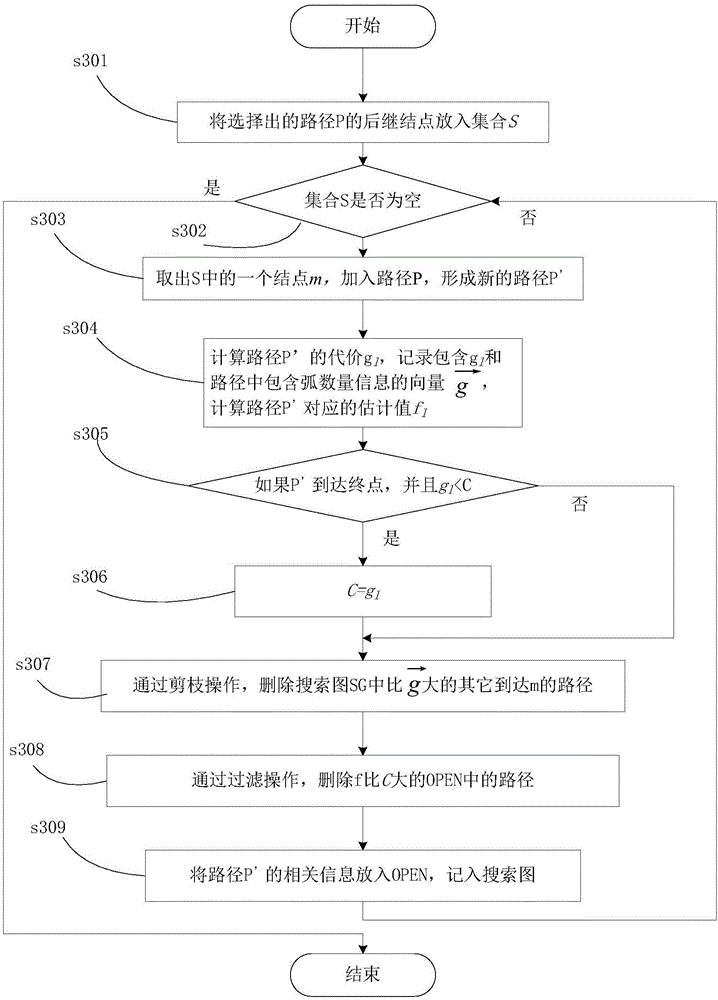
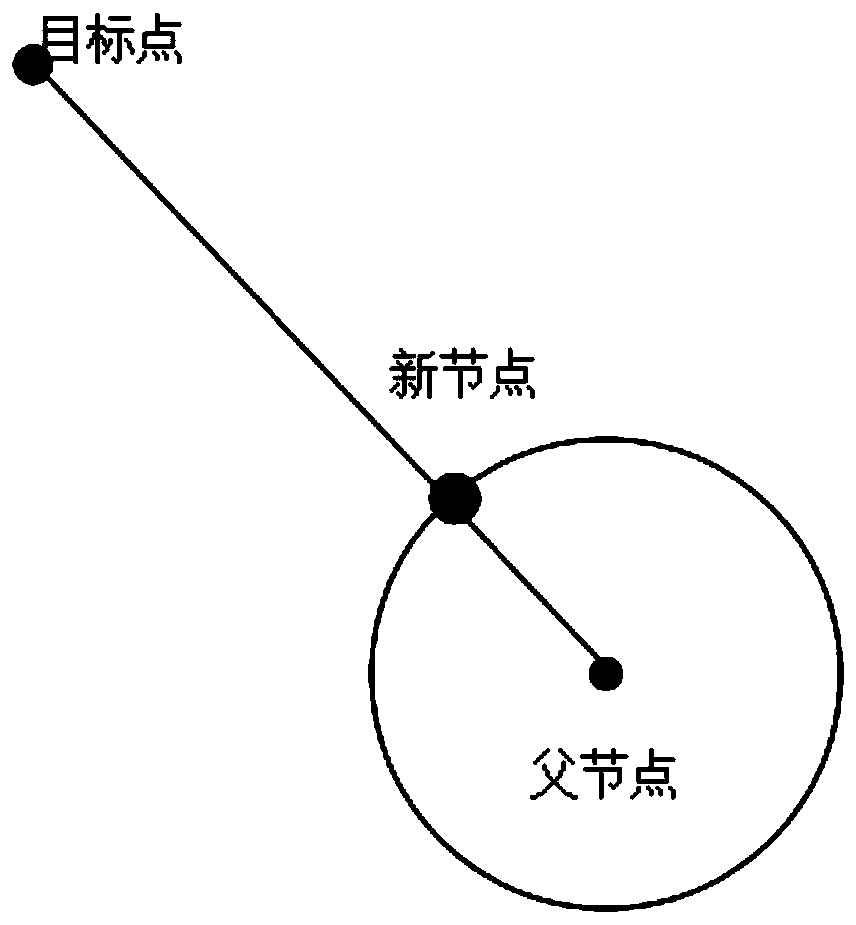
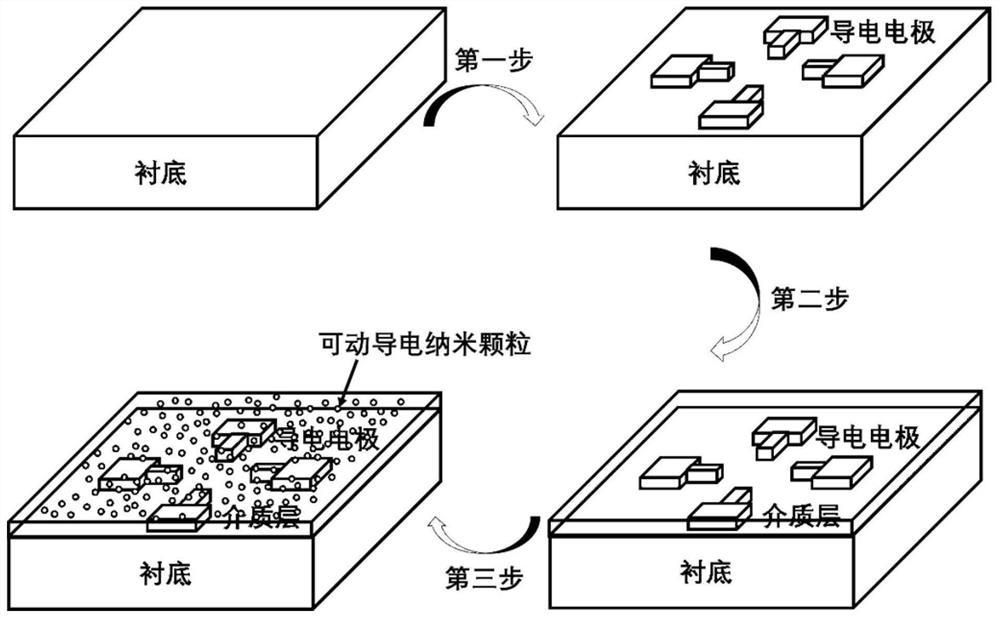
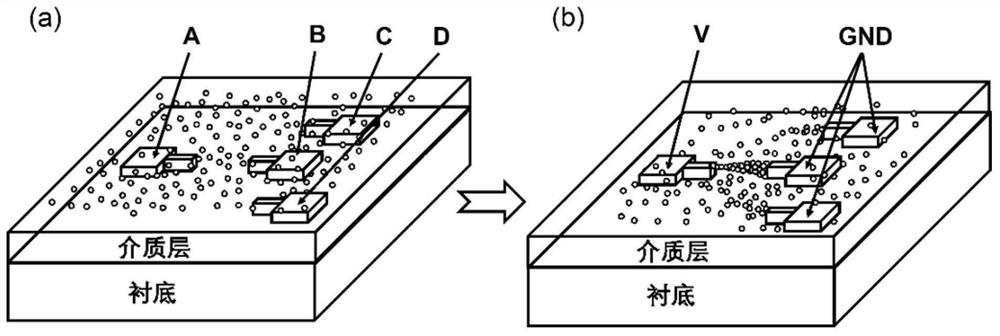
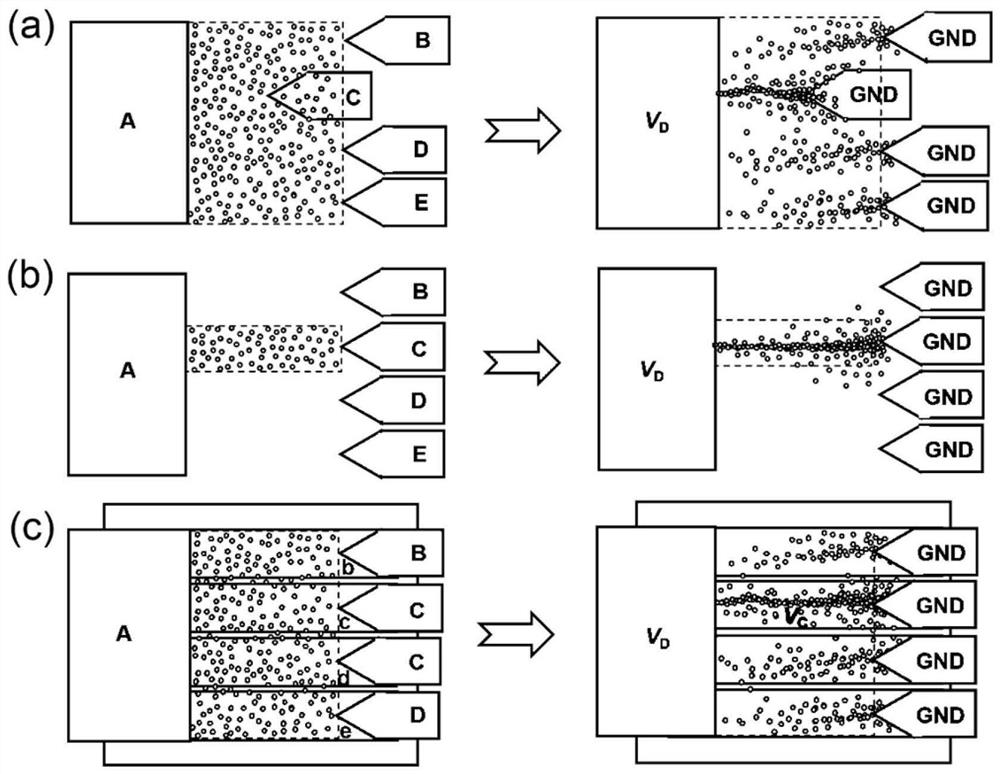
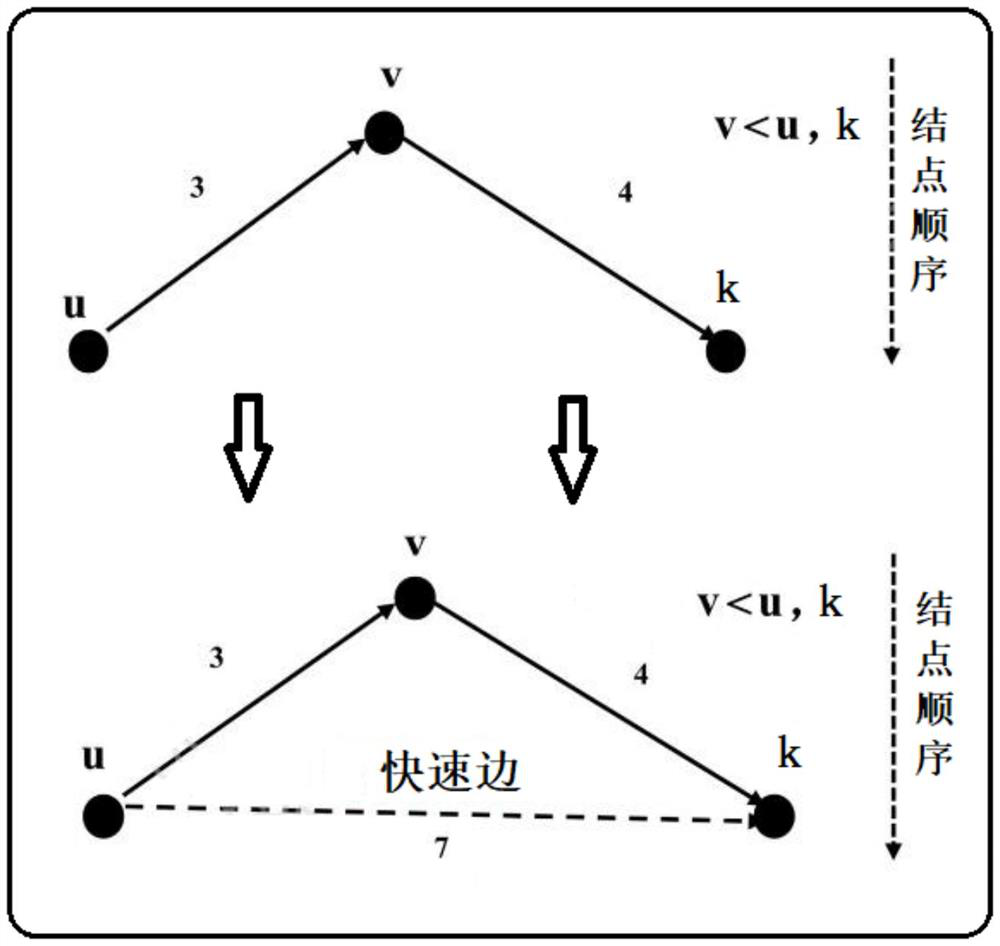
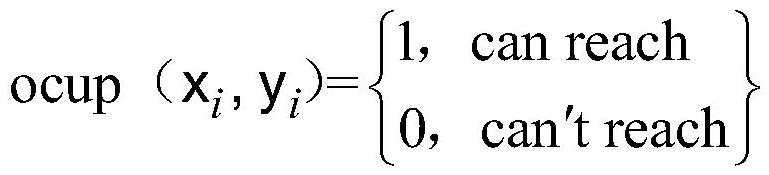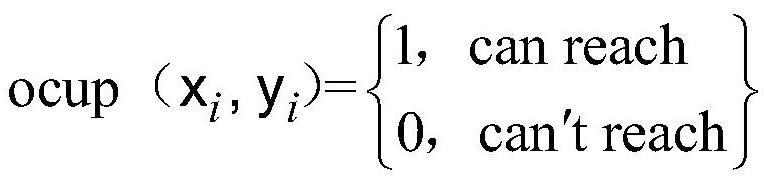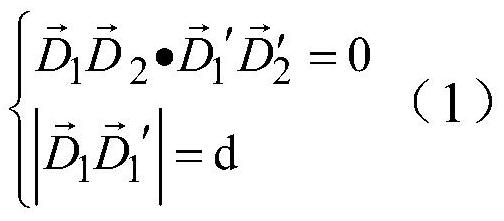Patents
Literature
48 results about "Shortest path problem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In graph theory, the shortest path problem is the problem of finding a path between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph such that the sum of the weights of its constituent edges is minimized. The problem of finding the shortest path between two intersections on a road map may be modeled as a special case of the shortest path problem in graphs, where the vertices correspond to intersections and the edges correspond to road segments, each weighted by the length of the segment.
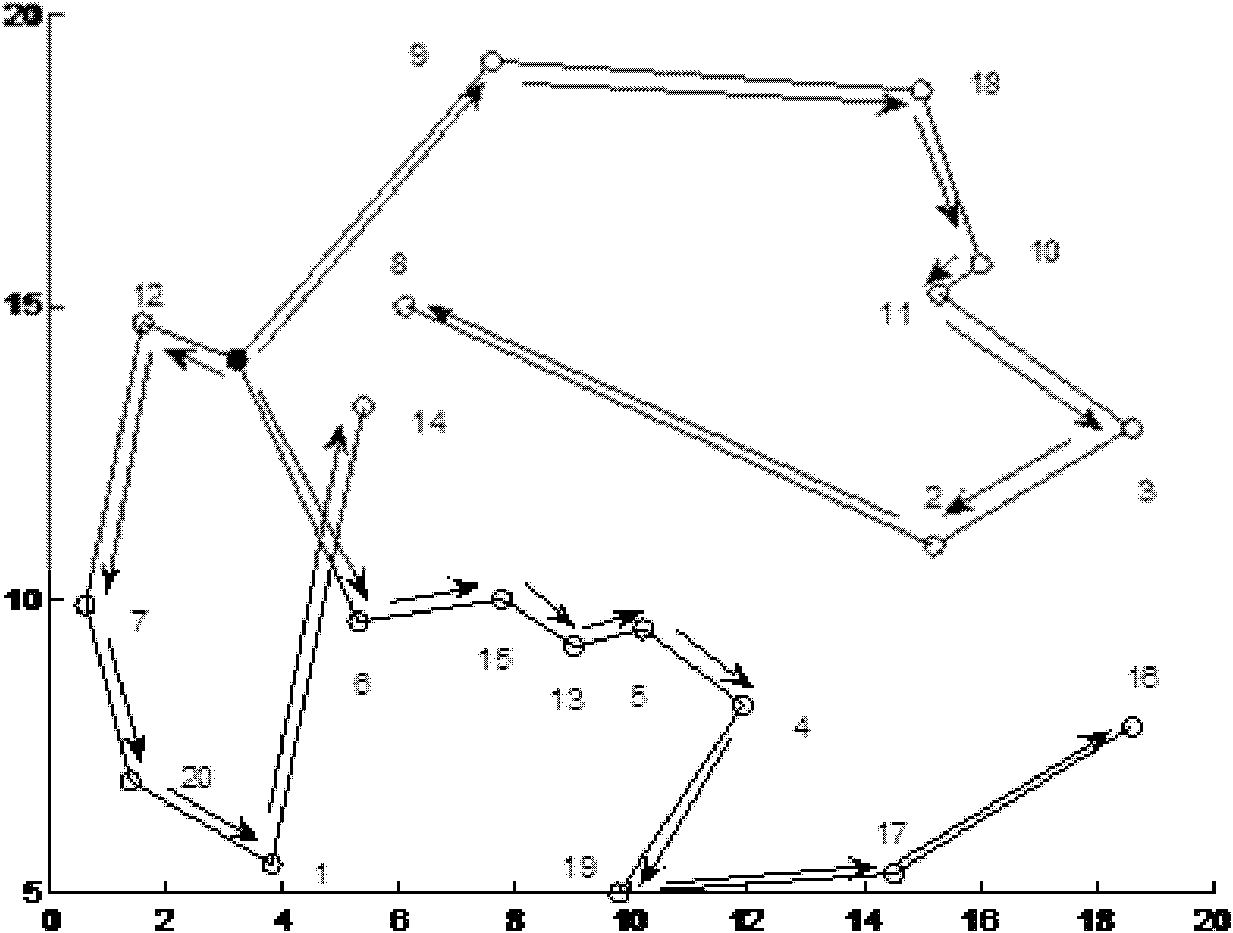
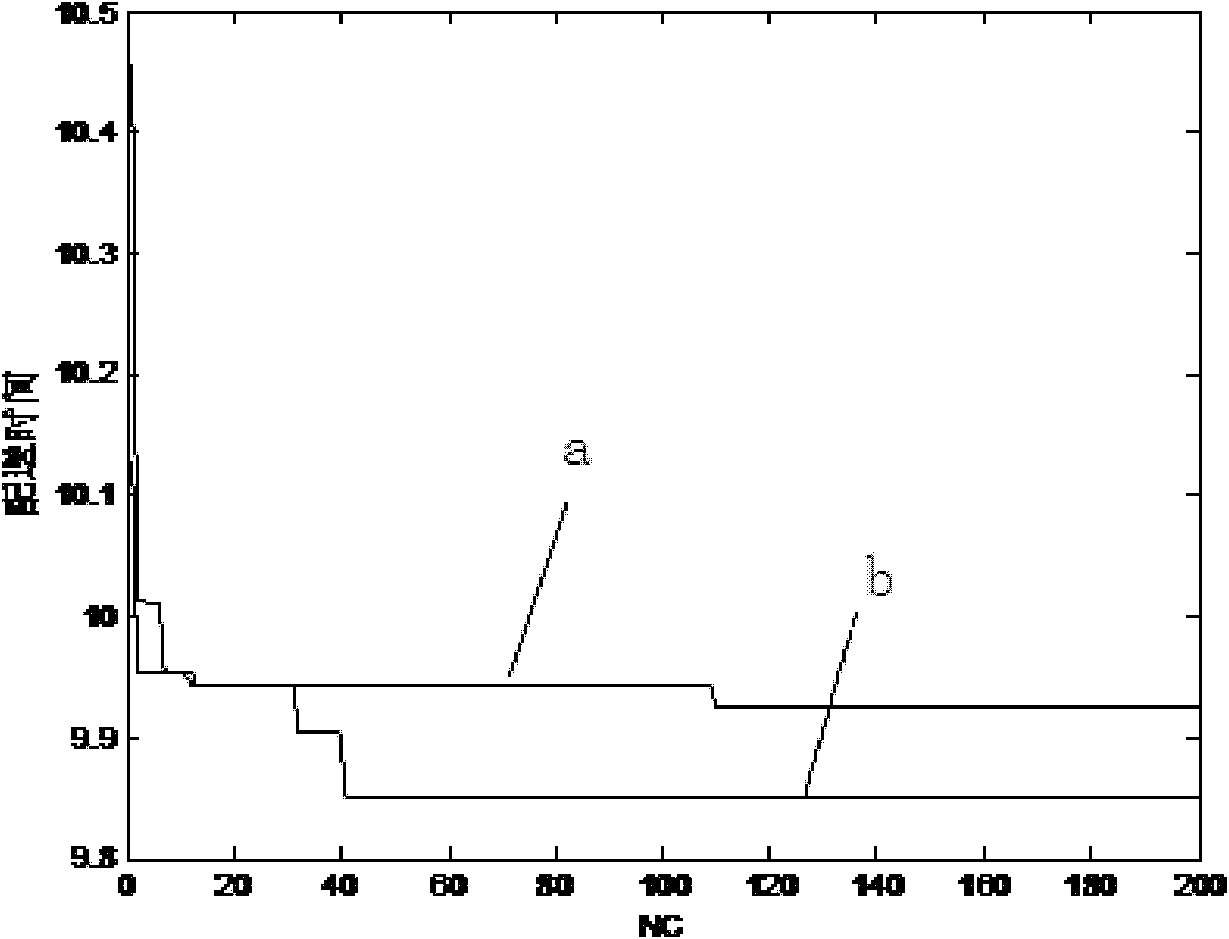
Optimization method of emergency logistics path with the shortest time based on fish swarm ant colony algorithm
InactiveCN102289712AAvoid precocityAvoid stagnationData processing applicationsBiological modelsLocal optimumEmergency logistics
The invention discloses an optimization method of the shortest emergency logistics path based on the fish swarm ant colony algorithm. The congestion factor is introduced into the basic ant colony algorithm to solve the optimization problem of the shortest emergency logistics path and enhance the search for emergency logistics. The ability to optimize the best solution for the path reduces the possibility of the basic ant colony algorithm falling into a local optimum. (1) Input the number of ants, the maximum number of iterations and the maximum load capacity of the vehicle, select the emergency situation, and input the importance of residual pheromone, the importance of heuristic pheromone, evaporation coefficient and intensity coefficient; (2) Find the shortest emergency logistics route : (1) Establish the model of the shortest emergency logistics route optimization problem; (2) The solution process of the model; (3) Display the distribution route results and the performance comparison results of the algorithm in solving the shortest emergency logistics route optimization problem. The optimization scheme for finding emergency logistics routes in the present invention is more efficient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
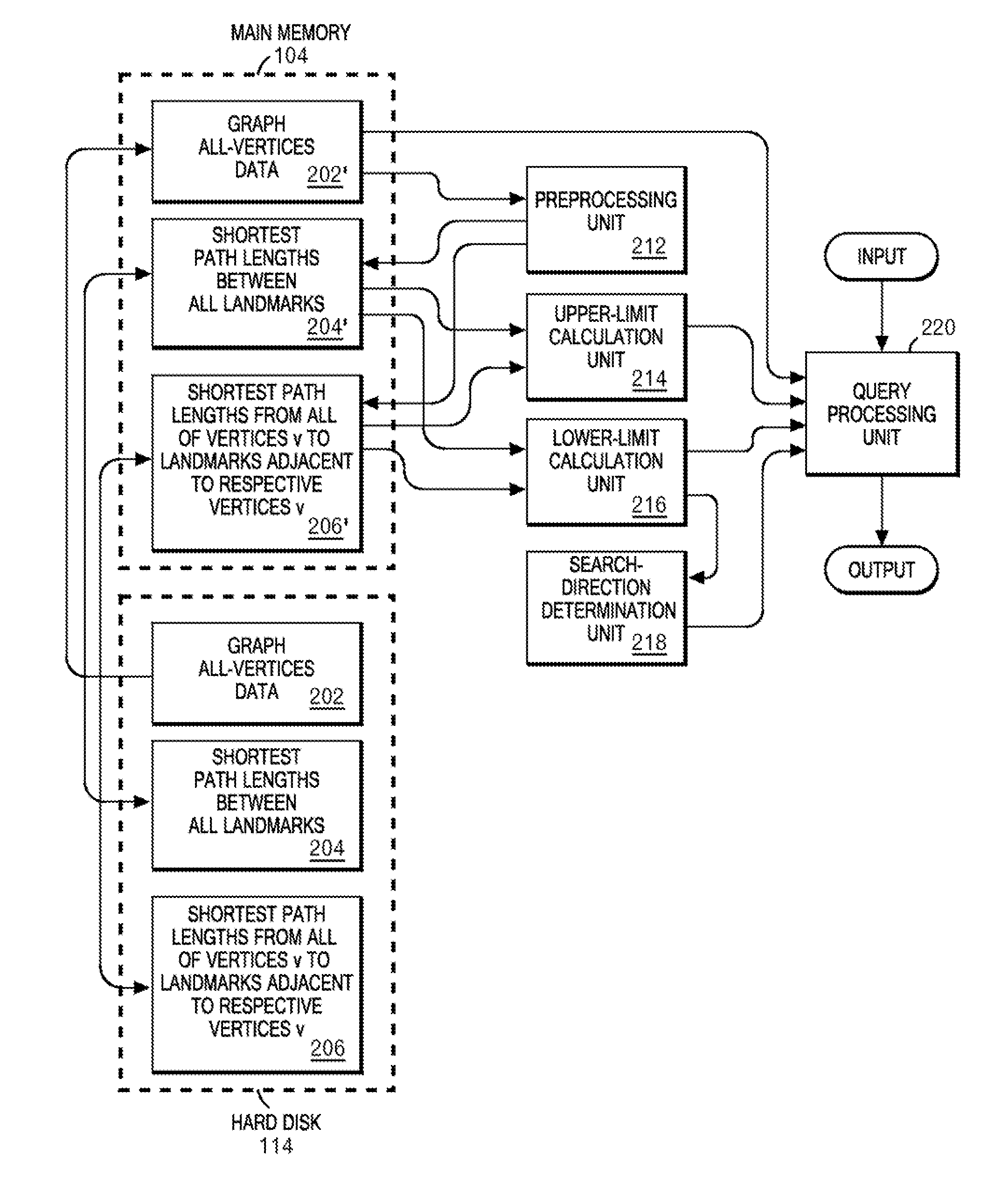
Fast algorithm for peer-to-peer shortest path problem
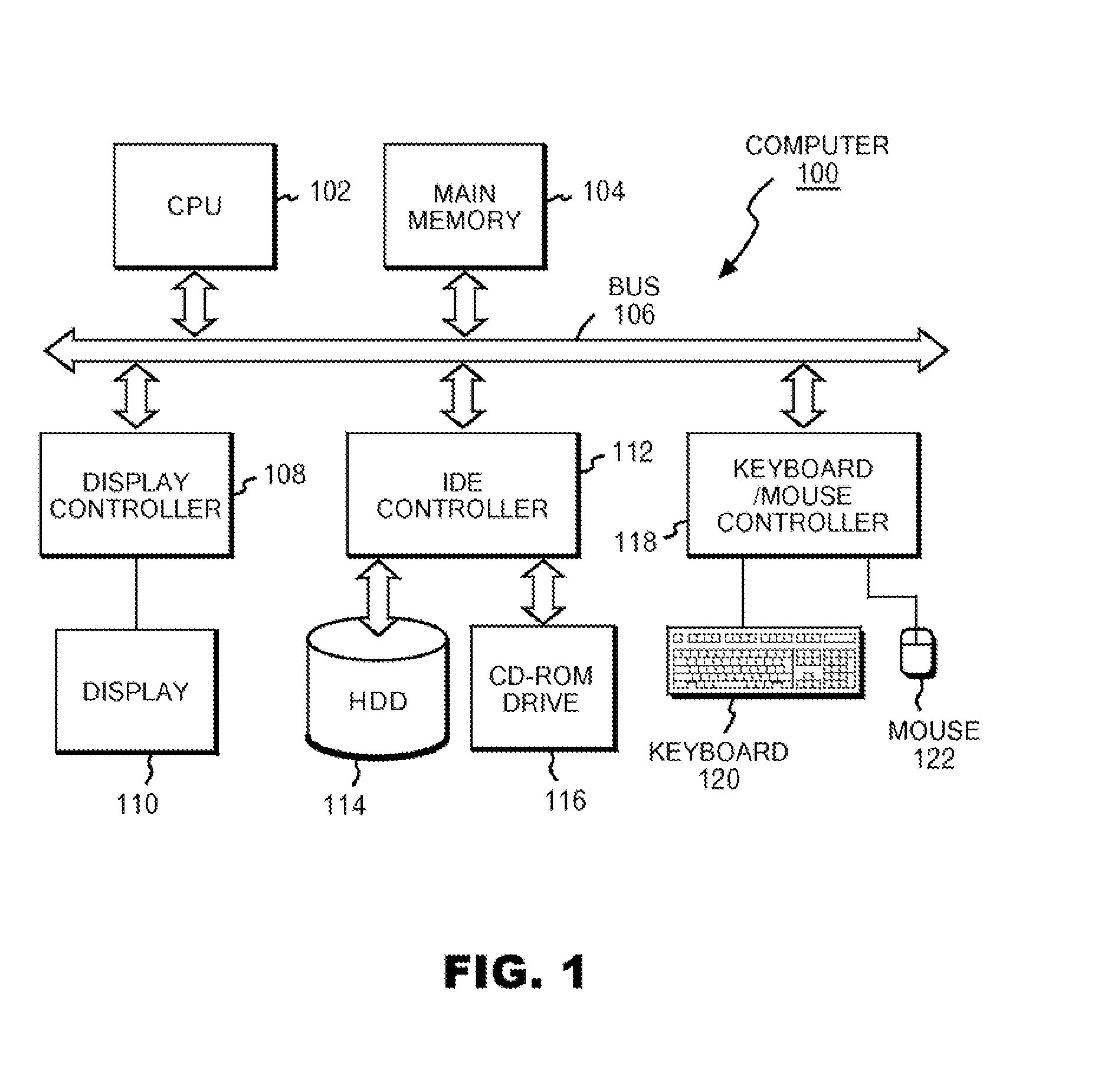
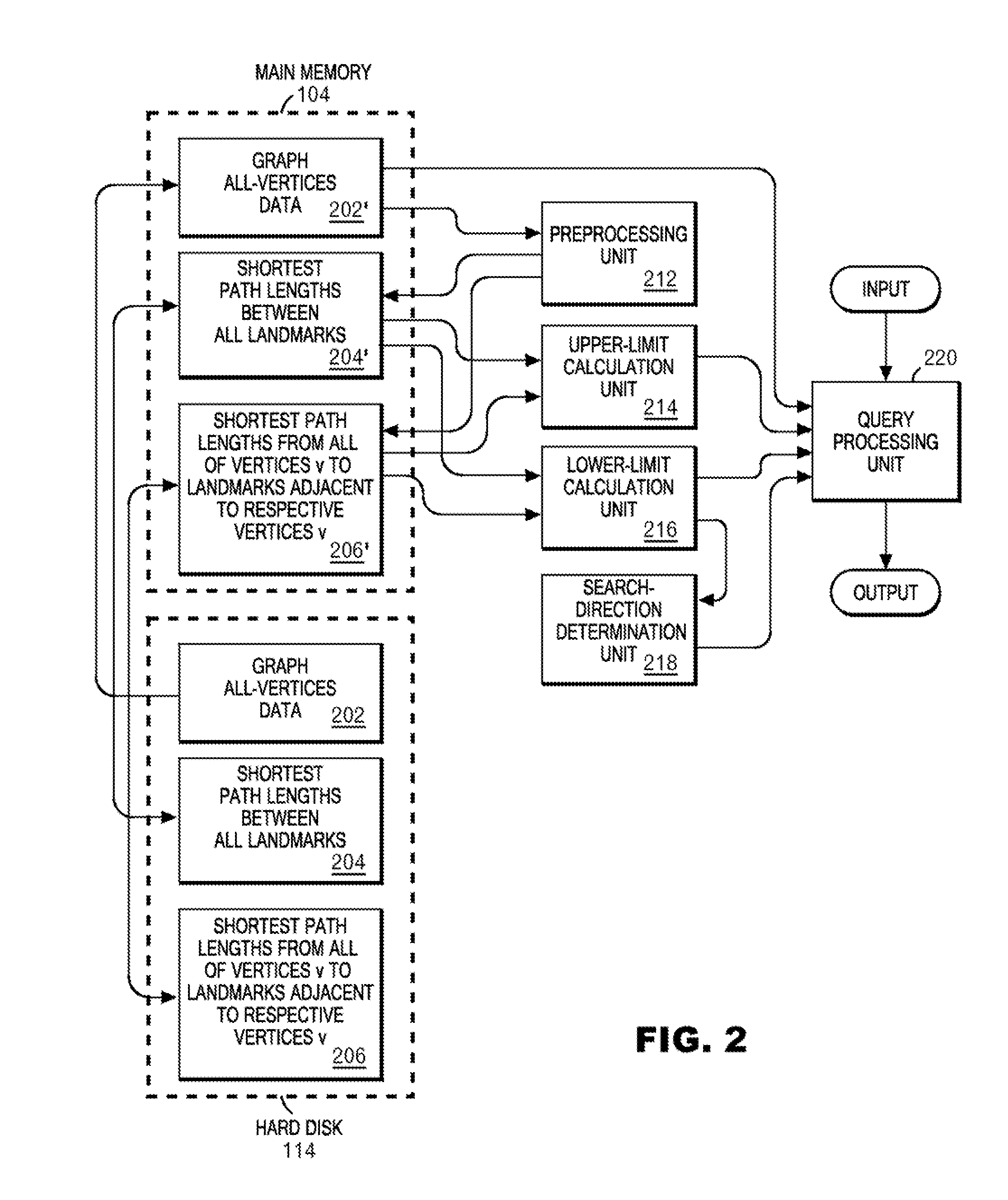
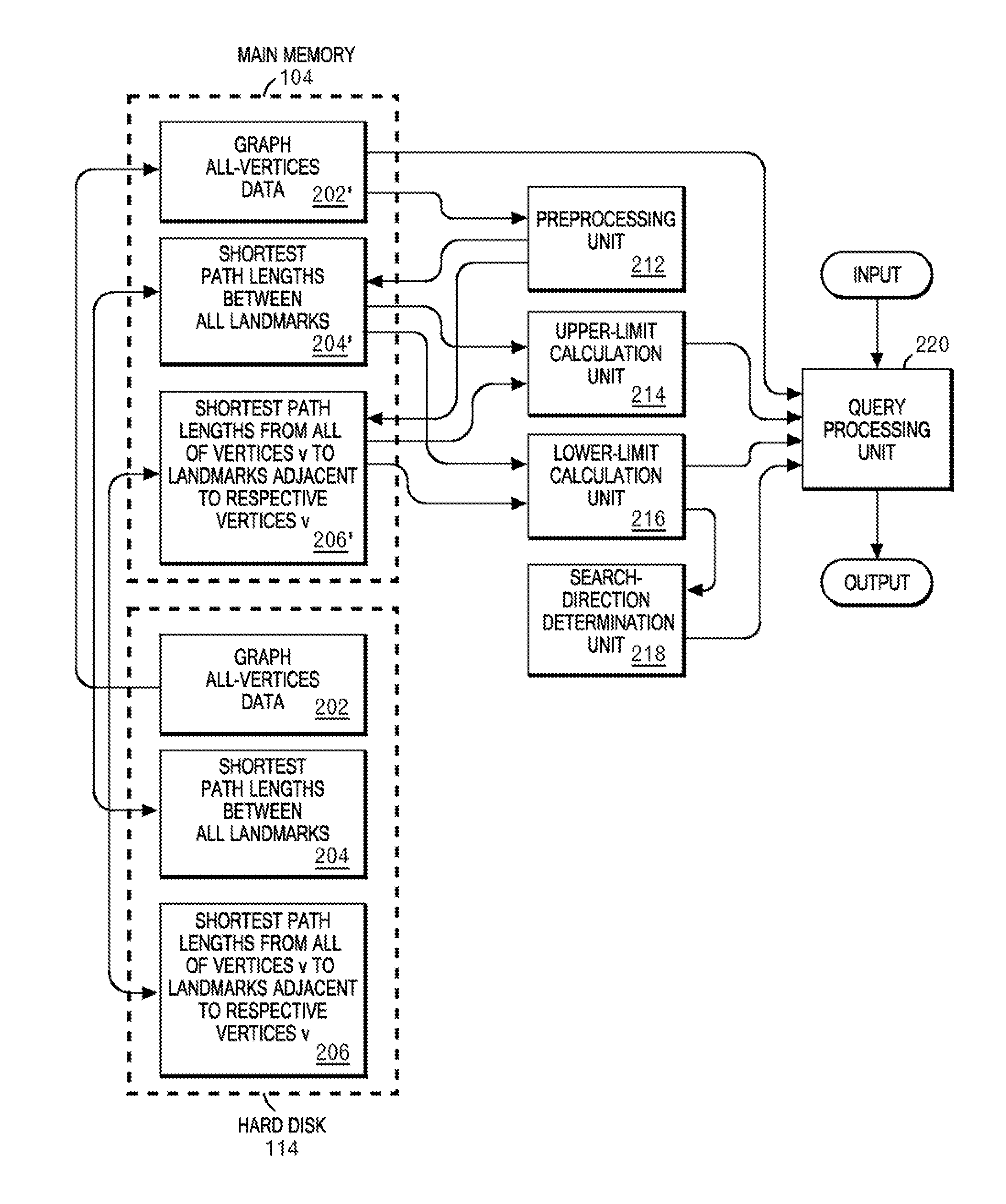
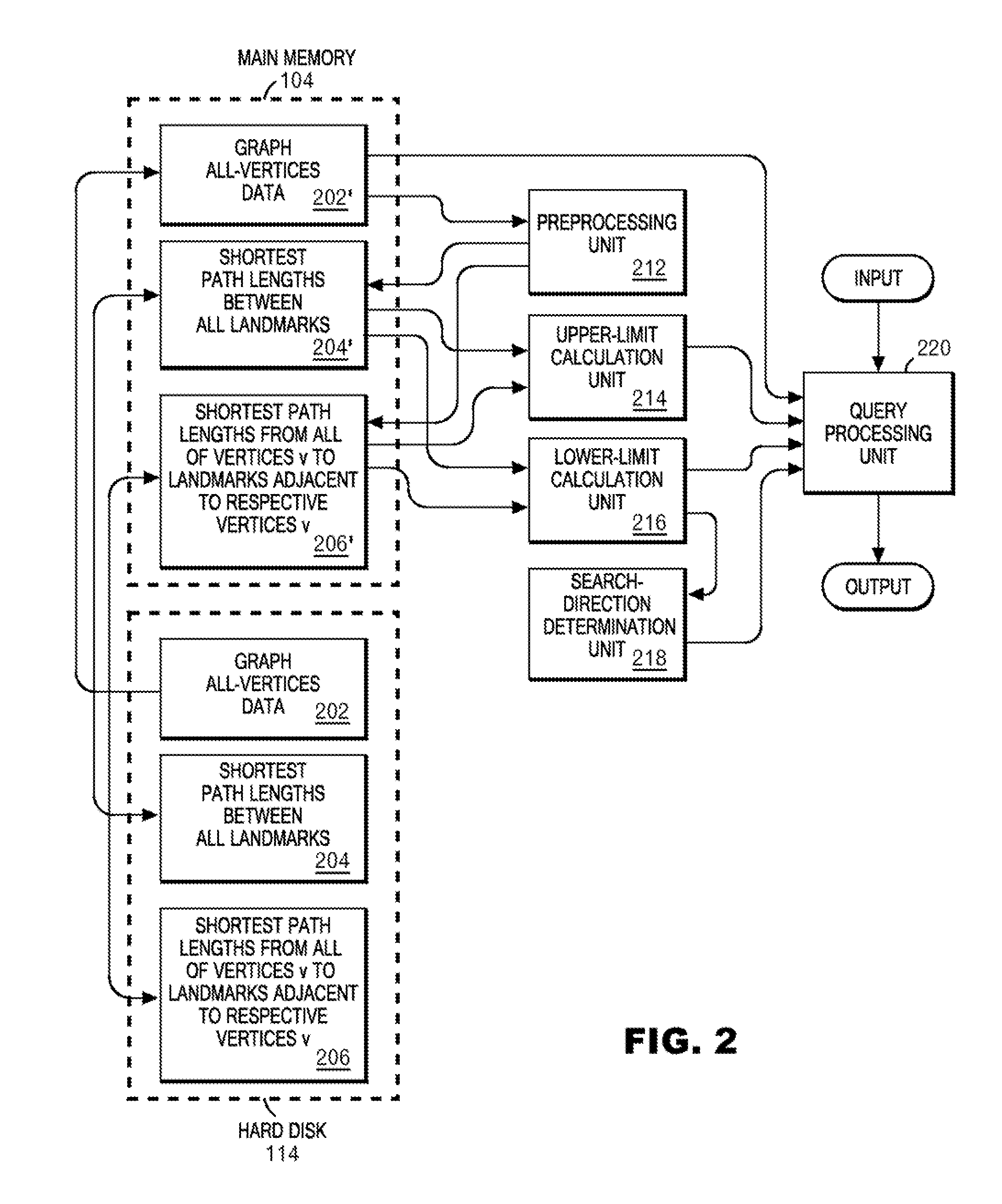
InactiveUS20080155119A1Speeding up path searchSpeedMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionLower limitPath length
A plurality of landmarks selected from a source weighed graph on which a path search is performed; and the shortest path lengths between landmarks, and the shortest path lengths from vertices to landmarks adjacent to the respective vertices are calculated, and are stored in a memory device so as to be later referable. Routines for calculating upper and lower limits of the shortest path length corresponding to two vertices v and w are prepared by using expressions derived from quadrangle inequalities formed of the two vertices v and w as well as two landmarks adjacent to the respective vertices v and w. In response to a call from an A* search program, these routines return the upper limit or the lower limit of the shortest path length corresponding to v and w by referring to the shortest path lengths between landmarks, and the shortest path lengths from vertices to landmarks adjacent to the respective vertices, which have been previously stored in the memory device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Novel moving object destination prediction algorithm
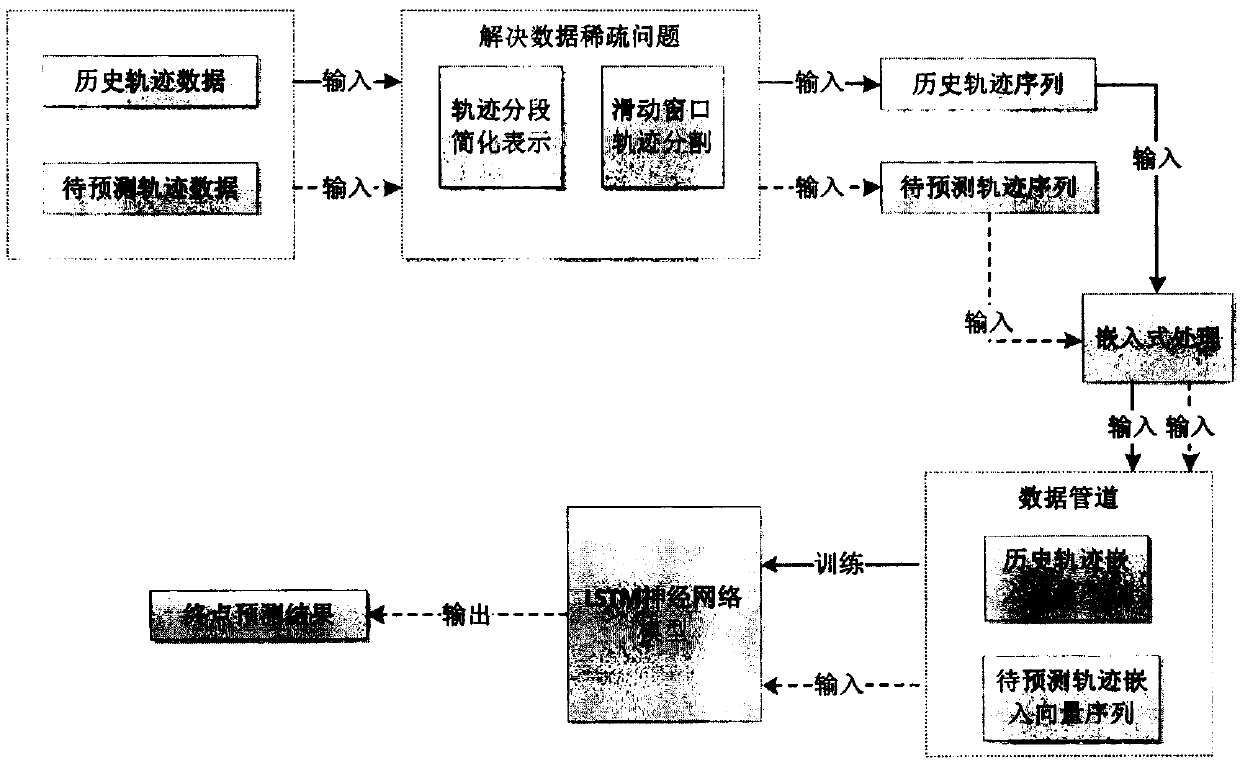
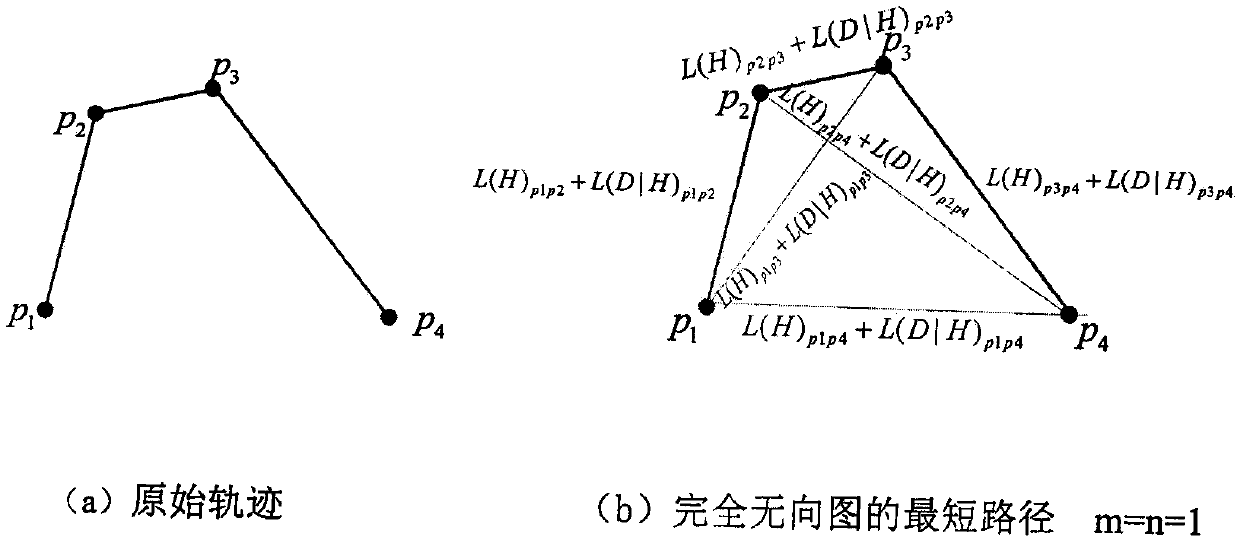
PendingCN110738370ASolve data sparsityAchieve dimensionality reductionForecastingGeographical information databasesPathPingPrediction algorithms
The invention discloses a moving object destination prediction algorithm. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an improved track segmentation method with the minimum description length (IMDL)is provided, weight parameters are introduced, meanwhile, a Dijkstra algorithm is used for converting the track segmentation problem into the shortest path problem of an undirected graph, the optimalsegmentation of a track is obtained, and therefore the track is simplified; then, a deep learning prediction model EP-LSTM based on embedded processing and long-short-term memory fusion is provided, and a high-dimensional input vector is converted into an embedded vector to serve as input of the model. The method has the advantages that the problems of data sparseness and long-term dependence in moving object destination prediction are effectively solved, and an excellent prediction effect is achieved by performing a large number of experimental verifications on a real data set.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Multi-pairs shortest path finding method and system with sources selection
InactiveUS8412660B2Quick fixNavigation instrumentsKnowledge representationGraphicsShortest path problem
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
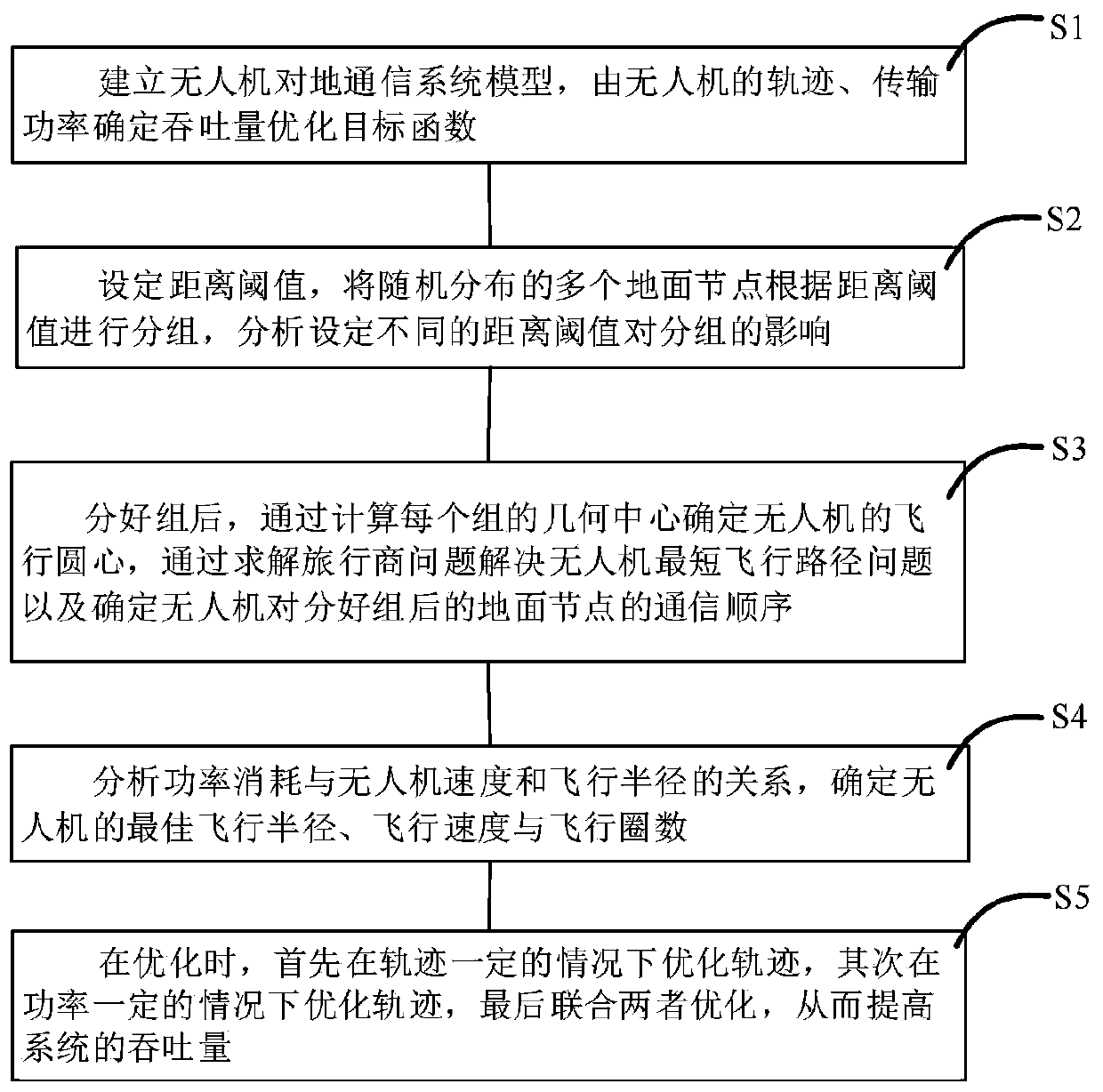
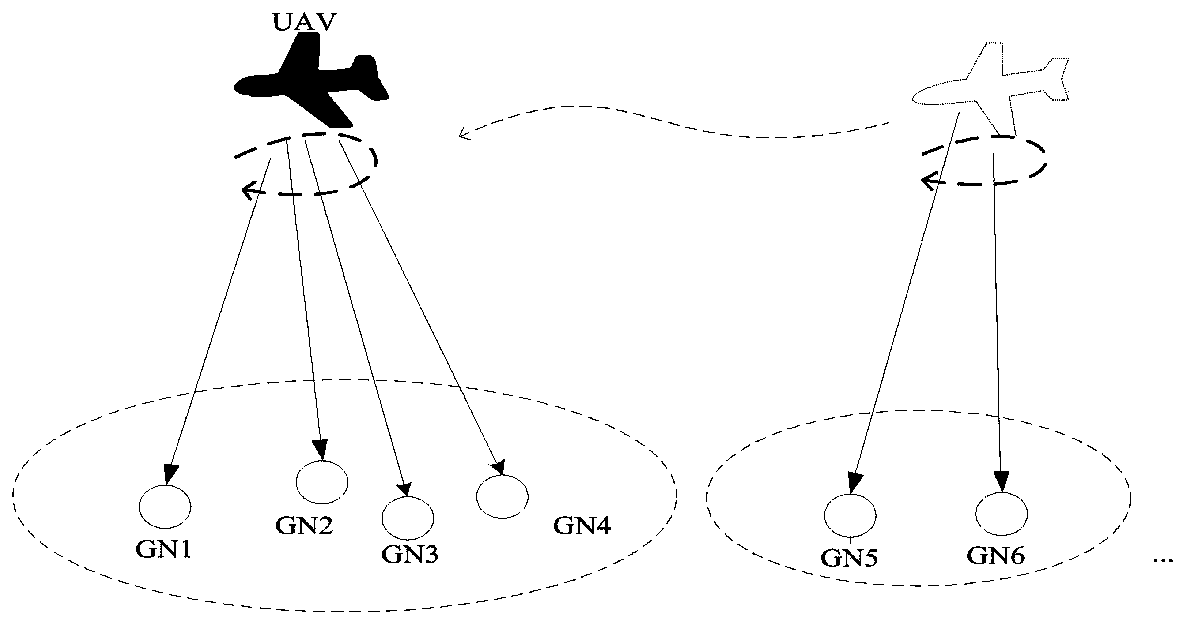
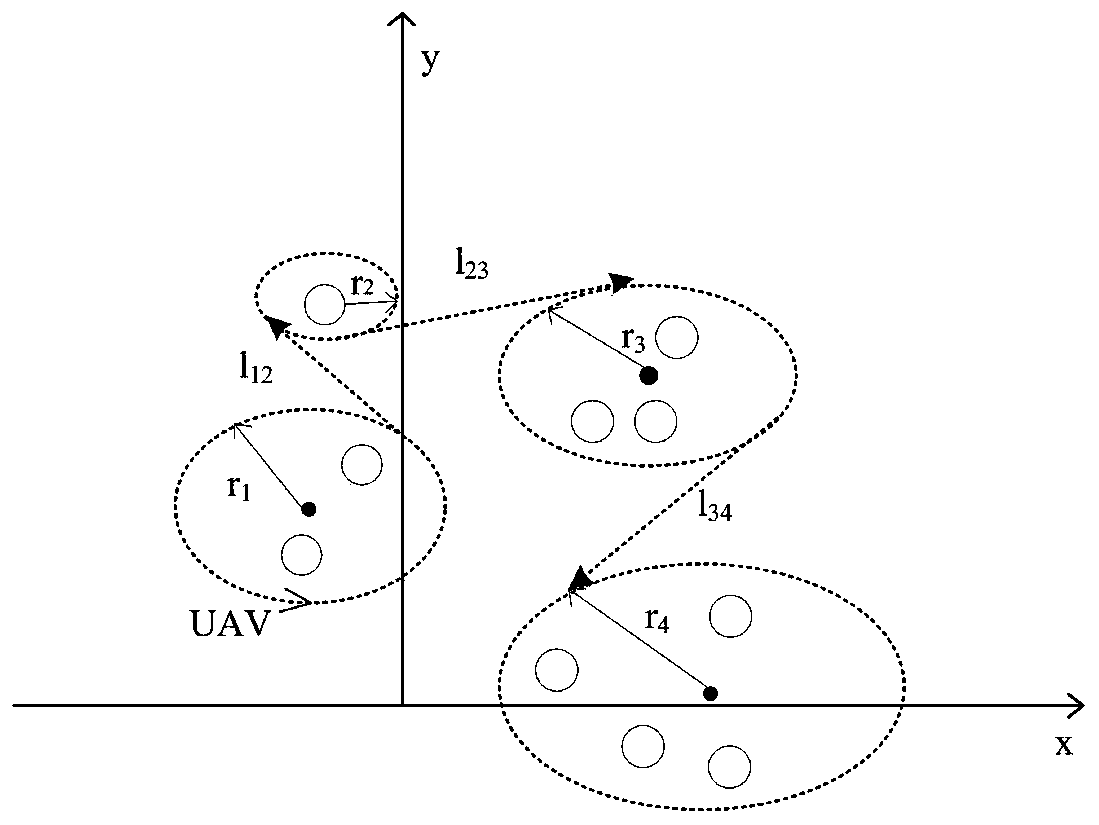
Throughput capacity-maximized unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory planning method
ActiveCN109857143AGuaranteed flight rangeMeet the needs of ground multi-point communicationPosition/course control in three dimensionsCapacity optimizationTravelling salesman problem
The invention discloses a throughput capacity-maximized unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory planning method, and belongs to the field of unmanned aerial vehicle communication. The method comprises thefollowing steps of: S1, establishing an unmanned aerial vehicle-ground communication system model, and determining a throughput capacity optimization target function via a track of the unmanned aerialvehicle and transmission power; S2, setting distance thresholds, grouping a plurality of randomly distributed ground nodes according to the thresholds, and analyzing influences, on the groups, of different distance thresholds; S3, after the grounding, calculating the geometric center of each group so as to determine a flight center of the unmanned aerial vehicle, solving traveling salesman problems to solve shortest flight path problems of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and determining a communication sequence, for the grouped ground nodes, of the unmanned aerial vehicle; S4, determining an optimum flight radius, an optimum flight speed and an optimum flight circle number of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and S5, during the optimization, firstly optimizing the track under the condition that the track is certain, optimizing the track under the condition that the power is certain, and finally carrying out combined optimization, so as to improve the system throughput.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
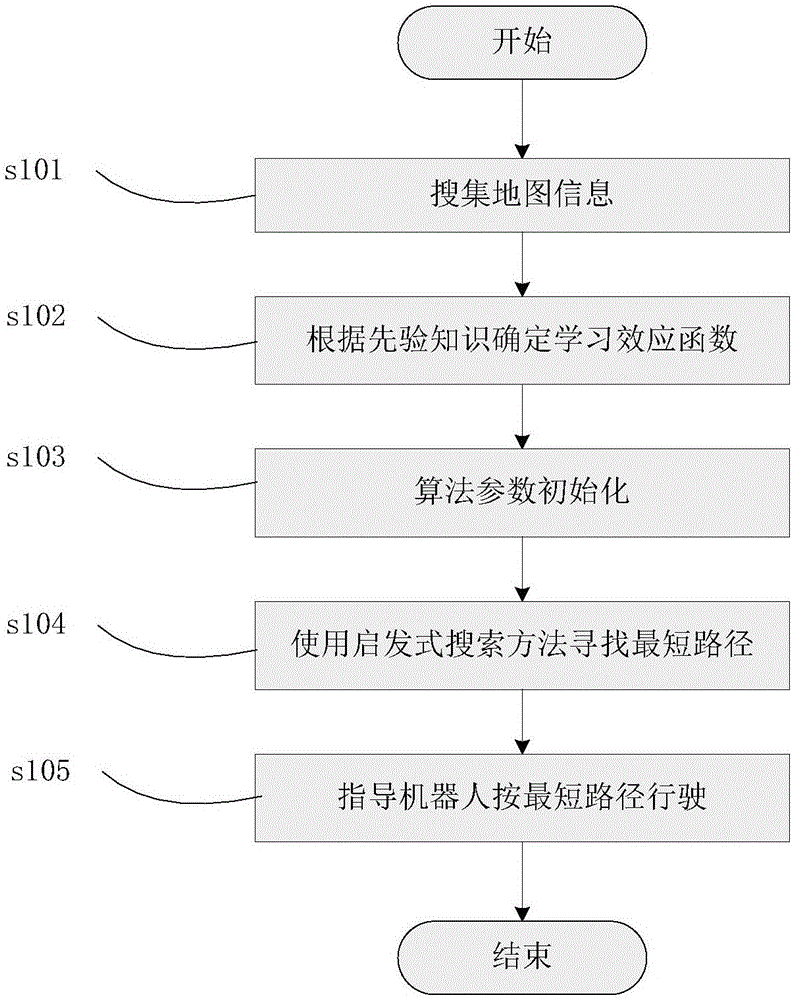
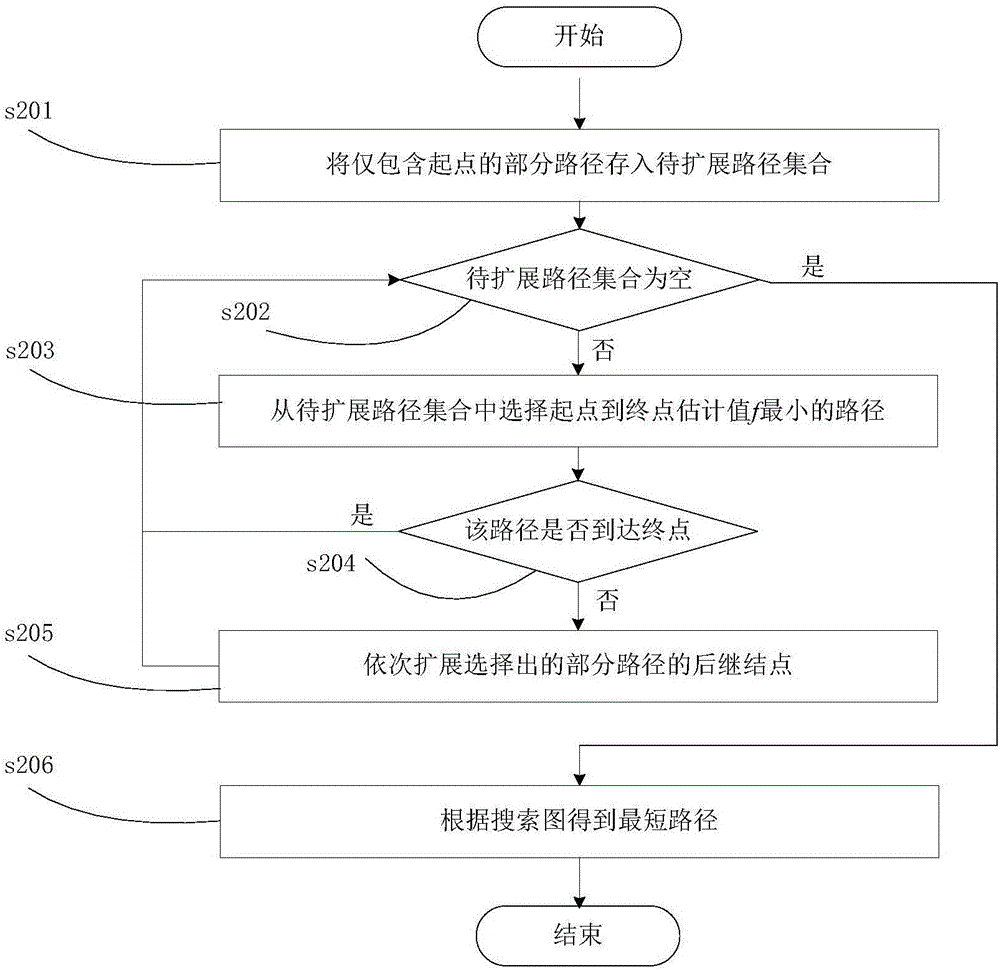
Heuristic search method of shortest path problems based on place learning effect
InactiveCN106779251AExact global shortest pathForecastingMachine learningEffect functionTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a heuristic search method with exact solutions to shortest path problems based on place learning effect, in particular to a robot path planning method. In finding a shortest path, a robot interacts with an environment to acquire experiences through reinforcement learning, which means the robot may acquire a same path at very low cost; therefore, in such case, the shortest path may be different from a shortest path with no learning effect. In order to solve the problem, after the robot acquires external environmental information and determines a learning effect function according to priori knowledge, pruning operation and filtering operation satisfactory to this problem are designed through heuristic information to eliminate in advance part of the paths which are determined not likely to present on the shortest path, the search process is accelerated, and the robot may find an exact global shortest path within reasonable effective time to guide its travelling.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
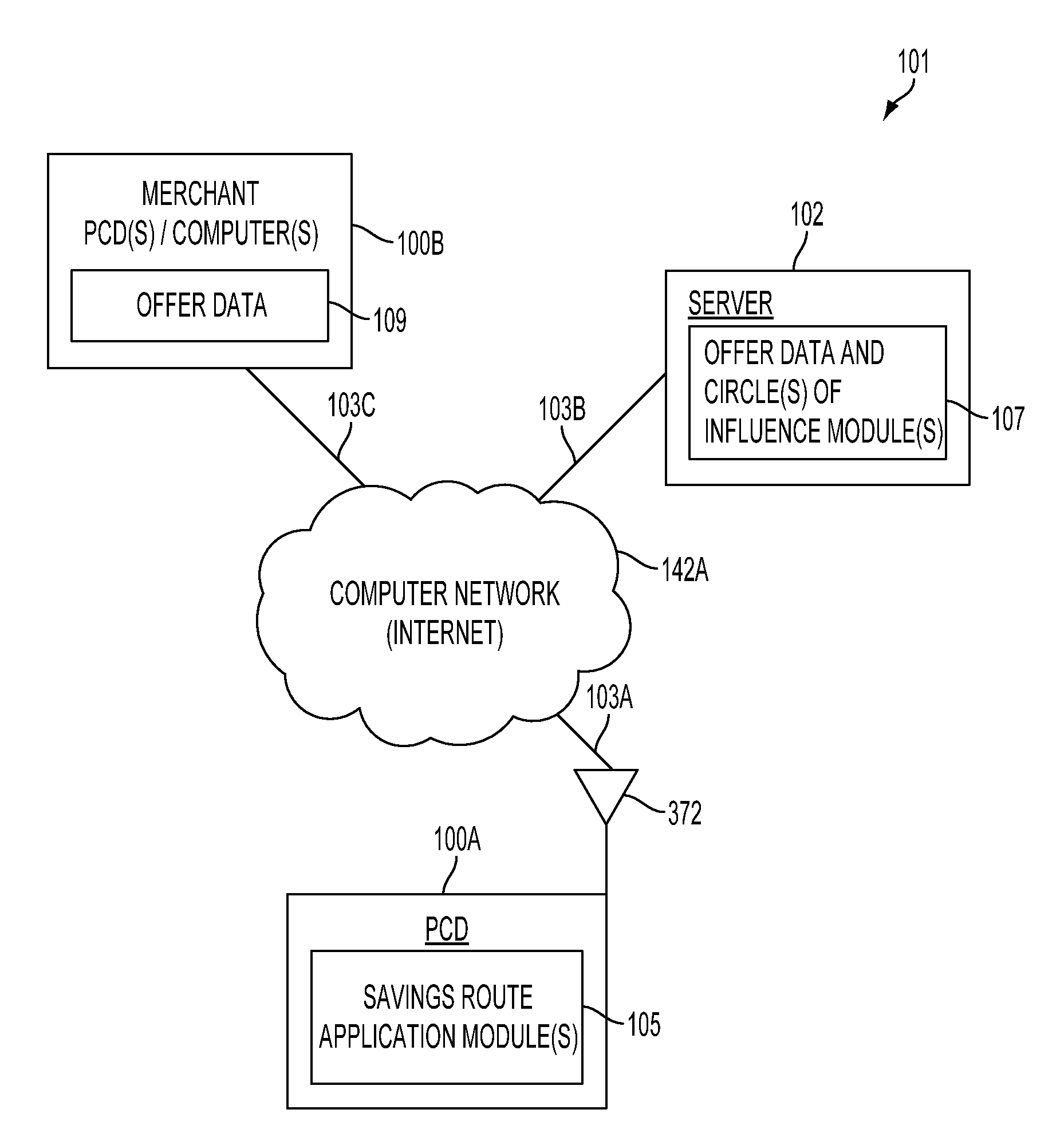
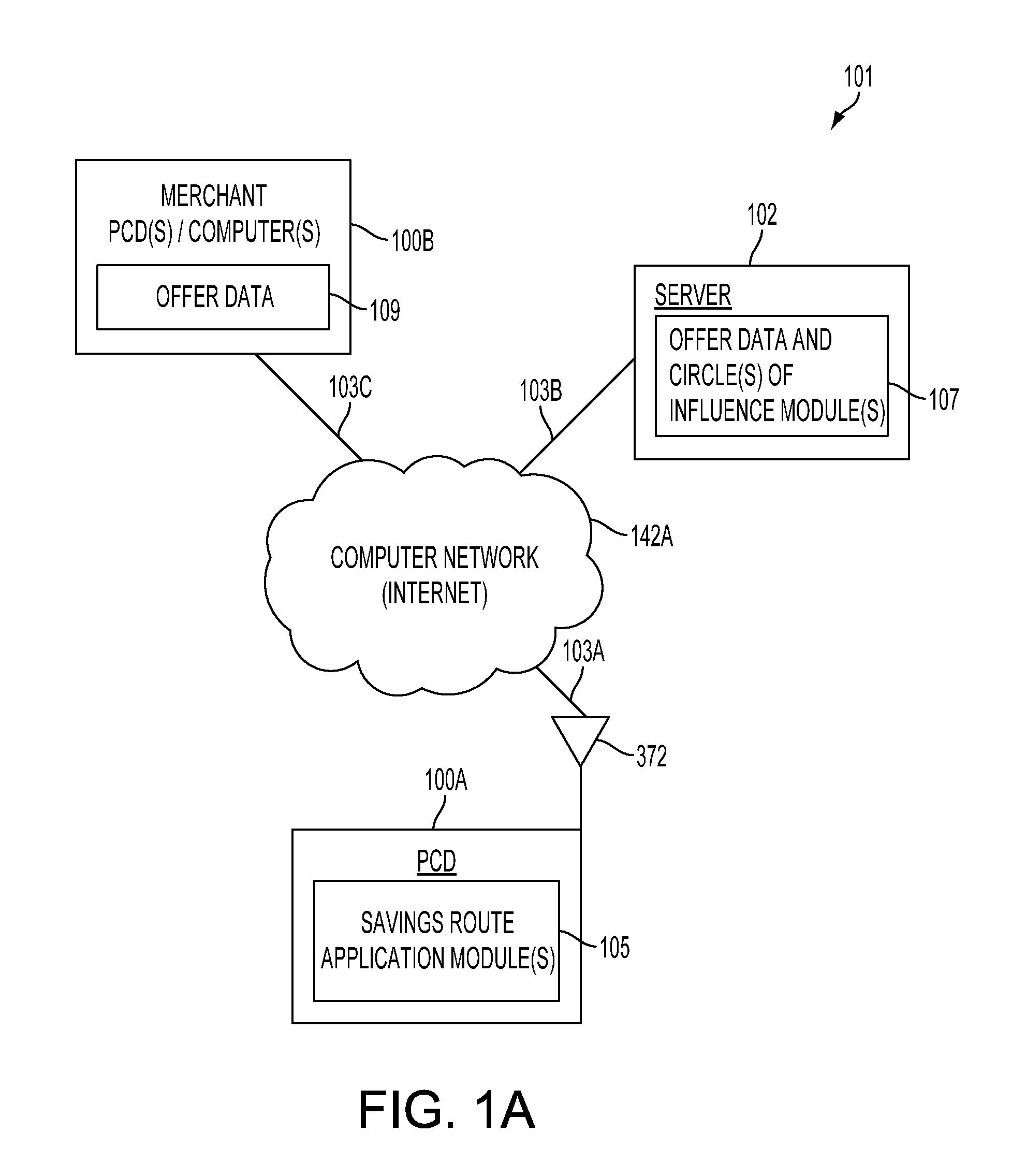
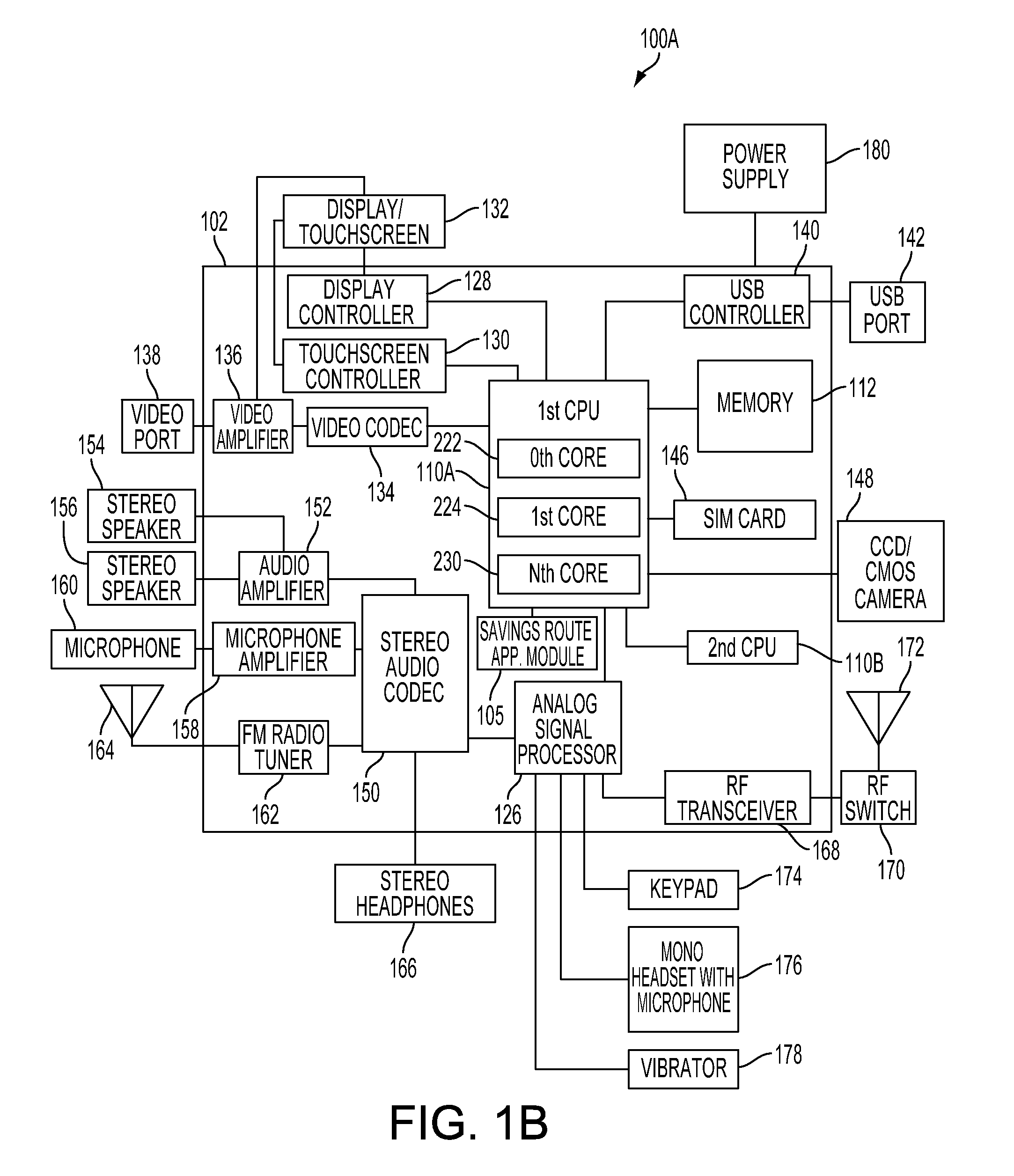
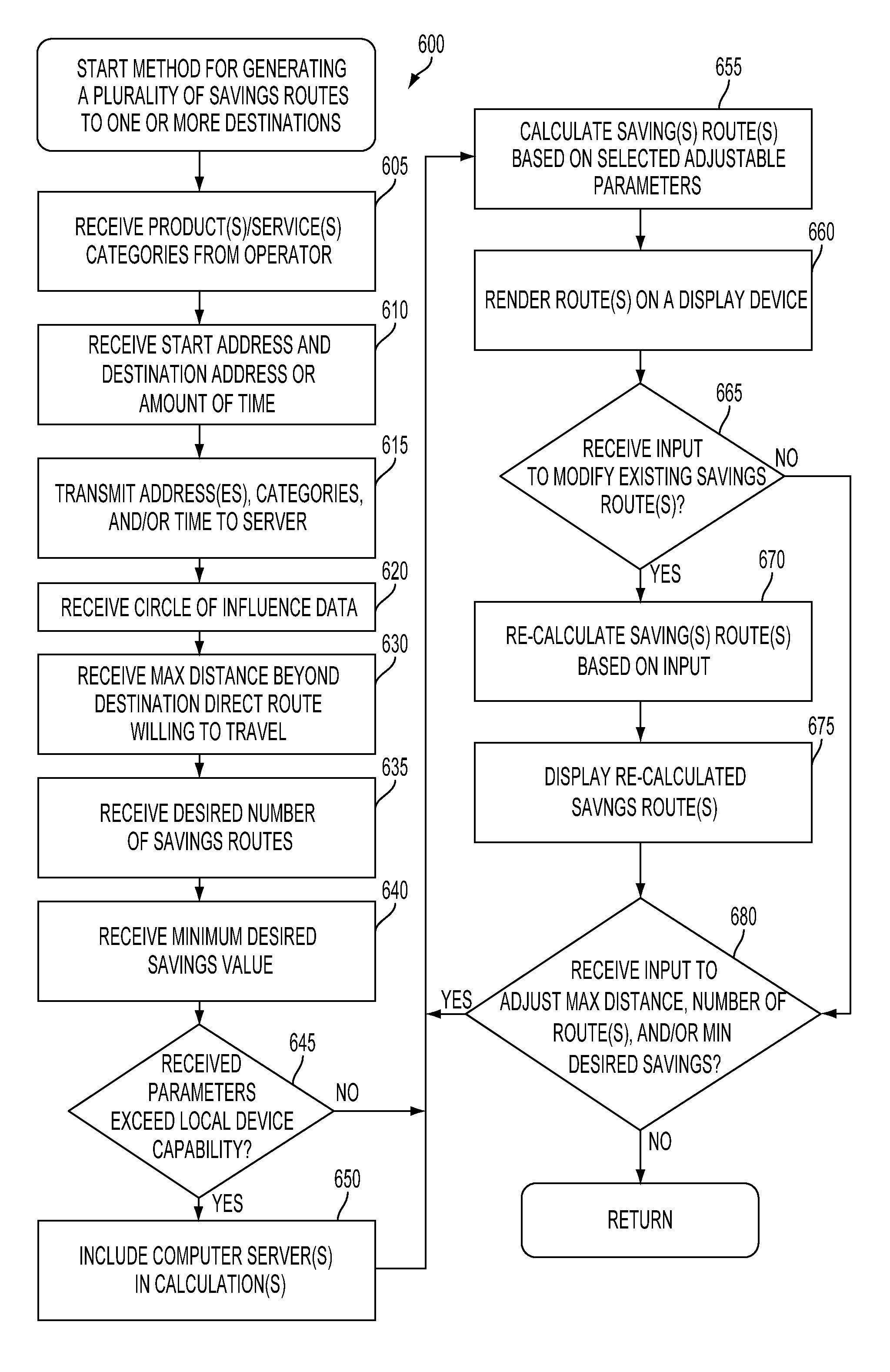
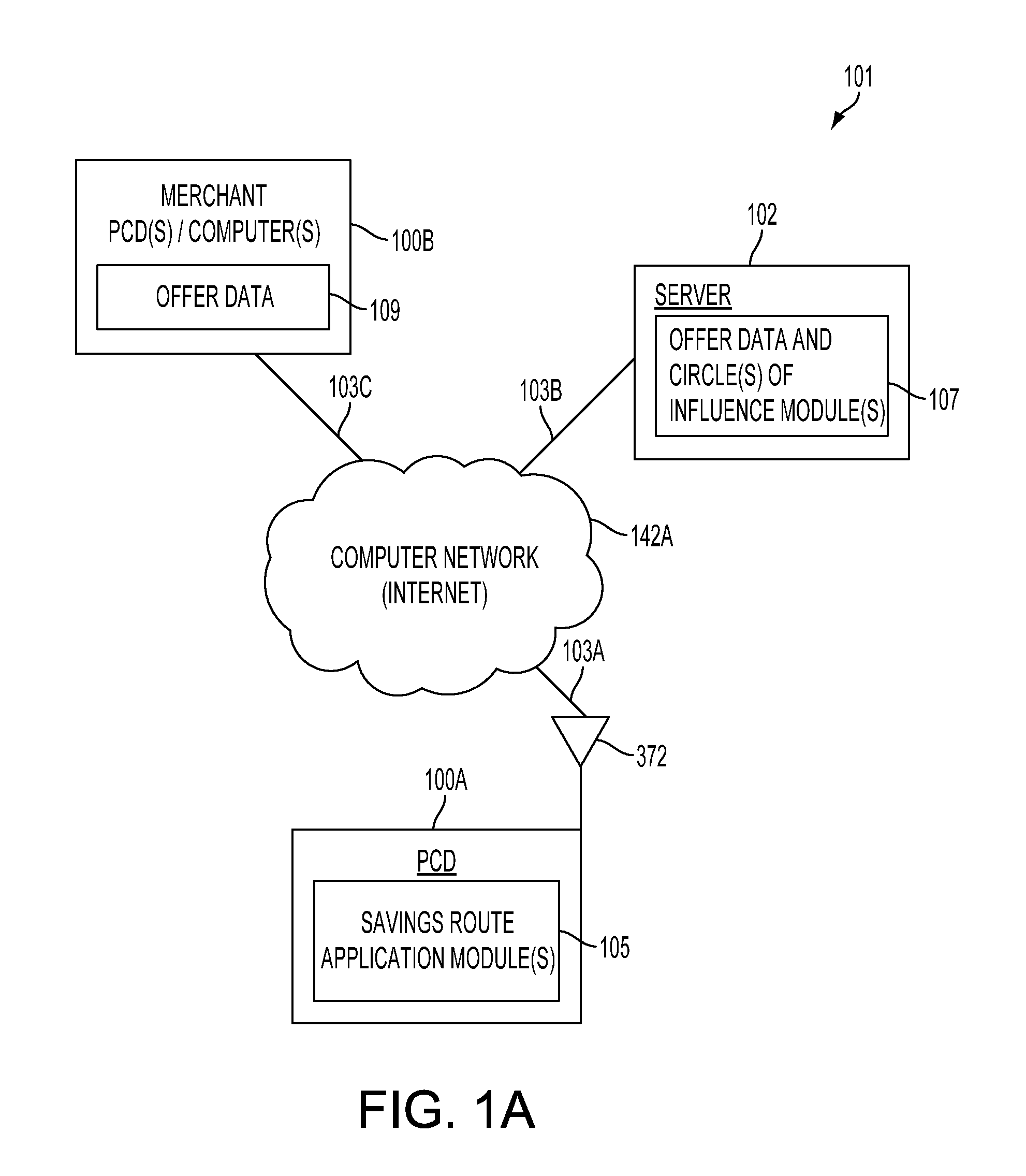
Method and system for generating savings routes with a portable computing device
ActiveUS20120239288A1Impact edge weightsInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsShortest path problemSearch algorithm
A method and system for calculating savings routes for display on a portable computing device (PCD) are described. The method includes receiving at least one of a product category and a service category from an operator of a PCD. The PCD may also receive a destination address. With this information, circle of influence data based on an offer for at least one product or service corresponding to the product category or service category may be generated and provided to the PCD. The circle of influence data may impact edge weights of a graph search algorithm. The graph search algorithm solves a single-source shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge path costs. The circles of influence in combination with the graph search algorithm allow a PCD to calculate one or more savings routes based on a start point and the desired destination address provided by the operator of the PCD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Optimized layout method of road section traffic monitors
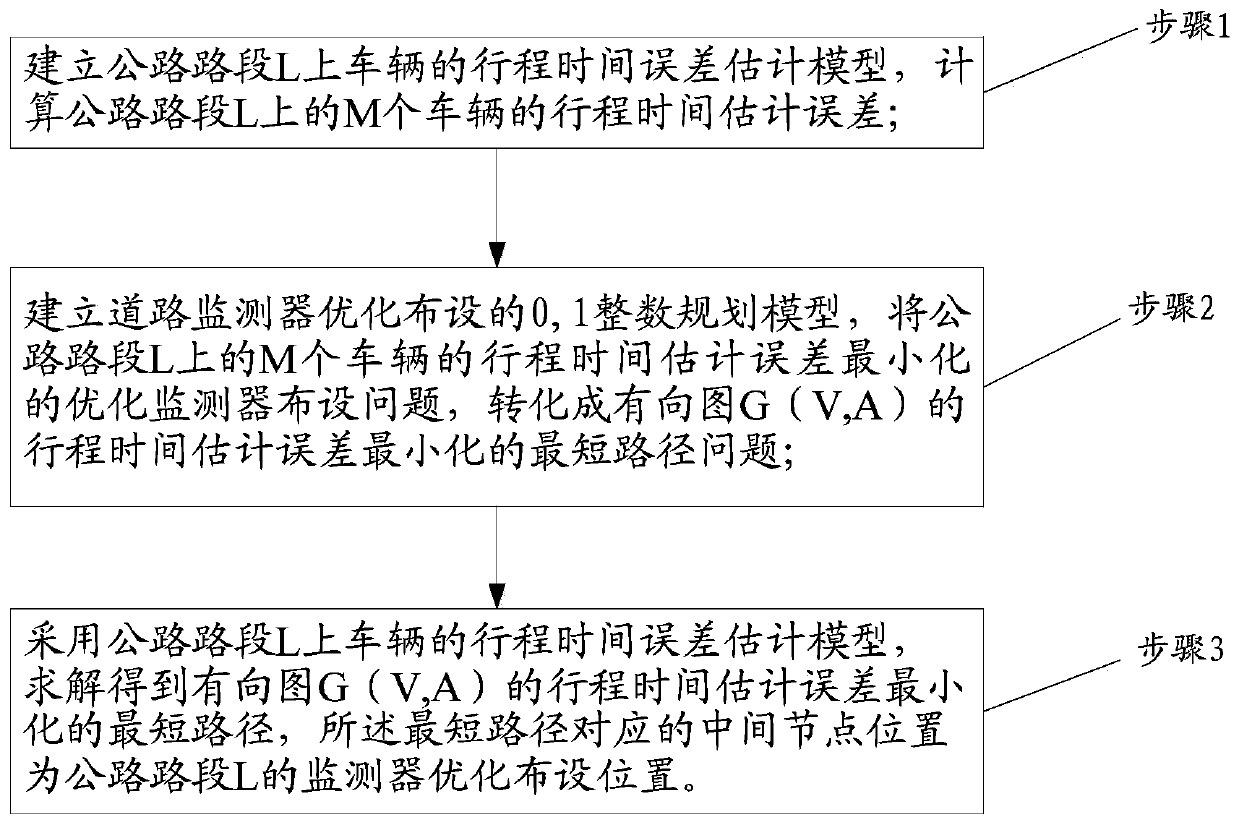
ActiveCN110322054ATravel time estimation error minimizationSolve the problem of large estimation errorInternal combustion piston enginesDetection of traffic movementDirected graphShortest path problem
The invention discloses an optimized layout method of road section traffic monitors. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a travel time error estimation model of vehicles ona road section L, and calculating travel time estimation errors of M vehicles on the road section L; establishing an optimized layout 0-1 integer programming model of road monitor and converting theoptimal monitor layout problem when the travel time estimation errors of M vehicles on the highway section L are minimum into the shortest path problem when the travel time estimation errors of the directed graph are minimum; and solving the shortest path when the travel time estimation error of the directed graph is minimum, wherein the node position corresponding to the shortest path is the optimal layout position of the monitor. According to the invention, on the premise that the number of the detectors is given, the optimal arrangement position of the traffic detectors can be optimally selected, the minimum estimation error of the whole journey time of the road section is ensured, the monitoring accuracy of the traffic monitor is improved, and the economical efficiency is very high.
Owner:CCCC FIRST HIGHWAY CONSULTANTS
AGV access path optimization method based on intelligent parking lot
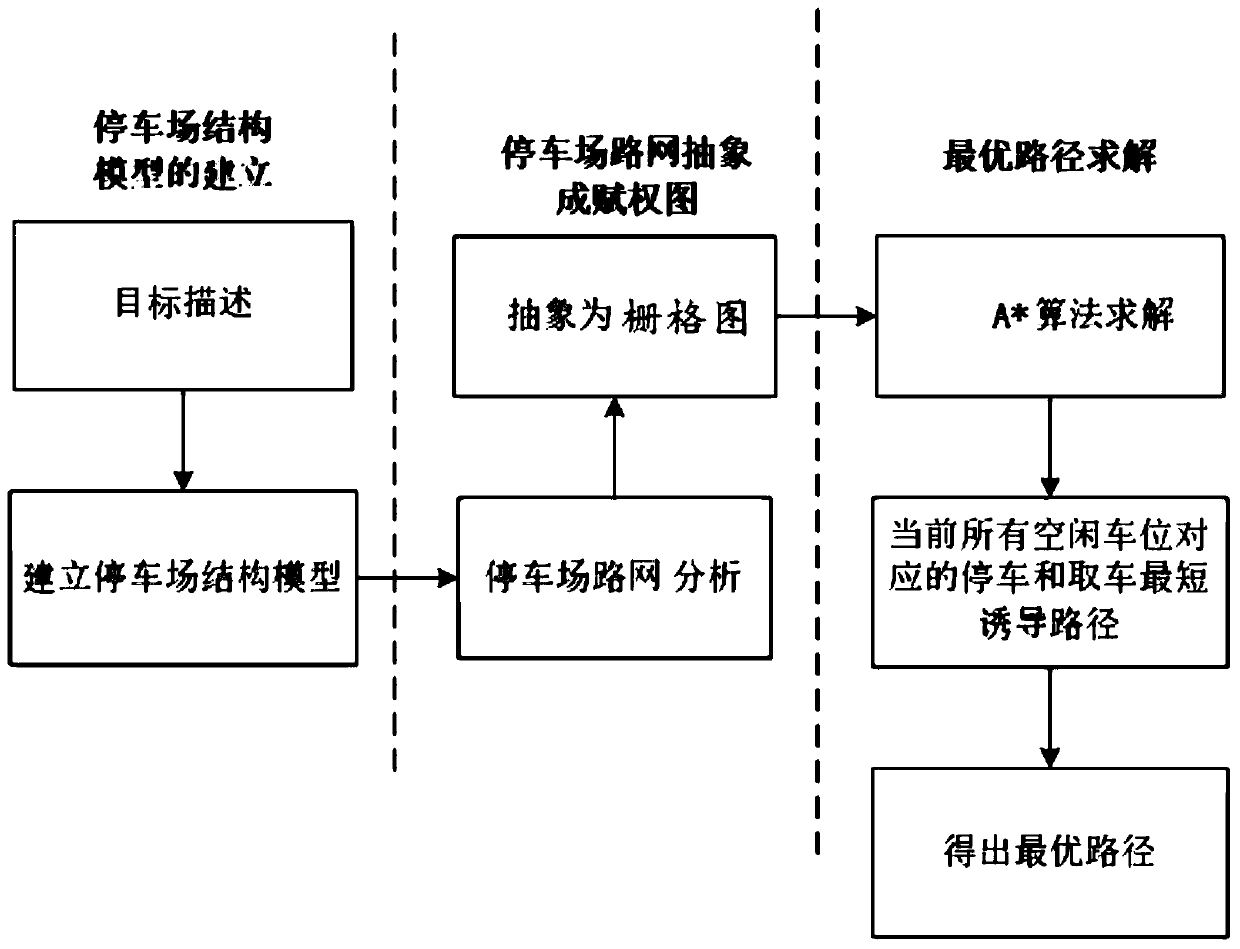
PendingCN110285821AShorten the timeImprove parking efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationParking spaceShortest path problem
The invention discloses an AGV access path optimization method based on an intelligent parking lot. An upper computer system quickly compares parking information of parking spaces and vehicles in the parking lot, and feeds back a detection signal to a main control computer; a parking space searching process is converted into a shortest path problem, and a heuristic A* algorithm is used for solving the problem. The main control computer can quickly obtain the optimal parking space through the A* algorithm and perform path planning, so that the time is shortened and the parking efficiency is improved. By means of grid map modeling, the visualization is better; the parking space utilization situation of the current parking lot and the position condition of an AGV can be checked in real time; and the monitoring and management of the parking lot are more convenient and intelligent.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for generating savings routes with a portable computing device
ActiveUS8494770B2Impact edge weightsInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsShortest path problemPath cost
A method and system for calculating savings routes for display on a portable computing device (PCD) are described. The method includes receiving at least one of a product category and a service category from an operator of a PCD. The PCD may also receive a destination address. With this information, circle of influence data based on an offer for at least one product or service corresponding to the product category or service category may be generated and provided to the PCD. The circle of influence data may impact edge weights of a graph search algorithm. The graph search algorithm solves a single-source shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge path costs. The circles of influence in combination with the graph search algorithm allow a PCD to calculate one or more savings routes based on a start point and the desired destination address provided by the operator of the PCD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
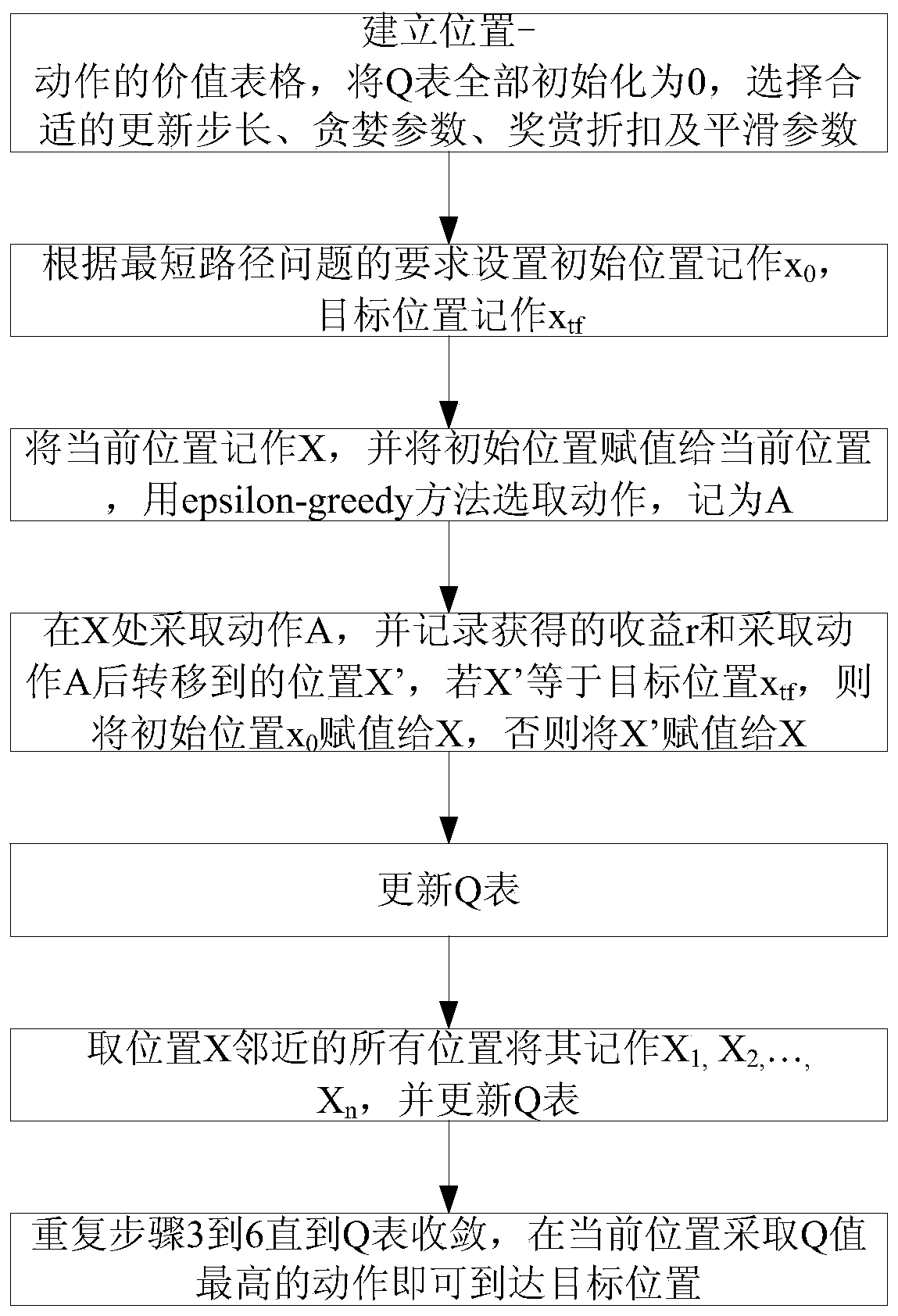
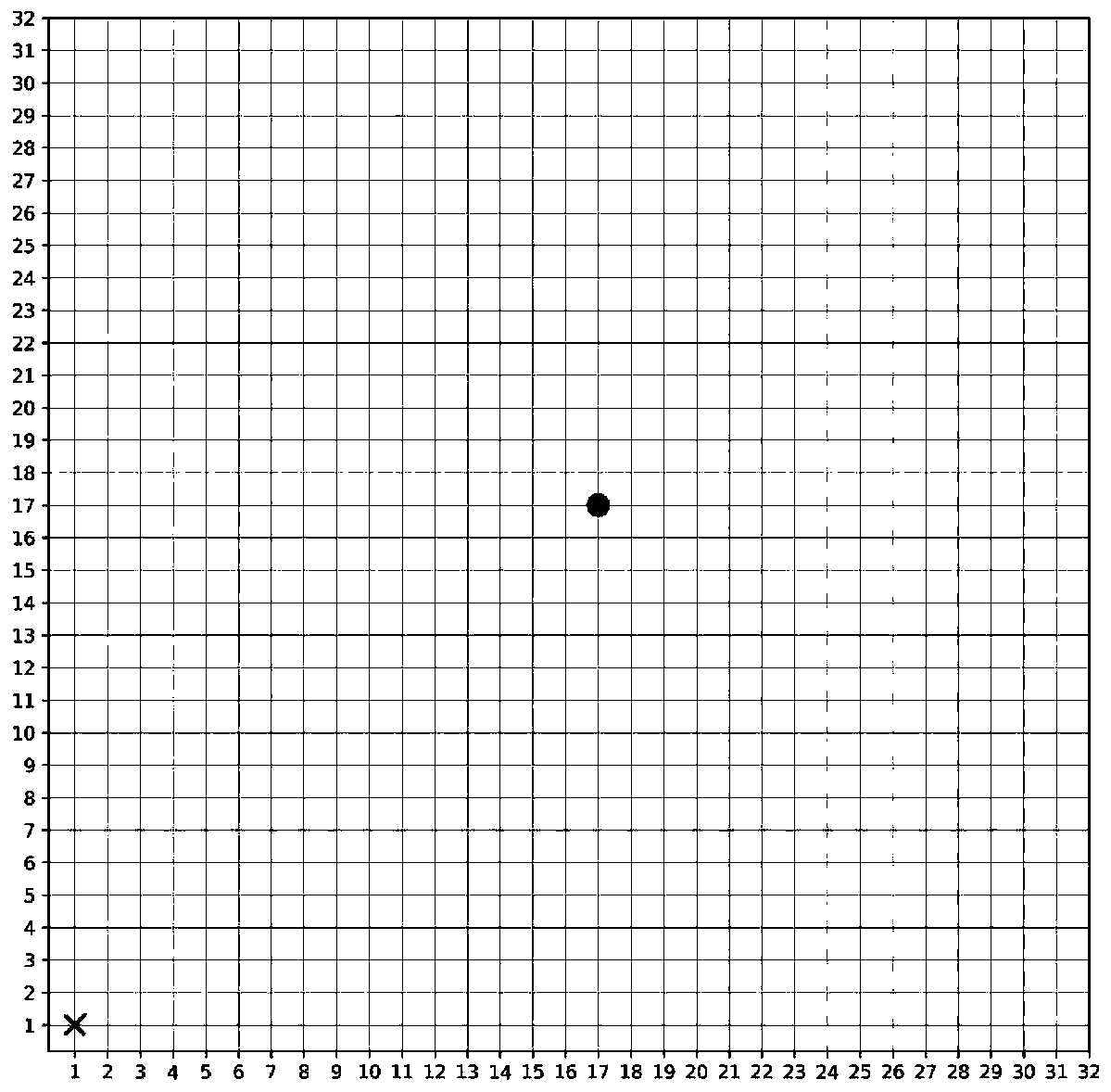
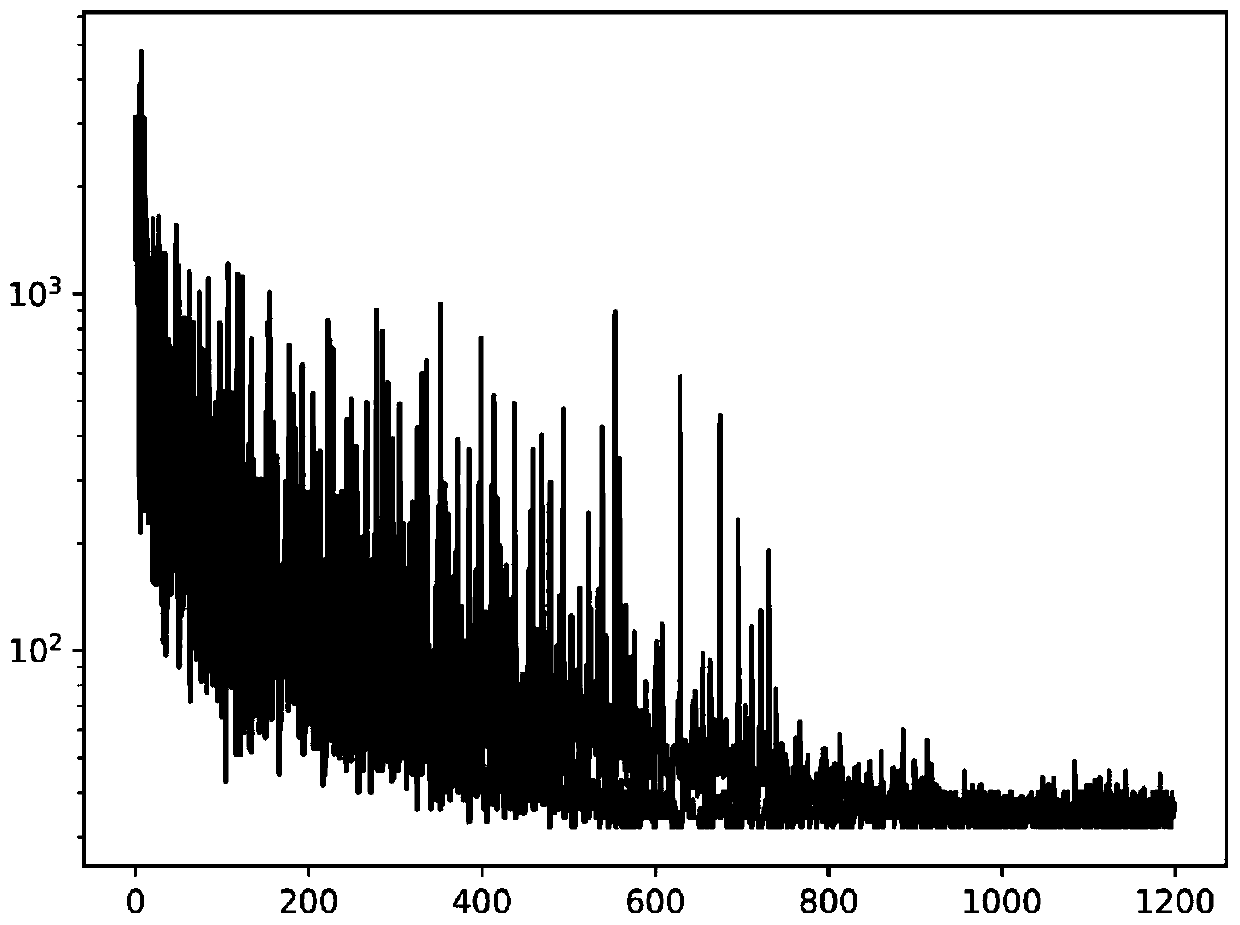
A method for solving the shortest path problem based on an improved Q-learning algorithm
InactiveCN109816115AEmbodies continuityFast convergenceMachine learningTheoretical computer scienceShortest path problem
The invention discloses a method for solving the shortest path problem based on an improved Q-learning algorithm. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: establishing a position-action value table, completely initializing the Q table to be 0, and selecting an appropriate updating step length, greedy parameters, reward discount and smooth parameters; setting an initial position tobe recorded as x0 and a target position to be recorded as xtf according to the requirement of the shortest path problem; The current position is marked as X, the initial position is assigned to the current position, and epson-is used for marking the current position as X; selecting an action according to a greedy method, and recording the action as A; Taking an action A at the X position, recording the obtained earnings r and the position X'transferred after the action A is taken, if X 'is equal to the target position xtf, assigning the initial position x0 to X, and otherwise assigning the X'to X; Updating the Q table; All positions adjacent to the position X are marked as X1, X2,..., Xn, and a Q table is updated; And repeating the above steps until the Q table converges. According to the invention, the existing Q-use at present is relieved; And the problem that the Q table convergence time is long when the problem of the shortest path is solved by the leader is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Fast algorithm for peer-to-peer shortest path problem
A plurality of landmarks selected from a source weighed graph on which a path search is performed; and the shortest path lengths between landmarks, and the shortest path lengths from vertices to landmarks adjacent to the respective vertices are calculated, and are stored in a memory device so as to be later referable. Routines for calculating upper and lower limits of the shortest path length corresponding to two vertices v and w are prepared by using expressions derived from quadrangle inequalities formed of the two vertices v and w as well as two landmarks adjacent to the respective vertices v and w. In response to a call from an A* search program, these routines return the upper limit or the lower limit of the shortest path length corresponding to v and w by referring to the shortest path lengths between landmarks, and the shortest path lengths from vertices to landmarks adjacent to the respective vertices, which have been previously stored in the memory device.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
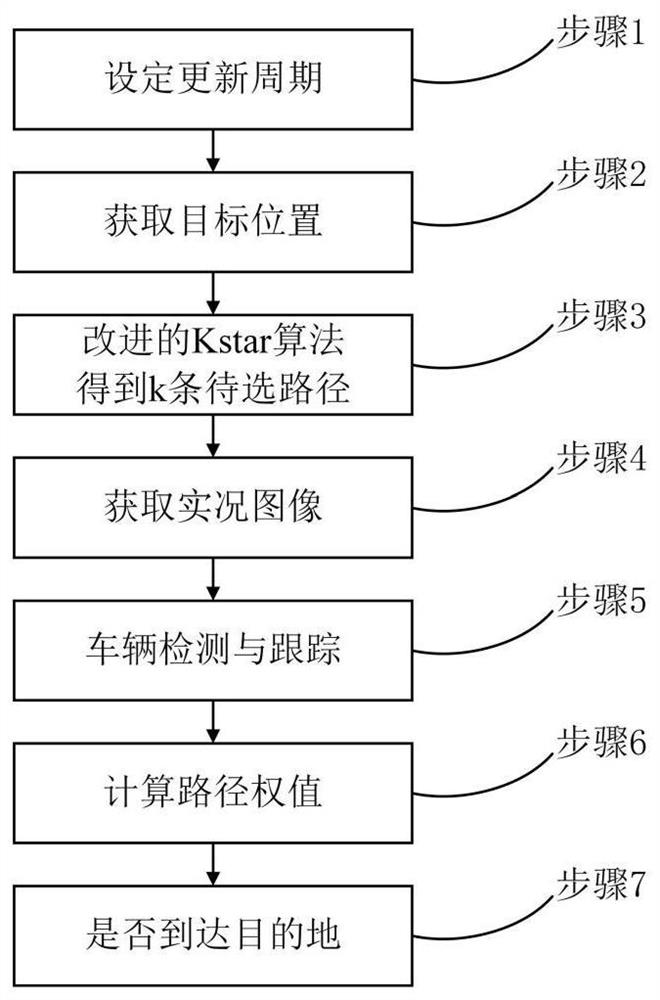
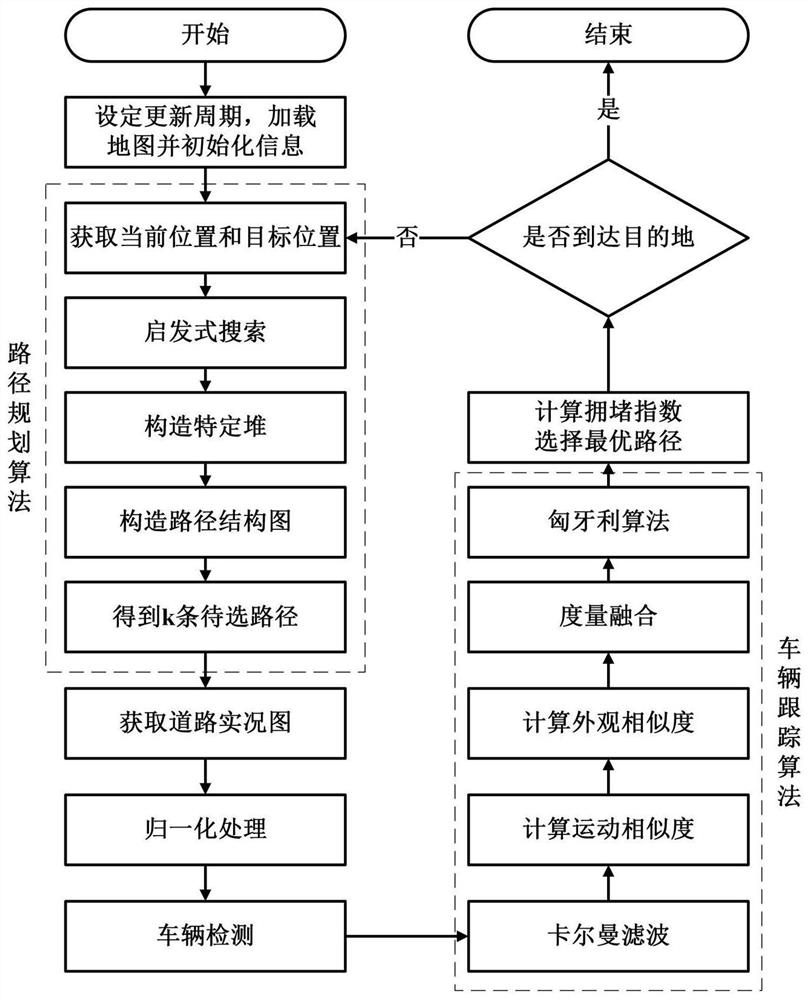
Real-time path planning method based on improved Kstar algorithm and deep learning
ActiveCN112748732AReduce planning timesHigh speedPosition/course control in two dimensionsRoad mapTerm memory
The invention discloses a real-time path planning method based on an improved Kstar algorithm and deep learning. According to the real-time path planning method, a k-shortest paths problem is combined into real-time path planning, k excellent to-be-selected paths are quickly and efficiently found out by improving the Kstar algorithm, a more reasonable road evaluation formula is put forward, the time for passing through the road and the congestion index of the road are comprehensively considered, and the traffic pressure is relieved while the optimal path is found out. The improved Kstar algorithm is used for regionalizing a road map, the speed of heuristic search is greatly increased, efficient data structures such as heaps and path structure diagrams are constructed, unnecessary memory waste is optimized, a plurality of to-be-selected paths are quickly obtained under the condition that the time complexity of the method is close to that of a conventional optimal path algorithm, and the number of unnecessary navigation route planning times is effectively reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
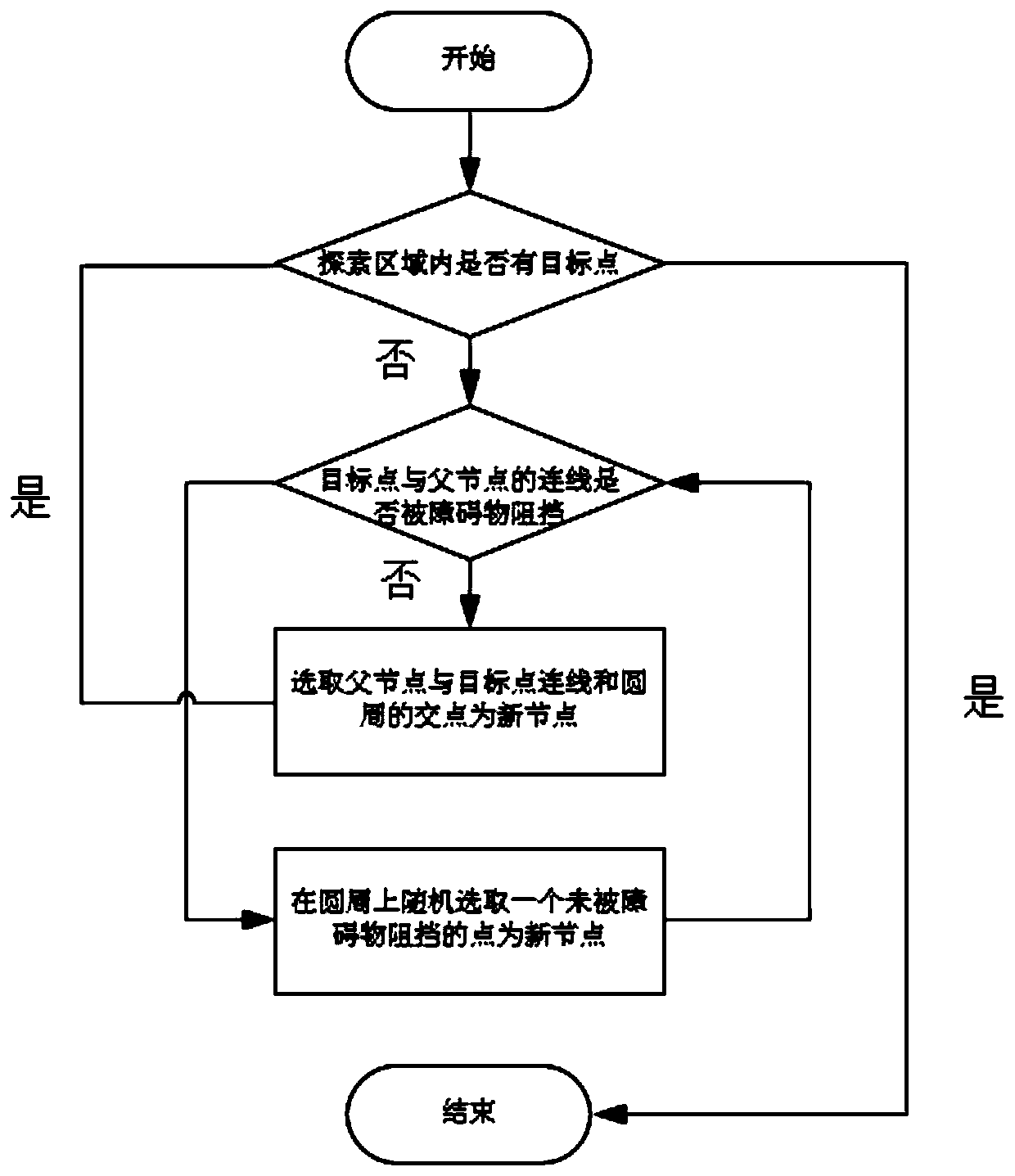
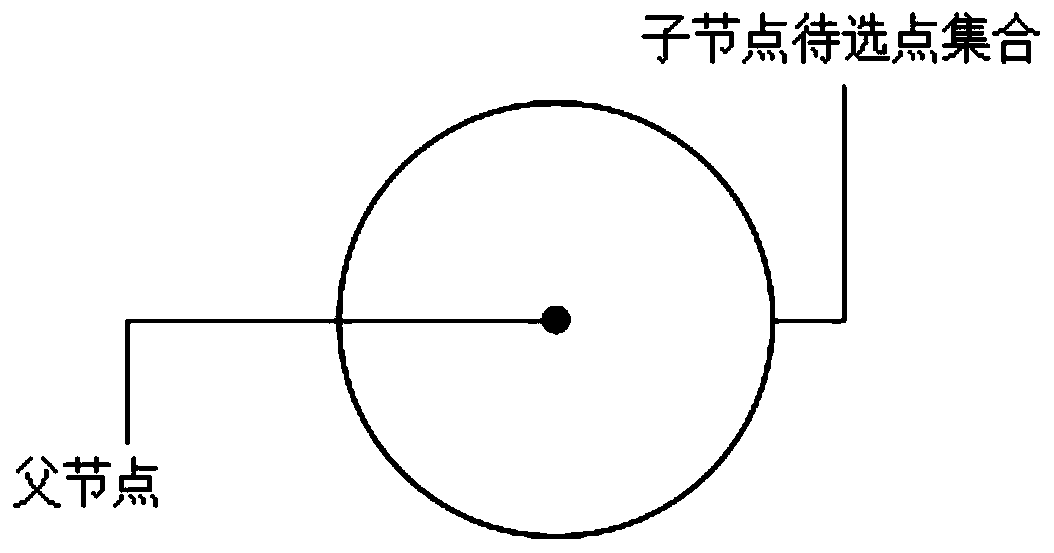
Myxomycetes RRT navigation method and system based on two-dimensional static path planning
ActiveCN110906947AImprove performanceIncrease roughnessInstruments for road network navigationPathPingSimulation
The invention discloses a myxomycetes RRT navigation method and system based on two-dimensional static path planning, and the method comprises the steps: taking a point where a mobile robot is locatedas an original point, and taking a step length as a radius for making a circle; taking the circle as an exploration range, and taking points on the circle as a to-be-selected node set; when no obstacle exists in the exploration range, using the intersection point of the straight line connecting the starting point and the terminal point and the circle as a new node; making a circle by taking the node as an original point and the step length as a radius. According to the method, the new node is reselected, so that the obtained path is shortest. According to the method, the problems of unsmoothpath and non-shortest path of the RRT algorithm can be improved, so that the performance of the RRT algorithm is improved, and a better and shorter path is obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI INST OF AUTOMATION
Memristive network based on movable conductive nanoparticles and self-organizing evolution operation application
PendingCN113675334ASmall sizeEfficient Self-Organizing Evolutionary ComputingElectrical apparatusNanoparticleEngineering
The invention discloses a memristor network based on movable conductive nanoparticles and a self-organizing evolution operation application. The memristive network comprises a substrate, a plurality of conductive electrodes, a dielectric layer and movable conductive nanoparticles; the conductive electrodes are located on the substrate and serve as signal input and output ends of the memristive network; the dielectric layer is filled between the conductive electrodes; the movable conductive nanoparticles are dispersed on the surface and / or inside the dielectric layer, and the movable conductive nanoparticles can migrate in the dielectric layer under the action of an electric field, so that the emergence behavior of the self-evolution network can be highly mapped, and advantages in solving some classic complex operation problems which are difficult to solve by a traditional computer are achieved. The invention further provides application of the memristor network based on the movable conductive nanoparticles in solving classical optimization problems, including solving of the shortest path problem and the maze problem, and the time complexity and the space complexity of operation can be greatly reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
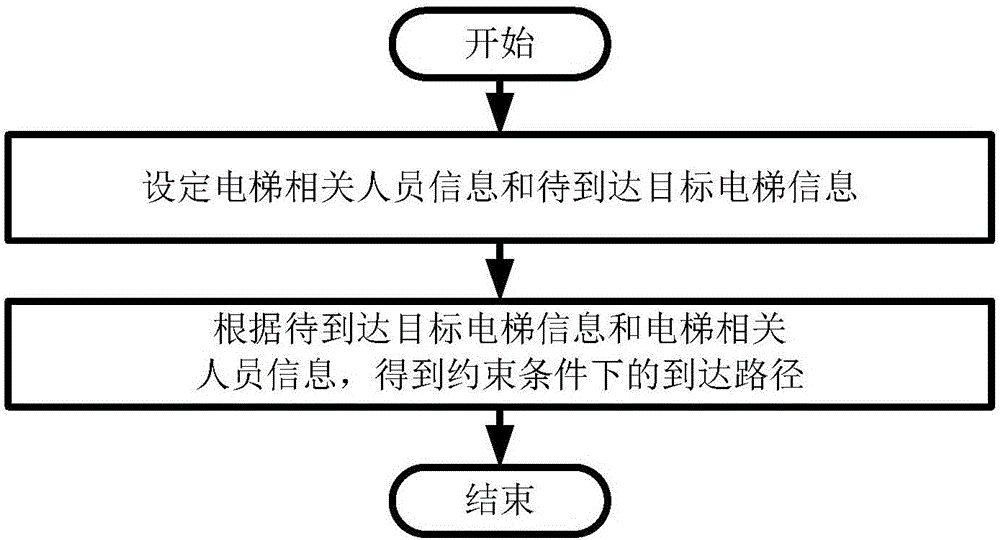
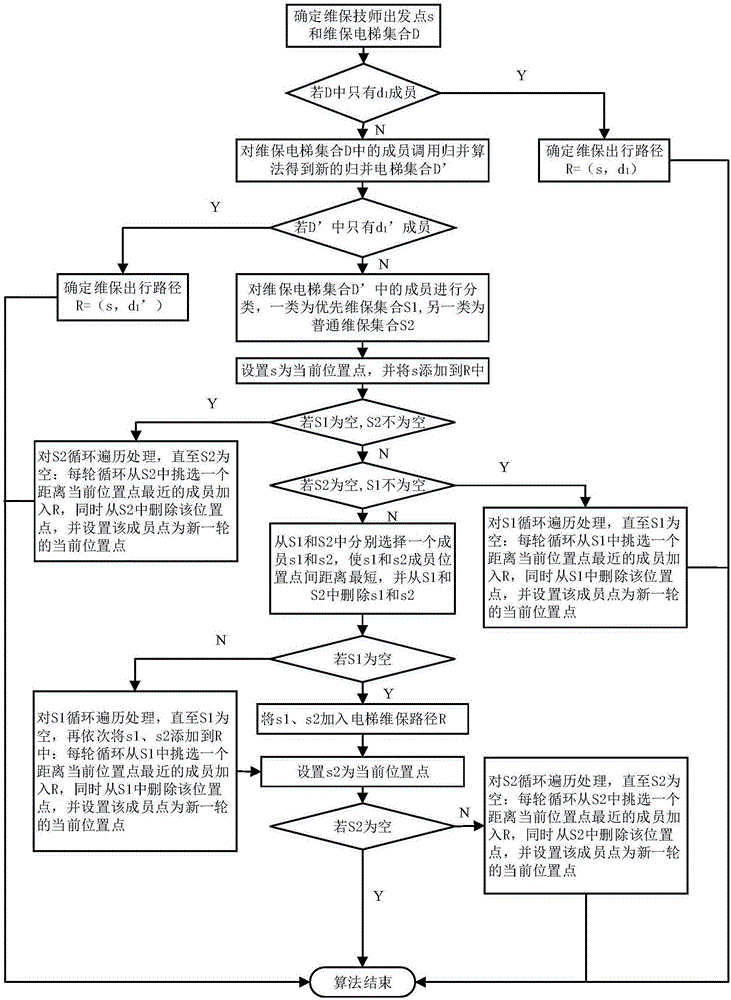
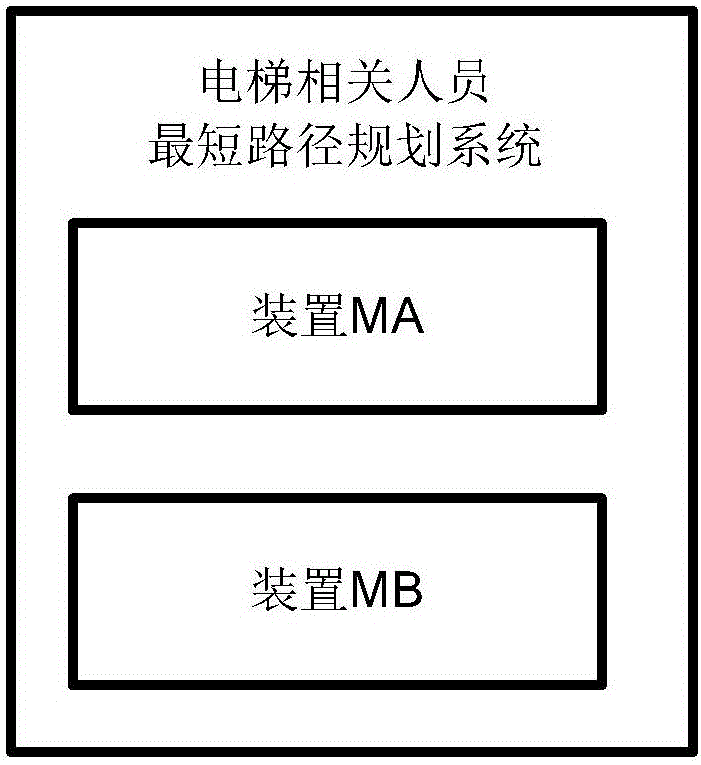
Elevator related personnel shortest path planning system
ActiveCN106197431AImprove timelinessShorten the transition journeyNavigational calculation instrumentsShortest path planningSimulation
The invention provides an elevator related personnel shortest path planning system which comprises a device MA and a device MB. The device MA is used for setting elevator related personnel information and target elevator information. The device MB is used for obtaining a reach path under constraint conditions according to the target elevator information and the elevator related personnel information. A calculation scheme of the shortest path problem within the constraint time is provided, all to-be-processed elevators are traversed by starting from starting points of elevator related personnel, an effective path spending shortest predicted elevator processing time for the elevators can be obtain, and a calculation result can be sent to mobile phones of elevator related personnel for path prompt. The system is applied to platforms for elevator maintenance, check and the like, the processing path planning method can be practically applied, a method is provided for elevator related personnel for planning a path, elevator daily processing work timeliness is improved, and the transition path in elevator daily processing work is shortened.
Owner:安徽奥里奥克科技股份有限公司
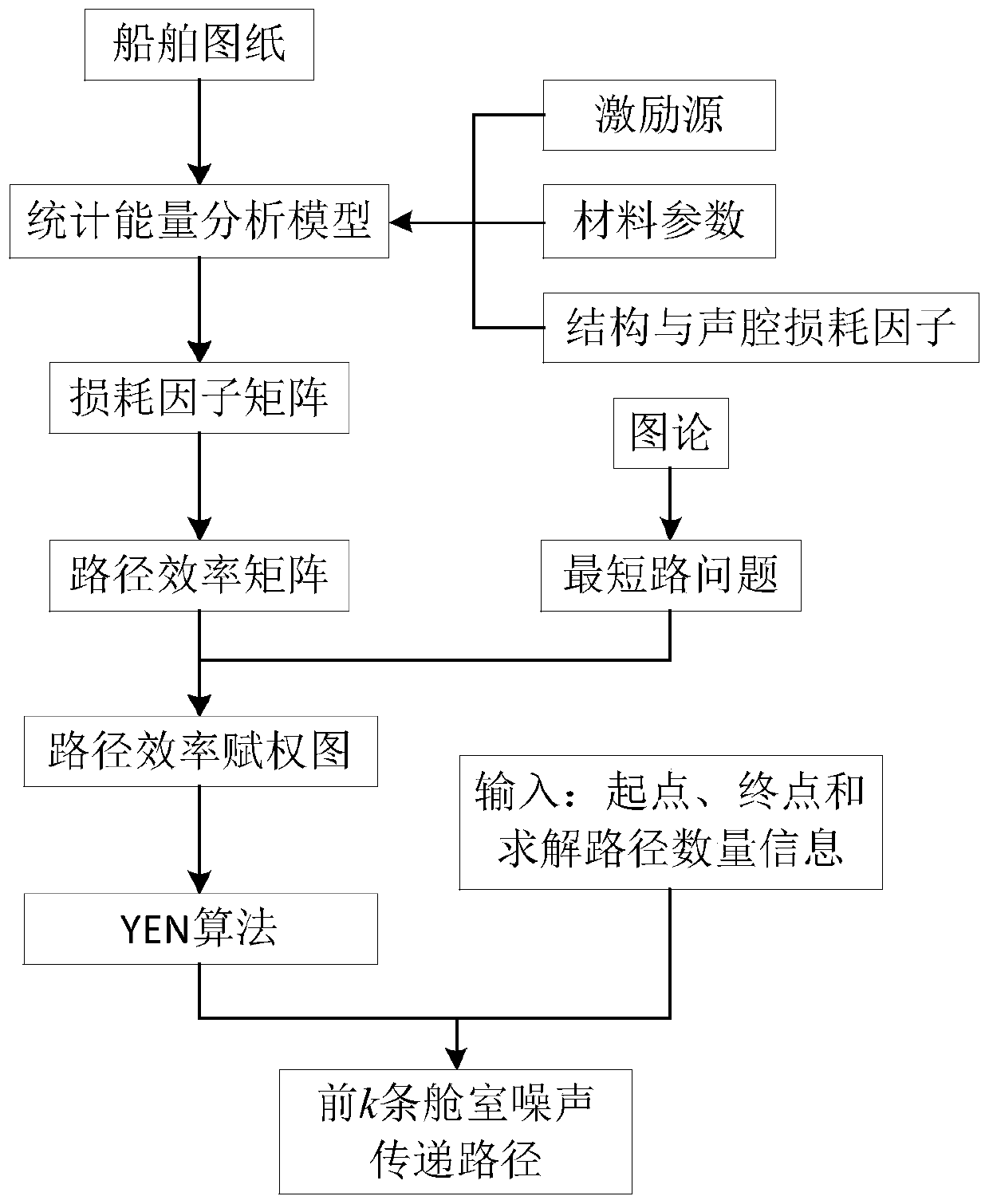
Ship cabin noise transmission path analysis method
PendingCN110826241AImprove noise reductionImprove economyDesign optimisation/simulationSimulationTest analysis
The invention discloses a ship cabin noise transmission path analysis method, which comprises the steps of establishing a statistical energy analysis model according to a ship drawing; setting attributes of each subsystem in the statistical energy analysis model according to drawings and data; calculating an internal loss factor of each subsystem and a coupling loss factor between the subsystems,and establishing a loss factor matrix of the whole system; converting the loss factor matrix into a path efficiency matrix, and establishing a path efficiency weighting graph for noise transmission path analysis; and solving the first k shortest paths of the weighted graph by using an algorithm of the shortest path problem, so as to obtain the first k noise energy transfer paths from the noise source to the target cabin. The cabin noise transmission path analysis work can be completed at the initial stage of ship design, the limitation that real ship test analysis can only be conducted after aship is built is overcome, guidance can be provided for subsequent noise reduction design, and the cabin noise transmission path analysis method has the obvious effects of saving cost and reducing space and weight occupation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MERCHANT SHIP DESIGN & RES INST
Network anonymity method for modifying graph structure based on optimal grouping of degree sequence
ActiveCN110378150AImplement anonymous processing operationsAnonymous processing operations applyDigital data protectionNetwork structureShortest path problem
The invention discloses a network anonymity method for modifying a graph structure based on optimal grouping of a degree sequence. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, converting an optimal grouping problem of anonymity of a network node degree value sequence into a shortest path problem of a directed packet network; carrying out anonymity on a network node degree value sequence according to the shortest path of the directed packet network; modifying a network structure according to the anonymous information of the network node degree value sequence to realize anonymous operation of the network node degree value. The calculation amount in the network data anonymization process can be effectively reduced. The method is suitable for large-scale network data anonymization processing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Path planning method and device passing through necessary point set and having extra hard constraint
ActiveCN112965500ACutting costsSimple calculationPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPathPingShortest path problem
The invention relates to a path planning method and device passing through a necessary point set and having extra hard constraint, wherein the path planning method comprises the following steps: S1, a preprocessing stage: converting the actual application environment information into mathematical description, and completing the processing and modeling of an undirected weighted graph of a problem; and S2, a shortest path solving stage: carrying out shortest path solving by using a random search algorithm, carrying out real-time judgment on the feasibility of the path in the search process, solving the shortest path problem of the necessary point set under the condition of meeting the requirement of extra hard constraint, and finally obtaining the shortest path meeting the requirement. According to the method, the additional hard constraint can be added, and the calculation result meeting the engineering requirements under the actual physical limitation condition can be ensured to be obtained within the short calculation time.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Laser filling method and device for multilayer contour pattern based on contour lines
ActiveCN113793351AReduce search volumeSave time and costImage analysisManufacturing computing systemsGrid patternComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a laser filling method and device for a multilayer contour pattern based on contour lines, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: performing outer contour inner offset operation on a to-be-filled pattern according to an equidistant offset algorithm to obtain a contour offset pattern; performing grid method environment modeling on the contour offset pattern to obtain a preprocessed grid pattern; performing inner and outer contour discrimination on the grid pattern to obtain a to-be-filled grid; for the to-be-filled grid, constructing a shortest path problem set; and solving the shortest path problem set by using an A* algorithm to obtain an optimal filling path of the to-be-filled grid. By adopting the method, the laser filling efficiency of the pattern can be improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Traffic shortest reliable path method driven by random GIS network
PendingCN114186410AImprove calculation accuracyImprove interactivityDesign optimisation/simulationGeographical information databasesTraffic networkShortest path problem
The shortest path problem and the traffic N shortest path problem in the prior art consider a scene with determined travel time, but in a congested urban traffic network, the travel time has high uncertainty, and travelers tend to select paths with high reliability under the condition that the travel time is uncertain, so that the traffic efficiency is improved. According to the method, the shortest reliable path problem and the shortest reliable path expansion problem in the random traffic network are solved, and the shortest reliable path in the large GIS traffic network is efficiently searched by reducing the calculation scale of the shortest reliable path; for a general looped network, the first N shortest reliable paths are solved, the improvement advantages are obvious, firstly, the travel time determinacy limitation is few, the maneuverability is high, and flexibility and convenience are achieved; secondly, the first N shortest reliable paths are efficiently solved, and the reliability and availability of the shortest reliable paths are enhanced; and thirdly, the GIS network type is high in interactivity, high in precision and relatively low in algorithm complexity, and the development, popularization and application of the ITS and the ATIS are powerfully promoted.
Owner:王彬
Fast-forward path optimization method for leather multi-contour processing
InactiveCN107798413BReduce conversionGuaranteed global search capabilityForecastingArtificial lifeReal arithmeticTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a method for optimizing the fast-forward path of leather multi-contour processing. The sample processing sequence sequence is obtained through quantum coding and quantum observation, and the problem of fast-forward path optimization is transformed into the problem of solving the shortest path of a multi-segment graph. Fitness evaluation solution. The method of the present invention has the following advantages: the quantum chromosomes encoded by real numbers can directly decode the sample processing order sequence expressed in decimal form, reducing the conversion process from binary to decimal; the individual fitness evaluation method based on the dynamic programming method has effectively established The relationship between multi-contour machining and multi-segment graph makes the fast-forward path problem easy to solve; the quantum update strategy of dynamic rotation angle effectively guarantees the global search performance of the algorithm. The method of the invention can effectively avoid the phenomenon of premature convergence, can quickly converge to the global optimal solution, and improve the quality and convergence speed of the solution.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIV
Online service placement method with data refreshing function based on value space estimation
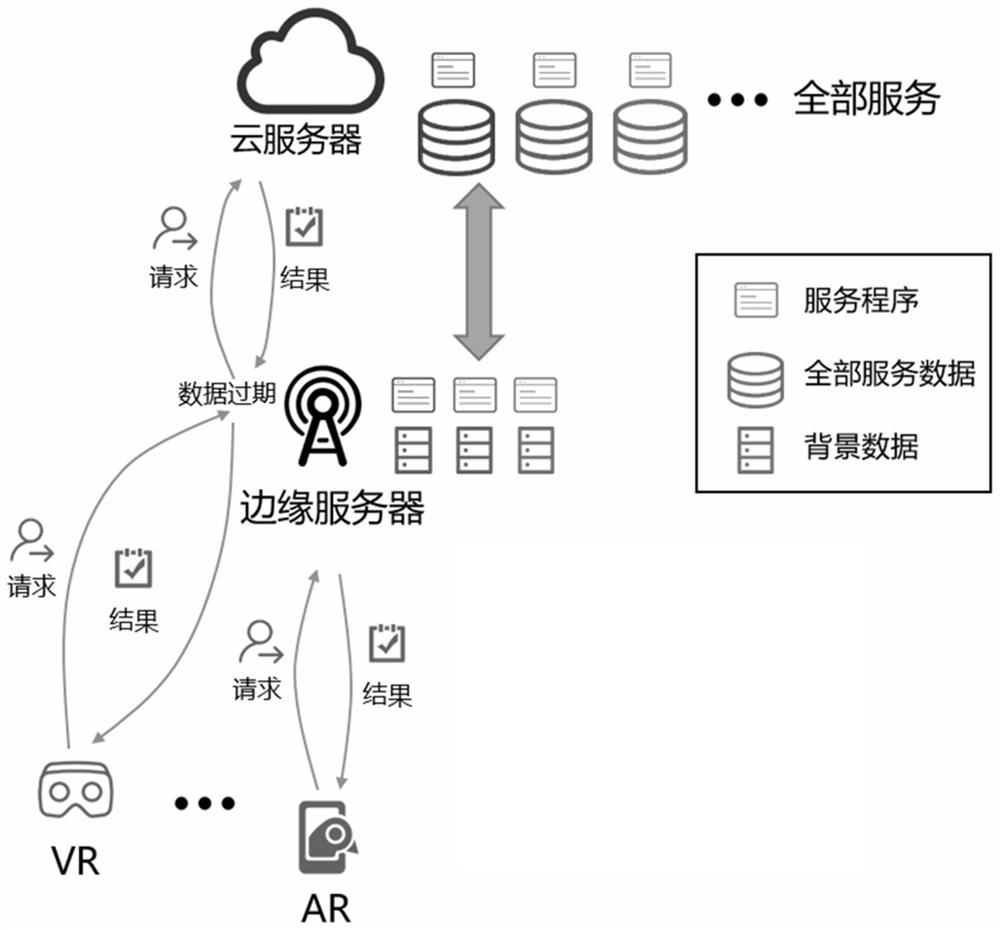
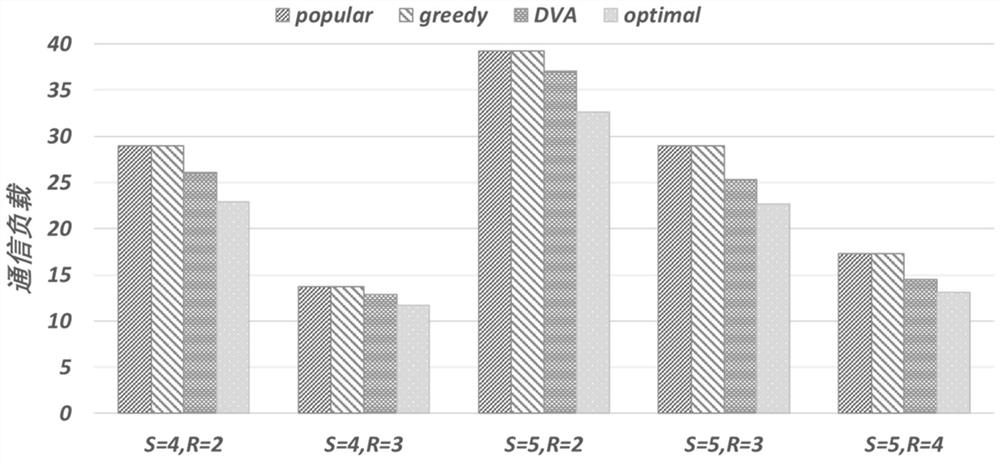
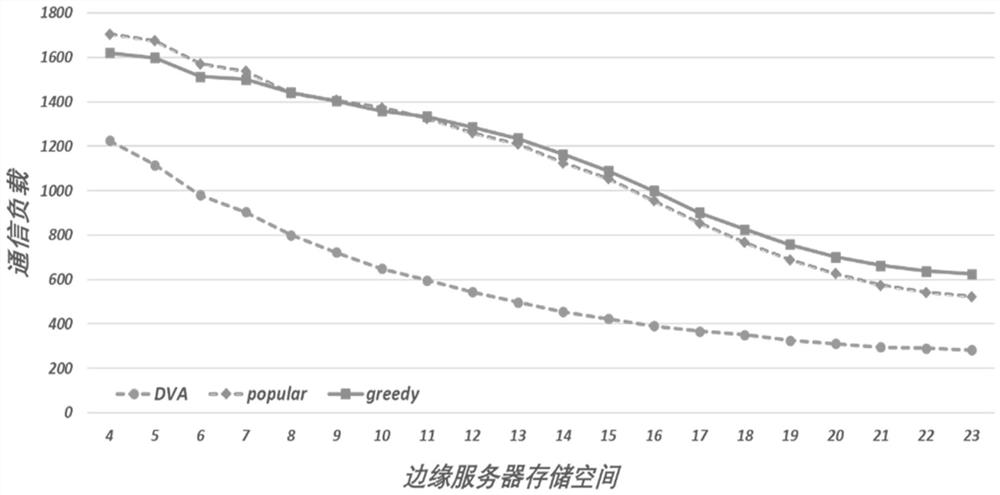
ActiveCN113572848AReduce time complexityService provisioningNetwork traffic/resource managementPathPingEdge server
The invention discloses an online service placement method with data refreshing based on value space estimation. The method comprises the following steps: in a mobile edge computing scene, under the condition that service background data is refreshed, determining how to select a service to be placed by an edge server, and adopting the manner to minimize a communication load between the edge server and a cloud server; converting a service placement problem into a shortest path problem; estimating a node value in the shortest path problem, and obtaining a service placement strategy of a next time slice during operation; finally, serving the user in the edge server so as to reduce the communication load between the edge server and the cloud server.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
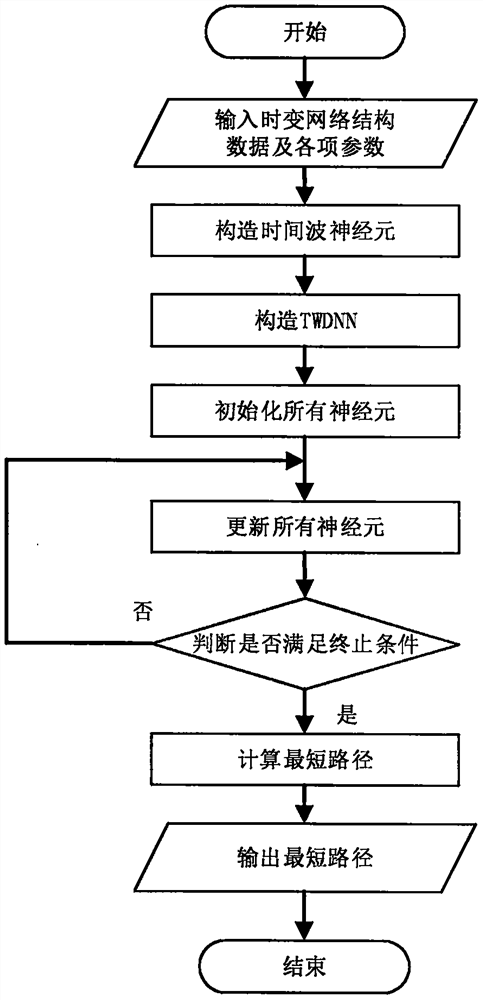
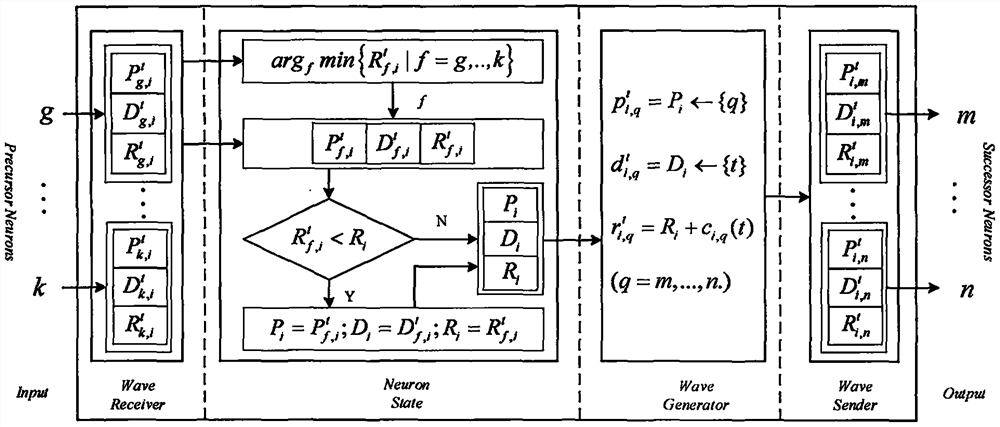
Constraint time-varying shortest path solving method based on time wave delay neural network
The invention discloses a constrained time-varying shortest path solving method based on a time wave delay neural network, and the method comprises the steps of solving a constrained time-varying shortest path problem(CTSPP for short) through the construction of a time wave delay neural network (TWDNN for short). The designed TWDNN is a novel neural network based on time wave delay neurons, the difference between the TWDNN and a traditional neural network is that the TWDNN does not need any training, and the design of the TWDNN comprises neuron structure design and neural network structure design. Each neuron on the time wave delay neural network is composed of an input part, a wave receiver part, a neuron state part, a wave generator part, a wave transmitter part and an output part. The wave is a medium for exchanging information among the neurons, the propagation delay of the wave among the neurons is equivalent to the transmission delay of a data packet on a network, and the output of the shortest path is based on the time wave received by the target neuron. Experimental results show that the method provided by the invention is superior to the existing method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
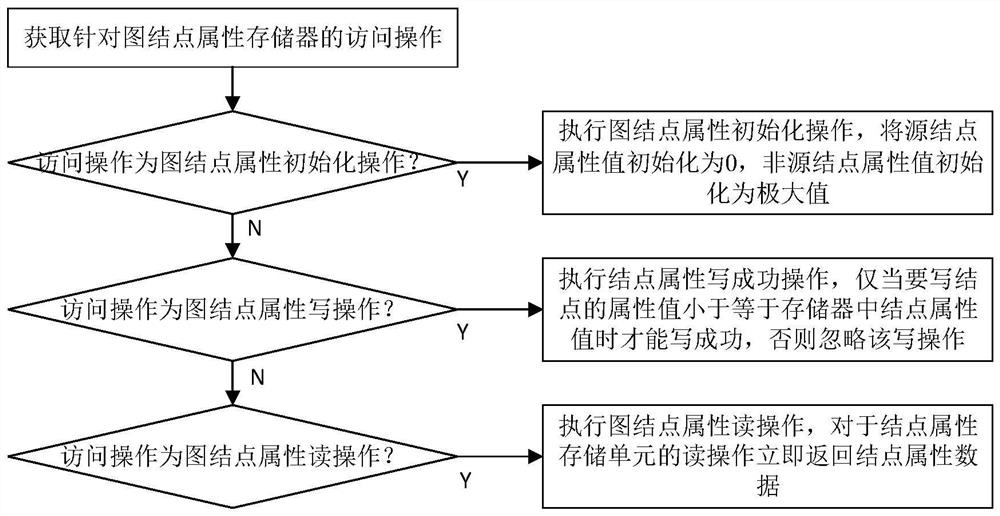
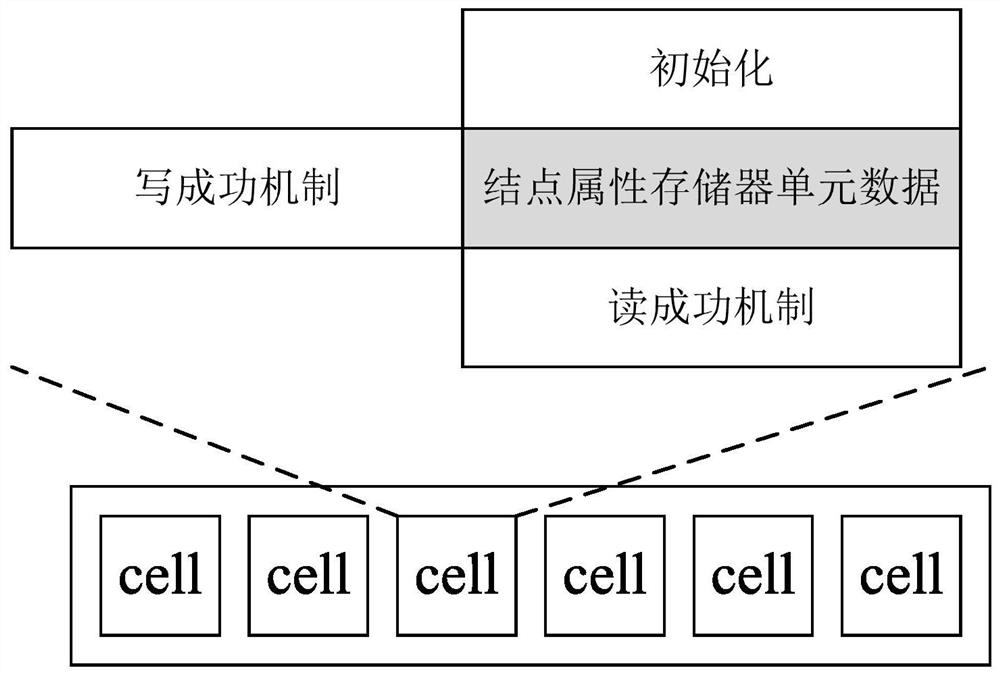
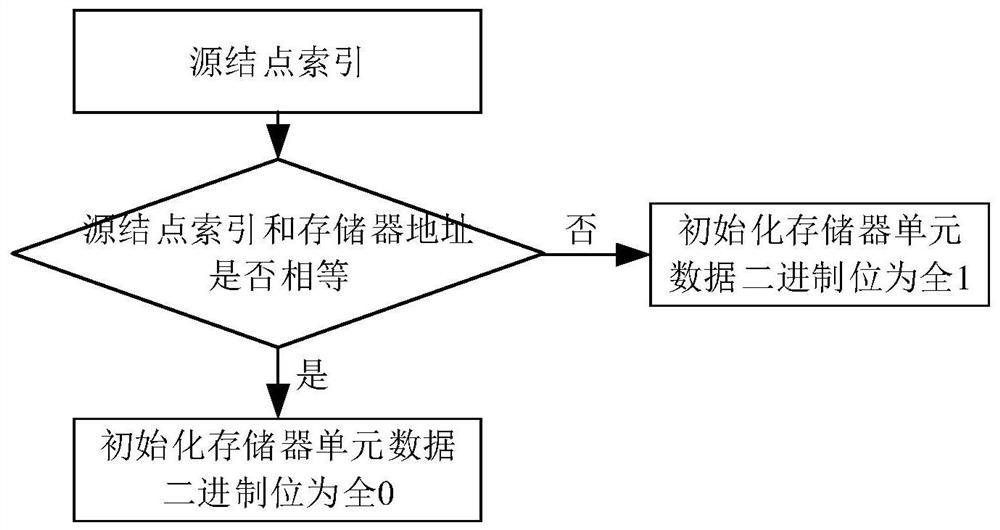
Method and device for realizing graph node attribute storage for shortest path problem
ActiveCN110647663BReduce the number of timesAdd some processing logicOther databases indexingSpecial data processing applicationsPathPingMemory cell
The invention discloses a method and device for realizing a graph node attribute memory for the shortest path problem. The graph node attribute memory of the present invention includes a plurality of graph node attribute memory units; each memory unit includes a graph node attribute Initialization, node attribute write success, read success mechanism; graph node attribute initialization, source node attribute value is initialized to 0, non-source node attribute value is initialized to positive infinity (all binary bits in the storage data area are initialized to all 1s); The node attribute writing is successful, if and only when the attribute value of the node to be written is less than or equal to the node attribute value in the memory, the writing can be successful, otherwise the write operation is ignored; the graph node attribute read, for the node attribute storage unit A read operation returns the node attribute data immediately. The present invention implements a method for realizing a graph node attribute memory for the shortest path problem, and reduces the impact of random read operations on performance.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
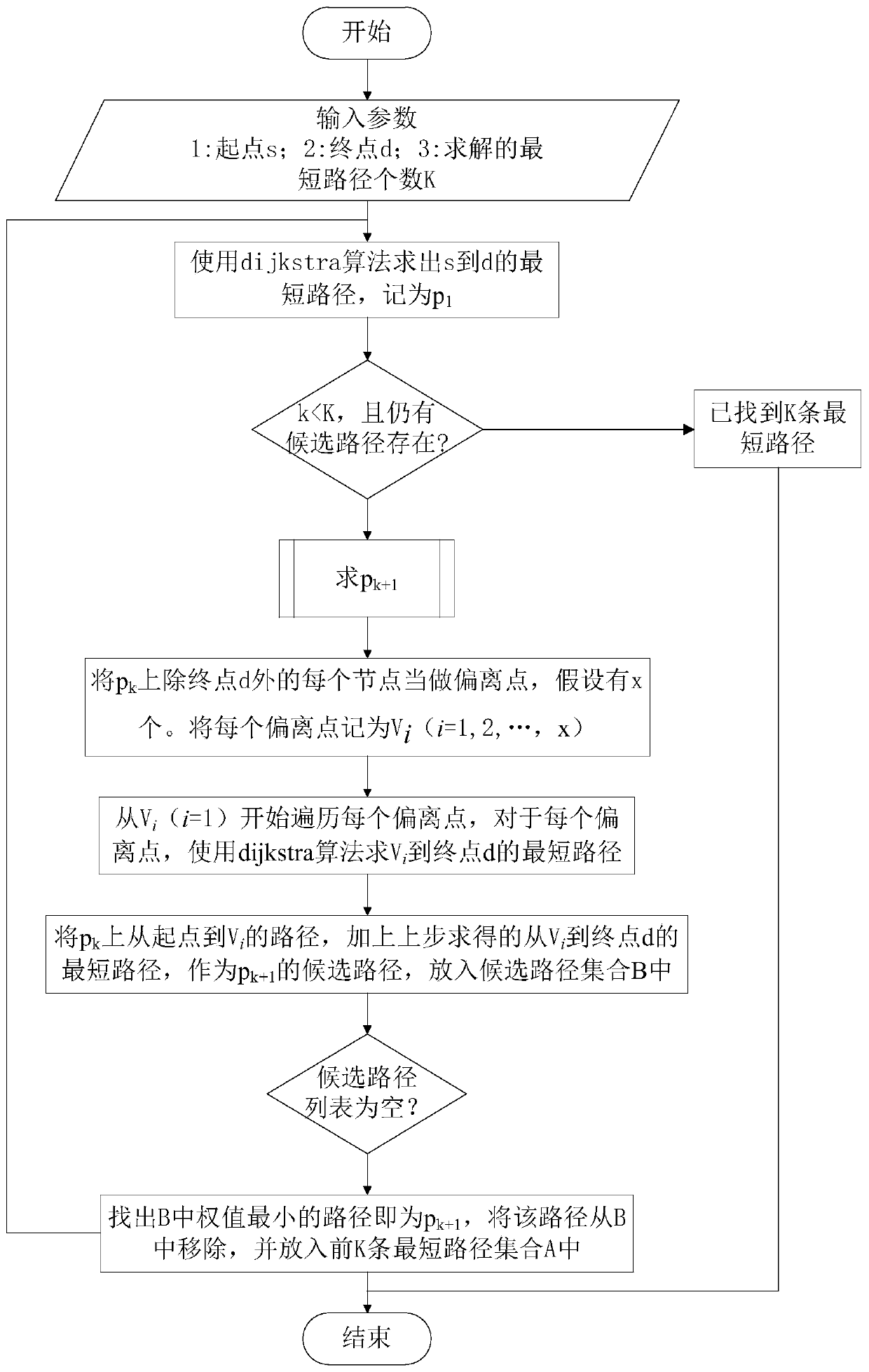
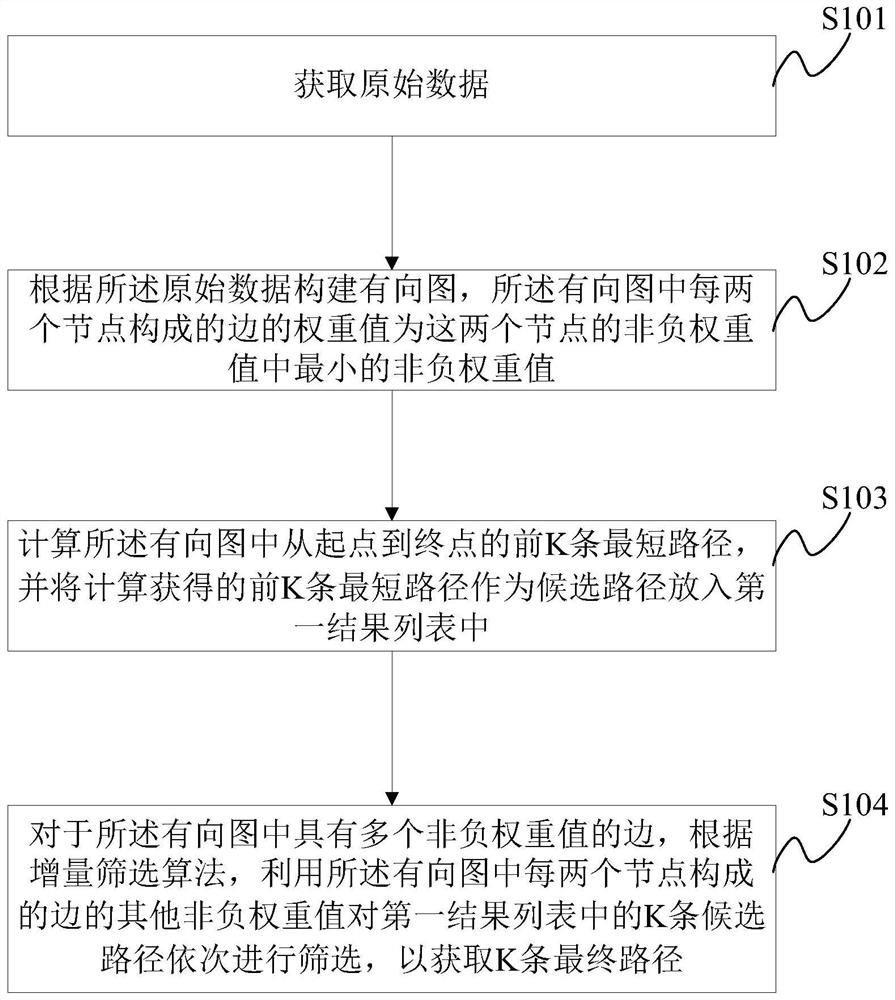
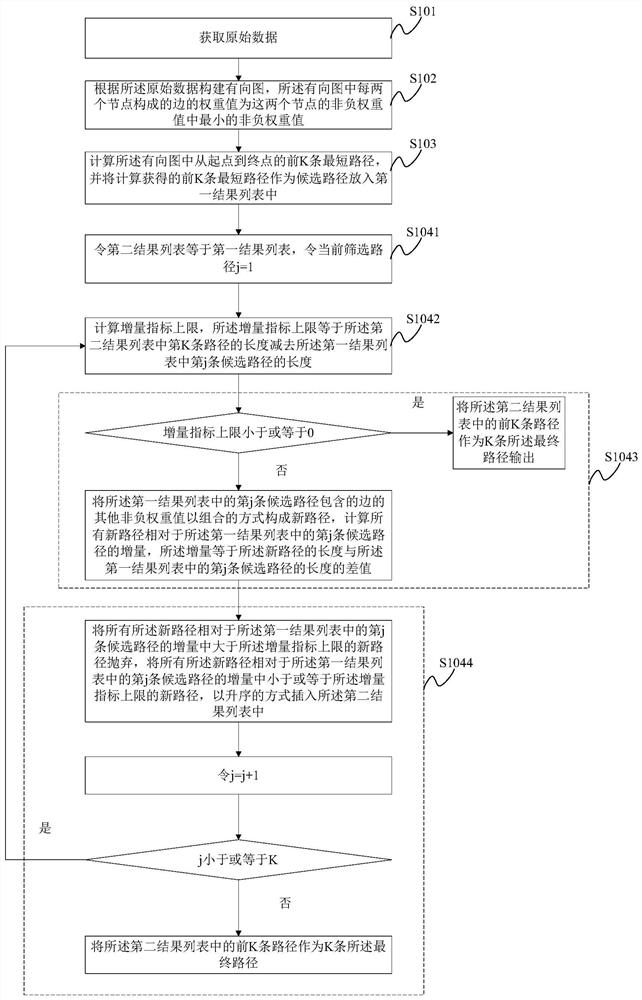
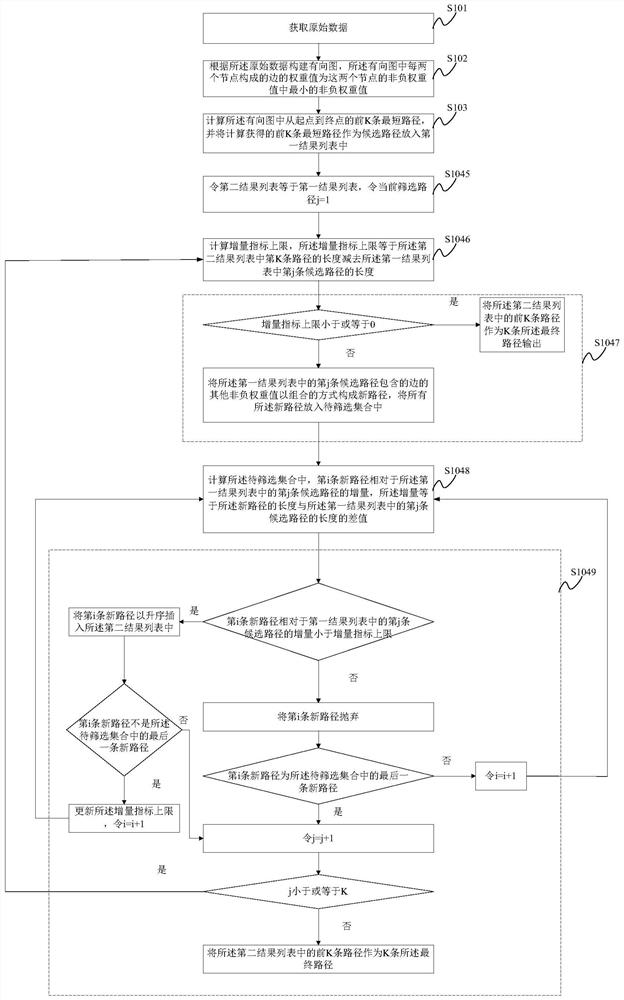
Shortest path generation method and related device
PendingCN112116136AAvoid large-scale problemsProblem Solving for Non-Negative Weight ValuesForecastingPathPingDirected graph
The invention discloses a shortest path generation method and a related device, and the method comprises the steps of simplifying a generation problem of a shortest path with a plurality of non-negative weight values of a sideband into a problem of a single non-negative weight value of the sideband; sequentially screening the K candidate paths by using other non-negative weight values of each edgein the directed graph to obtain K final paths, thereby solving the problem of multiple non-negative weight values of a sideband; according to the method, the shortest path problem of a single non-negative weight value of a sideband is restored to the shortest path problem of a plurality of non-negative weight values of the sideband through an incremental screening algorithm, virtual nodes do notneed to be introduced in the process, the problem that the scale of a graph is huge after the virtual nodes are introduced is avoided, and the purposes of reducing time complexity and improving timeliness are achieved.
Owner:SAIC MOTOR
Laser filling method and device for single-layer contour pattern based on contour lines
ActiveCN113793352AFast and accurate fillingImprove laser filling efficiencyImage analysisManufacturing computing systemsGrid patternComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a laser filling method and device for a single-layer contour pattern based on contour lines, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: performing outer contour inner offset operation on a to-be-filled pattern according to an equidistant offset algorithm to obtain a contour offset pattern; performing grid method environment modeling on the contour offset pattern to obtain a preprocessed grid pattern; aiming at the grid pattern, constructing a shortest path problem set; and solving the shortest path problem set by using an A * algorithm to obtain an optimal filling path of the grid pattern. By adopting the method, the laser filling efficiency of the pattern can be improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
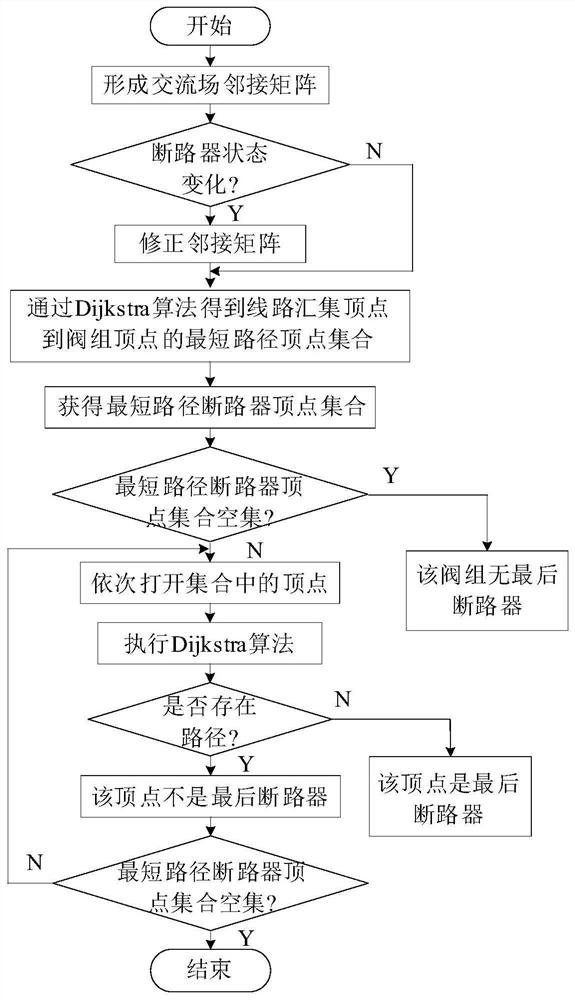
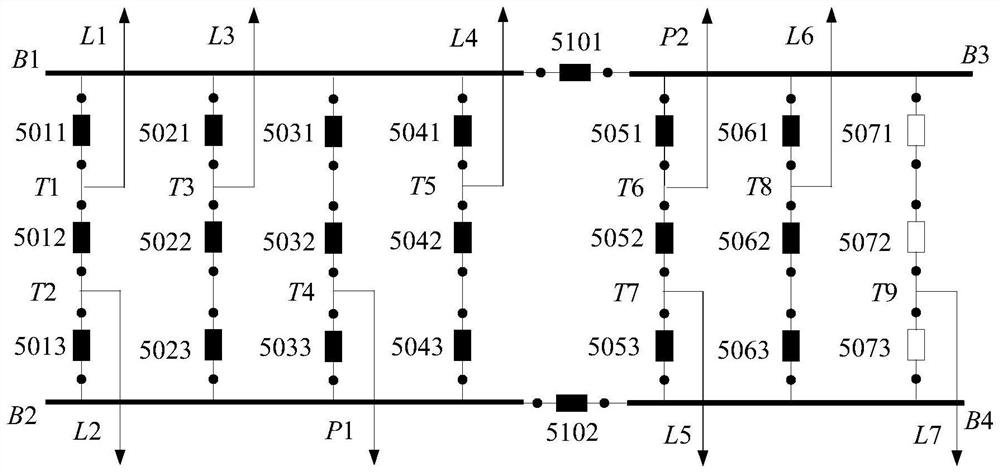
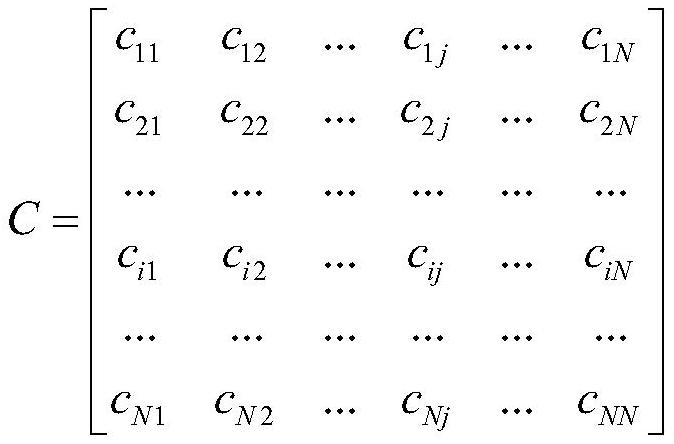
A method for identifying the last circuit breaker of valve group based on Dijkstra algorithm
ActiveCN110137911BThe identification method is simpleImprove operational efficiencyEmergency protection data processing meansComplex mathematical operationsAc fieldEngineering
The invention discloses a method for identifying the final circuit breaker of a valve group based on the Dijkstra algorithm. According to the topological structure of the AC field, it is abstracted into an undirected connected graph, and an adjacency matrix is constructed; the switching state of the circuit breaker in the AC field collected in real time is updated. Adjacency matrix, transforming the final circuit breaker judgment problem into Dijkstra algorithm to solve the problem of the shortest path from the valve group vertex to the AC line collection vertex; when a certain circuit breaker vertex on the path is set to open state, continue to search the valve group vertex to the AC line Convergence vertex, if there is a path between the valve group vertex and the AC line convergence vertex, then this vertex is the last circuit breaker; otherwise, this vertex is not the last circuit breaker. The invention is simple and effective, and can judge the last circuit breaker of the valve group in real time when the operation mode of the AC field changes, without preparing the last circuit breaker retrieval table in all operating states of the AC field in advance, and has good flexibility and versatility .
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Device for displaying road navigation track
ActiveCN100535600CSolve the distinctionSolve the problem of not getting the correct shortest pathInstruments for road network navigationTransceiverEngineering
Owner:XIAMEN YAXON NETWORKS CO LTD
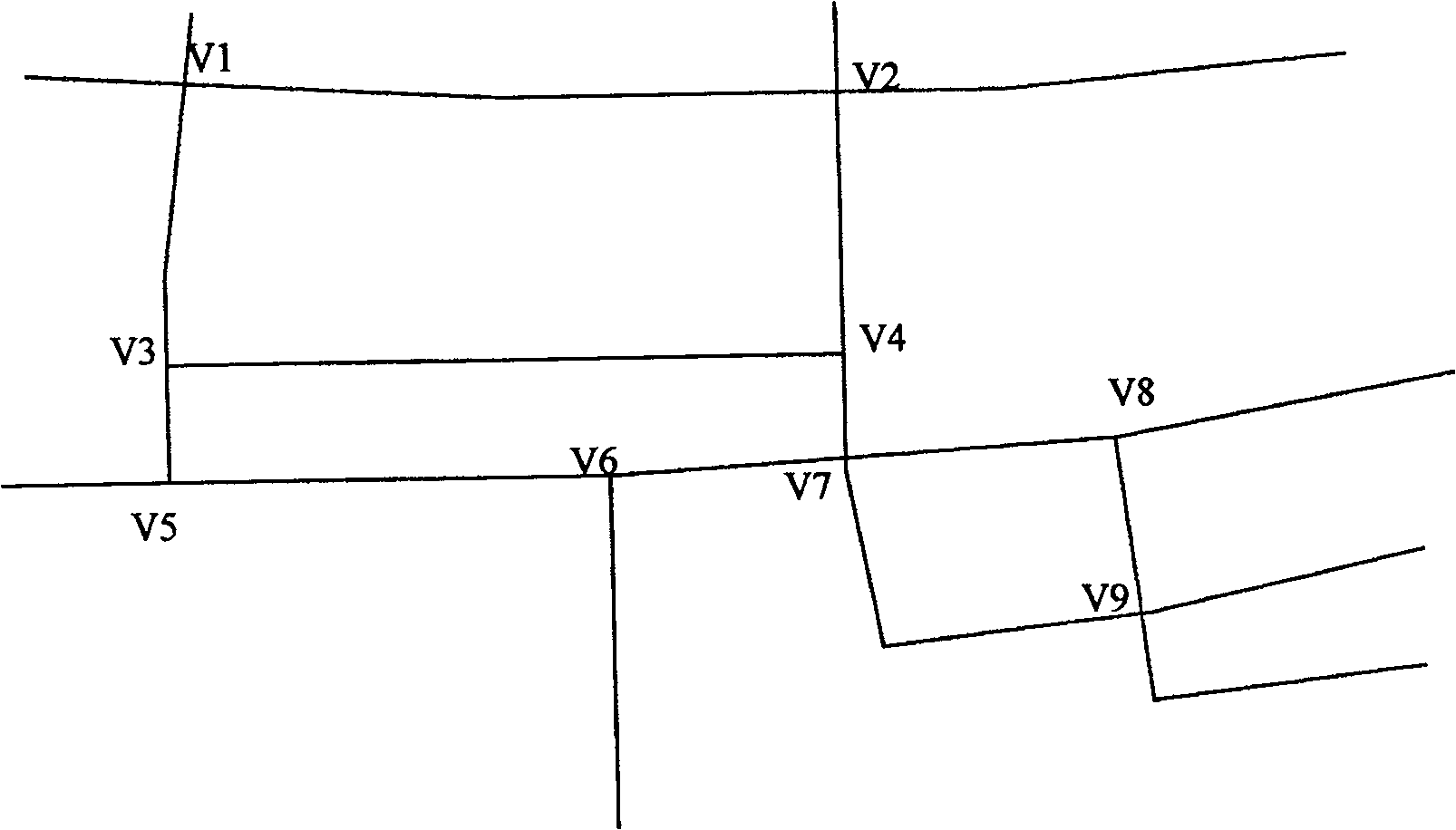
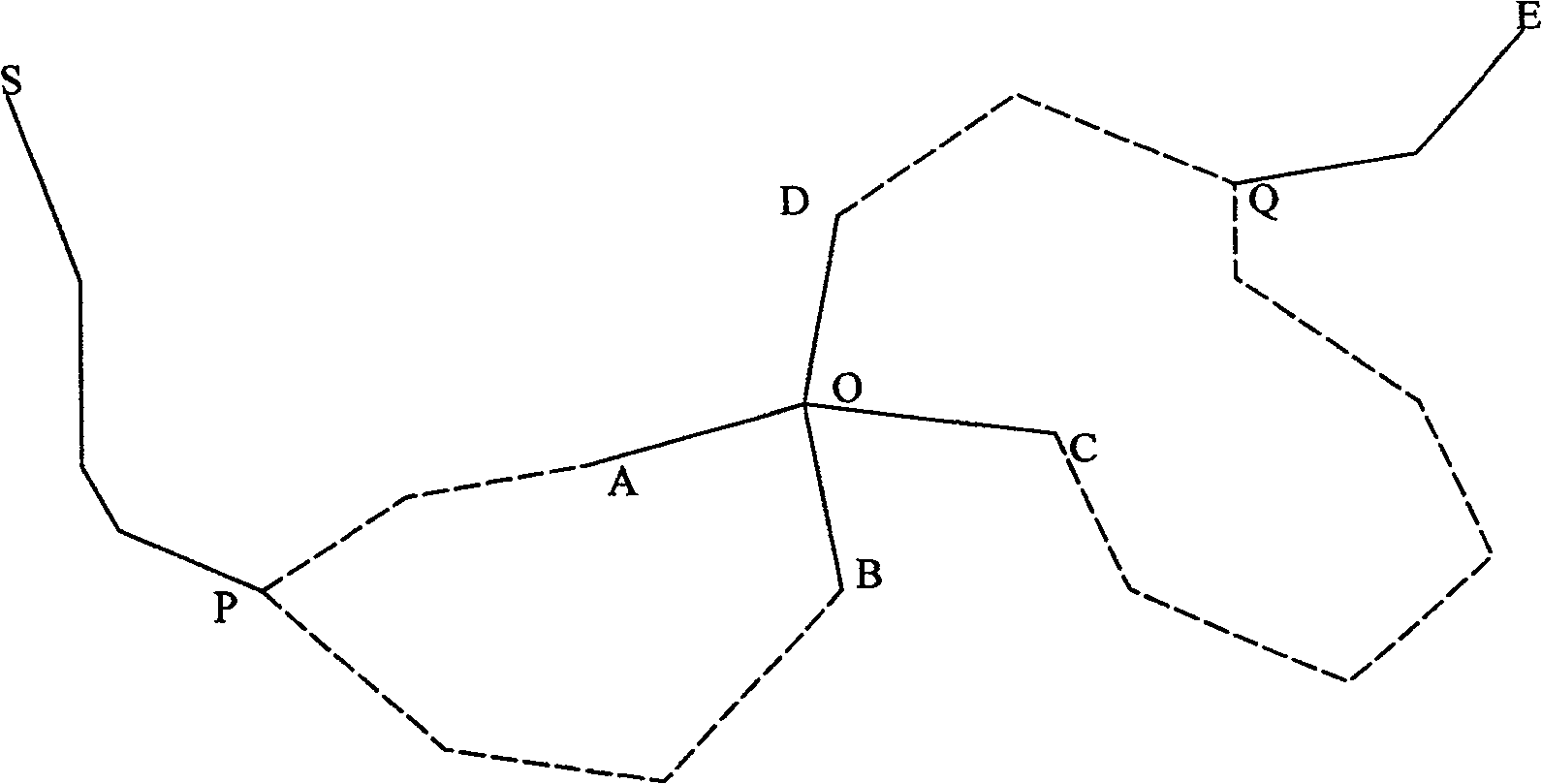
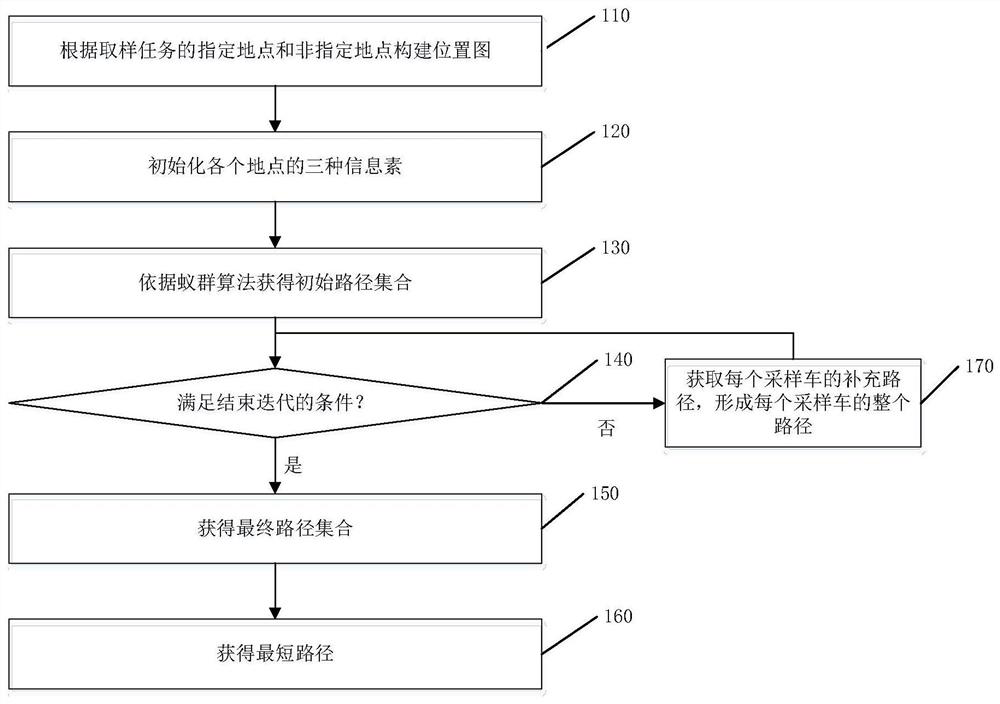
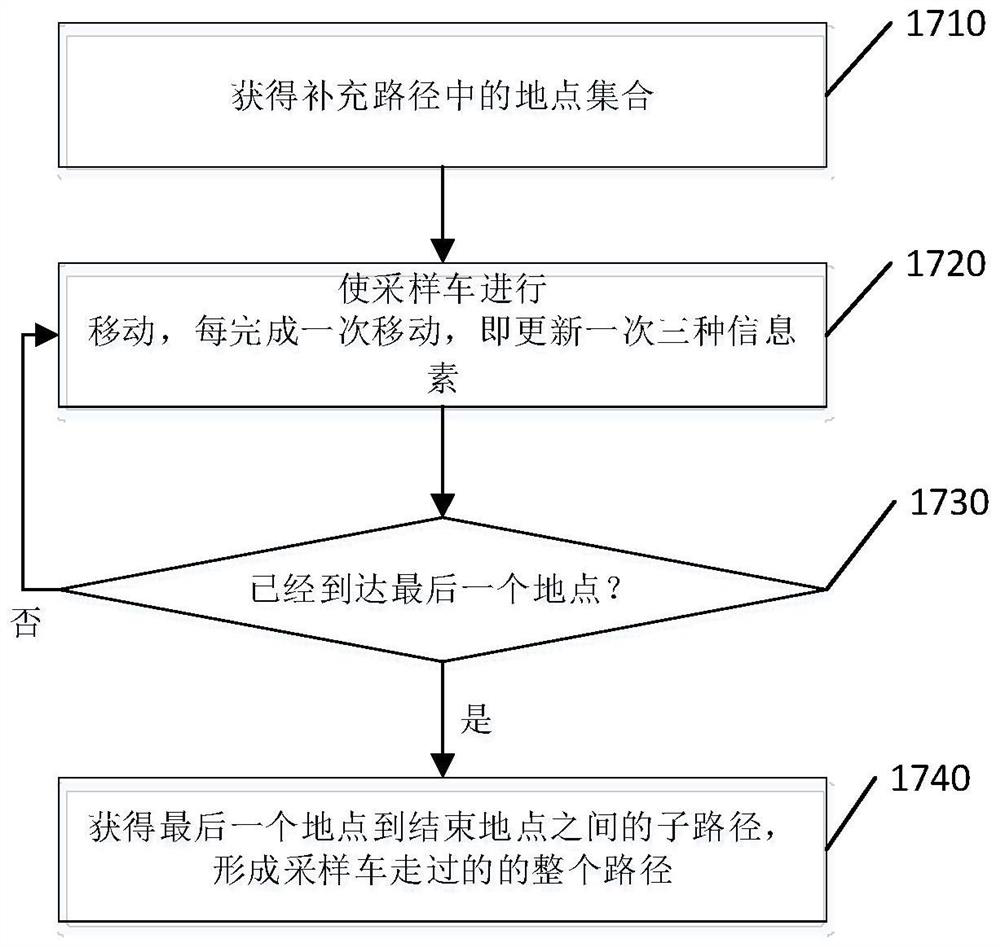
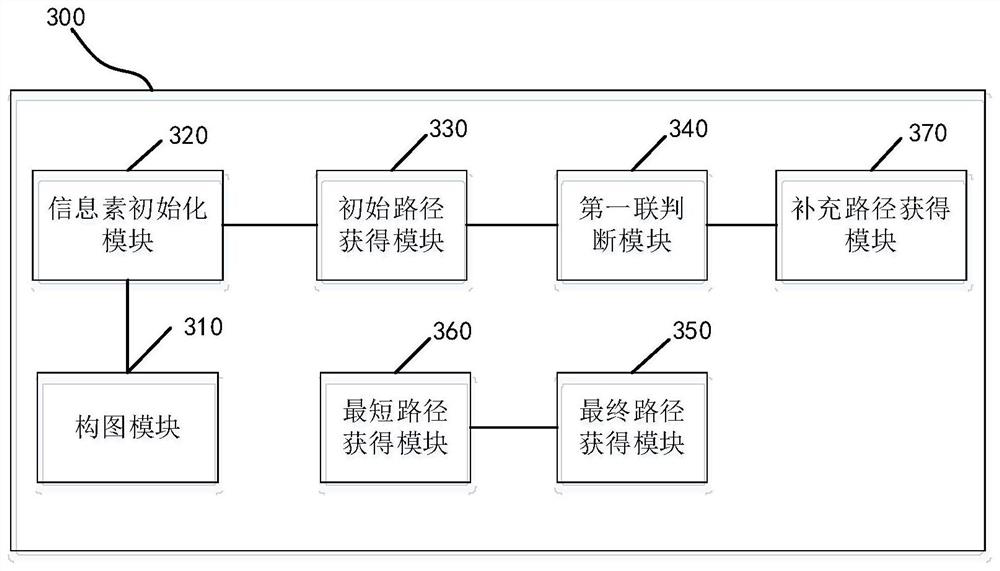
A method and system for obtaining the shortest path for sampling
The present application provides a method and system for obtaining the shortest path for sampling, the method includes: constructing a location map according to the sampling task; initializing the three pheromones at each location; The supplementary path of each sampled car forms the entire path of each sampled car until the condition for ending the iteration is met; the collection of the entire paths of all sampled cars is used as the final path set; the shortest path is obtained from the final path set. The addition of location pheromones and path pheromones in this application has changed the problem that the traditional ant colony algorithm cannot handle the shortest path through a designated location.
Owner:CHINA NAT ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com