Traffic shortest reliable path method driven by random GIS network
A network-driven, path technology, applied in the field of GIS traffic shortest reliable path, random GIS network-driven traffic shortest reliable path, can solve the shortest reliable path availability, poor accuracy and reliability, high algorithm time complexity and space complexity, Computational redundancy and other issues to achieve the effect of strengthening reliability and availability, promoting development and popularization, and ensuring traffic safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
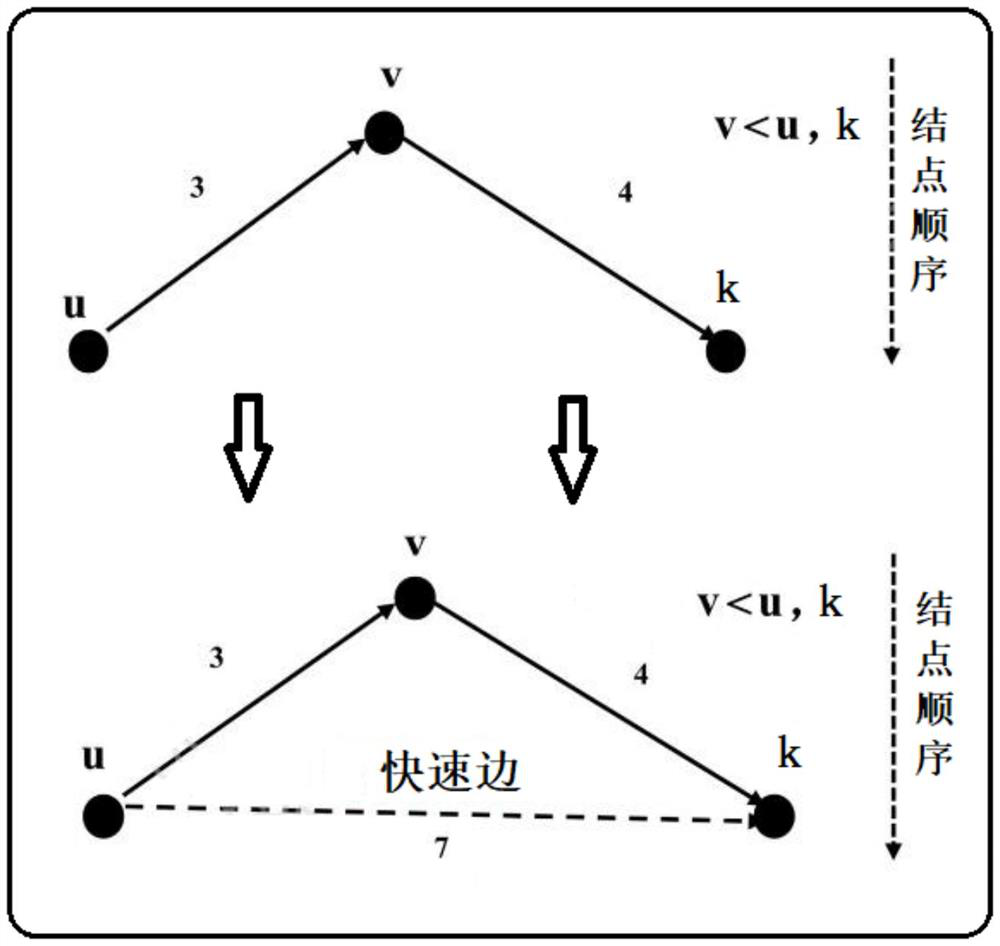
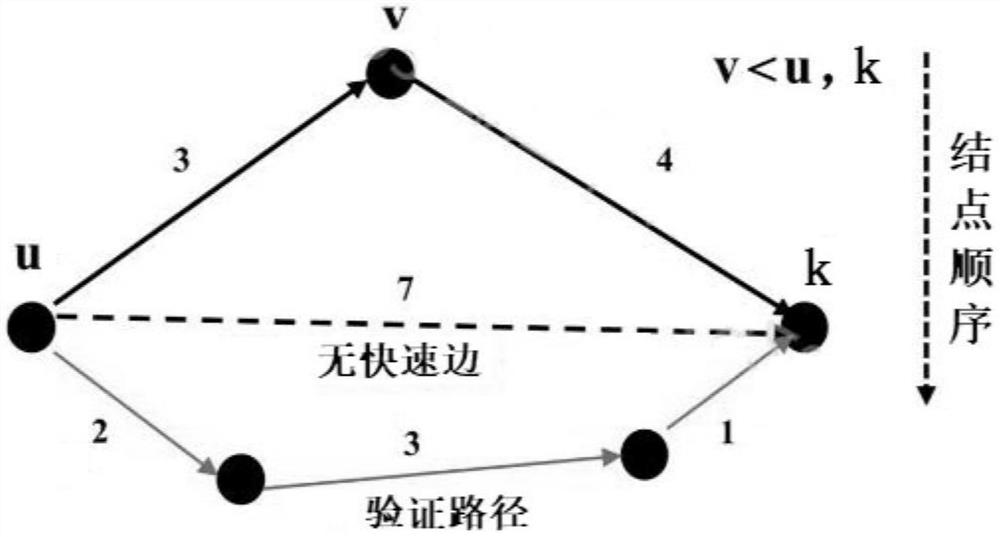
[0101] The following is a further description of the technical solution of the random GIS network-driven traffic shortest reliable route method provided by the application in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the application and implement it.
[0102] The shortest path problem and traffic N shortest path problem in the prior art are scenarios that consider the determination of travel time. However, in a congested urban traffic network, the travel time is highly uncertain, and the traveler has an uncertain travel time. It is more inclined to choose the path with high reliability, that is, the shortest reliable path. This application proposes a solution to the shortest reliable path problem and the shortest reliable path expansion problem in a random traffic network. By reducing the scale of the shortest reliable path calculation, it can efficiently find the shortest reliable path in a large-scale GIS traffic networ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com