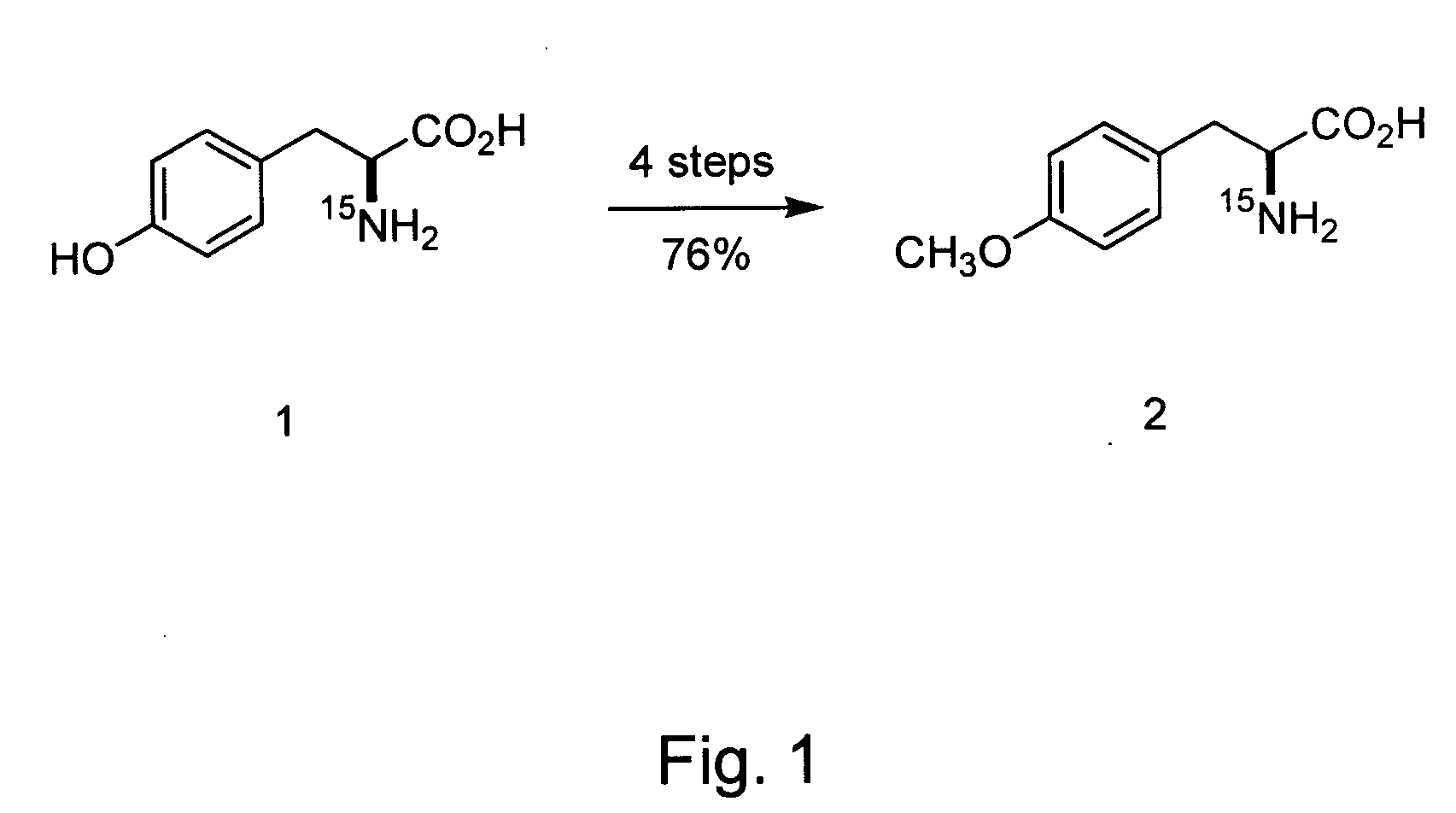
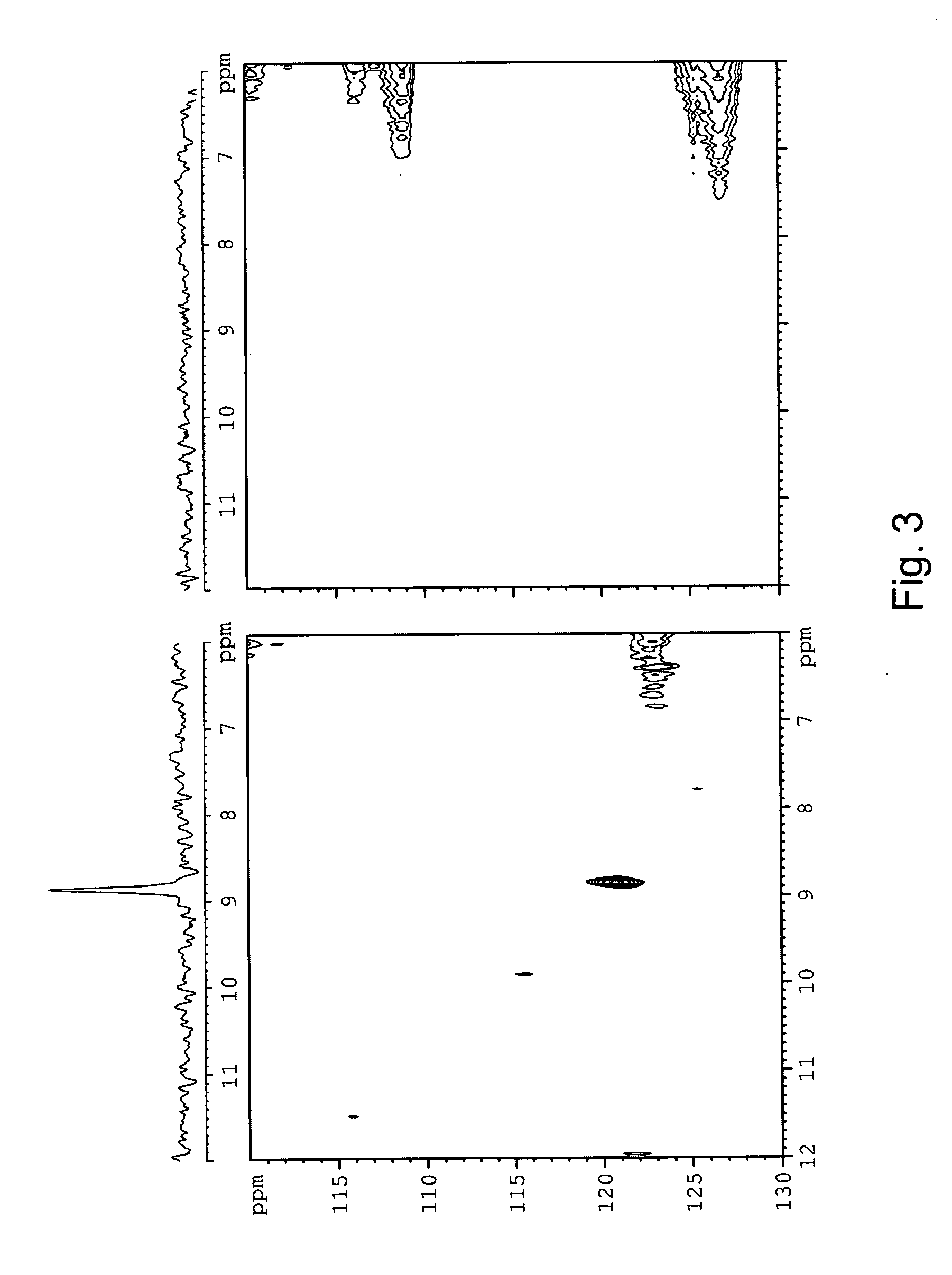
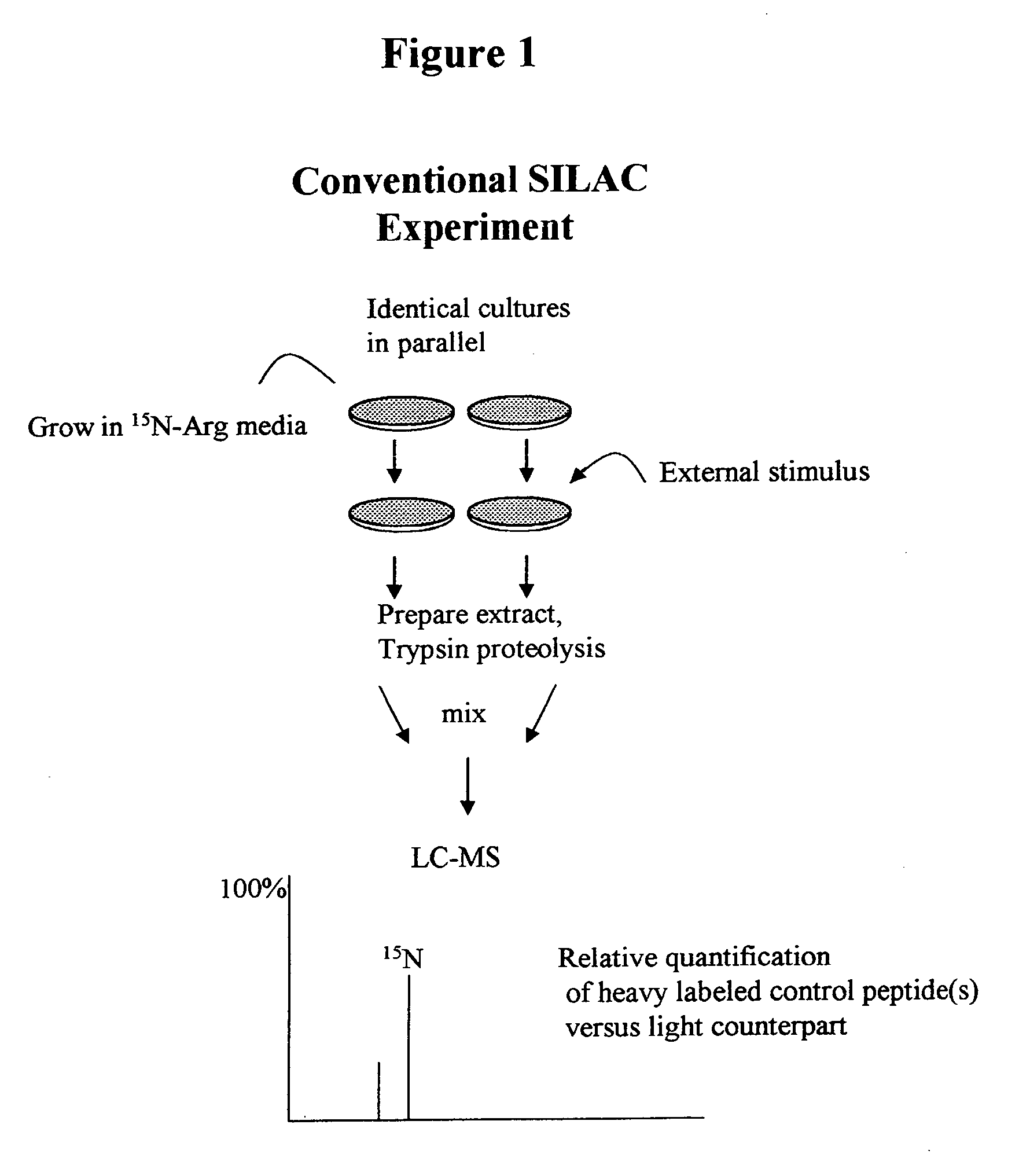
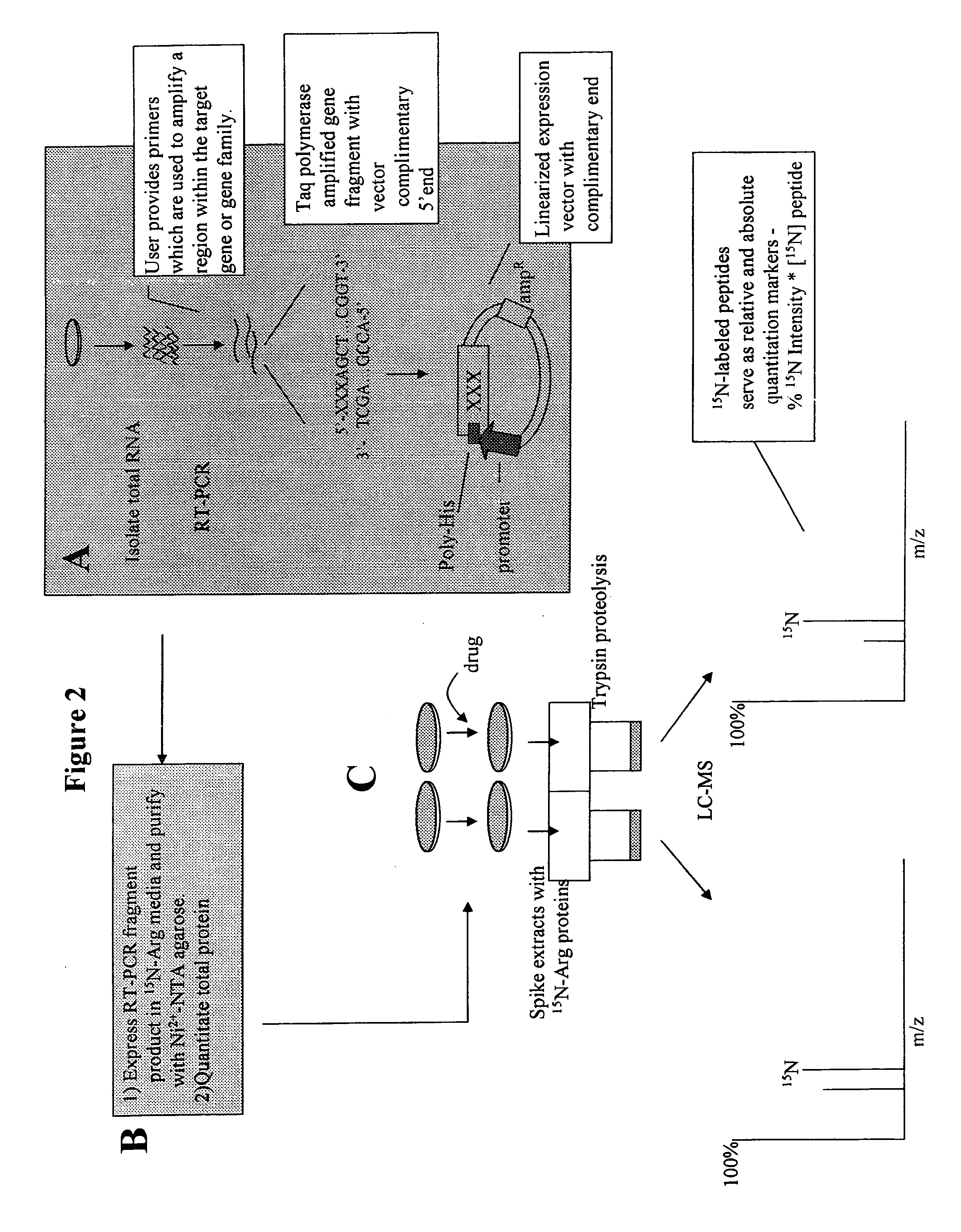
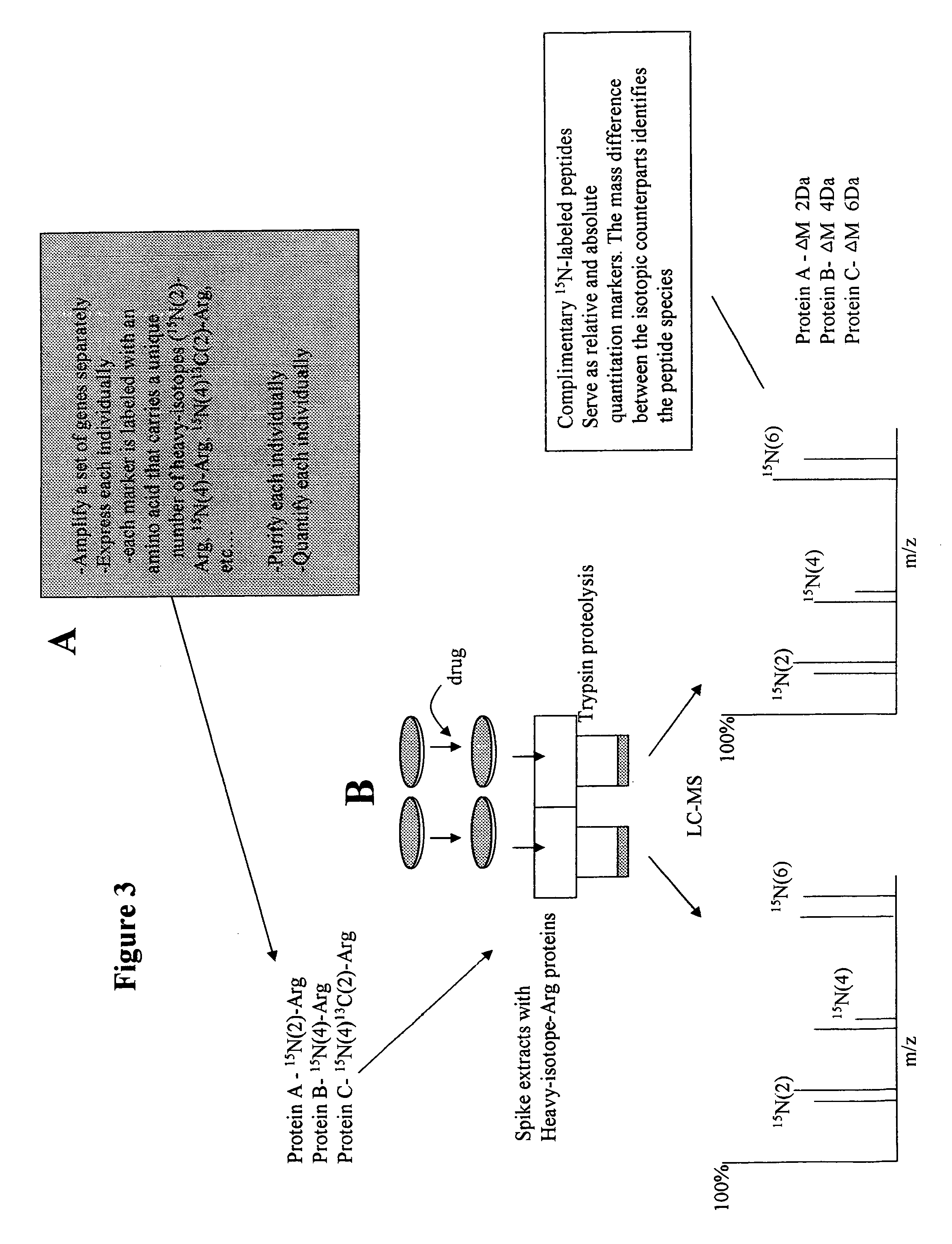
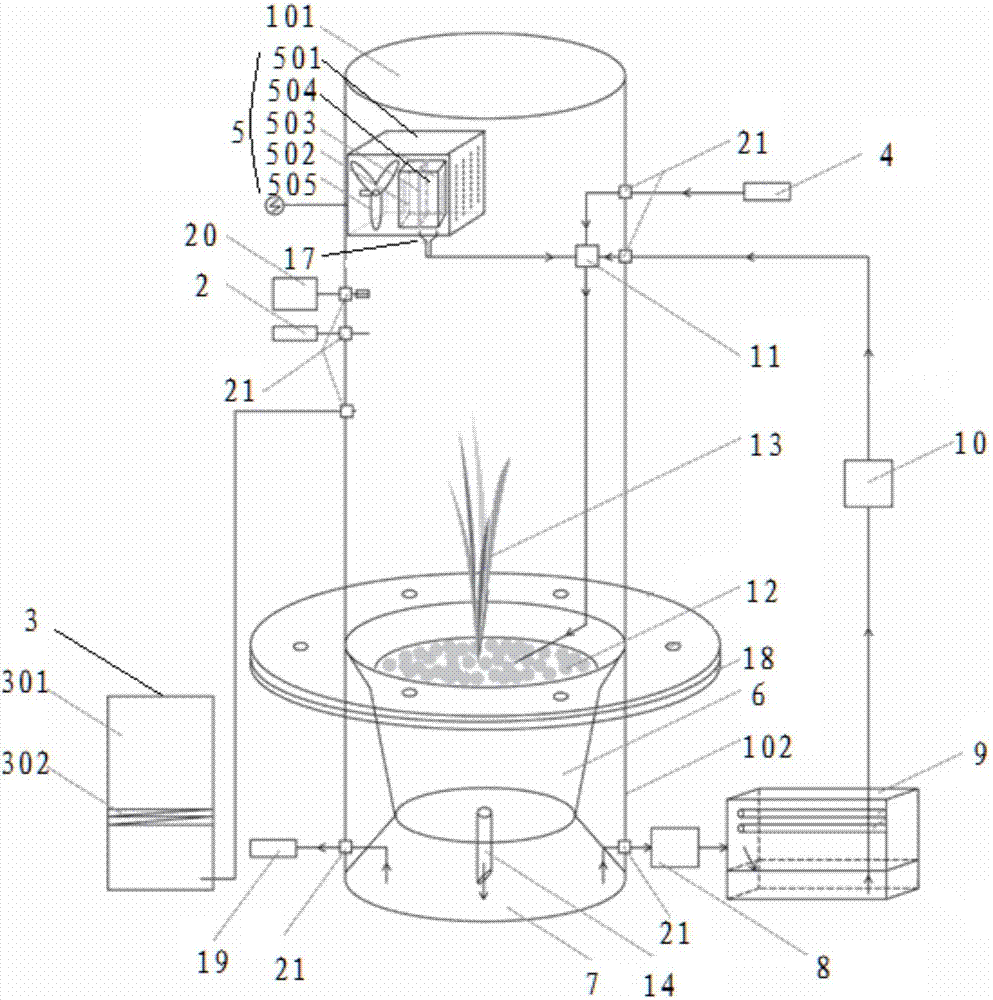
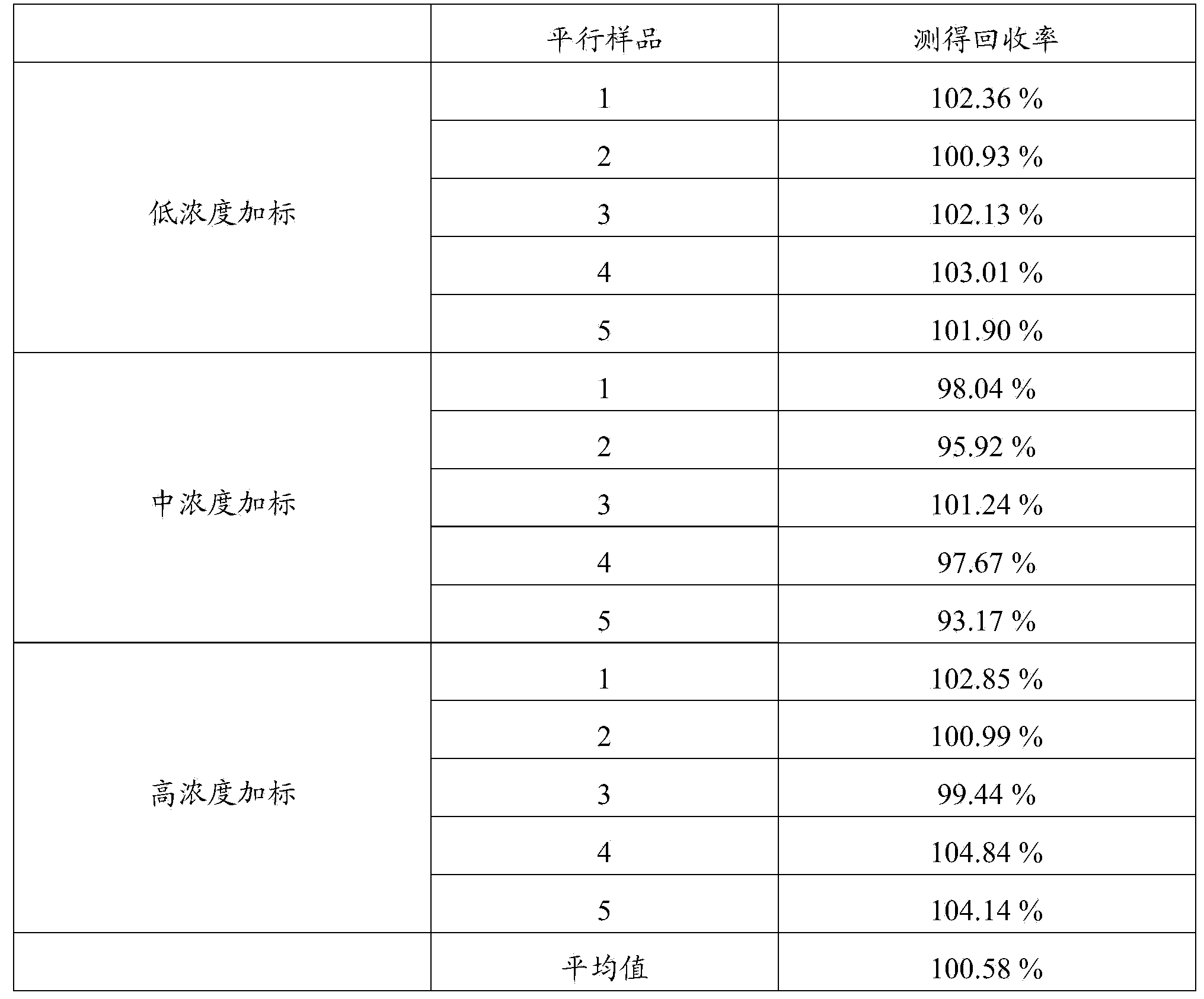Patents
Literature
151 results about "Isotopic signature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
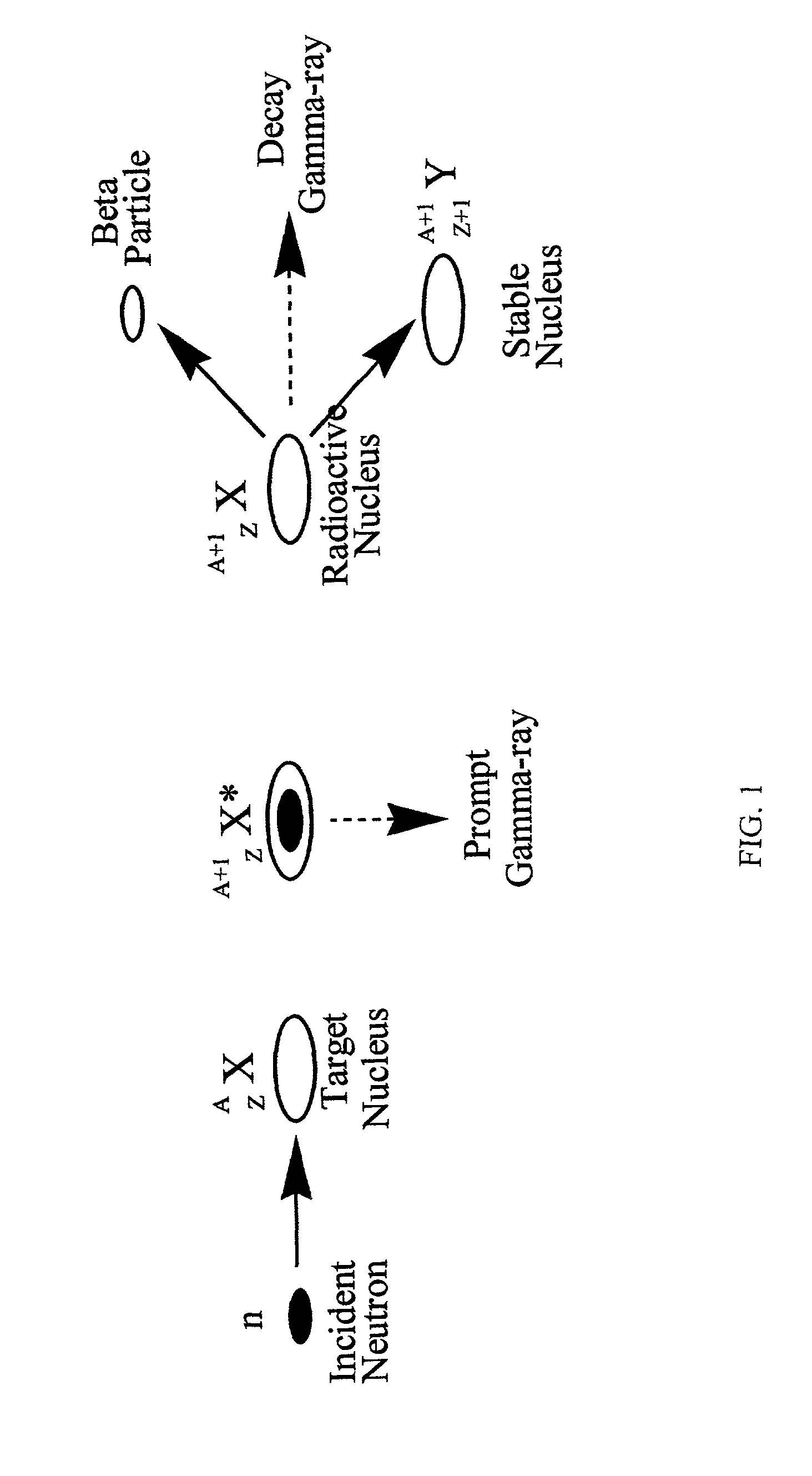
An isotopic signature (also isotopic fingerprint) is a ratio of non-radiogenic 'stable isotopes', stable radiogenic isotopes, or unstable radioactive isotopes of particular elements in an investigated material. The ratios of isotopes in a sample material are measured by isotope-ratio mass spectrometry against an isotopic reference material. This process is called isotope analysis.
Site-specific labeling of proteins for NMR studies
Methods of producing and / or analyzing spectroscopically labeled proteins, e.g., proteins site-specifically labeled with NMR active isotopes, spin-labels, chelators for paramagnetic metals, and the like, are provided. The labeled proteins are produced in translation systems including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthetase / tRNA pairs. Methods for assigning NMR resonances, e.g., methods using isotopically labeled proteins, are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
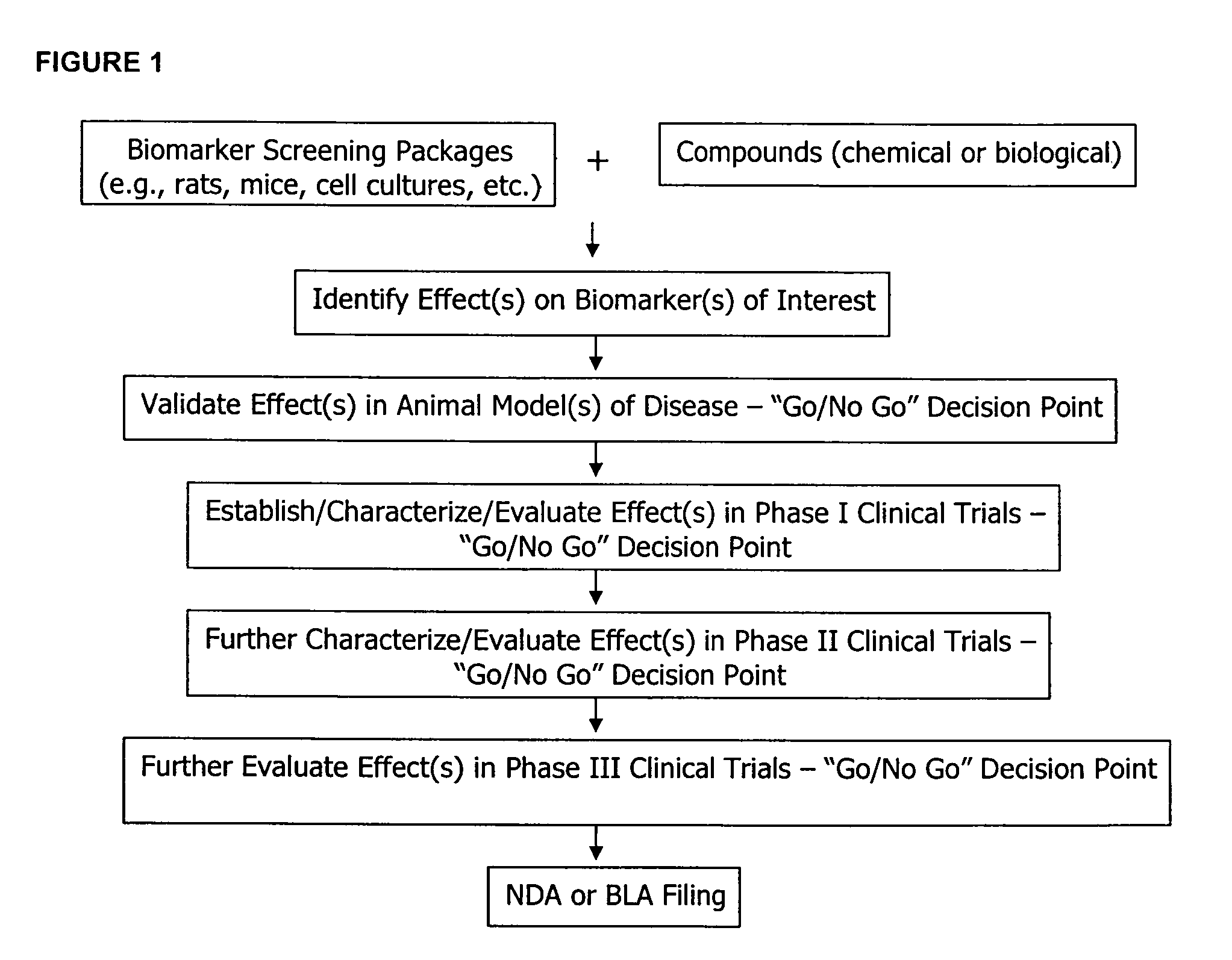
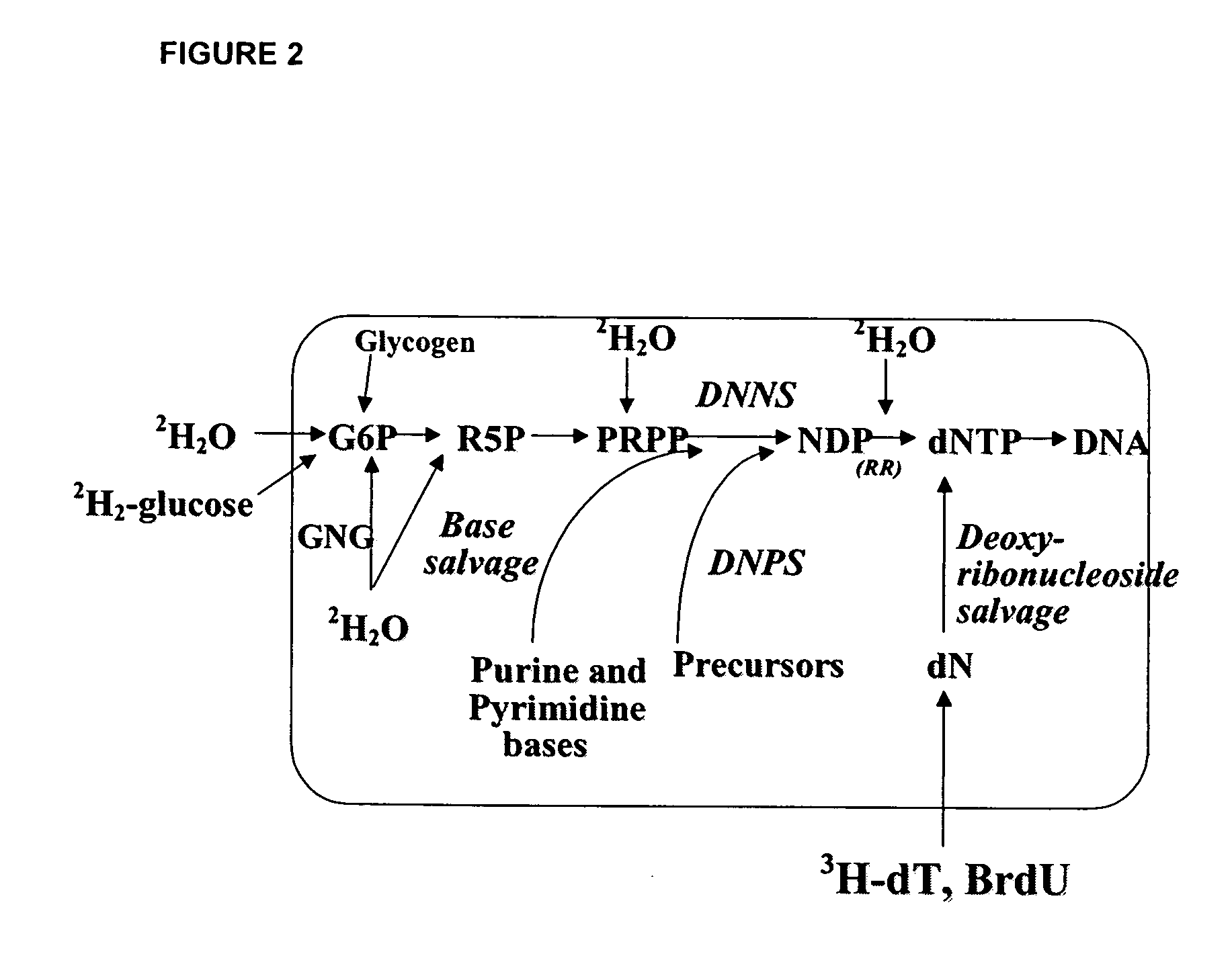
Molecular flux rates through critical pathways measured by stable isotope labeling in vivo, as biomarkers of drug action and disease activity
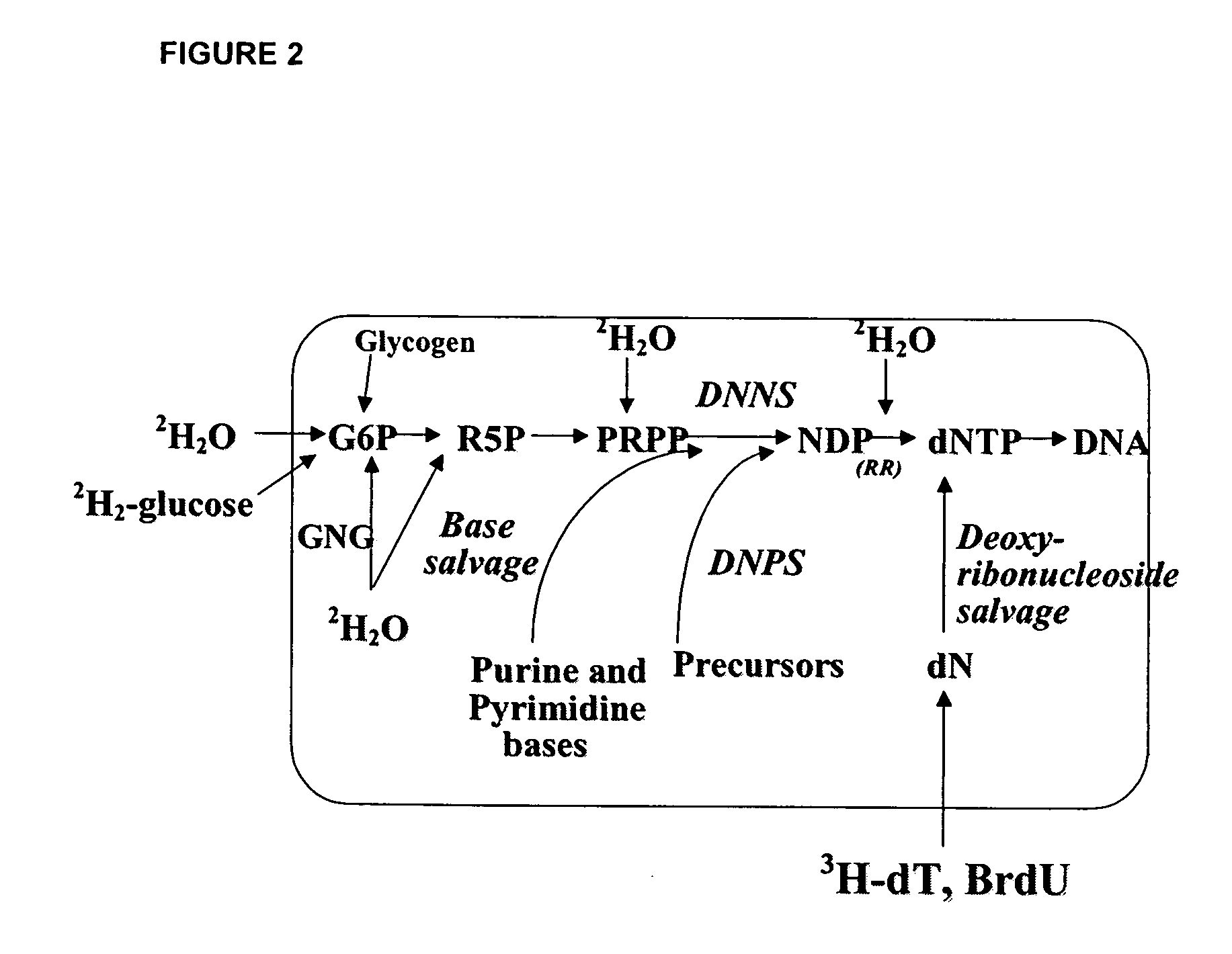
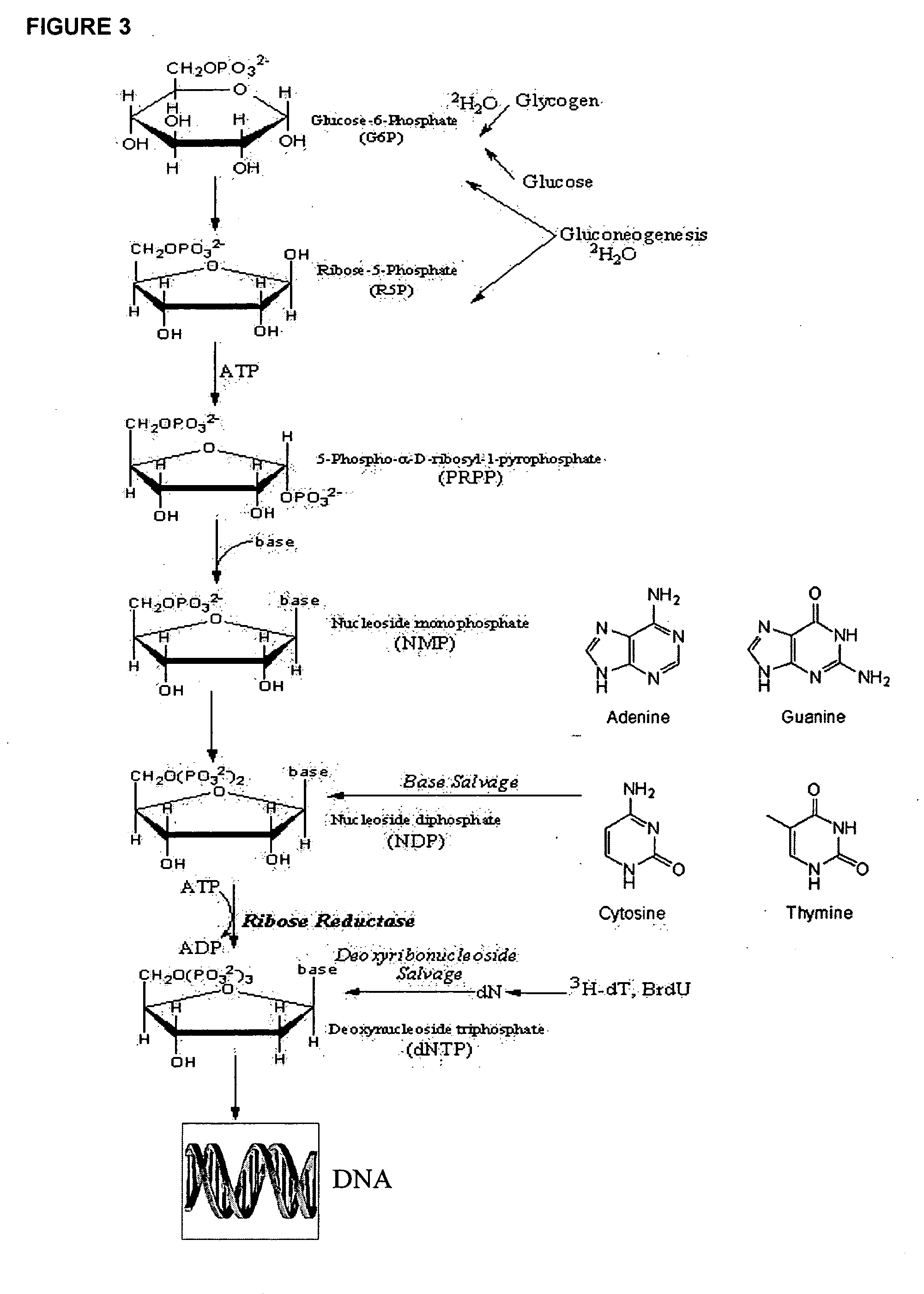
The methods described herein enable the evaluation of compounds on subjects to assess their therapeutic efficacy or toxic effects. The target of analysis is the underlying biochemical process or processes (i.e., metabolic process) thought to be involved in disease pathogenesis. Molecular flux rates within the one or more biochemical processes serve as biomarkers and are quantitated and compared with the molecular flux rates (i.e., biomarker) from control subjects (i.e., subjects not exposed to the compounds). Any change in the biomarker in the subject relative to the biomarker in the control subject provides the necessary information to evaluate therapeutic efficacy of an administered drug or a toxic effect and to develop the compound further if desired. In one aspect of the invention, stable isotope-labeled substrate molecules are administered to a subject and the label is incorporated into targeted molecules in a manner that reveals molecular flux rates through one or more metabolic pathways of interest. By this method, a comparison between subjects and control subjects reveals the effects of the chemical entity or entities on the biomarkers. This, in turn, allows for the identification of potential therapeutic uses or toxicities of the compound. Combinations of compounds can also be systematically evaluated for complementary, synergistic, or antagonistic actions on the metabolic pathways of interest, using the methods of the present invention as a strategy for identifying and confirming novel therapeutic or toxic combinations of compounds.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
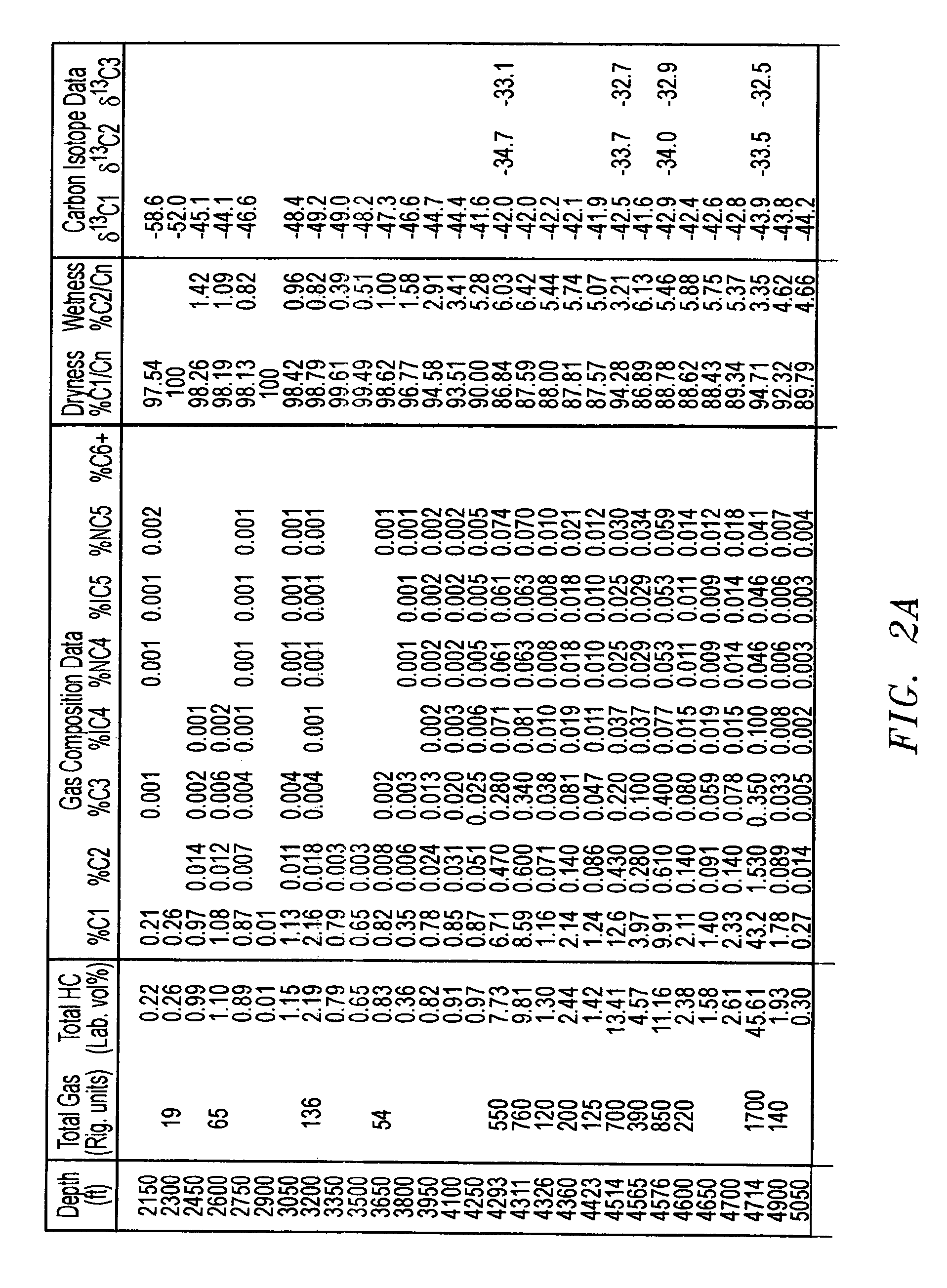
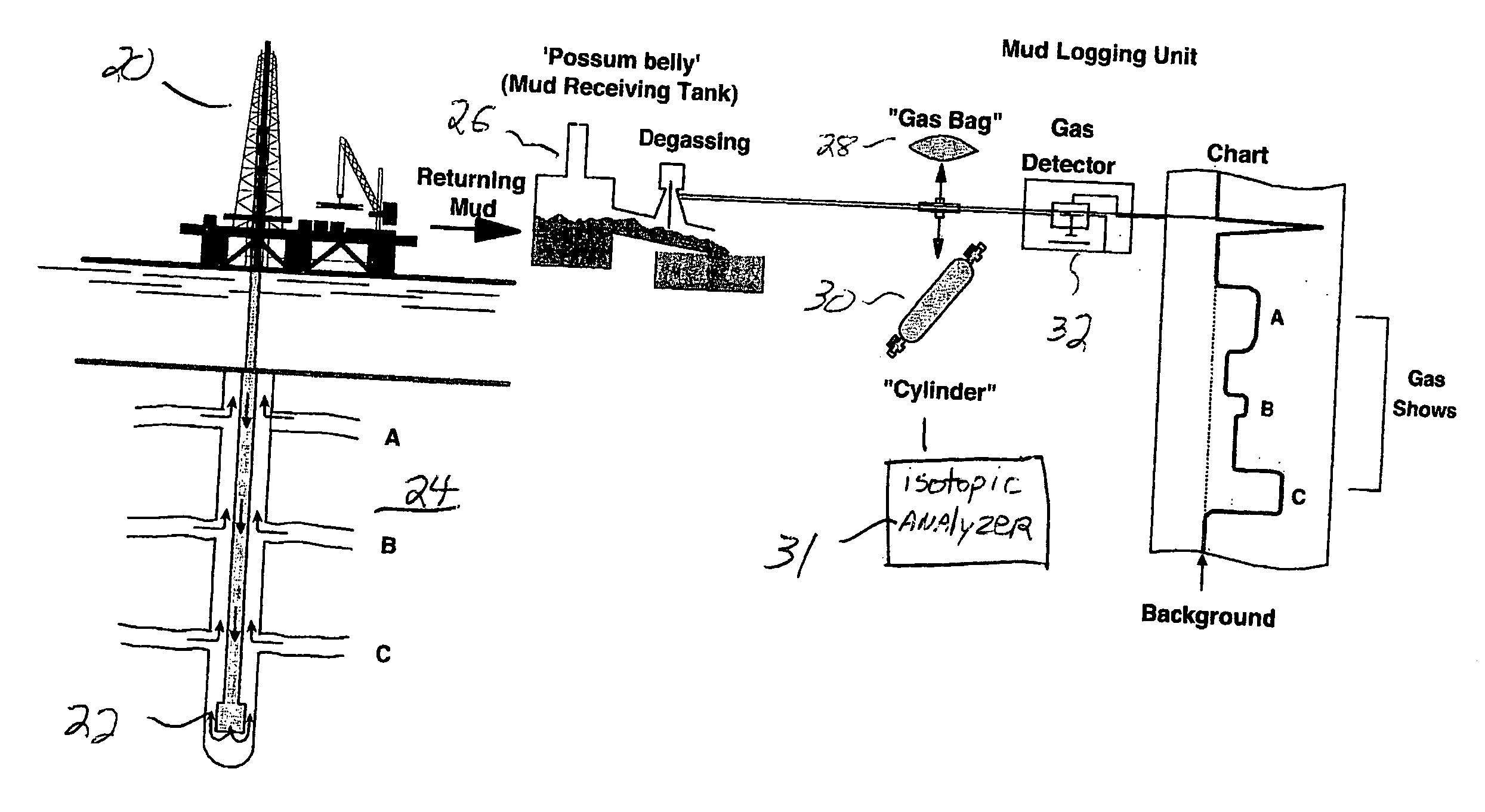
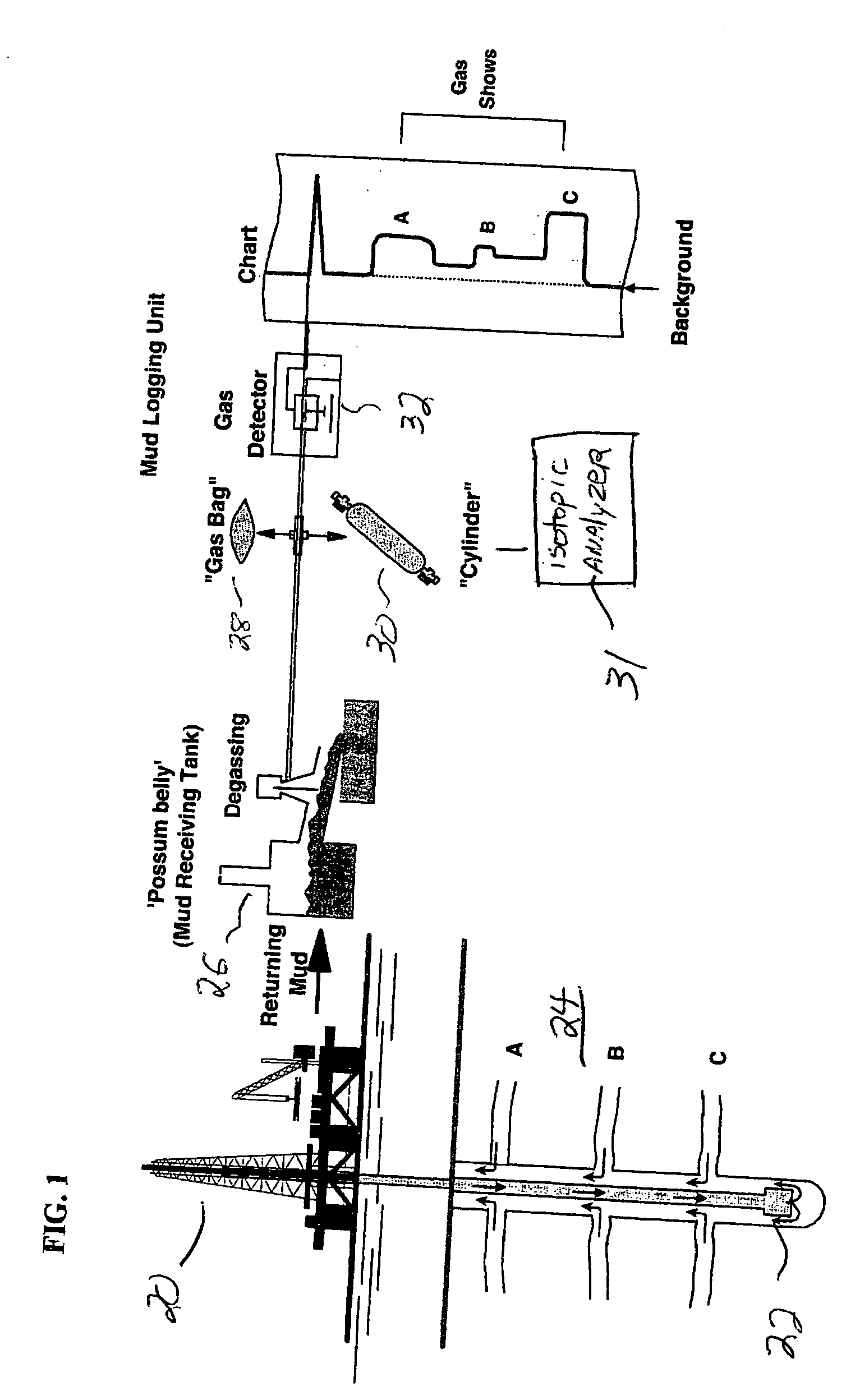
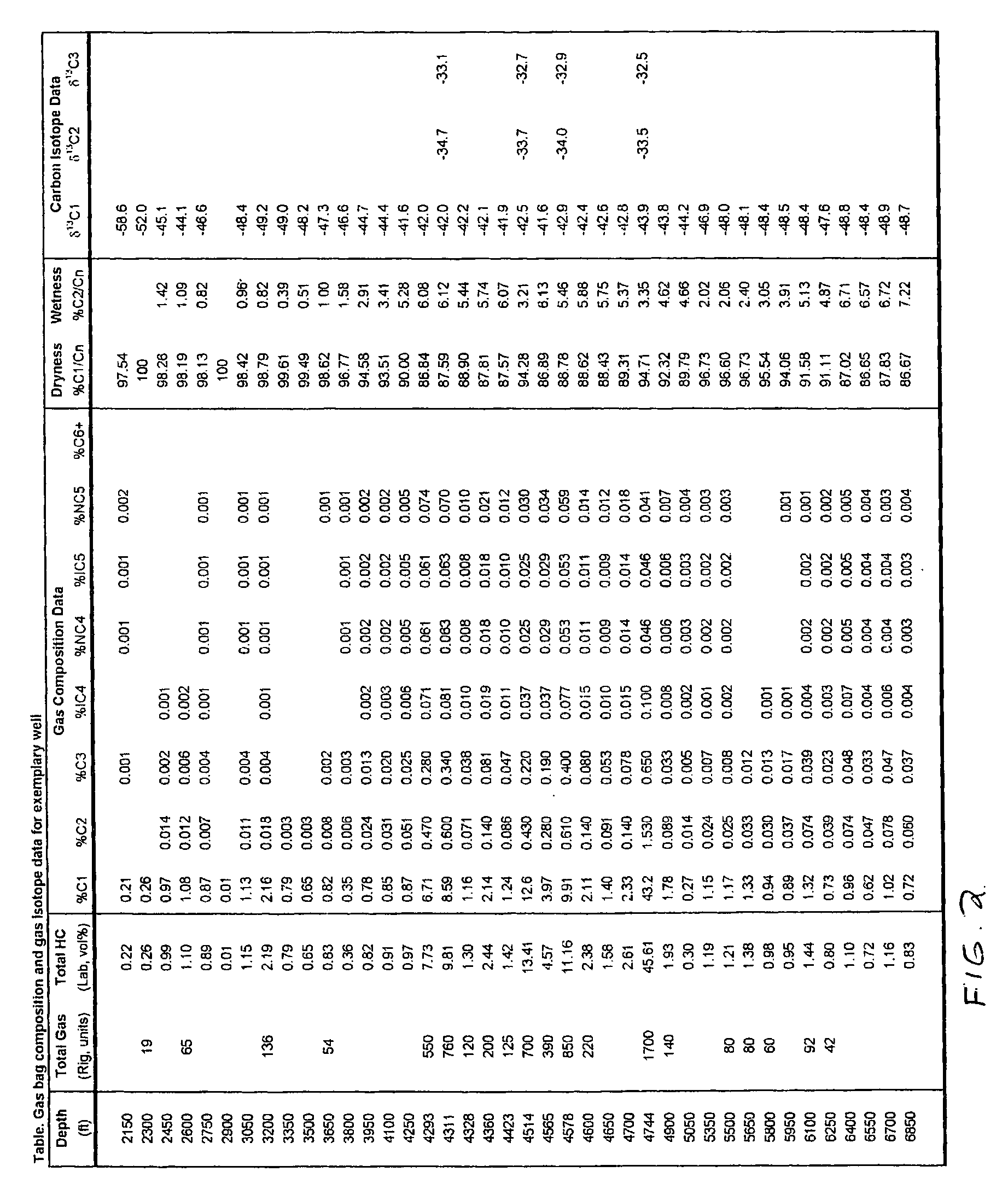
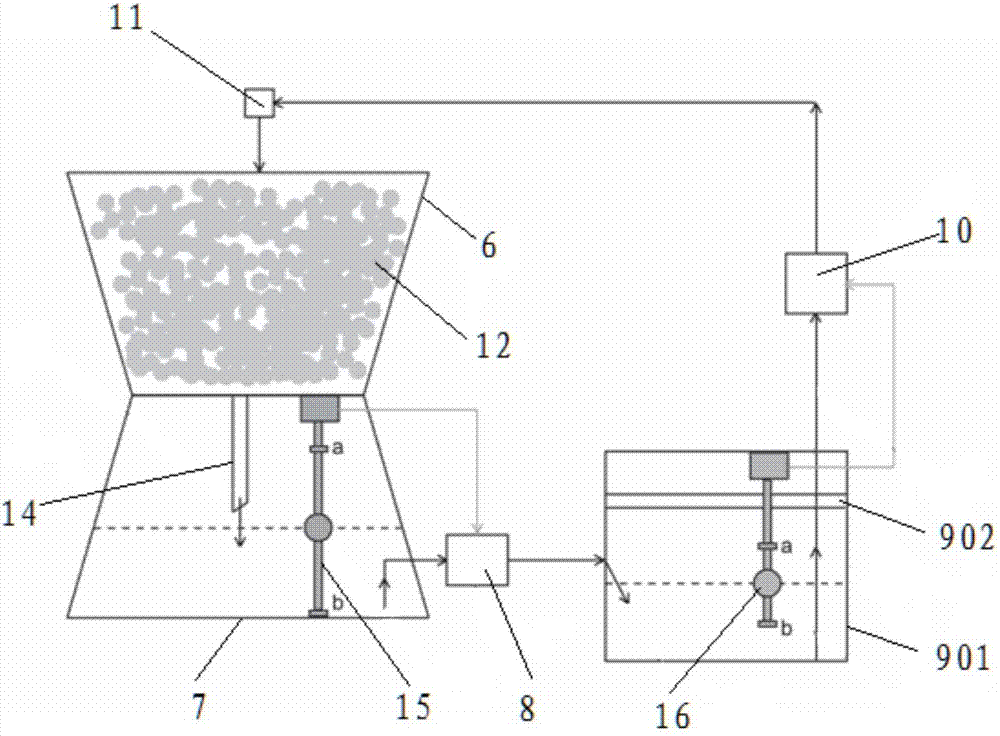
Mud gas isotope logging interpretative process utilizing mixing lines in oil and gas drilling operations
InactiveUS7174254B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingLine tubingCompositional data
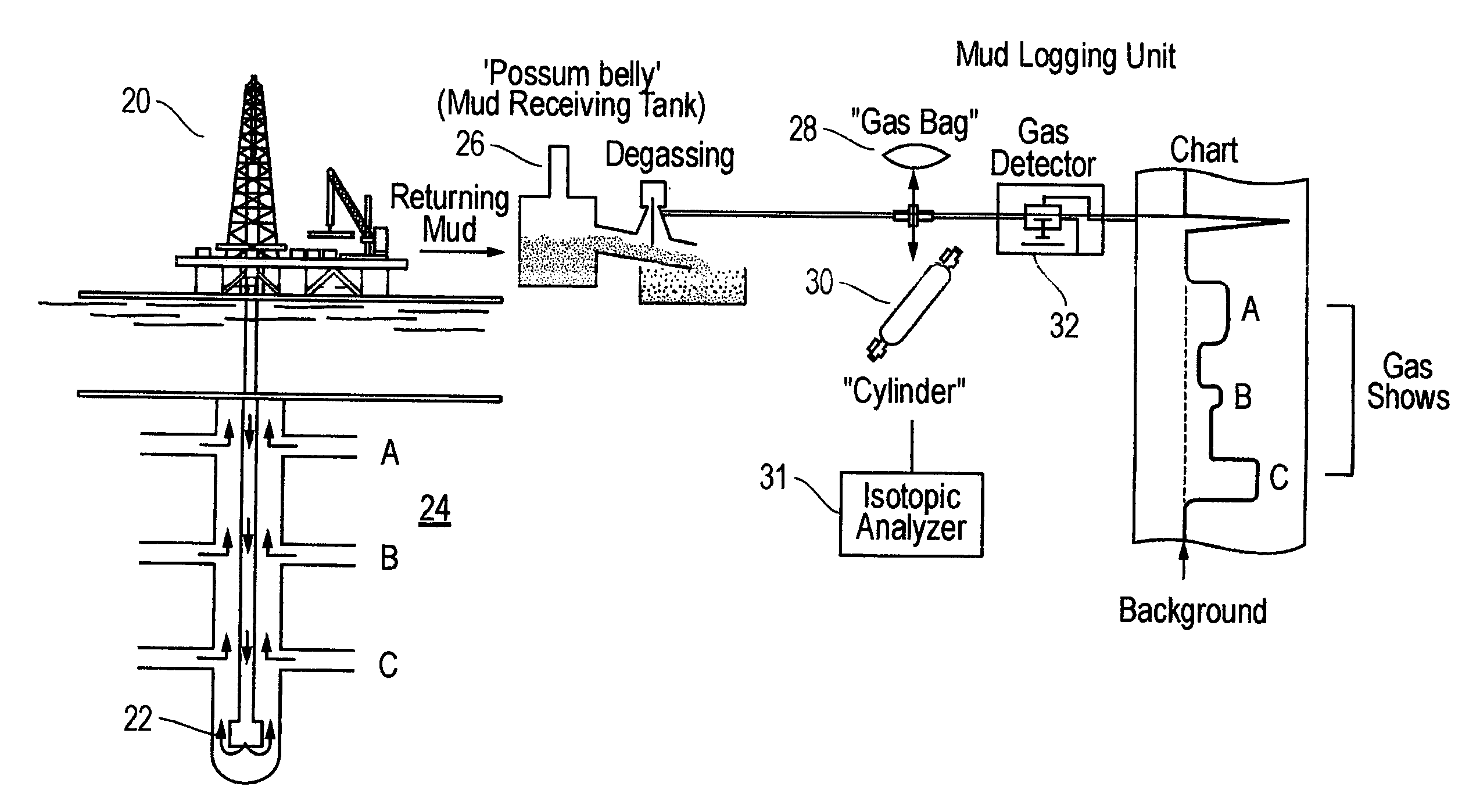
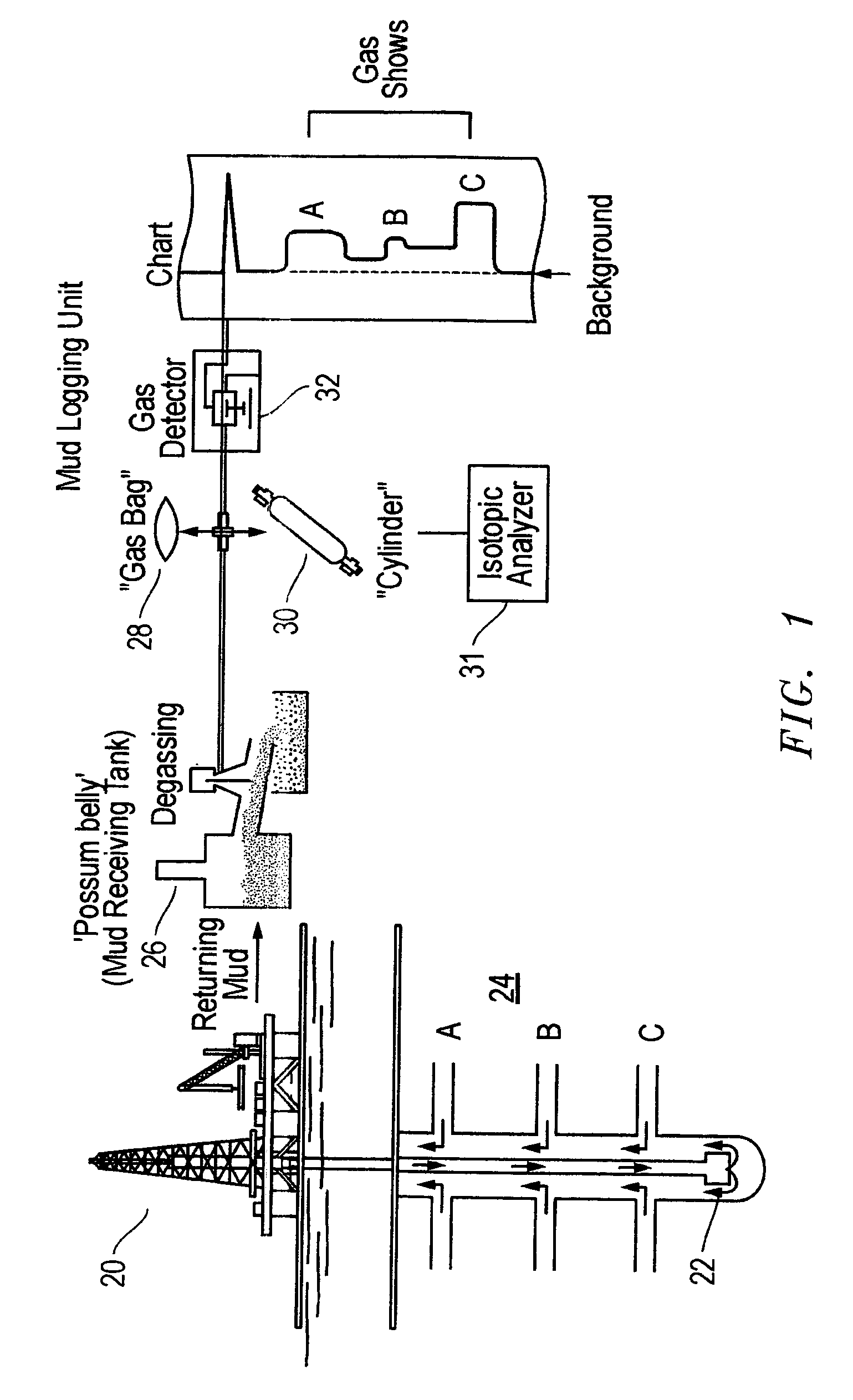
The present invention is a method of interpreting sampled mud gas compositional and isotopic data from a target area in a drilling operation. The compositional and isotopic data is plotted on a chart. The chart preferably illustrates methane compositional data together with isotopic composition, such as δ13C1. From this chart, mixing lines are determined. The mixing lines are determined by finding data points plotted on the chart which approximate a straight line or other trend. The mixing lines are then analyzed to determine reservoir isotopic signature, hydrocarbon communication and any interference to this communication within the target area.
Owner:ELLIS LEROY
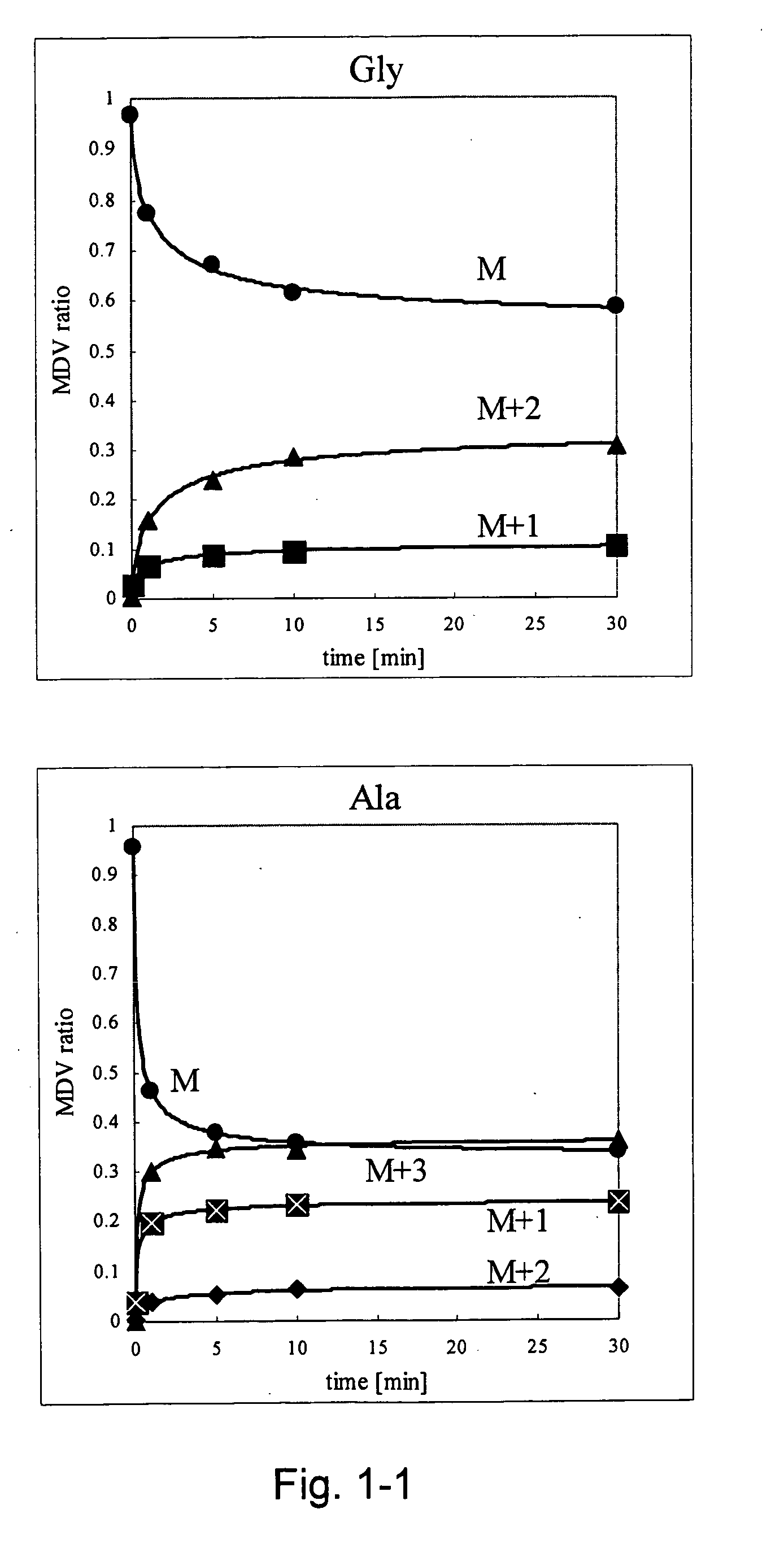
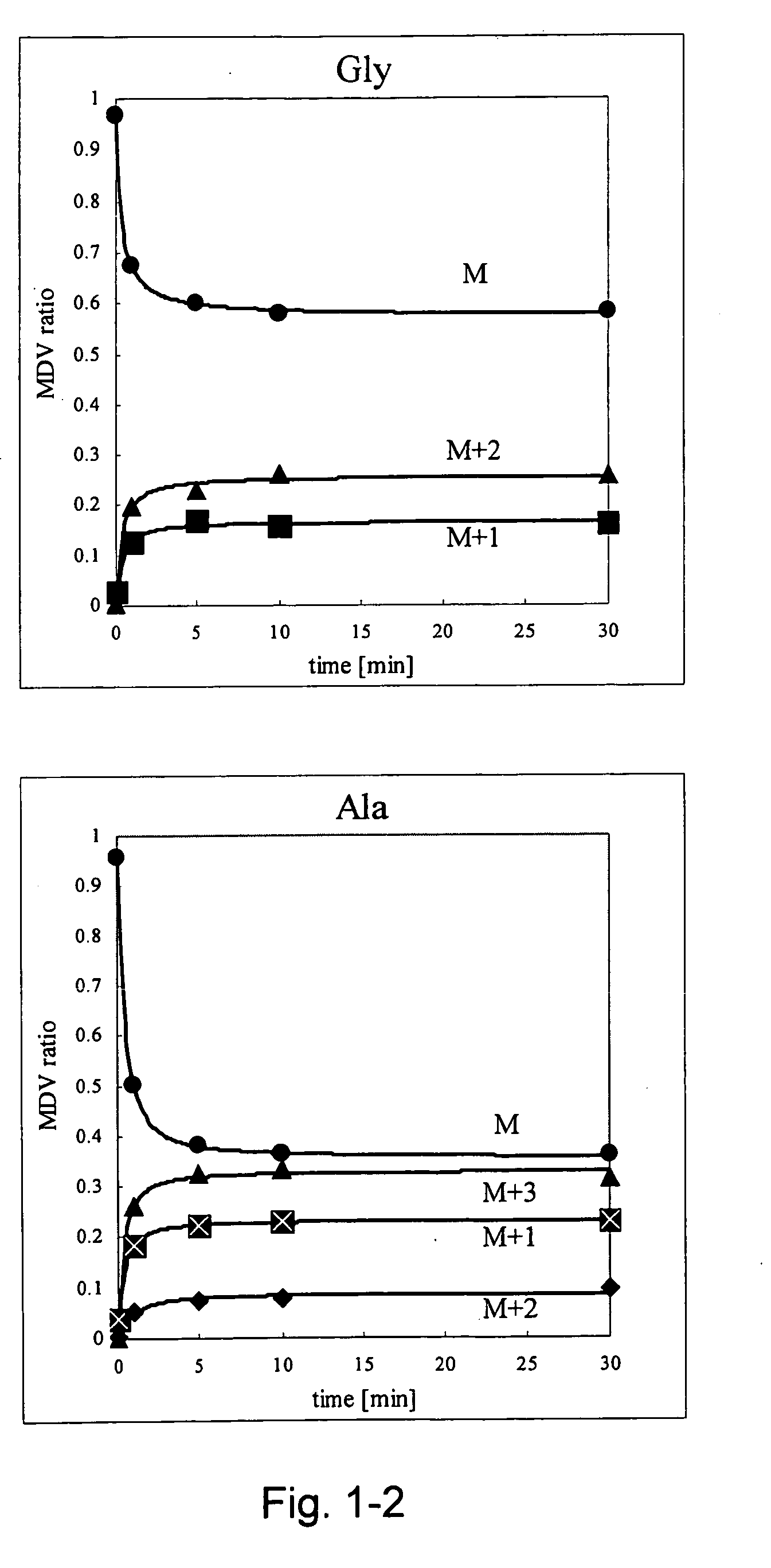
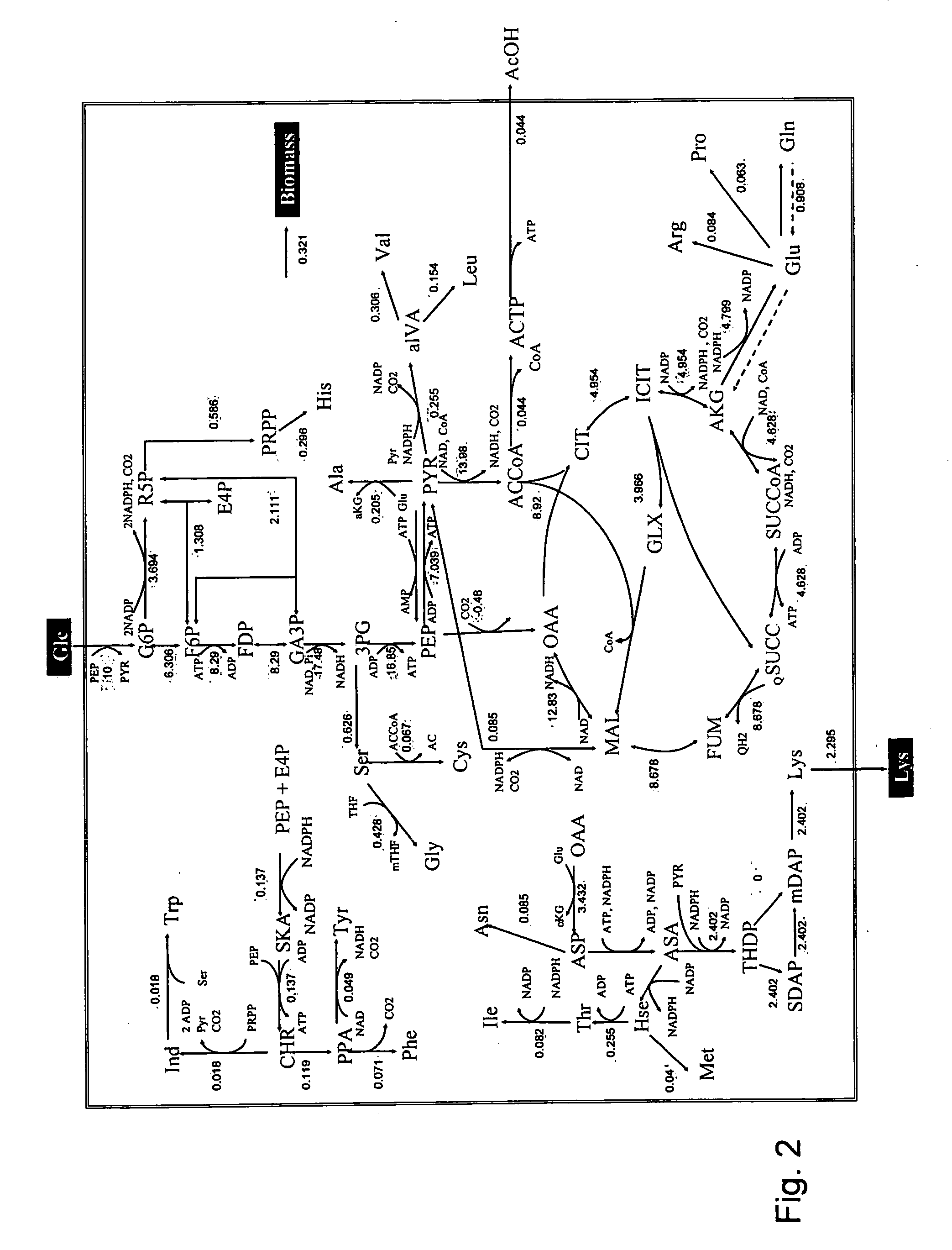
Intracellular metabolic flux analysis method using substrate labeled with isotope
InactiveUS20050175982A1Low costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDrug metabolismTime course
A method for intracellular metabolic flux analysis comprising (a) culturing cells in a medium not containing any isotope-labeled substrate to a target phase of the metabolic flux analysis, (b) adding an isotope-labeled substrate to the medium, and continuing culture and collecting samples from the medium in time course, (c) measuring isotope distribution in an intracellular metabolite contained in the samples collected in time course, (d) performing a regression analysis for measured data and calculating an isotope distribution ratio in a steady state, and (e) analyzing a metabolic flux of the cultured cells by using the calculated isotope distribution ratio.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
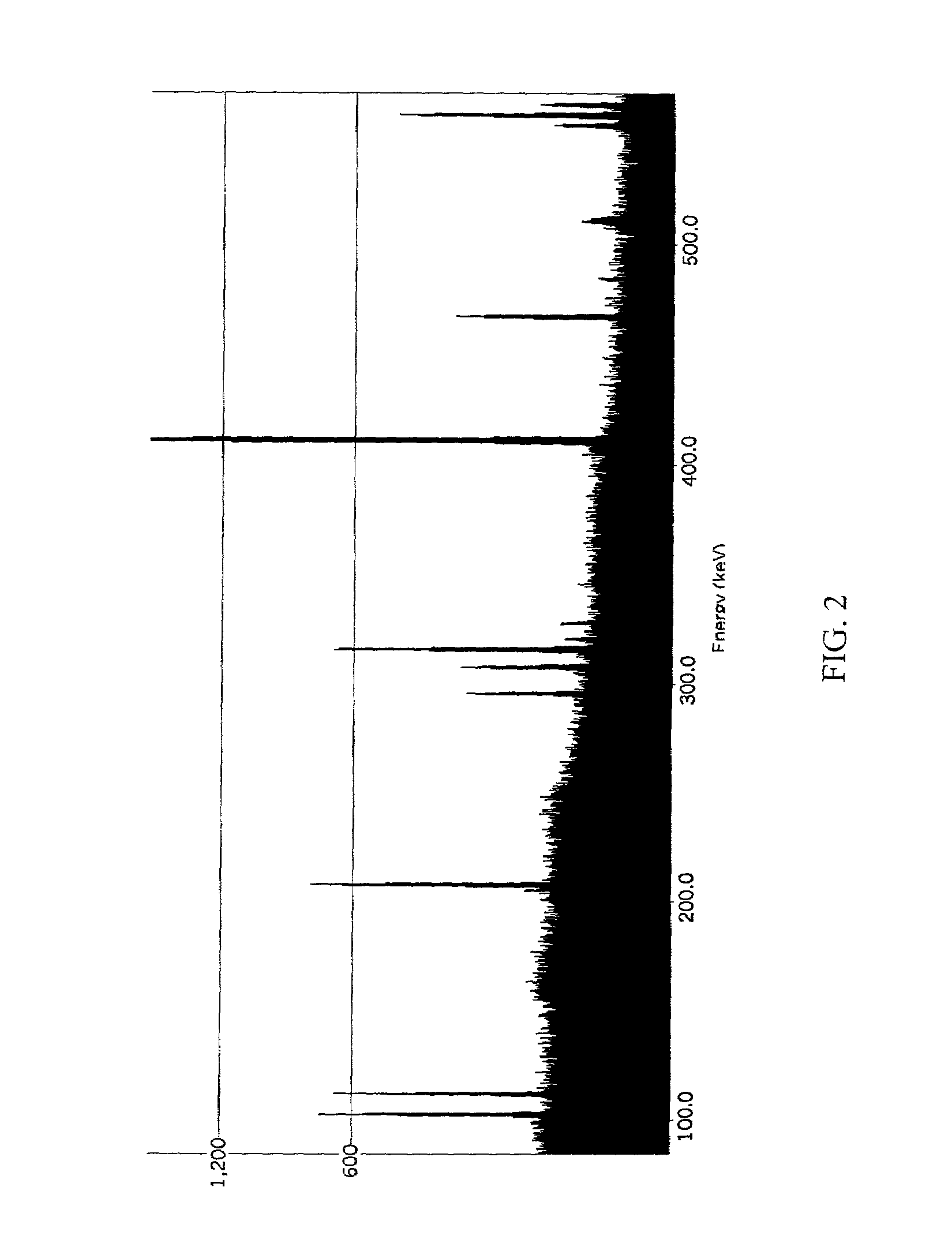
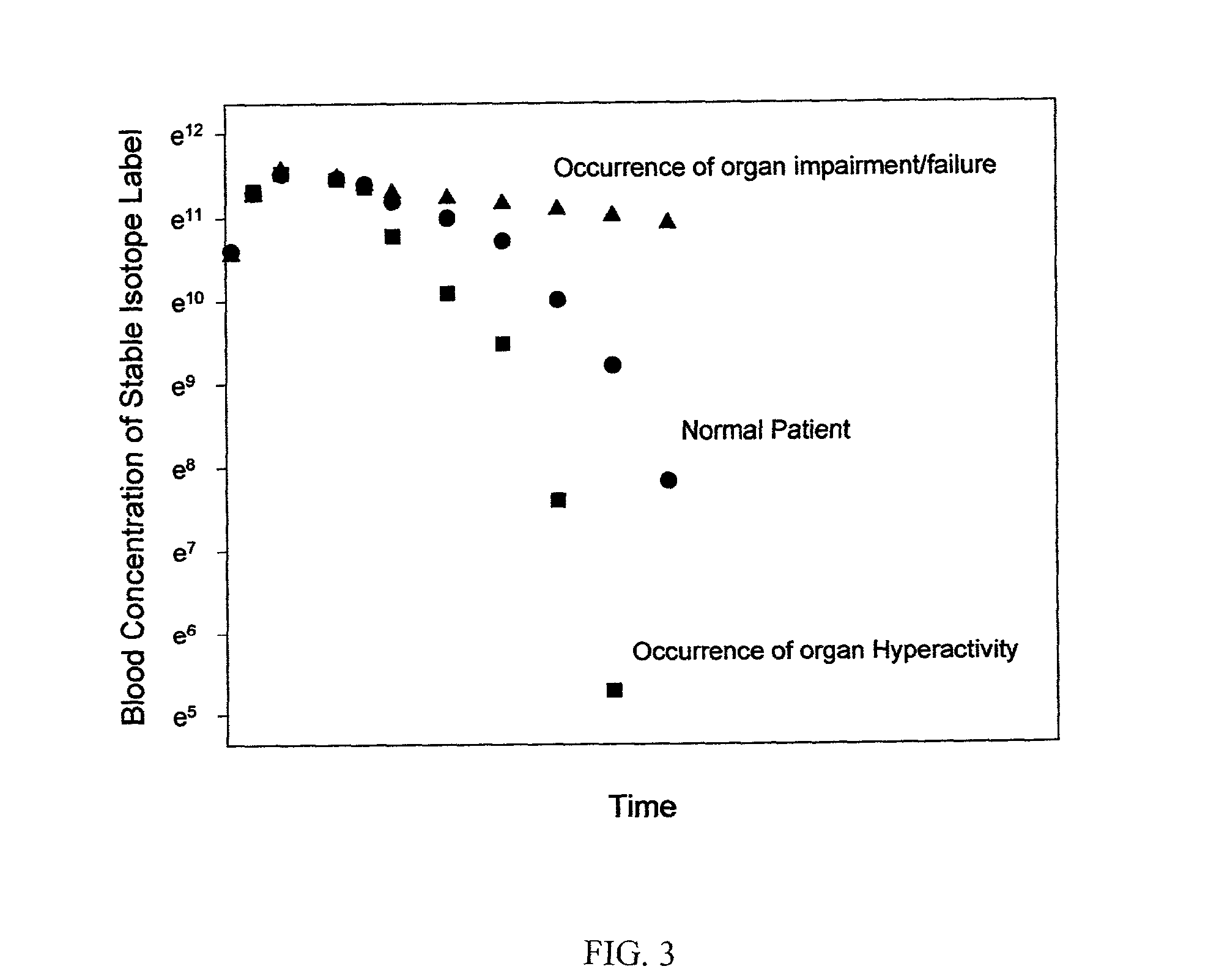
Synthesis, compositions and methods for the measurement of the concentration of stable-isotope labeled compounds in life forms and life form excretory products
Stable isotope labeling and neutron activation to measure biological functions are provided, as are the use and method of adding a chemical monitor to correct for neutron flux to sample vials prior to the addition of sample is presented, and the use of stable isotopes as a chemical bar code for vials and other items. Methods are provided also for measuring glomerular filtration rate and glomerular sieving function in a subject, and for measuring other physiological functions.
Owner:BIOPAL
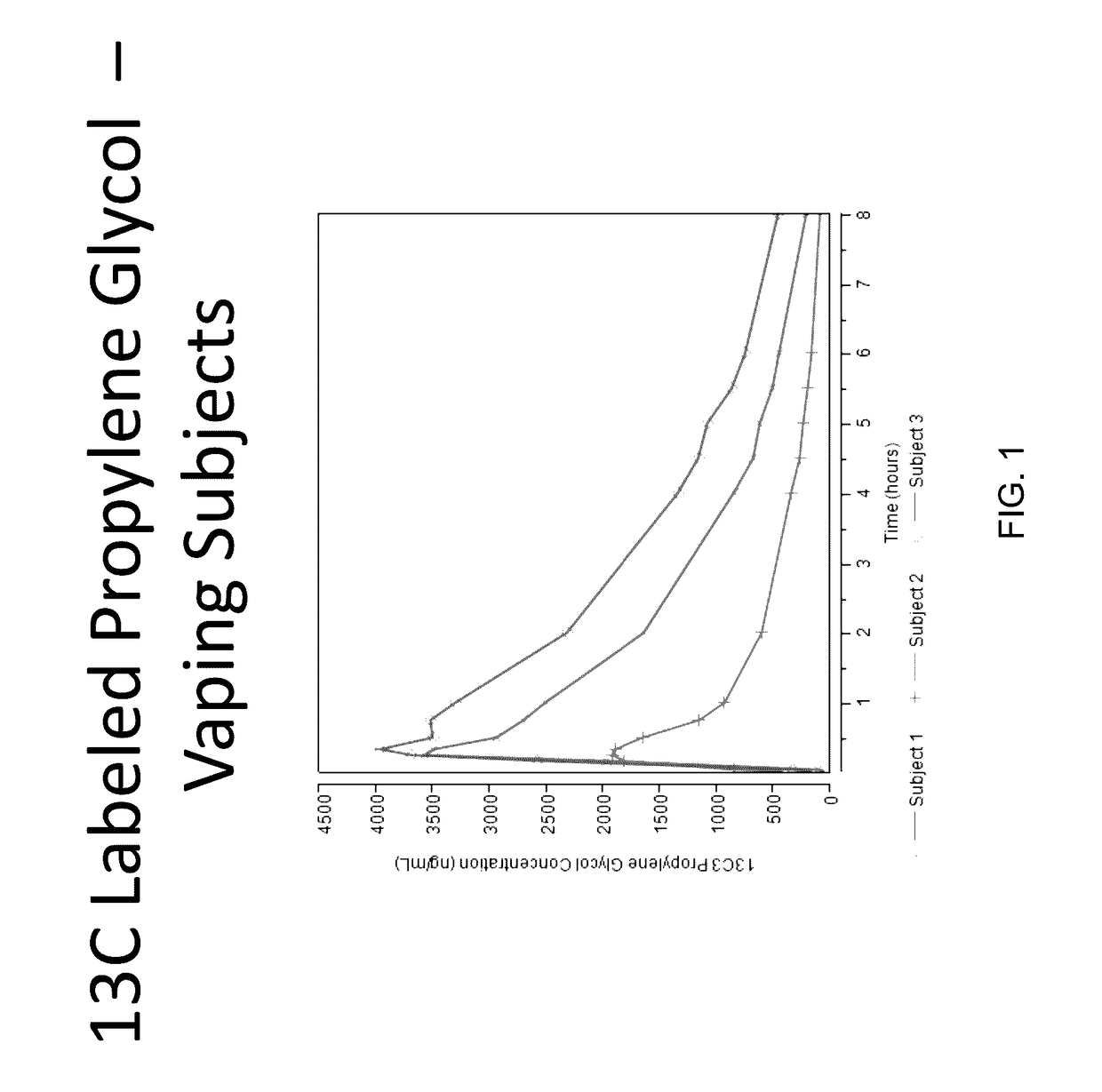
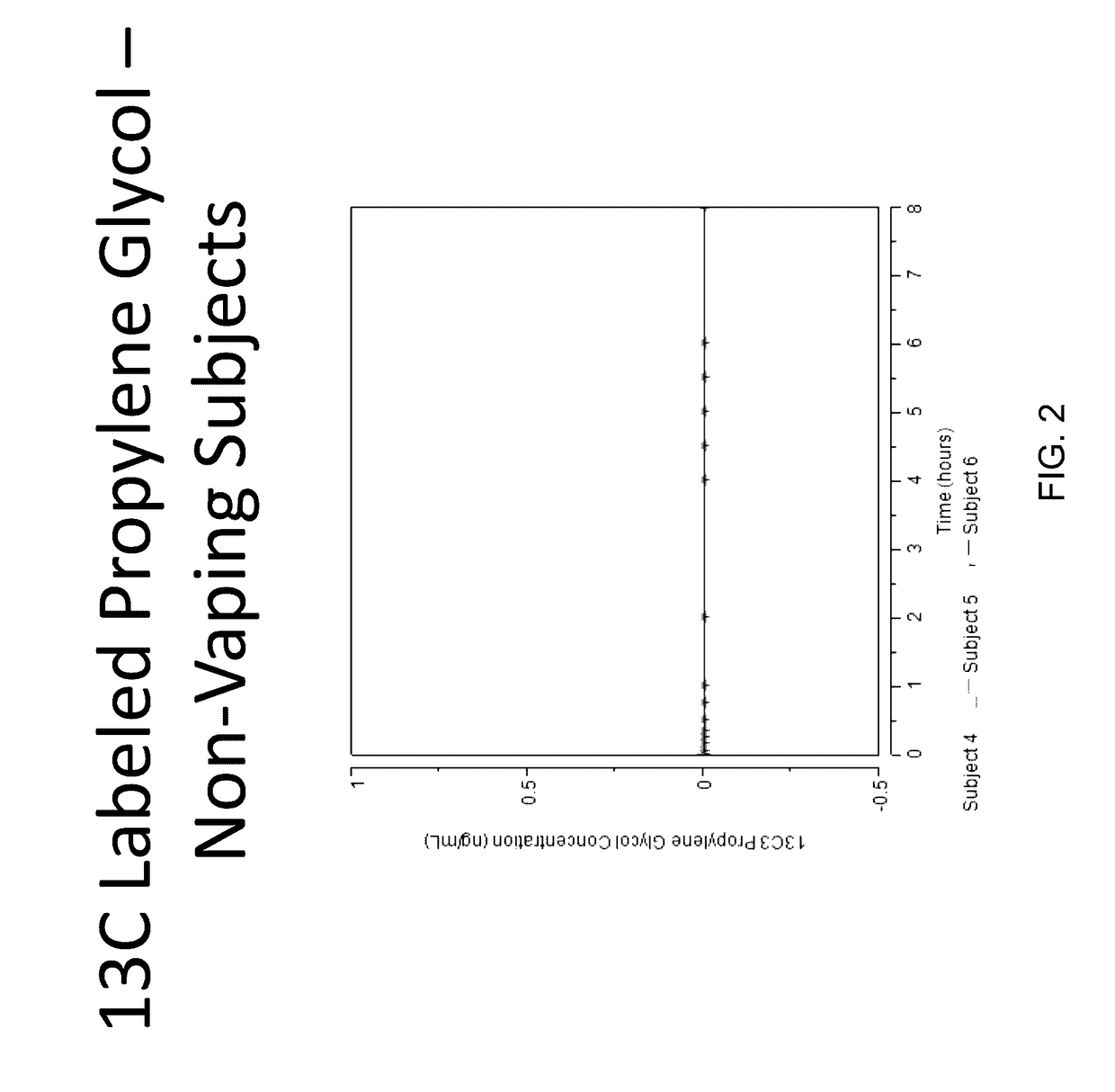
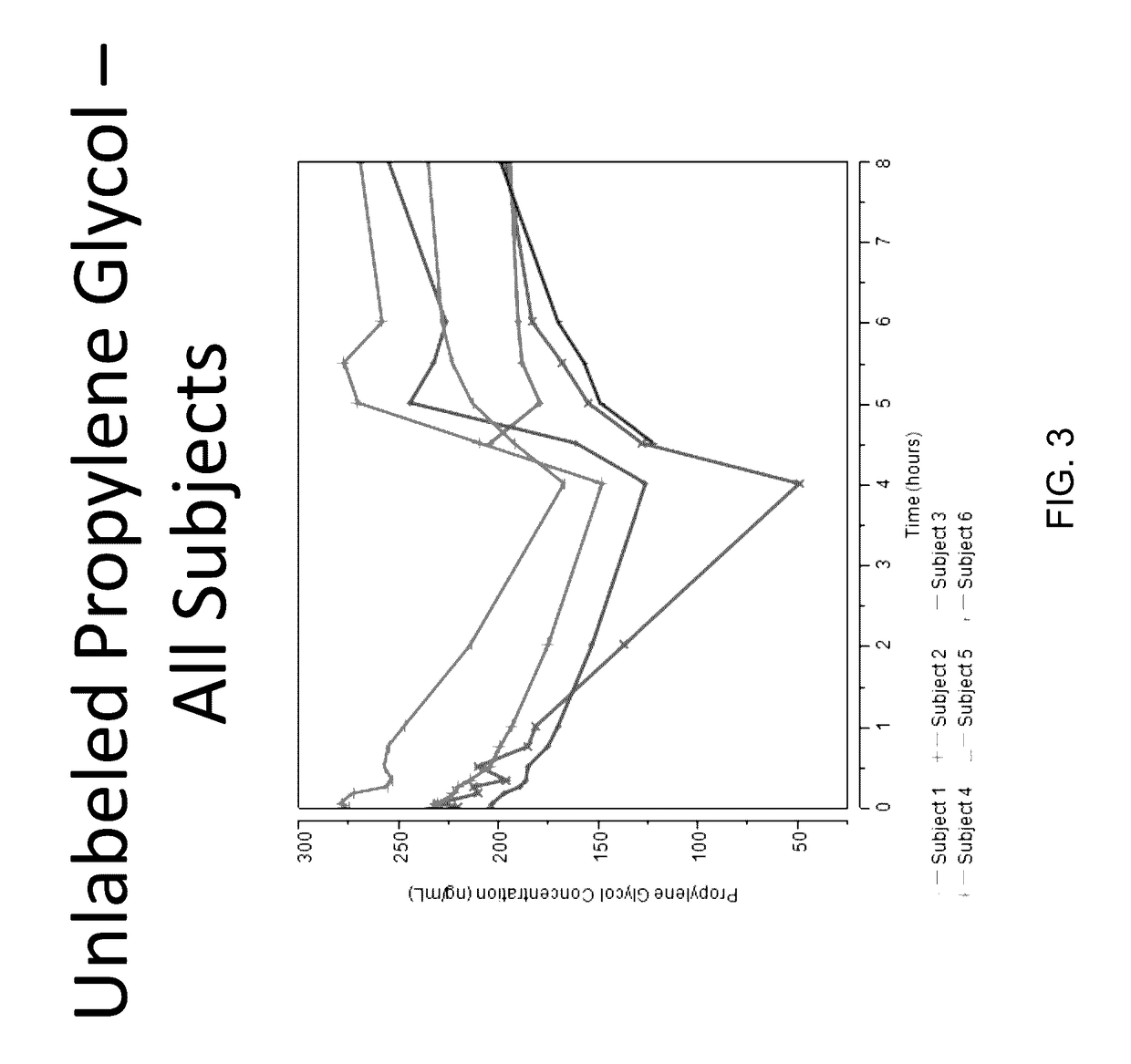
Isotopically-labeled solvents and the use of same in testing e-cigarettes
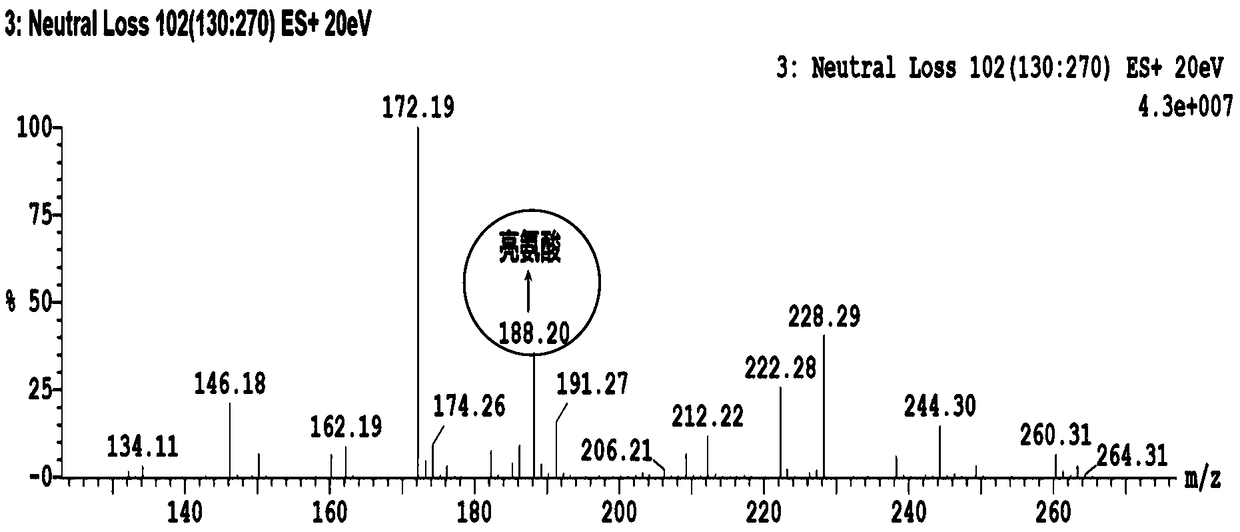
Isotopically-labeled species of propylene glycol and glycerol are provided as solvents for use in electronic nicotine delivery systems (e.g., as disposed in a cartridge in an e-cigarette). The isotopically-labeled species are distinguishable from the non-isotopically-labeled species (e.g., by mass spectrometry). Thus, methods are provided for the measurement of the quantity of solvent or of a solvent heating by-product (e.g., formaldehyde, acetaldehyde), or of a metabolite of the drug, delivered to a user by analysis of blood samples taken subsequent to dosing by use of the electronic nicotine delivery system. An example of an isotopically-labeled species of propylene glycol for use in such measurement methods is [13C]3H8O2. A clinical study of e-cigarettes loaded with this isotopically-labeled species resulted in the following blood plasma concentration profiles in “vaping” subjects.
Owner:CELERION INC
Molecular flux rates through critical pathways measured by stable isotope labeling in vivo, as biomarkers of drug action and disease activity
The methods described herein enable the evaluation of compounds on subjects to assess their therapeutic efficacy or toxic effects. The target of analysis is the underlying biochemical process or processes (i.e., metabolic process) thought to be involved in disease pathogenesis. Molecular flux rates within the one or more biochemical processes serve as biomarkers and are quantitated and compared with the molecular flux rates (i.e., biomarker) from control subjects (i.e., subjects not exposed to the compounds). Any change in the biomarker in the subject relative to the biomarker in the control subject provides information to evaluate therapeutic efficacy of an administered drug or a toxic effect and to develop the compound further if desired. In one aspect of the invention, stable isotope-labeled substrate molecules are administered to a subject and the label is incorporated into targeted molecules in a manner that reveals molecular flux rates through metabolic pathways of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
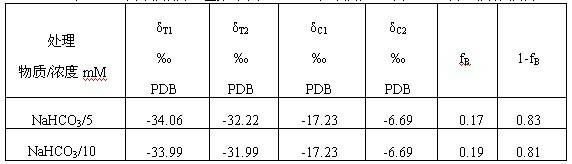
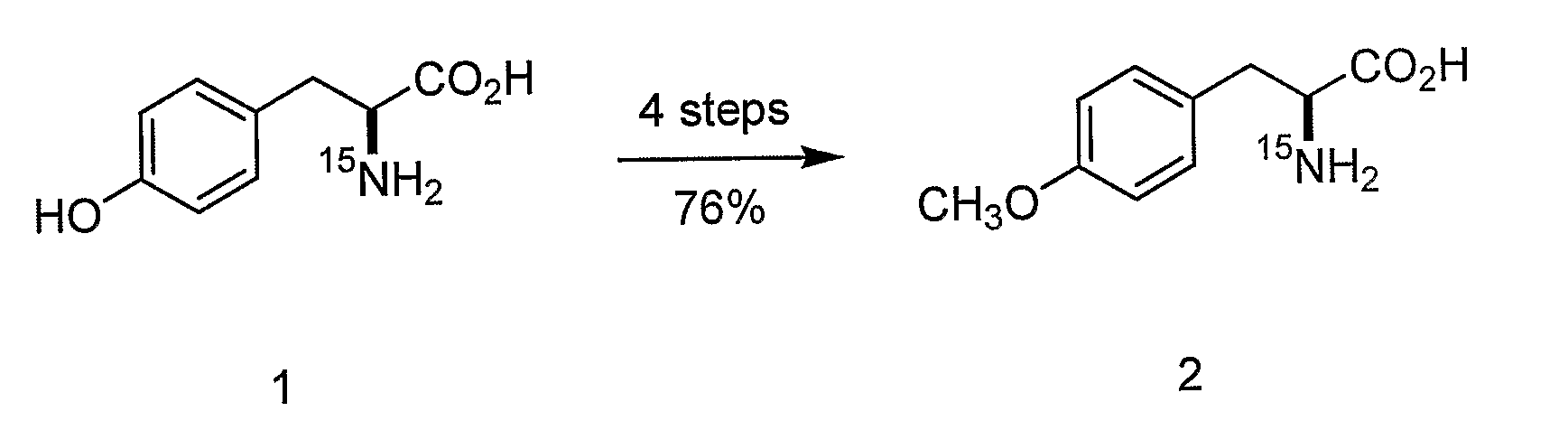
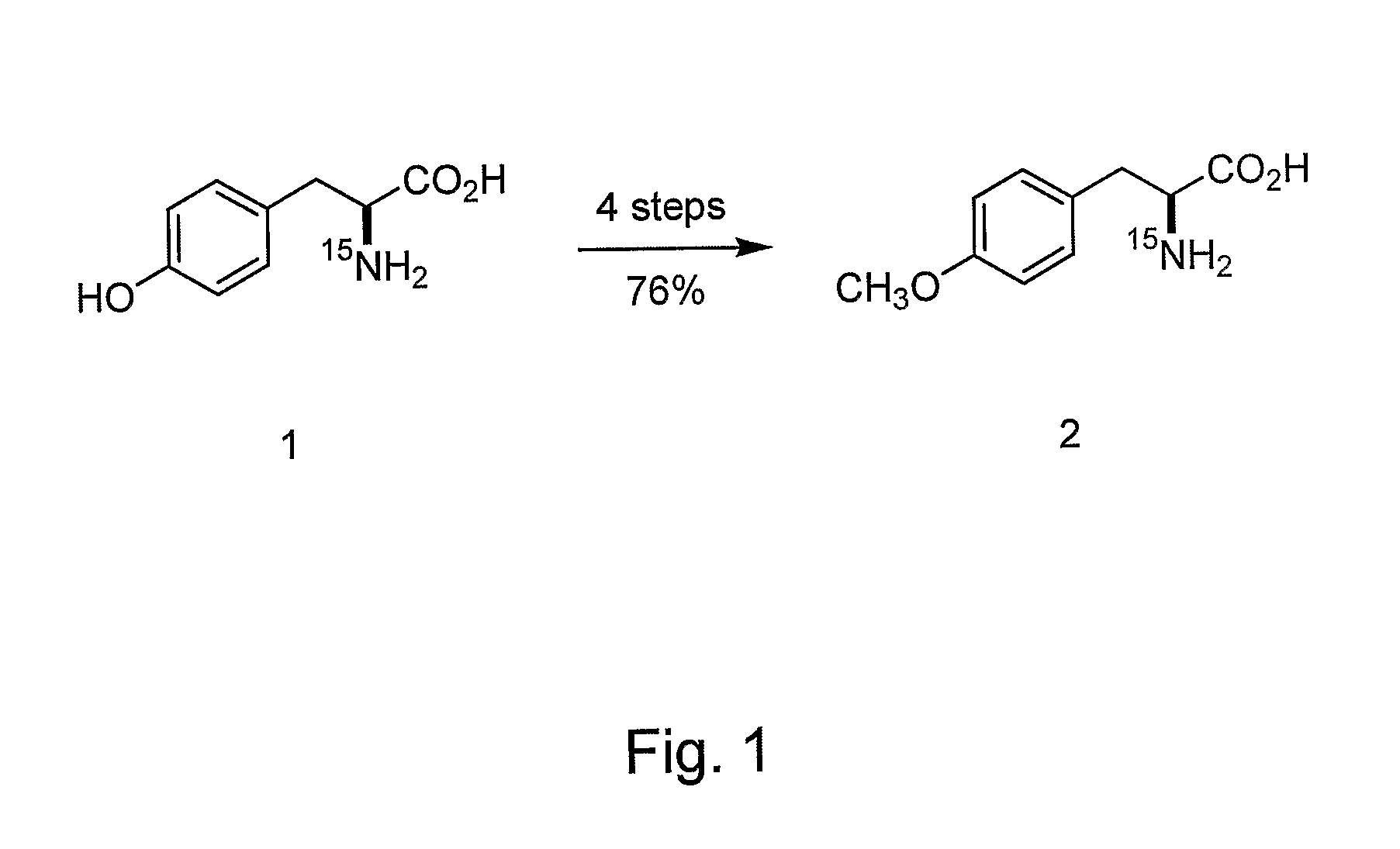
Method by utilizing double markers to acquire share of inorganic carbon source utilized by plants
ActiveCN102511362AFew stepsSimple calculationCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationSodium bicarbonateCulture fluid
The invention discloses a method by utilizing double markers to acquire share of inorganic carbon source utilized by plants, which comprises the following steps that: A. sodium bicarbonate produced by different manufacturers is determined, two types of sodium bicarbonate with delta 13C difference being more than eight thousandths are used as an isotopic marker 1 and an isotopic marker 2 to be respectively added into nutrient fluid to culture plants; delta 13C value of bicarbonate ion in nutrient fluid of the isotopic marker 1 is delta C1, and delta 13C value of bicarbonate ion in nutrient fluid of the isotopic marker 2 is delta C2; and B. after more than four leaves appear, the values of delta 13C consisting of stable carbon isotopes of plant leaves to be observed correspondently culturedby the nutrient fluid of the two types of isotopic markers are respectively determined as delta T1 and delta T2; and C. delta C1, delta C2, delta T1 and delta T2 are brought into equation fB= to calculate the share fB of the carbonate ions utilized by the plants. Due to the adoption of the method, the share of the inorganic carbon source utilized by the plants can be rapidly acquired, the steps are fewer, simplicity in calculation can be realized, and data is reliable.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Mud gas isotope logging interpretative process utilizing mixing lines in oil and gas drilling operations
InactiveUS20050256647A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingLine tubingIsotopic composition
The present invention is a method of interpreting sampled mud gas compositional and isotopic data from a target area in a drilling operation. The compositional and isotopic data is plotted on a chart. The chart preferably illustrates methane compositional data together with isotopic composition, such as δ13C1. From this chart, mixing lines are determined. The mixing lines are determined by finding data points plotted on the chart which approximate a straight line or other trend. The mixing lines are then analyzed to determine reservoir isotopic signature, hydrocarbon communication and any interference to this communication within the target area.
Owner:ELLIS LEROY
Site-Specific Labeling of Proteins for Nmr Studies
Methods of producing and / or analyzing spectroscopically labeled proteins, e.g., proteins site-specifically labeled with NMR active isotopes, spin-labels, chelators for paramagnetic metals, and the like, are provided. The labeled proteins are produced in translation systems including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthetase / tRNA pairs. Methods for assigning NMR resonances, e.g., methods using isotopically labeled proteins, are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
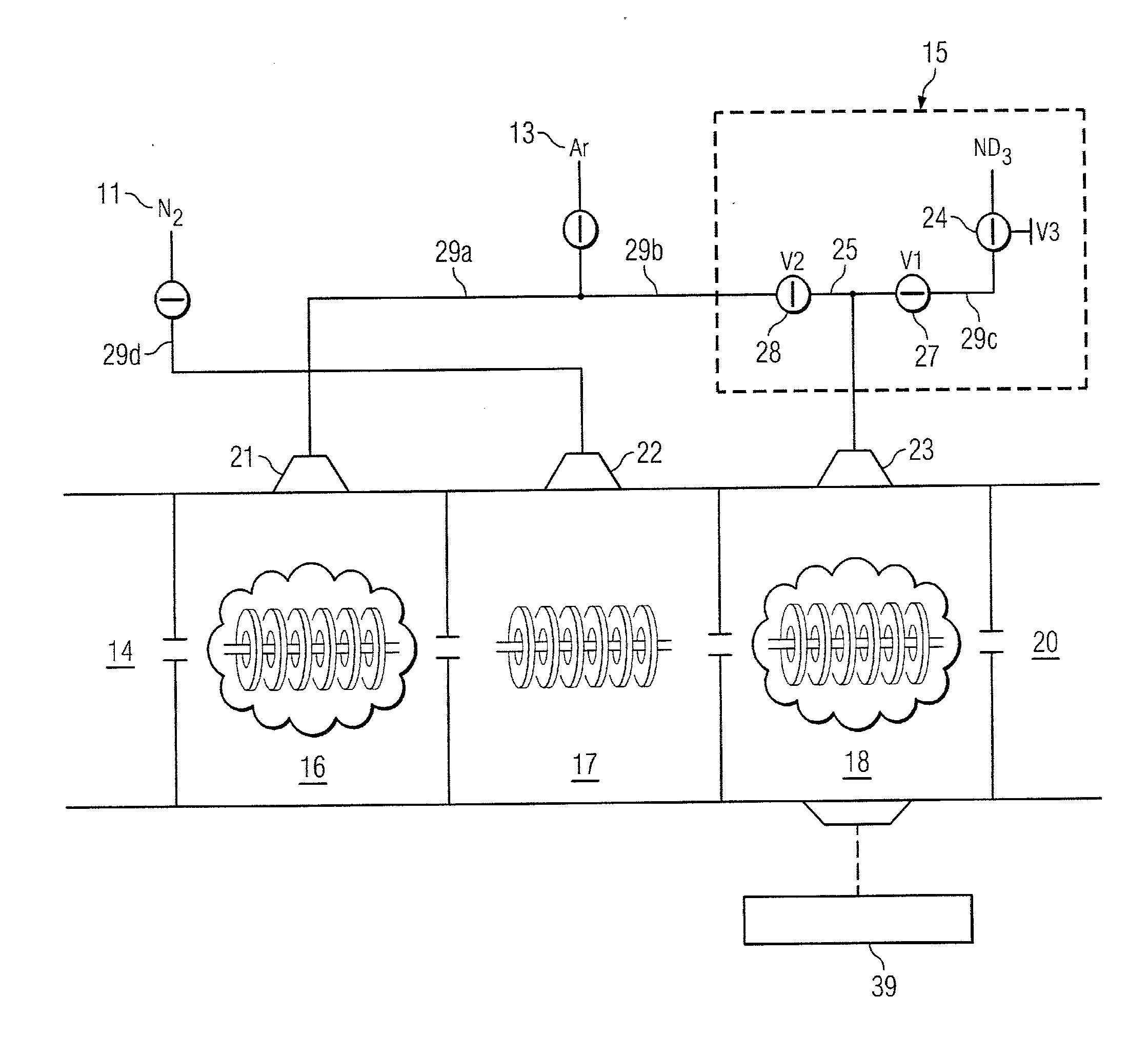
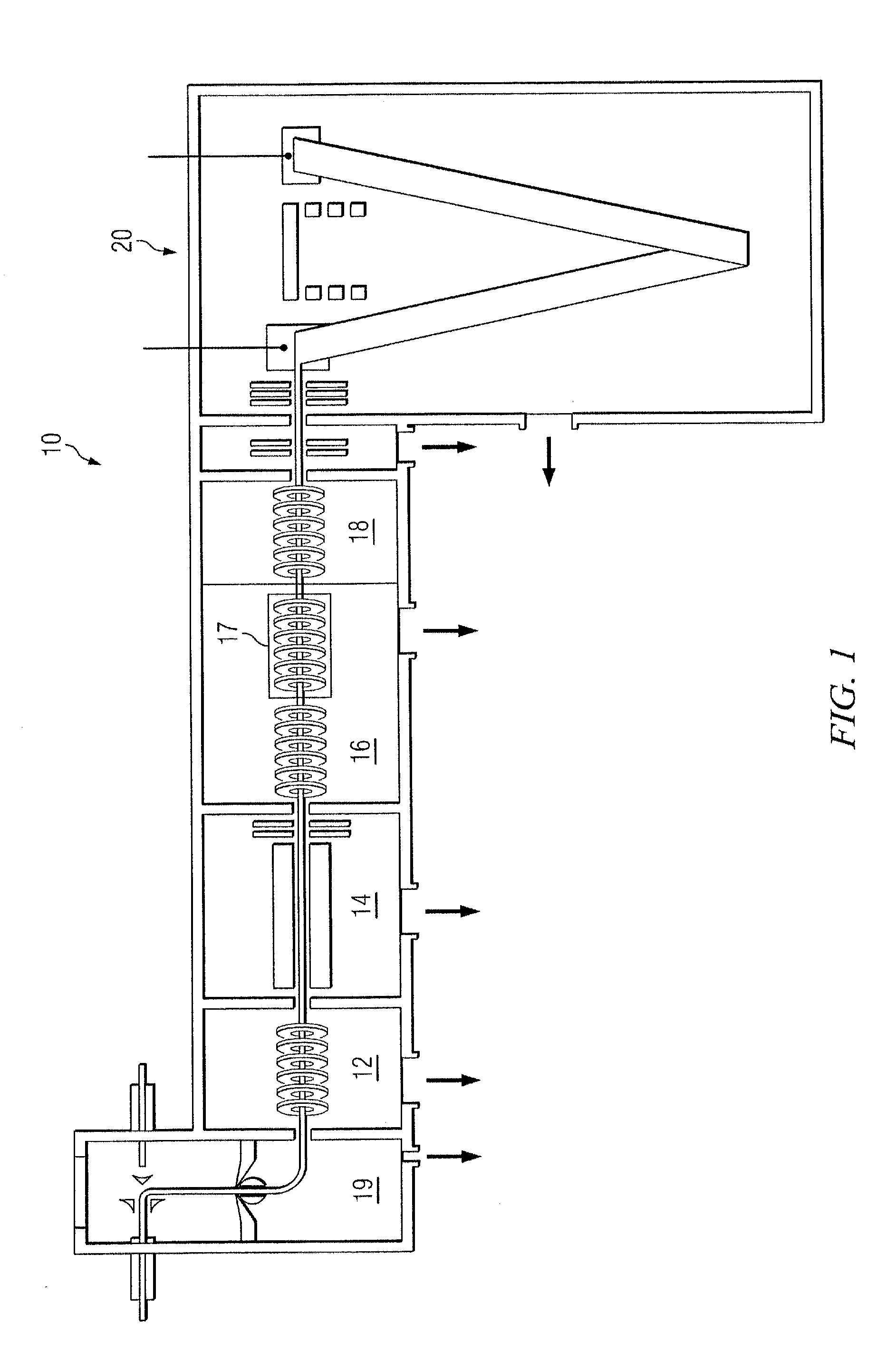
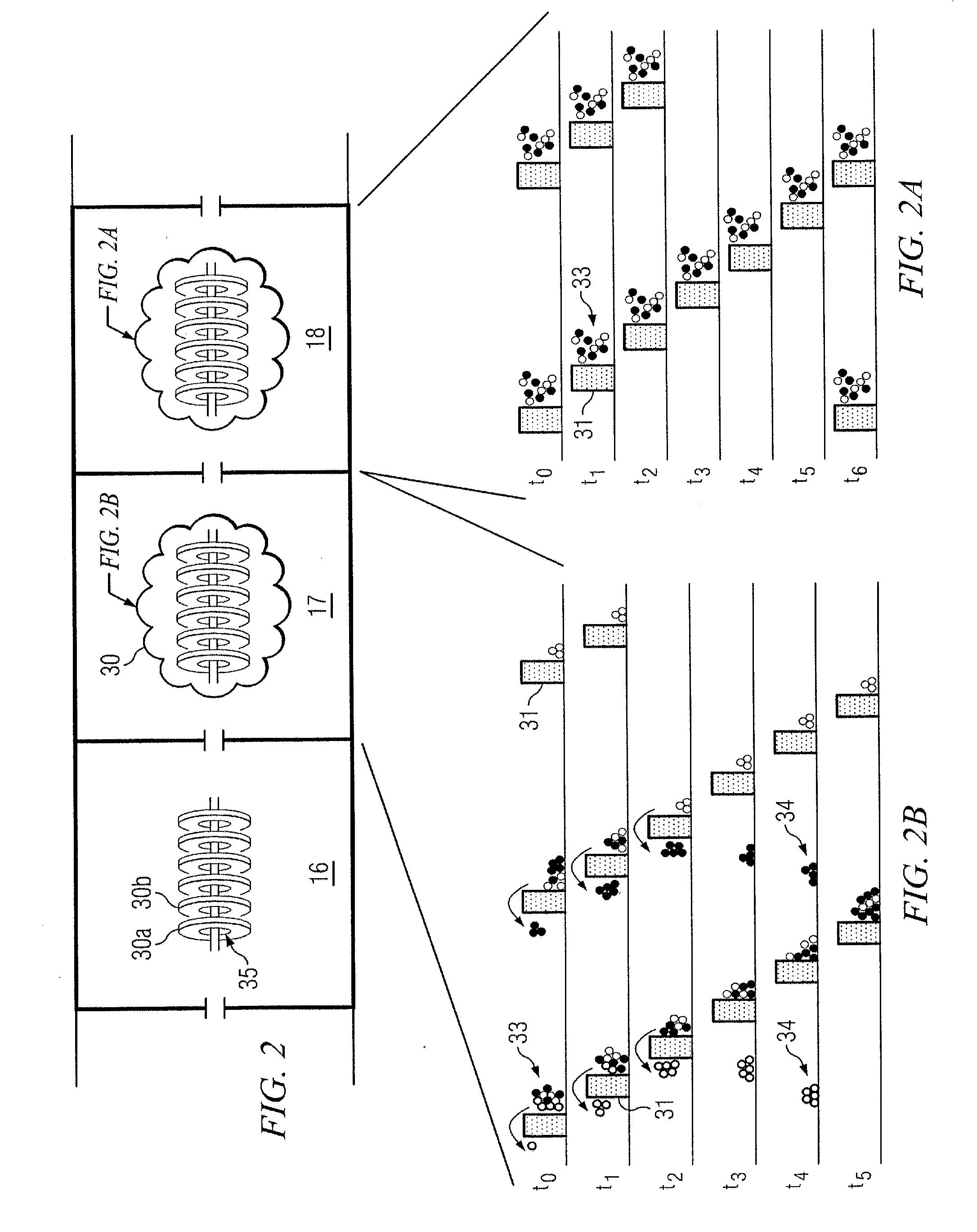
Rapid gas-phase isotopic labeling for enhanced detection of protein conformations
ActiveUS20120032073A1High resolution detectionIon sources/gunsIsotope separationPotential wellGas phase
A mass spectrometer (MS) that is adapted to allow rapid gas-phase hydrogen / deuterium exchange (HDX) labeling of ions in one or more traveling wave ion guides (TWIGs) with or without ion mobility separation. The addition of isotopic labeling by gas-phase HDX offers a sensitive alternative dimension for conformational detection, which enables high resolution detection of gaseous conformations based on shape and surface reactivity. Gas-phase, isotopic HDX labeling or “curtain” labeling, can be performed by infusing a reactive, isotopic labeling gas, e.g., ND3, into one or more of the traveling-ion wave guides (TWIG) in the MS. Analyte ions retained in the potential wells of a traveling wave generated by one or more of the TWIGs can be isotopic labeled at adjustable gas pressures. Labeling times can also be controlled by adjusting the speed of the traveling wave and can be performed within milliseconds of ionizations, probing protein conformations present in solution.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Site-specific labeling of proteins for NMR studies
Methods of producing and / or analyzing spectroscopically labeled proteins, e.g., proteins site-specifically labeled with NMR active isotopes, spin-labels, chelators for paramagnetic metals, and the like, are provided. The labeled proteins are produced in translation systems including orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthetase / tRNA pairs. Methods for assigning NMR resonances, e.g., methods using isotopically labeled proteins, are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST & IRM
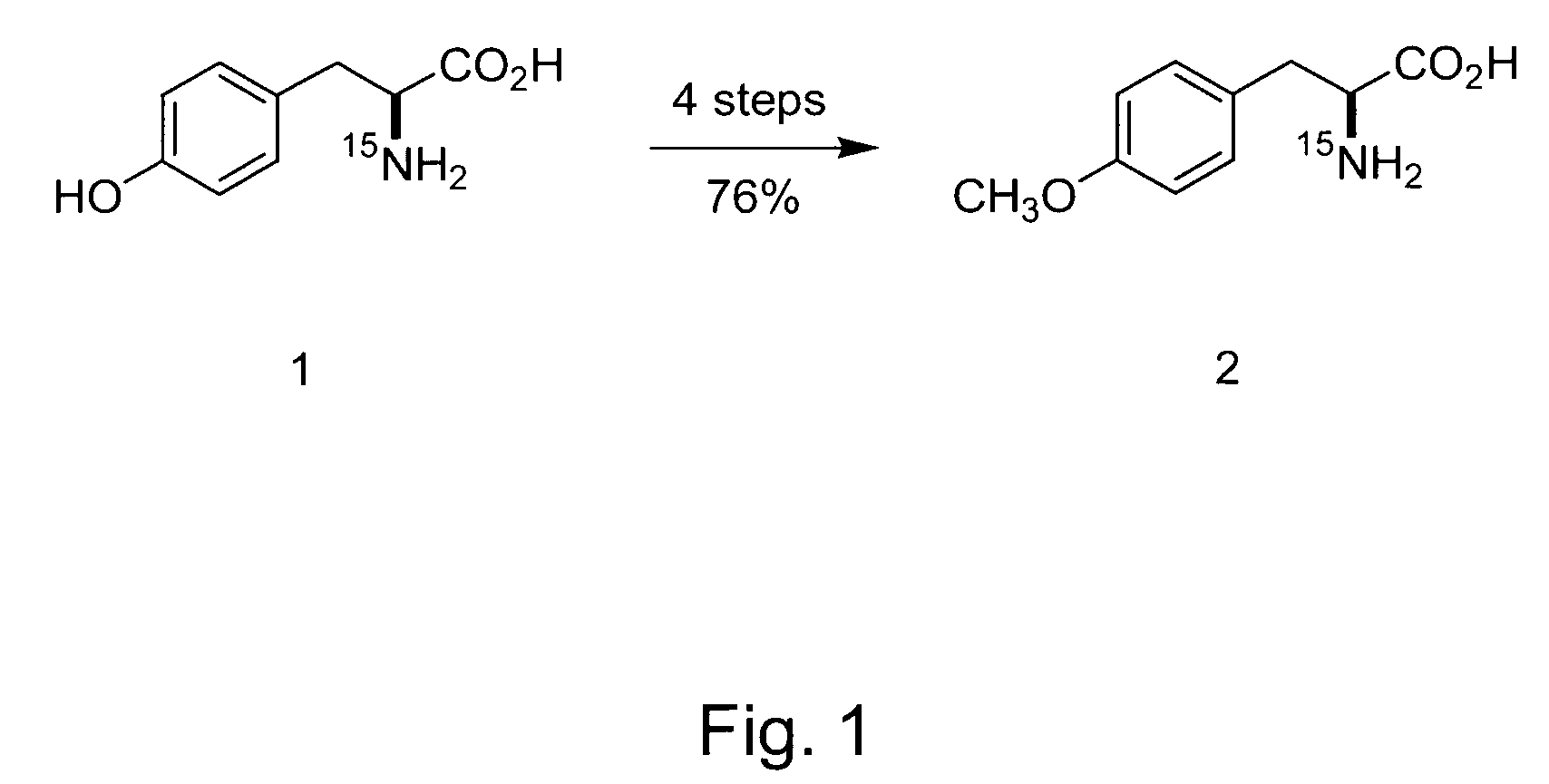
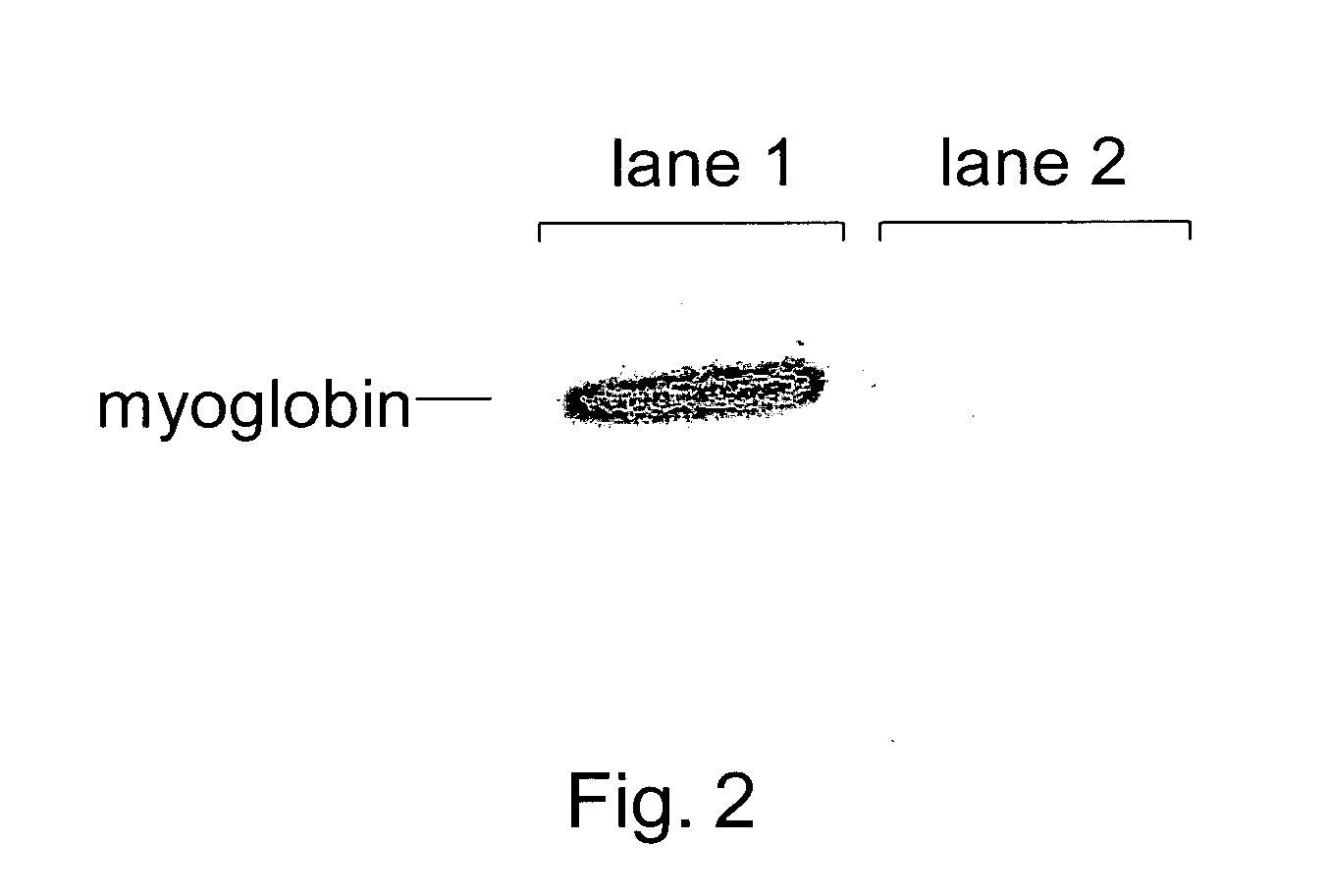
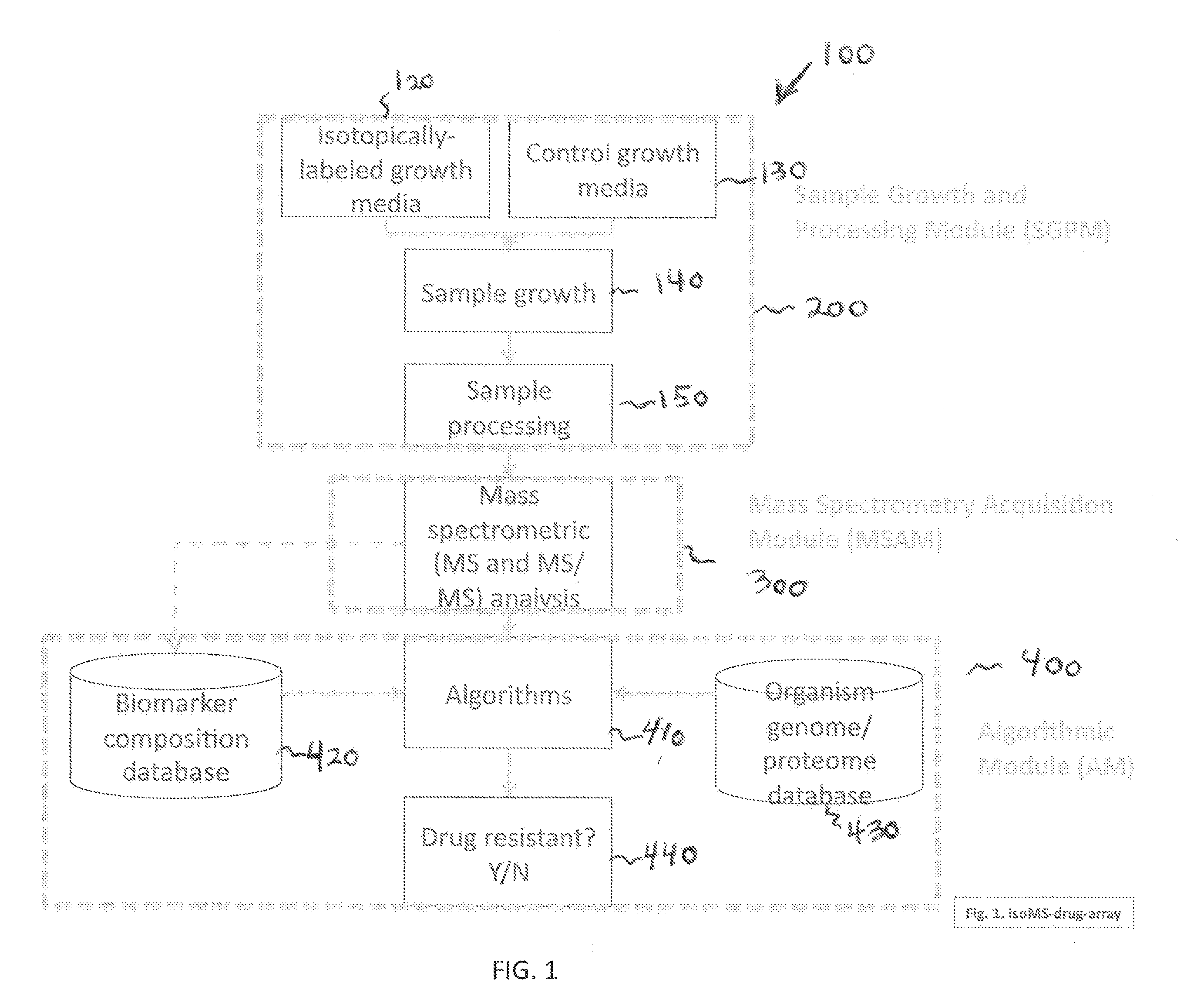
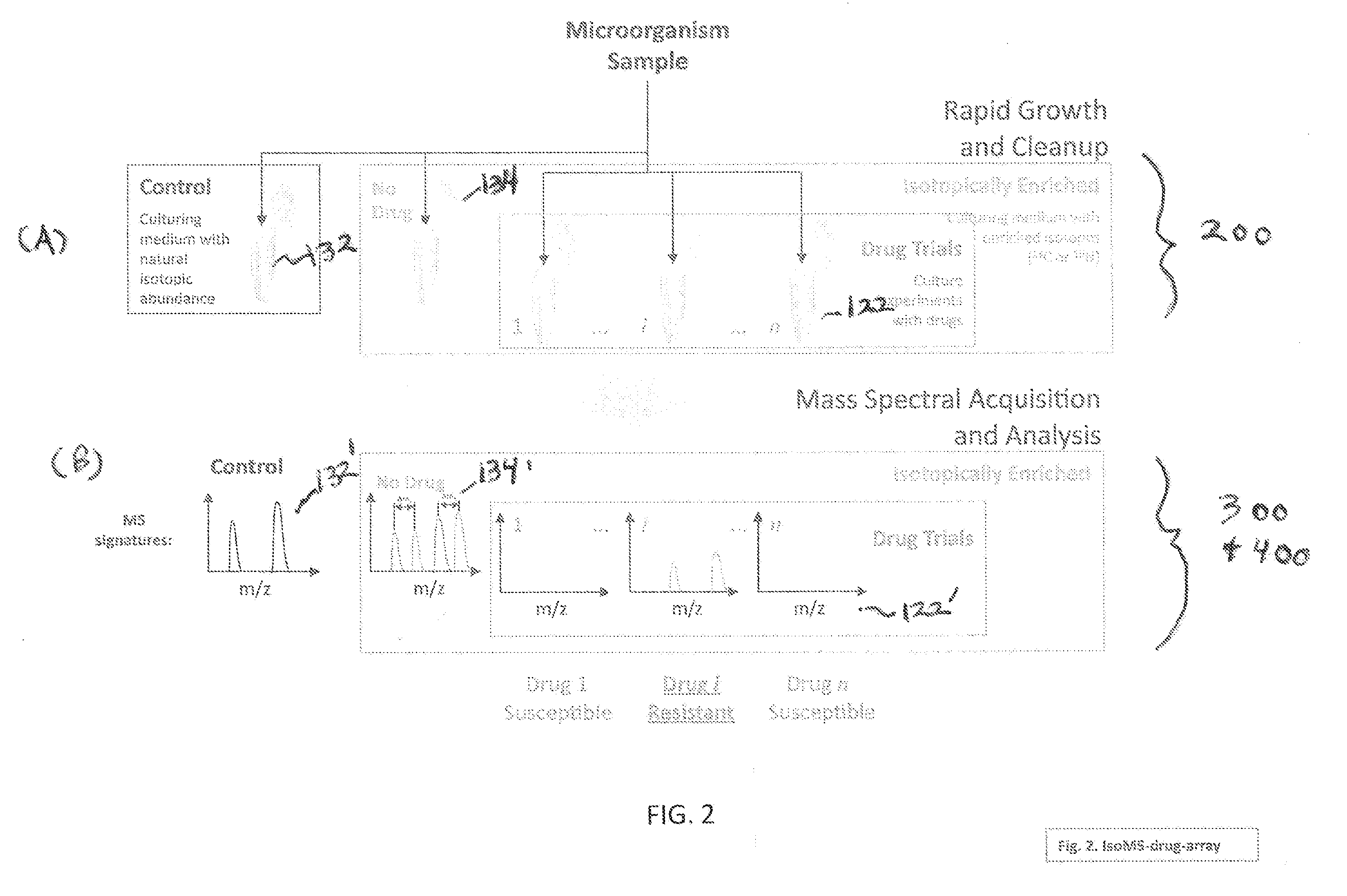
Systems and Methods for Determining Drug Resistance in Microorganisms
ActiveUS20110300552A1Accurately predict and confirmSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementMicroorganismMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention is based on the discovery that drug resistance in microorganisms can be rapidly and accurately determined using mass spectrometry. A mass spectrum of an intact microorganism or one or more isolated biomarkers from the microorganism grown in drug containing, isotopically-labeled media is compared with a mass spectrum of the intact microorganism or one or more isolated biomarkers from the microorganism grown in non-labeled media without the drug present. Drug resistance is determined by predicting and detecting a characteristic mass shift of one or more biomarkers using algorithms. The characteristic mass shift is indicative that the microorganism is growing in the presence of the drug and incorporating the isotopic label into the one or more biomarkers, resulting in change in mass.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Identification and localization of explosives and other material
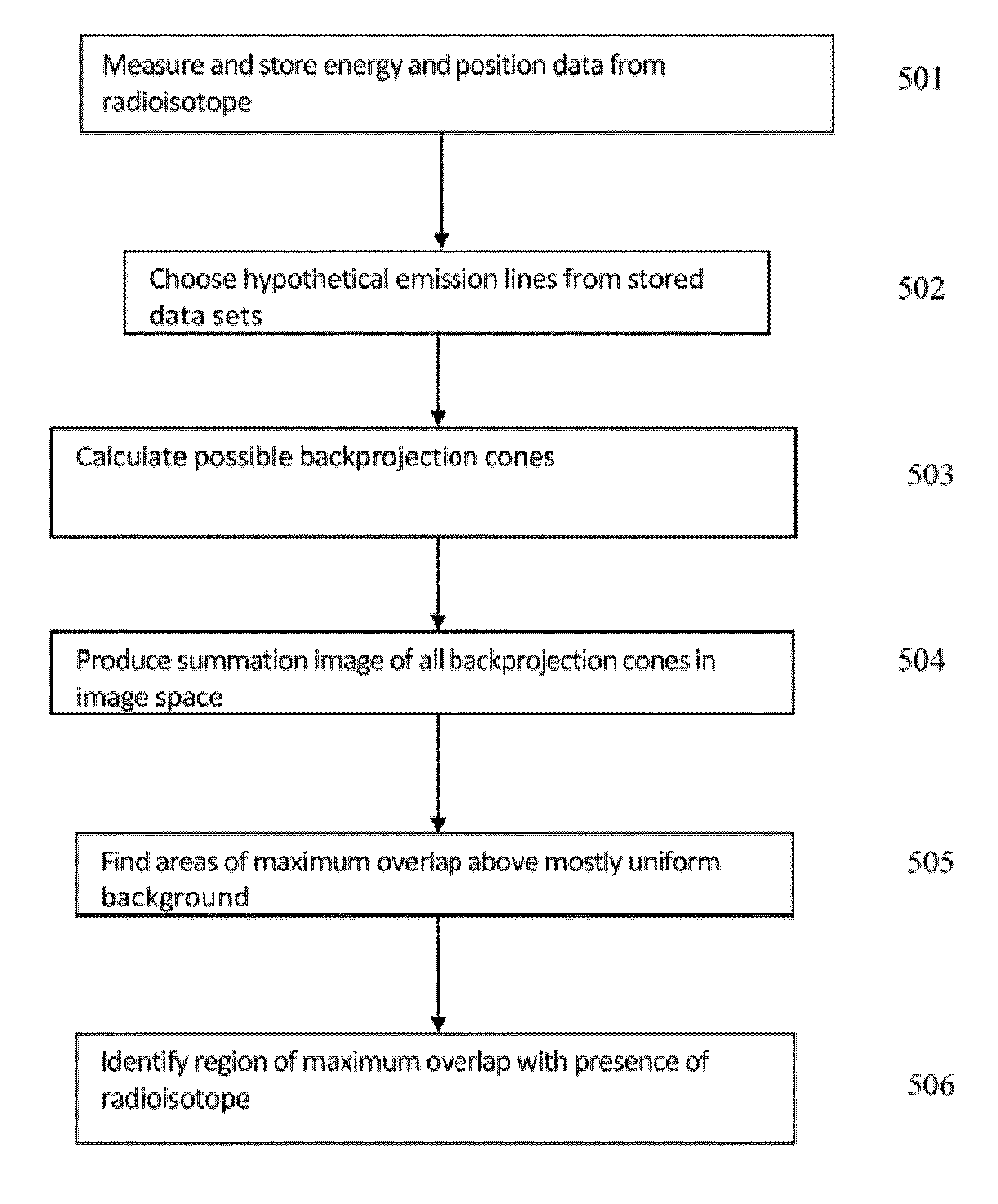
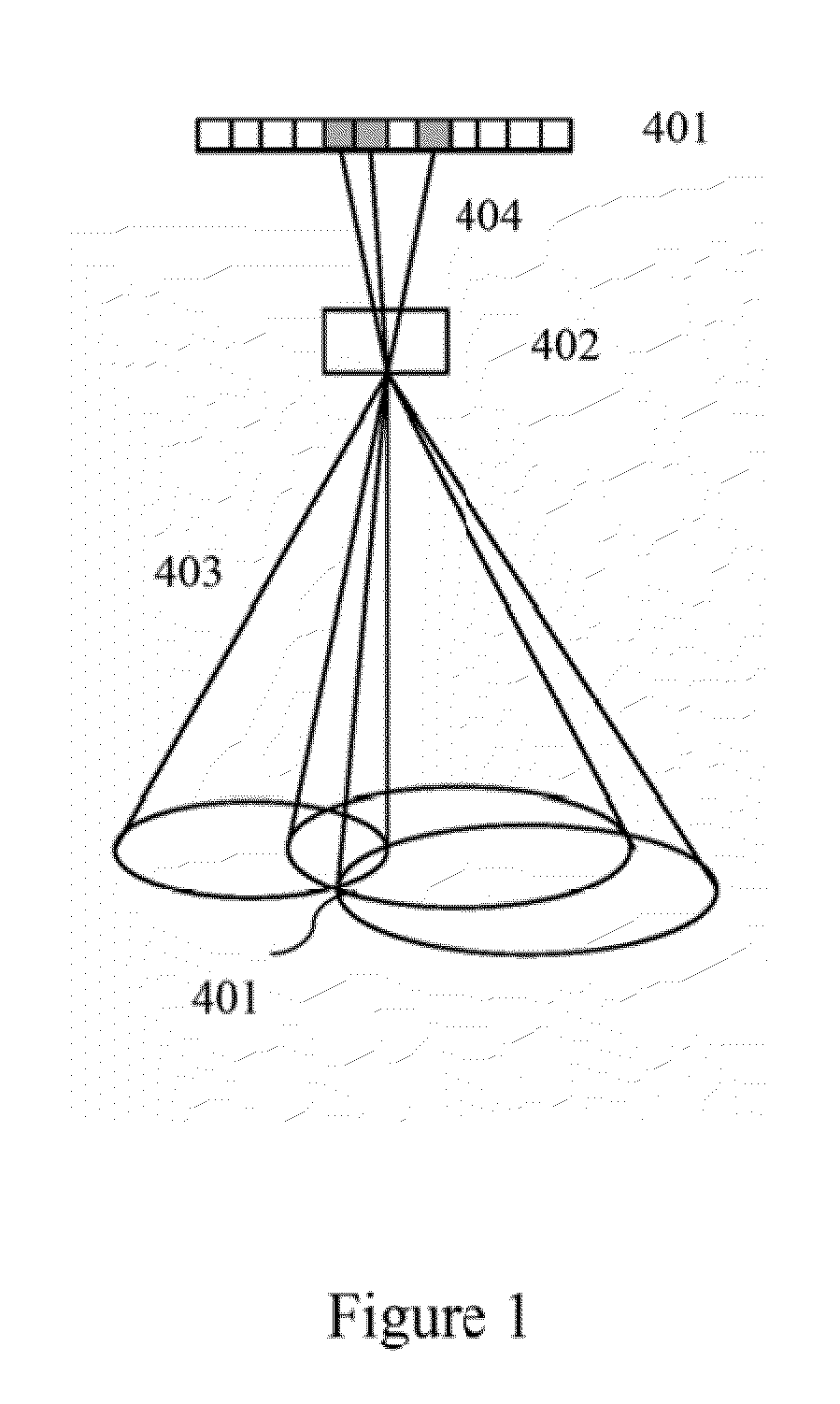
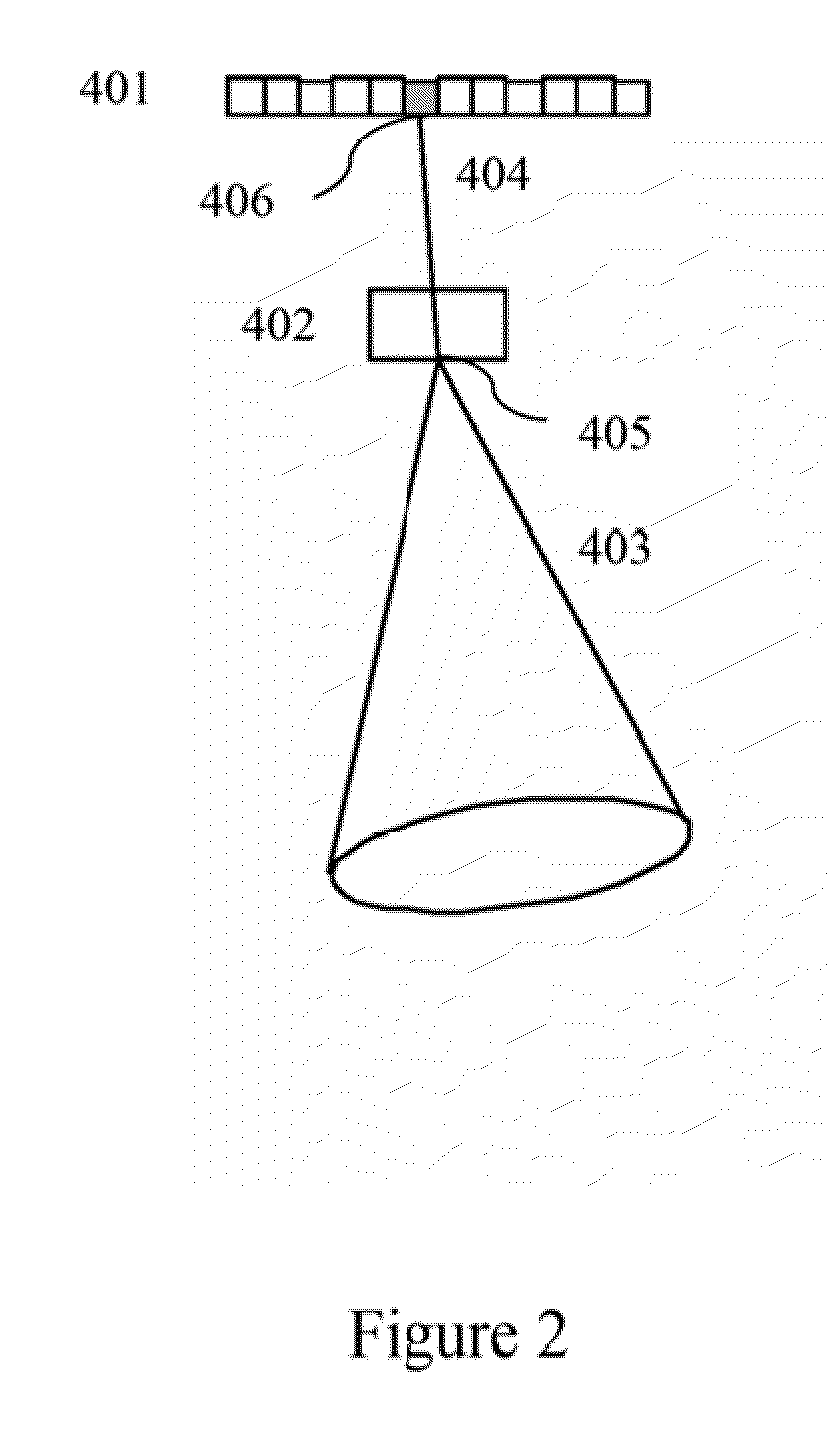
InactiveUS20100038550A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsNuclear engineeringGamma ray
A neutron source illuminates suspect material leading to emission of gamma rays characteristic of the isotopes present. The system measures Compton scattering of emitted gamma rays using detectors with three dimension event localization capability. Detection does not require full energy deposition. A spatial correlation of projection vectors is computed by a reconstruction that searches for solutions that generate spatial correlation. Identification and location for contraband material is determined from solutions that generate spatial correlation.
Owner:INNOVATIVE WORKS LLC
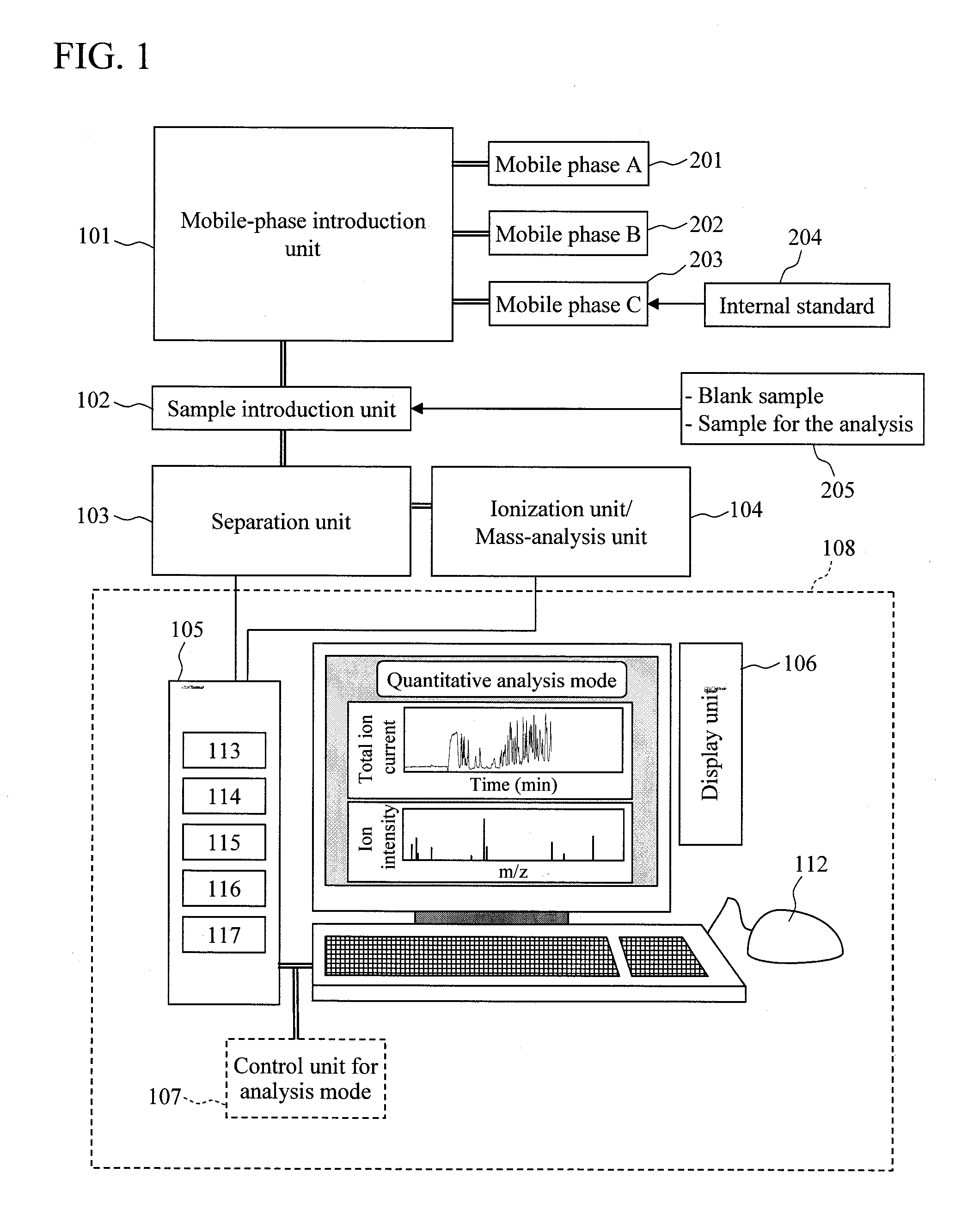
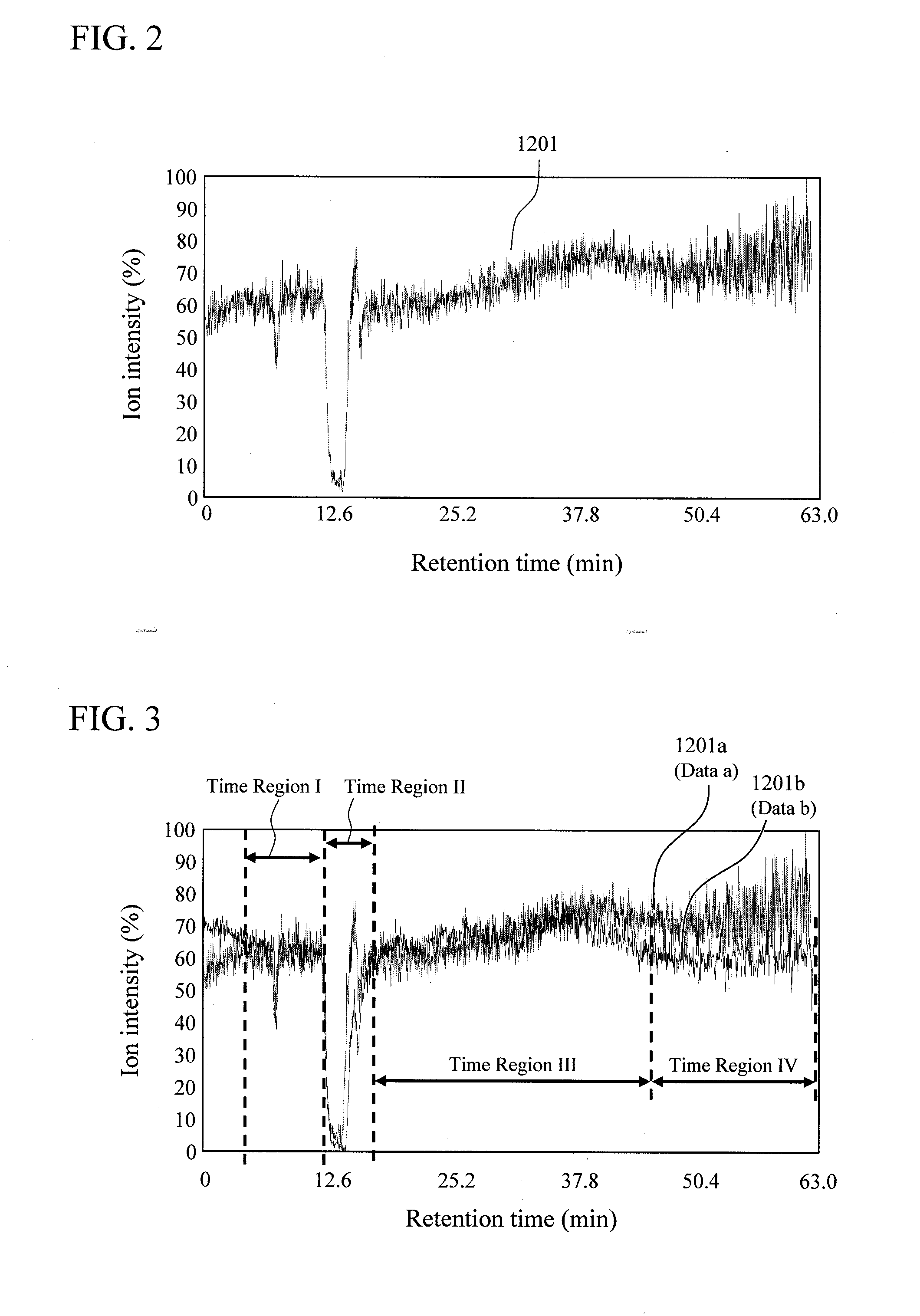
Quantitative analysis method using mass spectrometer
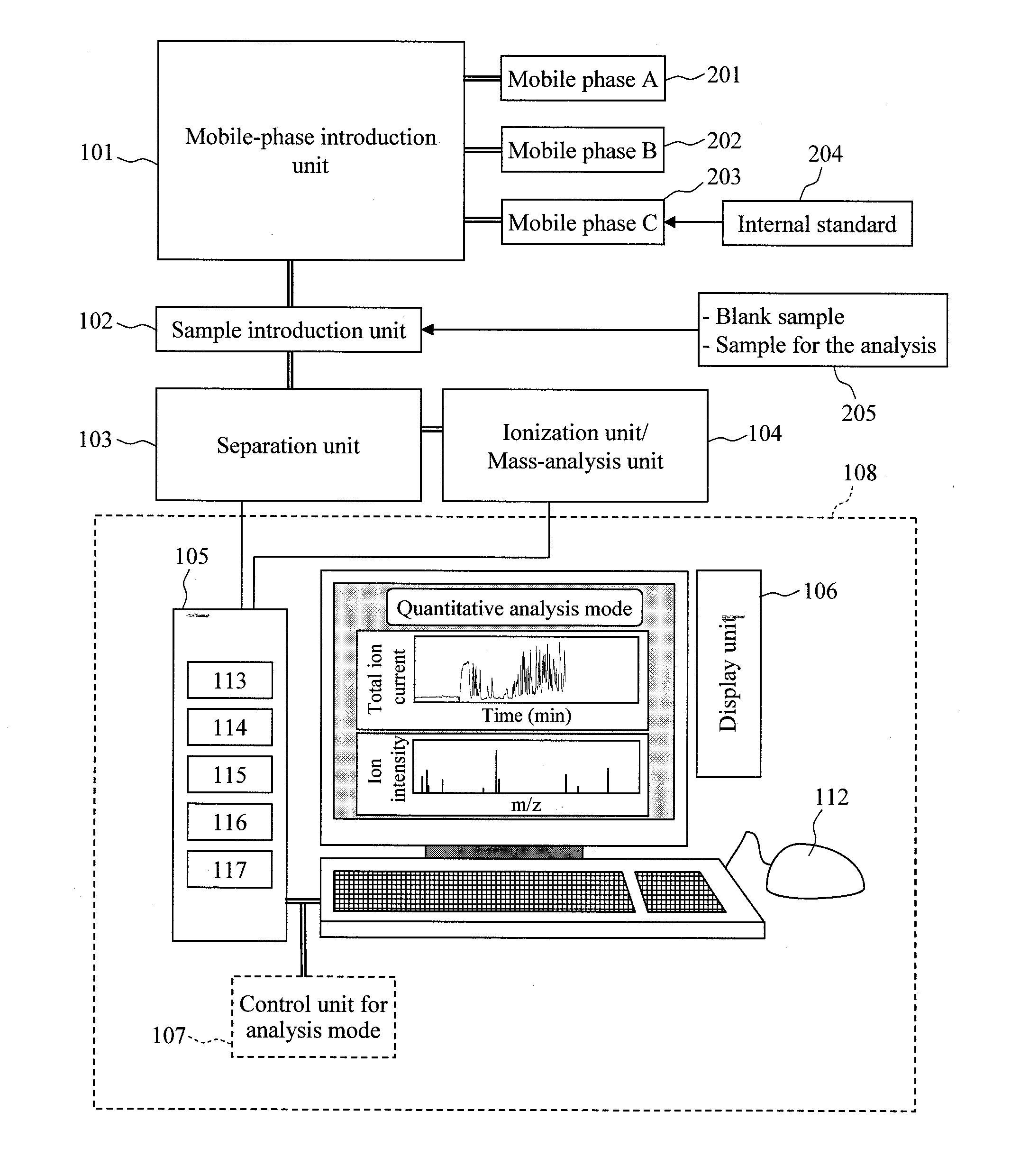
InactiveUS20110101215A1Improve accuracyError in quantitative dataComponent separationIsotope separationData setReal time analysis
In quantitation without using the isotope labeling technique, there is no means to detect the presence / absence and the time region of the occurrence of quantitative analysis-inhibitory factors in data for the analysis, and the reliability of the data for the analysis cannot be evaluated. Also, the error of the data due to the occurrence of the quantitative analysis-inhibitory factors cannot be evaluated. In order to solve the problems, first, an internal standard to be detected simultaneously with a component for the analysis is mixed in a mobile phase or an eluate of a liquid chromatograph; under the condition where no quantitative analysis-inhibitory factors occur, a blank sample is analyzed to acquire a mass chromatogram of ions originated from the internal standard; and the result is stored in a data storage unit. Then, a sample for the analysis is mixed to acquire data for the analysis of the sample; and the intensity of ions originated from the internal standard is compared with that of the blank sample in the analysis real time in a data analysis unit. At this time, if an inconsistency exceeding a predetermined threshold is detected, the occurrence of the quantitative analysis-inhibitory factors can be detected. Further, based on the inconsistency, the error range of the data can be given to a data set and the like.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
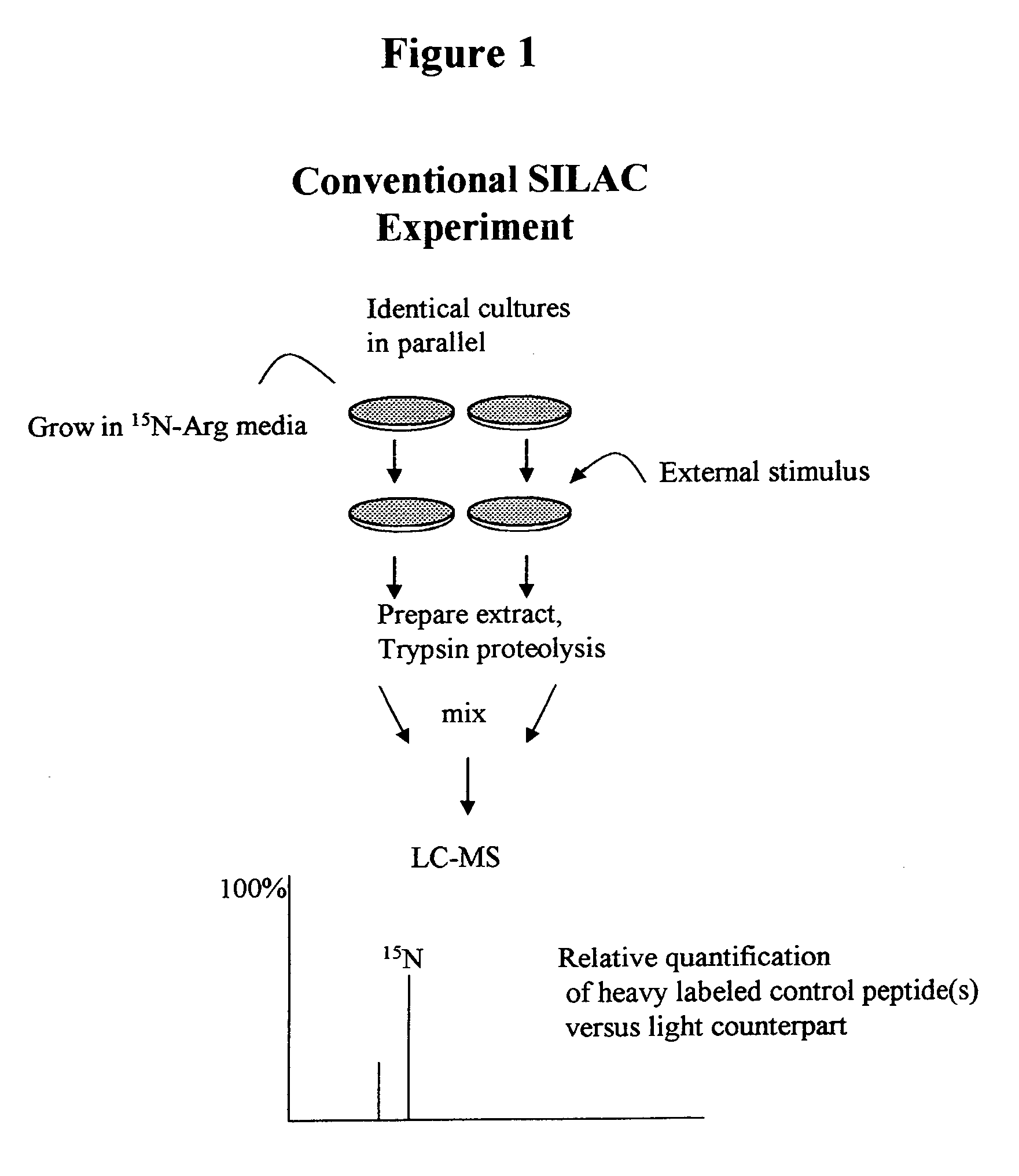
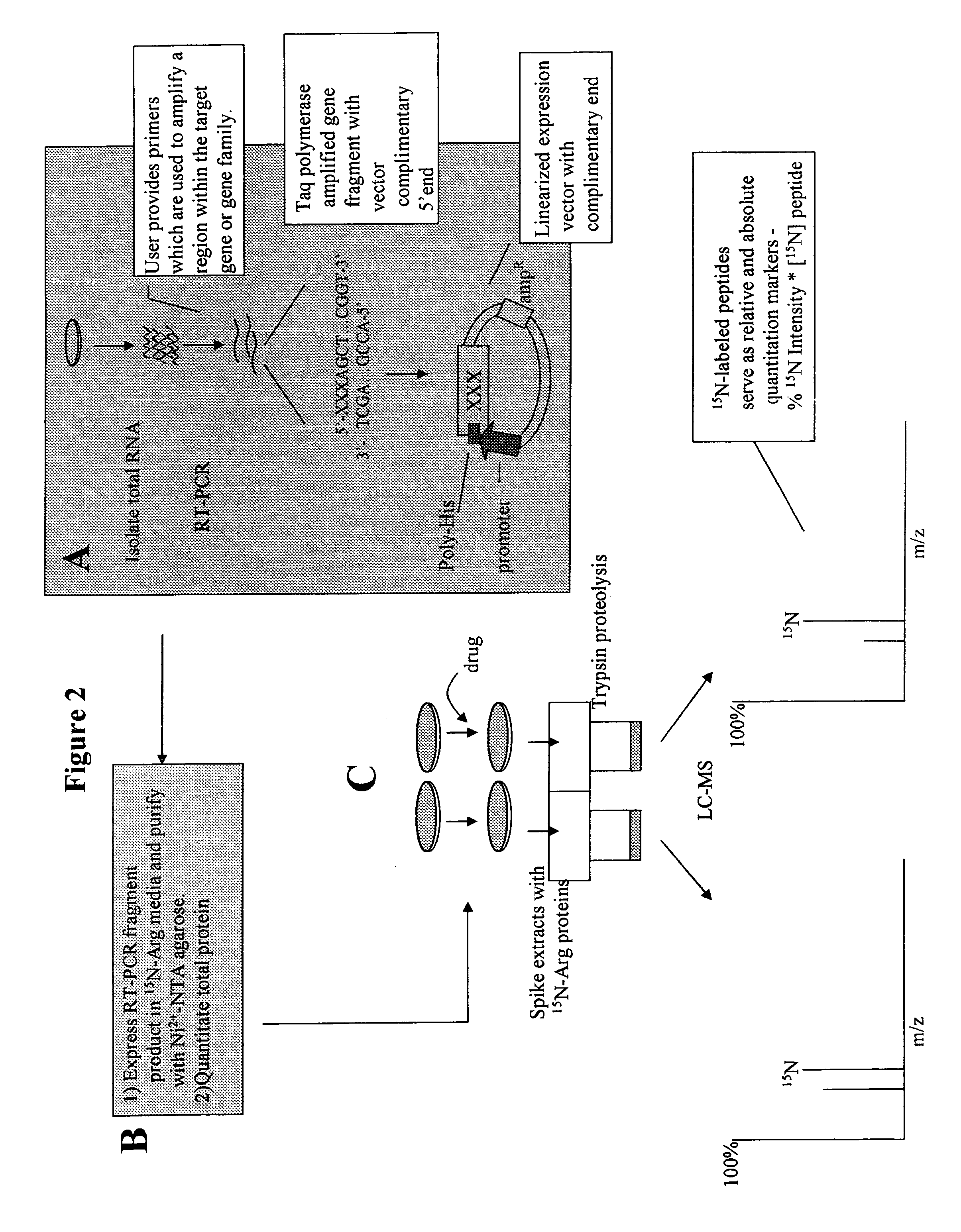
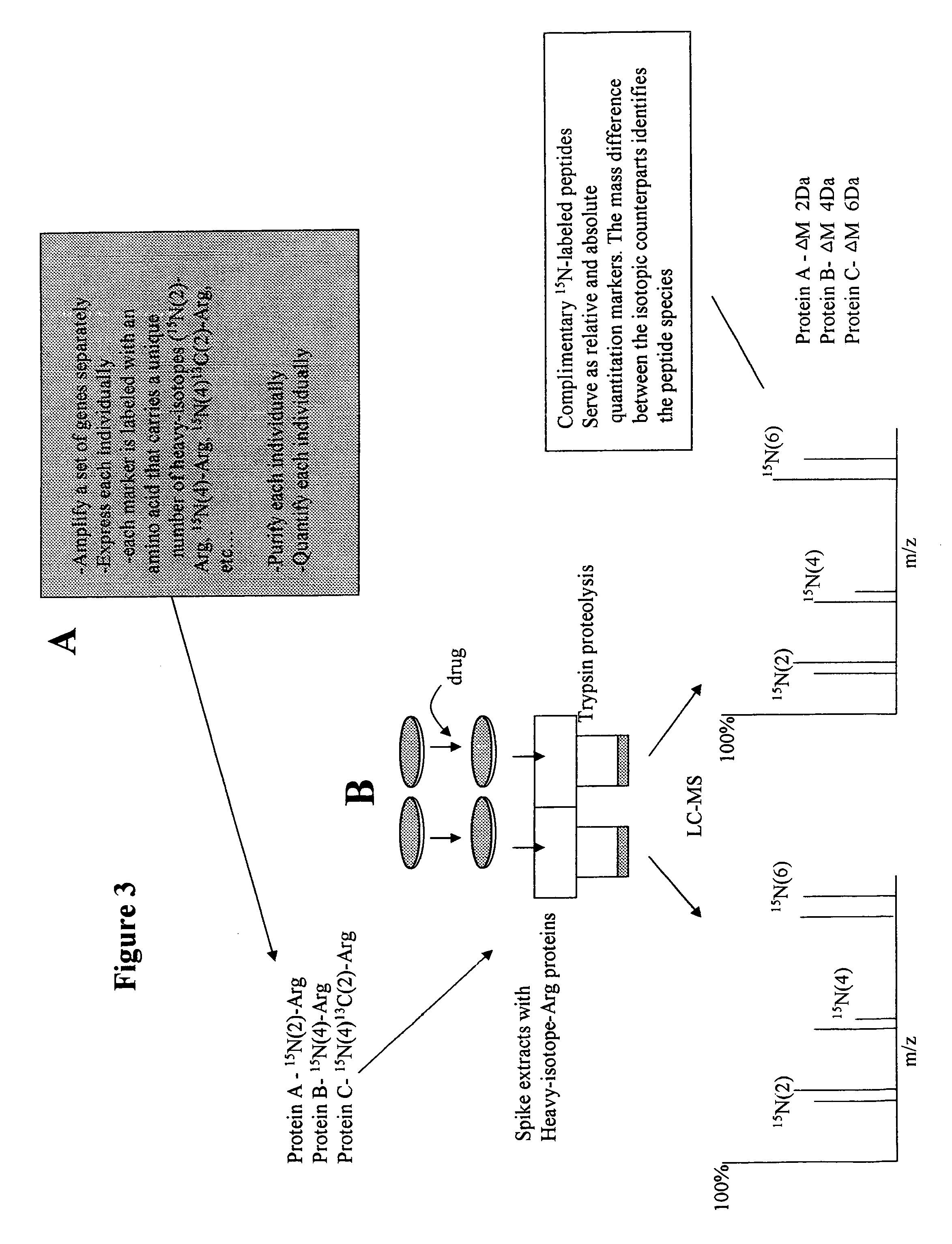
Isotopically-labeled proteome standards
ActiveUS7939331B2Quantitative precisionEnhanced advantageComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometricIsotopic signature
The invention provides methods for quantifying biomolecules, such as polypeptides in mass spectrometric analysis. The methods include use of a biomolecule standard having at least one atomic isotope different than that of the naturally occurring isotopes in the biomolecule of interest. Methods of the present invention also include methods for quantifying biomolecules where the copy biomolecule standard is made by expressing the biomolecule using a recombinant cell. Further included are the biomolecule standards themselves, method for making such standards, kits, systems, reagents, and engineered cells relating to the use of biomolecule standards in mass spectrometric analysis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
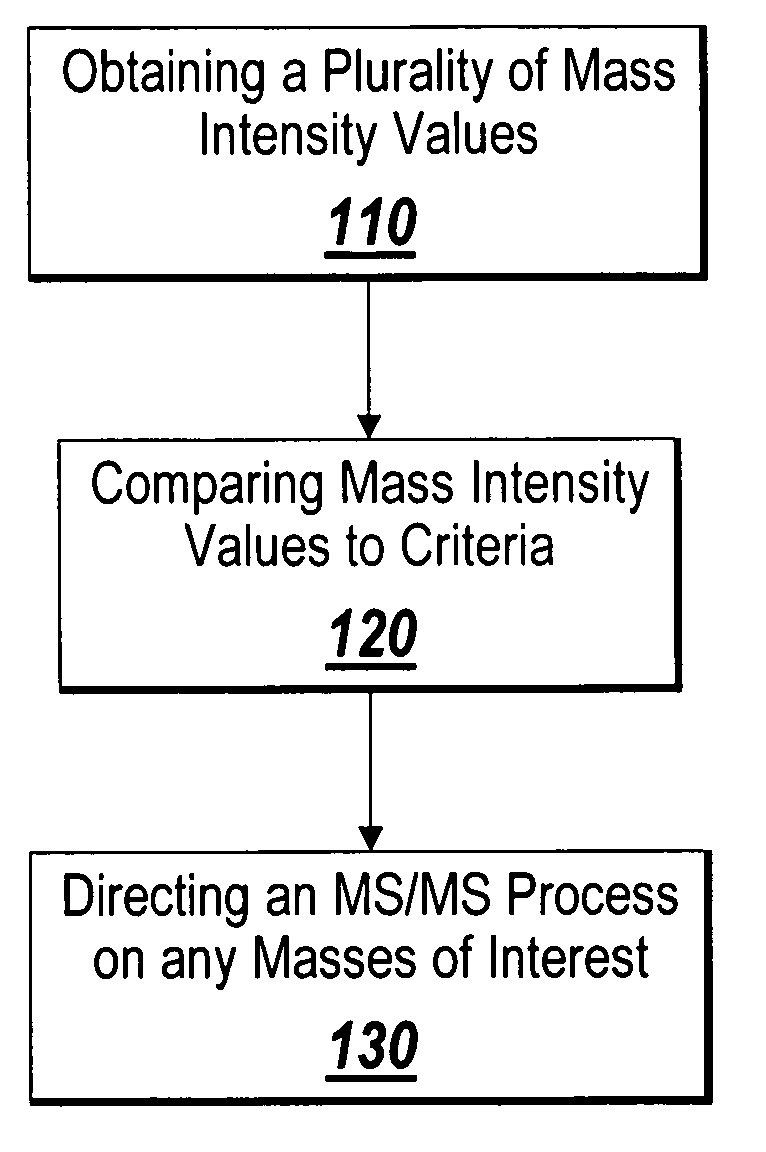
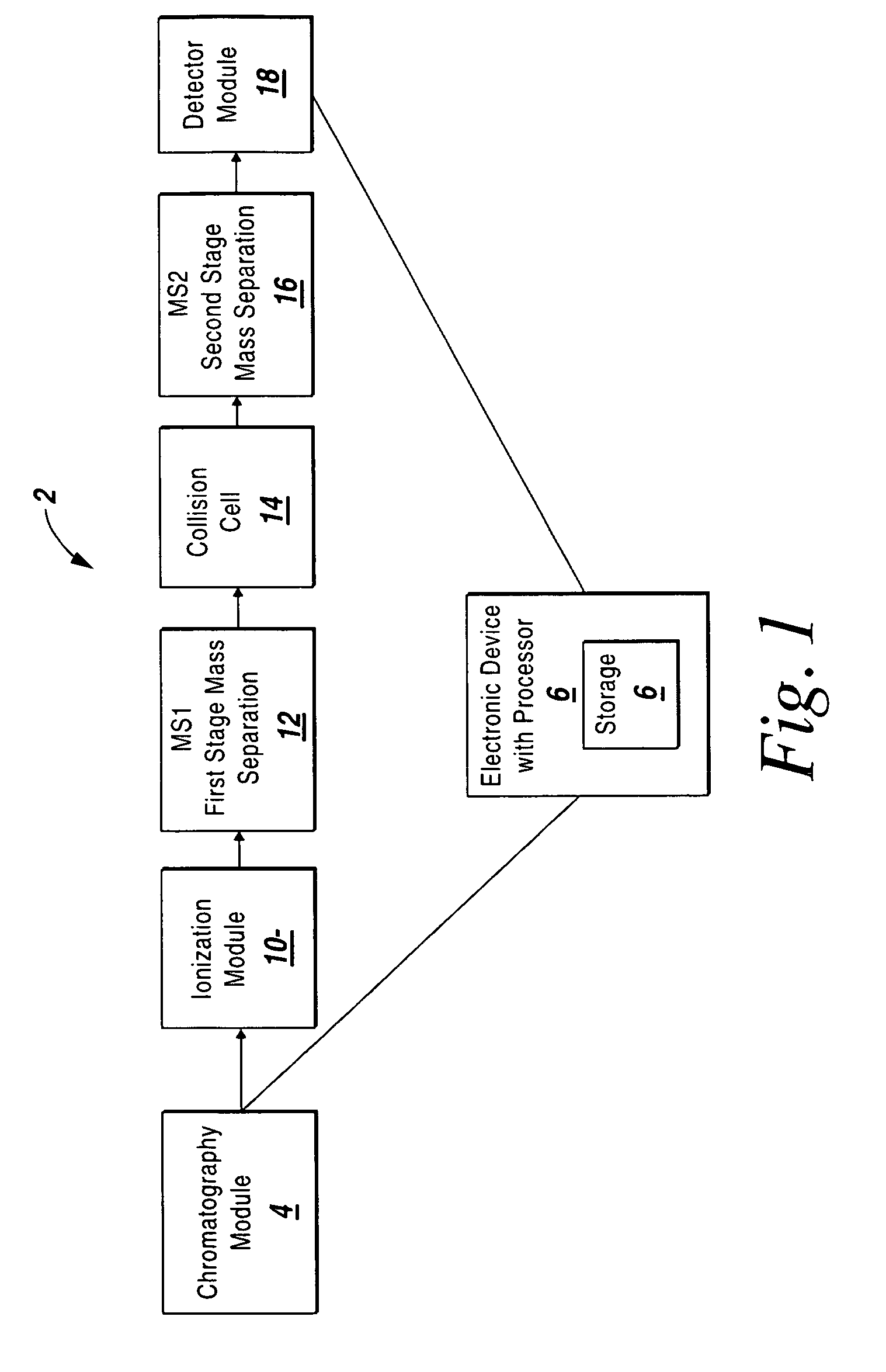
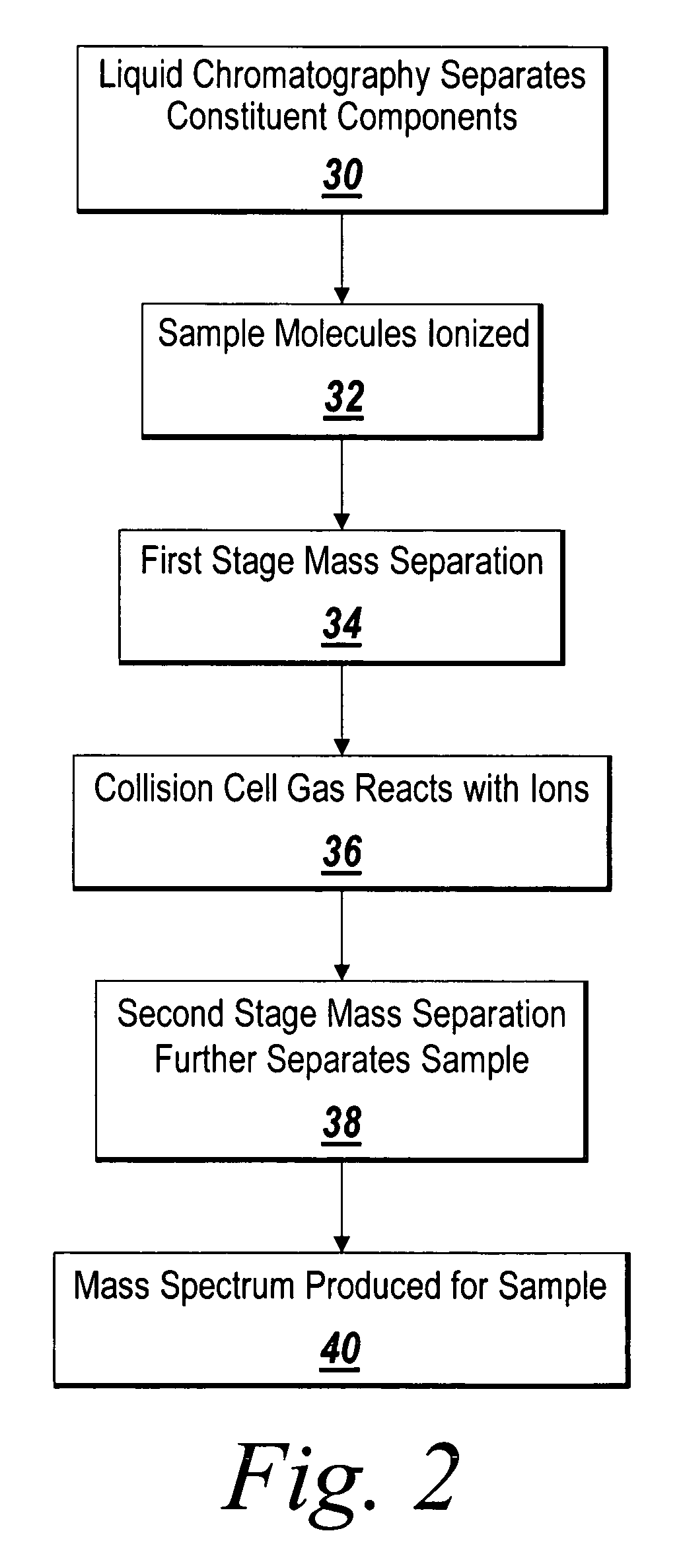
System and method for isotopic signature and mass analysis
Mass intensity values, isotopic ratios and exact mass differences between isotopes may be obtained and analyzed to determine if there are one or more masses of interest. In one implementation, a method will look among the mass intensity values for peaks of interest. The mass intensity values, representative of isotopic signatures, will be compared to a criteria in order to determine which of the masses are of interest. Although the invention is not so limited, examples of such criteria include mass intensity values above a specified threshold, within a certain ratio of another mass intensity value, and / or separation between the masses themselves. Optionally, a tolerance may be applied to the criteria. If masses are found to be of interest, MS / MS can automatically be triggered for one or all of the masses of interest, when an analyzing system such as an LC-MS-MS, GC-MS-MS or MALDI-MS-MS system is used.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Method and kit for quantitatively detecting human beta-casein content
ActiveCN103616454AAvoid defectsImprove accuracyComponent separationInternal standardIsotopic signature
The invention relates to the field of analytical chemistry, and discloses a method and a kit for quantitatively detecting human beta-casein content. According to the method and the kit, by utilizing a specific peptide sequence VMPVLK obtained after enzymolysis of human beta-casein, isotope labeled specific peptide and a sequence of an isotope labeling internal standard substance are designed, and a new accurate quantitative detection method is provided based on an internal standard method for quantitatively detecting the human beta-casein, with high accuracy, high precision and high sensitivity.
Owner:贝因美(杭州)食品研究院有限公司
Double-channel SPE column and application of double-channel SPE column in quantitative proteomics
ActiveCN104076114ASimple and fast operationGuaranteed retentionComponent separationAlkyl transferQuantitative Result
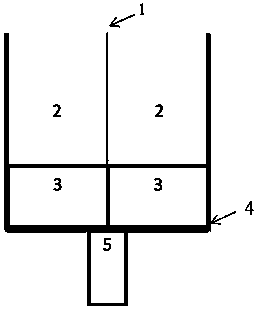
The invention relates to a novel solid phase extraction (SPE) device capable of achieving the whole process of quantitative analysis pretreatment of protein. According to the device, an SPE tube is partitioned into two chambers with the same capacity through a partition plate, and after the chambers are filled with chromatographic packing, the whole process of sample treatment in quantitative proteomics can be achieved in situ, wherein the treatment comprises denaturation, reduction, alkylation, enzymolysis, isotope labeling and mixing of protein samples. The device is easy and convenient to manufacture and low in manufacturing cost, and has the advantages that the recovery rate is high, operation is easy, the accuracy of quantitative results is good and the precision is high when the samples are treated.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
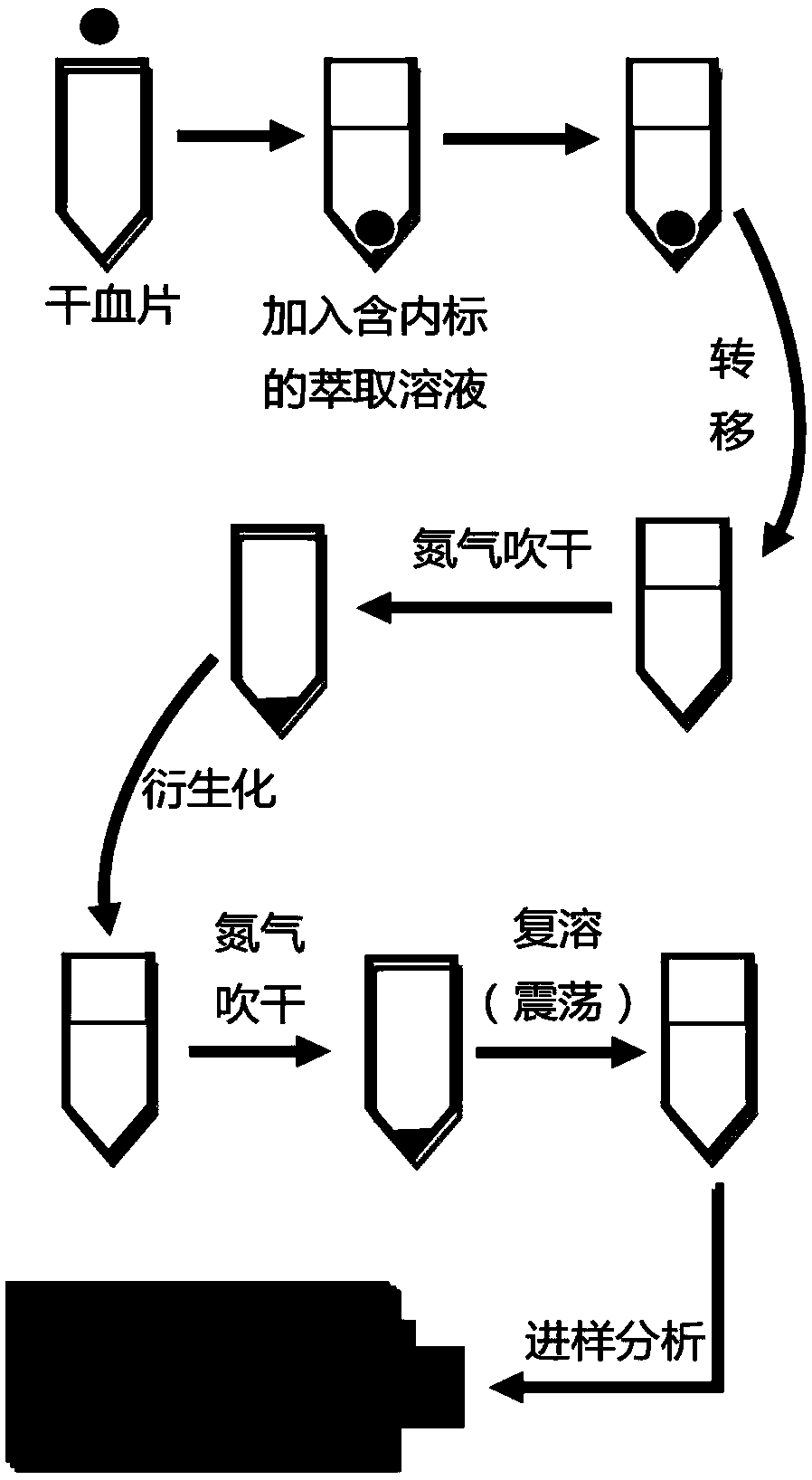
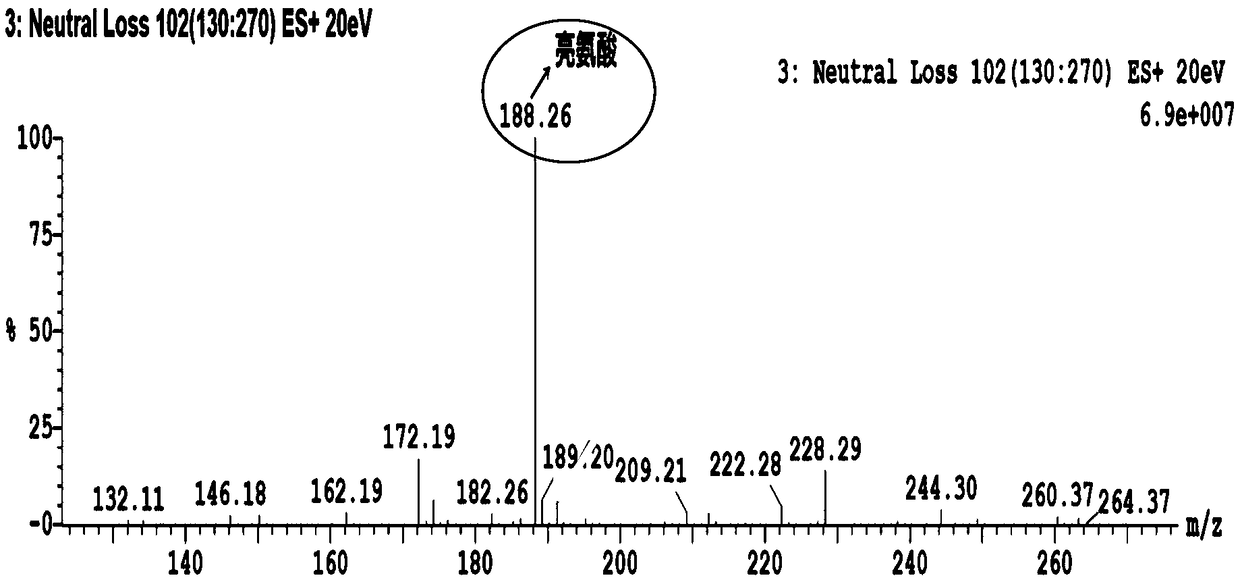
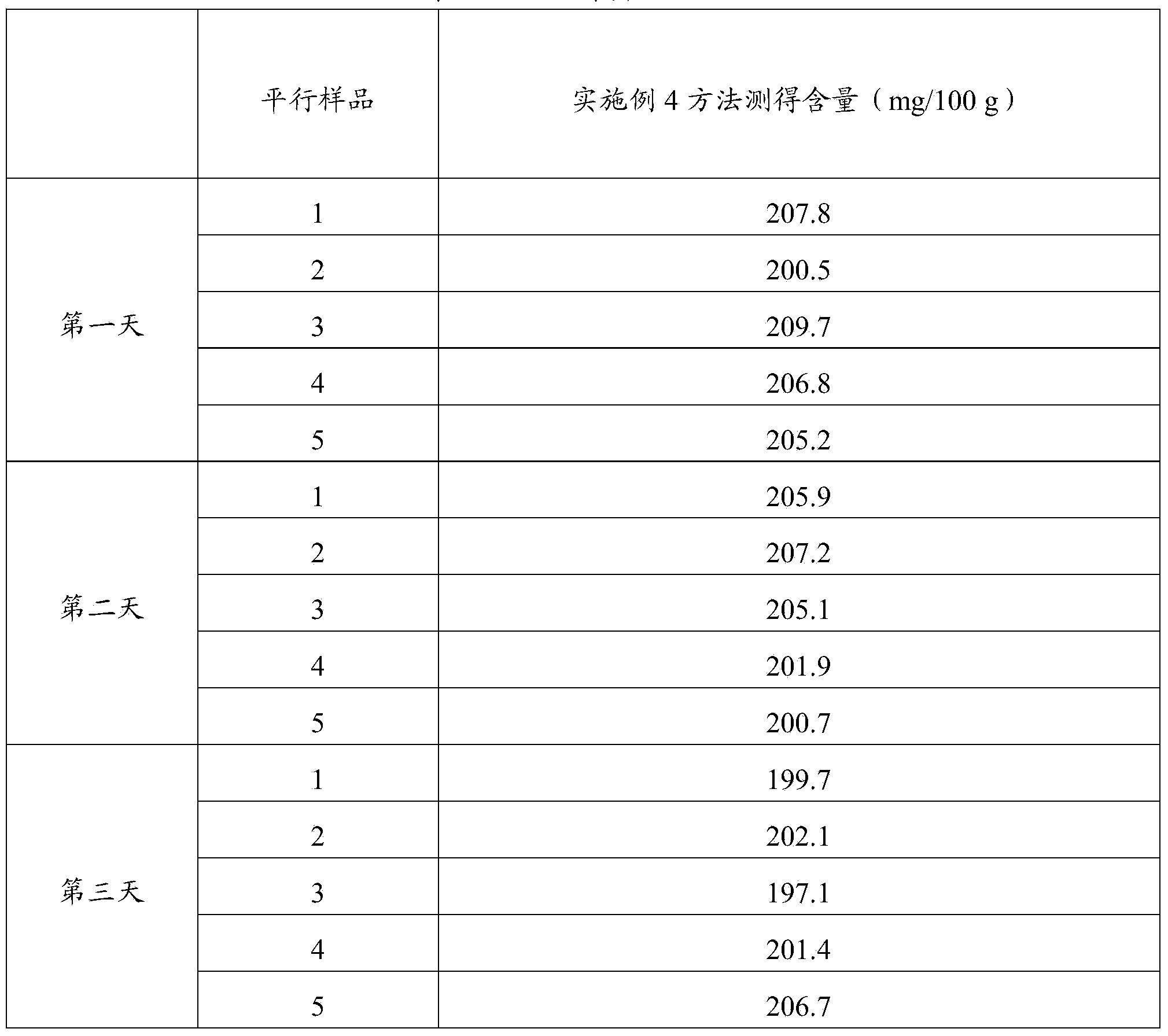
Method for detecting neonatal metabolites based on ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
ActiveCN108645924ASuitable for analytical applicationsHigh sensitivityComponent separationHigh concentrationPositive control
The invention provides a method for joint detection of metabolic markers based on ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of more than 134 metabolites including amino acids and carnitines is completed only through one-time detection of only an extremely low amount, being 3 [mu]L, of a blood sample by adopting an isotope-labeled amino acid standard substance and an isotope-labeled carnitine standard substance as internal standard substances, a high-concentration quality control blood tablet and a low-concentration quality control blood sheet as positive control substances and an acetonitrile-water solution as a mobile phase through reasonably setting parent ion scanning, neutral loss scanning and multi-reaction ion monitoring scanning combined ultra performance liquid chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer detection conditions. The method has the advantages of small sample volume, high sensitivity, high accuracy, highthroughput and high repeatability, and is suitable for large-scale analysis of clinical dried blood tablet samples.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
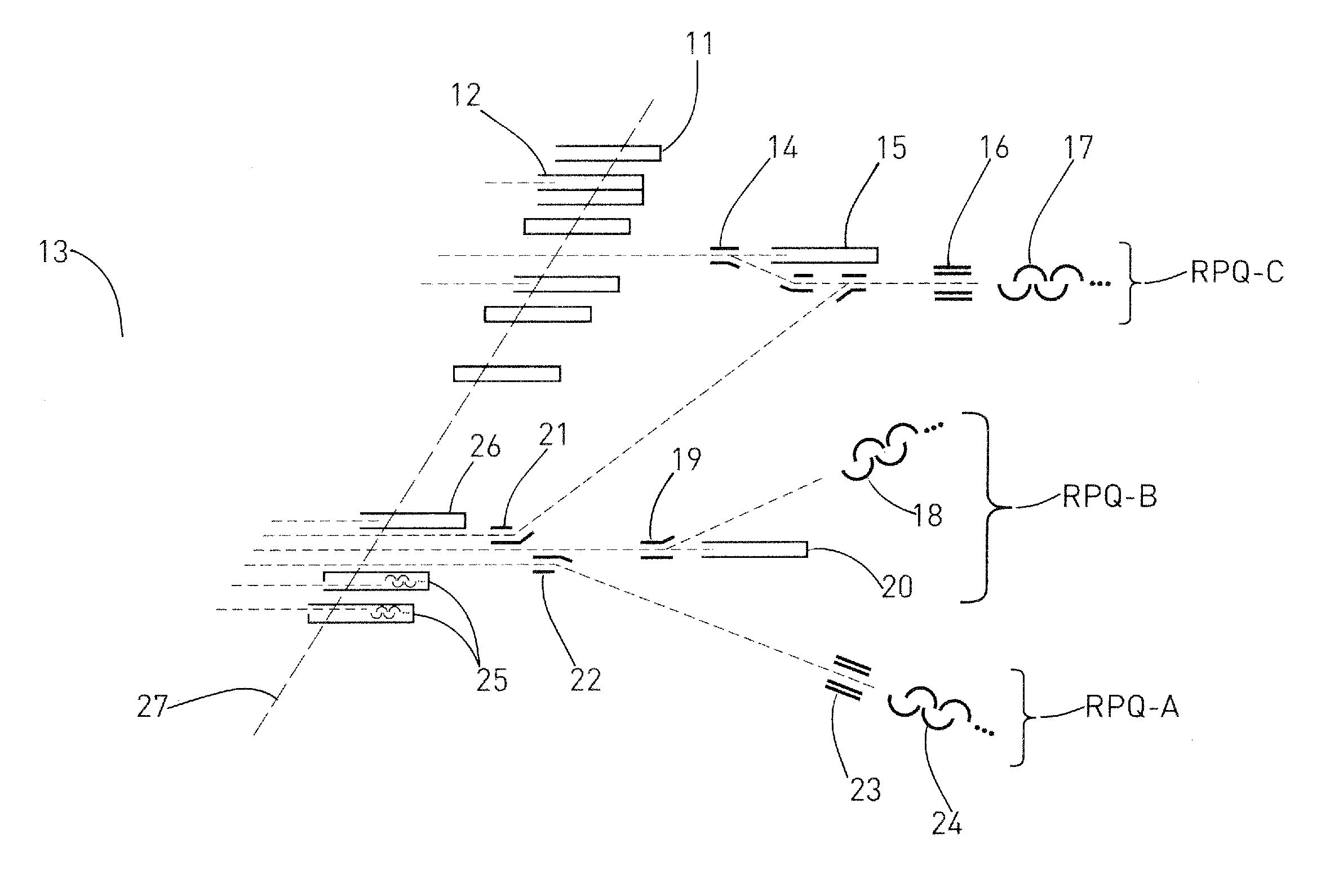
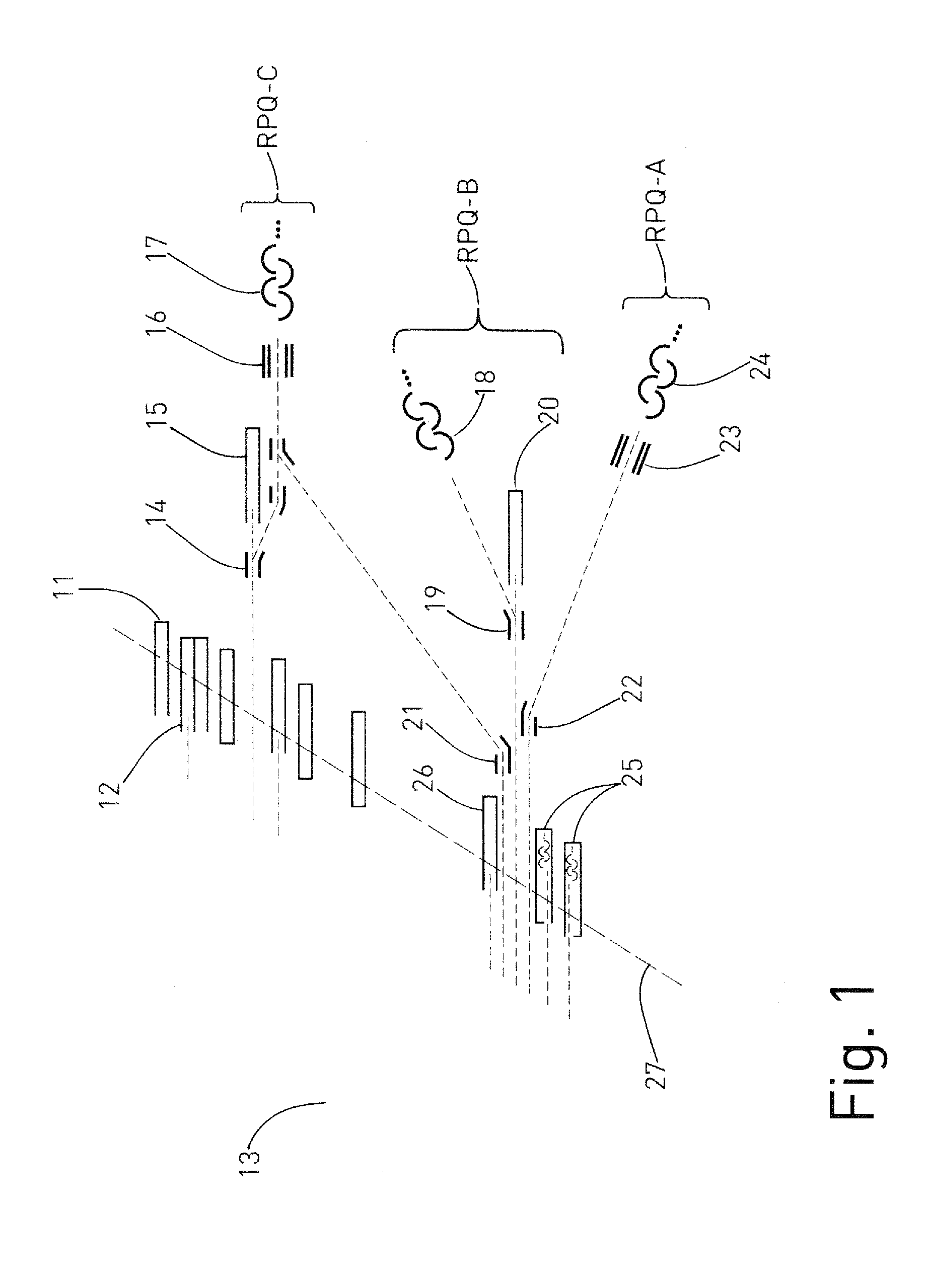
Mass spectrometer and method for isotope analysis
ActiveUS20120085904A1Easy to detectRaise the possibilitySpectrometer detectorsIsotope separationIon beamMass analyzer
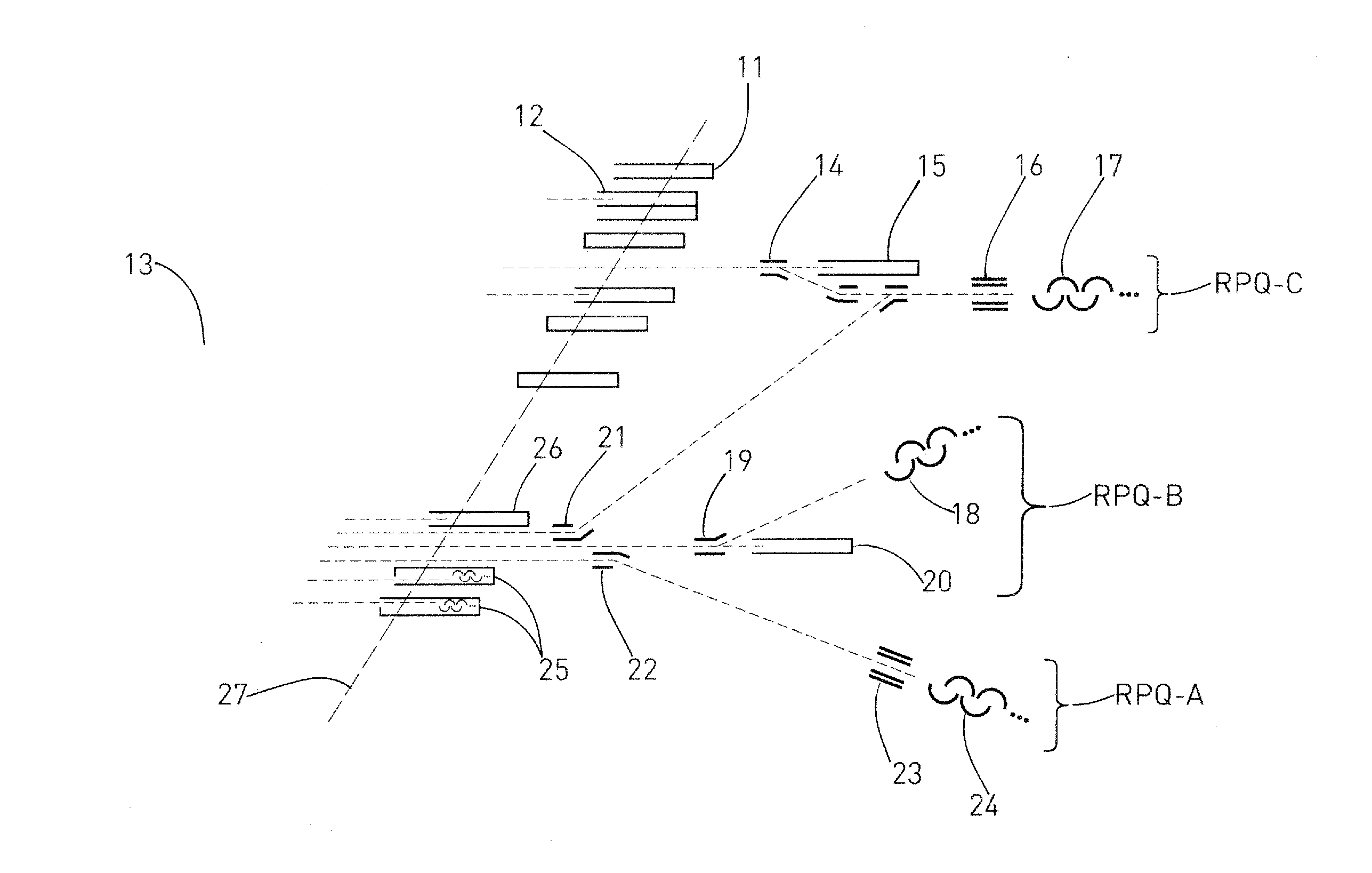
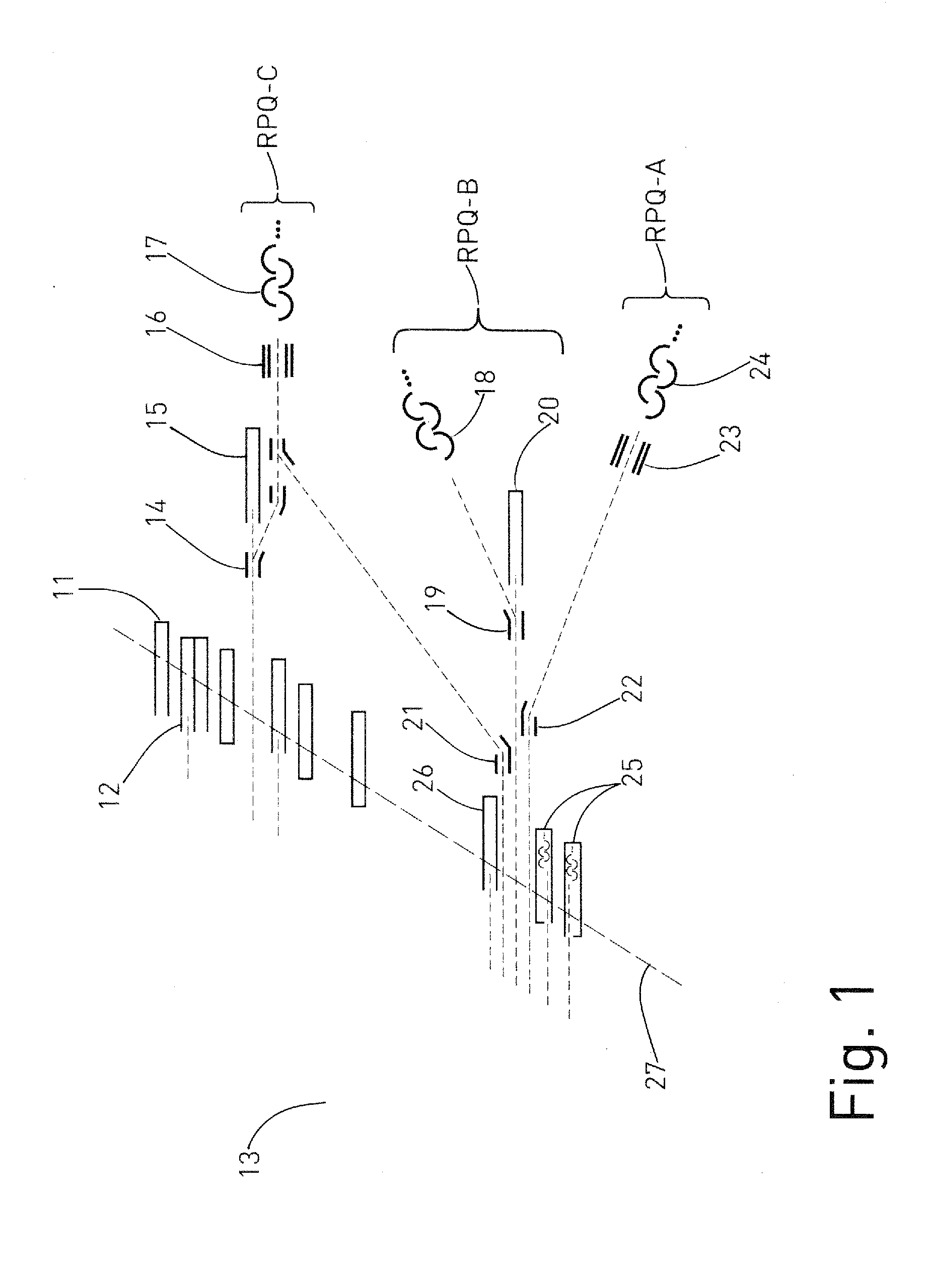
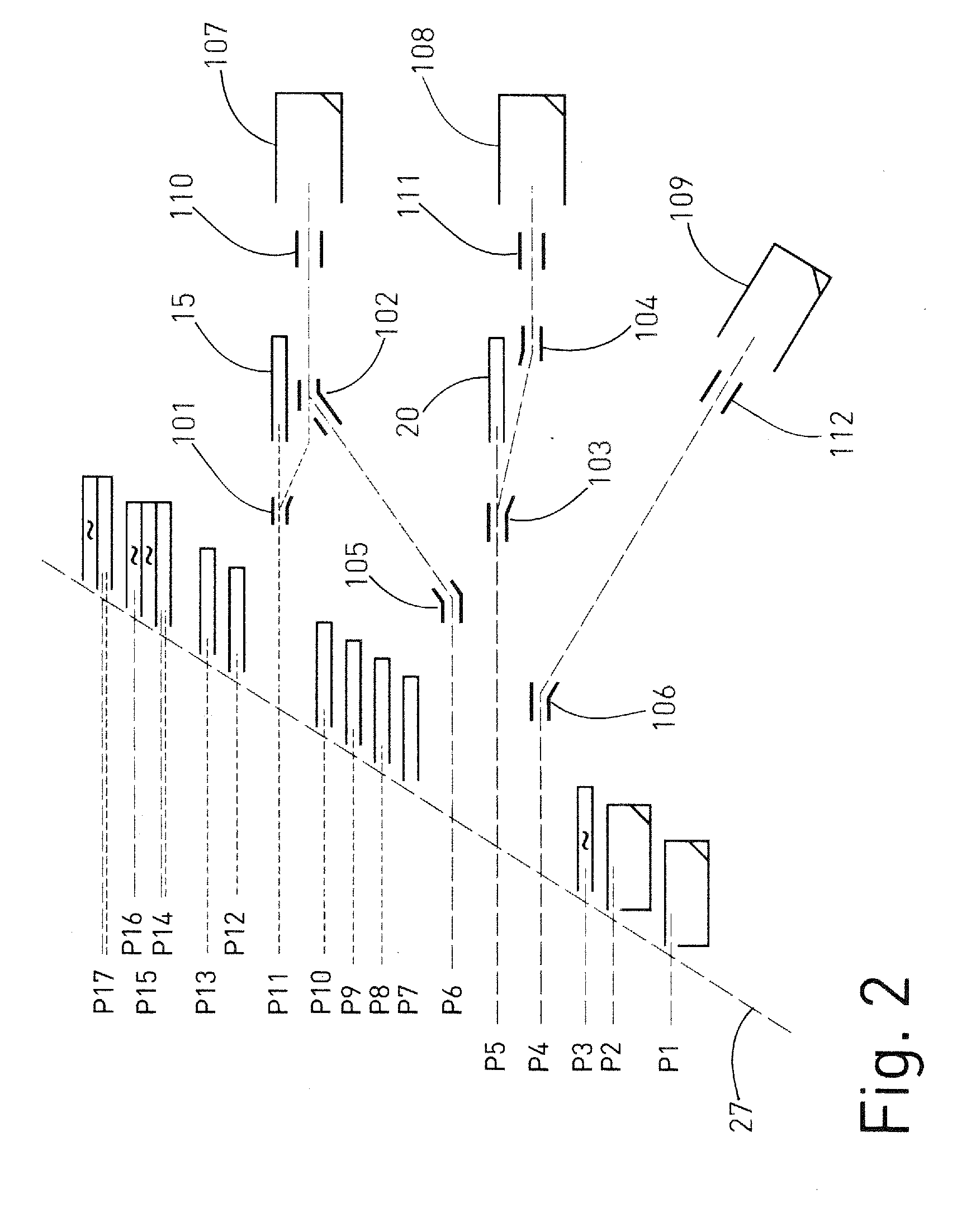
A mass spectrometer for analyzing isotopic signatures, with at least one magnetic analyzer and optionally with an electric analyzer as well, with a first arrangement of ion detectors and / or ion passages and, arranged downstream thereof in the direction of the ion beam, a second arrangement of ion detectors, with at least one deflector in the region of the two arrangements of ion detectors or between these arrangements. Additionally, a multi-collector arrangement, special uses and a method for analyzing isotopes in a sample. The mass spectrometer according to the invention has a control for the at least one deflector such that ion beams of different isotopes can be routed to at least one ion detector in the second arrangement.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
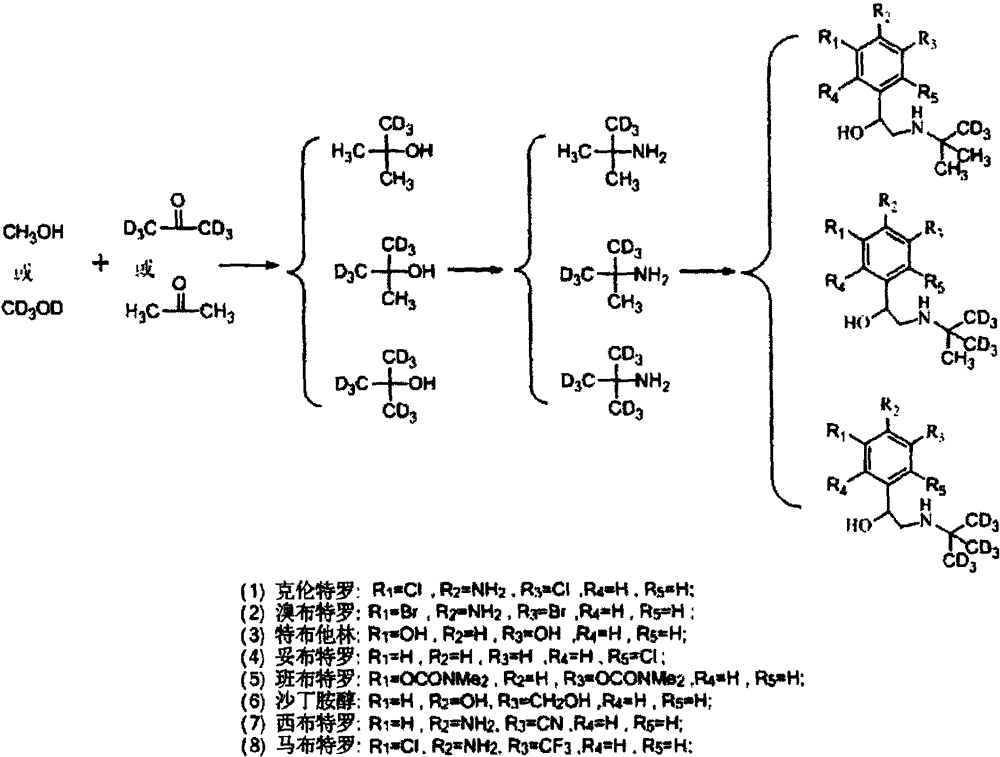
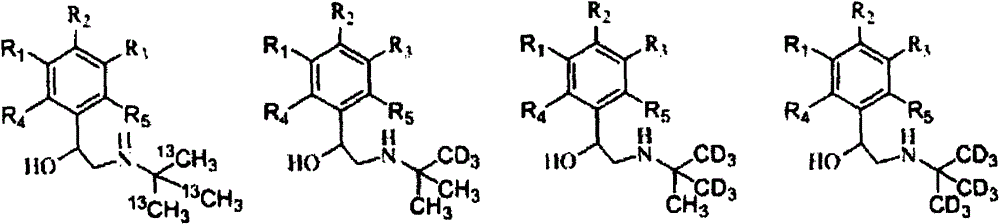
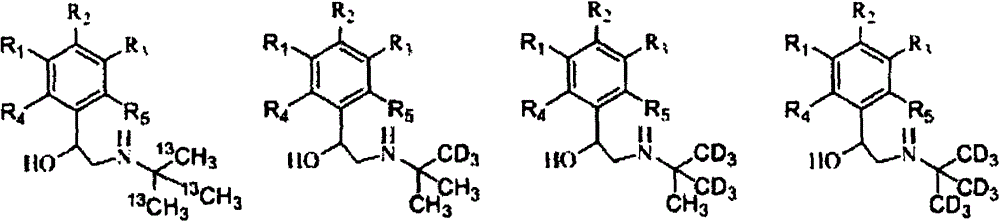
Synthesis method of stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist type compound
ActiveCN104478740AEasy to synthesizeSimple process routeCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationStable Isotope LabelingTert-Butylamine
The invention relates to a synthesis method of a stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist type compound. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: (1) by taking stable isotope-labeled methanol as a raw material, reacting with acetone or stable isotope-labeled acetone, and ammonifying to obtain stable isotope-labeled tert-butylamine; and (2) by taking a bromoketone type compound as a precursor of the beta receptor agonist type compound, reacting with stable isotope-labeled tert-butylamine to prepare the stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist type compound. Compared with the prior art, the method for preparing the stable isotope-labeled beta receptor agonist, provided by the invention, is simple, safe and reliable, the chemical purity of the product after separation and purification is above 99.0%, the isotopic abundance is above 98.0% atom, and the product can fully meet the requirements of residual detection in the field of food safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
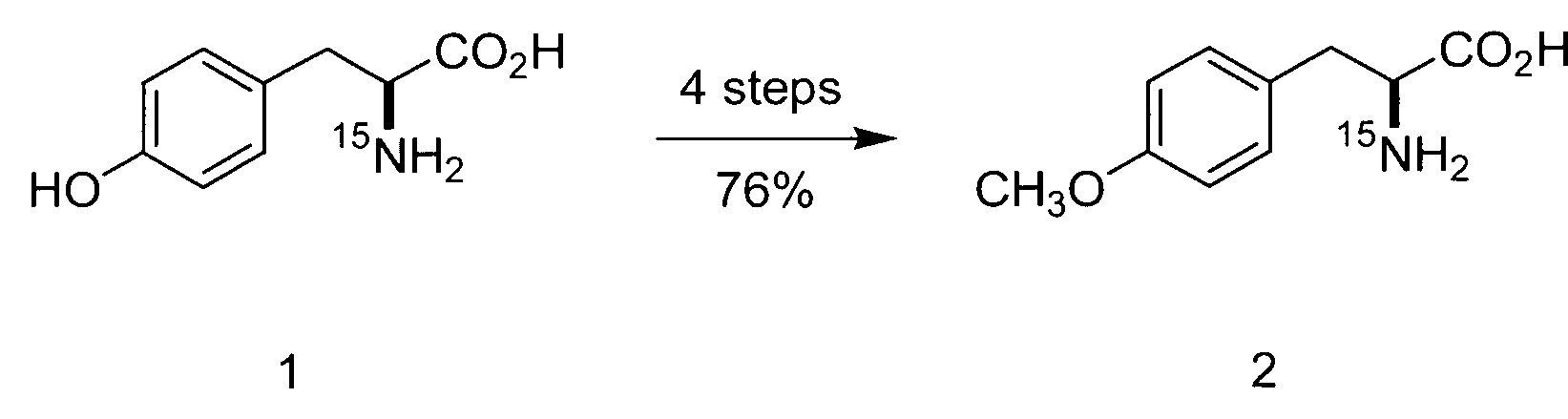
Synthesis and use of isotopically labeled macrocyclic compounds
Disclosed herein are isotopically labeled antifungal antibiotics and related compounds. Also disclosed are methods for synthesizing these isotopically labeled molecules and using the same to study the distribution of these compounds in the biosphere as well as the products formed by the breakdown of these isotopically labeled compounds.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Nondestructive reading method for isotopic label
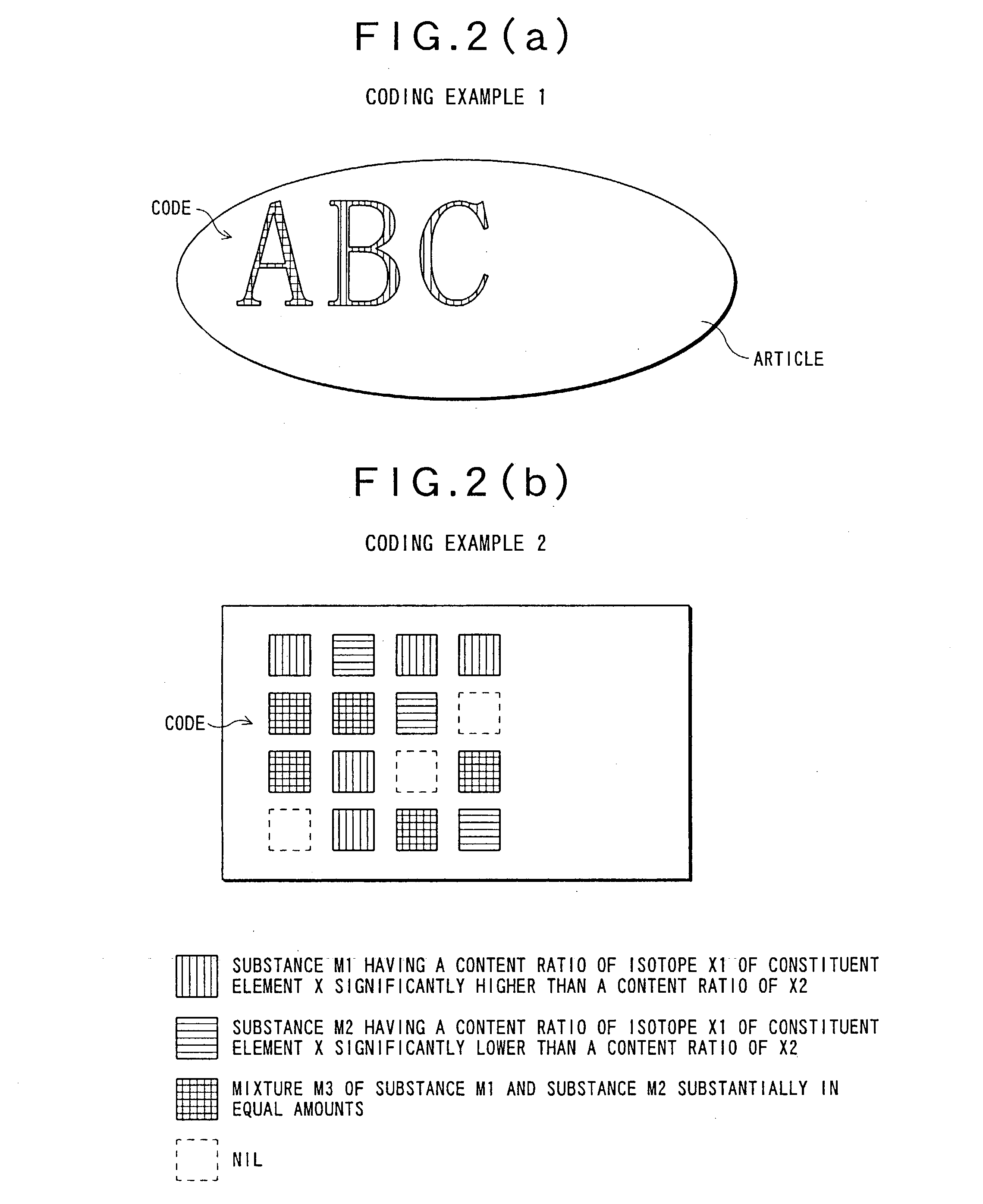
InactiveUS20030178561A1Particle separator tubesPaper-money testing devicesComputer scienceIsotopic signature
A nondestructive reading method for an isotopic label, capable of easily and quickly reading information on an isotopic label imparted to an article in advance without destroying the label, and a nondestructive reading-use isotopic label suitably using this method. In addition, information obtained by this nondestructive reading method is used to easily and quickly judge the authenticity of an article.
Owner:TOKYO GAS CO LTD
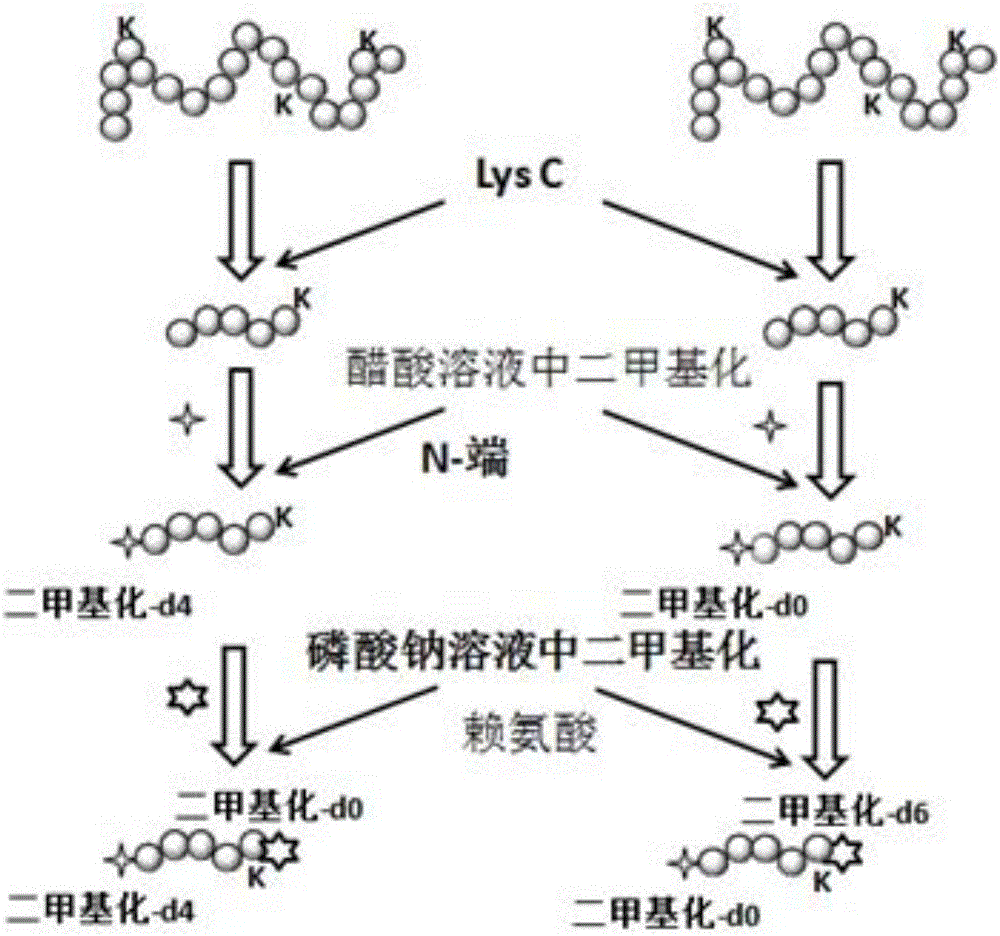
Protein identification method based on two-end equal-weight label and database search
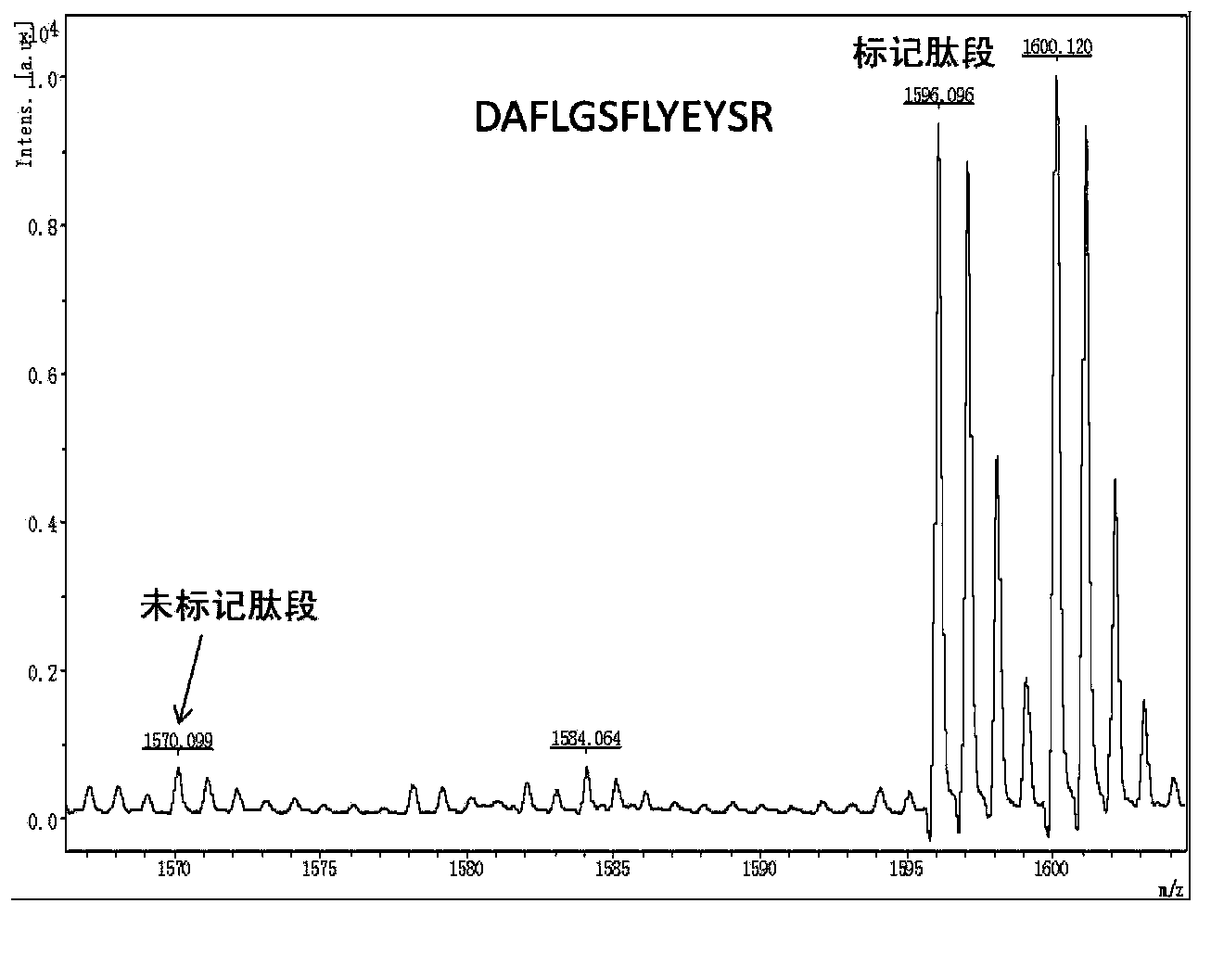
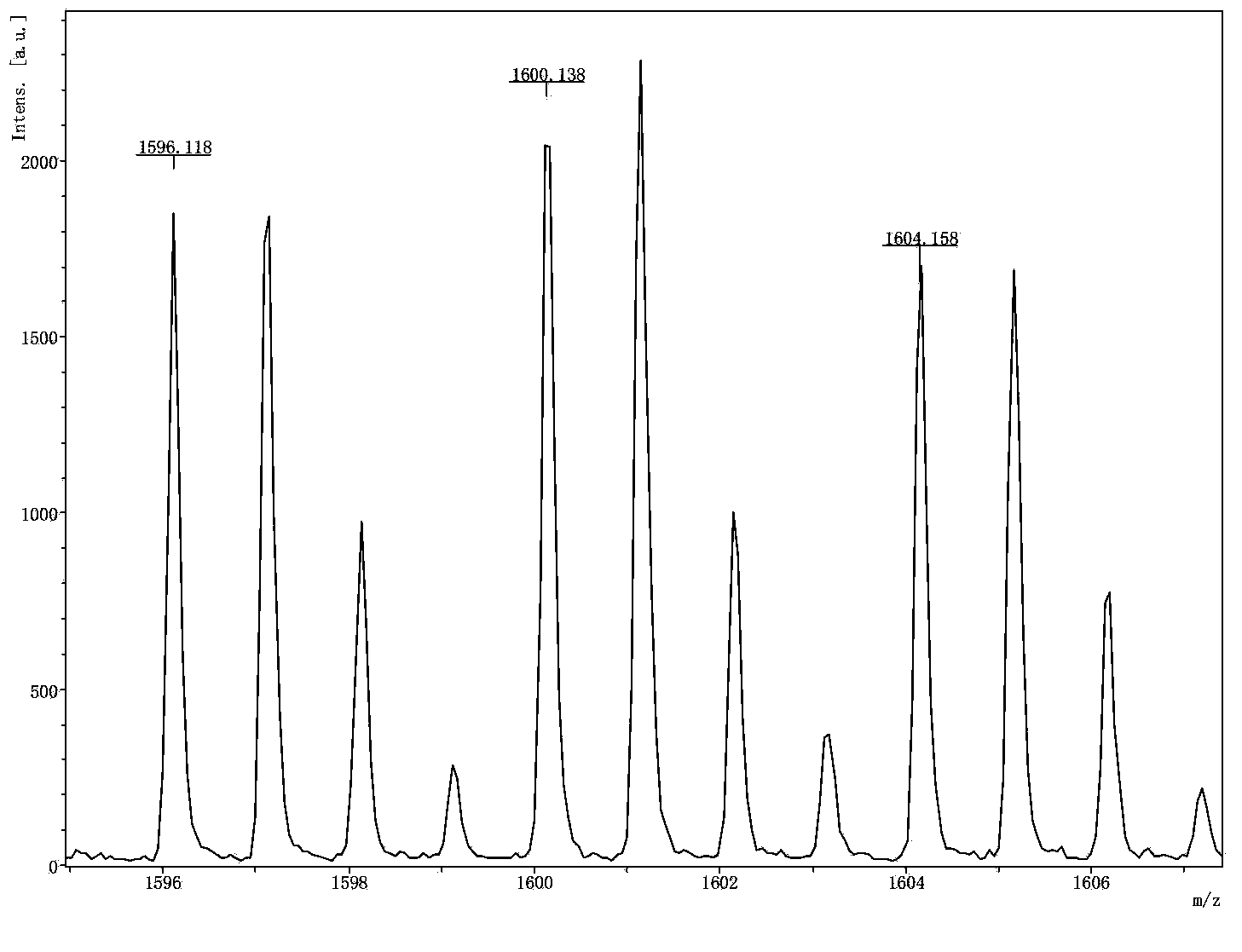
InactiveCN106596760ATake advantage ofImprove identification efficiencyComponent separationPeptide fragmentIsotopic signature
The invention relates to a protein identification method based on a two-end equal-weight label and database search and belongs to the technical field of biological information. According to the identification method, a protein enzymolysis product obtained by performing isotoplabelling at the two ends of polypeptide is subjected to separation and detection through liquid chromatogram-mass spectrum combination; when identification is conducted by a database search method, identification of polypeptide is realized by establishing a peptide fragment theory spectrogram containing all the fragment ions of the peptide section formed by two labels and matching with the experimental mass spectrogram, so that the protein is obtained through identification, the identification efficiency of polypeptide and the protein is improved, and the method can be used for efficiently identifying the protein sample of the database.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and kit for quantitative detection of content of human alpha-lactalbumin
ActiveCN103642895AImprove accuracyHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementInternal standardBiology
The invention relates to the field of analytical chemistry and discloses a method and kit for quantitative detection of content of human alpha-lactalbumin. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a specific polypeptide sequence CELSQLLK obtained after enzymolysis of the human alpha-lactalbumin is utilized to design the sequences of an isotope-labeled specific peptide and an isotope-labeled internal standard substance, a brand new accurate quantitative detection method is provided on the basis of an internal standard method to perform the quantitative detection of the human alpha-lactalbumin, and the accuracy, precision and sensitivity are relatively high.
Owner:贝因美(杭州)食品研究院有限公司
Isotopically-labeled proteome standards
ActiveUS20070031911A1Enabling useQuantitative precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotopic signatureMass spectrometric
The invention provides methods for quantifying biomolecules, such as polypeptides in mass spectrometric analysis. The methods include use of a biomolecule standard having at least one atomic isotope different than that of the naturally occurring isotopes in the biomolecule of interest. Methods of the present invention also include methods for quantifying biomolecules where the copy biomolecule standard is made by expressing the biomolecule using a recombinant cell. Further included are the biomolecule standards themselves, method for making such standards, kits, systems, reagents, and engineered cells relating to the use of biomolecule standards in mass spectrometric analysis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Circular system for cultivating abundant isotope carbon and nitrogen double-labeling plant sample
ActiveCN107047265ASimultaneous markingAchieve recyclingAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsPeristaltic pumpCircular loop
The invention relates to the technical field of the isotope labeling and in particular to a circular system for a cultivating abundant isotope carbon and nitrogen double-labeling plant sample. The circular system for the cultivating abundant isotope carbon and nitrogen double-labeling plant sample comprises a sealed cultivation chamber, a CO2 injector, a gas balancing device, a nutrient solution injector and a nutrient solution circular system. The sealed cultivation chamber comprises a transparent cover and a base. The transparent cover is internally provided with a semiconductor condensation dehumidification device. The transparent cover is connected with the CO2 injector and the gas balancing device. A cultivation basin, a liquid storage chamber, an external peristaltic pump, an ultraviolet sterilizing device, a circular peristaltic pump and a converging pool are successively connected to form a circular loop of the nutrient solution circular system. The converging pool is connected with the semiconductor condensation dehumidification device and the nutrient solution injector. The cultivation basin and the liquid storage chamber are installed in the base. The top of the cultivation basin is communicated with the transparent cover. Silica sand is installed in the cultivation basin. The circular system for the cultivating abundant isotope carbon and nitrogen double-labeling plant sample is capable of simultaneously labeling the carbon and nitrogen isotope, and realizing the cyclic utilization. The pollution of normal 12 C and 14 N is avoided, and an abundant carbon and nitrogen isotope double-labeling plant can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Mass spectrometer and method for isotope analysis
ActiveUS8592757B2Increase flexibilityImprove performanceSpectrometer detectorsIsotope separationIon beamMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer for analyzing isotopic signatures, with at least one magnetic analyzer and optionally with an electric analyzer as well, with a first arrangement of ion detectors and / or ion passages and, arranged downstream thereof in the direction of the ion beam, a second arrangement of ion detectors, with at least one deflector in the region of the two arrangements of ion detectors or between these arrangements. Additionally, a multi-collector arrangement, special uses and a method for analyzing isotopes in a sample. The mass spectrometer according to the invention has a control for the at least one deflector such that ion beams of different isotopes can be routed to at least one ion detector in the second arrangement.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
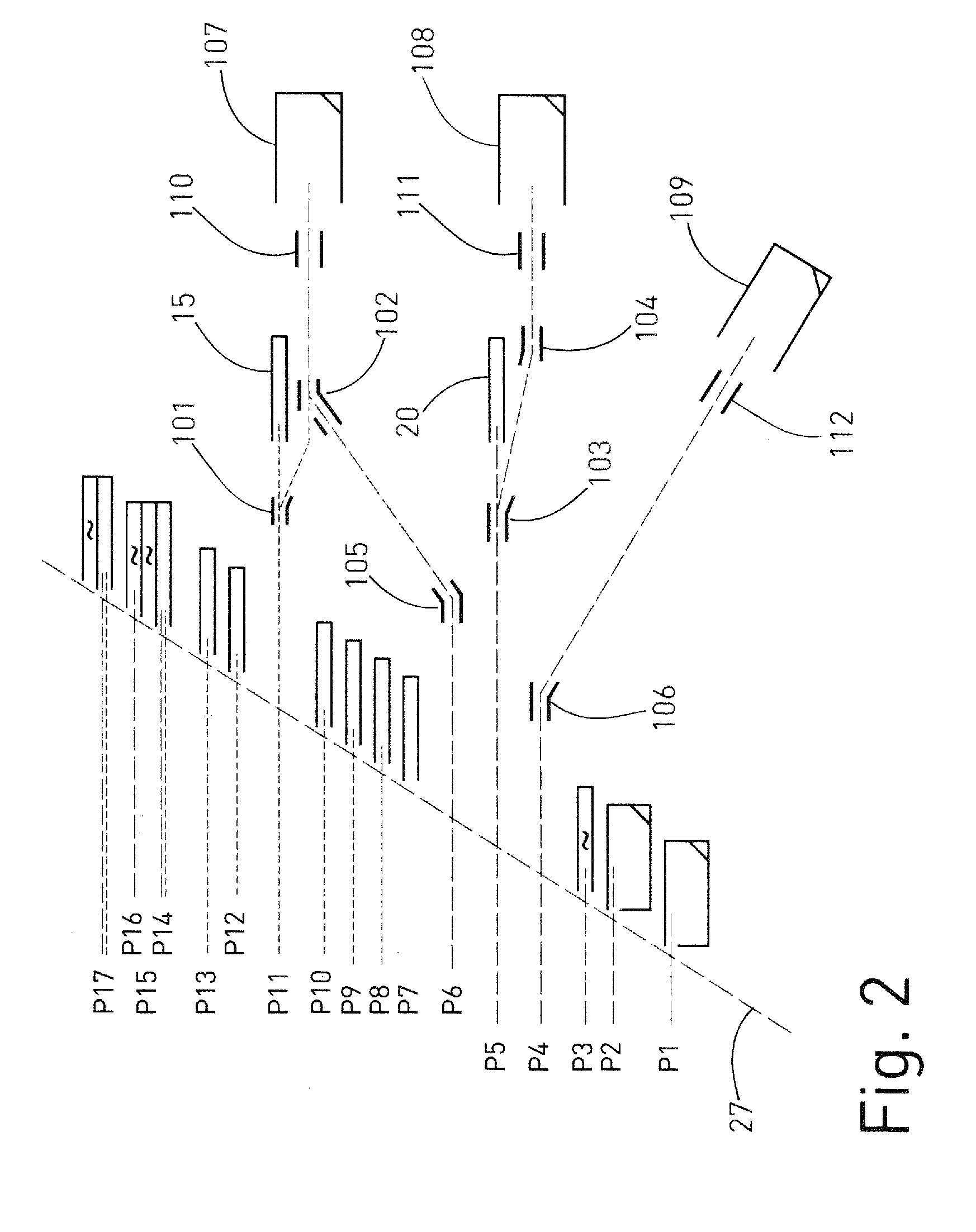
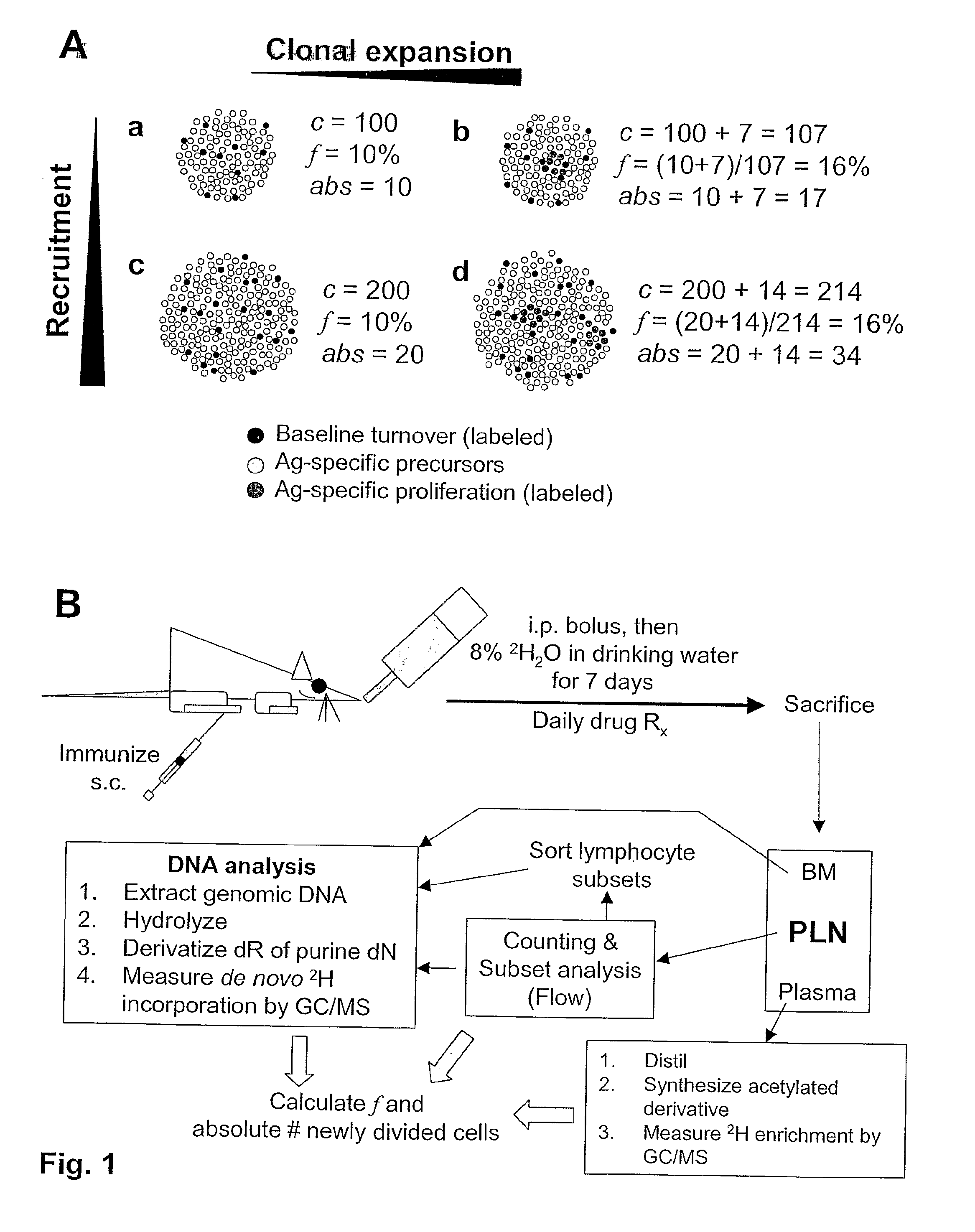
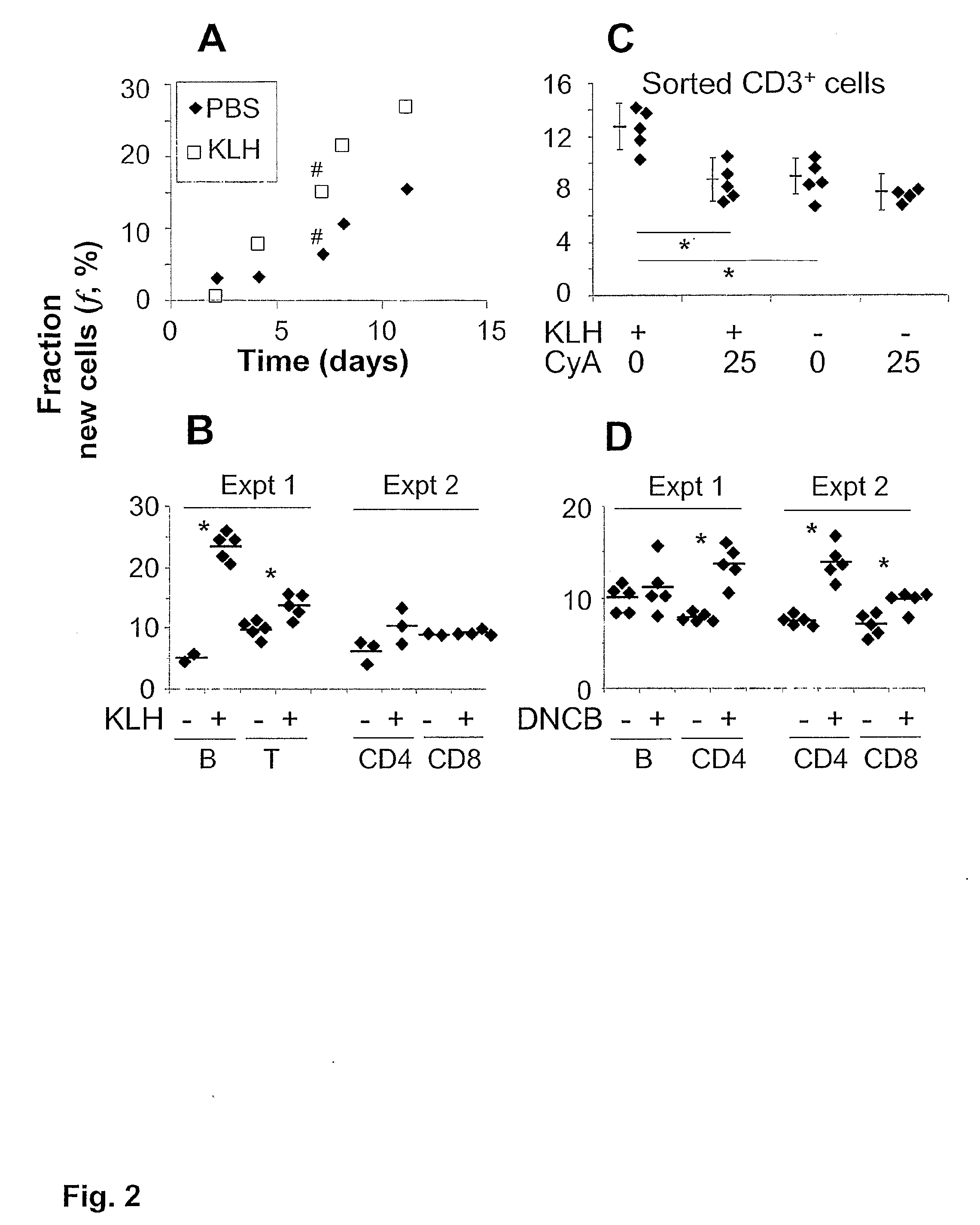
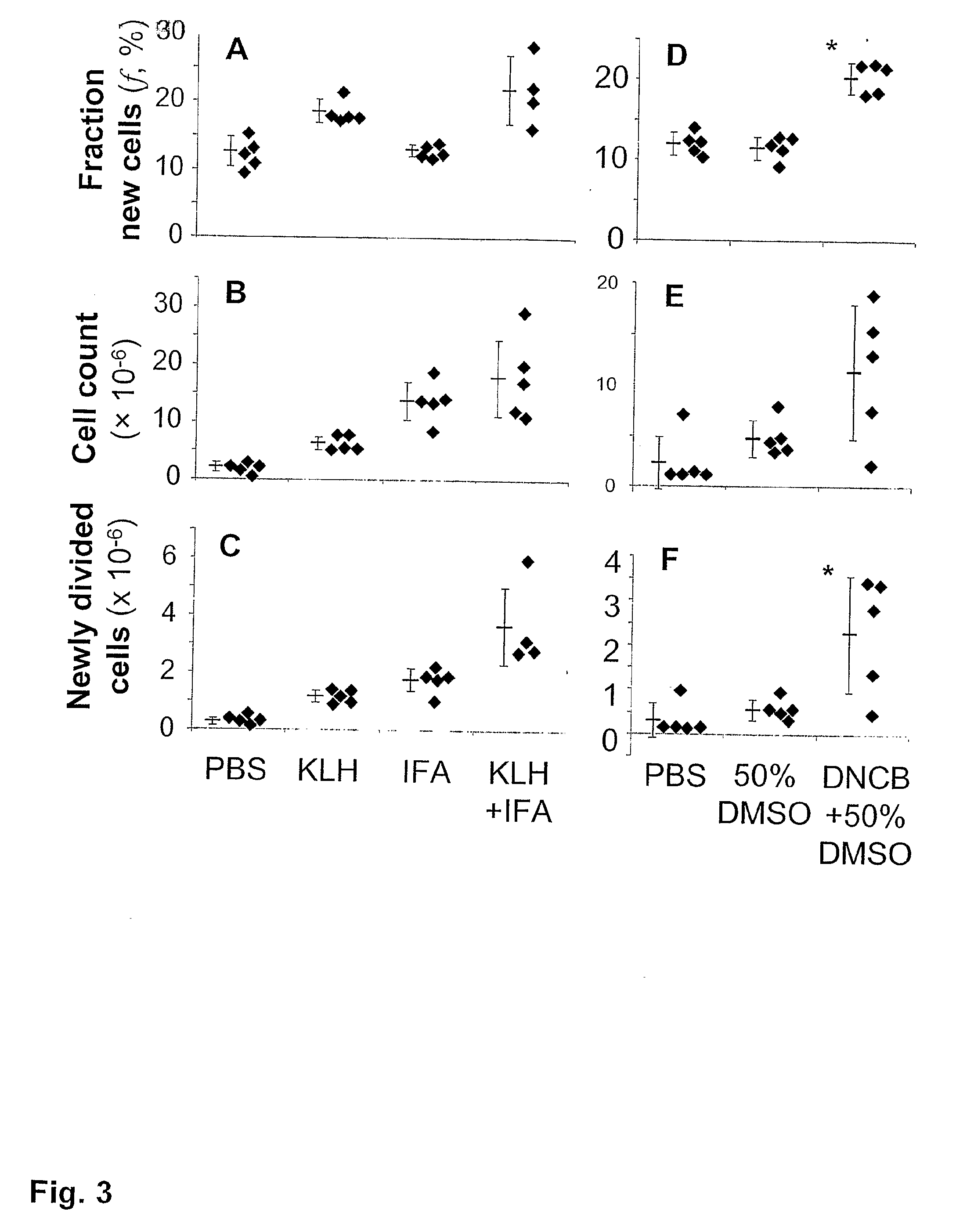
Kinetic biomarker for quantification of lymphoproliferation, clonal expansion, recruitment and trafficking in lymphoid tissues and of the in vivo actions of antigens and modulating thereon
InactiveUS20090155179A1Reduction of immune activationShorten the progressIn-vivo testing preparationsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseStable Isotope Labeling
Owner:KINEMED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com