cSNP molecular marker detection kit and method for scylla paramamosain disease-resistant characters
A technology of pseudo-cave blue crabs and molecular markers, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, etc., and can solve the problems of heavy workload and poor application effect of molecular markers related to disease resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Example 1: Acquisition of the full-length nucleic acid sequence and amino acid sequence of the disease resistance factor SpALF6 of Scylla pseudomae
[0071] Total RNA was extracted from the blood cell samples of Scylla pseudocarpus, and after testing to meet the requirements, the cDNA sequences of a large number of genes were obtained through transcriptome sequencing and data analysis. Using the online software blastx to analyze one of the full-length 756bp sequences, it was found that the sequence was 78% homologous to Portunus trituberculatus PtALF6 in the Genbank database, indicating that the sequence was a new member of the ALF family of Scylla cryptae, named SpALF6, its nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence are shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2, respectively.
[0072] Among them, the full-length cDNA of SpALF6 (SEQ ID NO: 1) contains 681 bp, wherein the 79th to 426th nucleotides are the open reading frame (SEQ ID NO: 5) encoding the amino acid ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2: Acquisition of SpALF6 single nucleotide mutant SpALF6-M sequence
[0075] The DNA sequence of the single nucleotide mutant SpALF6-M was obtained by fusion PCR technology. The primers SpALF6EF:5'-TACTCAGAATTCTTCGTGAAGGAACTACTCT-3'(SEQ ID NO:6) and SpALF6MR:5'-TACTCGGTAGTTACAGACACGGTC-3'(SEQ ID NO:8) were paired, and the mutation site was obtained by PCR using the SpALF6 nucleic acid sequence as a template (Containing) the upstream nucleic acid fragment; SpALF6MF:5'-TCCTTGACCGTGTCTGTAACTAC-3'(SEQ ID NO:9) and primer SpALF6ER:5'-TACTCACTCGAGCTATTCTAAGAAGAGTCG-3'(SEQ ID NO:7) are paired, using the SpALF6 nucleic acid sequence as a template, Obtain nucleic acid fragments downstream of the mutation site (including) by PCR; take 0.5 μL of the above two PCR products, mix them as subsequent PCR templates, and use SpALF6EF and SpALF6ER as paired primers to obtain the corresponding SpALF6-M mature peptide region by PCR. nucleic acid sequence. Finally, compared with th...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3: Construction of SpALF6 and SpALF6-M prokaryotic expression vector
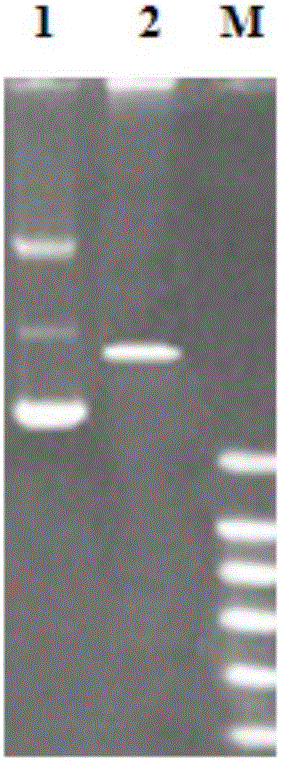
[0077] The DNA sequence corresponding to the SpALF6 mature peptide was amplified with the upstream primer SpALF6EF and the downstream primer SpALF6ER. The PCR reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 53°C for 45 s, extension at 72°C for 45 s, a total of 35 cycles, and a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. PCR products were analyzed by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis and positive fragments were recovered.
[0078] The above-mentioned purified and recovered nucleic acid fragments and the expression vector pET30a were respectively digested with endonucleases EcoRI and XhoI, and after digesting at 37°C for 3 hours, 1 μL of the digested products were subjected to 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the digestion effect. The electrophoresis results of the purified and recovered nucleic acid fragments and the expression vector...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com