Patents
Literature
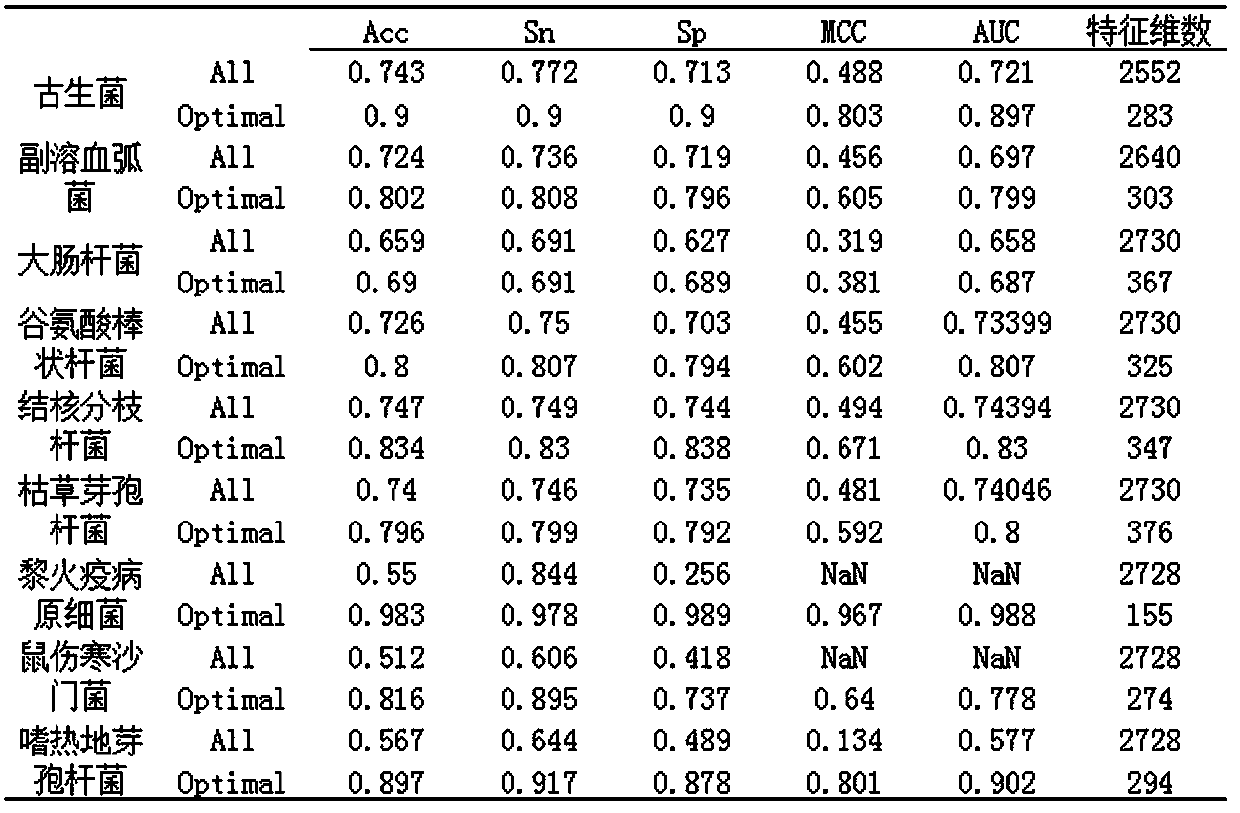
52 results about "Protein primary structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
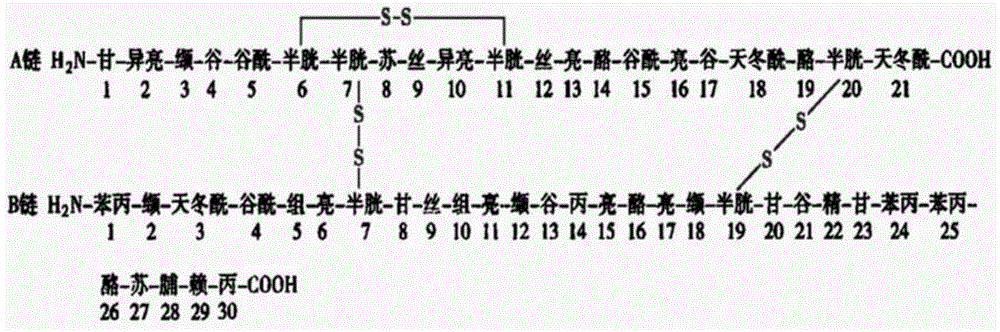
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced, or inferred from DNA sequences.
Method for identifying protein functions based on protein-protein interaction network and network topological structure features
InactiveCN105138866ARobustSignificant predictive advantageSpecial data processing applicationsNODALData set
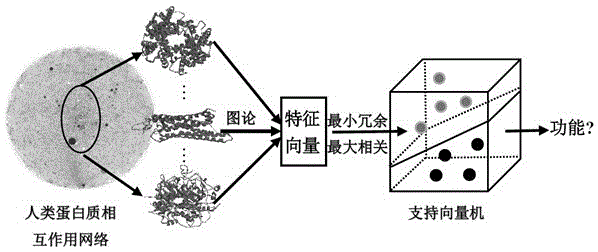
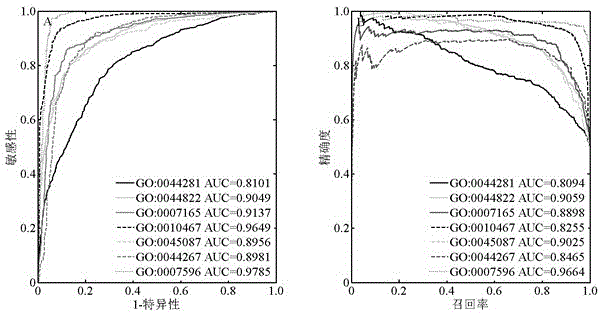
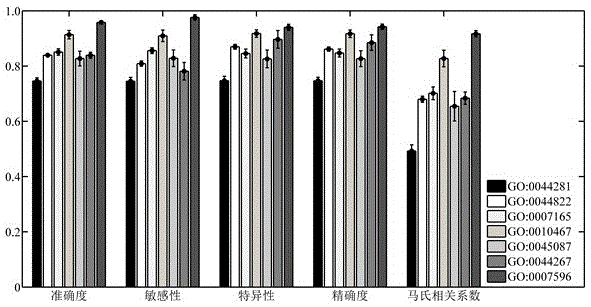
The invention discloses a method for identifying protein functions based on a protein-protein interaction network and network topological structure features. Firstly, a node and side-weighted protein-protection interaction network is established, wherein the node represents protein while the edge represents the interaction; then the nodes and the sides in the network are weighted by protein first-grade structural description and protein-protein interaction trust scoring; protection functional annotation data is collected to establish a data set, and a new protein with overall and local information network topological structure features is provided based on a graph theory; and finally, the protein functions are predicated by choosing features through adopting a minimum-redundancy maximum-correlation method and by modeling through a support vector machine. The protein function predication method is greatly better than the prior art, and has robustness on sequence similarity and sampling; and meanwhile, information of three-dimensional structure and the like of protein is not required, so that the method is simple, rapid, accurate and efficient, and the method is expected to be applied in the research fields of proteomics and the like.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +2
Latex Adhesives Derived From Ionic Strength Induced Soy Protein Complexes
InactiveUS20080287635A1Easy to operateHigh strengthPeptide preparation methodsFiberProtein molecules
Macro hydrophobic clusters and complexes of soybean globular proteins were observed using TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). Upon unfolding, hydrophobic groups of the proteins became exposed toward the surface of the protein and actively interacted with other hydrophobic groups of other protein molecules, thereby forming hydrophobic bonding. The hydrophobic bonding resulted in hydrophobic protein clusters, the formation of which was affected by the degree of protein unfolding, protein structure, and hydrophobic components. Such hydrophobic clusters followed the global minimum free energy theory and formed spherical like structures with diameters ranging from 100 nm to 3000 nm. Such an understanding lends applicability to many uses in adhesives, molding composites, surfactants for oil-water systems, bio-based interior construction paints and paper coatings, fiber production, and metal powder molding applications.
Owner:SUN XIUZHUI +2
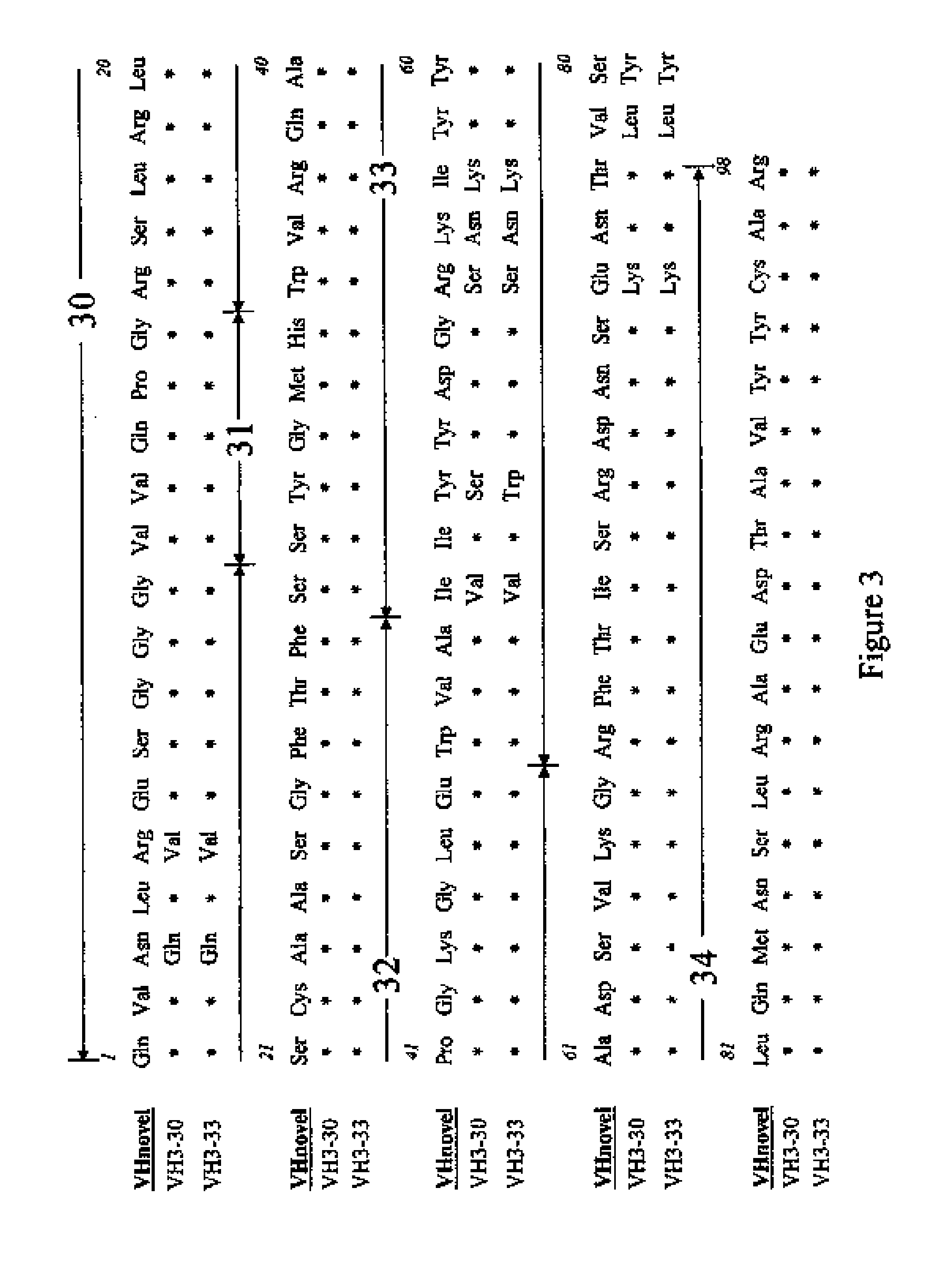
Novel antibody structures derived from human germline sequences
InactiveUS20130267688A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationHeavy chainMonoclonal antibody
In order to provide necessary information for the production of complete human monoclonal antibodies capable of human CD152 (CTLA-4) binding, the primary structures of heavy and light chains have been elucidated. The novel amino acid sequence of identified heavy and light chains are derived from VH3 and Vλ germline genes, respectively. Antibodies comprising such novel structures cause specific binding to soluble recombinant human CD152 as well as to activated human peripheral T cells, where the expression of CD152 has been elevated.
Owner:CHIN LI TE +2
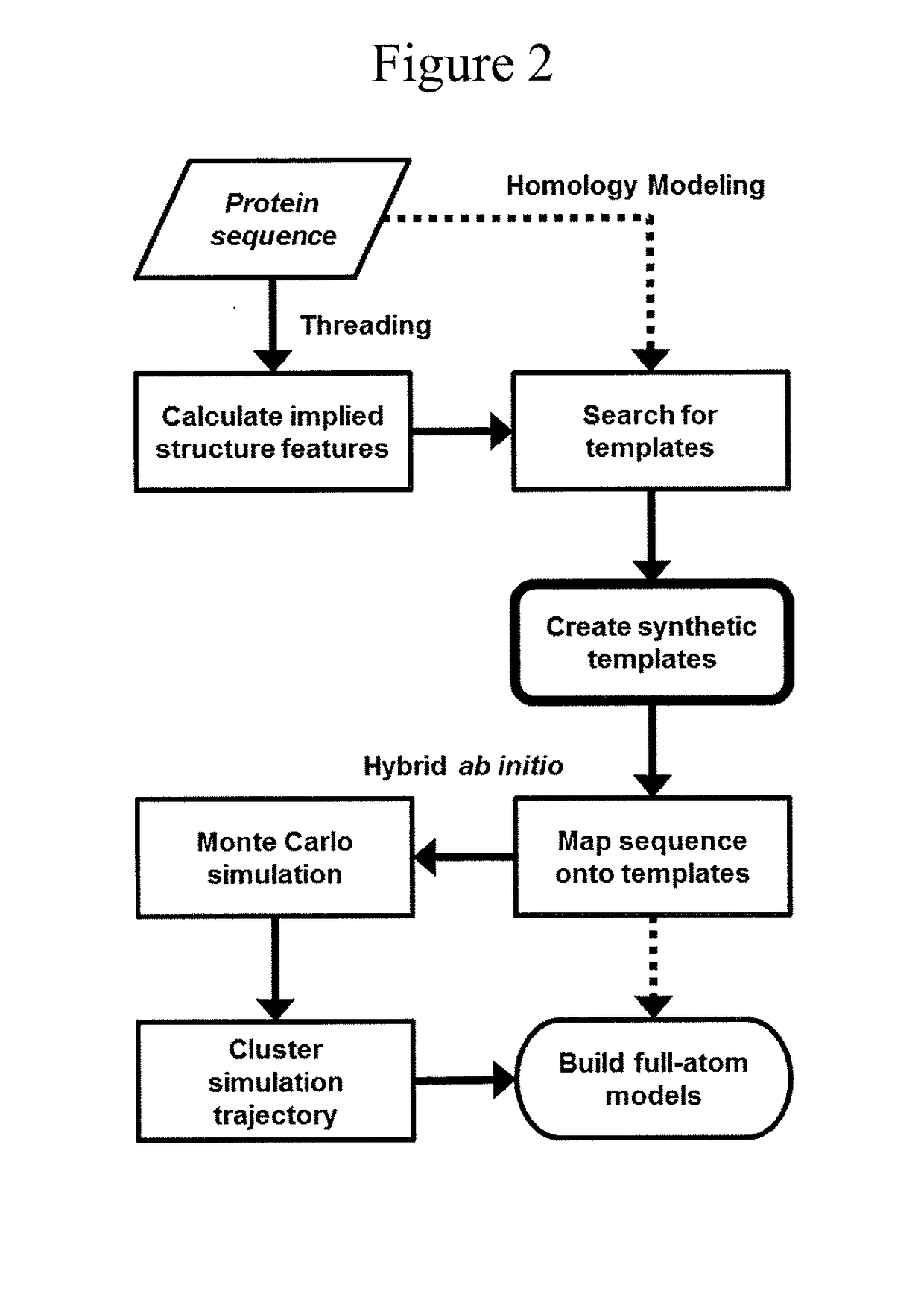
Protein structure prediction system
ActiveUS20180260517A1Increase structural diversityImprove discovery rateChaos modelsNon-linear system modelsEnergy minimizationTarget peptide
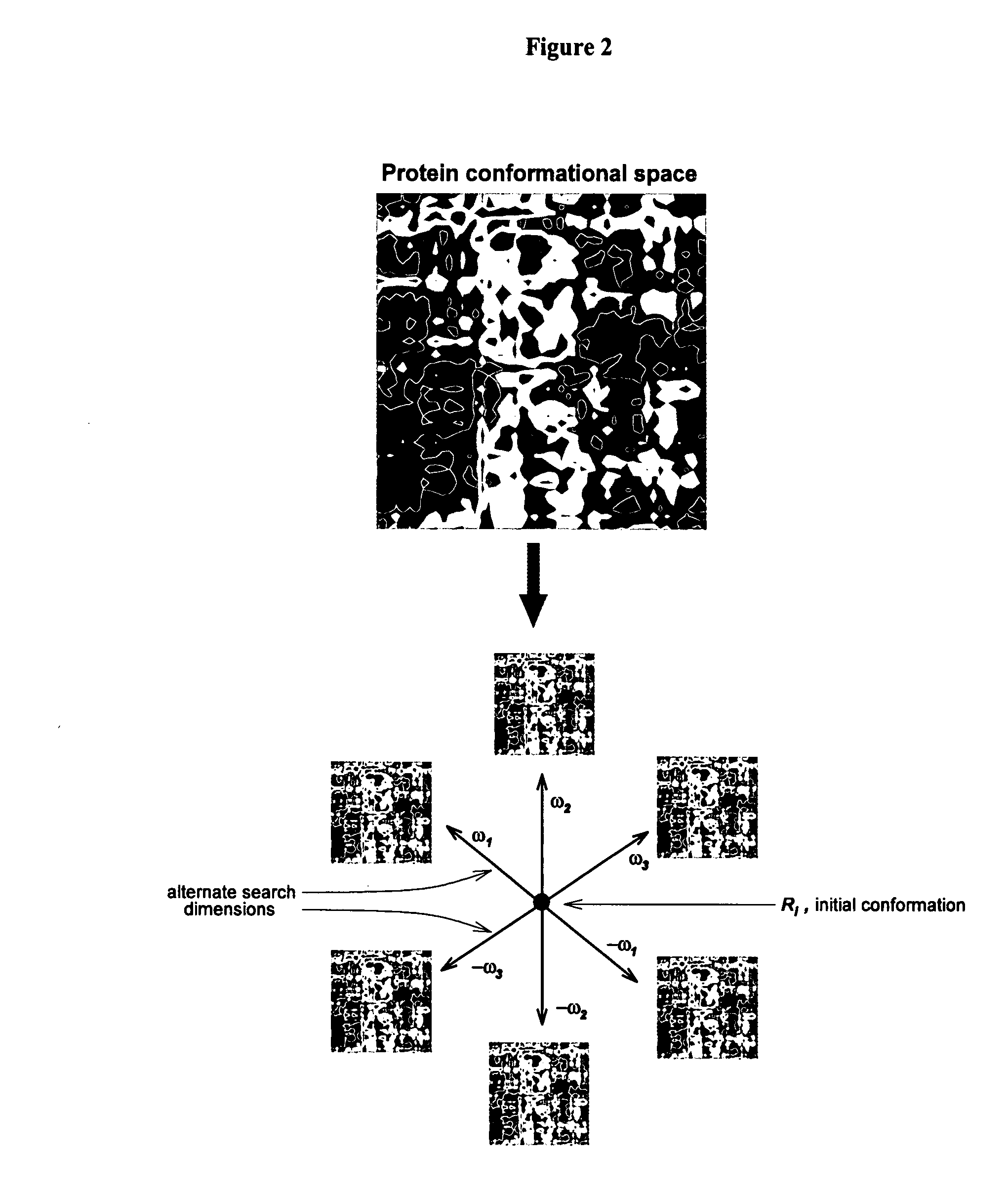
The present invention is an accelerated conformational sampling method for predicting target peptide and protein structures comprising a process of determining energy minimized synthetic templates using a simple system for modeling individual molecular bonds within the subject peptide or protein. Use of these synthetic templates greatly reduces the computational resources necessary for optimally determining structural features of the target peptide or protein. The present invention also provides methods for rapid and efficient analysis of the effect of mutations on target peptides and proteins.
Owner:DNASTAR
Methods and apparatus for predicting protein structure
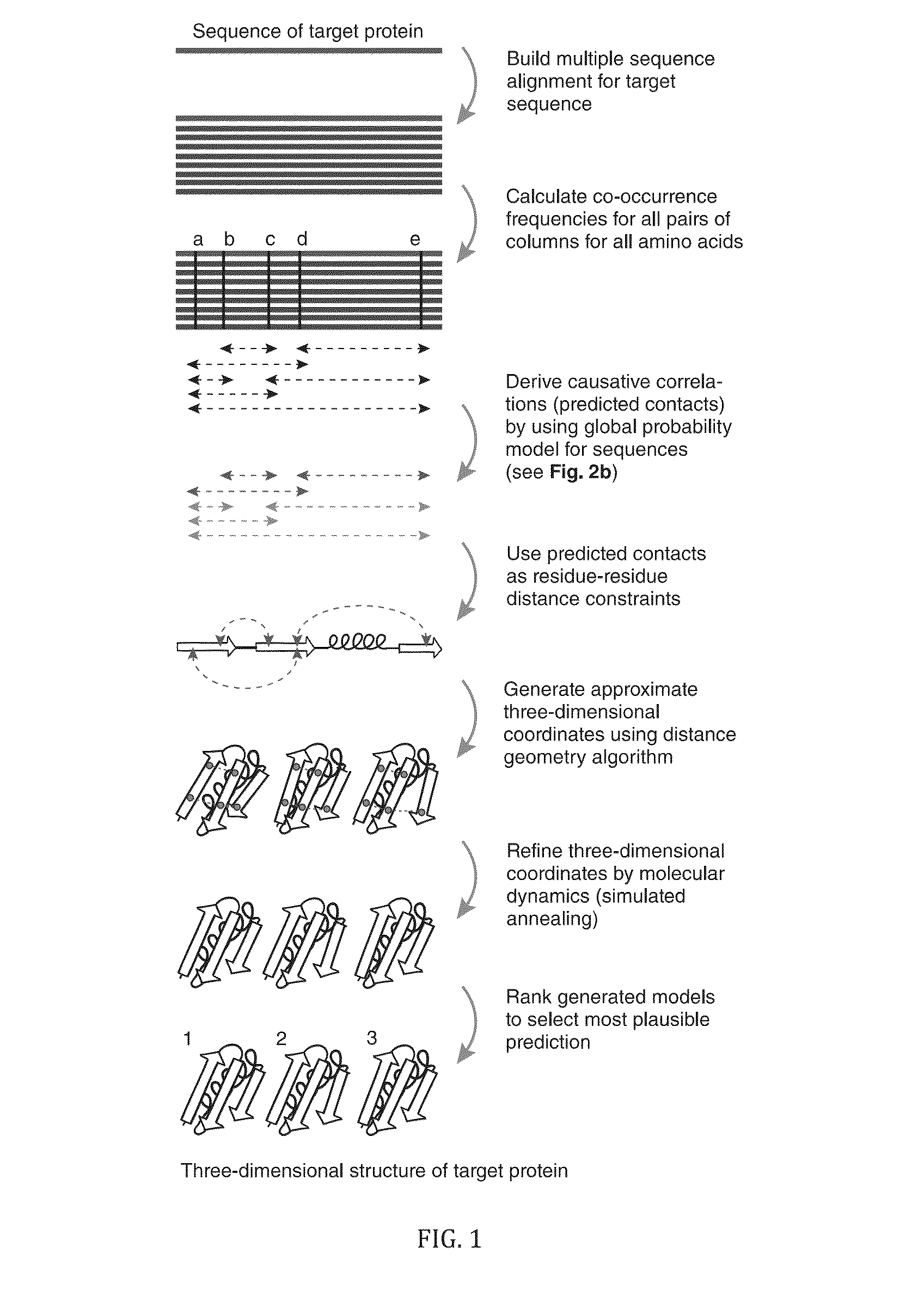
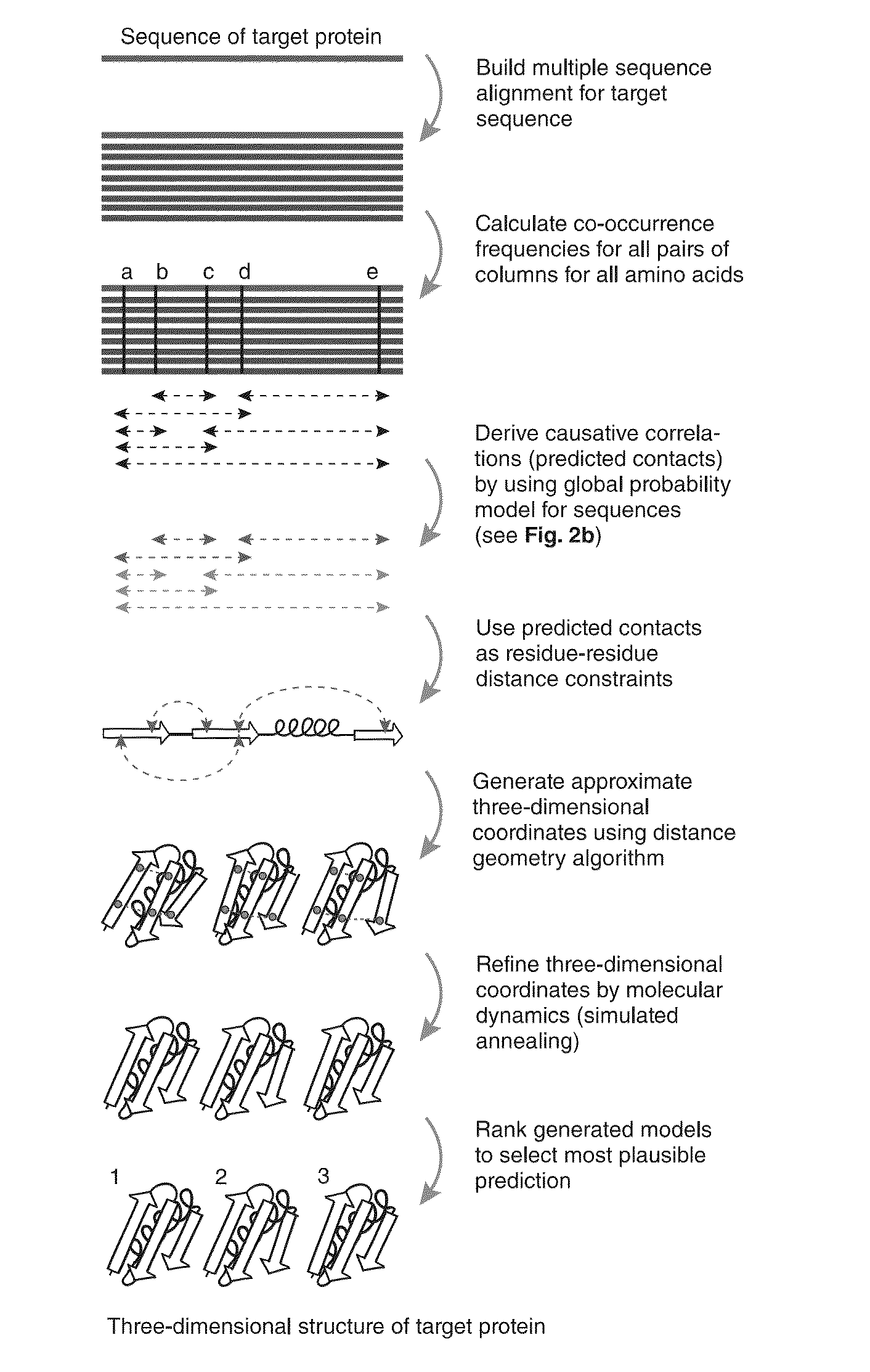
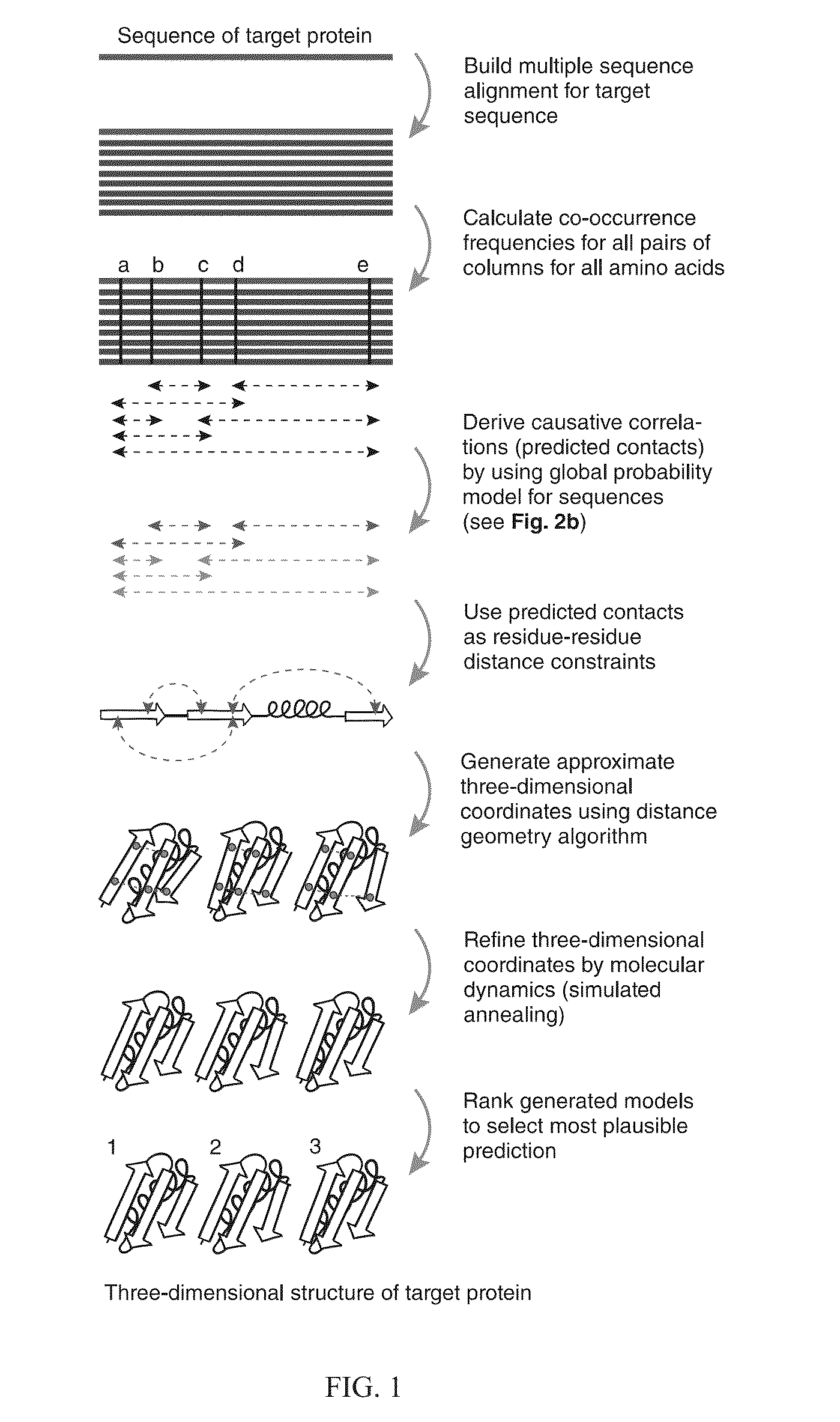
InactiveUS20130304432A1Remove constraintsComputation using non-denominational number representationSequence analysisChain structureProtein structure
The present invention relates to a method for predicting three-dimensional structure of a protein from its sequence. Three-dimensional structure may be determined by: (a) generating a multiple sequence alignment for a candidate protein having a known sequence; (b) identifying a covariance matrix between all pairs of sequence positions in the multiple sequence alignment; (c) inverting the covariance matrix and identifying predicted evolutionary constraints using a statistical model of the candidate protein; and (d) simulating folding of an extended chain structure of the candidate protein using the predicted constraints.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Prokaryotic protein acetylation site prediction method
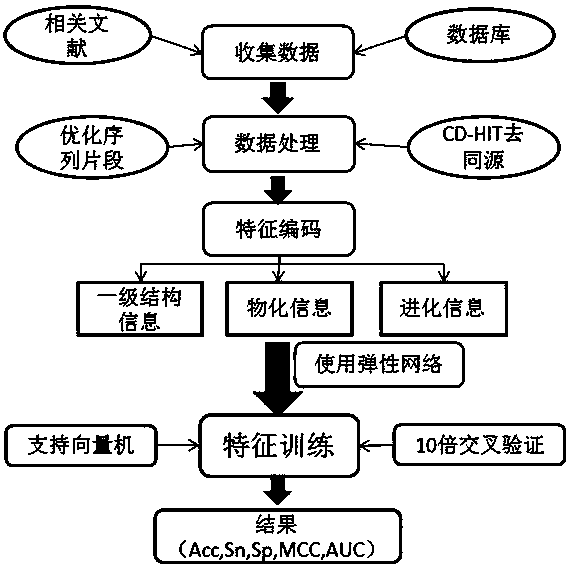
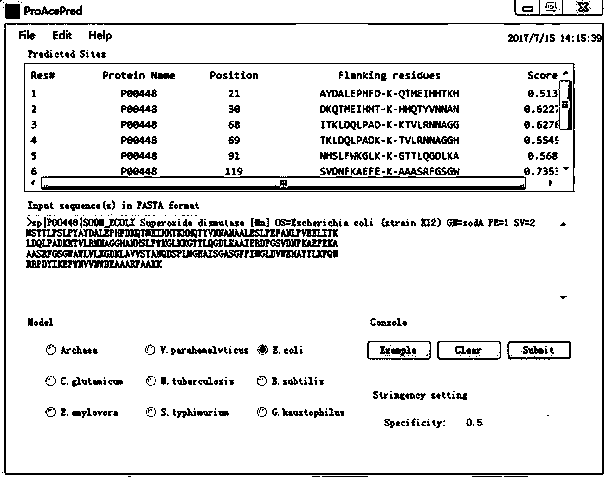
InactiveCN107463802AReduce dimensionalityImprove forecast accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsAlgorithmProtein insertion
The present invention discloses a prokaryotic protein acetylation site prediction method. The method comprises the steps of: collecting data; processing the data; performing feature coding: feature training; and constructing a prediction model. The present invention further discloses an application of the prokaryotic protein acetylation site prediction method. The method disclosed by the present invention comprises: based on multi-dimensional feature coding of protein primary structure information, physicochemical information and evolutionary information, extracting a feature of prokaryotic protein acetylation sequence; optimizing and selecting an optimal eigenvector by using an Elastic Net; and by combining a support vector machine (SVM), constructing a prediction model of a prokaryotic acetylation site, which significantly improves prediction performance of the prediction model for the prokaryotic acetylation site. A developed prediction software platform ProAcePred realizes high-throughput prediction of the prokaryotic protein acetylation site, provides an accurate, simple and rapid researching tool for study on protein acetylation, and offers valuable reference information to further experimental researches.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method for predicting protein structure based on phased multi-strategy copy exchange
ActiveCN106055920AImprove forecast accuracyReduce complexitySpecial data processing applicationsMolecular structuresMetapopulationPhases of clinical research
This invention discloses a method for predicting protein structure based on phased multi-strategy copy exchange. In the frame of differential evolution (DE), generate initial conformation populations with a variety of folding types in each temperature layer; to each temperature layer, divide a conformation search into two phases according to iterations; randomly select a conformation as a target unity from the populations in the first phase; divide the populations into two parts according to energy in the second phase; randomly select one unity as the target unity from first 50% of populations with low energy; randomly select three conformation unities different from the target unity to generate a testing unity through variation, cross and section combination strategy; judge whether to accept the testing unity according to the energy of the conformation so as to perform copy exchange to corresponding unities of adjacent temperature layers; and, under the guidance of the phased strategy and the supplement of copy exchange strategy, acquire a series of metastable conformation through updating continuously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
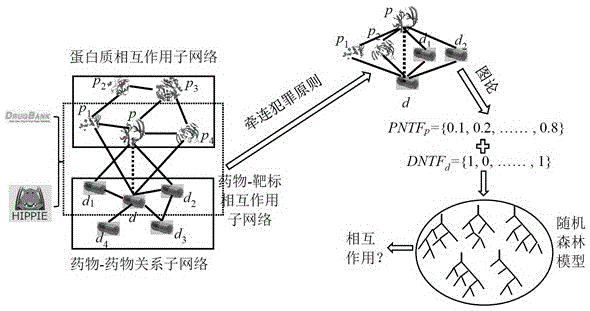
Implicated crime principle and network topological structural feature based recognition method for drug-target interaction
ActiveCN105117618AGood predictionReasonable representationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALPathology study
The present invention discloses an implicated crime principle and network topological structural feature based recognition method for drug-target interaction. The method comprises: firstly, according to human protein-protein interaction data and drug-target interaction data, constructing a drug-target interaction group network which comprises a protein-protein interaction sub-network, a drug-target interaction sub-network and a drug-drug relationship sub-network; according to information of a protein primary structure descriptor, a fingerprint feature of drug molecules and the reliability of interaction, weighting nodes and edges in the network; proposing a new network topological structural feature for characterizing a drug-target interaction pair based on an implicated crime principle and a graph theory; and finally, constructing a model by using a random forest algorithm and predicting a potential drug-target interaction effect in a proteome scale. The method does not require information of three-dimensional structures and the like of protein and drug molecules, is simpler, quicker and more accurate, and has high potential for application to the fields of new drug research and development, pathological study and the like.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +2
Fast computational methods for predicting protein structure from primary amino acid sequence
InactiveUS20080270094A1Analogue computers for chemical processesSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy minimizationProtein structure
The present invention provides a method utilizing primary amino acid sequence of a protein, energy minimization, molecular dynamics and protein vibrational modes to predict three-dimensional structure of a protein. The present invention also determines possible intermediates in the protein folding pathway. The present invention has important applications to the design of novel drugs as well as protein engineering. The present invention predicts the three-dimensional structure of a protein independent of size of the protein, overcoming a significant limitation in the prior art.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Recombinant large-tooth flounder interleukin-6 protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101805404AHigh purityHigh yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliInterleukin 6
The invention discloses a recombinant large-tooth flounder interleukin-6 protein and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: according to a DNA sequence of the large-tooth flounder interleukin-6 protein of paralichthys olivaceus, designing a primer and extracting the total RNA of the kidney fresh by a TRIzol Reagent method, carrying out RT-PCR augmentation, connecting a PCR product and a Pmd19T vector to form a recombinant plasmid, connecting with an expression vector Pet-32a(+) by double digestion, obtaining the recombinant plasmid and transforming the recombinant plasmid into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3); and realizing the soluble expression of the recombinant protein. As the expression process does not generate an inclusion body, the fusion protein for expressing the plasmid has histidine tags, thus being convenient to identification and purification of samples, avoiding the denaturation and renaturation of the samples, having simple operation, reducing the manufacturing cost, and more importantly, having no damage to a protein structure; and the invention has good purity of recombinant protein, high yield and difficult degradation, is applicable to industrial production and lays the foundation of studying the large-tooth flounder interleukin-6 protein of the paralichthys olivaceus.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Polynucleotide encoding a mouse choline transporter
InactiveUS7338799B2Enhances cholinergic signalingEnhanced signalBiocideBacteriaNucleic acid detectionNucleotide
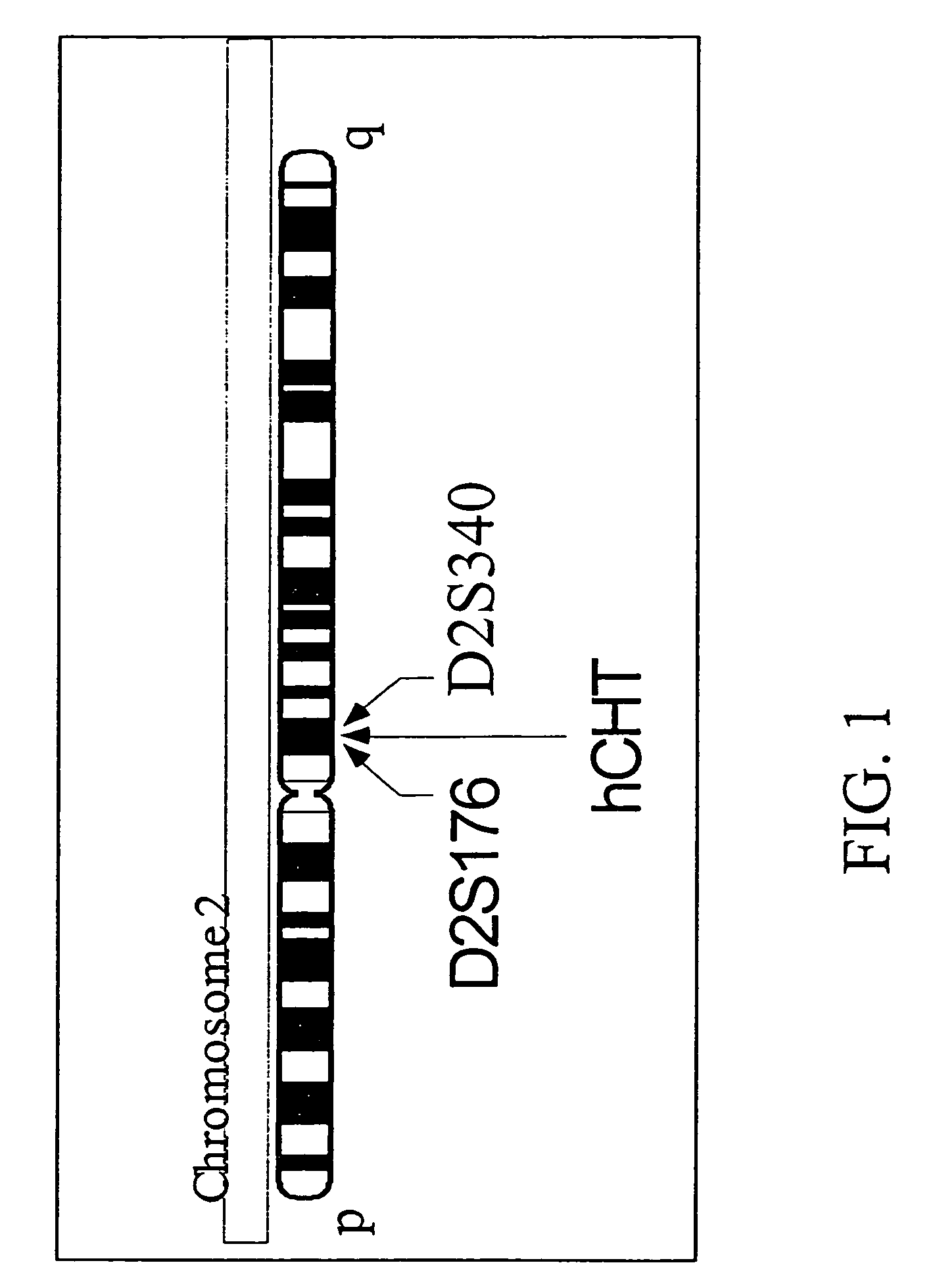
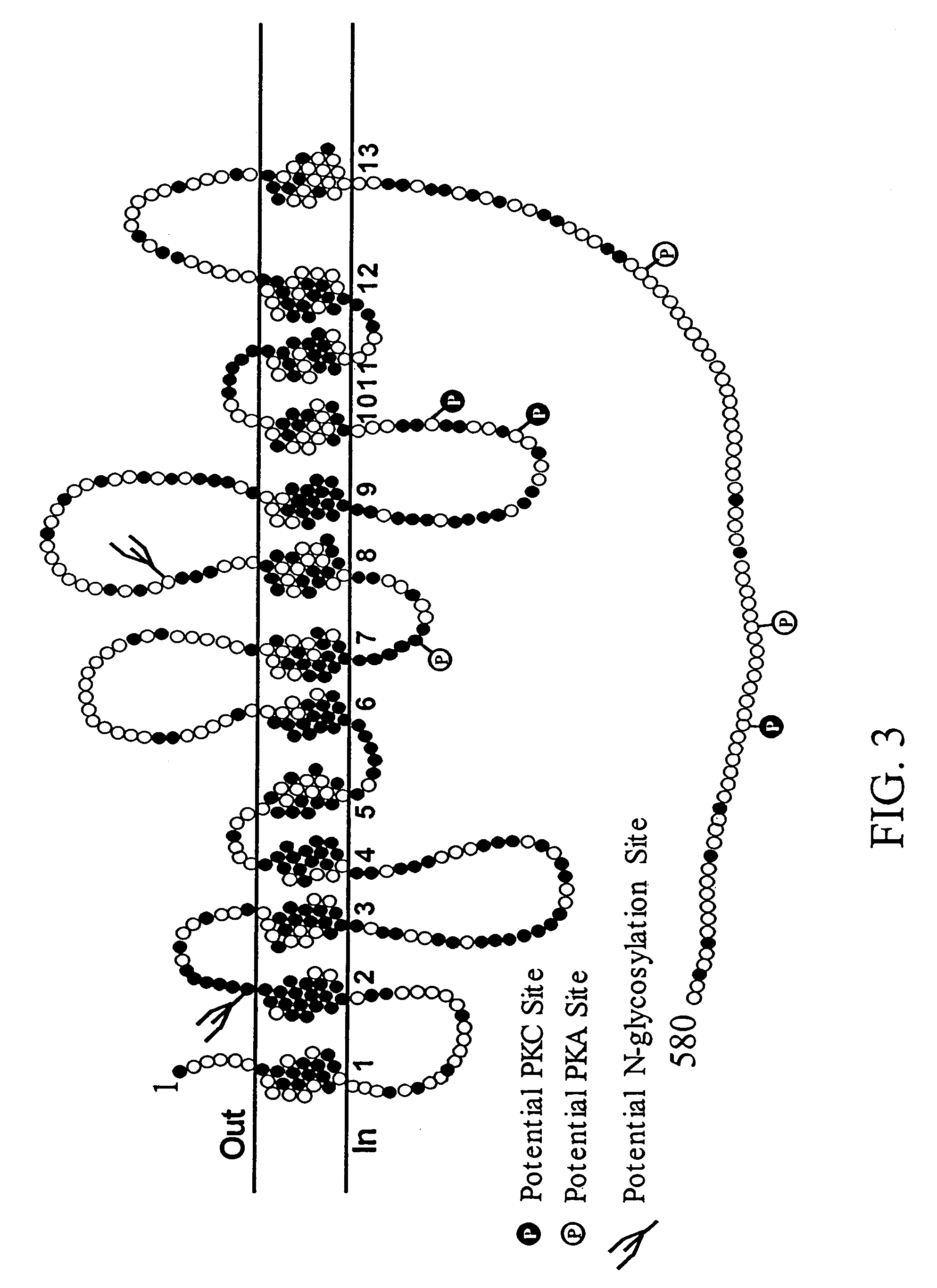
Human high affinity choline transporter (CHT) cDNA was cloned from spinal cord and the primary structure and chromosomal localization have been determined. Mouse high affinity CHT cDNA was also cloned and characterized. An isolated polynucleotide, an isolated polypeptide, a recombinant host cell, a recombinant vector, a purified protein, an antibody, a nucleic acid detection kit, a method for screening cholinergic therapeutics, a method of treating a patient, a method of gene therapy and transgenic CHT mice are discussed.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Proteolytically resistant hydrogen bond surrogate helices
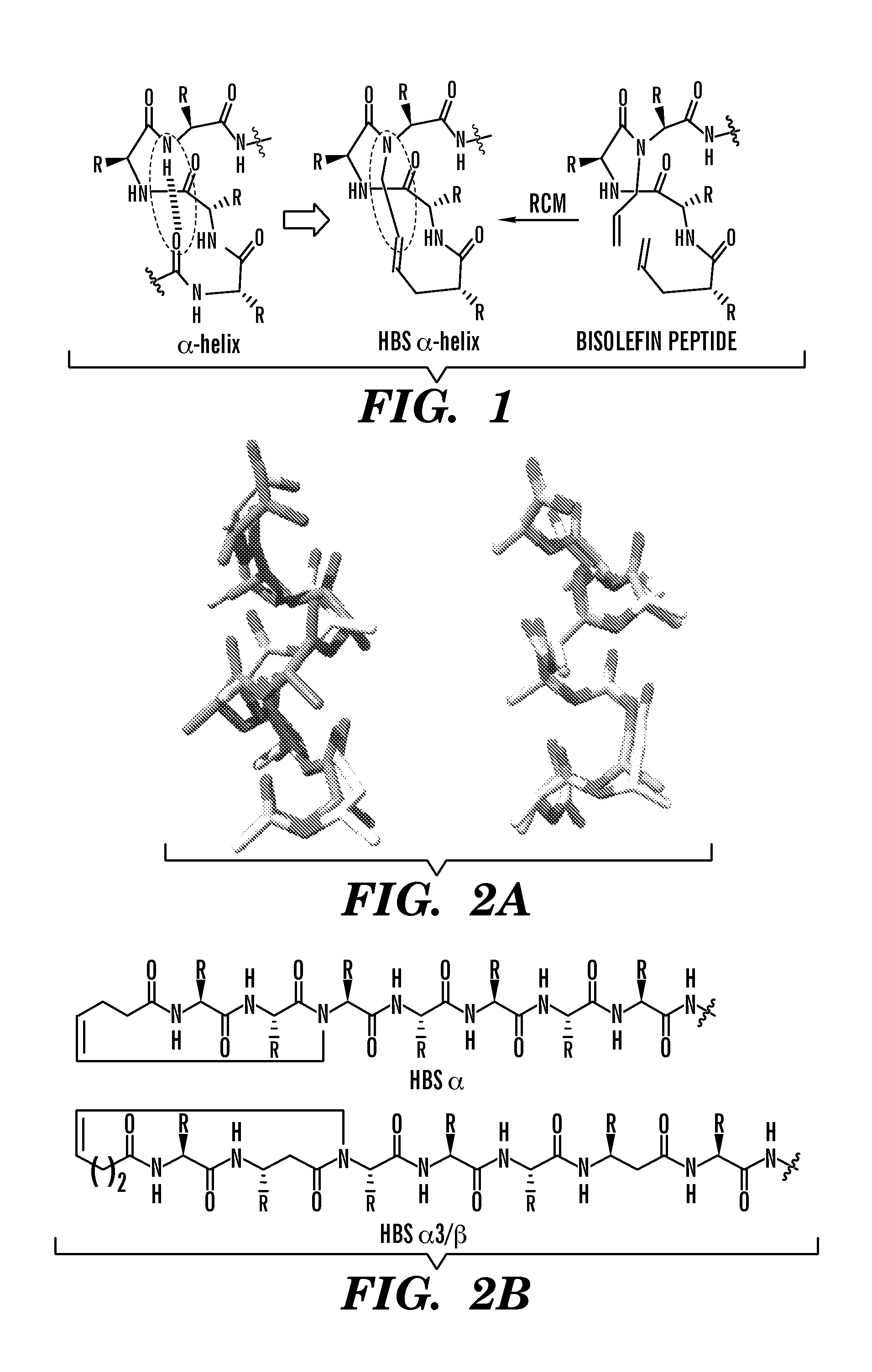
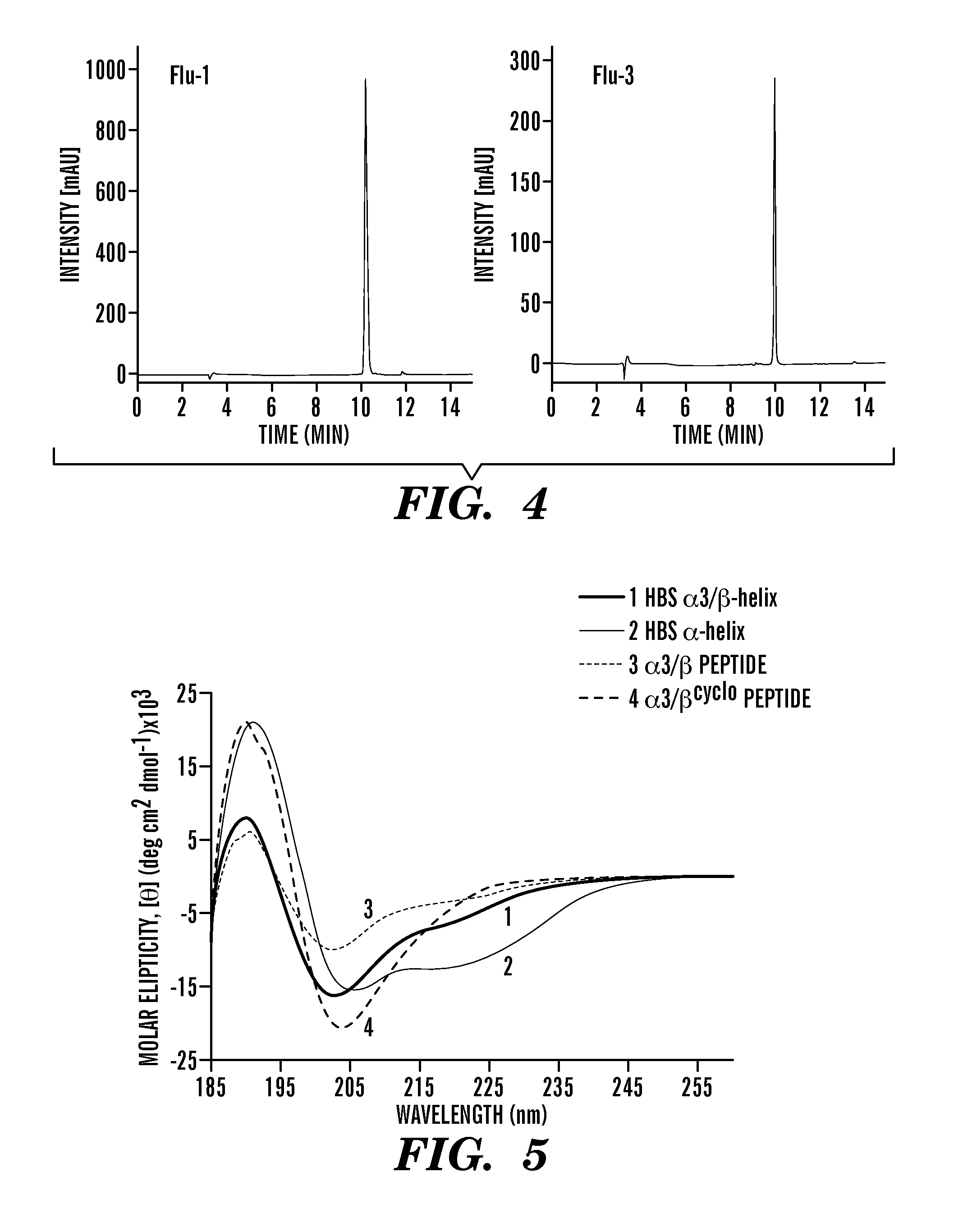
ActiveUS20130210144A1High affinityStrong specificityPeptide sourcesTissue cultureProtein secondary structureProteolysis
The present invention relates to peptidomimetics having a stable, internally constrained protein secondary structure, where the peptidomimetics contain a hydrogen bond surrogate in the internal constraint, and at least one beta amino acid. Methods for promoting cell death using peptidomimetics that inhibit p53 / hDM2 are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Protein medicine-carrying nano particle synthesis method
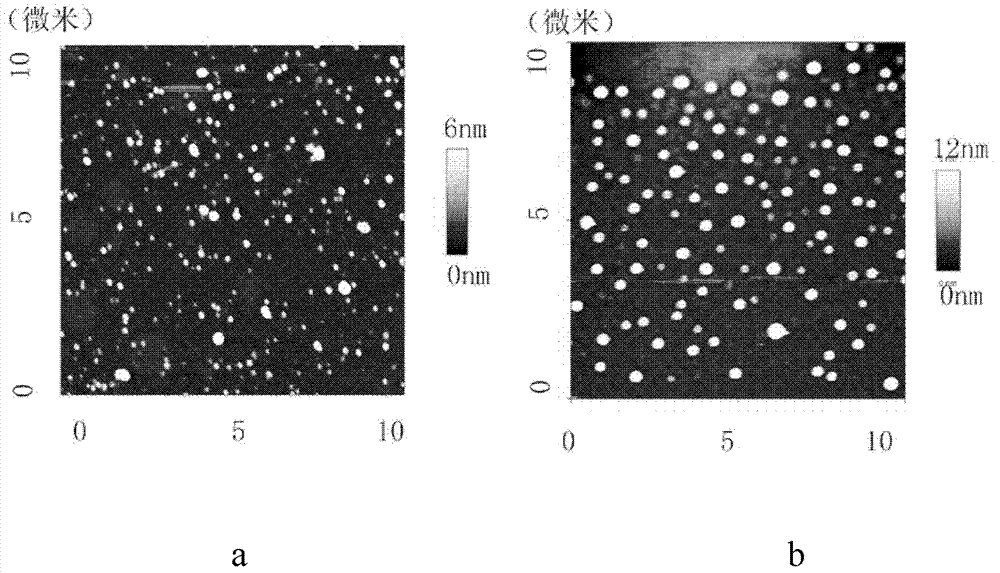
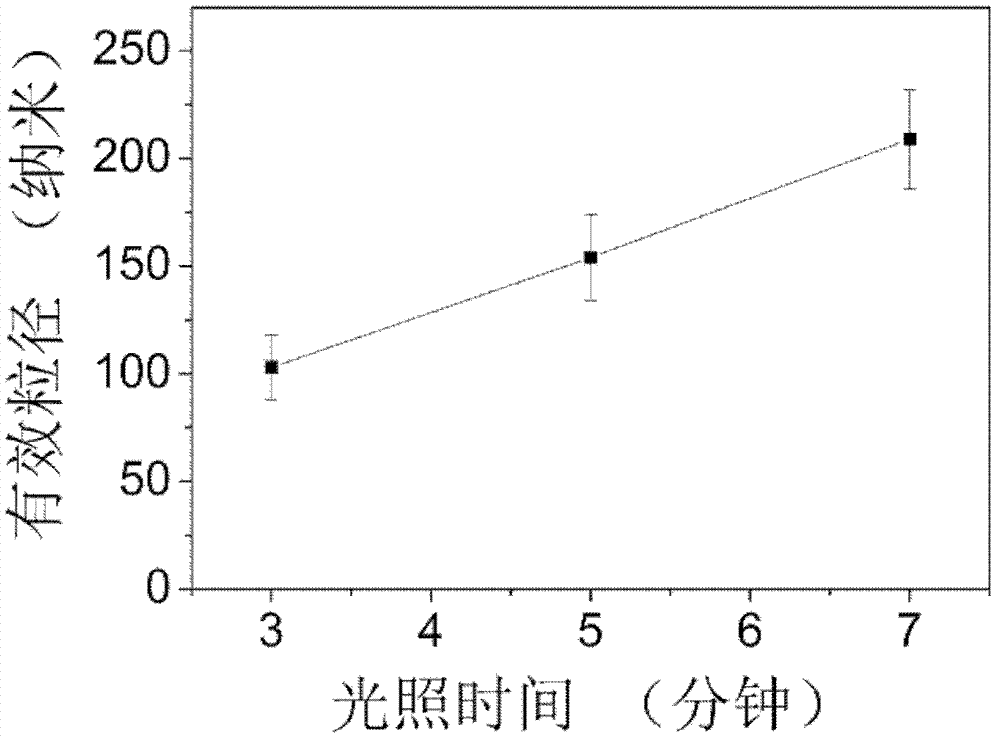
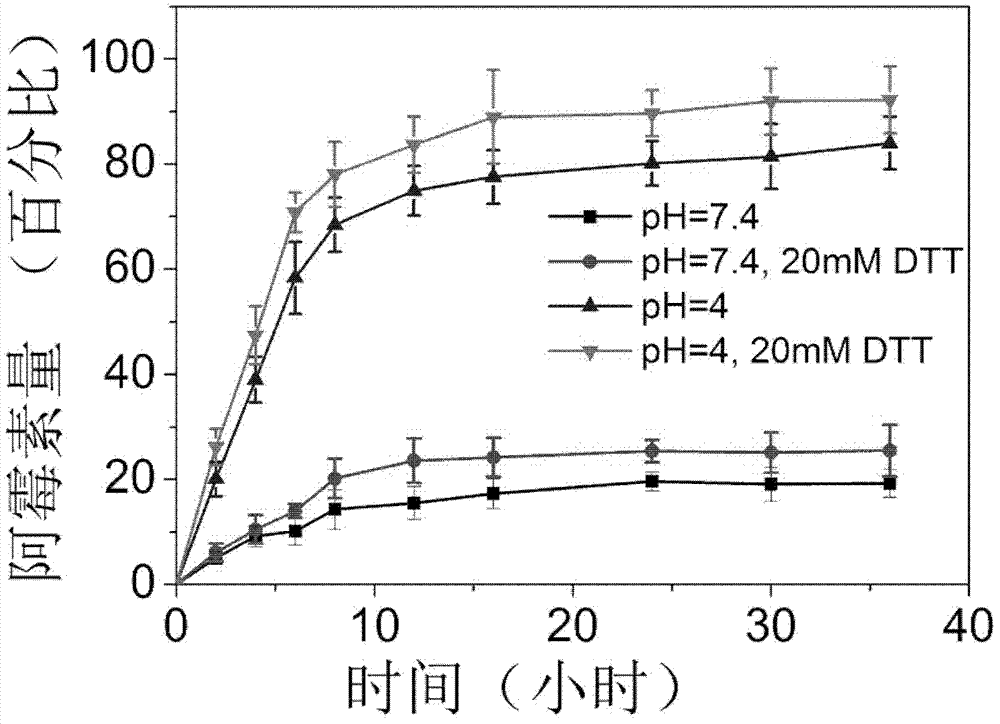
InactiveCN102949346AGuaranteed stabilityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryZeta potentialSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a protein medicine-carrying nano particle synthesis method. Without auxiliaries such as adding denaturant, reductant or crosslinking agent, synthesis and medicine carrying of nano particles are synchronously completed. The protein medicine-carrying nano particle synthesis method includes irradiating mixed solution of protein and hydrophobic medicines for 3-10 minutes by ultraviolet light, so that disulfide bonds in the protein are opened, variation of circular dichroism spectrum of the protein secondary structure is within 10%, a small amount of exposed protein hydrophobic base group and the hydrophobic medicines are gathered, medicine-carrying nano particles are formed at one step, protein contains tryptophan and disulfide bonds, absolute value of zeta potential on the surface of the protein is not smaller than 15mV, and the protein concentration in the mixed solution ranges from 0.5mg / ml to 5mg / ml. The synthesized nano particles are controllable in size, uniform and good in stability, and medicine carrying quantity can reach 20% maximally.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Application of group of cobra neurotoxin molecules having high affinity with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors for rapid acting on pain easing
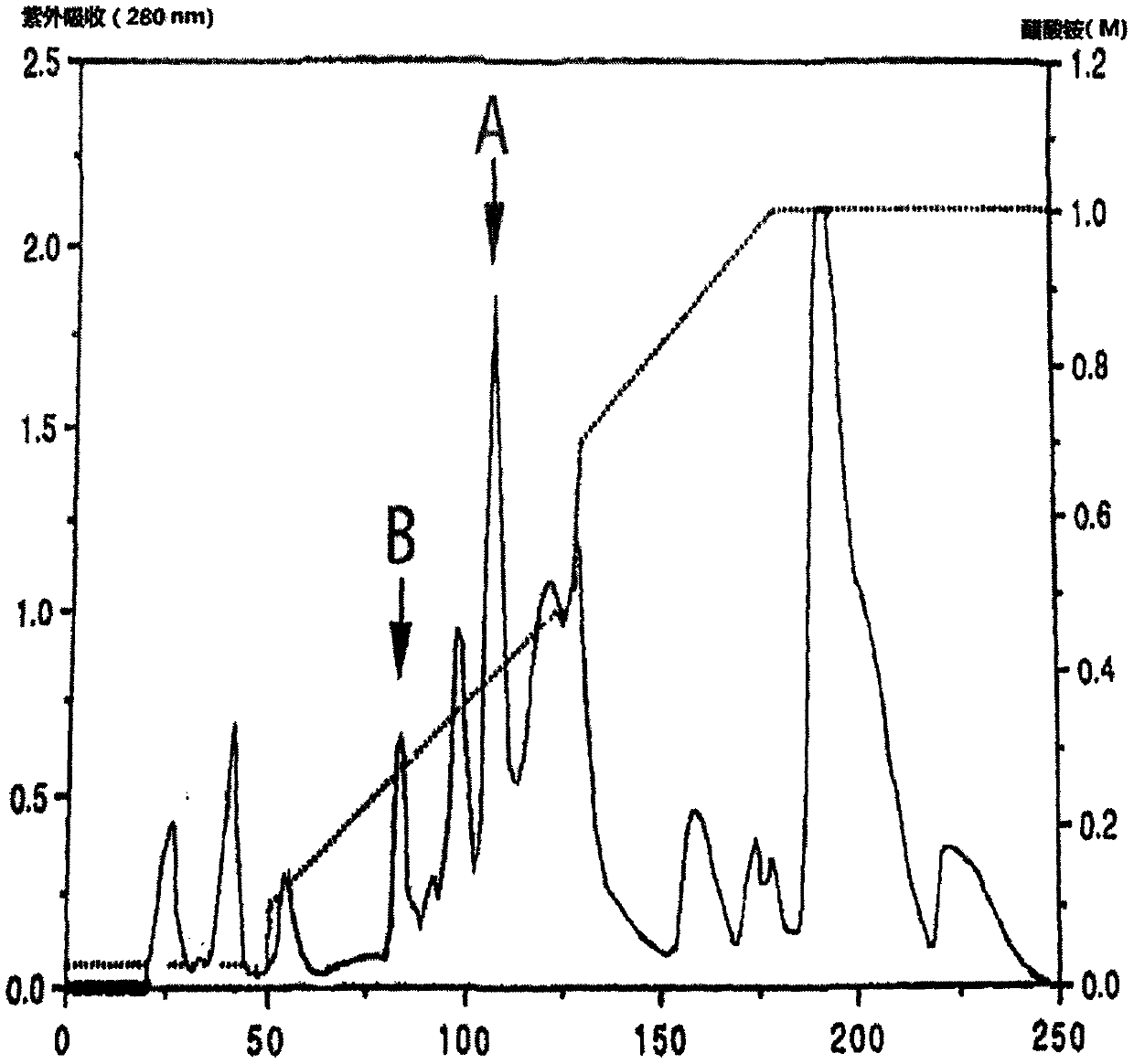
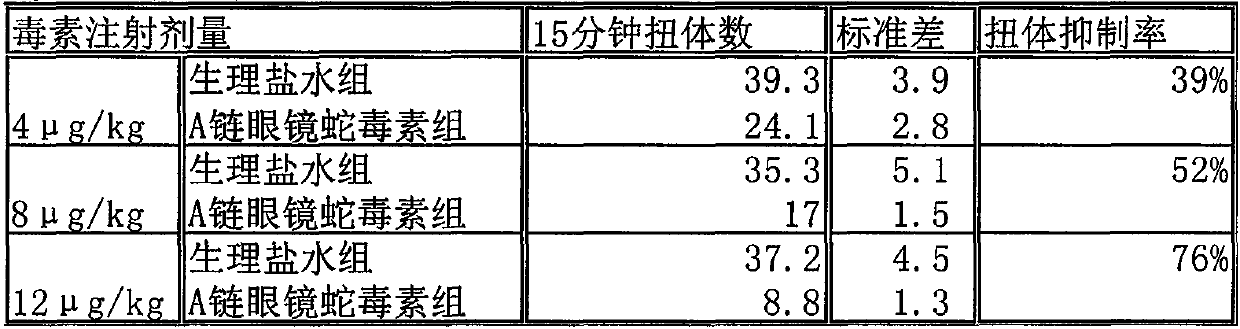
The cobra neurotoxin is capable of binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors after nerve synapses to block neuronal caudal ion flow to realize analgesic effect, however, the product on the market takes 2 hours to be effective and the curative effect is unstable, which cannot meet clinical requirement. The neurotoxins need to pass a blood cerebral barrier in the brain to play an analgesic effect, and the product on the market has no clear components, including various molecular weight proteins, so the speed for permeating the blood cerebral barrier is slow; and at the same time, affinity with the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is also inconsistent. The application screens a group of neurotoxin molecular monomers having high affinity with the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, can quickly pass the blood cerebral barrier, and has analgesic effect and stable therapeutic effect in 30 minutes. The neurotoxin molecular monomer overcomes the defects that a mixture cannot specify which neurotoxin is present, the protein primary structure is not existed, the quality cannot be precisely controlled; according to the invention, the quality is controlled, clinical safety and effectiveness are better guaranteed.
Owner:祁展楷
Novel apoptosis test regent and related kit
ActiveCN101665537AEfficient detectionSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliBio engineering
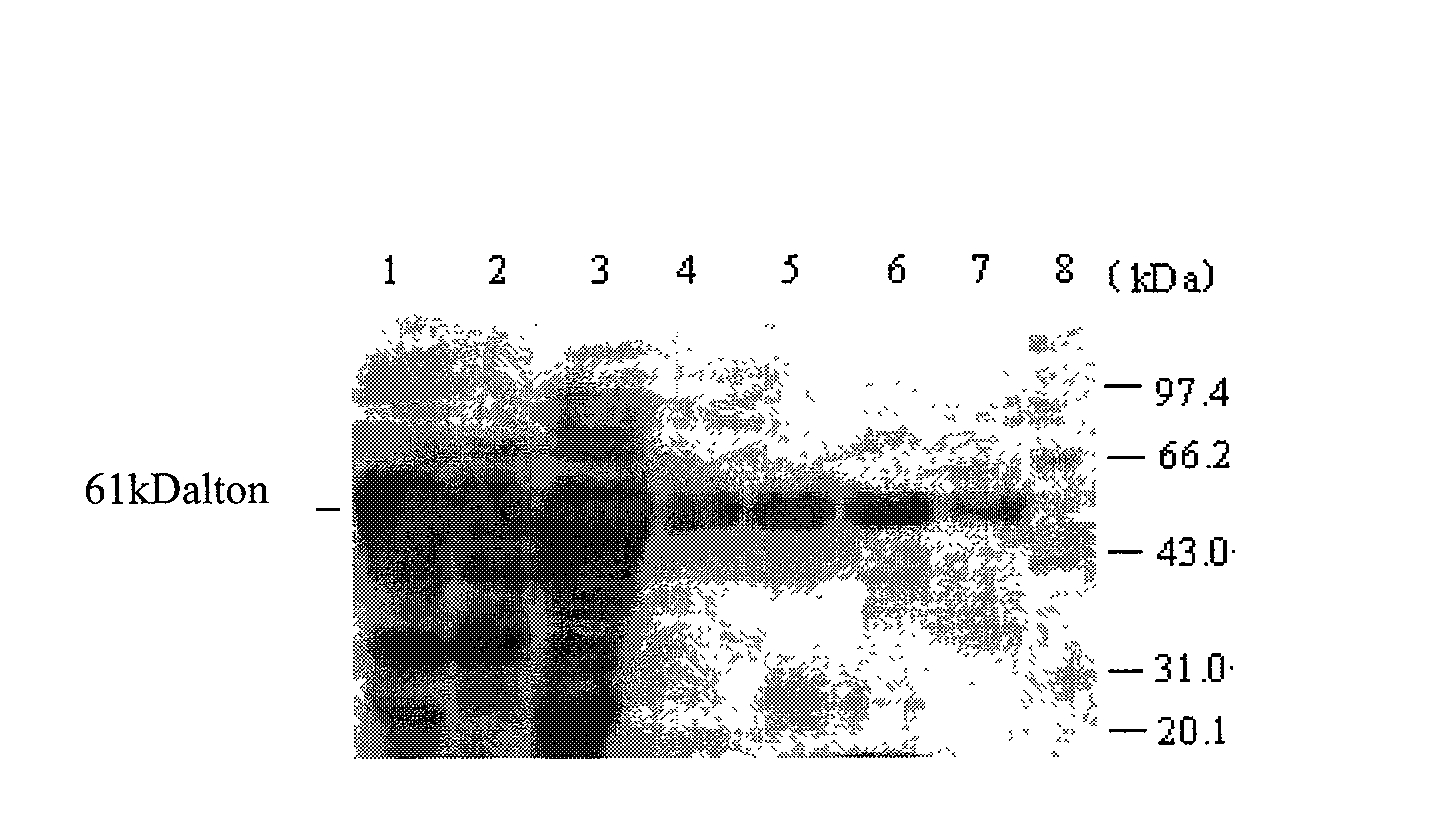
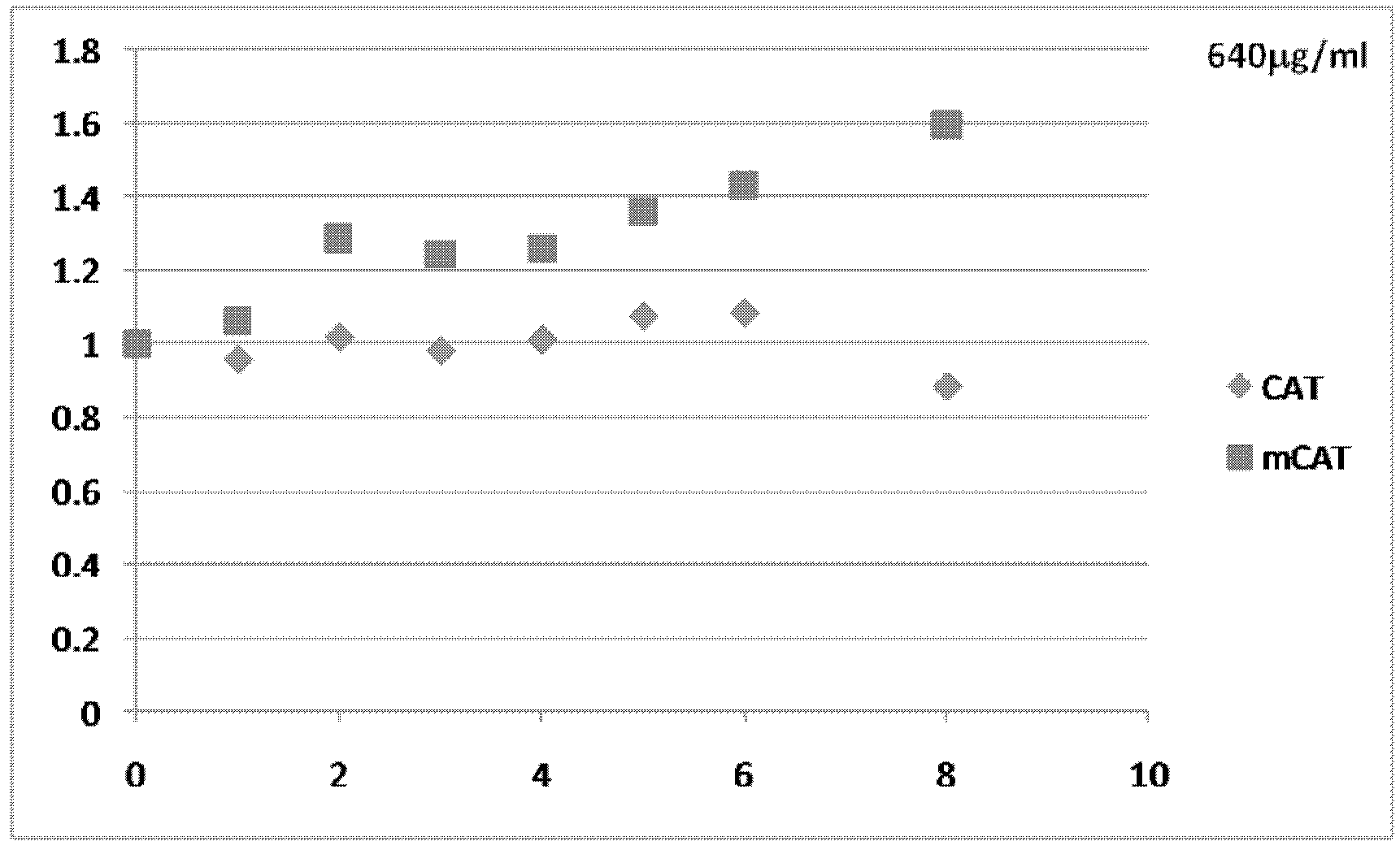
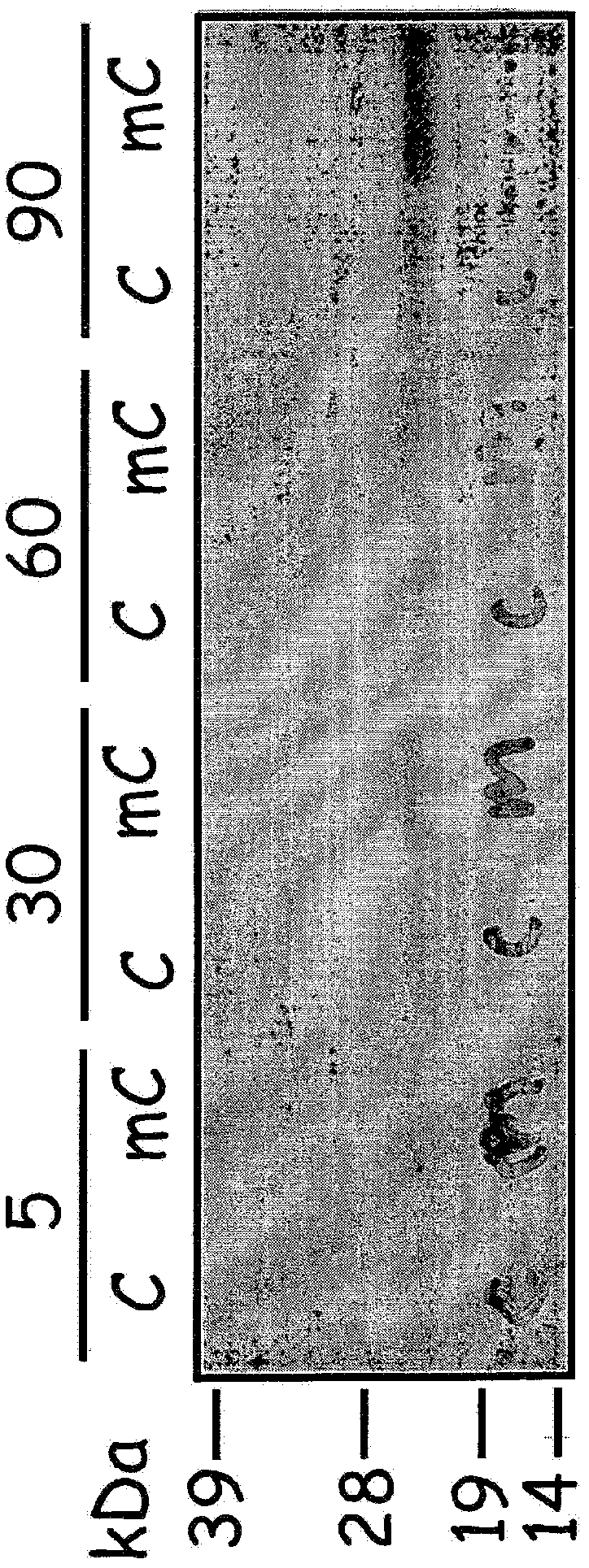
The invention relates to the development of a novel apoptosis test regent and a related kit. On the basis of modern biology engineering technology, glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and human annexin V are coupled to form a novel recombinant fusion protein GPPAN-V, and the primary structure diagram of the protein is shown as attached diagram 1. Efficient expression product GPPAN-V recombinant fusion protein after being induced by colibacillus host cell containing a GPPAN-V recombinant gene expression vector can exist in a soluble form, and GPPAN-V recombinant fusion protein with higher purity can be prepared by affinity chromatography purification. After being chemically coupled, the GPPAN-V recombinant fusion protein and the fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) can form a novel apoptosis testregent FITC-GPPAN-V for testing apoptosis. The novel apoptosis test kit formed by taking FITC-GPPAN-V as the core has the advantages of economy, sensitivity and efficiency.
Owner:井健
Stabilization method for biological samples by combination of heating and chemical fixation
ActiveUS20120122150A1Efficient heatingReduce acquisition timePreparing sample for investigationArtificial cell constructsPost translationalProtein phosphorylation
The present invention provides methods for stabilizing a biological sample for analysis. The invention more particularly provides methods combining heat treatment and chemical fixation of biological samples in order to maintain protein primary structure and post-translational modifications, such as protein phosphorylations.
Owner:DENATOR +1
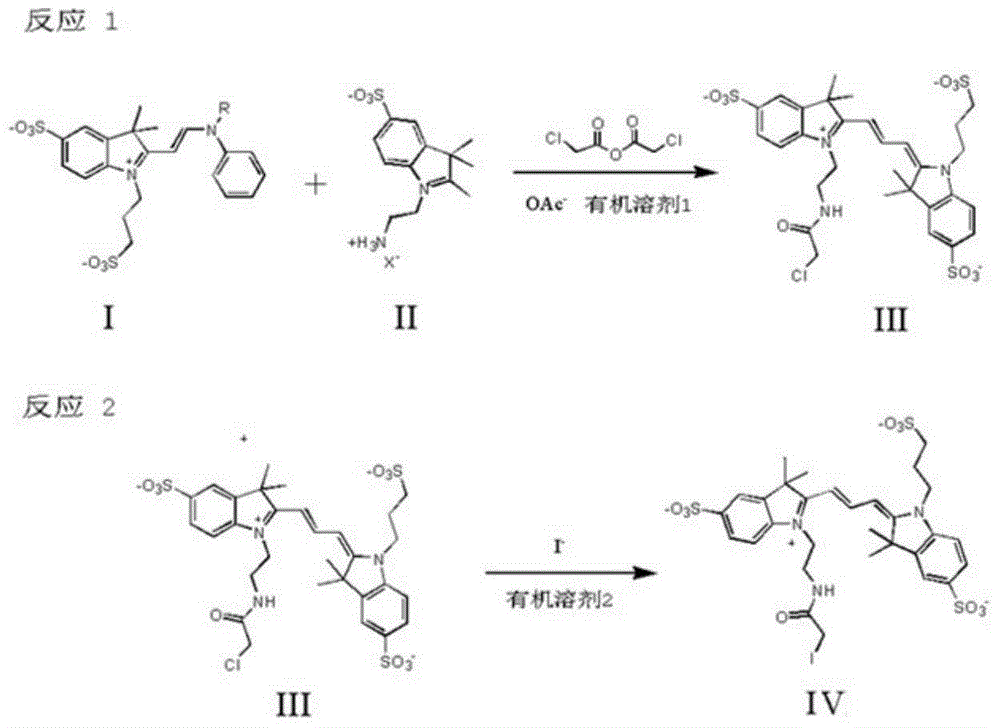
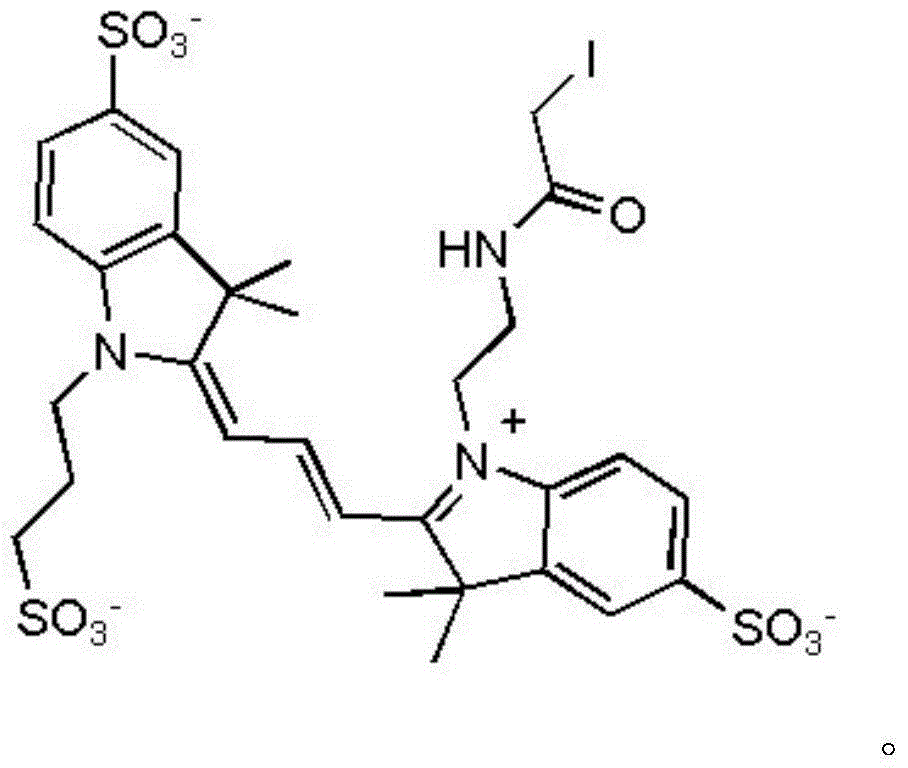
Trimethyl cyanine fluorescence probe used for protein labeling and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN103952143AImprove rigidityLittle flexibilityMethine/polymethine dyesPeptide preparation methodsSolubilitySynthesis methods
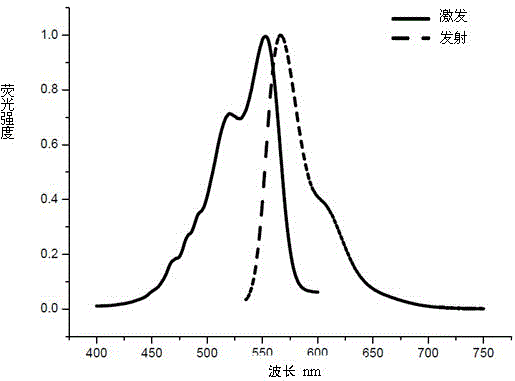
The invention relates to a new fluorescence probe used for protein labeling and a synthetic method thereof. The compound is prepared by the condensation of two water soluble indole compounds, by reaction of an iodoacetamide group of the compounds and mercapto groups of proteins, fixed-point fluorescent labeling of the proteins can be realized. The compound has the advantages of good water solubility, high molar absorptivity, longer excitation wavelengths, easy synthesis, mild protein labeling conditions, and the like. The probe can be used for fixed-point fluorescent labeling of the proteins, and has a great help for the study on protein structure, function and dynamics characteristics. Excitation emission wavelength of the probe is in the range of 500-600nm, the probe has a short linking group, can be used for more accurate description on the protein structure, dynamics characteristics and biological functions.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-2 protein and production method thereof
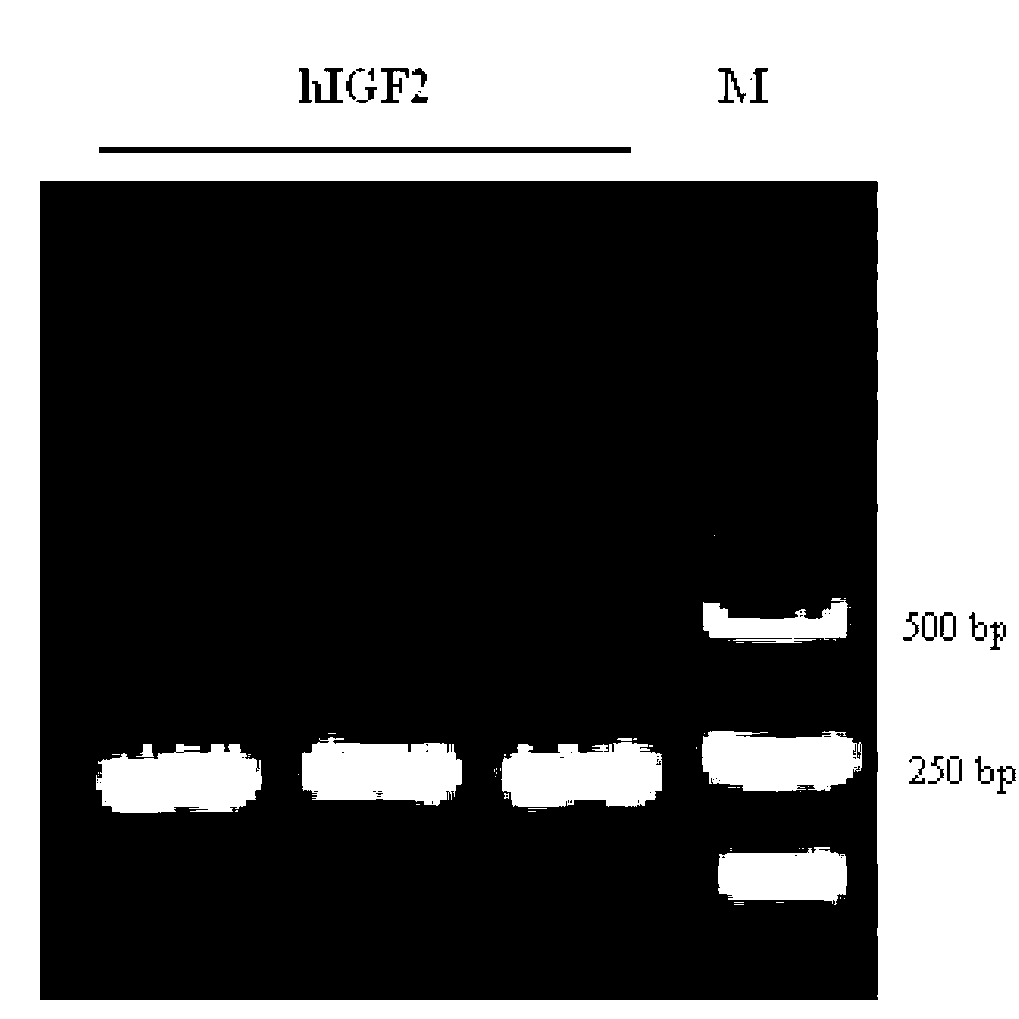
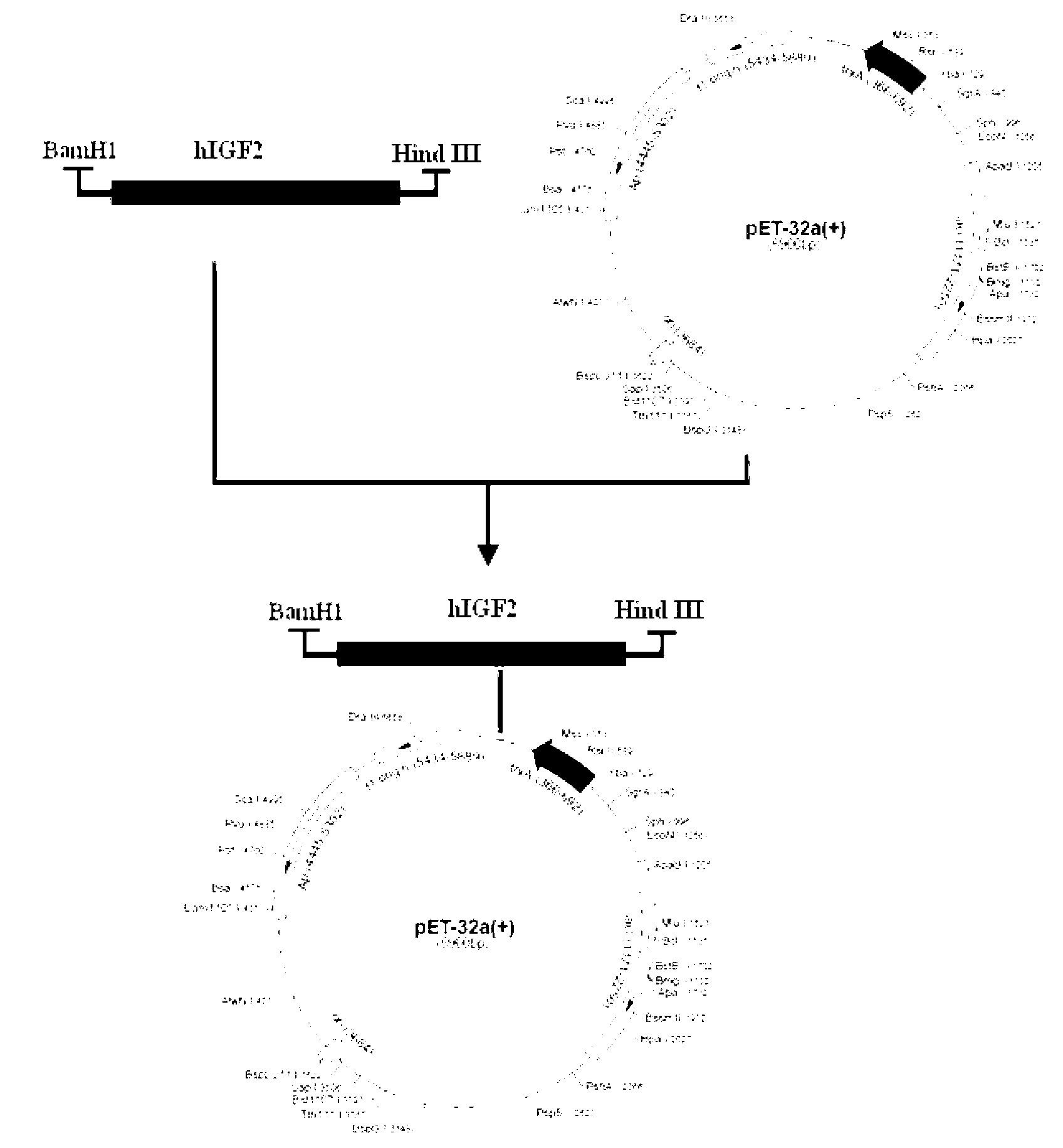
InactiveCN102936602AOptimizing expression conditionsHigh purityInsulin-like growth factorsVector-based foreign material introductionInsulin-like growth factorEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-2 (hIGF2) protein and production method thereof. An expression host is BL21 (DE3), and a vector is pET32-a(+). The method comprises the steps that: hIGF2 gene is cloned; a prokaryotic expression vector is constructed; expression of soluble Trx-hIGF2 fusion protein with an N terminal with a His*6 mark is carried out; Trx-hIGF2 fusion protein purification is carried out; and enterokinase with the His*6 mark is used for carrying out enzyme digestion upon the Trx-hIGF2 protein, such that high-purity hIGF2 is obtained. According to the invention, BL21 (DE3) and pET32-a(+) are adopted for a first time for realizing hIGF2 high-efficiency soluble fusion expression; His*6 mark and enterokinase cutting technologies are adopted, such that the preparation of a recombinant hIGF2 completely same with hIGF2 on a protein primary structure is realized; and an expression product has bioactivity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
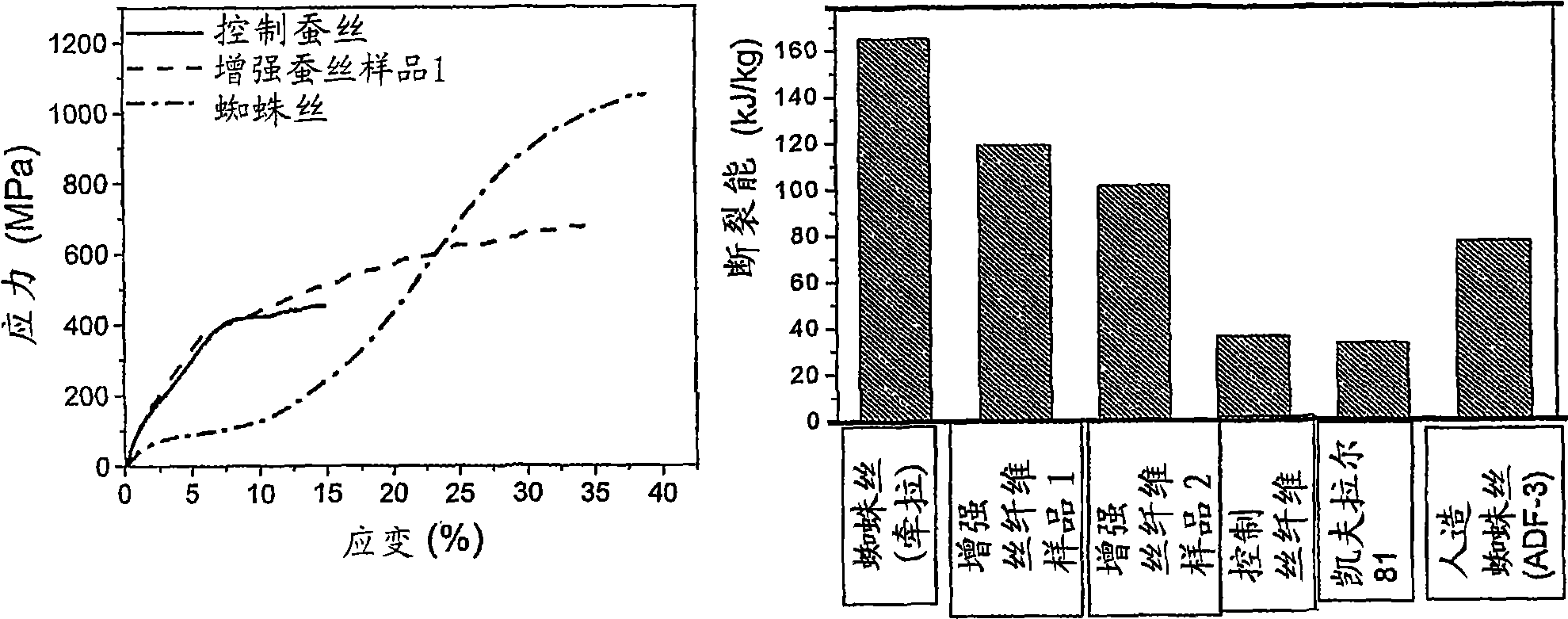
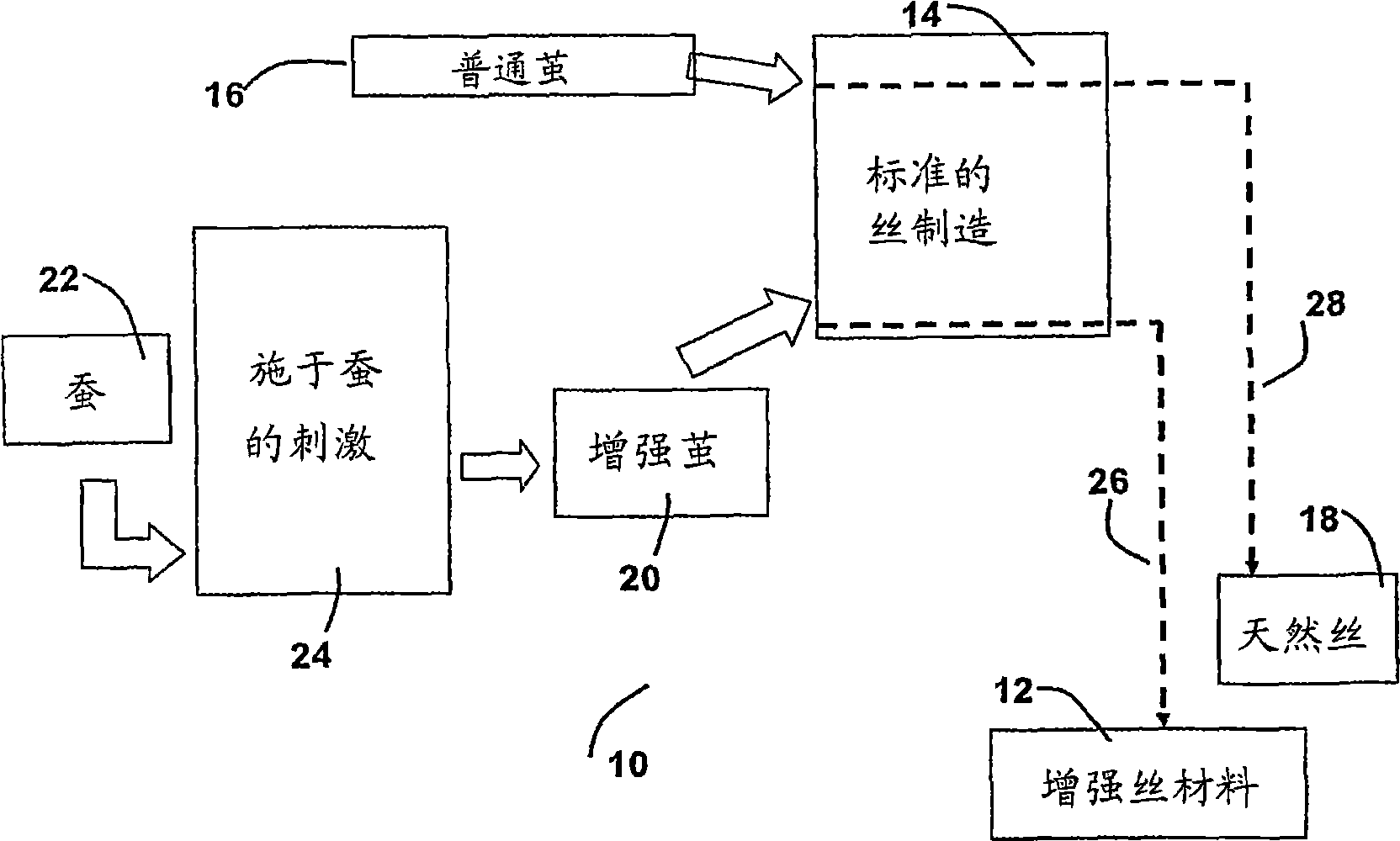
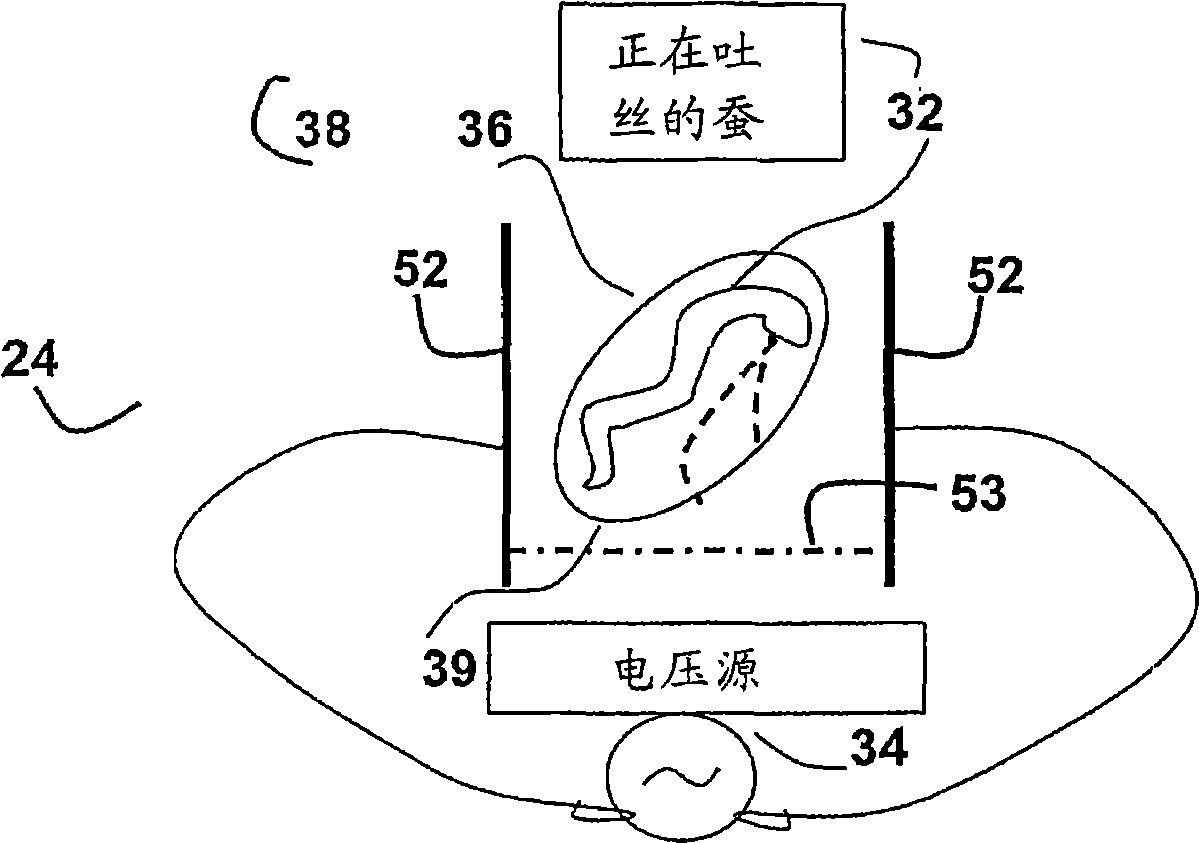
Enhanced silk protein material having improved mechanical performance and method of forming the same.
The invention provides an enhanced silk fiber rivaling spider silk in mechanical performance, in combination with a very low-cost method for producing it from the usual silkworms. The method provides for the simple application of an electric field which results in an enhancement of over 40% in the strength, and of 200% in the breaking energy with respect to ordinary silkworm silk. The critical elasticity is enhanced to the level of the dragline spider silk. The provided enhanced silk protein material has the same protein primary structure, fiber diameter and length of the customary silk. The method of formation offers the following advantages in comparison to other methods available in the prior art. Industrial scale production can be readily and cost-effectively achieved, given the wide-range availability of silkworms. The provided method relies largely on the present standard production processes of silkworm silk, and hence a low level of investment is required. Since no additional chemicals are required, the provided method is environmentally friendly.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Brain tissue membrane protein extraction method
InactiveCN108383901AEfficient extractionSimple recipePeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesProtein structureReducing agent
The invention provides a brain tissue membrane protein extraction method, and relates to the technical field of biology. A used scale removal agent is very mild; in addition, the concentration is verylow; a reducing agent and a protein allosteric agent are not used; the protein structure and activity can be maintained. Membrane lipid surrounding the extracted protein is not completely lost; a tertiary structure of the protein can be effectively remained, so that the combination state of the protein with other protein can be stabilized. By using the extraction method provided by the invention,80 percent of membrane protein or more can be effectively dissolved. The formula of a used buffer solution system is simple; only conventional reagents and instrument equipment in a laboratory are needed; the result and the activity of the protein are not influenced at all by the used stain removal agent and the dosage; the extracted membrane protein can be used for biochemical tests with higherdifficulty in co-immunoprecipitation and the like and higher protein extraction requirements.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
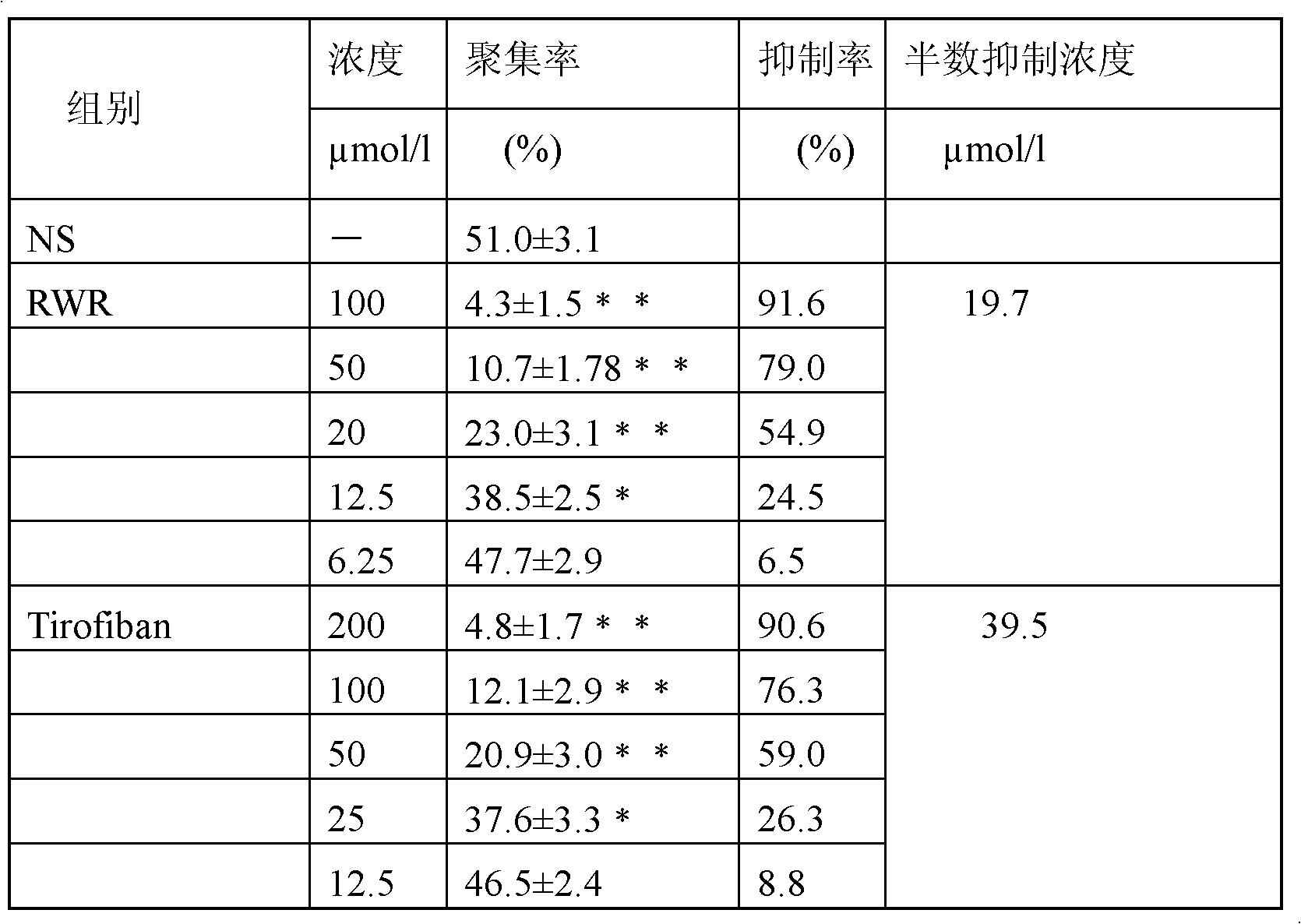
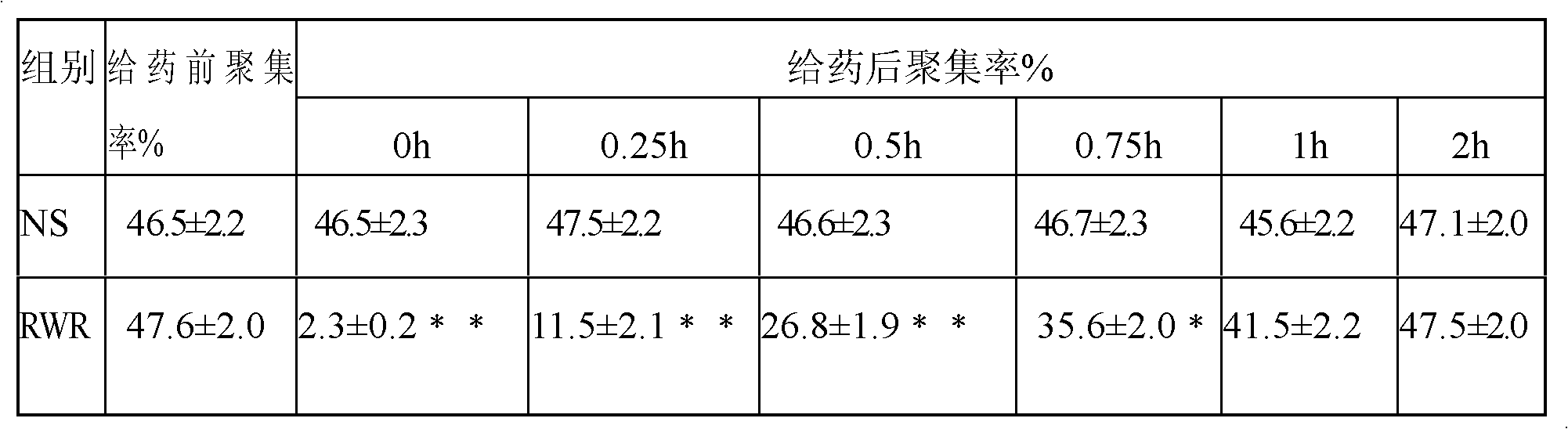
Antithrombotic medicine RWR for specifically identifying platelet alpha<IIb>beta3
InactiveCN102351948AHigh biological activityLittle side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSmall peptideArg-Gly-Asp
The invention provides a small molecular polypeptide for reforming RGD tripeptide. According to the characteristic that the RGD is specifically combined with alpha<IIb>beta3, a hydrophobic amino acid and a basic amino acid are added at the N end of the RGD, a hydrophobic amino acid W is added in the fourth site, a basic amino acid R is added in the fifth site, the small peptide sequence is Arg-Gly-Asp-Trp-Arg, the protein primary structure is RGDWR, the capability for specifically being combined with the alpha<IIb>beta3 can be improved, the immunogenicity can also be reduced by smaller molecular weight, and the defects of the existing antithrombotic preparations are overcome.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
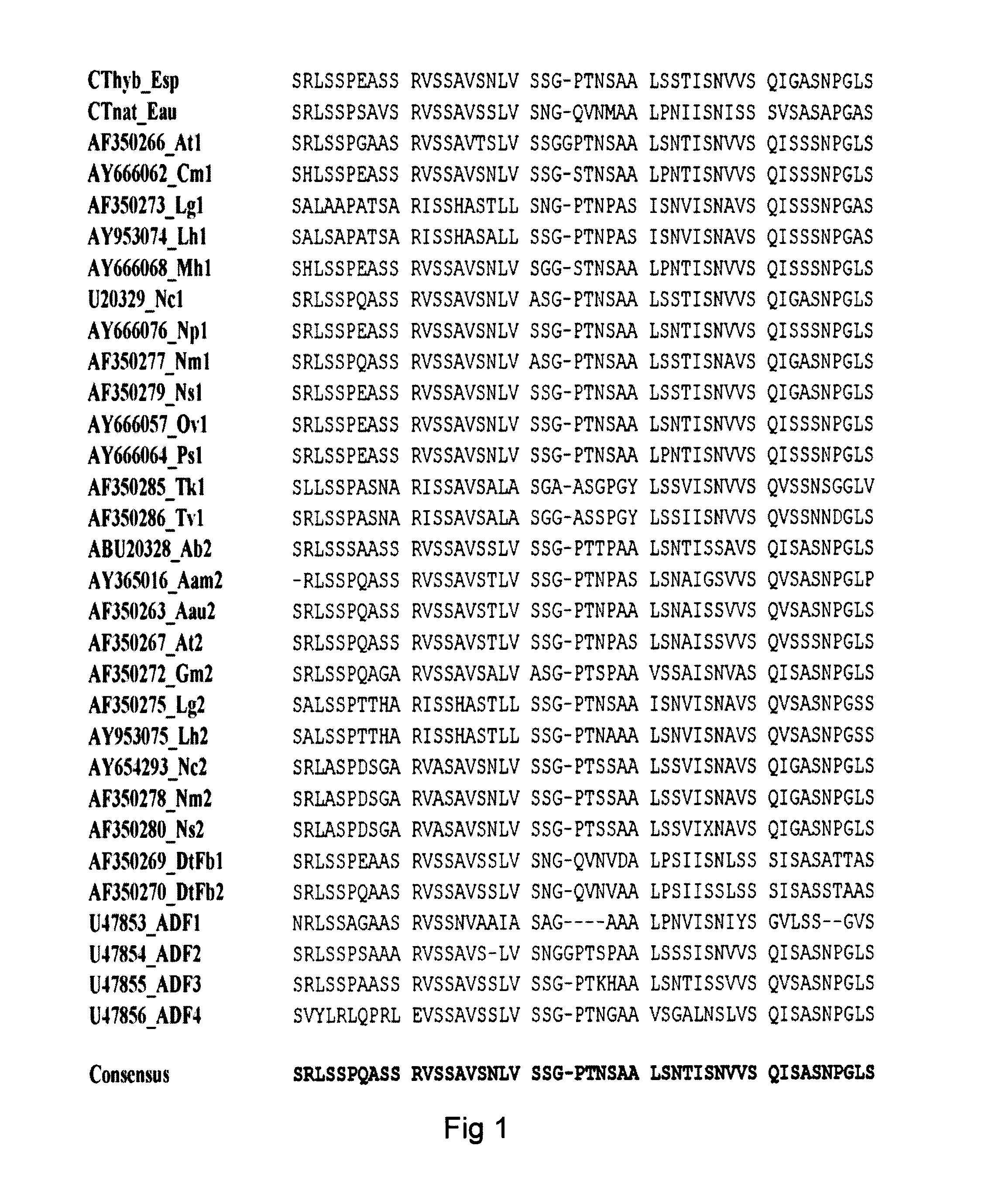
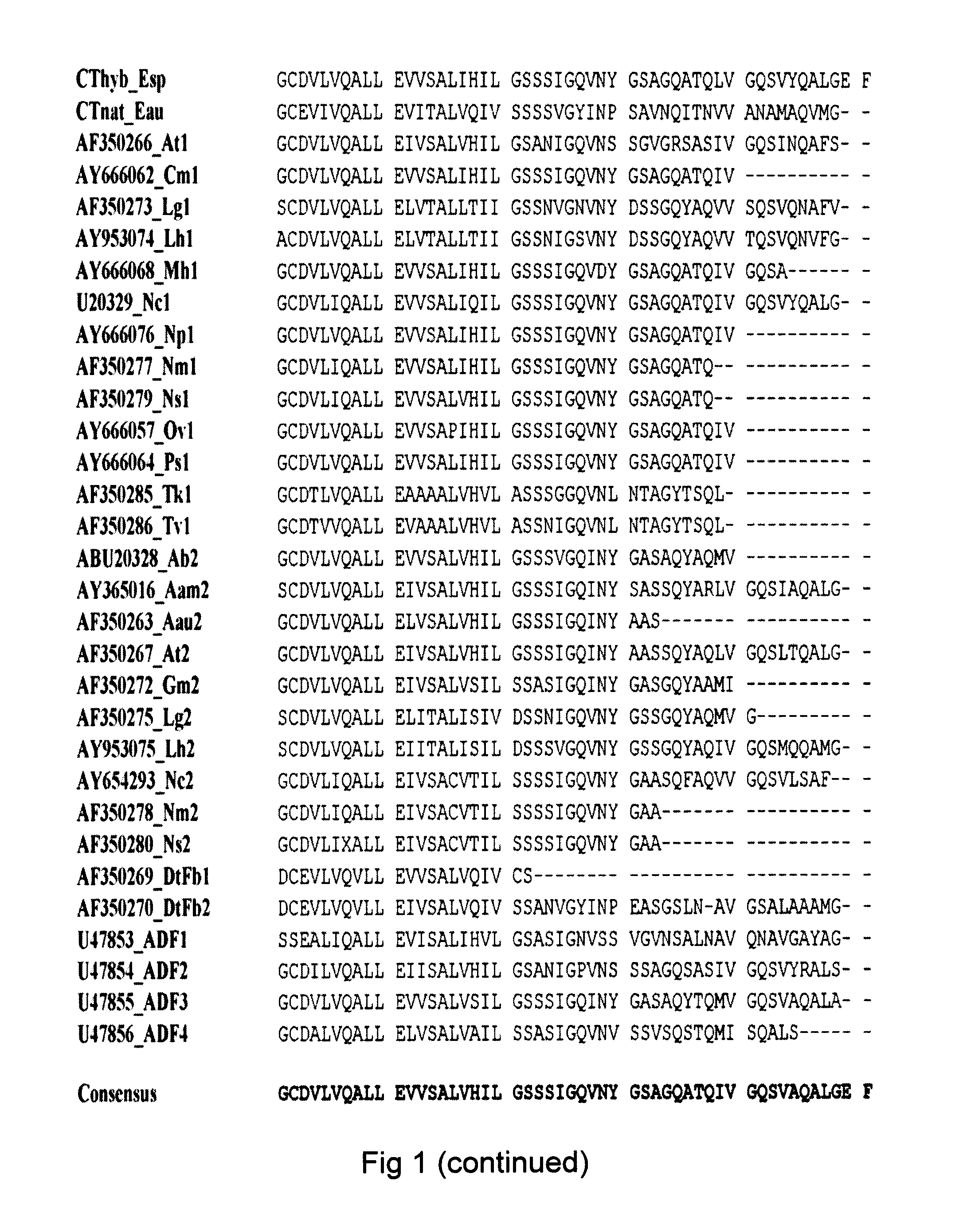
Spider silk fusion protein structures for binding to an organic target
ActiveUS9115204B2Promote regenerationStable structurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSpider ProteinsStructural unit
A protein structure capable of selective interaction with an organic target is provided. The protein structure is a polymer comprising as a repeating structural unit a recombinant fusion protein that is capable of selective interaction with the organic target. The fusion protein is comprising the moieties B, REP and CT, and optionally NT. B is a non-spidroin moiety of more than 30 amino acid residues, which provides the capacity of selective interaction with the organic target. REP is a moiety of from 70 to 300 amino acid residues and is derived from the repetitive fragment of a spider silk protein. CT is a moiety of from 70 to 120 amino acid residues and is derived from the C-terminal fragment of a spider silk protein. NT is an optional moiety of from 100 to 160 amino acid residues and is derived from the N-terminal fragment of a spider silk protein. The fusion protein and protein structure thereof is useful as an affinity medium and a cell scaffold material.
Owner:SPIBER TECHNOLOGIES AB
Modularly-assembled protein structure model
ActiveCN104882056AConducive to standardized manufacturingEasy to understandEducational modelsCrystallographySide chain
The invention discloses a modularly-assembled protein structure model which is formed by repeatedly connecting common modules (peptide planar modules) and amino acid feature modules ([alpha] carbon atoms and side chain modules) in sequence, and connecting an amino module and a carboxyl module at two ends, namely, the amino module-an amino acid feature module 1-a common module 1-an amino acid feature module 2-a common module 2...an amino acid feature module n-the carboxyl module. According to the modularly-assembled protein structure model provided by the invention, peptide planes and [alpha] carbon atoms are taken as basic structure modules; a module which can accurately display spatial configuration of a primary structure, a secondary structure, a tertiary structure, a quaternary structure and the like of protein is established; and standard production and manufacturing of the model, understanding of students, and application to scientific research are facilitated.
Owner:台州达辰药业有限公司
Methods and apparatus for predicting protein structure
InactiveUS20160210399A1Computation using non-denominational number representationSequence analysisChain structureProtein structure
The present invention relates to a method for predicting three-dimensional structure of a protein from its sequence. Three-dimensional structure may be determined by: (a) generating a multiple sequence alignment for a candidate protein having a known sequence; (b) identifying a covariance matrix between all pairs of sequence positions in the multiple sequence alignment; (c) inverting the covariance matrix and identifying predicted evolutionary constraints using a statistical model of the candidate protein; and (d) simulating folding of an extended chain structure of the candidate protein using the predicted constraints.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Stabilization method for biological samples by combination of heating and chemical fixation
ActiveUS8986947B2Efficient methodEfficient heatingPreparing sample for investigationArtificial cell constructsBiological pumpPost translational
The present invention provides methods for stabilizing a biological sample for analysis. The invention more particularly provides methods combining heat treatment and chemical fixation of biological samples in order to maintain protein primary structure and post-translational modifications, such as protein phosphorylations.
Owner:DENATOR +1
Method of analyzing change in primary structure of nucleic acid
InactiveCN101316936AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyReceptor for activated C kinase 1Protein primary structure
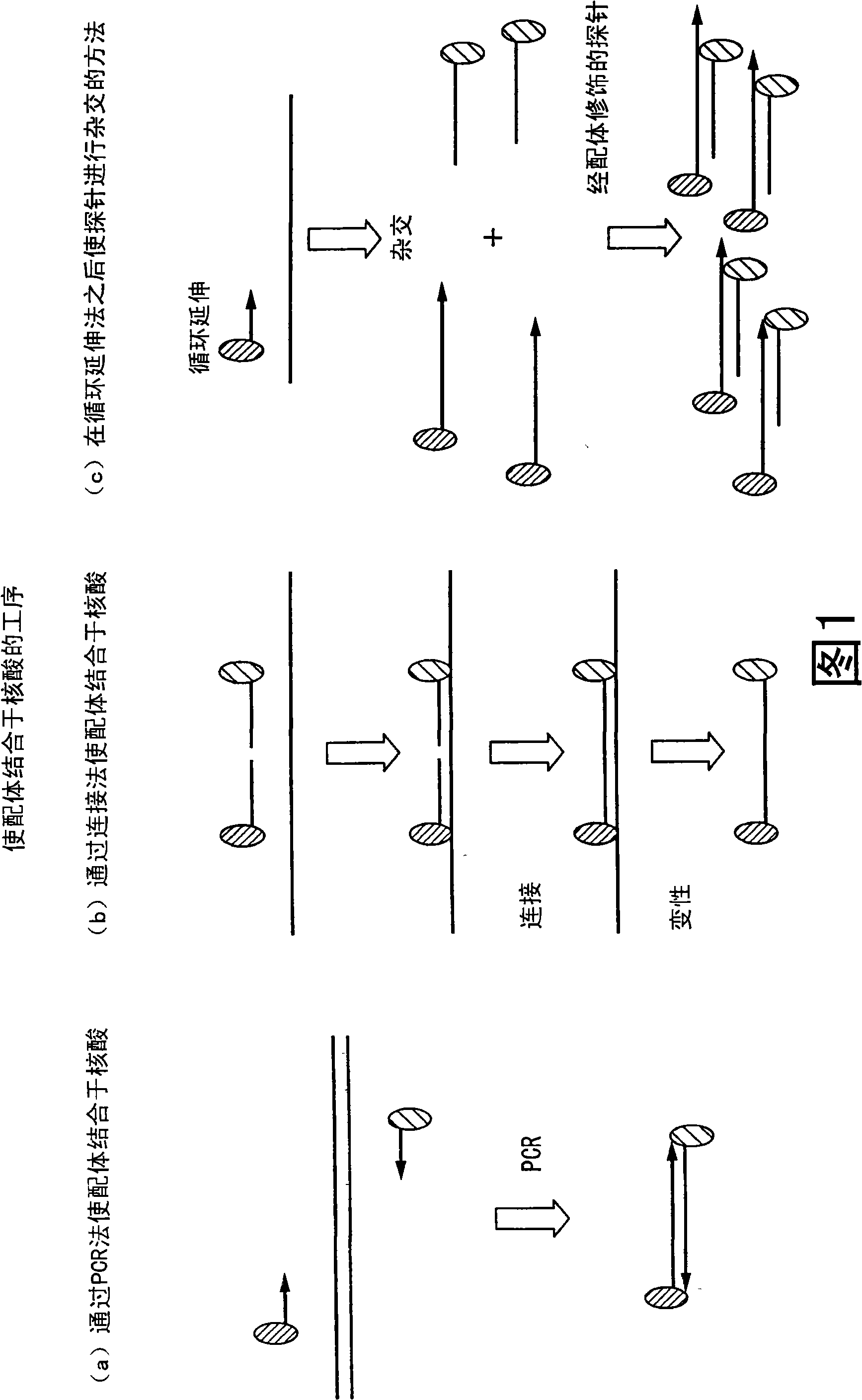
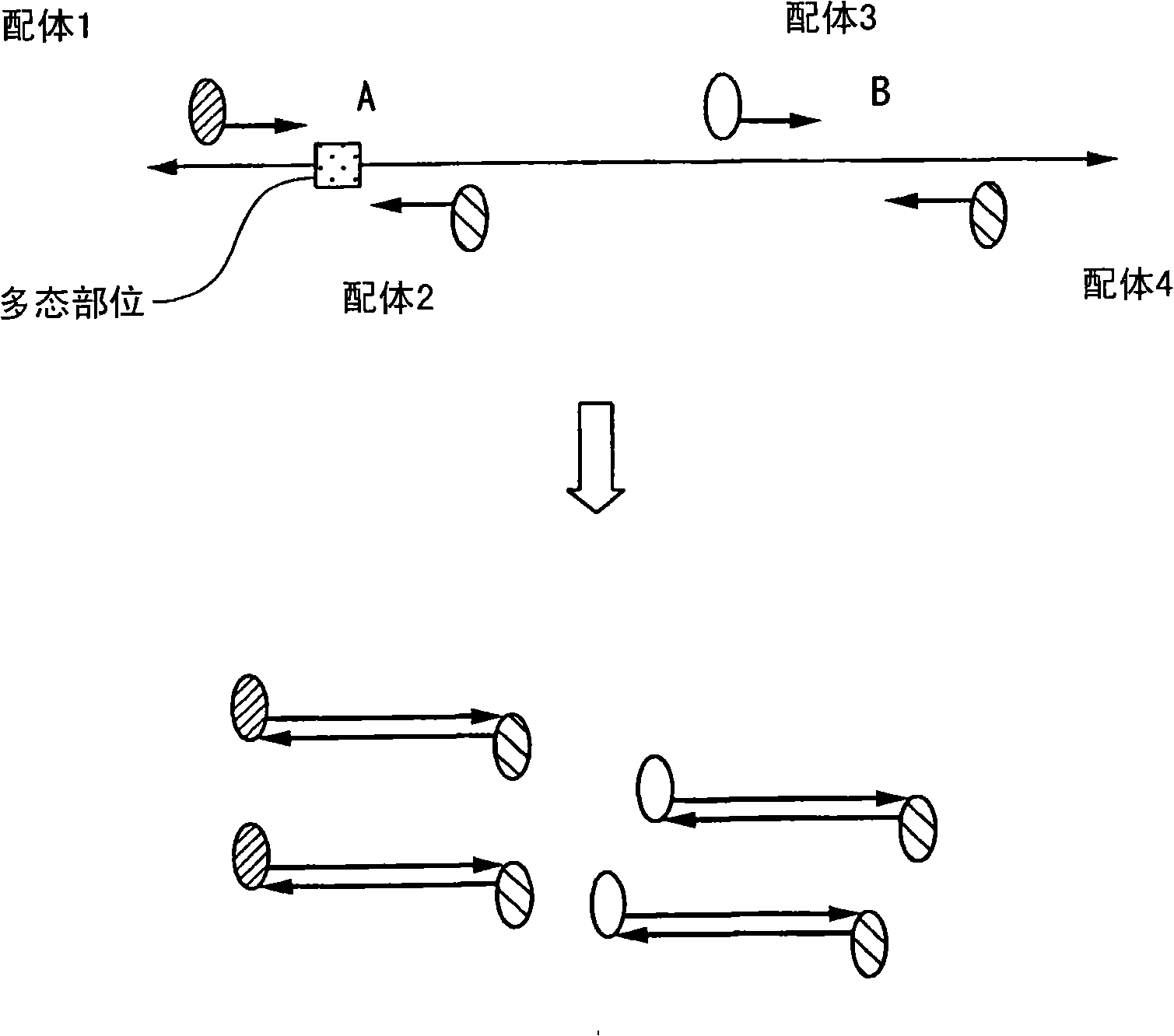
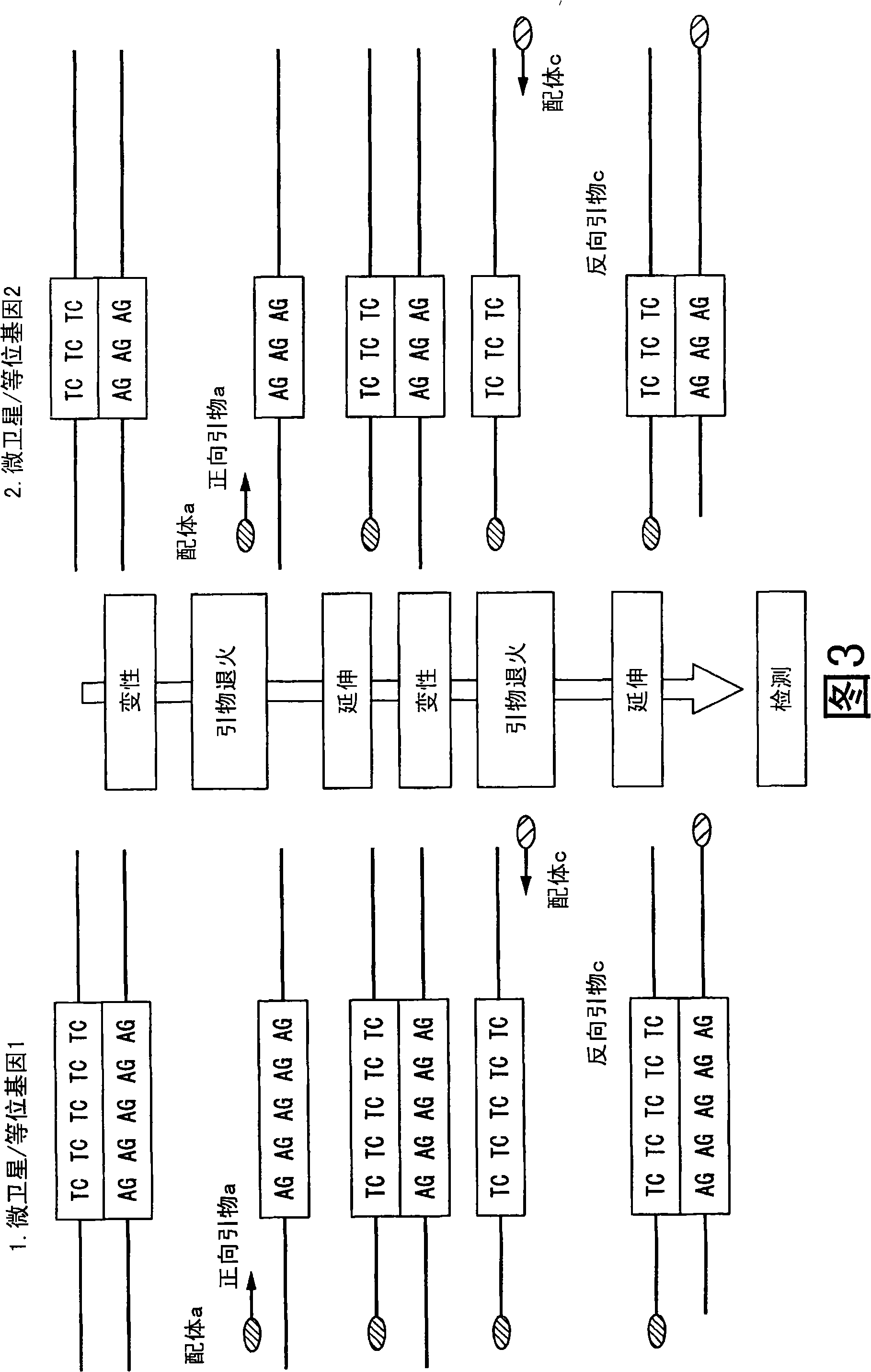
It is intended to provide a method of analyzing a change in the primary structure of a nucleic acid which is excellent in quantification properties, achieves a high sensitivity and a high reproducibility and can be quickly conducted at a low cost. Namely, a method of analyzing a change in the primary structure of a nucleic acid characterized by comprising: the step of obtaining nucleic acids wherein a first ligand and a second ligand differing from each other in nucleic acid type are bound to the standard sequence in a standard nucleic acid and a target sequence in a subject nucleic acid to be analyzed; the step of specifically binding the first ligand to a receptor held on a support to thereby immobilize the standard sequence and the target sequence to the support; the step of specifically binding a labeled receptor to the second ligand in the nucleic acids thus immobilized; the step of detecting the label to thereby detect the standard sequence and the target sequence; the step of determining the ratio of the standard sequence in the standard nucleic acid and the target nucleic acid to be analyzed, thus calculating a coefficient for correcting the detection data of the target sequence followed by the correction; and the step of confirming an increase or a decrease in the amount of the target sequence in the subject nucleic acid to be analyzed compared with the target sequence in the standard nucleic acid.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Protein crystal structure of magnaporthe oryzae mitogen-activated protein kinase Mpsl and application of protein crystal structure in bactericide target
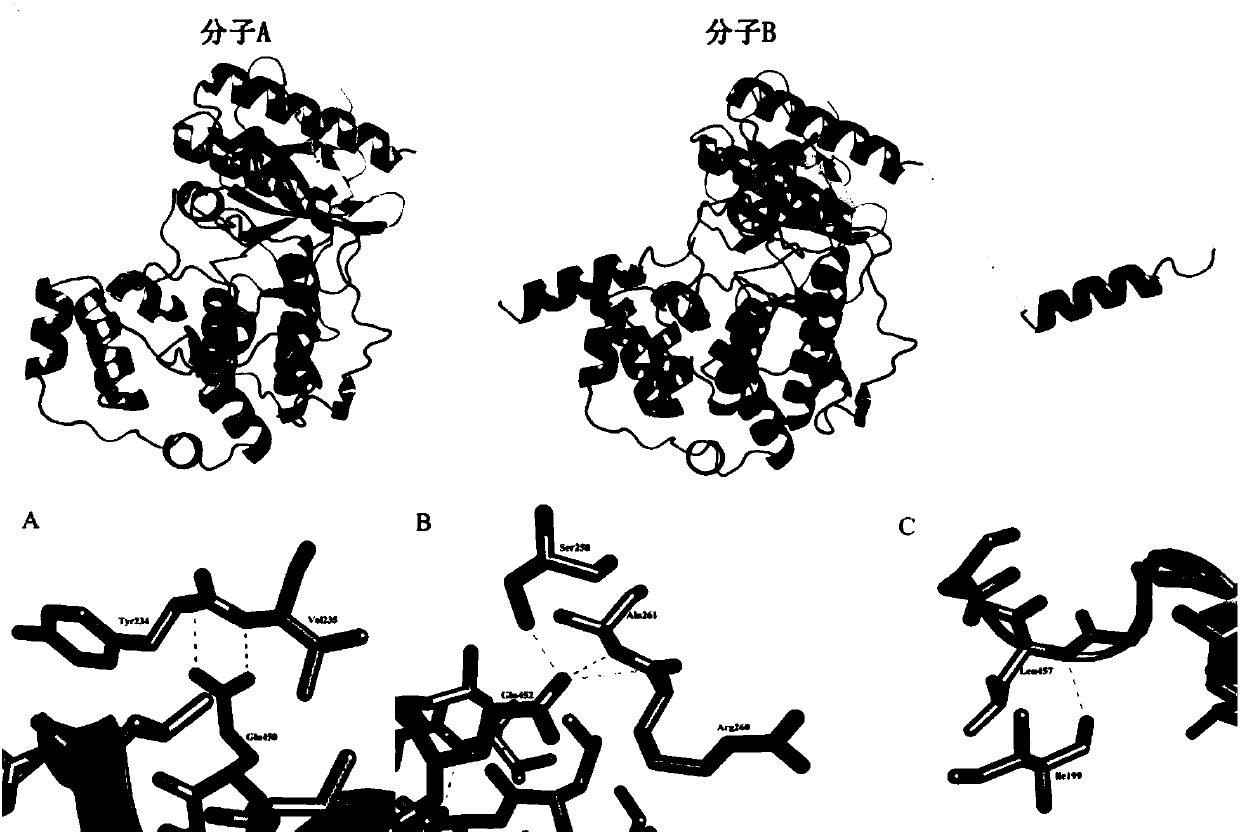
PendingCN107904217AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh activityTransferasesProtein structureADAMTS Proteins
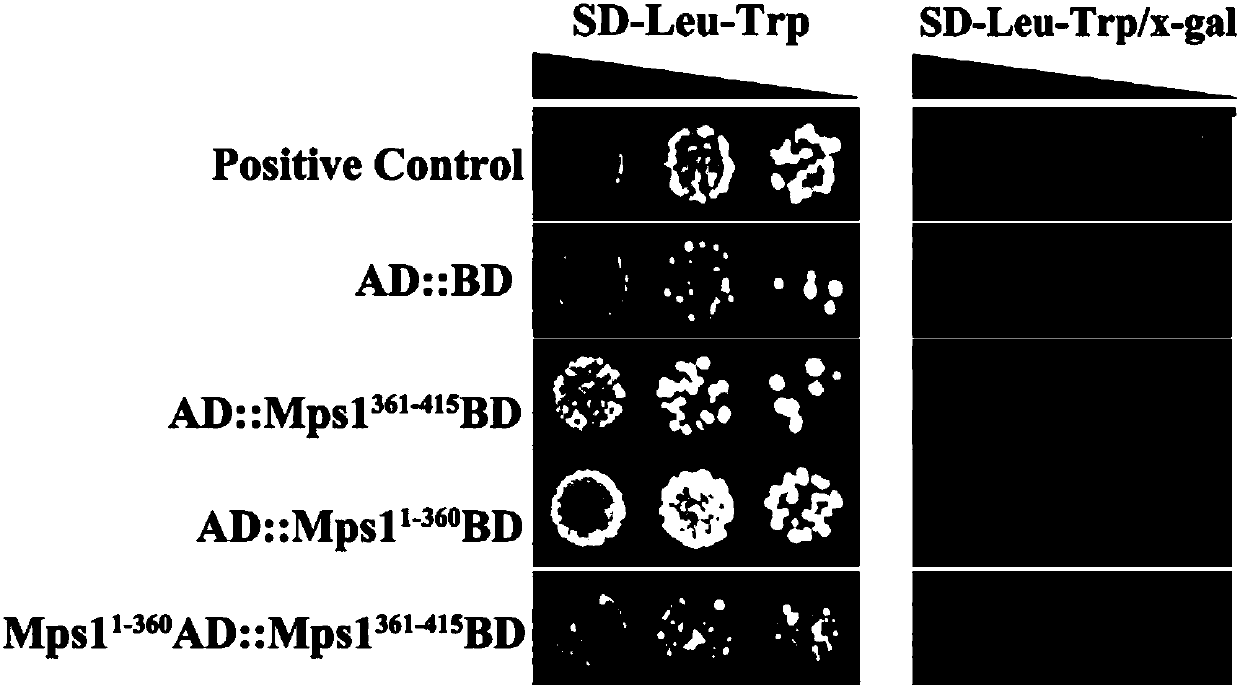
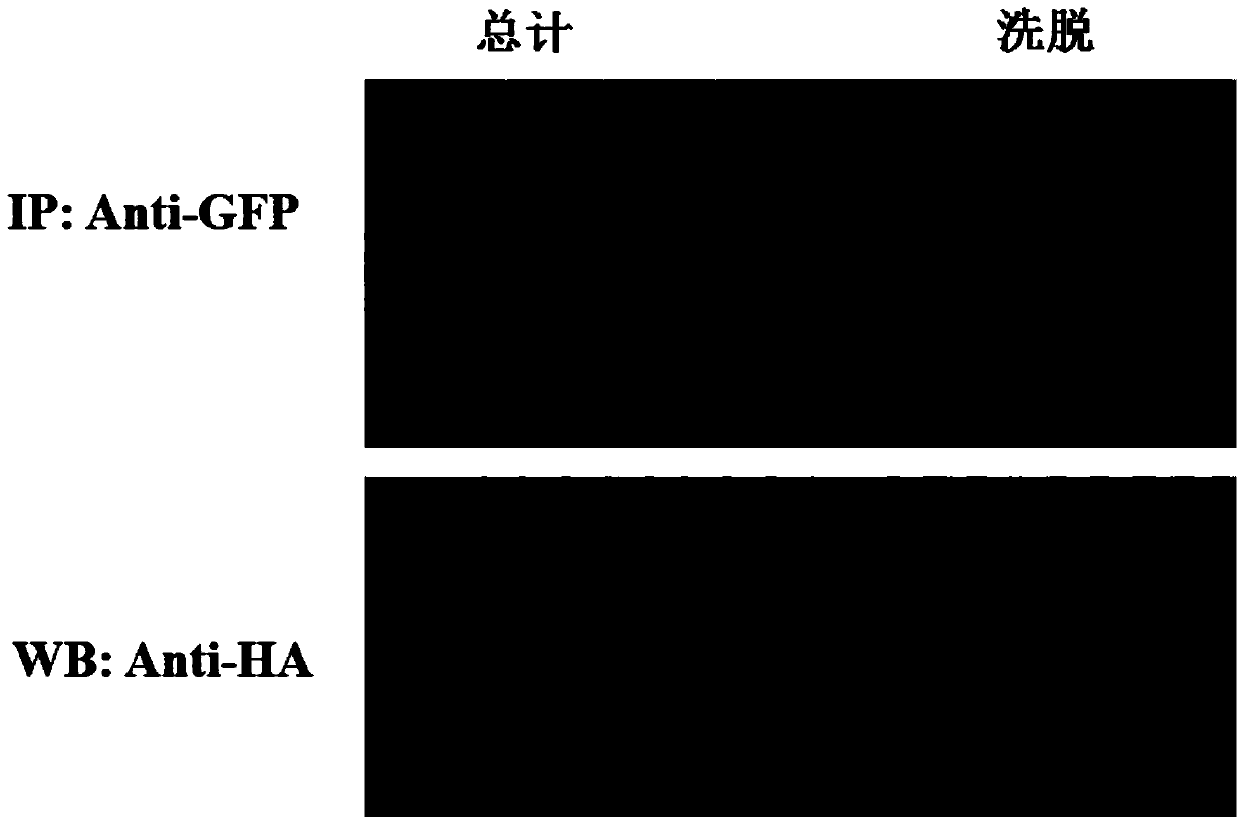
The invention discloses a protein crystal structure of magnaporthe oryzae mitogen-activated protein kinase Mpsl and application of the protein crystal structure in a bactericide target. The protein crystal structure of the magnaporthe oryzae mitogen-activated protein kinase Mpsl consists of two molecules. By analysis of the protein crystal structure of the magnaporthe oryzae mitogen-activated protein kinase Mpsl, the protein crystal structure has a self-interaction effect based on structural speculateion; an experiment further verifies that the protein crystal structure has interaction betweenthe carboxyl terminal non-kinase domain (Mpsl 401-415) and the autokinase domain (Mspl 1-360), and relevant experiments verify that the carboxyl terminal non-kinase domain (Mpsl 401-415) of Mpsl hasan outstanding inhibition effect on the phosphorylation level of Mpsl, so that design, screening and optimization are performed further through the protein space structure of the carboxyl terminal non-kinase domain of Mpsl to provide a structural guidance for a small-molecular inhibitor with relatively activity of Mpsl, and a foundation is laid for development of relevant researches based on the space structure, which serves as the bactericide target, of Mpsl.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
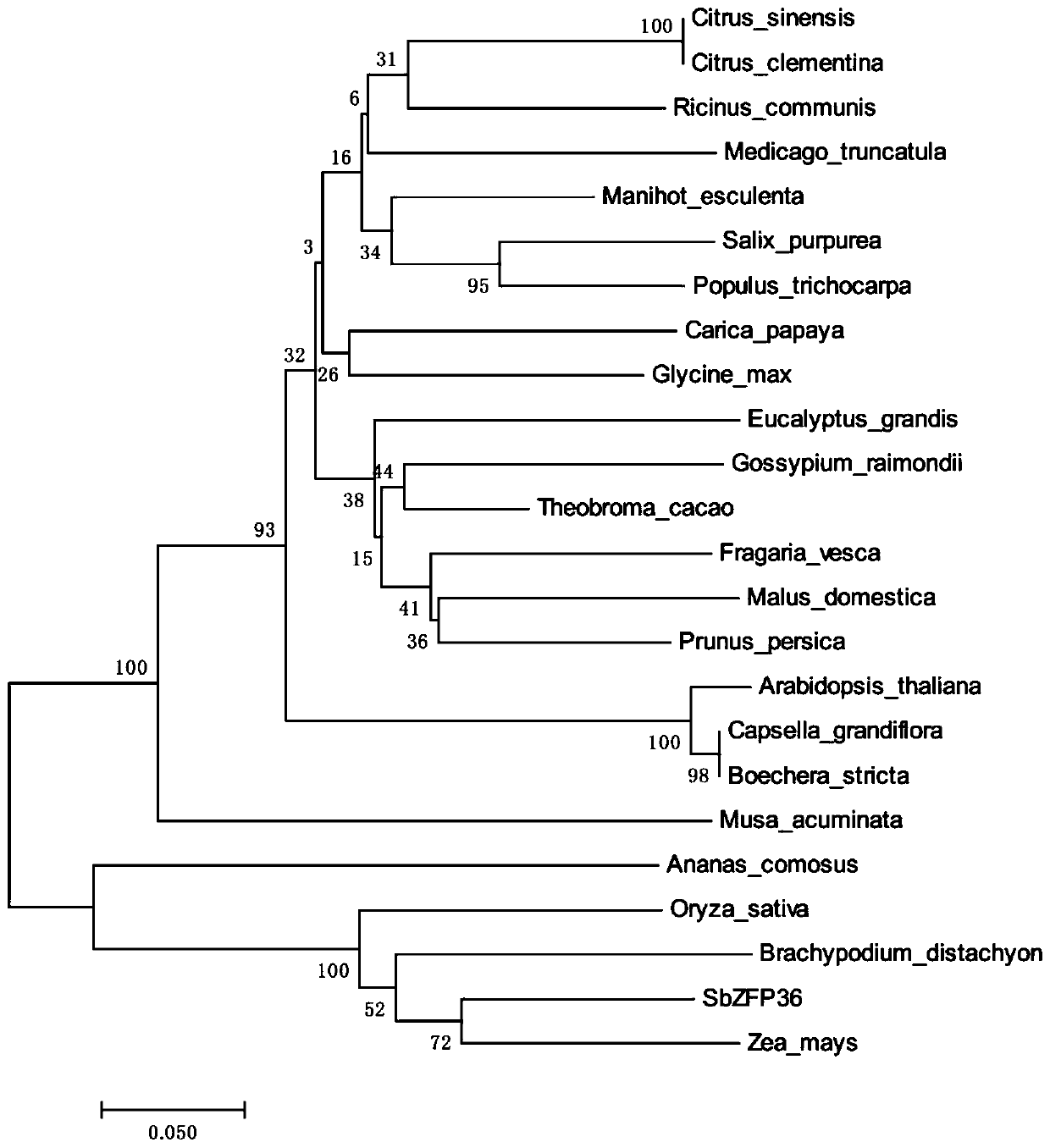
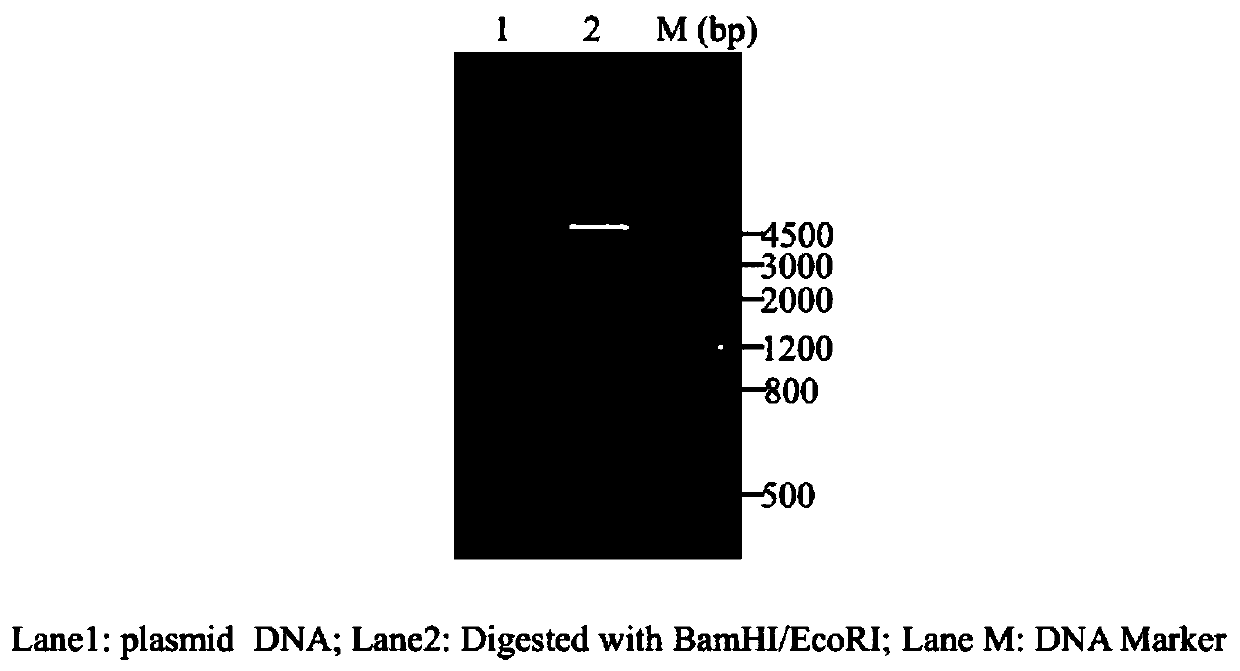
Sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36 and recombinant vector and expression method thereof
InactiveCN109971770AImprove stress resistanceHigh expressionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36. The nucleotide sequence of the sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention also discloses a protein encoded by the sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses a recombinant vector containing the sorghum C2H2 zinc finger protein gene SbZFP36 and an expression method. According to the invention, a sorghum homologous gene SbZFP36 is obtained from a sorghum genome database through theprotein sequence of a rice ZFP gene, the full length of the gene is 711bp, a prokaryotic expression vector is constructed according to the gene, a protein purification system is used for purifying theprokaryotic expression vector, the result lays a foundation for further researching the protein crystal structure and biological characteristics, and a basis is further provided for improving the disease resistance of sorghum through a gene editing method.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
Chamomile farnesyl diphosphatesynthase gene clone and prokaryotic expression
InactiveCN102703397AIncrease productionHigh homologyTransferasesFermentationOpen reading frameProtein target
The invention discloses a chamomile farnesyl diphosphatesynthase and a construction and expression method of a recombinant expression vector thereof, the amino acid sequence of the chamomile farnesyl diphosphatesynthase is shown as SEQ NO2, and the nucleotide sequence of the chamomile farnesyl diphosphatesynthase is shown as SEQ NO1. The ORF (open reading frame) of the chamomile FPS (frames per second) gene is 1032bp, and the chamomile FPS gene has higher homology compared with other plant sesquiterpene synthase genes through sequence comparison; and Westerning verification can be carried out by constructing a prokaryotic expression vector pET-30a(+) / FPS and inducting for expressing soluble protein to obtain a target protein with molecular weight of 38KDa, so that a foundation is established to further studies on FPS protein purification and protein structure and characteristics, and a reference is provided for improving the yield of chamomile chamazulene by a transgene method. Furthermore, the condition for induction expressing of protein is optimized in the method, the optimal induction time is six hours, and the optimal induction temperature is 37 DEG C.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Reengineering mrna primary structure for enhanced protein production
Described herein are rules to modify natural mRNAs or to engineer synthetic mRNAs to increase their translation efficiencies. These rules describe modifications to mRNA coding and 3' UTR sequences intended to enhance protein synthesis by: 1) decreasing ribosomal diversion via AUG or non-canonical initiation codons in coding sequences, and / or 2) by evading miRNA-mediated down-regulation by eliminating one or more miRNA binding sites in coding sequences.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com