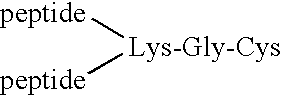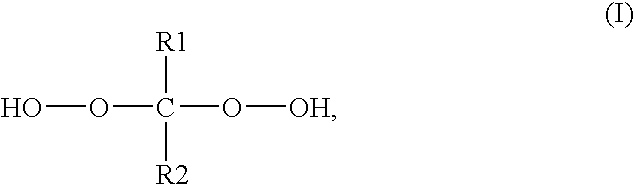Patents
Literature
98 results about "Sheep prion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Prions composed of the prion protein (PrP) are hypothesized as the cause of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), including scrapie in sheep and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cattle—known popularly as "mad cow disease".
Active immunization of AScr for prion disorders
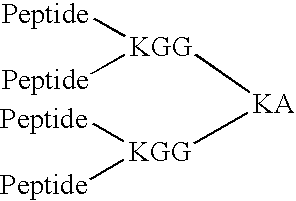
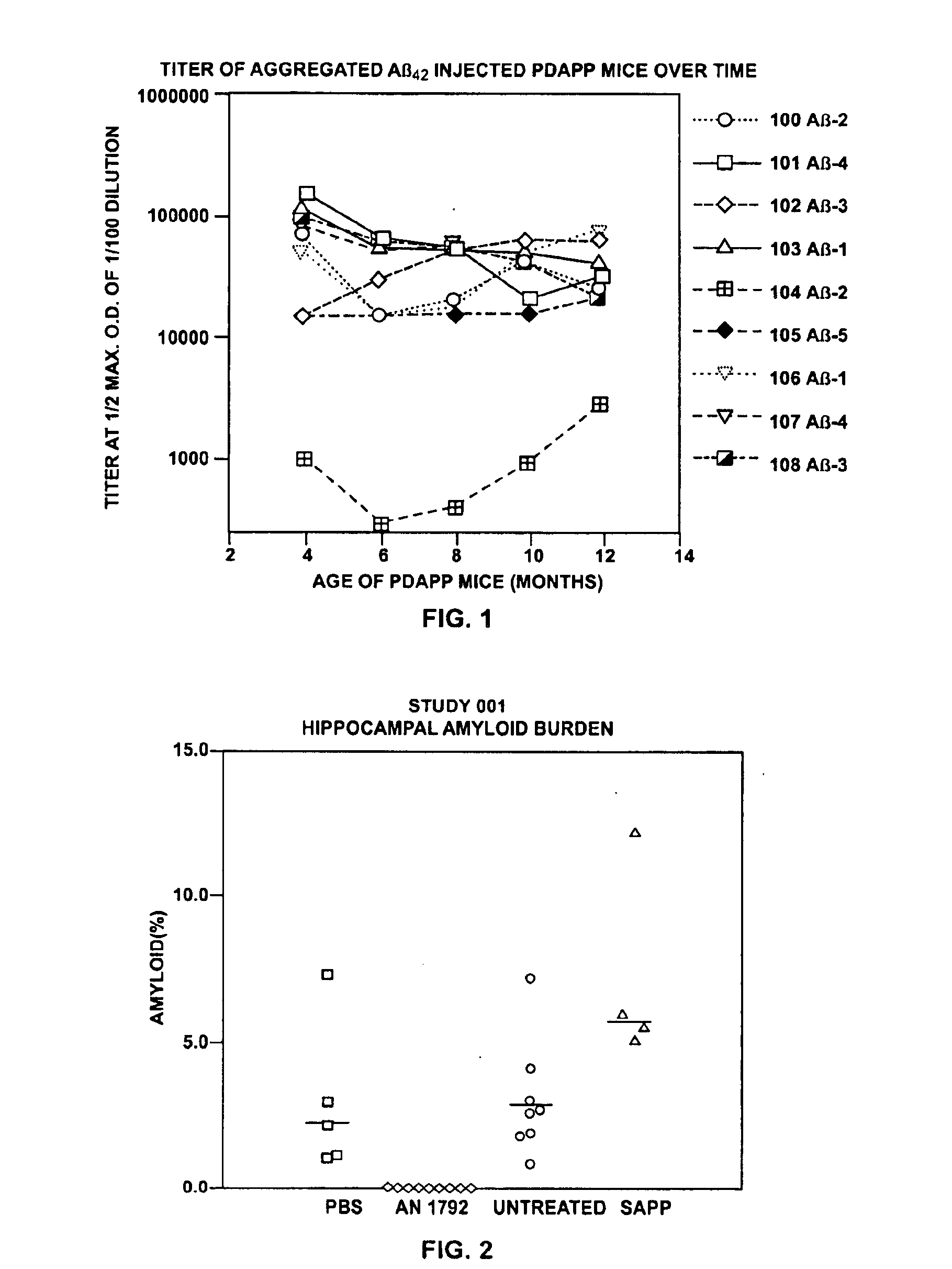
Disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods for preventing or treating a number of amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, prion diseases, familial amyloid neuropathies and the like. The pharmaceutical compositions include immunologically reactive amounts of amyloid fibril components, particularly fibril-forming peptides or proteins. Also disclosed are therapeutic compositions and methods which use immune reagents that react with such fibril components.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Method for fixing tissue
A method of preparing a fixed biological tissue includes, shaping the biological tissue, cross-linking the biological tissue, sterilizing the biological tissue, and inactivating prions in the biological tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Immunological detection of prions
The presented invention relates to monoclonal antibodies useful in sensitive and specific immunological assays for the identification of prions in various tissues and body fluids, the production of such monoclonal antibodies by means of immunization of PrP<0 / 0 >mice by means of a new recombinant fragment of PrP and the use of the antibodies, e.g. for therapeutic and preventive treatments of humans and animals suffering from prion diseases.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Coatings
ActiveUS20060150862A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCoated surfaceMedicine
This invention relates to coating a surface wherein the coated surface inhibits foulants such as cell and / or protein and / or prion adhesion or formation. In particular, the coated surface may be part of a medical device which inhibits bacterial adhesion and colonisation, thrombus formation and / or prion, blood protein and / or protein formation.
Owner:DUNDEE UNIV OF THE UNIV COURT OF THE
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for gnrh-II and gnrh-II modulation of t-cell activity, adhesion, migration and extravasation
Methods and compositions comprising GnRH-I and GnRH-II, GnRH-I and GnRH-II antibodies, anti-receptor antibodies, polynucleotide constructs and GnRH-I and GnRH-II analogs for immune enhancement and suppression, prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions characterized by abnormal T-cell activity, treatment of viral and prion-related diseases, and treatment of T-cell related neoplastic diseases are disclosed.
Owner:KOCH YITZHAK PROF +1
Device and method of use for detection and characterization of pathogens and biological materials
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for the detection of a target material. The method and apparatus includes providing a substrate with a surface and forming a domains of deposited materials thereon. The deposited material can be placed on the surface and bound directly and non-specifically to the surface, or it may be specifically or non-specifically bound to the surface. The deposited material has an affinity for a specific target material. The domains thus created are termed affinity domains or deposition domains. Multiple affinity domains of deposited materials can be deposited on a single surface, creating a plurality of specific binding affinity domains for a plurality of target materials. Target materials may include, for example, pathogens or pathogenic markers such as viruses, bacteria, bacterial spores, parasites, prions, fungi, mold or pollen spores. The device thus created is incubated with a test solution, gas or other supporting environment suspected of containing one or more of the target materials. Specific binding interactions between the target materials and a particular affinity domain occurs and is detected by various methods.
Owner:BIOFORCE NANOSCI
Prion protein binding materials and methods of use
ActiveUS7510848B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHamsterProteinaceous infectious particle
Prion protein binding materials and methods for using the binding materials to detect or remove a prion protein from a sample, such as a biological fluid or an environmental sample. The binding materials are capable of binding to one or more forms of prion protein including cellular prion protein (PrPc), infectious prion protein (PrPsc), recombinant prion protein (PrPr), and proteinase resistant prion protein (PrPres). Prions from various species, including humans and hamsters, are bound by the binding materials.
Owner:PATHOGEN REMOVAL & DIAGNOSTIC TECH +1
Prion-specific peptide reagents
InactiveUS20050118645A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinaceous infectious particleAntibody
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Methods of sterilizing biological mixtures using stabilizer mixtures
InactiveUS20050106728A1Reducing residual solvent contentEffective protectionBiocideDead animal preservationFungal microorganismsBiological materials
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing biological materials to reduce the level of one or more biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, single or multicellular parasites, and / or prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs. These methods involve the use of stabilizer mixtures in methods of sterilizing biological materials with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Assay for Prions
InactiveUS20130196356A1Avoid treatmentPrevent steppingDisease diagnosisBiological testingBovine serum albuminUrine production
The invention relates to a method for detection of abnormal PrP in a sample of blood or urine, said method comprising: (a) diluting the sample with buffer to comprise final concentrations of (i) 10 mM to 500 mM buffer agent; (ii) 1% to 10% w / v bovine serum albumin; and (iii) 1% to 8% w / v CHAPS; (b) adding steel particles and incubating to allow PrP binding; (c) washing the steel particles to remove diluted sample; and (d) detecting abnormal PrP captured on the steel particles using antibody capable of binding said abnormal PrP. The invention also provides compositions and kits.
Owner:D GEN
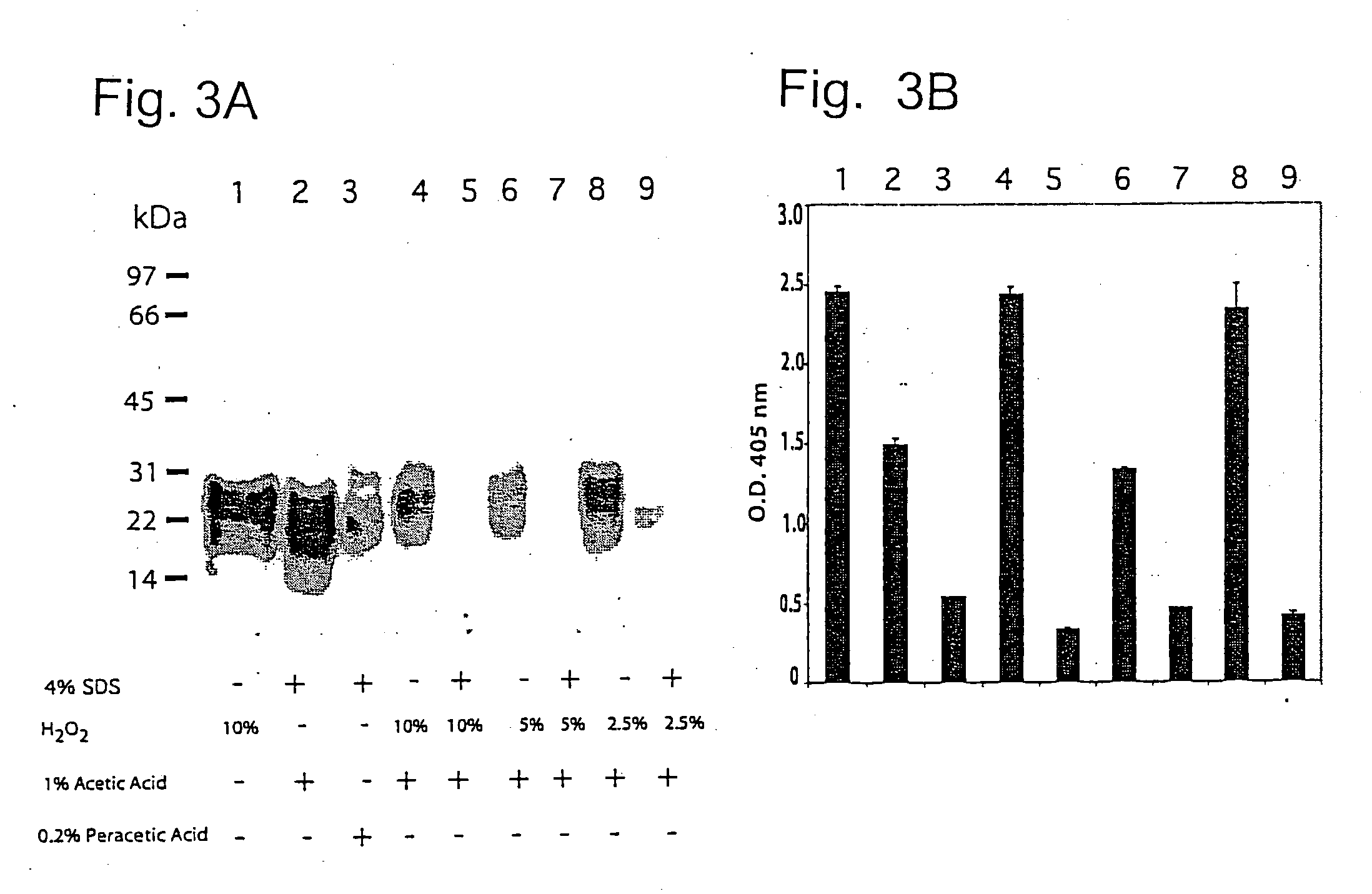
Complete inactivation of infectious proteins
InactiveUS20060008494A1Short timeInactivate the infectivity of the proteinBiocideDead animal preservationEthylic acidSolvent
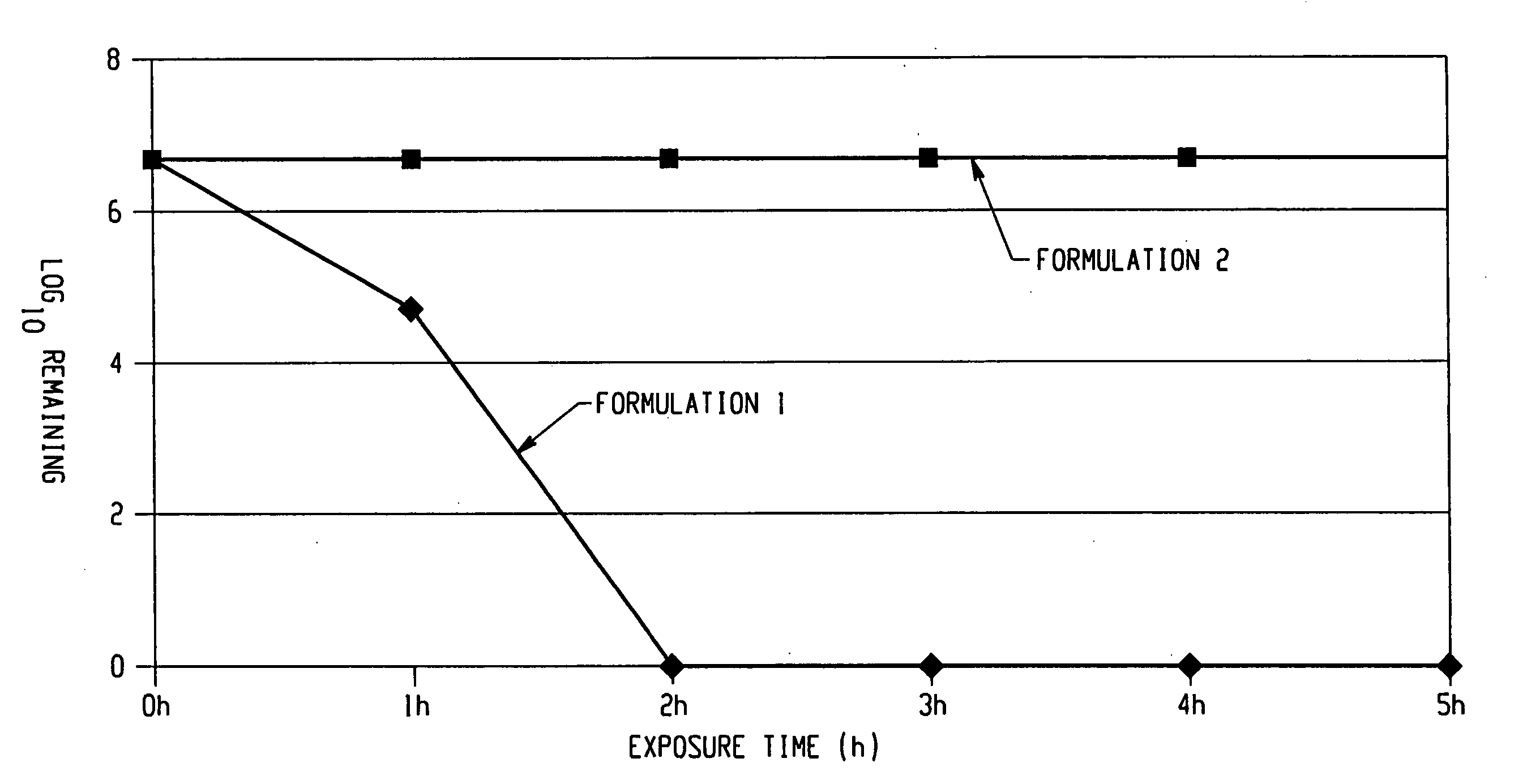
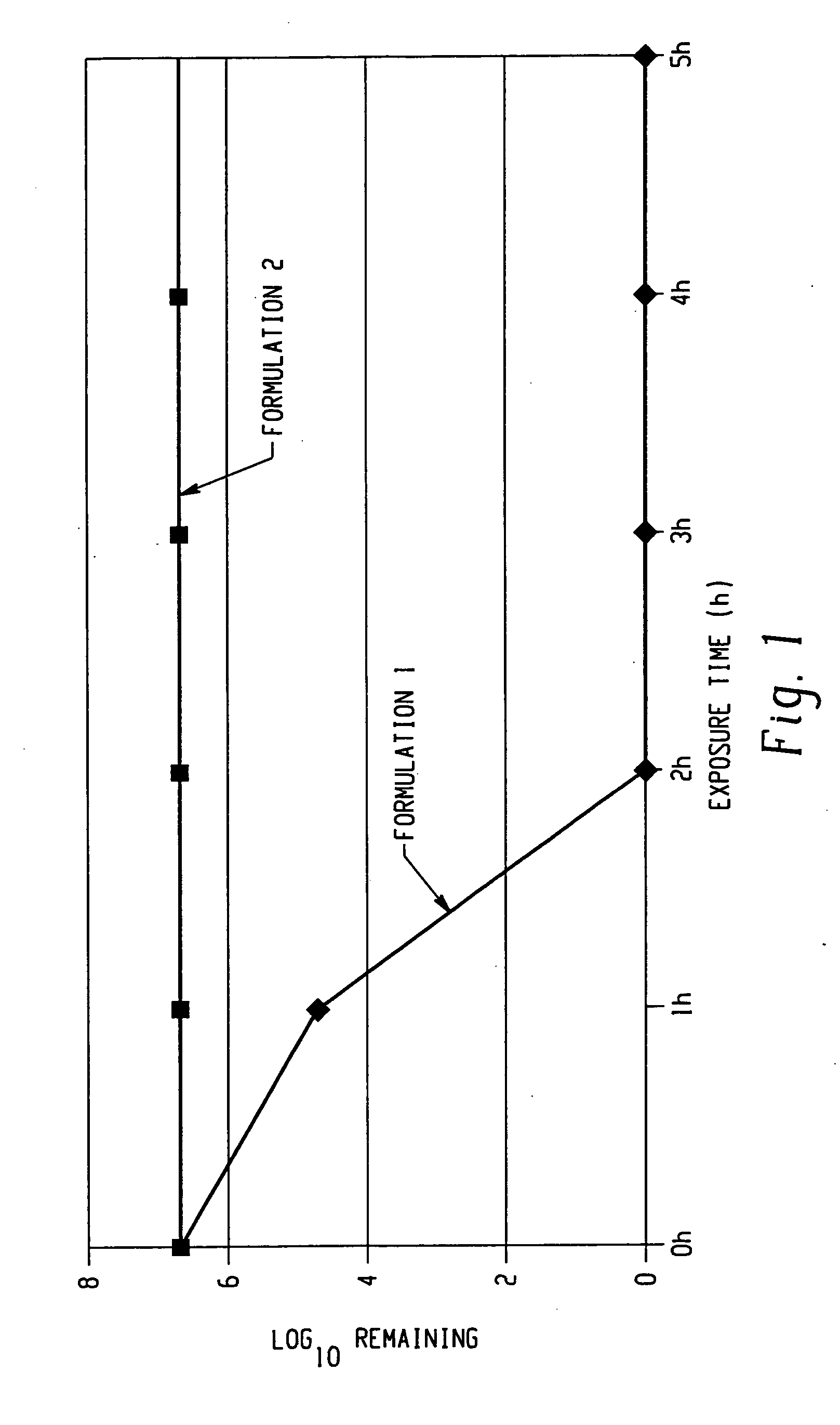
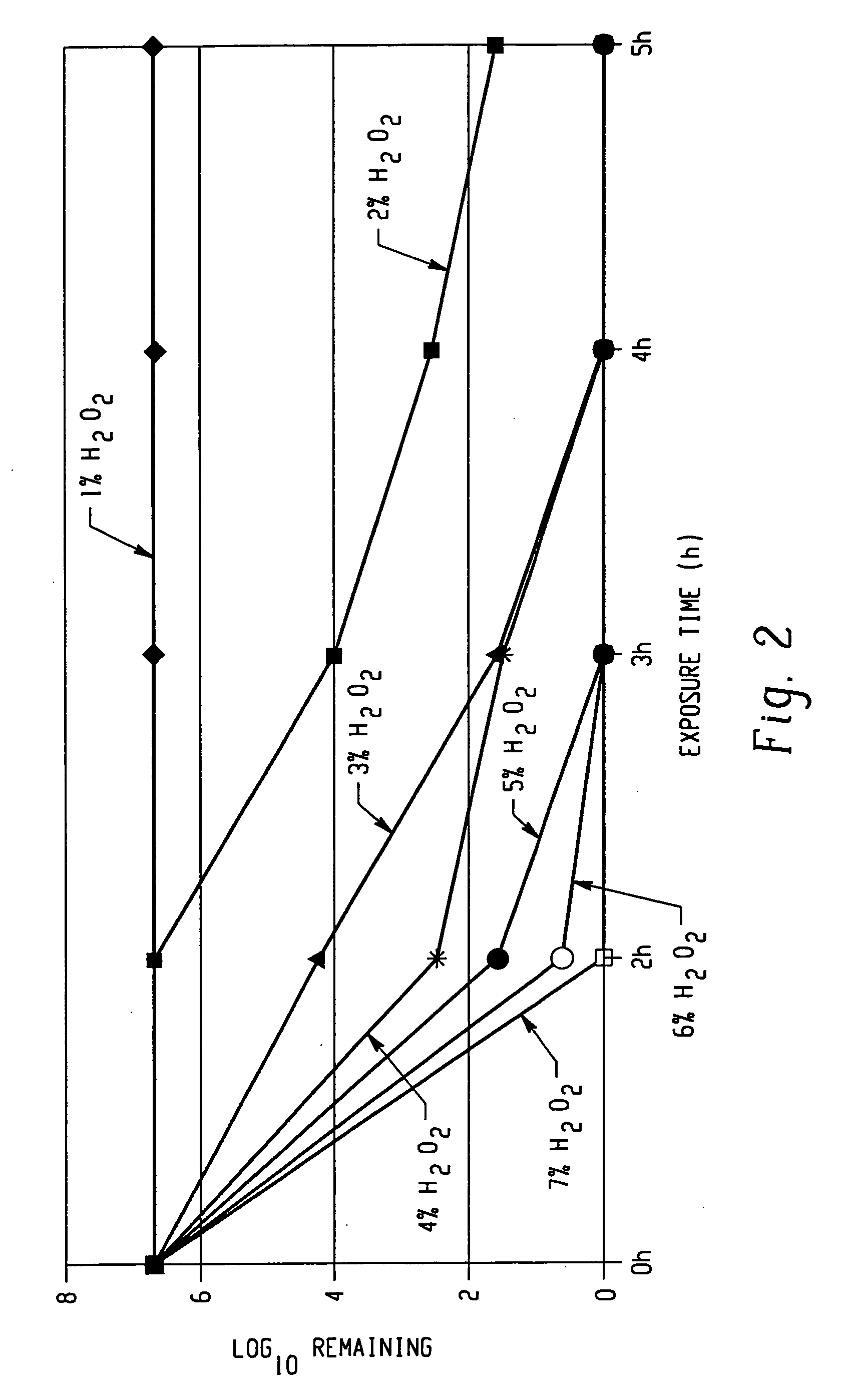
The invention comprises a formulation and a method which uses the formulation. The formulation is comprised of an aqueous or alcohol solvent having therein (1) a detergent such as SDS; (2) a weak acid such as acetic acid; and (3) a chemical modification reagent such as hydrogen peroxide. The formulation can be modified to substitute other detergents for the SDS, other acids for the acetic acid and other oxidants for the peroxide provided the substitute results in a total formulation which completely inactivates the infectivity of infectious proteins such as prions in a relatively short period of time (e.g. less than two hours) and under relatively mild temperatures (e.g. 60° C. or less).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
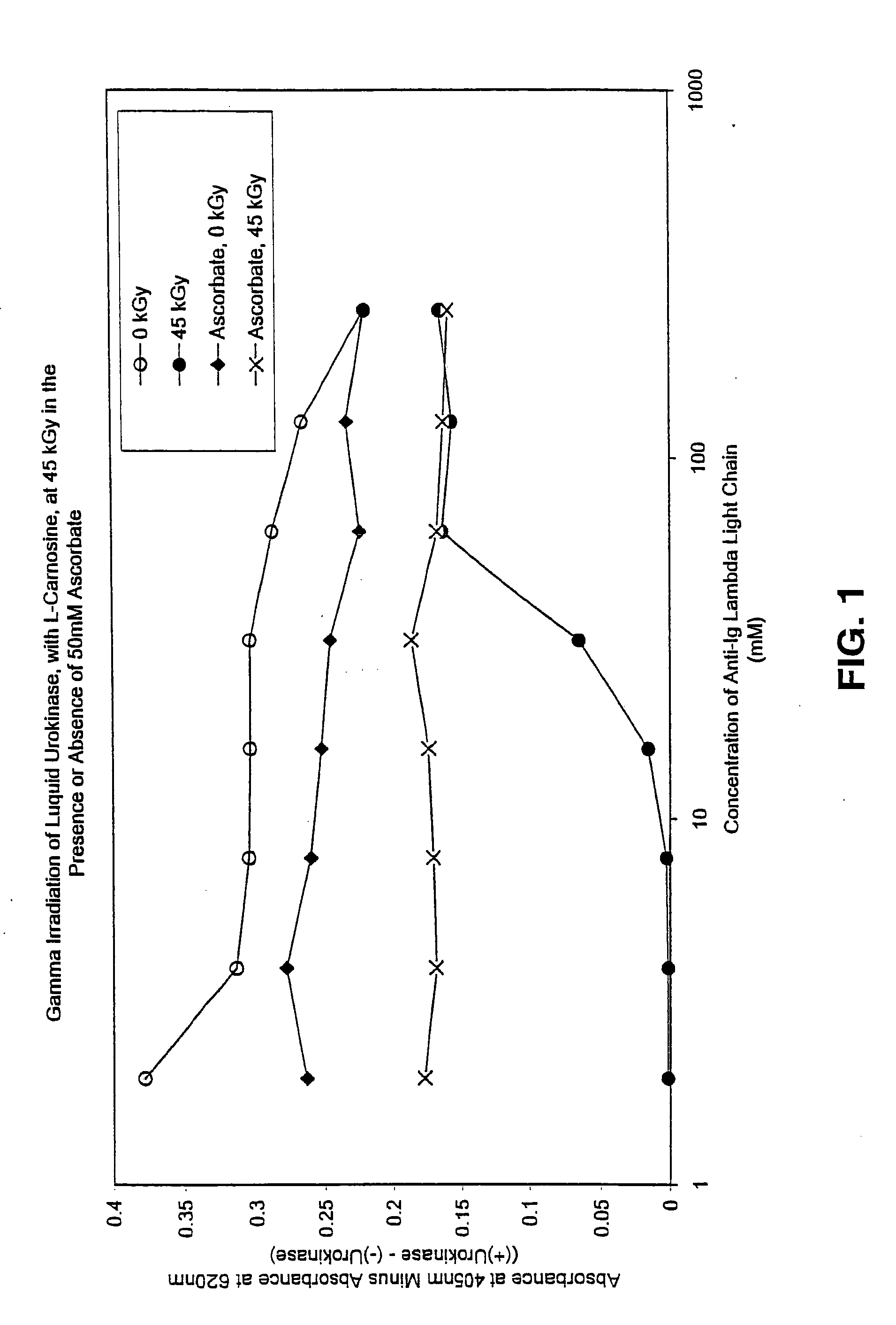
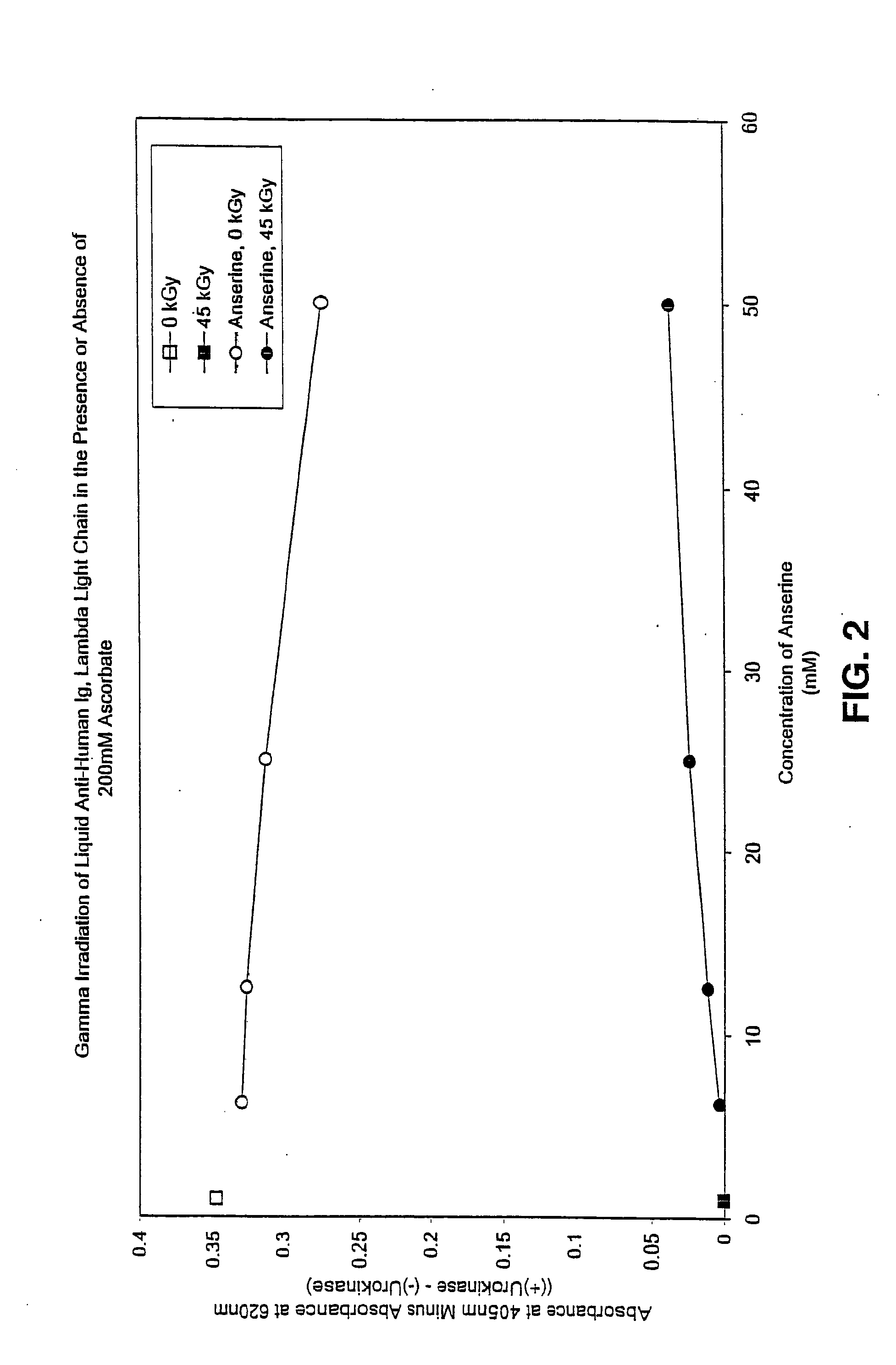
Methods for sterilizing preparations of urokinase
InactiveUS20050069453A1Effective sterilizationAvoid radiationLavatory sanitoryEnzymesUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorFungal microorganisms
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing preparations of urokinase to reduce the level therein of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia and rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, single or multicellular parasites, and prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs. These methods involve sterilizing preparations of urokinase with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Methods and composition for treating a material
ActiveUS20090324514A1Unprecedented speedUnprecedented economyBiocideCosmetic preparationsMicroorganismCompound (substance)
A composition and method are described for sanitizing or otherwise treating a material such as a non-living surface, living tissue, soil or atmosphere which may be contaminated by a toxin, chemical warfare agent, insect, prion, microorganism or other infectious agent. The composition generally includes an aqueous composition mixture that includes: (a) lower alkanol; (b) an alkalinating agent, and (c) a fatty acid salt and / or ester. The components are present in an effective amount to sanitize (or treat) a material (or modifying a chemical contained thereon) to which the composition is applied. Also described are methods of making the composition.
Owner:URTHTECH
Genomic editing of prion disorder-related genes in animals
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences encoding proteins that are associated with cognitive disorders. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. Also provided are methods of using the genetically modified animals or cells disclosed herein to screen agents for toxicity and other effects.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Epitope protection assay and method for detecting protein conformations
InactiveUS20070003977A1Simple methodNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeProteinaceous infectious particle
The invention relates to an epitope protection assay for use in diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic intervention in diseases, for example, involving polypeptide aggregation, such as prion infections. The methods of the invention first block accessible polypeptide target epitope with a blocking agent. After denaturation of the polypeptide, a detecting agent is used to detect protein with target epitope that was inaccessible during contact with the blocking agent.
Owner:AMORFIX LIFE SCI
Prion-specific peptide reagents
InactiveUS7439041B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseProteinaceous infectious particle
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Early diagnosis of conformational diseases
InactiveUS7351526B2Increase the number ofEasy to adaptPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnosis earlyProteinaceous infectious particle
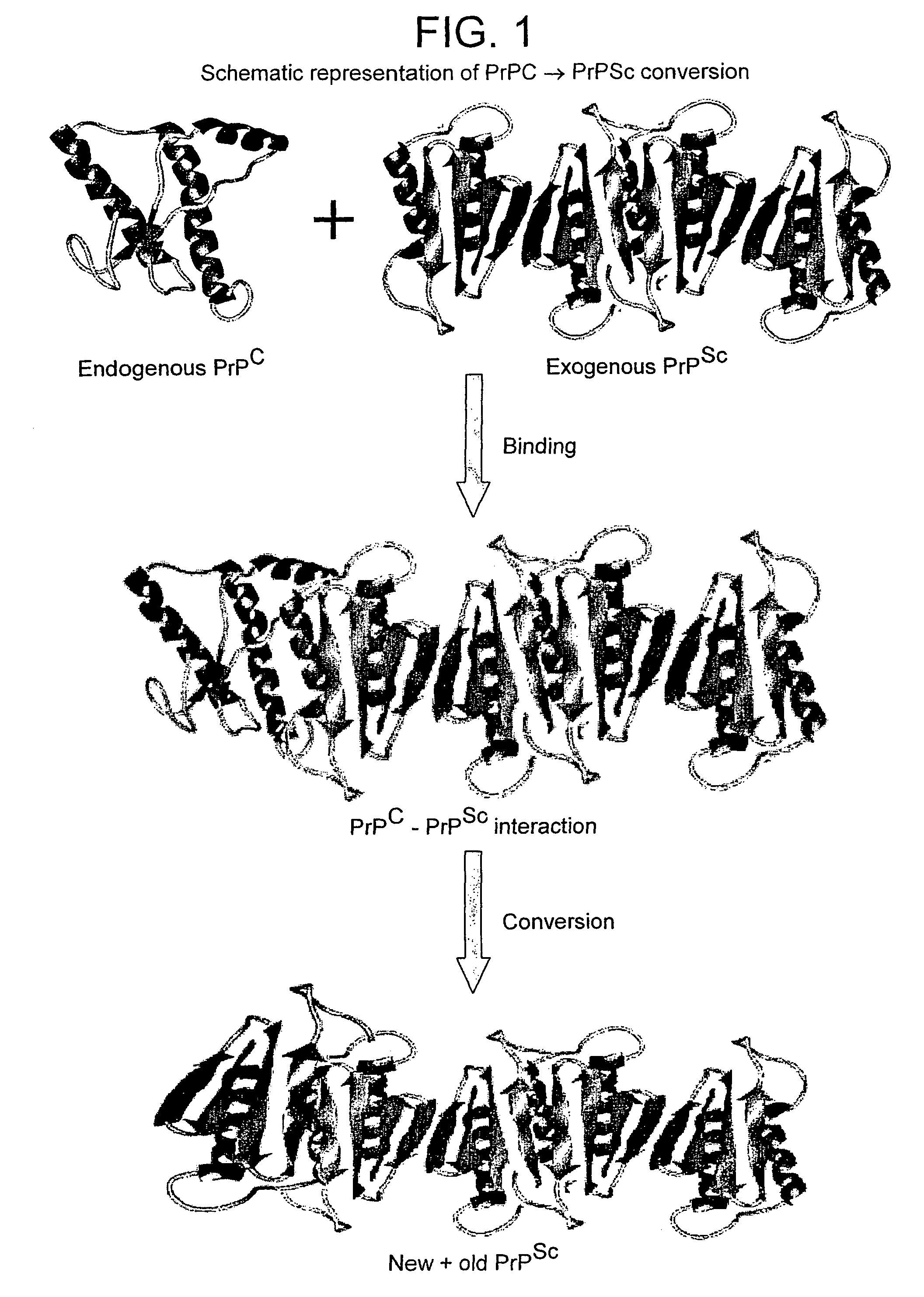
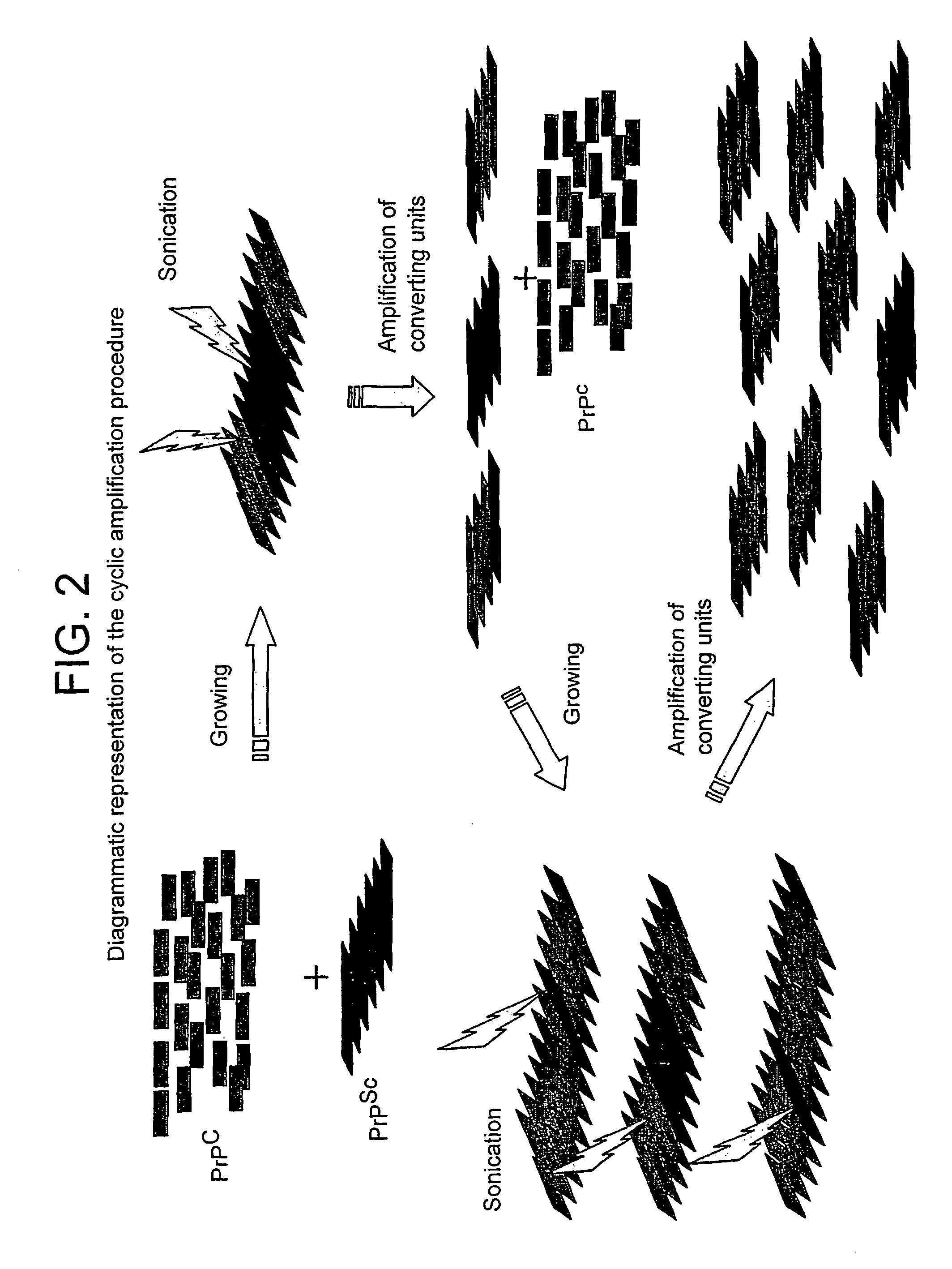
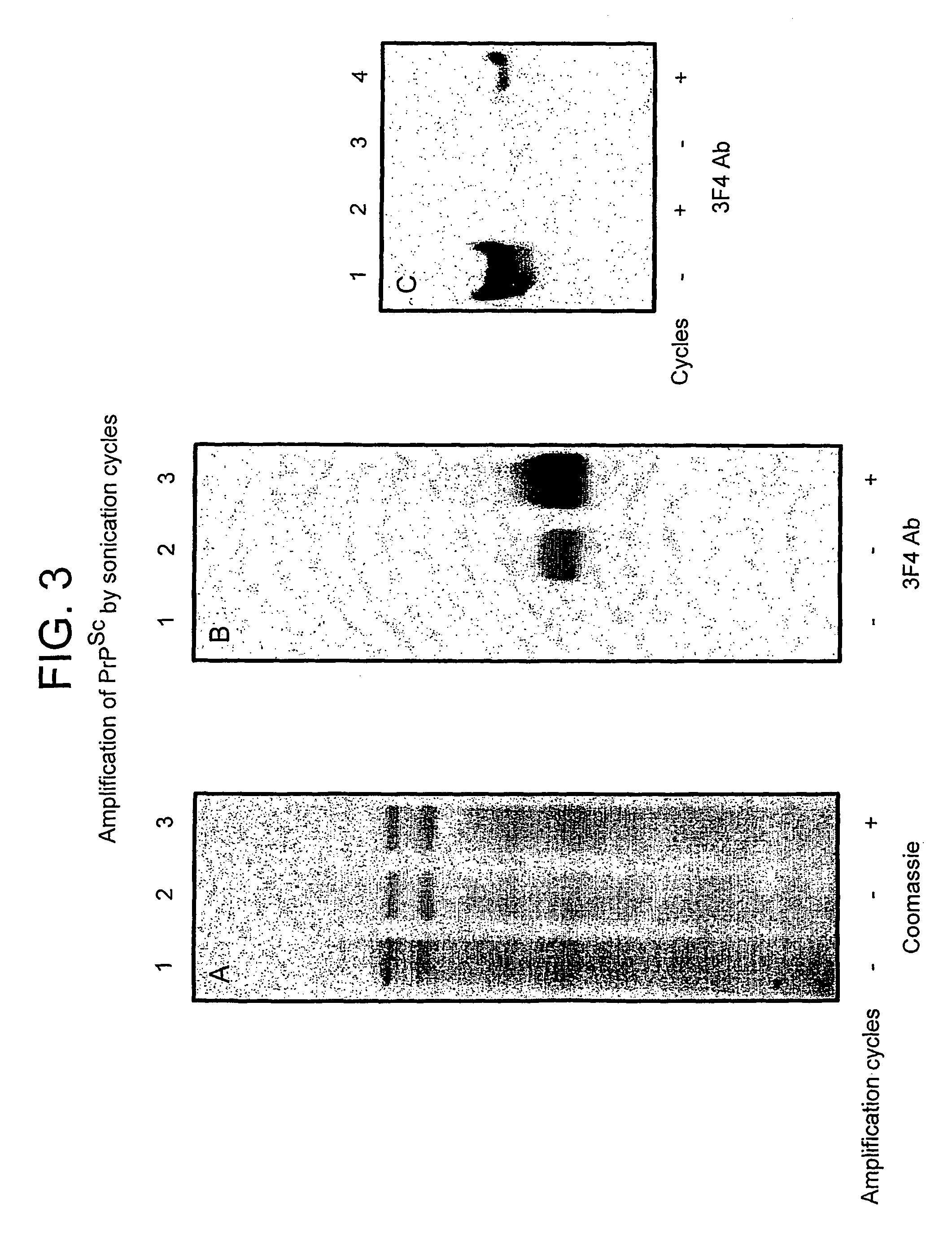
A method for the diagnosis or detection of conformational diseases by assaying for a marker (the pathogenic conformer) of such diseases in a sample is described, which method comprises a cyclic amplification system to increase the levels of the pathogenic conformer which causes such diseases. In particular, such transmissible conformational diseases may be prion encephalopathies. Assays, diagnostic kits and apparatus based on such methods are also disclosed.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
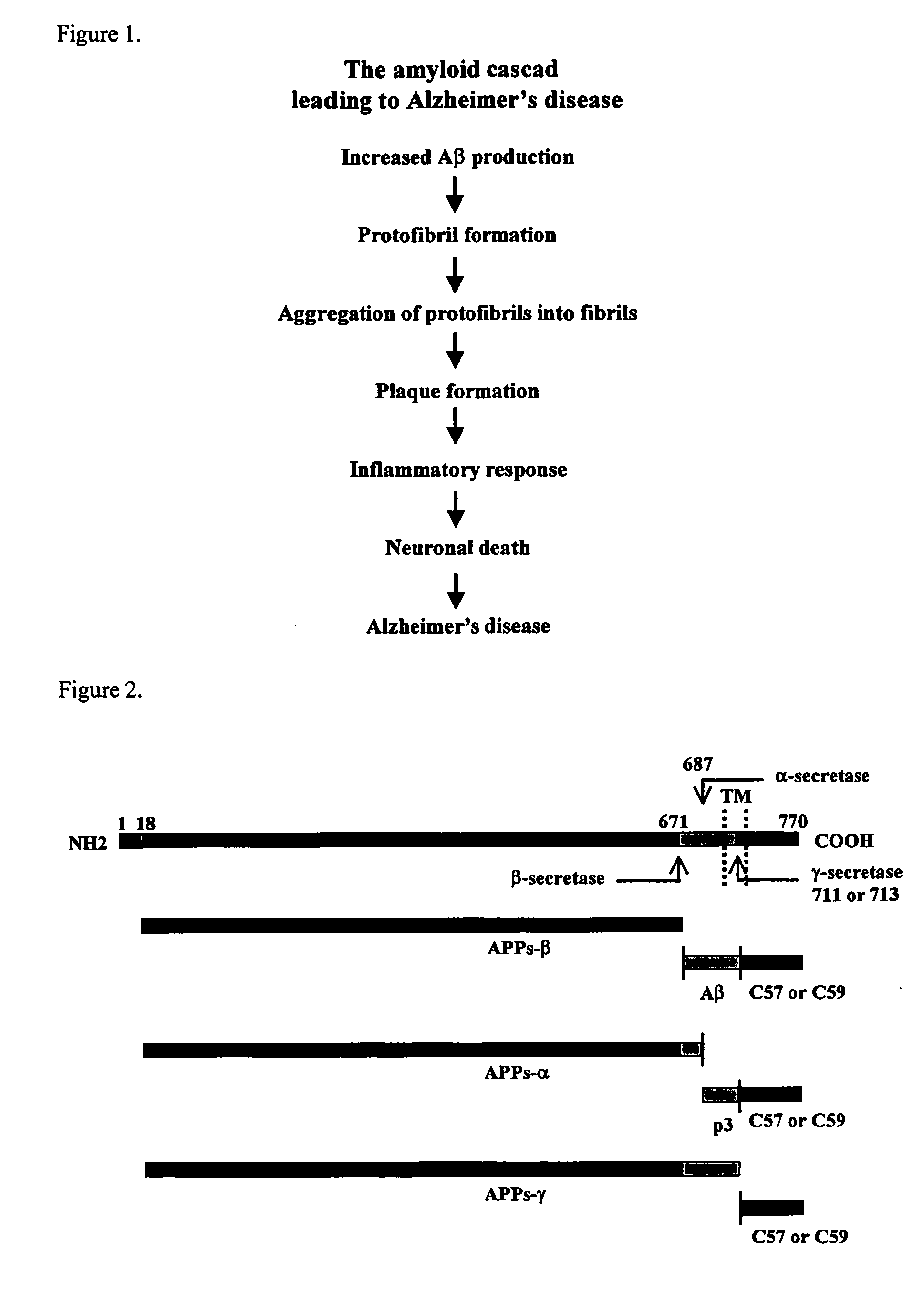
Methods for the identification of agents that modulate the structure and processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein
The present invention provides methods for the screening and identification of agents from a large library of molecular structures that can alter the cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (AP). Agents identified by the methods of the present invention that modify the cleavage of APP can be used in the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer's disease. The methods select for and identify effector agents that bind to APP causing a structural change in the structure of APP in such a way that the efficiency of the cleavage of a secretase is modulated. Further, the methods are carried out in an in vivo system that provides for physiological conditions similar or identical to conditions for APP processing. Agents can be selected for their ability to cause a decrease in the amount of B-secretase or β-secretase cleavage of APP, or for an increase in a-secretase cleavage of APP. The agents can be, particularly peptide agents, can be converted into a peptidominetic, an isosteric replacement compound, a D-amino acid analog, or non-peptidyl compound for treating Alzheimer's disease or any other amyloid related or prion related disease. The agents or derivatives thereof can be formulated for intravenous, parenteral, topical, sustained release, intranasal, or inhalation use.
Owner:ICOGENEX CORP
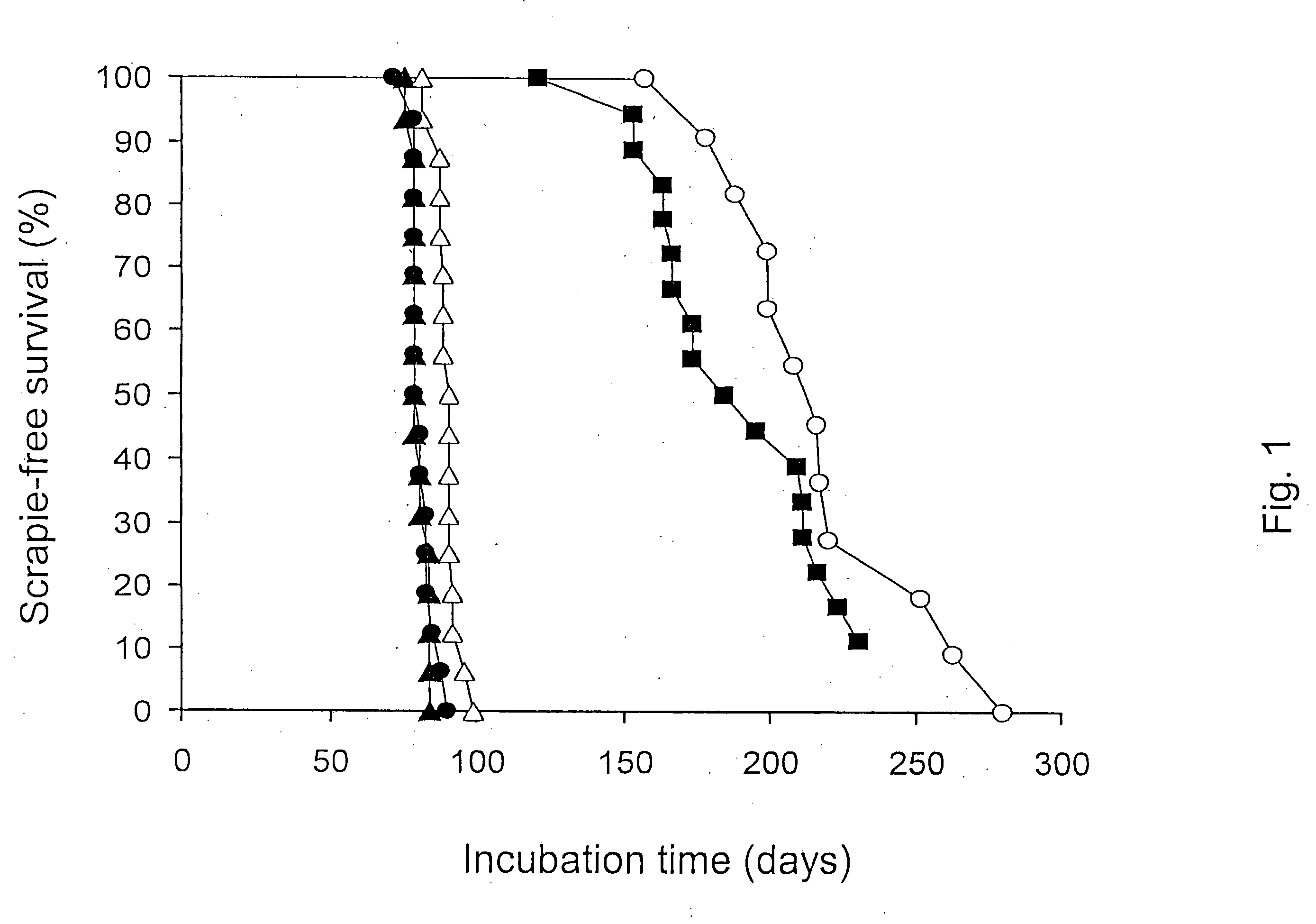
Method for diagnosing a transmissible spongiform subacute encephalyopathy caused by an unconventional transmissible agent strain in a biological sample
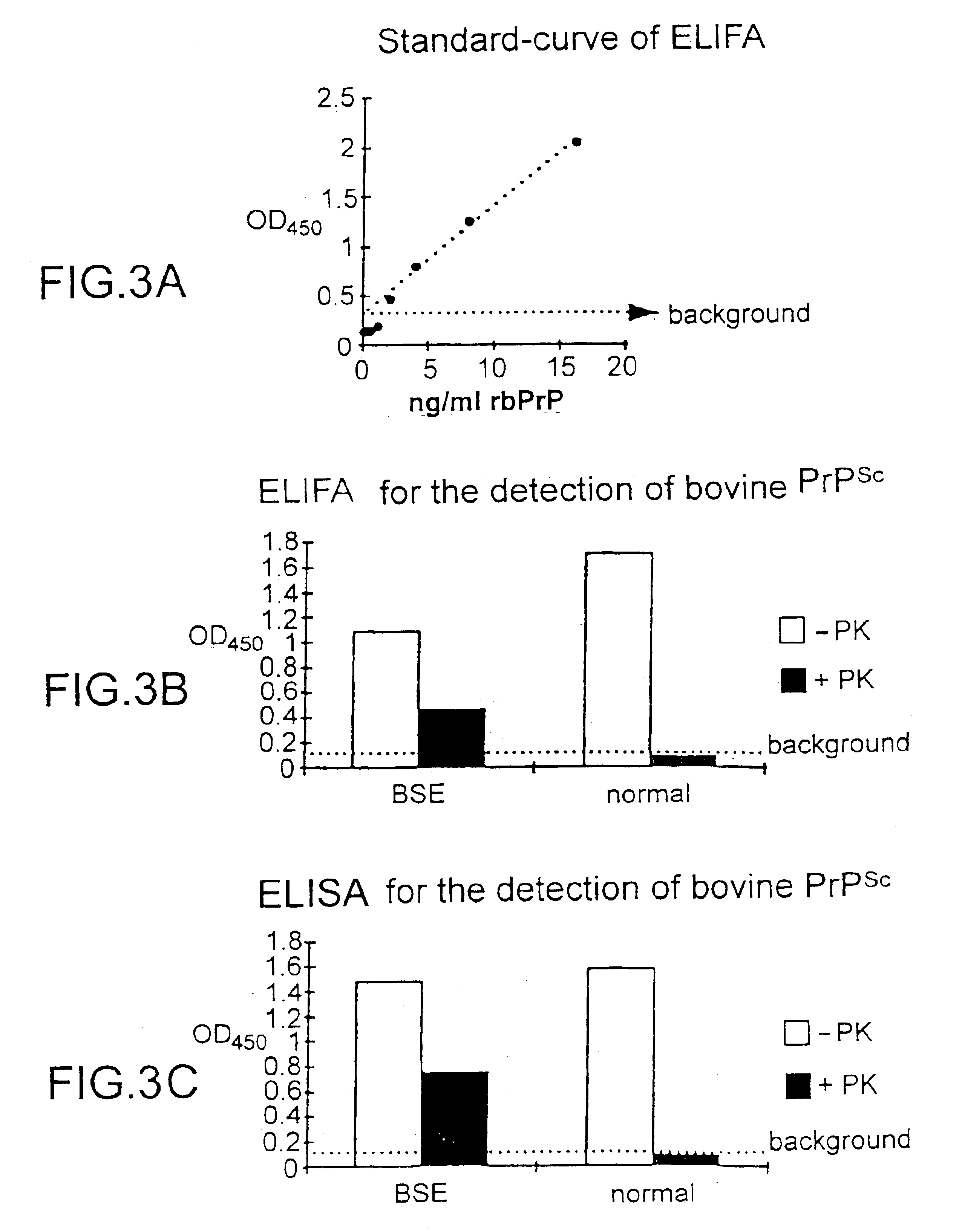
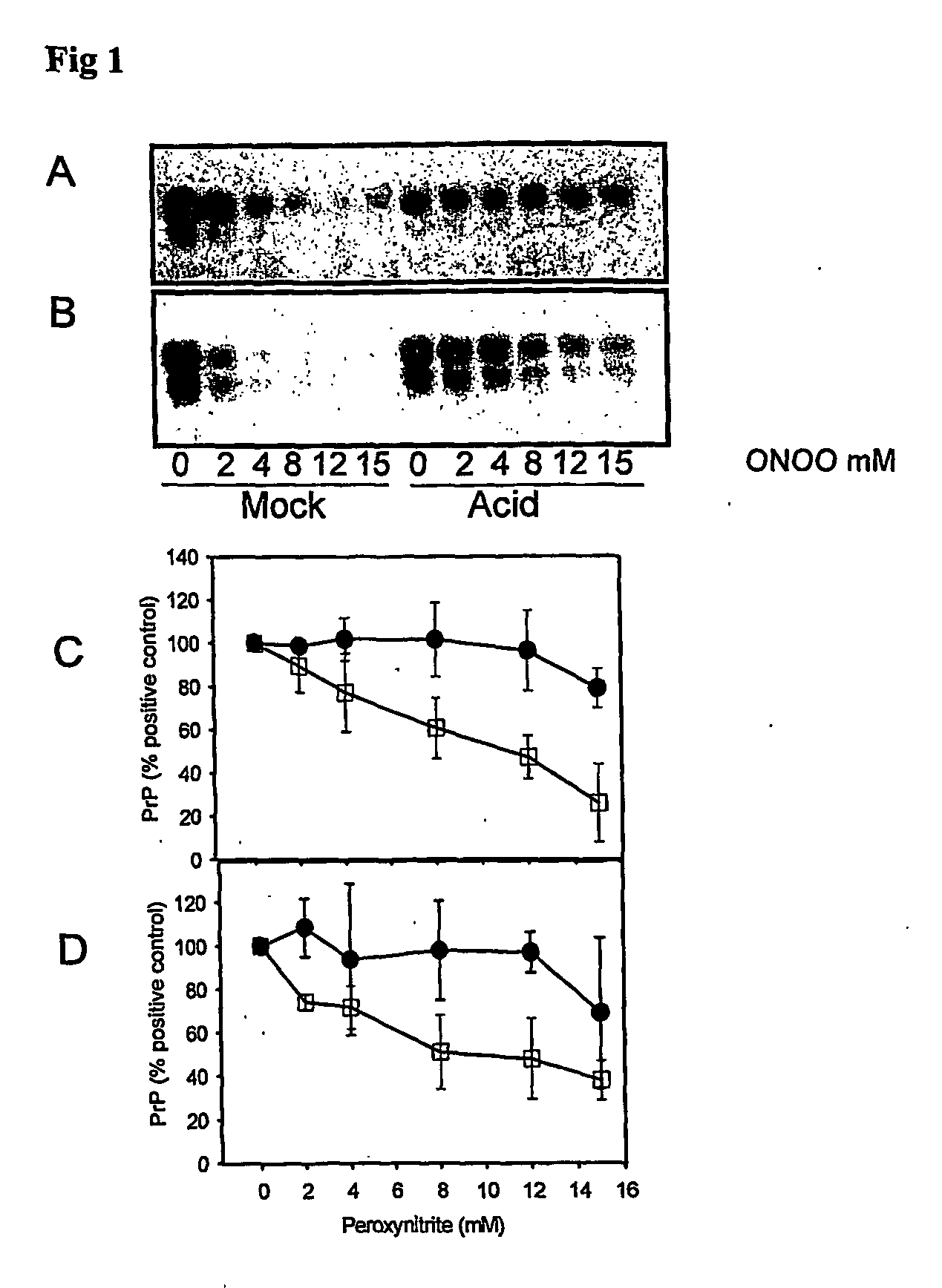
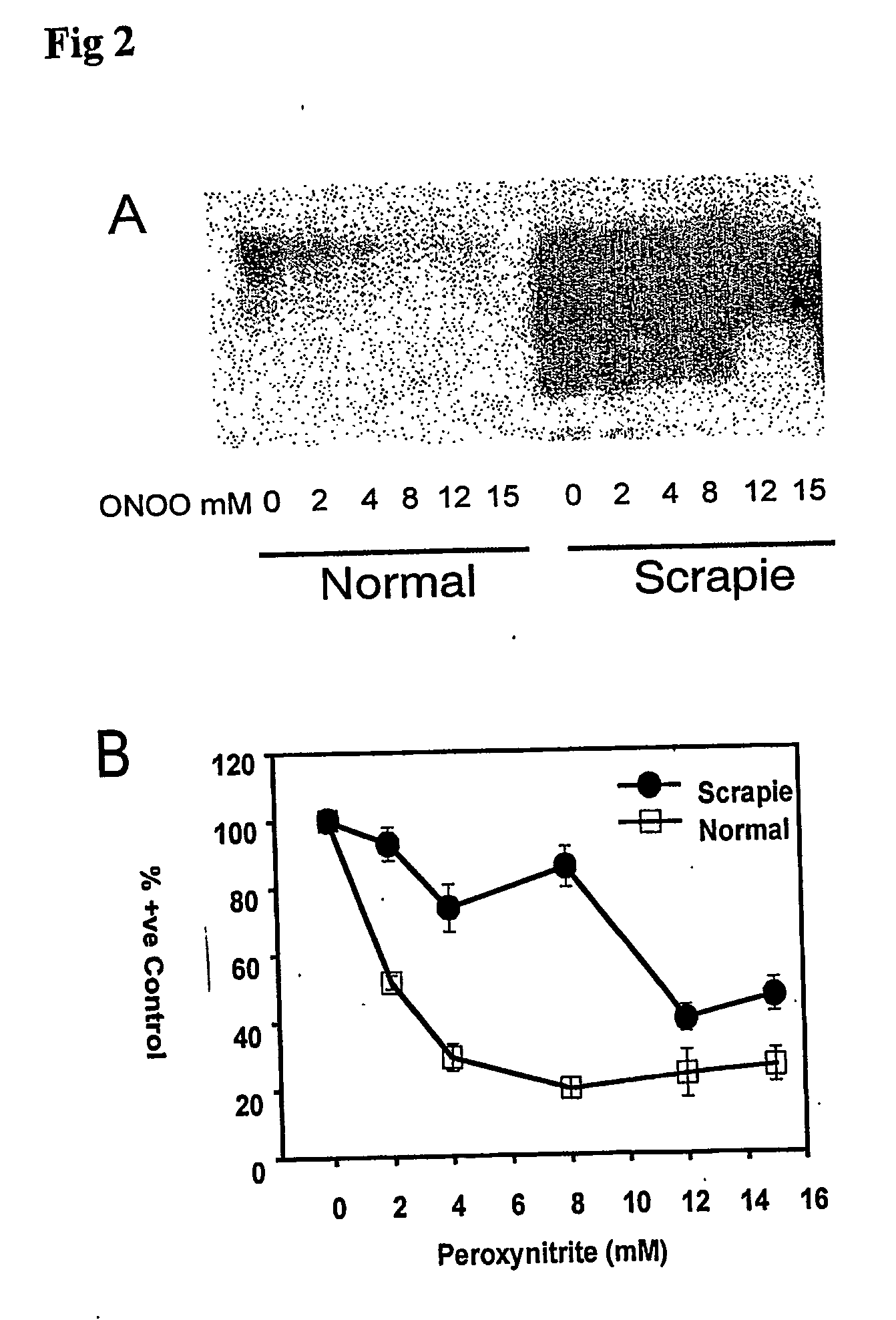
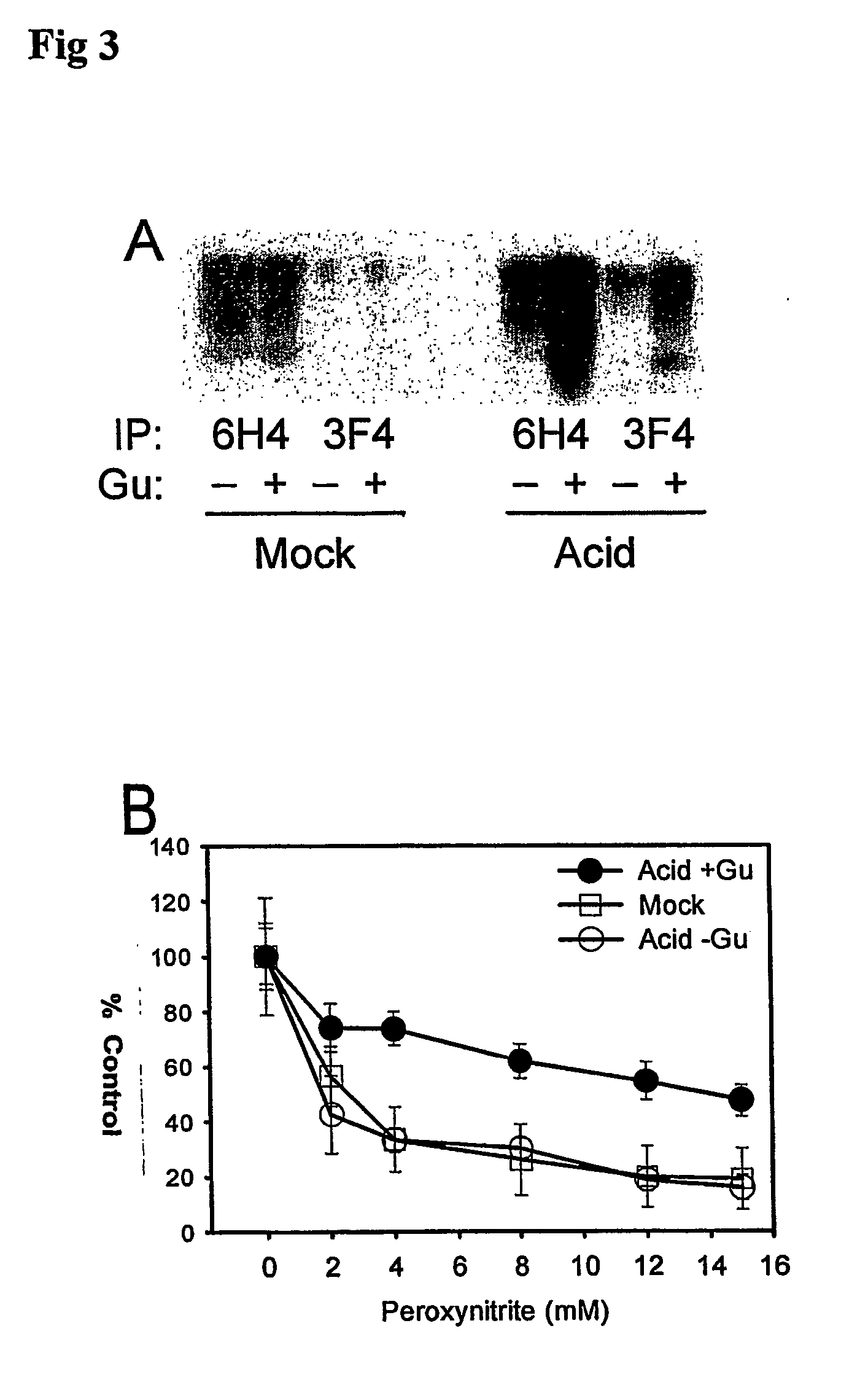
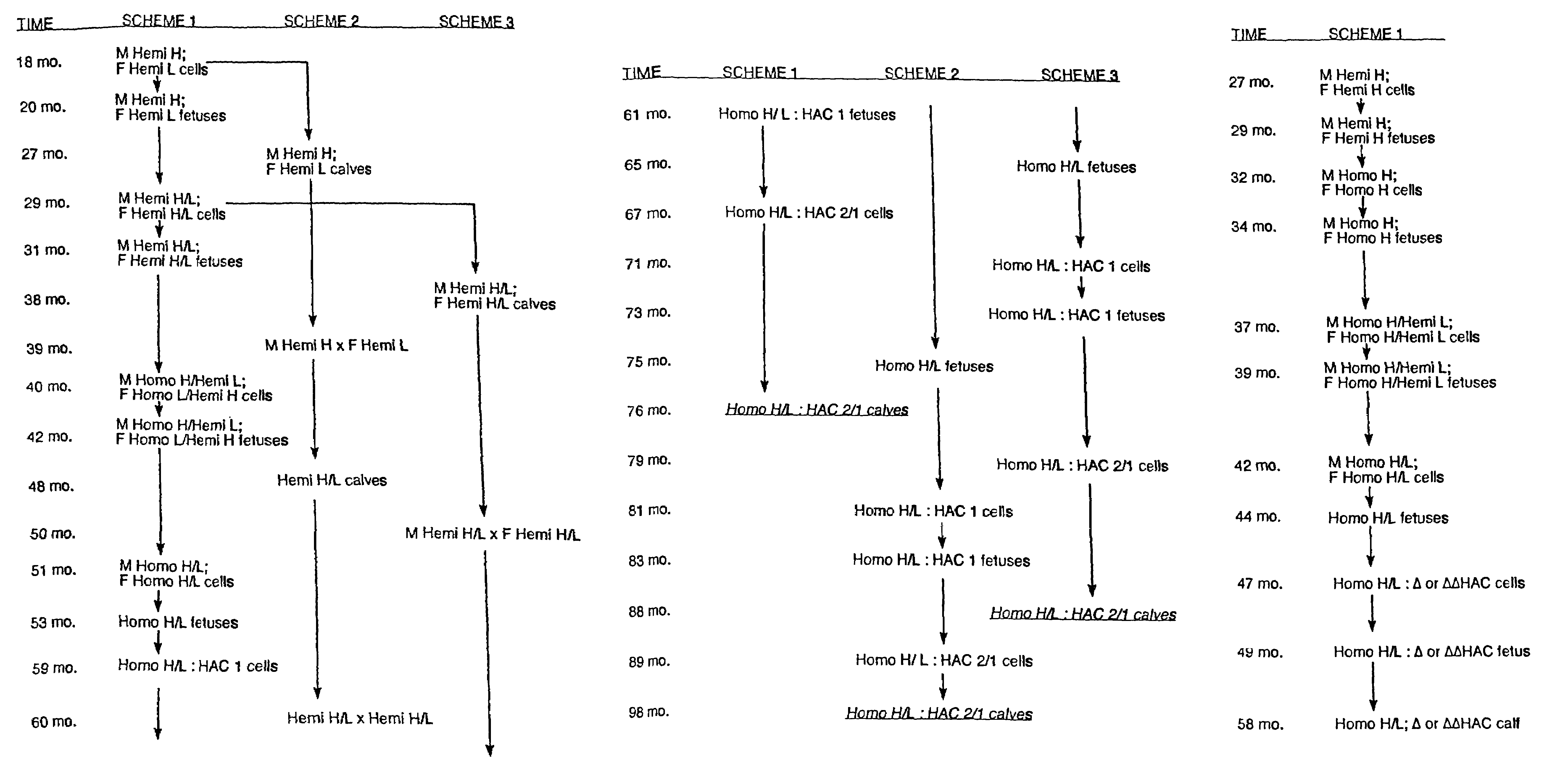
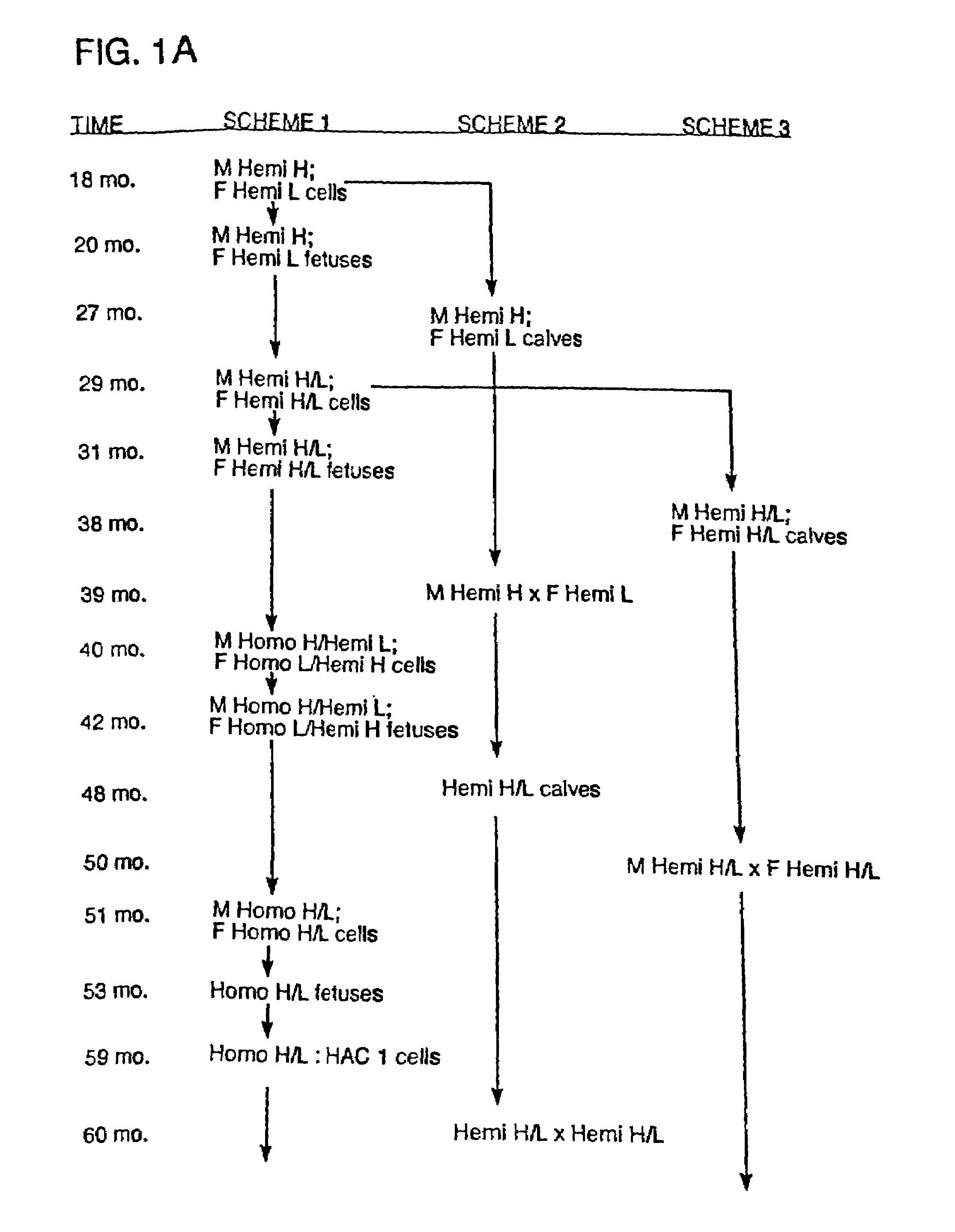
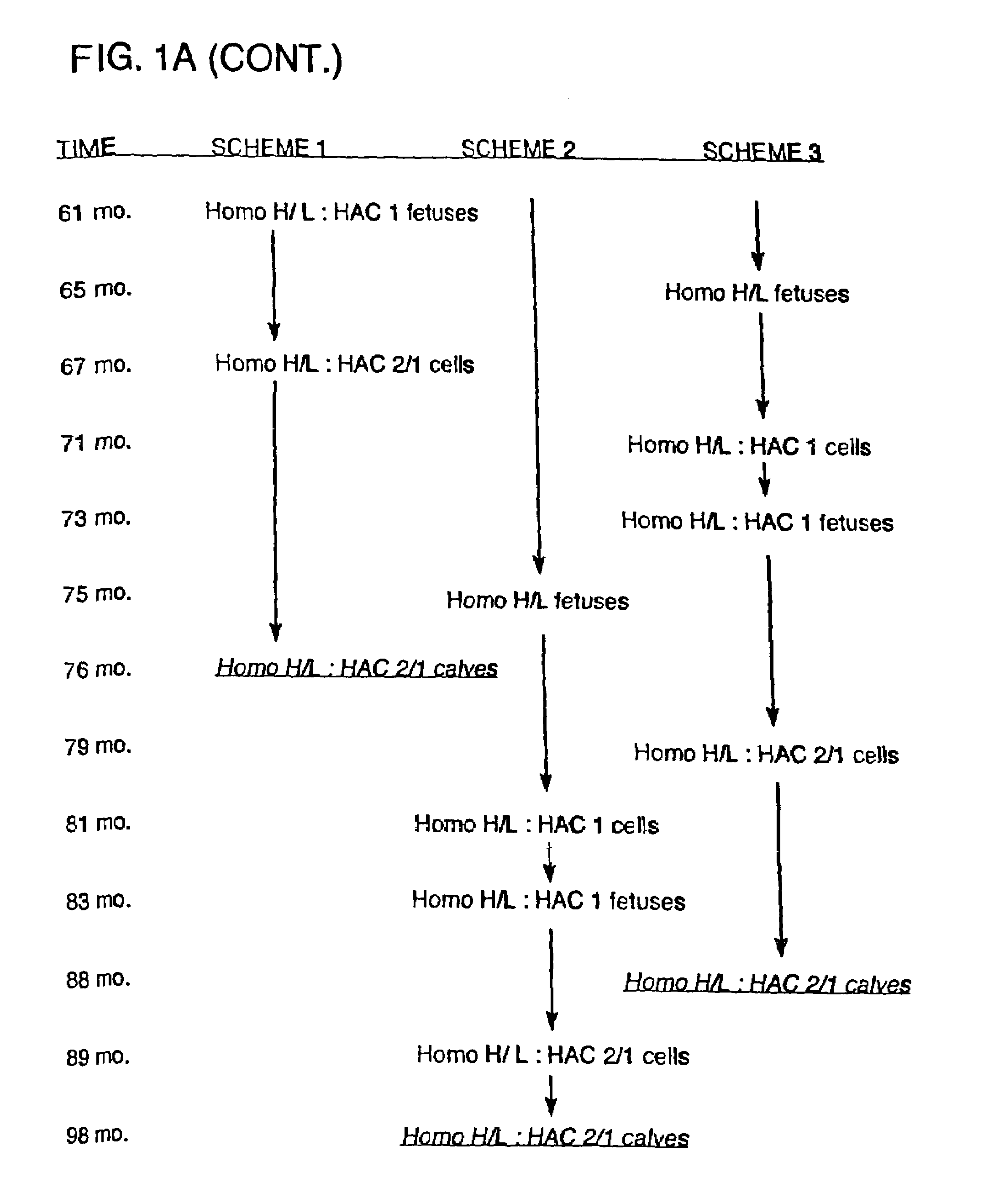
InactiveUS7097997B1High detection sensitivityHigh affinityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPrion ProteinsSheep prion
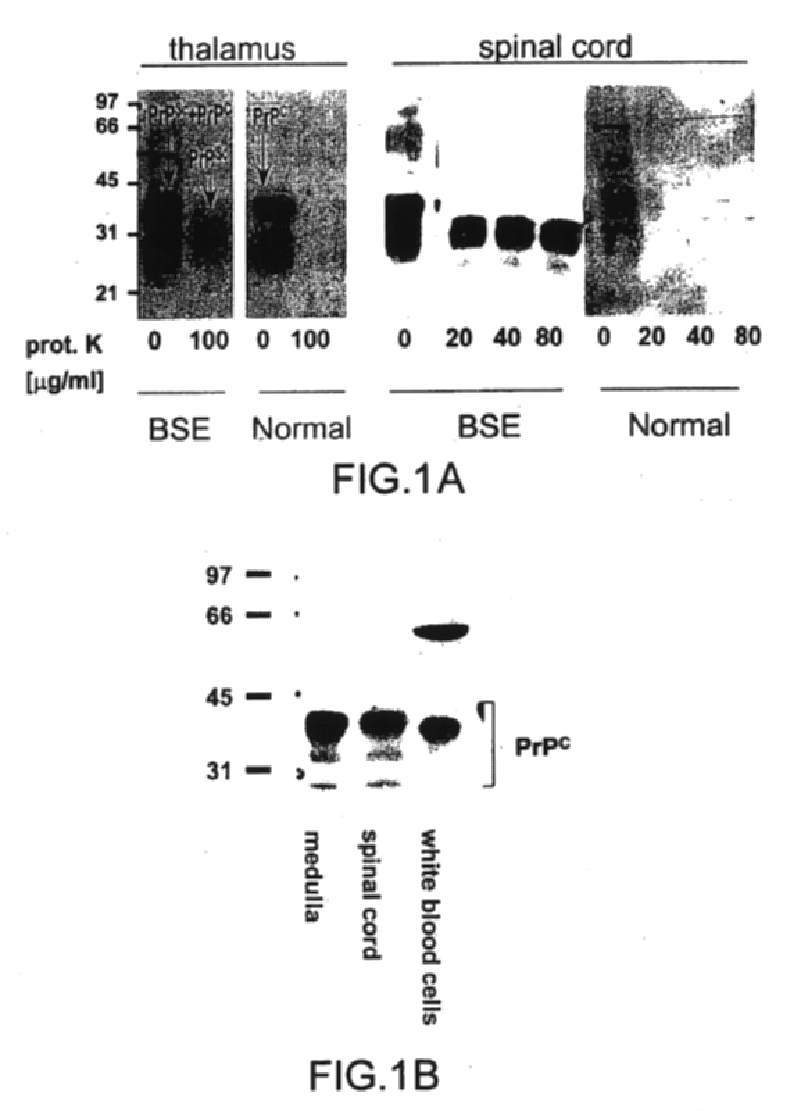
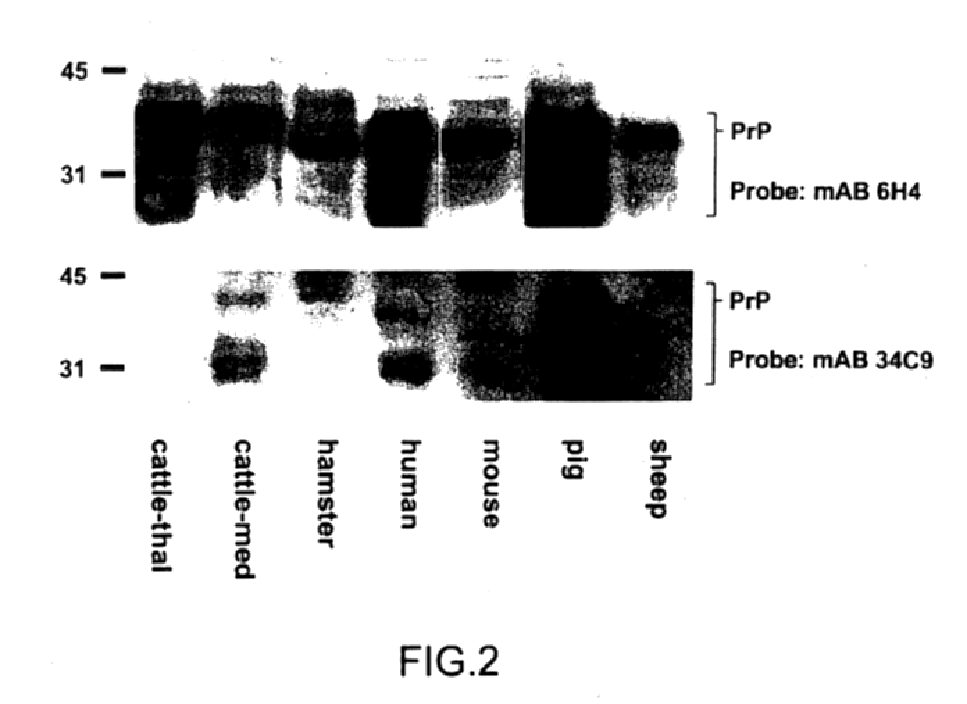
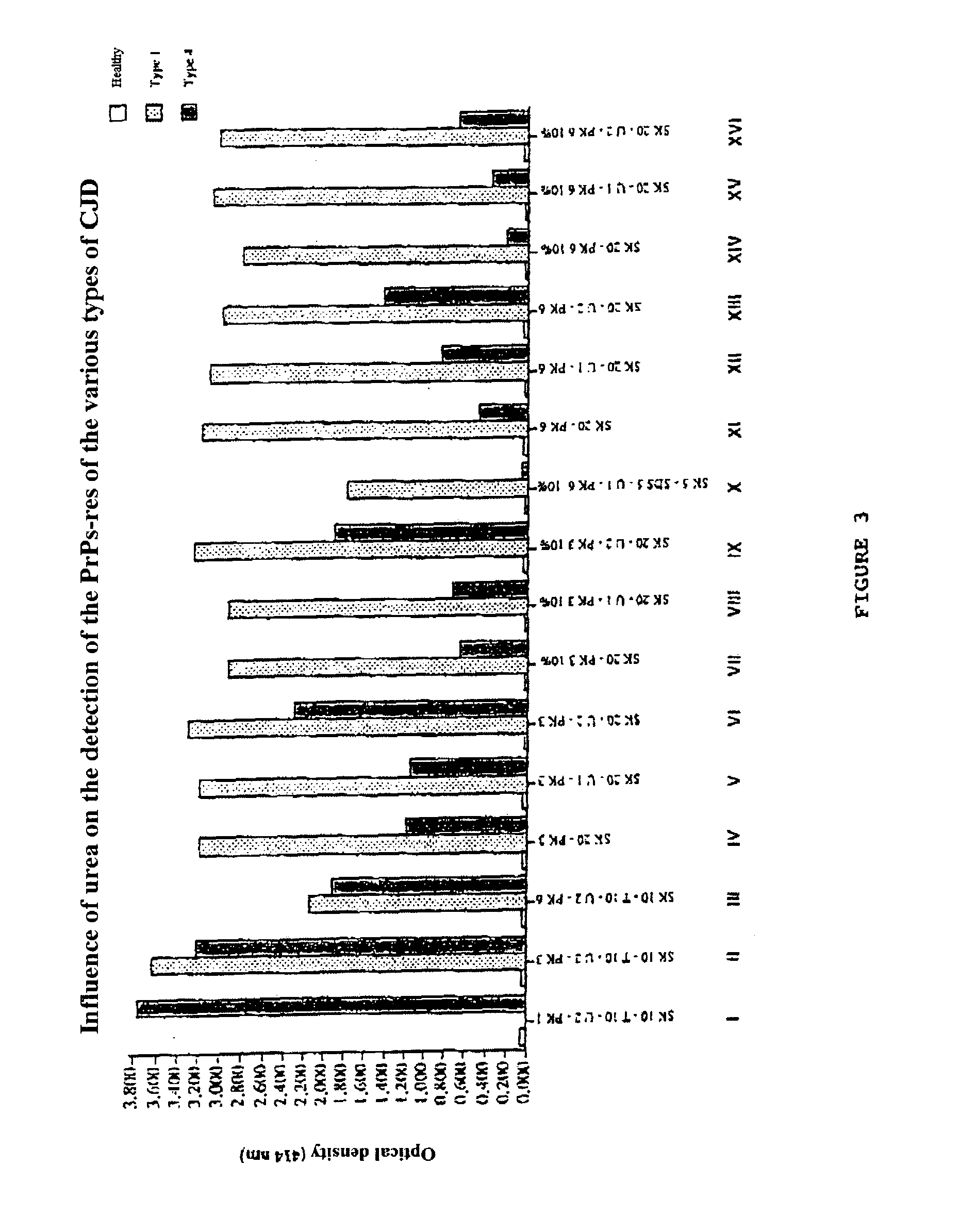
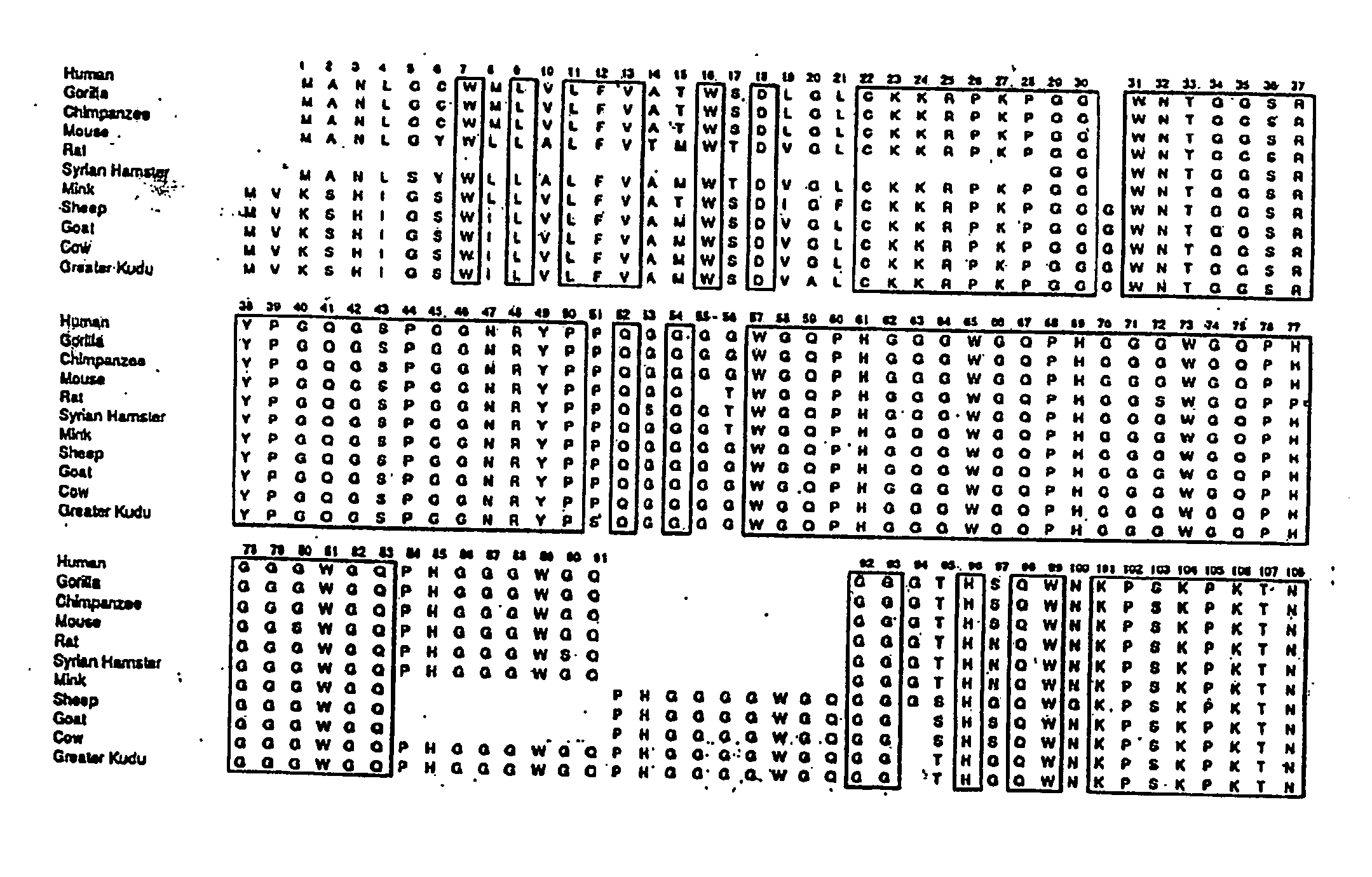
The invention relates to a method for diagnosing a transmissible spongiform subacute encephalopathy (TSSE) caused by an unconventional transmissible agent (UTA) or prion. The method involves treating a sample suspected of containing a prion with proteinase K for a time and under conditions that completely degrade normal prion protein (Prp-sen), but which only partially digest abnormal prion protein (PrP-res) so that all or some of the octapeptide motif repeats comprising P(H / Q)GGG(- / T)WGQ (SEQ ID NO: 1) in the abnormal prion protein (Prp-res) are retained.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
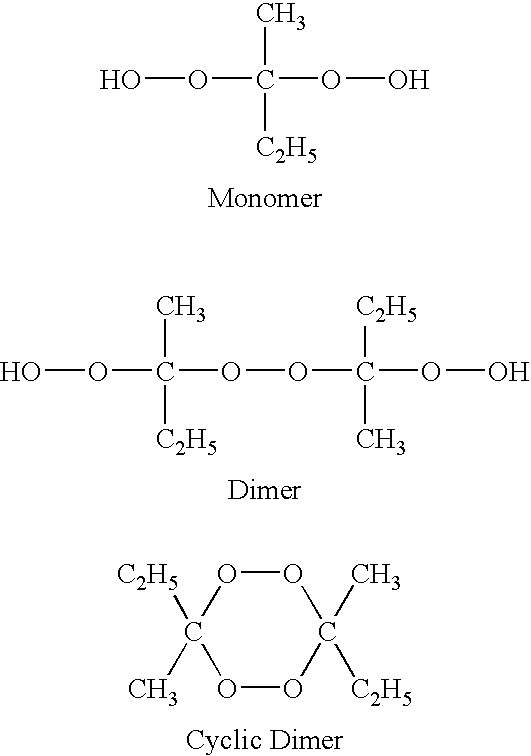
Use of dialkylketone peroxide as biocidal, sterilizing, antiseptic, disinfecting and anti-parasitic agent
The invention presented here establishes the use of a dialkyl ketone peroxide as a sterilizing, antiseptic, disinfecting and anti-parasitic agent, with no apparent toxicity nor ecotoxicity, and a very wide spectrum of activity in terms of the type of organisms on which it acts (bacteria, virus, fungi, spores, mycobacteria, protozoa, algae, prions, arachnids, mites, insects, etc.), and in terms of the type of applications in which it can be employed (human and animal therapy, hygiene, packing, medical and industrial instruments, sanitary surfaces and healthcare environments, premises, surfaces in general, industrial installations, refrigeration towers, sanitary hot water systems, purification of drinking water for human or animal consumption, etc.). Likewise, the current invention illustrates the use of a composition comprising such dialkyl ketone peroxides. Finally, the invention presented here provides a method of sterilisation, disinfection, asepsia or deparasitisation that involves the application of said composition.
Owner:NEOCHEMICAL DESARROLLOS AVANZADOS SA
EB Matrix production from fetal tissue and its use for tissue repair
InactiveUS20050013802A1Improve suppression propertiesTissue strength is preservedBiocideHepatocytesCross-linkTissue repair
A method of forming and preserving a bioremodelable, biopolymer scaffold material by subjecting animal tissue, particularly fetal or neo-natal tissue, to chemical and mechanical processing. The process includes, but is not limited to, harvesting the tissue, optionally extracting growth and differentiation factors from the tissue, inactivating infective agents of the tissue, mechanically expressing undesirable components from the tissue, delipidizing the tissue, washing the tissue, optionally drying the tissue, optionally cross-linking the tissue not necessarily in the order described. The resulting product, EBM, is characterized by its microbial, fungal, viral and prion inactivated state. EBM is strong, bioremodelable, drapable and does not undergo calcification. EBM supplants previous inventions because of its unique method of preparation and broad applicability in tissue reengineering.
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
Mucosal immunization to prevent prion infection
Vaccines against prion disease eliciting a humoral immune response when administered mucosally are described. The vaccines comprise a prion protein, a prion protein fragment, or a non-amyloidogenic prion protein homolog and an adjuvant suitable for inducing a humoral immune response after mucosal administration. Suitable adjuvants include cholera toxin subunit B, heat-labile enterotoxin and aluminum hydroxide. Alternatively, the vaccine comprises a vector encoding a prion protein, fragment, or homolog in an attenuated Salmonella host. The vaccines can be used to prevent or treat prion disease in humans and other mammals.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Binary compositions and methods for sterilization
InactiveUS20070264355A1Raise the potentialRapid detoxifyingBiocideSpecific water treatment objectivesHypochloriteFungal microorganisms
The present invention relates to binary methods and compositions comprising hypohalite (preferably hypochlorite) and peroxide (preferably hydrogen peroxide) directed to the killing of pathogenic microbes such as parasites, bacteria, fungi, yeast, and prions, the oxidation of toxins, and the preparation of potable water. The binary methods and compositions extend the microbicidal potency of conventional hypochlorite by providing additional singlet molecular oxygen generated in situ, and offer more control over reactive chlorination exposure than hypochlorite alone. This combination is a highly effective disinfecting and decontaminating agent, capable of disinfection, detoxification, or deactivation of biological contamination and many chemical toxins, facilitating the sterilizing of surfaces and solutions, and the production of potable water.
Owner:BINARY
Epitope protection assay
ActiveUS20060246517A1Prevents and reduces reactionReduced responseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The invention relates to an epitope protection assay for use in diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic intervention in diseases, for example, involving polypeptide aggregation, such as prion infections. The methods of the invention first block accessible polypeptide target epitope with a blocking agent. After denaturation of the polypeptide, a detecting agent is used to detect protein with target epitope that was inaccessible during contact with the blocking agent. The invention also relates to novel amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-specific epitopes and their uses to make antibodies, and to the novel antibodies and uses thereof.
Owner:PROMIS NEUROSCI
Rapid prion-detection assay
Assays are provided for rapid detection, with high specificity of the pathogenic form of prion protein responsible for neurodegenerative diseases affecting humans and animals, such as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in bovine, sheep, and cats. Also provided are assays for testing animal feedstock, such as animal feed, for the presence or concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Results are available in from about 0.5 to about 20 minutes and preferably within from about 5 to about 10 minutes. The assays employ proteinase-K to remove normal prion protein from a biological sample, so that the sample may be analyzed by immunochromatography to determine the presence and concentration of pathogenic prion protein. Because the proteinase-K is immobilized on a solid support for in situ removal of interfering components, the present invention obviates the need for subsequent extraction of the desired analyte. All aspects of the present invention are suitable for quantifying the minimal detectable amount of pathogenic prion protein in a biological sample. Moreover, the simplicity of sample preparation makes the present invention suitable for use in the field.
Owner:PRION DEVAL LAB
Cleaning and decontamination formula for surfaces contaminated with prion-infected material
ActiveUS20060105930A1Efficient modelingReadily culturedBiocideNon-surface-active detergent compositionsProteinaceous infectious particleContamination
A method of treating the surfaces of medical instruments which are contaminated with prions includes contacting the surface with a composition containing a source of peroxide ions, such as hydrogen peroxide, at a molar concentration of at least 1.5M peroxide (equivalent to approximately 5% hydrogen peroxide) and preferably, about 2M peroxide (approximately 7% hydrogen peroxide). The composition is optionally in the form of a gel. The composition is retained in contact with the surfaces for about 1-2 hours until all or substantially all prion contamination is removed.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Composite peptide compounds for diagnosis and treatment of diseases caused by prion proteins
InactiveUS20060057636A1Low detection sensitivityAvoid detectionApolipeptidesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTherapeutic treatmentDisease cause
The present invention relates to diseases caused by prion proteins, Novel composite peptide compounds are disclosed which comprise two or more peptides or peptide fragments optionally linked to a backbone and the peptides or peptide fragments are spatially positioned relative to each other so that they together form a non-linear sequence which mimics the tertiary structure of one or more PrPSc-specific epitopes as evidenced by the test described herein. The use of such conjugates as immunogens for the production of antibodies that specifically bind to the pathogenic form of a prion protein is revealed. Other uses of the composite peptide compounds are also disclosed, such as use in diagnostic assays, production of antibodies and uses as vaccine immunogens for the prophylactic protection and therapeutic treatment of subjects against transmissible prion disease.
Owner:COPENHAGEN BIOTECH ASSETAB
Prion inhibiting peptides and derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20050181998A1Nervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsTransmissible spongiform encephalopathyProteinaceous infectious particle
Short peptides and derivatives or analogs thereof for the treatment or prevention of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, in particular CJD are herein described. These peptides and / or their derivatives have been designed to block the conformational changes that occur in the prion protein (PrP) and which are implicated in the pathogenesis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies as well as to dissolve the fibrillar deposits already formed
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
New method for partition and inactivation of viral and prion contaminants
InactiveUS20050250935A1Peptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesBuffer solutionProteinaceous infectious particle
Herein is described a new method for partition and inactivating of viral and prion contaminants contained in a solution. The method is based on ultracentrifugation of the solution in a centrifuge tube at the bottom of which a high molarity urea solution is layered. The system can include a cushion solution interposed as an intermediate liquid phase between the starting solution and the urea solution.
Owner:IBSA INSTITUT BIOCHIM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com