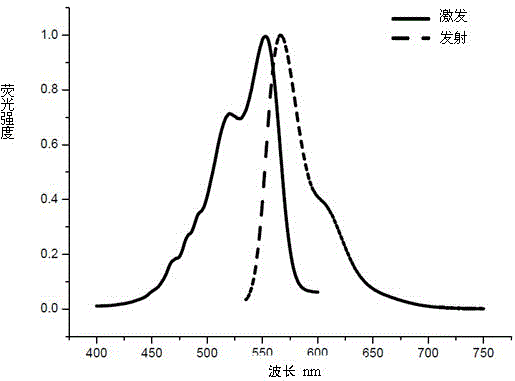
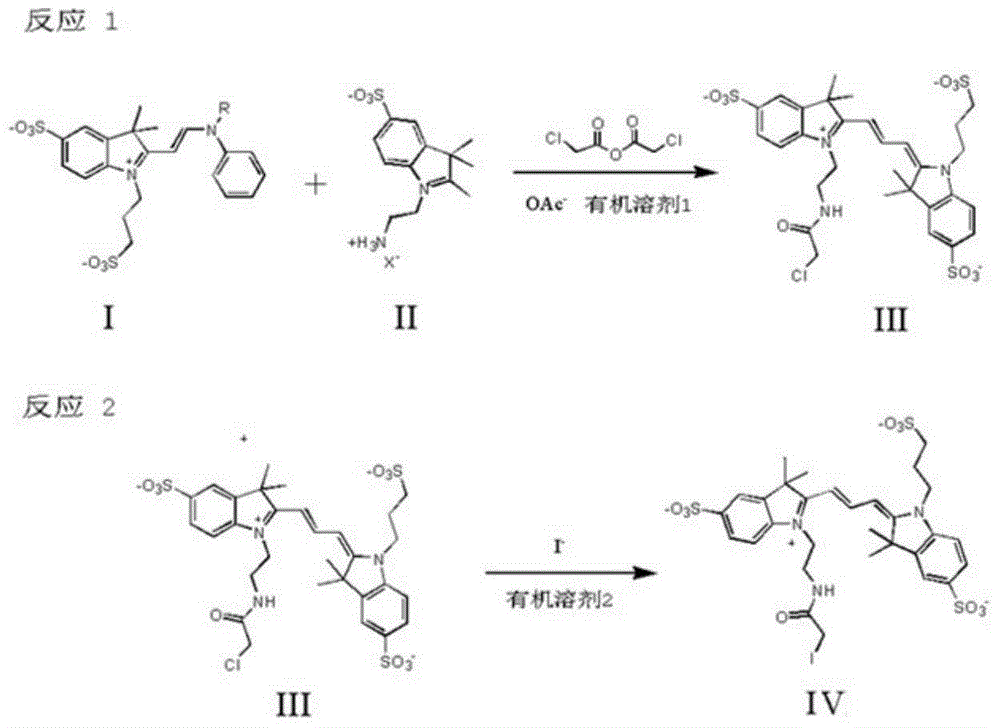
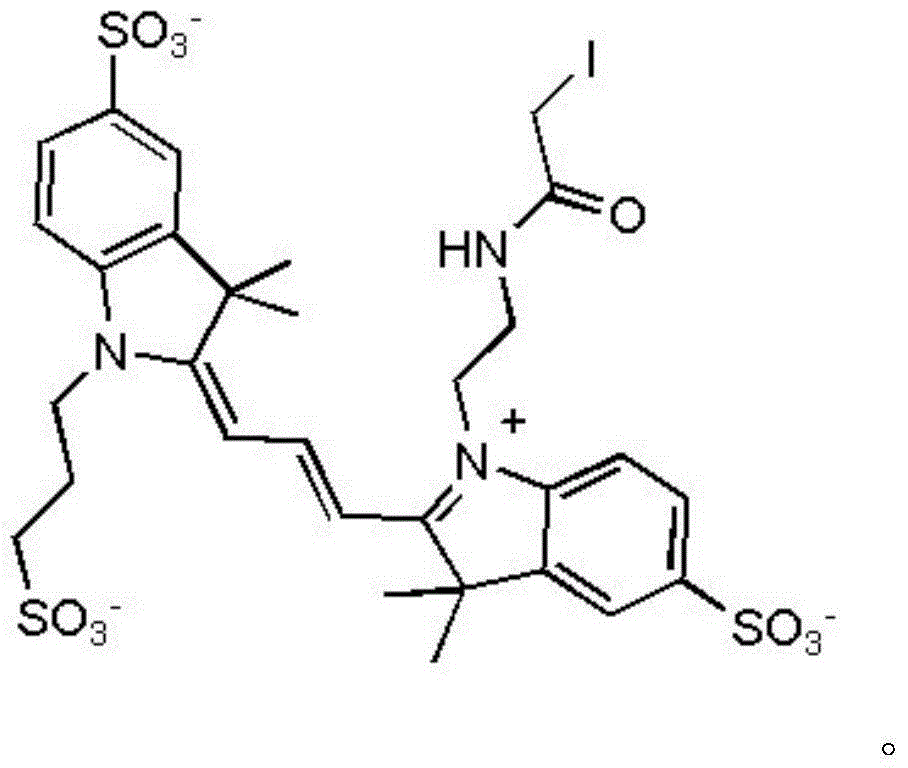
Trimethyl cyanine fluorescence probe used for protein labeling and synthetic method thereof
A technology of fluorescent probe and synthesis method, applied in the field of biological macromolecular labeling, can solve problems such as poor water solubility and long linking group, and achieve the effects of small flexibility, improved rigidity, and poor water solubility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A method for synthesizing a trimethylcyanine fluorescent probe for protein labeling, the method is carried out in the following steps:
[0039] Take 1 equivalent of the potassium salt of Compound I with R=H and 1.2 equivalents of the sodium salt of Compound II with X=Cl, dissolve them in acetonitrile, add 1.5 equivalents of sodium acetate and 1.5 equivalents of chloroacetic anhydride, and stir at room temperature for 1 hour. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and column chromatography was eluted with methanol: acetone = 1:7 to obtain the corresponding compound III. The resulting 1 equivalent of compound III was reacted with 1.1 equivalent of potassium iodide in a solvent of methanol:chloroform=1:1 at 60°C for 24 hours, filtered, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain the corresponding final product IV. It was confirmed by NMR that it was consistent with the target product.
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for synthesizing a trimethylcyanine fluorescent probe for protein labeling, the method is carried out in the following steps:
[0042] Take 1 equivalent of the sodium salt of compound I with R=H and 1.2 equivalents of the sodium salt of compound II with X=Br, dissolve them in chloroform, add 2 equivalents of sodium acetate and 2 equivalents of chloroacetic anhydride, and stir at room temperature for 1.2 hours. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and column chromatography was eluted with methanol: acetone = 1:5 to obtain the corresponding compound III. The resulting 1 equivalent of compound III was reacted with 1.5 equivalents of sodium iodide in a solvent of methanol:chloroform=1:2 at 70°C for 20 hours, filtered, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain the corresponding final product IV. NMR showed that it was consistent with the target product.
Embodiment 3
[0044] A method for synthesizing a trimethylcyanine fluorescent probe for protein labeling, the method is carried out in the following steps:
[0045] Take R=-COCH 3 0.7g of potassium salt of compound I and 0.38g of potassium salt of compound II of X=Br are dissolved in 10ml of N,N-dimethylformamide, and 0.43g of chloroacetic anhydride and 0.2g of acetic acid are added sodium, and stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and column chromatography was eluted with methanol: acetone = 1:5 to obtain the corresponding compound III. The obtained 0.30 g of compound III was reacted with 1 g of sodium iodide in a solvent of methanol:chloroform=1:1 at 65°C for 24 hours, filtered, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain 0.32 g of the corresponding final product IV. NMR showed that it was consistent with the target product.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com