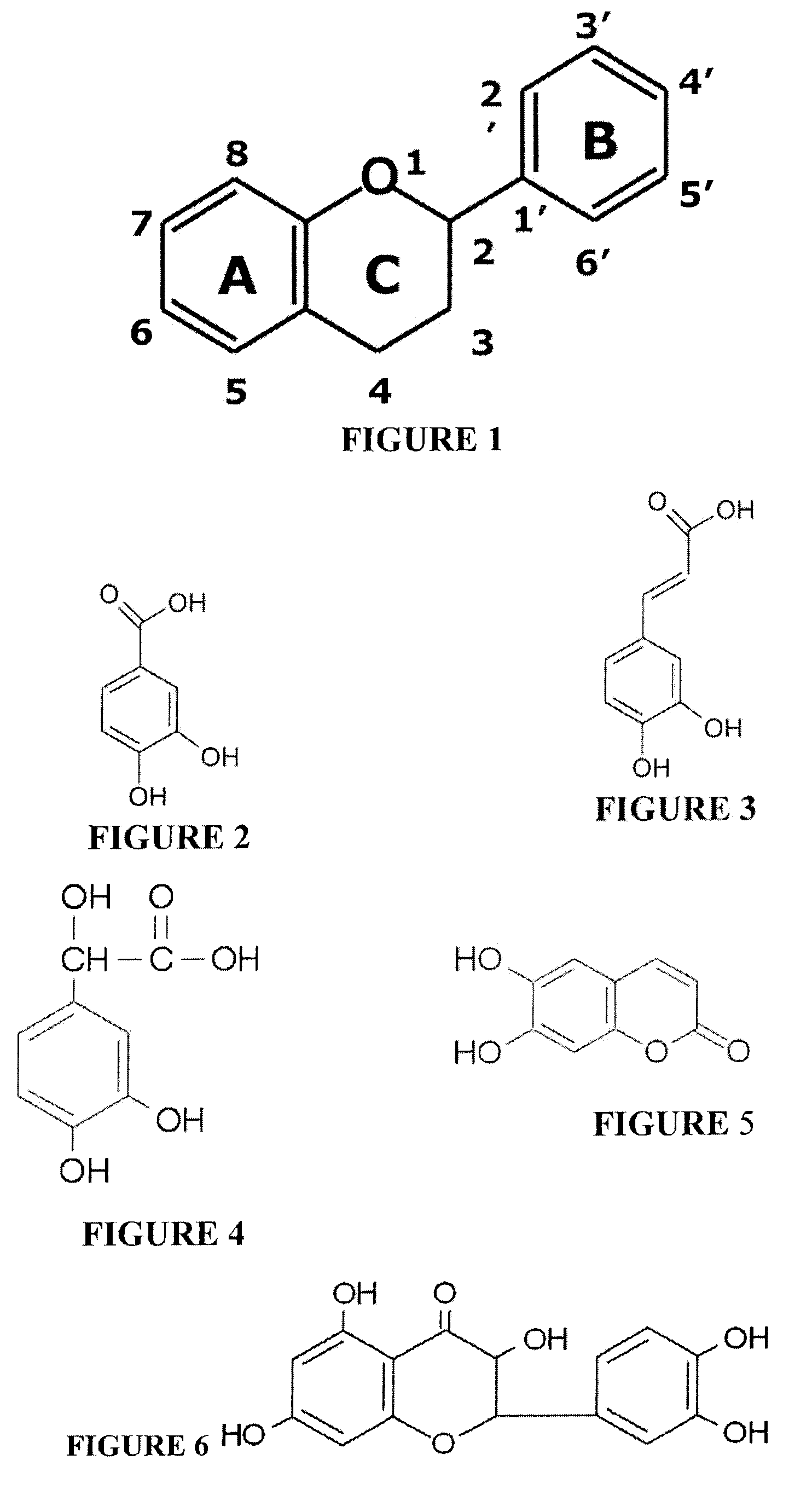
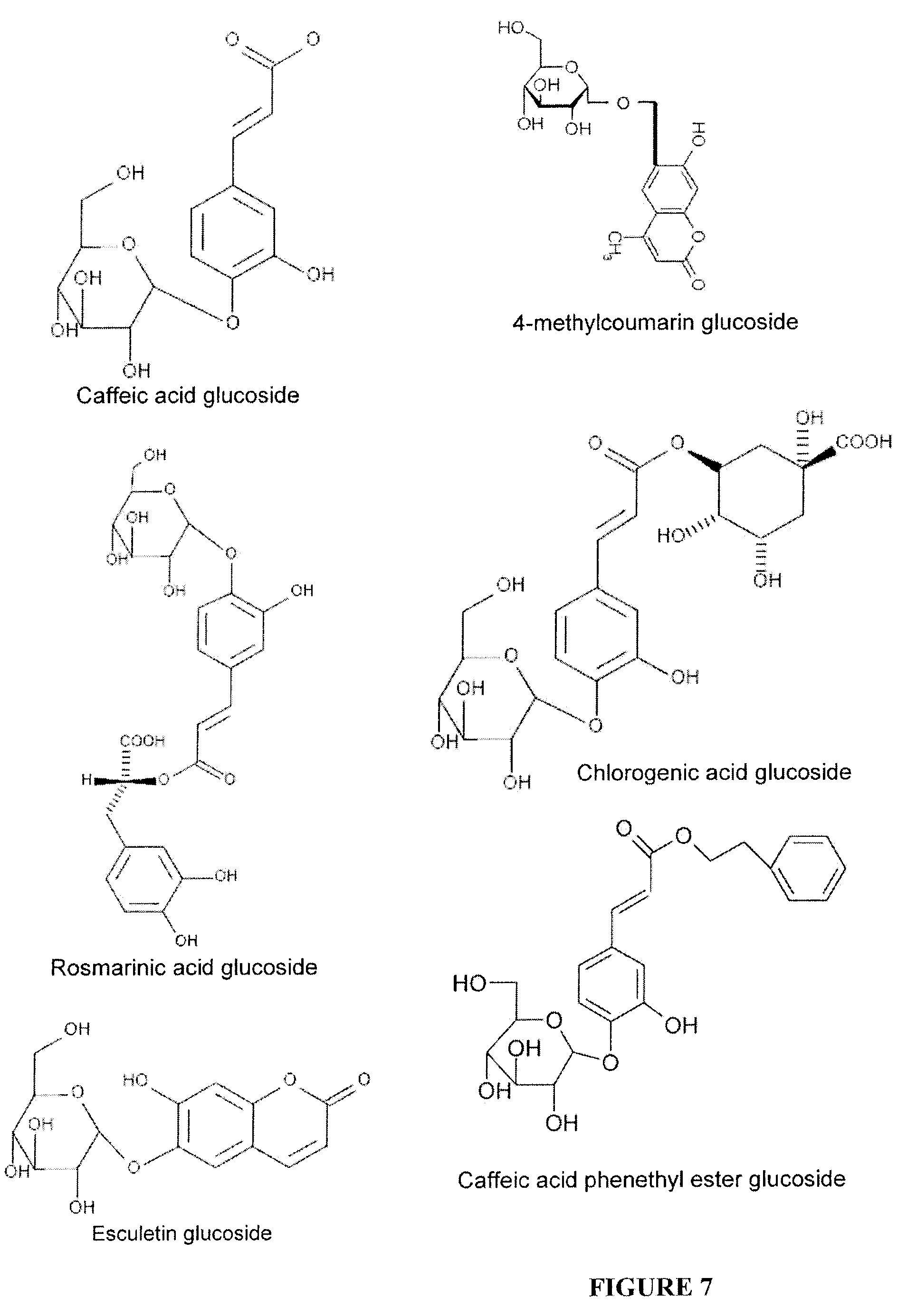
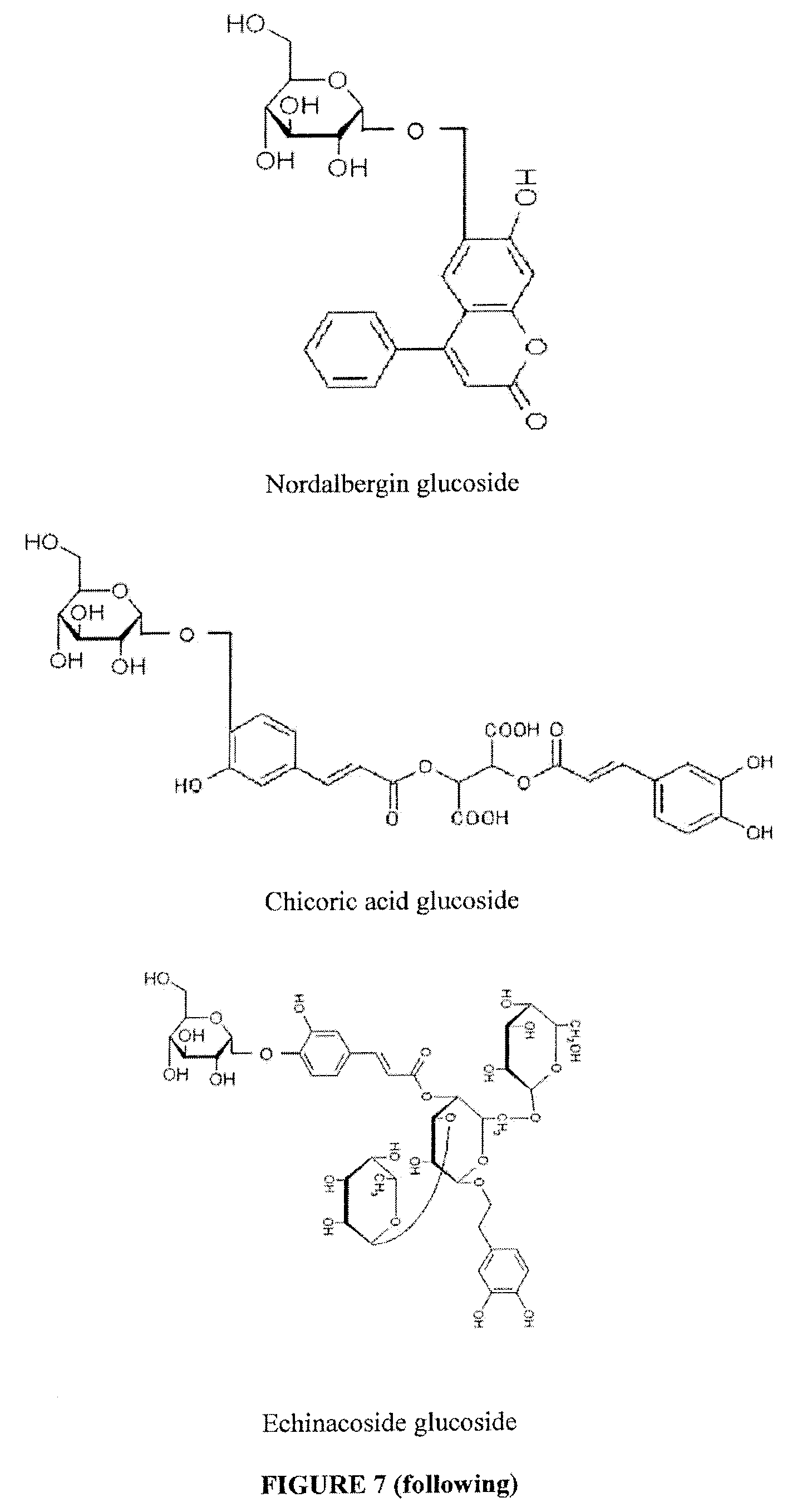
Water Soluble and Activable Phenolics Derivatives with Dermocosmetic and Therapeutic Applications and Process for Preparing Said Derivatives
a technology of activation and phenolics, applied in the field of preparation of phenolics derivatives, can solve the problems of difficult to reach concentration and stability, difficult to achieve concentration and stability, and difficult to achieve oxidation resistant forms of phenolics, so as to prevent carcinogenesis, reduce allergic reactions, and potent immunosuppressive effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Glucosylated Taxifolin; Solubility in Water of Highly Purified Glucosylated Taxifolin and Stability of the Glucosylated Derivative Molecule at Temperatures Ranging from 4° C. to 45° C.
[0441]The conditions that were carried out for the synthesis of glucosylated Taxifolin are as follows (amounts for 1 liter of reaction medium):
IngredientOriginAmountConcentrationSolution of Taxifolin atTaxifolin: SIGMA T 4512100mlTaxifolin: 9 g / L90 g / L in pure DMSODMSORiedel de Haën 60153250mlTotal DMSO:350 ml / LSodium acetate bufferAcetic acid:40mlSodium acetate:500 mM pH 5.2Prolabo 20104.29820 mMSodium hydroxide:Riedel de Haën 6203Sucrose at 500 g / LProlabo 27478.296300ml150 g / L(1,462 M)0.439 MWaterDeionizedQsp 1.00L#Calcium chloride,Merck 1.02382.050010mg10 mg / Ldihydrate(can also be introduced inthe reaction medium in theform of a solution at 2 g / L;the dose is then 5 ml / L)DextransucrasePurified from L. mesenteroides170ml3.1 U / mlpreparation (18 U / ml)NRRL B-512F culture broth
[0442]The react...
example 2
Influence of the DMSO Concentration on the Efficiency of the Synthesis of Taxifolin Glucoside
[0469]Taxifolin glucoside enzymatic synthesis was carried out as described in Example 1 with the following exceptions:
[0470]enzyme concentration was 1 U / ml
[0471]DMSO concentration was 35%, 25%, 15% or 5%.
[0472]After 22 hours of incubation, relative Taxifolin glucoside concentrations in the four reaction medium are reported in the following table.
DMSO, %3525155Taxifolin glucoside10013316117(relative concentration), %
[0473]The optimal DMSO concentration for the synthesis of Taxifolin glucoside appears to be at a value significantly lower than 30% and close to 15%.
example 3
Activation of Taxifolin Glucoside by Human Skin Micro-Flora
[0474]Cutaneous flora was separately collected from 5 donors. The forearms and forehead of each donor were scraped with a cotton-wool swab saturated with NaCl solution (v=5 mL, 8 g / l). After each scraping, the swab was divided into the remaining NaCl solution and squeezed to deliver the sampled material. After two cycles of scraping / squeezing on both forearms and three on the forehead, the obtained trouble preparation was filtered (40 μm) to eliminate squama and finally centrifuged (4° C., 5000 g, 15 min). The microbial pellets were resuspended in a NaCl solution (v=1 mL, 8 g / l) and characterized by OD at 600 nm.
[0475]The five microbial samples were mixed to form the final microbial suspension used for the test. Microbial cells were cultivated using the Hickey-Tresner culture medium (yeast extract at 1.0 g / L, meat extract at 1.0 g / L, casein peptone at 2.0 g / L, starch at 10.0 g / L, cobalt chloride hexahydrate at 20 mg / l; pH=6)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com