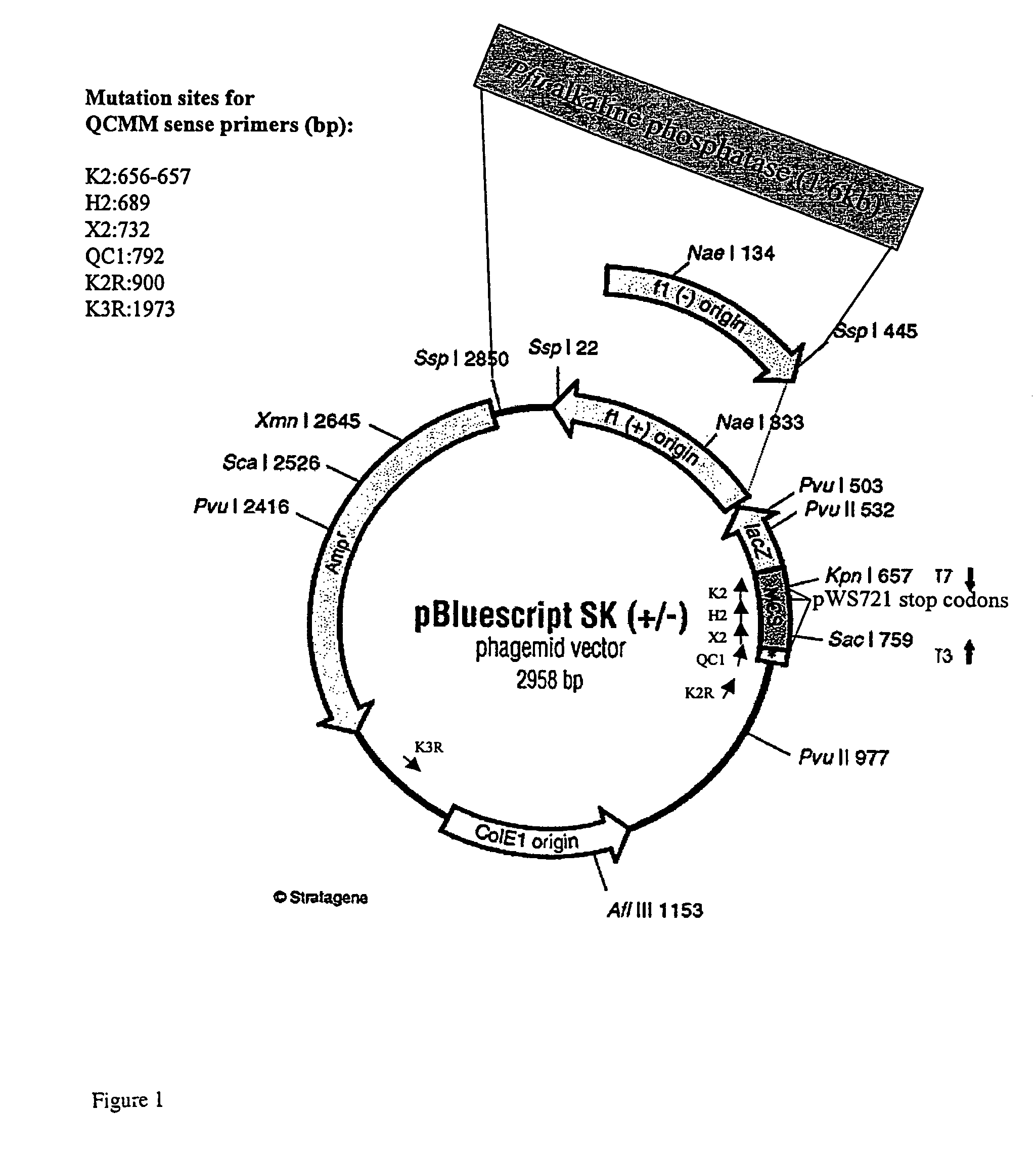
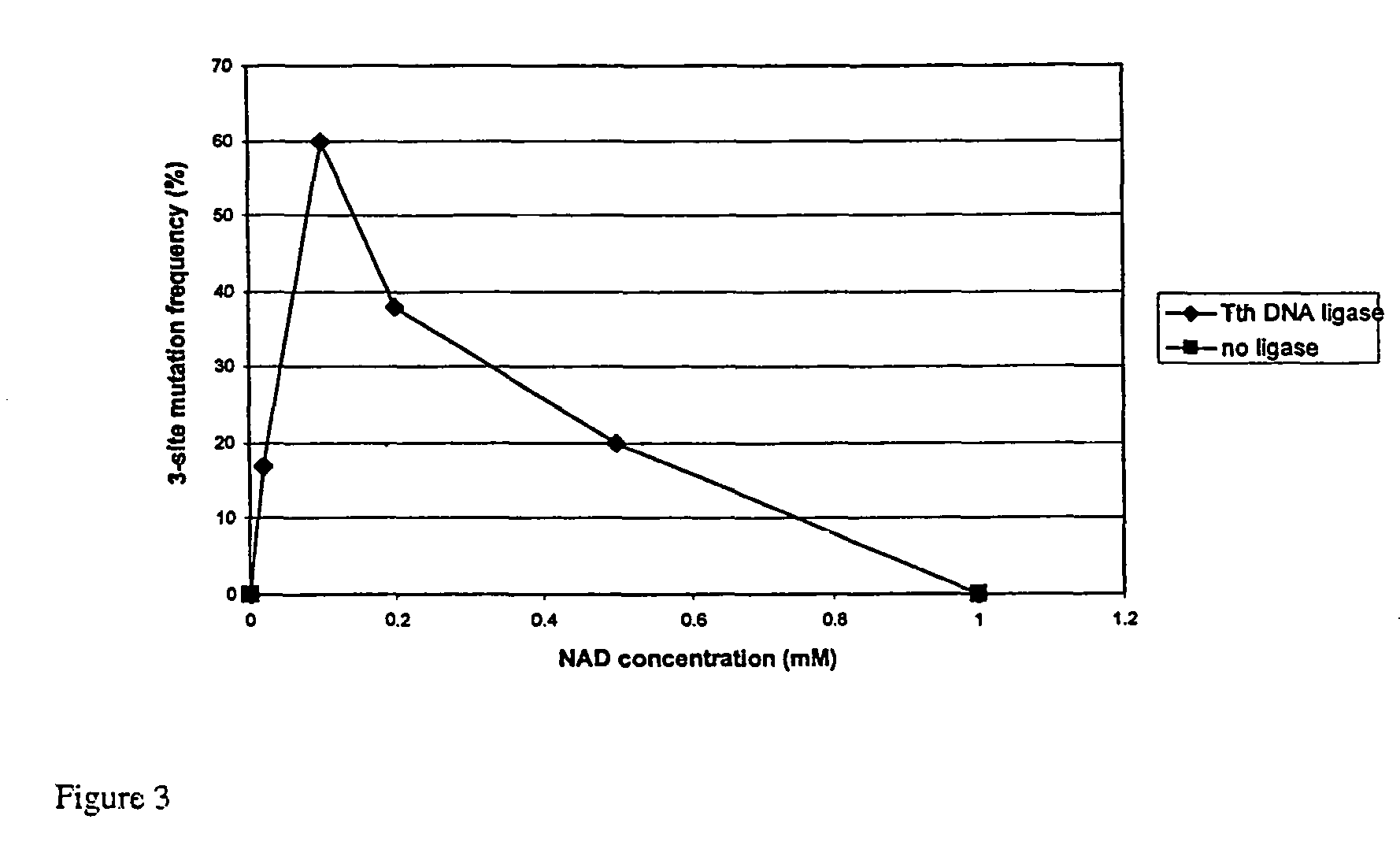
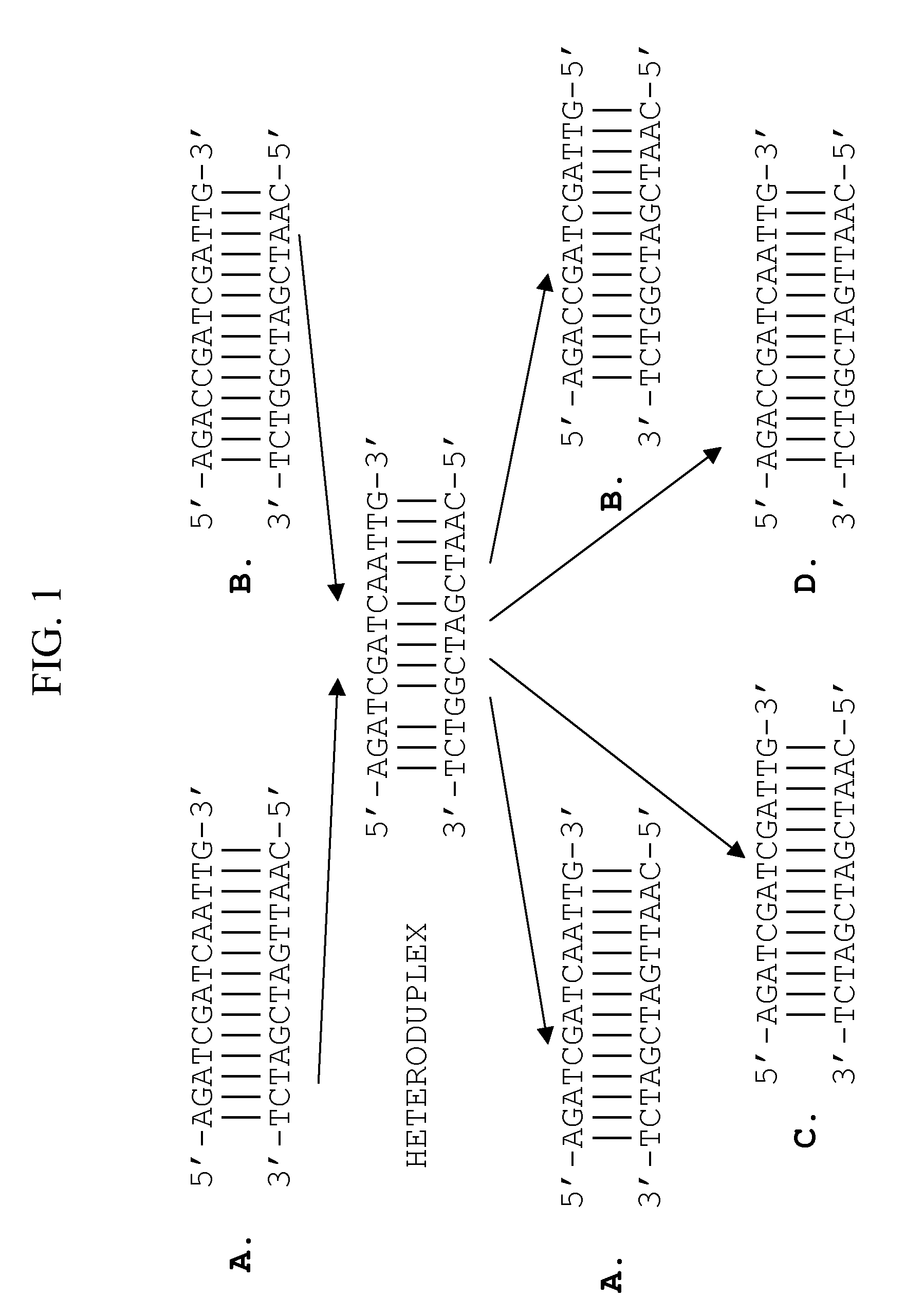
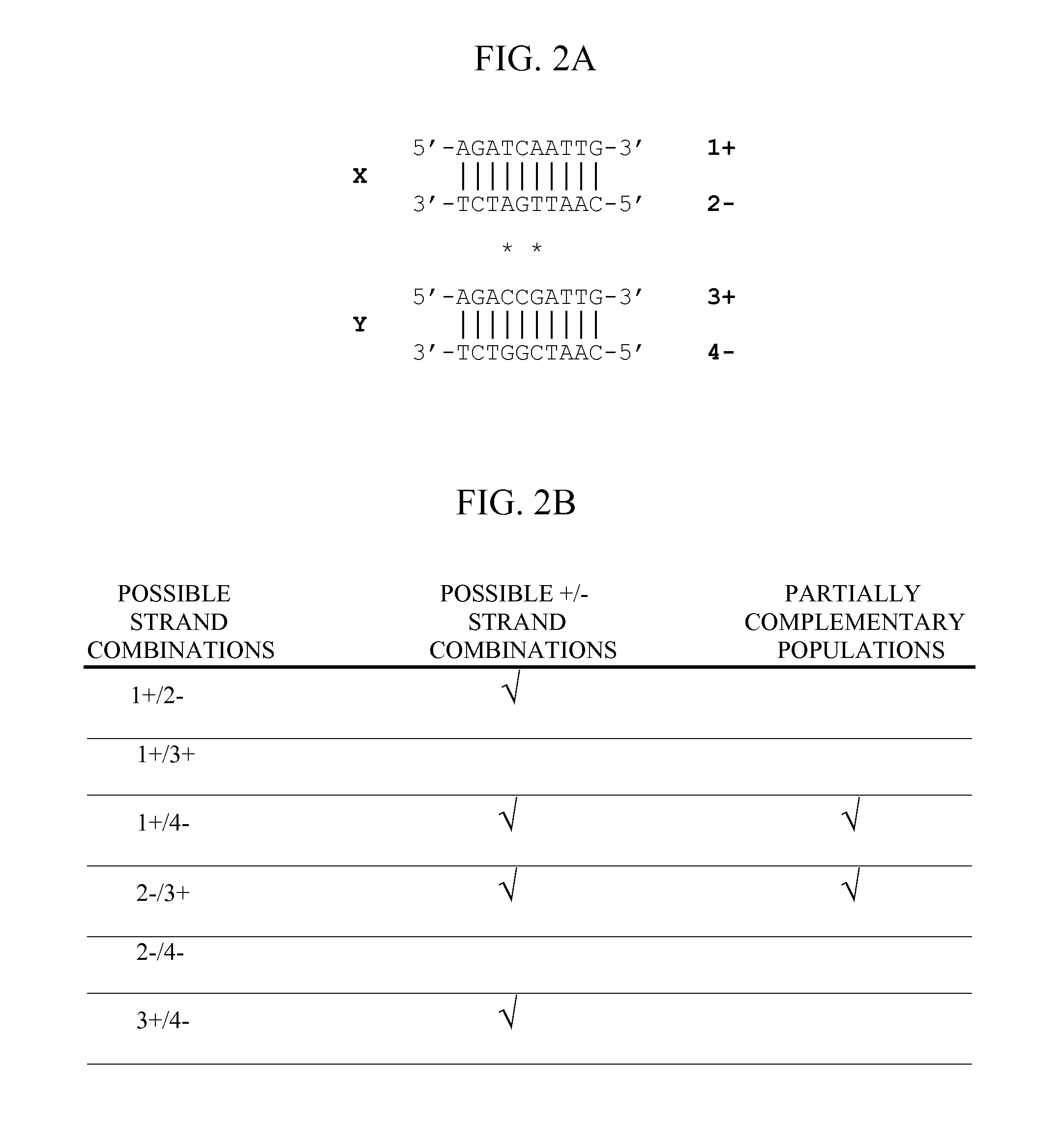
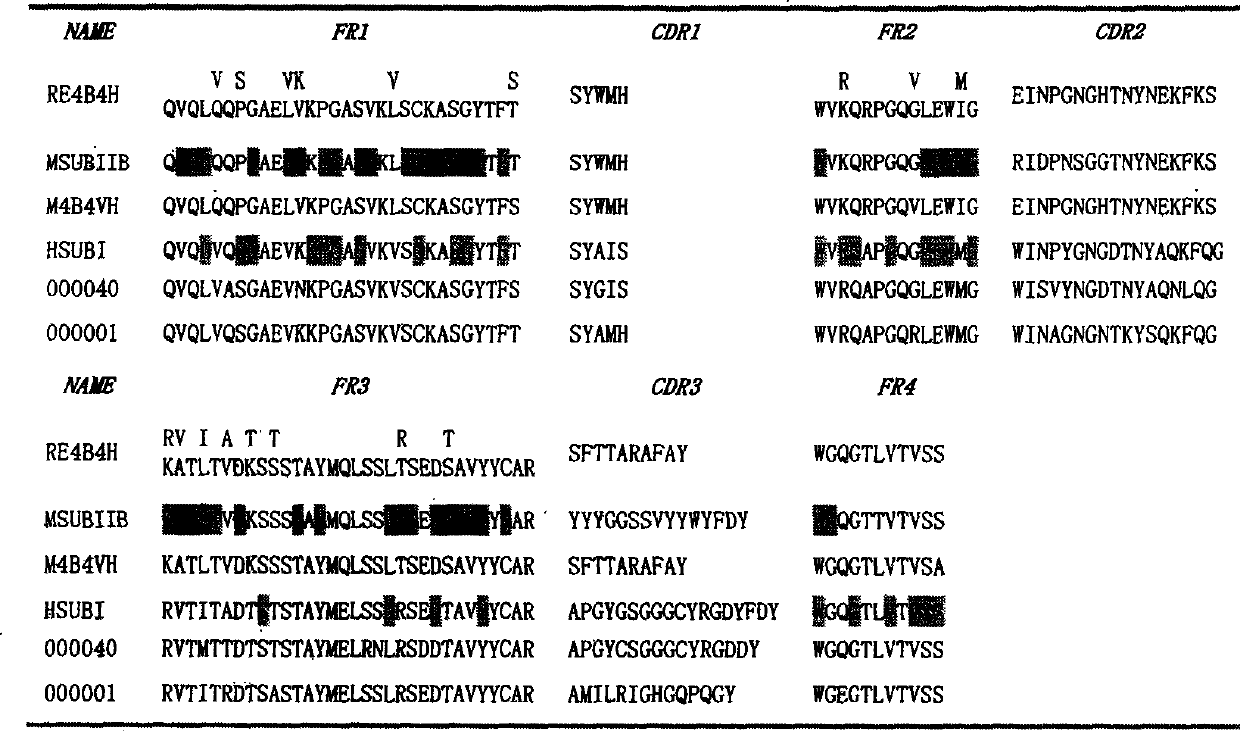
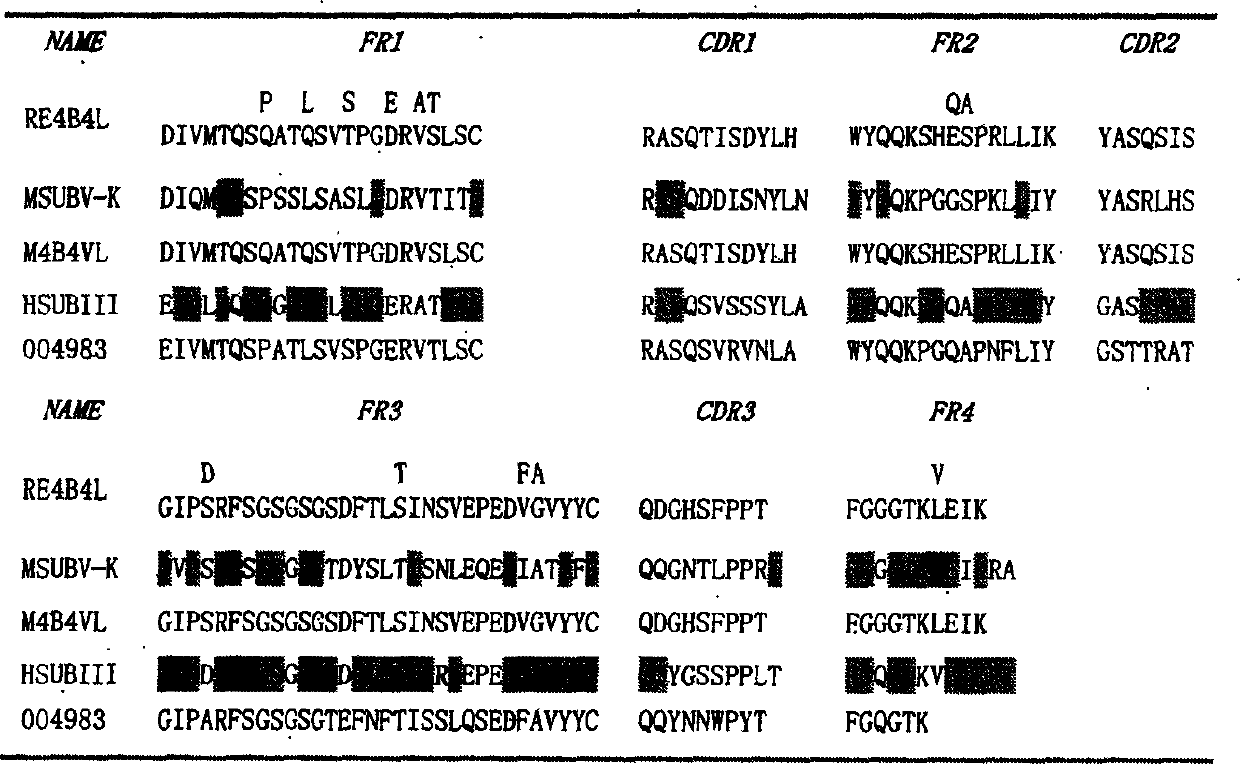
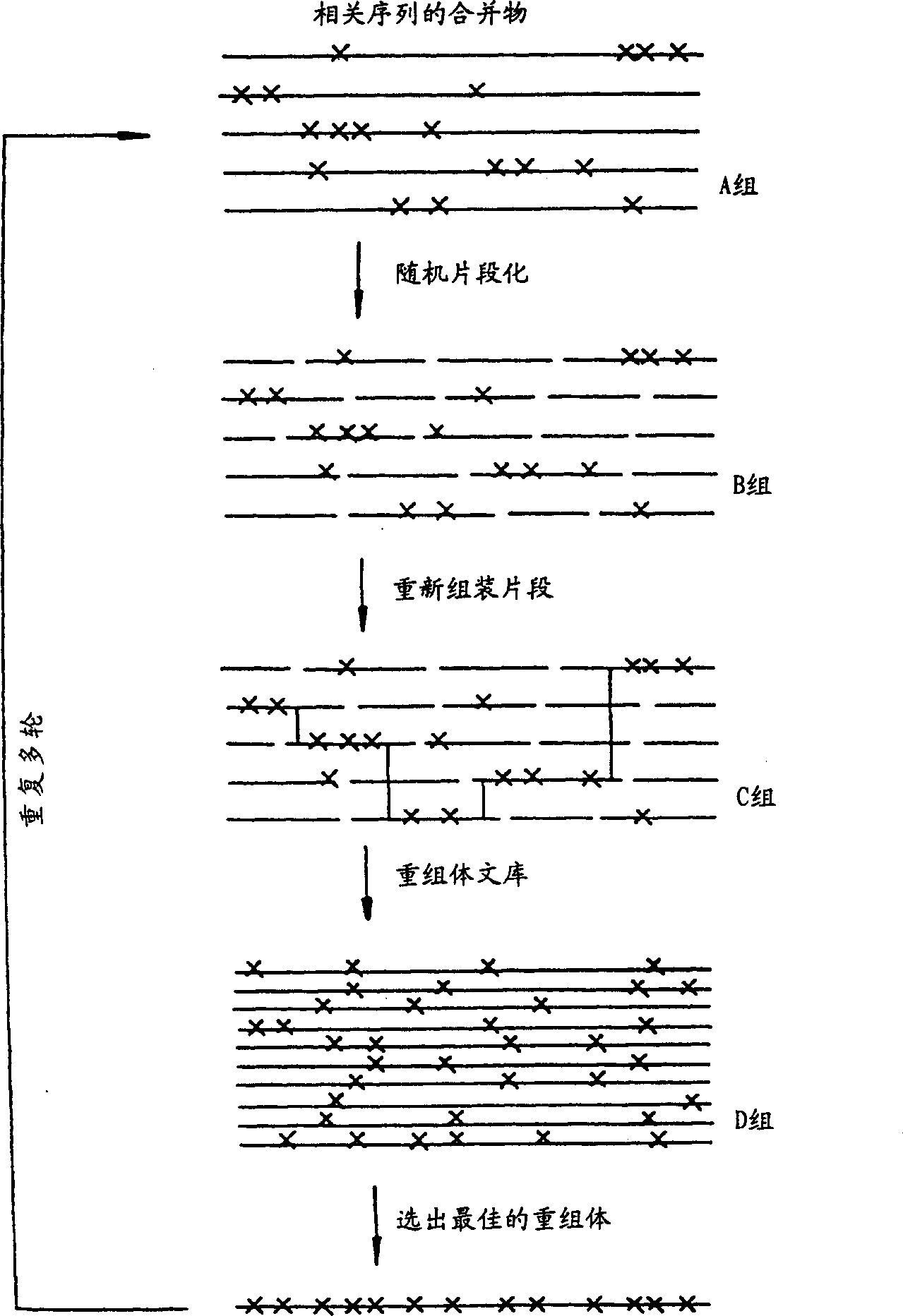
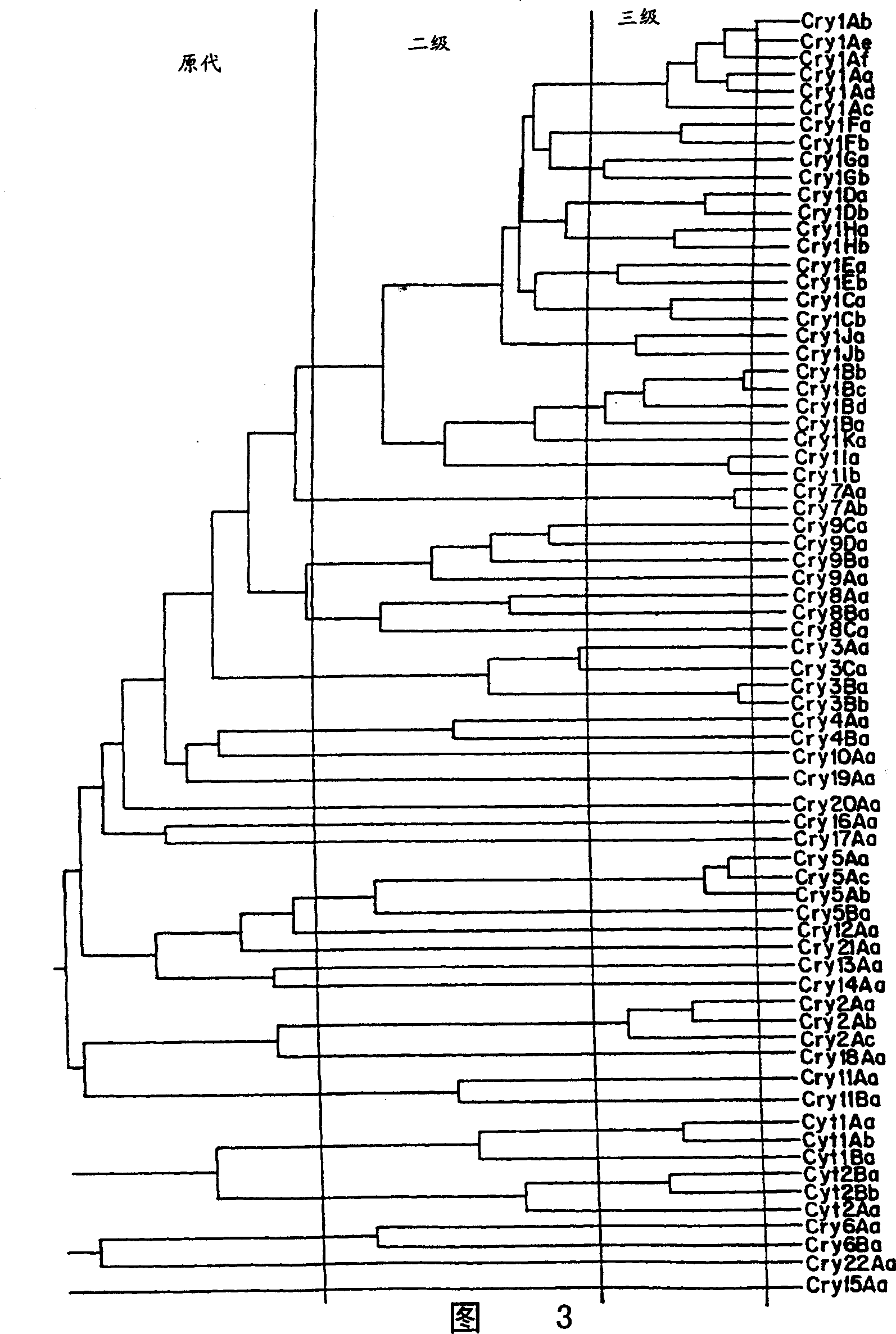
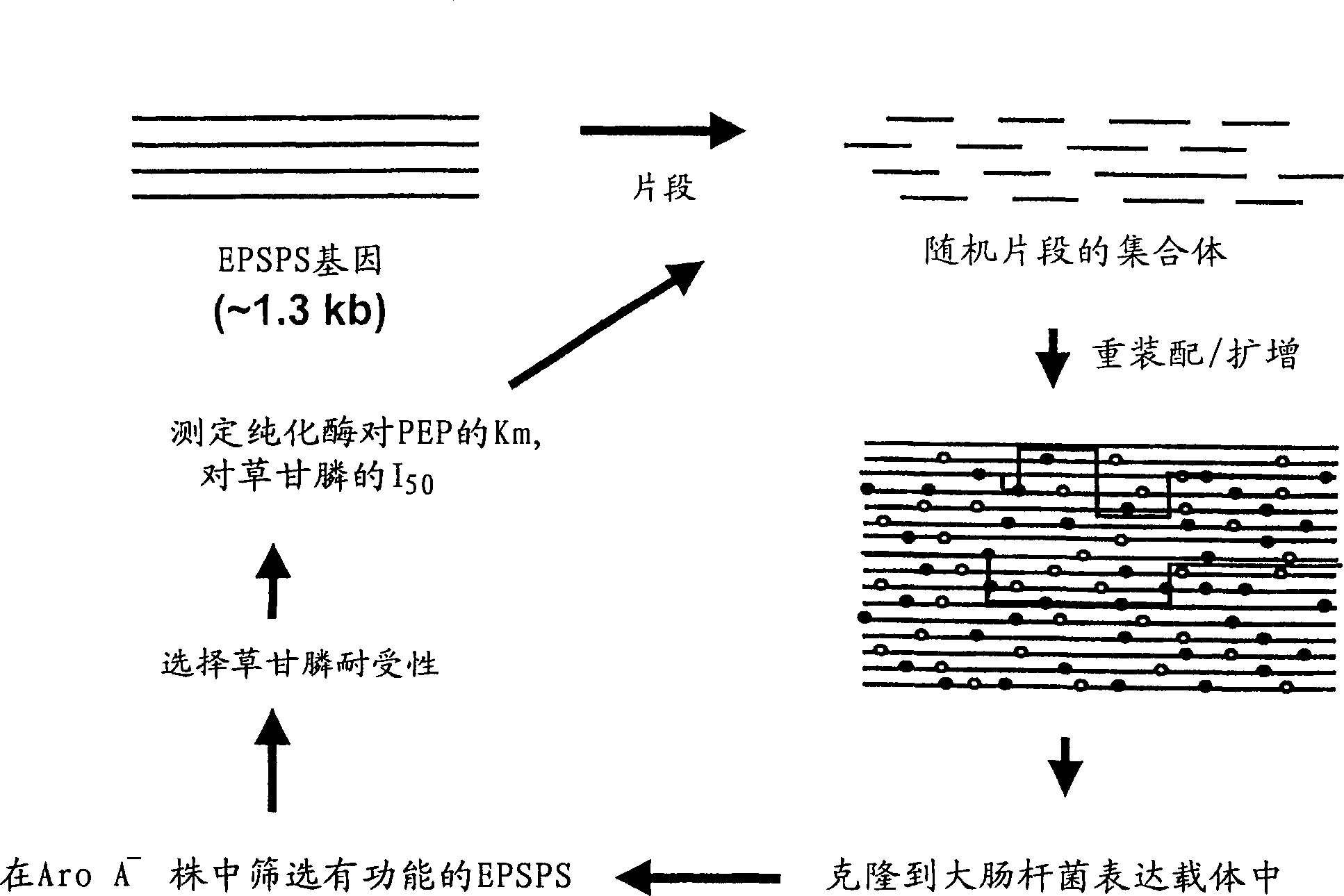
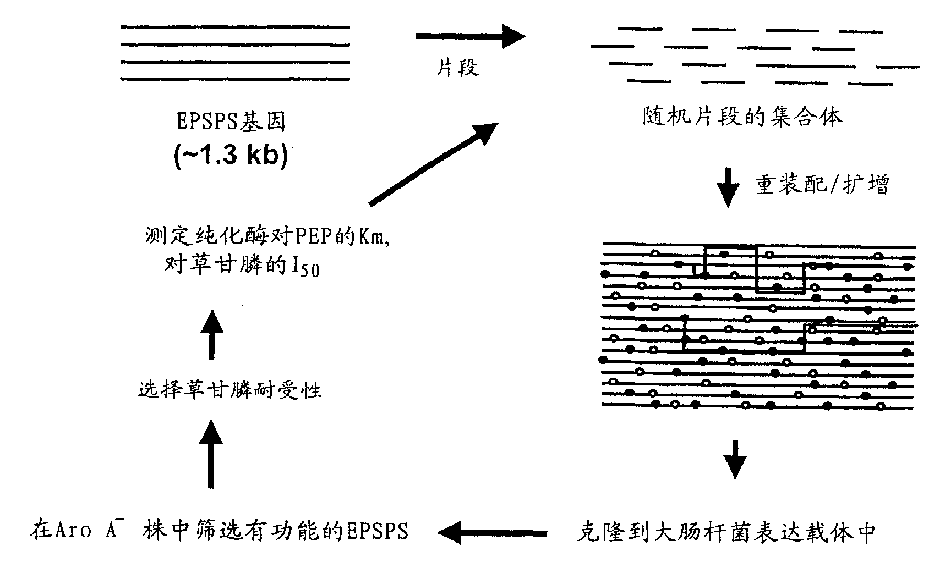
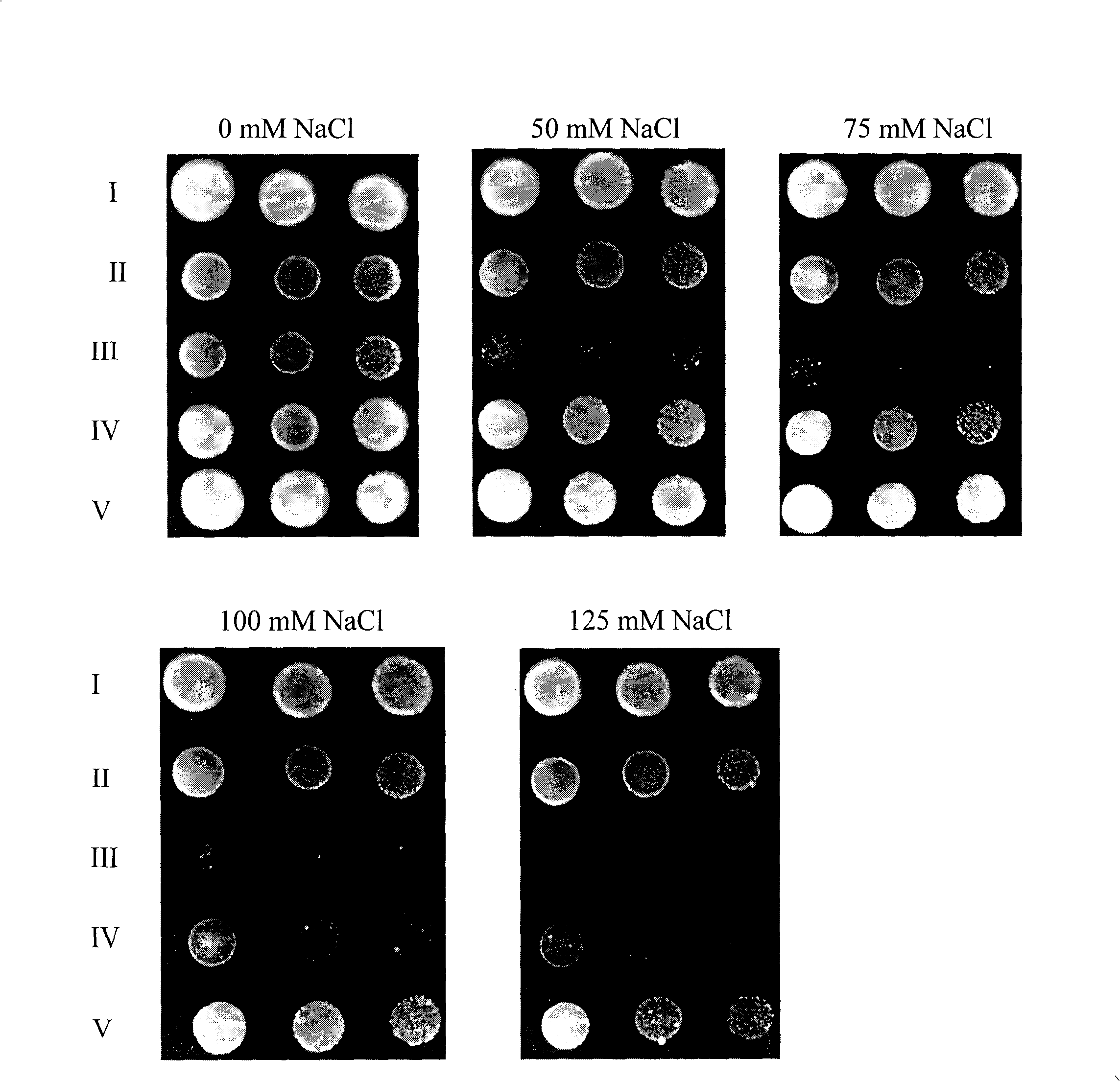
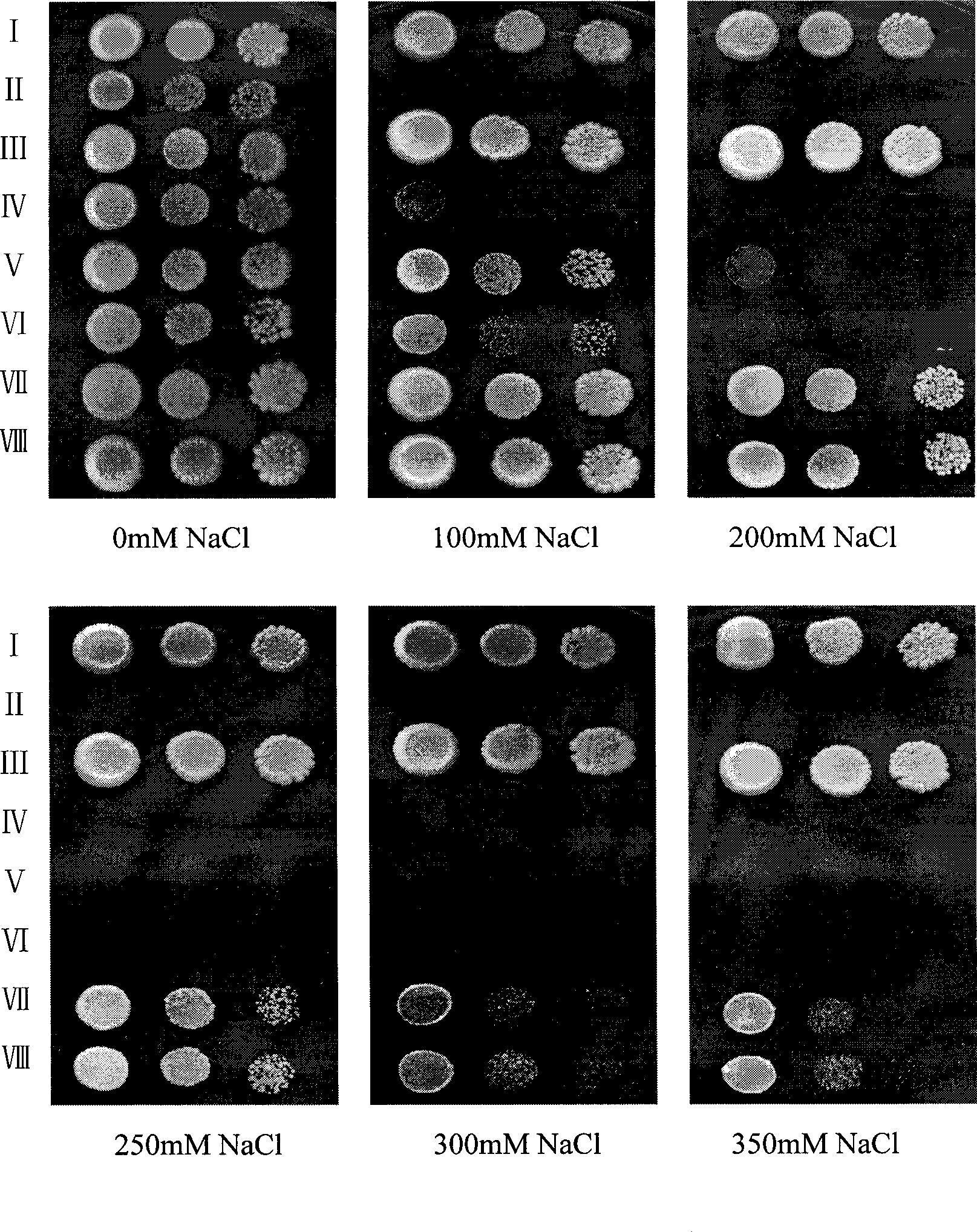
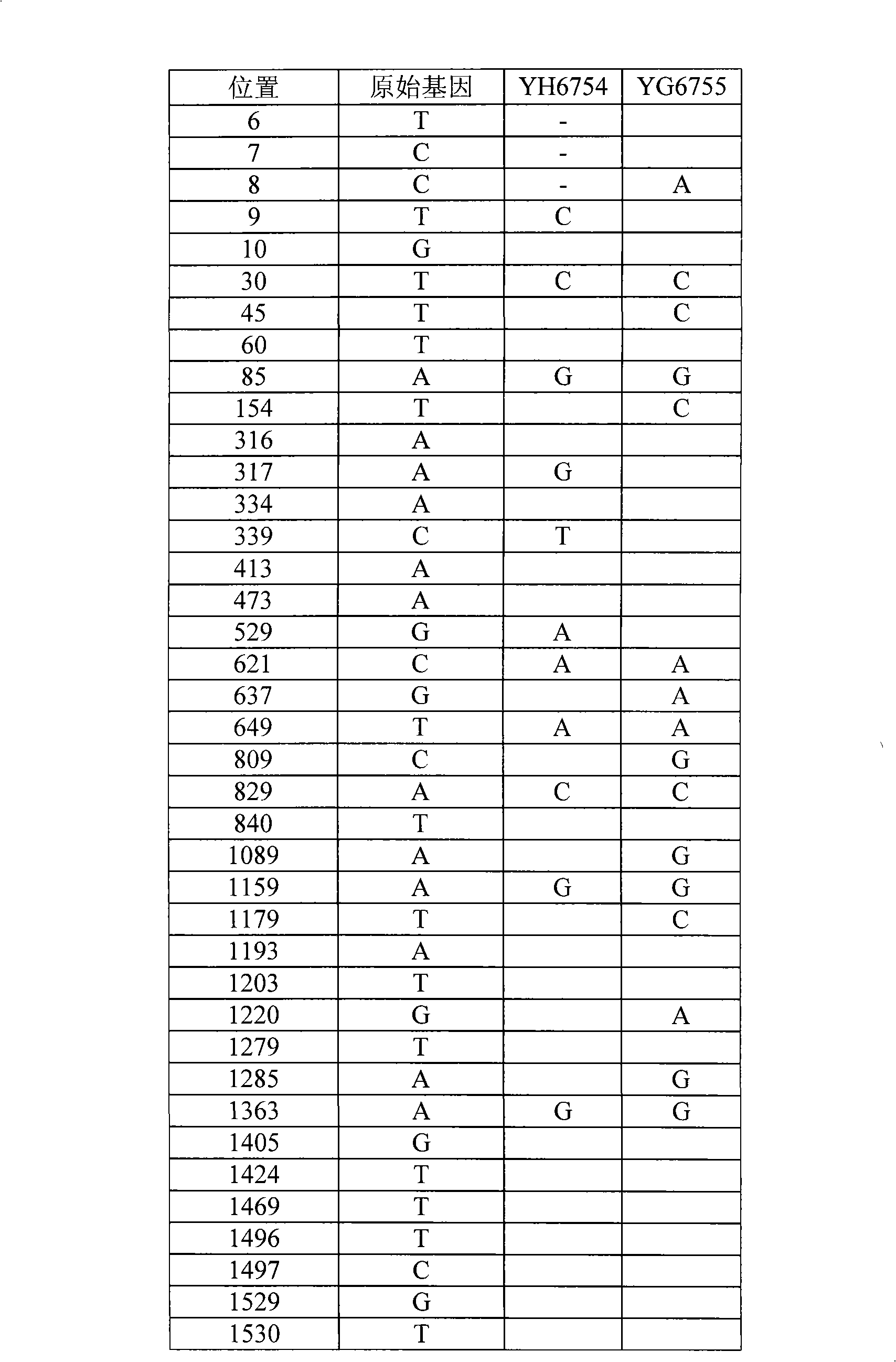
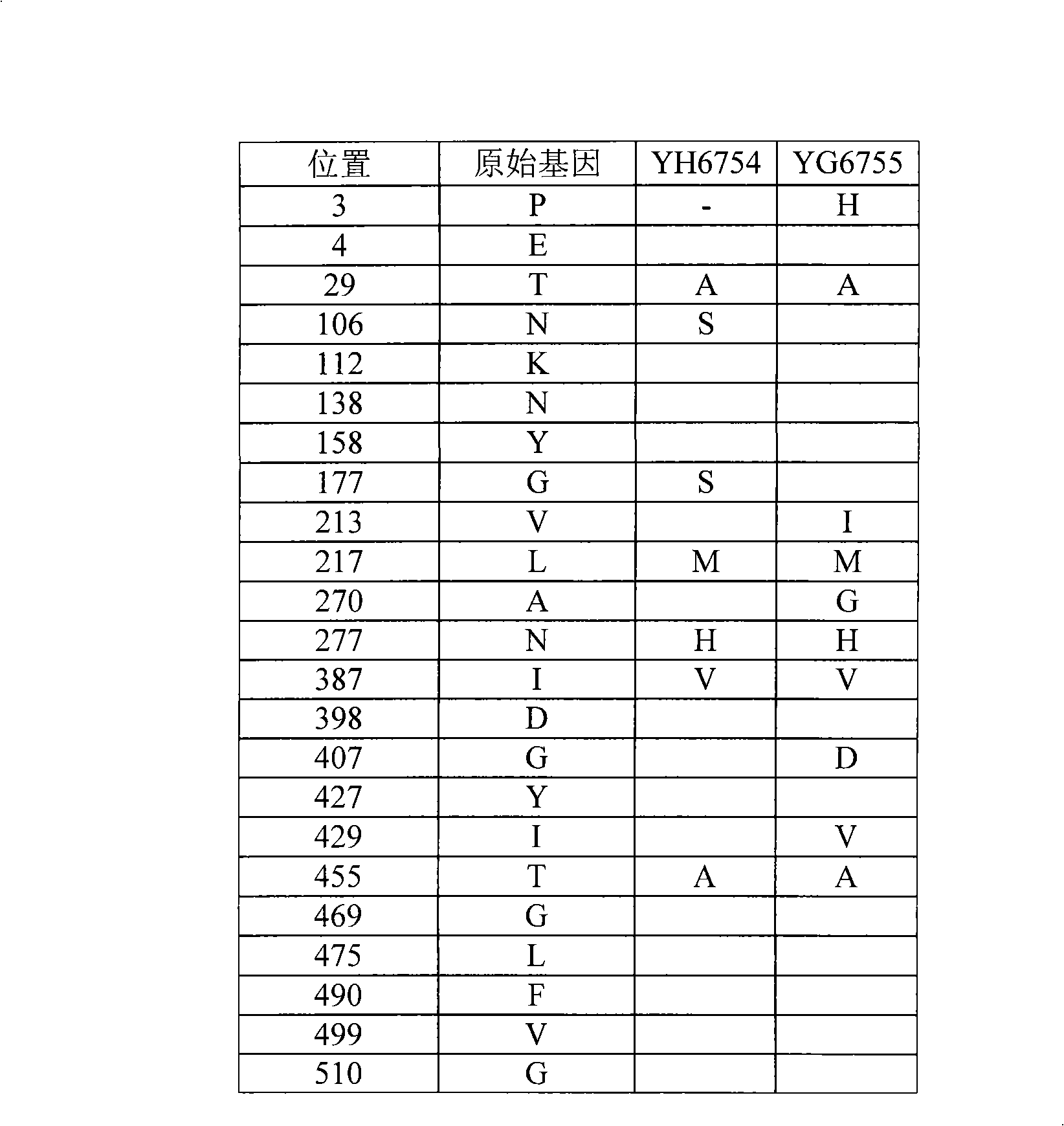
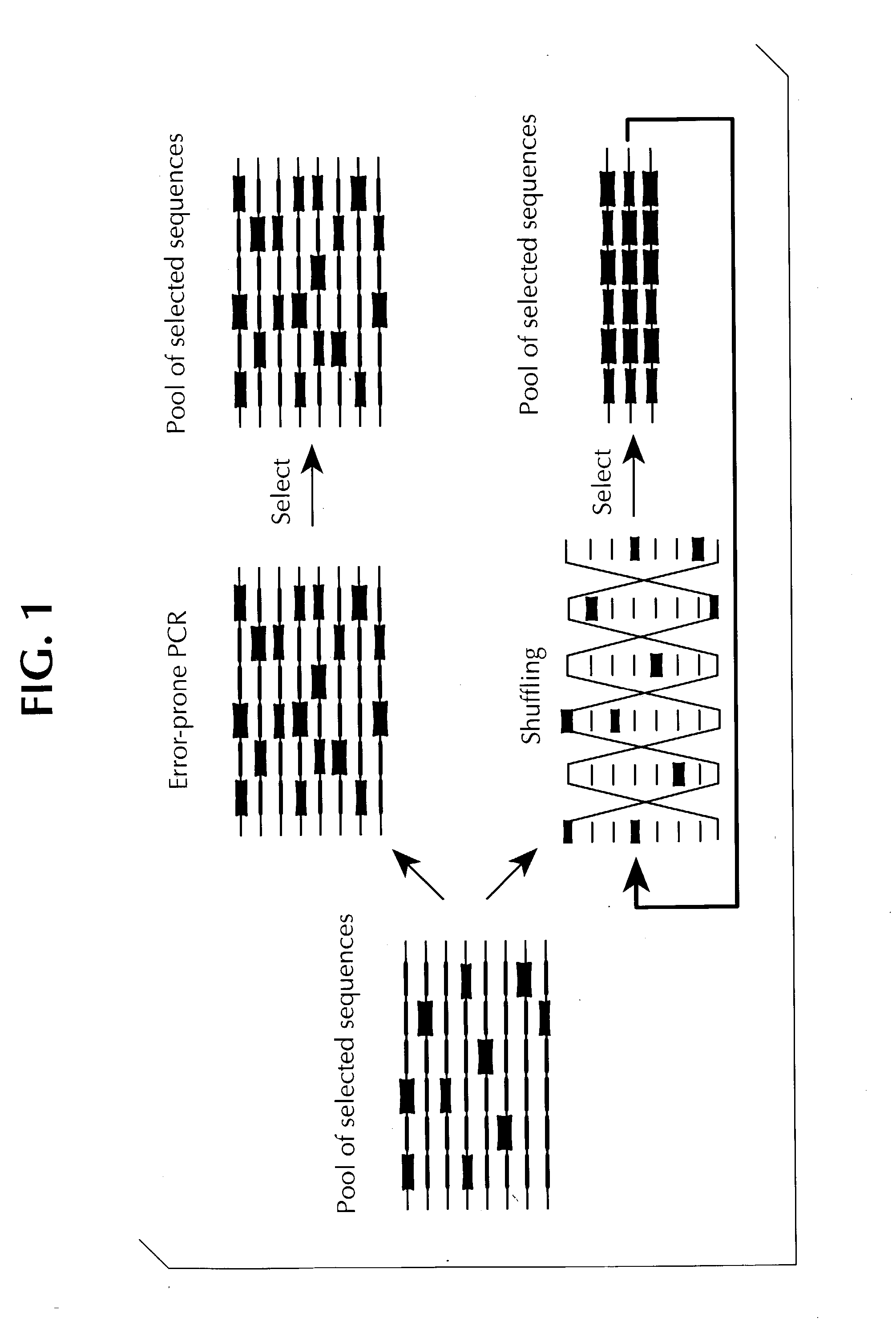
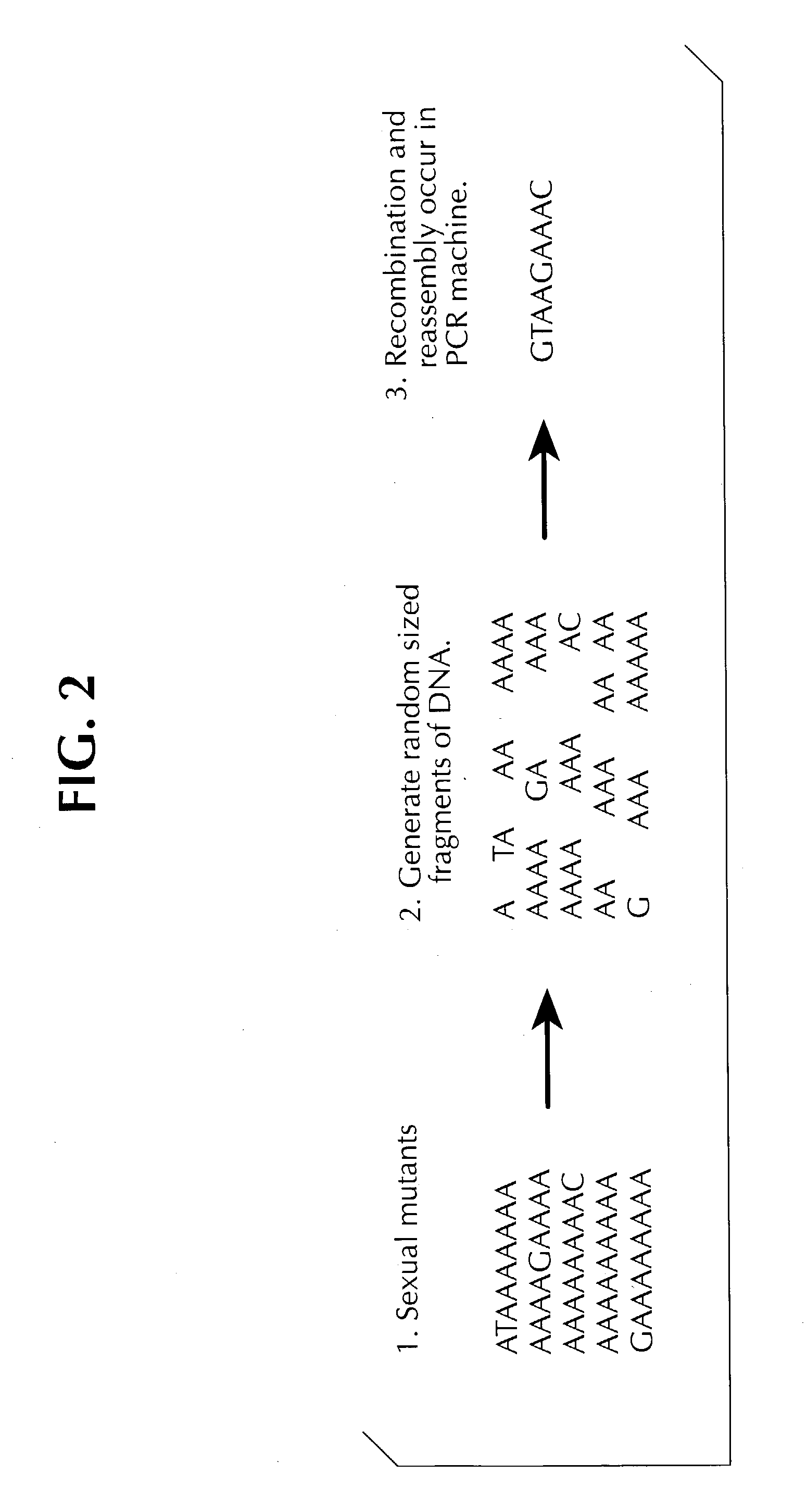
Patents
Literature
54 results about "DNA shuffling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
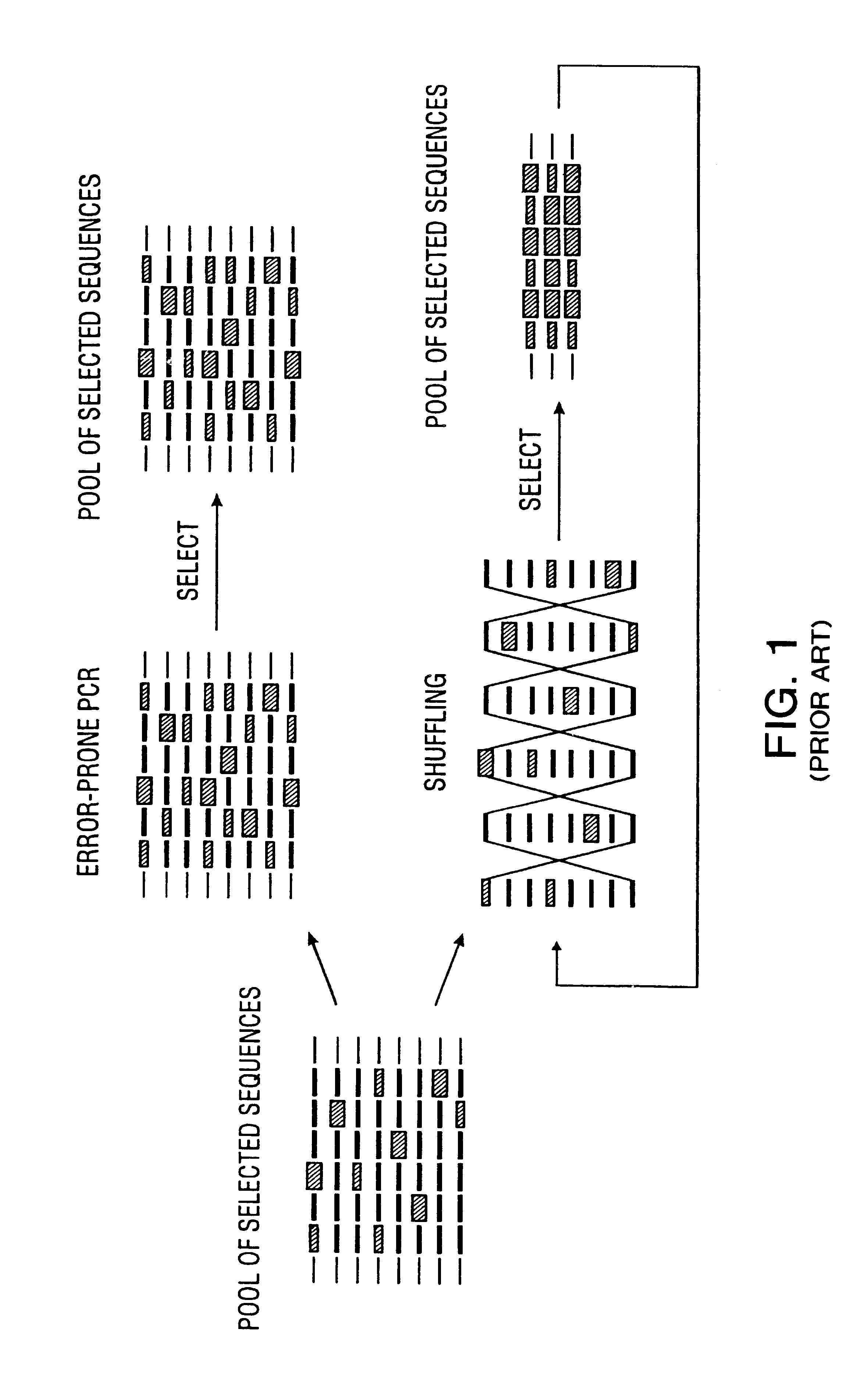
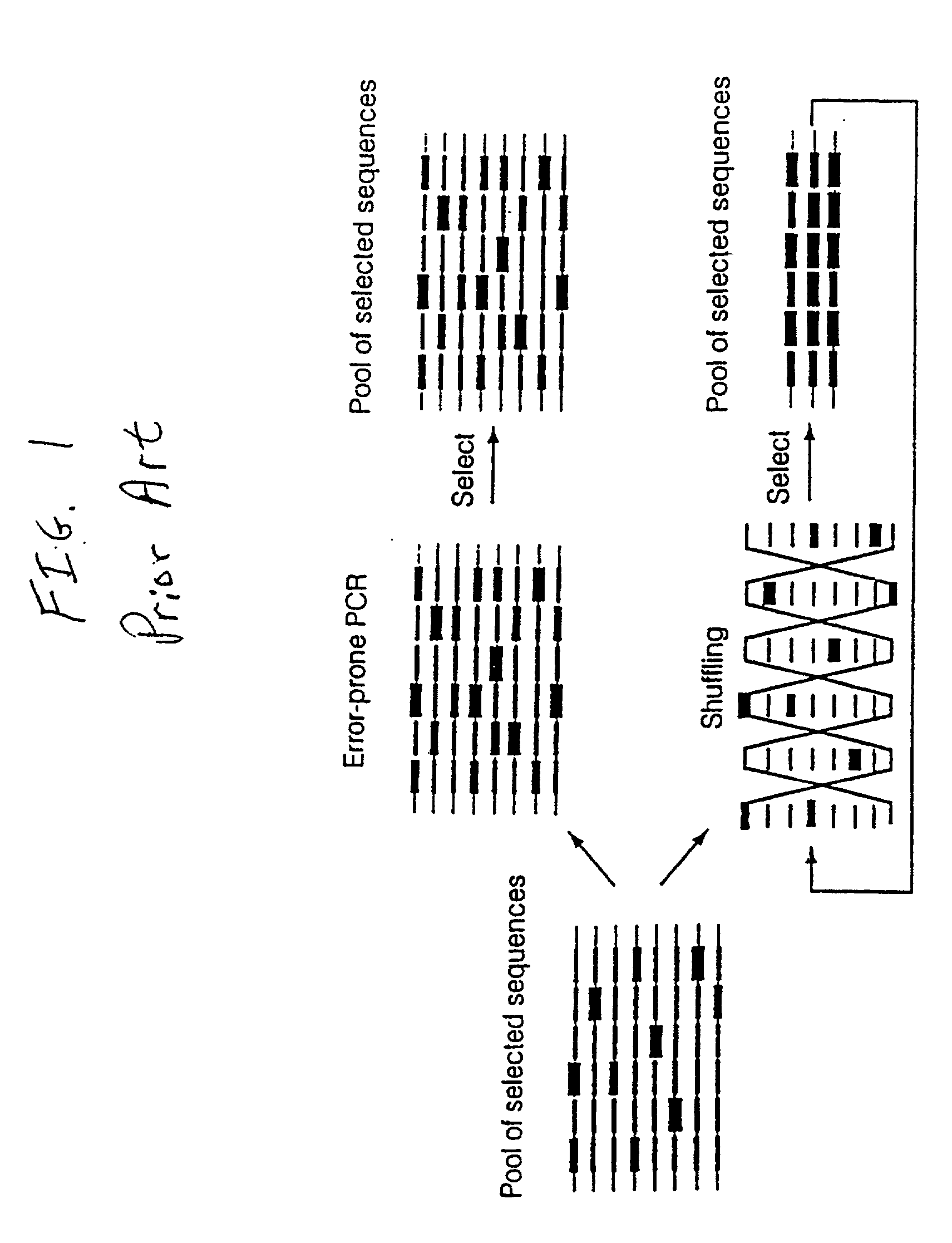
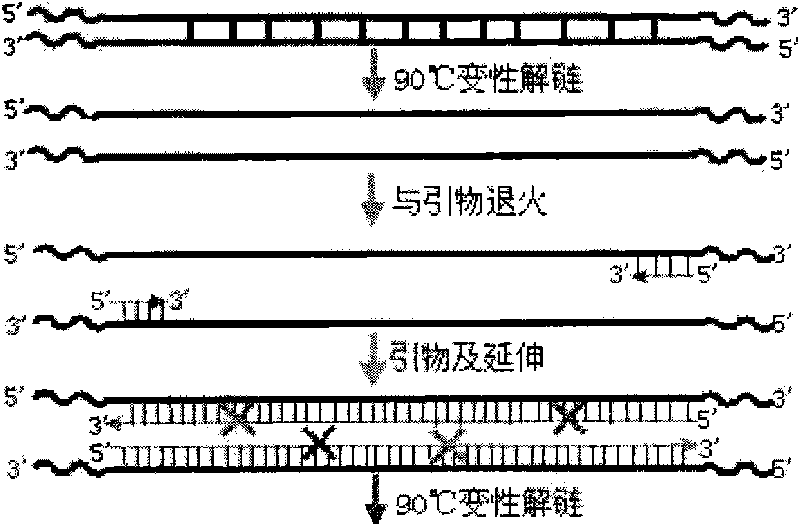
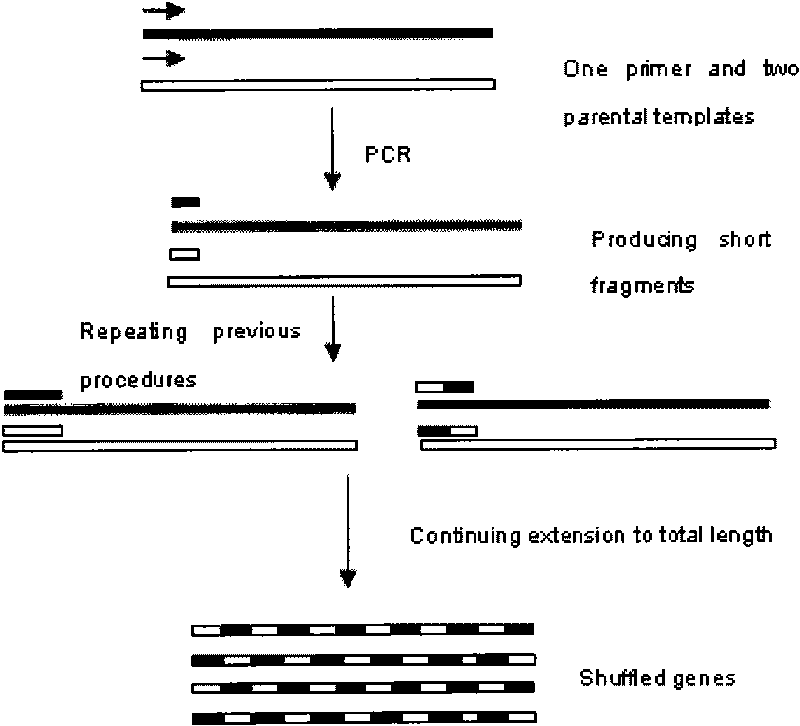
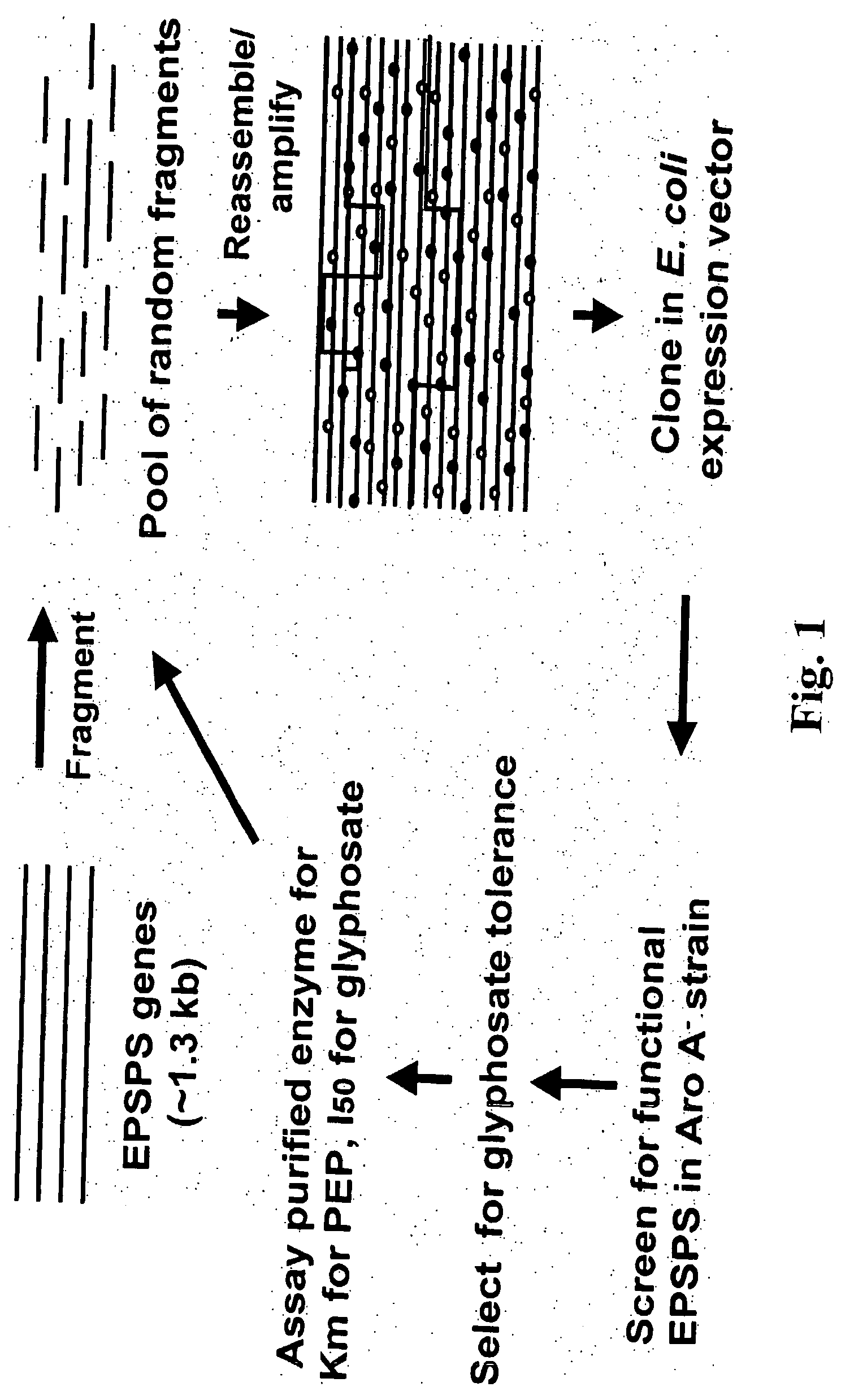
DNA shuffling is a way to rapidly propagate beneficial mutations in a directed evolution experiment. It is used to rapidly increase DNA library size.
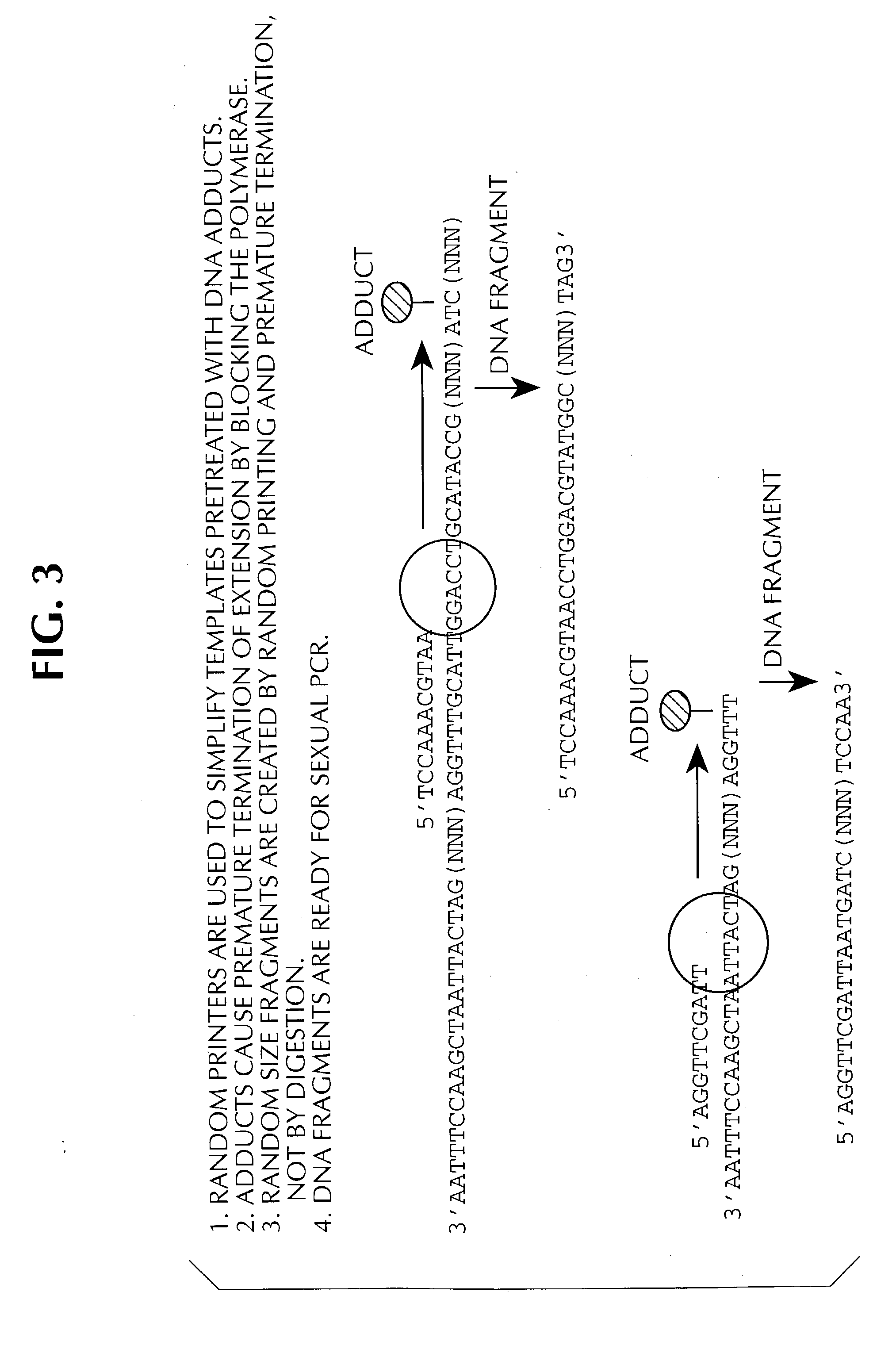
Method of DNA shuffling with polynucleotides produced by blocking or interrupting a synthesis or amplification process
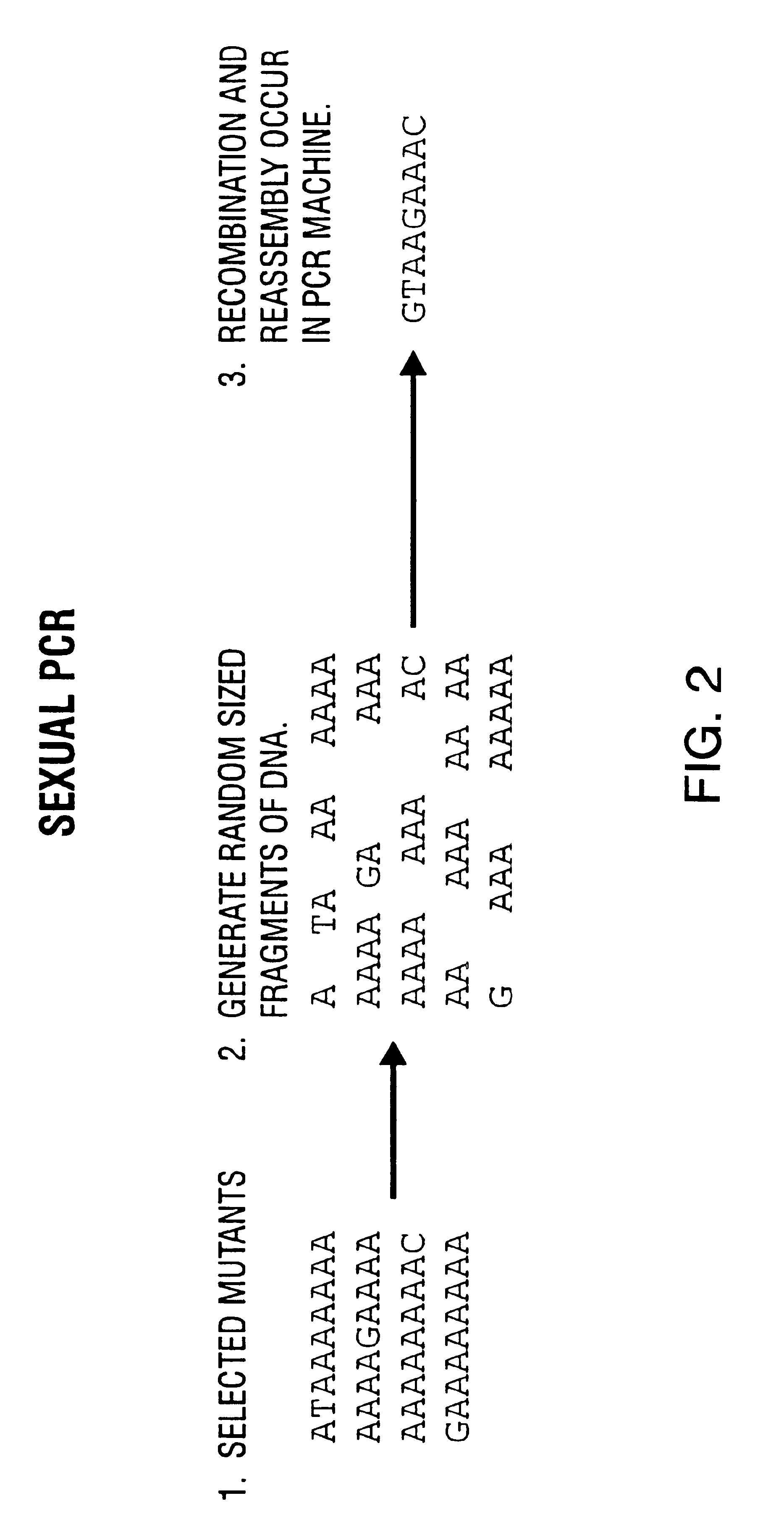
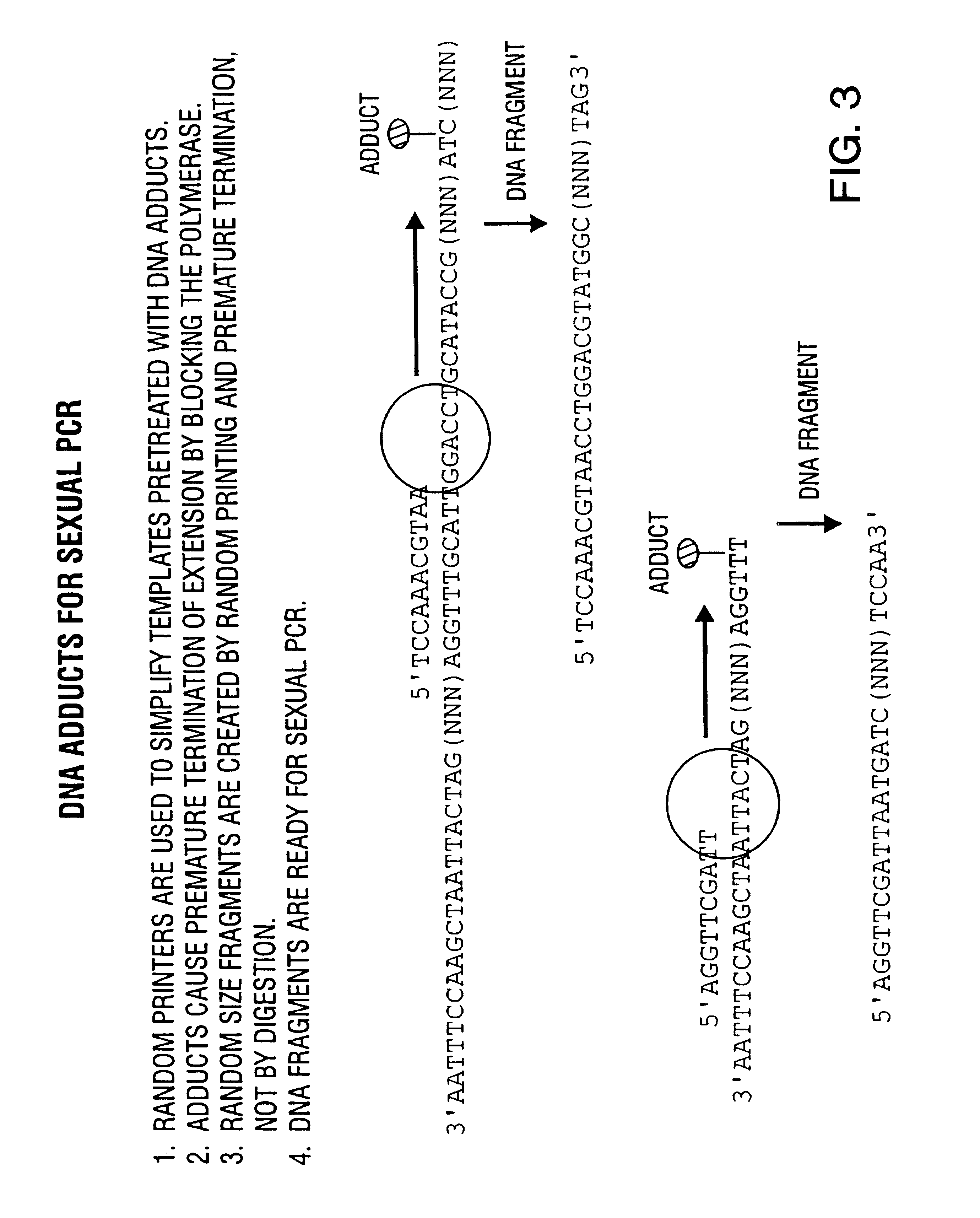
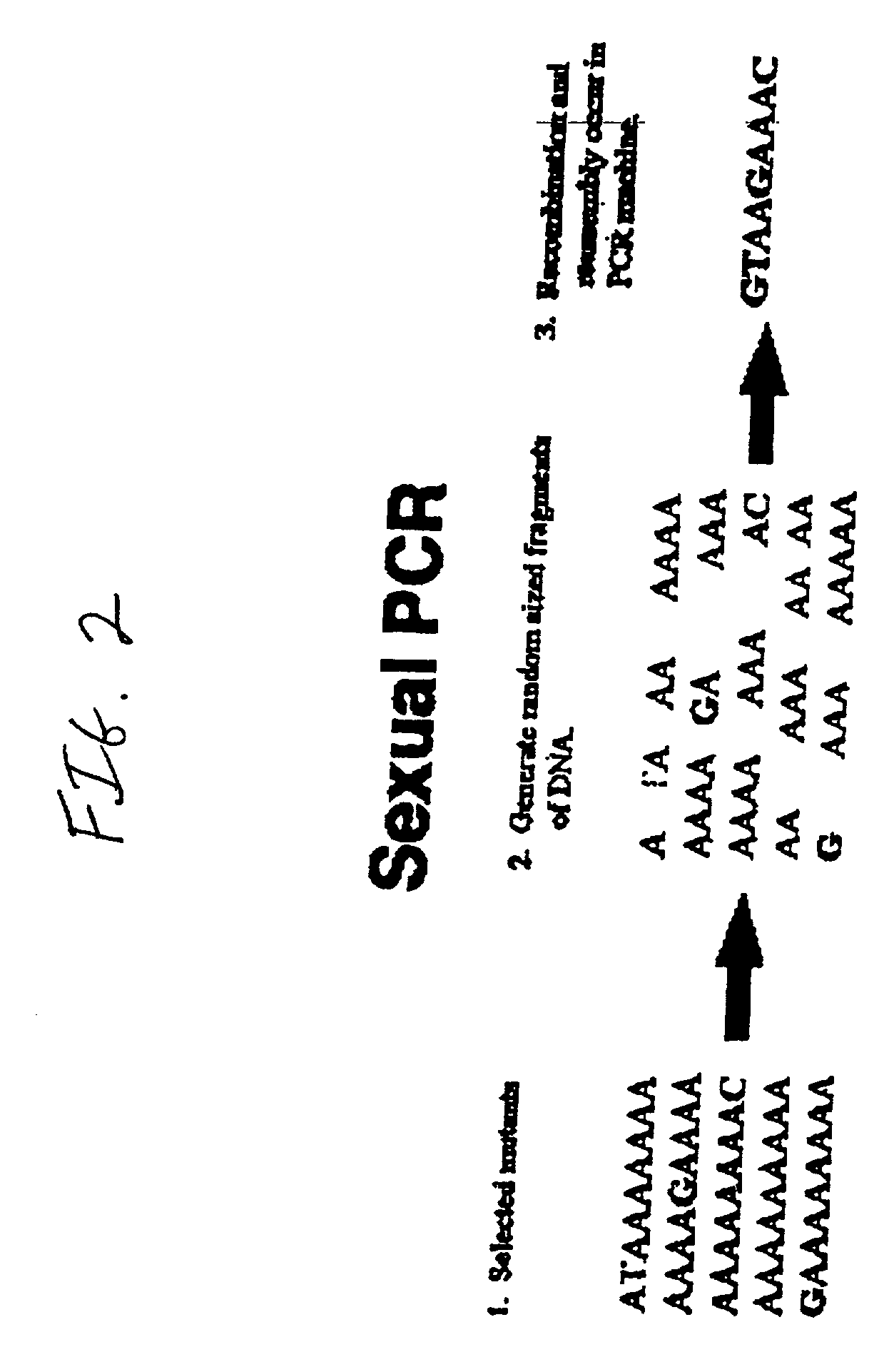
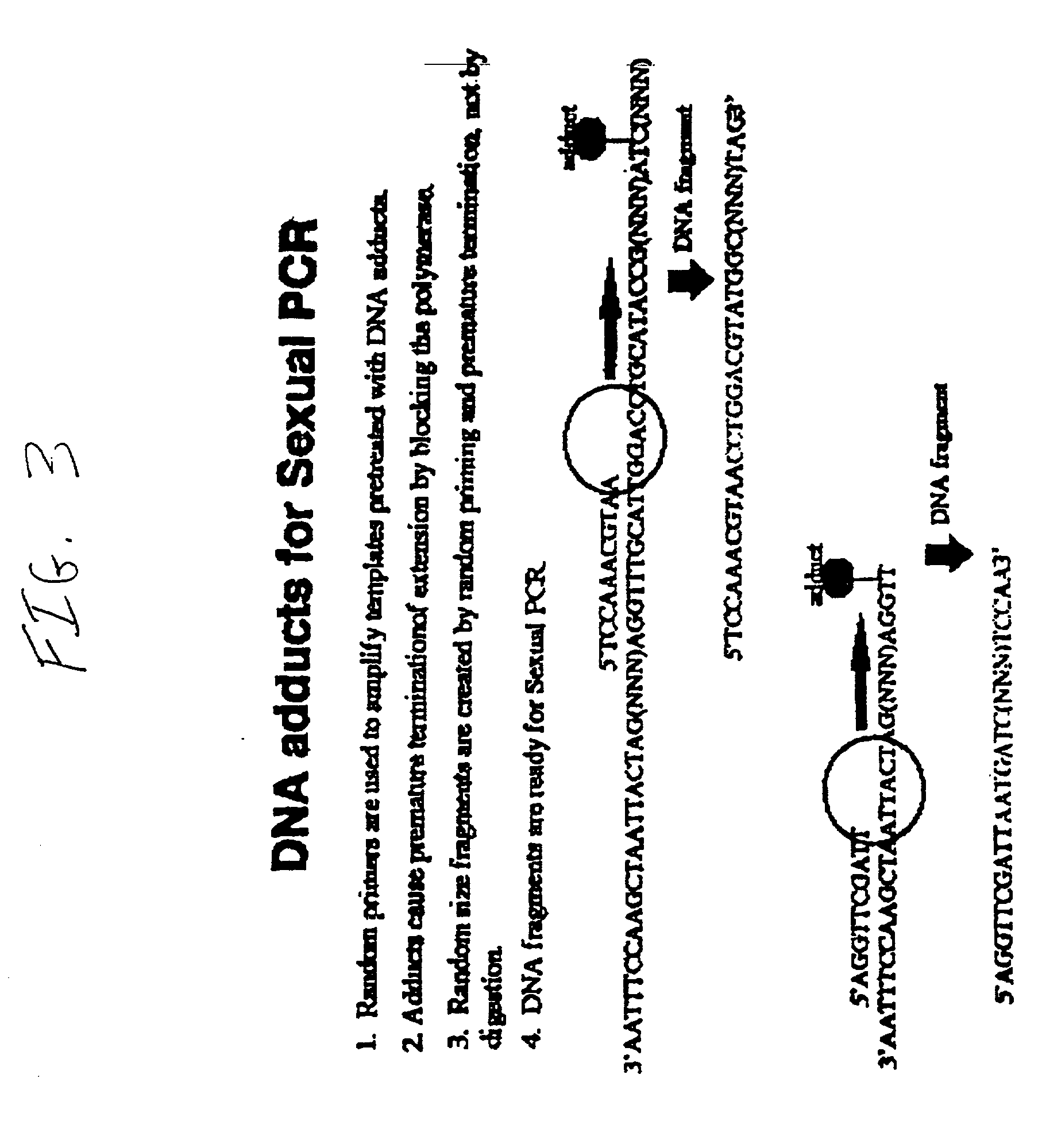
Disclosed is a process of performing Sexual PCR which includes generating random polynucleotides by interrupting or blocking synthesis or amplification process to slow or halt synthesis or amplification of at least one polynucleotides, optionally amplifying the polynucleotides, and reannealing the polynucleotides to produce random mutant polynucleotides. Also provided are vector and expression vehicles including such mutant polynucleotides, polypeptides expressed by the mutant polynucleotides and a method for producing random polypeptides.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
DNA shuffling to produce herbicide selective crops
InactiveUS20050060767A1Improve abilitiesReduce sensitivityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGMO PlantsDNA shuffling
Owner:SUBRAMANIAN VENKITESWARAN +4
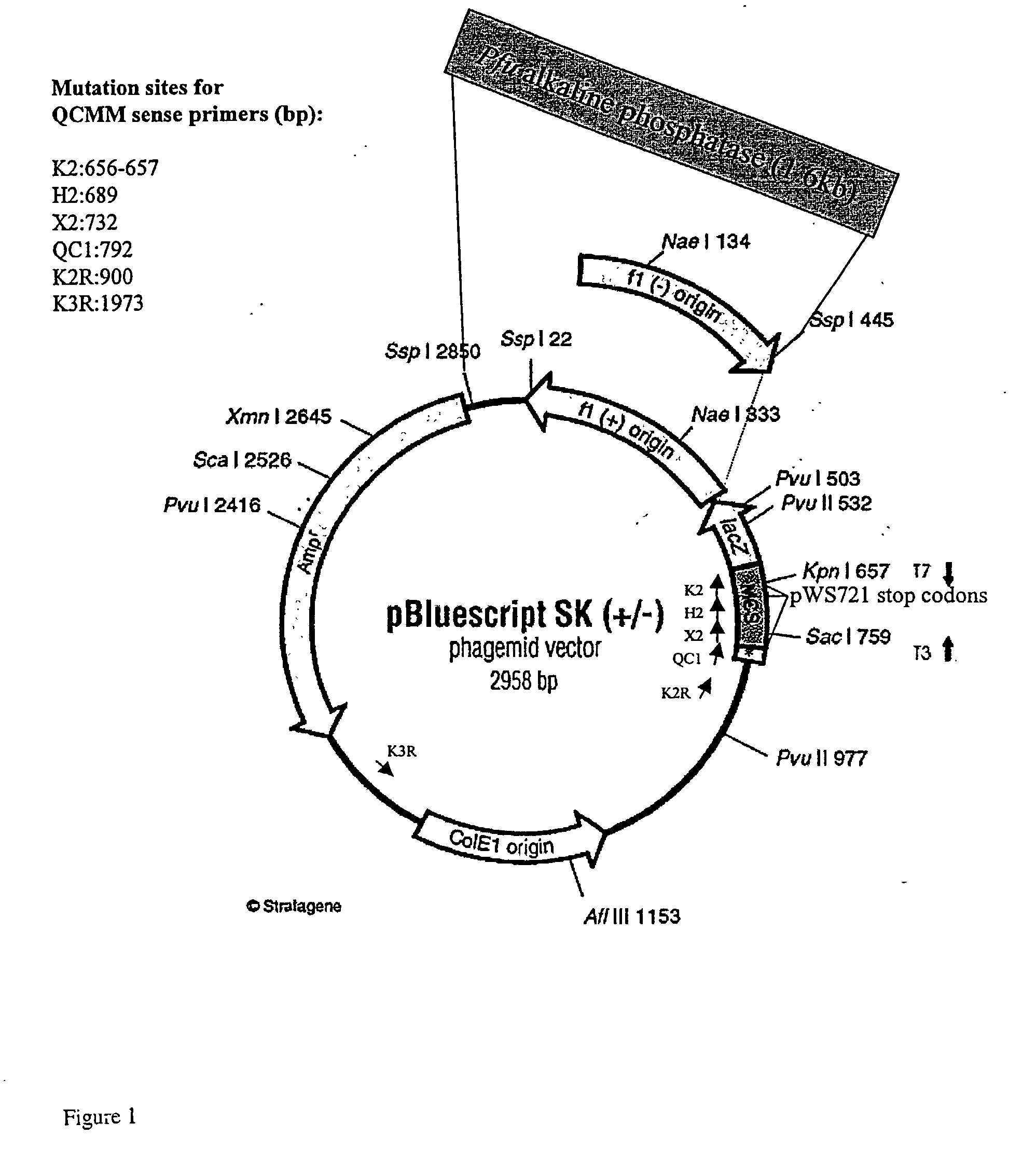
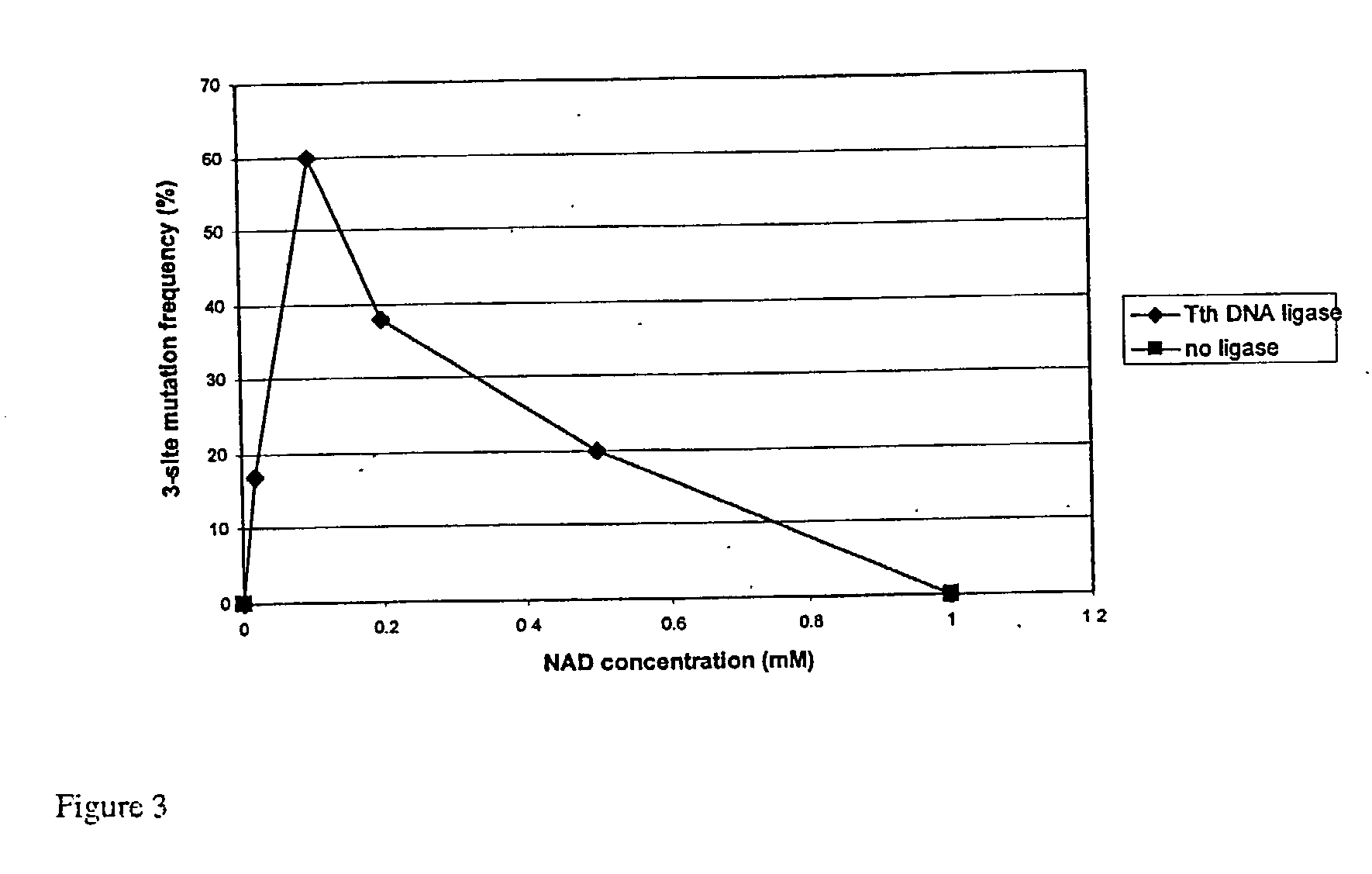
Multi-site mutagenesis
The present invention provides compositions and improved methods for multi-site directed mutagenesis and DNA shuffling. The present compositions and methods provide increased mutation frequency and increased number of transformants which allow one to sequence only a few clones in order to identify the correct mutants and to obtain the desired mutant by screening large number of transformants in a short time. Moreover, the inclusion of FEN-1, PEF and optimized buffer and cycling conditions provided in the present invention should also facilitate random mutagenized library construction and the mutagenesis of large or difficult templates.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method of optimizing codon usage through DNA shuffling
InactiveUS20110111413A1Enough timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGeneCodon optimization
The present invention relates to codon optimization utilizing DNA shuffling. A method of producing gene sequences optimized for a desired functional property is described involving synthesizing a library of parental codon variant genes encoding some or all codon choices at some or all amino acid positions of a gene, reassorting the variant codons among the parental codon variant genes using DNA shuffling thereby forming progeny codon variant genes, expressing the progeny codon variant genes in a host; and screening or selecting for progeny codon variant genes encoding a desired functional property.
Owner:PADGETT HAL S +3
Multi-site mutagenesis
ActiveUS20060051748A1Optimized cycling conditionSimple methodSugar derivativesHydrolasesMulti siteMutation frequency
The present invention provides compositions and improved methods for multi-site directed mutagenesis and DNA shuffling. The present compositions and methods provide increased mutation frequency and increased number of transformants which allow one to sequence only a few clones in order to identify the correct mutants and to obtain the desired mutant by screening large number of transformants in a short time. Moreover, the inclusion of FEN-1, PEF and optimized buffer and cycling conditions provided in the present invention should also facilitate random mutagenized library construction and the mutagenesis of large or difficult templates.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Directed evolution of recombinant monooxygenase nucleic acids and related polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20060051782A1Improve abilitiesIncrease rangeBacteriaLibrary screeningNitrobenzeneMonooxygenase
The present invention relates to novel monooxygenase nucleic acids and polypeptides created using mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, or both, in a single iteration or multiple iterations, and methods for their creation and use. The monooxygenase enzymes of the present disclosure have particular utility as biocatalysts in industrial chemical redox reactions, such as the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons, for example, toluene, benzene, or nitrobenzene, into industrially desirable products. The systems and processes of the present invention are especially useful for the coupled synthesis and recovery of catechols, methylcatechols, resorcinols, methylresorcinols, hydroquinones, methylhydroquinones, hydroxybenzenes, cresols, nitrobenzenes, and nitrohydroxyquinones.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Method of DNA shuffling with polynucleotides produced by blocking or interrupting a synthesis or amplification process
InactiveUS20020028443A1Less immunogenicSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleotide
Disclosed is a process of performing "Sexual" PCR which includes generating random polynucleotides by interrupting or blocking a synthesis or amplification process to show or halt synthesis or amplification of at least one polynucleotide, optionally amplifying the polynucleotides, and reannealing the polynucleotides to produce random mutant polynucleotides. Also provided are vector and expression vehicles including such mutant polynucleotides, polypeptides expressed by the mutant polynucleotides and a method for producing random mutant polypeptides.
Owner:DIVERSA
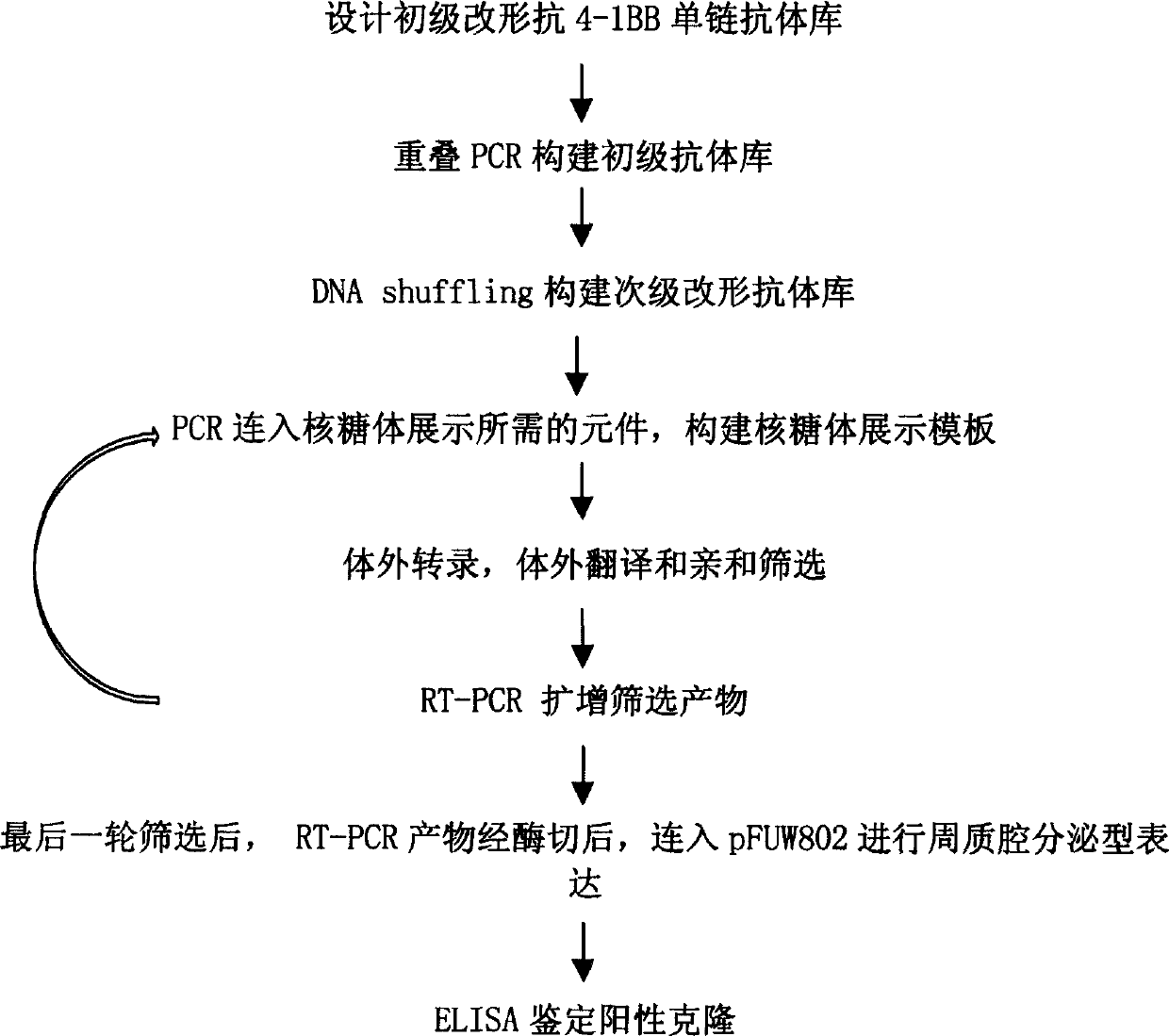
In vitro molecular directed evolution method for reshaping antibody
InactiveCN1566341AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSingle-Chain AntibodiesNucleotide
The invention relates to an in vitro molecular directed evolution method for reshaping antibody, which integrates ribosome displaying technology with DNA reorganization technology by designing reshaped antibody molecules, thus directly obtaining the extracorporal molecules of the single-chain antibody reshaped orientation.
Owner:BEIJING ABT GENETIC ENG TECH +1
Optimization of pest resistance genes using DNA shuffling
InactiveCN1314911APromote growthSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAgricultural scienceA-DNA
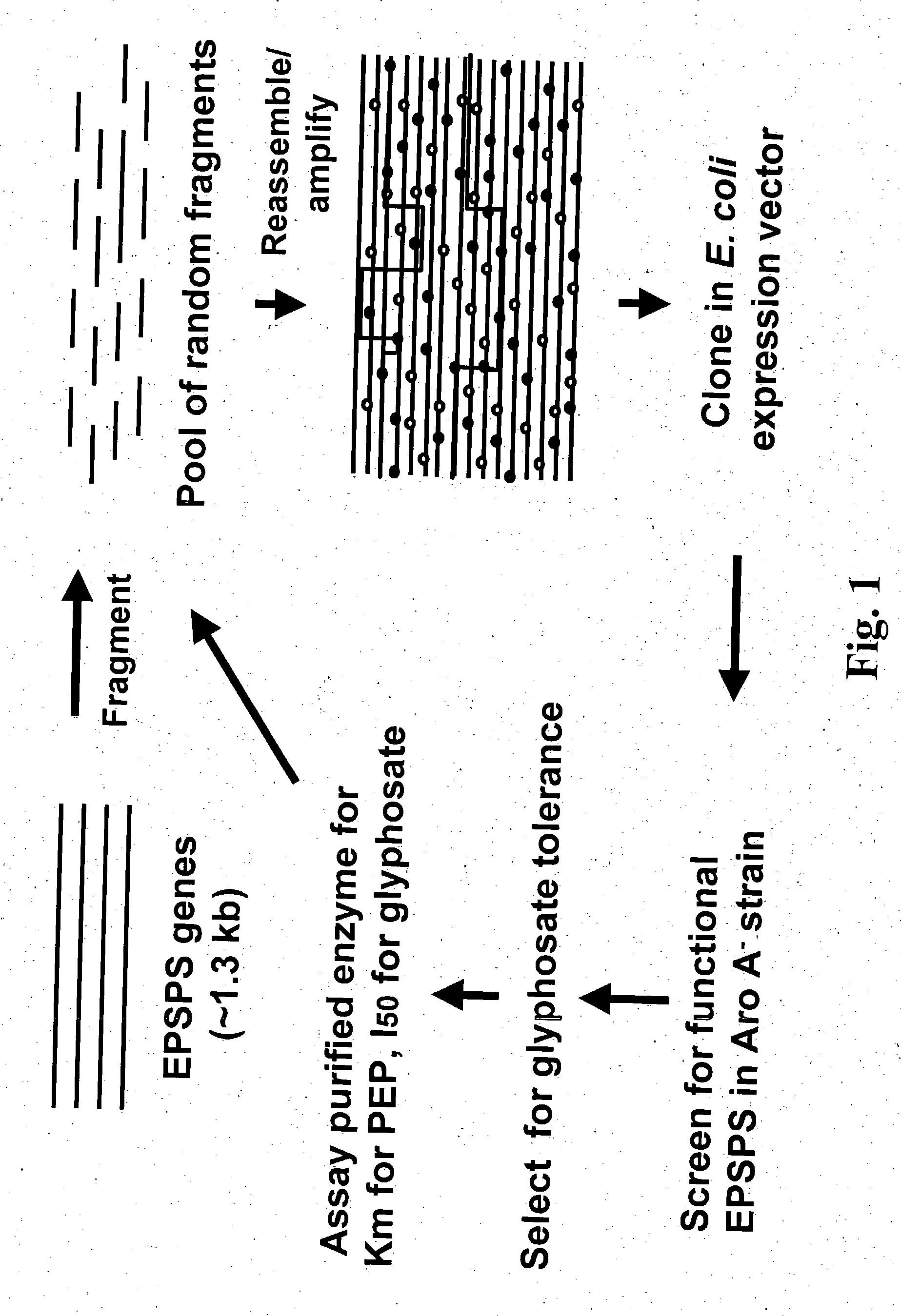
The present invention provides methods for obtaining pest resistance genes that are improved over naturally occurring genes for conferring pest resistance to plants. The method involves the use of DNA shuffling of pest resistance genes to generate a library of recombinant pest resistance genes, and then screening the library to identify those genes that show an improved property of interest.
Owner:MAXYGEN
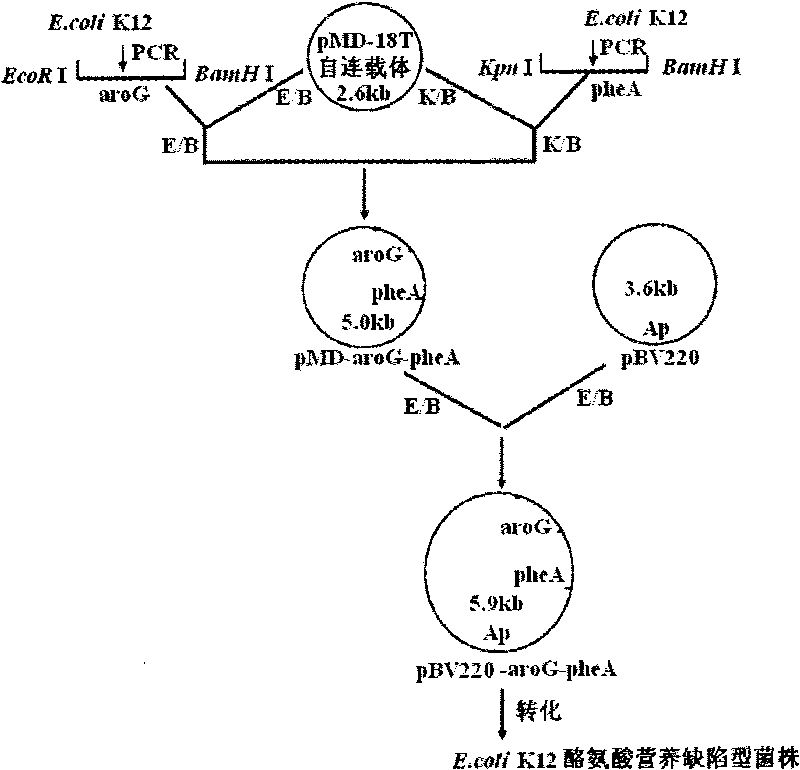
In-vitro directed coevolution method for modifying L-phenylalanine gene engineering strains
InactiveCN101698853ASpeed up evolutionHigh catalytic activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhenylalanineMetabolic balance
The invention relates to an in-vitro directed coevolution method for modifying L-phenylalanine gene engineering strains, which is realized in a way that: using genes aroG and pheA on an L-phenylalanine gene engineering strain constructed in the room as a whole; carrying out the in-vitro directed coevolution modification by using an error-prone PCR technology and a recombinant DNA technology; and screening to obtain a mutant strain, of which the yield of L-phenylalanine is increased by 114%. In the invention, by modifying the gene formed by coupling and connecting aroG and pheA in series, the key genes aroG and pheA in the metaboly process of the L-phenylalanine are used as a whole to carry out the directed modification, thereby obtaining a new metabolic balance, so that the expressed enzyme has high-efficiency catalytic activity and can resist the feedback inhibition of the L-phenylalanine, thereby obtaining the new modified high-yield L-phenylalanine gene engineering strain by screening. The method can provide an example for modifying the acid production rate of any amino acid gene engineering strain.
Owner:MAIDAN BIOLOGICAL GROUP FUJIAN
Defensin variants and methods of use
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
Resistance gene capable of degrading herbicide glyphosate and encoded protein of resistance gene
InactiveCN103421824AIncrease vitalityHigh activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringFunctional identificationNucleotide
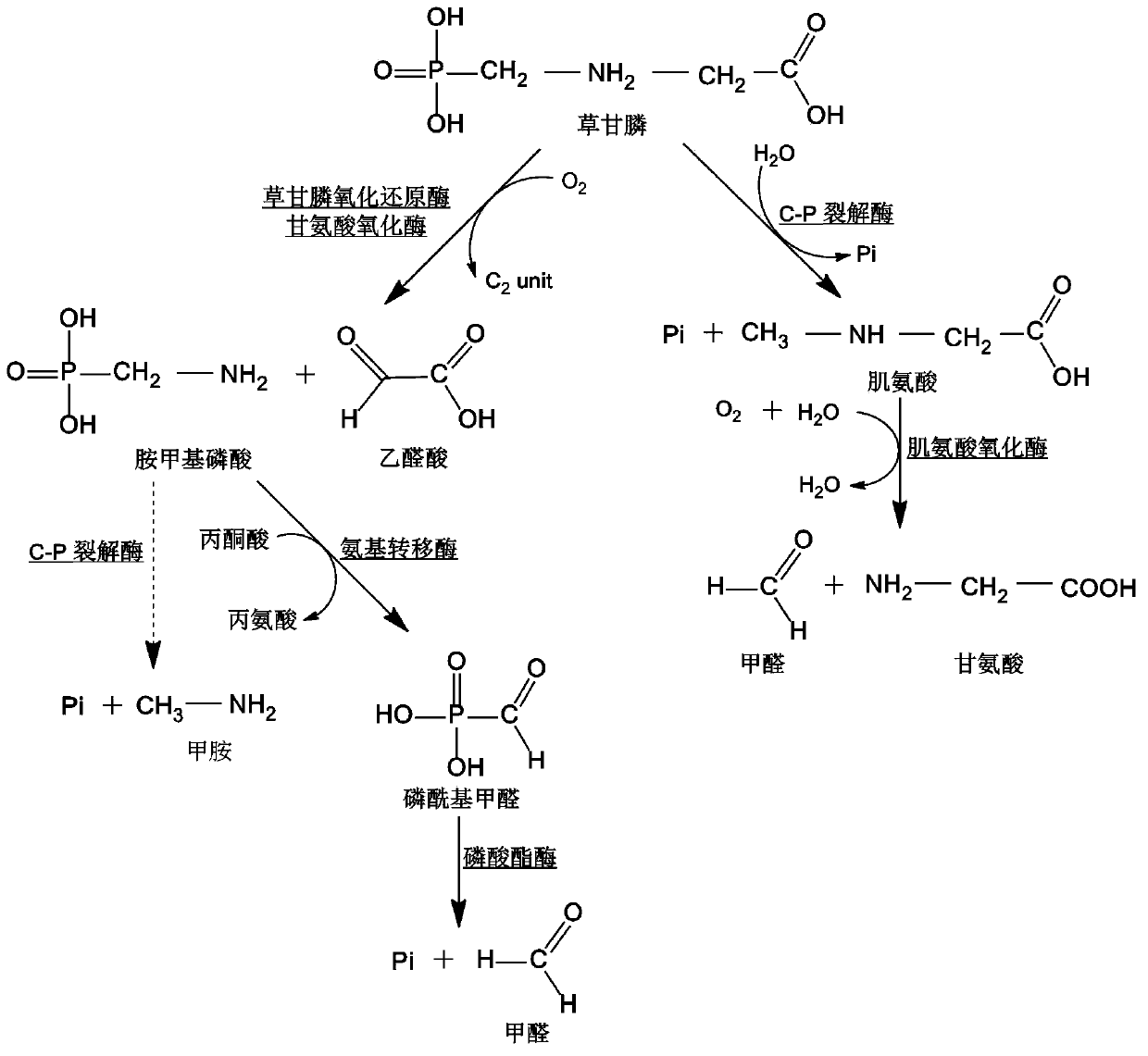
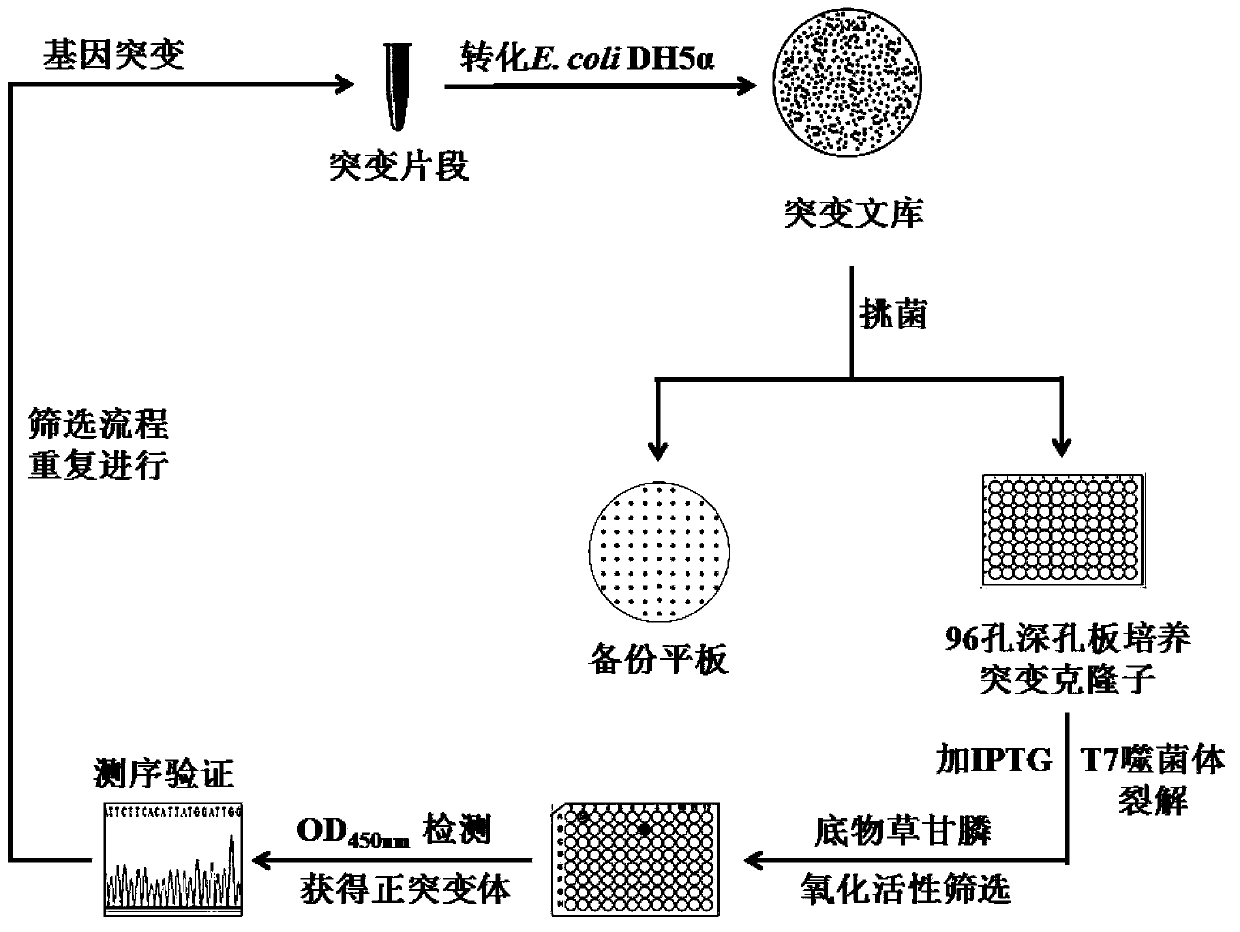
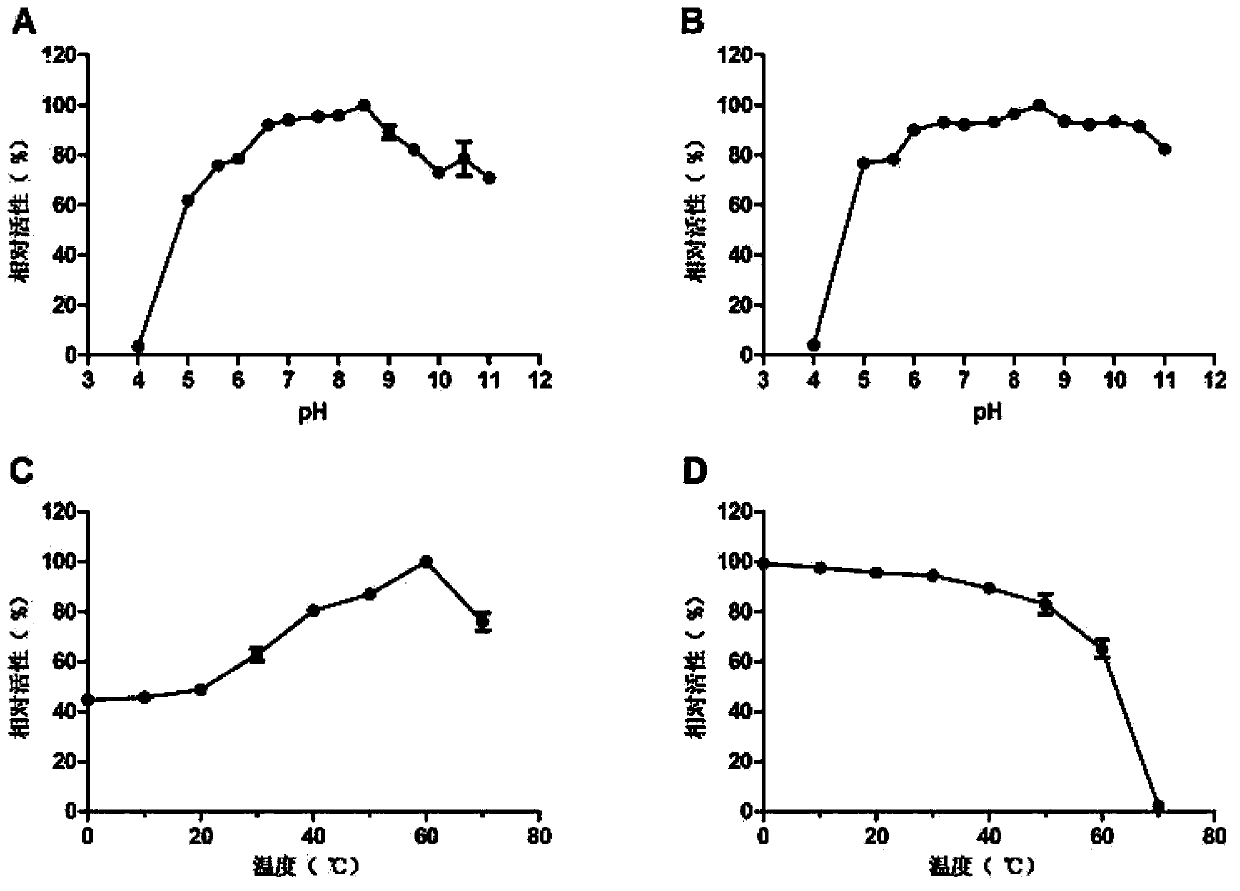
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, relates to separation, determinate evolution in vitro and functional identification of a resistance gene capable of degrading herbicide glyphosate efficiently, and further relates to the resistance gene capable of degrading herbicide glyphosate in plants. The nucleotide sequence of the gene B3S1 is as shown in the figure SEQ ID NO: 1; the amino acid sequence of encoded protein of the resistance gene is as shown in the figure SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the invention, the glycine oxidase (thiO) from marine bacteria bacillus cereus (Bacillus cereus) is amplified, and two rounds of random mutagenesis and a round of DNA shuffling test are performed continuously on the glycine oxidase (thiO), and combined with an activity screening technology on the basis of T7 phage pyrolysis-horseradish peroxidase / dianisidine enzyme coupling, the final glyphosate oxidase mutant B3S1 is obtained. The function of the gene and the application approach of the gene in degrading the resistance of herbicide glyphosate are proved in the invention.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for obtaining high-vitality superspectrum beta-lactam enzyme by directional anagenesis in vitro
InactiveCN101104858ABroad substrate spectrumIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCefotaxime
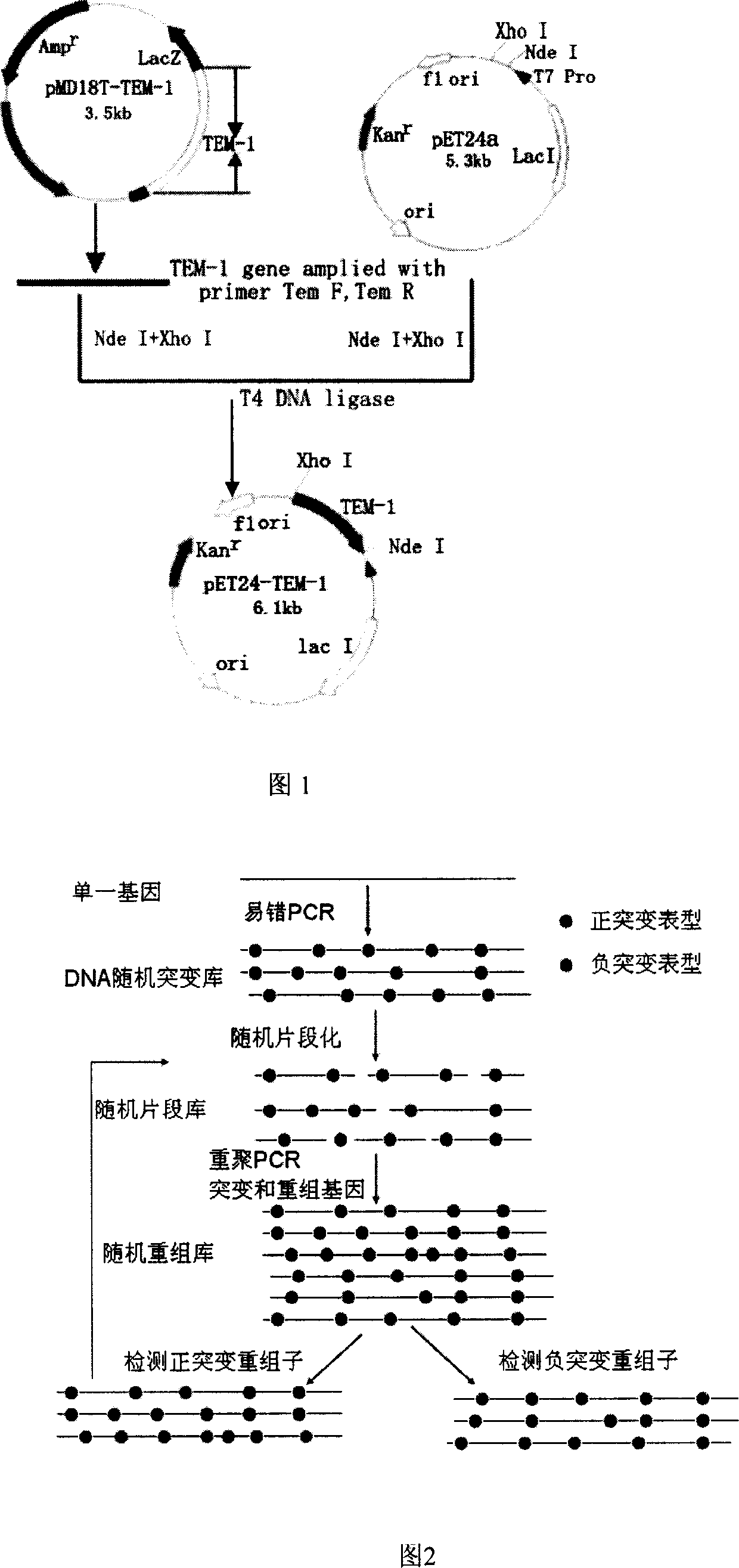
The method to prepare high active extended spectrum beta-lactamase through directed evolution in vitro of the invention belongs to medical bioengineering technical field. In particular, the invention adopts two directed evolution strategies of error-prone PCR and DNA shuffling to transform a lab strain plant which contains TEM-1 gene. The substrate spectrum enzymes of the mutated strain plant and the wild strain plant, and the activity of the substrate spectrum enzymes are compared, showing that the original substrate spectrum is enlarged because of mutation and the degradability of the third representative generation of beta-lactam antibiotics ceftazidime (CAZ) and the cefotaxime (CTX) is improved from zero to a specific activity of 43IU / mg to 78IU / mg.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method for isolation of soluble polypeptides
InactiveUS20090220485A1Improved biophysical propertyHigh throughput screeningAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticSolubilityDiagnostic agent
Polypeptides with desirable biophysical properties such as solubility, stability, high expression, monomericity, binding specificity or non-aggregation, including monomeric human VHs and VLs, are identified using a high throughput method for screening polypeptides, comprising the steps of obtaining a phage display library, allowing infection of a bacterial lawn by the library phage, and identifying phage which form larger than average plaques on the bacterial lawn. Sequences of monomeric human VHs and VLs are identified, which may be useful for immunotherapy or as diagnostic agents. Multimer complexes of human VHs and VLs are also identified. The VHs and VLs identified may be used to create further libraries for identifying additional polypeptides. Further, the VHs and VLs may be subjected to DNA shuffling to select for improved biophysical properties.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Novel Defensin Variants and Methods of Use
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for novel variants of antipathogenic polypeptides generated through DNA shuffling that exhibit improved antipathogenic activity. Polynucleotides that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the polynucleotides disclosed herein is further provided. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a microorganism comprising an antipathogenic polynucleotide of the invention in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising an antipathogenic polynucleotide or polypeptide of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
Method for isolation of soluble polypeptides
InactiveUS8293233B2Improved biophysical propertyImprove throughputAntibacterial agentsPeptide librariesSolubilityDiagnostic agent
Polypeptides with desirable biophysical properties such as solubility, stability, high expression, monomericity, binding specificity or non-aggregation, including monomeric human VHs and VLs, are identified using a high throughput method for screening polypeptides, comprising the steps of obtaining a phage display library, allowing infection of a bacterial lawn by the library phage, and identifying phage which form larger than average plaques on the bacterial lawn. Sequences of monomeric human VHs and VLs are identified, which may be useful for immunotherapy or as diagnostic agents. Multimer complexes of human VHs and VLs are also identified. The VHs and VLs identified may be used to create further libraries for identifying additional polypeptides. Further, the VHs and VLs may be subjected to DNA shuffling to select for improved biophysical properties.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
DNA shuffling to produce herbicide selective crops
InactiveCN1314945AImprove performanceBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyTransgene
The present invention provides a method for shuffling DNA to obtain a recombinant herbicide tolerance nucleic acid, the protein encoded by the nucleic acid has new or improved herbicide tolerance activity, and the invention also provides the shuffled herbicide tolerance nucleic acid Libraries, transgenic plants and DNA shuffling mixtures.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Plant strong salt-resistant gene AtNHXS1 and its coding protein and application
The invention provides a novel plant strong salt tolerant gene AtNHXS1 acquired through DNA reshuffling technology, and the ionic transport activity of Na+ / H+ antiporter protein coded by the gene is stronger than that of wild Na+ / H+ antiporter protein ATNHX1. A nucleotide sequence of the gene as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 also comprises genes of the nucleotide sequence of sequence 1 in a sequence table with the homology between 70 and 100 percent, or a nucleotide sequence of an amino acid sequence of sequence 2 in a coded sequence table. The new Na+ / H+ antiporter has a protein of the amino acid sequence of sequence 2 in the sequence table, protein of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2 with the homology between 70 and 100 percent, or protein which replaces, deletes or adds one or a plurality of amino acids in the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2 with the same homology. The invention also provides the construction of recombinant vector, the transgenic plant and other methods so as to apply the gene and the protein, thereby cultivating a novel variety of transgenic plant with strong capacity of salt tolerance or other improved biologic characters.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Novel plant strong-salt resistance gene NHXFS1, encoding protein and use thereof
InactiveCN101413004AImprove salt resistanceCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPlant peptidesNucleotideWild type
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering and provides a novel plant strong salt-tolerant gene NHXS1 obtained by a restructuring technology. A nucleotide sequence of the plant strong salt-tolerant gene NHXS1 is SEQ ID NO: 1, or a DNA sequence which has 70 to 100 percent homology with the SEQ ID NO: 1 nucleotide sequence or a DNA sequence for coding a protein sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2. Na + / H + antiporter NHXS1 colded by the gene has stronger ion transport activity than the wild-type Na + / H + antiporter AtNHX1. The invention also provides methods for construction of recombinant vectors and transgenic plants to apply the genes and proteins, and can culture a novel breed of transgenic plant with stronger salt-tolerant property or other improved biological characteristics.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Mutant blue fluorescent protein and method of using the same for fluorescence resonance energy transfer and blue fluorescent fish
InactiveUS20120238726A1High fluorescence quantum yieldHigh fluorescence intensityBacteriaSugar derivativesWild typeA-DNA
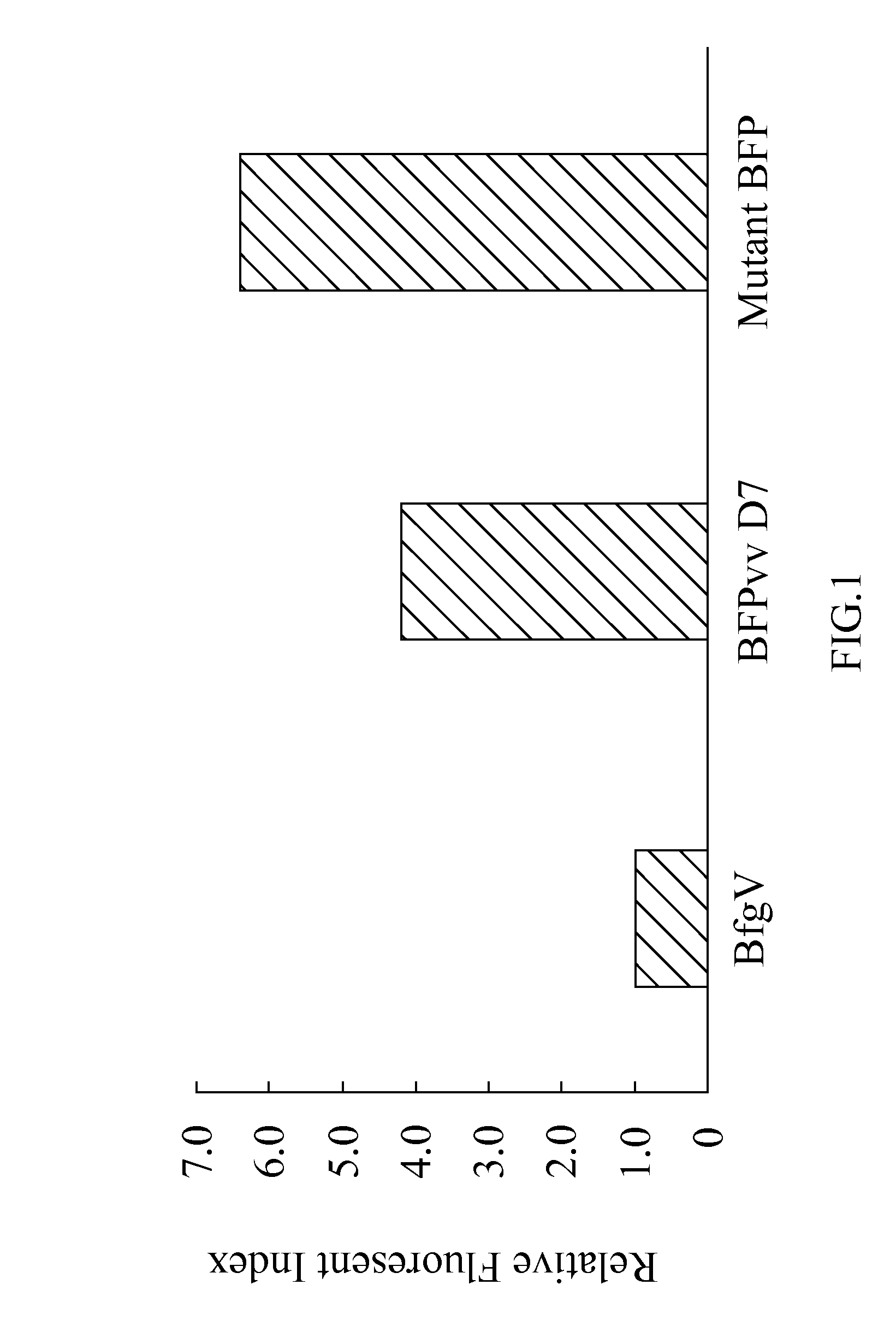
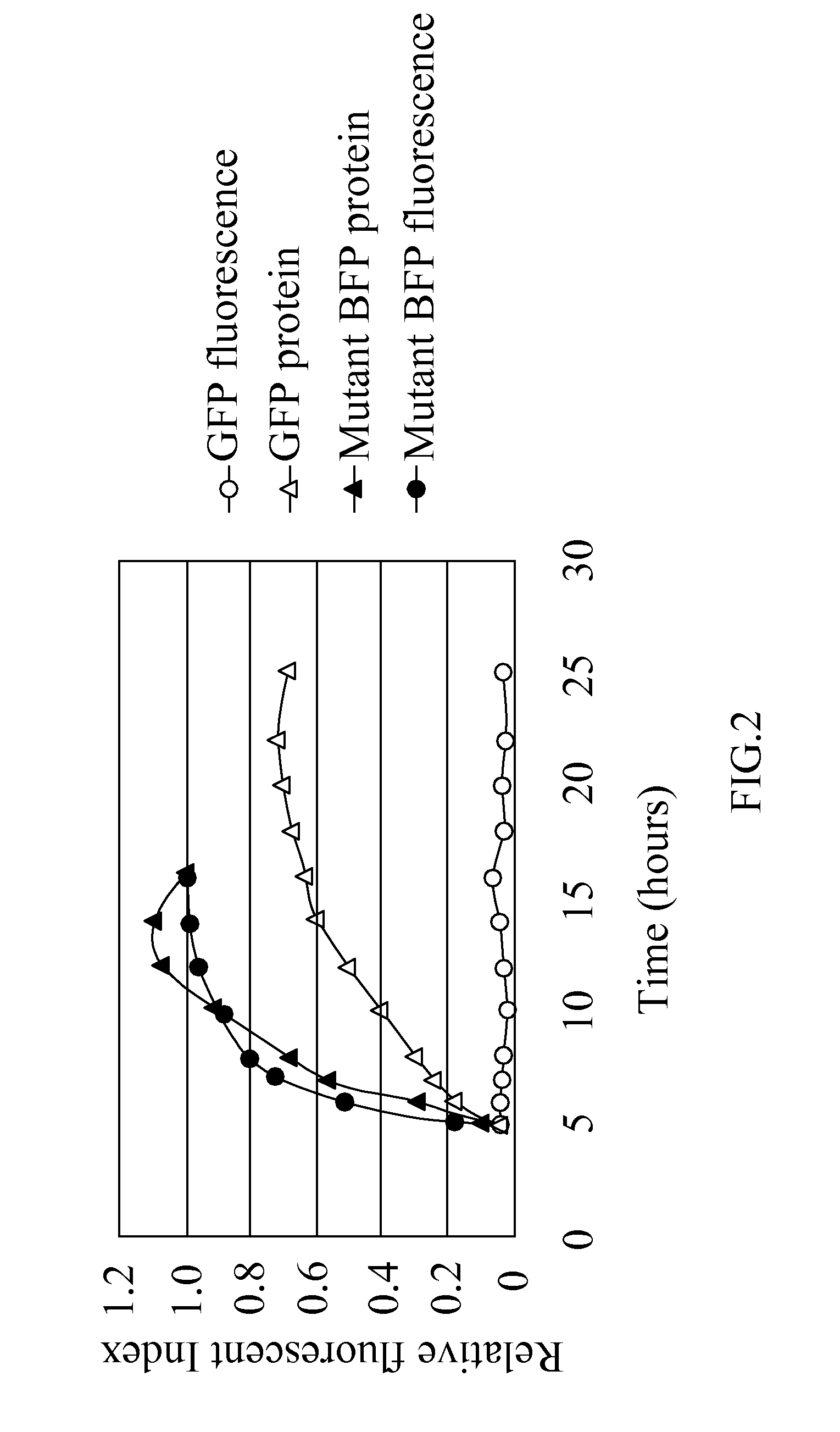
The present invention discloses a mutant blue fluorescent protein (BFP), mutated by an error-prone PCR method or a DNA shuffling method with using a BFPvv D7 of SEQ ID NO:2 as parents, obtained from a wild type blue fluorescent protein BfgV of SEQ ID NO:1, obtained from Vibrio vulnificus, wherein a set of mutation positions of the mutant BFP corresponding to SEQ ID NO:2 comprises position 176 and position 178. In a preferred embodiment, the set of mutation positions of the mutant BFP corresponding to SEQ ID NO:2 comprises a S176R mutation or a V178I mutation. Moreover, methods of using the blue fluorescent proteins from Vibrio vulnificus for fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and a blue fluorescent fish are also provided.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Artificially modified glucose oxidase gene and expression application thereof
The invention relates to an artificially modified glucose oxidase gene and expression application thereof, belonging to the fields of protein or enzyme preparation modification engineering and glucose oxidase production. The artificially modified glucose oxidase gene aims to further enhance enzyme activity on the basis of the existing glucose oxidase. An irrational means DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) shuffling technique in protein or enzyme preparation modification engineering is utilized to modify a glucose oxidase gene derived from Aspergillus niger Z-25; and a gene segment subjected to DNaseI random cutting is subjected to the DNA shuffling technique to recombine the segment into a complete variant gene, and the complete variant gene is connected with a shuttling expression plasmid and integrated into the yeast genome. The strain with obviously higher enzyme activity is screened from the mutant library, and the variant sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. In a 3L scale-up experiment of yeast, the end enzyme activity of the glucose oxidase reaches the higher level. Finally, in the aspect of enzyme activity and genes, the obtained high-enzyme-activity expression strain has favorable hereditary.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
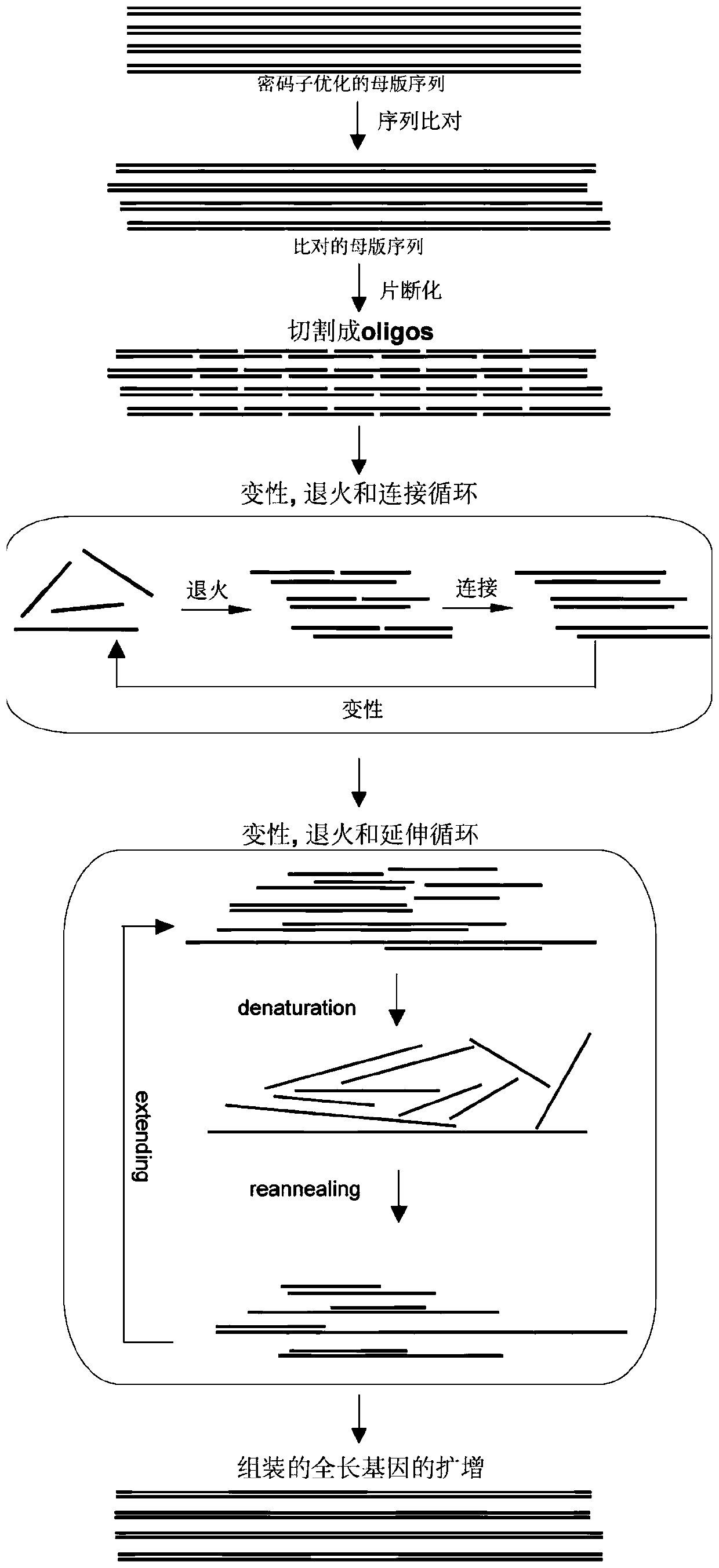
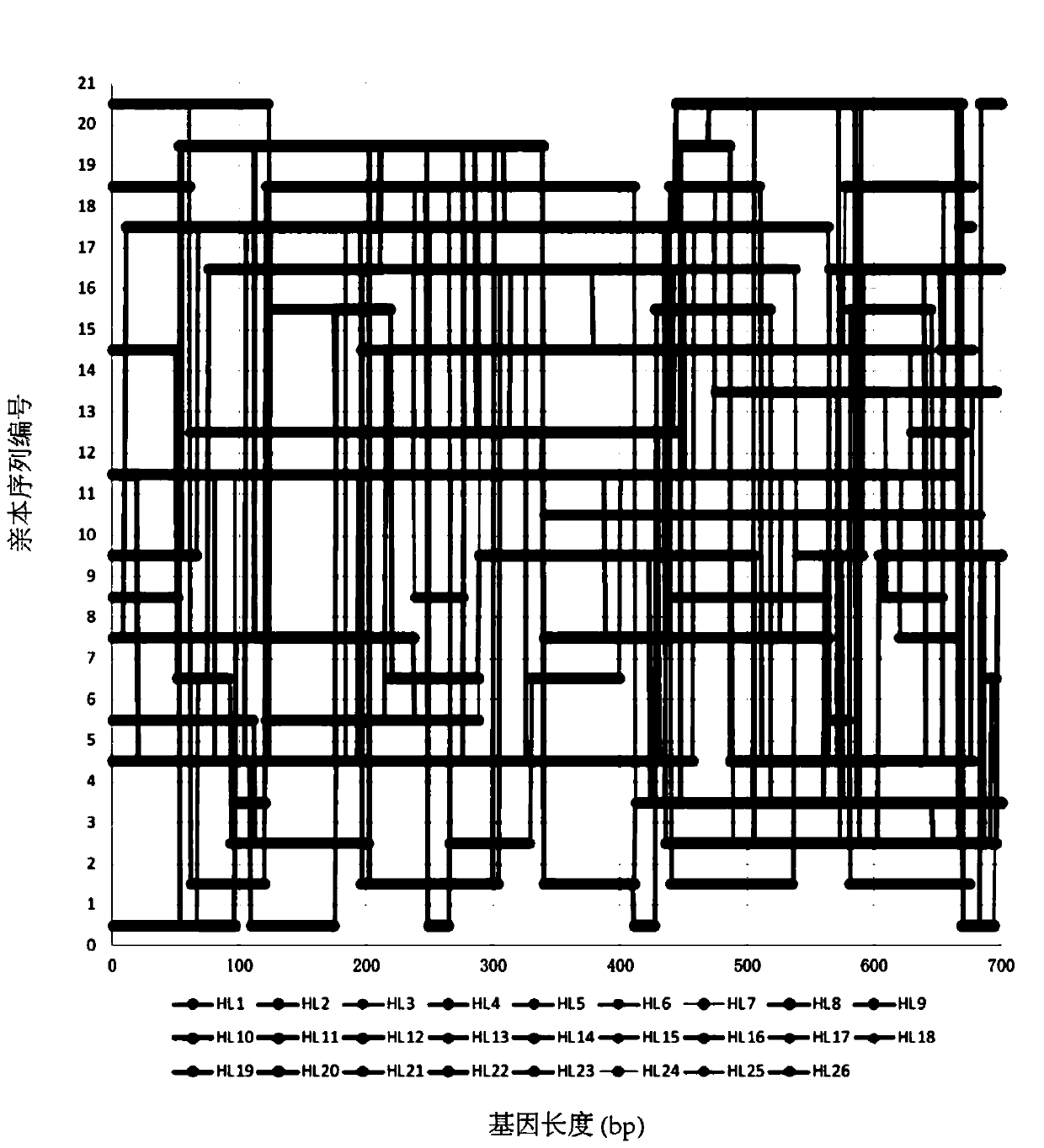
Method for de novo synthesis of library by using chip synthesized oligonucleotide library for DNA shuffling
ActiveCN109868271AImprove recombination rateEasy to assembleLibrary creationDNA preparationCelluloseRecombination rate
The invention discloses a method for de novo synthesis of a library by using a chip synthesized oligonucleotide library for DNA shuffling. The method mainly comprises the following steps: cutting a parent sequence into oligonucleotide sequences by combining comparison software; carrying out high-throughput error correction on an oligonucleotide library by using a mismatch binding protein MutS immobilized cellulose column; and carrying out full-length recombinant library assembly by using the cut oligonucleotides. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention has theadvantages of high recombination rate, reduced difficulty of assembling into a full-length gene sequence, reduced synthesis cost, improved diversity of the sequence, improved accuracy of the oligo pool, improved fidelity of the synthesized gene library and improved probability of recombination.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
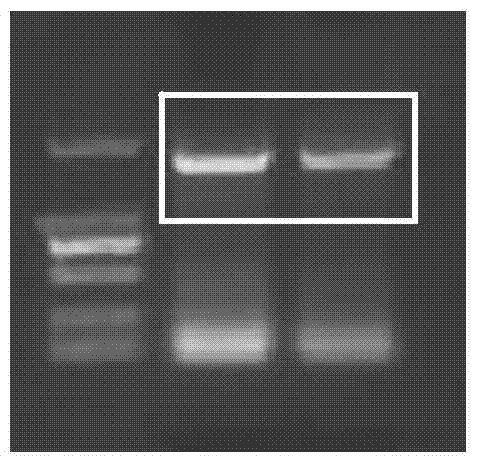
Method for carrying out directional evolution on gene promoter
ActiveCN107338241AImprove efficiencyIncrease productionDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationMutation frequencyA-DNA
The invention provides a method for carrying out directional evolution on a gene promoter. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying the promoter by adopting an error-prone PCR technology, thus obtaining a group of promoter sequences with high mutation frequency; removing harmful mutation by adopting a DNA shuffling technology, and collecting beneficial mutation, thus obtaining the promoter after shuffling; forming an expression cassette by adopting the recombinant promoter and a galactosidase gene, transforming host cells by adopting the expression cassette, and carrying out blue and white spot screening and enzyme activity determination, thus obtaining the target mutation promoter. With the method provided by the invention, the functional region of the gene promoter does not need to be analyzed, the cost is low, the operation is efficient, rapid, easy and convenient, the success rate is high, and the method is suitable for carrying out directional evolution on gene promoters of escherichia coli or other bacteria, fungi and mammalian cells.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Gene directed molecular evolution system in vitro based on half-rational evolutionary design
InactiveCN101311185ACombined screening system is simpleSimple and efficientSugar derivativesDNADNA shuffling
The invention relates to a simple and efficient gene in vitro directed evolution system based on half-reasoning design; the system can achieve larger mutation potential and more definite mutation region compared with the conventional reshuffle mutation by combining DNA reshuffle mutation and the half-reasoning design and can provide more diversified mutant population for the modification of gene and protein, wherein, the mutant sites of the diversified mutant population are positioned in critical area.. With the combination of a screening system, reliable improved gene or protein can be obtained more easily; moreover, the system of the invention has effectiveness as well as simple and convenient operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel Antifungal Proteins and Methods of Use
Compositions and methods for protecting a plant from a pathogen, particularly a fungal pathogen, are provided. Compositions include amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for novel variants of antipathogenic polypeptides generated through DNA shuffling that exhibit improved antipathogenic activity. Polynucleotides that encode the antipathogenic polypeptides are also provided. A method for inducing pathogen resistance in a plant using the polynucleotides disclosed herein is further provided. Compositions comprising an antipathogenic polypeptide or a microorganism comprising an antipathogenic polynucleotide of the invention in combination with a carrier and methods of using these compositions to protect a plant from a pathogen are further provided. Plants, plant cells, seeds, and microorganisms comprising an antipathogenic polynucleotide or polypeptide of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
Method of DNA shuffling with polynucleotides produced by blocking or interrupting a synthesis or amplification process
InactiveUS20030113759A1Less immunogenicMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationNucleotidePolynucleotide
Owner:SHORT JAY M
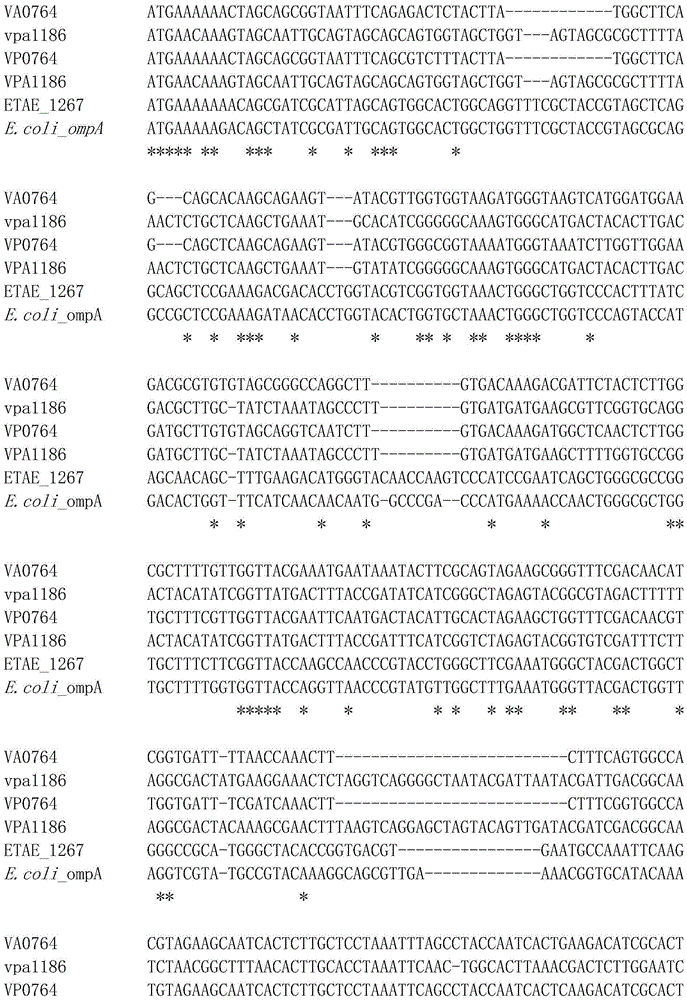
Bacterial outer membrane protein ompAs-19 after DNA shuffling and application thereof as an immunomodulator
InactiveCN105566461AGood immune protectionShow cross-immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsResearch ObjectVibrio parahaemolyticus
The present invention belongs to the technical field of DNA shuffling, and specifically discloses a bacterial outer membrane protein ompAs-19 after DNA shuffling and application thereof as an immunomodulator. The invention for the first time uses the DNA shuffling technology combined with immunological research; the outer membrane proteins of OmpA vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Edwardsiella tarda and Escherichia coli are research objects; DNA shuffling technology is employed to obtain the bacterial outer membrane protein ompAs-19 after DNA shuffling, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The bacterial outer membrane protein ompAs-19 after DNA shuffling has high immune protection to vibrio alginolyticus, and reaches relative immune protective rate (RPS) of 100%. In addition, the bacterial outer membrane protein ompAs-19 after DNA shuffling also shows cross immunogenicity to Edwardsiella tarda and the reaches immune protective rate (RPS) of 85.71%. The results indicate that No.19 shuffled OmpA (ompAs-19) can be used as a vaccine component.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
DNA shuffling to produce herbicide selective crops
InactiveUS20060253923A1Improve abilitiesImprove expression levelBacteriaLibrary screeningGMO PlantsDNA shuffling
Owner:SUBRAMANIAN VENKITESWARAN +4
Directed evolution of recombinant monooxygenase nucleic acids and related polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS7723498B2Improve abilitiesIncrease rangeBacteriaUnicellular algaeNitrobenzeneMonooxygenase
The present invention relates to novel monooxygenase nucleic acids and polypeptides created using mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, or both, in a single iteration or multiple iterations, and methods for their creation and use. The monooxygenase enzymes of the present disclosure have particular utility as biocatalysts in industrial chemical redox reactions, such as the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons, for example, toluene, benzene, or nitrobenzene, into industrially desirable products. The systems and processes of the present invention are especially useful for the coupled synthesis and recovery of catechols, methylcatechols, resorcinols, methylresorcinols, hydroquinones, methylhydroquinones, hydroxybenzenes, cresols, nitrobenzenes, and nitrohydroxyquinones.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
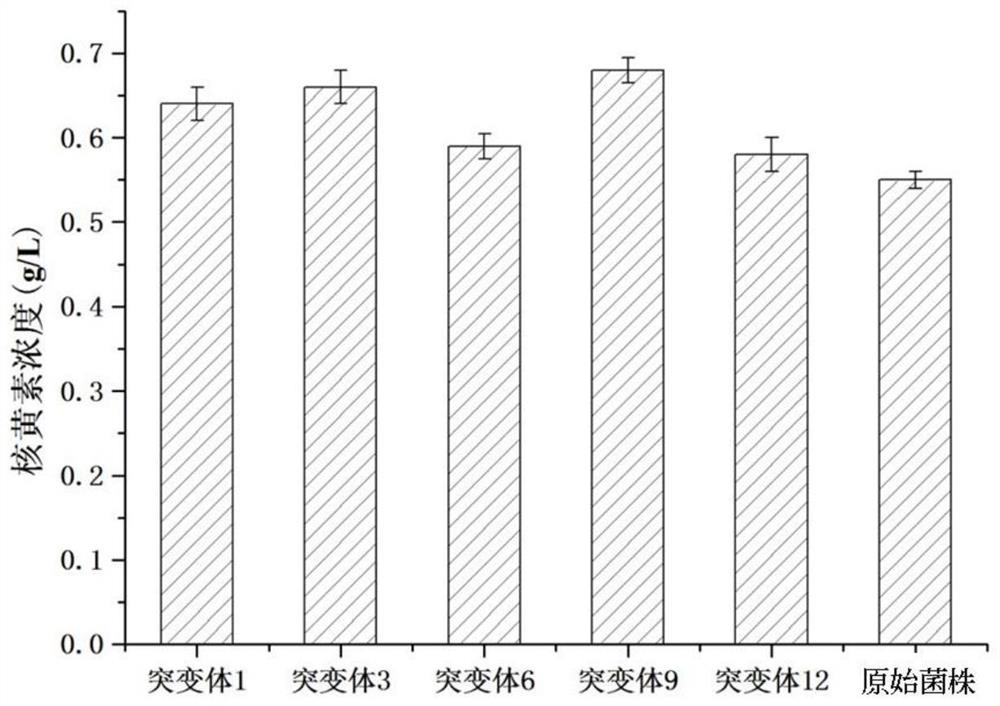
Method for improving riboflavin production capacity of escherichia coli engineering bacteria by DNA shuffling
PendingCN114181963ALow toxicityEliminate Feedback InhibitionTransferasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRiboflavin biosynthesis
The invention provides a method for improving riboflavin production capacity of escherichia coli engineering bacteria by using DNA shuffling, and relates to the field of genetic engineering, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing riboflavin-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing 26 genes; carrying out DNA rearrangement and directional screening on the T7RNA polymerase gene expression unit, and extracting to obtain a first batch of positive plasmids; carrying out DNA rearrangement and directional screening on a riboflavin biosynthesis and transport system, and extracting to obtain a second batch of positive plasmids; carrying out DNA rearrangement and directional screening on the Escherichia coli sigma factor gene, and extracting to obtain a third batch of positive plasmids; introducing the third batch of plasmids into different chassis cells to obtain recombinant strains; and selecting the positive strain with the highest riboflavin yield. The toxicity problem of T7RNAP to an escherichia coli host in the construction process of the riboflavin-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria, the feedback inhibition problem of a product and the moderate and coordinated expression problem of a constructed riboflavin biosynthetic gene are effectively eliminated. The efficiency and the yield of biosynthesis of riboflavin by the escherichia coli engineering strain are further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com