A Mass Spectrometry De novo Sequencing Method Based on Peptide C-terminus Selective Enzyme Labeling
An enzyme labeling and selective technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to splice sequence information and obtain fragment ion information, and achieve good selectivity, improve sequencing efficiency, and avoid reactions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
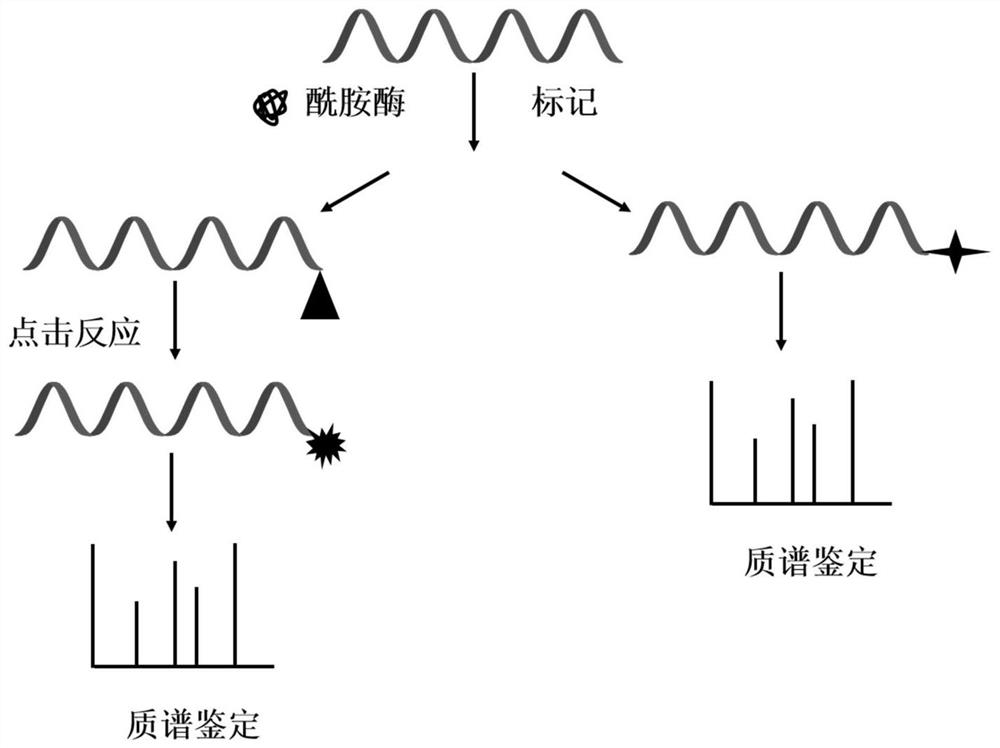
[0015] Weigh 1 mg of peptide powder from bovine pancreas, and add 50 μL of N,N-dimethylformamide to make peptide mother solution. Take another centrifuge tube, add 243 μL of acetonitrile and 2 μL of hydrazine solution, mix well, add 5 μL of peptide mother solution to the centrifuge tube, and mix well. Transfer to 100mg of peptide C-terminal amidase, and react at 50°C for 18h. After the reaction is completed, centrifuge at 16000 g for 10 min, and take the supernatant for freeze-drying. After freeze-drying, 20 μL of 2% formic acid aqueous solution was added to redissolve for mass spectrometric identification. According to the characteristics of the fragmentation law of fragment ions in the secondary mass spectrometry, the sequence of the peptide segment was deduced.
Embodiment 2
[0017] Weigh 5 mg of the peptide mixture powder produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of bovine serum albumin, and prepare the peptide mother solution with 50 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide. Take another centrifuge tube, add 240 μL of acetonitrile and 5 μL of tris(2-aminoethyl)amine solution, mix well, add 5 μL of polypeptide mother solution to the centrifuge tube, and mix well. Transfer to 150mg of peptide C-terminal amidase, and react at 50°C for 24h. After the reaction is completed, centrifuge at 16000 g for 10 min, and take the supernatant for freeze-drying. After freeze-drying, 20 μL of 2% formic acid aqueous solution was added to redissolve for mass spectrometric identification. According to the characteristics of the fragmentation law of fragment ions in the secondary mass spectrometry, the sequence of the peptide segment was deduced.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Weigh 1 mg of peptide powder from mouse brain and add 50 μL of acetonitrile to make peptide mother solution. Take another centrifuge tube, add 243 μL of acetonitrile and 2 μL of ethylenediamine solution, mix well, add 5 μL of peptide mother solution to the centrifuge tube, and mix well. Transfer to 150mg of peptide C-terminal amidase and react at 50°C for 18h. After the reaction is completed, centrifuge at 16000 g for 10 min, and take the supernatant for freeze-drying. After freeze-drying, 20 μL of 2% formic acid aqueous solution was added to redissolve for mass spectrometric identification. According to the characteristics of the fragmentation law of fragment ions in the secondary mass spectrometry, the sequence of the peptide segment was deduced.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com