Method for constructing artificial algal crusts by utilizing mixed algae
A technology of algae and crust, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, application, seaweed cultivation, etc., can solve the problems of large investment and long cultivation process cycle, and achieve the effect of huge application potential.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Using mixed algae to construct artificial algae crust
[0020] The present invention specifically provides a method for constructing an artificial algae crust by using mixed algae, and its specific construction method steps are as follows:
[0021] (1) Preparation of inoculation materials: select fully developed algal crusts in the desert, collect them, air-dry them, grind them, and then collect soil samples. The algae contained in the soil samples were dominated by Microcoletheca, Coleopsis, Matella, Oscillatoria, Nostoc, Monofidophyta, and Pseudocladon filamentous cyanobacteria, among which Microcoletheca was the dominant species. , Chlorella terrestris, Chlorella, Chromococcus and other common species of spherical algae.
[0022] (2) Cultivation: Insert the prepared BG into the culture plate 11 For liquid culture medium, pass the bare sand through a 0.2mm sieve and add 100g of bare sand to the medium per liter of medium, add bare sand to cover the bottom...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: The present invention utilizes mixed algae to construct the effect test of artificial algae crust
[0028] The content of chlorophyll a in the soil is used to represent the algae biomass. For the measurement method, refer to the literature (Xie et al., 2007, Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 567-572). The biomass of the harvested algae is the product of the biomass content of the algae and the soil weight of the harvested algae.
[0029]
[0030] The method for constructing artificial algae crusts provided by the present invention can rapidly proliferate algae species, and the natural algae crusts collected from the field have an average biomass of 0.016 ± 0.005mg chlorophyll a / gram of dry soil, in BG 11 After 2-3 weeks of indoor cultivation in liquid medium, the biomass of algae species and sand grains is 0.663±0.054 mg chlorophyll a / gram of dry soil after collection and drying, and the biomass has increased by as much as 124 times.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: The present invention utilizes mixed algae to construct the effect test of artificial algae crust
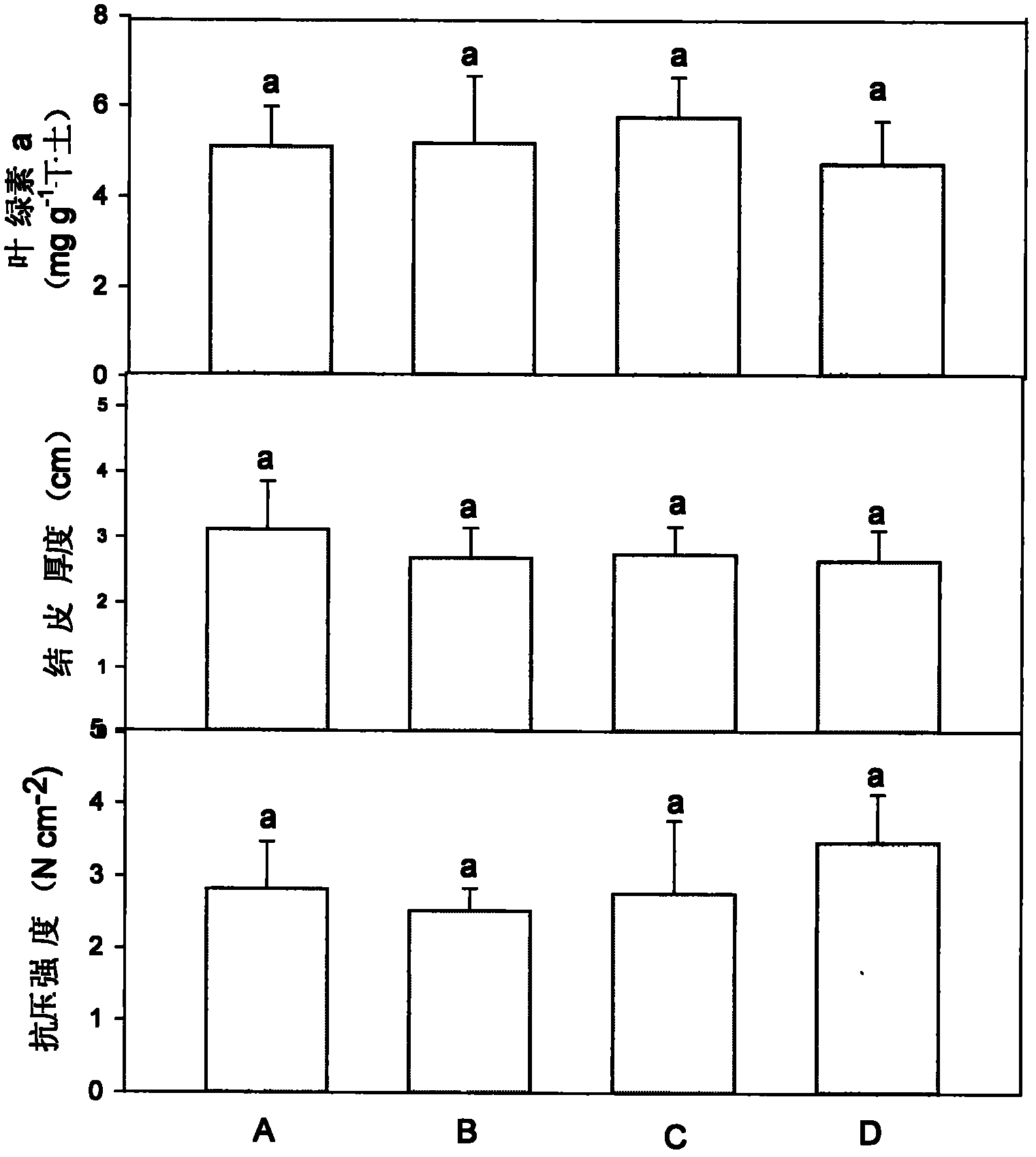
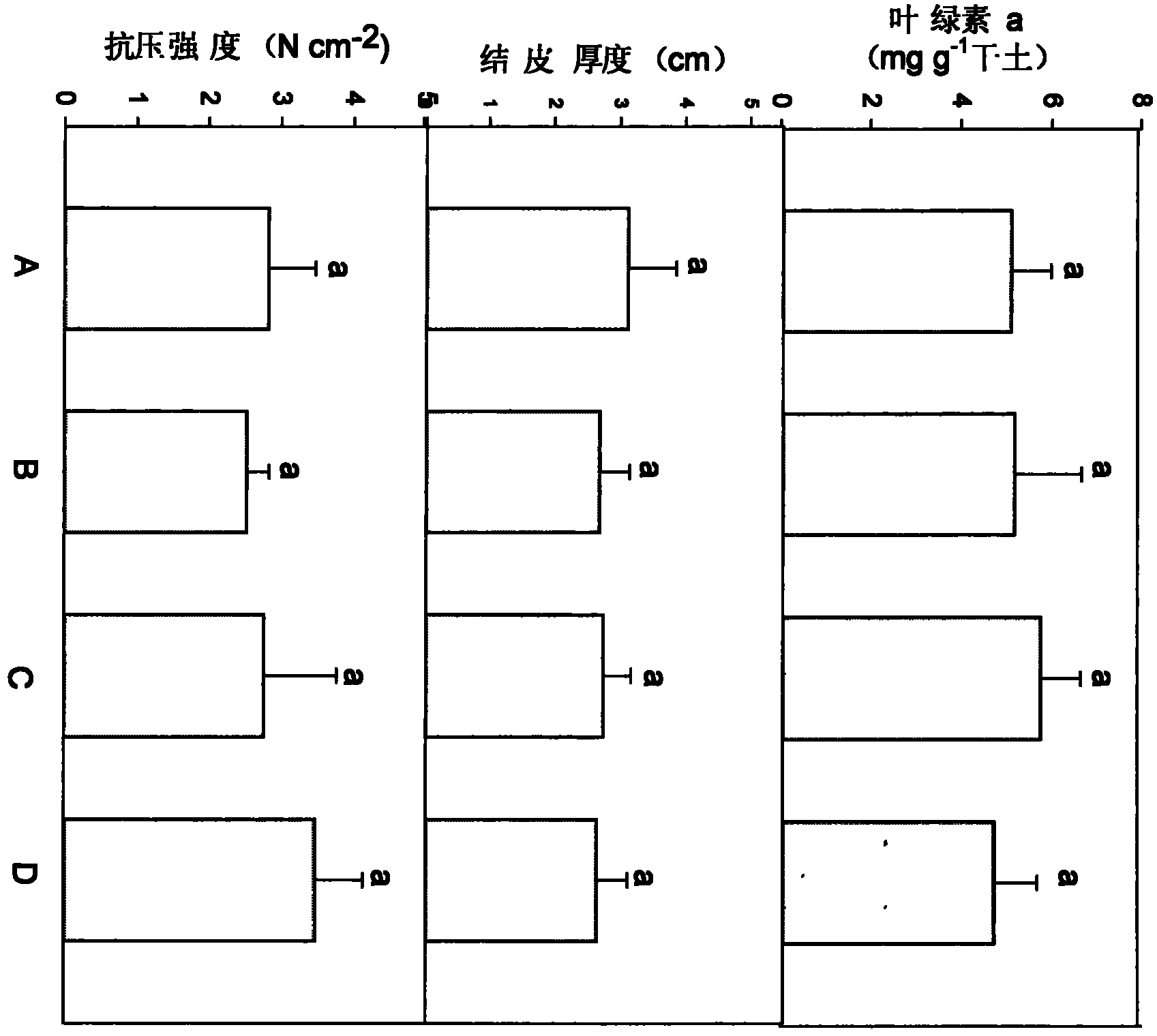
[0032] In this experiment, four 2.5m×2.5m squares were set up in the greenhouse, covered with quicksand with a thickness of 10cm, and then treated with different algae species:
[0033] Microsheatha
[0034] B: The common dominant algae species in several biological crusts are mixed in a regular ratio
[0035] C The mixed algal species formed by natural algal crusts through liquid culture
[0036] D: Natural algal crust alga species.
[0037] After the algae were ground, the chlorophyll content was measured, and the algae biomass was converted to be equal, and the algae whose total biomass was 100 mg chlorophyll a were used for inoculation, and other conditions were the same. After cultivating for 3 months, soil samples were collected at a depth of 0.5 cm, and the content of chlorophyll a was determined after natural drying. The thickness of the formed a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com