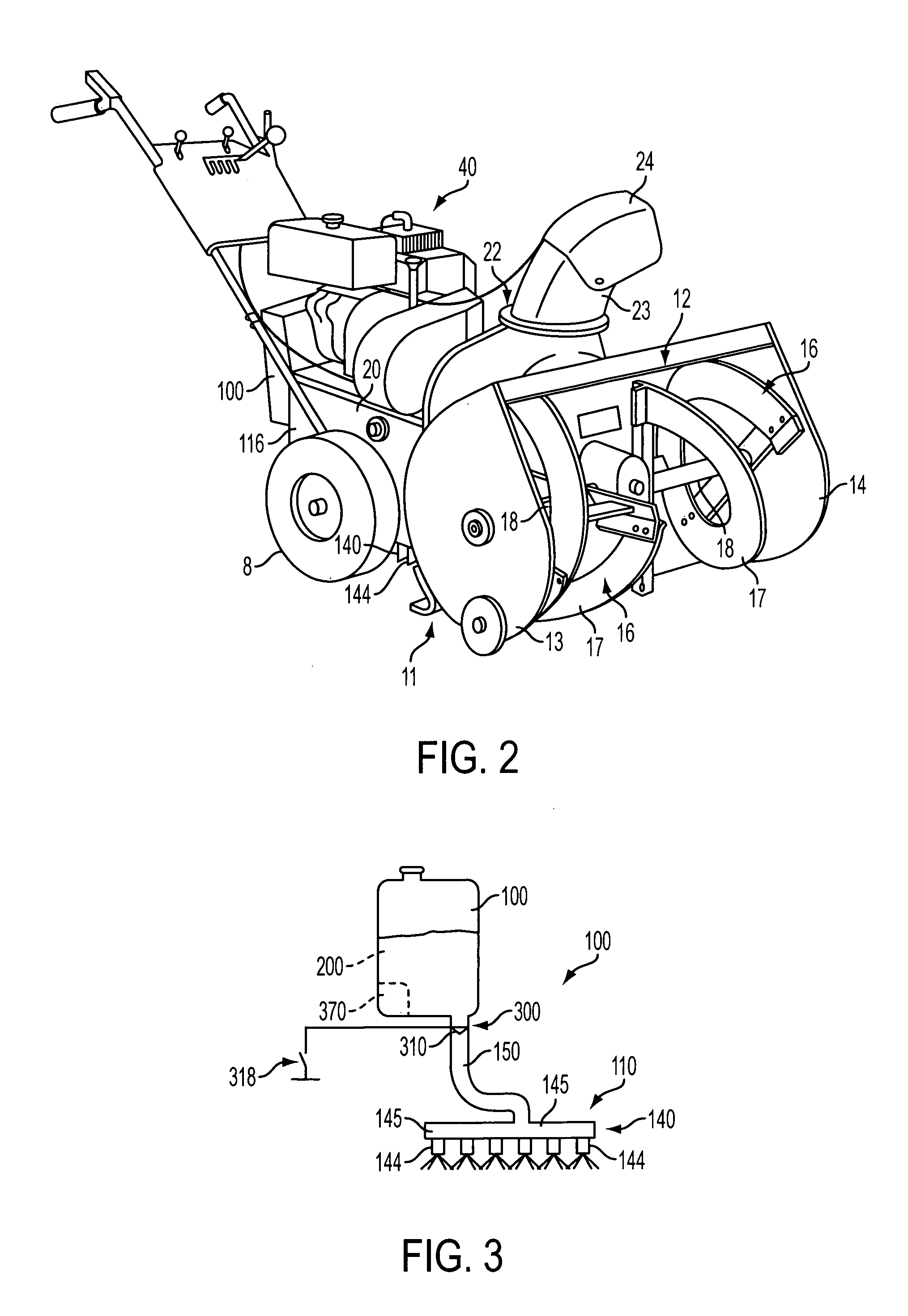
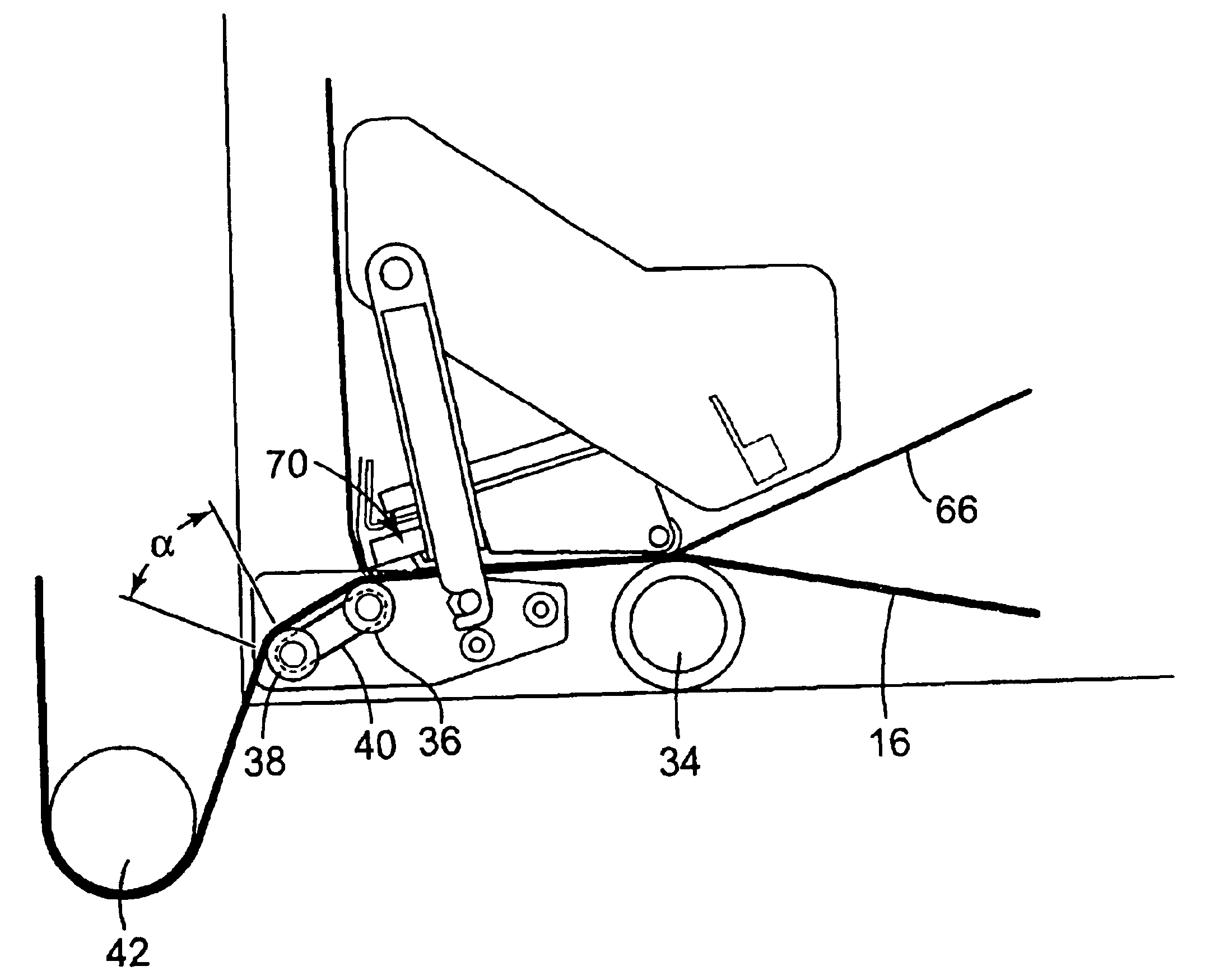
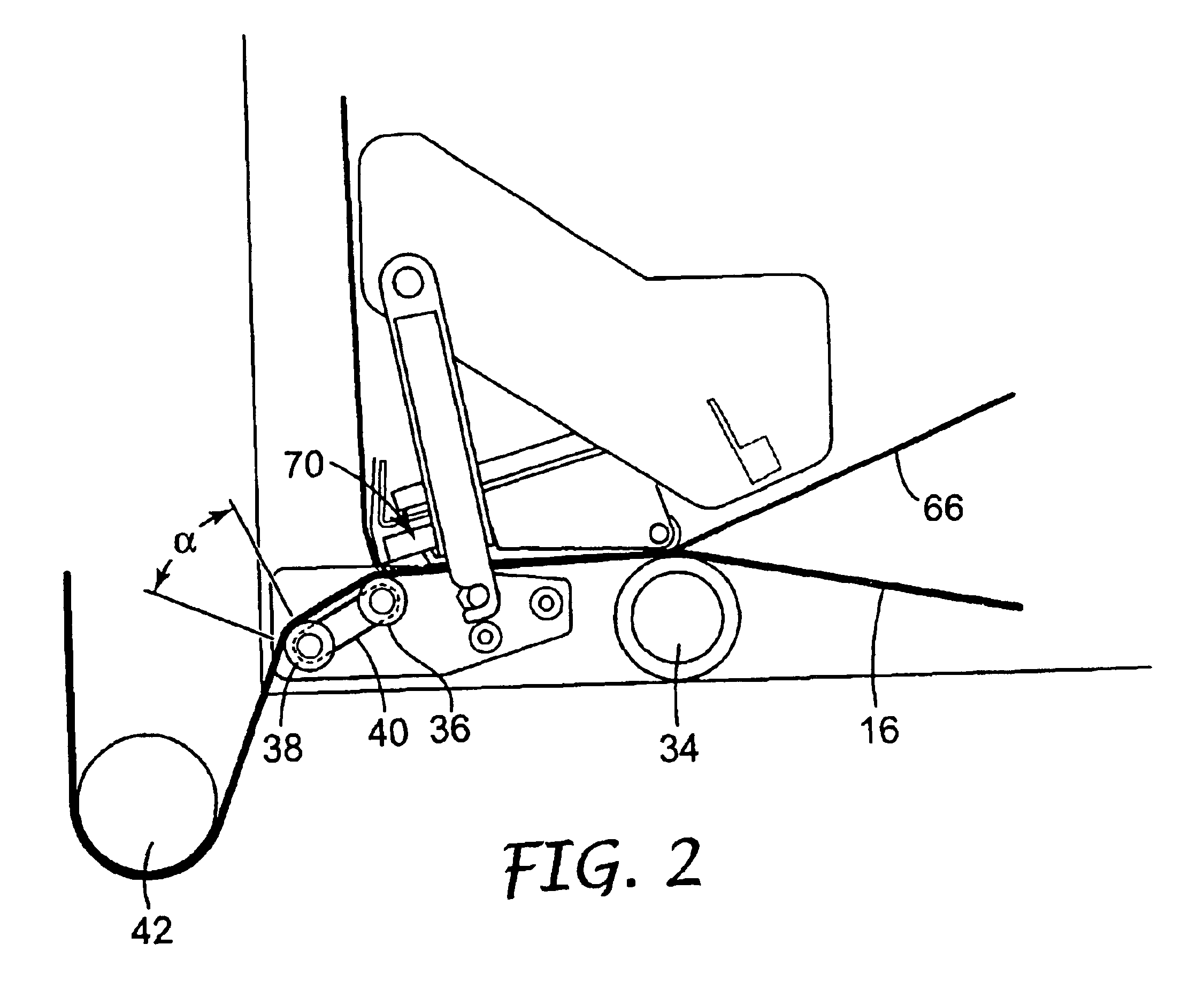
InactiveUS7137214B2Minimize adhesionLow costSki bindingsFertiliser distributersSnow removalEngineering
A snow removal machine including a housing with a forward opening through which snow enters the snow removal machine. At least one rotatable member is positioned and rotatably secured within the housing for engaging and eliminating the snow from within said housing. The snow removal machine also includes a surface treatment application system with a treatment material dispensing system connected to the housing for dispensing a liquid or solid deicer and / or anti-icing treatment material over an area from which snow has been removed.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Charging device and image forming apparatus
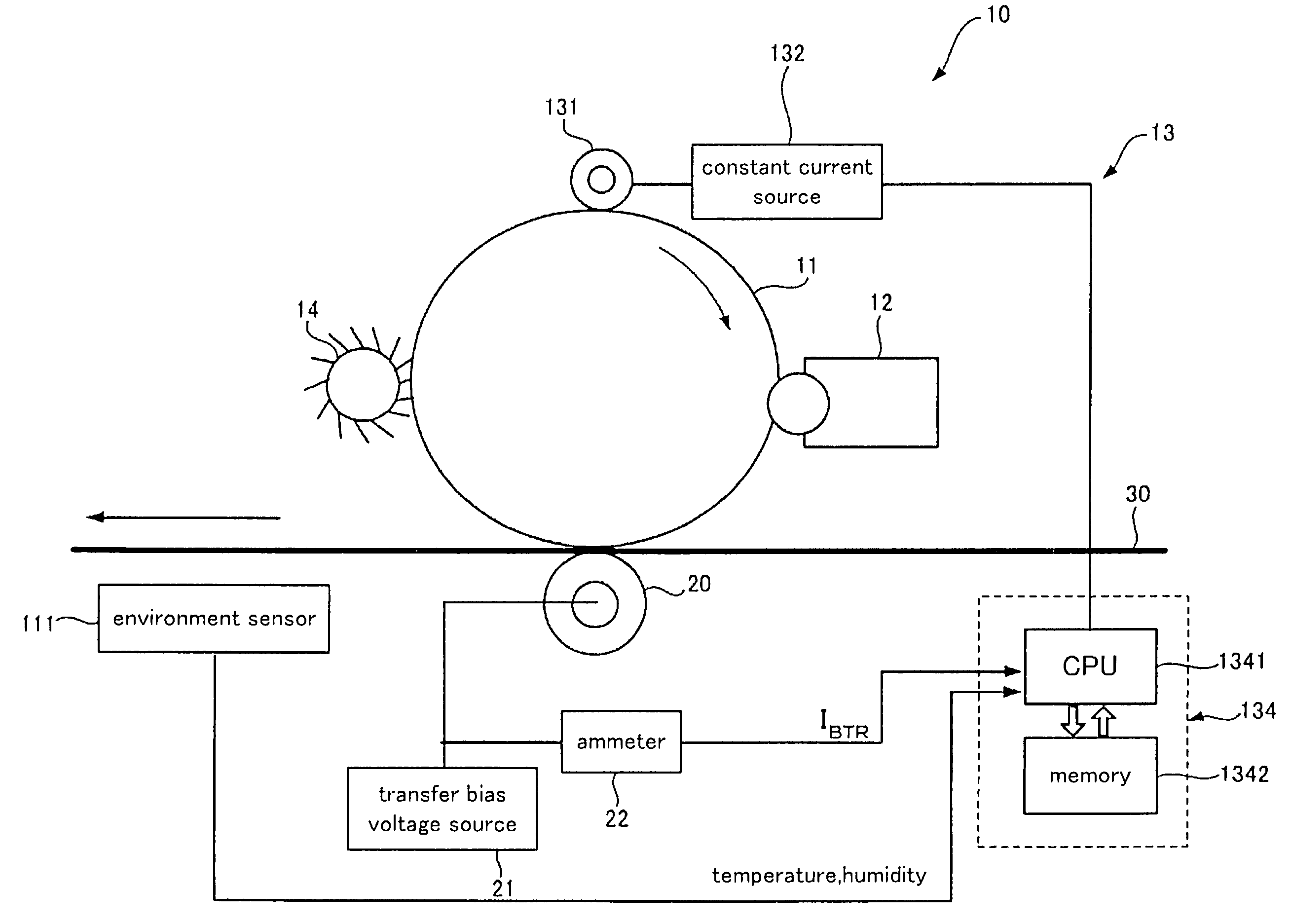
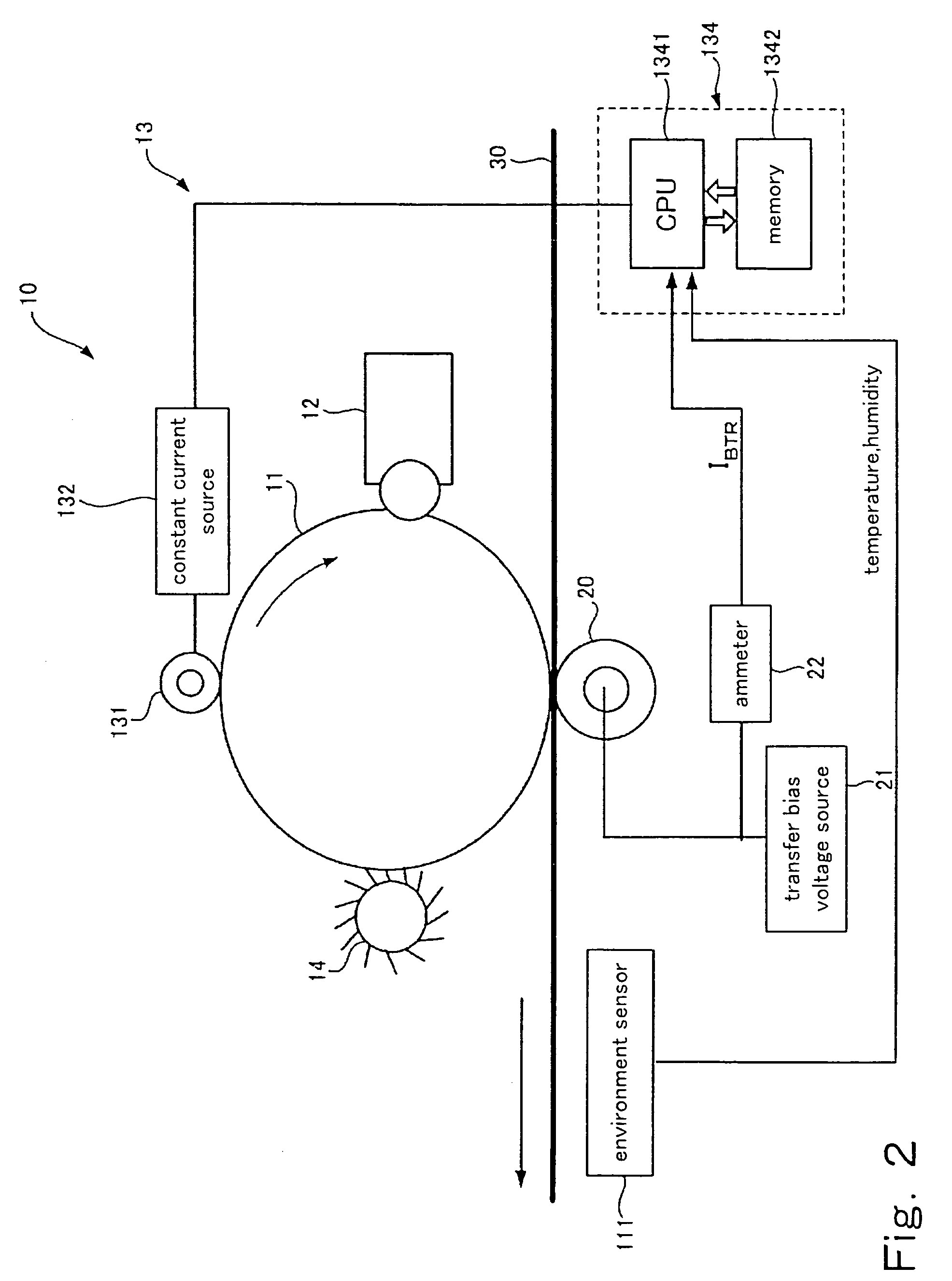
InactiveUS7024125B2Suppress excessive electric dischargeUniform chargeElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeCurrent meterImage formation
The present invention is a charging device that electrically charges an object that is charged while being moved in a predetermined direction and an image forming device having such a charging device. The charging device has: a charging member that electrically charges the charged object; a power source that supplies electric power to the charging member in order to electrically charge the charged object; a contact member arranged downstream relative to the charging member as viewed in the moving direction of the charged object and adapted to contact the charged object directly or by way of a predetermined intermediary medium; an ammeter that gauges an electric current caused to flow through the contact member due to an electric charge on the charged object electrically charged by the charging member; and a power source control section that controls the power source based on the electric current gauged by the ammeter.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Image forming apparatus
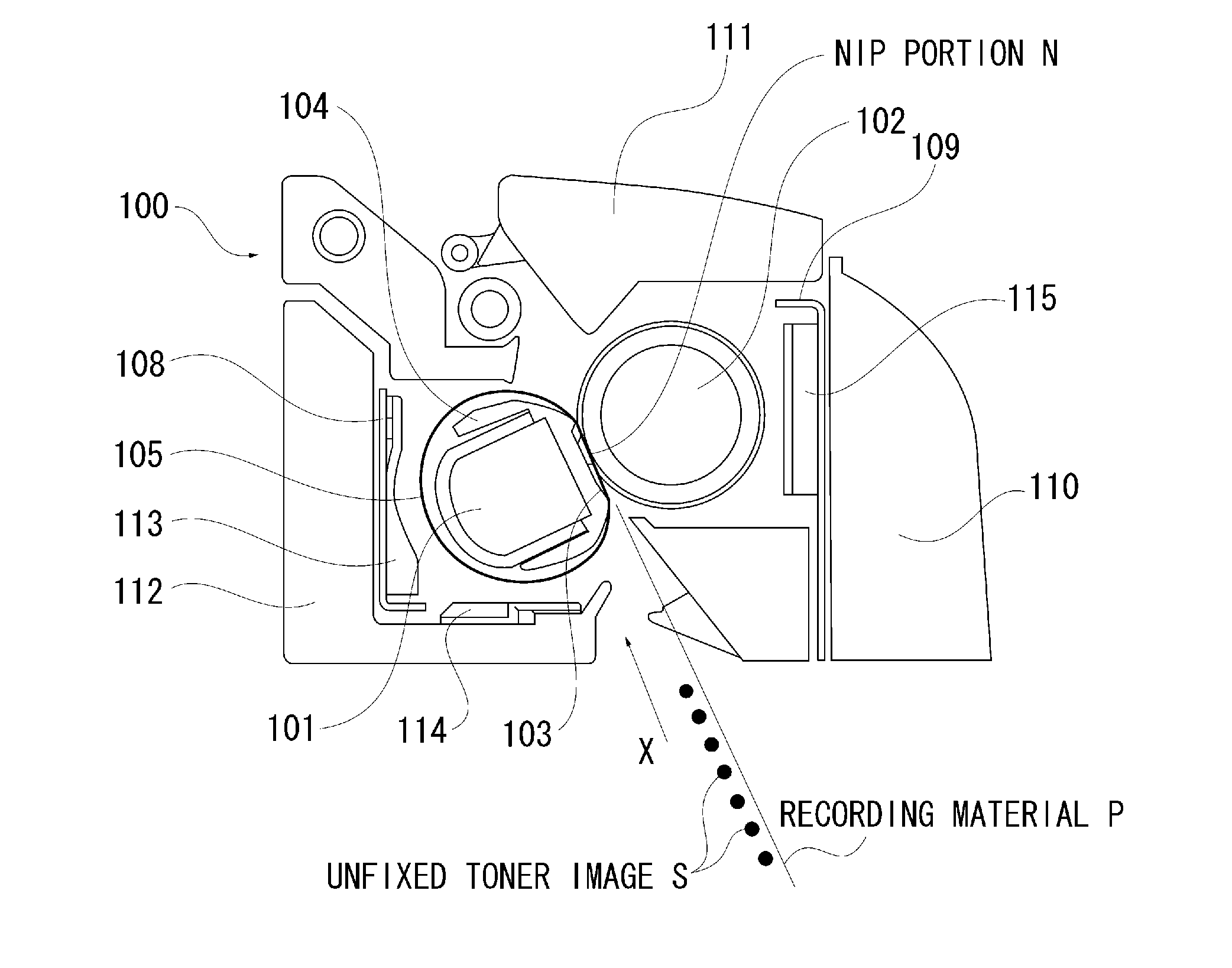
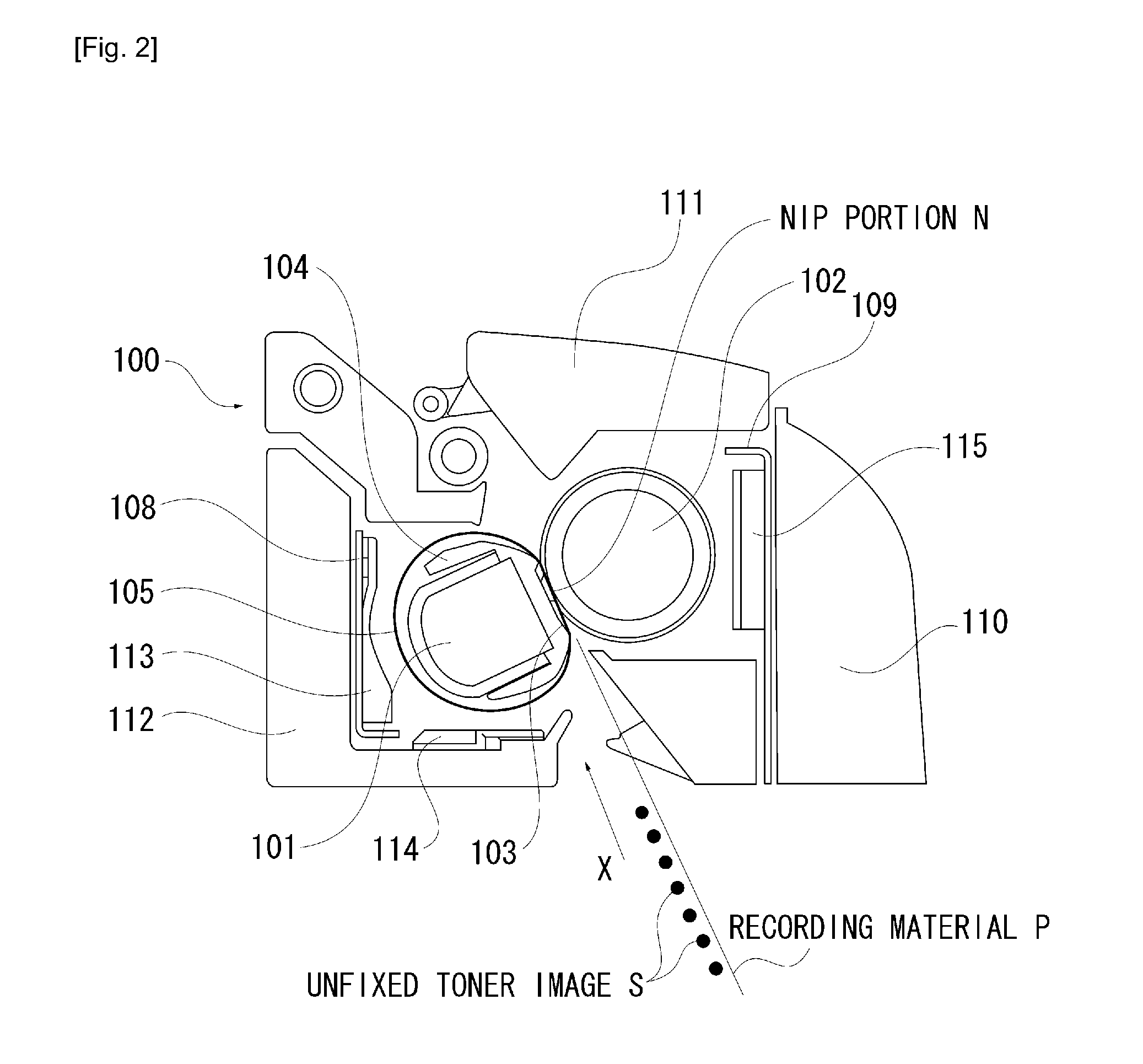
ActiveUS20110243598A1MinimizingMinimize adhesionElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringBiomedical engineering
There is provided an image forming apparatus capable of minimizing the adhesion of a mold release wax vaporized at the time of heating a toner image to components excluding a fixing device inside the image forming apparatus. The mold release wax vaporized at the time of heating and fixing a toner image to a recording material is collected by a collection member, which is provided between a nip portion forming member and the frame of the fixing device, and kept at a temperature between the melting point and the sublimation point of the mold release wax.
Owner:CANON KK
Article of clothing with buoyant material
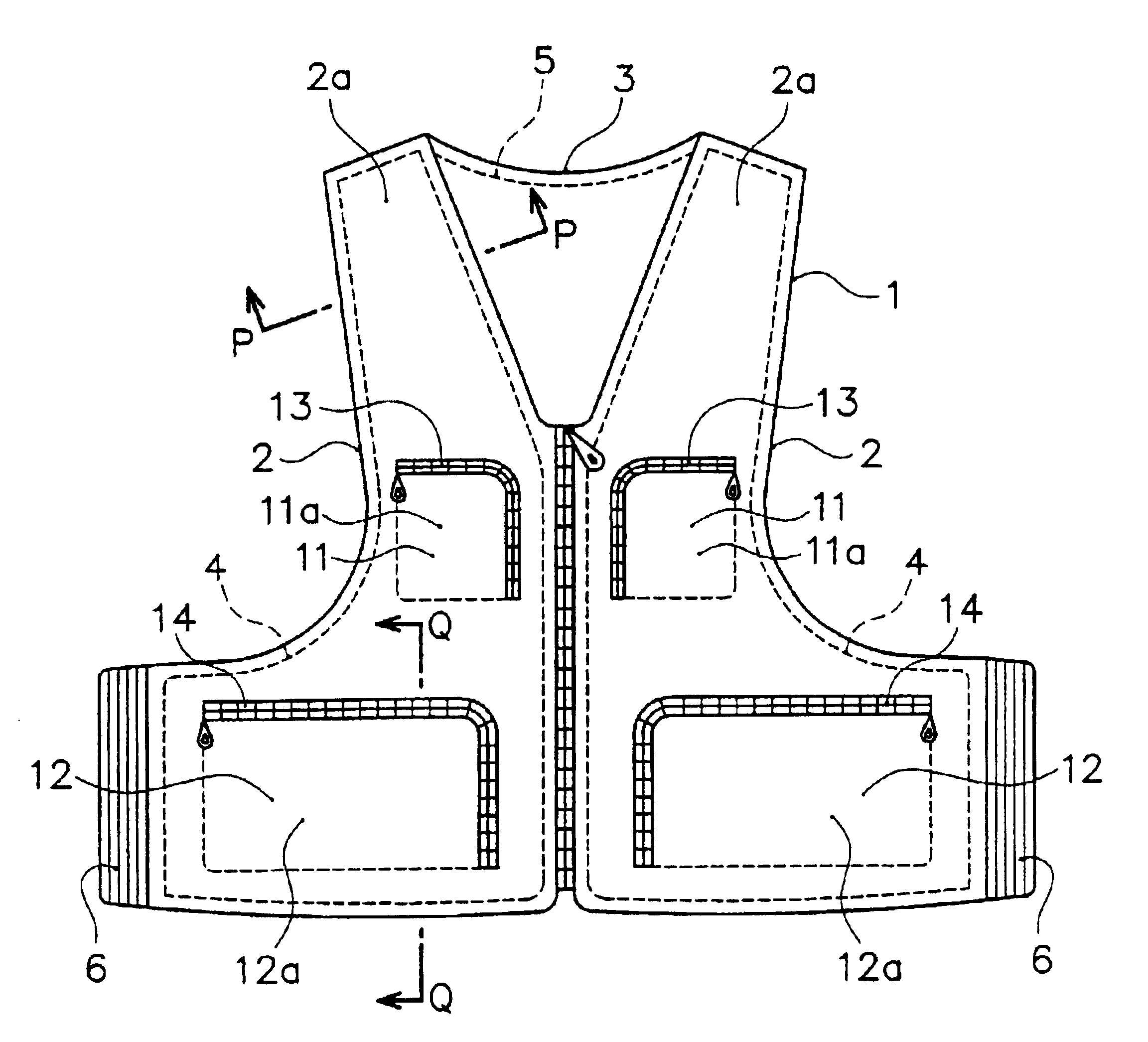
InactiveUS6910224B2Minimize adhesionEasy to fixChemical protectionHeat protectionTextileMechanical engineering
An article of clothing such as a vest incorporating buoyant material is configured to reduce pocket bulging when carried items that are placed in pockets and to allow the wearer to move freely. The article of clothing includes a main clothing unit having one or more pockets and one or more buoyant material sections coupled to the main clothing unit. One or more of the buoyant material sections has at least one concavity formed at a position on the outside and / or inside surfaces of the buoyant material sections at positions that correspond to one the pockets such and at least part of each the carrying spaces of the pockets are formed in one of the concavities. Preferably, buoyant material sections are generally plate-shaped. Preferably, the pockets are made of cloth and located at prescribed positions on the outside and / or the inside of the buoyant material sections.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Electrical connectors adapted to reduce or prevent adherence of conductive material to contact portions as the connector
InactiveUS6450821B2Minimize adhesionEliminate disadvantagesPrinted circuit assemblingElectric discharge tubesElectricityElectrical connection
An electrical connector includes a first connector having a connector plate and a plurality of electric contacts thereon, and a second connector having a plurality of electric contact elements provided on conductors arranged on a board. The board is formed with slits around the conductors to support the conductors elastically by parts of said board surrounded by the slits. The first and second connectors are brought into detachable abutment against each other to electrically connect to electric contacts and the electric contact elements of the first and second connectors. The electric contact elements of the second connector each are provided with at least one ridge, preferably plural ridges facing to the electric contact of the first connector. The ridges preferably extend in parallel with the direction of sliding movement of the electric contacts caused by the elastic support of the conductors. With this arrangement, after repeated connections between two connectors a great many times more than thousands, no foreign substance can adhere to the electric contact elements and no longer is there any incorrect electrical connection between the contacts.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Apparatus and method for handling linerless label tape
InactiveUS6910820B2Minimize adhesionArea minimizationRecording apparatusPrinting mechanismsEngineeringHead parts
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
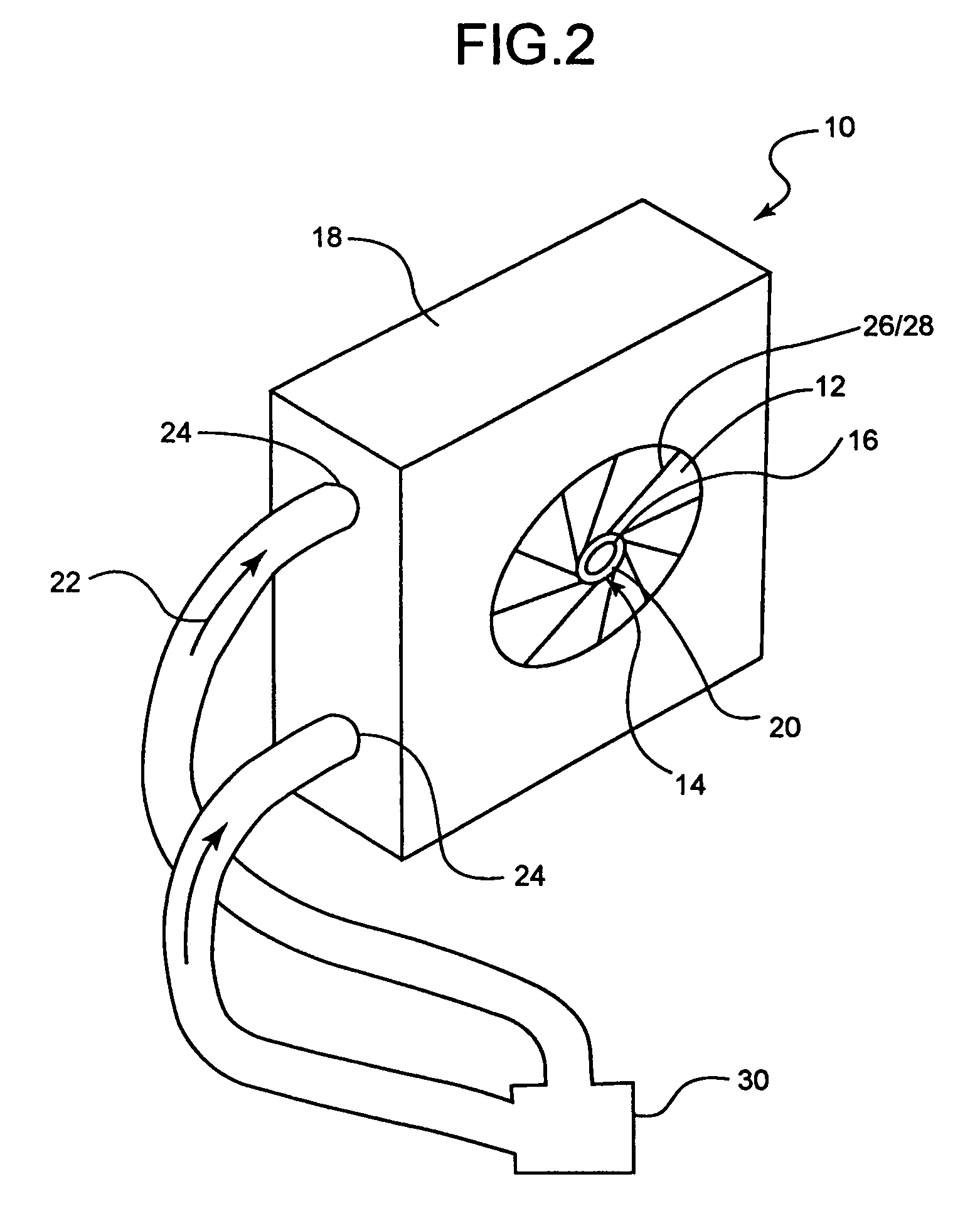
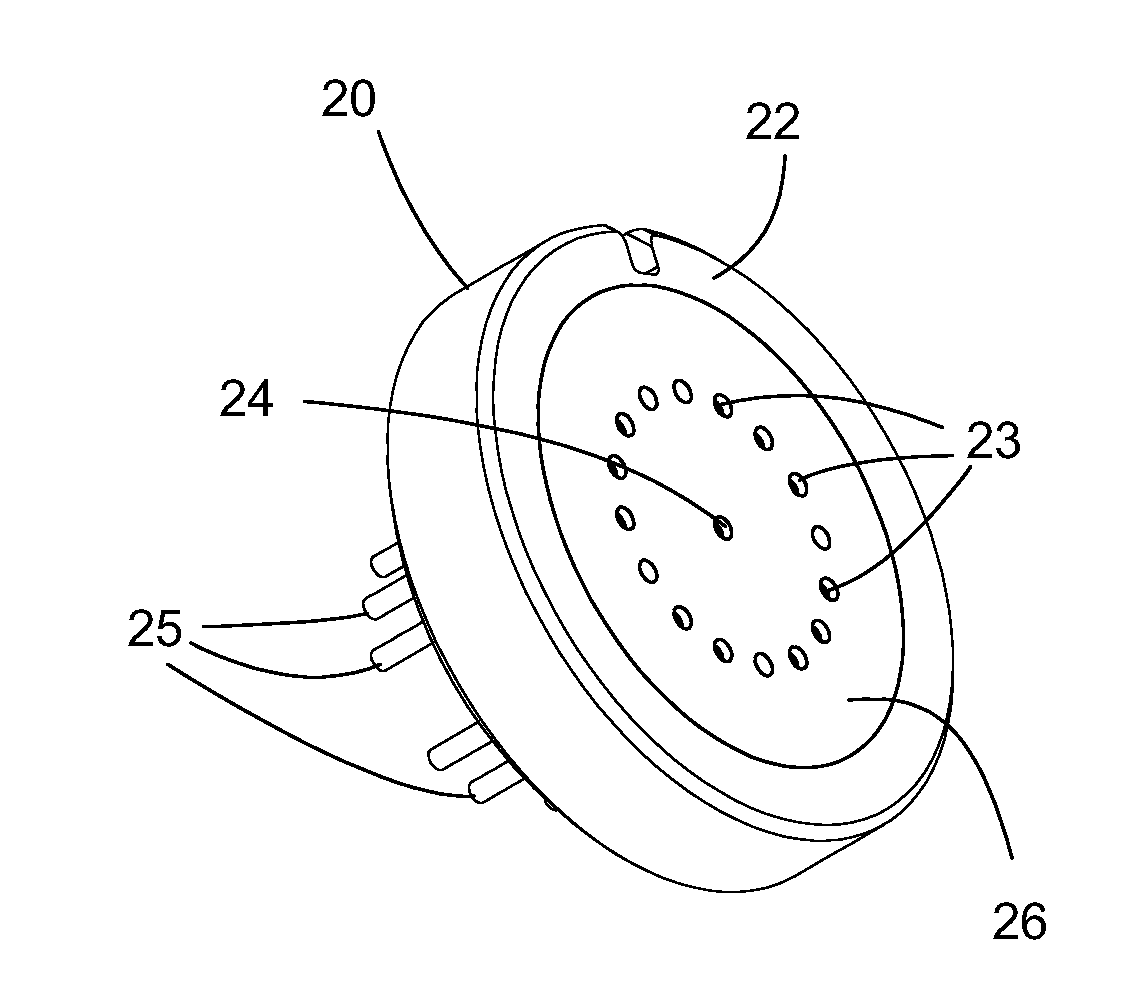
Multi-lumen vascular catheter and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7223254B2Avoid recyclingMinimize adhesionMulti-lumen catheterMedical syringesGuide wiresBlood vessel
A multilumen vascular catheter (1) having a flexible catheter tube (16) with a distal end-portion (12) which is terminated by a guide-wire opening (26). The catheter tube (16) has a first lumen (18) for extraction of fluid from the vessel (1) and a second lumen (20) for introducing fluid to the blood vessel (14). One or more suction openings (22) communicate with the first lumen (18) and are located upstream of one or more outlet openings (24), which in turn communicate with the second lumen (20). The distal end-portion (12) is permanently bulbous and has a first, widening section (A) starting distally from the catheter tube (16) with a gradually increasing external cross-section to a shoulder (30) with a maximum external diameter into a second, narrowing section (B) having a gradually decreasing external cross-section distally. One or more of the suction openings (22) are located in the first, widening section (A) of the distal end-portion (12) while one or more of the outlet openings (24) are located in the second, narrowing section (B).
Owner:NORDIC MED COM
Halation-Free Light-Emitting Diode Holder
InactiveUS20100277932A1Reduce adhesionImprove luminance uniformityLighting support devicesSolid-state devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A halation-free light-emitting diode holder includes a body and a retaining portion. The body has a die holder, which includes a first surface, a second surface, and an opened end. The retaining portion is provided on the second surface. By using the retaining portion, the optical gel in the die holder is blocked from capillary movement up along the second surface. Furthermore, having nano-material layers further formed on the second surface or having the area of the first surface made greater than the area of the opened-end also prevents the optical gel from climbing along the second surface. Thereby, a light halation circling a light pattern of the resultant light-emitting diode is avoided and the light-emitting diode is improved in luminance uniformity.
Owner:HELIO OPTOELECTRONICS
Miniaturized contact spring
InactiveUS7137830B2High strengthMinimize adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padMiniaturization
Owner:ADVANTEST SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Treatment method for reverse osmosis filtration systems
InactiveUS20090050563A1Increase calciumHigh calcium concentrationSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAlkalinityFiltration
A method for cleaning and maintaining reverse osmosis membrane filters by injecting sulfurous acid into water and then sequentially filtering the acidified water through membrane filters to reduce alkalinity scaling, add sufficient SO2 as a biocide to attack bacteria and other micro organisms to prevent membrane fouling, and reduce iron to prevent iron deposit build-up.
Owner:EARTH RENAISSANCE TECH
Preparation for wound healing and prevention of bandage adhesion to the wound
InactiveUS20050181025A1Promote wound healingMinimize adhesionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBandagePotassium iodine
Preparation for wound healing and prevention of adhesion to the wound containing a physiologically acceptable salt of hyaluronic acid, iodine and potassium iodine.
Owner:CPN SPOL SRO
Pre-treatment reverse osmosis water recovery method for brine retentate metals removal
ActiveUS8101083B2Minimize adhesionPrevent bacterial growthMembranesOther chemical processesPretreatment methodFiltration
Owner:EARTH RENAISSANCE TECH
Shear valve apparatus and methods to improve leakage and wear
InactiveUS20100102264A1Minimize adhesionReduce coefficient of frictionPlug valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTime extensionDrive shaft
A shear valve assembly includes a stationary valve manifold having a manifold planar surface containing a plurality of manifold input ports and one or more manifold output ports, a movable valve switch having a switch planar surface in slidable, interactive contact with the manifold planar surface forming an interactive contact junction, the switch planar surface having a fluid switching channel capable of connecting one of the plurality of manifold input ports with one of the one or more manifold output ports, a surface modifying component disposed at the interactive contact junction that provides a period of extended useful life of the manifold planar surface and the switch planar surface beyond the useful life of pre-lubricated interactive contact junction, a drive shaft connected to the valve switch, and a valve housing supporting the stationary valve manifold, the movable valve switch, and the drive shaft.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
System and method for delivering an Anti-adhesive substance to a body cavity
InactiveUS20130211320A1Minimize adhesionPrevent tissue adhesionMulti-lumen catheterAerosol deliveryAnti adhesiveDrug
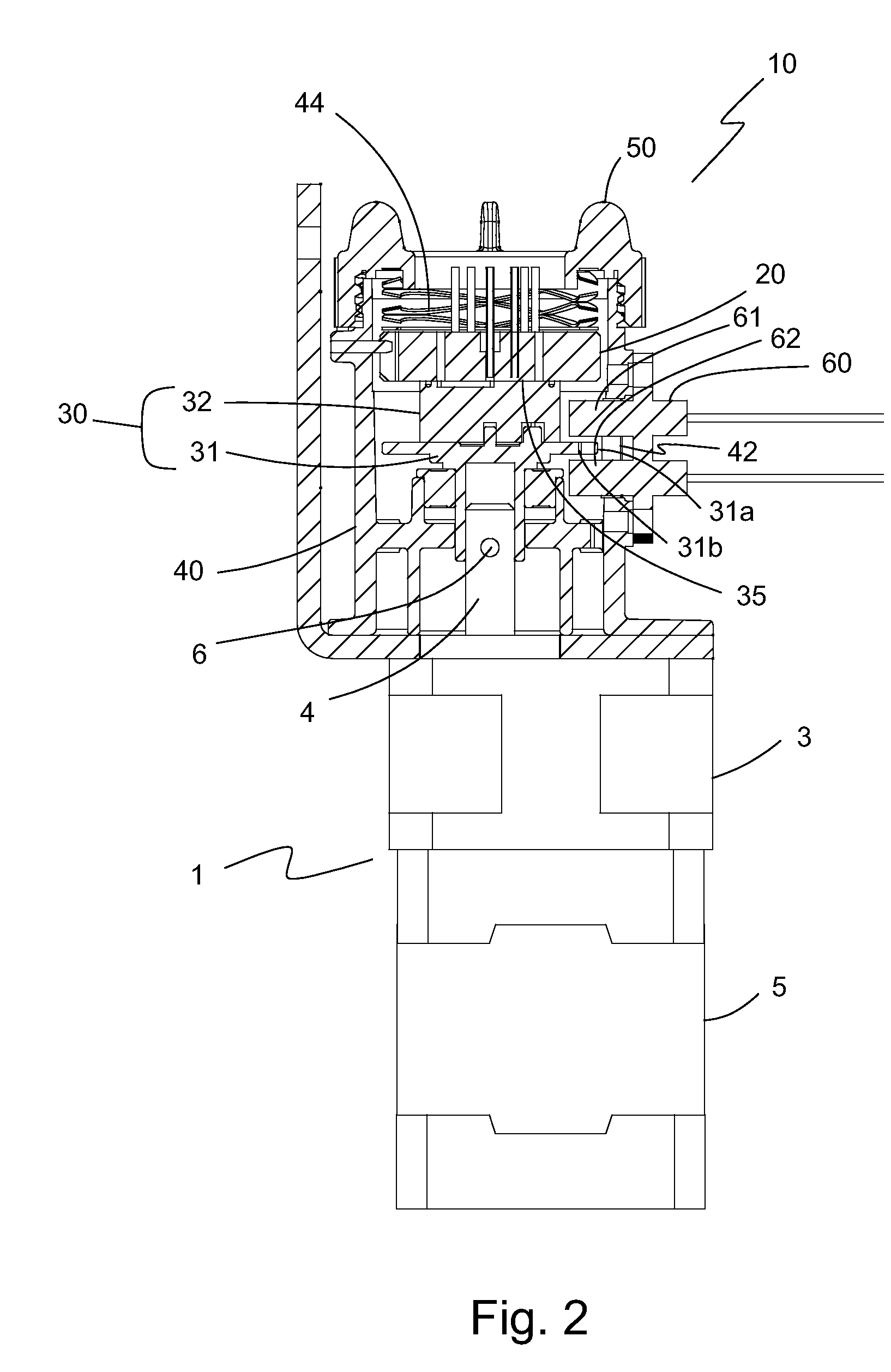
A system and method for creating a medicated atmosphere in an organ, or body cavity is disclosed. The system includes a flexible nebulization catheter that can be manipulated during use, a device for the introduction of the nebulization catheter, a medication delivery apparatus configured to control delivery of a medication to the catheter, a gas delivery apparatus in communication with the catheter, a gas pressure relief apparatus configured to relieve pressure in the organ or body cavity, and a central controller. The system may include a liquid source having a mixture of hyaluronic acid and heparin that, in conjunction with the nebulizing catheter, are designed to generate an aerosol with a particle size of 10-25 microns in a body cavity. The method includes providing an aerosol of anti-adhesive medication to an organ or body cavity while controlling overall pressure in the organ or cavity.
Owner:NORTHGATE TECH
Reverse osmosis water recover method
ActiveUS8236178B2Minimize adhesionPrevent bacterial growthMembranesSedimentation separationAlkalinityFiltration
A method for cleaning and maintaining reverse osmosis membrane filters by injecting sulfurous acid into water to form sulfurous acid (H2SO3), and then sequentially filtering the acidified water through membrane filters to reduce alkalinity and mineral scaling, add sufficient SO2 as a biocide to attack bacteria and other micro organisms to prevent membrane fouling, reduce iron to prevent iron deposit build-up, scavenge and remove dissolved oxygen prior to filtration to prevent membrane oxidation, and prevent concentrated salts within the retentate from precipitating out of solution during transport for land application.
Owner:EARTH RENAISSSANCE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com