High throughput detection of molecular markers based on AFLP and high throughput sequencing
A molecular marker, high-throughput technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and biology, nucleic acid detection and identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
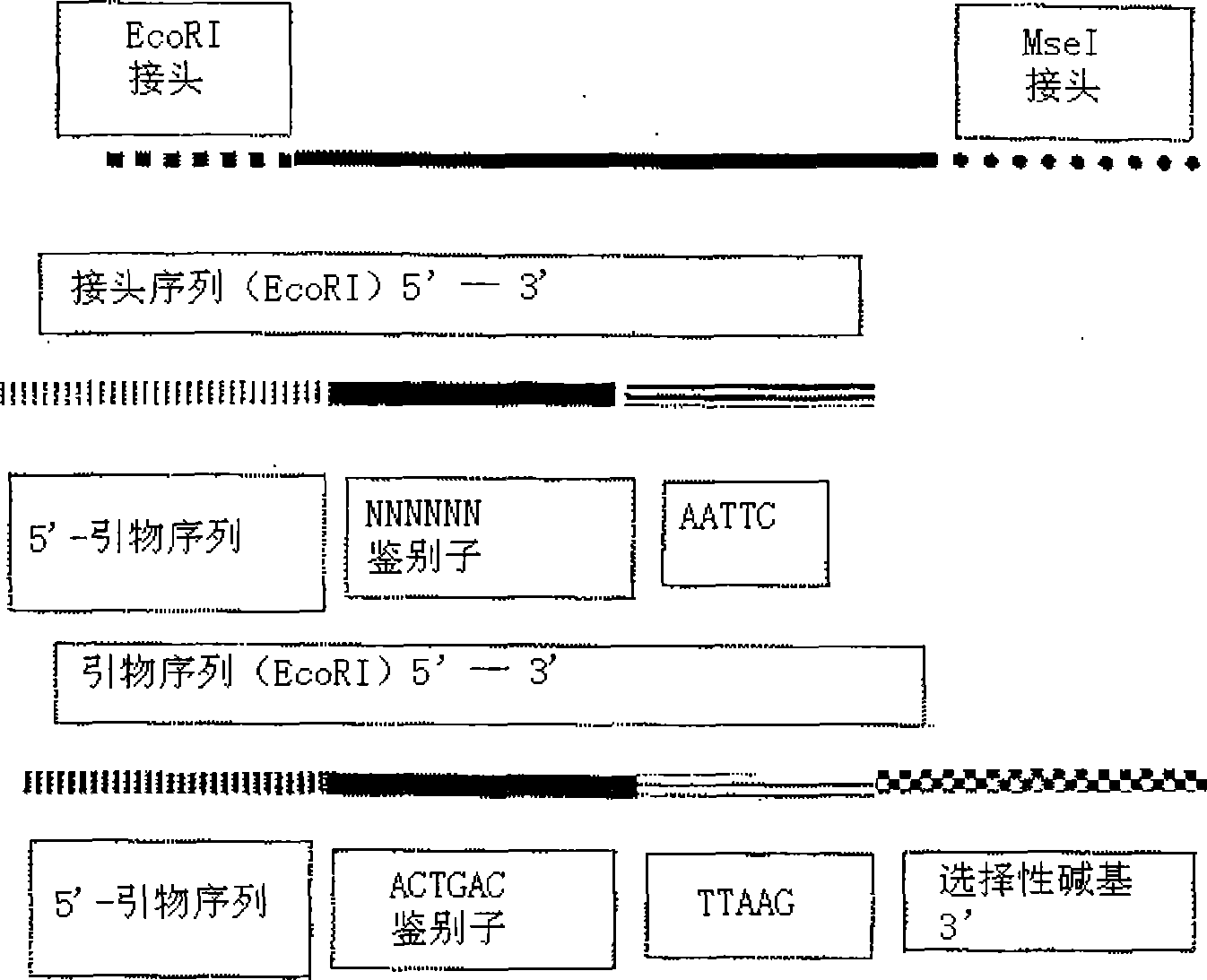
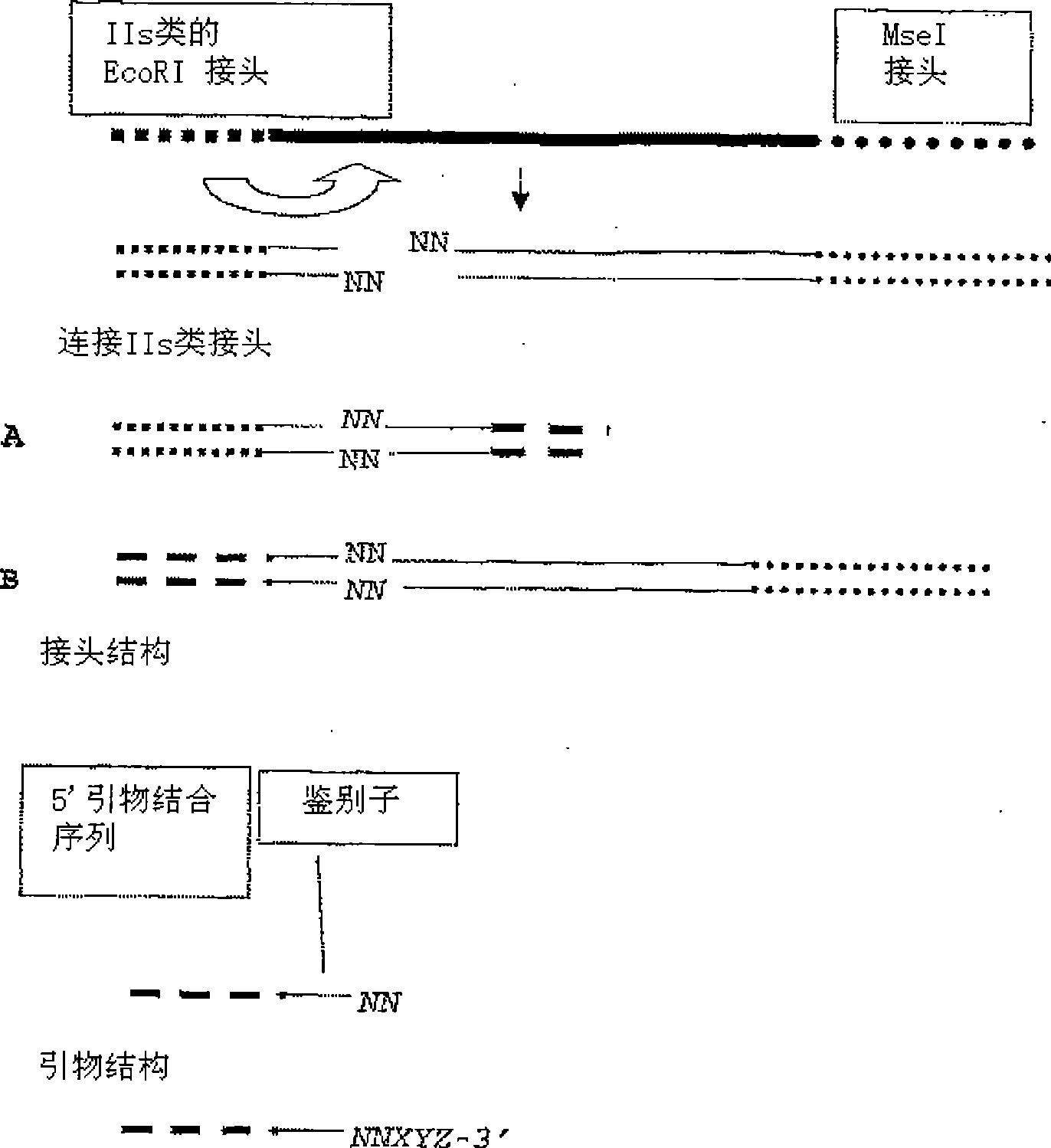
[0098] For each DNA sample, a restriction ligation step was performed with EcoRI and MseI. The linker is based on the hybridization sequence located on the surface of the Slexa high-throughput sequencing system. More specifically, the EcoRI linker contains the P5 sequence (sequence primer part), and the MseI linker contains the P7 sequence (bridge PCR primer sequence). EcoRI adapters also contain sample identity tags. 96 different EcoRI adapters and 1 MseI adapter were used. A degenerate EcoRI linker can be used. Template preparation included a size selection step: After the restriction digestion (EcoRI+MseI) step but before the adapter ligation step, the mixture was incubated at 80°C for 10 minutes. Fragments smaller than 130 nt were removed (in one corn sample).
[0099] The complexity of the mixture is reduced by a selective preamplification: using a +1 primer (i.e., containing a random selective nucleotide at the 3' end), using 96 EcoRI+1 primers and 1 MseI+1 primer (o...
Embodiment 2
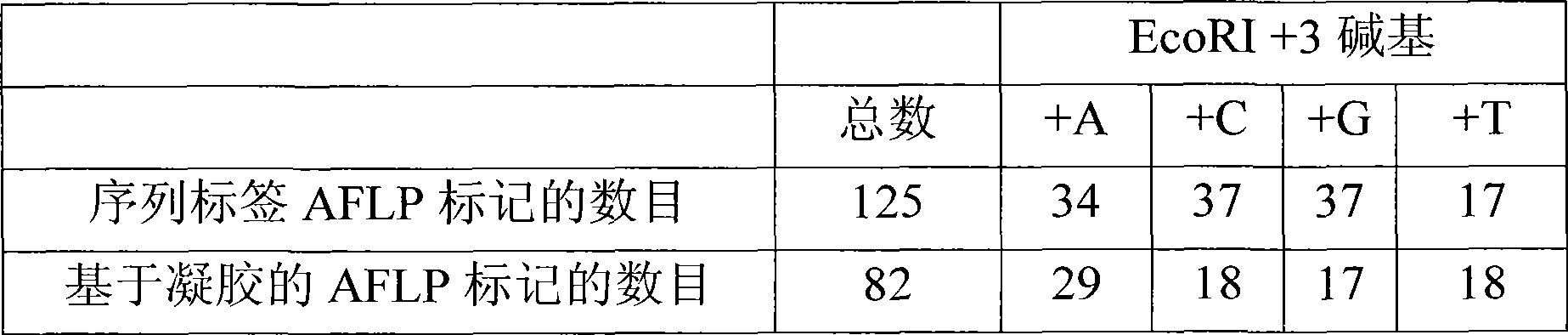
[0104]Sequence-based detection of AFLP fragments was performed with Solexa's Clonal SingleMolecule Array (CSMATM) technology, a sequencing-by-synthesis platform capable of analyzing up to 40,000,000 individual fragments in a single sequence run. The experimental procedure included: AFLP template preparation, selective (AFLP) amplification, single-molecule bridge amplification, and sequencing of thousands of sequence tags from one restriction enzyme end of the AFLP fragment. Maize parental lines B73 and Mo17 and 87 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) were used and sequenced, and more than 8,900,000 EcoRI AFLP fragment ends were sequenced to provide proof-of-principle for sequence-based AFLP detection. The parental lines B73 and Mo17 and 87 RILs were selected. AFLP templates were performed with the restriction enzyme combination EcoRI / MseI. Selective amplification was performed with +2 / +3 AFLP primers. Solexa CSMA bridge amplified template fragments were prepared with a second res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com