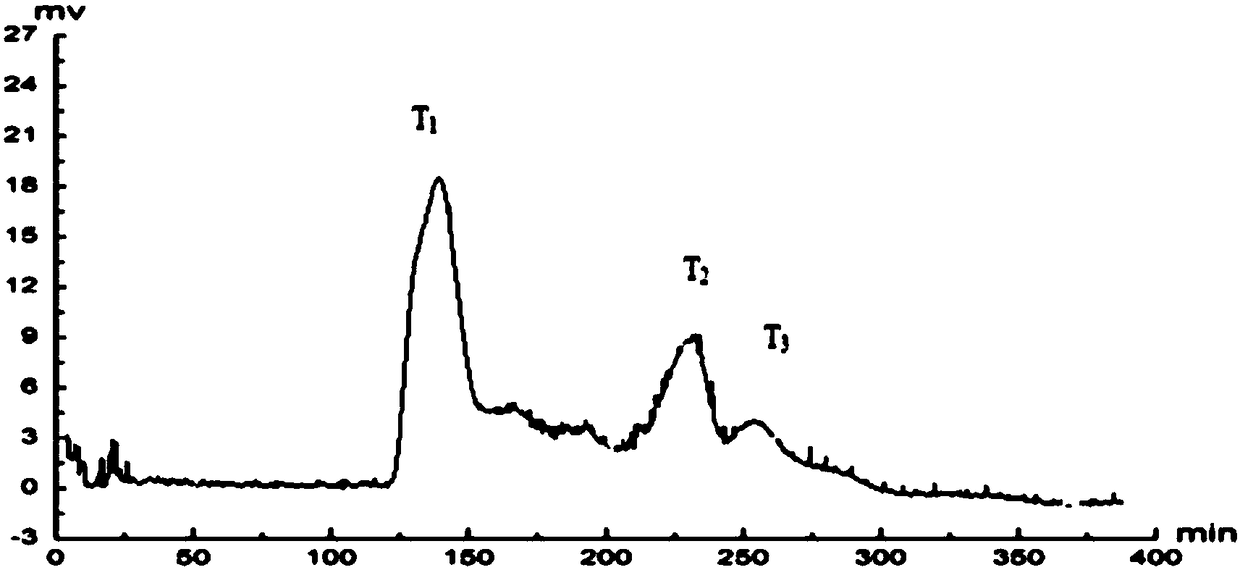
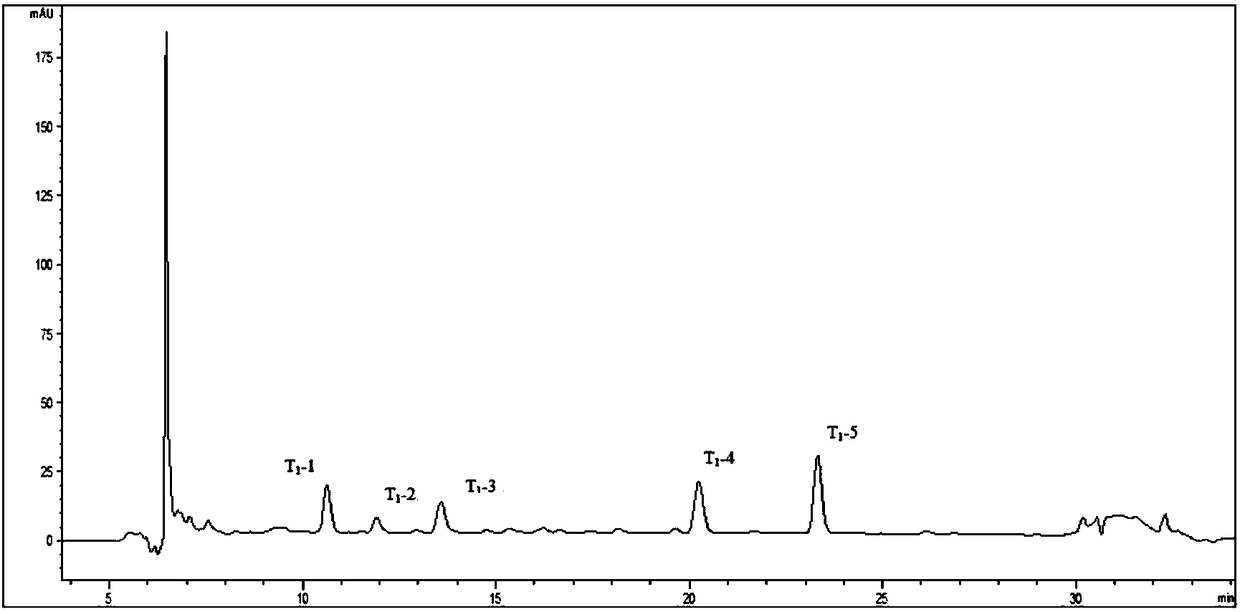
Separation and purification method of antibacterial peptides in bodily wall of Apostichopus japonicus
A technology for separation, purification and antimicrobial peptides, applied in the field of separation and purification of antimicrobial peptides in the body wall of Apostichopus japonicus, can solve problems such as toxicity, and achieve the effects of small molecular weight, stable effect, and reduced drug residues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The fresh and live imitation japonicus was temporarily raised in seawater for 10 days in a holding tank, and Bacillus subtilis was added to the seawater to stimulate it to produce more antimicrobial peptides. After 10 days, it was rinsed with filtered seawater, removed from the intestinal tract, weighed, and cut. Grinding with a colloid mill, and then using a tissue masher for three consecutive times, each time for 3 minutes, and then using a cell wall crusher for three consecutive times, and set aside.
[0033] Add 5% acetic acid to the crushed imitation sea cucumber body wall tissue at a volume ratio of 1:1, mix with a high-speed disperser, place it in a 4°C refrigerator for extraction for 24 hours, then put the mixture into a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge, and centrifuge Rotate at 8000r / min, centrifuge at 4°C for 20min, take the supernatant, and store at 4°C. Add the same amount of 5% acetic acid to the precipitate again, leaching again at 4°C for 24 hours, cent...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The fresh and live imitation japonicus was temporarily raised in seawater for 8 days in a holding tank, and Bacillus subtilis was added to the seawater to stimulate it to produce more antimicrobial peptides. After 8 days, it was rinsed with filtered seawater, removed from the intestinal tract, weighed, and cut. Grinding with a colloid mill, and then using a tissue masher for 2 consecutive times, each time for 5 minutes, and then using a cell wall crusher for 5 consecutive crushing times, for later use.
[0043] Add 5% acetic acid to the crushed imitation sea cucumber body wall tissue at a volume ratio of 1:0.8, mix evenly with a high-speed disperser, place it in a refrigerator at 3°C for extraction for 28 hours, then put the mixture into a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge, and centrifuge Rotate at 8000r / min, centrifuge at 3°C for 25min, take the supernatant, and store at 3°C. Add the same amount of 5% acetic acid to the precipitate again, leaching again at 3°C f...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Fresh and live imitation sea cucumbers were temporarily raised in seawater for 12 days in a holding tank, and Bacillus subtilis was added to the seawater to stimulate them to produce more antimicrobial peptides. After 12 days, they were rinsed with filtered seawater, removed from the intestinal tract, weighed, and cut. Grinding with a colloid mill, and then using a tissue masher for 4 consecutive crushes, each time for 2 minutes, and then using a cell wall crusher for 1 consecutive crush, for later use.
[0050] Add 5% acetic acid to the crushed imitation sea cucumber body wall tissue at a volume ratio of 1:1.2, mix evenly with a high-speed disperser, place it in a refrigerator at 5°C for extraction for 20 hours, then put the mixture into a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge, and centrifuge Rotate at 8000r / min, centrifuge at 5°C for 15min, take the supernatant, and store at 5°C. Add the same amount of 5% acetic acid to the precipitate again, extract again at 5°C for 20 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com