Blood cells having modified antigenicity
a technology of blood cells and antigens, applied in the field of blood cells having modified antigens, can solve the problems of only converting the more abundant a cells, the lack of blood type o donors, and the development and utilization of enzyme conversion universal o cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Characterization of Fine Substrate Specificities of Alpha-N-Acetylgalactosaminidases and Alpha-Galactosidases Previously Used in A / B Blood cell Conversions
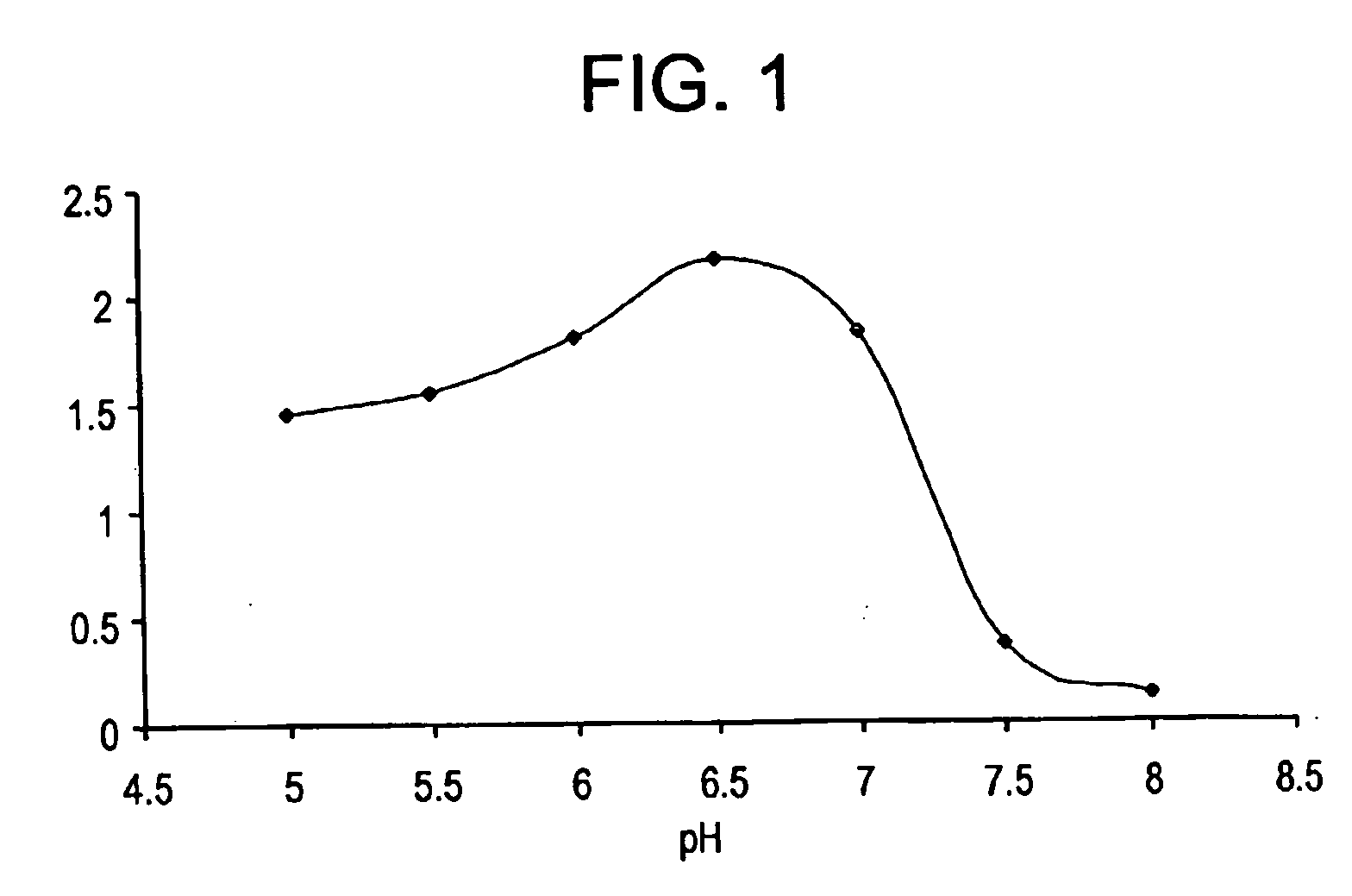
[0089] To eliminate the B and A antigenic activities of red cells, the most efficient exoglycosidases used in the past have been the coffee bean alpha-galactosidase and the chicken liver alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, respectively. These enzymes have been studied extensively and their characteristics and performance in red cell conversion described in the literature and in patent applications as referenced above.
[0090] (i) Specific Activity with Different Substrates (U / mg).
[0091] Table II lists reported specific activities of these enzymes with p-nitrophenyl monosaccharide derivatives. One unit is defined as the activity converting one micromole of substrate in one minute under the optimal assay conditions defined. Assays with p-nitrophenyl substrates were evaluated at initial velocity with less than 10% of the substrates use...
example 2
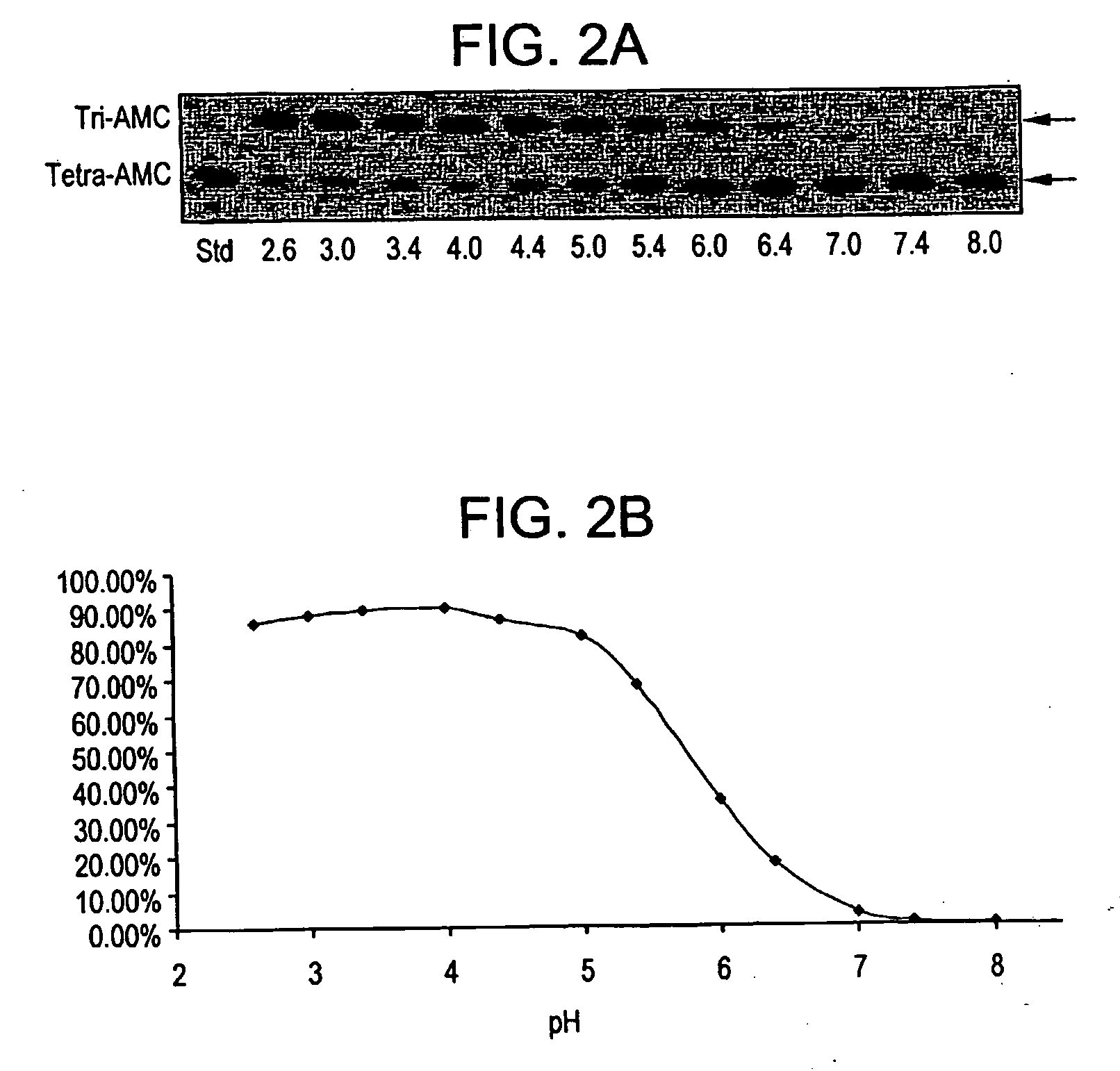
Identification of Alpha-N-Acetylgalactosaminidases and Alpha-Galactosidases with Highly Preferential or Exclusive Substrate Specificity for the Blood Group A and / or B Blood Group Structures at Neutral pH
[0108] In order to identify potential enzymes with preferred and / or exclusive specificity for blood group A and B structures, a large panel of fungal and bacterial isolates were analyzed. A protocol for initial screening with the blood group A / B tetrasaccharide AMC derivatives as well as the Gal / GalNAcalpha-pNP derivatives was developed. Briefly, preserved frozen stocks of cultures were inoculated onto YM slant cultures (tube size: 1.8×18 cm), grown at 27 degrees C. for 8 days, and the cultures (spores) harvested by washing down with 5 ml cryogen (10% glycerol+5% lactose), followed by maceration (strongly whirling with glass beads in the screwed tube, 1.3×13 cm). One ml of the slant cultures were inoculated to appropriate specific media for aerobic fermentation (25 degrees C. for fu...
example 3
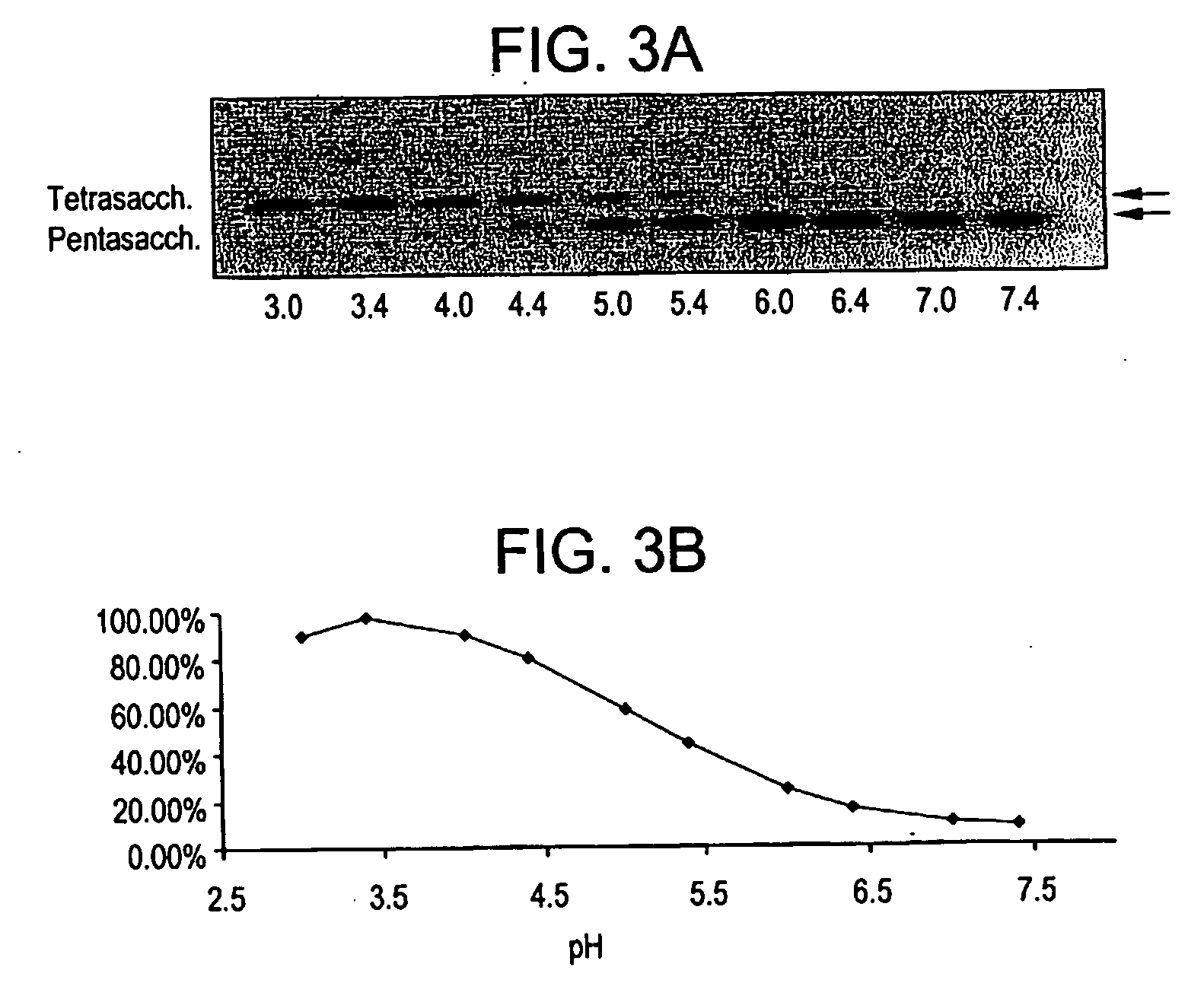
Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Alpha-Galactosidase Identified from Streptomyces Strain #2357, which has Exclusive Substrate Specificity for the Branched Blood Group B Antigens and with Unprecedented High Specific Activity with such Substrates
[0125] A 20-liter fermentation culture was processed by the French press method. The main alpha-galactosidase activity was determined to be present in the supernatant after centrifugation at 10,000×g. The supernatant was fractionated by ammonium sulfate precipitation and approximately 70% activity was found in the 20-60% fraction. The precipitate of the 20-60% cut was dissolved in 20 mM Tris (pH 7.5) and clarified by centrifugation. The supernatant was sequentially fractionated by chromatography on Q-sepharose (buffer 20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, with a gradient of 0-1.5 M NaCl), S-sepharose (buffer 20 mM NaOAc, pH 5.3, with a gradient of 0-1.0 M NaCl), and by S 12 gel filtration chromatography (buffer 20 mM NaOAc, pH 5.3, with 0.5 M NaCl or ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com