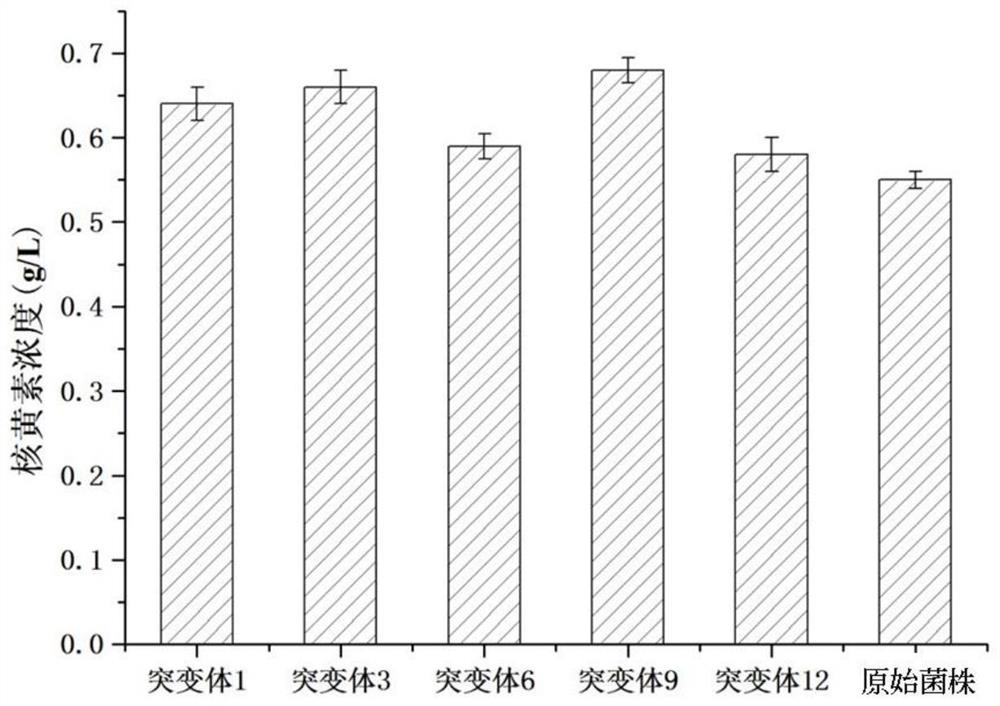
Method for improving riboflavin production capacity of escherichia coli engineering bacteria by DNA shuffling
A technology of Escherichia coli and riboflavin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, to achieve the effect of improving efficiency and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below. Those who do not indicate the specific conditions in the examples are carried out according to the conventional conditions or the conditions suggested by the manufacturer. The reagents or instruments used were not indicated by the manufacturer, and they were all conventional products that could be purchased from the market.
[0046] The characteristics and performance of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the examples.
[0047] The embodiment of the present invention provides a DNA rearrangement and directional screening method for increasing the yield of riboflavin-producing Escherichia coli engineering bacteria, comprising the following steps:
[0048] Construction of riboflavin-producing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com