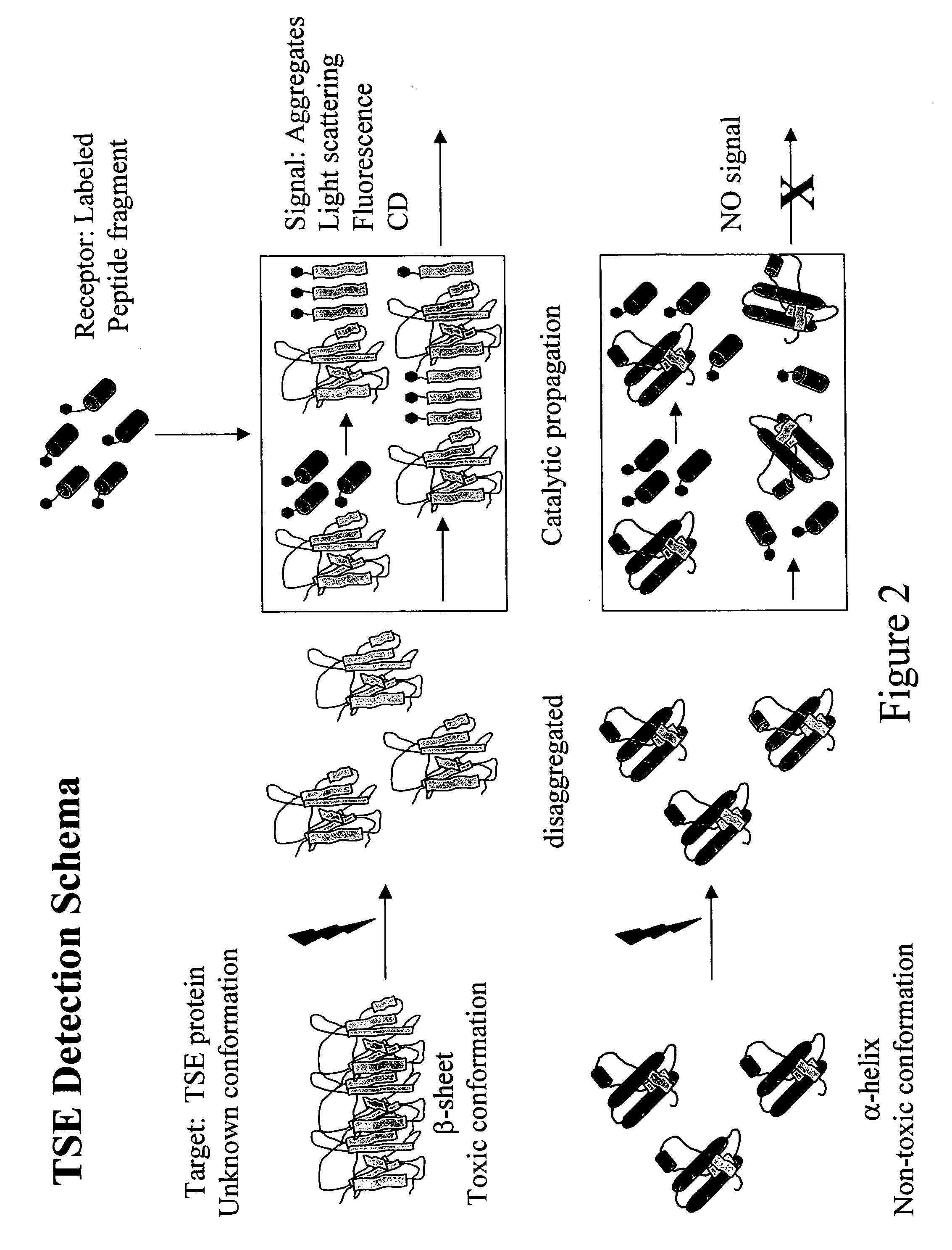
Detection of conformationally altered proteins and prions
a technology applied in the field of conformationally altered proteins and detection methods, can solve the problems of difficult diagnosis of prions, complicating detection, late detection, etc., and achieves the effects of convenient prophylactic or remedial treatment, rapid diagnosis, and reliable, affordable and safe methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0125]A sample may be obtained for testing and diagnosis through use of the instant invention as follows. A sample may be prepared from tissue (e.g. a portion of ground meat, or an amount of tissue obtained by a biopsy procedure) by homogenization in a glass homogenizer or by mortar and pestle in the presence of liquid nitrogen. The amount of material should be between about 1 mg and 1 gm, preferably between 10 mg and 250 mg, ideally between 20 and 100 mg. The material to be sampled may be suspended in a suitable solvent, preferably phosphate-buffered saline at a pH between 7.0 and 7.8. The addition of Rnase inhibitors is preferred. The solvent may contain a detergent (e.g., Triton X-100, SDS, or sarkosyl). Homogenization is performed for a number of excursions of the homogenizer, preferably between 10 and 25 strokes; ideally between 15 and 20 strokes. The suspended sample is preferably centrifuged at between 100 and 1,000 g for 5-10 minutes and the supernatant ...
example 2
[0130]Poly-lysine was used as a model peptide. Experiments were performed using model systems to illustrate the conformational changes involved in the transition from a predominately alpha-helix to a beta-rich form. The model system chosen used non-neurotoxic polyamino acid polylysine. The polyamino acid was chosen because of availability and safety; and normally evidences random coil conformation at pH values between 5 and 9.
[0131]FIG. 3 depicts a CD graph of an experiment in which poly-L-lysine 20 micro Molar (μμM) 52,000 molecular weight (MW) was used as a peptide model.
[0132]As also illustrated in FIG. 3:
Sample 24, which was maintained at pH 7, 25° C., exhibited a minimum at approximately 205 nanometers (nm), indicating a random coil structure;
Sample 26 which was maintained at pH 11 (near the isoelectric point), at 50° C., resulted in a minimum at approximately 216 nanometers (nm) indicating a β-sheet structure (see FIG. 11 for exemplary CD spectra of protein conformations);
Samp...
example 3
[0133]FIG. 4 illustrates general CD results of experiments that were conducted: (1) using poly-L-lysine; and (2) at varying temperatures and pH, to observe the effect of random coil to beta-sheet conformational changes under varying environmental conditions. The results indicate that both temperature and pH play an important role in the transition. The results also indicate that the addition of a relatively small amount of β-sheet peptide to a random coil sample can result in a shift towards a β-rich conformation and that such changes can be accelerated depending on the temperature and pH environment of the samples.
[0134]More specifically, FIG. 4 illustrates an absorbance graph generated using a poly-L-lysine of 52,000 molecular weight (MW) at 70 micromolar (μM) as a peptide probe in accordance with the experimental technique described in Examples 1-3. FIG. 4 illustrates that:
Sample 32 (pH 11, 25° C.) evidenced a plateau at approximately 0.12, indicating a pre-dominantly α-helical s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com