Reengineering mrna primary structure for enhanced protein production
A protein and protein expression technology, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, genetic engineering, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as inability to generate immune responses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
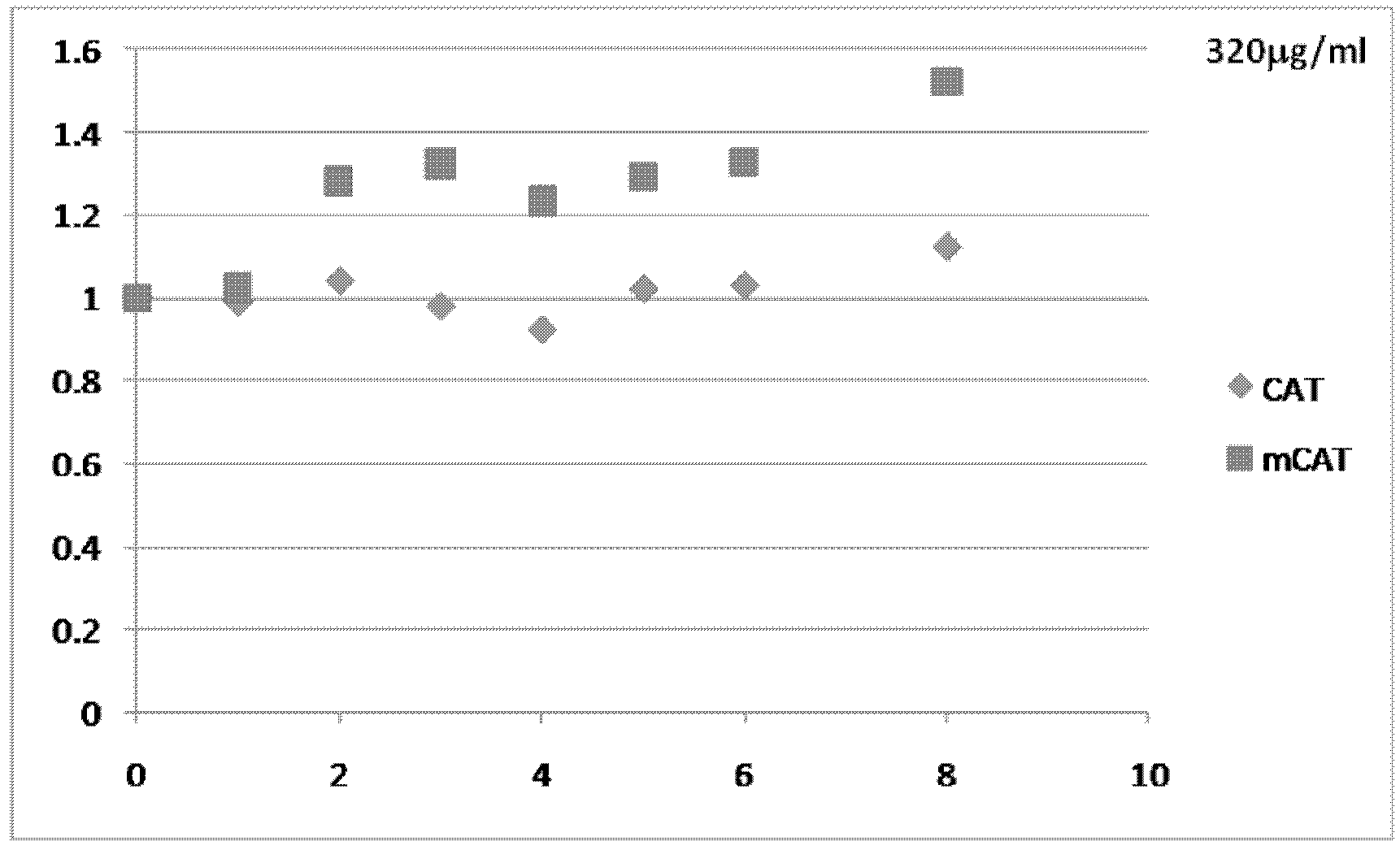
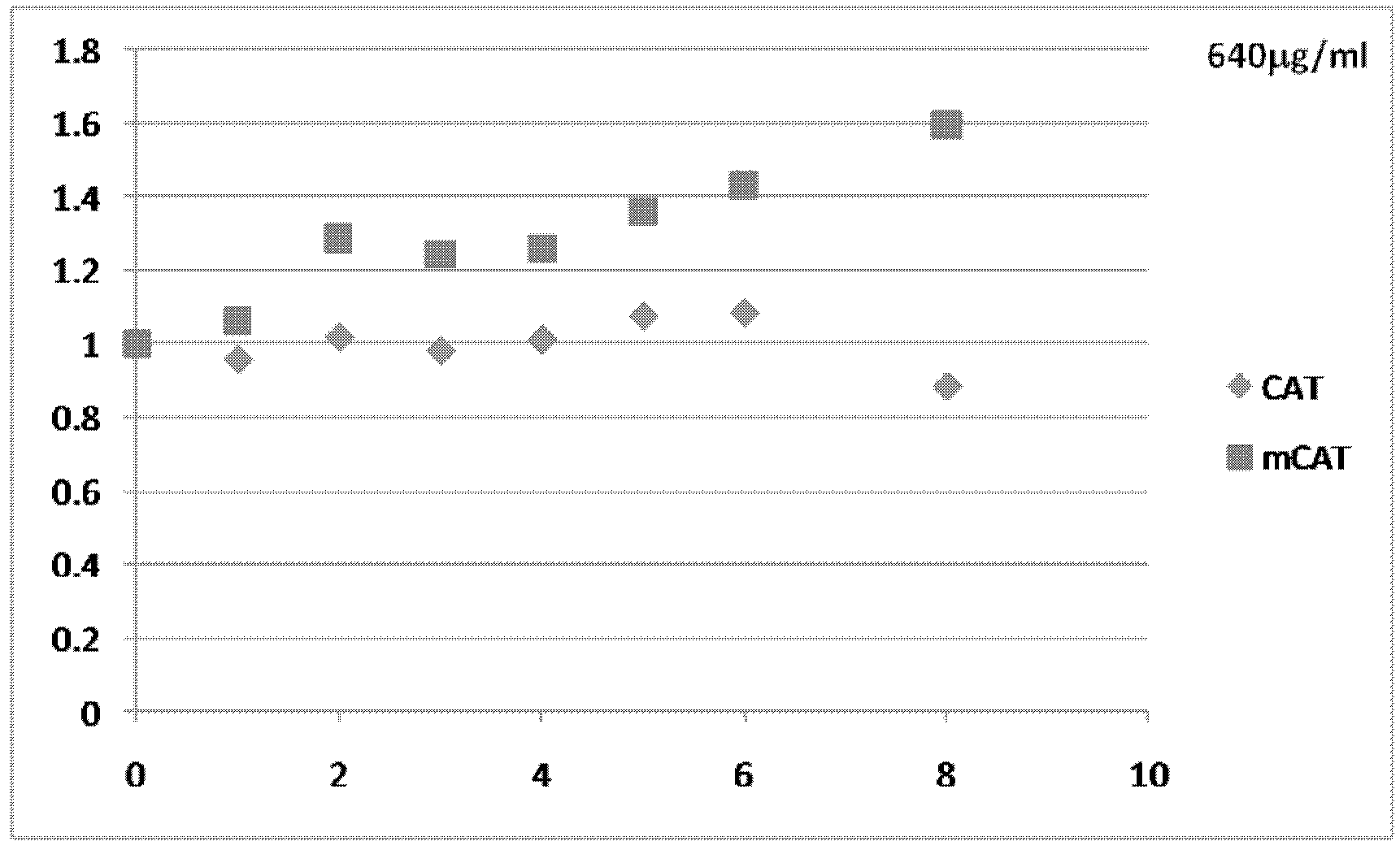
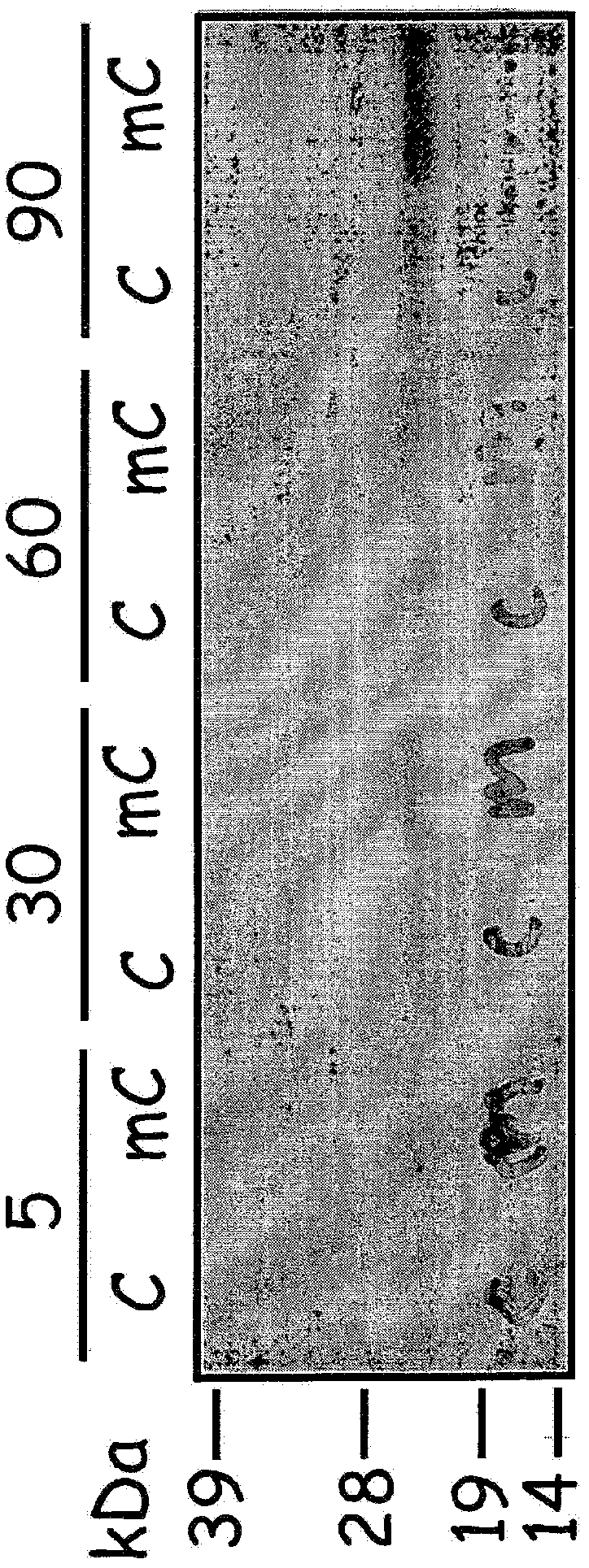
[0075] Example 1: Modification of multiple translation initiation sites within mRNA transcripts
[0076] The presence of multiple translation initiation sites within the 5′-UTR and coding regions of mRNA transcripts can reduce translation efficiency, for example by shifting ribosomes away from true or proven translation initiation codons. Alternatively or additionally, the presence of multiple translation initiation sites downstream of a true or proven translation initiation codon can induce translation of one or more protein isoforms that reduce the translation efficiency of the full-length protein. To increase translation efficiency of mRNA transcripts encoding commercially valuable human proteins, potential translation initiation sites in all reading frames upstream and downstream of true or proven translation initiation codons were mutated to eliminate these sites . In preferred aspects of this method, the mRNA sequence is altered, but the resulting amino acids encoded ...
Embodiment 2
[0151] Example 2: Modification of miRNA binding sites within mRNA transcripts
[0152] MicroRNAs (miRNAs) that bind to target mRNA transcripts reduce translation efficiency by inducing degradation of the target mRNA transcript or by preventing translation of the target mRNA transcript. To increase the translation efficiency of mRNA transcripts encoding commercially valuable human proteins, first identify the target mRNA within the 5' leader sequence, 5' untranslated region (UTR) sequence, coding sequence, and 3' untranslated region (UTR) sequence. All known or predicted miRNA binding sites are then mutated or altered in order to inhibit miRNA binding.
[0153] In a preferred aspect of the method, a seed sequence comprising the first 8 5'-nucleotides of the mature miRNA sequence is specifically targeted. The seed sequence comprises 5' nucleotides 1-7 or 2-8 of the mature miRNA sequence. Therefore, the seed sequences used in this method encompass both alternatives. The miRN...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com