Protein identification method based on two-end equal-weight label and database search
A technology of protein identification and database, which is applied in the field of protein identification based on equal weight tags at both ends and database search, can solve the problems of reducing the score of candidate peptides, poor quality of fragment ions, and affecting the identification efficiency of peptides and proteins, etc., to achieve The effect of improving identification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
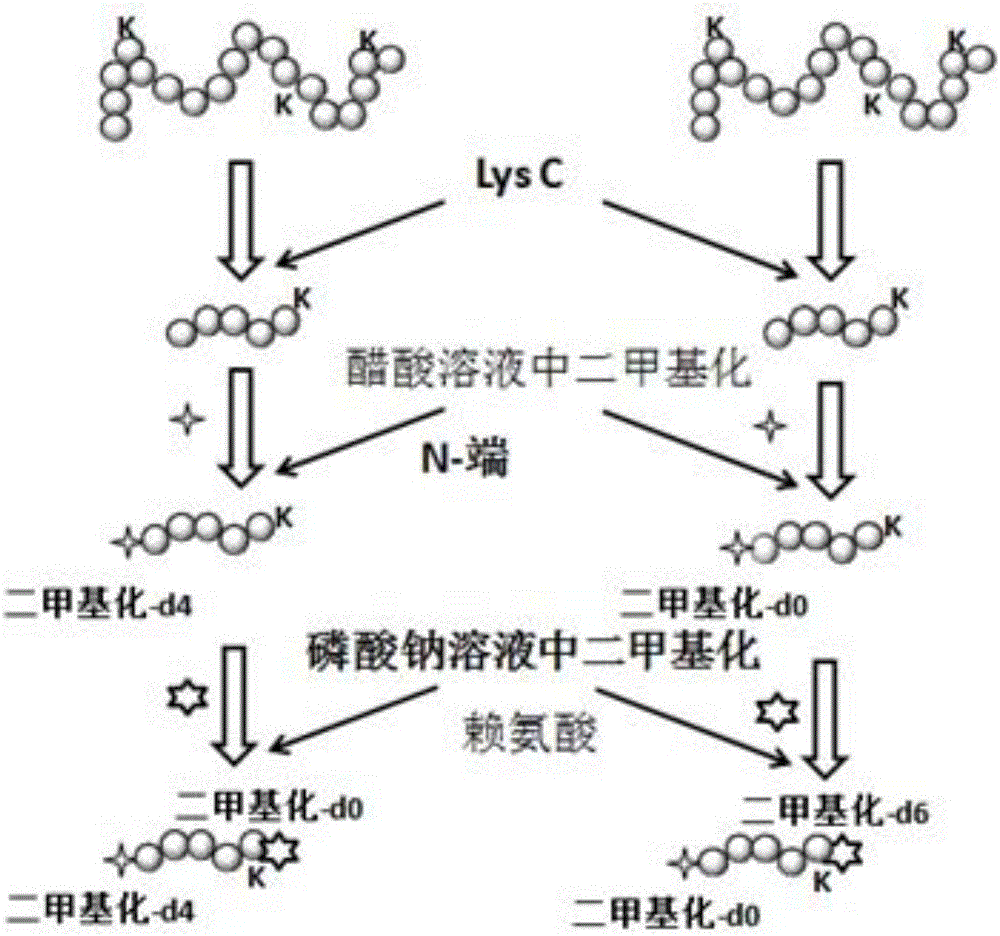
[0028] (1) Treat the protein as follows: dissolve 100 μg of bovine serum albumin in 1 mL of urea with a concentration of 8 M; then add 100 μL of dithiothreitol with a concentration of 10 mM and place it in a water bath at 56°C for 2 hours; then add 100 μL of dithiothreitol with a concentration of 10 mM 20mM iodoacetamide, placed in the dark for 1h to obtain the treated protein; dilute the urea concentration in the treated protein to 0.8M with 50mM sodium phosphate with a pH value of 7.5, and then add the intracellular protease lysine Acid-C, the mass ratio of bovine serum albumin to intracellular protease lysine-C is 25:1, incubated overnight at 37°C for enzyme digestion to obtain polypeptides.
[0029] (2) Divide the polypeptide obtained in step (1) into two equal parts. After the first part of the polypeptide is desalted with a C18 pre-column, the N-terminus is labeled with a formaldehyde solution containing H. Specifically: 5 μL of 0.6M cyanide Sodium borohydride and 55 μL ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) The protein is processed as follows:
[0045] 1) Protein C-terminal metabolic labeling
[0046] HeLa cells were cultured with cell culture medium containing lysine with different light and heavy isotopes. A cell culture medium containing 13 C-labeled lysine, another cell fluid containing 12 C-labeled lysine; HeLa cells were passaged 8 times to ensure 12 C and 13 C mark completely.
[0047] 2) Extract proteins from the light and heavy isotope-labeled HeLa cells obtained in 1), respectively; take 100 μg of the light and heavy isotope-labeled HeLa cell proteins, respectively, and perform the following operations: dissolve in 1 mL of 8M urea, add 100 μL Dithiothreitol at a concentration of 10 mM was placed in a water bath at 56°C for 1 hour, then 100 μL of iodoacetamide at a concentration of 20 mM was added, and placed in the dark for 0.5 hour to obtain the treated protein, which was treated with 50 mM phosphoric acid at a pH of 7.5 Sodium Dilute the urea concentr...
Embodiment 3
[0059] (1) Treat the protein as follows: Dissolve 100 μg of yeast extract protein in 1 mL of urea with a concentration of 8 M; then add 100 μL of dithiothreitol with a concentration of 10 mM, and place it in a water bath at 56°C for 2 hours; then add 100 μL of dithiothreitol with a concentration of 10 mM 20mM N-ethylmaleimide was placed in the dark for 10min to obtain the treated protein; the urea concentration in the treated protein was diluted to 0.8M with 50mM sodium phosphate with a pH value of 7.5, and then added to the cell Endoprotease lysine-C, the mass ratio of yeast extract protein to intracellular protease lysine-C is 25:1, incubated overnight at 37°C for enzyme digestion to obtain polypeptides.
[0060] (2) Divide the polypeptide obtained in step (1) into two equal parts. After the first part of the polypeptide is desalted with a C18 pre-column, the N-terminus is labeled with succinic anhydride containing H. Specifically: 100 μL of 0.1M The succinic anhydride solut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com