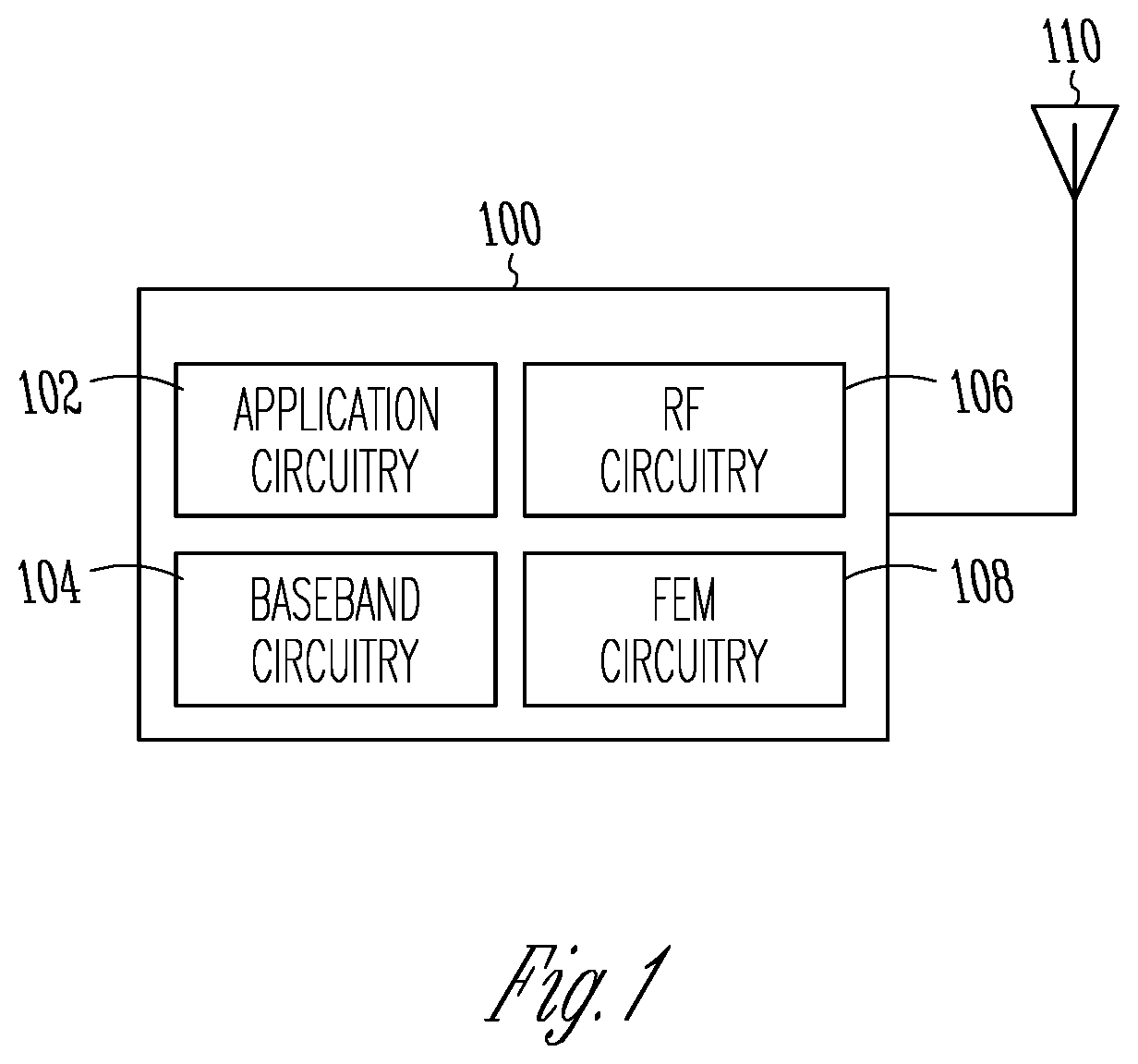
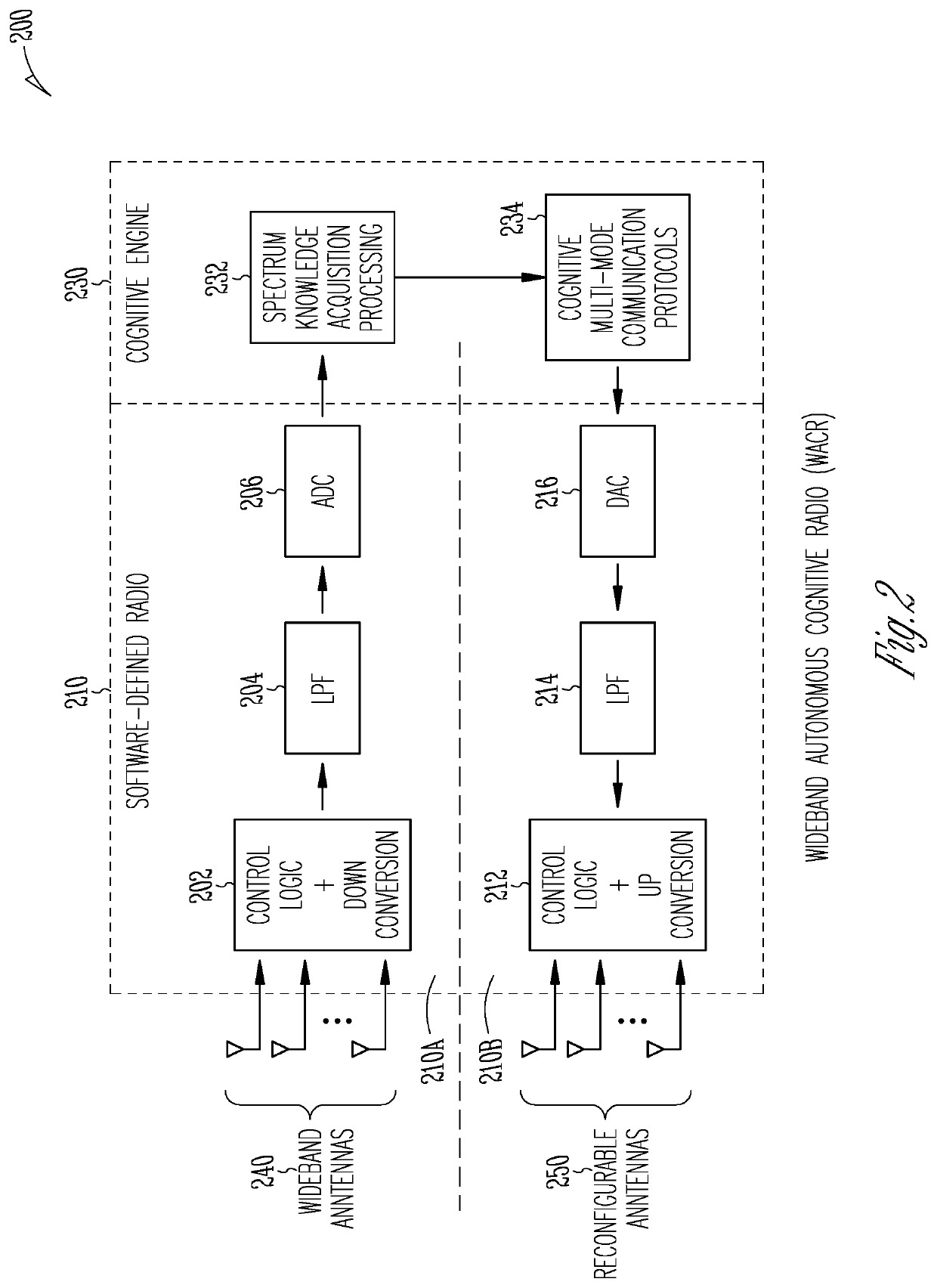
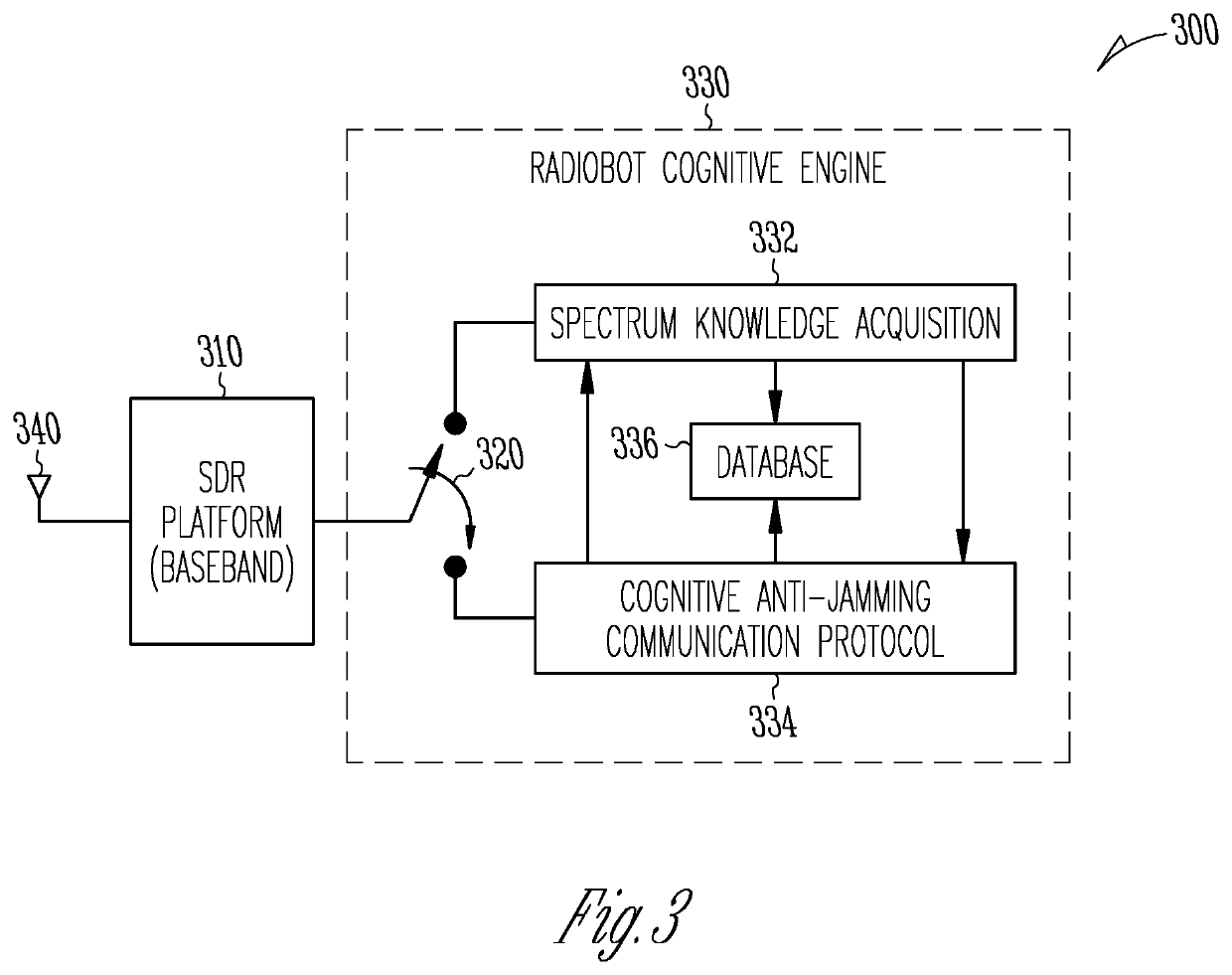
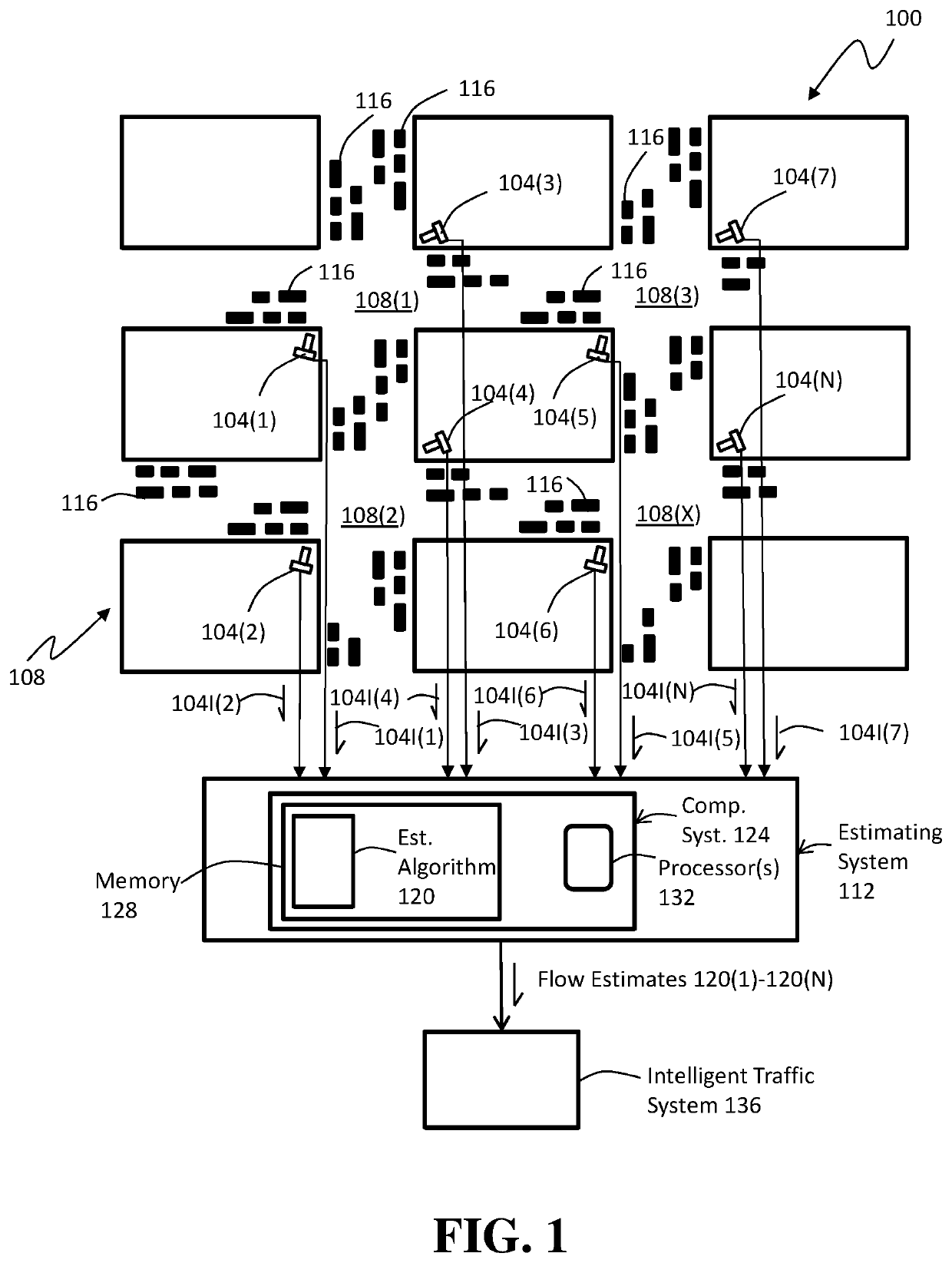
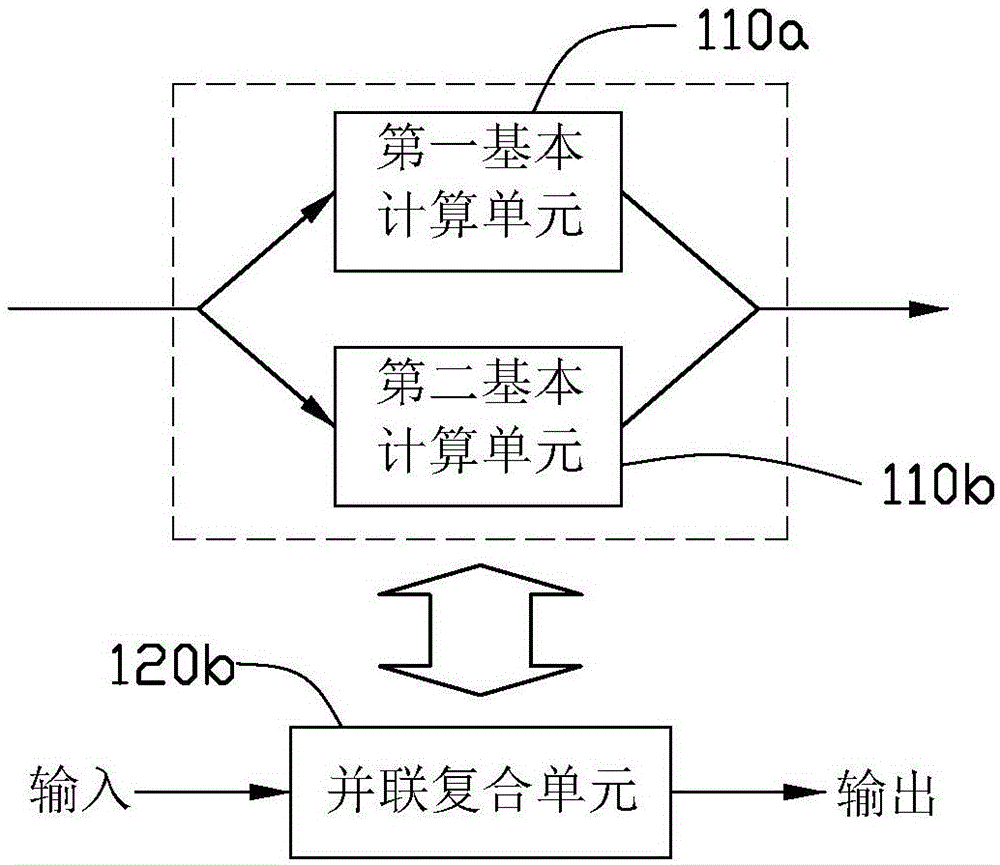
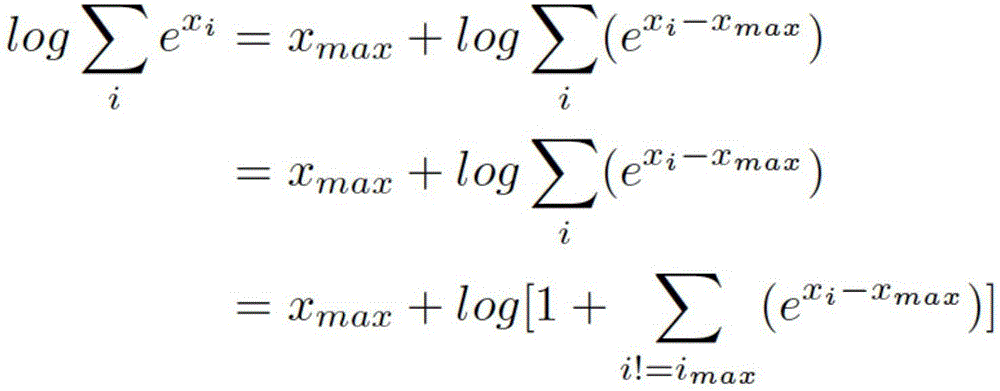Patents
Literature
2237 results about "Artificial neuronal network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
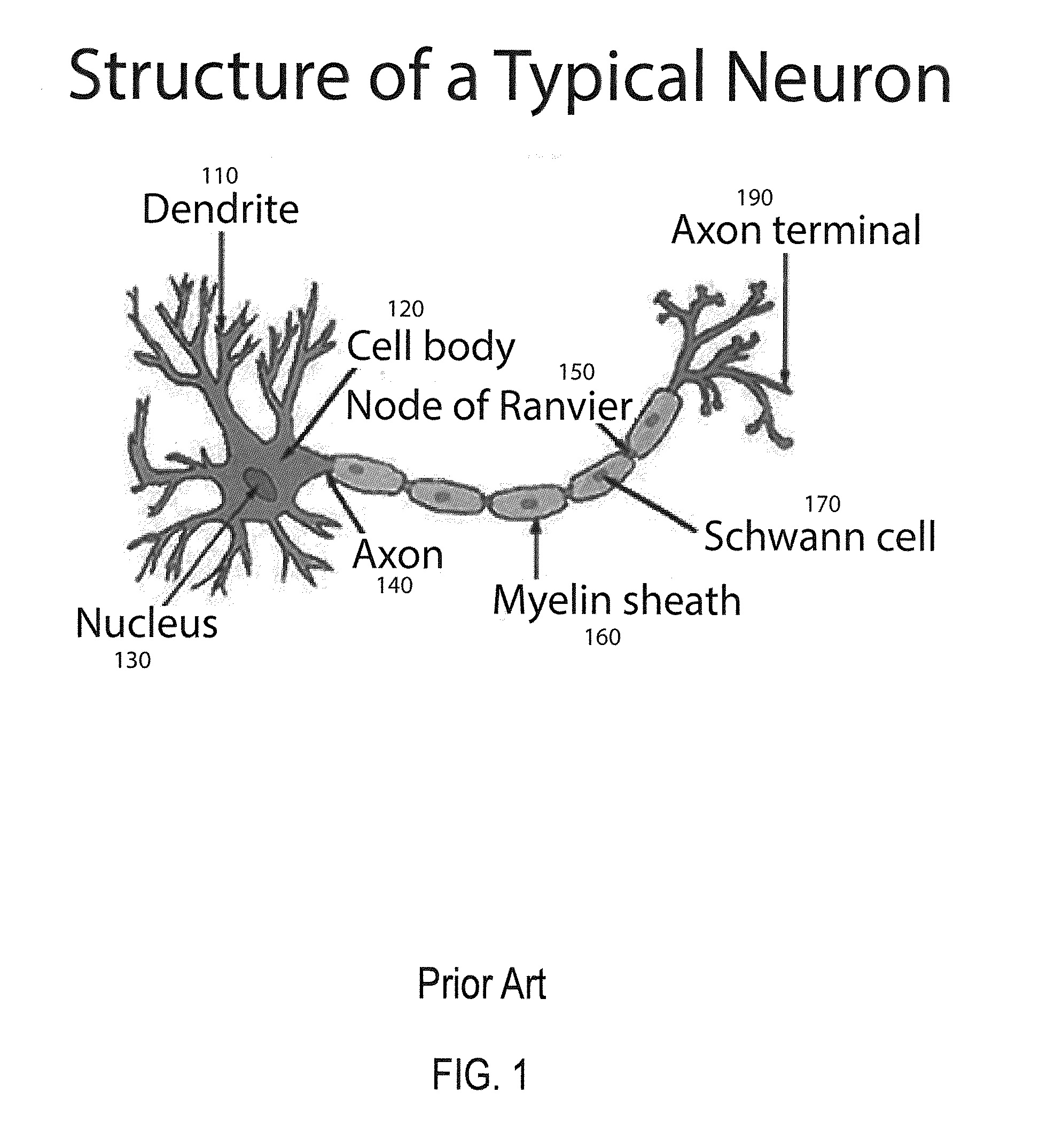
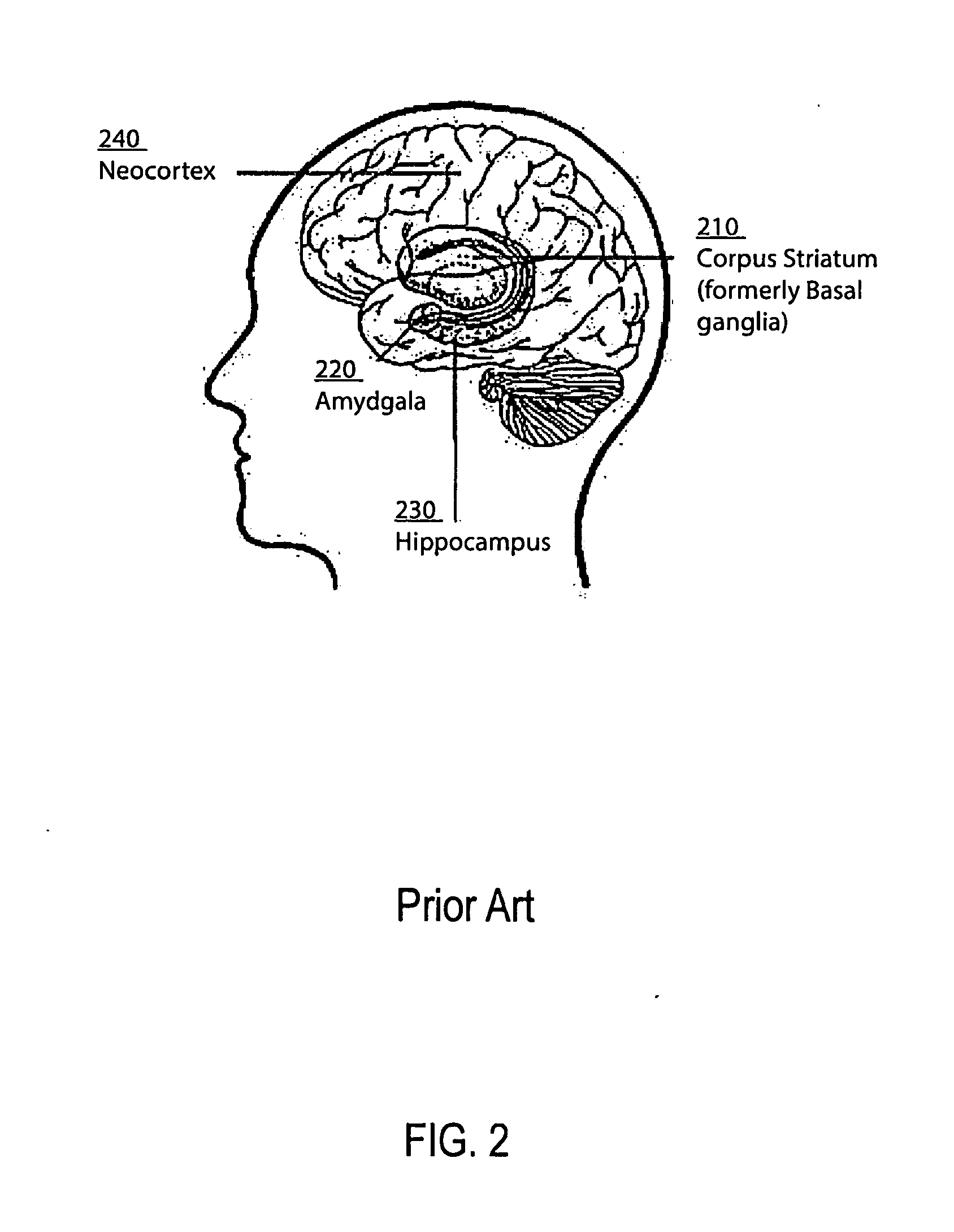
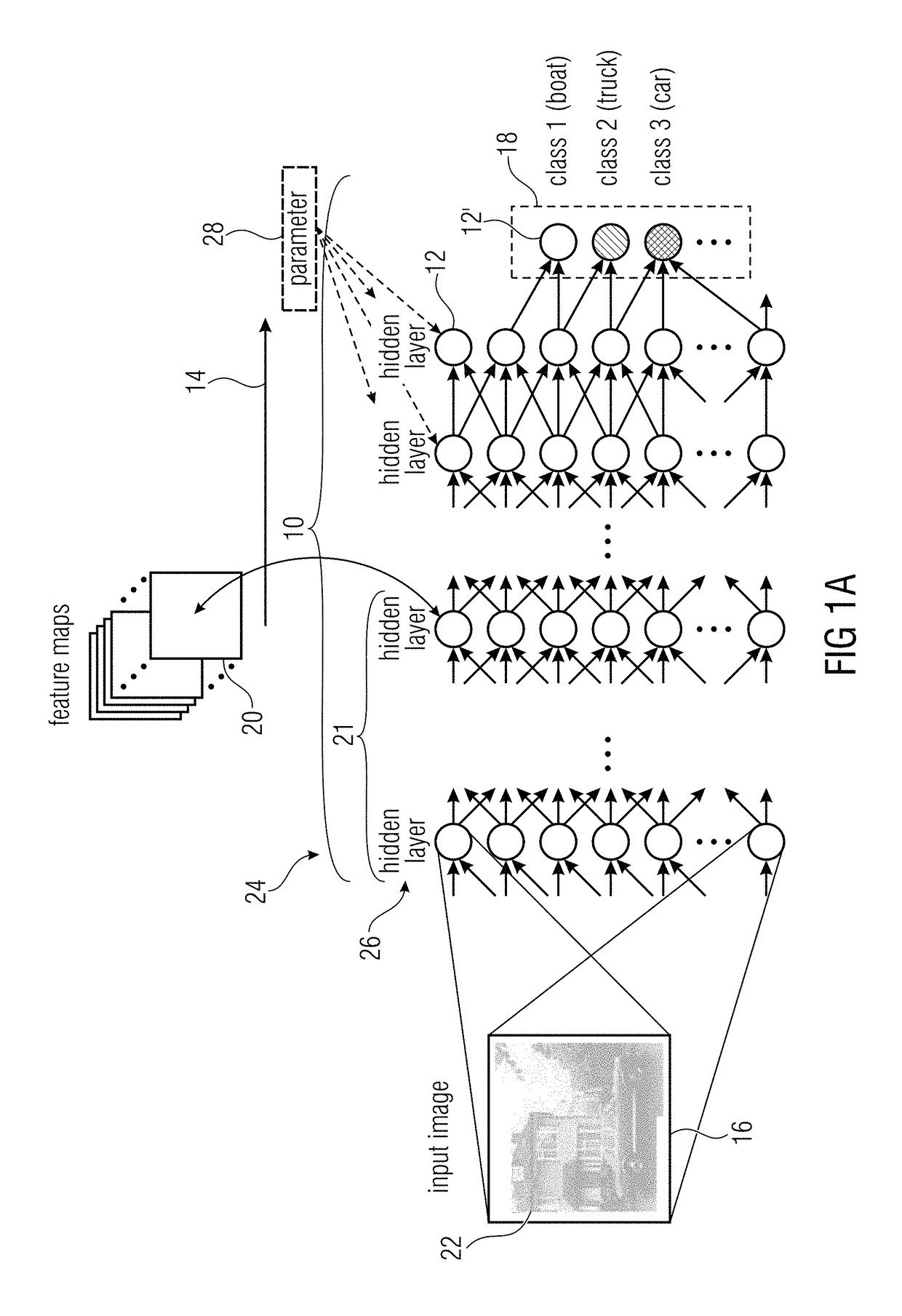
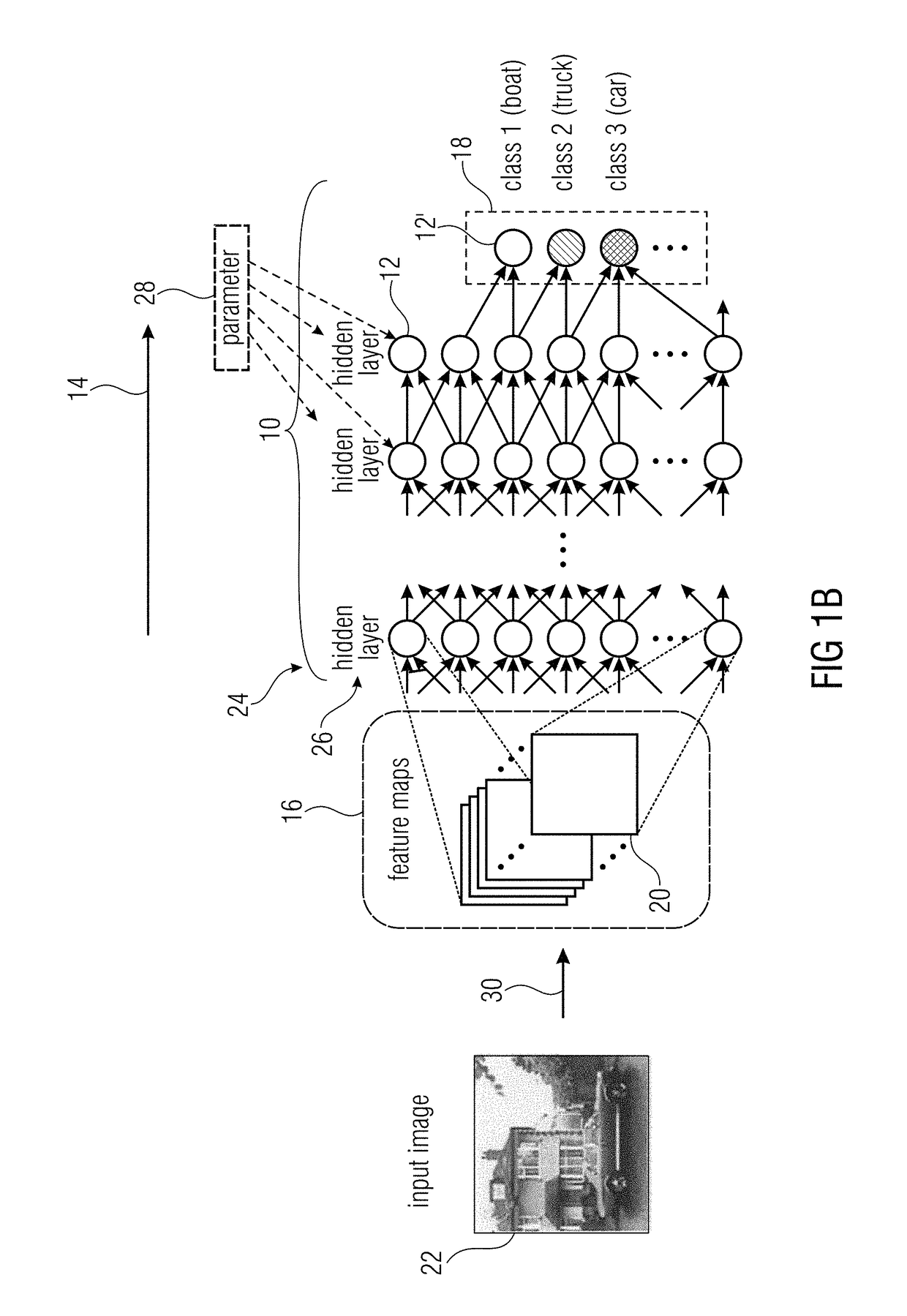
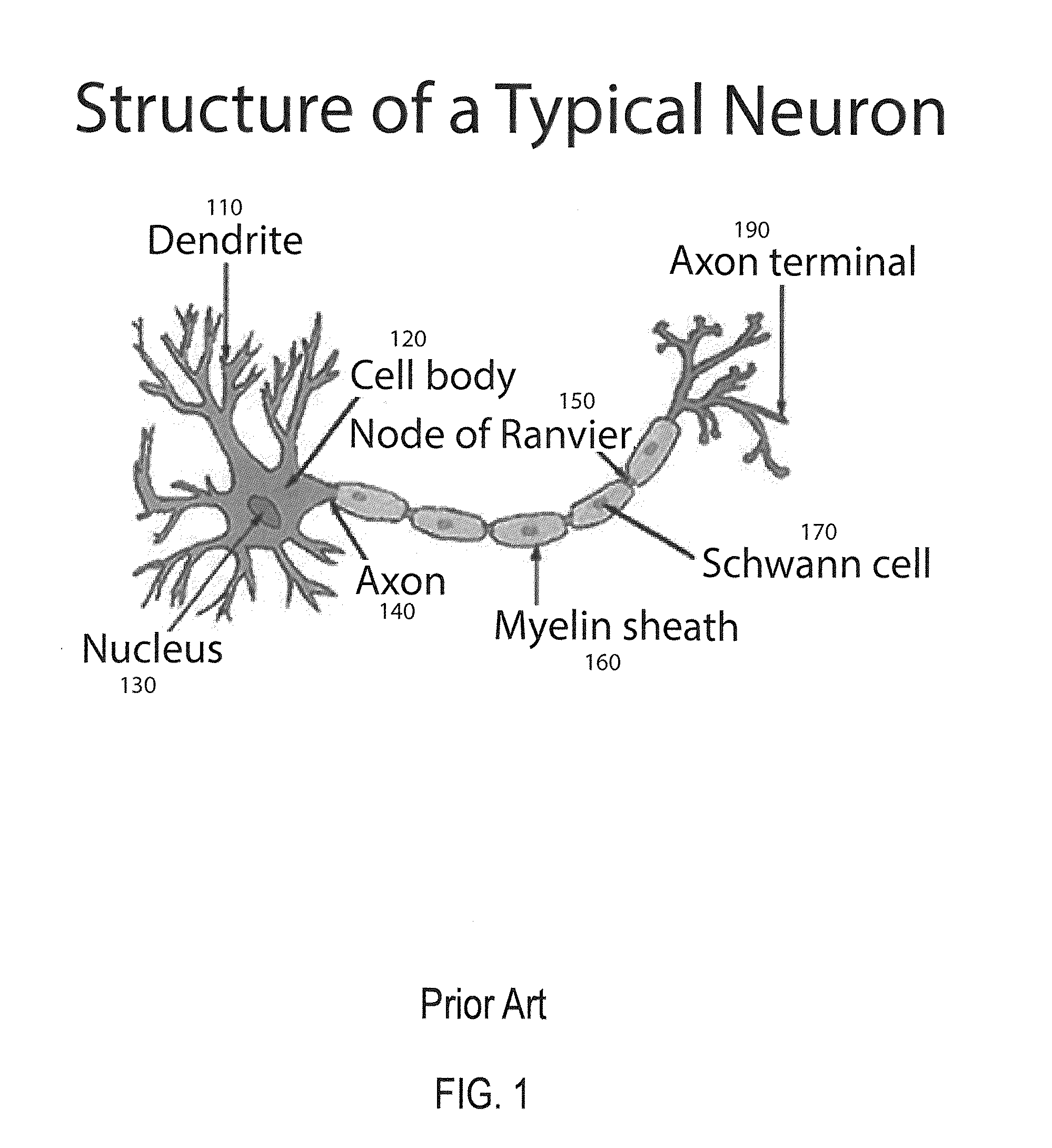
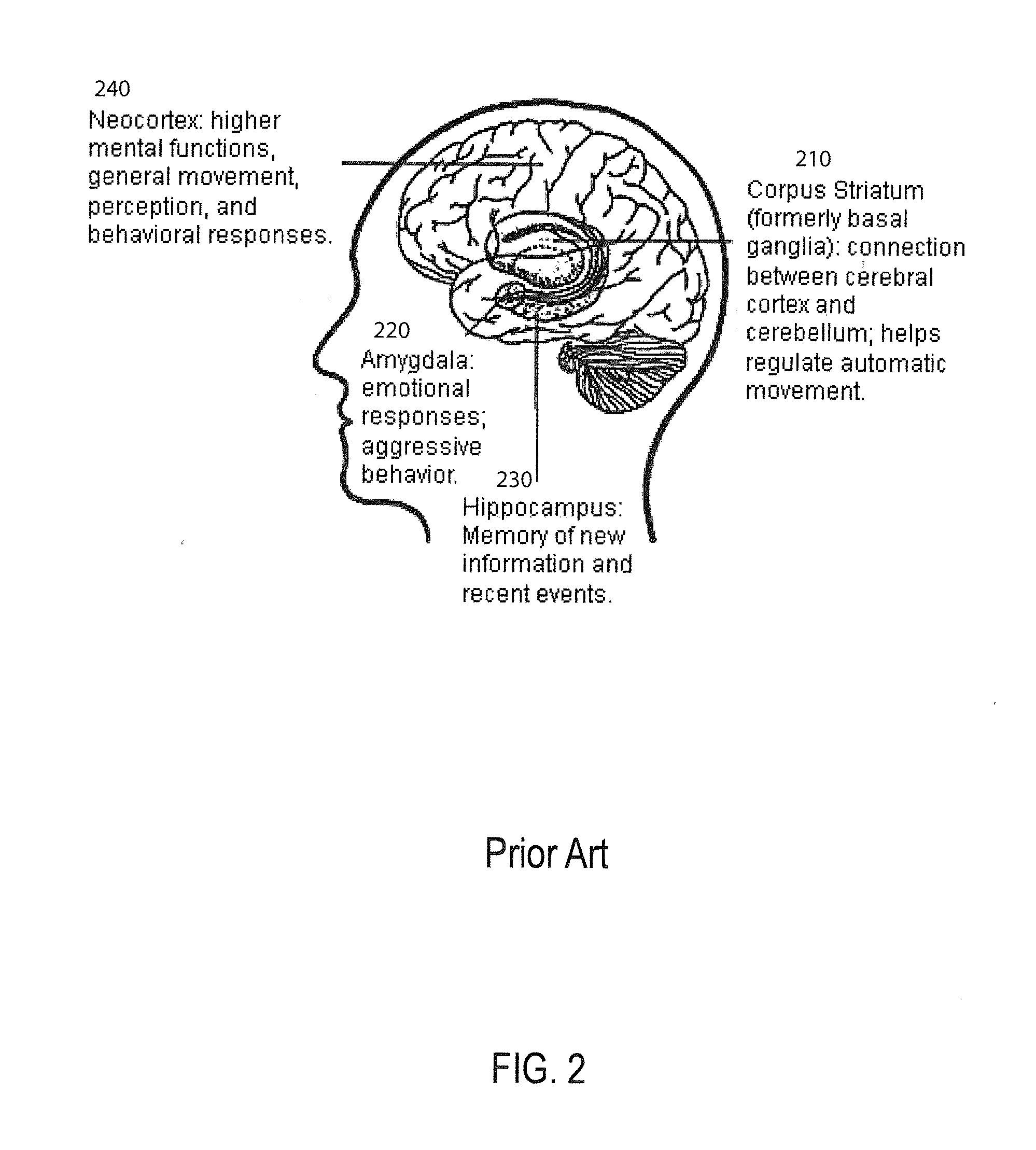
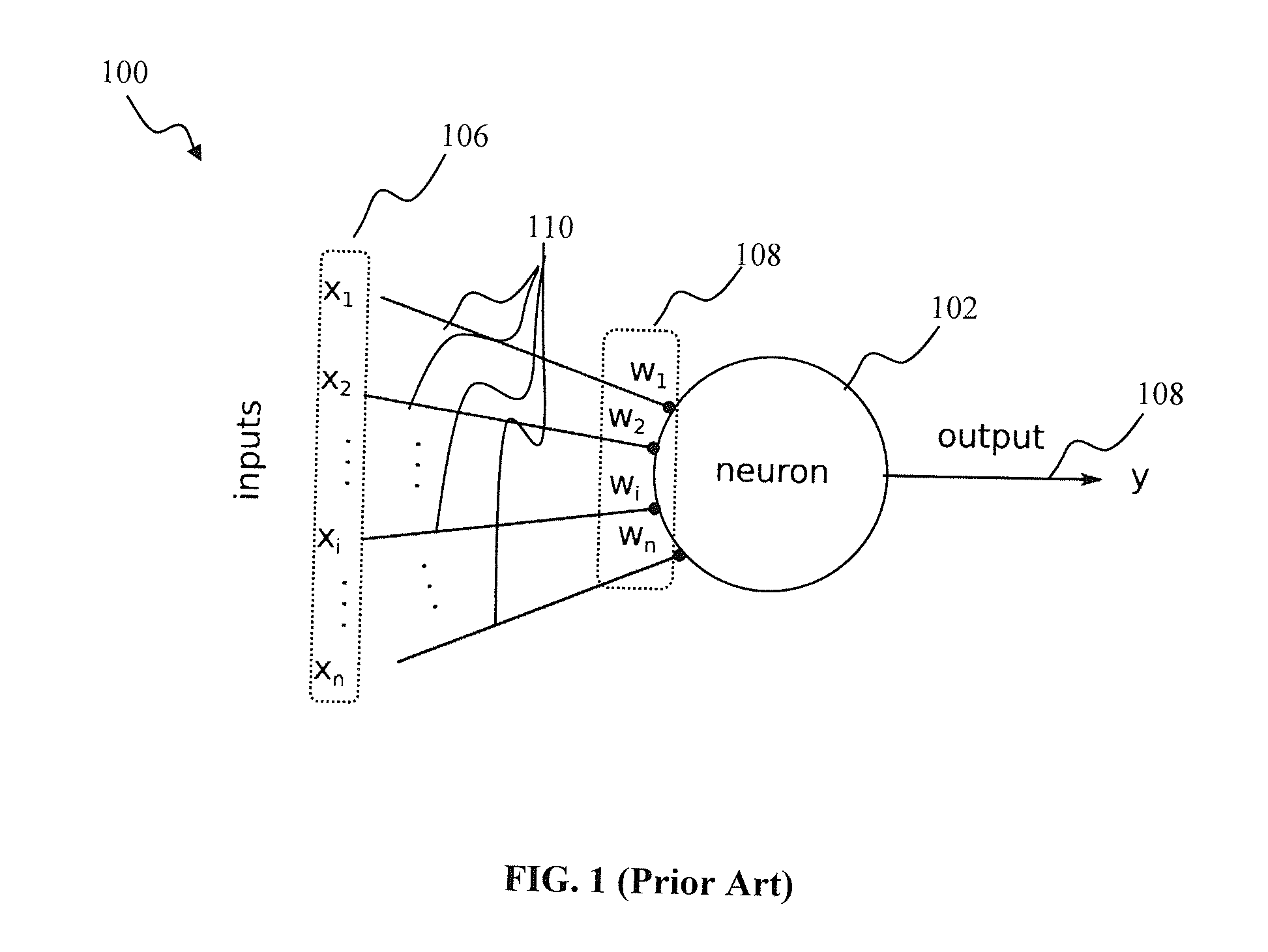
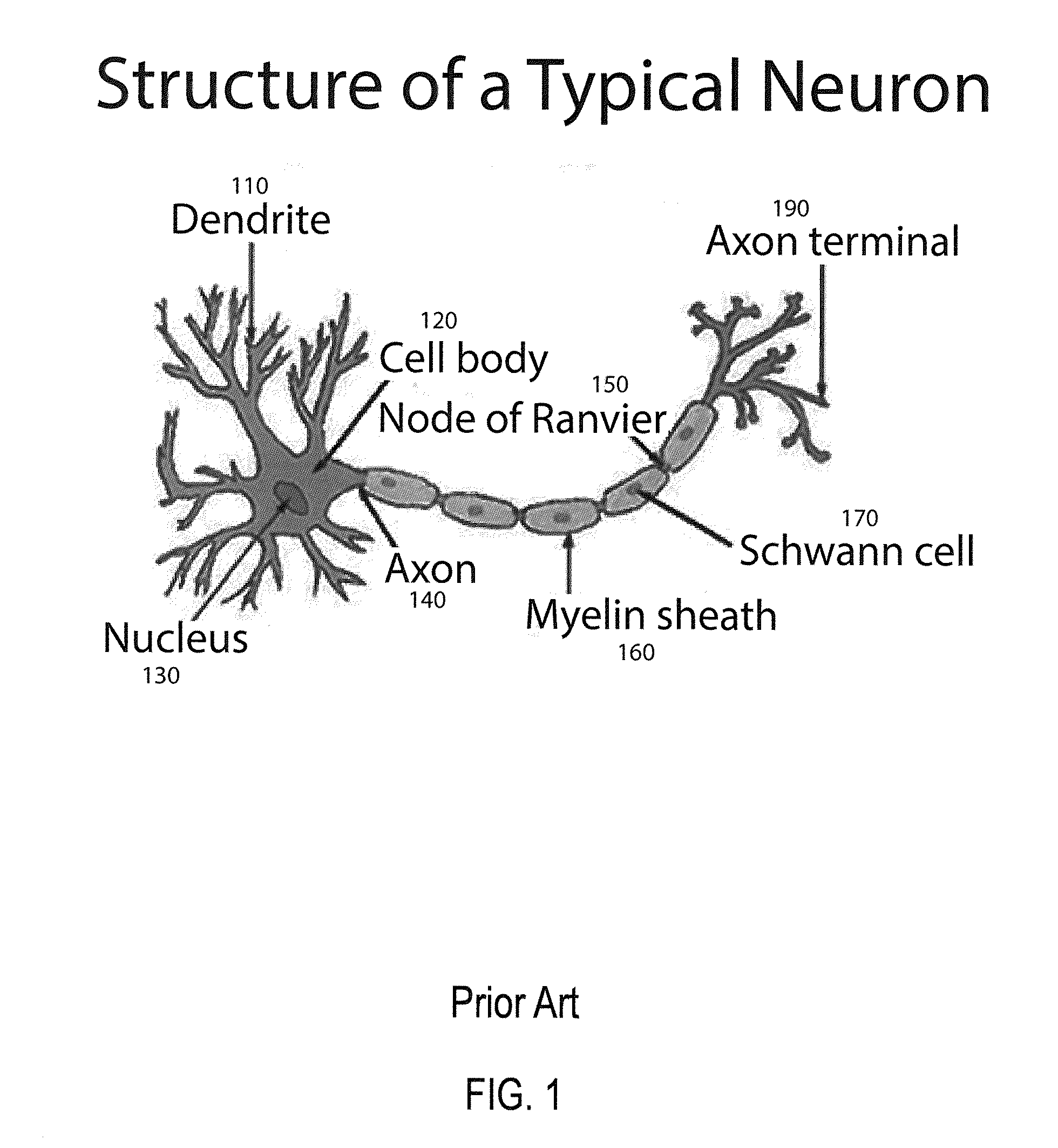
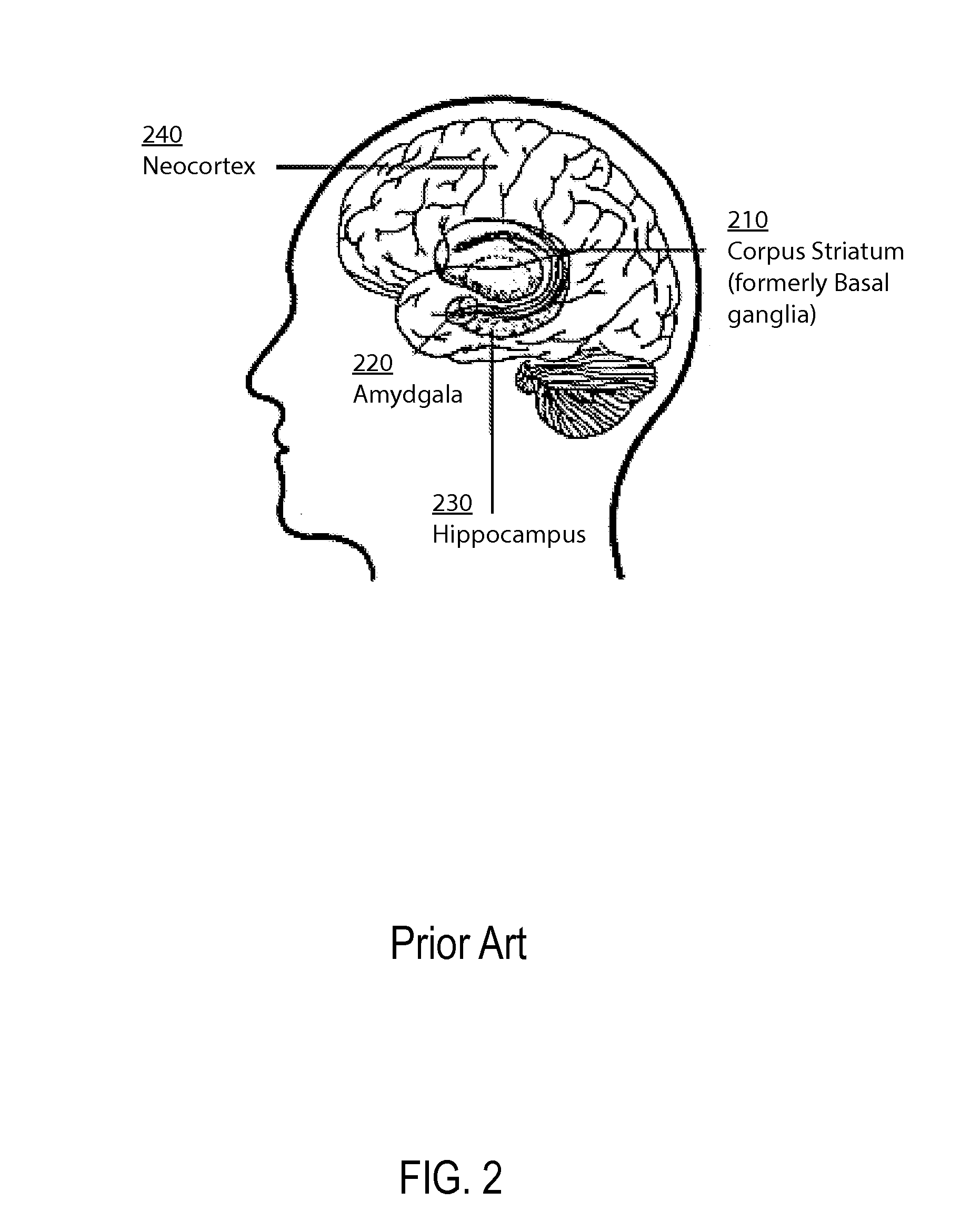
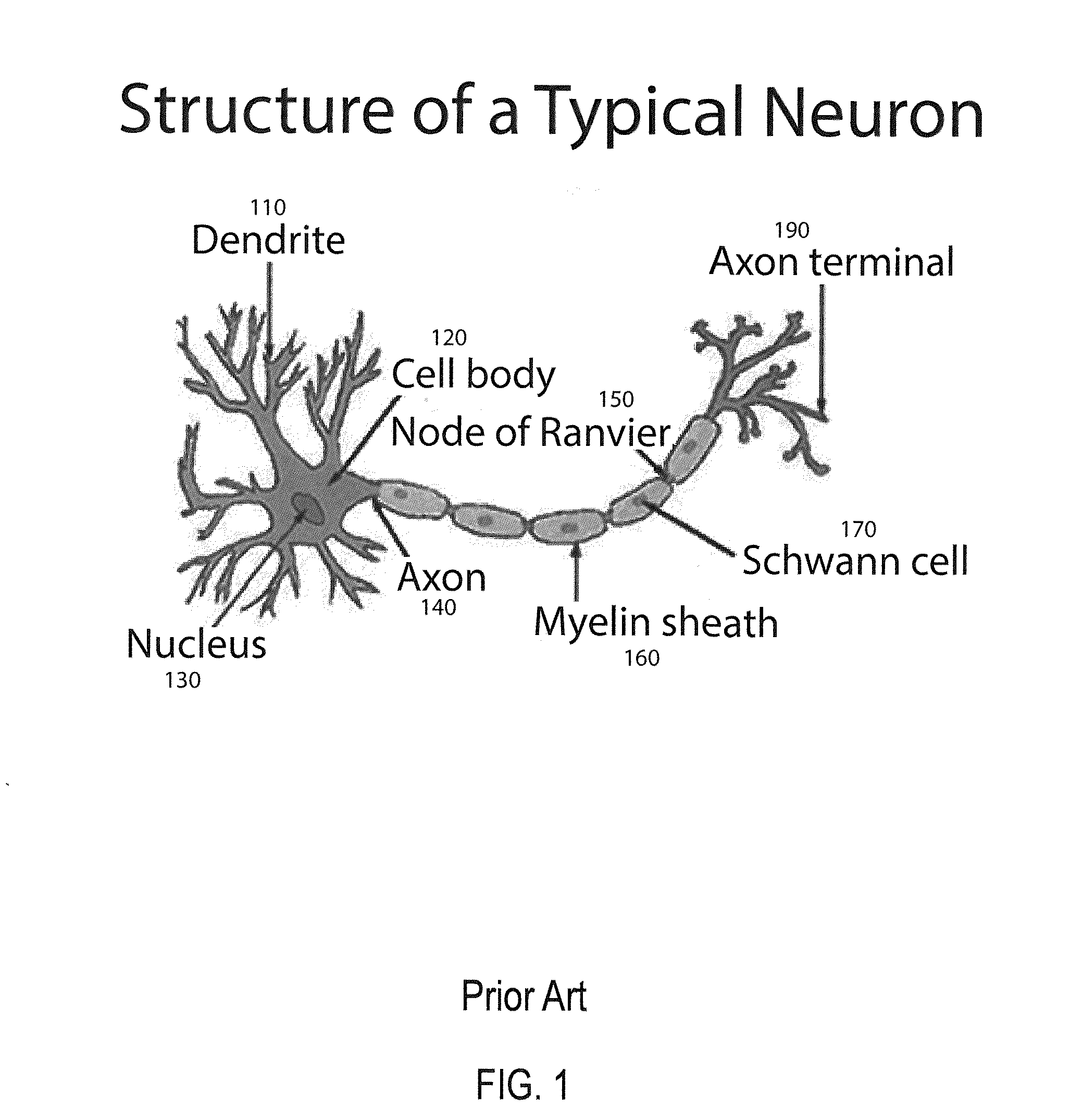
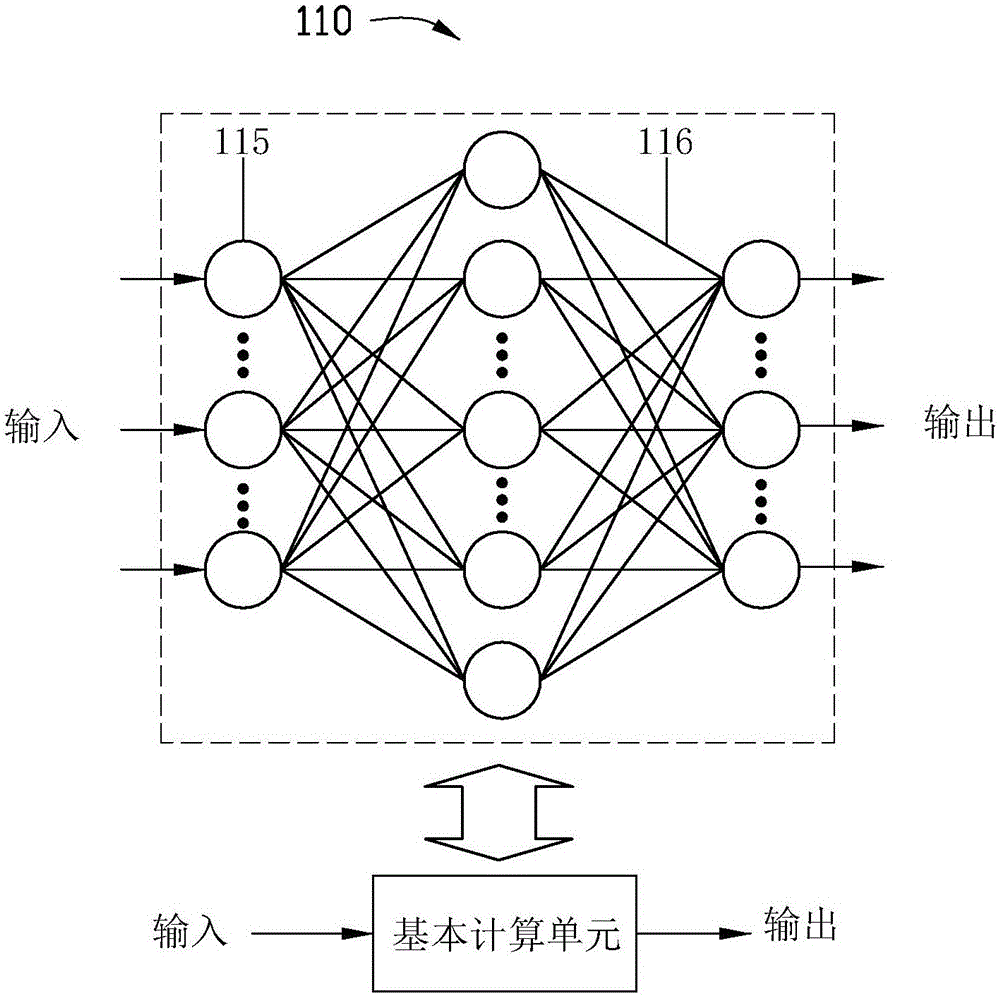
An artificial neural network is an attempt to simulate the network of neurons that make up a human brain so that the computer will be able to learn things and make decisions in a humanlike manner. ANNs are created by programming regular computers to behave as though they are interconnected brain cells.
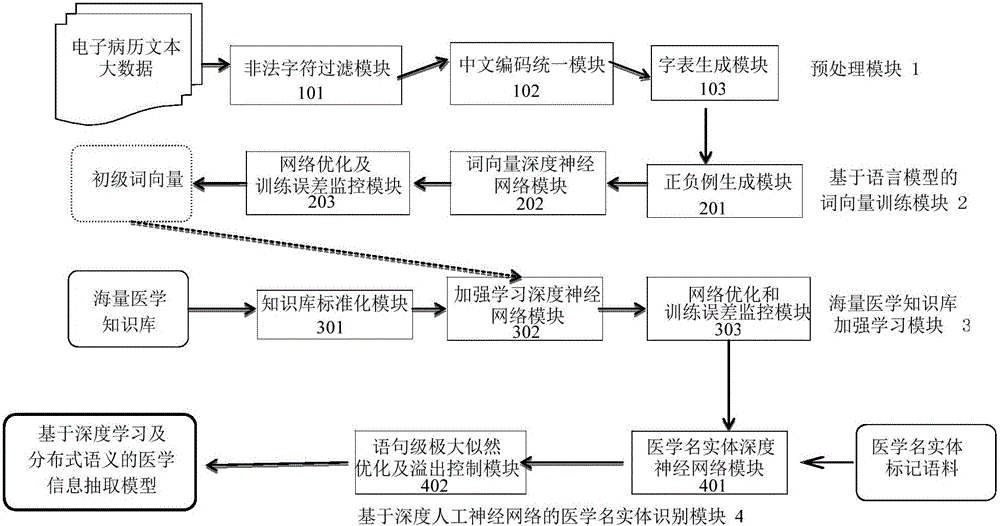
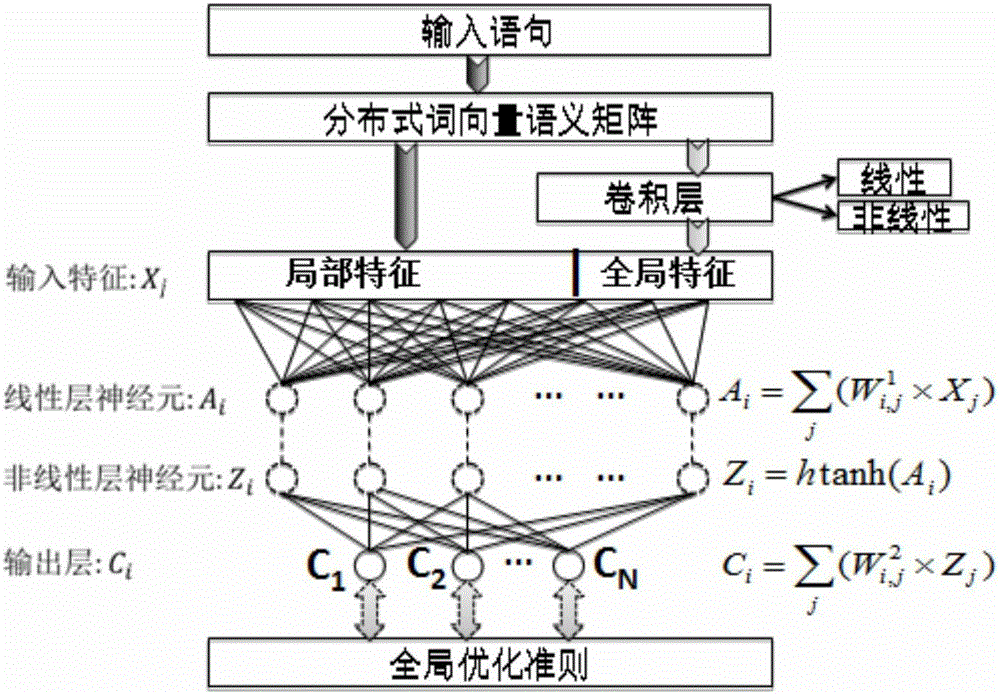
Medical information extraction system and method based on depth learning and distributed semantic features
ActiveCN105894088AAvoid floating point overflow problemsHigh precisionNeural learning methodsNerve networkStudy methods
he invention discloses a medical information extraction system and method based on depth learning and distributed semantic features. The system is composed of a pretreatment module, a linguistic-model-based word vector training module, a massive medical knowledge base reinforced learning module, and a depth-artificial-neural-network-based medical term entity identification module. With a depth learning method, generation of the probability of a linguistic model is used as an optimization objective; and a primary word vector is trained by using medical text big data; on the basis of the massive medical knowledge base, a second depth artificial neural network is trained, and the massive knowledge base is combined to the feature leaning process of depth learning based on depth reinforced learning, so that distributed semantic features for the medical field are obtained; and then Chinese medical term entity identification is carried out by using the depth learning method based on the optimized statement-level maximum likelihood probability. Therefore, the word vector is generated by using lots of unmarked linguistic data, so that the tedious feature selection and optimization adjustment process during medical natural language process can be avoided.
Owner:神州医疗科技股份有限公司 +1
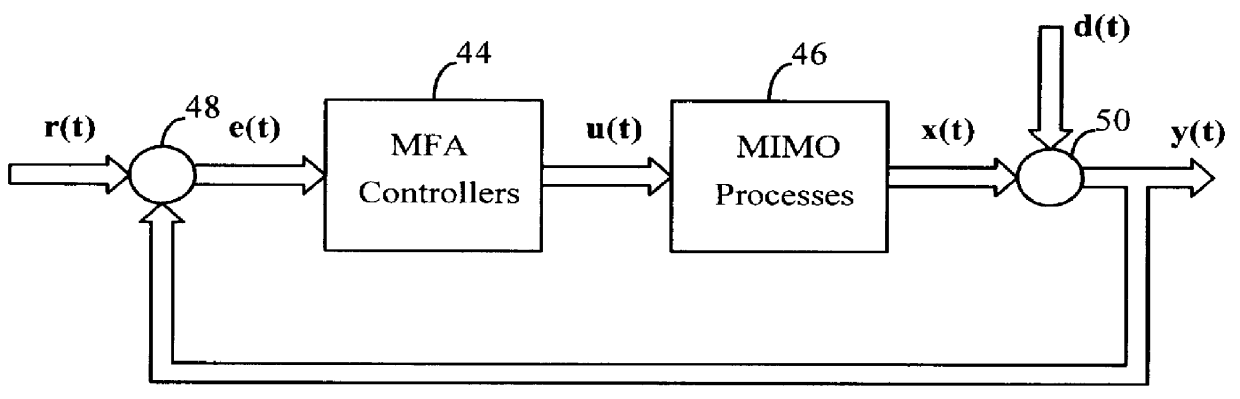
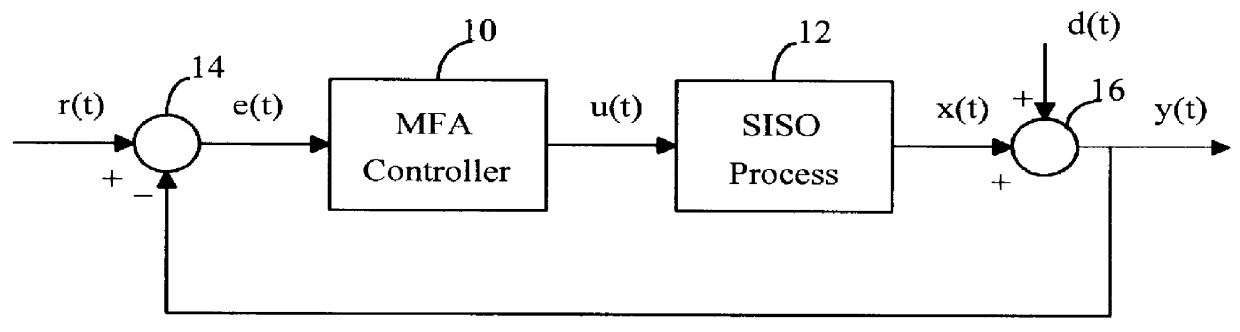
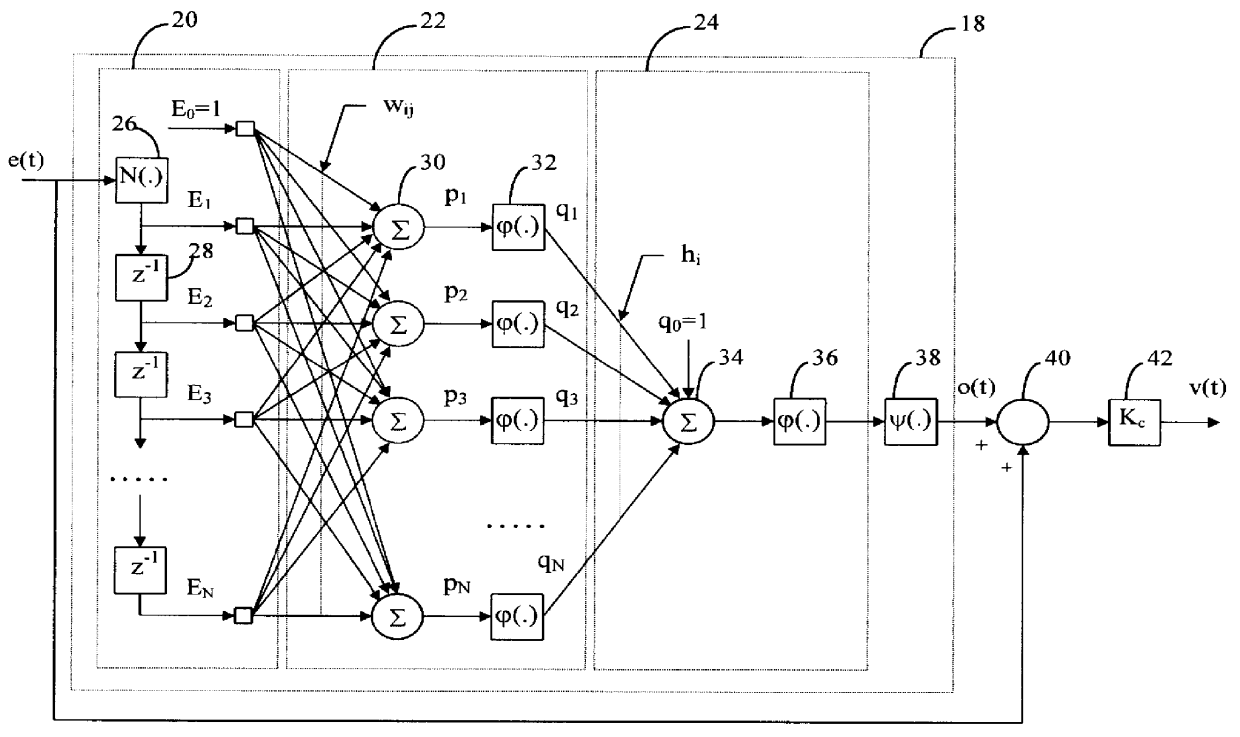
Model-free adaptive process control
InactiveUS6055524ALong response delayOvercome limitationsDigital computer detailsDigital dataData miningSelf adaptive
A model-free adaptive controller is disclosed, which uses a dynamic artificial neural network with a learning algorithm to control any single-variable or multivariable open-loop stable, controllable, and consistently direct-acting or reverse-acting industrial process without requiring any manual tuning, quantitative knowledge of the process, or process identifiers. The need for process knowledge is avoided by substituting 1 for the actual sensitivity function .differential.y(t) / .differential.u(t) of the process.
Owner:GEN CYBERNATION GROUP
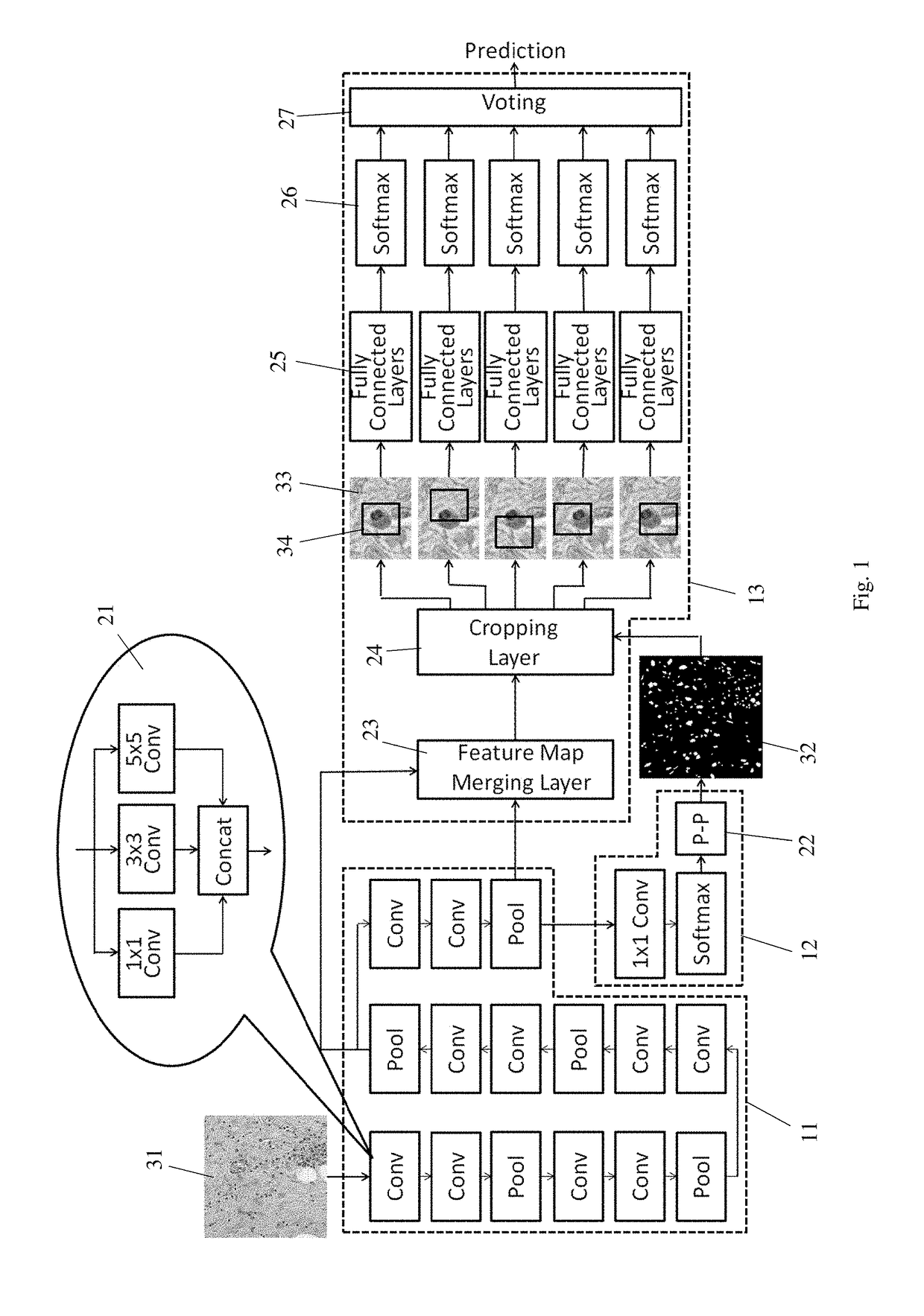
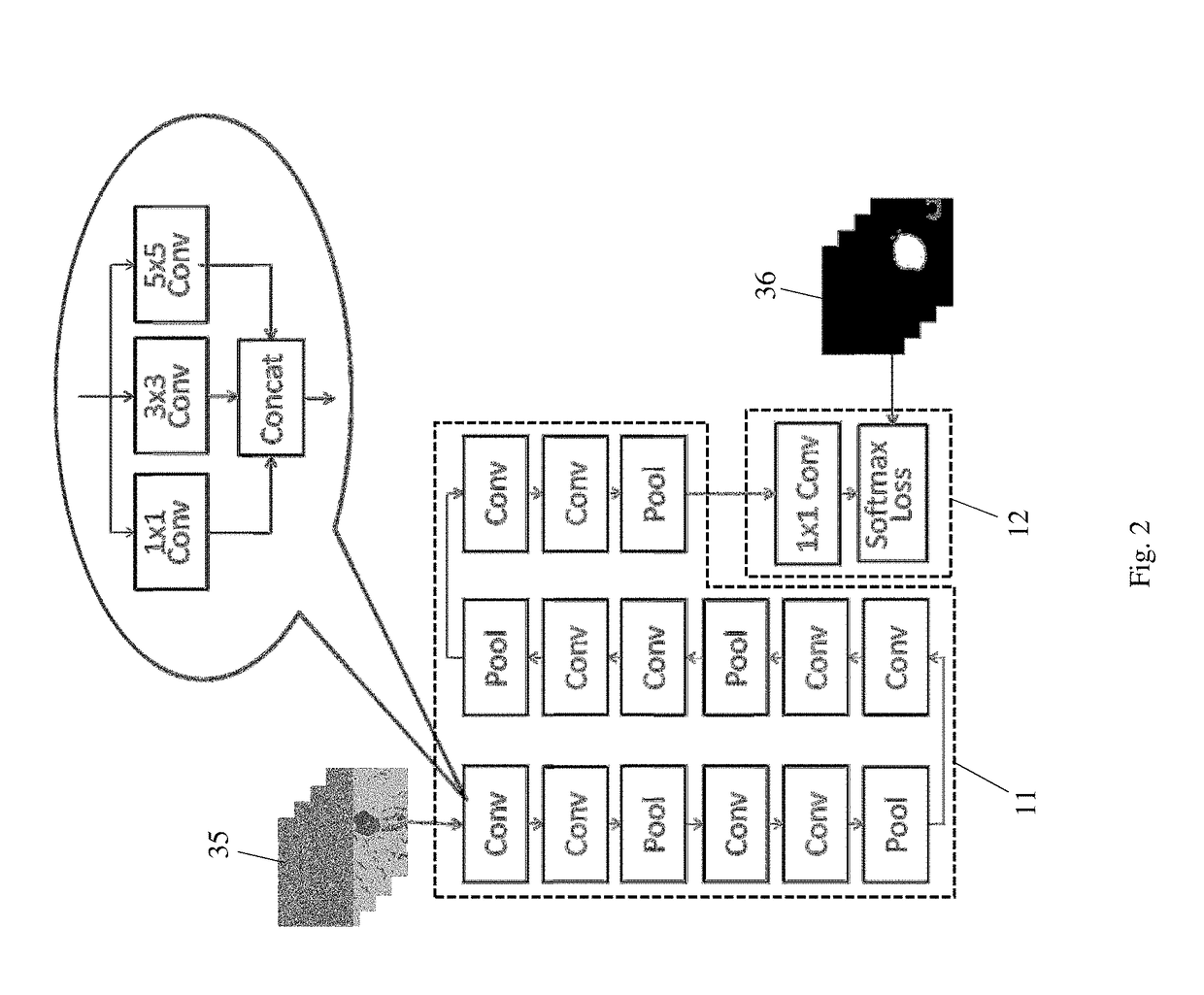
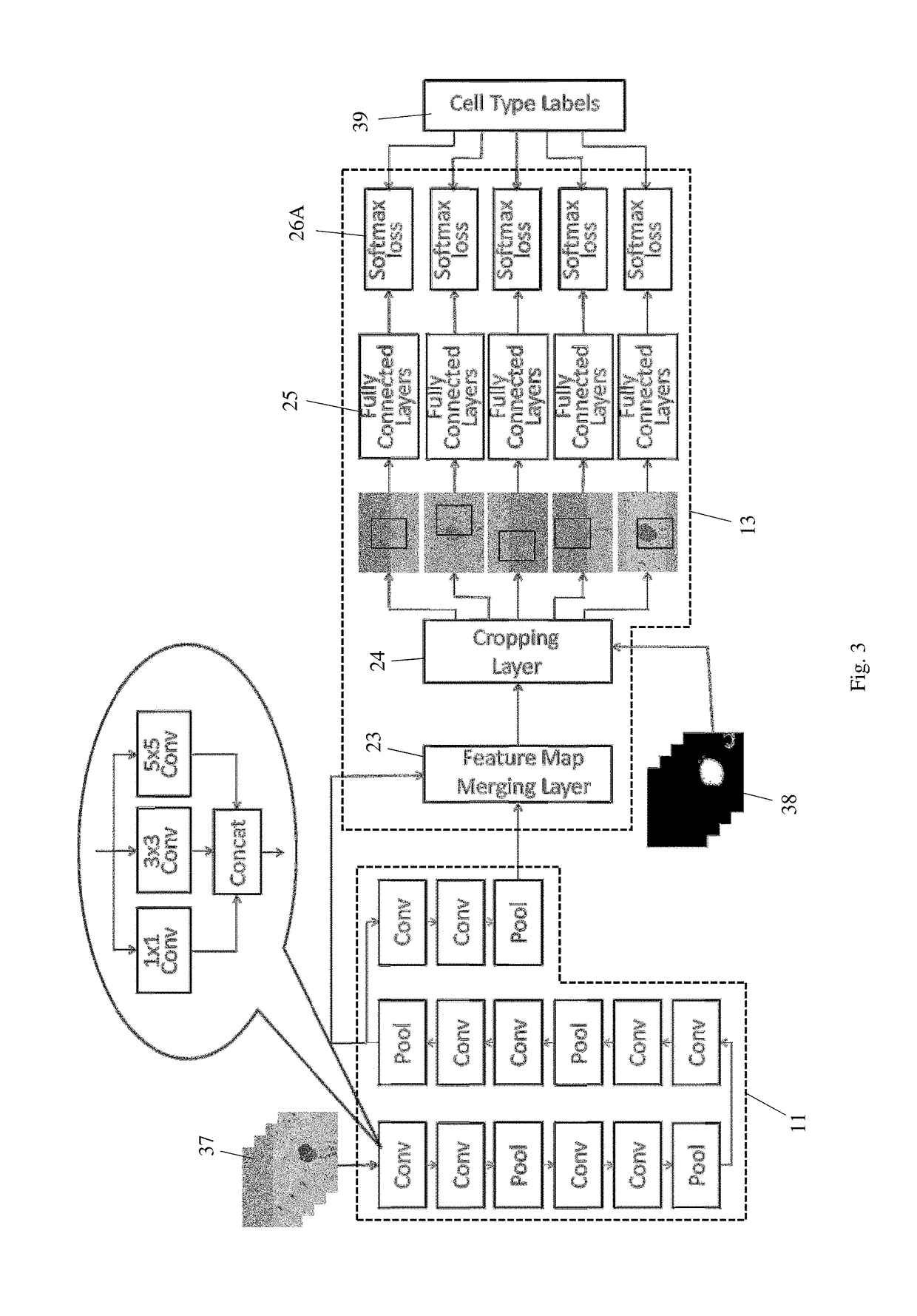
Method and system for detection and classification of cells using convolutional neural networks
ActiveUS20190065817A1Accurate cell segmentationAccurate classificationImage enhancementImage analysisFeature mappingArtificial neural network
An artificial neural network system implemented on a computer for cell segmentation and classification of biological images. It includes a deep convolutional neural network as a feature extraction network, a first branch network connected to the feature extraction network to perform cell segmentation, and a second branch network connected to the feature extraction network to perform cell classification using the cell segmentation map generated by the first branch network. The feature extraction network is a modified VGG network where each convolutional layer uses multiple kernels of different sizes. The second branch network takes feature maps from two levels of the feature extraction network, and has multiple fully connected layers to independently process multiple cropped patches of the feature maps, the cropped patches being located at a centered and multiple shifted positions relative to the cell being classified; a voting method is used to determine the final cell classification.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
Method and apparatus for providing real-time monitoring of an artifical neural network
ActiveUS20150106316A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesProcessor registerMulti dimensional
A circuit element of a multi-dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such circuit elements, (wherein a circuit element may be digital), a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension to form linked columns and rows of neuron / synapse circuit elements. In one embodiment, the rows and columns of circuit elements have read registers that are linked together by signal lines and clocked and controlled so as to output columnar data to an output register when a neuron / synapse data value is stored in the read register.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Method and system for detecting malicious behavioral patterns in a computer, using machine learning
InactiveUS20070294768A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer wormComputerized system
Method for detecting malicious behavioral patterns which are related to malicious software such as a computer worm in computerized systems that include data exchange channels with other systems over a data network. Accordingly, hardware and / or software parameters are determined in the computerized system that is can characterize known behavioral patterns thereof. Known malicious code samples are learned by a machine learning process, such as decision trees and artificial neural networks, and the results of the machine learning process are analyzed in respect to the behavioral patterns of the computerized system. Then known and unknown malicious code samples are identified according to the results of the machine learning process.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
Relevance score assignment for artificial neural networks
The task of relevance score assignment to a set of items onto which an artificial neural network is applied is obtained by redistributing an initial relevance score derived from the network output, onto the set of items by reversely propagating the initial relevance score through the artificial neural network so as to obtain a relevance score for each item. In particular, this reverse propagation is applicable to a broader set of artificial neural networks and / or at lower computational efforts by performing same in a manner so that for each neuron, preliminarily redistributed relevance scores of a set of downstream neighbor neurons of the respective neuron are distributed on a set of upstream neighbor neurons of the respective neuron according to a distribution function.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
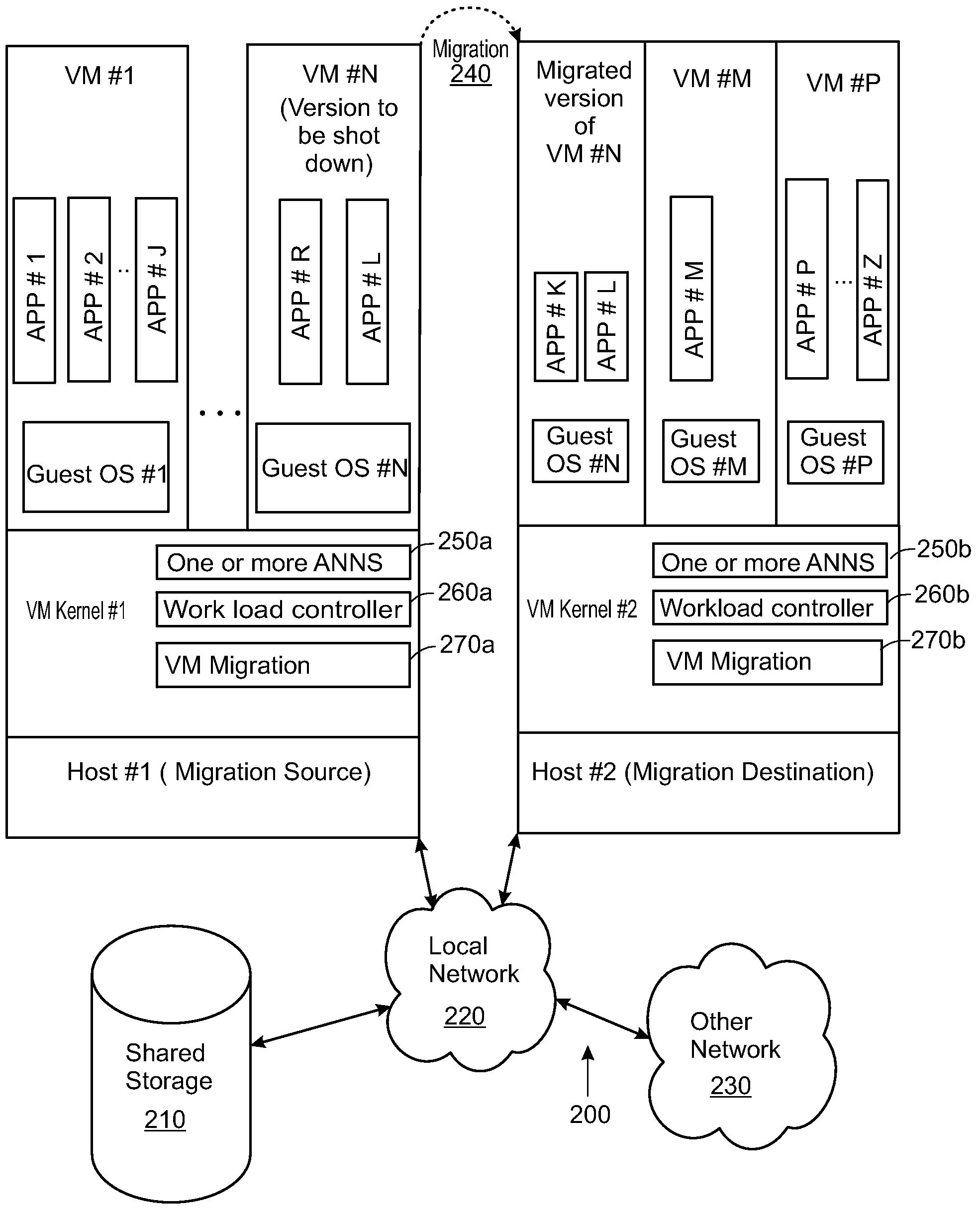
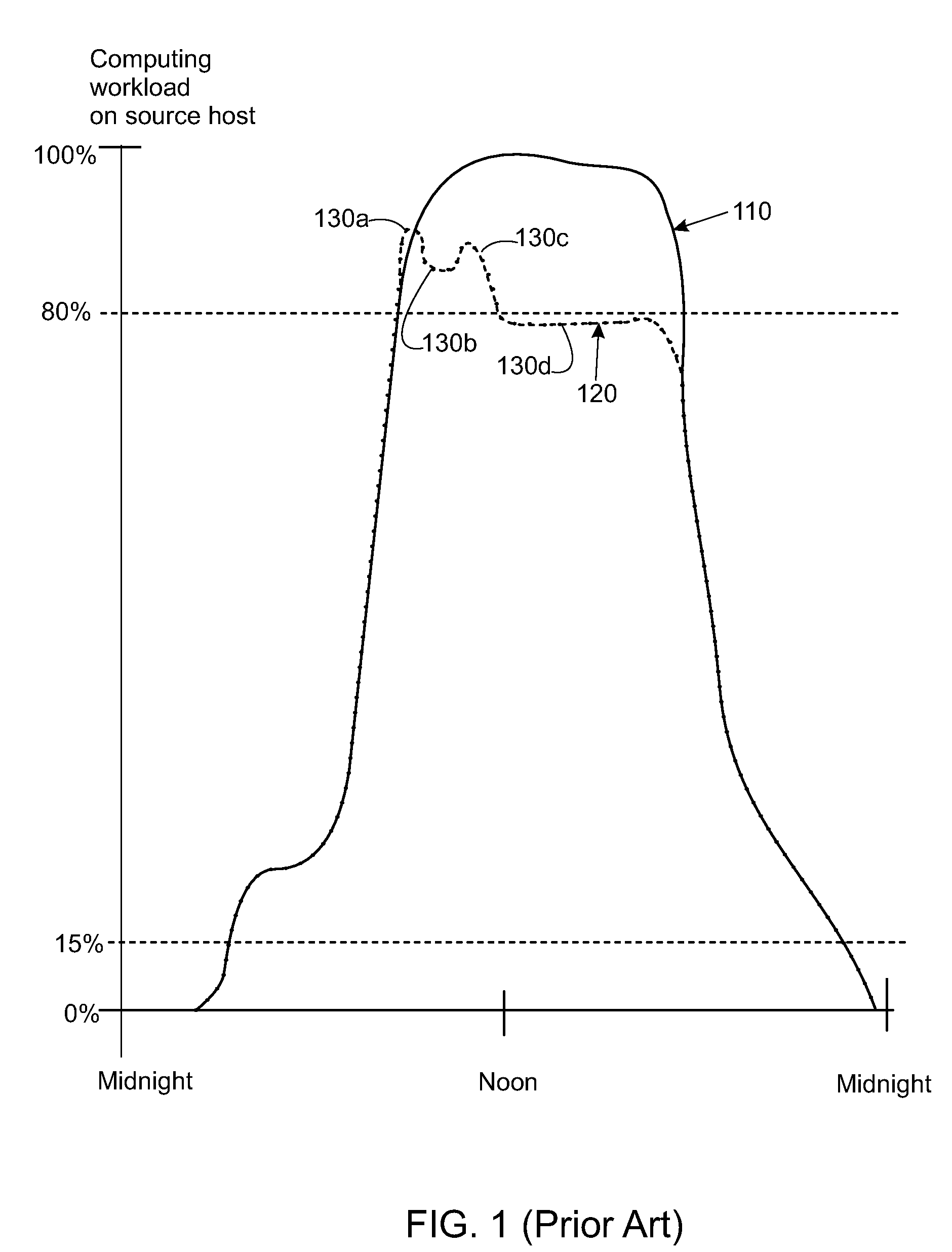
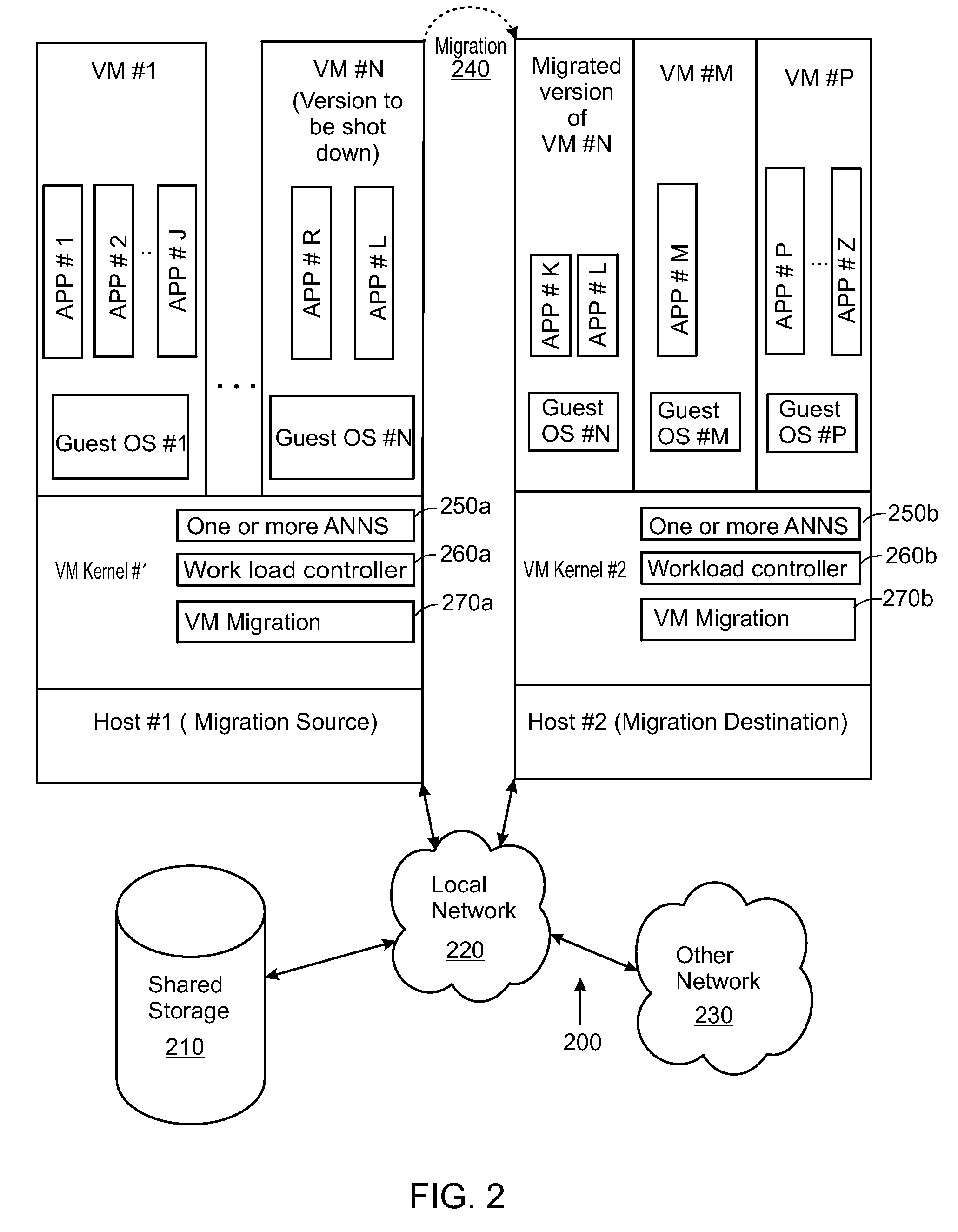
Artificial neural network for balancing workload by migrating computing tasks across hosts
Methods and apparatuses for balancing computing workload via migrating computing tasks are disclosed. An artificial neural network (ANN) is trained based on the workload distribution over time for a host. The ANN predicts the workload for the host, and an indication may be sent to migrate at least one computing task away from the host. The indication is sent when the method is operating in a proactive mode and when the predicted workload is outside of a desired operating range. Some embodiments monitor the workload; and automatically switch the method to the proactive mode, when a difference between the monitored workload and the predicted workload is small. Other embodiments monitor the workload; and automatically switch the method to a reactive mode, when the monitored workload is outside of a failsafe operating range for the particular host.
Owner:VMWARE INC
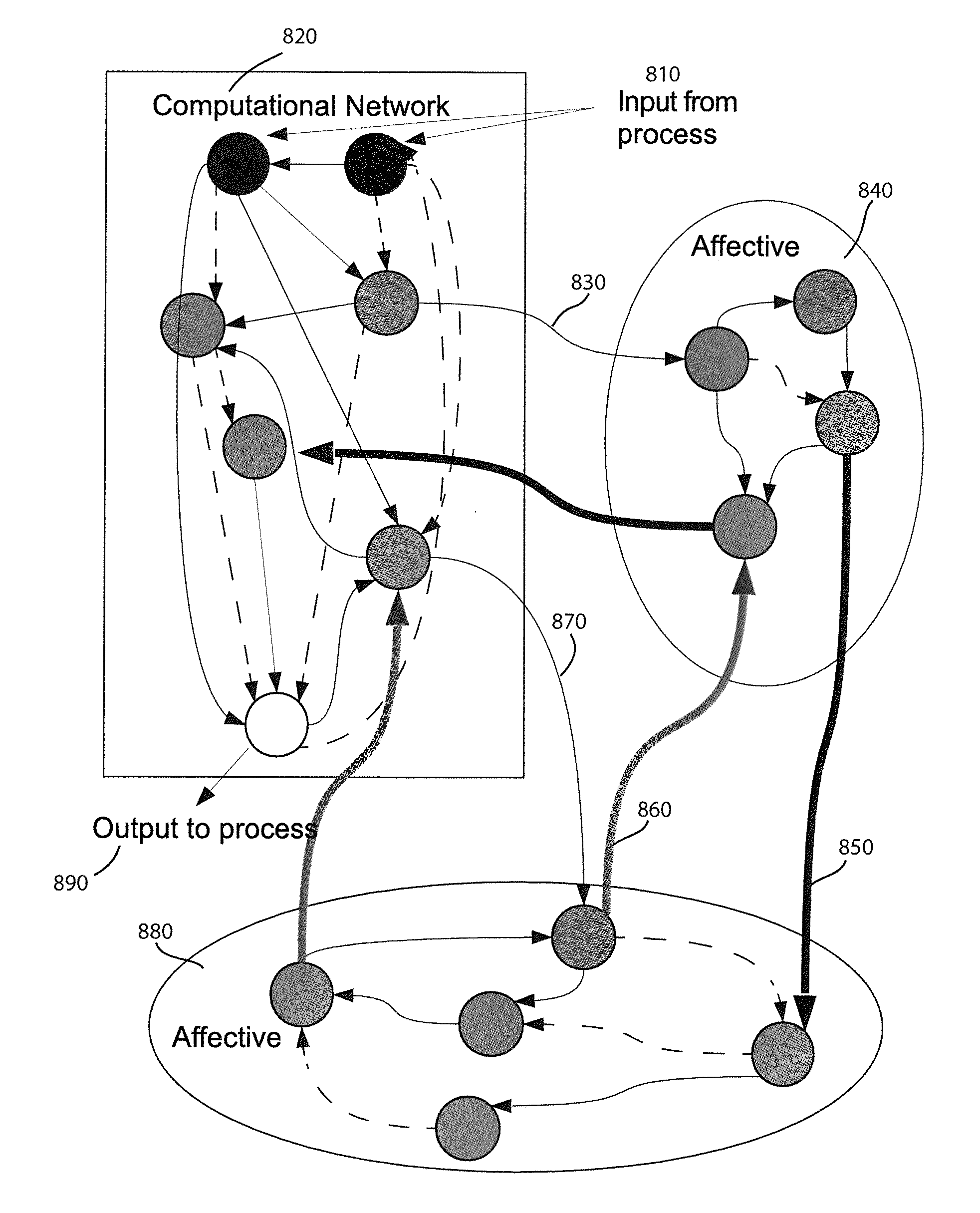
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network
ActiveUS20150106310A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsDigital dataComputational neuroscienceAnomaly detection
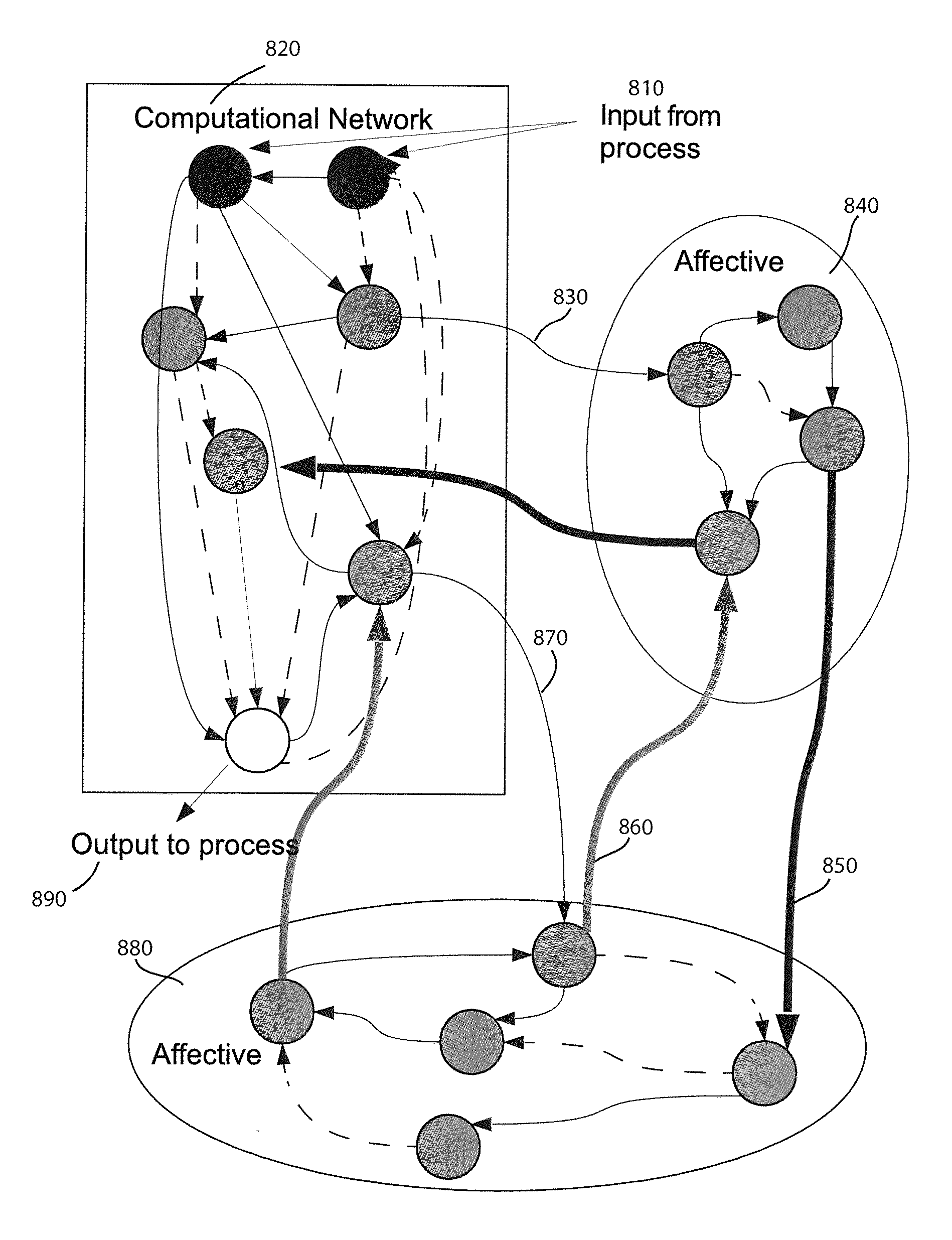
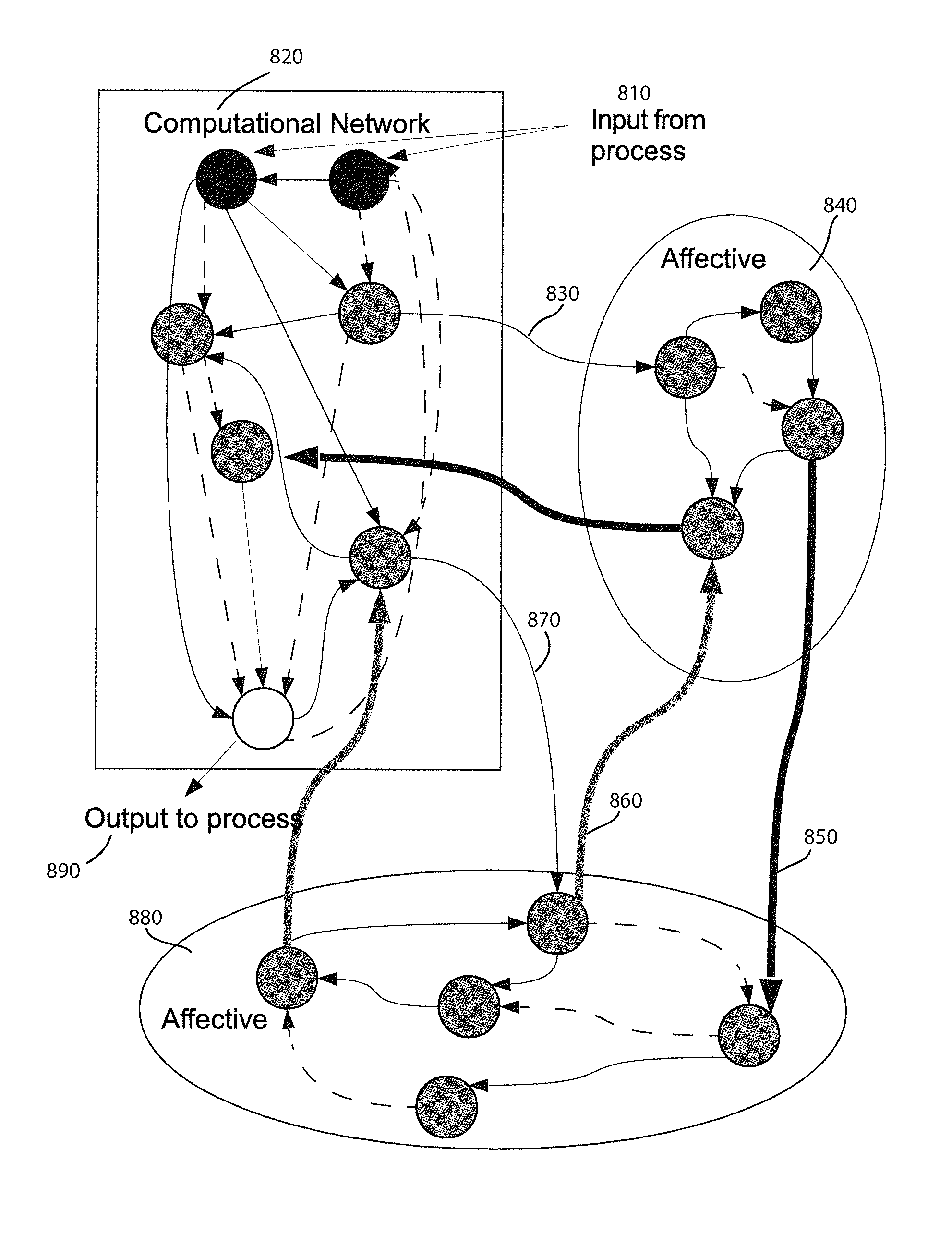
A method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture (NIDA) for an artificial neural network is disclosed. The method comprises constructing, in one embodiment, an artificial neural network embodiment in a multi-dimensional space in memory such that a neuron is connected by a synapse to another neuron. The neuron and the synapse each have parameters and have features of long-term potentiation and long-term depression. Furthermore, crossover and mutation are employed to select children of parents. Through learning, an initial network may evolve into a different network when NIDA is applied to solve different problems of control, anomaly detection and classification over selected time units. The apparatus comprises in one embodiment a computational neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with at least one affective network coupled to receive input data from an environment and to output data to the environment.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
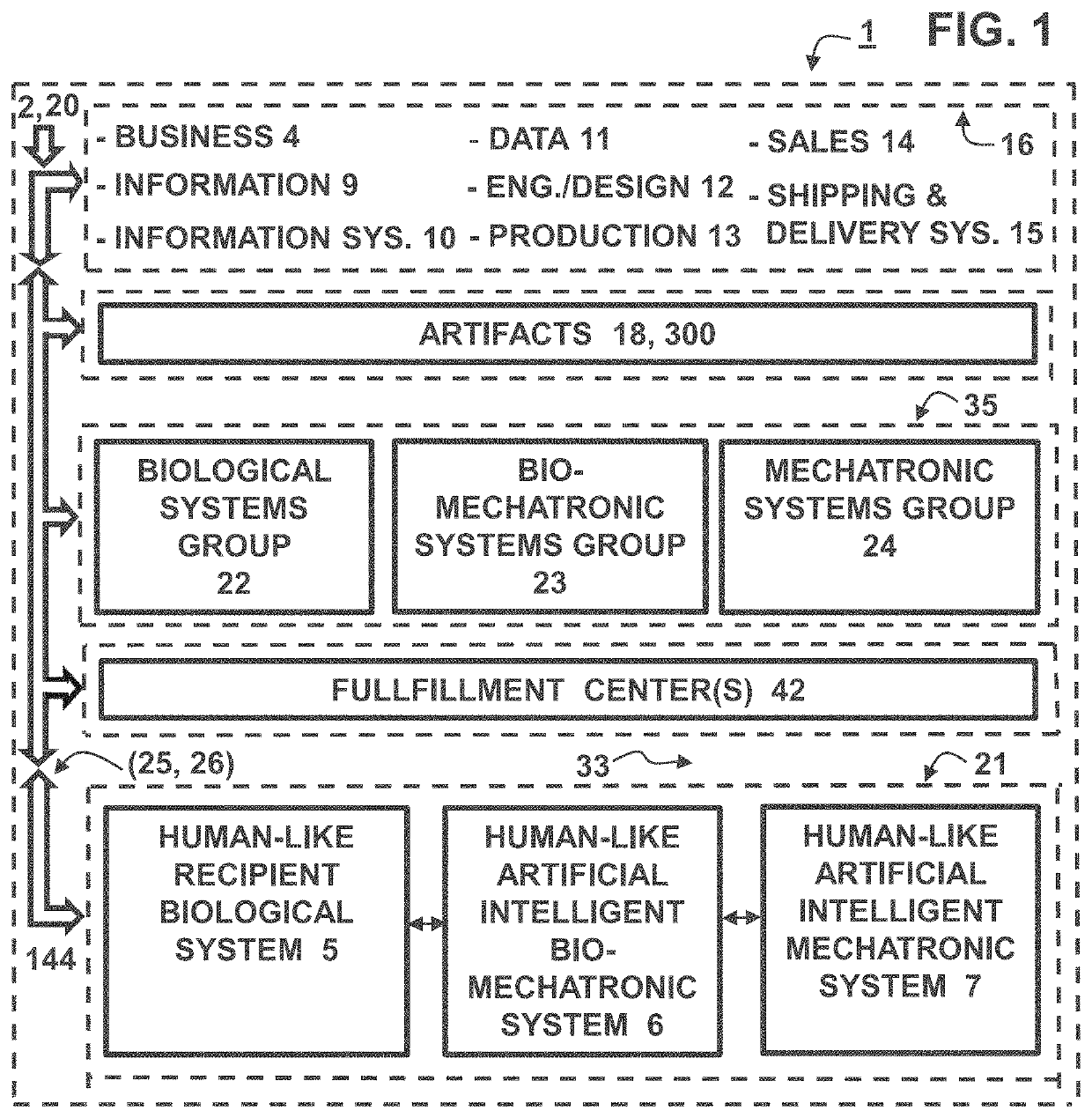
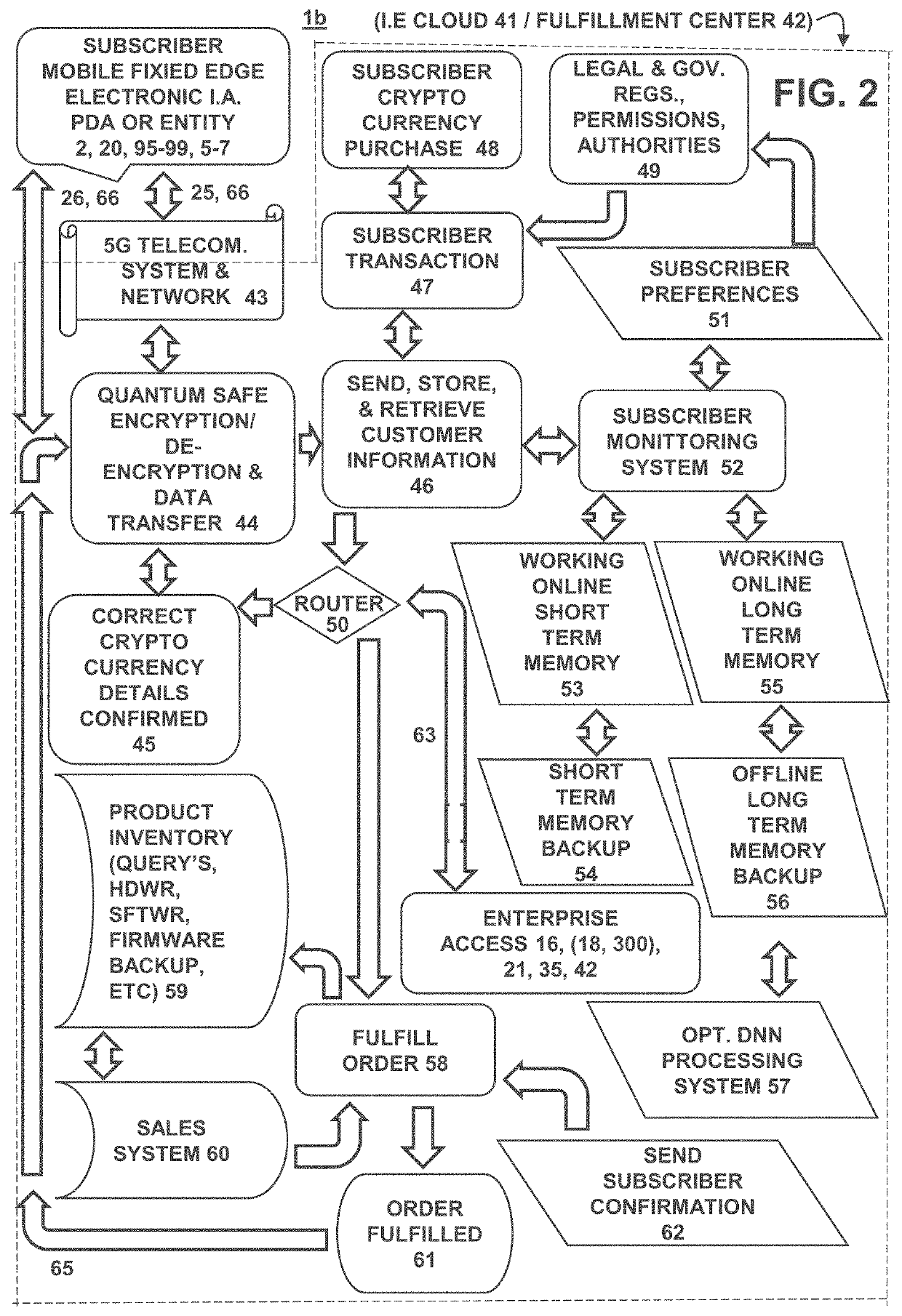
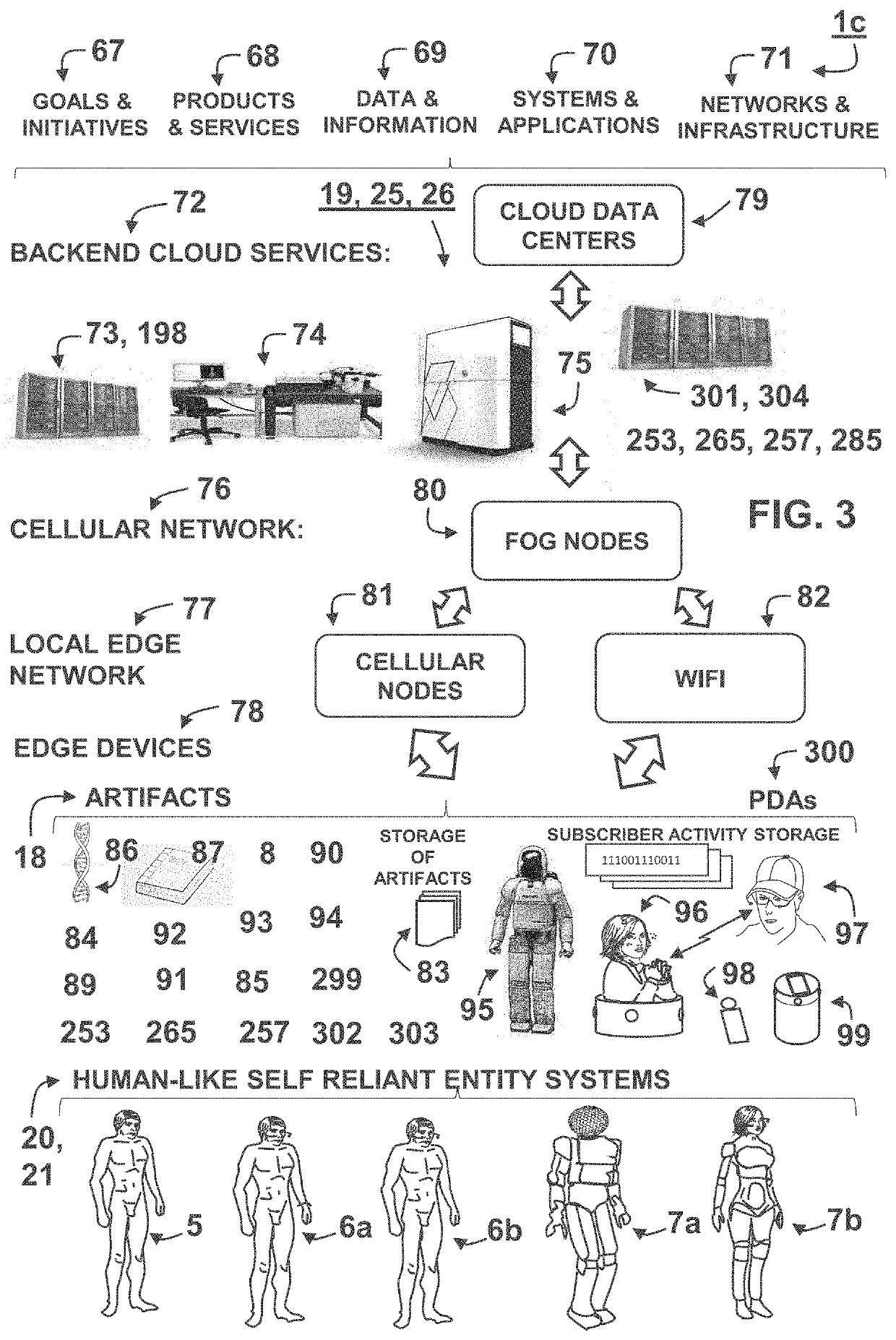
Human-like emulation enterprise system and method
ActiveUS20200218767A1Television system detailsBioelectric signal measurementBusiness enterpriseEngineering
An enterprise system and method for maintaining and transitioning humans to a human-like self-reliant entity is presented. Said system including at least one a biological, biomechatronic, and mechatronic entity with a biological or artificial neural network to at least one transform or maintain. Embodiments are provided to assist in the transition of human between a biological state to a bio-mechatronic and mechatronic entity. Said entity's biological, biomechatronic, and mechatronic subsystems are configured to communicate and interact with one another in order for said enterprise system to manage, configure, maintain, and sustain said entity throughout the entity's life-cycle. Subsystem embodiments and components supported by the enterprise system are presented.
Owner:VIRTUAL VIDEO BY RITCHEY LLC
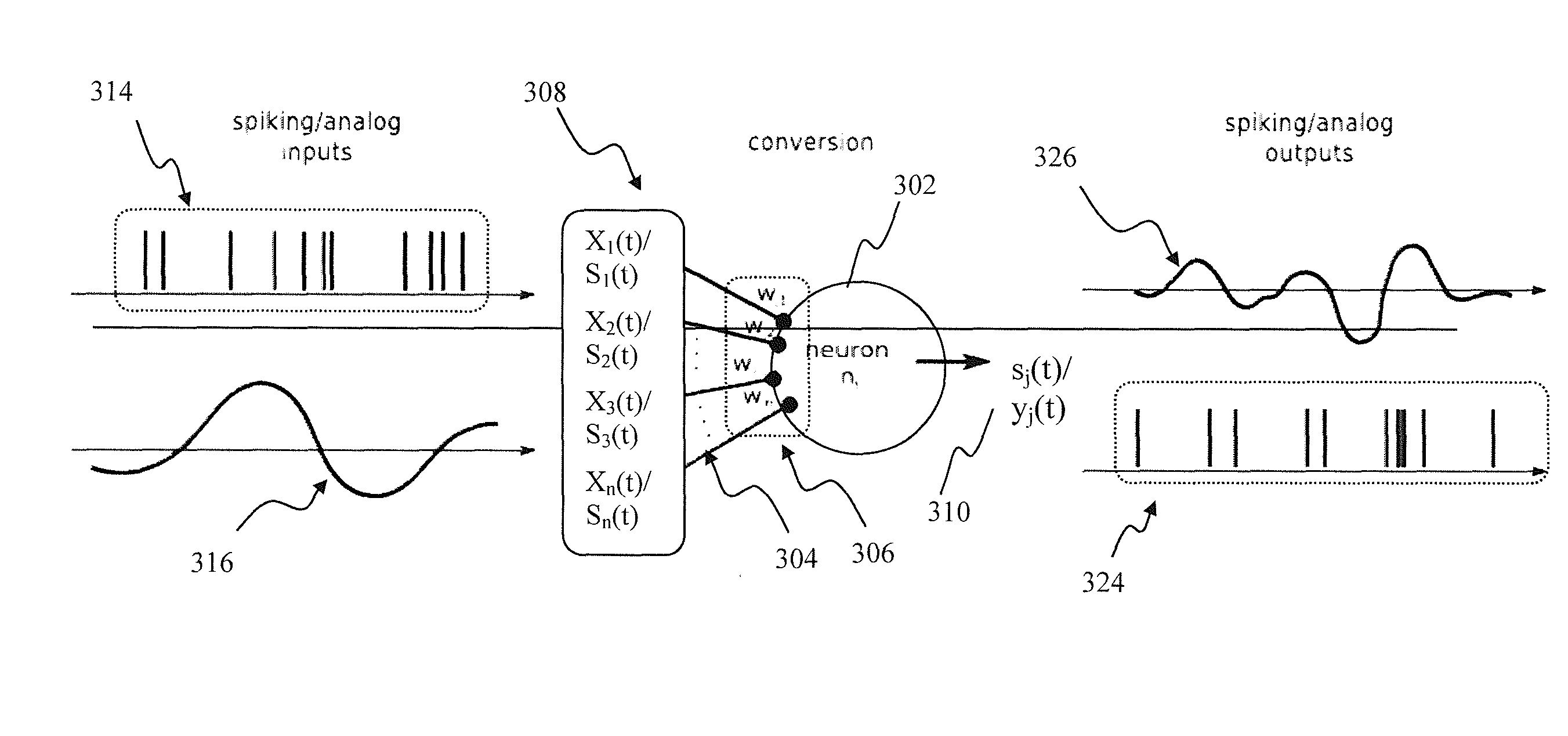
Apparatus and methods for implementing learning for analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Computational method for identifying adhesin and adhesin-like proteins of therapeutic potential
ActiveUS20050288866A1Easy to identifyLaborious and time-consume and expensiveBiological material analysisSurgeryDipeptideMicrobiology
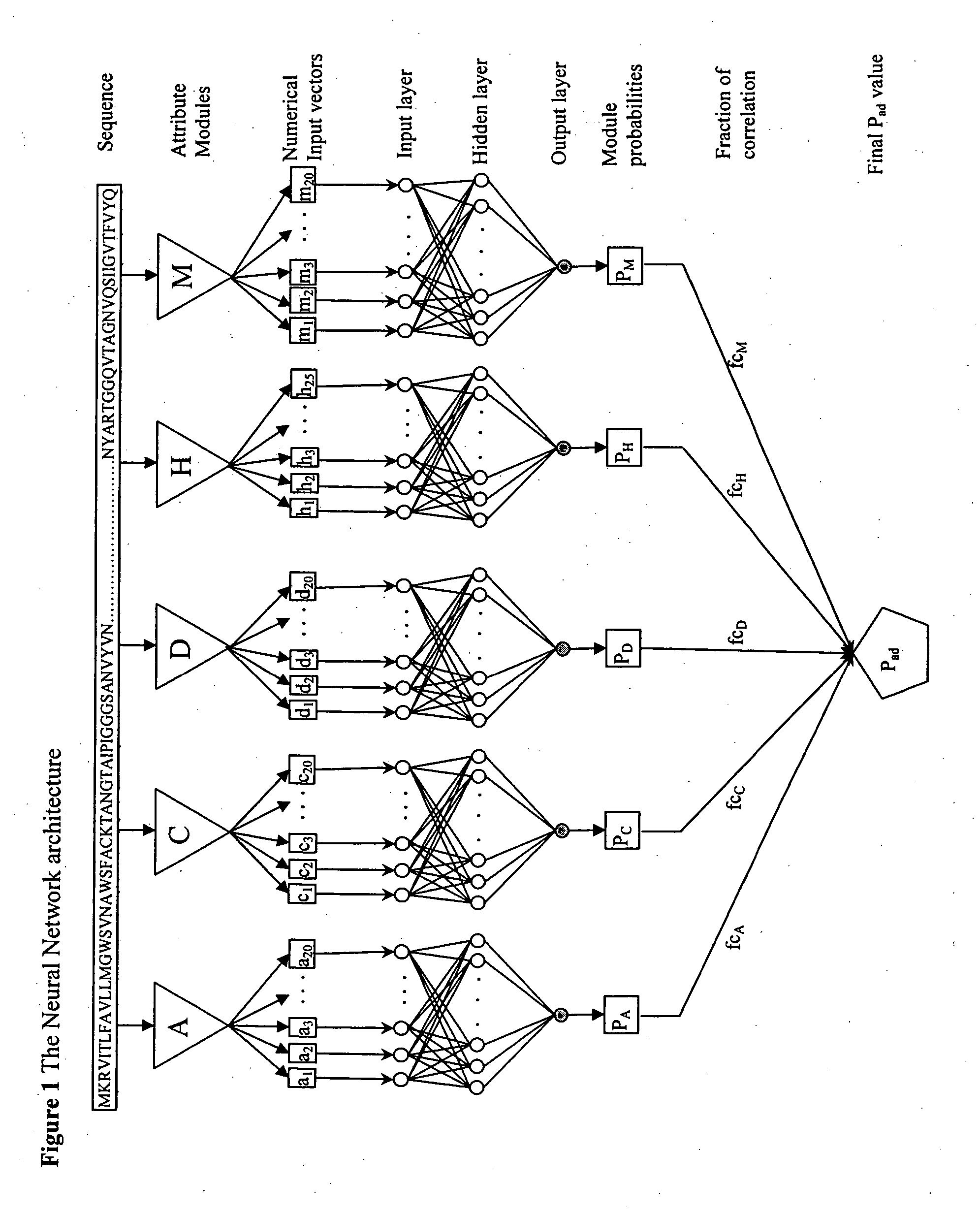
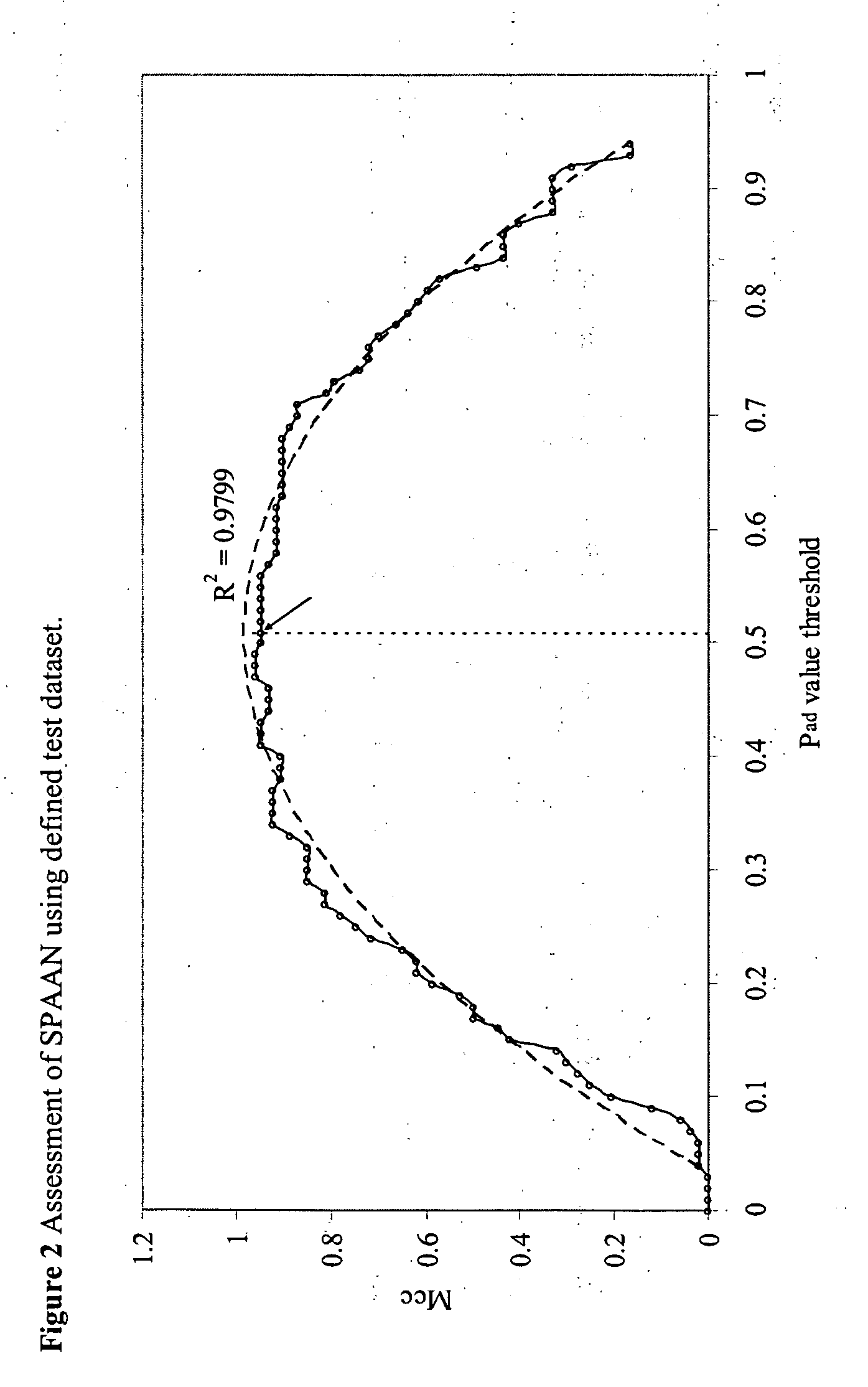
A computational method for identifying adhesin and adhesin-like proteins, said method comprising steps of computing the sequence-based attributes of a neural network software wherein the attributes are (i) amino acid frequencies, (ii) multiplet frequency, (iii) dipeptide frequencies, (iv),charge composition, and (v) hydrophobic composition, training the artificial neural Network (ANN) for each of the computed five attributes, and identifying the adhesin and adhesin-like proteins having probability of being an adhesin (Pad) as ≧0.51; a computer system for performing the method; and genes and proteins encoding adhesin and adhesin-like proteins.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
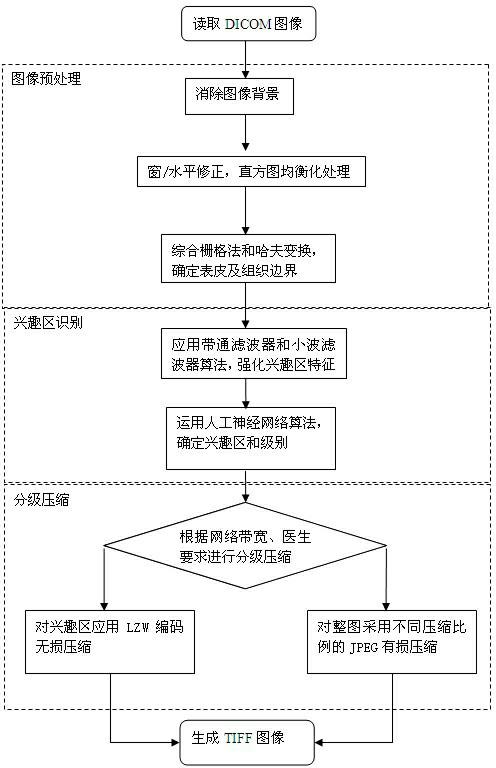
Method for automatic recognition and stage compression of medical image regions of interest based on artificial neural network
InactiveCN102332162AEasy to readIncrease transfer rateImage analysisBiological neural network modelsHuman bodyTagged Image File Format
The invention relates to a method for automatic recognition and stage compression of medical image regions of interest based on an artificial neural network. Medical image files in a digital diagnostic system are generally larger, and due to the limitation by factors of bandwidth and the like, the transmission speed is low, the effect is not good, and the diagnosis quality is influenced. By the method, medical digital images are subjected to noise elimination, the tissue outline of a human body is recognized, tissue images are subjected to multiple times of overlay operation, image features of the regions of interest are strengthened, feature values are extracted, classification is performed by using an artificial neural network method, the regions of interest and corresponding levels are determined, and tagged image file format (TIFF) images are generated in different compression modes according to different levels of the regions of interest and non-regions of interest. By the method, the medical image files are greatly lessened, the transmission speed is increased, and effective necessary information used for diagnosis and treatment in the images is kept, so the method facilitates the reading of doctors, and can be applied to the digital diagnostic system and a remote medical system, and improve the diagnosis and treatment efficiency and effect.
Owner:BAILEAD TECH CO LTD
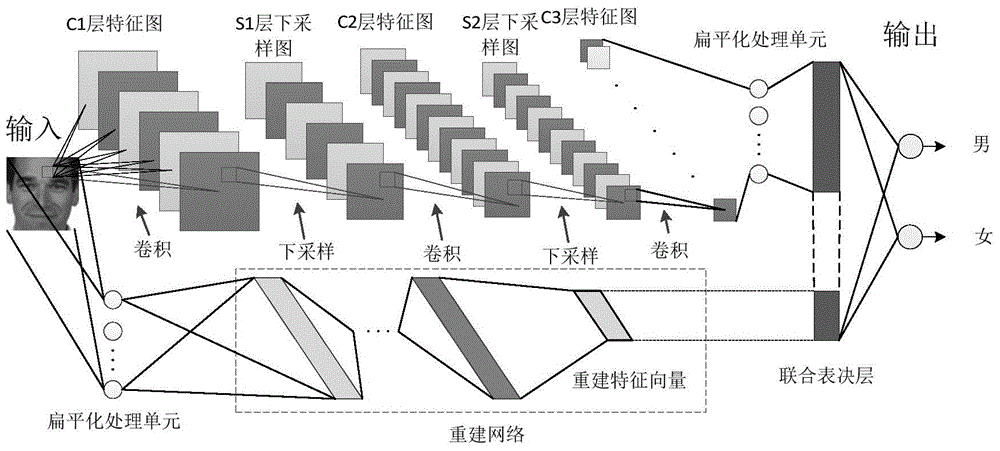
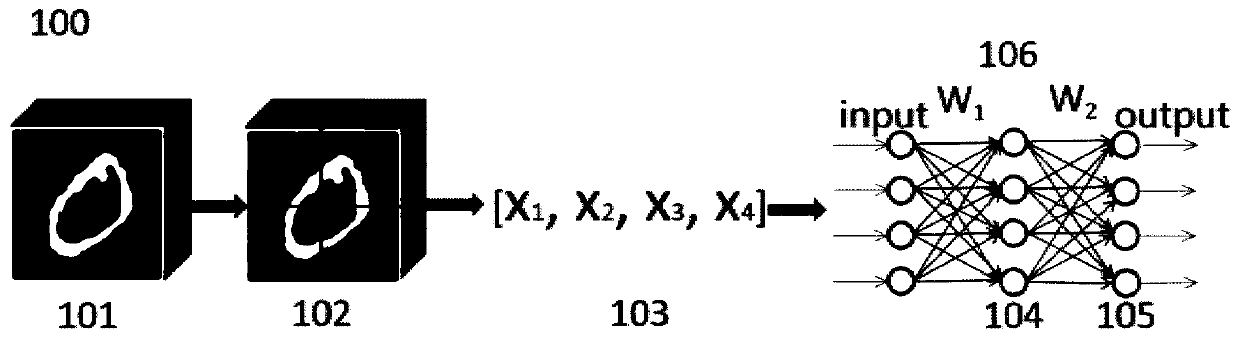
Network constructing method for human face identification, identification method and system
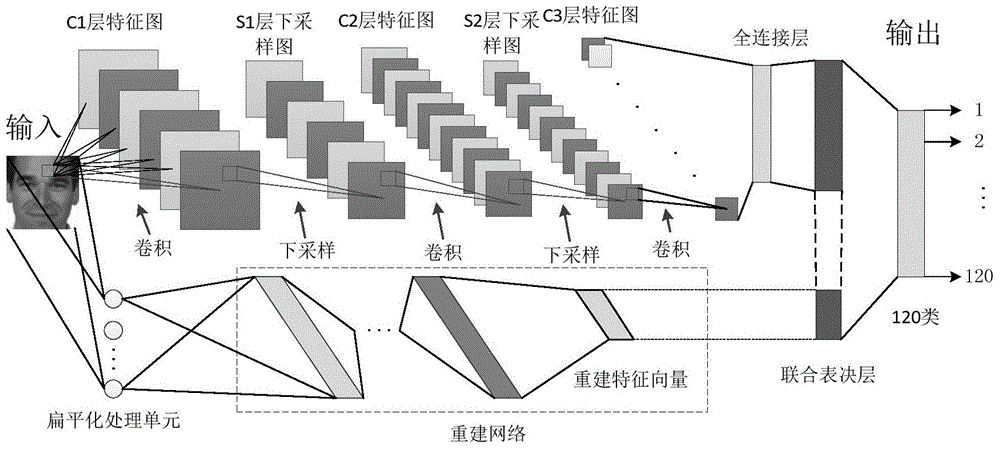
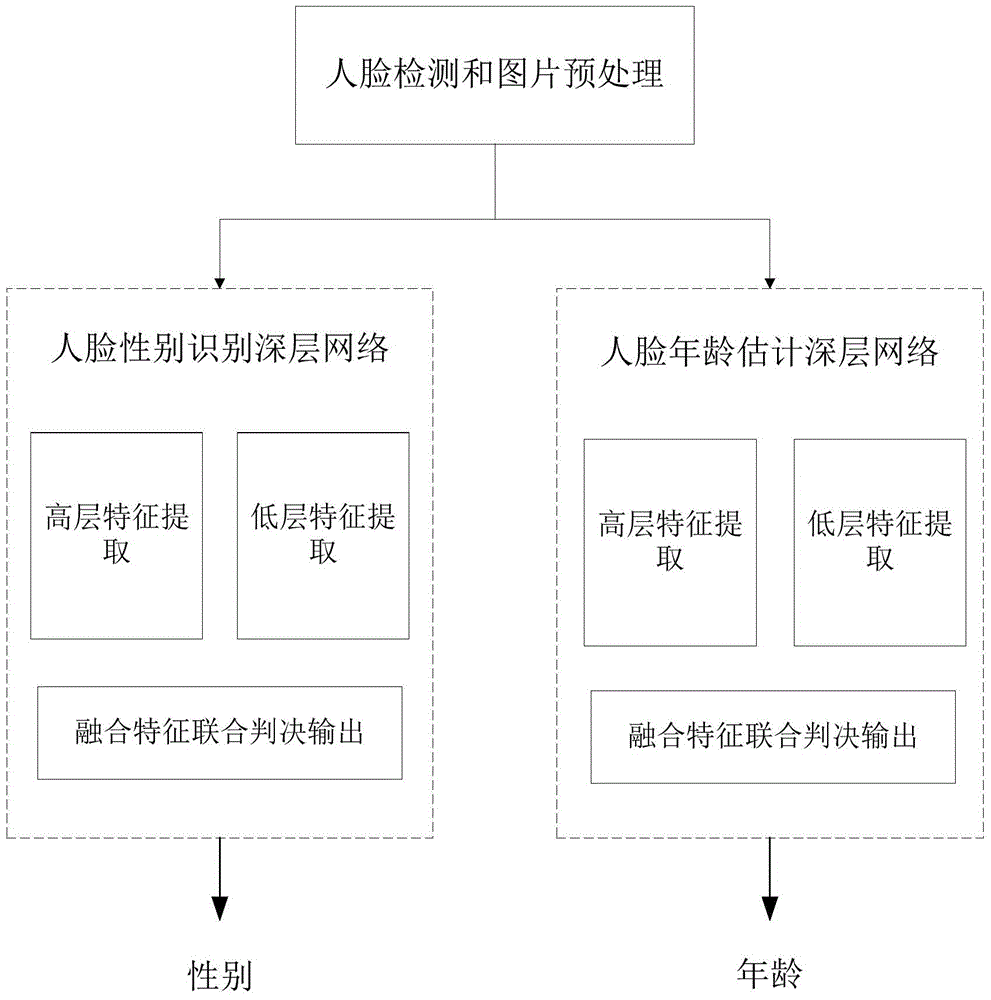
ActiveCN105095833AImprove learning abilityImprove generalization abilityBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionAge estimationGroup of pictures
The invention discloses a deeper layer network constructing method used for gender identification or age estimation based on human face. The method includes a step (101) dividing all training pictures into a plurality of groups; (102) extracting high layer features of a group of pictures based on a convolution neural network and thereby obtaining a first matrix composed of the high layer feature vectors, and extracting low layer and global features of the same group of the training images based on an artificial neural network and thereby obtaining a second matrix composed of the low layer feature vectors, obtaining a group of gender identification or age estimation results based on the extract first matrix, the second matrix and the defined judgment formula, wherein the values of a first weight matrix W1, a second weight matrix w2, an offset matrix b and an adjusting weight beta in the defined judgment formula are updated by utilizing an error back propagation algorithm and the final values of the parameters are obtained and the network construction is completed. Judgment of age and gender of a human face is performed based on the judgment formula determined according to the values of the parameters when the network construction is completed.
Owner:HENGFENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with visualization of neural pathways
ActiveUS20150106306A1Slow visualizationUnderstand biological neural system behaviorNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNerve networkPartition of unity
A method and apparatus for constructing one of a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network and a neural network array comprises one of a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture, a dynamic artificial neural network array and a neural network array of electrodes associated with neural tissue such as a brain, the method and apparatus having a special purpose display processor. The special purpose display processor outputs a display over a period of selected reference time units to demonstrate a neural pathway from, for example, one or a plurality of input neurons through intermediate destination neurons to an output neuron in three dimensional space. The displayed neural network may comprise neurons and synapses in different colors and may be utilized, for example, to show the behavior of a neural network for classifying hand-written digits between values of 0 and 9 or recognizing vertical / horizontal lines in a grid image of lines.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
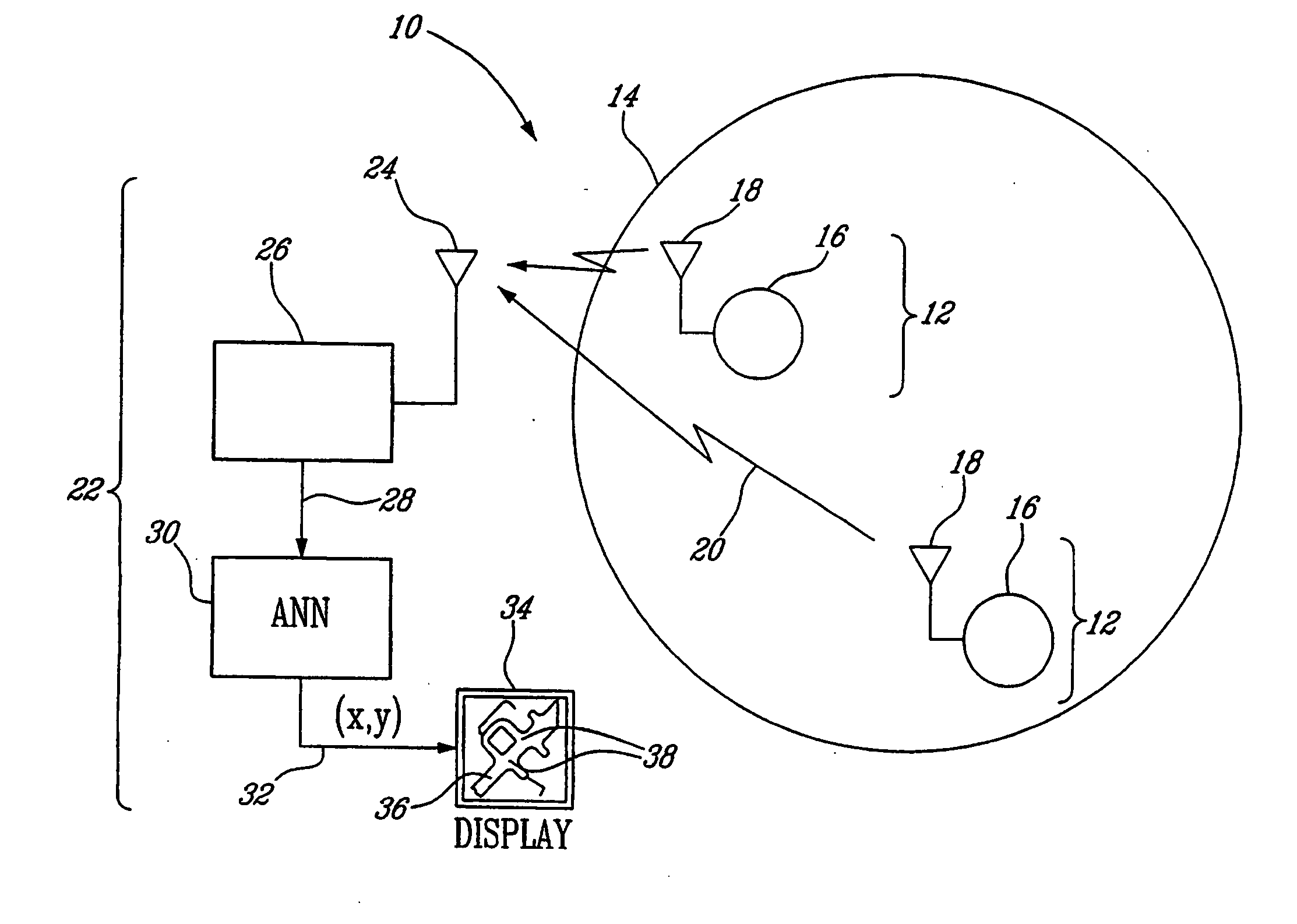
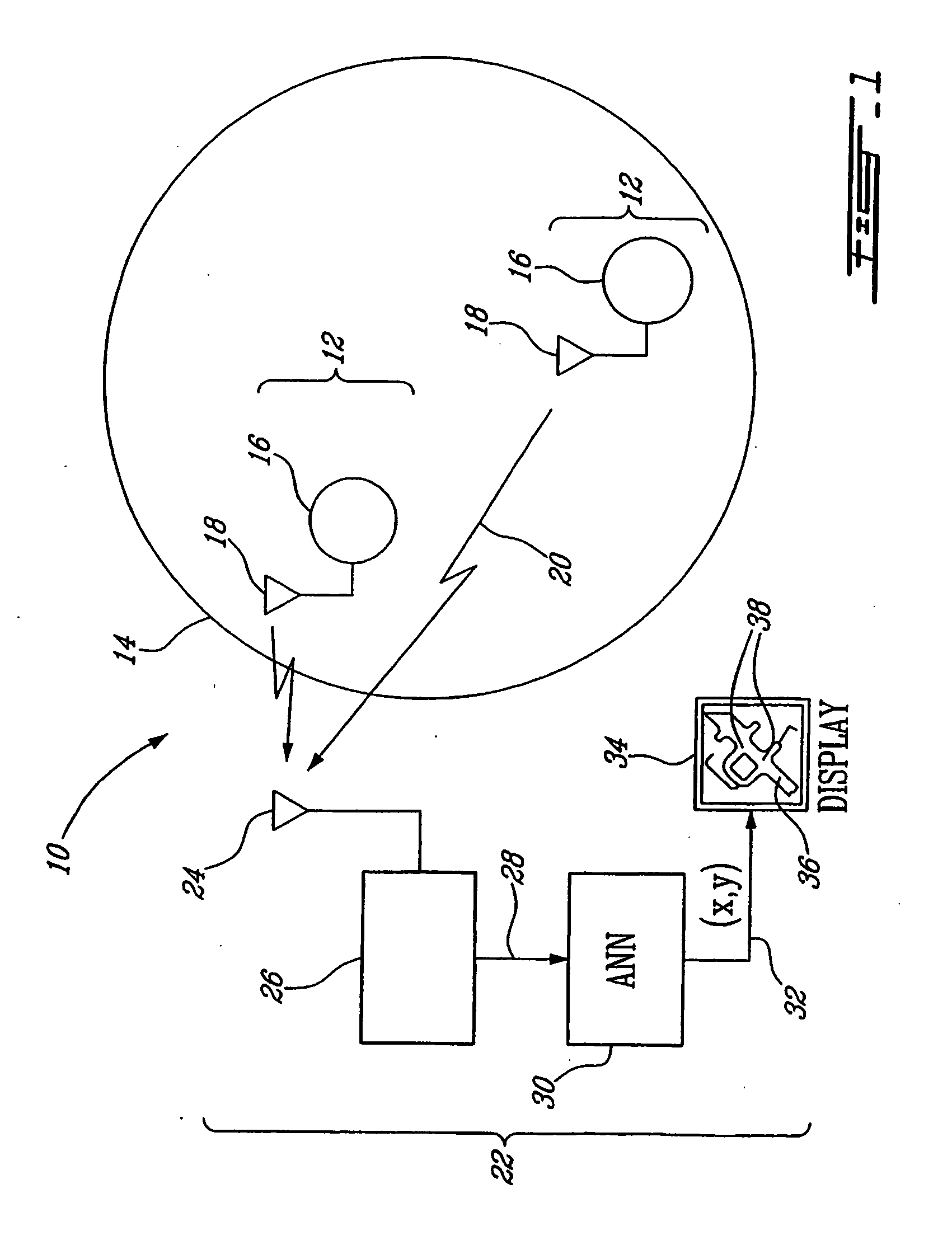
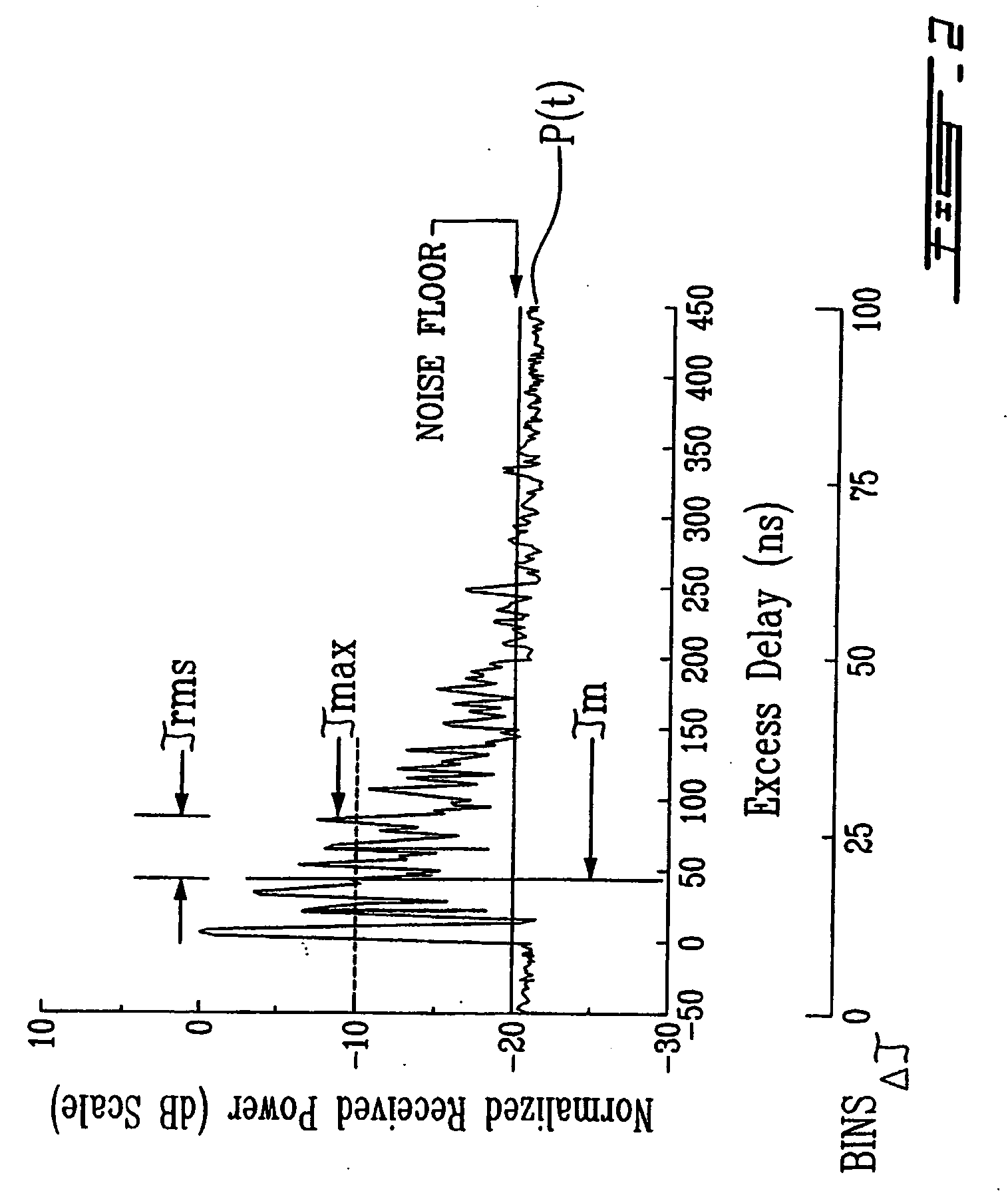
Method and system for indoor geolocation using an impulse response fingerprinting technique
ActiveUS20070010956A1Minimize error functionPolarisation/directional diversityDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionData setIndoor geolocation
A system and method for predicting the location of a transmitter in an indoor zone of interest, including fixed receiver for receiving a signal from the transmitter, the receiver deriving a fingerprint from the received signal, and a trained neural network. The trained neural network predicts the transmitter location from the fingerprint. The method includes receiving a signal transmitted from the transmitter at a fixed-location receiver, deriving a fingerprint from the received signal, supplying the fingerprint to a trained neural network, and reading the predicted location from the neural network. The artificial neural network may further be trained and include a plurality of weights and biases is also shown. The method may include collecting a training data set of fingerprints and corresponding locations, inputting the training data set to the neural network, and adjusting the weights and biases by minimising a sum of squares error function.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE +1
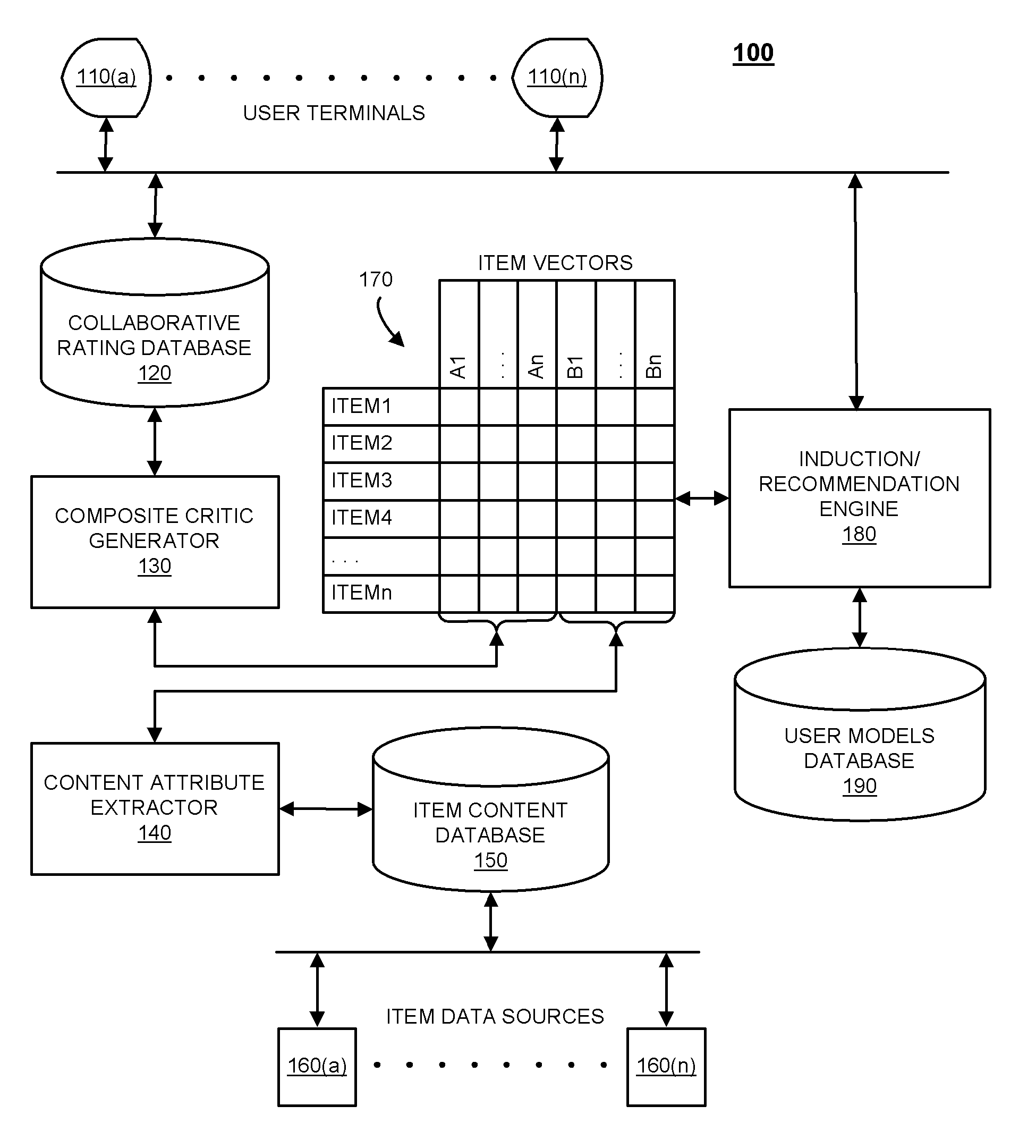
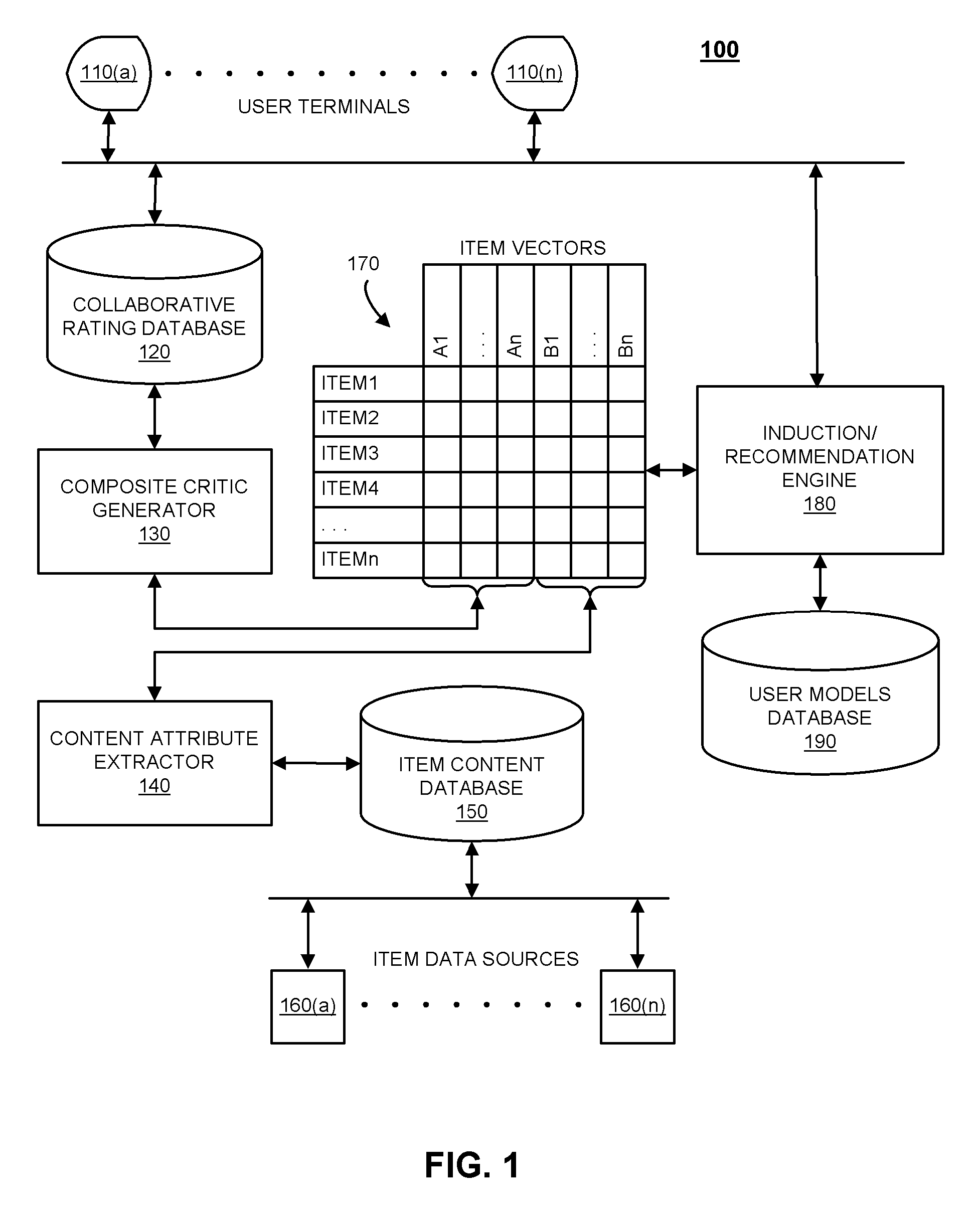
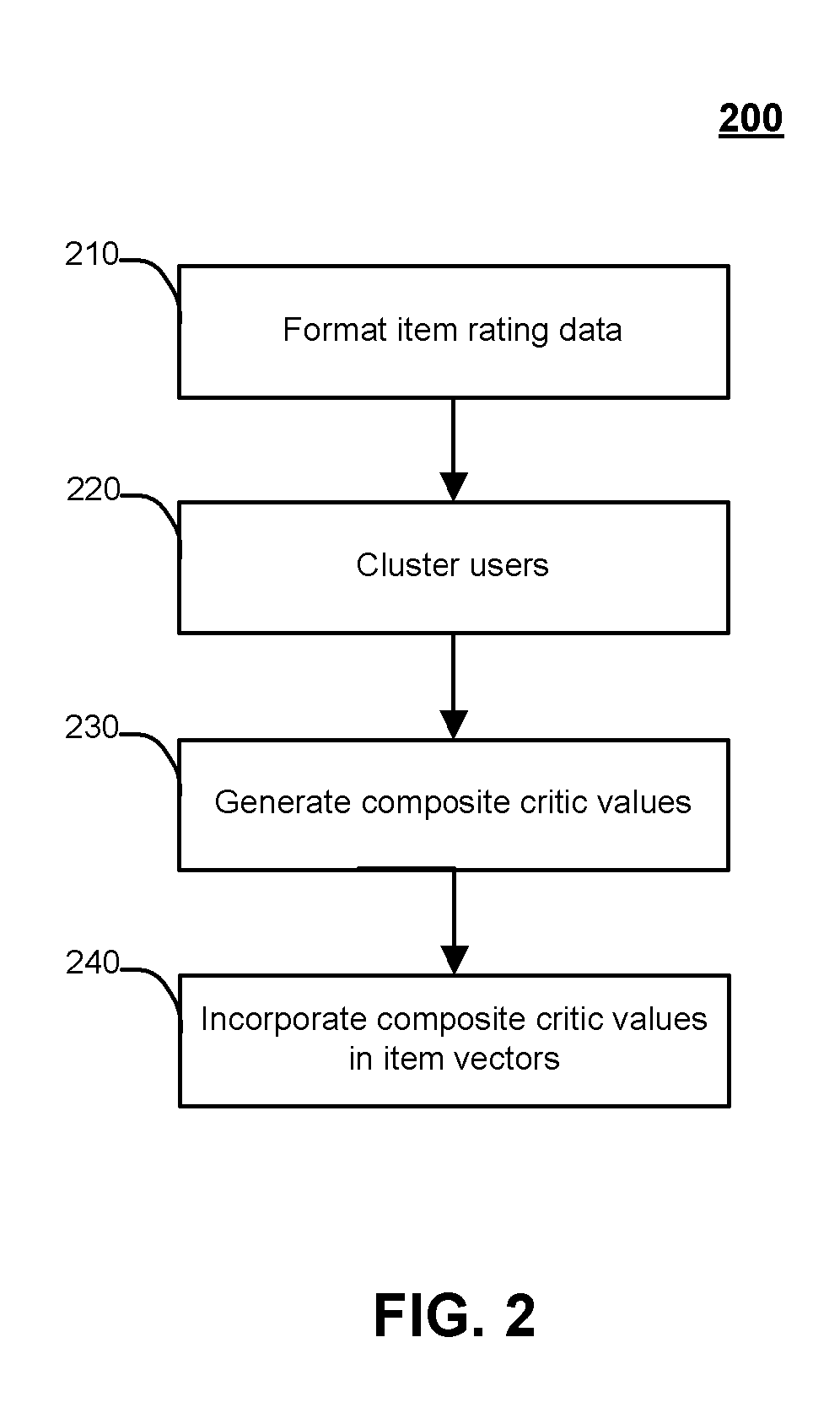
Systems and methods for supplementing content-based attributes with collaborative rating attributes for recommending or filtering items
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for supplementing content-based attributes with collaborative rating attributes for recommending or filtering items. Collaborative rating data may be consolidated into “composite critics” which serve as item quality rating attributes. These attributes may be used in conjunction with content-based attributes to generate user preference models. Composite critics may be formed using data clustering methods such that users with similar tastes may be grouped together. The user preference models may be induced using machine learning processes, such as decision trees, artificial neural networks, support vector machines, and / or statistical techniques. In some embodiments, composite critics may represent a small number of users or professional critics selected for having differing sensibilities and who rate most or all items according to those sensibilities.
Owner:FOURTHWALL MEDIA
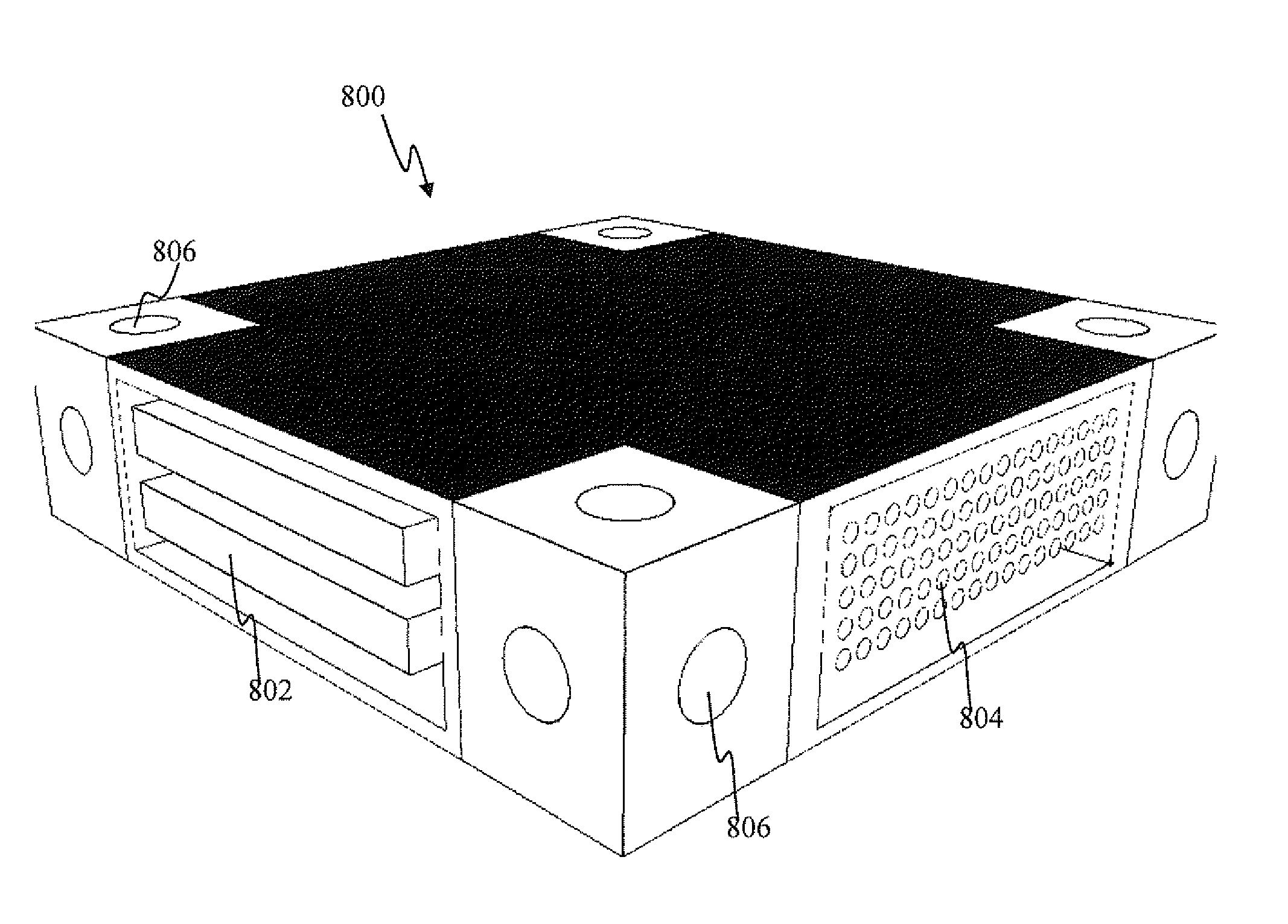
Intelligent modular robotic apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140019392A1Increased compact structureHigh densityDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNegative feedbackBiological body
Apparatus and methods for an extensible robotic device with artificial intelligence and receptive to training controls. In one implementation, a modular robotic system that allows a user to fully select the architecture and capability set of their robotic device is disclosed. The user may add / remove modules as their respective functions are required / obviated. In addition, the artificial intelligence is based on a neuronal network (e.g., spiking neural network), and a behavioral control structure that allows a user to train a robotic device in manner conceptually similar to the mode in which one goes about training a domesticated animal such as a dog or cat (e.g., a positive / negative feedback training paradigm) is used. The trainable behavior control structure is based on the artificial neural network, which simulates the neural / synaptic activity of the brain of a living organism.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for constructing a dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA)
ActiveUS20150106314A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkAnomaly detection
A circuit element of a multi-dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such circuit elements, (wherein a circuit element or component thereof may be analog or digital), a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension, a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension and, optionally, a third destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a third synapse. The DANNA may thus form multiple levels of neuron and synapse circuit elements. In one embodiment, multiples of eight inputs may be selectively received by the circuit element selectively functioning as one of a neuron and a synapse. The dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a special purpose processor for performing one of a control, anomaly detection and classification application and may comprise a first structure connected to a neuroscience-inspired dynamic artificial neural network (NIDA), comprise substructures thereof or be combined with other neural networks.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Apparatus and methods for implementing learning for analog and spiking signals in artificial neural networks
Apparatus and methods for universal node design implementing a universal learning rule in a mixed signal spiking neural network. In one implementation, at one instance, the node apparatus, operable according to the parameterized universal learning model, receives a mixture of analog and spiking inputs, and generates a spiking output based on the model parameter for that node that is selected by the parameterized model for that specific mix of inputs. At another instance, the same node receives a different mix of inputs, that also may comprise only analog or only spiking inputs and generates an analog output based on a different value of the node parameter that is selected by the model for the second mix of inputs. In another implementation, the node apparatus may change its output from analog to spiking responsive to a training input for the same inputs.
Owner:PONULAK FILIP
Contamination level estimation method for high voltage insulators
ActiveUS20160117845A1Affects colorReadily apparentImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
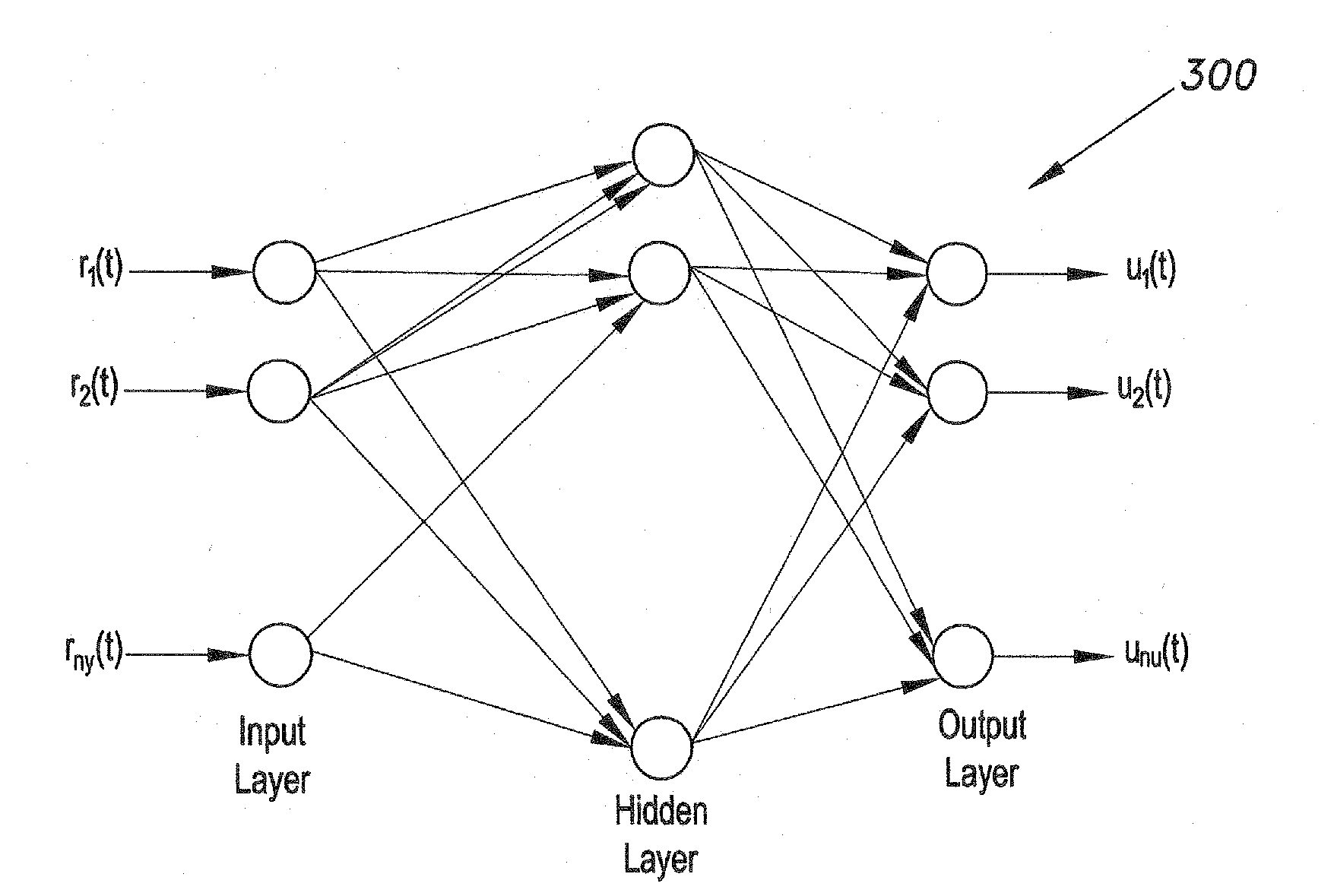
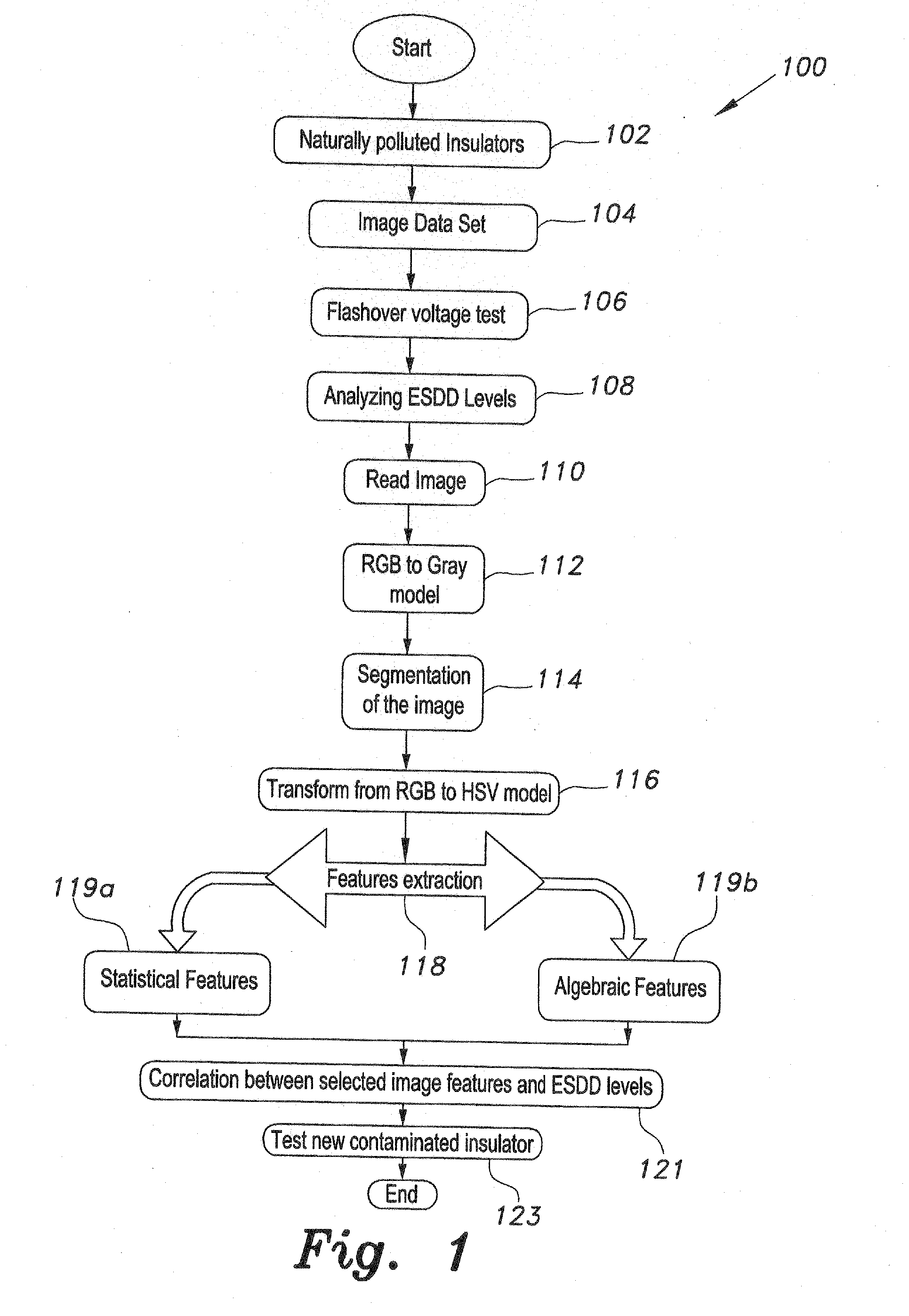
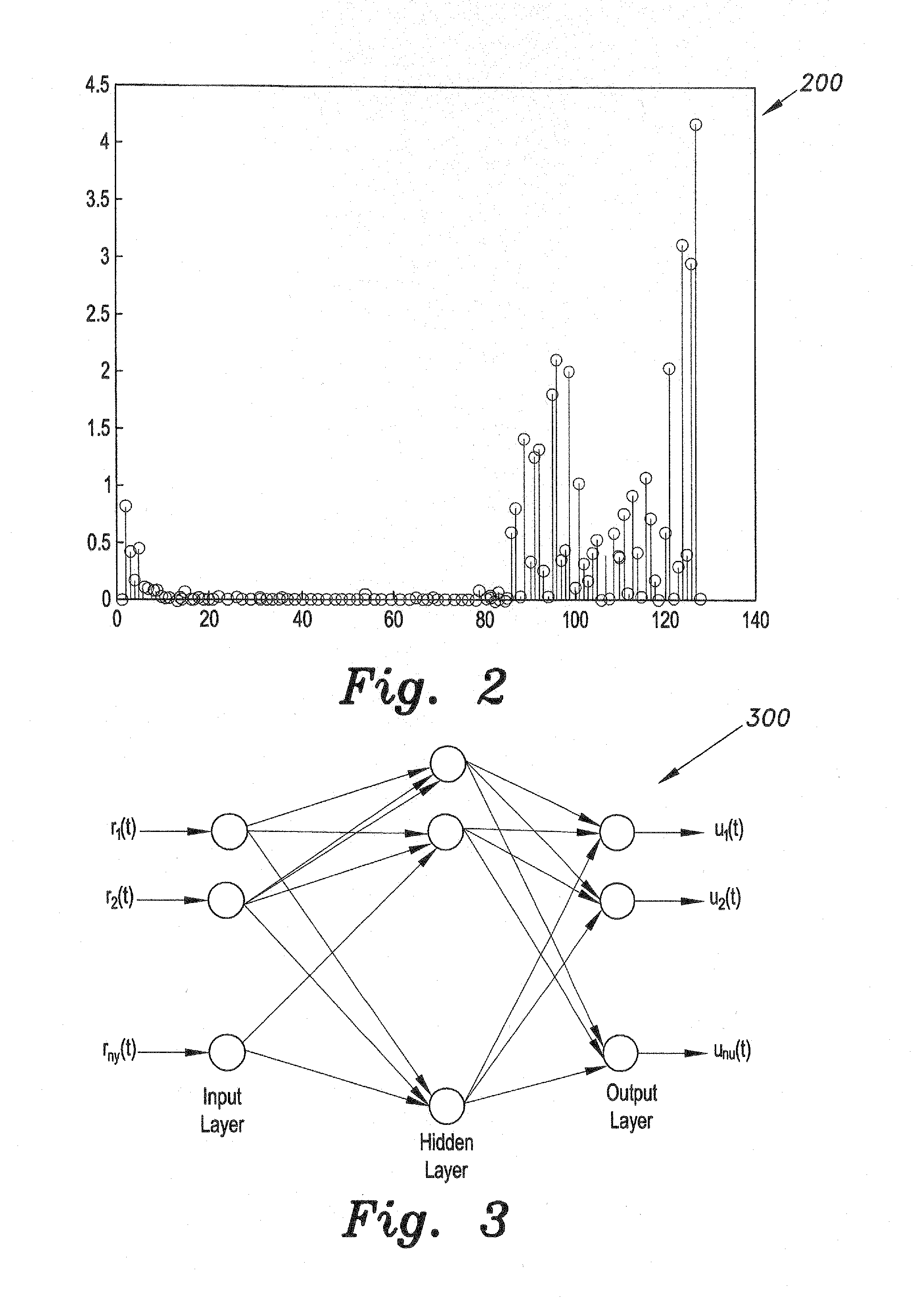
The contamination level estimation method for high voltage insulators collects samples of naturally contaminated insulators and builds an image data set for the collected insulators. Flashover voltages of several insulators samples are measured. ESDD levels of the collected insulators are estimated. Images are input to image processing algorithms to extract representative features. The images are segmented. Transforming the image from RGB color space into grayscale model excludes the background from the image. Subsequently, the segmented images are transferred back to RGB color space model using matrix manipulation. Since contaminants on the insulator surface affect the color of the insulator, the segmented image is transformed from RGB to HSV color space which is used for extracting statistical and linear algebraic features from the hue image. A trained artificial neural network correlates the extracted features to the contamination levels enabling testing of other contaminated insulators.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Image analysis neural network systems
A method includes determining object class probabilities of pixels in a first input image by examining the first input image in a forward propagation direction through layers of artificial neurons of an artificial neural network. The object class probabilities indicate likelihoods that the pixels represent different types of objects in the first input image. The method also includes selecting, for each of two or more of the pixels, an object class represented by the pixel by comparing the object class probabilities of the pixels with each other, determining an error associated with the object class that is selected for each pixel of the two or more pixels, determining one or more image perturbations by back-propagating the errors associated with the object classes selected for the pixels of the first input image through the layers of the neural network without modifying the neural network, and modifying a second input image by applying the one or more image perturbations to one or more of the first input image or the second input image prior to providing the second input image to the neural network for examination by the neurons in the neural network for automated object recognition in the second input image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
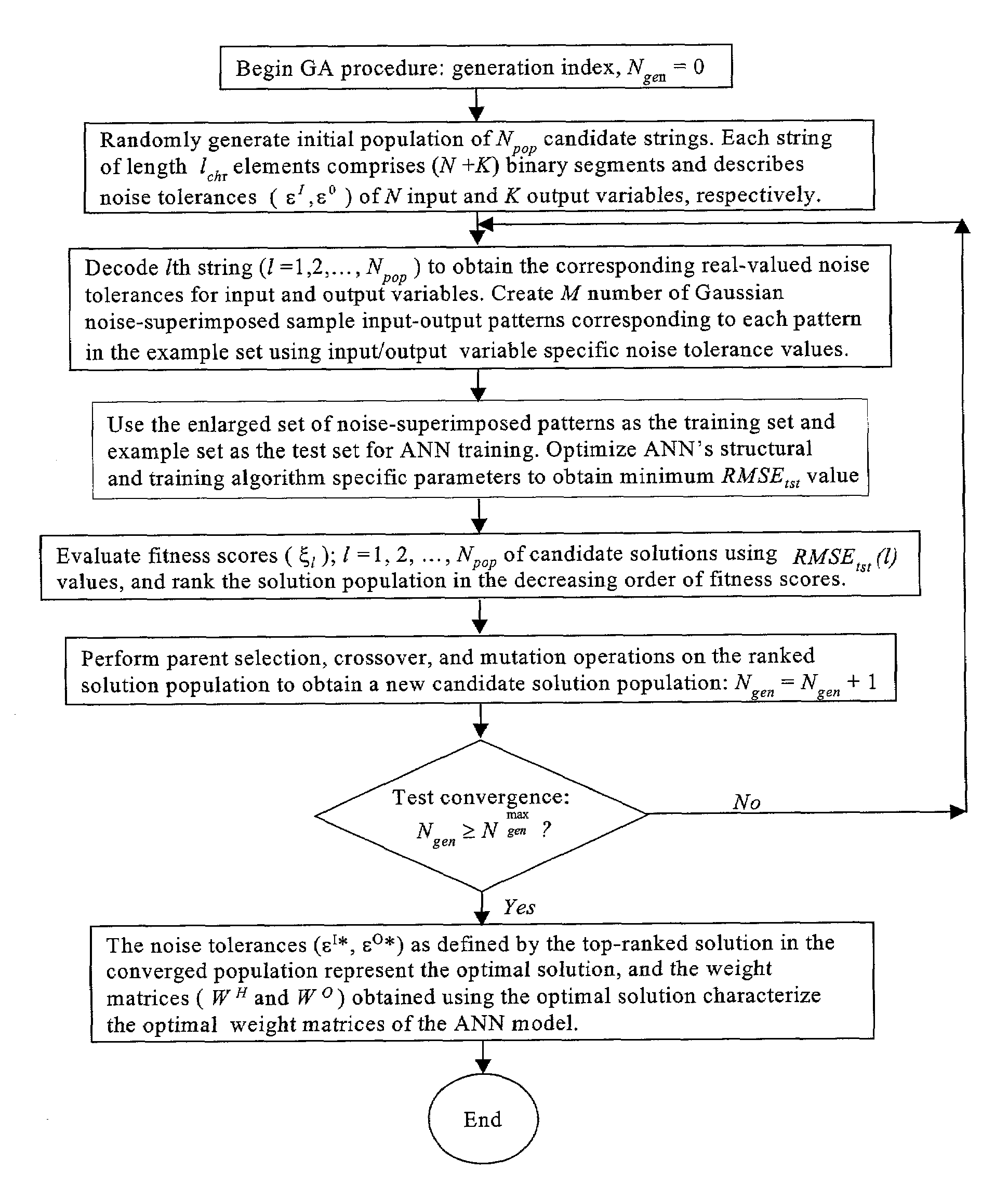
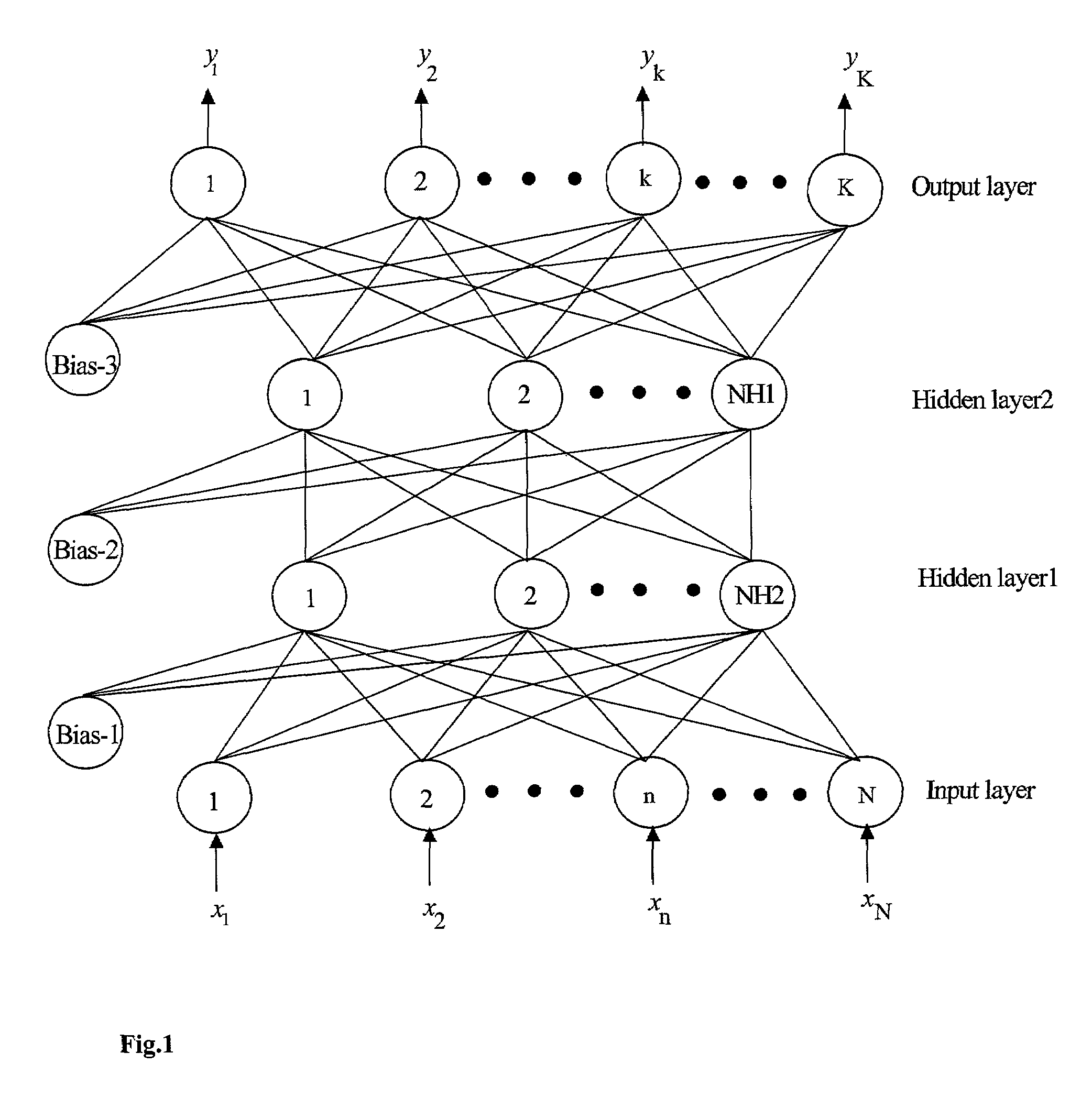
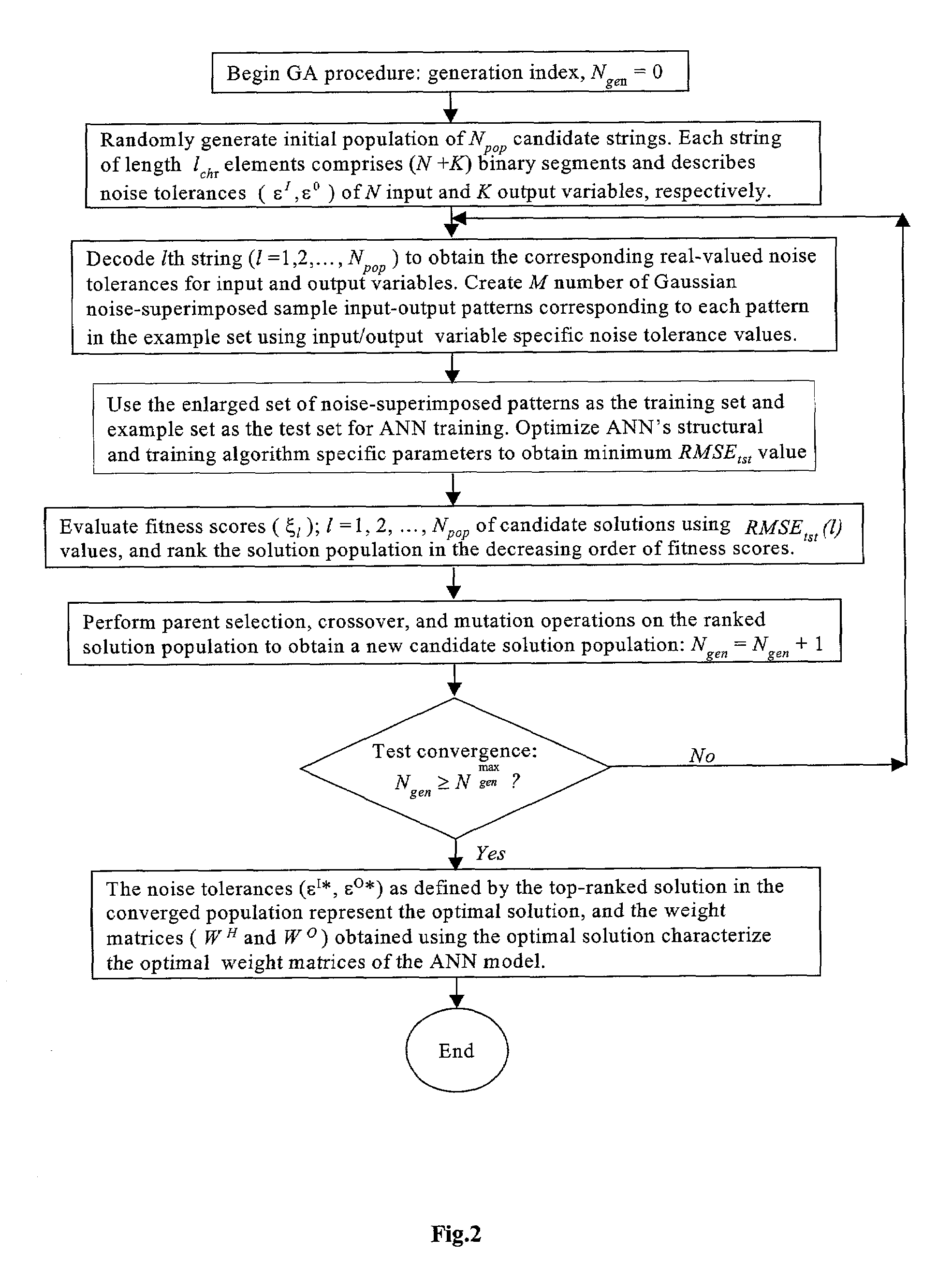
Performance of artificial neural network models in the presence of instrumental noise and measurement errors
InactiveUS7313550B2Improve accuracyImprove performanceGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsObservational errorData set
A method is described for improving the prediction accuracy and generalization performance of artificial neural network models in presence of input-output example data containing instrumental noise and / or measurement errors, the presence of noise and / or errors in the input-output example data used for training the network models create difficulties in learning accurately the nonlinear relationships existing between the inputs and the outputs, to effectively learn the noisy relationships, the methodology envisages creation of a large-sized noise-superimposed sample input-output dataset using computer simulations, here, a specific amount of Gaussian noise is added to each input / output variable in the example set and the enlarged sample data set created thereby is used as the training set for constructing the artificial neural network model, the amount of noise to be added is specific to an input / output variable and its optimal value is determined using a stochastic search and optimization technique, namely, genetic algorithms, the network trained on the noise-superimposed enlarged training set shows significant improvements in its prediction accuracy and generalization performance, the invented methodology is illustrated by its successful application to the example data comprising instrumental errors and / or measurement noise from an industrial polymerization reactor and a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Auto CPAP
InactiveUS20030000528A1Simple methodRespiratorsMedical data miningSleep disordered breathingBreathing gas
A method for the detection and treatment of disordered breathing during sleep employs an artificial neural network (ANN) in which data related to breathing gas flow are analyzed. A respiratory circuit is established by connecting the patient to a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) system with pressurized breathing gas supply, the gas flow in the circuit is periodically sampled, one or several cepstrum parameters distinctive of various breathing patterns are periodically calculated; the parameter values are periodically fed to an ANN trained to recognize breathing patterns characteristic of sleep disordered breathing and are analyzed in the network, the CPAP pressurized breathing gas supply is controlled in response to the ANN output. Also disclosed is a corresponding apparatus.
Owner:BREAS MEDICAL
Reinforcement learning based cognitive Anti-jamming communications system and method
InactiveUS20200153535A1Random number generatorsCharacter and pattern recognitionAnti jammingCommunications system
Systems and methods of using machine-learning in a cognitive radio to avoid a jammer are described. Smoothed power spectral density is used to detect activity in a sub-band and basic characteristics of different signals therein extracted. If unable to classify the signals as either a valid signal or a jammer using the basic characteristics, ANN-based classification with cumulants features of the signals is used. Multiple periods are used to train sensing and communications (S / C) polices to track and avoid a jammer using RL (e.g. Q learning). The ANN has input neurons of higher order cumulants of a sensing channel and a single output neuron. The S / C polices are coupled during training and communication using negative or decreasing rewards based on the time the sensing policy takes to determine jammer presence and that the cognitive radio is jammed. A feedback channel provides a new communications channel to a radio transmitting to the cognitive radio.
Owner:BLUECOM SYST & CONSULTING LLC
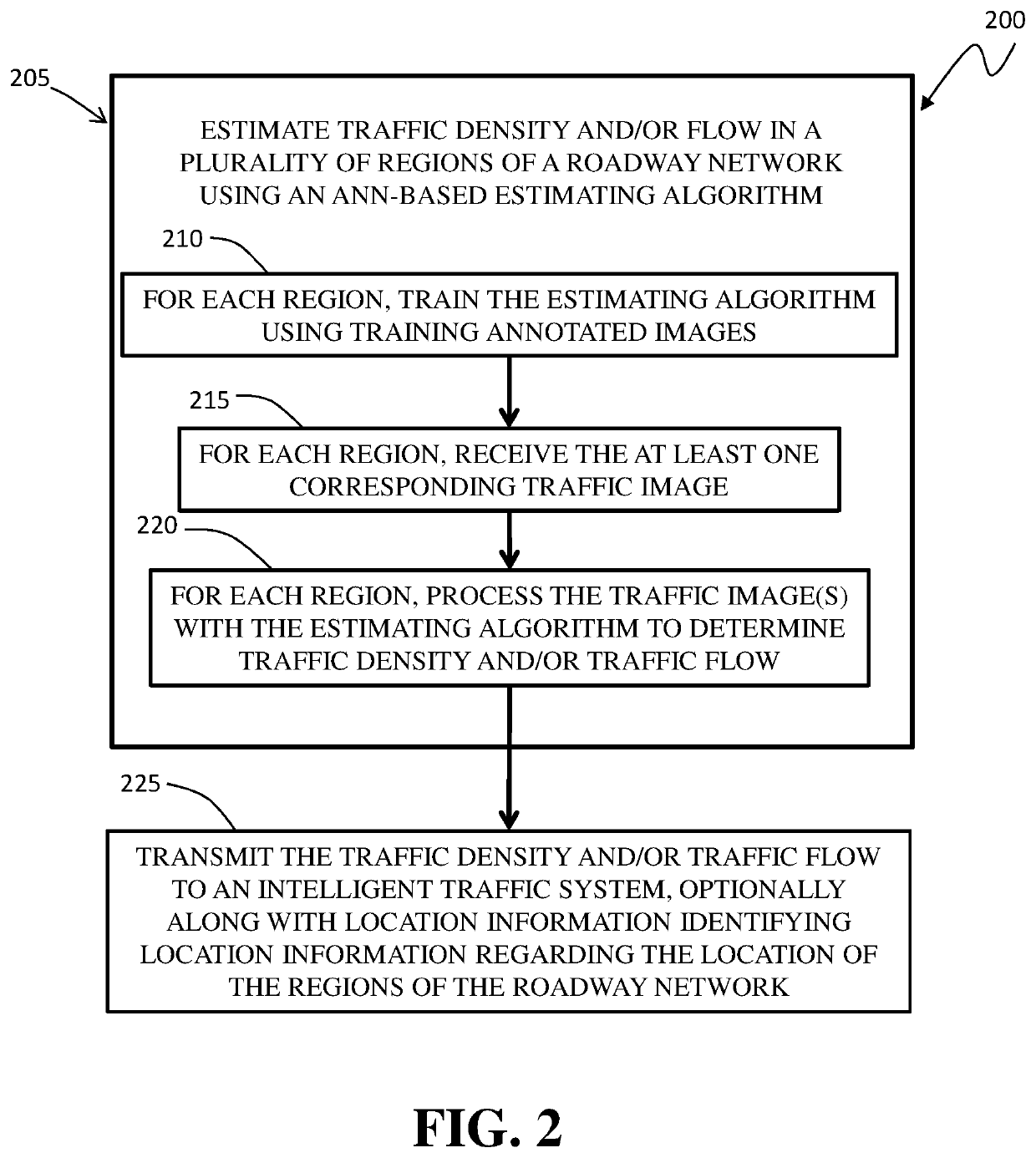
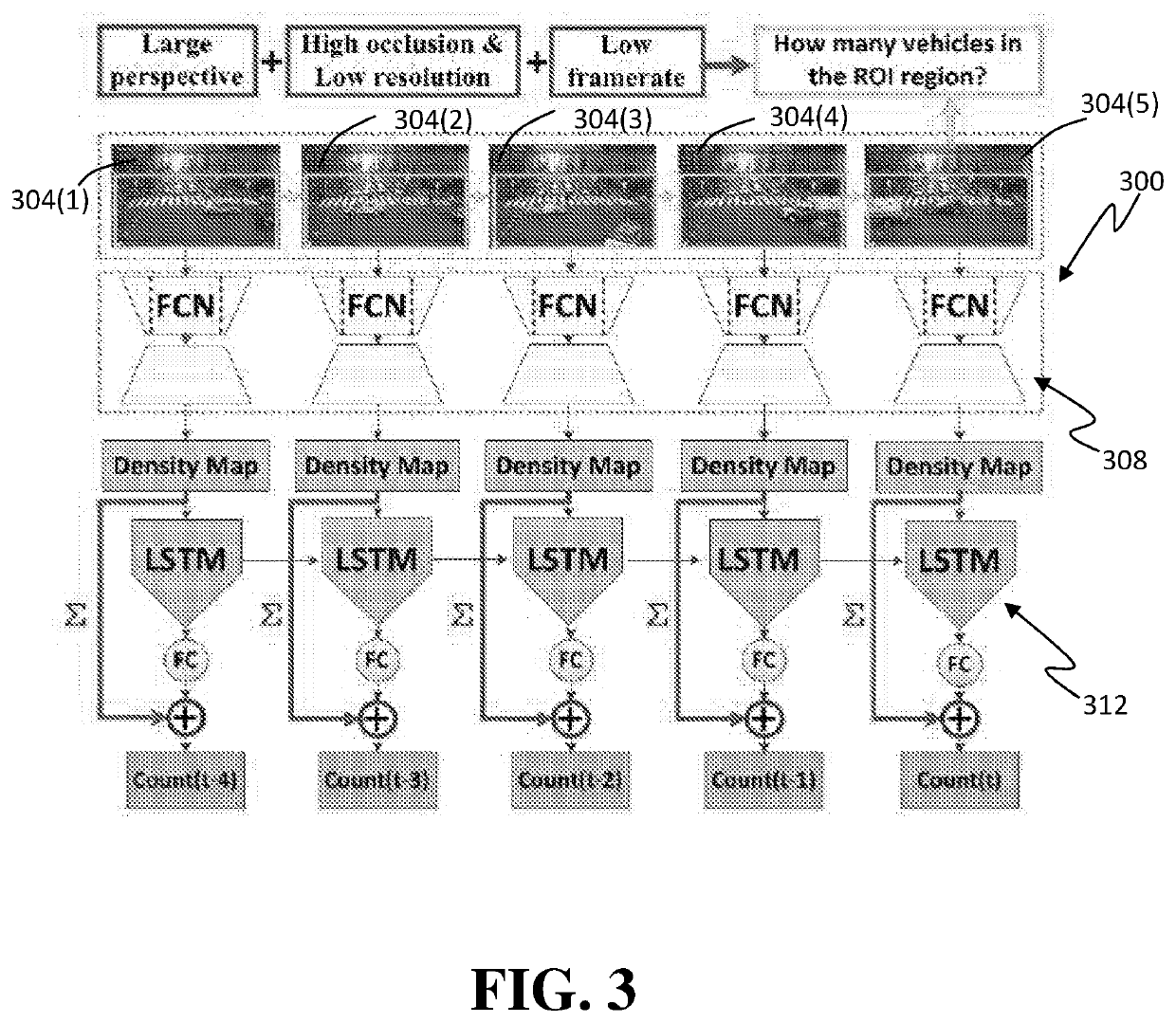
Deep Learning Methods For Estimating Density and/or Flow of Objects, and Related Methods and Software
ActiveUS20200118423A1Detection of traffic movementNeural learning methodsPattern recognitionEngineering
Methods and software utilizing artificial neural networks (ANNs) to estimate density and / or flow (speed) of objects in one or more scenes each captured in one or more images. In some embodiments, the ANNs and their training configured to provide reliable estimates despite one or more challenges that include but are not limited to, low-resolution images, low framerate image acquisition, high rates of object occlusions, large camera perspective, widely varying lighting conditions, and widely varying weather conditions. In some embodiments, fully convolutional networks (FCNs) are used in the ANNs. In some embodiments, a long short-term memory network (LSTM) is used with an FCN. In such embodiments, the LSTM can be connected to the FCN in a residual learning manner or in a direct connected manner. Also disclosed are methods of generating training images for training an ANN-based estimating algorithm that make training of the estimating algorithm less costly.
Owner:INST SUPERIOR TECH +1
Hybrid computing system of artificial neural network and impulsive neural network
ActiveCN105095966AReal-time computingGuaranteed accuracyNeural architecturesNerve networkData mining
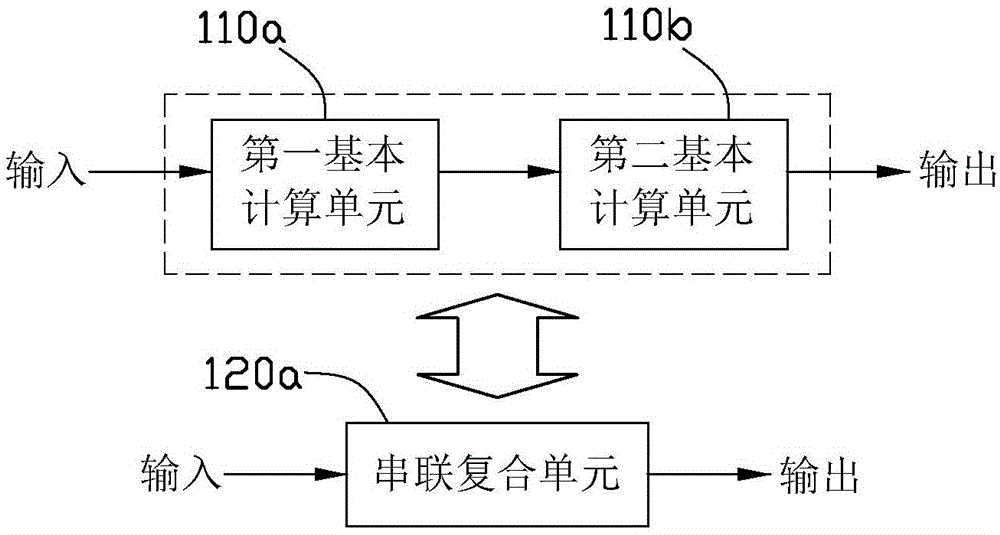
Provided in the invention is a hybrid computing system of an artificial neural network and an impulsive neural network. The hybrid computing system comprises a plurality of neural network computing units; one part of the neural network computing units is an artificial neural network computing unit being responsible for artificial neural network computing; and the other parts of the neural network computing units are impulsive neural network computing units responsible for impulsive neural network computing. The multiple basic computing units are mutually connected according a certain topological structure, thereby realizing a neural network computing function jointly. According to the hybrid computing system, the computing modes of the two kinds of neural networks containing the artificial neural network and the impulsive neural network are combined to realize real-time multi-mode or complex space-time signal calculation rapidly and guarantee the computing precision.
Owner:LYNXI TECH CO LTD
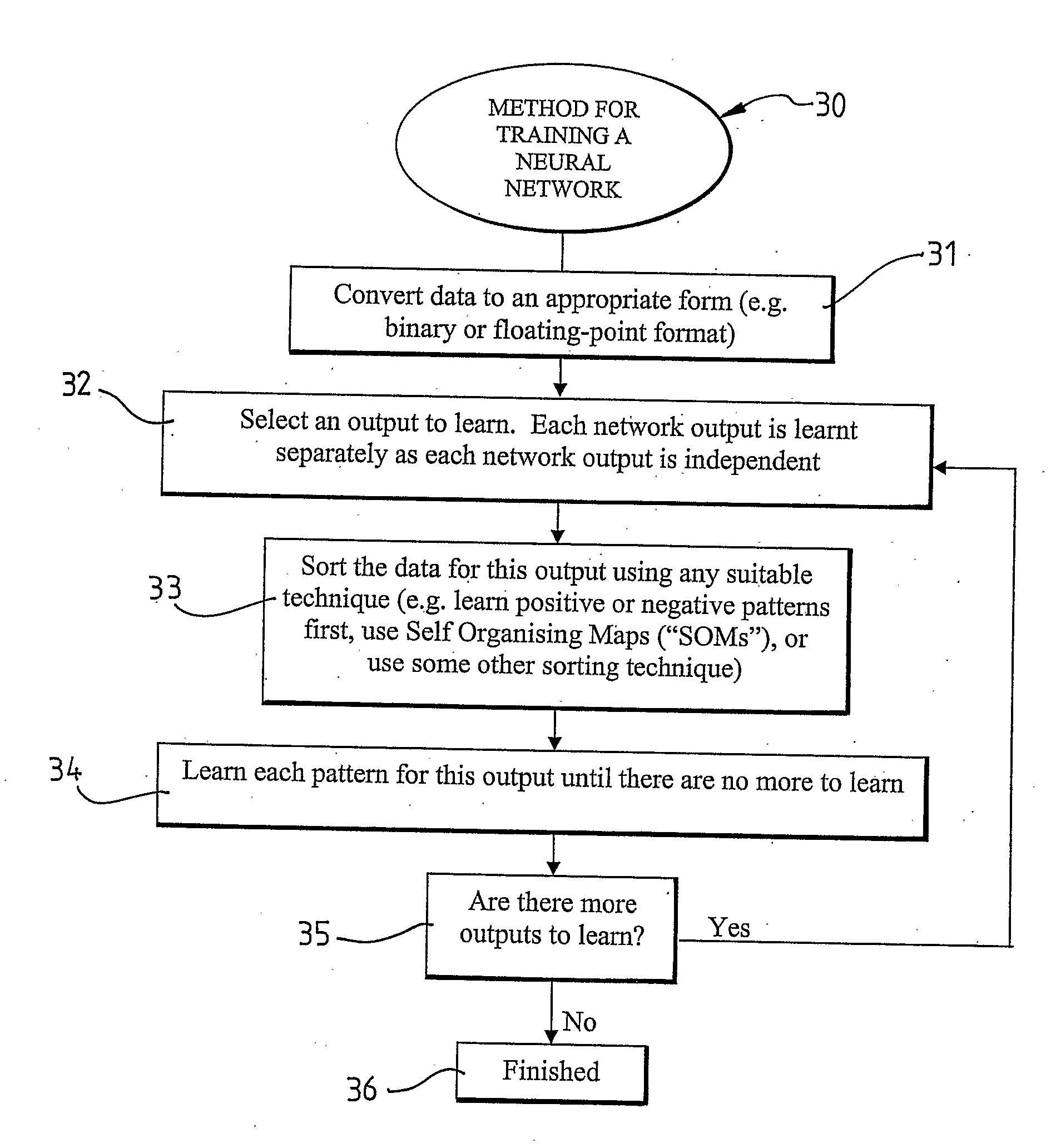
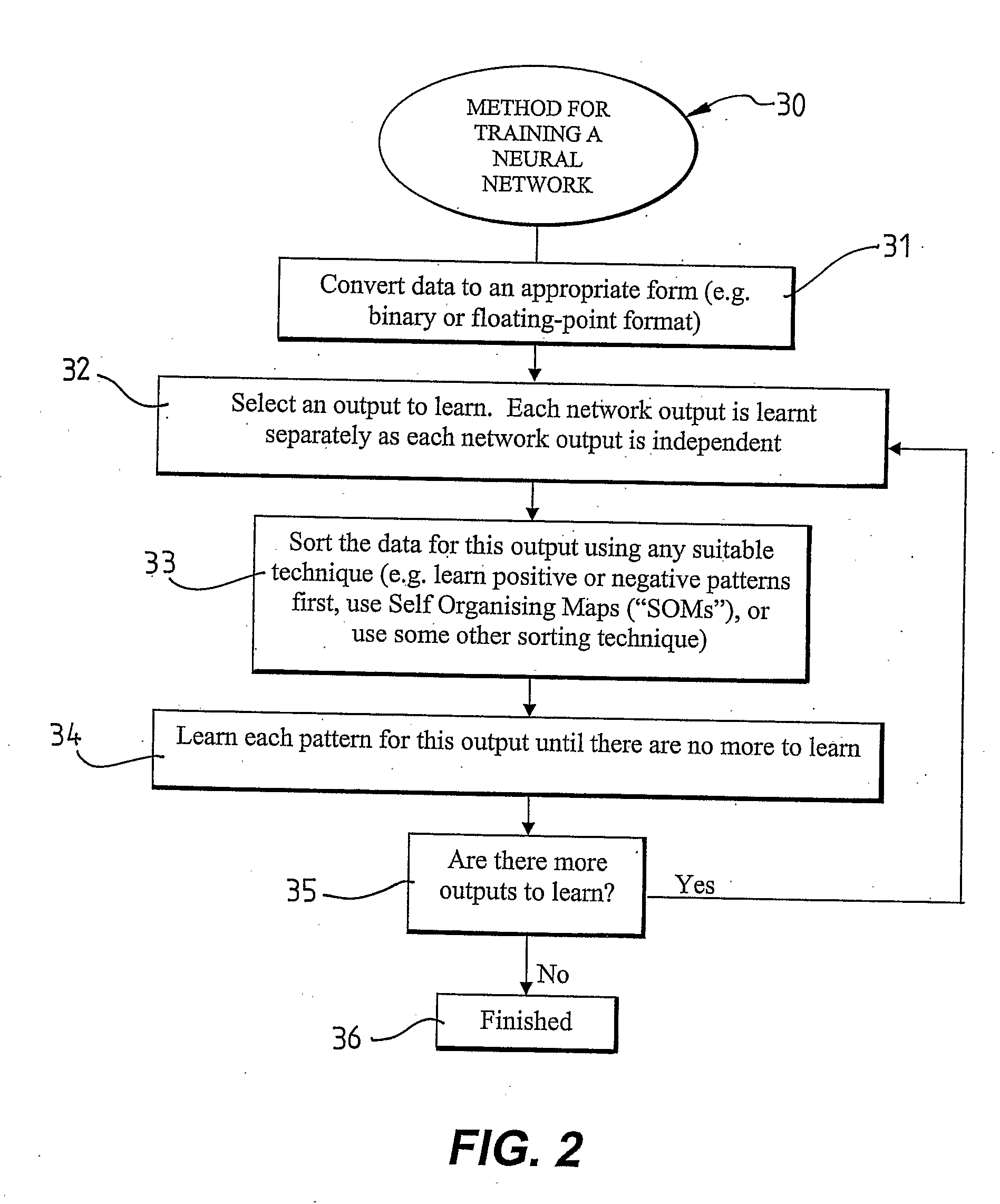
Method for Training Neural Networks
ActiveUS20080281767A1Simple processSimple taskDigital computer detailsProcessor architectures/configurationHidden layerData set
The present invention provides a method (30) for training an artificial neural network (NN). The method (30) includes the steps of: initialising the NN by selecting an output of the NN to be trained and connecting an output neuron of the NN to input neuron(s) in an input layer of the NN for the selected output; preparing a data set to be learnt by the NN; and, applying the prepared data set to the NN to be learnt by applying an input vector of the prepared data set to the first hidden layer of the NN, or the output layer of the NN if the NN has no hidden layer(s), and determining whether at least one neuron for the selected output in each layer of the NN can learn to produce the associated output for the input vector. If none of the neurons in a layer of the NN can learn to produce the associated output for the input vector, then a new neuron is added to that layer to learn the associated output which could not be learnt by any other neuron in that layer. The new neuron has its output connected to all neurons in next layer that are relevant to the output being trained. If an output neuron cannot learn the input vector, then another neuron is added to the same layer as the current output neuron and all inputs are connected directly to it. This neuron learns the input the old output could not learn. An additional neuron is added to the next layer. The inputs to this neuron are the old output of the NN, and the newly added neuron to that layer.
Owner:GARNER BERNADETTE
On-line measurement method and device for micro/nano deep trench structure
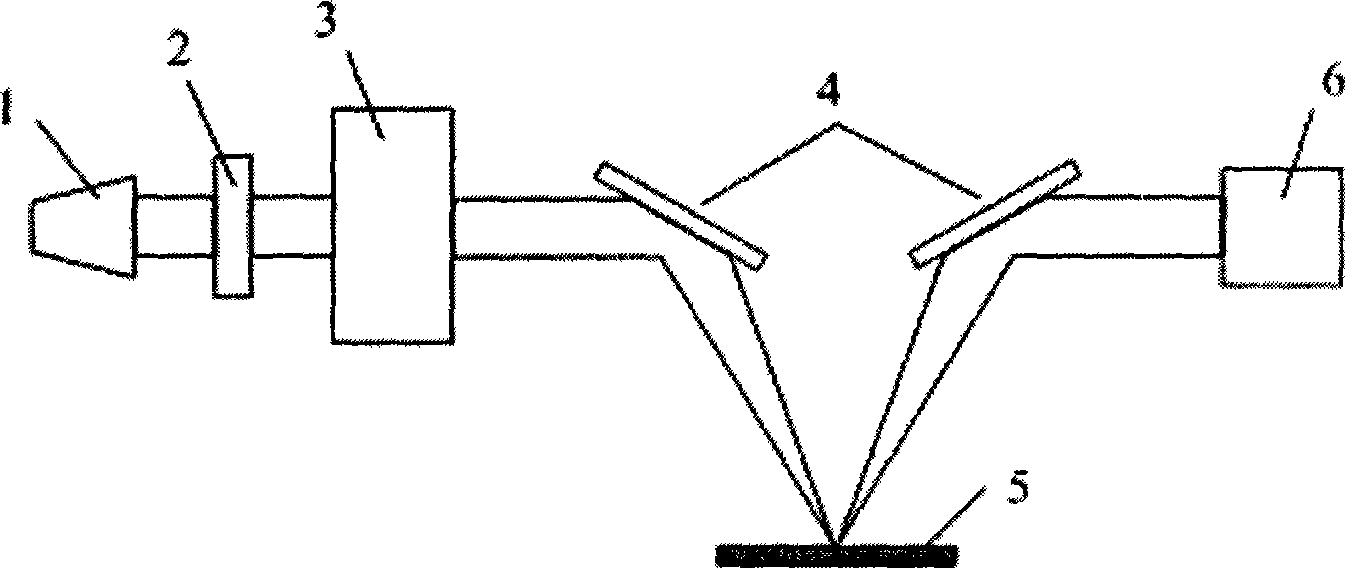
ActiveCN101393015ARealize onlineQuick measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansWidth ratioArtificial neural network
The invention discloses an online measuring method and an online measuring device for a micro-nano deep groove structure. The method comprises the following steps: linearly polarized infrared beams are projected to the surface of a sample piece which is provided with the deep groove structure, and measured reflection spectra are obtained after interference signals which are formed by reflected light on various interfaces of the groove structure are subjected to filtration and so on; an equivalent optical model of the deep groove structure is established by the polarization-based equivalent medium theory, and theoretic reflection spectra of the equivalent optical model of the deep groove structure are calculated; and the width and the depth of the groove are quickly extracted by the quick parameter extraction method of combination of an artificial neural network and a local search algorithm and through fitting of the theoretic reflection spectra and the measured reflection spectra, and precise online measurement of geometrical shape parameters of the deep groove is realized. The device comprises an infrared source, an infrared polaroid sheet, an interferometer, a plane mirror, two off-axis parabolic mirrors and an infrared detector. The device can realize online measurement of the depth and the width of the deep groove structure with high depth-width ratio in a field effect tube and a dynamic RAM during the manufacturing procedure, and has the characteristics of nondestructiveness, quickness and low cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
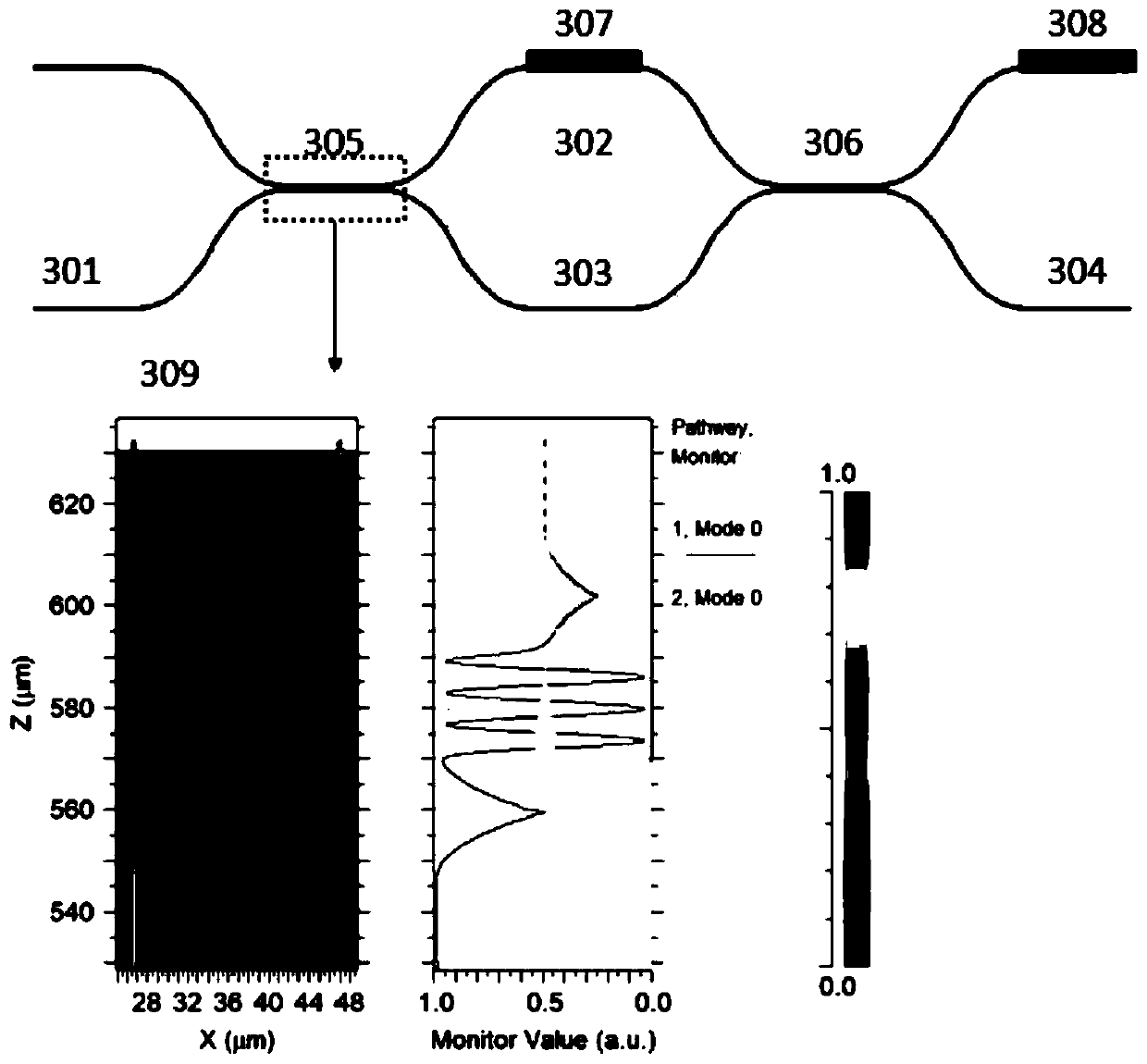
Optical neural network method for realizing digital recognition
InactiveCN110197277AReduce computing timeReduce computing energy consumptionNeural architecturesPhysical realisationActivation functionMach–Zehnder interferometer
The invention provides an optical neural network method for realizing the digital recognition. The optical neural network method comprises a step of acquiring digital image features and a step of constructing an optical neural network. The optical neural network is composed of an optical interference module, an optical nonlinear module and a detector array, and the optical interference module comprises a Mach-Zehnder interferometer array and a variable optical attenuator, and can realize any matrix multiplication. The optical non-linear module is composed of a saturable absorber and other devices with the non-linear effects, and can realize the function of an activation function in an artificial neural network. According to the method, the calculation time is shortened through optical calculation, and the calculation energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
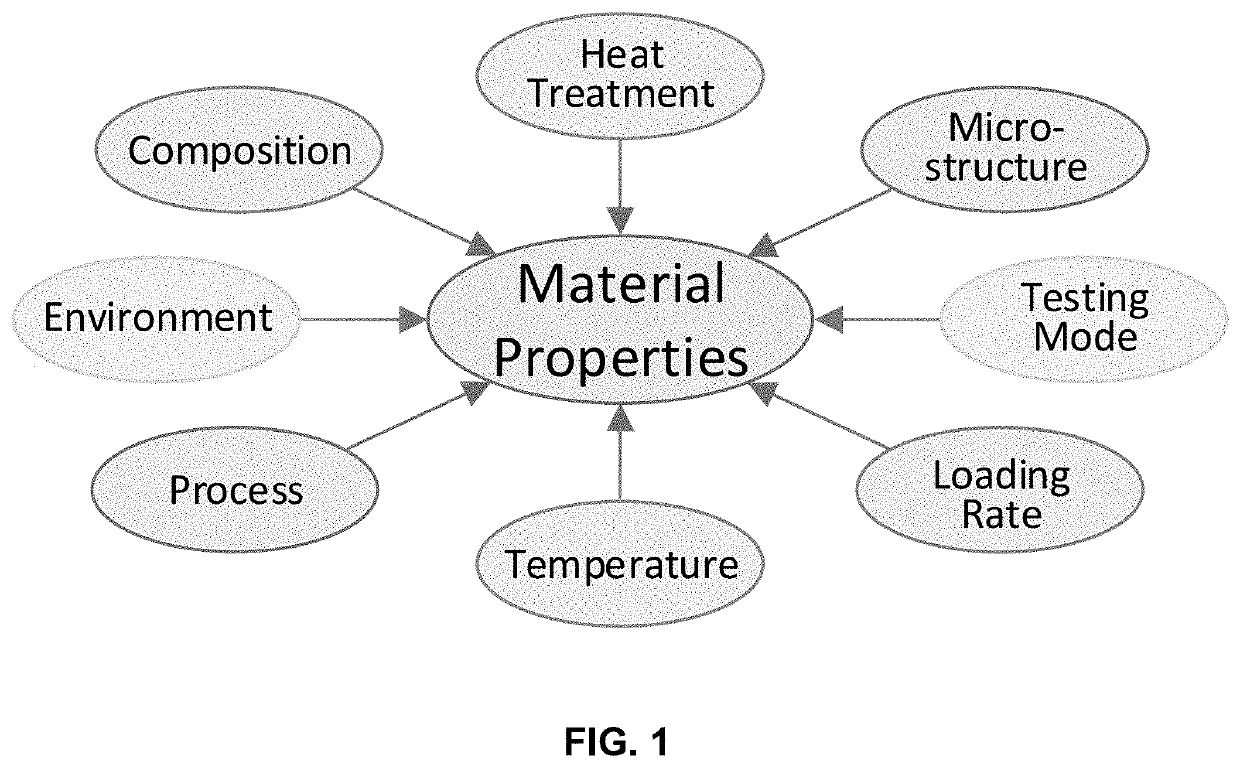
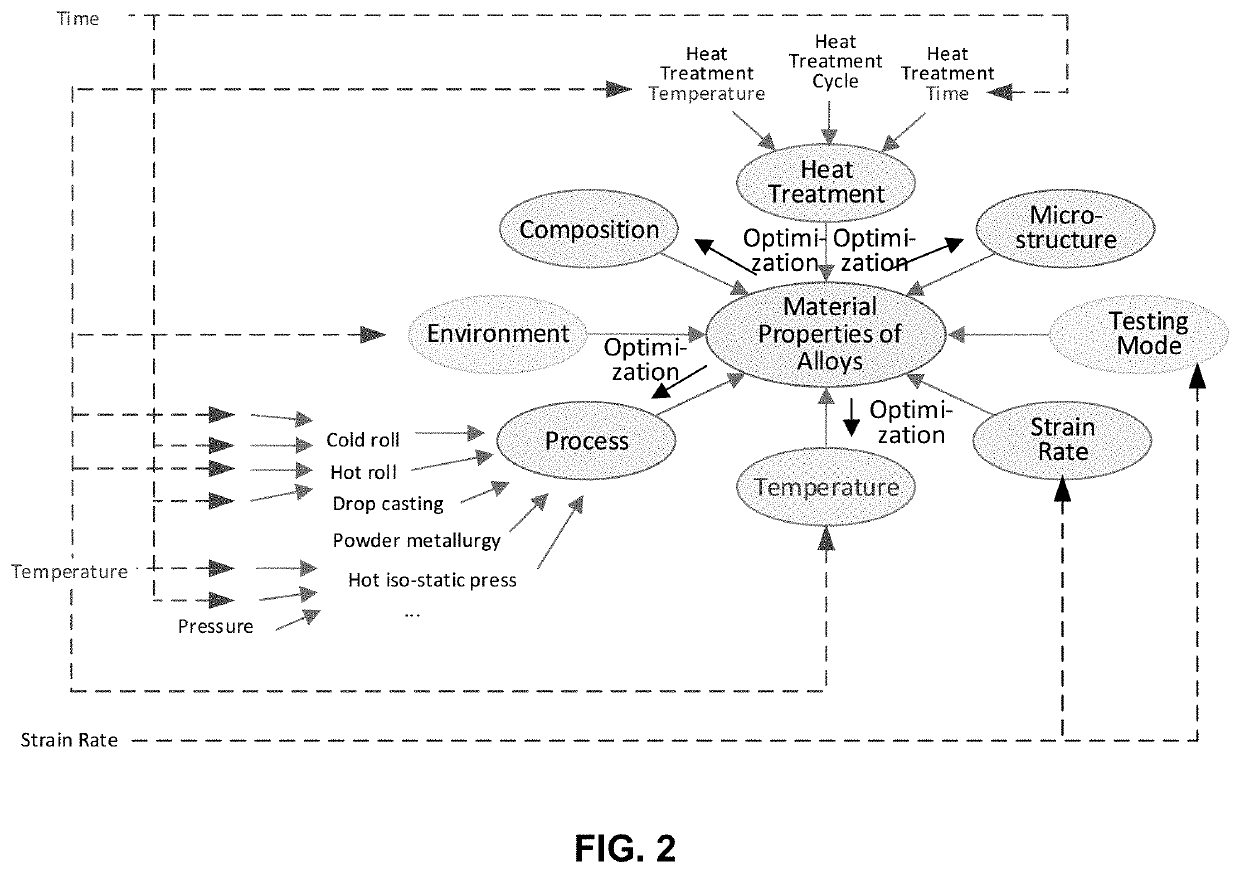
Machine Learning to Accelerate Alloy Design
PendingUS20200257933A1Tightly coupledEasy to predictChemical property predictionTurbinesPrior informationRegression analysis
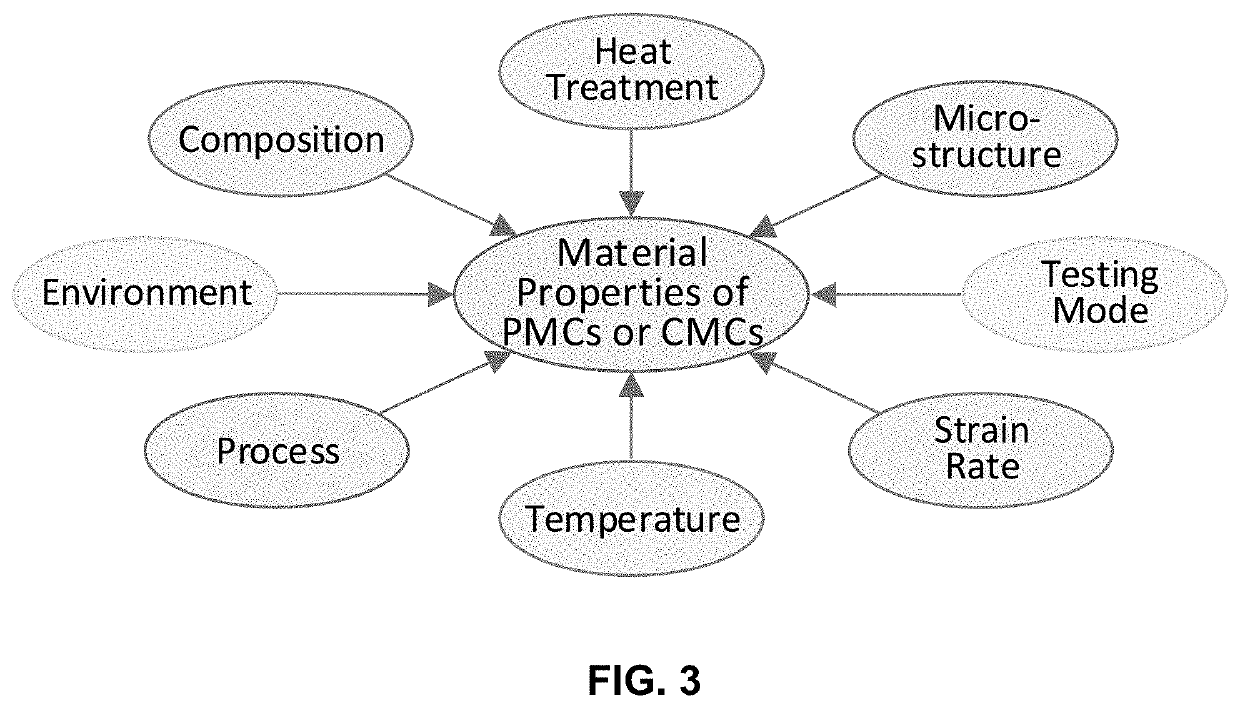
This invention presents an innovative framework for the application of machine learning for identification of alloys or composites with desired properties of interest. For each output property of interest, we identify the corresponding driving (input) factors. These input factors may include the material composition, heat treatment, process, microstructure, temperature, strain rate, environment or testing mode. Our framework assumes selection of optimization technique suitable for the application at hand and data available, starting with simple linear, or quadratic, regression analysis. We present a physics-based model for predicting the ultimate tensile strength, a model that accounts for physical dependencies, and factors in the underlying physics as a priori information. In case an artificial neural network is deemed suitable, we suggest employing custom kernel functions consistent with the underlying physics, for the purpose of attaining tighter coupling, better prediction, and extracting the most out of the—usually limited—input data available.
Owner:IMAGARS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com