Method for inducing spider to generate antibiotic activity substance
An antibacterial active substance, spider technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of simple and convenient operation and good antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1. Collect 90 horned fat spiders and divide them into two groups. The first group is 80 for induction, and the second group is 10 for control. The 80 spiders of the first group were placed in a petri dish, irradiated for 1 hour at a distance of 1 meter under a 20w ultraviolet lamp (50 spiders could be irradiated at a time), and then continued to be raised under normal conditions. The 10 spiders in the second group were not irradiated and were fed under normal conditions as a control.
[0034] 2. 80 spiders after ultraviolet irradiation and 10 spiders without induction were single-headed in glass finger tubes (length * diameter = 12cm * 4cm), and there was a sponge at the bottom of the tube to absorb enough water for the spiders to drink. Seal it with a cotton plug, and then place the glass vial containing the spider in a 25°C incubator with a light cycle of 12:12 (Light:Dark). Glass vials were cleaned every 2 days and fed with adult fruit flies (Drosophila sp.) and mid...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1. Collect 40 spiders, put them in a petri dish, and irradiate them at a distance of 1 meter under a 20w ultraviolet lamp for 1 hour.
[0042] 2. Raise 40 spiders single-headed in a glass finger tube (length×diameter=12cm×4cm) after ultraviolet irradiation. There is a sponge at the bottom of the tube to absorb enough water for the spiders to drink. The glass vials with spiders were placed in a 25°C incubator with a light cycle of 12:12 (Light:Dark). Glass vials were cleaned every 2 days and fed with adult fruit flies (Drosophilasp.) and midges (Tendipes sp.).
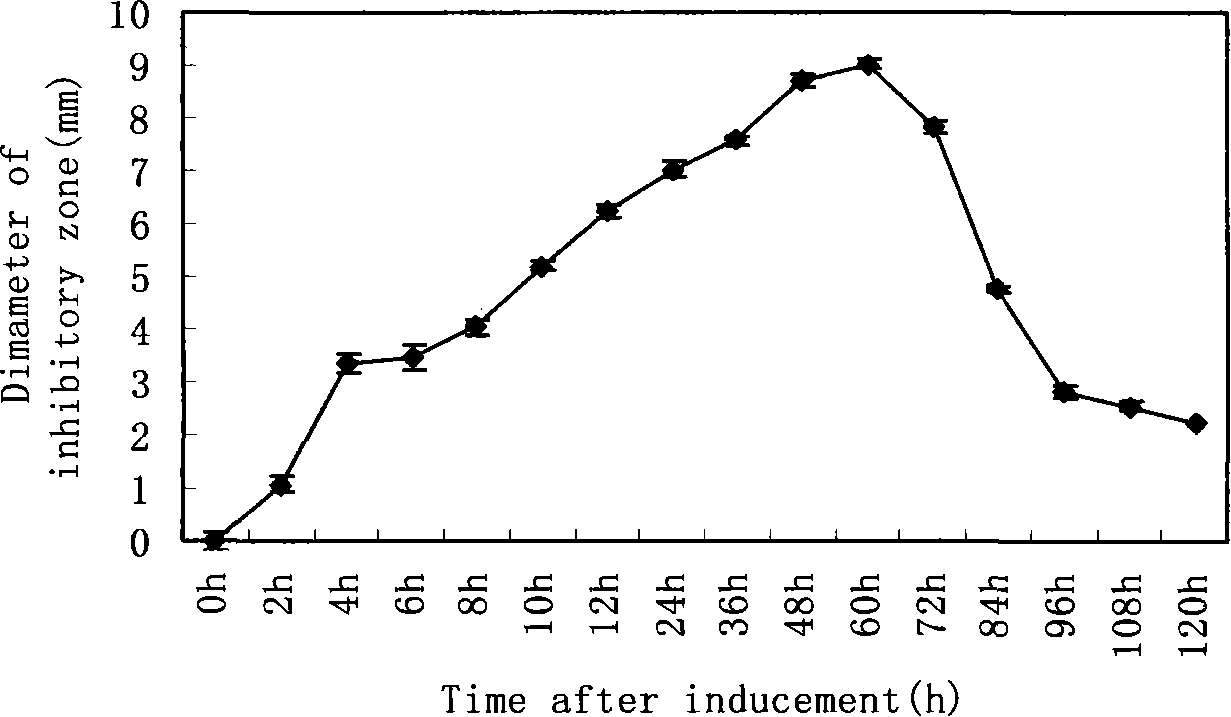
[0043] 3. After feeding the spiders irradiated by ultraviolet rays for 60 hours, take the spiders to extract hemolymph. Disinfect the spider with 75% alcohol, then place it in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube in an ice bath, add pre-cooled sterile water homogenate (when the external temperature is high, you need to add some mercaptoethanol to prevent the blackening of antibacterial substances) , The homogenate was centr...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1. Collect 40 horned fat spiders and divide them into four groups, 10 in each group. The first three groups were induced by ultraviolet irradiation, bacterial injection and starvation respectively, and the fourth group was not induced and served as the control group.
[0048] Ultraviolet radiation induction: put 10 test spiders in a petri dish, irradiate them at a distance of 1 meter under a 20w ultraviolet lamp for 1 hour, and then continue to raise them under normal conditions.
[0049] Bacterial injection method: After 10 test spiders were anesthetized on ice, they were injected on the abdomen with a micro-injector on the ultra-clean workbench, and each spider was injected with 1 μl of prepared Escherichia coli suspension (concentration of 1× 10 6 cfu / ml), and then continue to feed under normal conditions.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com