Patents
Literature
362results about How to "Avoid malfunction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image search apparatus for images to be detected, and method of controlling same
ActiveUS20060098875A1Avoid malfunctionAvoid failureCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation storageOperating system
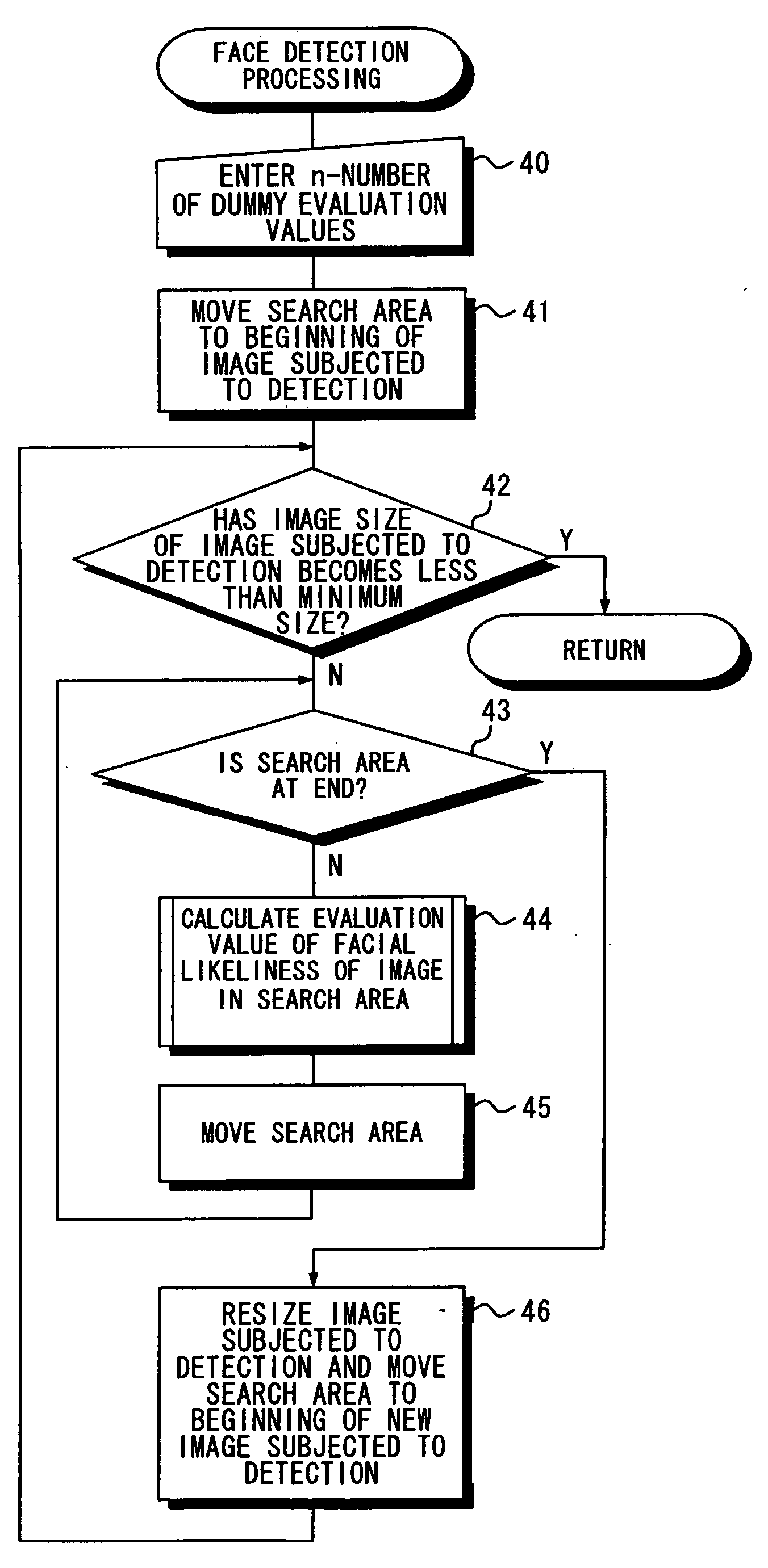
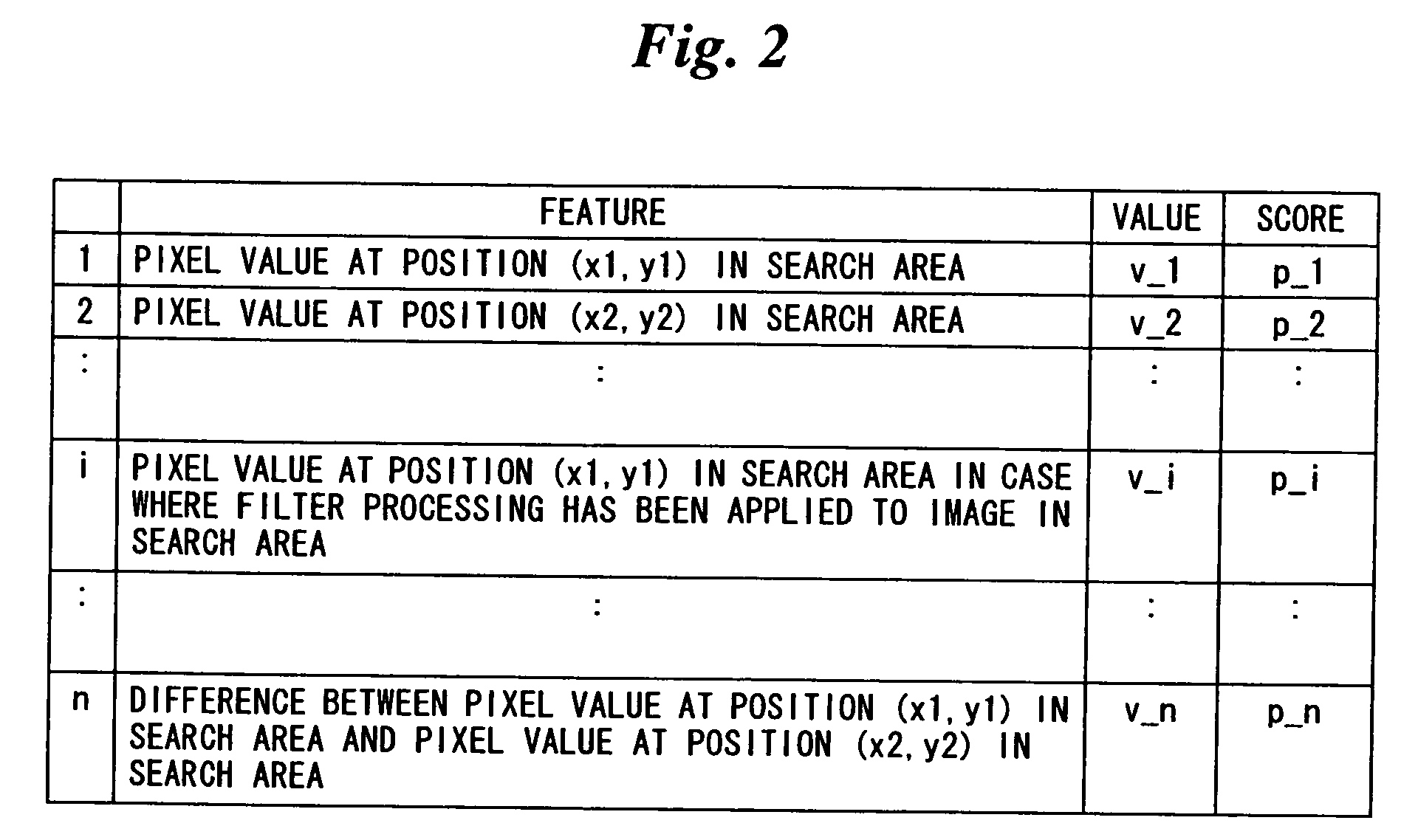
If a target-image portion to be detected is detected anew, an evaluation value of this target-image portion is calculated. If the target-image portion is detected anew, it is determined whether the number of target-image portions has exceeded n owing to such detection. If, in a case where n has been exceeded, information concerning a target-image portion having an evaluation value smaller than that of the newly detected target-image portion has been stored, then the information having this evaluation value is deleted from a list and the information concerning the newly detected target-image portion is stored in the list. Since the number of items of information stored in the list will not exceed n, it is possible to avoid a malfunction that can occur if processing is executed following storage of a large number of items of information.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Intelligent lock system and remote unlocking/locking method
InactiveCN102800140AEasy to operateNo need to carry keysIndividual entry/exit registersElectric machineryCode division multiple access
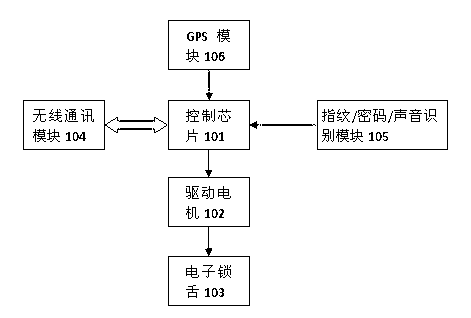
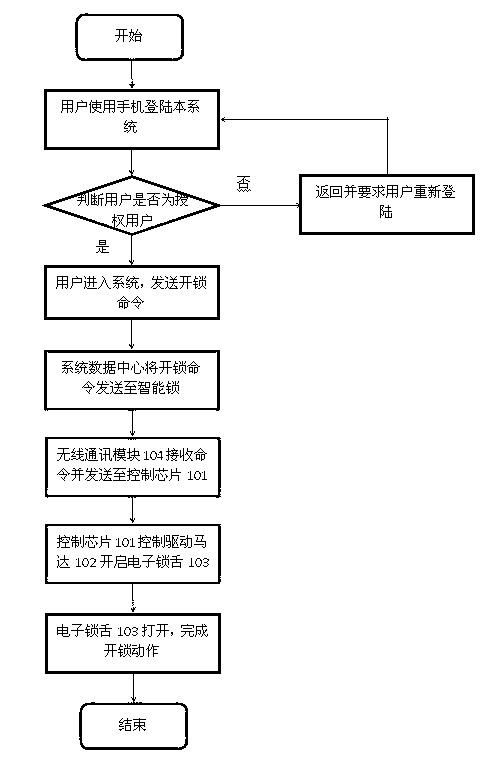
The invention relates to an intelligent lock system and a remote unlocking / locking method. The intelligent lock system is controlled by an intelligent mobile phone program, calling of phones, sending of short messages, fingerprints, passwords, sounds, inductive cards and the like and can be unlocked and locked in a remote manner. The intelligent lock system comprises an intelligent lock body, an intelligent mobile phone, a system data center and a user management system among which the communication is realized in a mobile communication mode implemented by an Internet, a global system for mobile communications (GSM), a general packet radio service (GPRS), wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA) or third-generation telecommunication (3G) and the like. The intelligent lock body comprises a control chip, a drive motor, an electric lock tongue, a wireless communication module, a fingerprint or password or sound or inductive card identification module and a GPS position module.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIUSHU NETWORK TECH
Intelligent automatic vending machine based on IOT technology
ActiveCN104992499AMake sure to leavePrivacy protectionCoin-freed apparatus detailsCash registersPaymentControl system
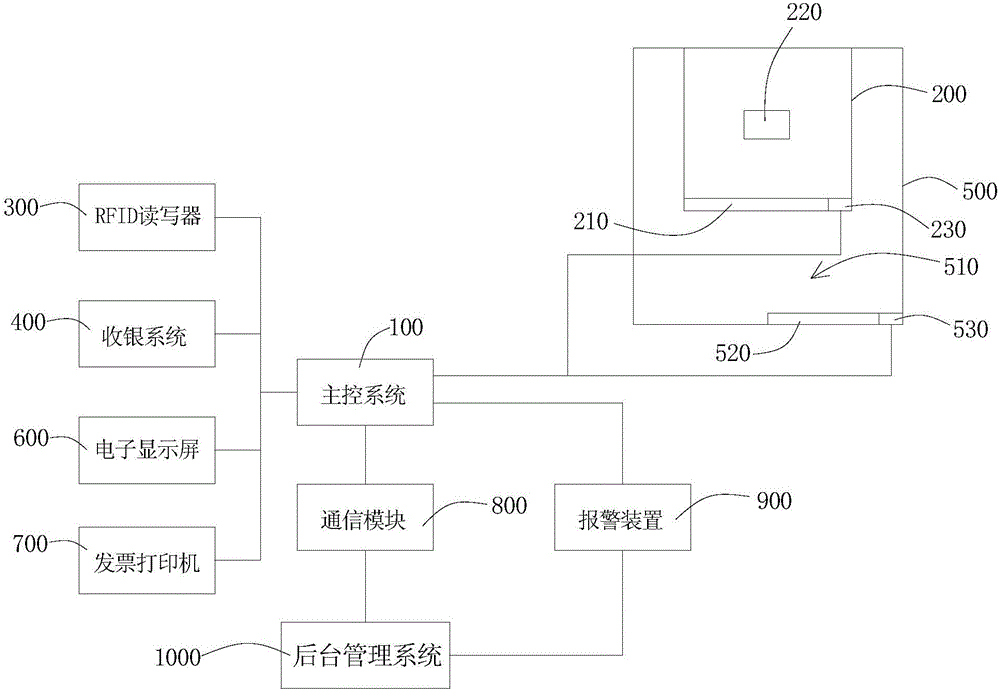
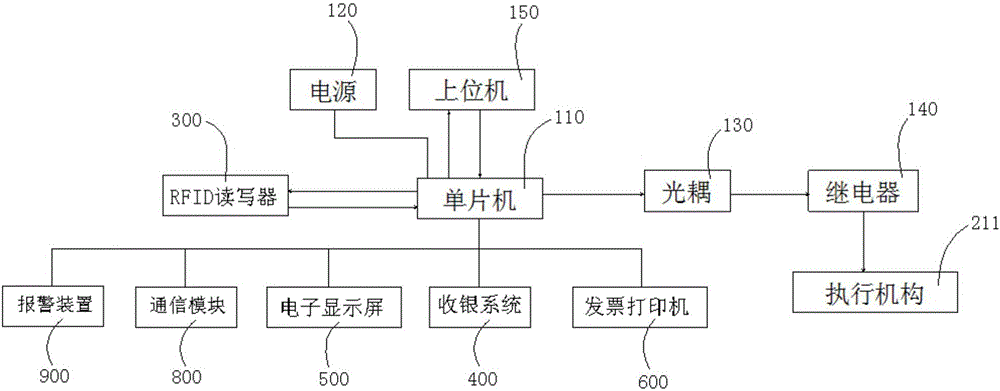
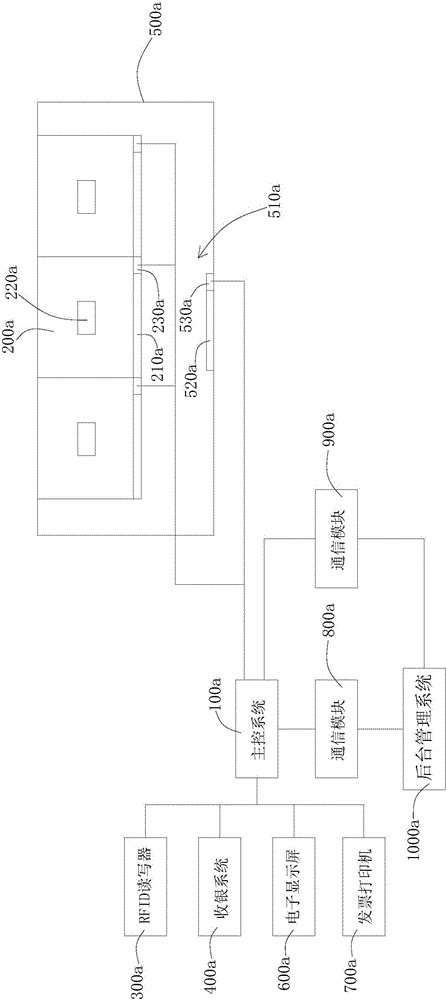
The invention discloses an intelligent automatic vending machine based on IOT technology. The intelligent automatic vending machine comprises a main control system, at least one cabinet storing RFID-labeled goods, an RFID reader connected with the main control system and reading information of RFID labels attached to the goods stored in the at least one cabinet via each RFID antenna, a cashier system connected with the main control system and further a peripheral enclosure structure at least accommodating each cabinet and the cashier system and forming an activity area for customers to selecting goods, wherein each cabinet is provided with a cabinet door connected with the main control system; one RFID antenna is disposed in each cabinet; and the peripheral enclosure structure is provided with a pass door communicated with a first electronic lock of the main control system and the activity area. With the peripheral enclosure structure, customers can be guaranteed to leave after payment and purchasing privacy of the customers can be protected.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUKE SMART TECH
Rotating transformer position measuring system and method
ActiveCN102721362AImplement redundant functionsImprove reliabilityUsing electrical meansMicrocontrollerCommunication interface
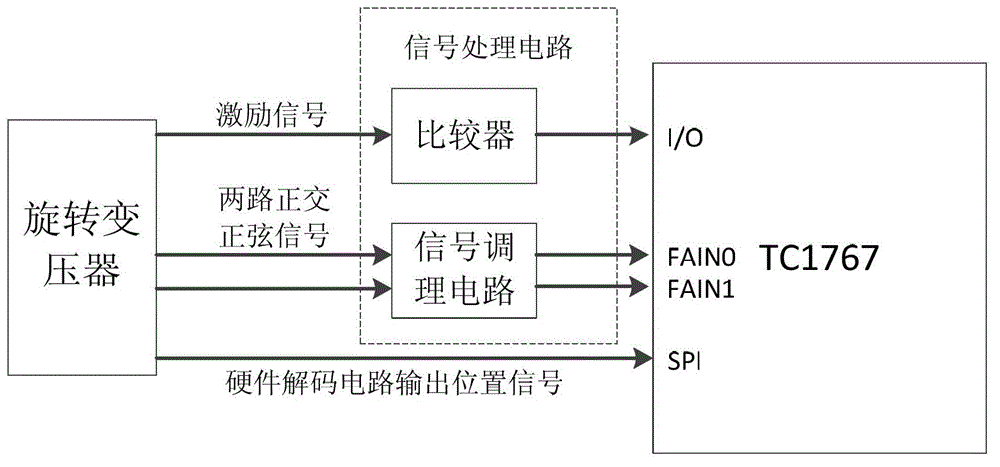
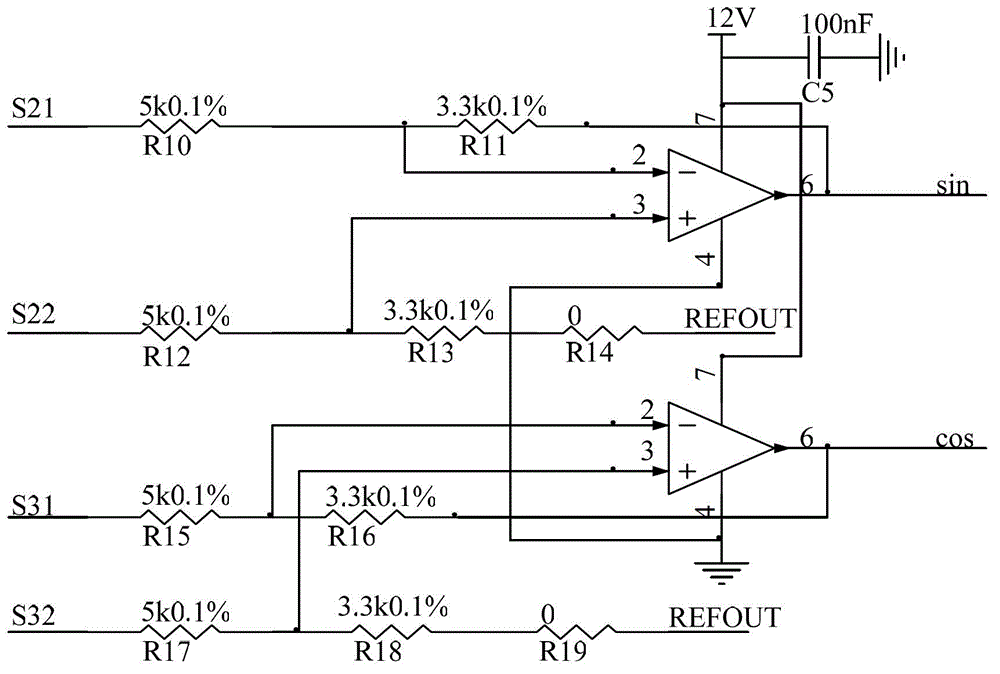
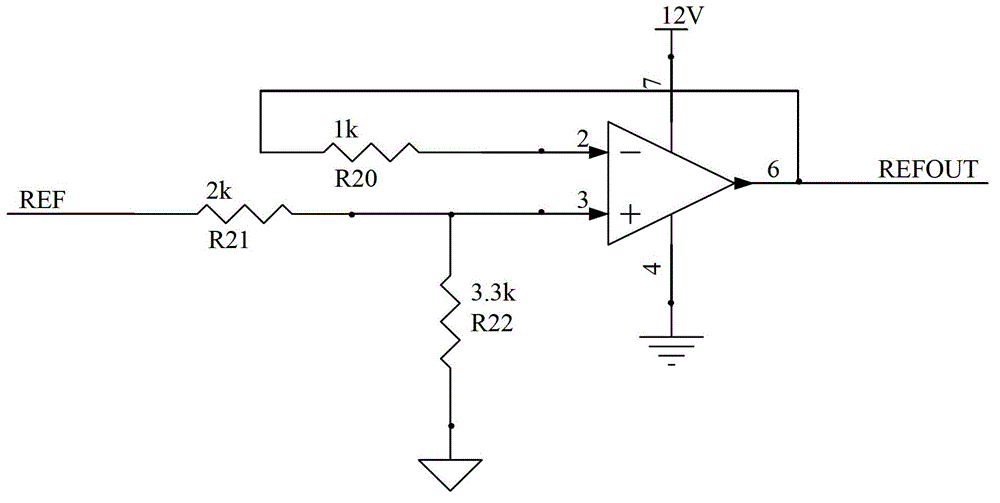
The invention discloses a rotating transformer position measuring system. The system comprises a signal processing circuit, a hardware decoding circuit and a singlechip, wherein the signal processing circuit is electrically connected with a rotating transformer and the singlechip, and is used for receiving and processing an excitation signal of the rotating transformer and two channels of orthogonal sinusoidal signals and outputting the signals to an input / output (I / O) port of the singlechip and two input channels of a quick analog / digital (A / D) sampling module; and the hardware decoding circuit is electrically connected with the rotating transformer and the singlechip, and is used for decoding rotating transformer position information and generating and outputting a position signal to a serial peripheral interface (SPI) communication interface of the singlechip. The quick A / D sampling function of the singlechip is used, the two channels of orthogonal sinusoidal signals of a secondary coil of the rotating transformer are acquired by the singlechip, the rest part of signal processing is finished in the singlechip through programming, and the redundancy function of the system can be realized by only a few peripheral circuits, so that the reliability of the system is greatly improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
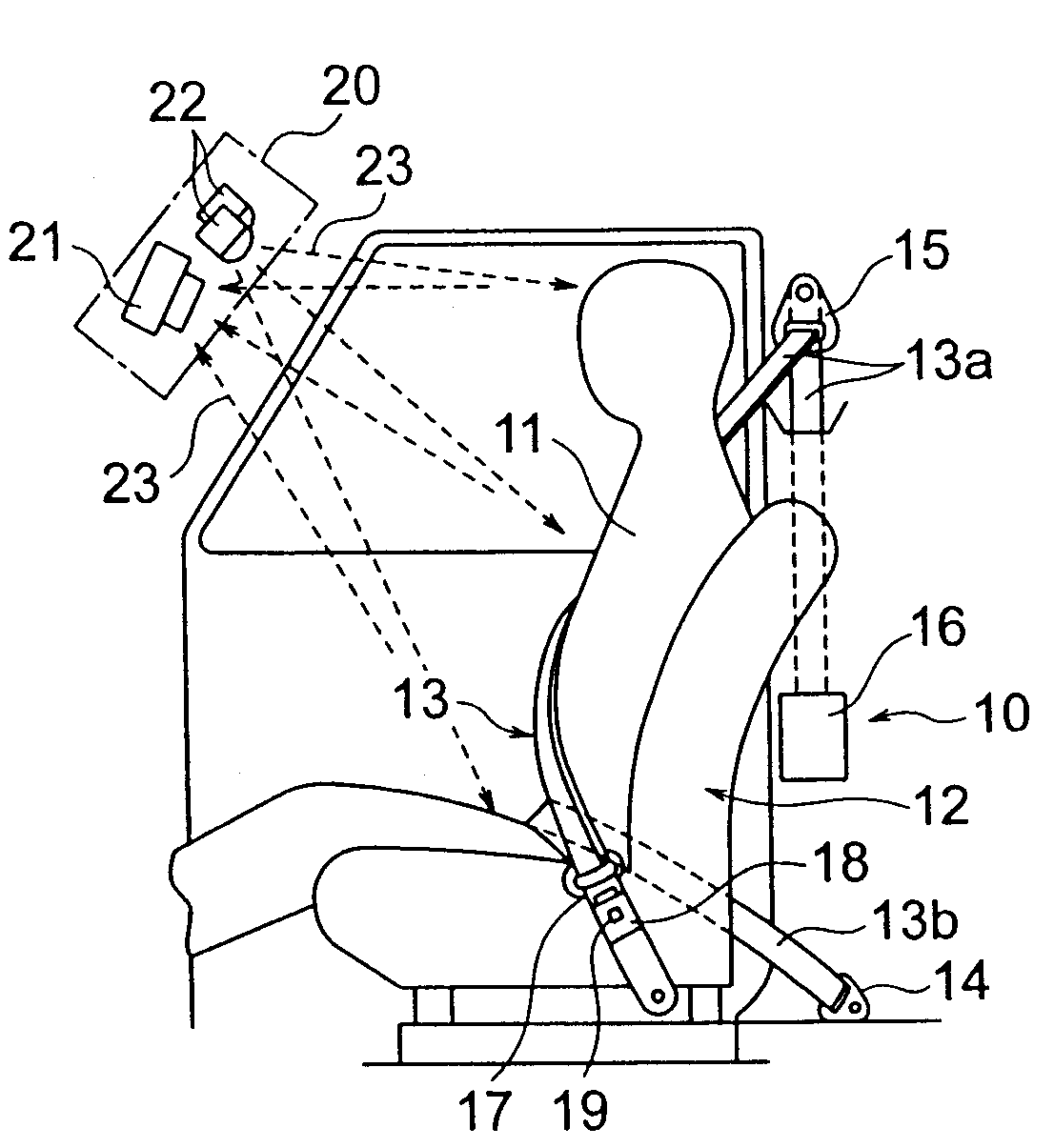
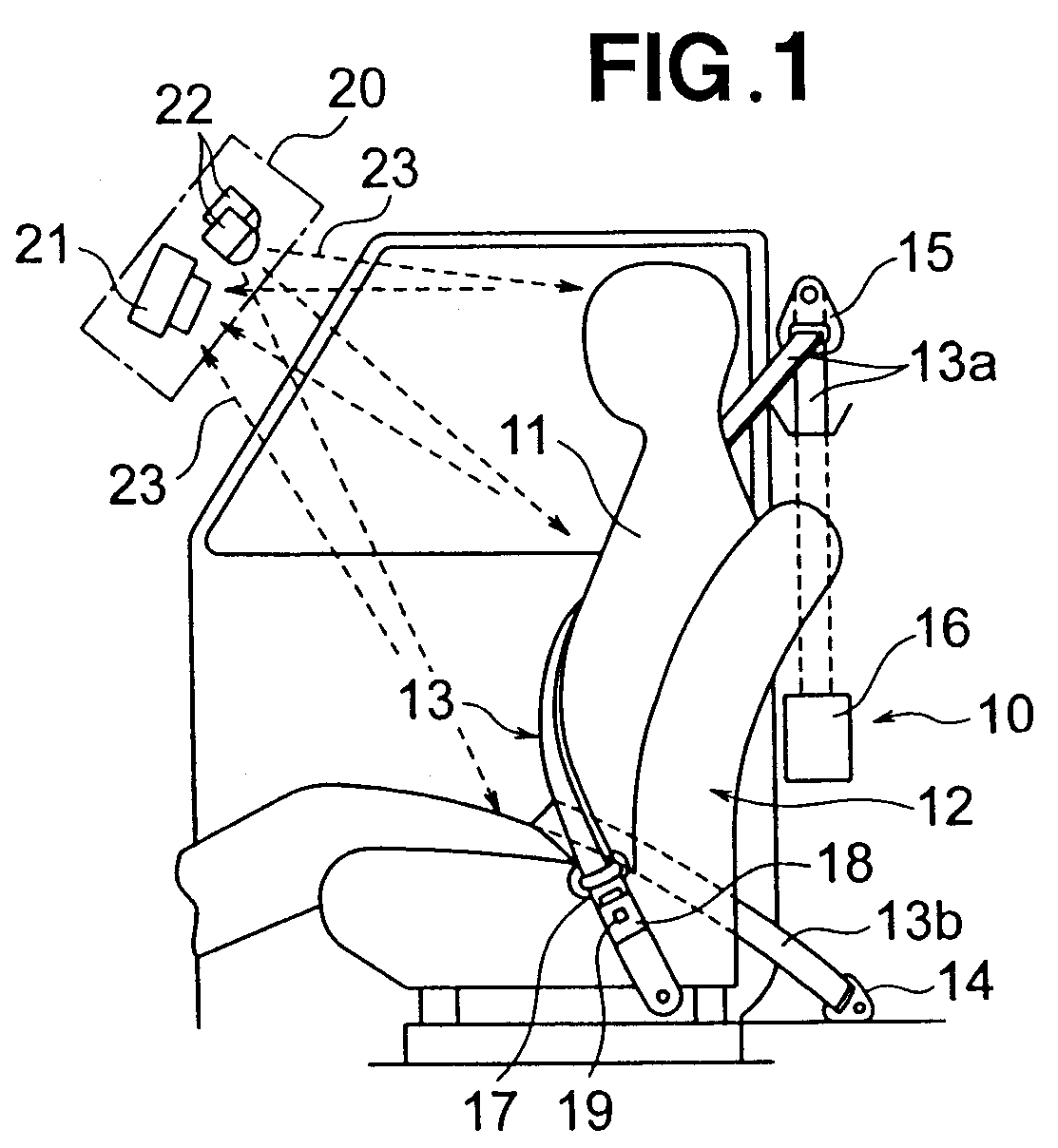
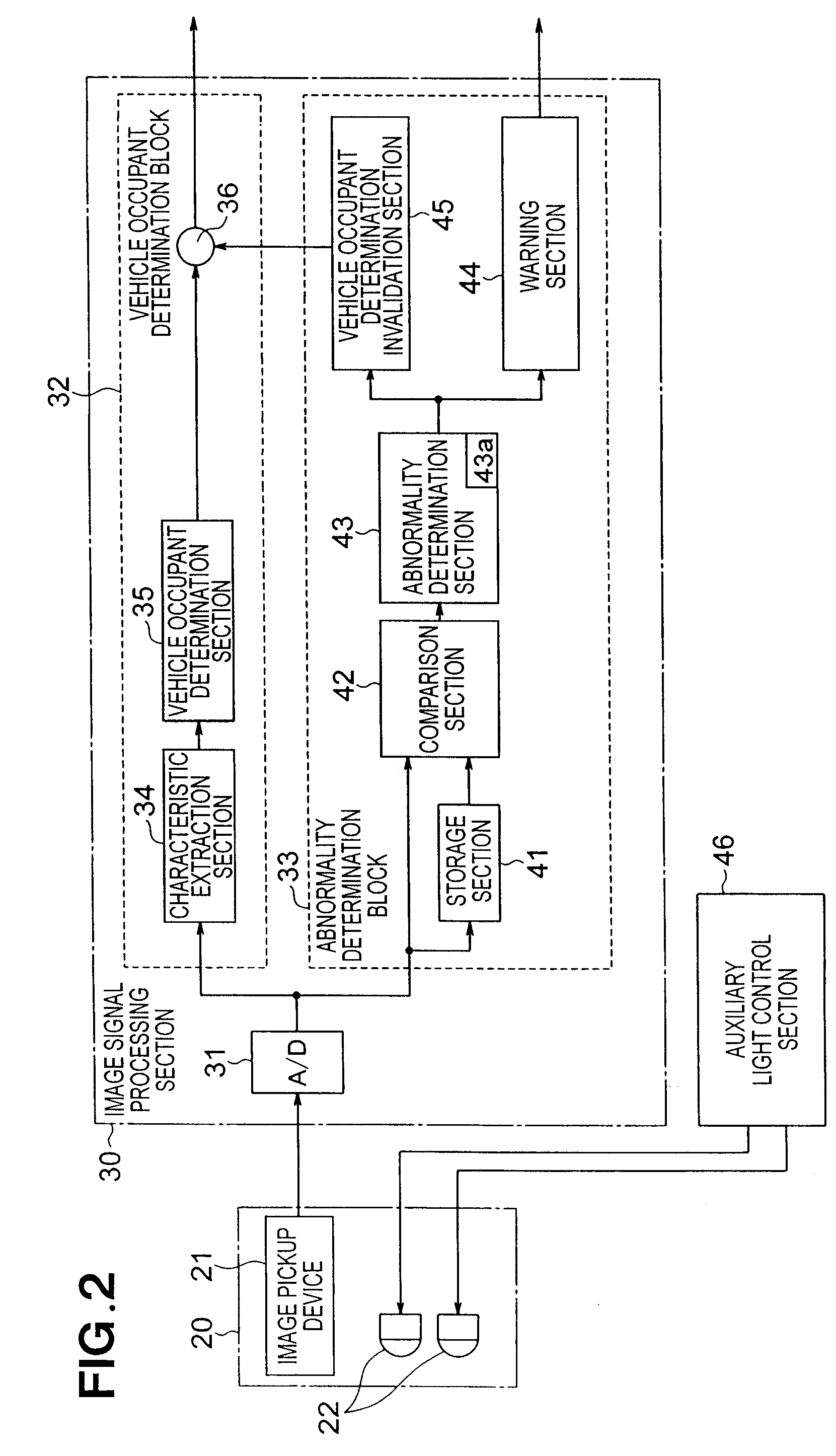
Vehicle occupant detection apparatus
InactiveUS20080094195A1Reliably determinedAbnormal operationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingEngineeringImage based
A vehicle occupant detection apparatus includes an image pickup device for imaging an area including a position of a vehicle occupant within a vehicle compartment, a light emitting element for emitting auxiliary light into the compartment that includes the imaging area of the pickup device, and a storage section for storing imaging information provided by the pickup device. The vehicle occupant detection apparatus further including a comparison section for comparing imaging information provided through further imaging by the pickup device and the imaging information stored in the storage section, to provide a difference between the imaging information provided through the further imaging and the stored imaging information, and an abnormality determination section for determining abnormality of the imaging information on the basis of the image information difference.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
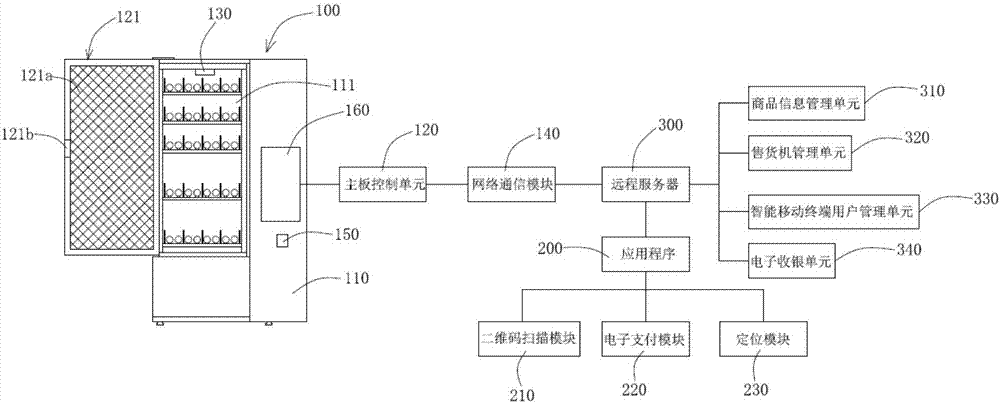
Self-service intelligent vending machine system
InactiveCN107134050AAvoid malfunctionLow mechanical failure rateCoin-freed apparatus detailsCo-operative working arrangementsElectronic cashNetwork communication
The invention discloses a self-service intelligent vending machine system. The system comprises vending machine, wherein the vending machine comprises a goods container, a mainboard control unit, a RFID reader, a network communications module and a two-dimensional bar code; an application program implantable in an intelligent mobile terminal, wherein the application program comprises a two-dimensional bar code scanning module and an electronic payment module; a remote server, wherein communications and interactions are conducted by the remote server through the network communications module with the mainboard control unit of the vending machine, the remote server comprises a goods information management unit, a management unit of the vending machine, a user management unit of the intelligent mobile terminal, and an electronic cash register unit. The self-service intelligent vending machine system has the profitable effects that more stable running of the vending machine is guaranteed, and buying experiences of the customers' are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUKE SMART TECH
Thermal management system of hybrid power heavy truck and control method
ActiveCN109927534AImprove economyReduce consumptionAir-treating devicesInternal combustion piston enginesPower batteryCost effectiveness
The invention discloses a thermal management system of a hybrid power heavy truck and a control method. According to the thermal management system, components with different thermal demands are integrated in different cooling subsystems respectively, and the thermal management system can be divided into a high-temperature-level cooling system, a low-temperature-level cooling system and an air conditioner cooling system, wherein the high-temperature-level cooling system comprises an engine water circulation cooling device and an engine oil circulation cooling device, the low-temperature-level cooling system comprises a power battery and a motor, and the air conditioner cooling system is provided with a double-drive air conditioner compressor. The provided thermal management system of the heavy truck provides a control method for vehicle warming, driving and post-cooling and can achieve distribution of heat dissipation amount of each component under various working conditions as required, reasonably utilize waste heat and reduce the energy consumption of accessories of the thermal management system, so that the cost-effectiveness of a whole vehicle is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Straight pushing plate type flow regulation damping cylinder for smart knee-joint
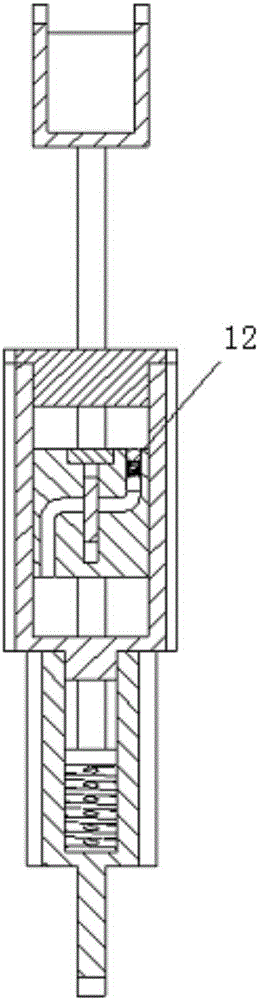
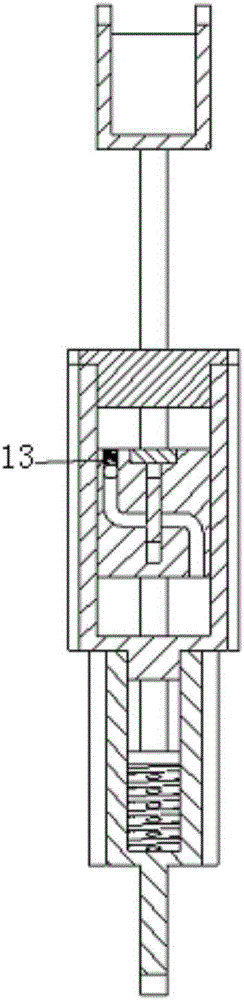
ActiveCN106539633ARealize two-way independent controlDamping adjustment continuousArtificial legsHydraulic cylinderKnee Joint
The invention relates to a straight pushing plate type flow regulation damping cylinder for a smart knee-joint. The straight pushing plate type flow regulation damping cylinder for the smart knee-joint comprises a motor support, a hollow piston rod, a plate type valve body, a hydraulic cylinder upper cover, a hydraulic cylinder body, a hollow piston block, a spring shell and an extending assisting spring. The upper cover is fixedly connected with one end of the hydraulic cylinder body through a thread, and the spring shell is fixedly connected with the other end of the hydraulic cylinder body through a thread; the extending assisting spring is stored in the spring shell; the hollow piston block is installed in the hydraulic cylinder body; one end of the hollow piston block is connected with the extending assisting spring through the piston rod, and the other end of the hollow piston block is connected with the motor support through the hollow piston rod; the plate type valve body is installed in the hollow piston block; two flat-key-shaped holes in parallel and two circular holes in parallel up and down are formed in the plate type valve body; hydraulic oil flowing passages which are bent and extended correspondingly and in parallel are formed in the hollow piston block; and the two hydraulic oil flowing passages are arranged in the axial direction with the heights being staggered and each provided with a one-way valve. According to the straight pushing plate type flow regulation damping cylinder, bi-directional independent control over a bend-extend damp of the artificial limb knee-joint can be achieved through one linear motor.
Owner:上海理工资产经营有限公司
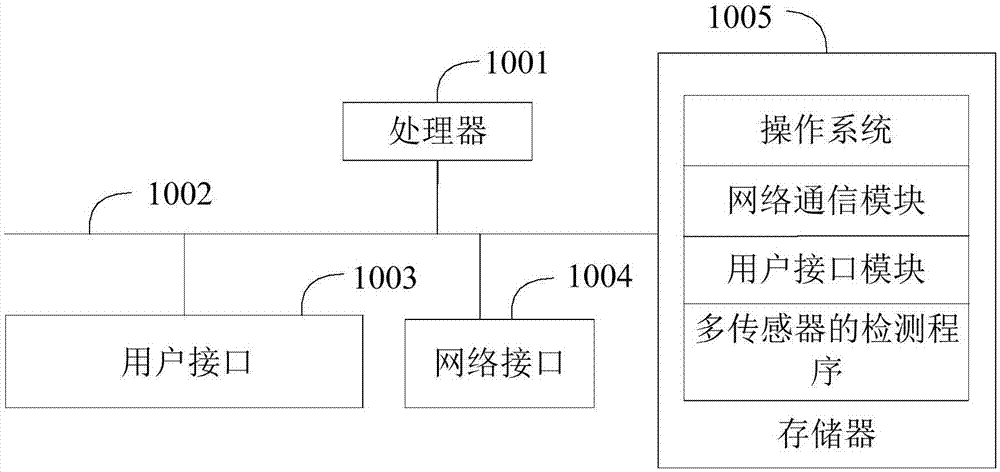
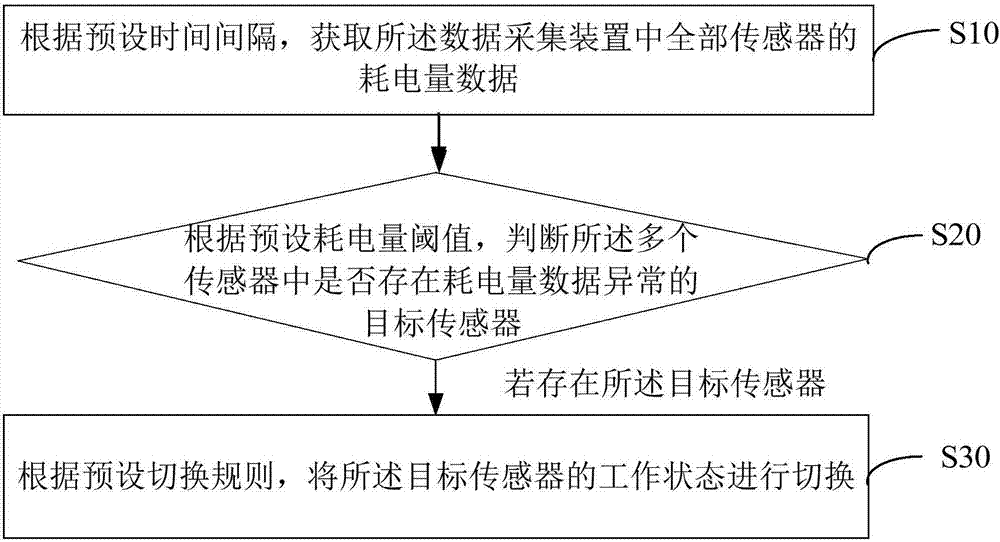
Multi-sensor detection method and device, and computer readable storage medium
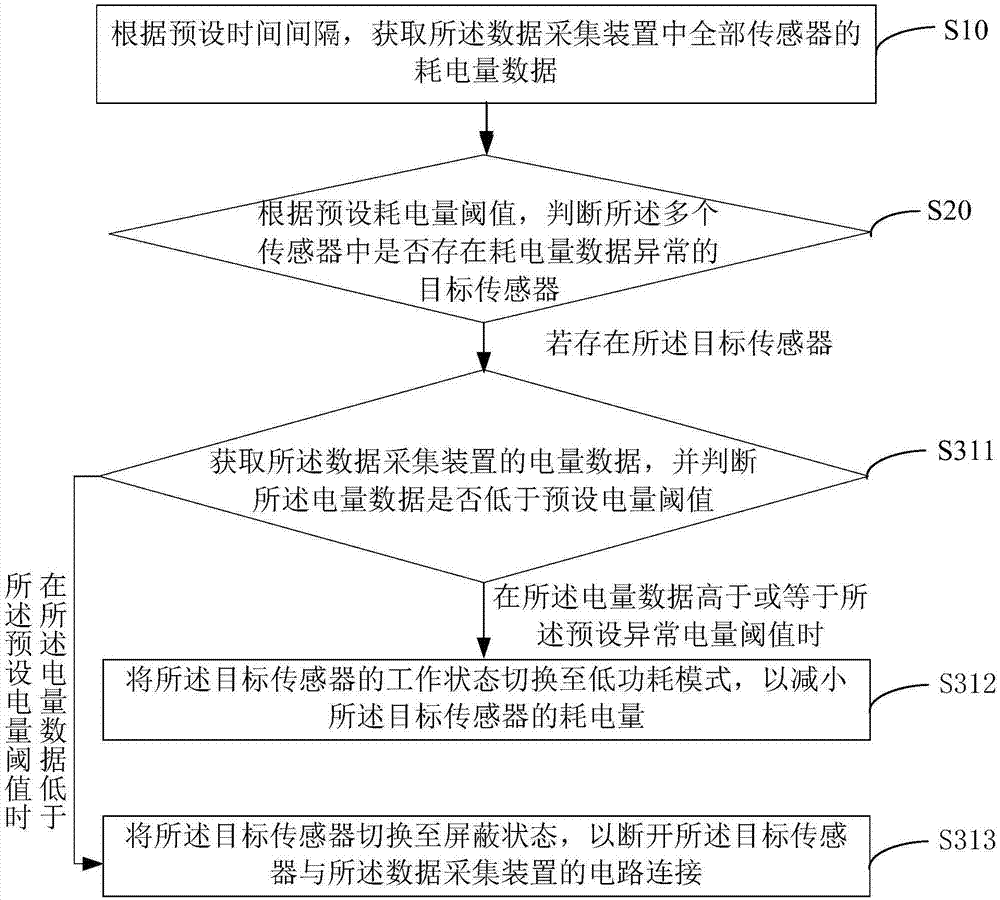
The invention provides a multi-sensor detection method and device, and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps: obtaining the power consumption data of a plurality of sensors in a data collection apparatus according to a preset time interval; judging whether there is a target sensor with the abnormal power consumption data in the sensors or not according to a preset power consumption threshold value; and switching the working state of the target sensor according to a preset switching rule if there is the target sensor. Through the above mode, the method achieves the control of the working state of the abnormal sensor when the sensor with the abnormal power consumption is detected, such as the switching off of the abnormal sensor or the reduction of the working frequency of the abnormal sensor, so as to avoid the quick consumption of the residual power, and guarantee the normal operation of other sensors. Therefore, a technical problem that a sampling apparatus cannot work normally caused by the excessively high power consumption of one or more sensors is solved.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD +1
Wireless headset role switching method, wireless headset and TWS headset
ActiveCN108696784AGuaranteed normal useImprove user experienceCordless telephonesService provisioningHeadphonesWireless connectivity
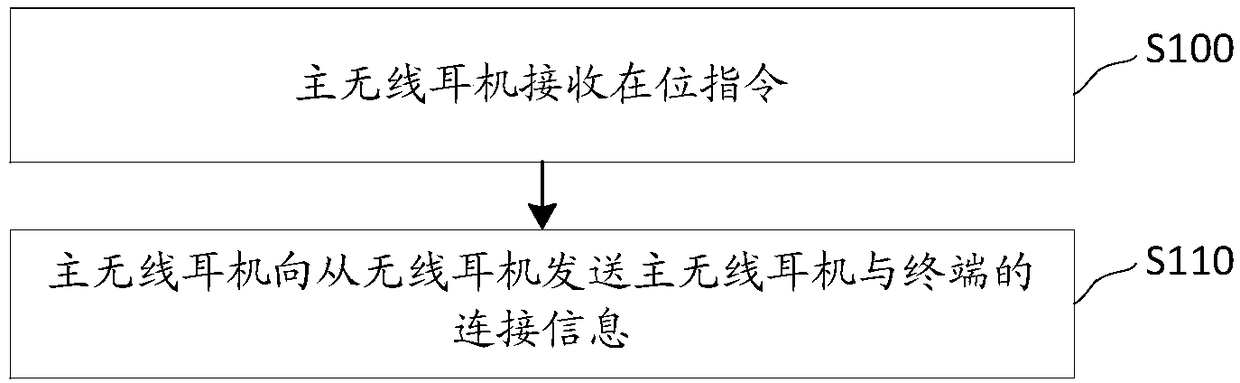
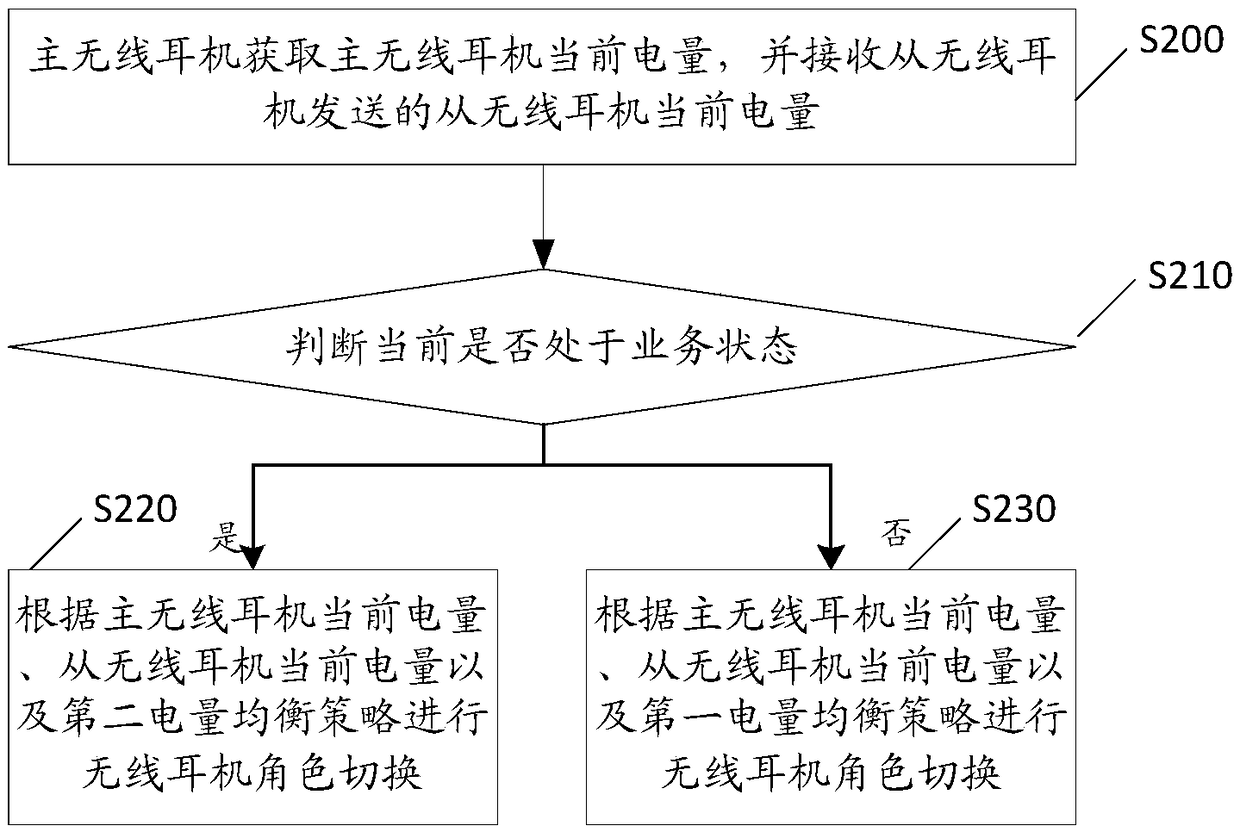
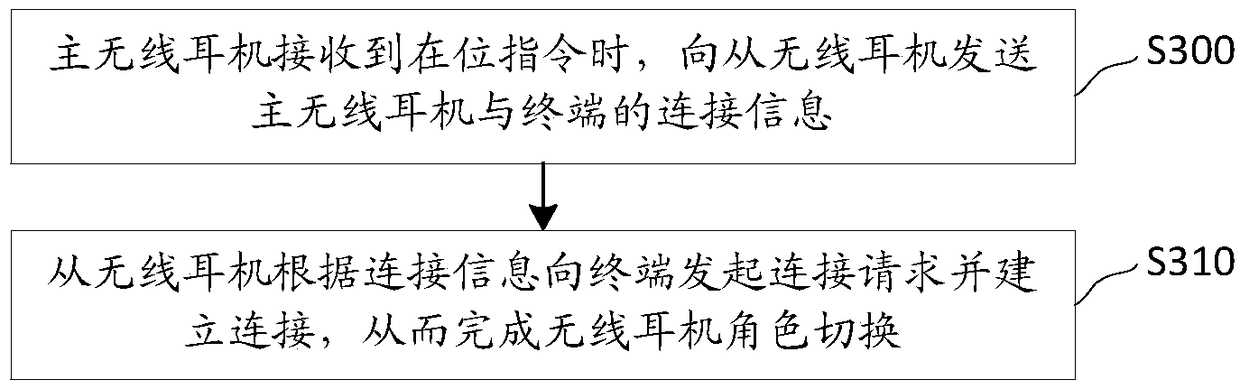
The invention discloses a wireless headset role switching method, and relates to the technical field of portable listening equipment. A main wireless headset is the headset establishing connection with a terminal at present, and a slave wireless headset is the headset not establishing connection with the terminal at present. The method comprises the steps that when the main wireless headset receives an in-place instruction, the main wireless headset sends connection information of the main wireless headset and the terminal to the slave wireless headset to enable the slave wireless headset to initiate a connection request to the terminal according to the connection information and establish connection with the terminal, and then wireless headset role switching is achieved. According to themethod, the slave wireless headset can achieve data interaction with the terminal by means of the connection information of the main wireless headset and the terminal to continue working; and the condition that in the prior art, after the main wireless headset stops working, the slave wireless headset cannot work is avoided, and therefore the user experience is improved. The invention further discloses the wireless headset, a wireless connection equipment role switching method, a TWS headset and a computer readable storage medium which have the above-mentioned advantages.
Owner:GEER TECH CO LTD
Valve control constant magnetic magnetorheological damper
ActiveCN102889331ASimple structureAvoid heat productionSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionCavity wallMagnet
The invention relates to a valve control constant magnetic magnetorheological damper and belongs to the technical field of magnetorheological dampers. The valve control constant magnetic magnetorheological damper consists of a cylinder body, a piston, a piston rod, a by-pass pipe and an electric-hydraulic proportional servo valve, wherein the piston consists of an annular permanent magnet, two magnetic rings, an annular magnetic isolating body and two magnetic isolating rings; the piston is arranged in a cavity of the cylinder body; two ends of the piston rod respectively extend out of central round holes of two end face plates of the cylinder body; a magnetorheological fluid flow gap is formed between the piston and a cavity wall of the cylinder body; two ends of the by-pass pipe which is connected with in series with the electric-hydraulic proportional servo valve are respectively communicated with a left cavity and a right cavity; magnetorheological fluid is filled in the cavity of the cylinder body, the magnetorheological fluid flow gap and the by-pass pipe; and the magnetorheological fluid in the magnetorheological fluid flow gap becomes a viscous plastic body with a certain shear yield strength under the action of a constant magnetic field, and normal flow of the magnetorheological fluid is blocked. The complex control algorithm of a power supply or a computer does not need to be controlled, and the damper can work, the structure is simple, and the reliability is high.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
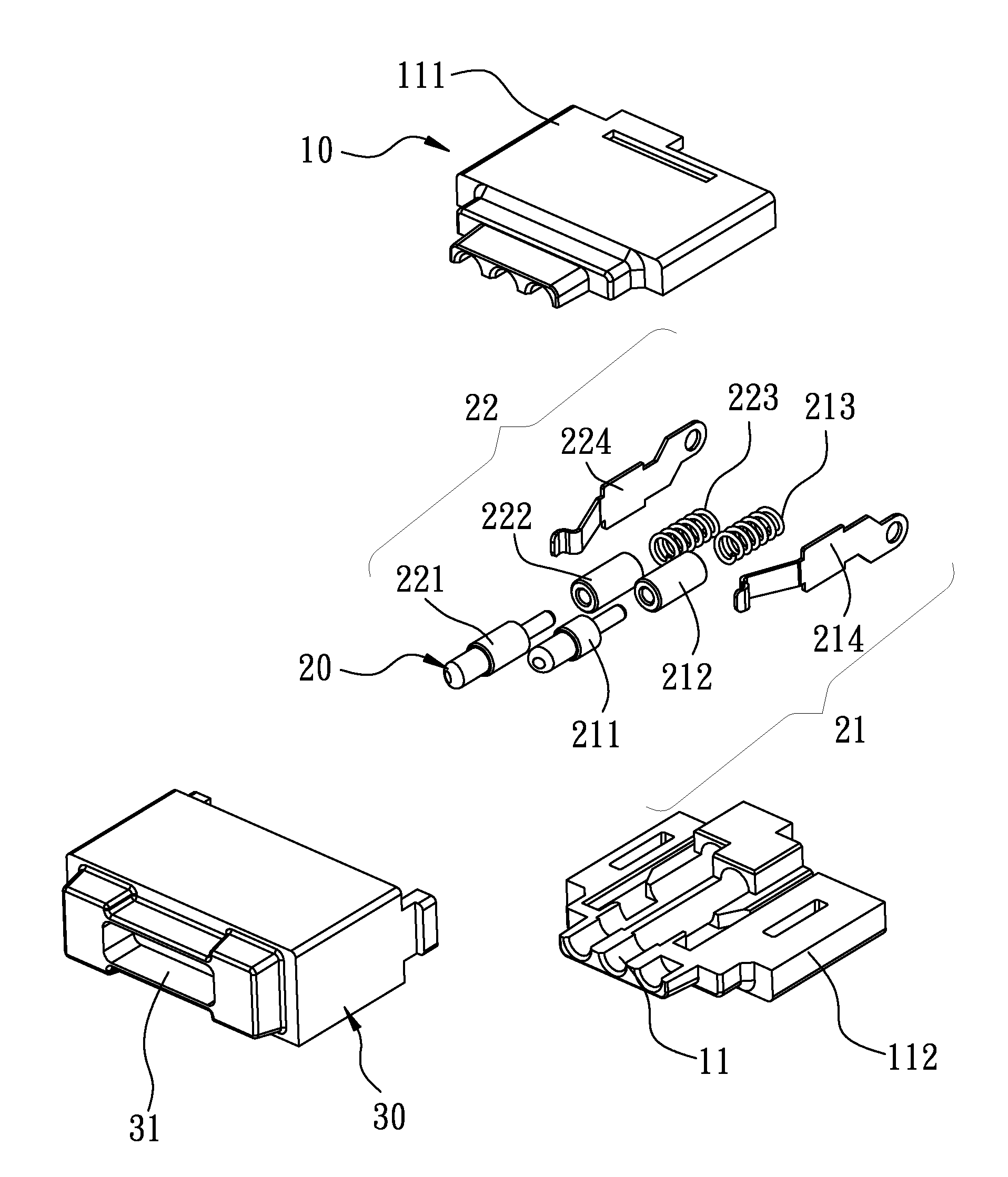
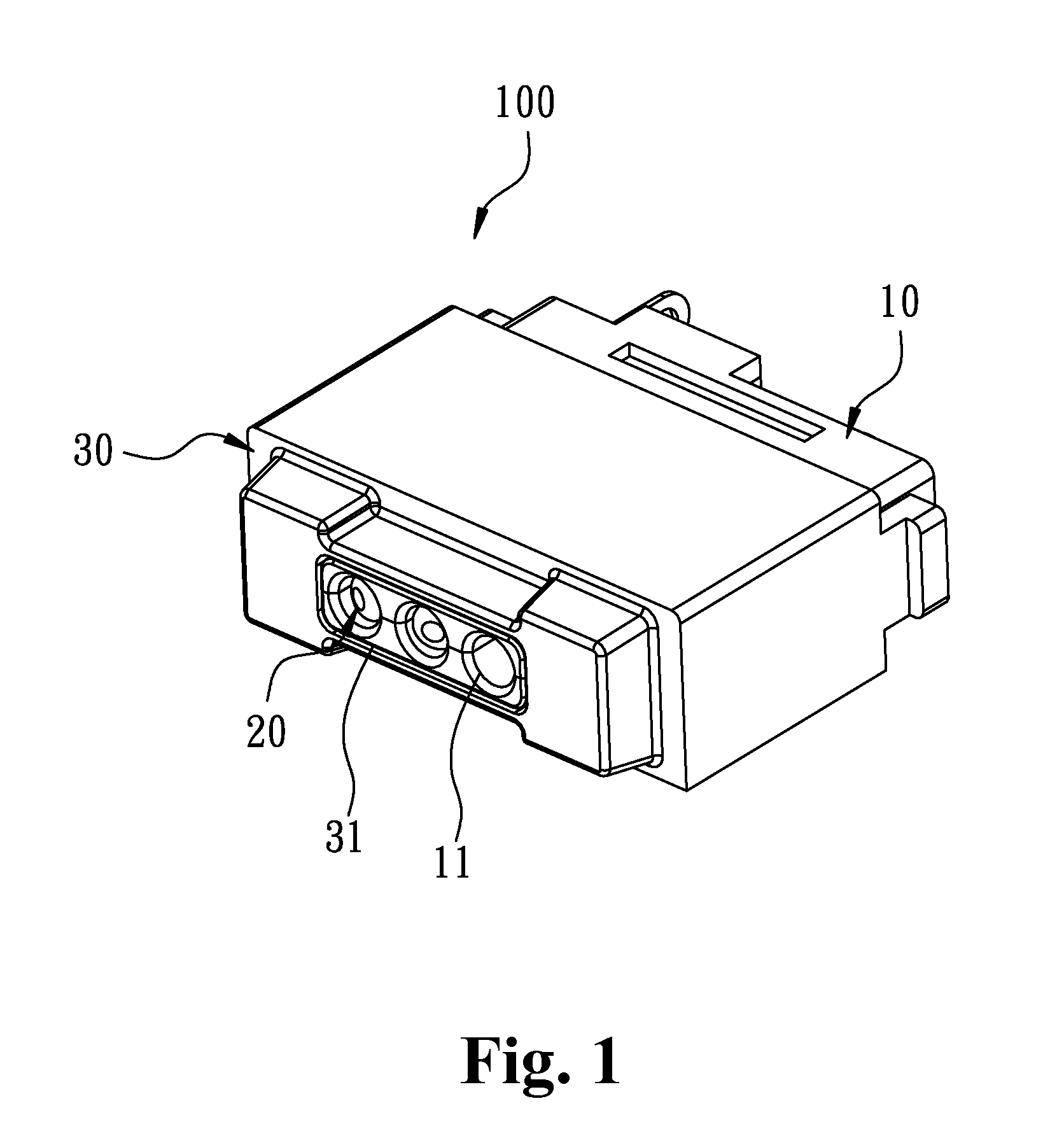
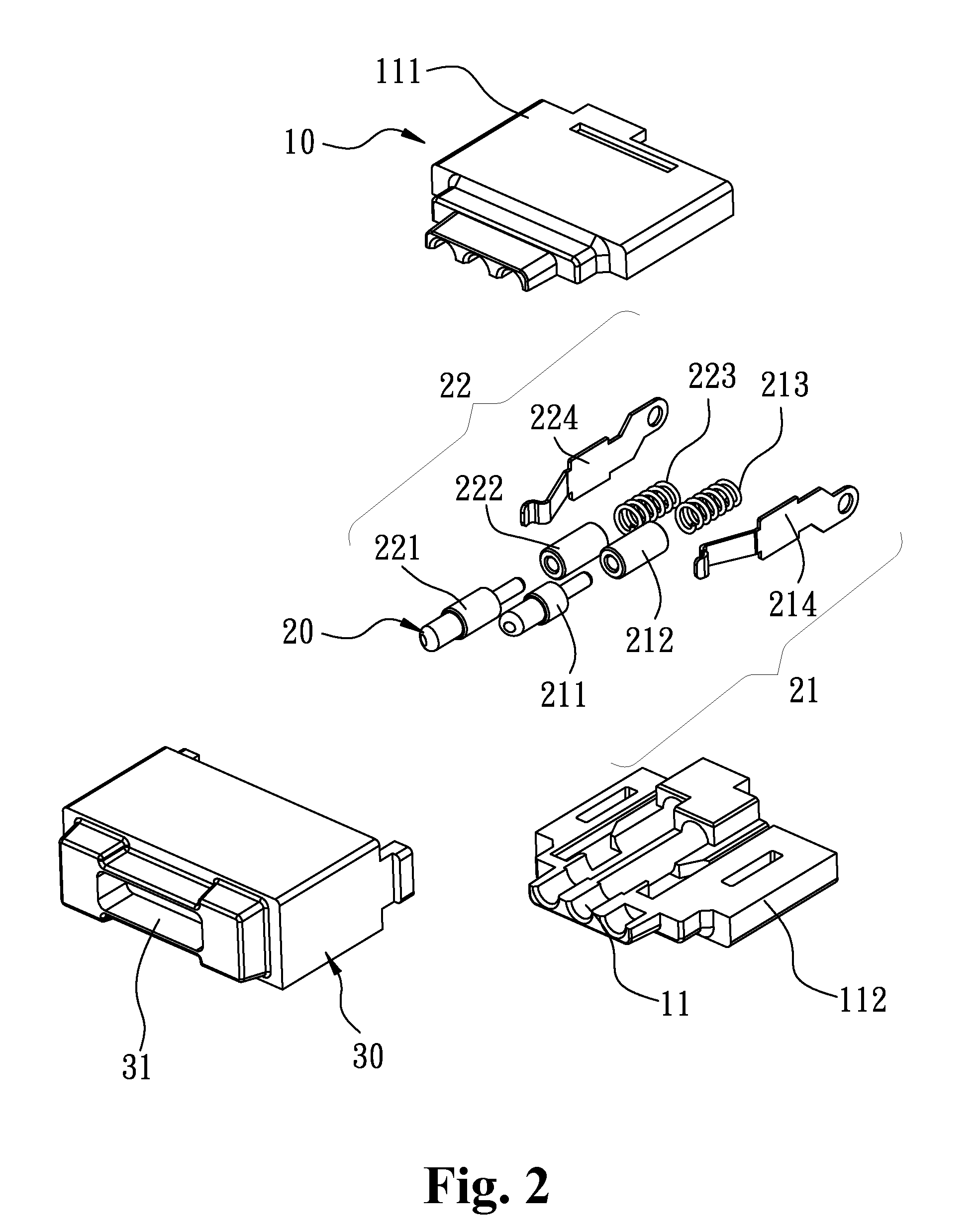
Magnetic power connector and an electronic system using the magnetic power connector assembly
InactiveUS9004924B2Extended service lifeReduce impactEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsCoupling contact membersElectricityElectronic systems
A magnetic power connector and an electronic system using a magnetic power connector are disclosed, wherein a magnetic element of the magnetic power connector is magnetically attracted to a matching magnetic connector to ensure a stable contact. In addition, the electrical conductive path created between the contact elements does not pass through any elastic elements, thereby avoiding heating and improving the lifespan of the elements. Furthermore, sealing can be disposed in the gaps between the connector elements to make the connector waterproof. In addition, a trigger signal can be generated by establishing an electrical connection between a signal contact element and the conductive element in the magnetic power connector so as to achieve the purpose of identification or control, thereby avoiding the functional failure caused by the damage of the contact element of the matching magnetic connector.
Owner:SINGATRON TECH HONG KONG CO
Automatic feeding device for stud welding
The invention discloses an automatic feeding device for stud welding. The automatic feeding device for stud welding comprises a machine frame, a longitudinal placing device for placing studs to be welded, a transverse pushing device for installing the longitudinal placing device and capable of transversely moving back and forth between a first position and a second position of a horizontal workstation of the machine frame, a longitudinal pushing device capable of longitudinally moving back and forth between a third position and a fourth position of a vertical workstation of the machine frame, a movable clamp fixed at the lower end of the longitudinal pushing device and capable of clamping a stud pushed to the second position by the transverse pushing device when the longitudinal pushing device moves to the third position, and a controller for performing data transmission and connected with the longitudinal placing device, the transverse pushing device, the longitudinal pushing device and the movable clamp. The automatic feeding device for stud welding is high in working efficiency, free of workpiece blockage, small in noise and electricity-saving, and can help to save the production cost.
Owner:佛山市玛雅数控设备有限公司
Bidirectional electromechanical static pressure control device
ActiveCN106337845AMeet job requirementsExcellent static pressure performanceServomotor componentsServomotorsElectric machineEngineering
The invention relates to the field of control equipment of an actuator, and discloses a bidirectional electromechanical static pressure control device. The bidirectional electromechanical static pressure control device comprises a motor pump assembly, a hydraulic oil tank and an integrated valve block which are arranged on a supporting plate, wherein the integrated valve block is provided with a control valve assembly; the motor pump assembly comprises a double-output-shaft motor; output shafts on two sides of the double-output-shaft motor are connected with a first screw pump and a second screw pump correspondingly; low-pressure oil openings of the first screw pump and the second screw pump are both connected with the hydraulic oil tank; high-pressure oil openings of the first screw pump and the second screw pump are connected with a first oil path and a second oil path correspondingly; the first oil path is used for being connected with an oil cavity of the actuator; and the second oil path is used for being connected with another oil cavity of the actuator. The motor pump is formed by the two screw pumps and the double-output-shaft motor, and when the bidirectional electromechanical static pressure control device works on the actuator, the vibration of the bidirectional electromechanical static pressure control device and air noise are lowered.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS
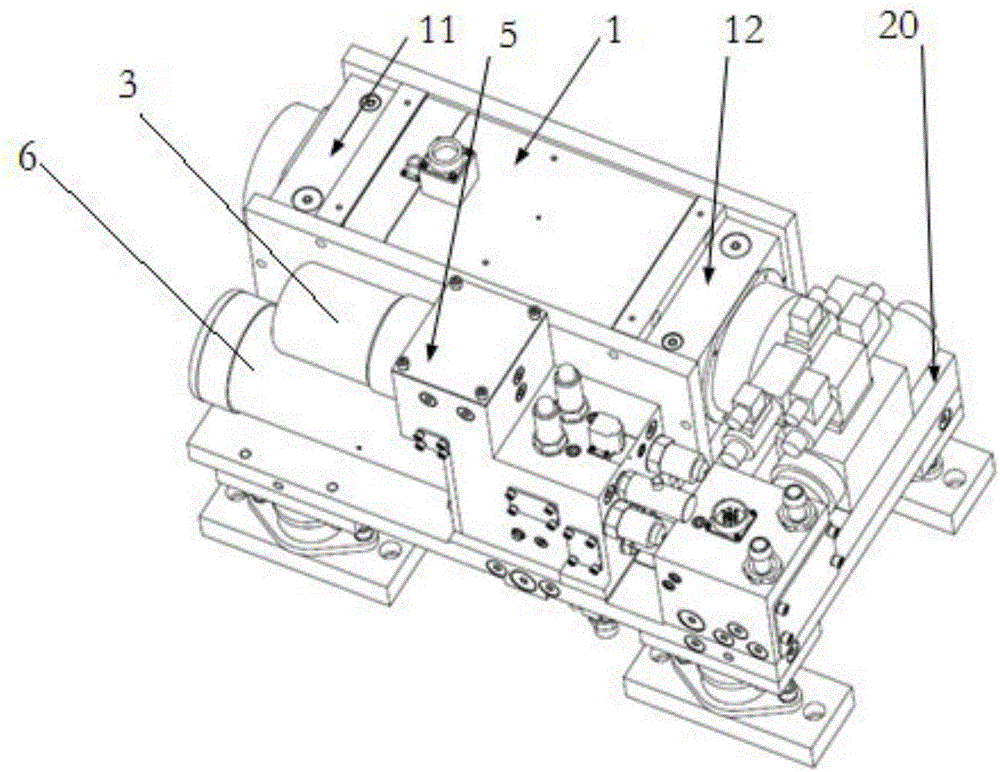
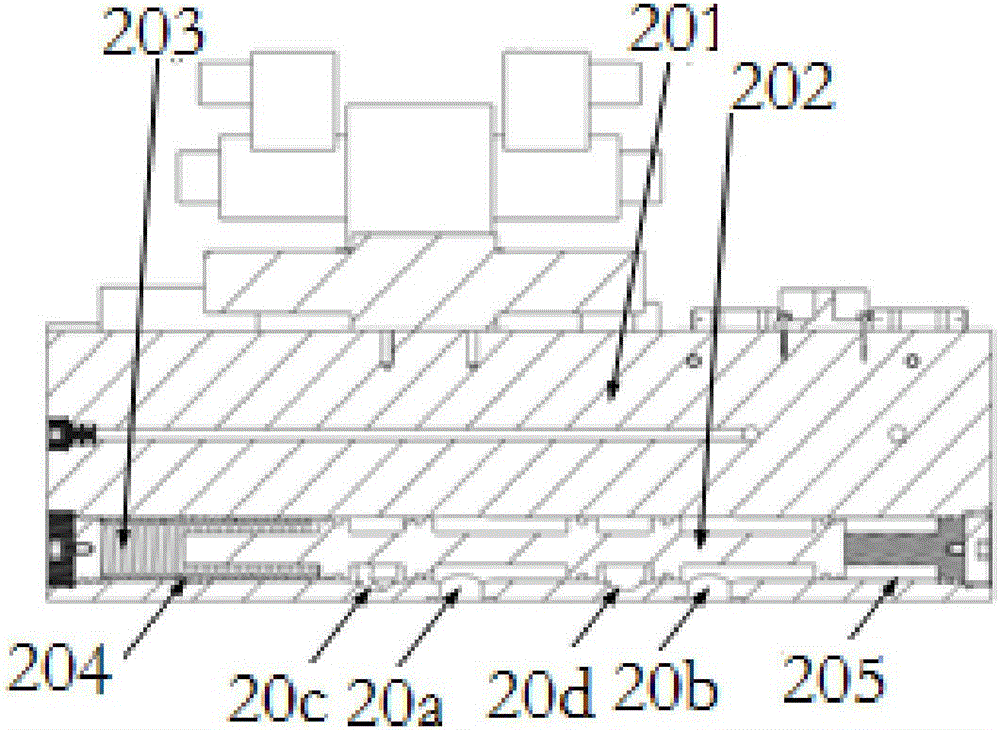
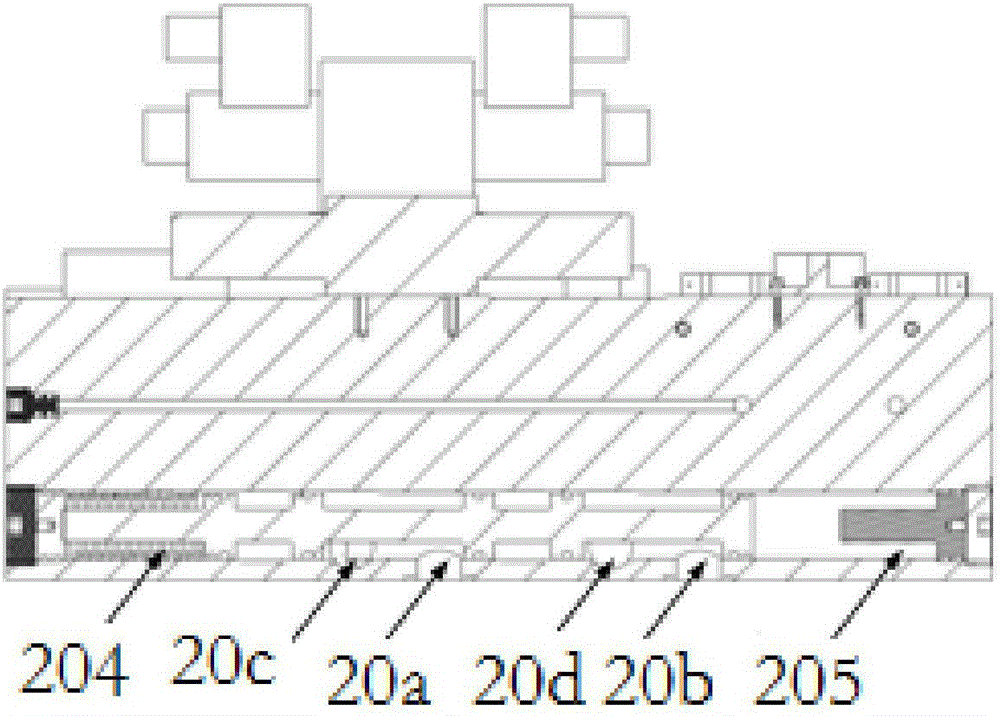
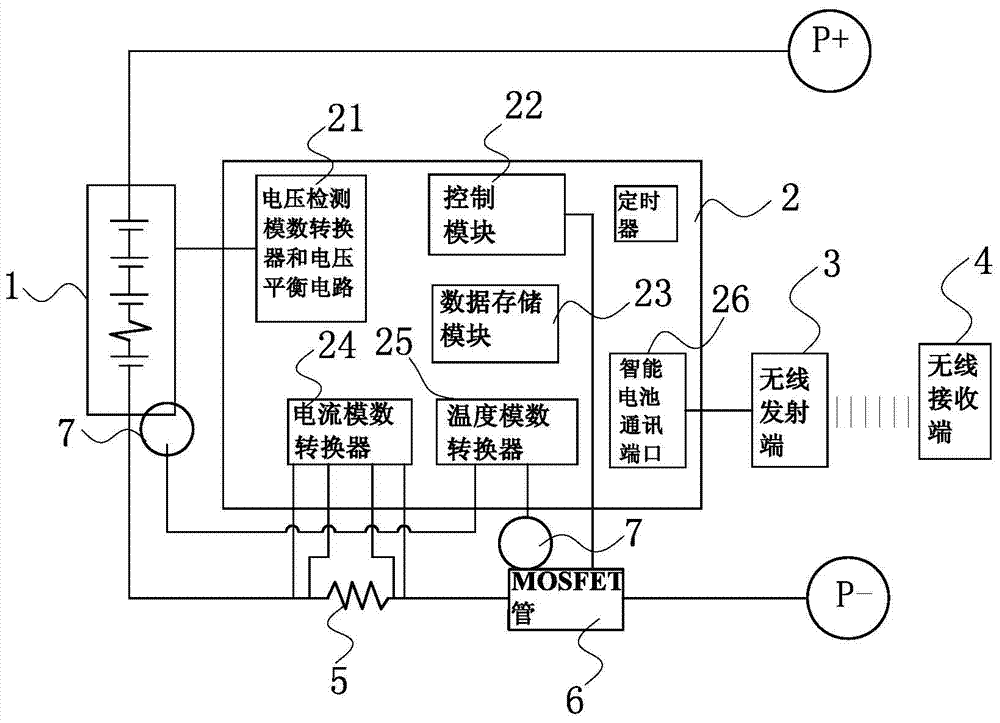
Battery pack monitoring system and monitoring method thereof
ActiveCN107017670AReduce volumeAvoid malfunctionSafety/protection battery circuitsElectric powerMOSFETMonitoring system
The invention provides a battery pack monitoring system. The battery pack monitoring system comprises battery package and a wireless receiving end, wherein the battery package comprises a battery pack, a battery management system (BMS) master control unit, a current detection resistor, a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET), a plurality of temperature detection probes and a wireless emission end, wherein the battery pack, the current detection resistor and the MOSFET are connected in series, the battery pack is formed by electrically connecting a plurality of single batteries and is provided with a positive connection end and a negative connection end, the plurality of temperature detection probes are respectively attached onto surfaces of the battery pack and the MOSFET, a control module, a data storage module and an analog-to-digital conversion module are integrated onto the BMS master control unit, the analog-to-digital conversion module is connected with the control module, the data storage module is connected with the control module, and the control module is connected with the MOSFET. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a monitoring method of the battery pack monitoring system. The battery pack monitoring system aims to solve the problems of insufficient monitoring on a temperature state, unreasonable module setting and unintuitive state information of an existing BMS.
Owner:BMTPOW LTD
Device for measuring material refractive index temperature coefficient under low temperature based on minimum deviation angle method
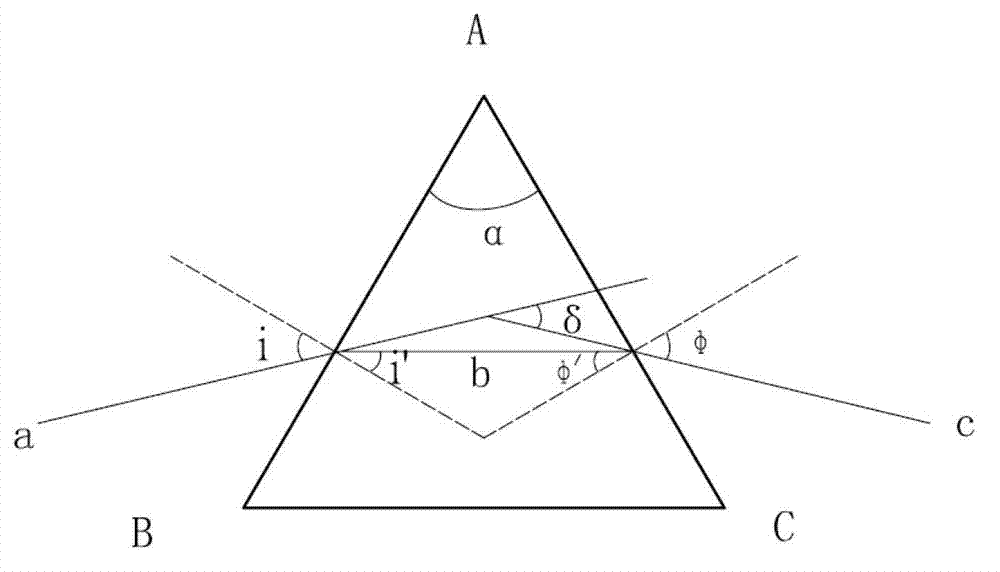
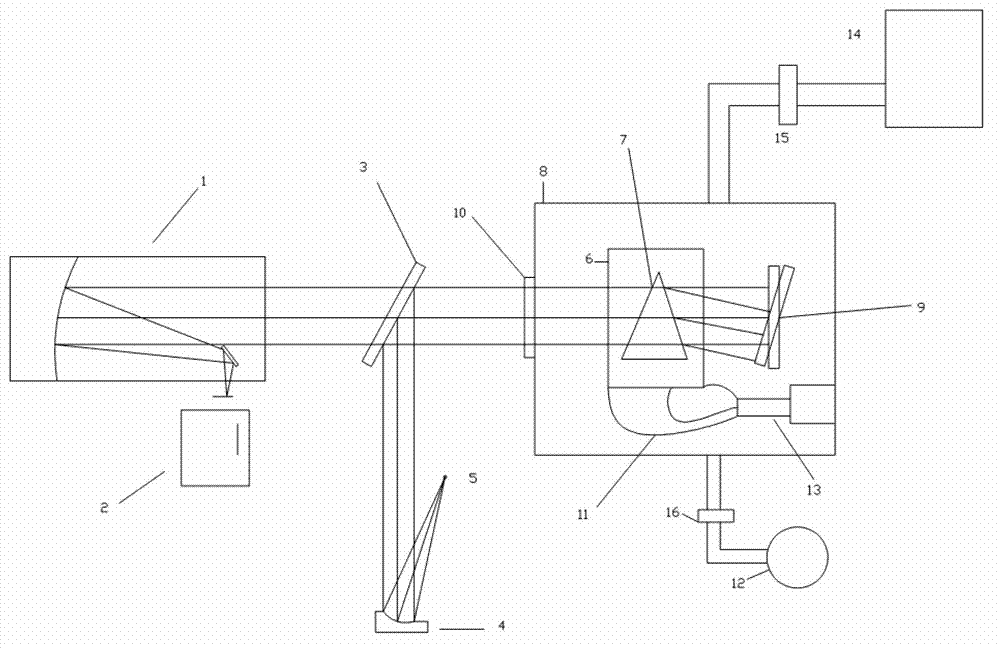
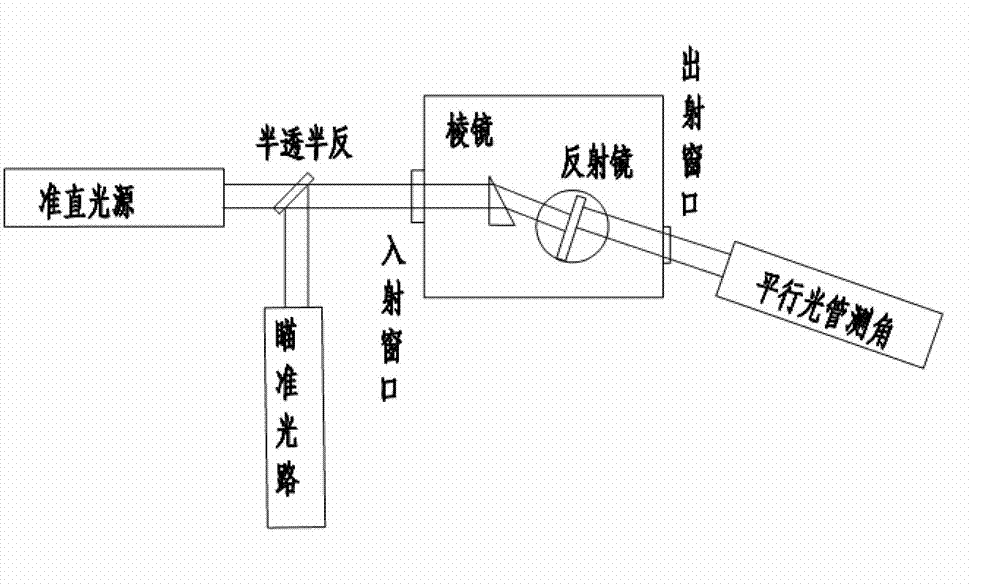
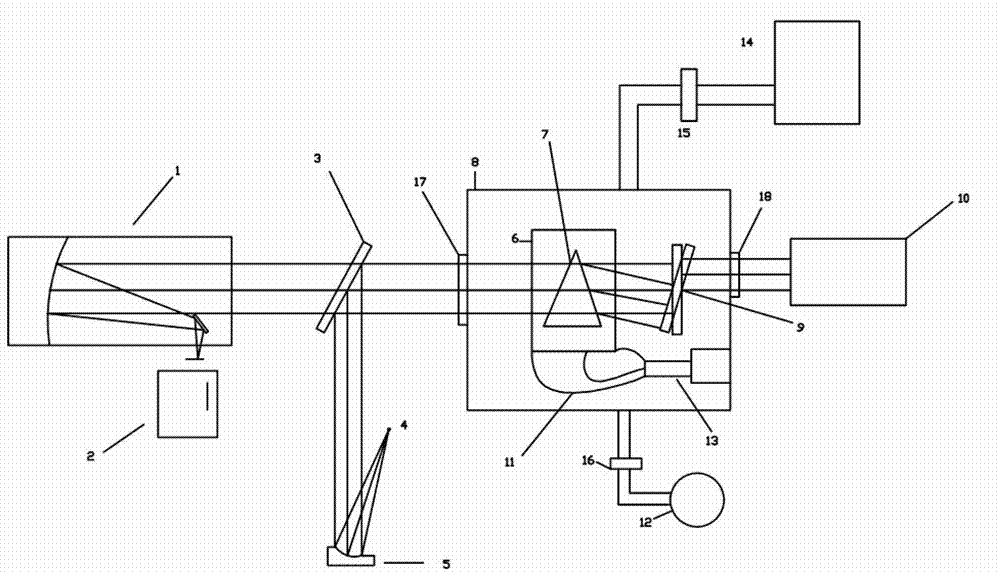
InactiveCN102788767AAvoid the effects of coolingIgnore the influence of the refractive index measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsLight beamMinimum deviation
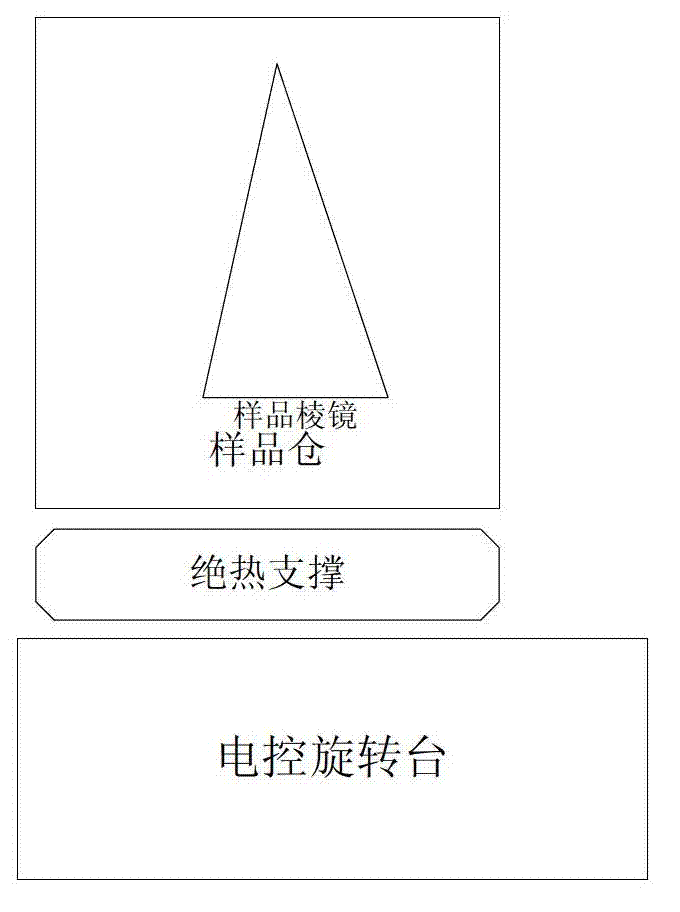
The invention provides a device for a measuring material refractive index temperature coefficient under low temperature based on a minimum deviation angle method. The device comprises a collimation light source system, a spectroscope, a collimation system, a low-temperature vacuum bin, a low-temperature vacuum system, a sample bin, a rotary reflection mirror, an electrically-controlled rotary table and an encoder. The low-temperature vacuum system, the sample bin, the rotary reflection mirror, the electrically-controlled rotary table and the encoder are subsidiary to the low-temperature vacuum bin. The sample bin and the rotary reflection mirror are driven by a motor respectively and are disposed in the low-temperature vacuum bin. When the device is used for measuring, quasi-monchromatic parallel light beams are emitted from a collimation light source and are emitted into the low-temperature vacuum bin after refection by the spectroscope, placement angles of reflection mirrors on a triple prism and the encoder are rotated to be adjusted to figure out a position of a minimum deviation angle, the light beams are perpendicularly emitted into the rotary reflection mirror, finally return to the spectroscope and enter the collimation system after being reflected. The traditional minimum deviation angle method is modified, the auto-collimation principle and the minimum deviation angle method are combined, demands for high precision of a shaft encoder are lowered within equal measuring precision ranges, and accordingly systematic cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for measuring material refractive index and refractive index temperature coefficient under low temperature
InactiveCN102830090AAvoid the effects of coolingIgnore the influence of the refractive index measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexPrism
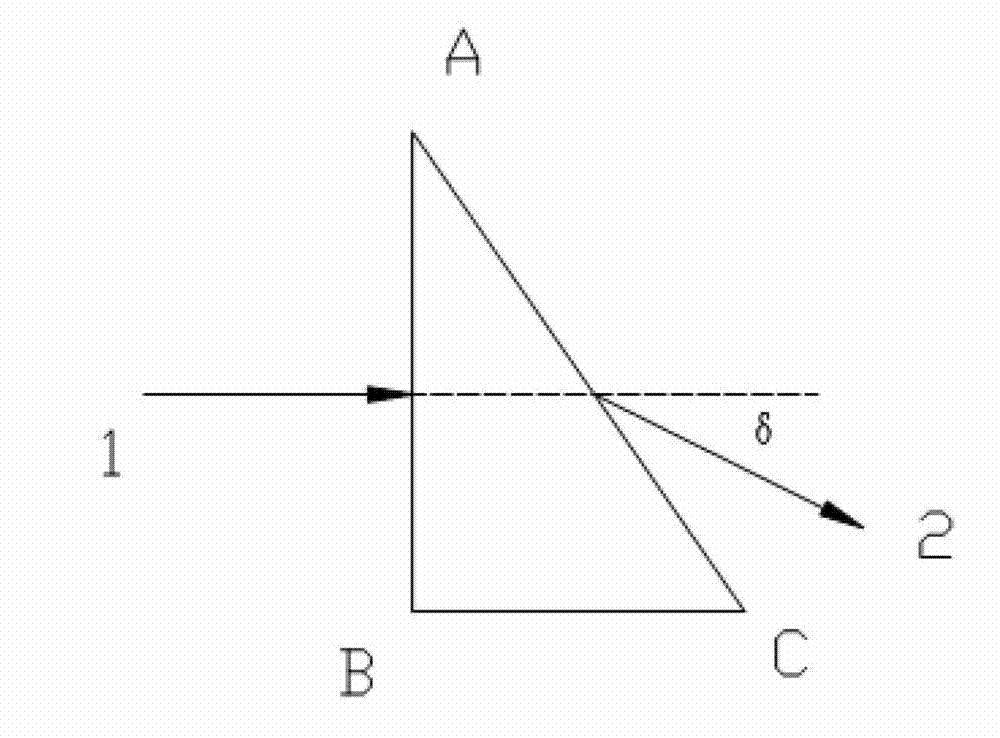
The invention provides a device for measuring a material refractive index and a refractive index temperature coefficient under a low temperature, and the device comprises a collimation light source system, an optical spectroscope, an aiming system, a low-temperature vacuum cabin, a sample cabin, a double-sided rotary reflection mirror, an electric-control rotary platform and a collimator. When the temperature inside the sample cabin is reduced, the refractive index of a sample is reduced, a deviation angle delta also has slight variation delta, and the variation quantity of the deviation delta can be measured by the collimator, so that the refractive index of the material under the low temperature is changed. The device is based on the most conventional vertical incidence method, simple in principle and convenient to operate, a measured sample prism can be made of infrared materials and also can be made of the material in the visible light band, the application range is wide, the collimator is used for substituting a conventional coder for the measurement, the collimator is precise for measuring the slight variation of the angle, the collimator can be well applied to the slight variation of the deviation angle caused by the variation of the material refractive index under the low temperature, the cost of the device is reduced, and the measurement precision of the deviation angle is improved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Automatic maintenance device for standby battery of uninterruptible power system (UPS)
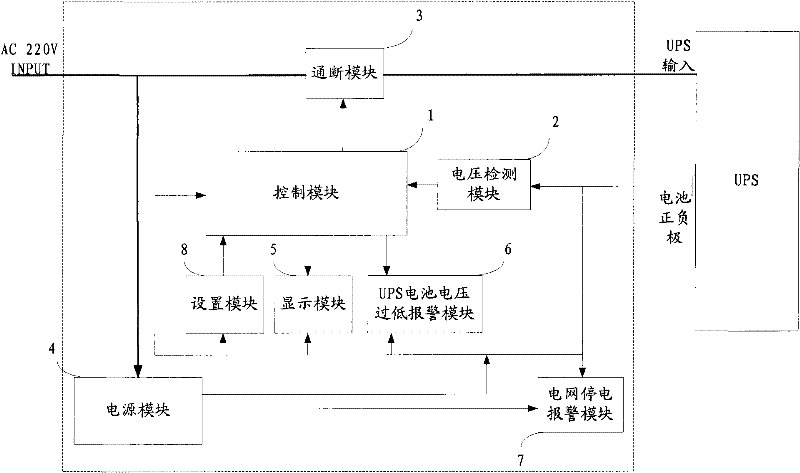
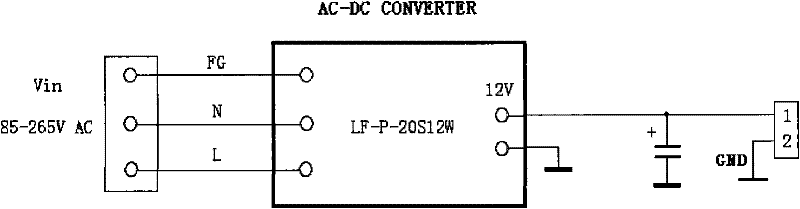
InactiveCN102244413AExtended service lifeReduce use costEmergency power supply arrangementsCharge and dischargeAC power
The invention relates to a device for automatically charging and discharging a standby battery of an uninterruptible power system (UPS). The device comprises a control module, a voltage detection module, a switching on / off module and the like, wherein the switching on / off module is arranged at the input end of an AC power supply which supplies power to the UPS; the voltage detection module detects the voltage of the standby battery of the UPS; the switching on / off module and the voltage detection module are both electrically connected with the control module; the control module performs timing according to set automatic maintenance time, controls the switching on / off module to cut AC off to discharge the standby battery of the UPS when time obtained by the timing is equal to the maintenance time, and controls the switching on / off module to switch the AC on and performs maintenance time timing again when the voltage detection module detects the voltage of the standby battery of the UPS is reduced to a certain set value. Manual intervention is not required by the whole maintenance process to save labor cost at the same time of prolonging the service life of the UPS. Simultaneously, the invention also provides a UPS battery under voltage alarming module and a power grid power failure alarming module, which aim to timely give an alarm in exceptions.
Owner:BEIJING JINGMEI GRP GENERAL HOSPITAL
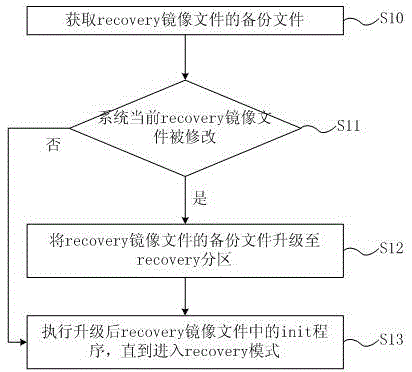
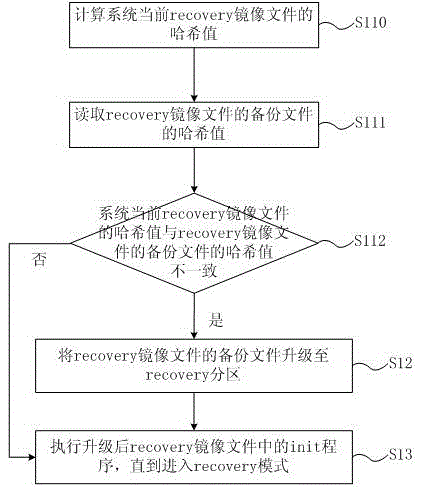
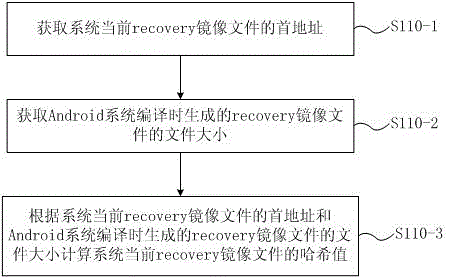
Android system protection method and apparatus
ActiveCN105468477AAvoid malfunctionImprove securityRedundant operation error correctionThird partyFile size
The invention discloses an Android system protection method and apparatus. The protection method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a backup file of a recovery image file, wherein the backup file of the recovery image file comprises a recovery image file generated in the compiling process of an Android system, and a hash value and a file size of the recovery image file; judging whether the current recovery image file of the system is modified; and if yes, upgrading the backup file of the recovery image file to a recovery partition. According to the Android system protection method and apparatus which are disclosed by the invention, a device is avoided being rooted by an OTA (Over-the-Air Technology) upgrade package after a third party recovery image file is flashed into the device; the condition that due to a user roots the device, the device cannot be normally used and even is bricked is prevented; safety of the device is improved; and normal use of the user and benefits of manufacturers are ensured.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
Magnetic power connector and an electronic system using the magnetic power connector assembly
InactiveUS20140256163A1Avoid malfunctionExtend your lifeEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsElectric connection structural associationsElectricityElectronic systems
A magnetic power connector and an electronic system using a magnetic power connector are disclosed, wherein a magnetic element of the magnetic power connector is magnetically attracted to a matching magnetic connector to ensure a stable contact. In addition, the electrical conductive path created between the contact elements does not pass through any elastic elements, thereby avoiding heating and improving the lifespan of the elements. Furthermore, sealing can be disposed in the gaps between the connector elements to make the connector waterproof. In addition, a trigger signal can be generated by establishing an electrical connection between a signal contact element and the conductive element in the magnetic power connector so as to achieve the purpose of identification or control, thereby avoiding the functional failure caused by the damage of the contact element of the matching magnetic connector.
Owner:SINGATRON TECH HONG KONG CO
Production method of high elasticity stainless steel belt for touch switch
The invention relates to a production method of a high elasticity stainless steel belt for a touch switch, and in particular discloses a production method of the stainless steel belt which is used for manufacturing touch switches of electronic products such as mobile phones and computers. The production method is characterized by sequentially comprising steps such as a sorting, primary rolling, primary cleaning, primary annealing, secondary rolling, secondary cleaning, secondary annealing, tertiary rolling, tertiary cleaning, pulling rectification, high temperature relief annealing, anti-corrosive treatment, quartic cleaning and reverse pulling rectification. The stainless steel band produced by the method has the advantages of light weight, high hardness, low and stable force, long fatigue life, unified hand feeling and low roughness, and the stainless steel band can normally reserve and can avoid wasting and can meet operating requirements of elastic buttons of the electronic products such as the mobile phones and the computers, and the service lives of the elastic buttons are prolonged.
Owner:无锡华生精密材料股份有限公司
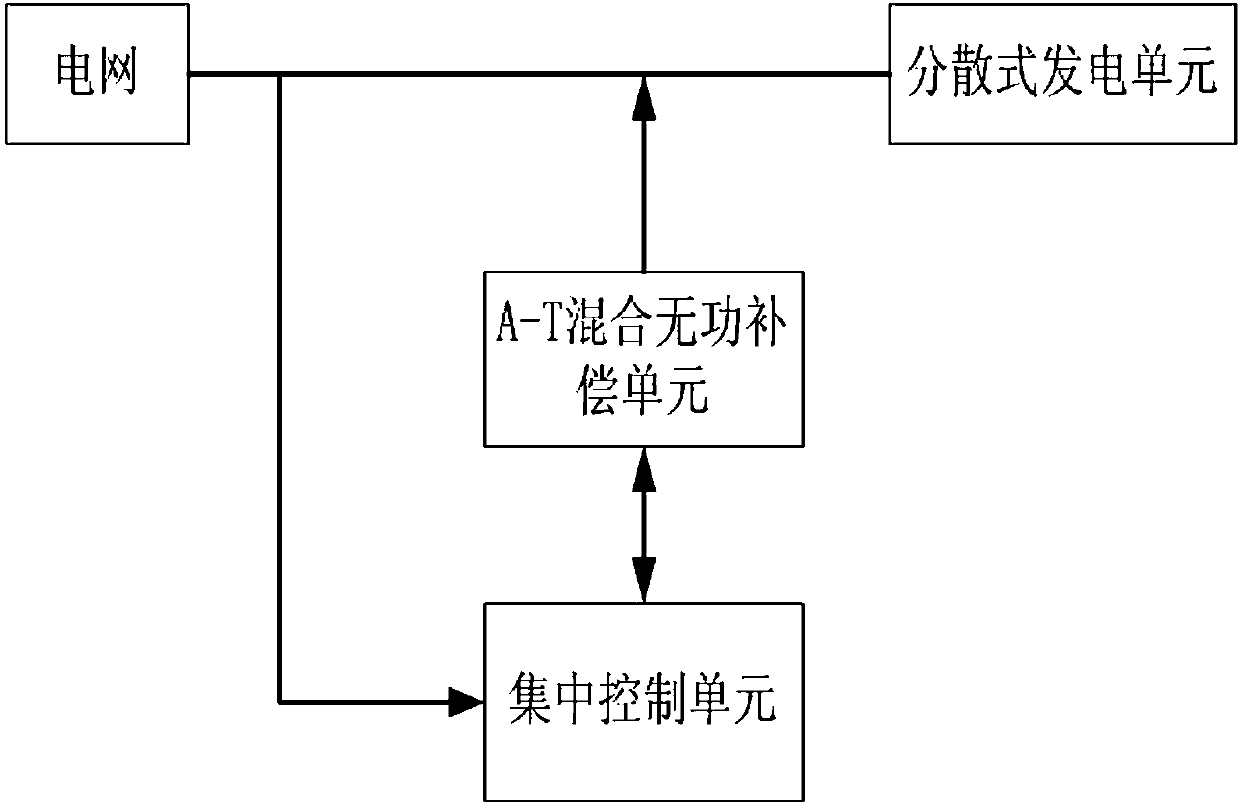
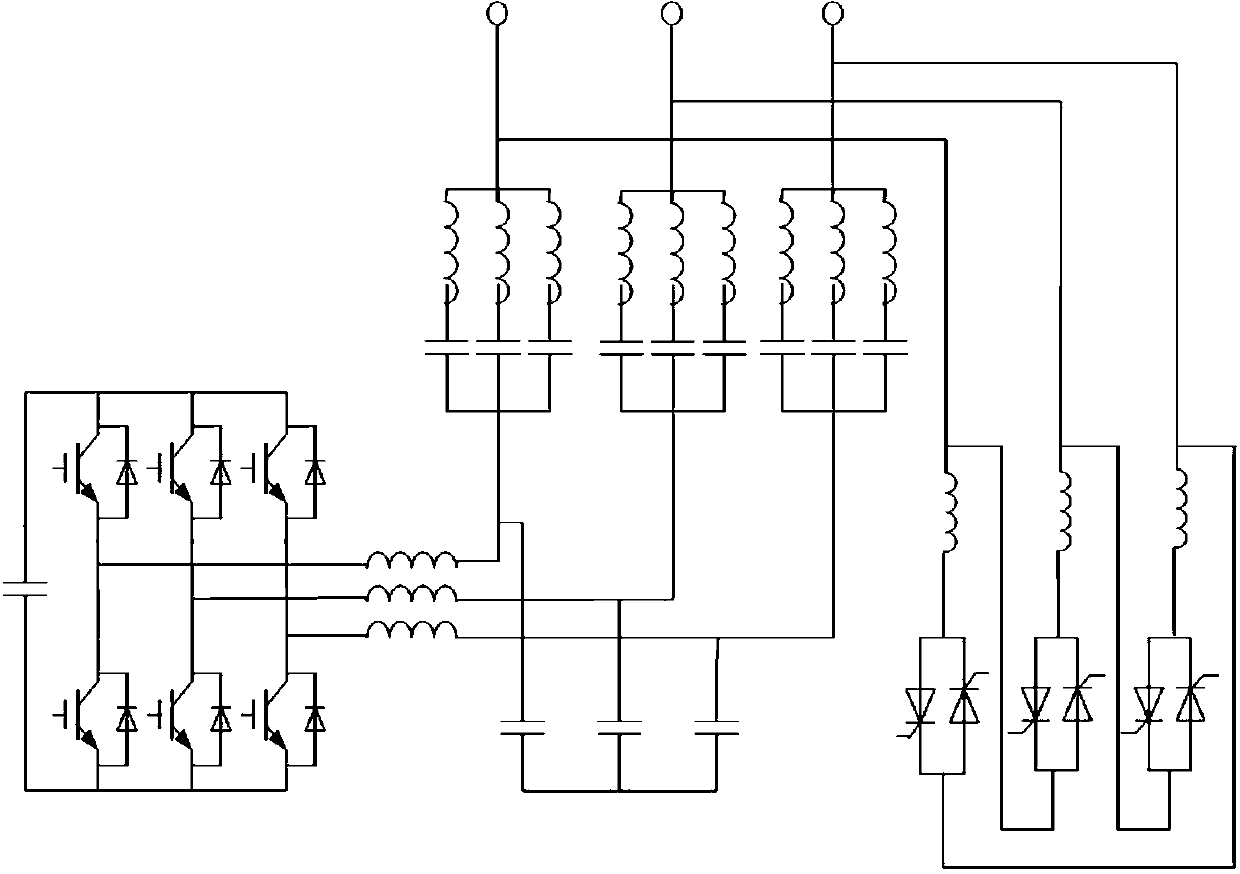
Scattered power generation reactive compensation device and method with harmonic suppression function
ActiveCN103219733ASuppress resonanceHigh accuracy of harmonic compensationFlexible AC transmissionActive power filteringAutomatic controlElectric power system
The invention belongs to the technical field of automatic control of a power system, in particular to a scattered power generation reactive compensation device and method with the harmonic suppression function. The scattered power generation reactive compensation device comprises an A-T mixing reactive compensation unit, a central control unit and a power supply module. The A-T mixing reactive compensation unit comprises a thyristor control reactor set (TCR), an active power filter (APF) and a passive filter set, wherein the thyristor control reactor set is connected with a compensation access point between the passive filter set and a power grid main line, and the active power filter and the passive filter set are in serial connection to form a mixing active filter. The central control unit can output pulse width modulation signals and triggering pulse signals which can respectively trigger an APF thyristor and a thyristor in the thyristor control reactor set. The scattered power generation reactive compensation device and method with the harmonic suppression function can effectively restrain resonance between the passive filter and the power grid, enables harmonic compensation accuracy to be higher and system response to be quick, improves reactive compensation safety and is economical and practical.
Owner:LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY LIMITED POWER SCI RES INSTION +3
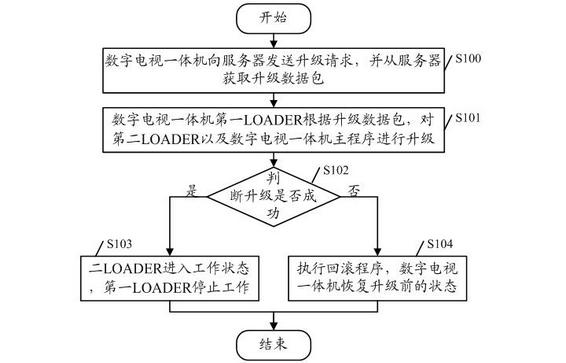
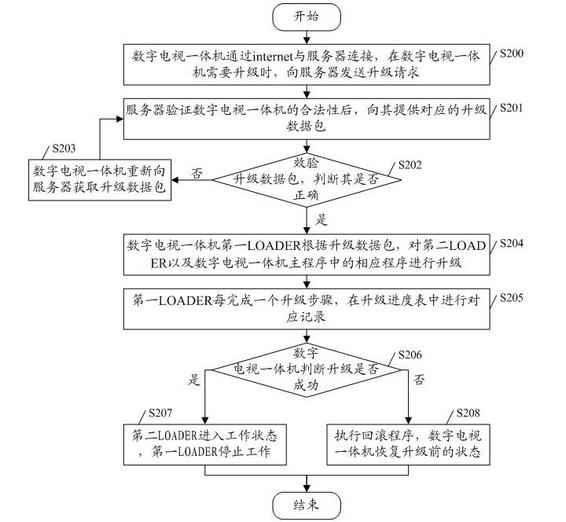
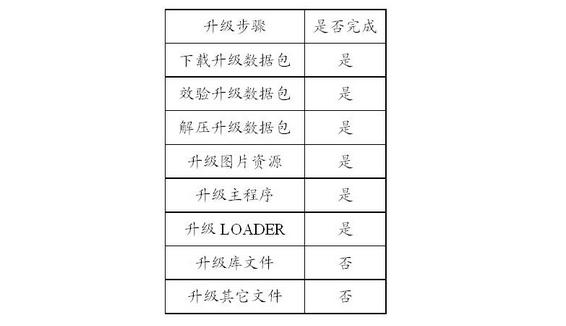
Digital television network system, digital television all-in-one machine and upgrading method thereof
ActiveCN102170536AGuaranteed reliabilityAvoid malfunctionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNetwork packetDigital television
The embodiment of the invention discloses a digital television network system, a digital television all-in-one machine and an upgrading method thereof. The method comprises the steps of: a digital television all-in-one machine sending an upgrading request to a server to obtain an upgrading packet from the server; and according to the upgrading packet, a first LOADER of the digital television all-in-one machine carrying out upgrading to a second LOADER and corresponding programs of a main program of the digital television all-in-one machine, wherein the first LOADER is currently in work state and the second LOADER is currently not in work state; and determining whether the upgrading is successful or not: if the upgrading is successful, then the second LOADER is in work state while the first LOADER stops working. The digital television network system, the digital television all-in-one machine and the upgrading method thereof provided by the embodiment of the invention adopt a double-LOADER structure, and can carry out upgrading on digital television all-in-one machines via internet, with reliability of the upgrading process guaranteed.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYWORTH DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
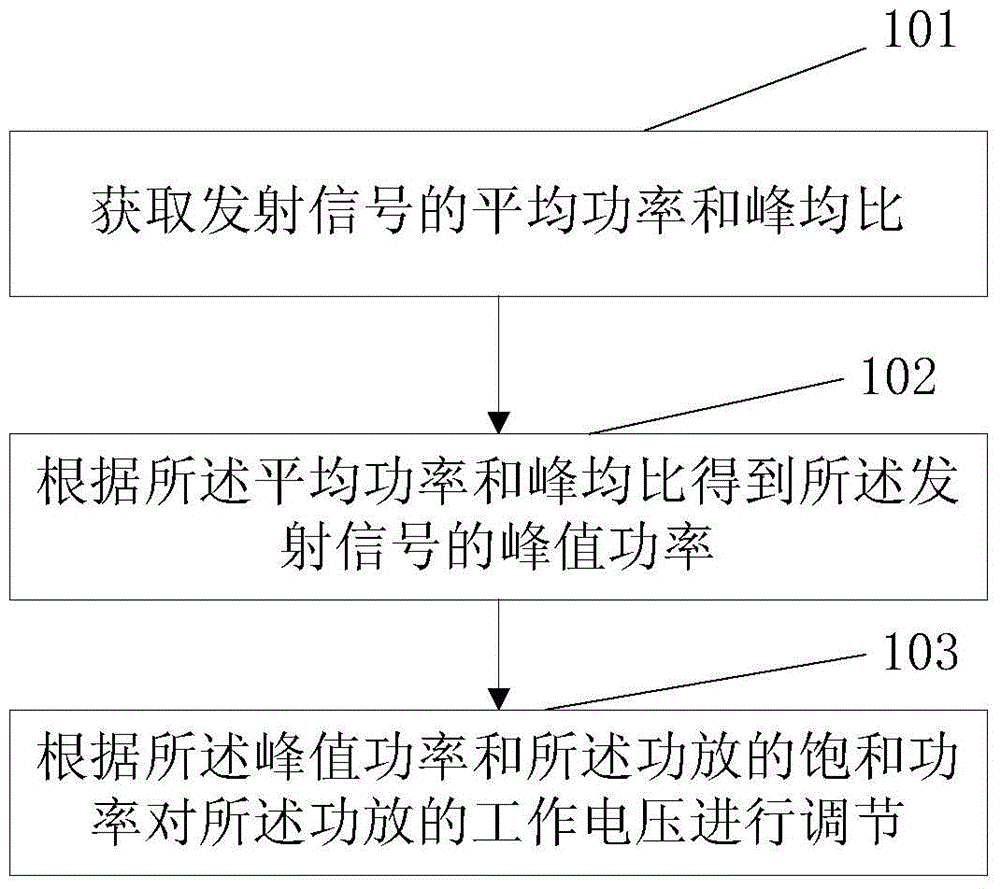
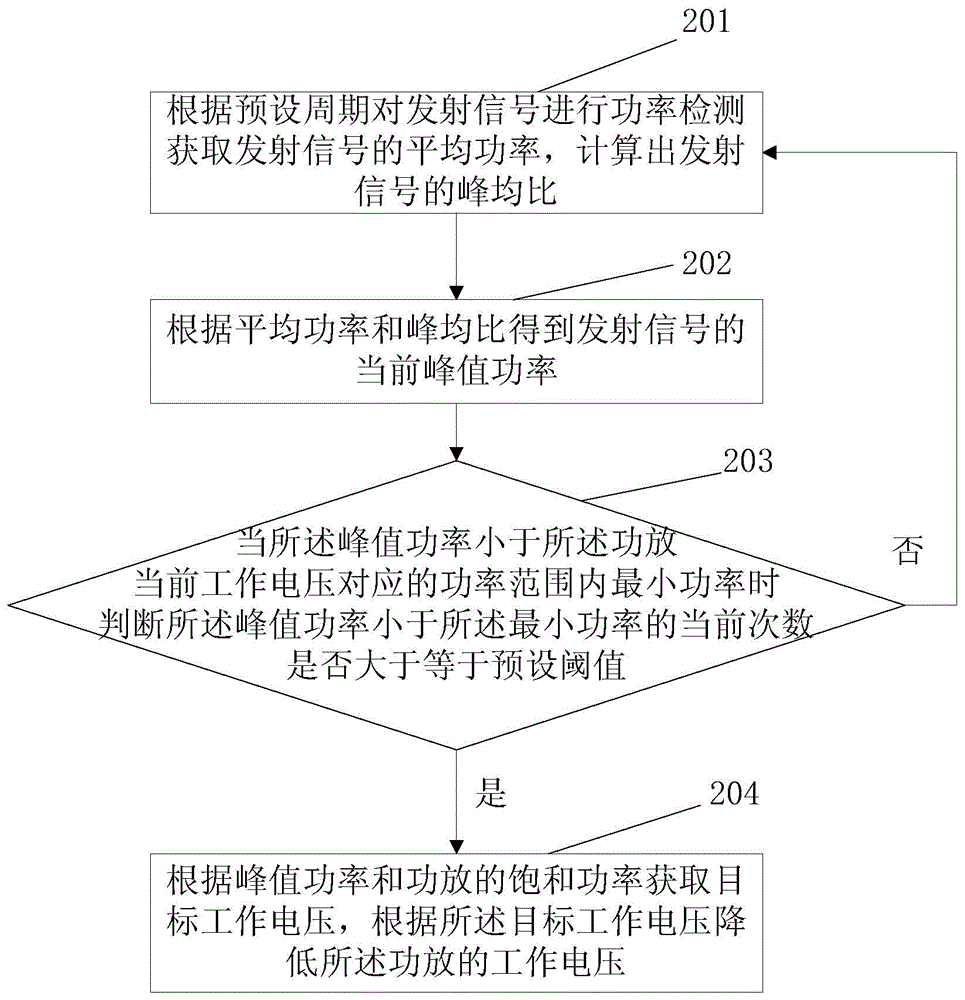
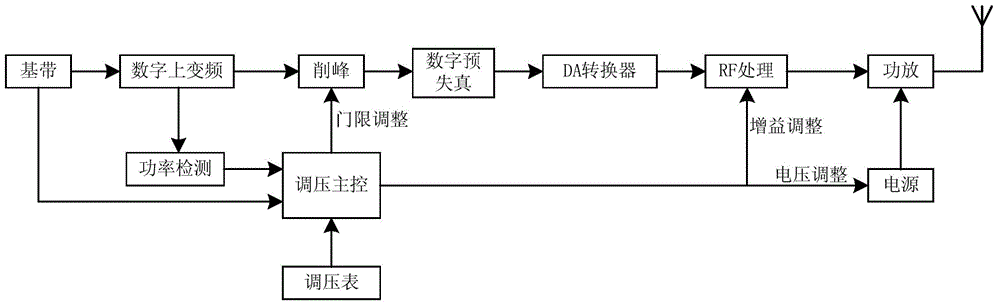
Method and device for adjusting power amplifier voltage
ActiveCN105611620AIncrease power consumptionImprove low power consumptionPower managementPower amplifiersPeak valueAmplifier
The invention discloses a method and a device for adjusting a power amplifier voltage. The power amplifier voltage adjusting method is applied to a multi-system base station. The method comprises steps: the average power and the peak-to-average power ratio of transmitted signals are acquired; according to the average power and the peak-to-average power ratio, the peak power of the transmitted signals is obtained; and according to the peak power and the saturation power of the power amplifier, the working voltage of the power amplifier is adjusted. The power amplifier voltage adjusting method provided by the invention solves the technical problems that a transmitter can not work normally after power amplifier voltage adjustment is carried out and the existing power amplifier voltage adjusting technology can not be applied to the multi-system base station.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Environment-friendly intelligent semi-concealed monitoring device
InactiveCN105430355AUse monitoring to operate intelligentlyAutomate using monitoring operationsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExternal energyGlass cover
The invention discloses an environment-friendly intelligent semi-concealed monitoring device which belongs to the technical field of monitoring equipment. The environment-friendly intelligent semi-concealed monitoring device comprises the components of a monitor, a solar power generating system, a self cleaning system and an intelligent control system. The monitor comprises a housing with a closed inner chamber, a reflection imaging system and a stepping motor, wherein the reflection imaging system and the stepping motor are fixed in the closed inner chamber. The reflection imaging system comprises a total reflection prism, a total reflection prism rack and an image camera. The housing is provided with a perspective opening next to the total reflection prism. The perspective opening is provided with a high-transparency glass cover. The stepping motor is connected with and fixed with a central shaft of the total reflection prism rack through a magnetic coupling. The environment-friendly intelligent semi-concealed monitoring device can intelligently drive devices to perform monitoring operation and cleaning operation through the intelligent control system, thereby realizing intelligent and automatic monitoring operation, and improving imaging effect and monitoring quality. Through the solar power generating system, self driving electric energy can be supplied, thereby realizing no requirement for external energy, preventing a use limitation caused by independence to an external power supply, and enlarging application range.
Owner:CHONGQING REAL ESTATE COLLEGE
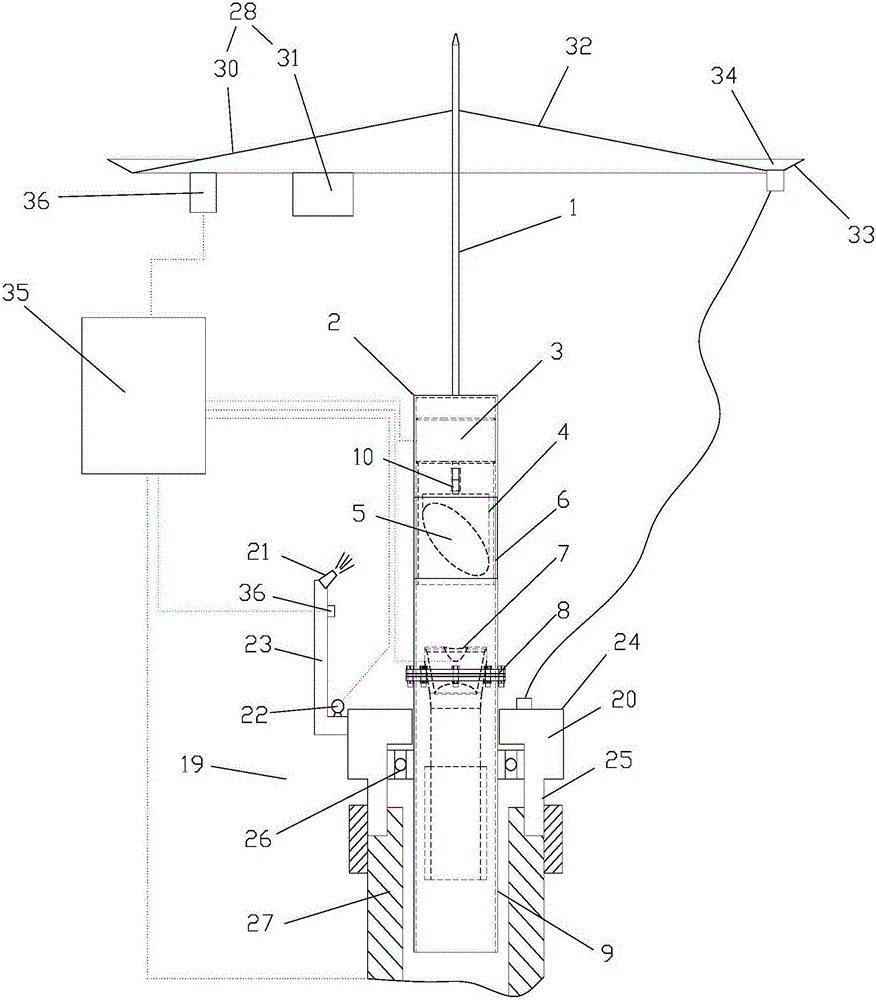
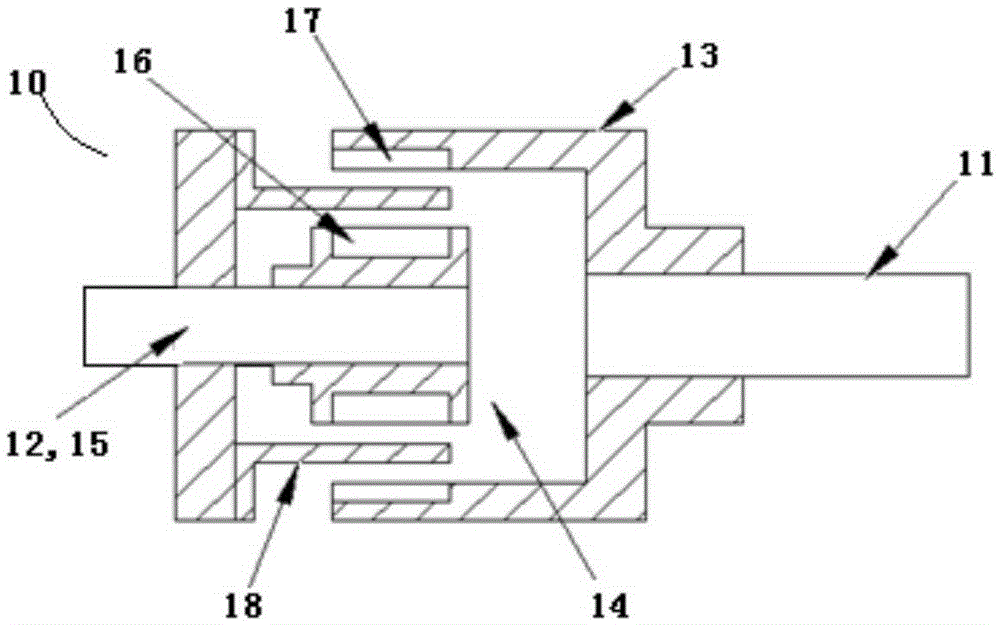
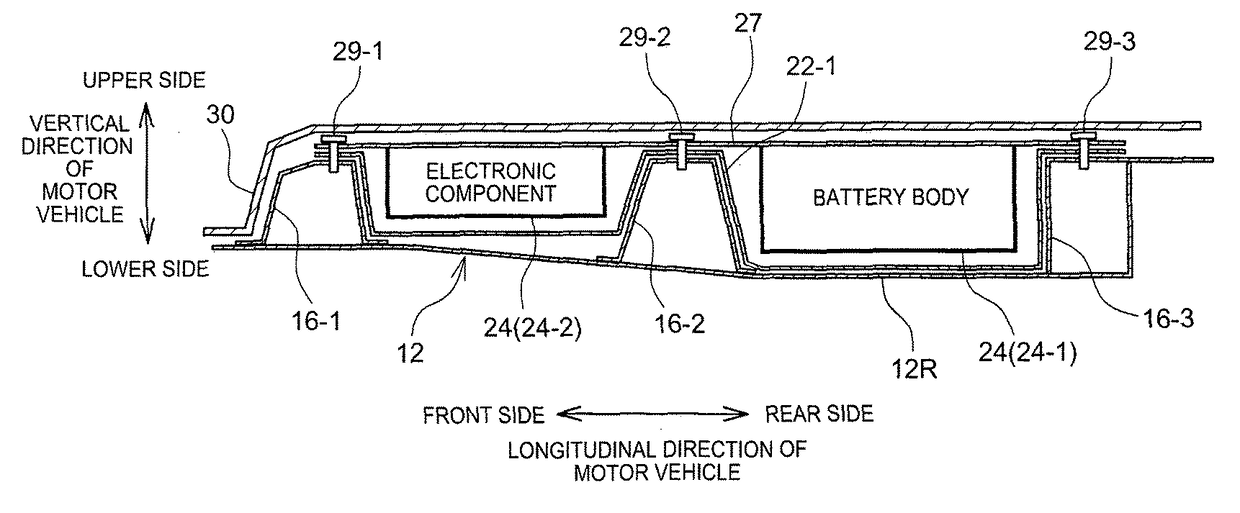
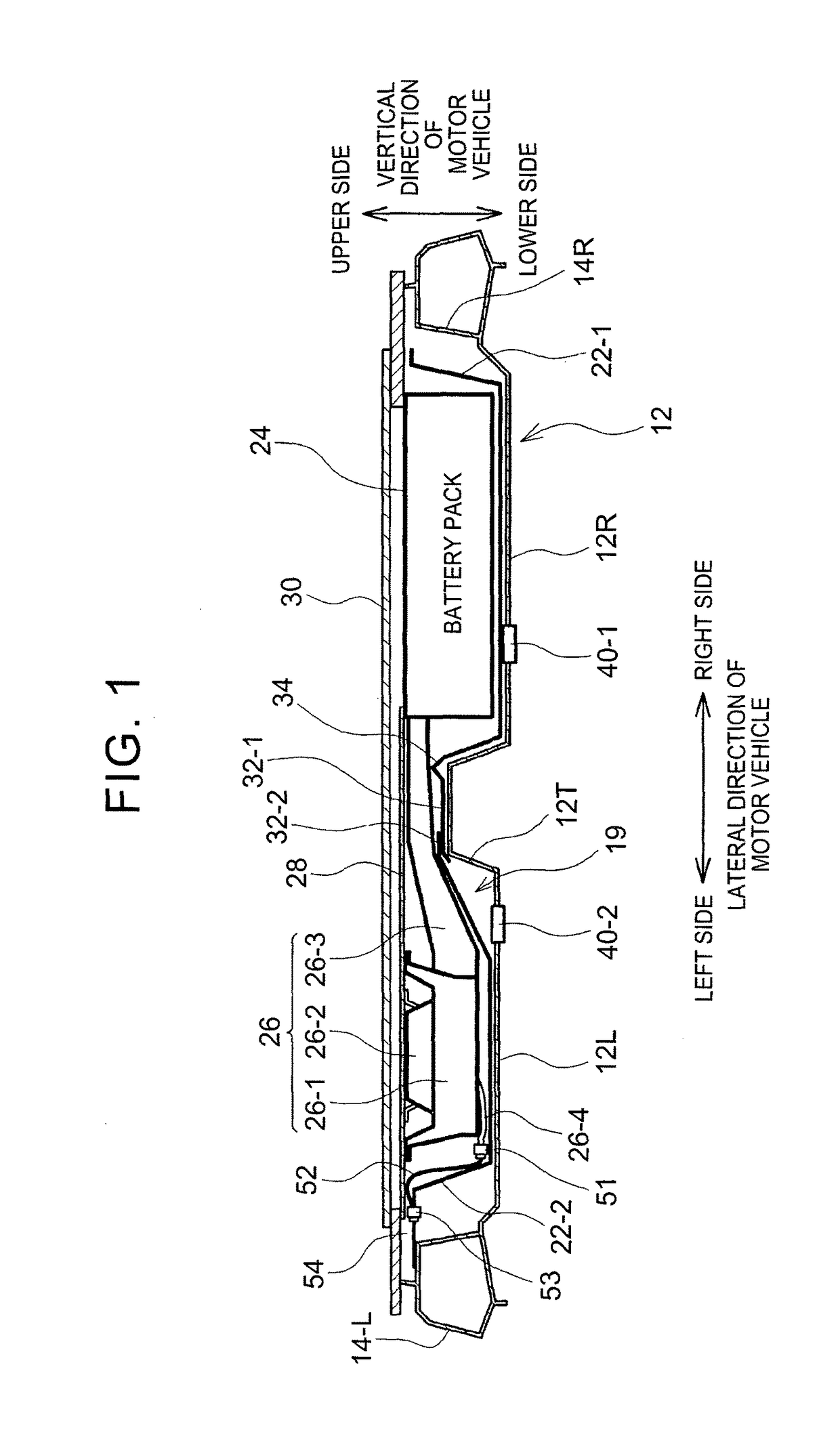
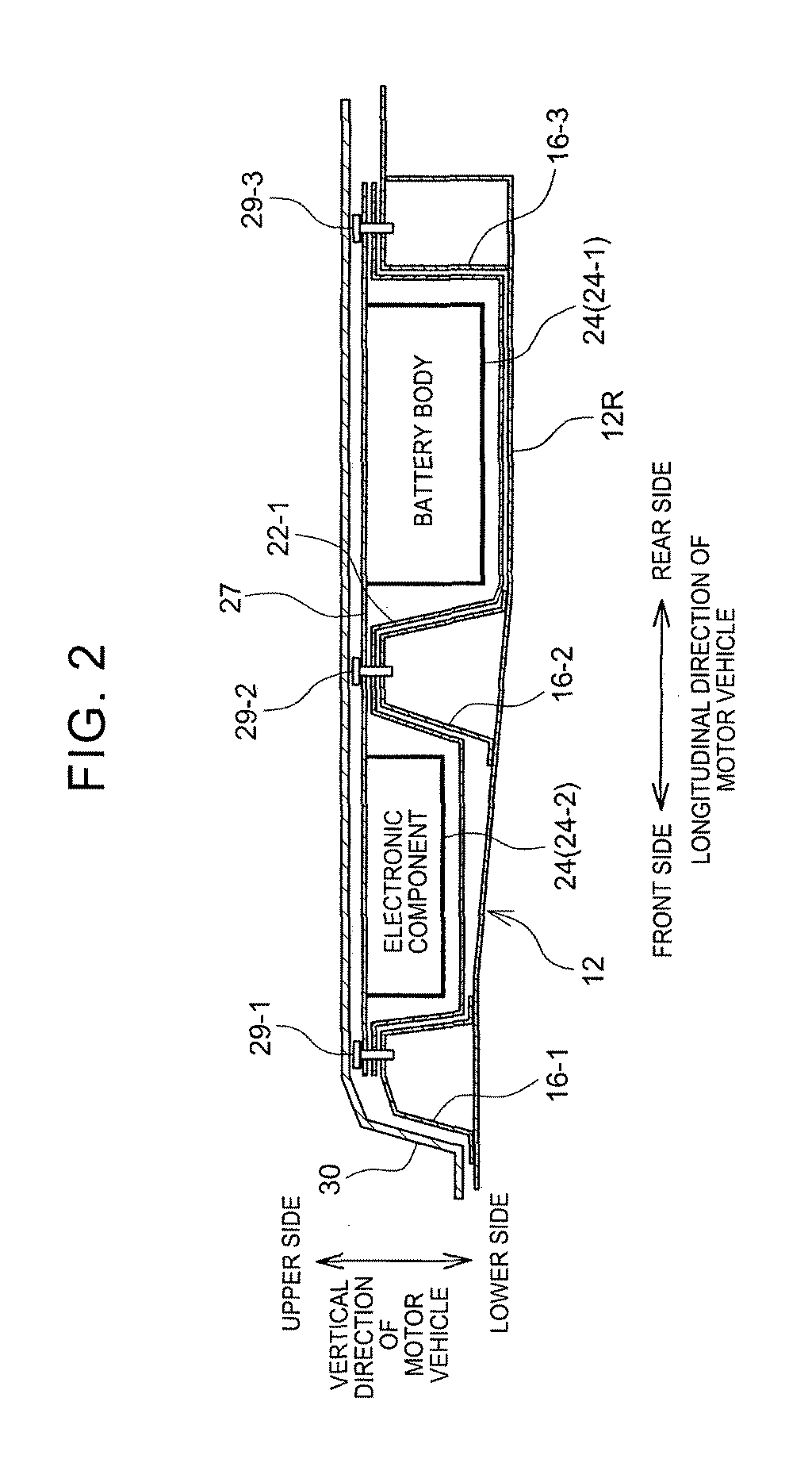
Motor vehicle
ActiveUS9821645B2Avoid malfunctionElectric propulsion mountingSuperstructure subunitsMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Pressure threshold determination method and device and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN110266876AAvoid malfunctionAvoid accidental touchDevices with sensorSubstation equipmentTerminal equipmentComputer terminal
The invention relates to a pressure threshold determination method and device and a computer readable storage medium, the pressure threshold determination method is used for terminal equipment, at least one pressure sensor is arranged on the terminal equipment, and the pressure threshold determination method comprises the following steps: obtaining a pressure value detected by the pressure sensor and an initial pressure threshold; when the pressure value is greater than the pressure threshold value, recording the change trend of the pressure value within a first preset time length; and determining a target pressure threshold value according to the change trend, and updating the initial pressure threshold value into the target pressure threshold value. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, whether the current pressing operation is the mistaken touch operation or not is judged by recording the change trend of the pressure value, then the change trend of the pressure value is adjusted to adjust the pressure threshold value, and finally, an intelligent and accurate pressure value correction scheme is realized.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Transformer fault monitoring method
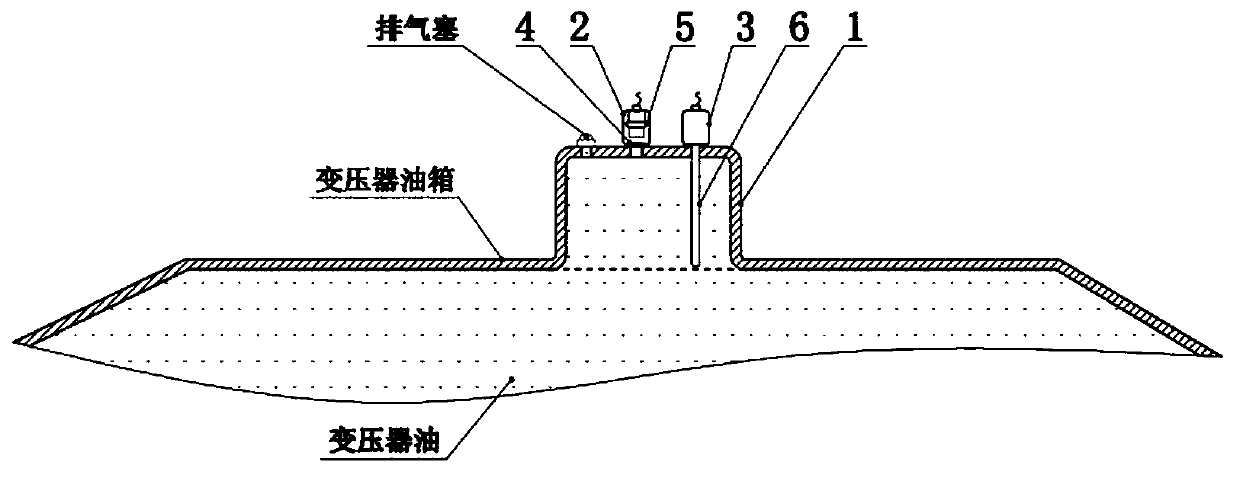
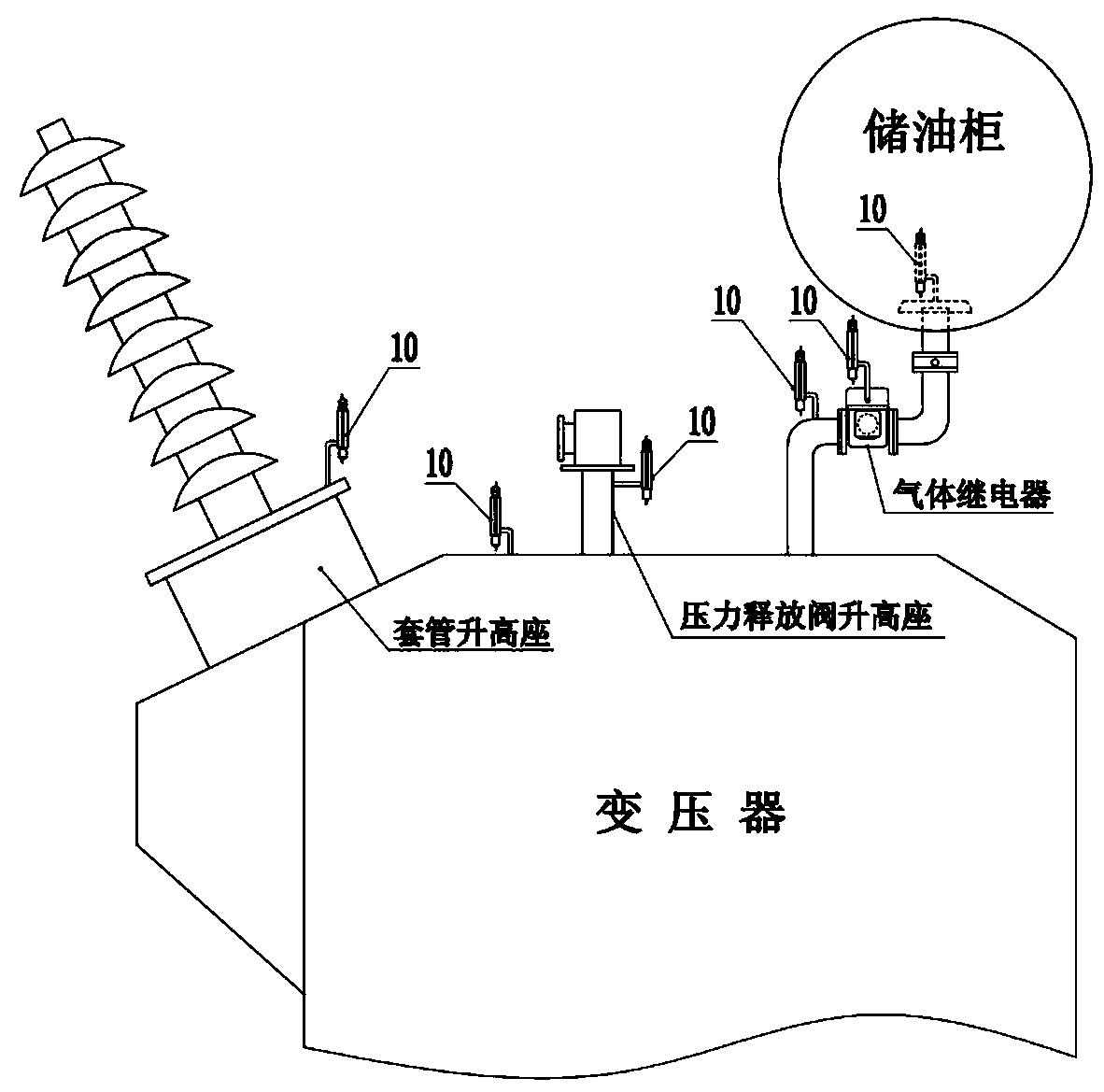
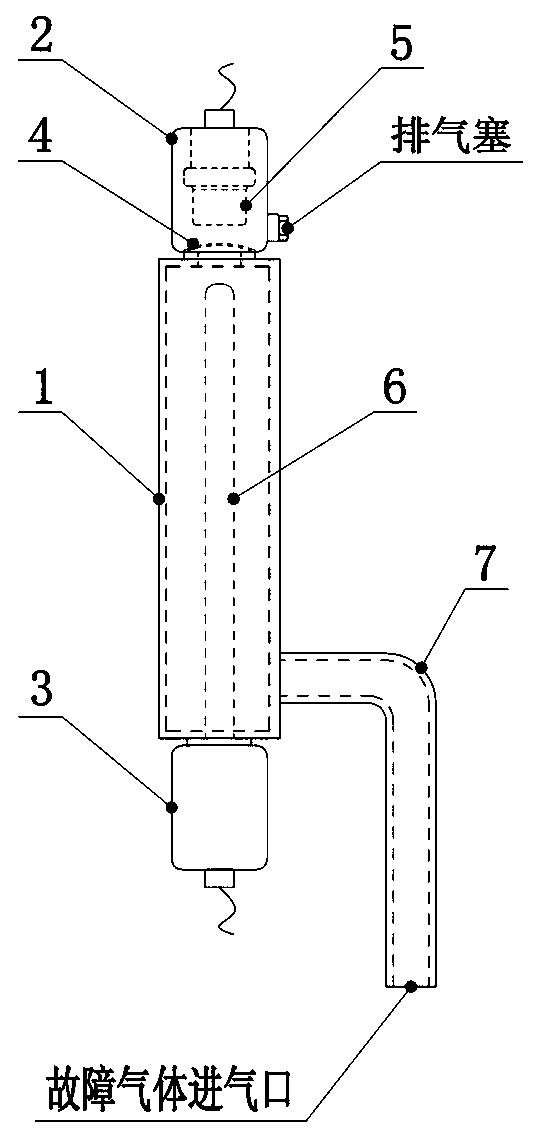
PendingCN111308257AImprove detection efficiency and effectivenessAvoid malfunctionAnalysing gaseous mixturesElectrical testingAutomotive engineeringFault severity
The invention relates to a transformer fault monitoring method. A gas collection cavity is arranged at a position where transformer fault gas floats upwards to pass or remain, a gas component detection device and a gas quantity detection device are connected to the gas collection cavity, and gas components and gas production speed in the gas collection cavity are directly detected. A transformer fault is found and a fault type is diagnosed by detecting a fault characteristic gas; and the fault severity is judged by detecting the gas production speed. When acetylene gas is detected and the gasproduction speed reaches a dangerous value, power-off protection is started. The method can quickly and accurately discover sudden faults of a transformer and timely diagnose whether chronic faults enter a dangerous period, effectively changes the current situation of serious lag of oil chromatography monitoring at present, and has important significance for improving the safety level of the transformer. The system is convenient to install and suitable for transformation of existing equipment and selection of new equipment.
Owner:孙铭阳
Material performance test device applicable to high-temperature vacuum environment
ActiveCN106248717AAvoid malfunctionImprove accuracyInvestigating phase/state changeEngineeringTest fixture
The invention discloses a material performance test device applicable to a high-temperature vacuum environment. The material performance test device applicable to the high-temperature vacuum environment comprises a vacuum furnace box body. A heating device, a fixture for fixing a sample, and a deformation measurement component for measuring the deformation of a sample gauge length are arranged in the vacuum furnace box body; the heating device is used for heating the sample; the vacuum furnace box body comprises a first vacuum chamber and a second vacuum chamber; the heating device and the fixture are arranged in the first vacuum chamber; the deformation measurement component is arranged in the second vacuum chamber; a heat shield is arranged between the first vacuum chamber and the second vacuum chamber. According to the device, the deformation measurement component is kept in a normal operating temperature environment, so that the accuracy of an experiment test result is improved.
Owner:中机试验装备股份有限公司
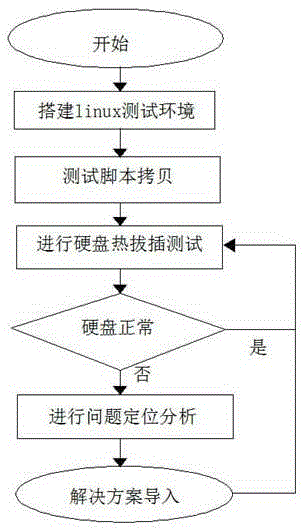
Linux-based hard disk random hot plug stability detection method
InactiveCN105260274ASimple and efficient operationEasy to useDetecting faulty computer hardwareSoftware testing/debuggingConfiguration systemComputer engineering
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com