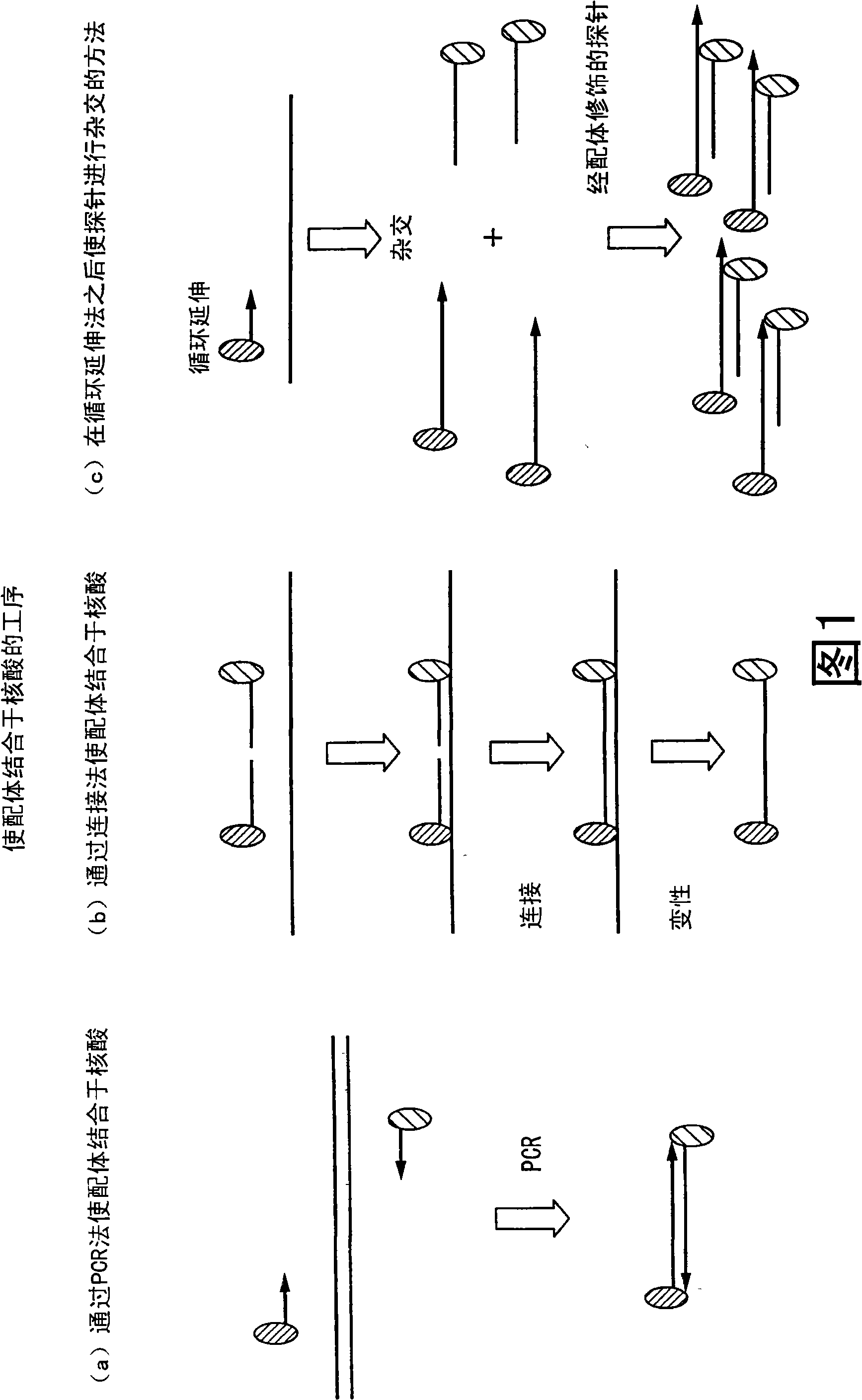
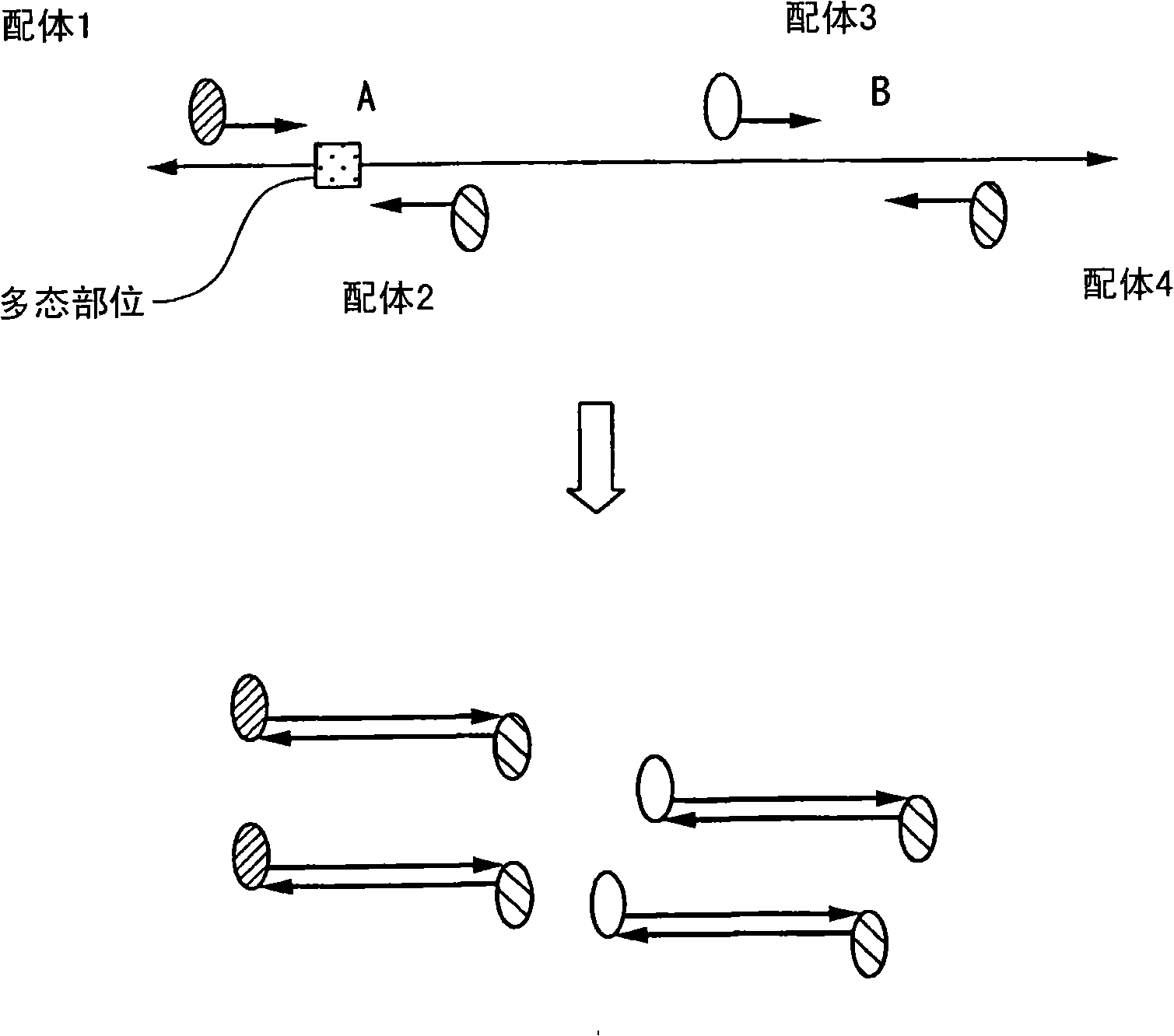
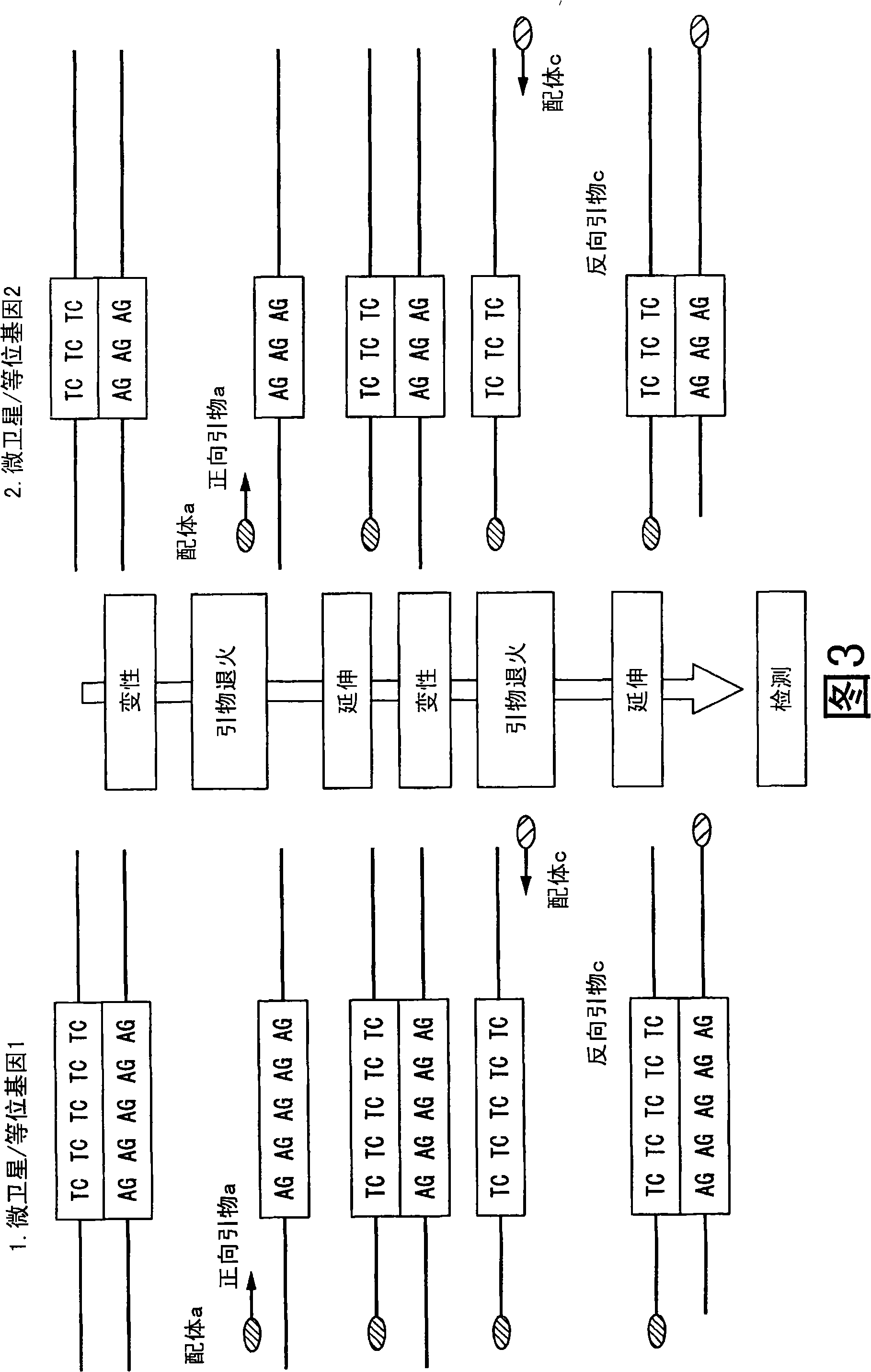
Method of analyzing change in primary structure of nucleic acid
A technology of structural change and analytical methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as complex experimental operations, difficult quantification of target genes, time required, etc., and achieve excellent quantitative performance , high sensitivity and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 11
[0180] [embodiment 1] 1. preparation reagent
[0181] Prepare the following reagents.
[0182] (Sample 1, Reference Nucleic Acid Solution 1): A sample containing the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 6 at 2 nM each, which is a sample with a normal chromosome structure
[0183] (Sample 2, Analytical Target Nucleic Acid Solution 2): A sample containing 2 nM of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5 and 1 nM of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 6, and a sample with an abnormal chromosome structure in which LOH occurred in the region of SEQ ID NO: 6
[0184] (PCR reagent): "Accuprime Super Mix II" catalog No. 12341-012 manufactured by Invitrogen Corporation
[0185] (PCR primers): Combinations of the primers shown below
[0186] ・The 5' end of the primer a shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 was modified with FITC
[0187] Those who modified the 5' end of the primer b shown in Sequence 2 with biotin
[0188] The 5' end of the primer c shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 was modified with digoxige...
Embodiment 2
[0210] Nucleic acids containing one-base polymorphisms are detected by ligation reactions. Before performing the ligation reaction, in order to remove similar sequences and improve detection sensitivity, it is assumed that the base sequence before and after the above-mentioned basic polymorphic site was amplified by multiplex PCR, and samples with base sequences of 80bp and 85bp were prepared. . The carrier uses magnetic particles to detect the sequence through an enzyme-substrate reaction. In addition, when the template DNA is present in a sufficient amount to enable direct detection of ligation, direct detection without amplification by the PCR method can more accurately reflect the presence ratio of the nucleic acid.
[0211] 1. Preparation of Reagents
[0212] Prepare the following reagents.
[0213] (Sample 1): A sample containing the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 and SEQ ID NO: 8 at 100 nM each, which is a sample with a normal chromosome structure
[0214] (Sample ...
Embodiment 3
[0238] The nucleic acid used in Example 1 was detected by measuring aggregation of the microparticles using dispersible microparticles.
[0239] 1. Preparation of Reagents
[0240] Prepare the following reagents.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com