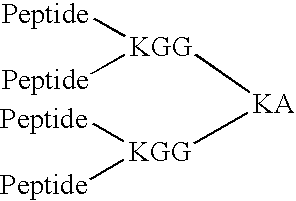
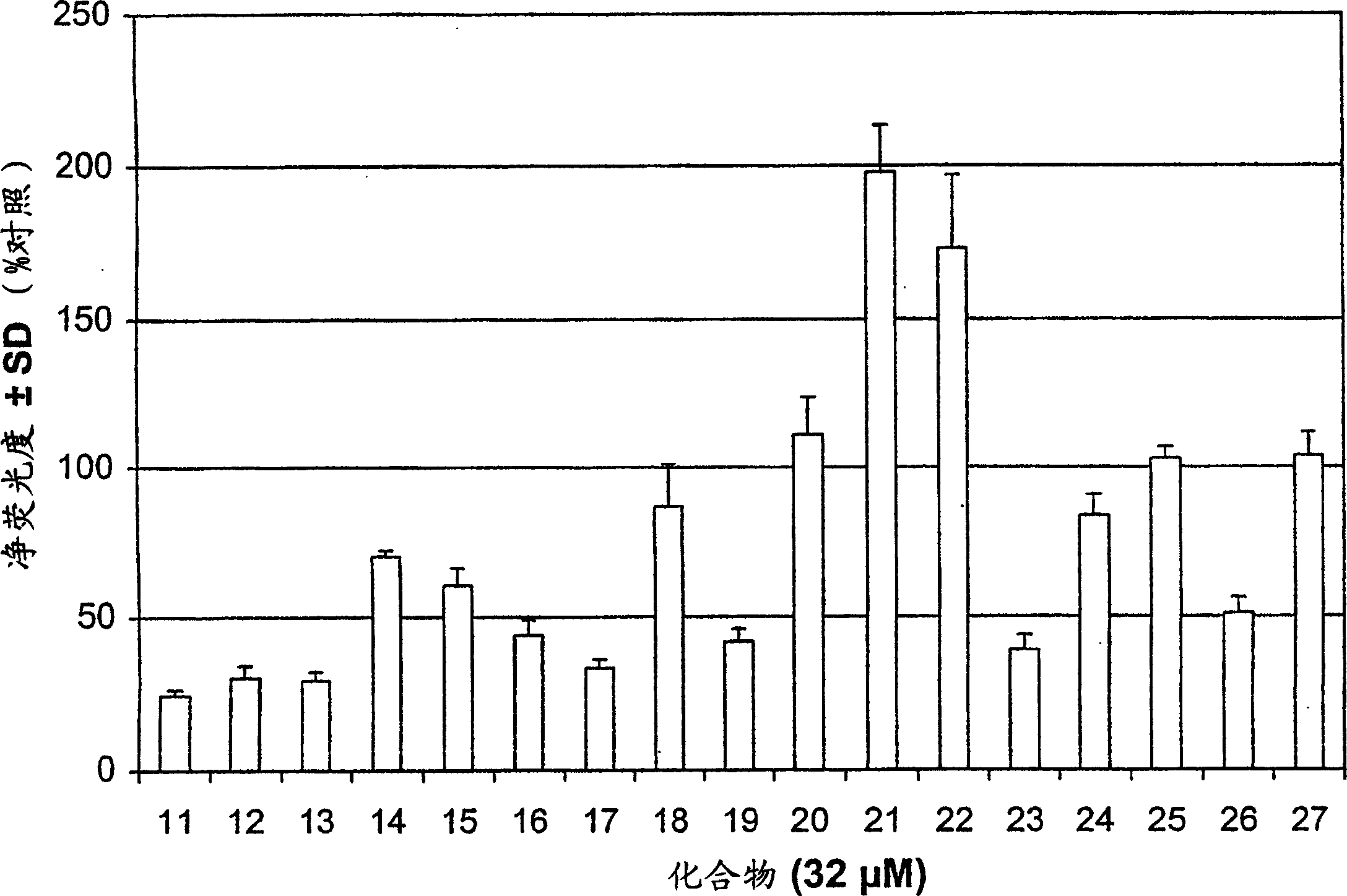
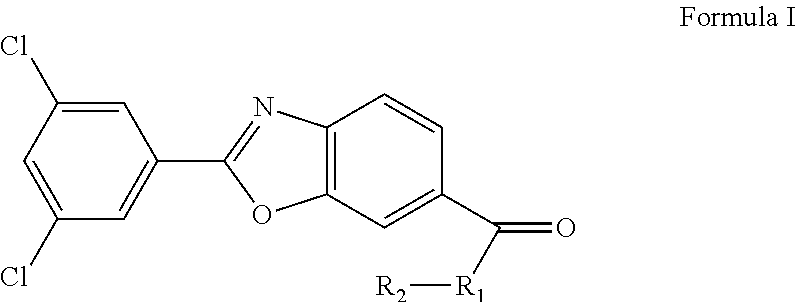
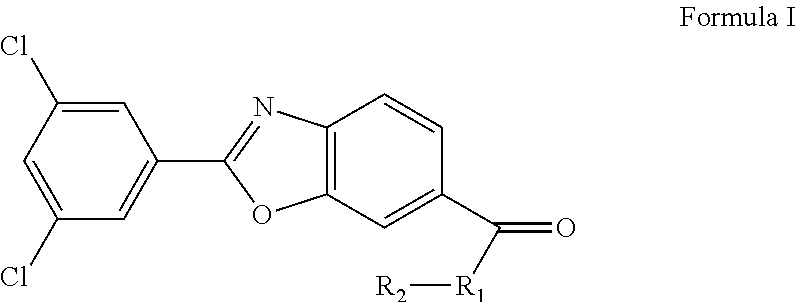
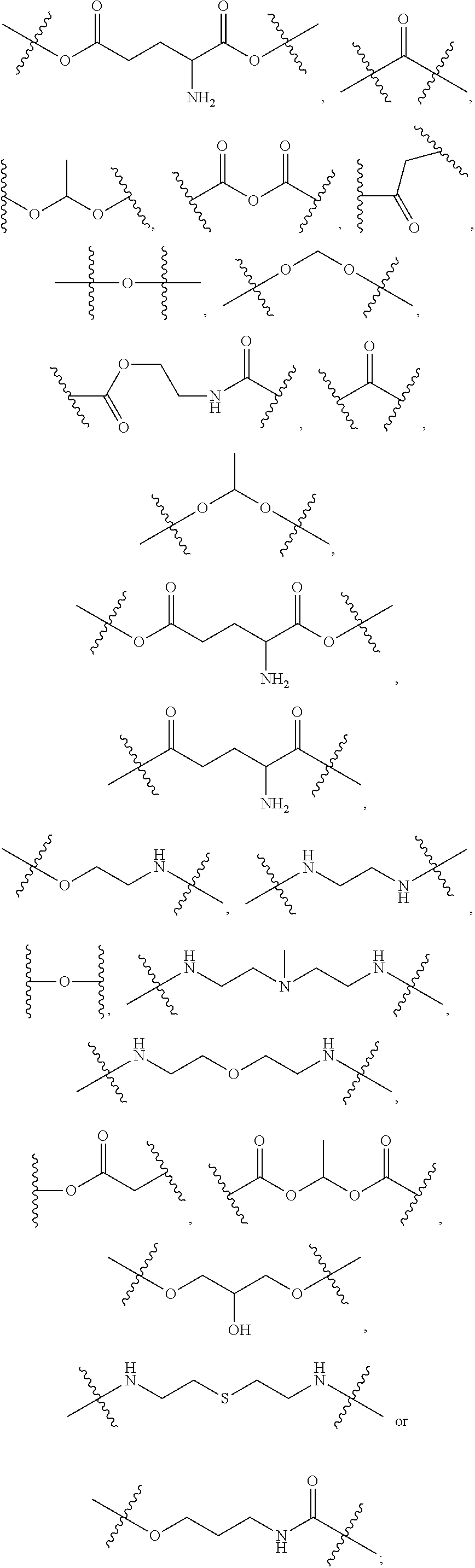
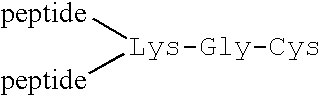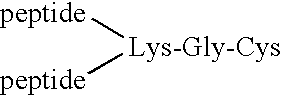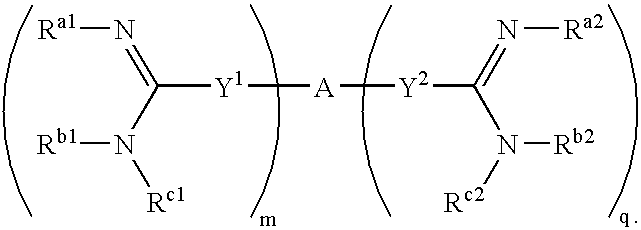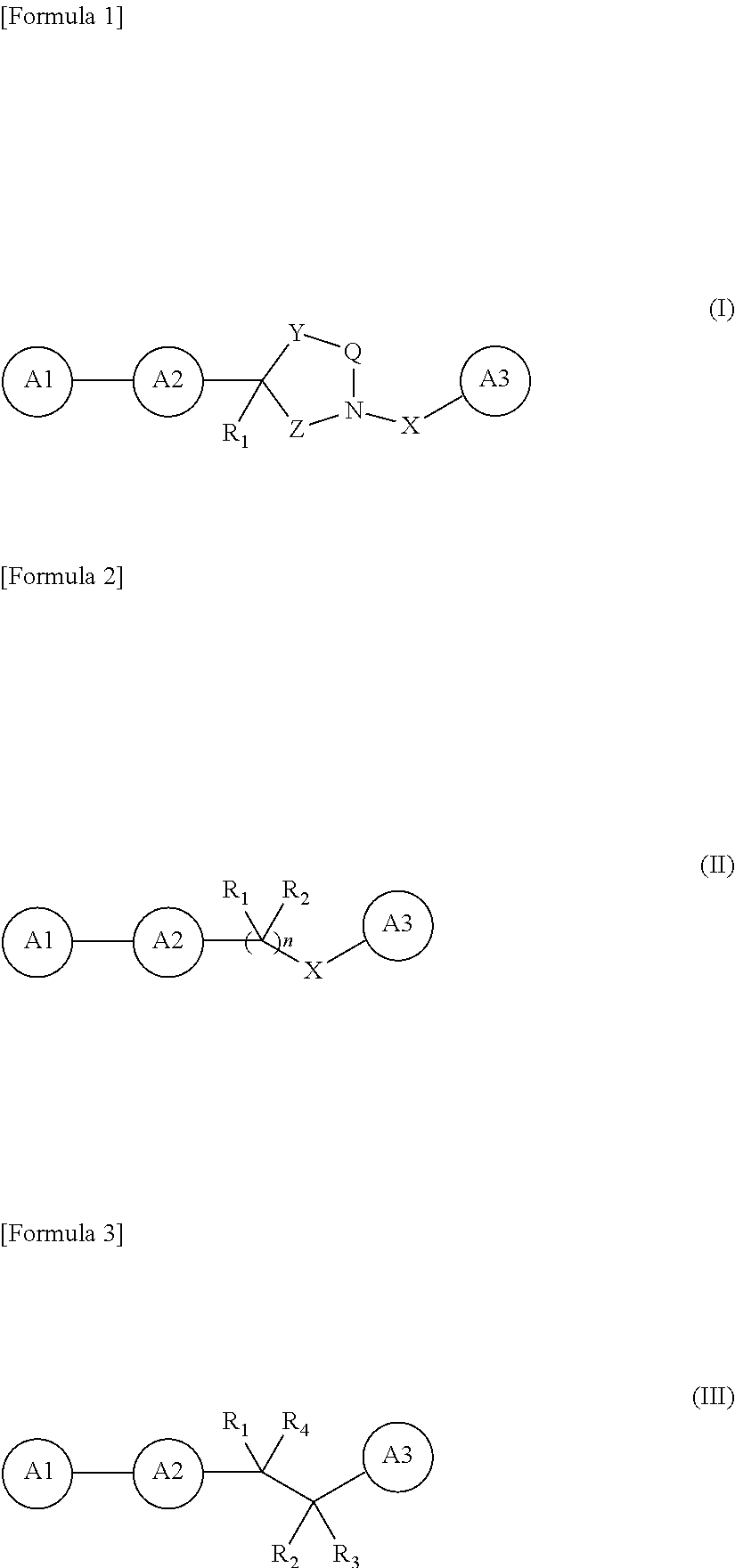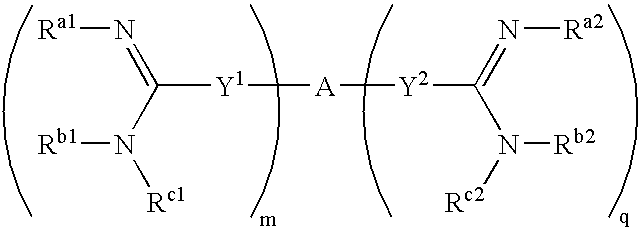Patents
Literature
68 results about "Amyloid fibril" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
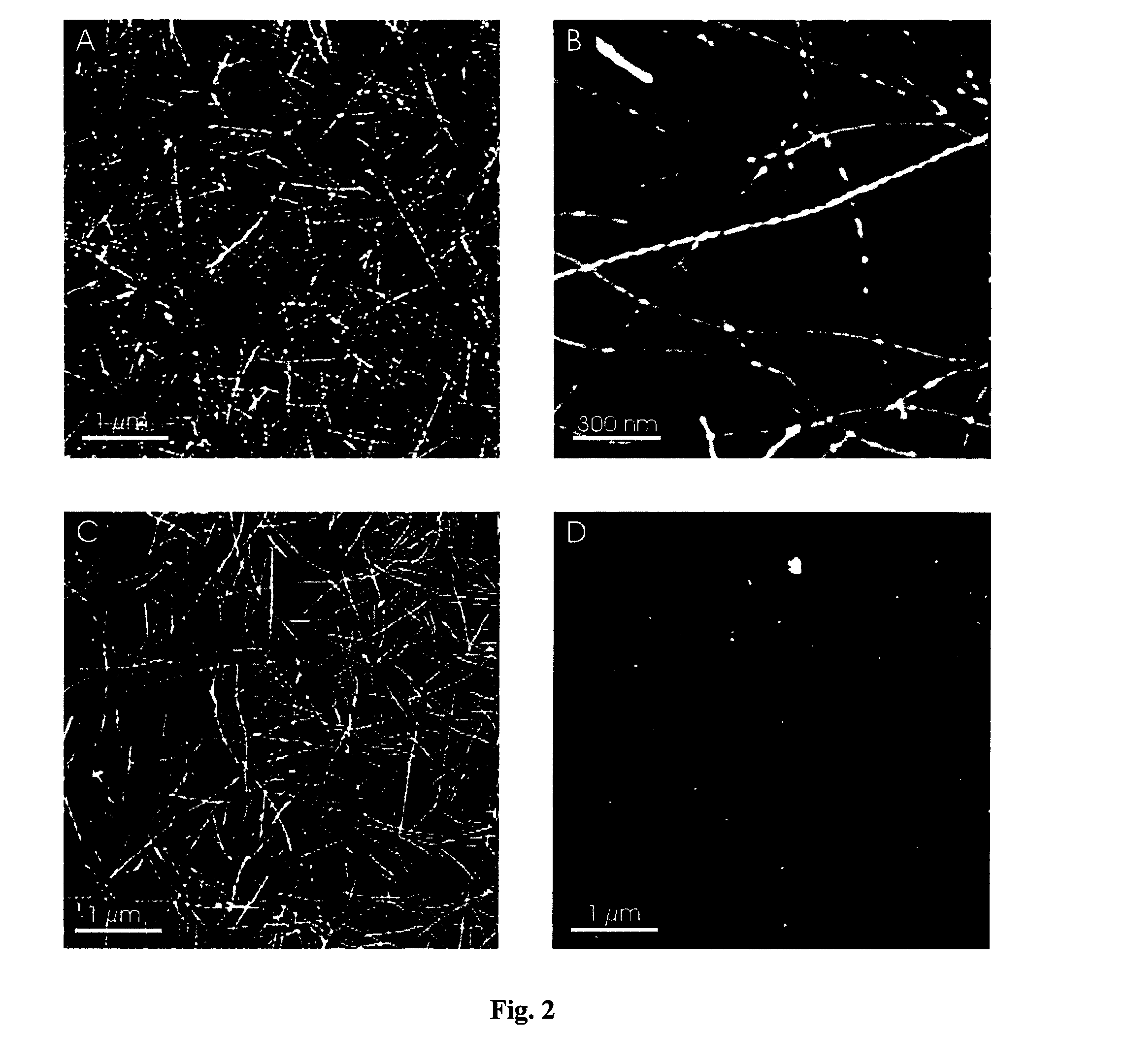
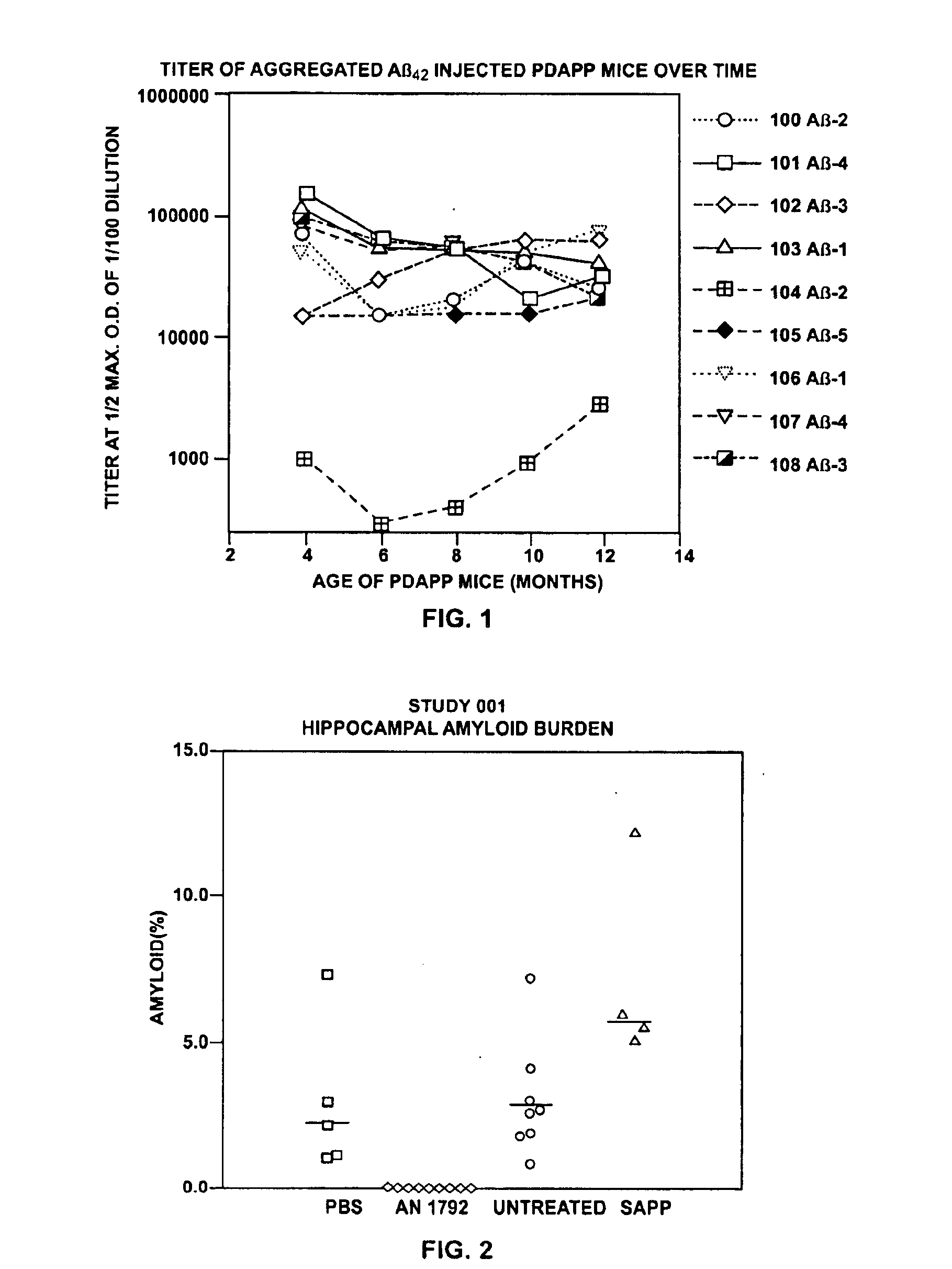
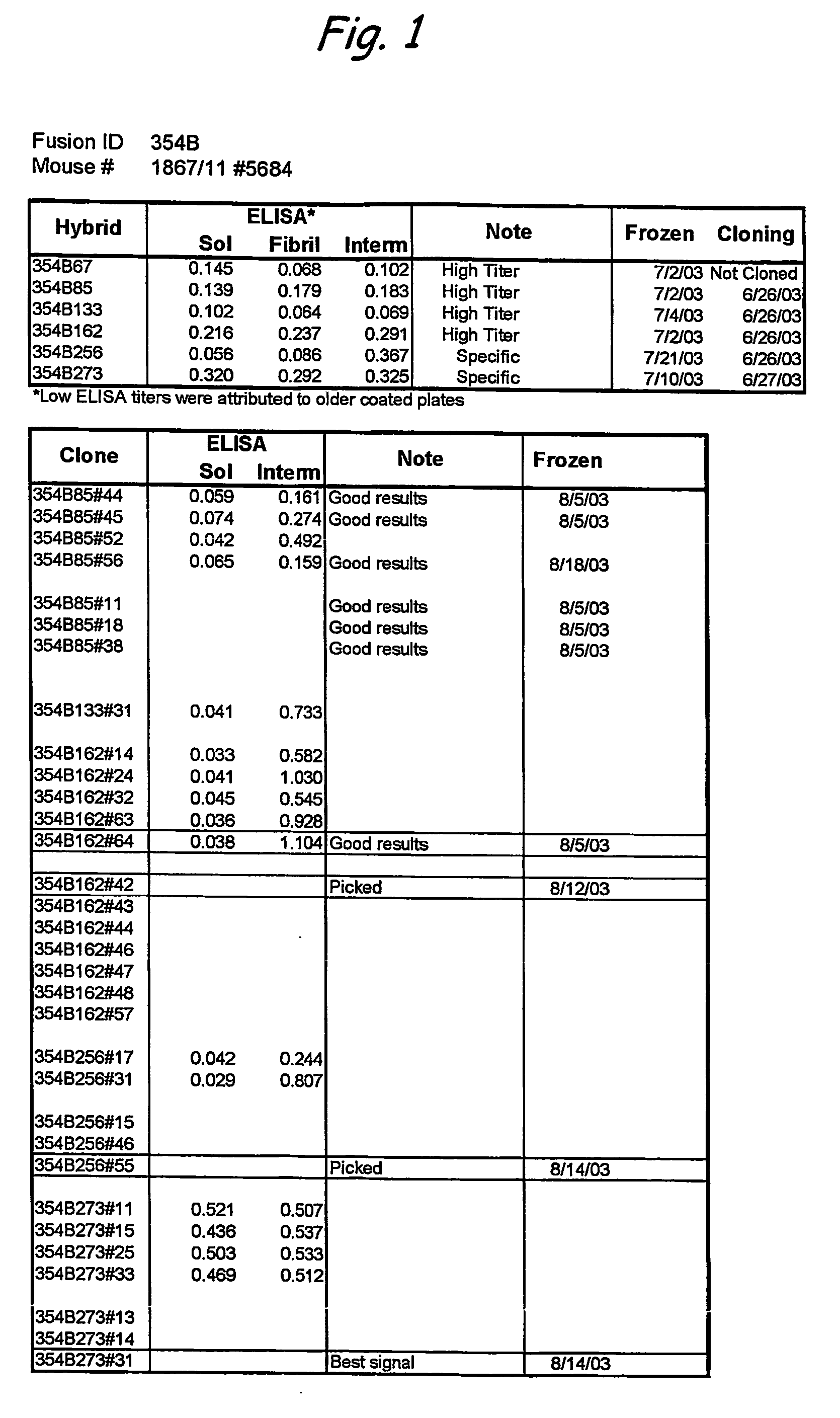
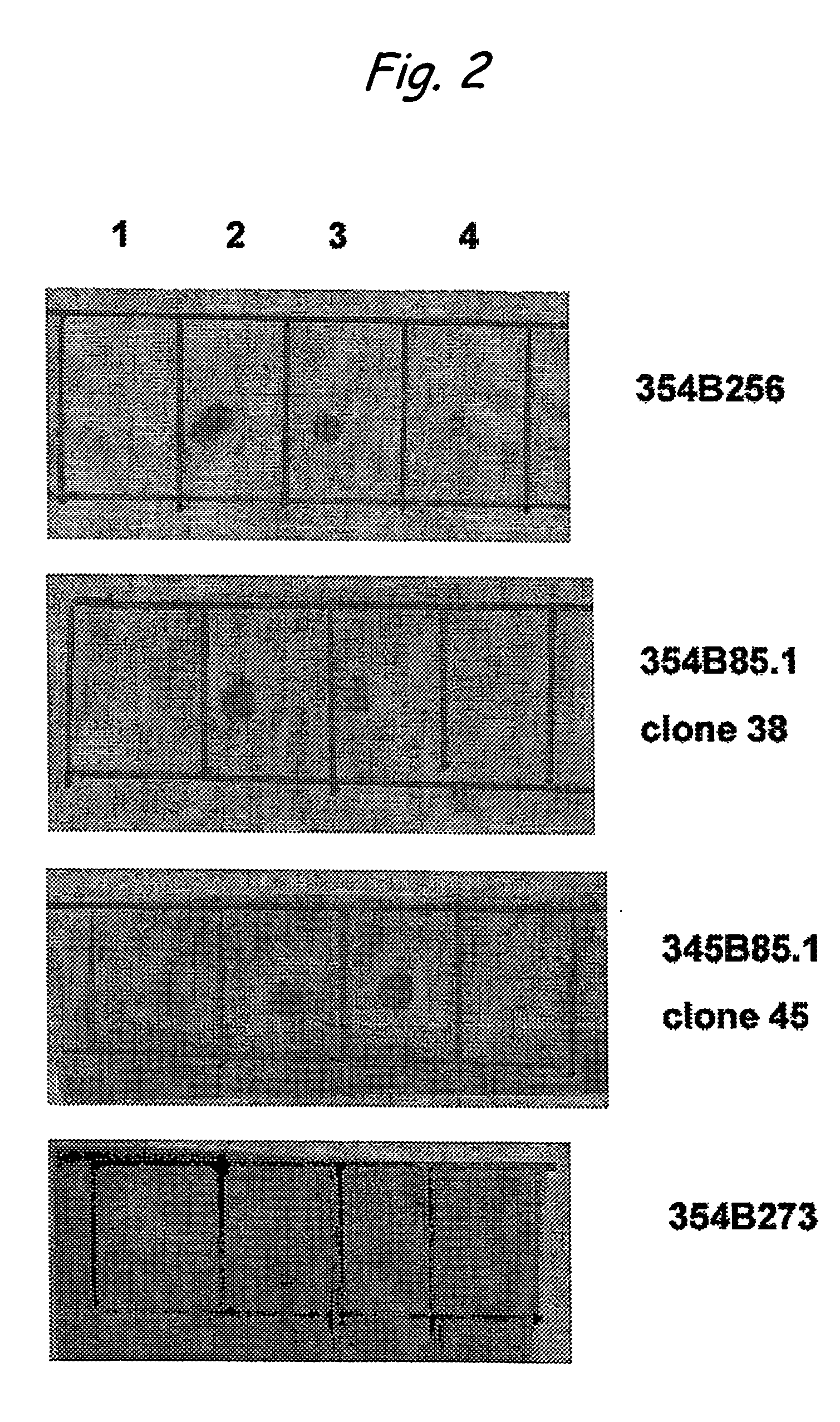
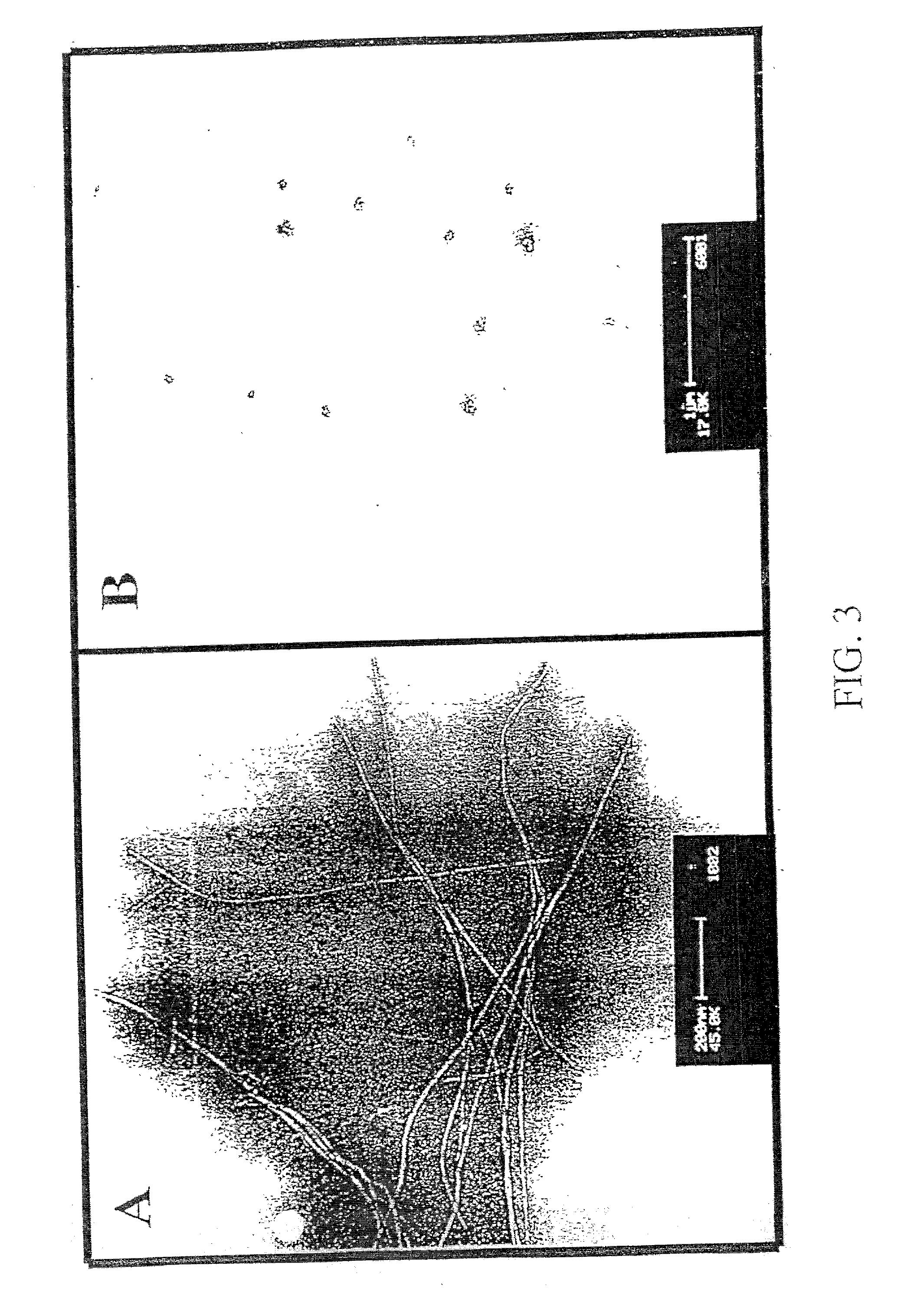
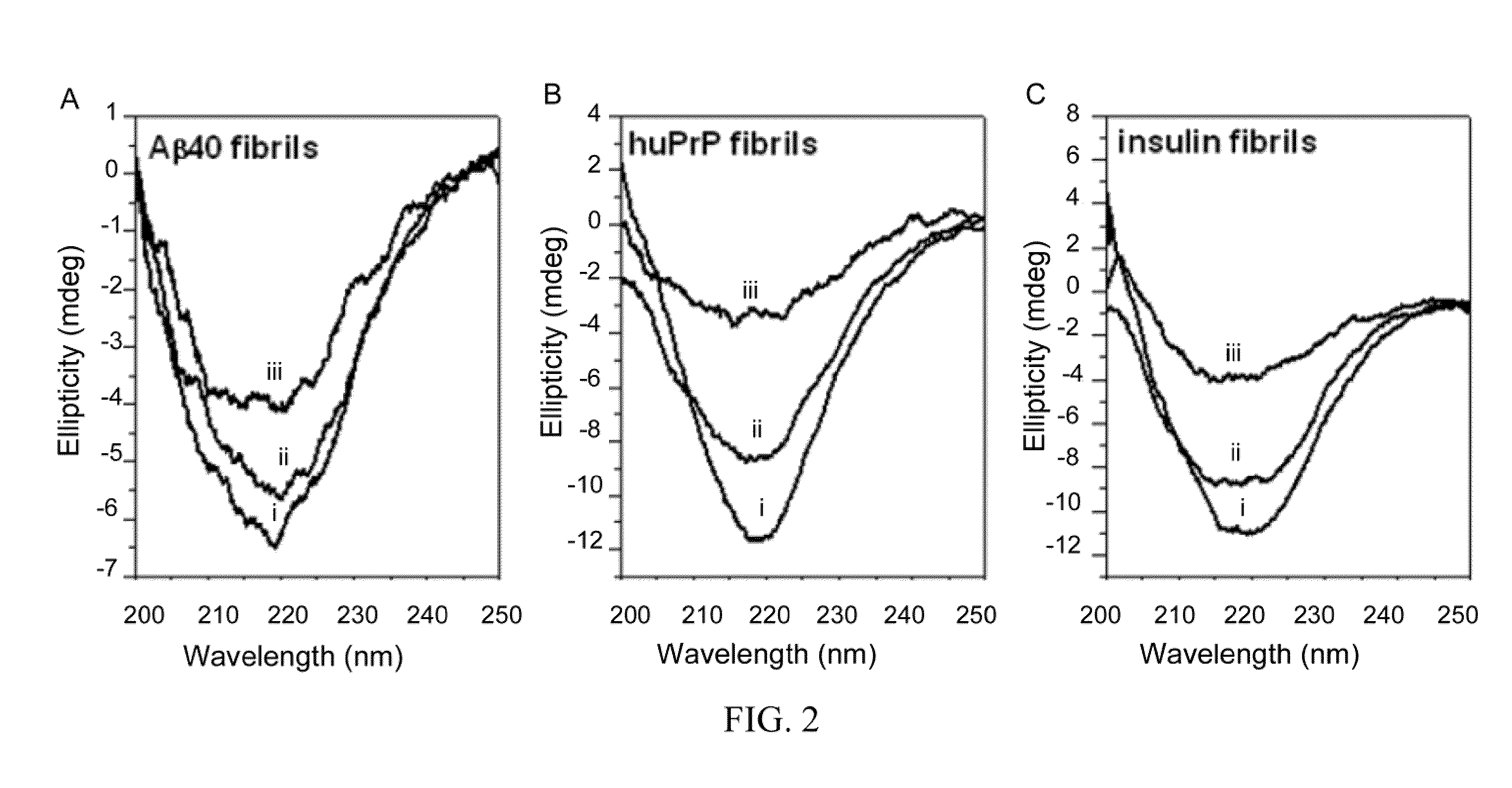
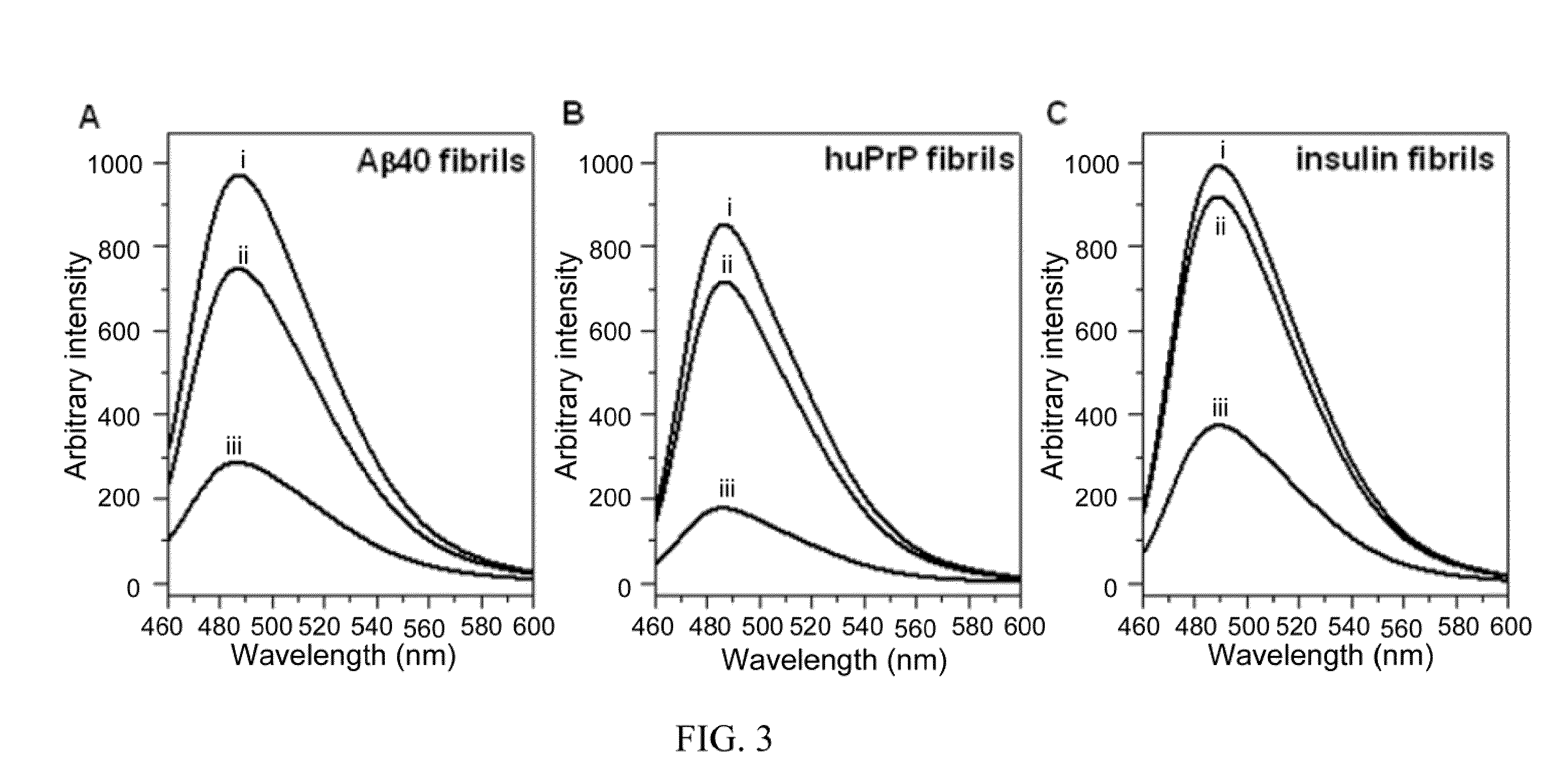
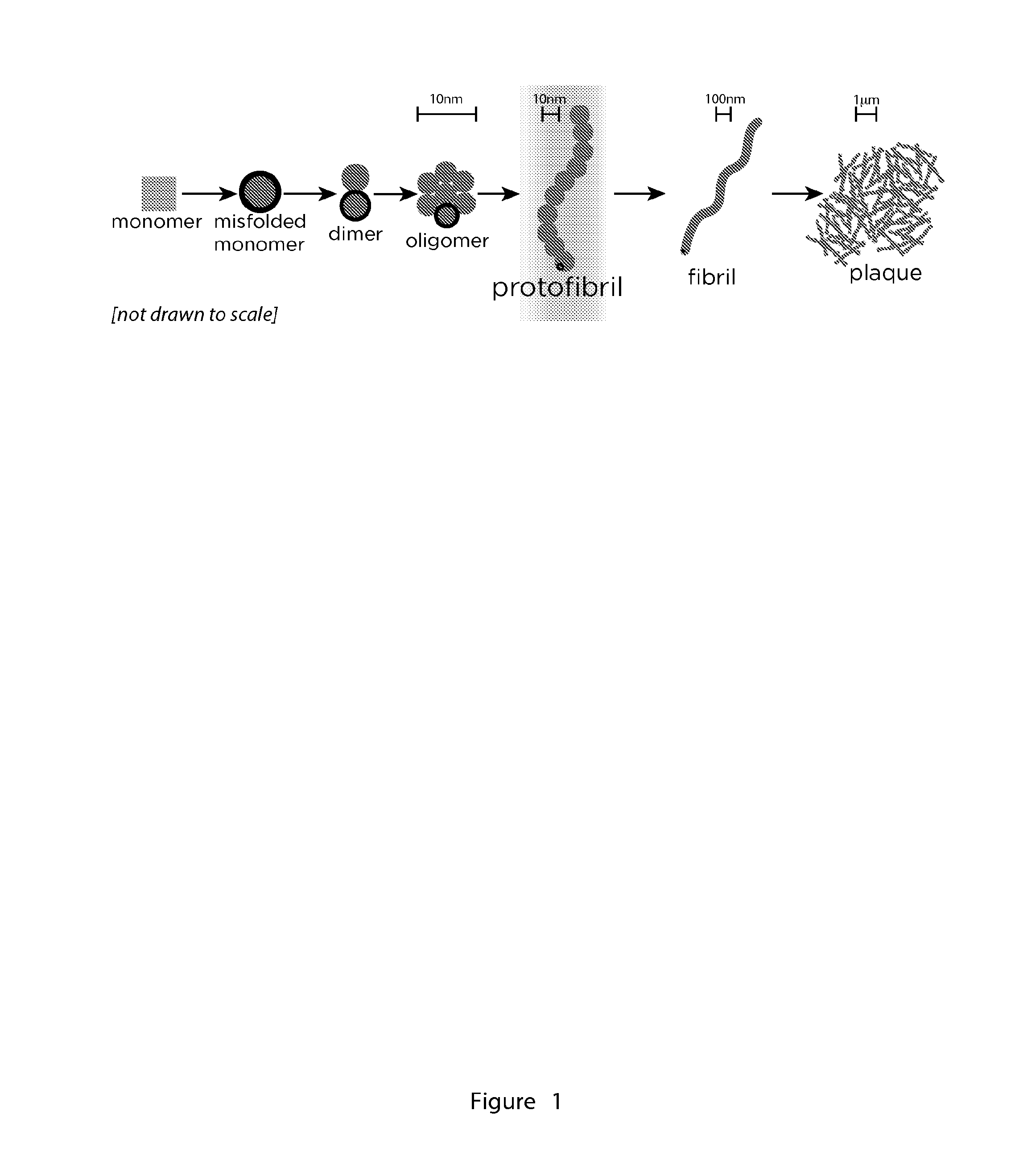
Amyloid fibrils are peptide or protein aggregates that form under certain conditions in vitro or in vivo. For example, the amyloid fibril plaques found in brain tissue of Alzheimer patients are formed from the peptide Aβ and are associated with neurodegeneration.
Passive immunization of Alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS6913745B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPassive ImmunizationsAmyloid disease
Disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods for preventing or treating a number of amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, prion diseases, familial amyloid neuropathies and the like. The pharmaceutical compositions include immunologically reactive amounts of amyloid fibril components, particularly fibril-forming peptides or proteins. Also disclosed are therapeutic compositions and methods which use immune reagents that react with such fibril components.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of amyloid diseases
Disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods for preventing or treating a number of amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's disesase, prion diseases, familial amyloid neuropathies and the like. The pharmaceutical compositions include immunologically reactive amounts of amyloid fibril components, particularly fibril-forming peptides or proteins. Also disclosed are therapeutic compositions and methods which use immune reagents that react with such fibril components.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY
Active immunization of AScr for prion disorders
Disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions and methods for preventing or treating a number of amyloid diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, prion diseases, familial amyloid neuropathies and the like. The pharmaceutical compositions include immunologically reactive amounts of amyloid fibril components, particularly fibril-forming peptides or proteins. Also disclosed are therapeutic compositions and methods which use immune reagents that react with such fibril components.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Monoclonal antibodies specific for high molecular weight aggregation intermediates common to amyloids formed from proteins of differing sequence
InactiveUS20070110750A1Low toxicityPreventing and limiting formationSenses disorderNervous disorderAmyloid diseaseDisease cause
Methods for the production of monoclonal antibodies specific to conformational epitope(s) of a prefibrilar aggregate(s) which contribute to amyloid fibril formation in human or animal subjects who suffer from amyloid diseases (e.g. Alzheimer's Disease) and the hybridomas and monoclonal antibodies produced therefrom. Also, the use of such monoclonal antibodies in the immunization of human or animal subjects against Alzheimer's Disease or other amyloid diseases and / or for the diagnosis or detection of Alzheimer's Disease or other amyloid diseases. The monoclonal antibodies may be administered concomitantly or in combination with anti-inflammatory agents, such as gold or gold containing compounds, to decrease neural inflammation associated with amyloid diseases (e.g. Alzheimer's Disease).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
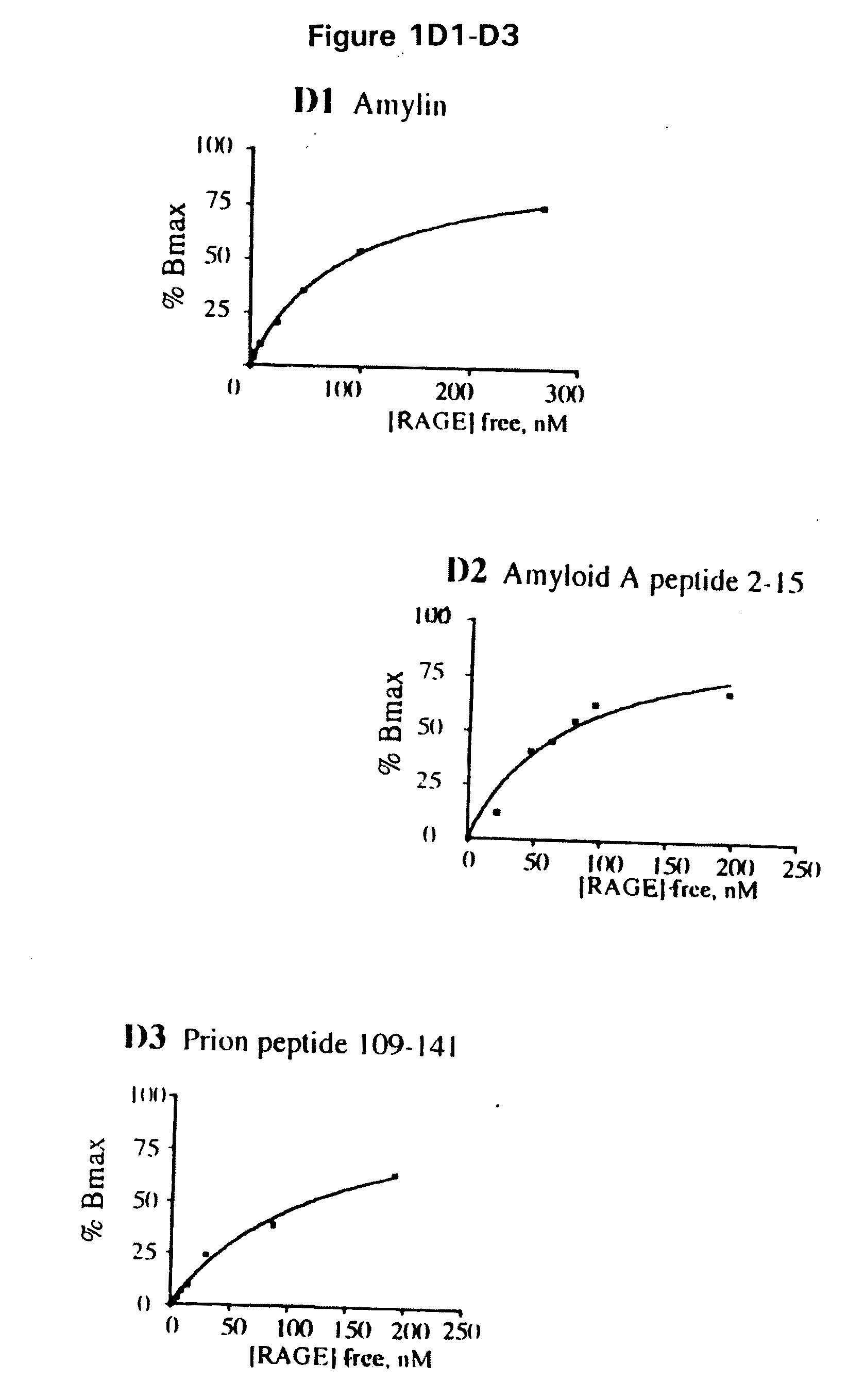
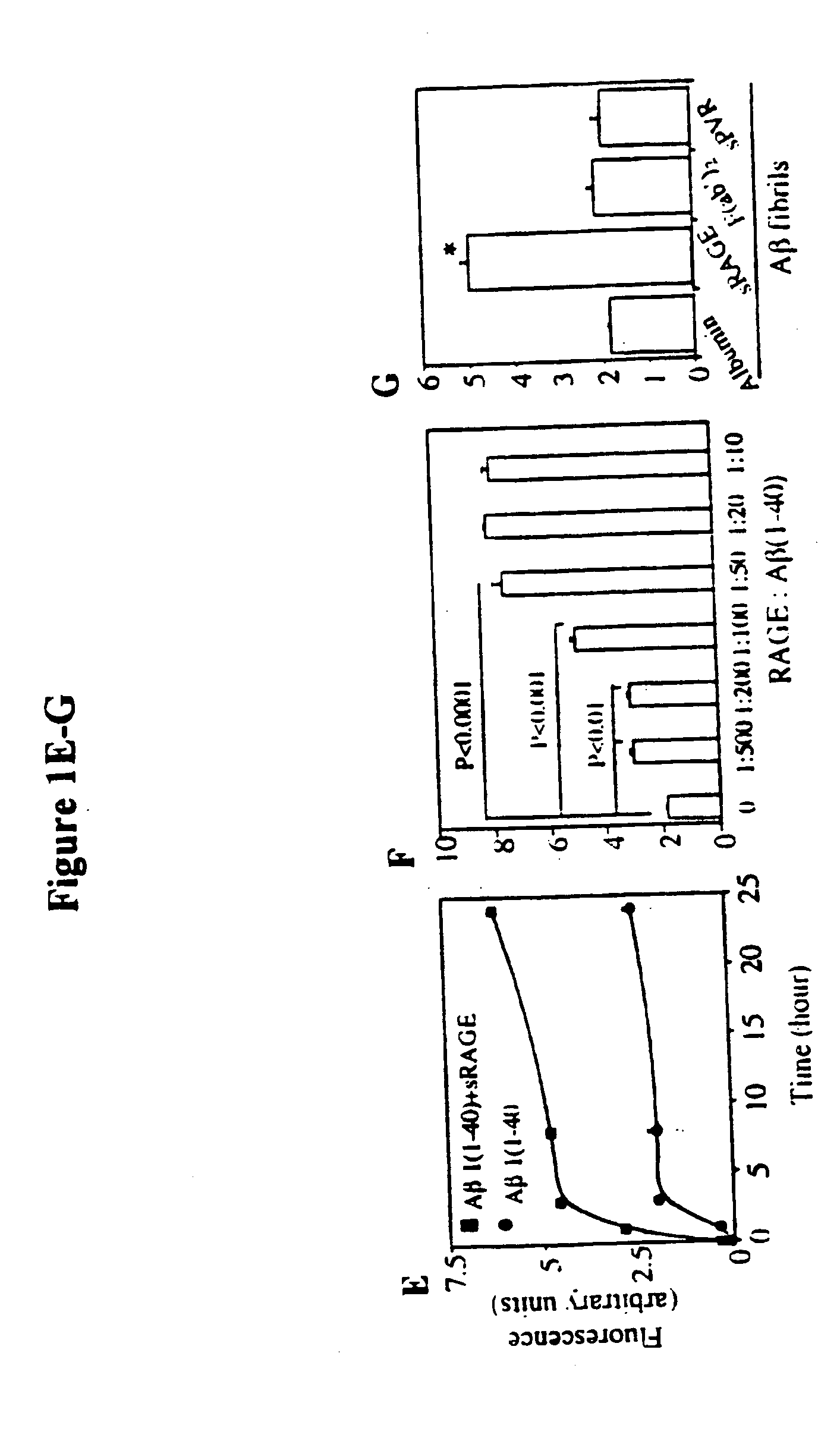
Methods of inhibiting binding of beta-sheet fibril to rage and consequences thereof
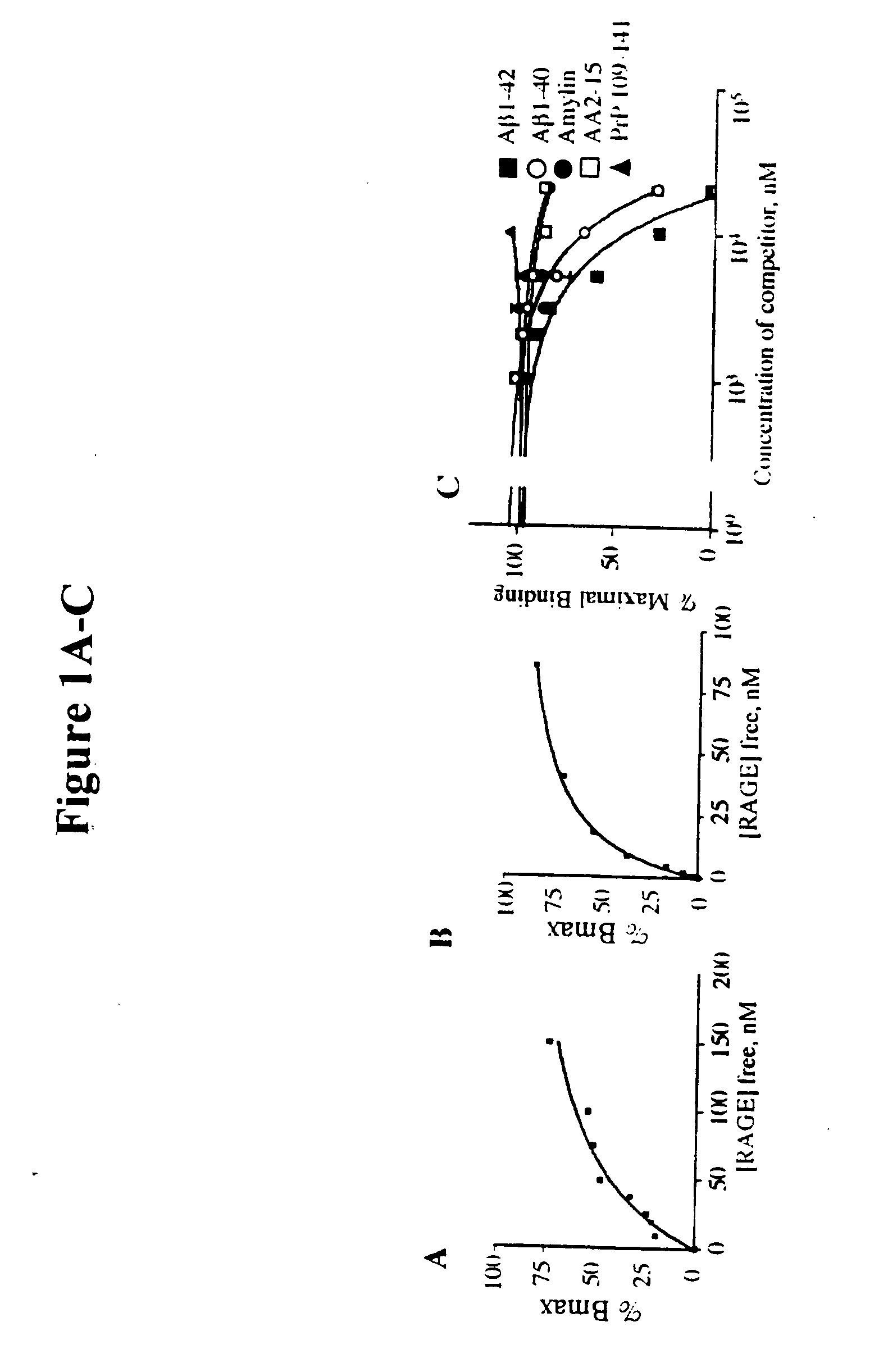
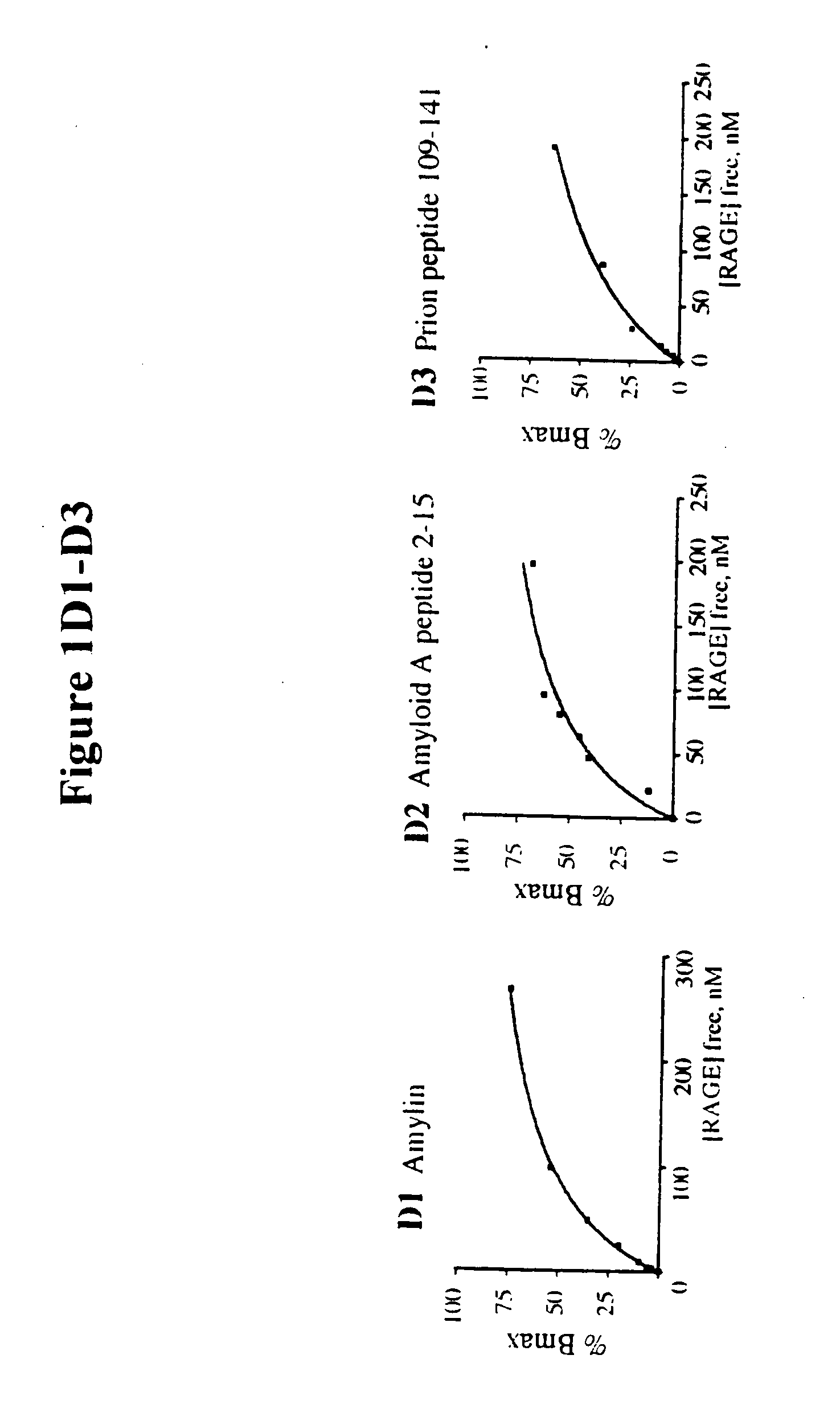
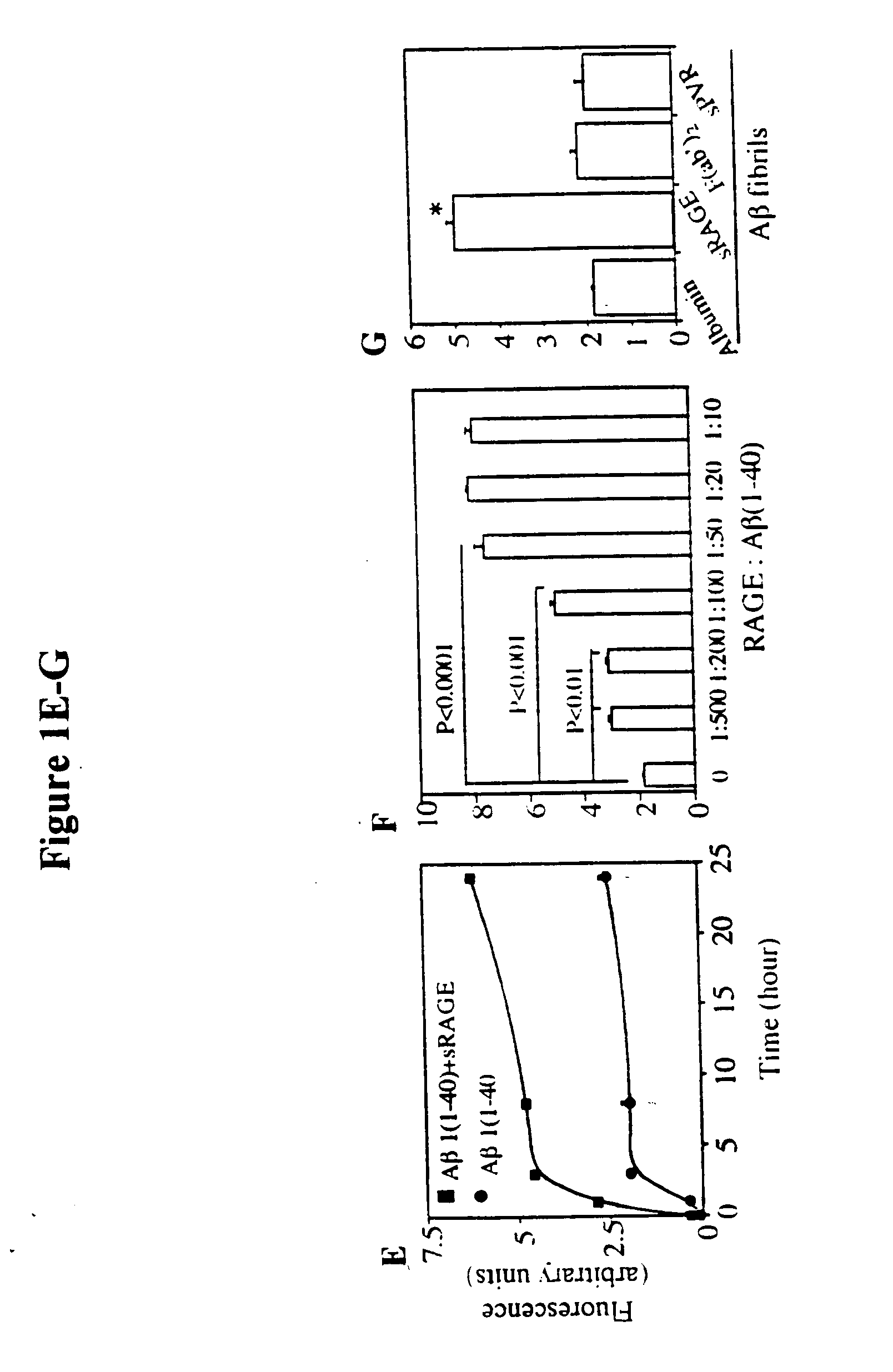
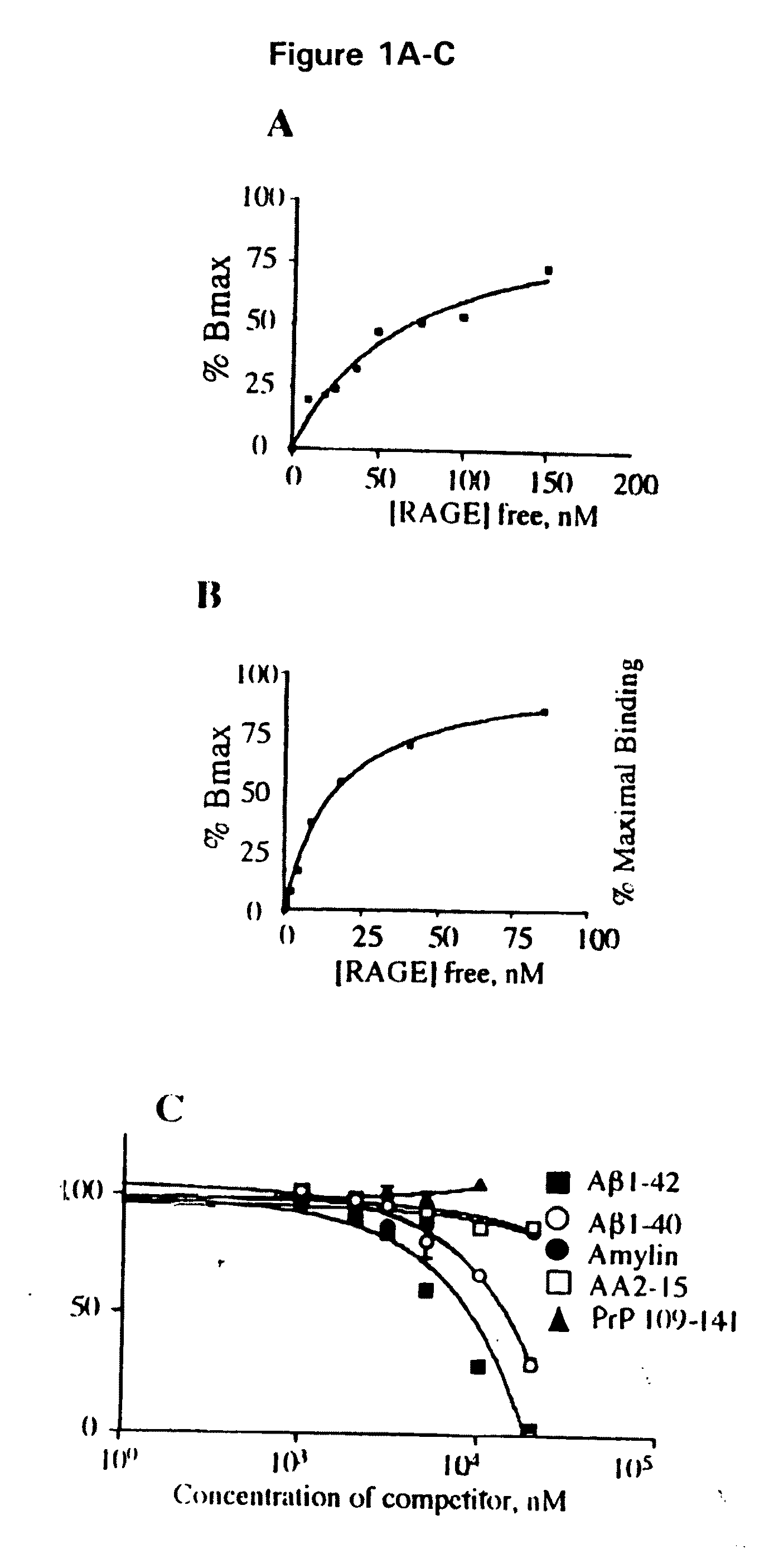
This invention provides a method of inhibiting the binding of a β-sheet fibril to RAGE on the surface of a cell which comprises contacting the cell with a binding inhibiting amount of a compound capable of inhibiting binding of the β-sheet fibril to RAGE so as to thereby inhibit binding of the β-sheet fibril to RAGE. In one embodiment the β-sheet fibril is amyloid fibril. In one embodiment, the compound is sRAGE or a fragment thereof. In another embodiment, the compound is an anti-RAGE antibody or portion thereof. This invention provides the above method wherein the inhibition of binding of the β-sheet fibril to RAGE has the consequences of decreasing the load of β-sheet fibril in the tissue, inhibiting fibril-induced programmed cell death, inhibiting fibril-induced cell stress. This invention also provides methods of determining whether a compound inhibits binding of a β-sheet fibril to RAGE on the surface of a cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
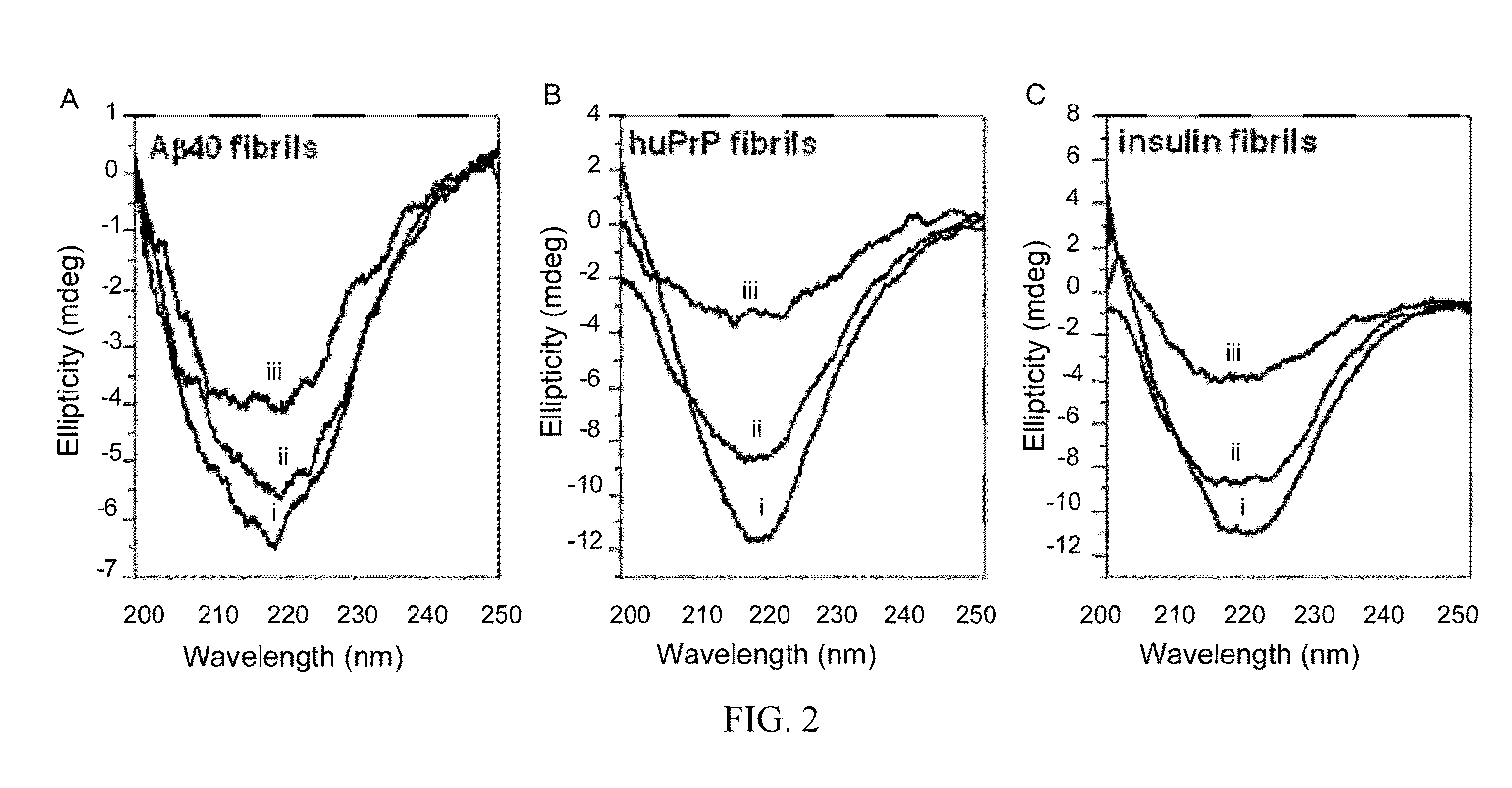
Methods for Determining Conformational Changes and Self-Assembly of Proteins
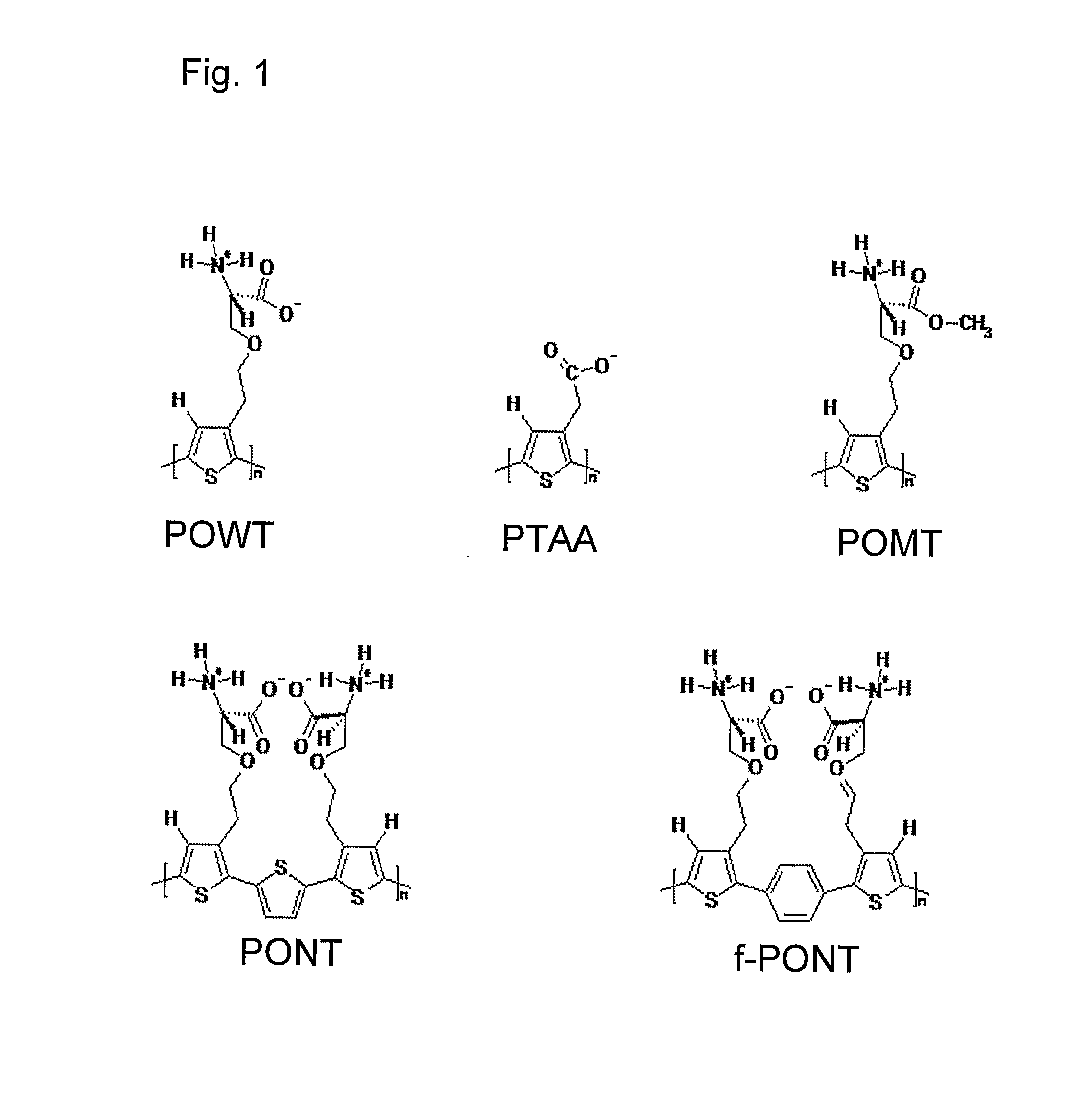
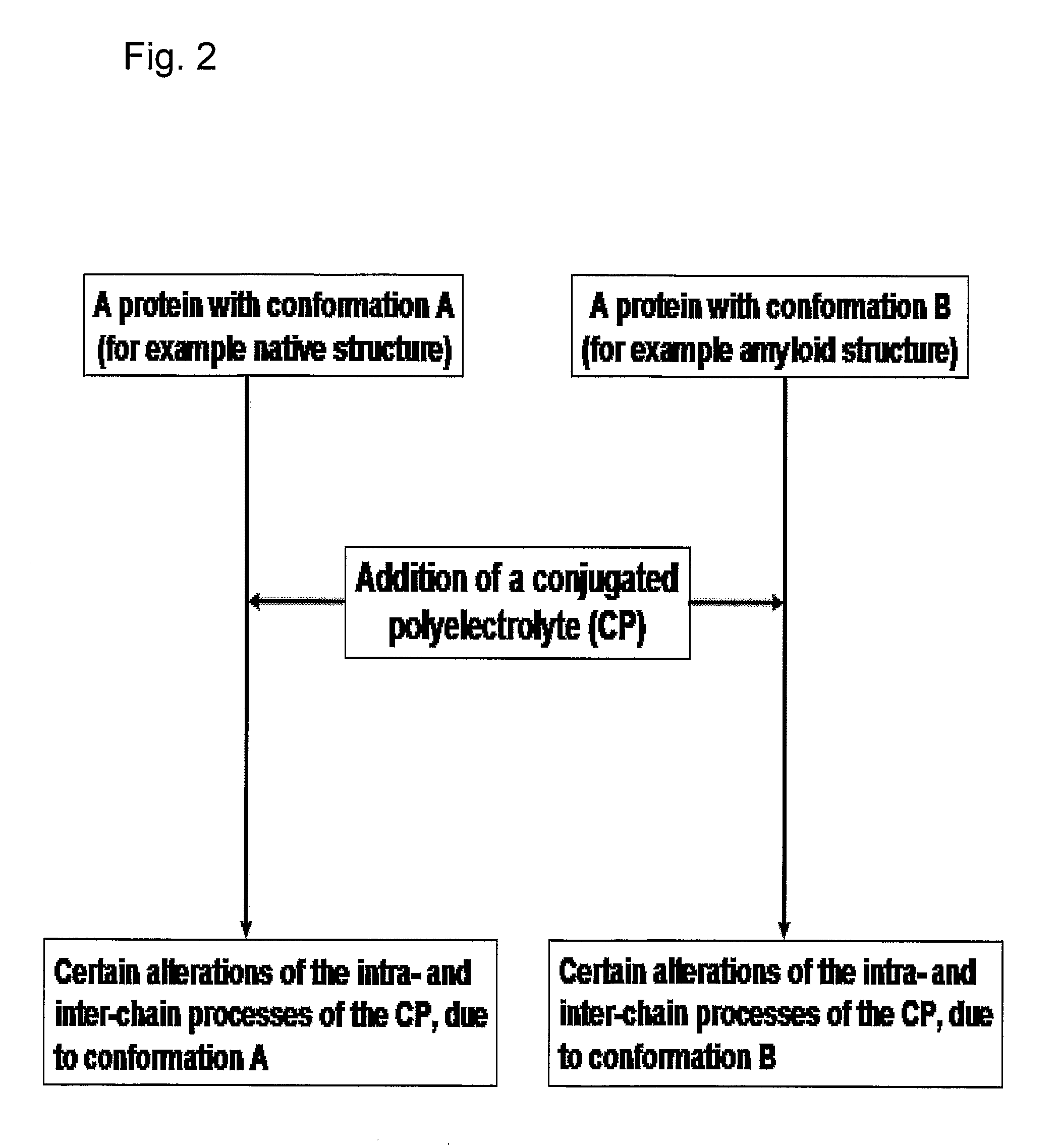
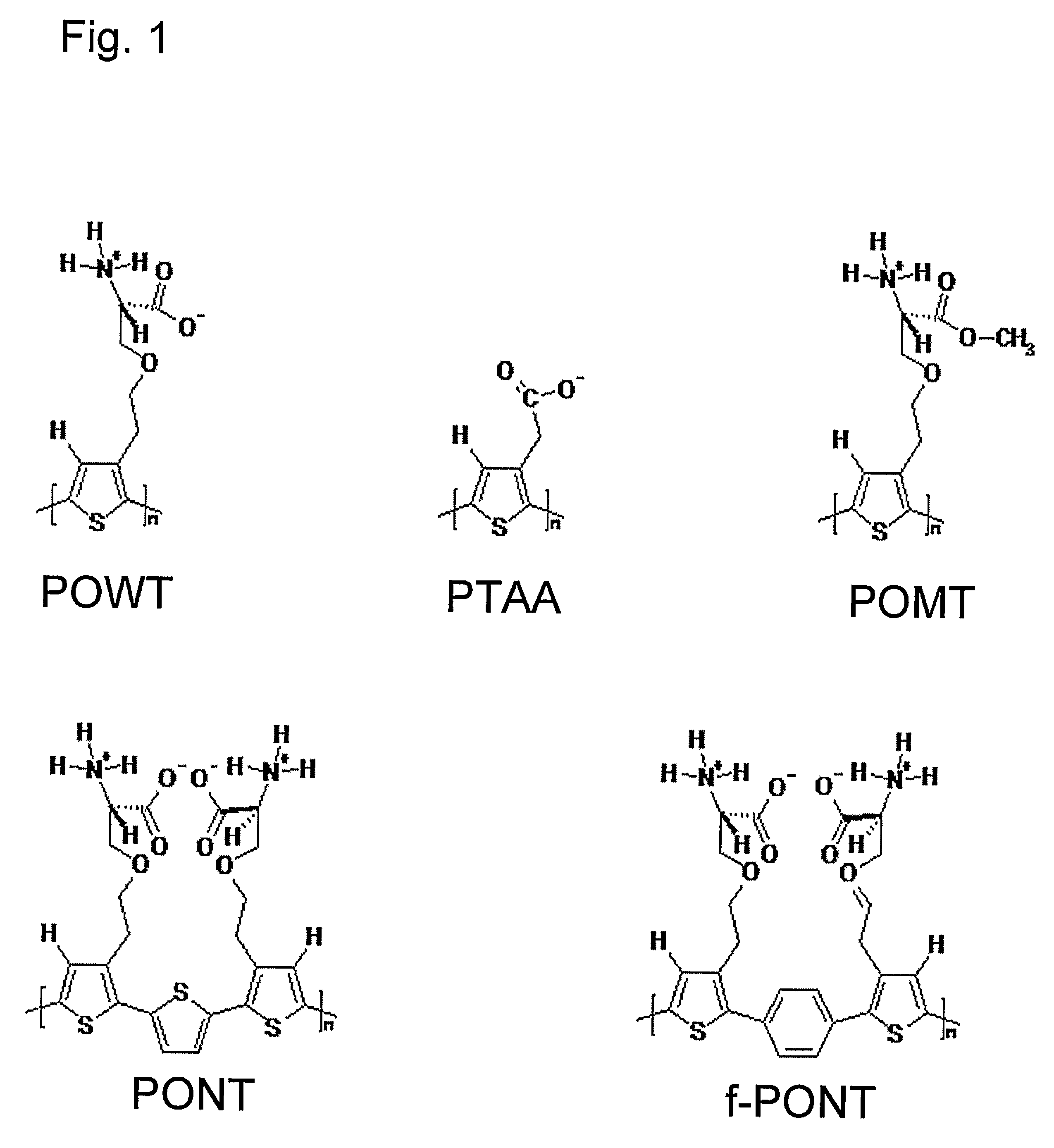
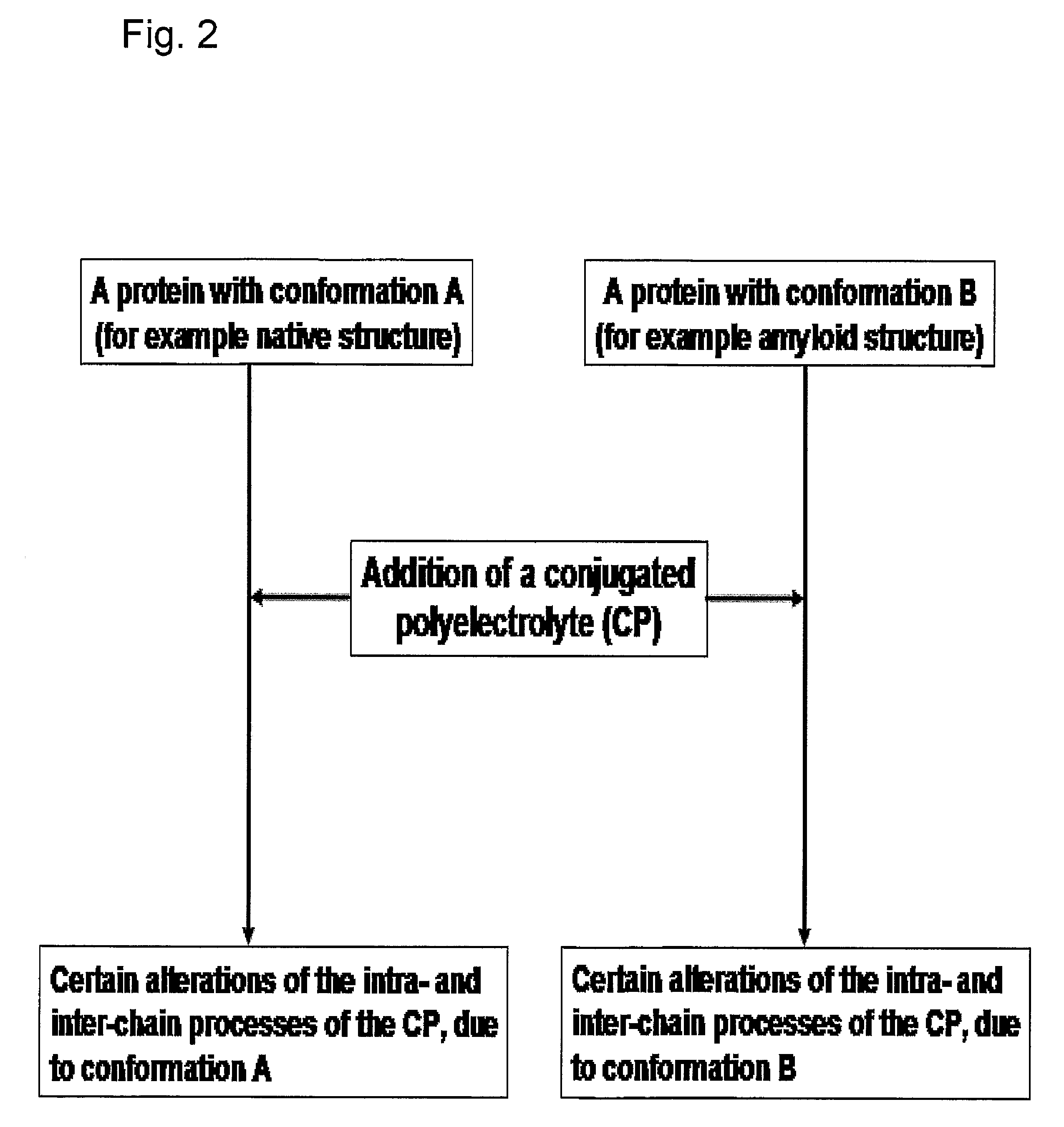
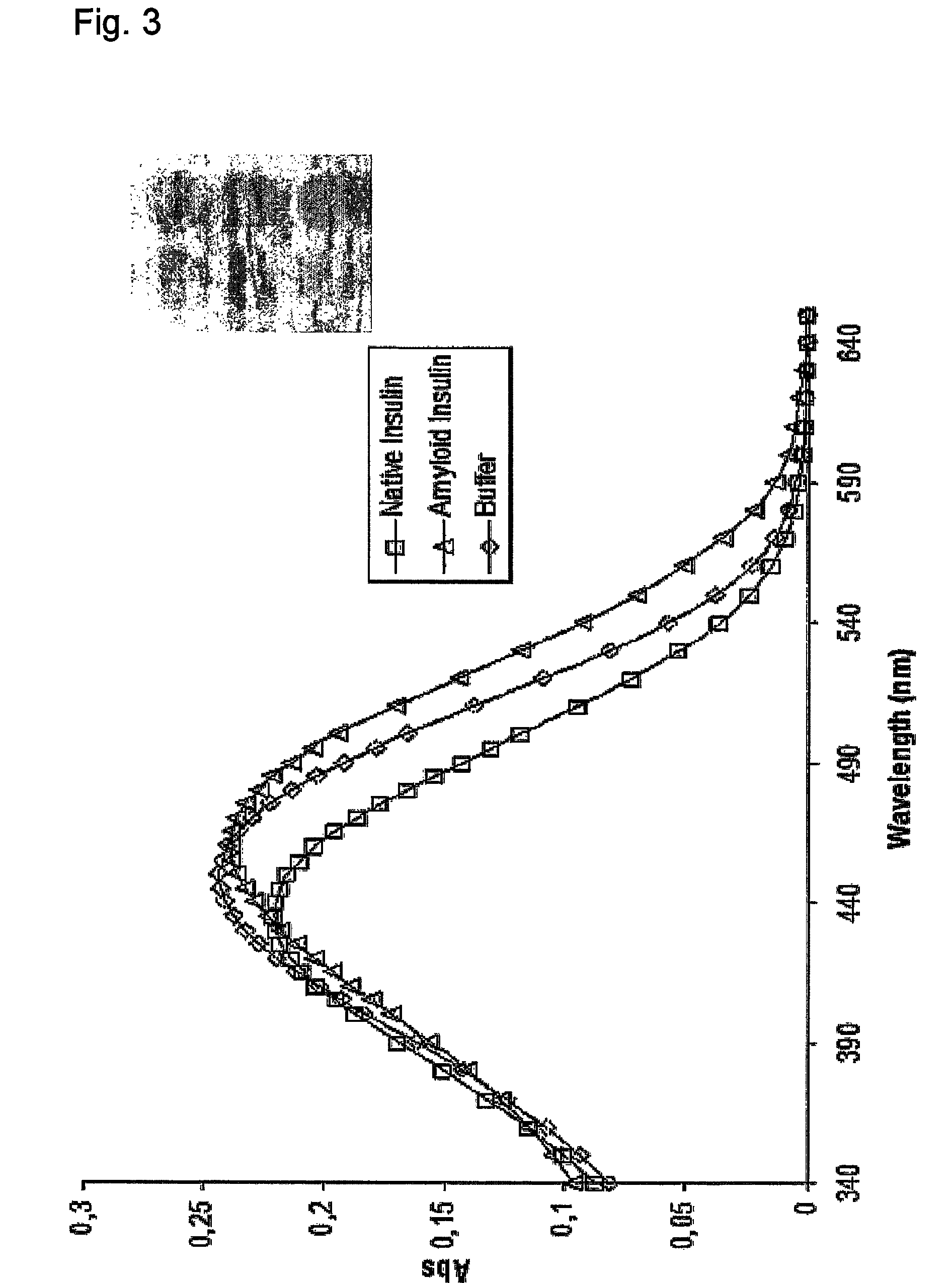
InactiveUS20080038751A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelf-assemblyConjugated polyelectrolyte
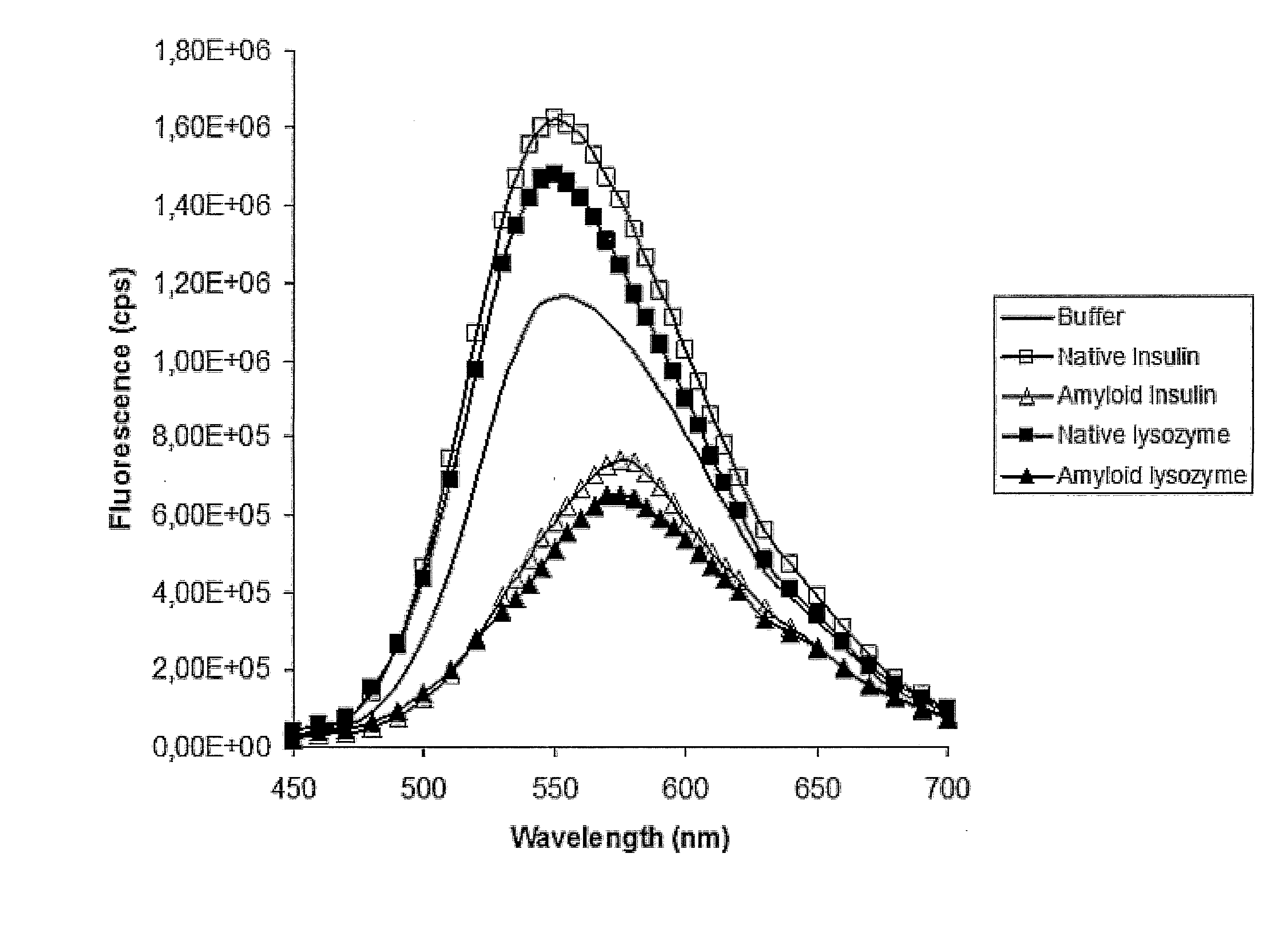
The invention relates to methods for measuring conformational changes and self-assembly / aggregation of proteins, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils, using conjugated polyelectrolytes. The conjugate polyelectrolyte is exposed to the protein whereby the conjugated polyelectrolyte and the protein of interest interact, and a change of a property of the polyelectrolyte in response to conformational changes of the protein is observed. The detected change is used to determine different conformations of the protein, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Inhibitors and disassemblers of fibrillogenesis
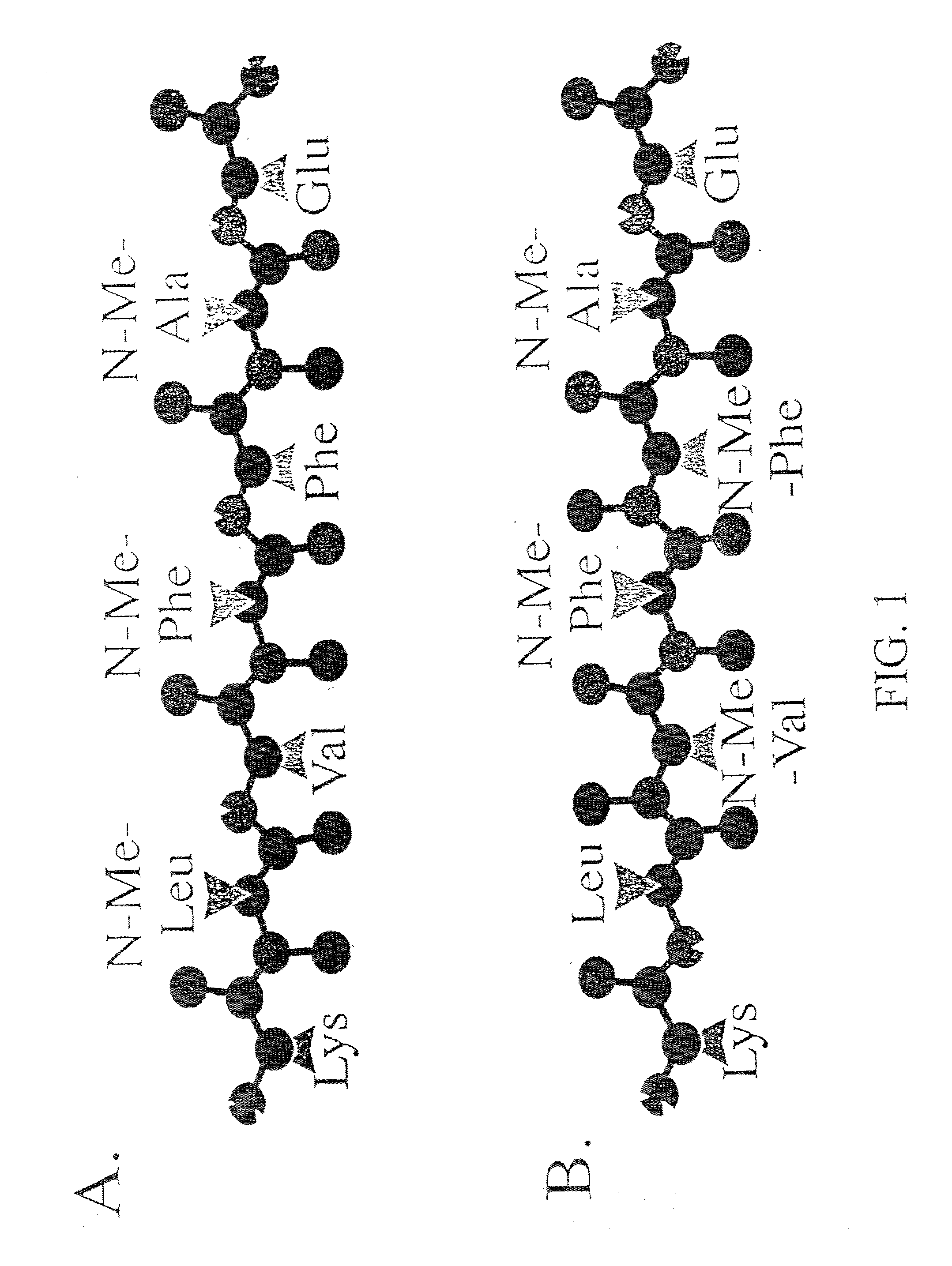
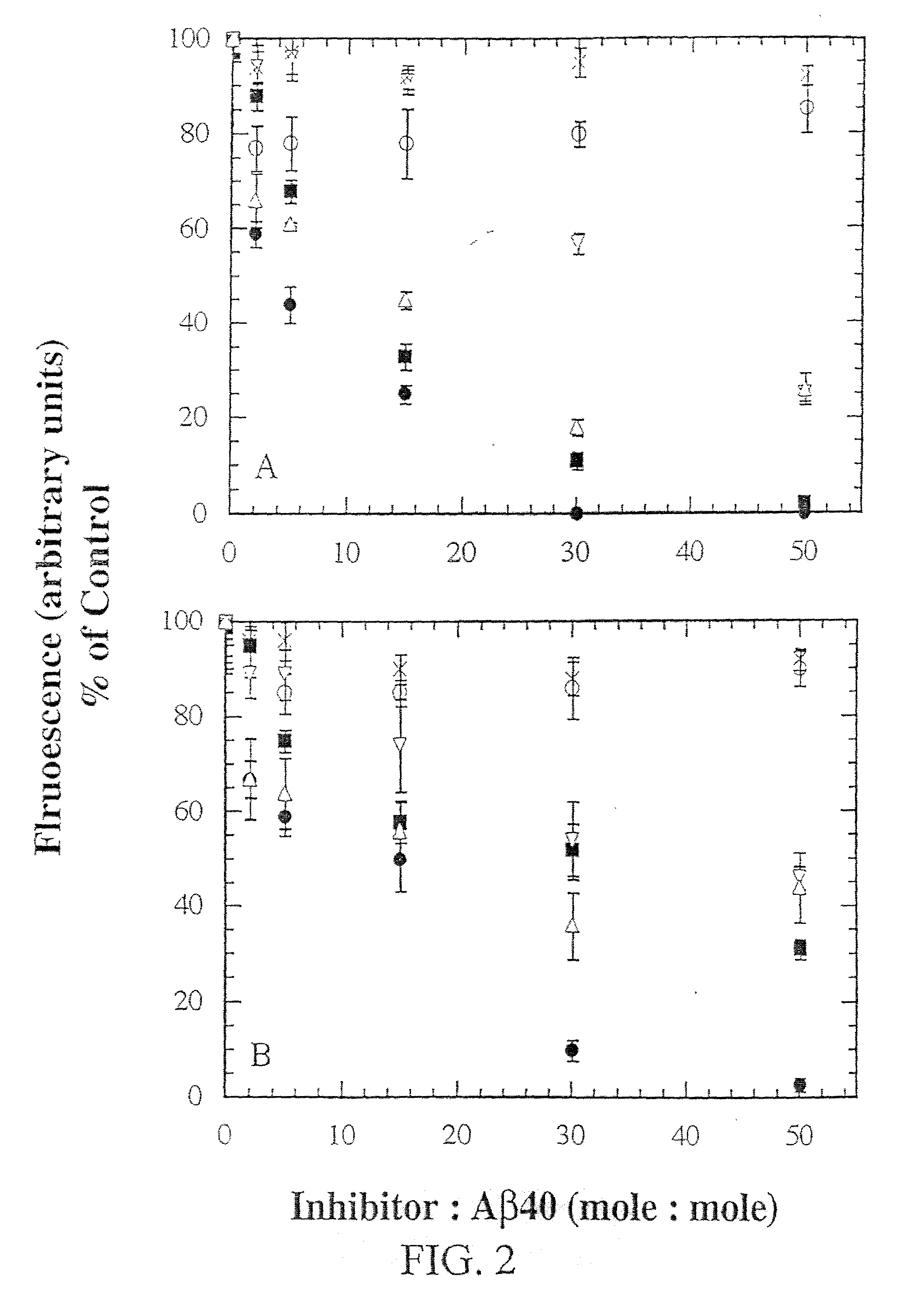
InactiveUS20030130484A1Highly effective at disassembling pre-formed fibrilsInhibition formationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFiberAmino acid
Methods and compositions are presented that inhibit fibril formation and / or bring about disassembly of pre-formed fibrils. Compositions include peptides with short beta-strands with two faces: one that can bind to beta-amyloids through hydrogen bonds, and one which blocks propagation of hydrogen bonding needed to form fibrils. Thus, short congeners of the fibril protein containing N-methyl amino acids or esters are provided for the inhibition of fibril formation and for the disassembly of pre-existing or pre-formed fibrils. Specific aspects address beta-amyloid fibrils; prion mediated fibrils; Huntington protein fibrils. Methods for screening for potential fibril inhibitors and disassemblers, diagnostic analysis and treatments are provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Apomorphine inhibitors of amyloid-beta (Abeta) fibril formation and their use in amyloidosis based disease
Described is a new class of small molecule inhibitors of amyloid beta protein (Abeta) aggregation, based on apomorphine. These molecules target the nucleation phase of Abeta self-assembly and interfere effectively with aggregation of Abeta 1-40 into amyloid fibrils in vitro as determined by transmission electron microscopy, Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence, and velocity sedimentation. Structure-activity studies using apomorphine analogues demonstrate that 10,11-dihydroxy substitutions of the D ring are preferred for the inhibitory effectiveness of these aporphines, and that methylation of these hydroxyl groups reduces their inhibitory potency. The ability of these small molecules to inhibit Abeta amyloid fibril formation appears to be linked to their ability to undergo auto-oxidation in solution, implicating an auto-oxidation product as the active Abeta inhibitor. Sedimentation velocity and electron microscopy studies demonstrate that apomorphine and analogues facilitate oligomerization of Abeta into short nonfibrillar soluble assemblies, but inhibit Abeta fibrillization.
Owner:CYTOKINE PHARMASCI
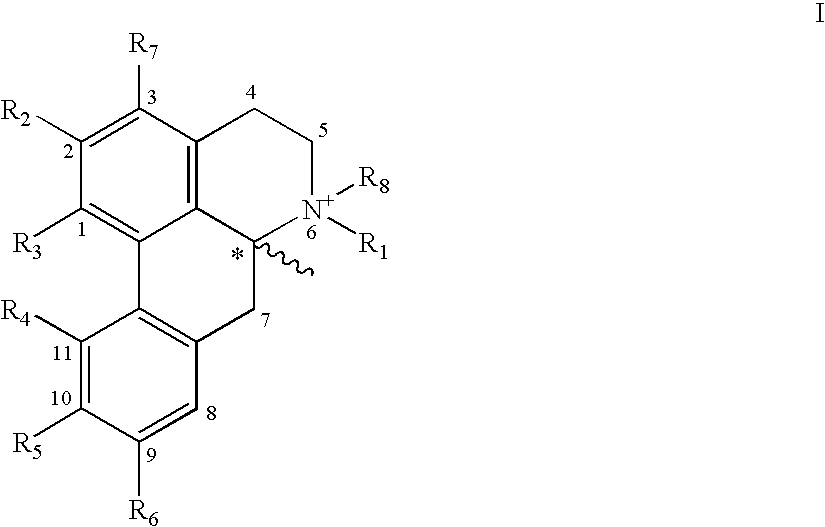
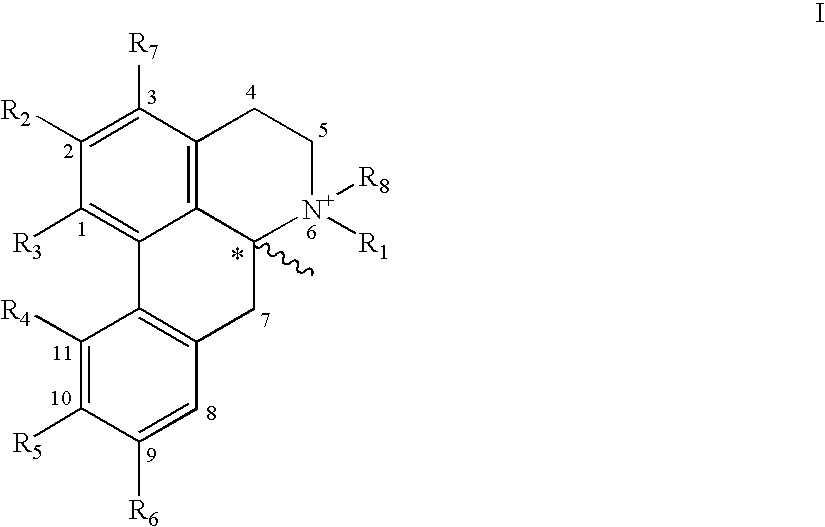
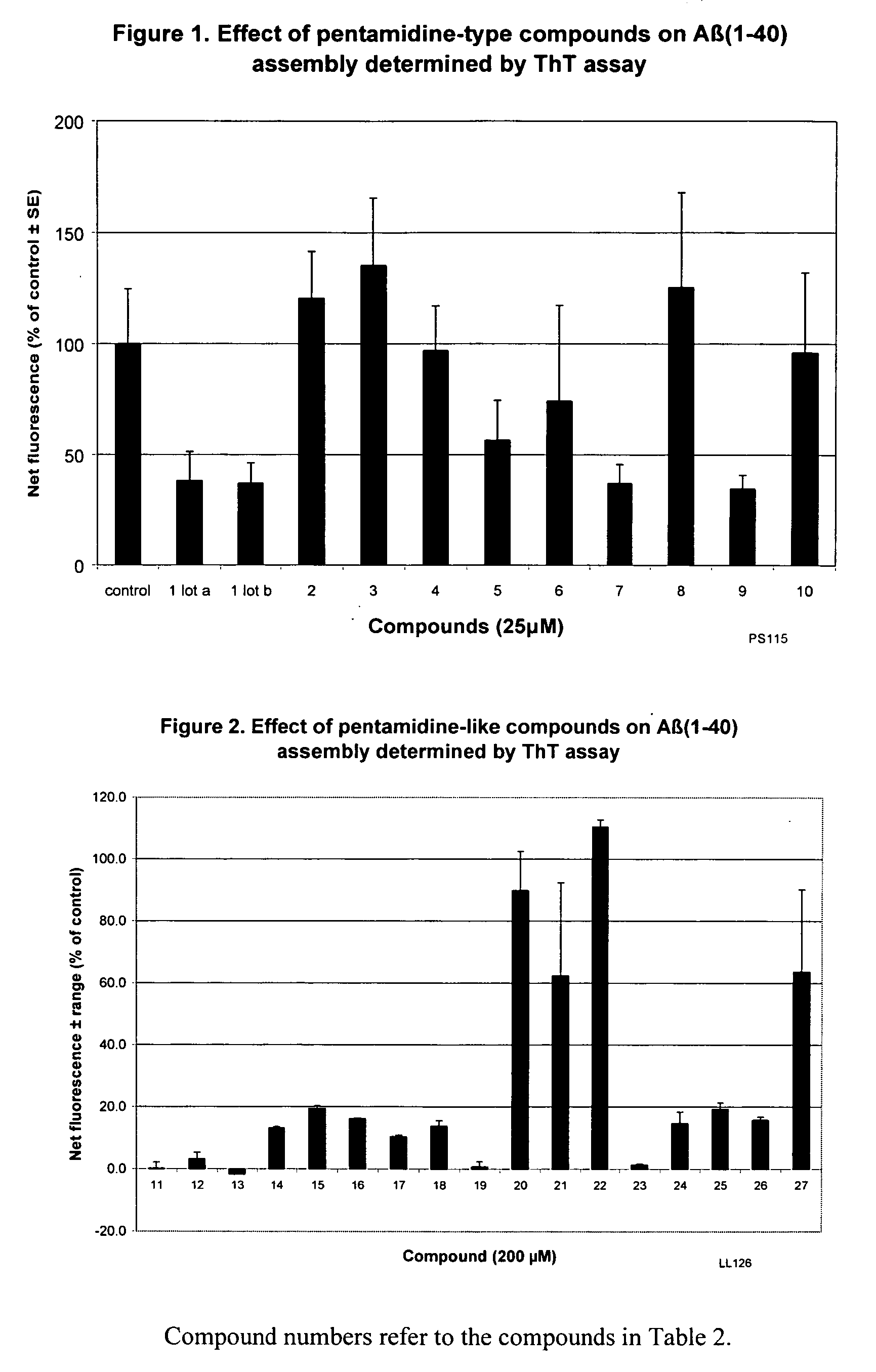
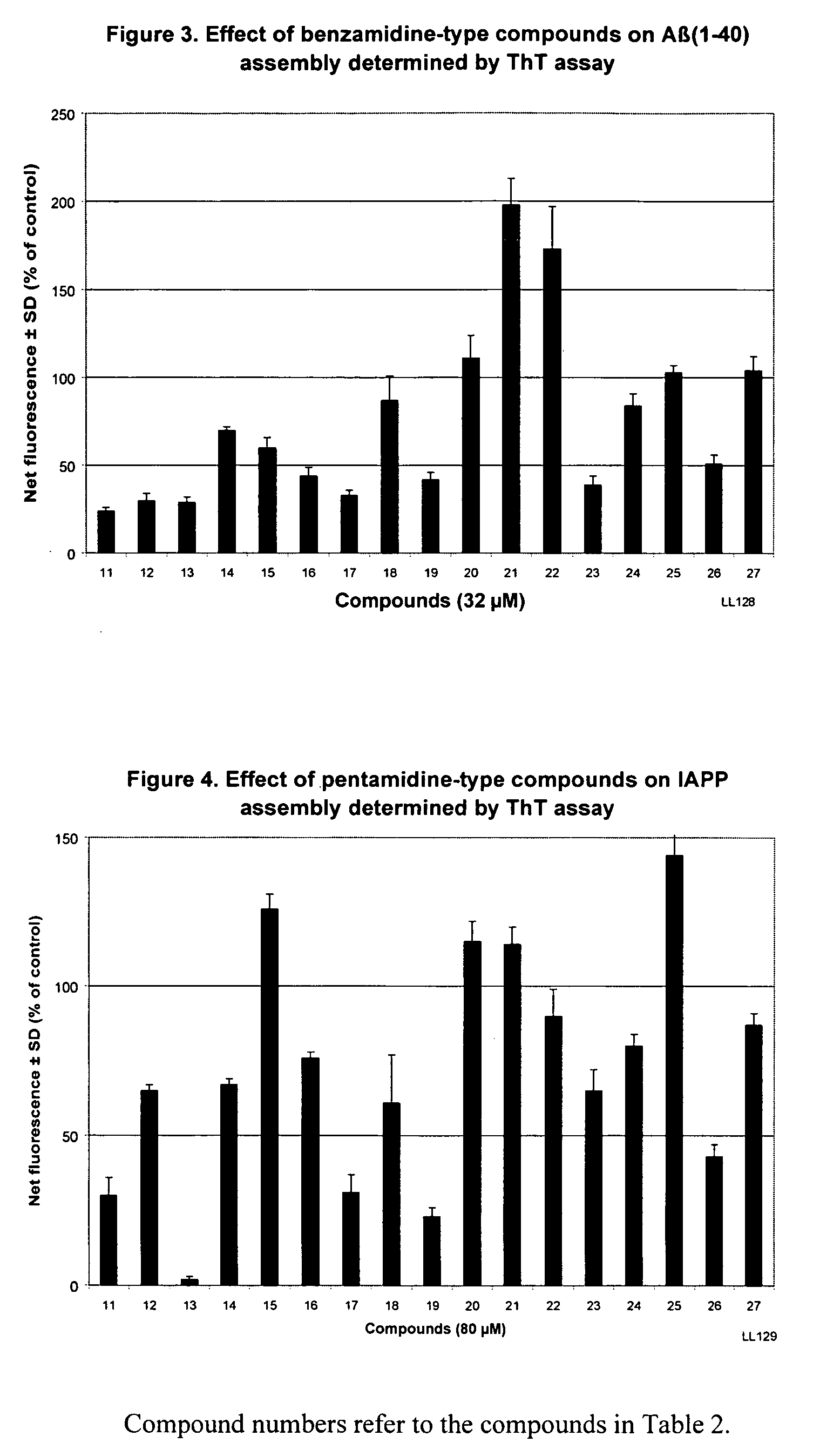
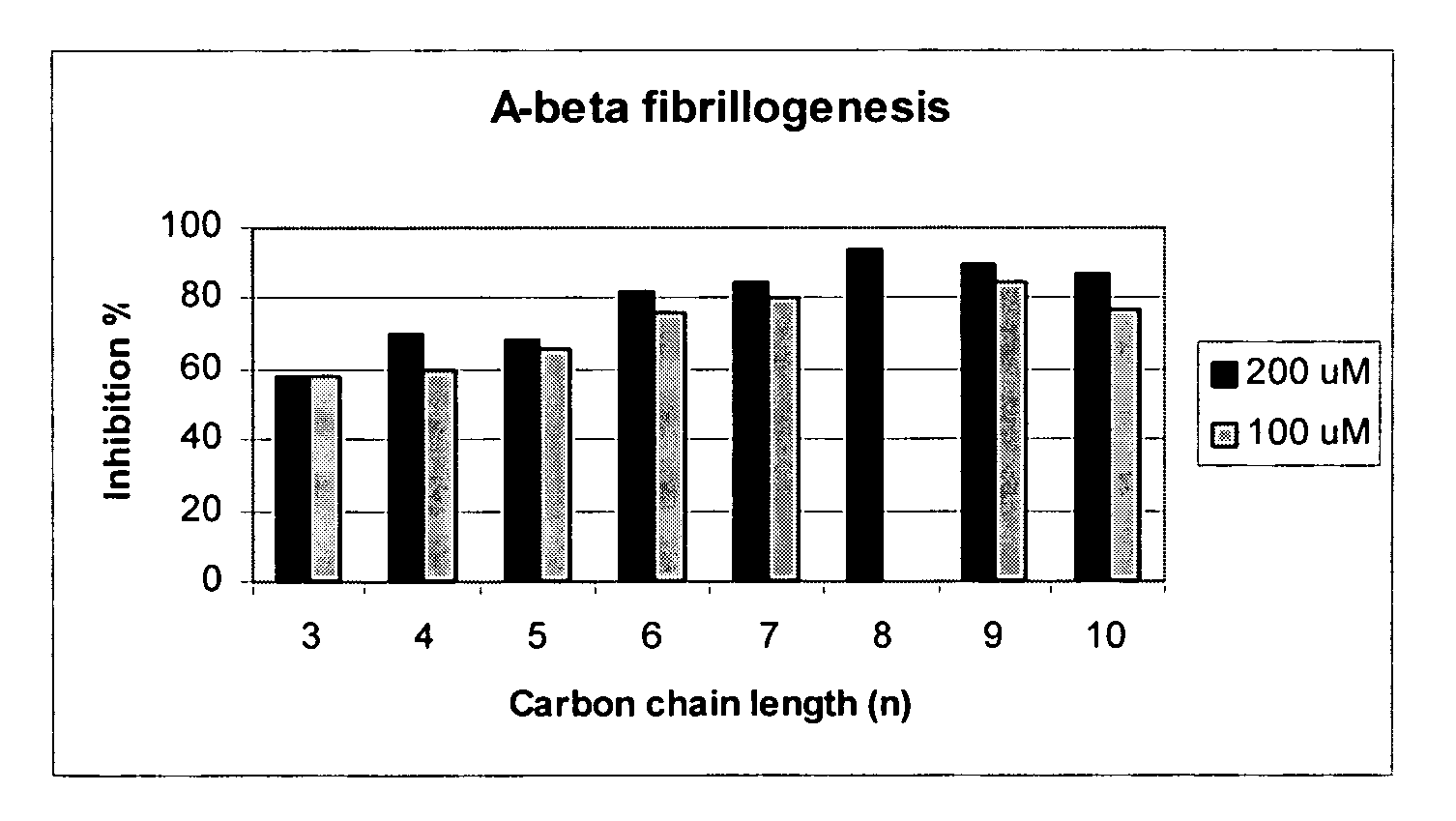
Amidine derivatives for treating amyloidosis
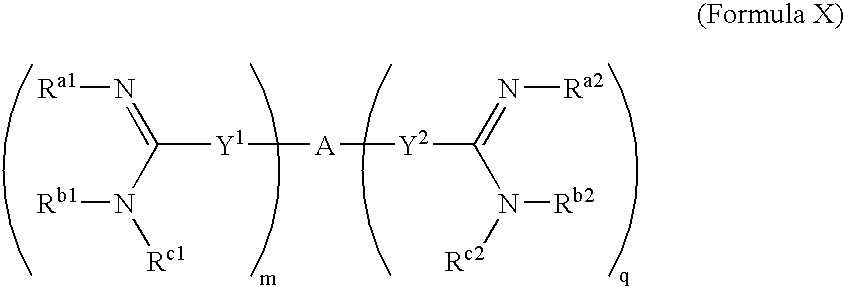
The present invention relates to the use of amidine compounds in the treatment of amyloid-related diseases. In particular, the invention relates to a method of treating or preventing an amyloid-related disease in a subject comprising administering to the subject a therapeutic amount of an amidine compound. Among the compounds for use according to the invention are those according to the following Formula, such that, when administered, amyloid fibril formation, neurodegeneration, or cellular toxicity is reduced or inhibited:
Owner:NEUROCHEM INT
Amidine derivatives for treating amyloidosis
The present invention relates to the use of amidine compounds in the treatment of amyloid-related diseases. In particular, the invention relates to a method of treating or preventing an amyloid-related disease in a subject comprising administering to the subject a therapeutic amount of an amidine compound. Among the compounds for use according to the invention are those according to the following Formula, such that, when administered, amyloid fibril formation, neurodegeneration, or cellular toxicity is reduced or inhibited:
Owner:BELLUS HEALTH (INT) LTD (CH)
Conjugates of amyloid proteins as vaccines for amyloid-related diseases
InactiveUS20070172496A1Treating, preventing and/or ameliorating amyloid-related diseasesPreventing or reducing amyloid-induced cellular toxicityBacterial antigen ingredientsNervous disorderAmyloid betaMammal
New conjugates comprising fragments of amyloid proteins, which may be used in vaccines for the treatment, prevention and / or amelioration of diseases associated with deposition of amyloid proteins, such as, e.g. Alzheimers disease. Methods for treating, preventing and / or ameliorating amyloid-related diseases, by administering a conjugate comprising fragments of an amyloid protein to a subject in need thereof, thereby enabling the production of antibodies in the subject. Antibodies—being capable of interacting with pathological regions within an amyloid protein, and thereby preventing e.g. the formation of amyloid fibrils, plaques and / or deposits, and methods for passive immunization wherein an antibody as described above is administered to a subject in need thereof. Furthermore is provided specific fragments of the C-terminal part of amyloid beta (1-42), that when administered to a mammal generates antibodies, which specifically targets the soluble form of the highly amyloidogenic amyloid beta (1-42).
Owner:CURIX
Methods for amyloid removal using anti-amyloid antibodies
InactiveUS8105594B2Nervous disorderSugar derivativesCell mediated immunityCell-mediated immune response
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for removal or destruction of amyloid fibril or amyloid adhesin comprising aggregates
InactiveUS20130115257A1Reduce riskFacilitate communicationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHuntingtons choreaAmyloid beta
Methods and compositions for treating biofilms and diseases associated with amyloidosis such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease, and Type 2 diabetes, by destroying amyloid fibrils in a two-step treatment are disclosed. The first step consists of binding to the amyloid fibril an intercalating molecule with a negatively charged group such as Congo red. The second step consists of adding metal ions, such as silver, gold(I), copper(I), palladium or lead ions or metal colloids of silver or gold, which destabilize the amyloid-dye complex. This process results in a disintegration of the fibril into peptide monomers and small aggregates of monomers.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Therapeutic formulations for the treatment of beta-amyloid related diseases
A method of preventing or treating an amyloid-β-related disease in an individual, the method comprising administering to an individual in need thereof an effective amount of a first therapeutic agent for preventing or treating an amyloid-β-related disease, and a second A therapeutic agent, the second therapeutic agent being (i) a peptide or peptidomimetic compound that modulates amyloid-beta fibril formation or induces a prophylactic or therapeutic immune response against amyloid-beta fibril formation, or (ii) Immune system modulator that prevents or inhibits amyloid-beta fibril formation.
Owner:NEUROCHEM INT
Novel oxadiazole derivative and pharmaceutical containing same
ActiveUS20180072708A1Easy to synthesizePreventing initiationNervous disorderOrganic chemistryHydrogen atomMedicinal chemistry
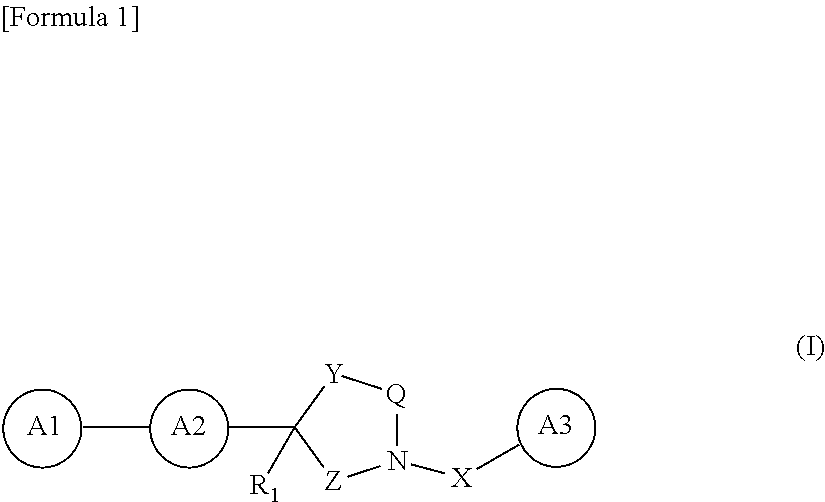
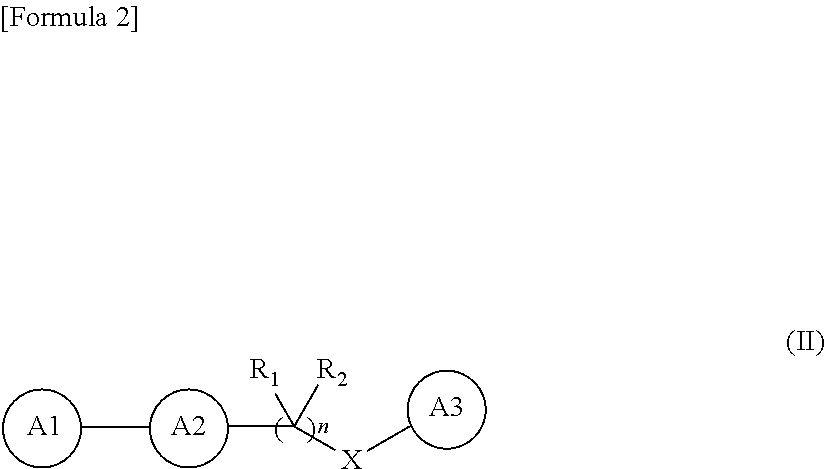
An amyloid fibril formation inhibitor comprising a compound represented by the following general formulae (I) to (III):whereinQ is —C(═O)—;X is —C(═O)—, —NH—C(═O)—;Y is —(CH2)m—;Z is —(CH2)n—;R1, R2, and R3 are each independently a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a hydroxyalkyl group, an alkylaminoalkyl group; andR4 is an amino group, an alkylamino group or the like;or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a solvate thereof.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR GERIATRICS & GERONTOLOGY
Methods of inhibiting binding of beta-sheet fibril to rage and consequences thereof
This invention provides a method of inhibiting the binding of beta-sheet fibril to RAGE on the surface of a cell which comprises contacting the cell with a binding-inhibiting amount of a compound capable of inhibiting binding of beta-sheet fibril to RAGE so as to thereby inhibit binding of beta-sheet fibril to RAGE.In one embodiment, the beta-sheet fibril is amyloid fibril. In one embodiment, the compound is sRAGE or a fragment thereof. In another embodiment, the compound is an anti-RAGE antibody or portion thereof.This invention provides the above method wherein the inhibition of binding of the beta-sheet fibril to RAGE has the consequences of decreasing the load of beta-sheet fibril in the tissue, inhibiting fibril-induced programmed cell death, and inhibiting fibril-induced cell stress.This invention also provides methods of determining whether a compound inhibits binding of a beta-sheet fibril to RAGE on the surface of a cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods and compositions for treatment of amyloid deposition diseases
ActiveUS20190038745A1Reduction in NT-proBNPImprovement in GLSNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAfter treatmentCardiac muscle
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of amyloid deposition diseases using chimeric (e.g., mouse-human) antibody are disclosed, including a method for treating amyloid deposition diseases with cardiac involvement by administering pharmaceutical compositions comprising a chimeric anti-amyloid fibril antibody. The methods herein can improve myocardial function in patients diagnosed with light chain amyloid light chain amyloidosis (ALA) having a cardiac involvement in as little as three weeks after treatment.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Compounds useful for the treatment of diseases associated with the formation of amyloid fibrils
The present invention provides new amyloidogenesis inhibiting compounds of formula (I): in which R1 is a —NRaRb group, where Ra and Rb, independently, are a hydrogen atom or a C1-C6 alkyl group; —ORc group, where Rc is a hydrogen atom or a C1-C6 alkyl group; a glycosyl; a C1-C6 polyhydroxyalkyl; or a —NH—CH(Rd)—COORe group, where Rd is a side chain of one of the 20 natural alpha-amino acids in either of their two enantiomerically pure forms L or D, and Re is a hydrogen atom or a C1-C6 alkyl group; and R2 is a hydrogen atom, a C1-C6 alkyl group, a glycosyl; a C1-C6 polyhydroxyalkyl; —C(═O)—Rf group, where Rf is a C1-C6 alkyl group; or a —CH2—COO—Rg group, where Rg is a hydrogen atom or a C1-C6 alkyl group; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, which are useful in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, among others.
Owner:INNOVAPROTEAN
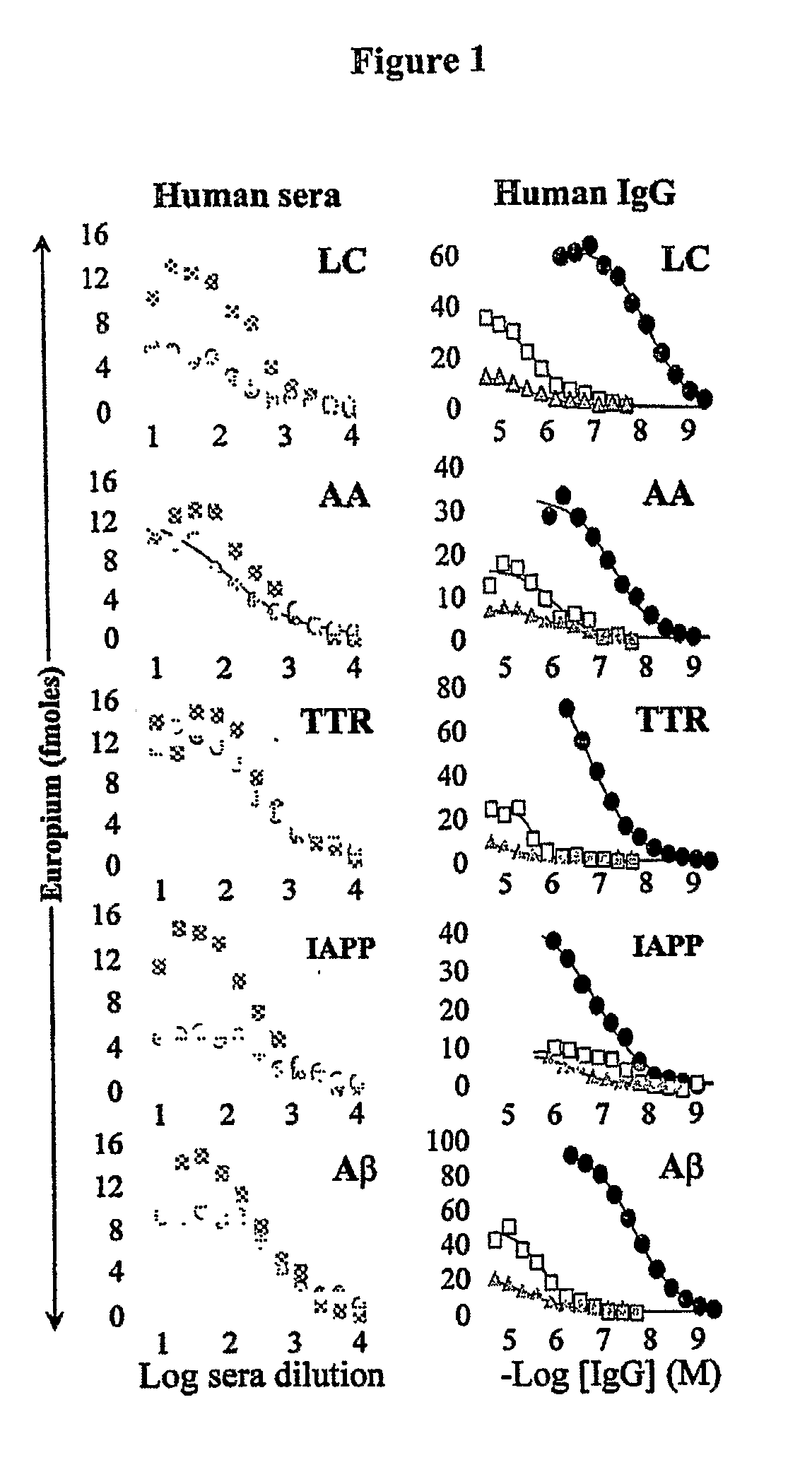
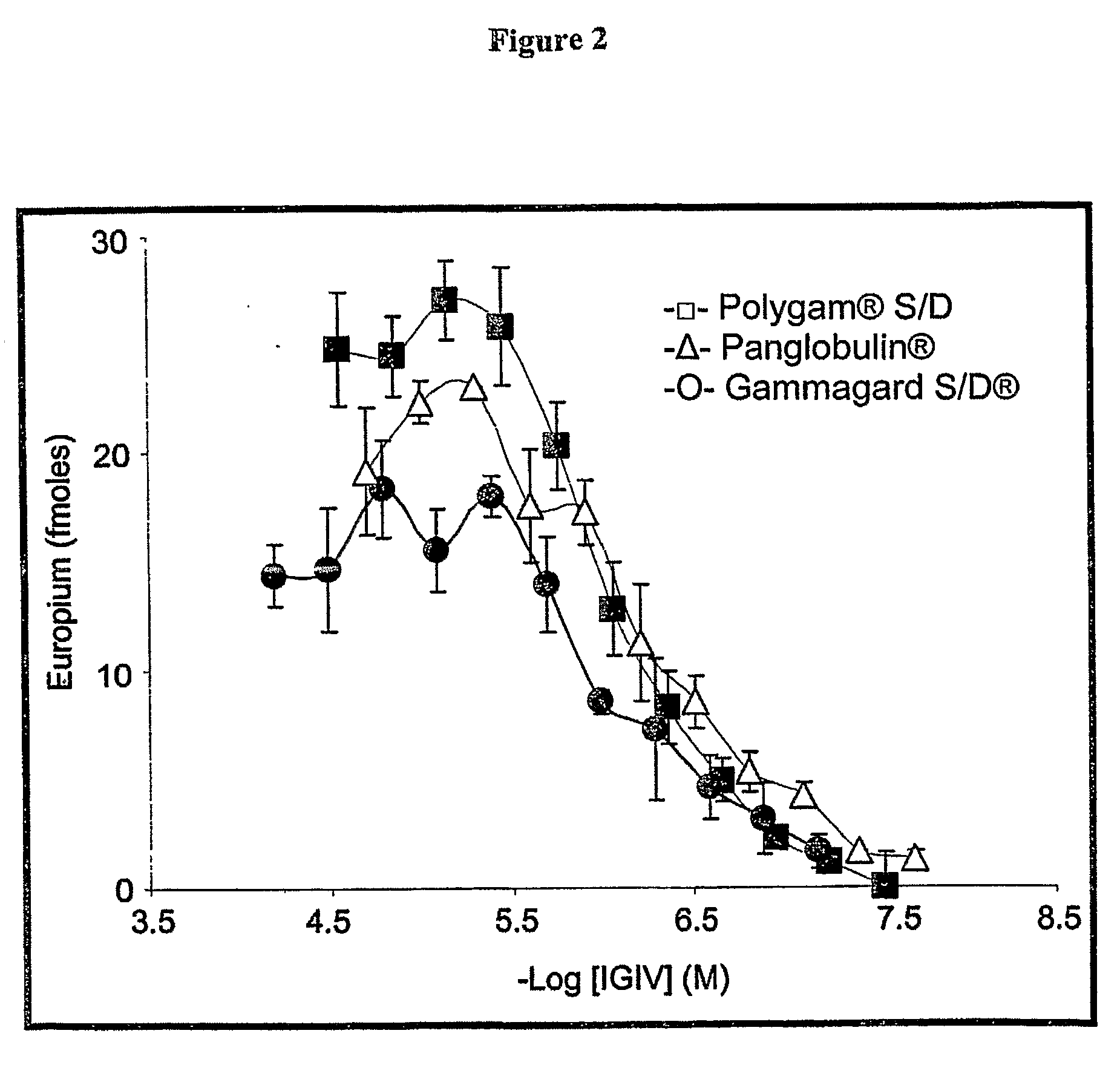
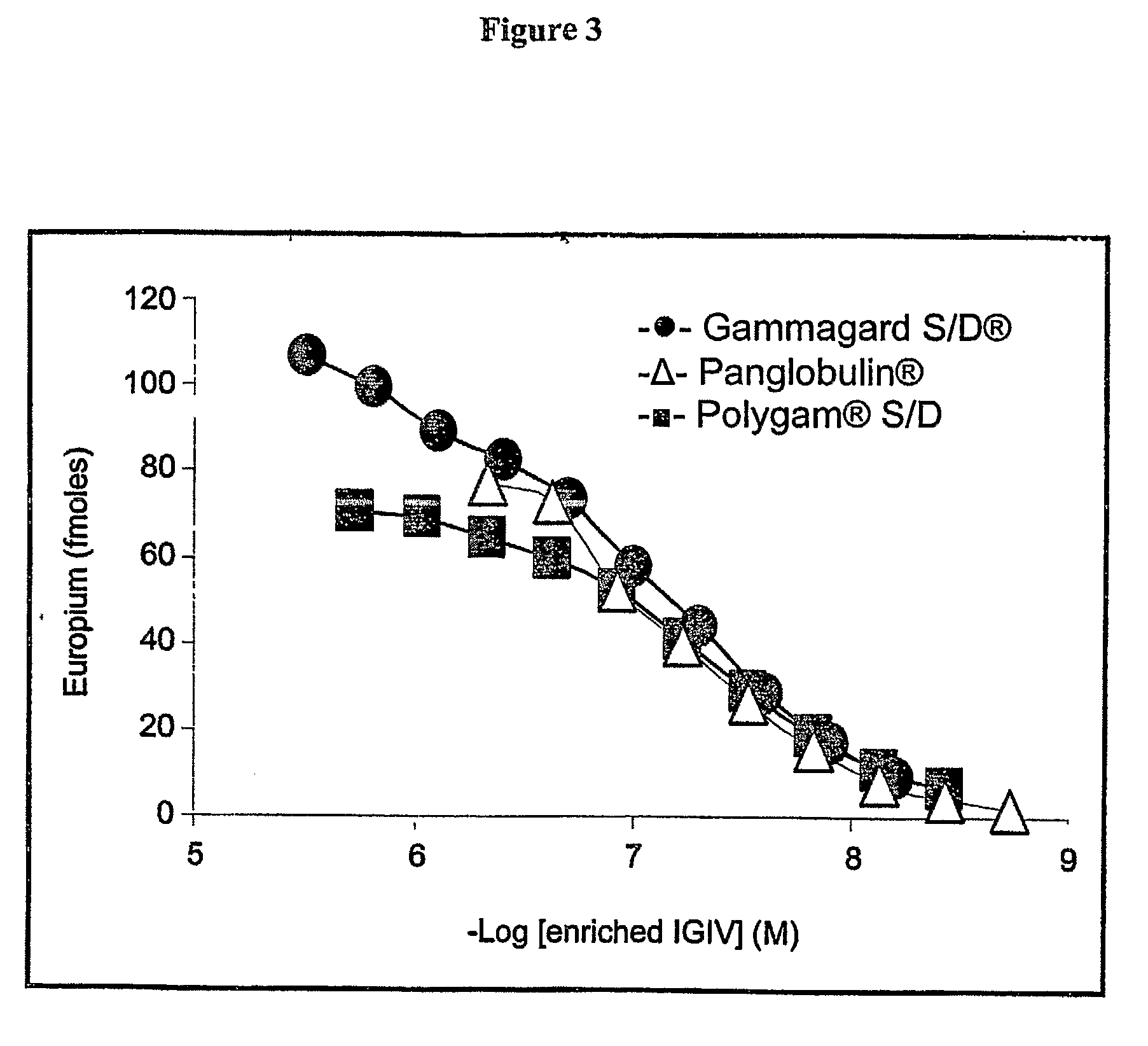
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of Immune Globulin Intravenous (IGIV) Products
InactiveUS20090232733A1Inhibit and prevent formationSmall sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideMedicineGlobulin
The present invention provides IGIV and IGIV enriched for binding to amyloid fibrils and to partially denatured amyloidogenic precursor polypeptides. The present invention also provides methods for obtaining IGIV enriched for binding to amyloid fibrils and to partially denatured amyloidogenic precursor polypeptides. The IGIV recognizes amyloid fibrils and partially denatured amyloidogenic precursor polypeptides. They are useful for treating diseases and conditions associated with amyloid deposition. The IGIV of the present invention also are useful for diagnosing and detecting amyloid deposition.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
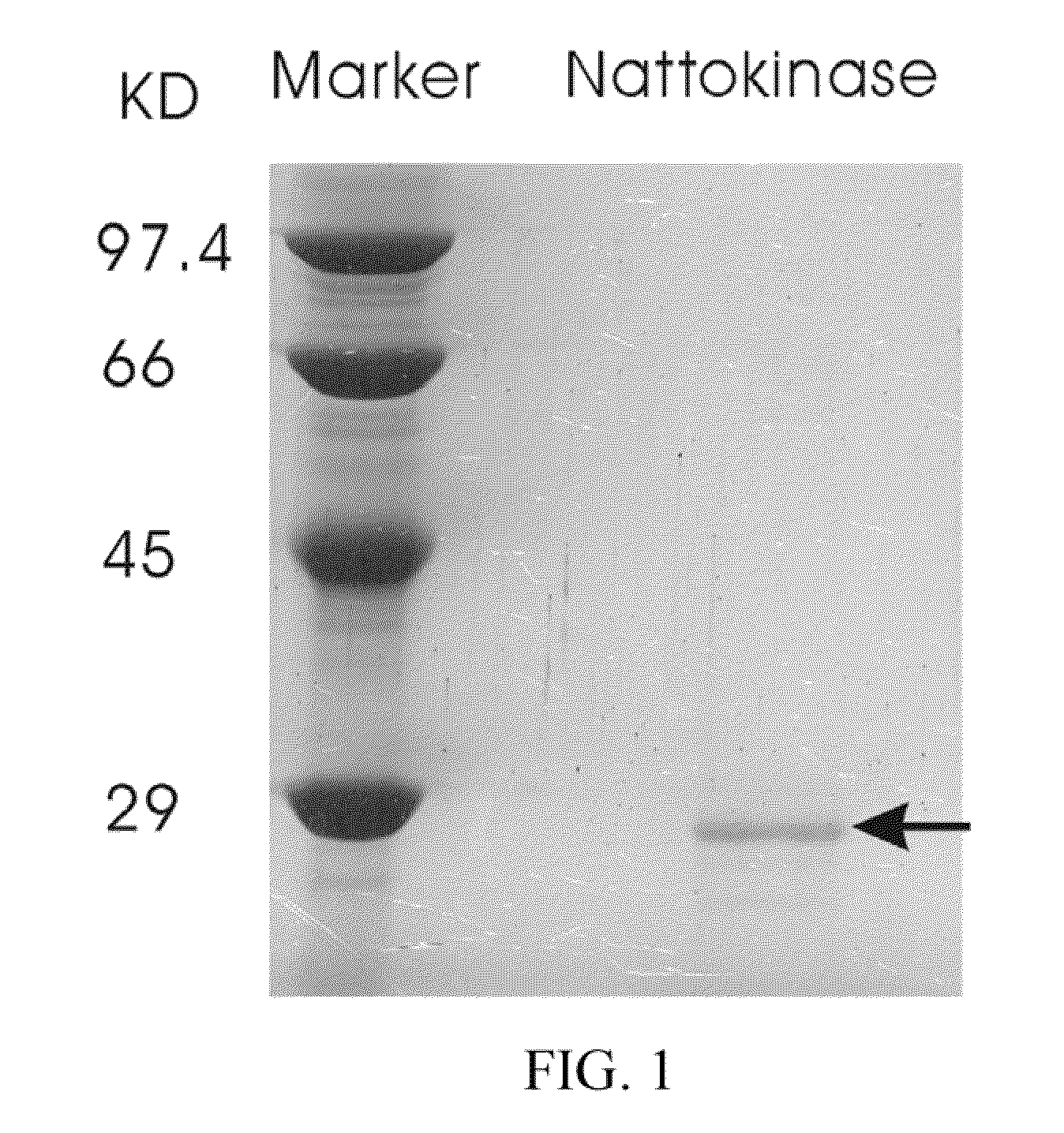
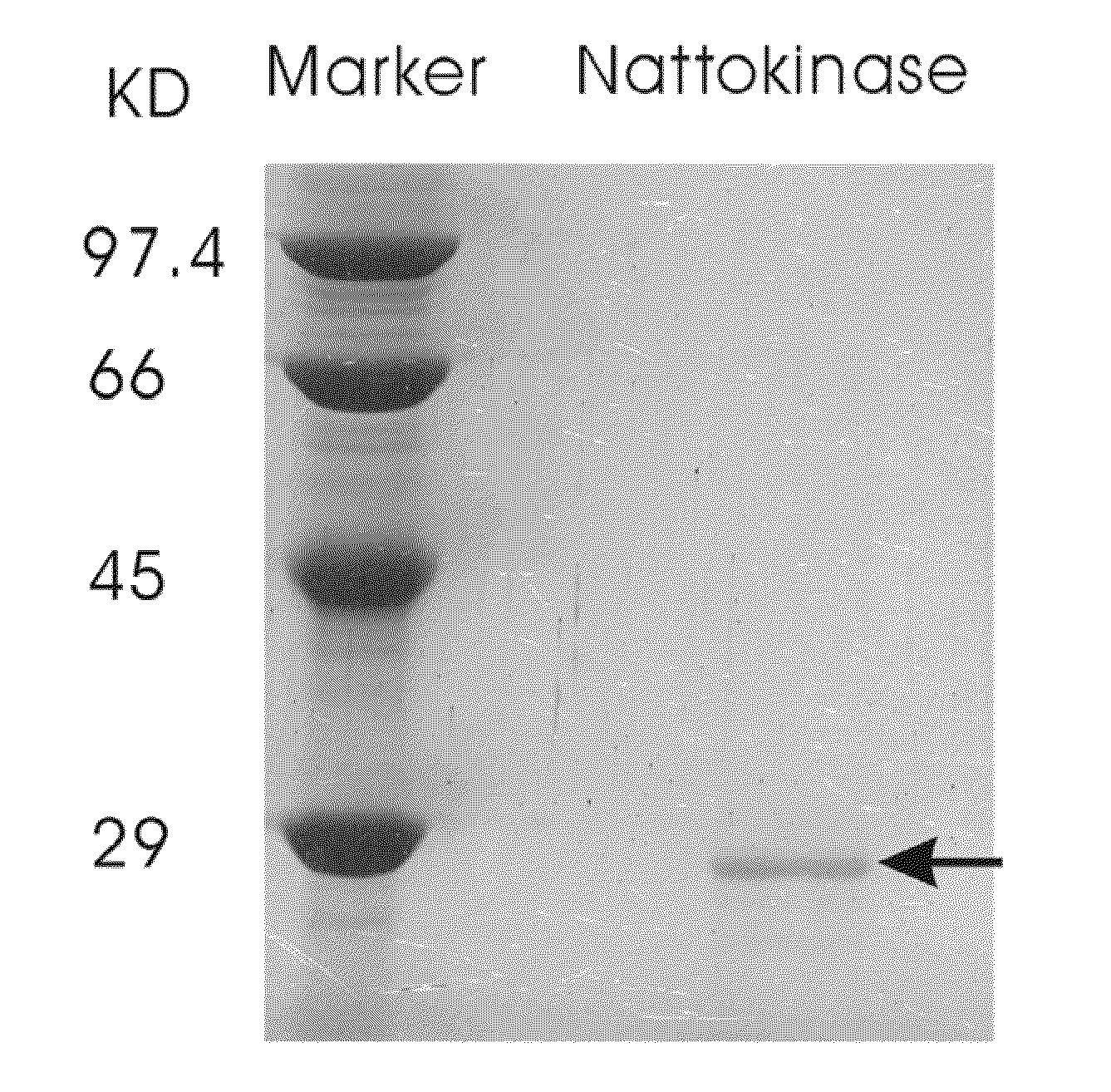
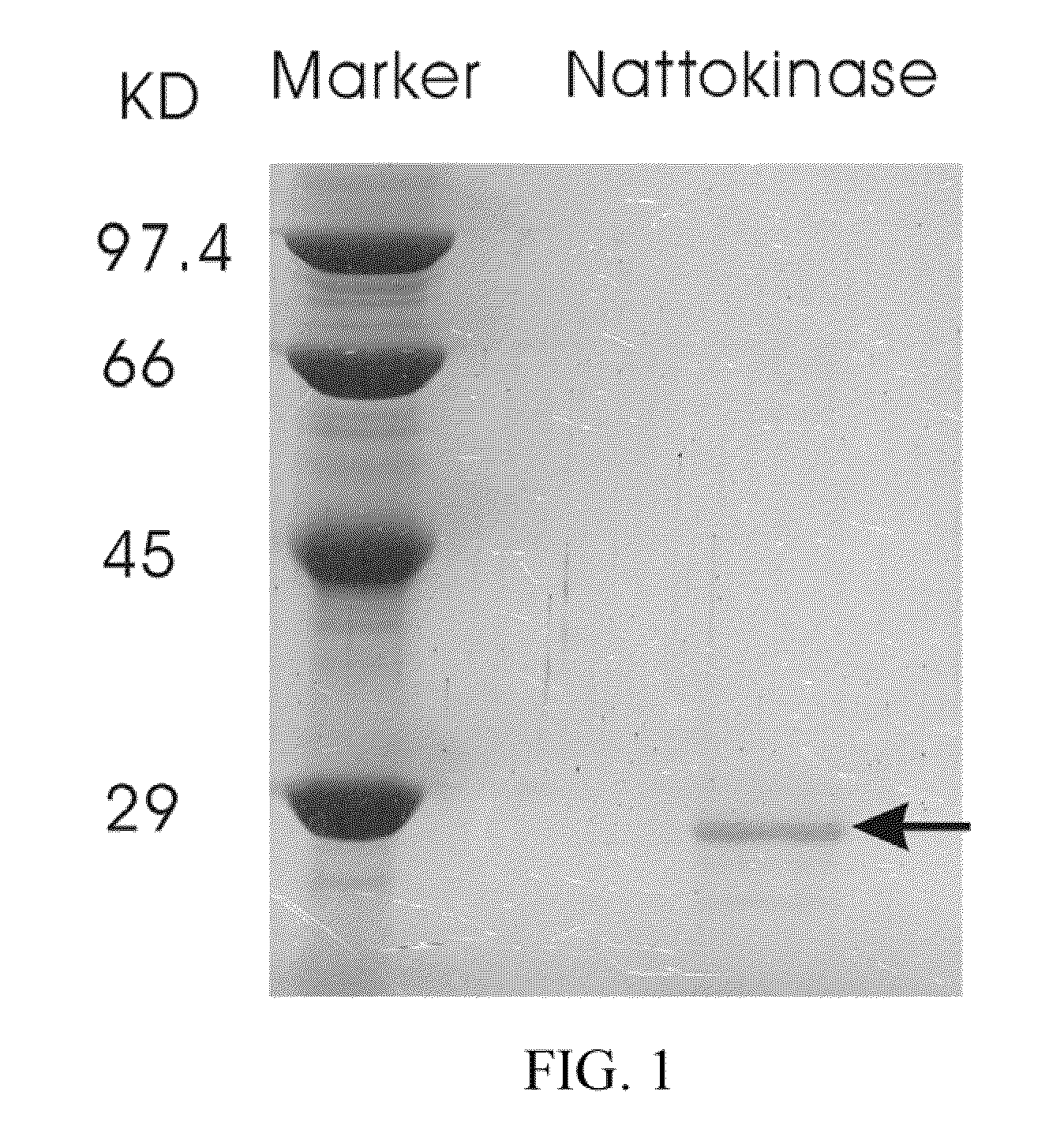
Nattokinase for degrading and reducing amyloid fibrils—associated with alzheimer's disease, prion diseases and other amyloidoses
ActiveUS8137666B2Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProteinaceous infectious particle
A method of dissolving or disrupting pre-formed or pre-deposited amyloid fibrils and / or inhibiting amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence in Alzheimer's disease, prion diseases and / or other amyloidoses in a mammalian subject is disclosed. In the method a therapeutically effective amount of nattokinase is administered.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
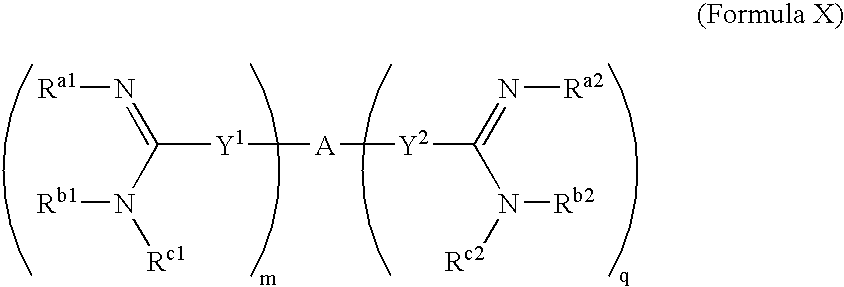
Amidine derivatives for treating amyloidosis
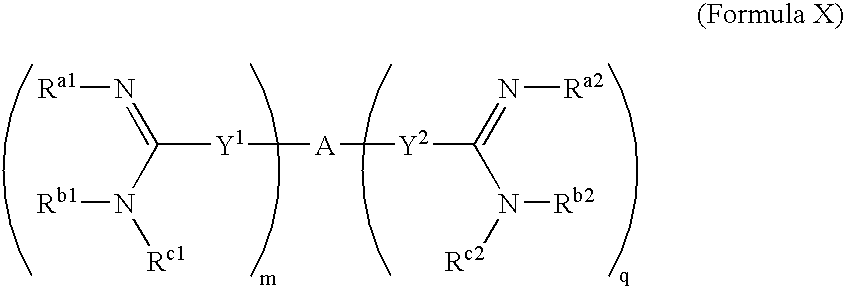
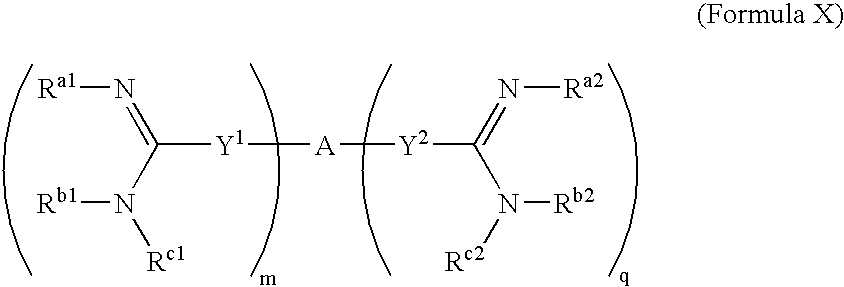
The present invention relates to the use of amidine compounds in the treatment of amyloid-related diseases. In particular, the invention relates to a method of treating or preventing an amyloid-related disease in a subject comprising administering to the subject a therapeutic amount of an amidine compound. Among the compounds for use according to the invention are those according to the following Formula (X), such that, when administered, amyloid fibril formation, neurodegeneration, or cellular toxicity is reduced or inhibited.
Owner:NEUROCHEM INT
Compositions and methods for the treatment of familial amyloid polyneuropathy
ActiveUS20150126567A1Treat and prevent and ameliorate effectBiocideNervous disorderEnantiomerMedicine
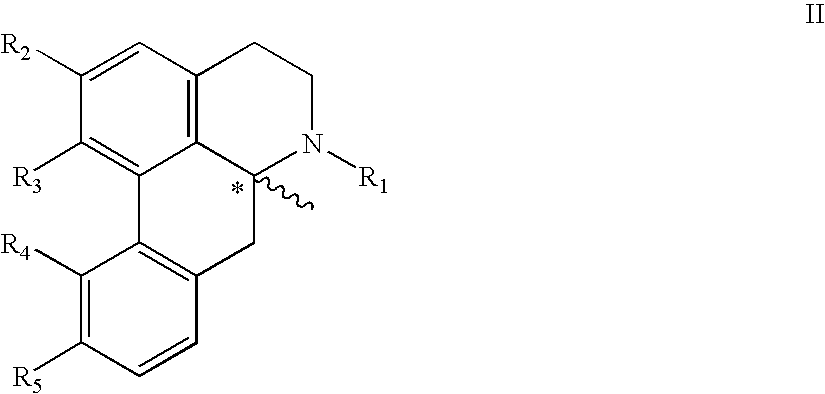
The invention relates to the compounds of formula I or its pharmaceutical acceptable salts, as well as polymorphs, solvates, enantiomers, stereoisomers and hydrates thereof. The pharmaceutical compositions comprising an effective amount of compounds of formula I, and methods for the treatment of familial amyloid polyneuropathy may be formulated for oral, buccal, rectal, topical, transdermal, transmucosal, intravenous, parenteral administration, syrup, or injection. Such compositions may be used to treatment of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, neurodegenerative diseases, amyloidosis, neuropathic pain, amyloid fibril formation and cardiomyopathy related diseases.
Owner:CELLIXBIO PTE LTD
Inhibitors of Amyloid Fibril Formation and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080004211A1Amyloid deposit formation and amyloidosis is inhibited, prevented, and/or reducedCompound screeningNervous disorderDiabetes mellitusDisease cause
The present invention provides new antifibrillogenic agents and peptides, compositions and cells containing same, compositions that bind to same, effective therapeutics for preventing or delaying the progression of, e.g., Alzheimer's disease and diabetes, methods for optimizing antifibrillogenic agents, and methods of using the antifibrillogenic agents, peptides, compositions, and cells of the invention for detecting and / or inhibiting amyloid fibril formation.
Owner:FRASER PAUL
Methods for amyloid removal using Anti-amyloid antibodies
InactiveUS20100322932A1Nervous disorderSugar derivativesCell mediated immunityCell-mediated immune response
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Antibody and use thereof
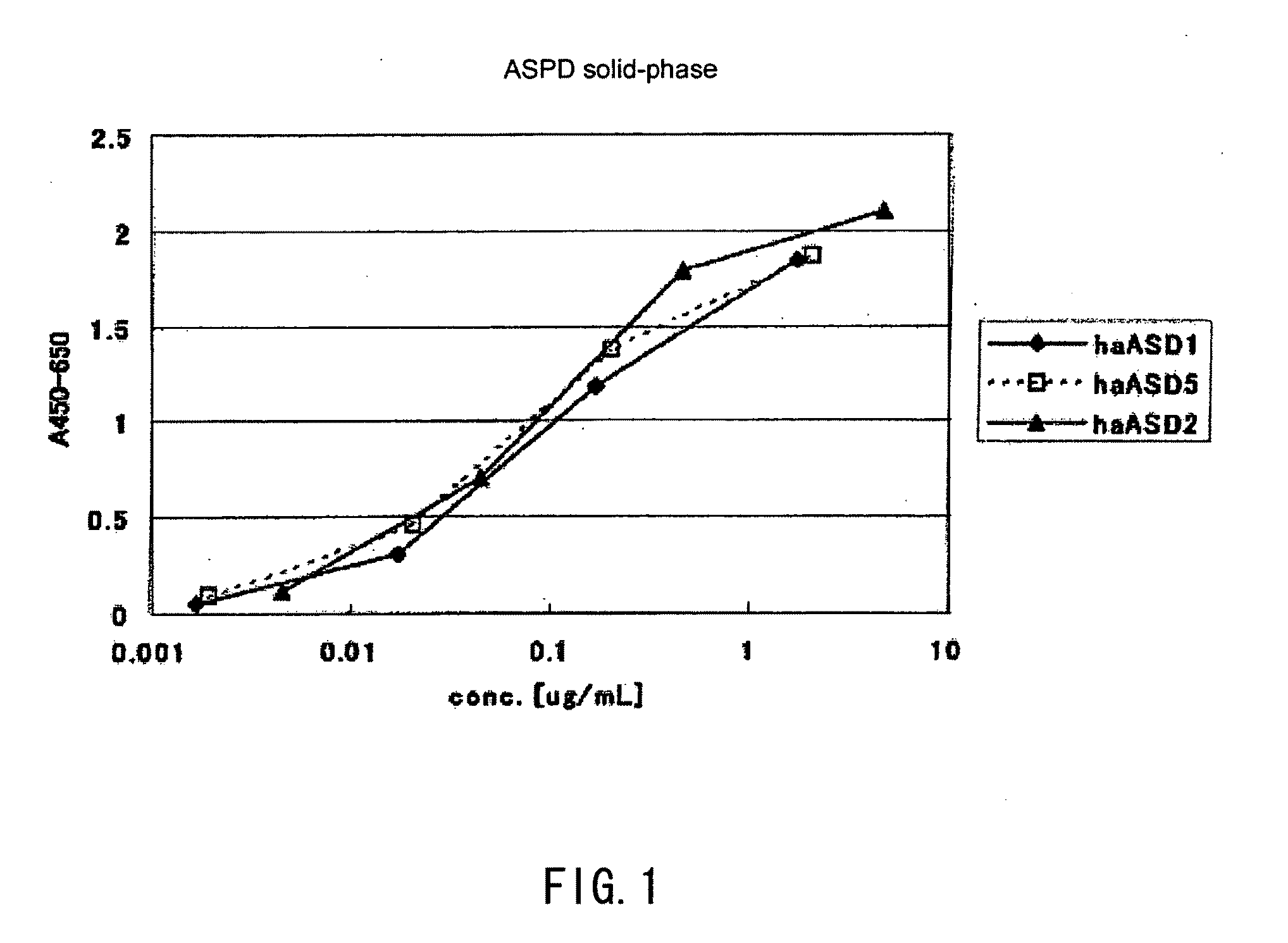
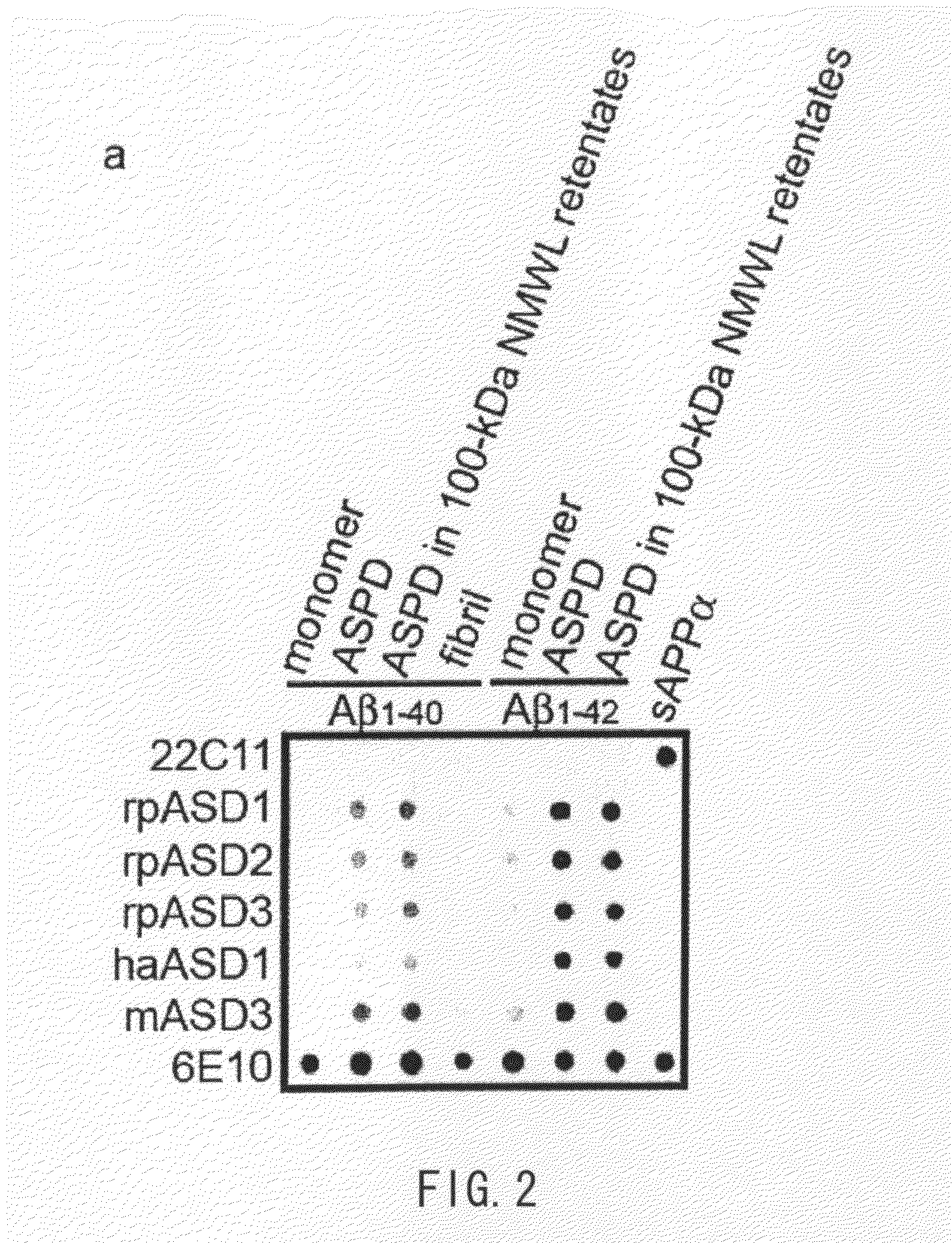
ActiveUS20100297662A1Avoid deathReduced responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderAmyloid betaHigh activity
An antibody provided by the present invention has a low reactivity with amyloid precursor proteins, and has a higher reactivity with amylospheroids than with amyloid β fibrils or monomeric amyloid β-proteins. According to the present invention, an antibody is provided that has a higher reactivity with amylospheroids than with amyloid precursor proteins, and has any one or more of the following properties: (i) a higher activity with amylospheroids than with amyloid β fibrils; (ii) a higher reactivity with amylospheroids than with monomeric amyloid β-proteins; and (iii) an activity of inhibiting neuronal cell death induced by amylospheroids.
Owner:FOUND FOR BIOMEDICAL RES & INNOVATION
Methods for determining conformational changes and self-assembly of proteins
The invention relates to methods for measuring conformational changes and self-assembly / aggregation of proteins, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils, using conjugated polyelectrolytes. The conjugate polyelectrolyte is exposed to the protein whereby the conjugated polyelectrolyte and the protein of interest interact, and a change of a property of the polyelectrolyte in response to conformational changes of the protein is observed. The detected change is used to determine different conformations of the protein, especially the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Owner:BIOCHROMIX
Nattokinase for degrading and reducing amyloid fibrils assoicated with alzheimer's disease, prion diseases and other amyloidoses
A method of dissolving or disrupting pre-formed or pre-deposited amyloid fibrils and / or inhibiting amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence in Alzheimer's disease, prion diseases and / or other amyloidoses in a mammalian subject is disclosed. In the method a therapeutically effective amount of nattokinase is administered.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Amidine derivatives for treating amyloidosis
InactiveUS20050182118A1Prevent and inhibit assemblyInhibition of activationBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicineCytotoxicity
The present invention relates to the use of amidine compounds in the treatment of amyloid-related diseases. In particular, the invention relates to a method of treating or preventing an amyloid-related disease in a subject comprising administering to the subject a therapeutic amount of an amidine compound. Among the compounds for use according to the invention are those according to the following Formula, such that, when administered, amyloid fibril formation, neurodegeneration, or cellular toxicity is reduced or inhibited:
Owner:BELLUS HEALTH (INT) LTD (CH)
Dissolution of amyloid fibrils by flavonoids and other compounds
Methods for disrupting amyloid fibrils in a subject, comprising combining an effective amount of a β-2 microglobulin fibril disrupting compound with a medium associated with the subject, are disclosed. The invention also relates to combining the β-2 microglobulin fibril disrupting compound ex vivo with the blood during dialysis treatment of an animal. It also relates to methods for determining which compounds are effective at disrupting amyloid fibrils in a medium.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Amyloid Protofibril Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20160251419A1Compounds screening/testingImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAmyloid disease
The invention relates to methods for obtaining antibodies that recognize amyloid protofibrils and antibodies that recognize one or more amyloid protofibrils. Also provided are methods of using the antibodies to prevent or inhibit amyloid disease in a subject, to diagnose amyloid disease in a subject, and to detect amyloid protofibrils in a sample.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com