Patents
Literature
170 results about "Mud motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
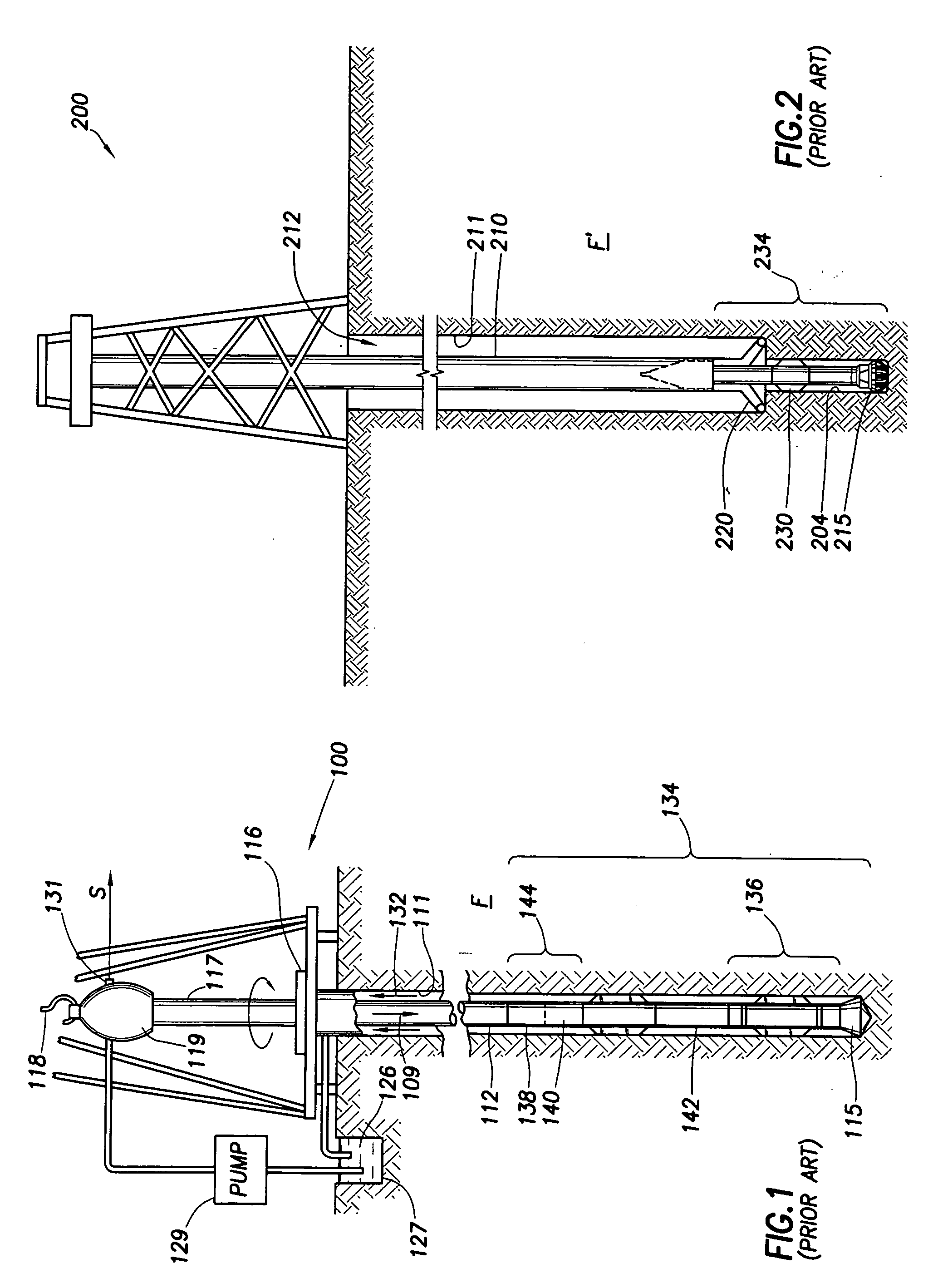
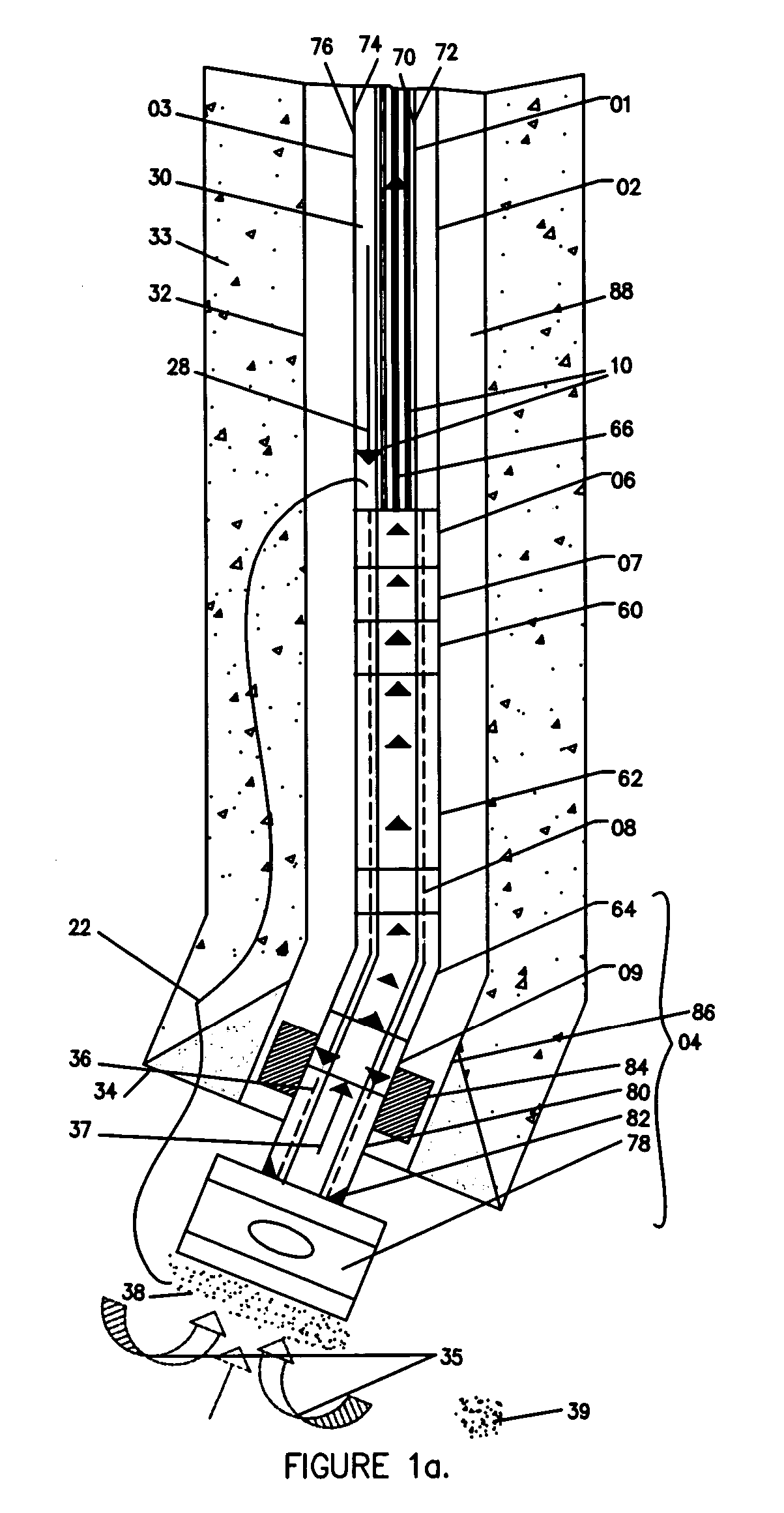
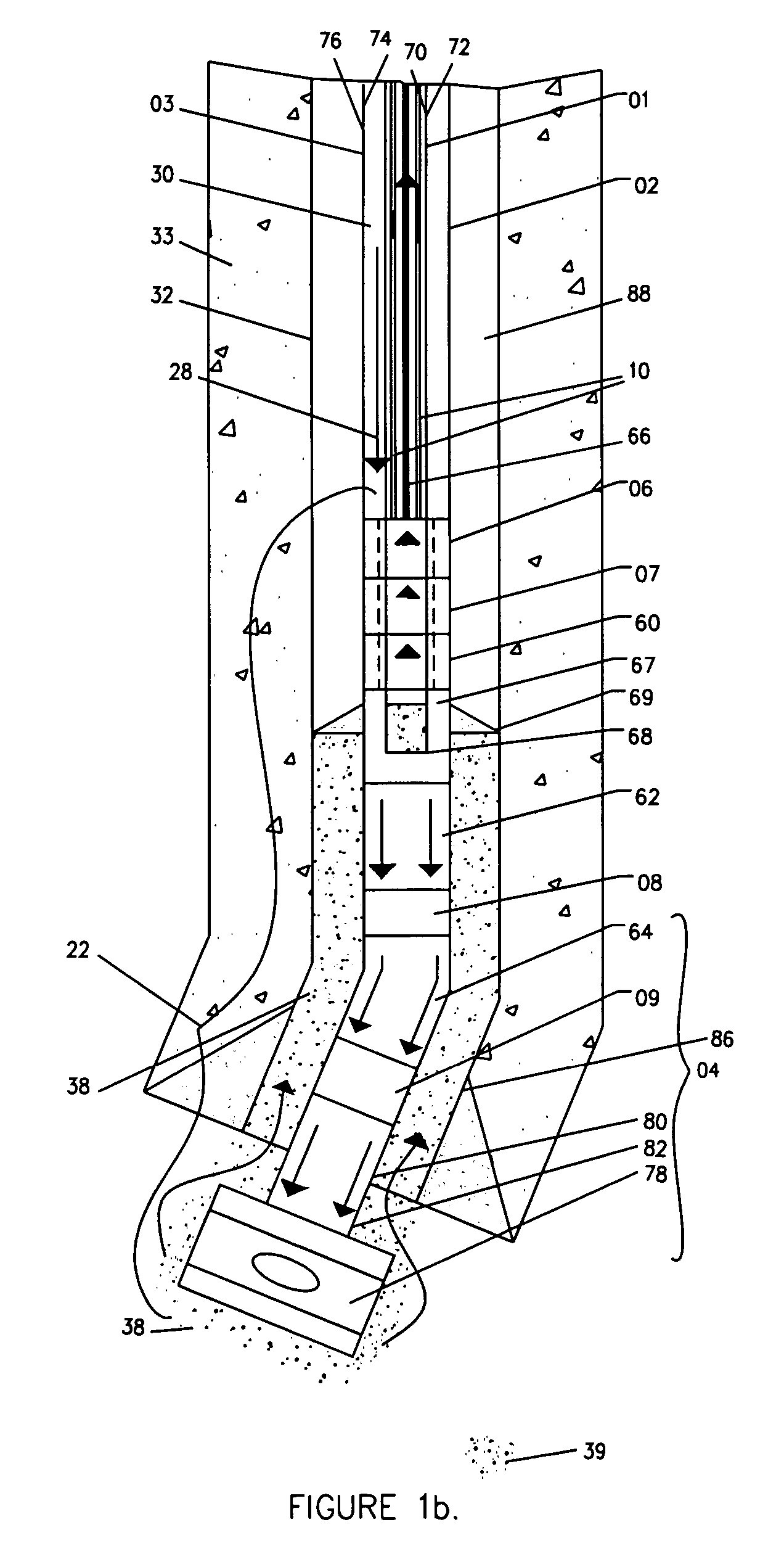
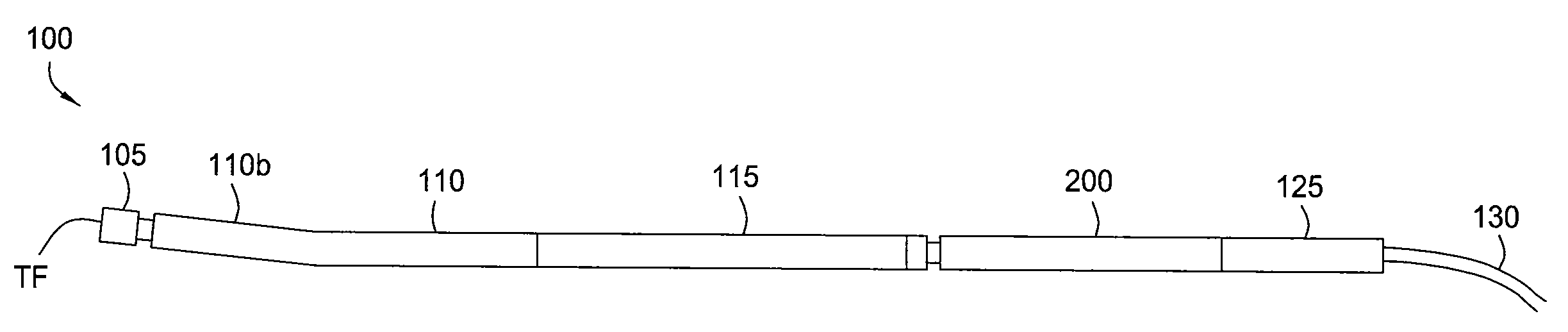
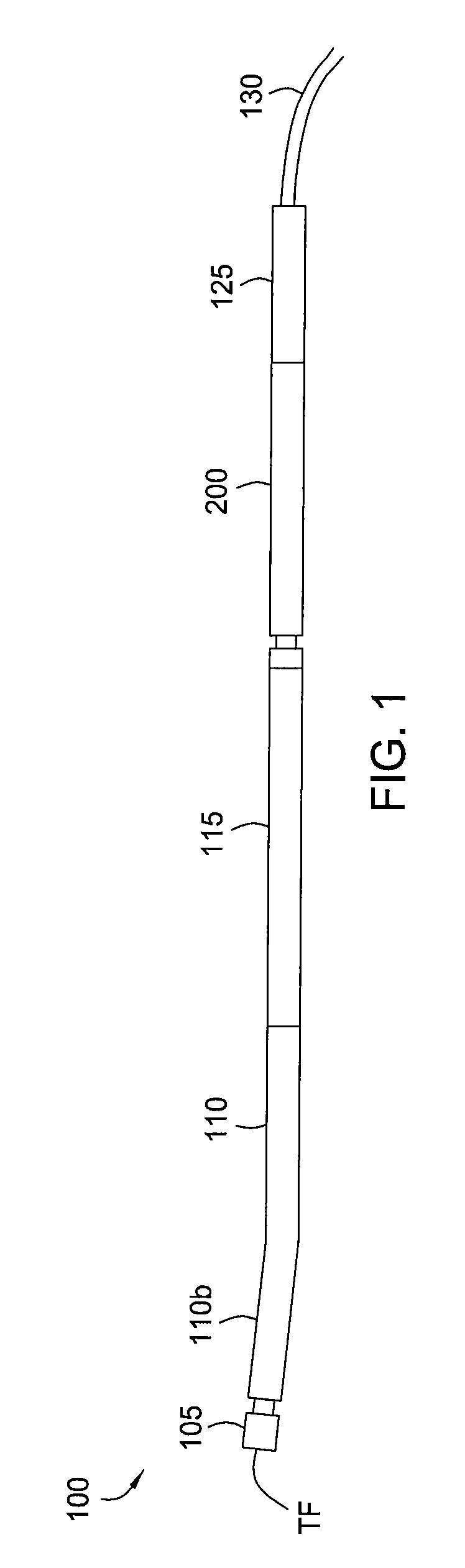
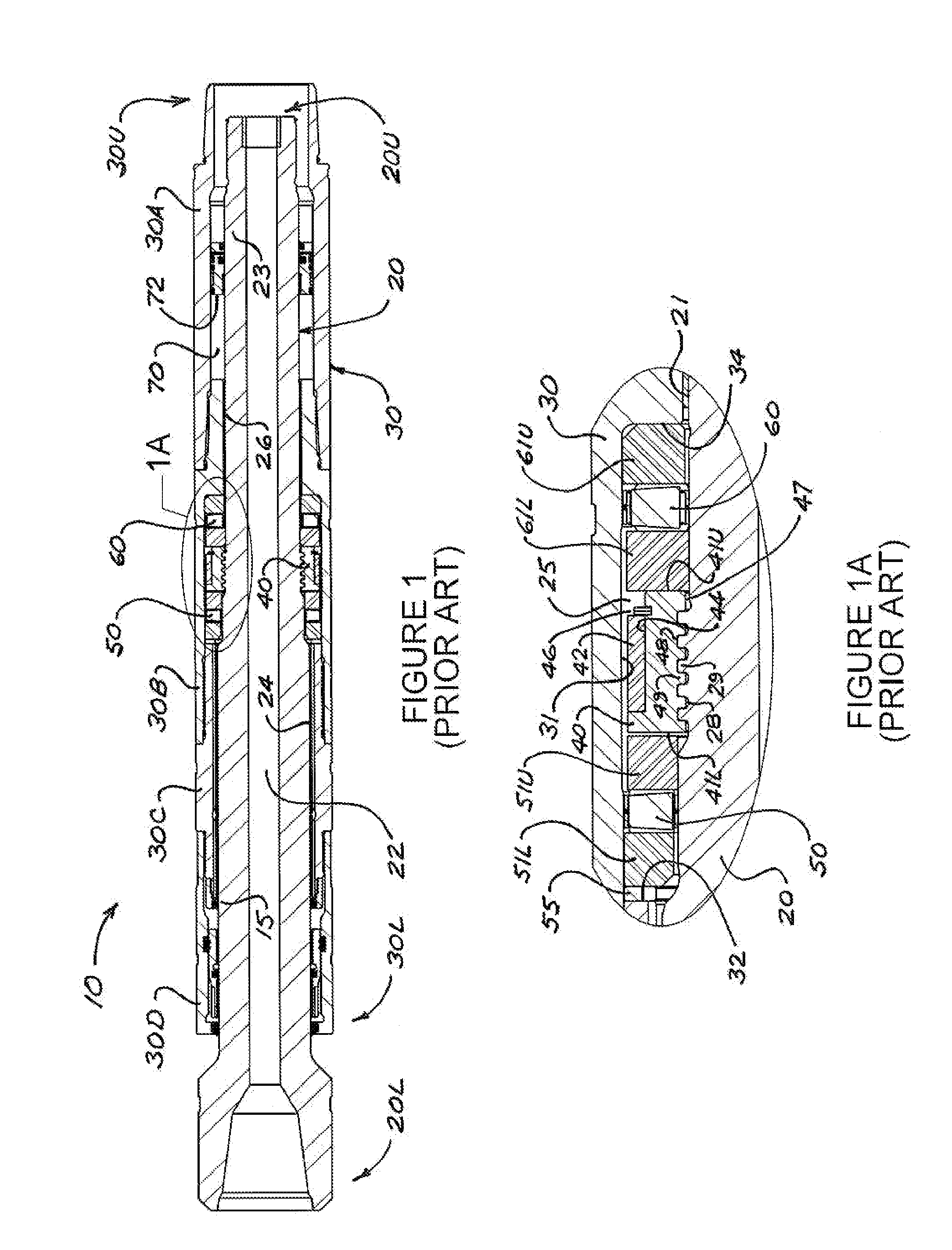
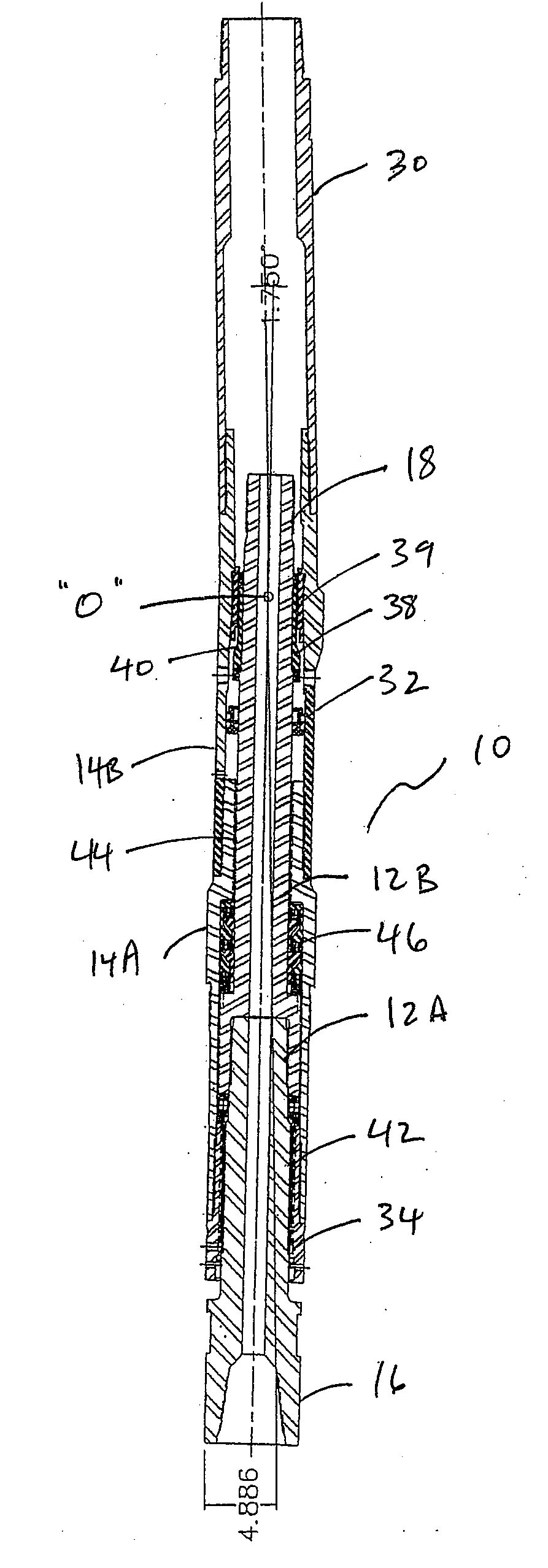
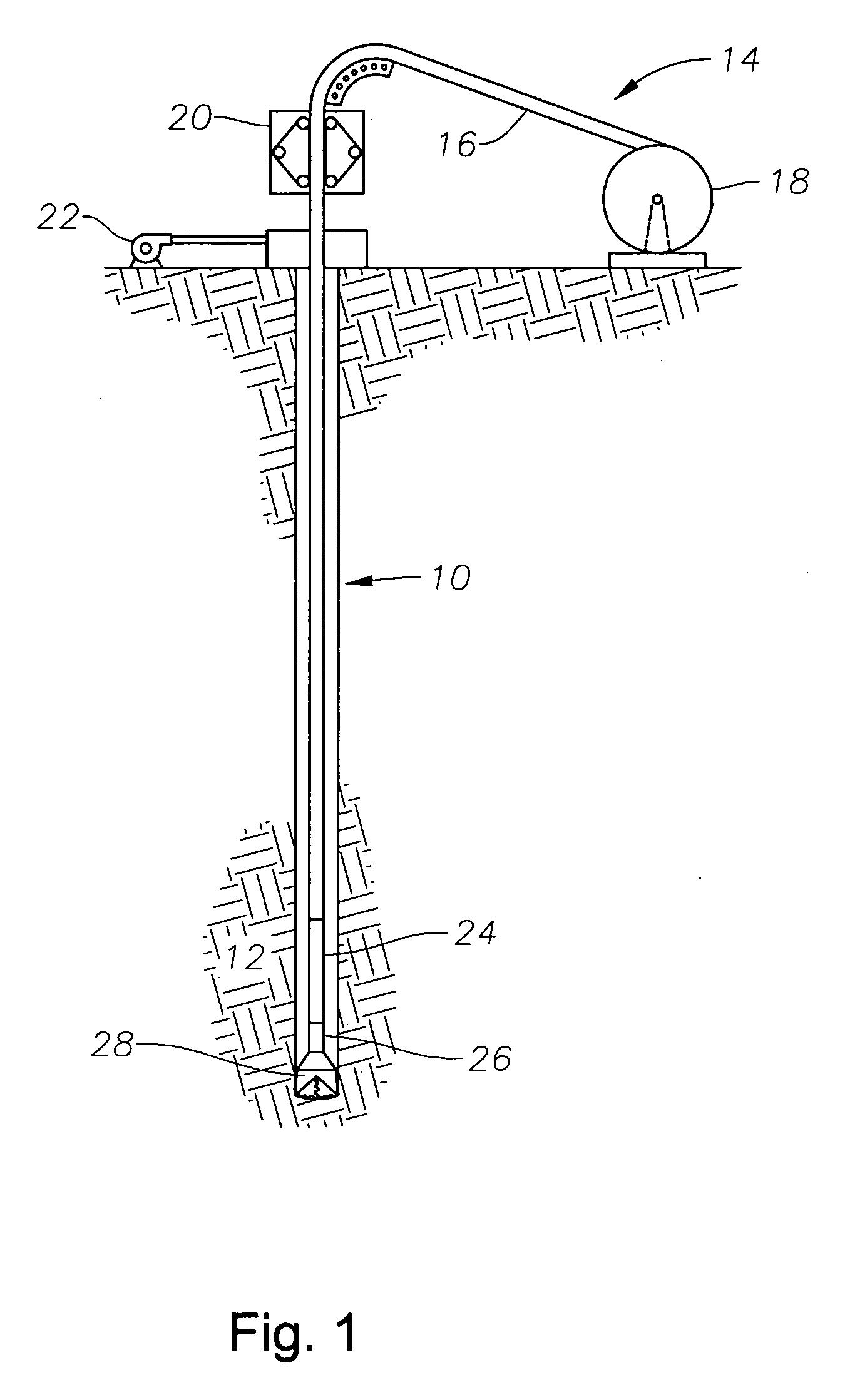
A mud motor (or drilling motor) is a progressive cavity positive displacement pump (PCPD) placed in the drill string to provide additional power to the bit while drilling. The PCPD pump uses drilling fluid (commonly referred to as drilling mud, or just mud) to create eccentric motion in the power section of the motor which is transferred as concentric power to the drill bit. The mud motor uses different rotor and stator configurations to provide optimum performance for the desired drilling operation, typically increasing the number of lobes and length of power assembly for greater horsepower. In certain applications, compressed air, or other gas, can be used for mud motor input power. Normal rotation of the bit while using a mud motor can be from 60 rpm to over 100 rpm.
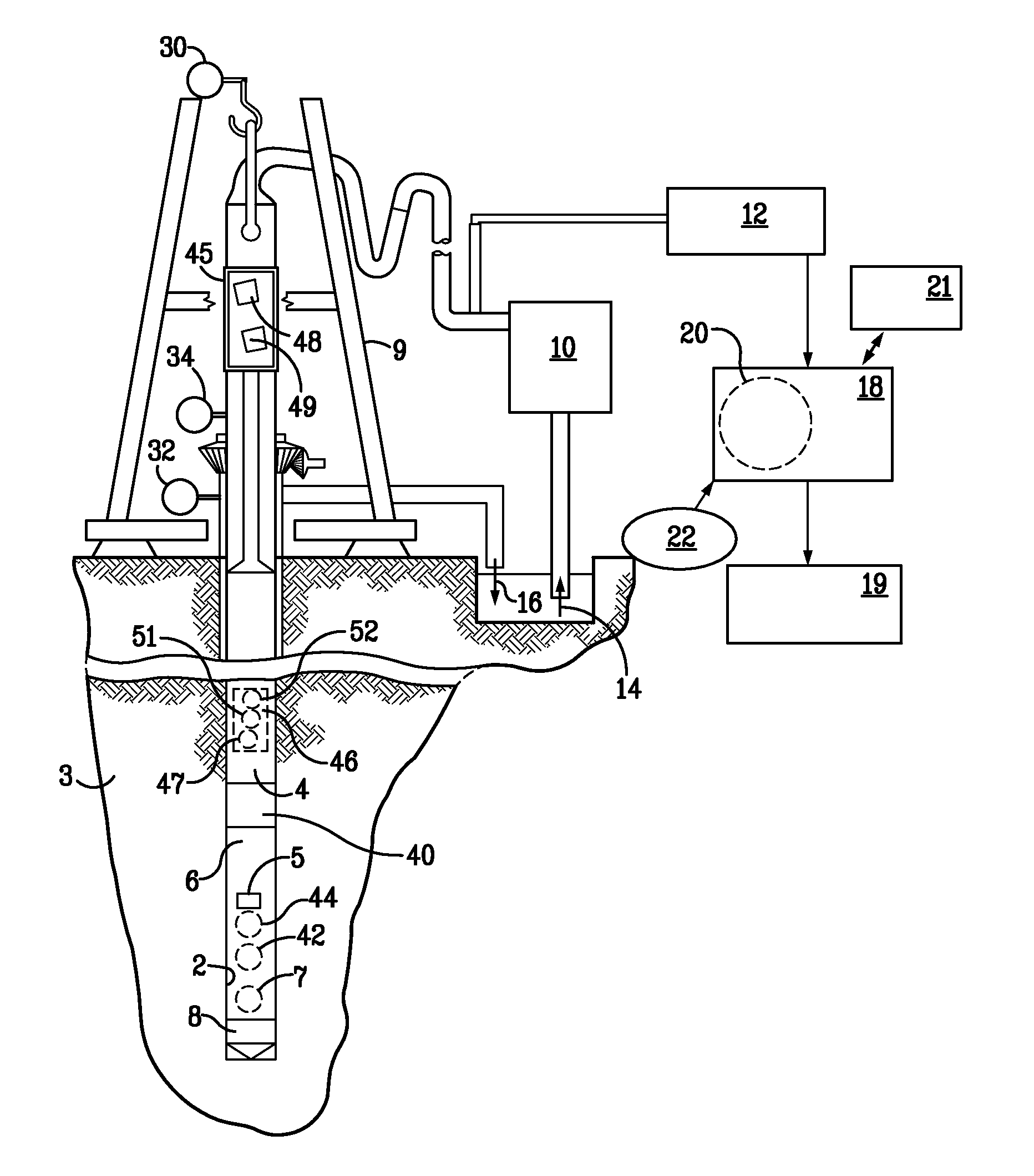
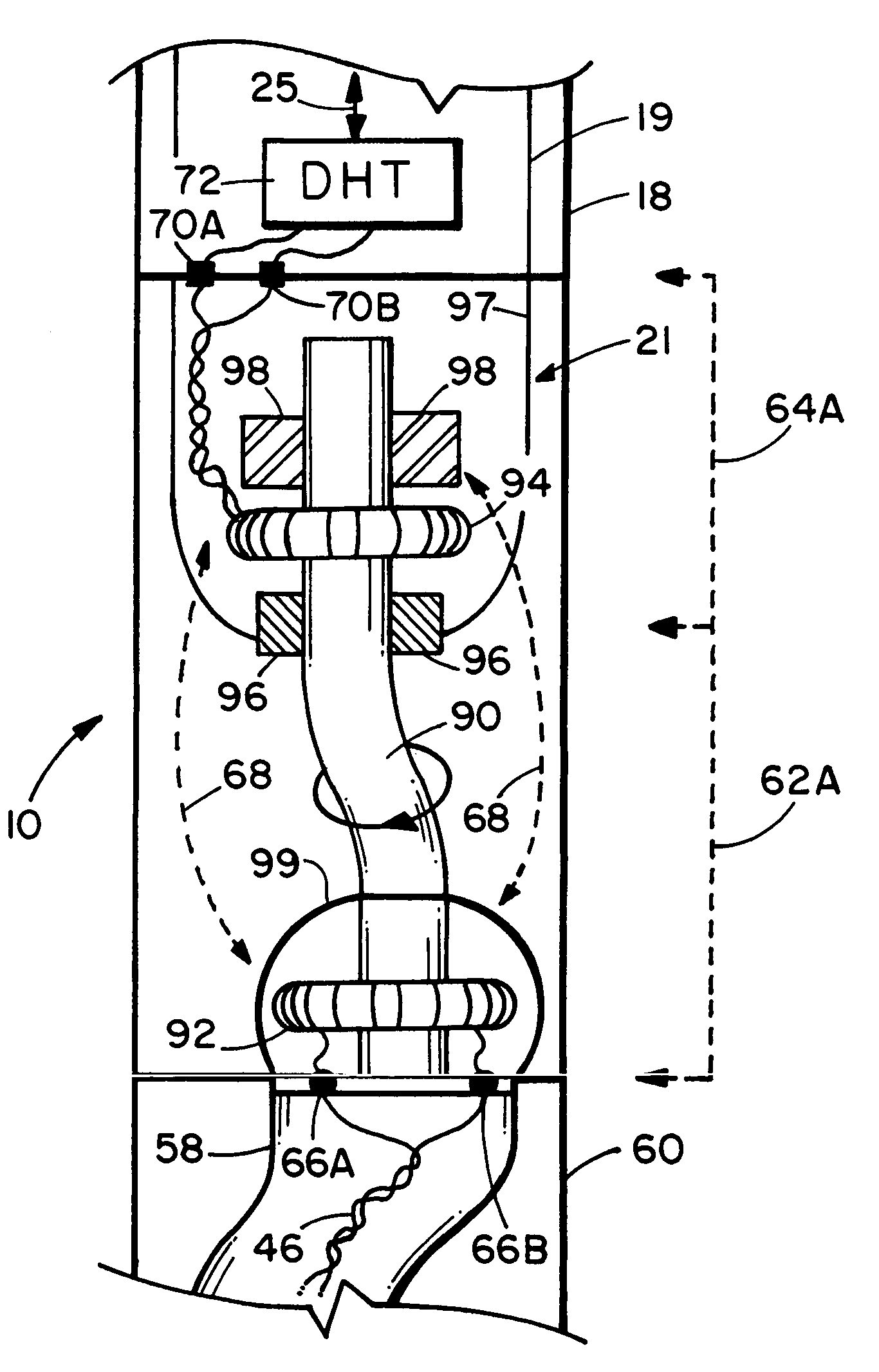
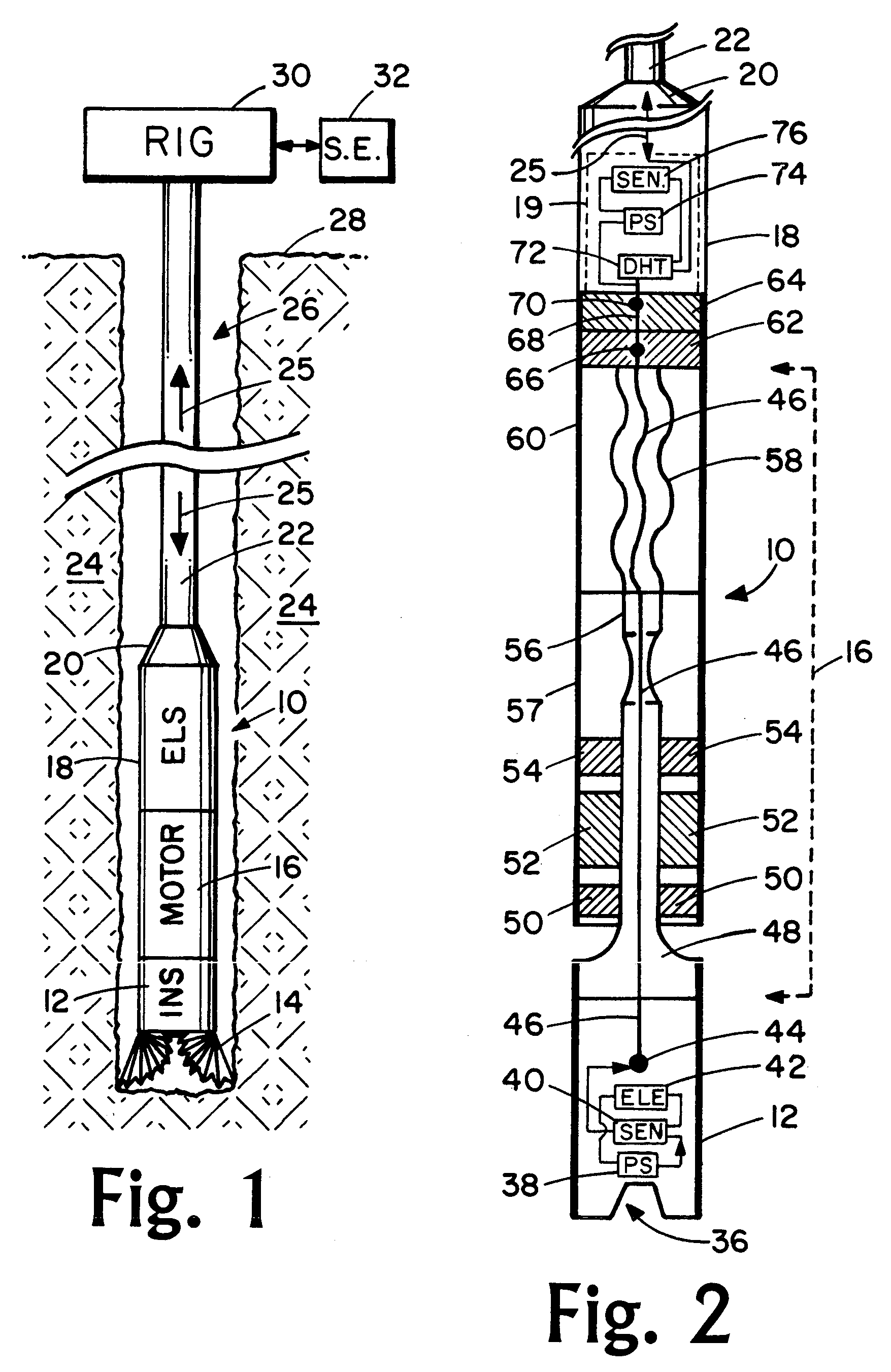
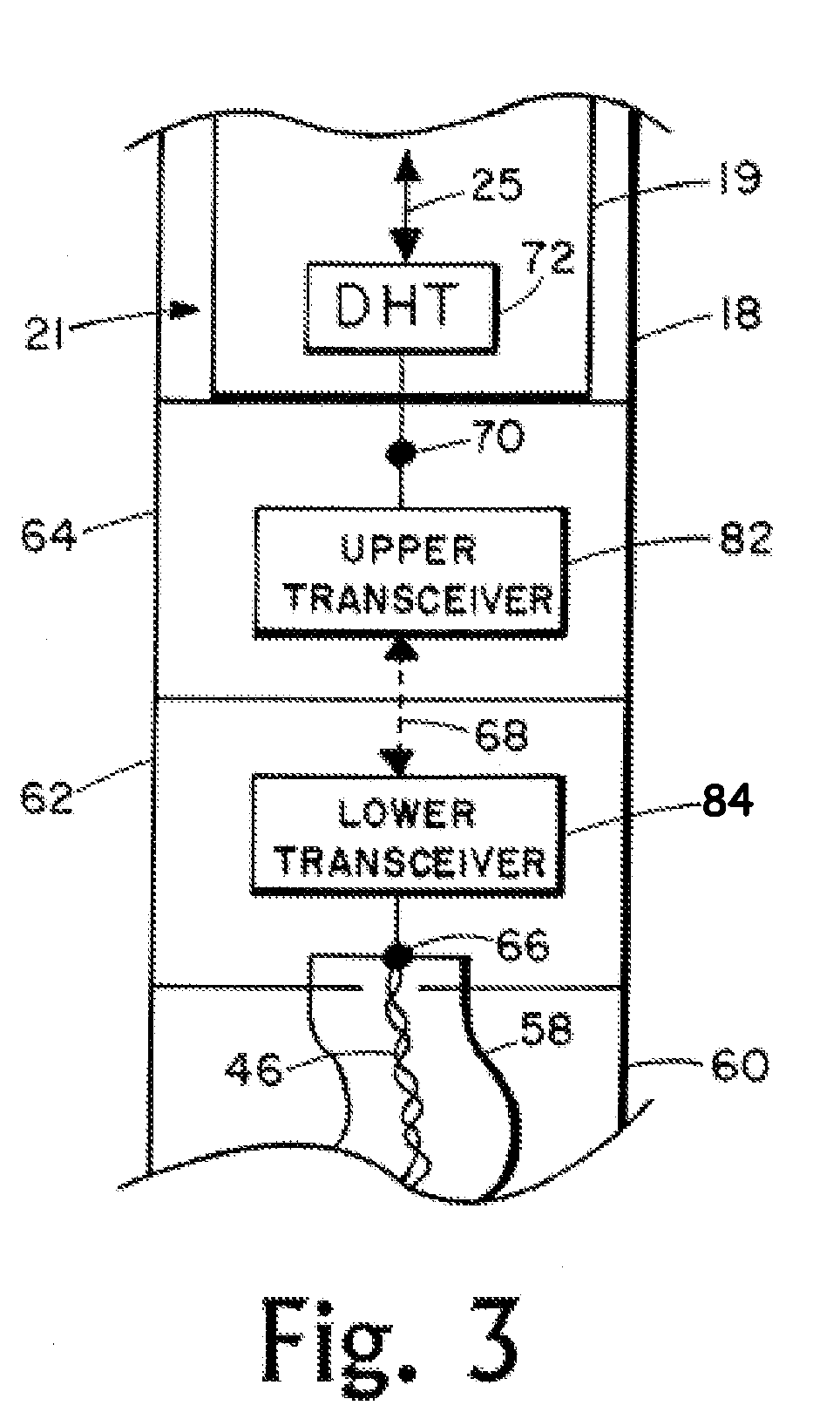
System and Method for Monitoring and Controlling Underground Drilling
ActiveUS20110186353A1Reduce the differenceVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingFinite element techniqueResonance
A system and method for monitoring underground drilling in which vibration is monitored by creating a model of the drill string using finite element techniques or finite difference techniques and (i) predicting vibration by inputting real time values of operating parameters into the model, and then adjusting the model to agree with measured vibration data, (ii) predicting the weight on bit and drill string and mud motor speeds at which resonance will occur, as well as when stick-slip will occur, so that the operator can avoid operating regimes that will result in high vibration, (iii) determining vibration and torque levels along the length of the drill string based on the measured vibration and torque at one or more locations, (iv) determining the remaining life of critical components of the drill string based on the history of the vibration to which the components have been subjected, and (v) determining the optimum drilling parameters that will avoid excessive vibration of the drill string.
Owner:APS TECH
Apparatus and method for directional drilling using coiled tubing
A steerable directional drilling tool assembly includes a bent housing defining a bend angle and having a mud motor in its upper section and a drill bit below its lower section, an orienting tool rotatably coupled to such upper section and suspended on coiled tubing that extends upward to the surface, an electric motor in the orienting tool operable to rotate the bent housing in either hand direction to change or adjust the tool face angle of the bit, or continuously rotate the bent housing so that the bit drills straight-ahead, and an electric cable extending throughout the coiled tubing to furnish power from the surface to the electric motor and transmit electric signals to and from the surface. A logging tool can be included in the assembly for measuring characteristics of the formation, the borehole, and the tool assembly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Apparatus and method for measuring while drilling
InactiveUS20060254819A1Improve cost efficiencyImprove drilling performanceSurveyConstructionsWell drillingMud motor
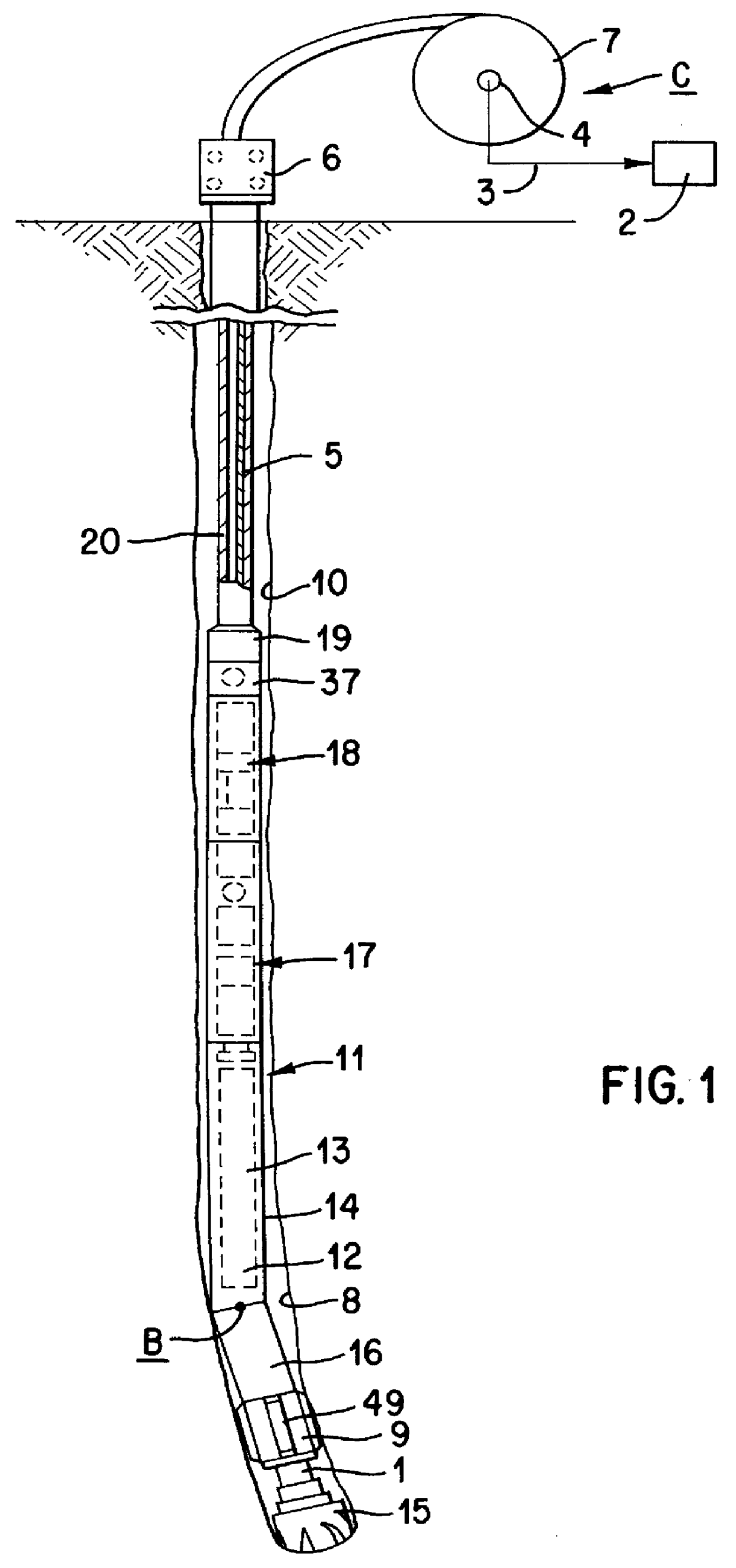
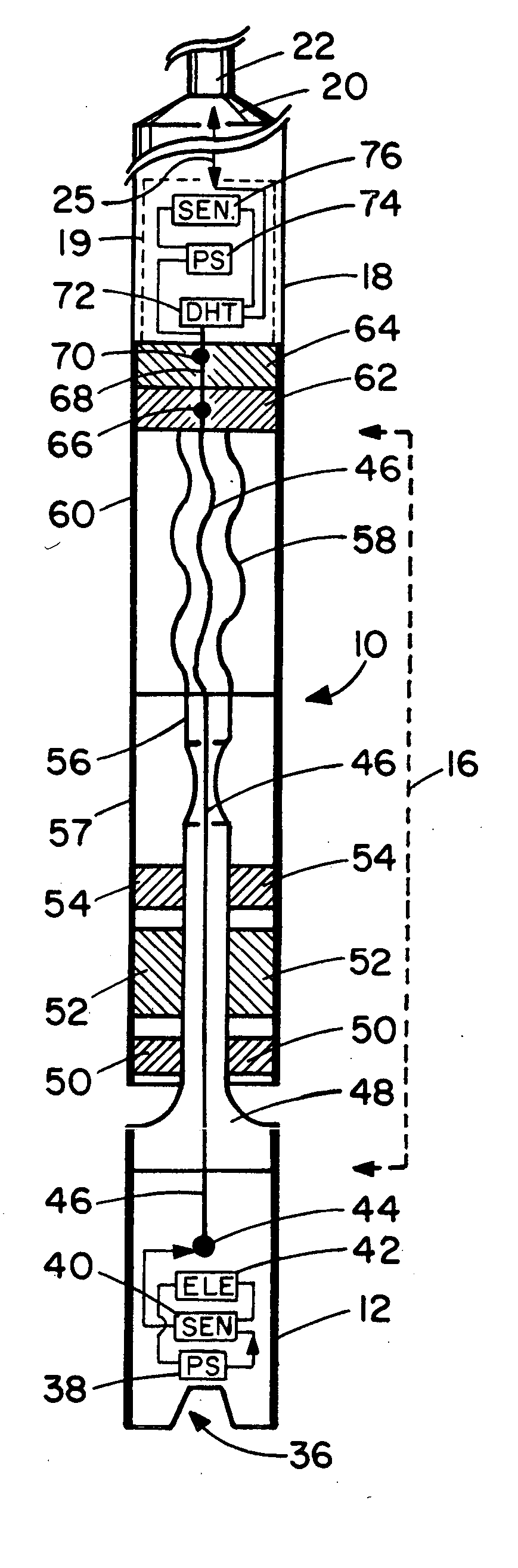
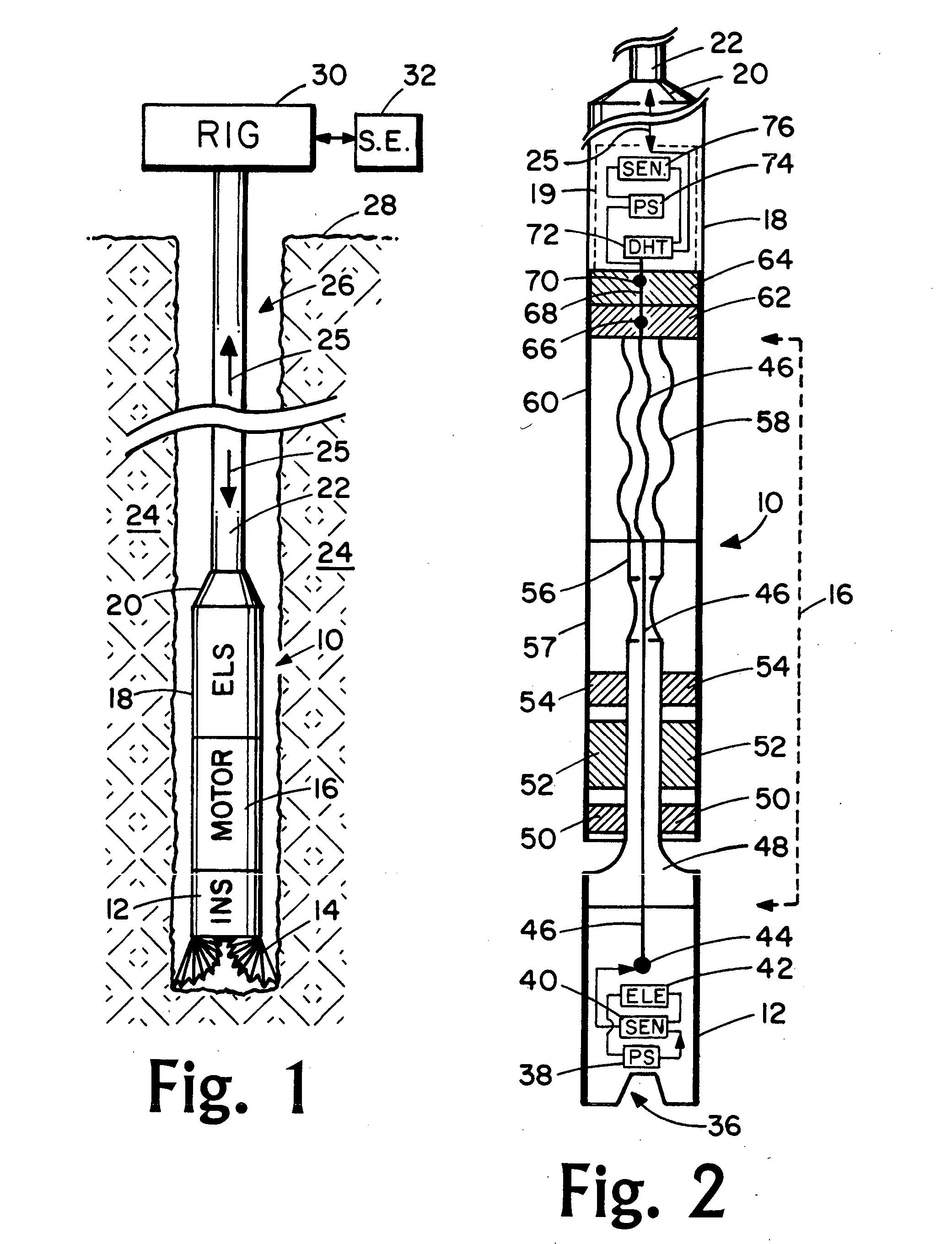
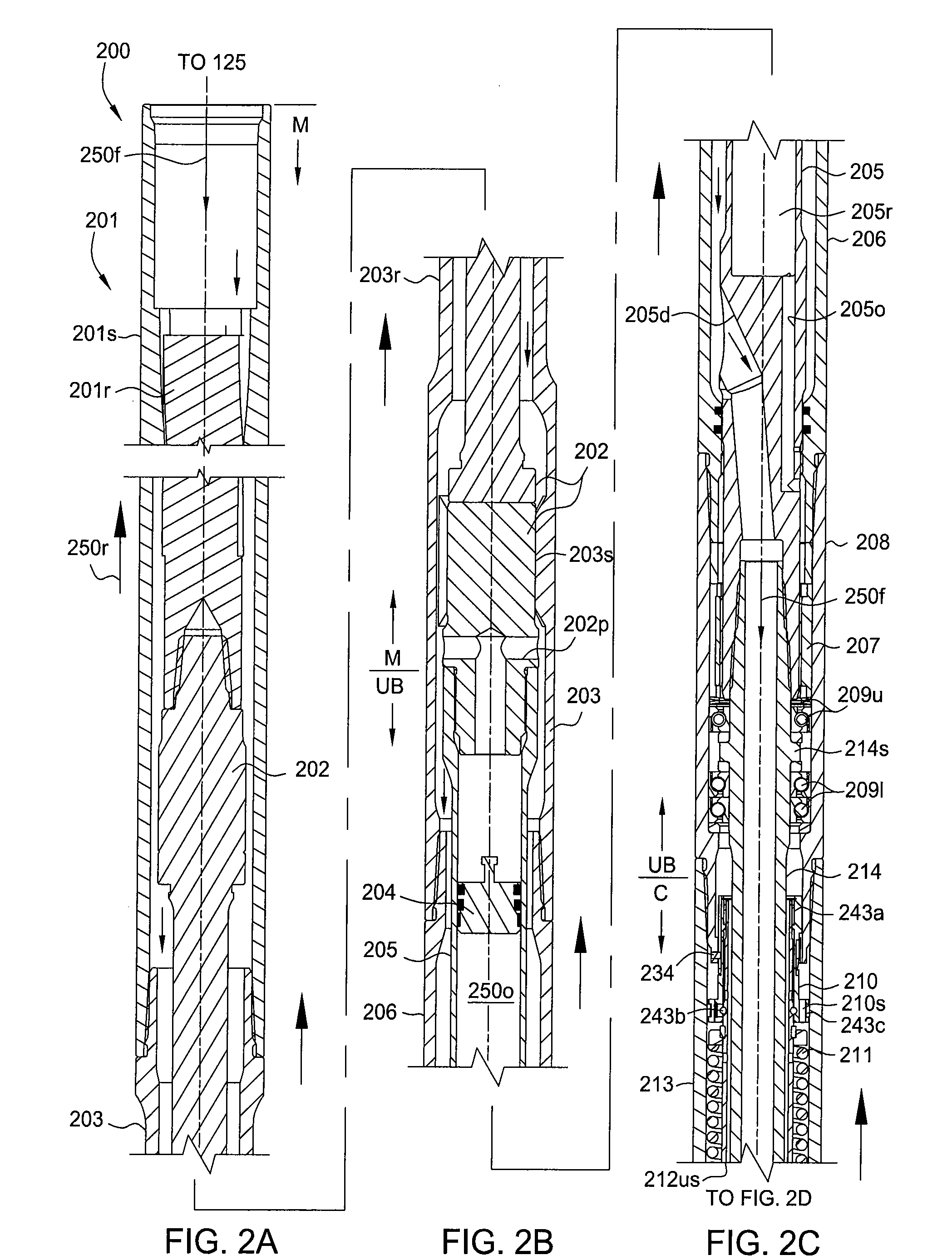
An apparatus, system, and method for transmitting measurements while drilling are adapted for use with a drill string equipped with a mud motor. The drill string may comprise a plurality of interconnected drill pipe joints or a plurality of interconnected casing joints. The apparatus comprises a measurement-while-drilling tool adapted for placement in the drill string beneath the mud motor. The measurement-while-drilling tool has a system for transmitting telemetry signals, such as mud-pulse telemetry signals, upwardly through the mud motor and the drill string. In particular embodiments, the measurement-while-drilling tool has a system for transmitting mud-pulse telemetry signals upwardly through the mud motor and the drill string at frequencies below approximately 1 Hz, although other frequencies may be employed to advantage. The apparatus may further comprise a rotary steerable system for placement in the drill string beneath the mud motor. The rotary steerable system may be a point-the-bit system or a push-the-bit system. In particular embodiments, the rotary steerable system and the measurement-while-drilling tool are integrated.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for transmitting sensor response data and power through a mud motor
InactiveUS7303007B2Save powerMush less affectedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
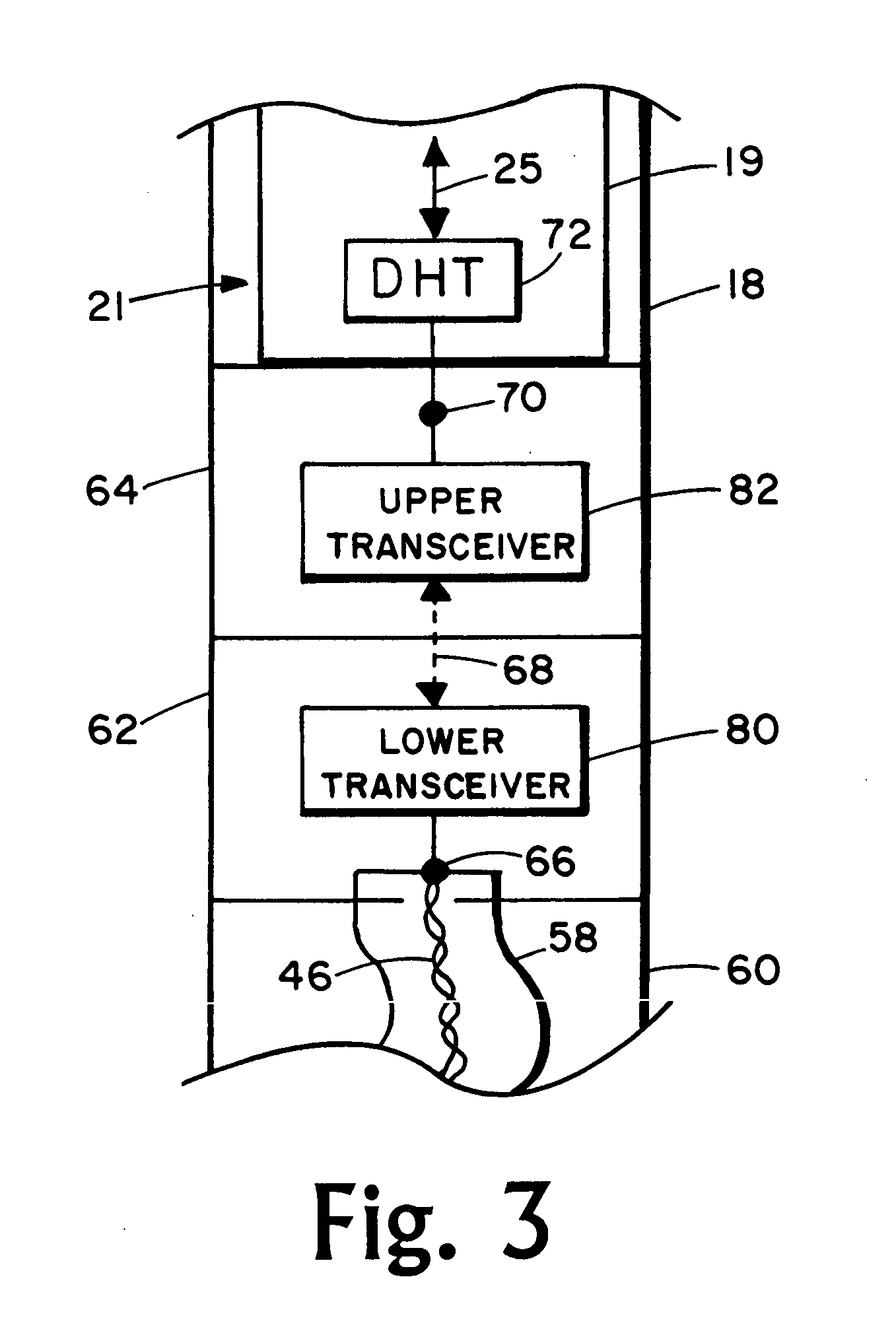
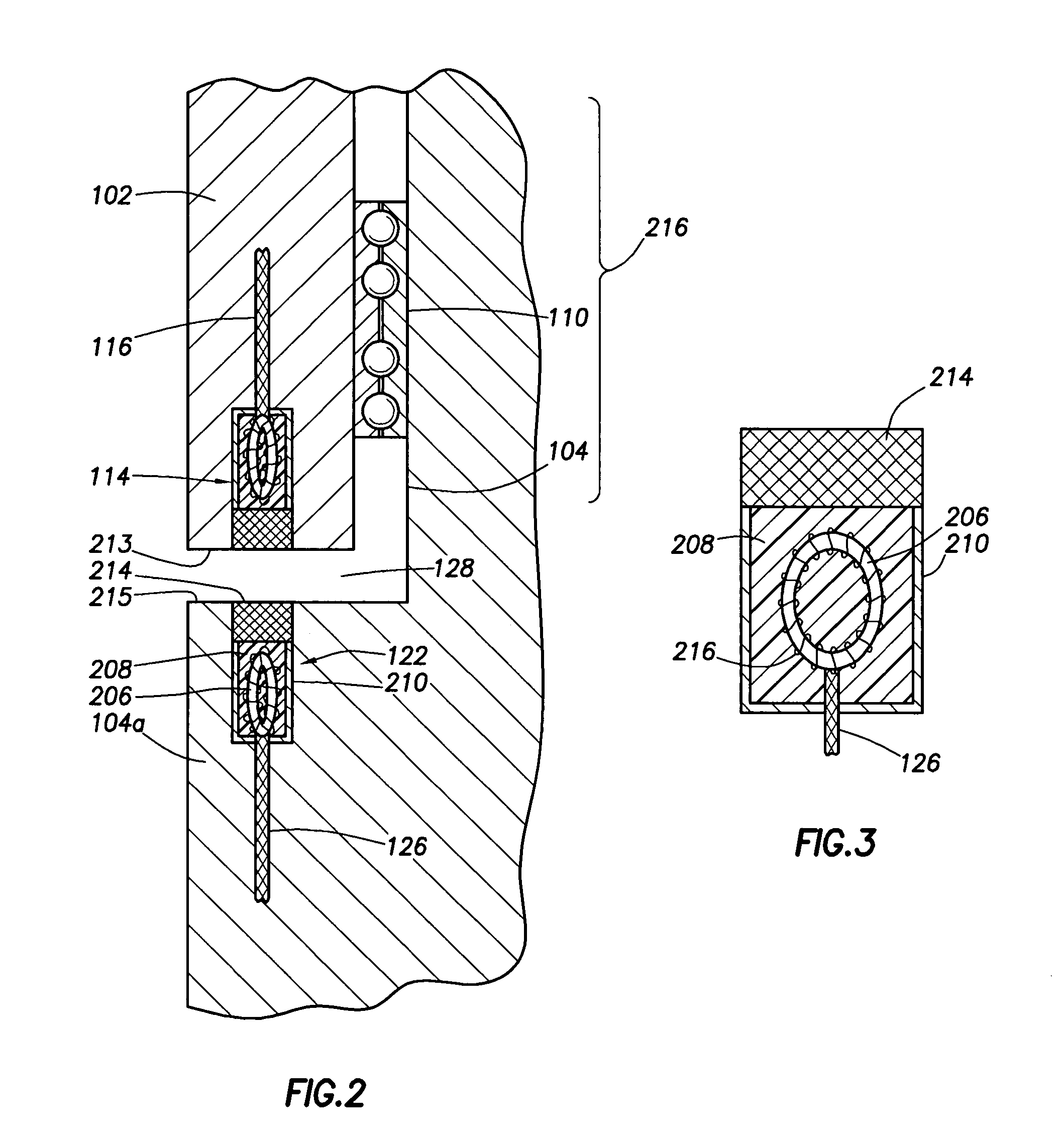
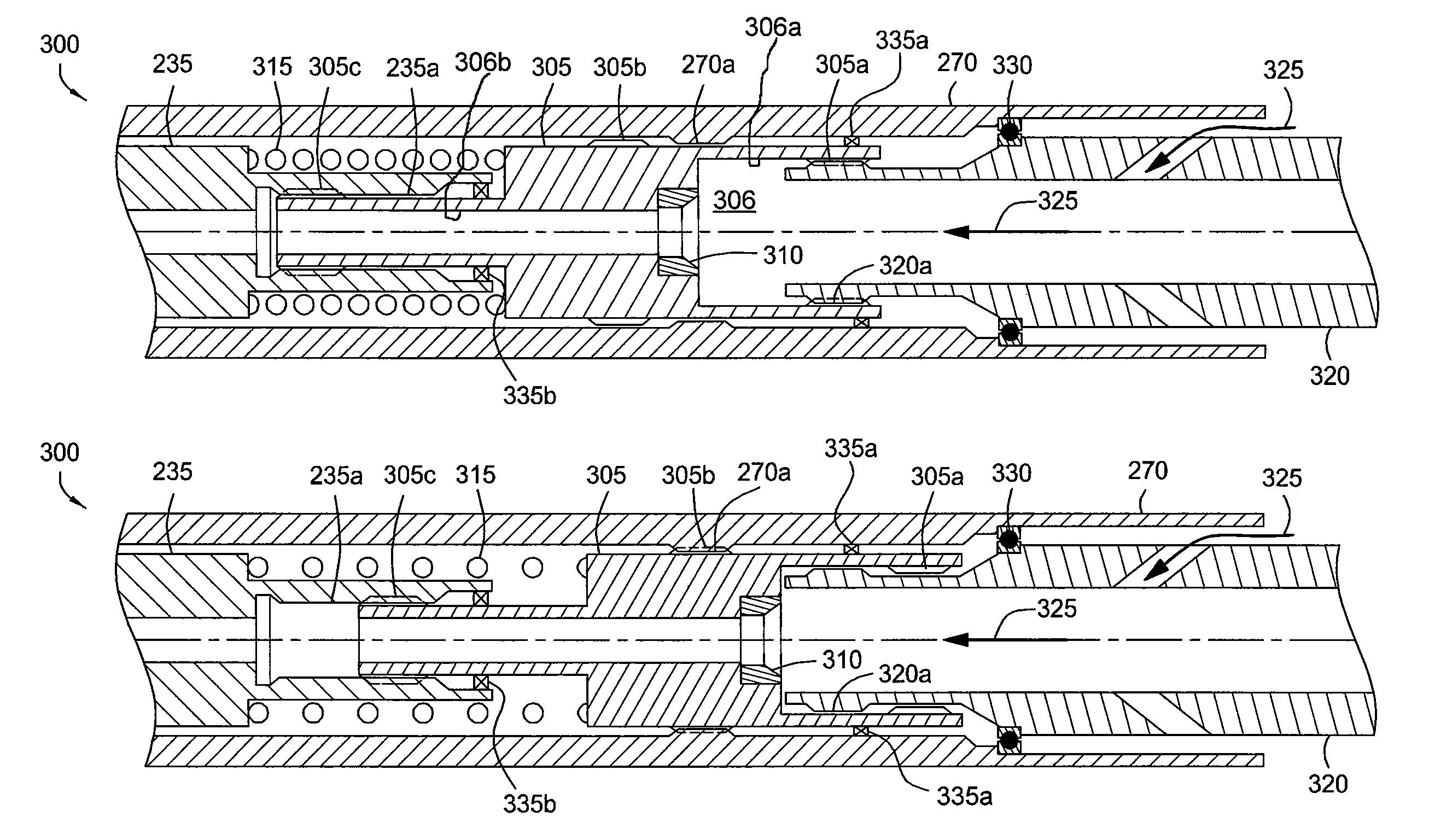
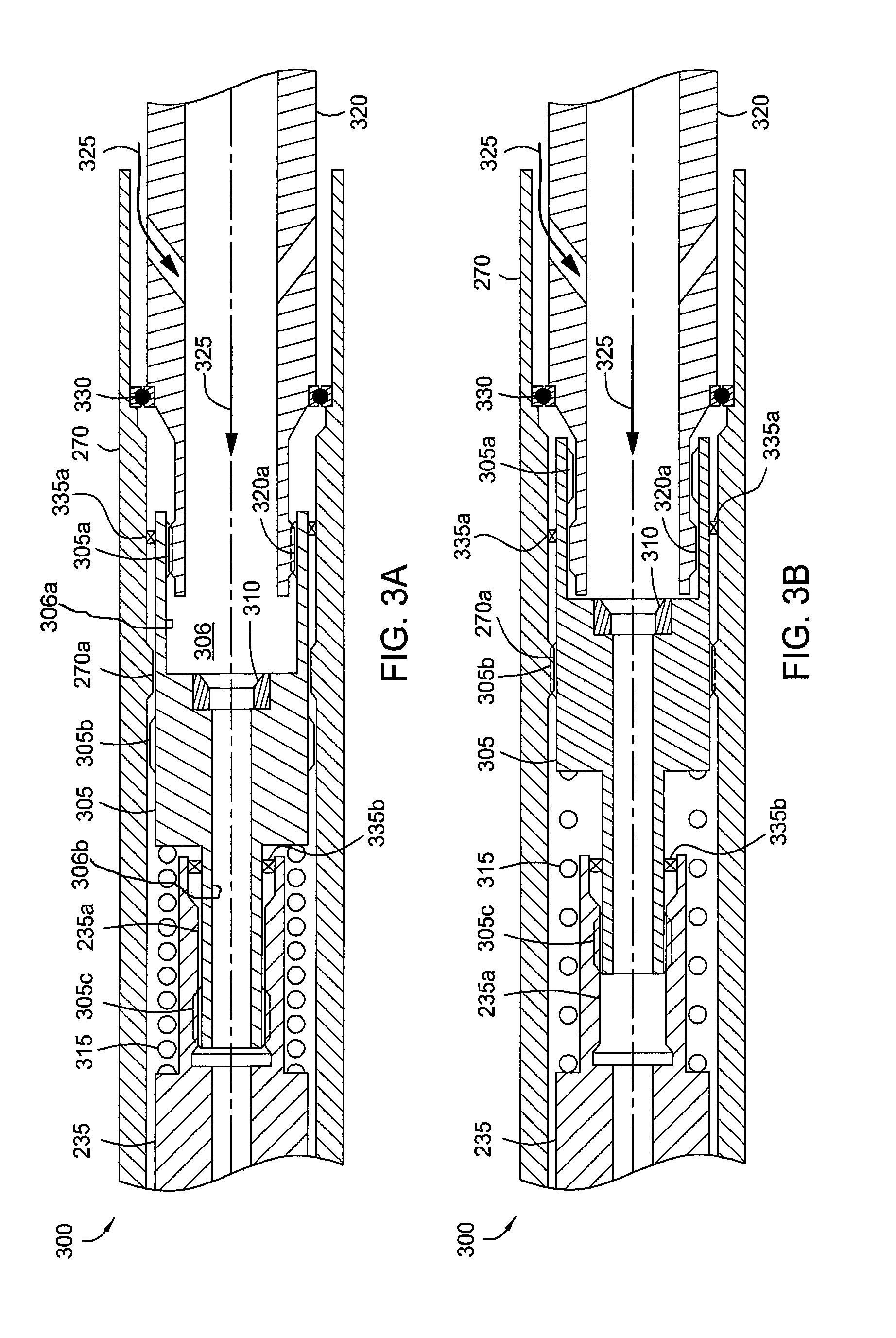
Apparatus and methods for establishing electrical communication between an instrument subsection disposed below a mud motor and an electronics sonde disposed above the mud motor in a drill string conveyed borehole logging system. Electrical communication is established via at least one conductor disposed within the mud motor and connecting the instrument sub section to a link disposed between the mud motor and the electronics sonde. The link can be embodied as a current coupling link, a magnetic coupling ling, an electromagnetic telemetry ling and a direct electrical contact link. Two way data transfer is established in all link embodiments. Power transfer is also established in all but the electromagnetic telemetry link.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA PARTNERSHIP
Method and apparatus for transmitting sensor response data and power through a mud motor
InactiveUS20070079988A1Save powerMush less affectedSurveyConstructionsElectric power transmissionElectrical conductor
Apparatus and methods for establishing electrical communication between an instrument subsection disposed below a mud motor and an electronics sonde disposed above the mud motor in a drill string conveyed borehole logging system. Electrical communication is established via at least one conductor disposed within the mud motor and connecting the instrument sub section to a link disposed between the mud motor and the electronics sonde. The link can be embodied as a current coupling link, a magnetic coupling ling, an electromagnetic telemetry ling and a direct electrical contact link. Two way data transfer is established in all link embodiments. Power transfer is also established in all but the electromagnetic telemetry link.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA PARTNERSHIP
Reverse circulation directional and horizontal drilling using concentric coil tubing
InactiveUS7066283B2Less and safe mannerAvoid damageArtificial islandsDrilling rodsWell drillingCoiled tubing
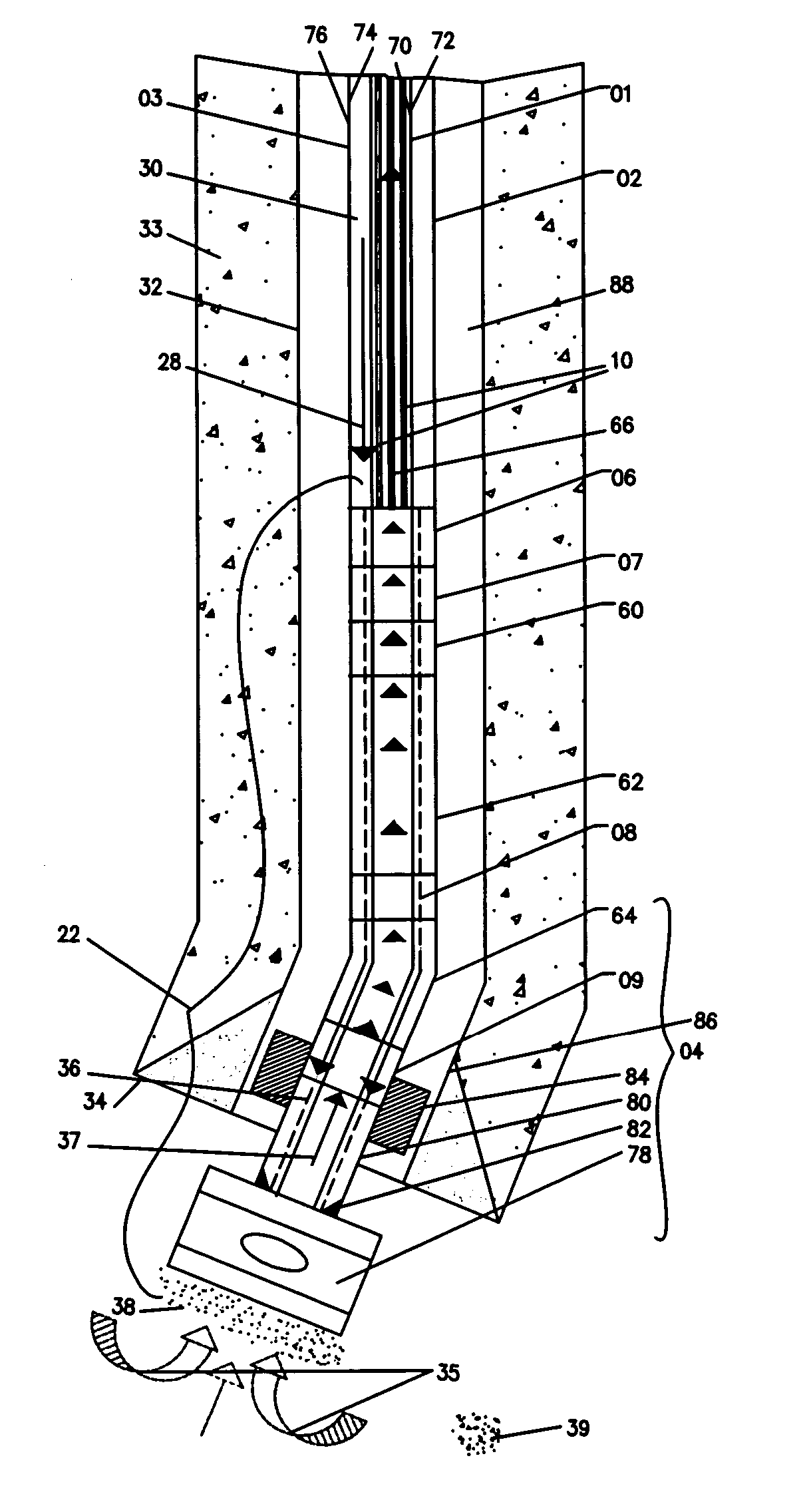
Method and apparatus for drilling a directional or horizontal wellbore in a hydrocarbon formation using concentric coiled tubing drill string having an inner coiled tubing string and an outer coiled tubing string defining an annulus there between. A bottomhole assembly comprising a directional drilling means is provided at the lower end of the concentric coiled tubing drill string for reverse circulation drilling. Directional drilling means comprises a reciprocating air hammer and a drill bit, a positive displacement motor and a reverse circulating drill bit, or a reverse circulating mud motor and a rotary drill bit, and a bent sub or housing. Drilling medium is delivered through the annulus or inner coiled tubing string for operating the directional drilling means to form the directional or horizontal wellbore. Exhaust drilling medium comprising drilling medium, drilling cuttings and hydrocarbons are removed from the wellbore by extraction through the other of the annulus or inner coiled tubing string.
Owner:PRESSSOL
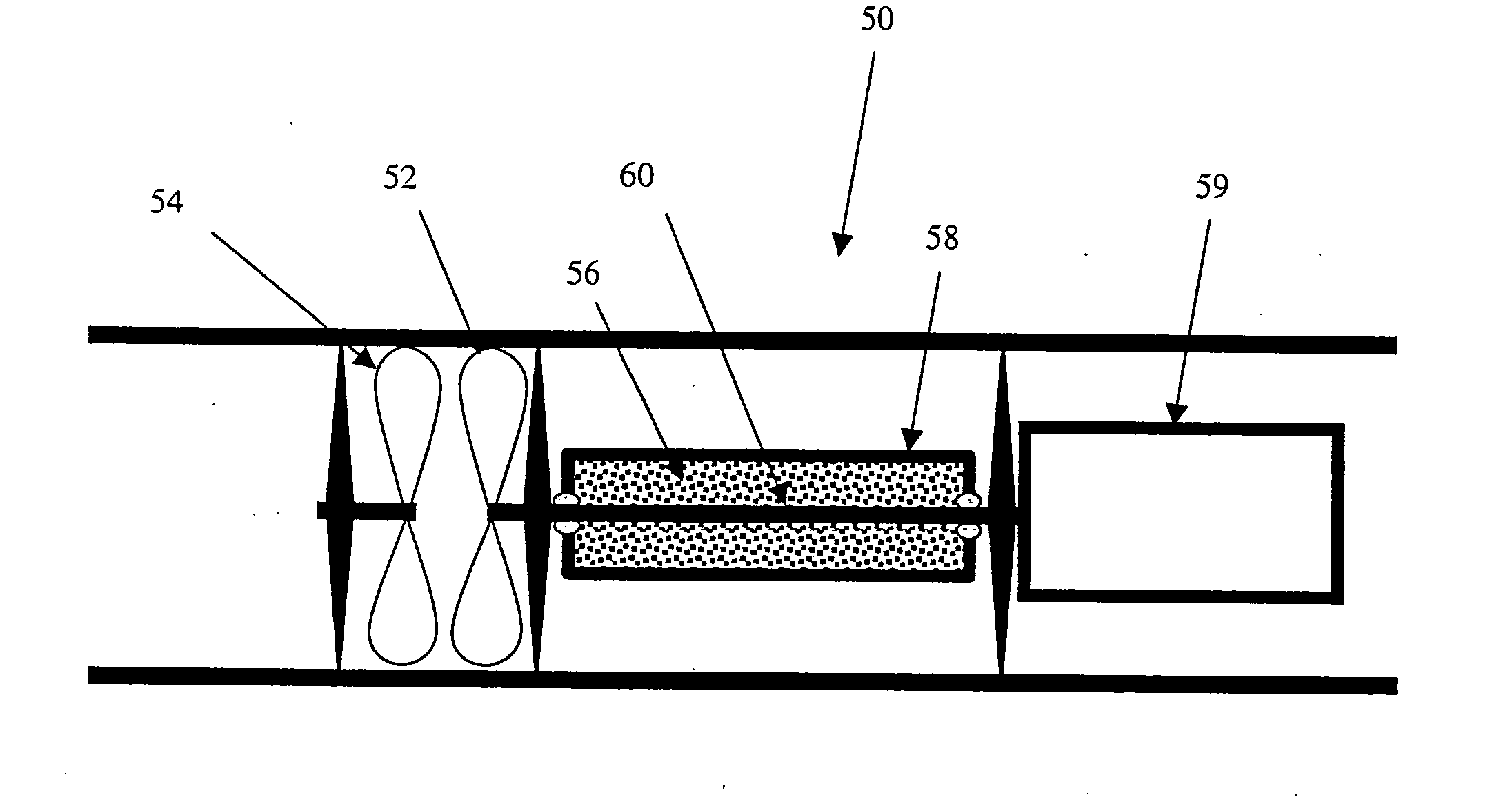
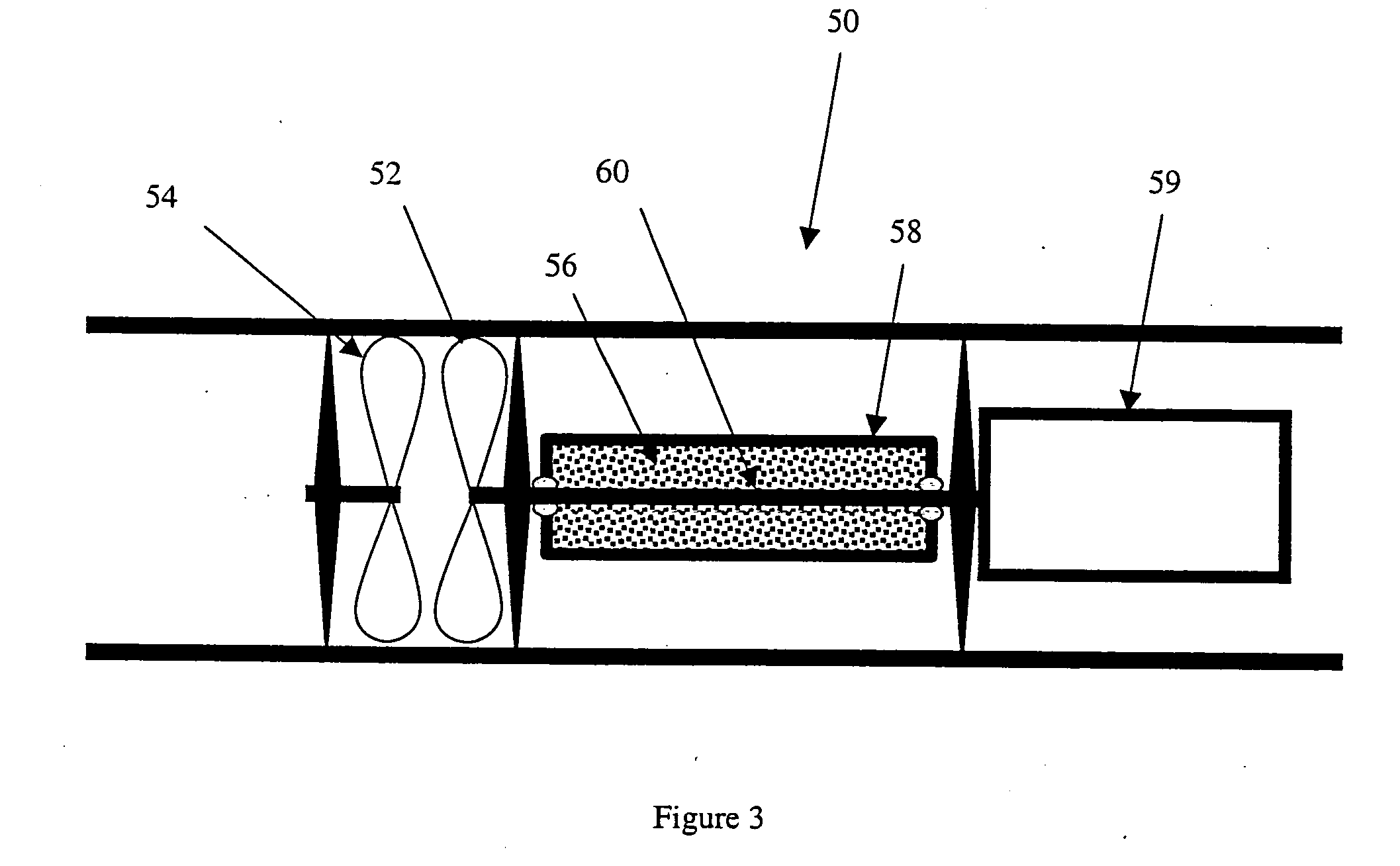
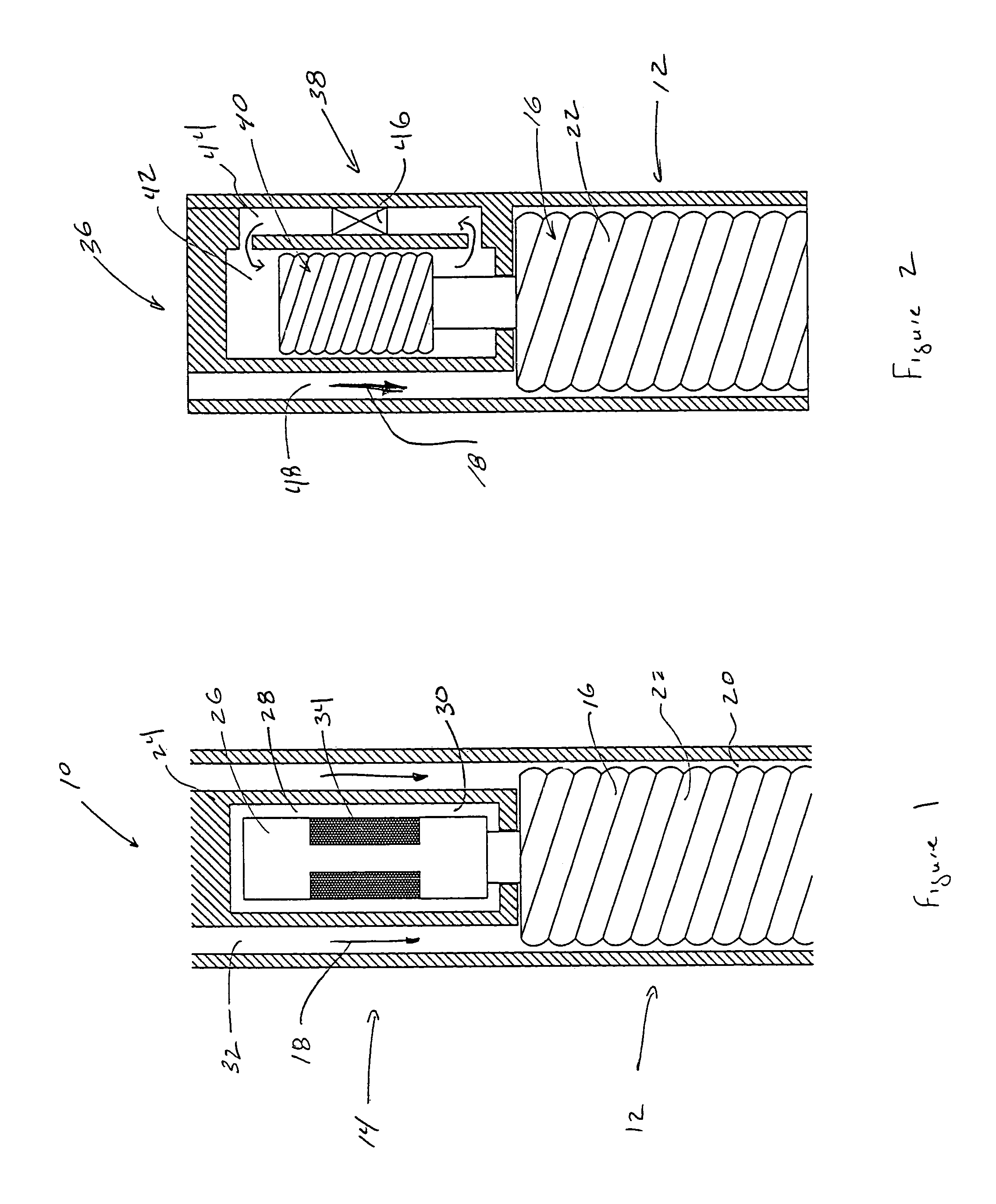
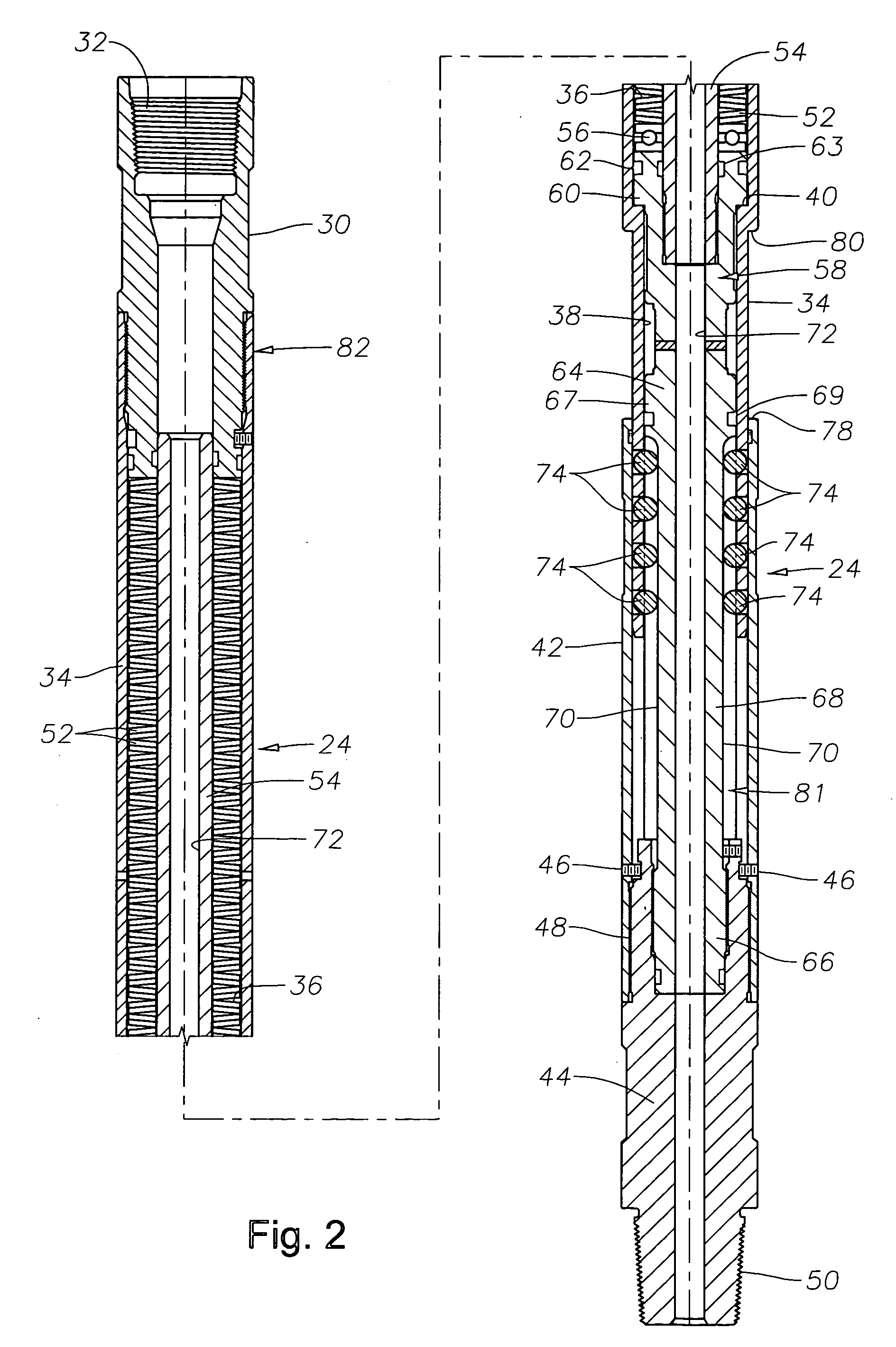
Mud motor with integrated percussion tool and drill bit
A downhole tool having a progressive cavity mud motor with an impact generator disposed within the mud motor rotor or bearing assembly. In one embodiment, the impact generator includes a mud turbine connected to a eccentric ring that encircles and periodically strikes an anvil surface of a percussion shaft. The eccentric ring is pivotable between an engaged striking position and a disengaged non-striking position. The percussion shaft is coupled to a drill bit though a splined connector that provides limited slip for transmitting rotation of the mud motor rotor to the drill bit and for transmitting percussion strikes against the anvil to the drill bit without the need to accelerate the entire drill string.
Owner:ULTERRA DRILLING TECH LP
Steering of bent housing mud motor downhole rotation device
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
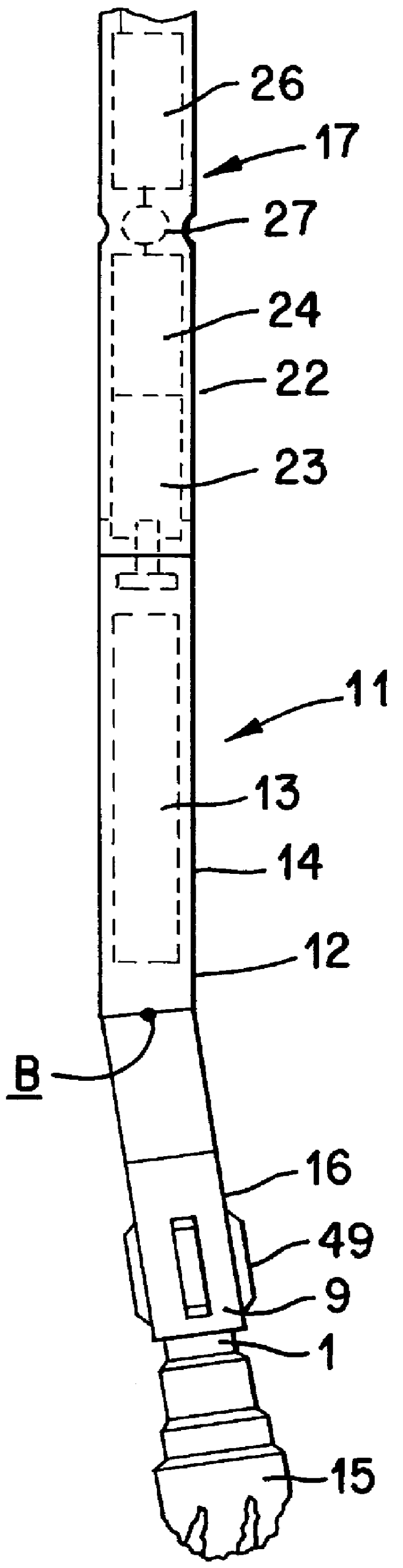
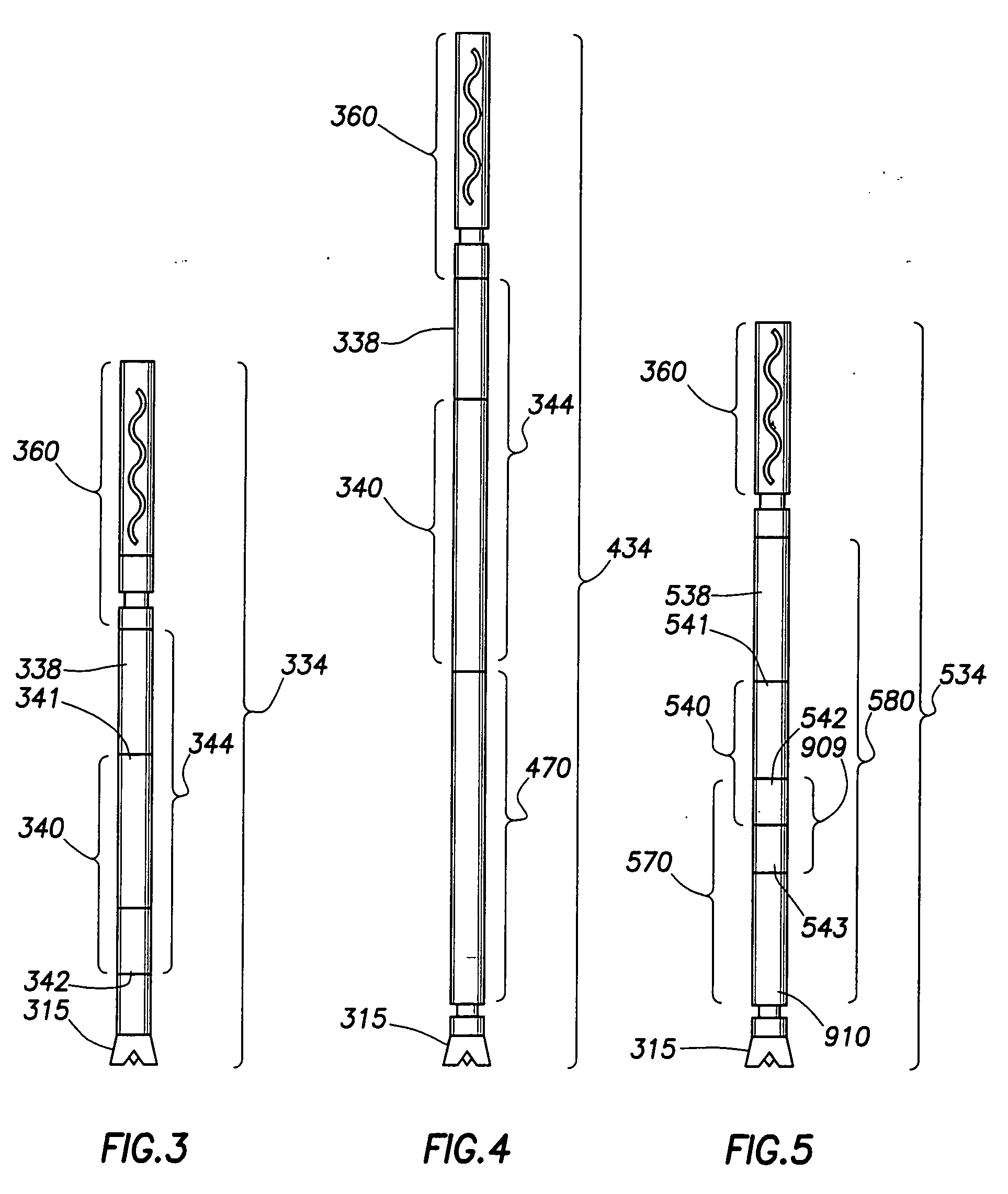
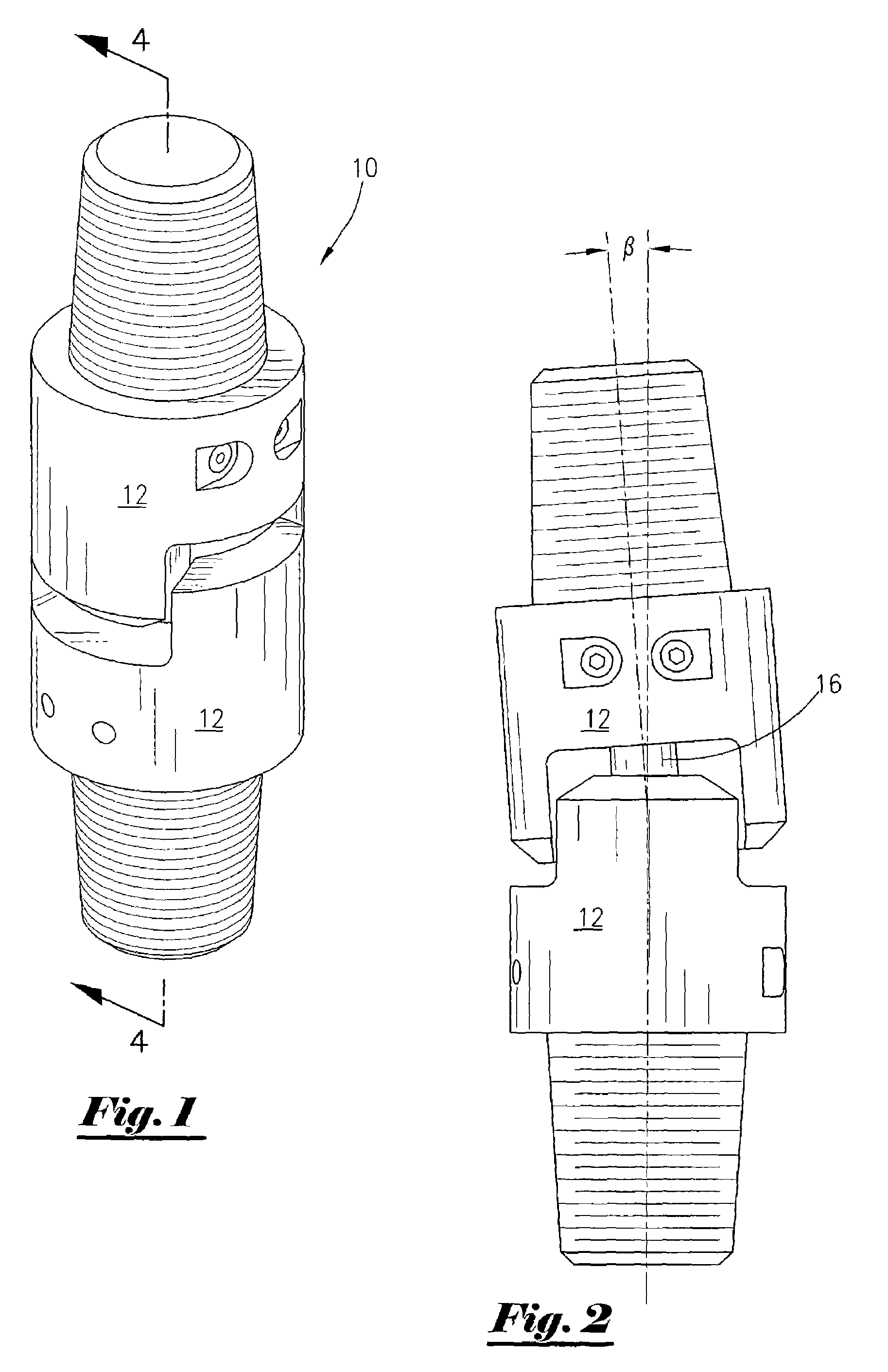
Drive line for down hole mud motor
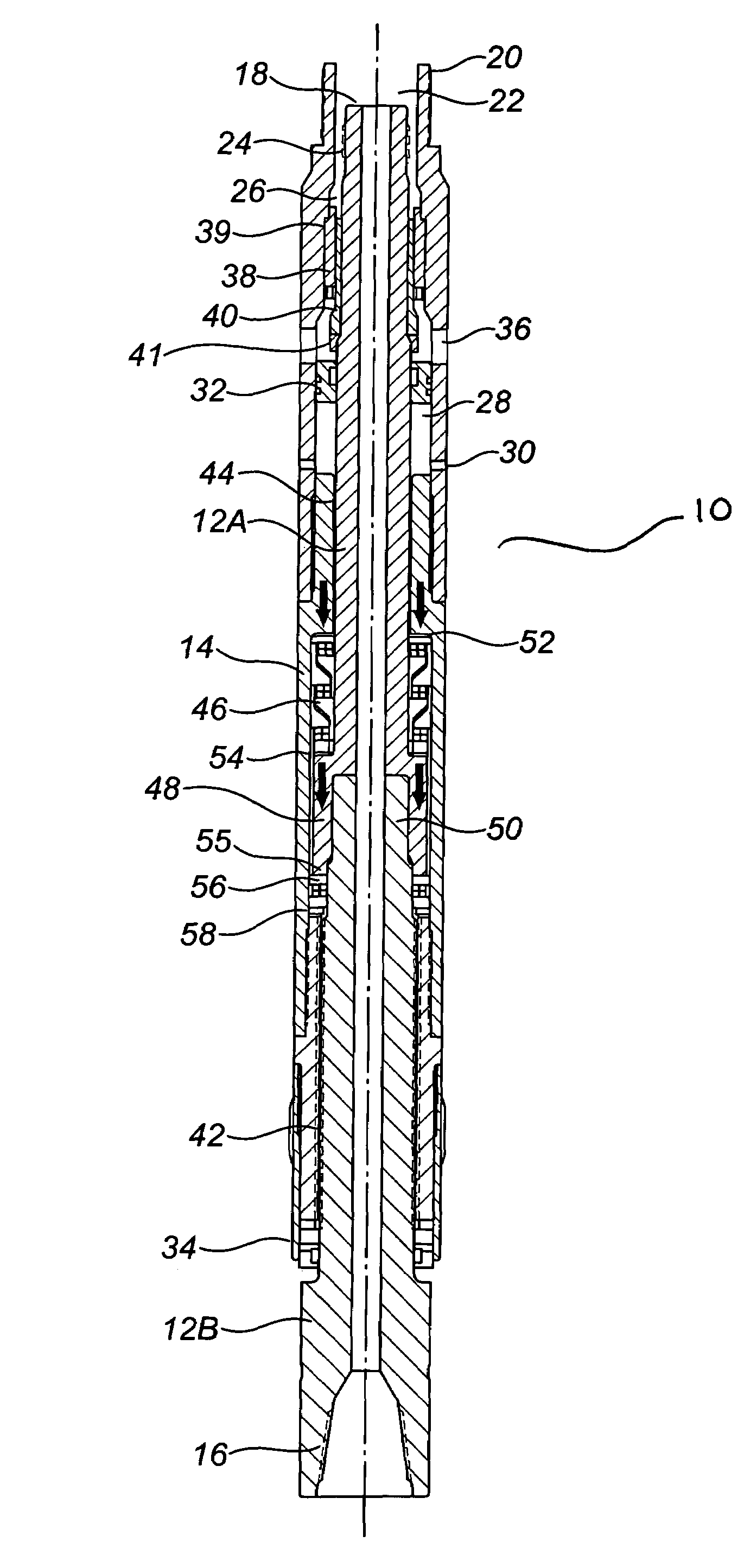
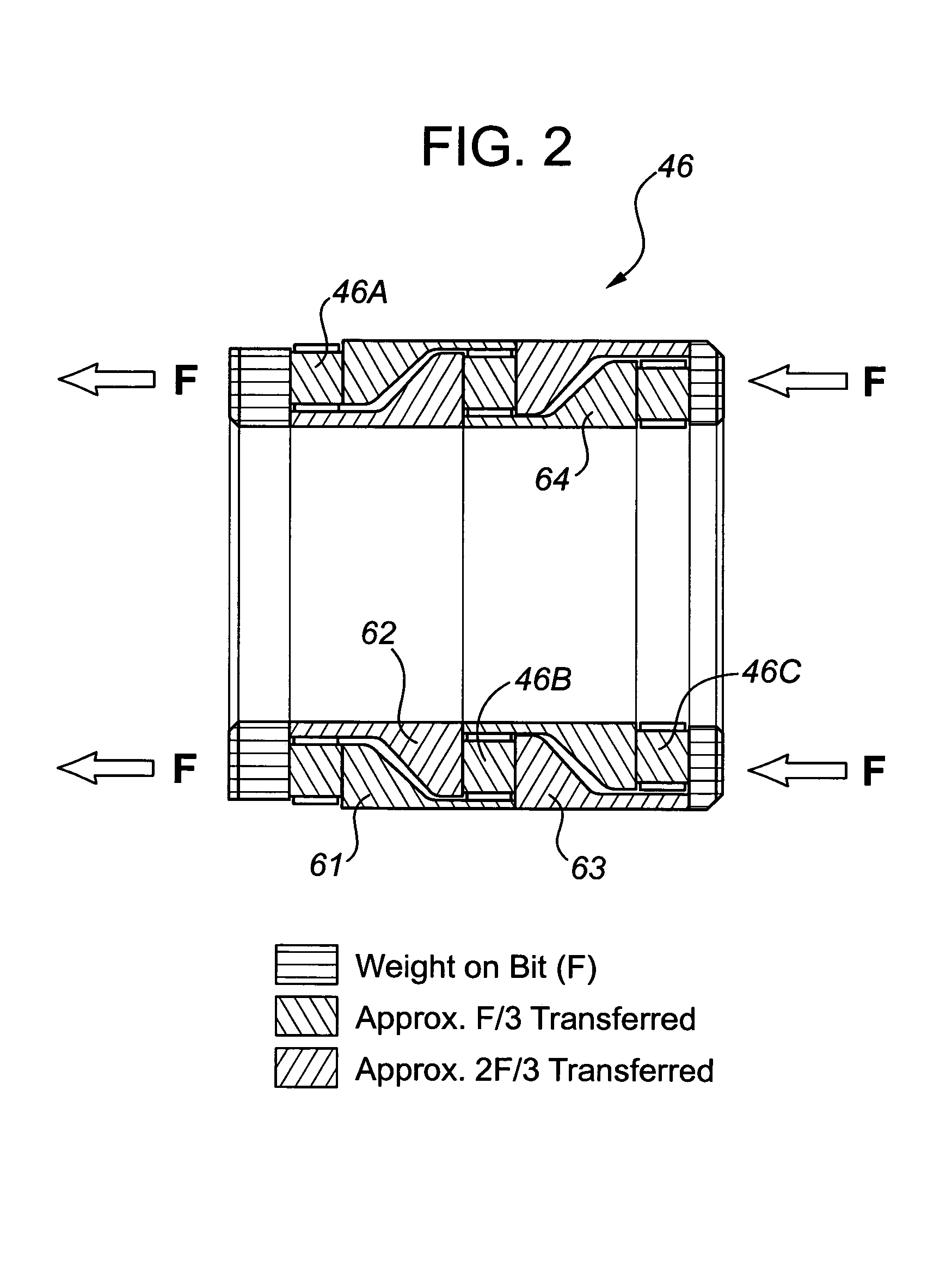
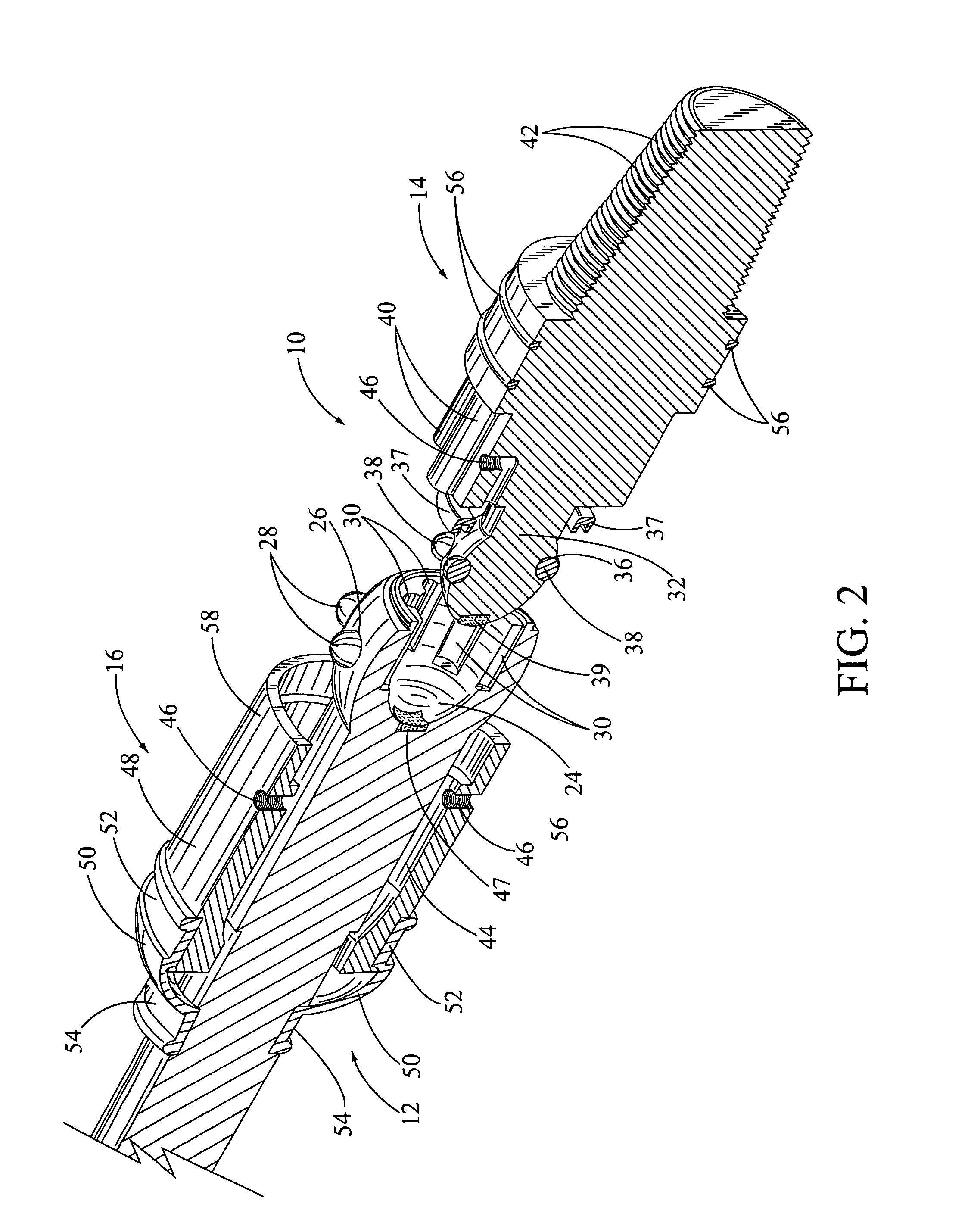
ActiveUS7186182B2Facilitating omni-directional pivotal movementIncrease surface contact areaYielding couplingDrilling rodsTorque transmissionMud motor
A drive line for a down hole mud motor has a plurality of elongate keys extending radially from an exterior surface of a central shaft for the purpose of transmitting torque. A plurality of circumferentially spaced axial keyways are provided in an interior surface of each end housing, which are adapted to receive the keys. Each of the keys has opposed sides, opposed ends and a front face. The front face is radiused both in a first direction between the opposed ends and in a second direction between the opposed sides, thereby accommodating the omni-directional pivotal movement of the shaft relative to the housing. The use of keys for torque transmission increases available contact area, with a corresponding increase in torque load capacity.
Owner:WENZEL DOWNHOLE TOOLS
Directional casing and liner drilling with mud motor
A directional casing drilling system includes a casing string, a mud motor operatively coupled to the casing string, a rotary steerable system operatively coupled to the mud motor, and a drill bit operatively coupled to the rotary steerable system.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Electrical transmission apparatus through rotating tubular members
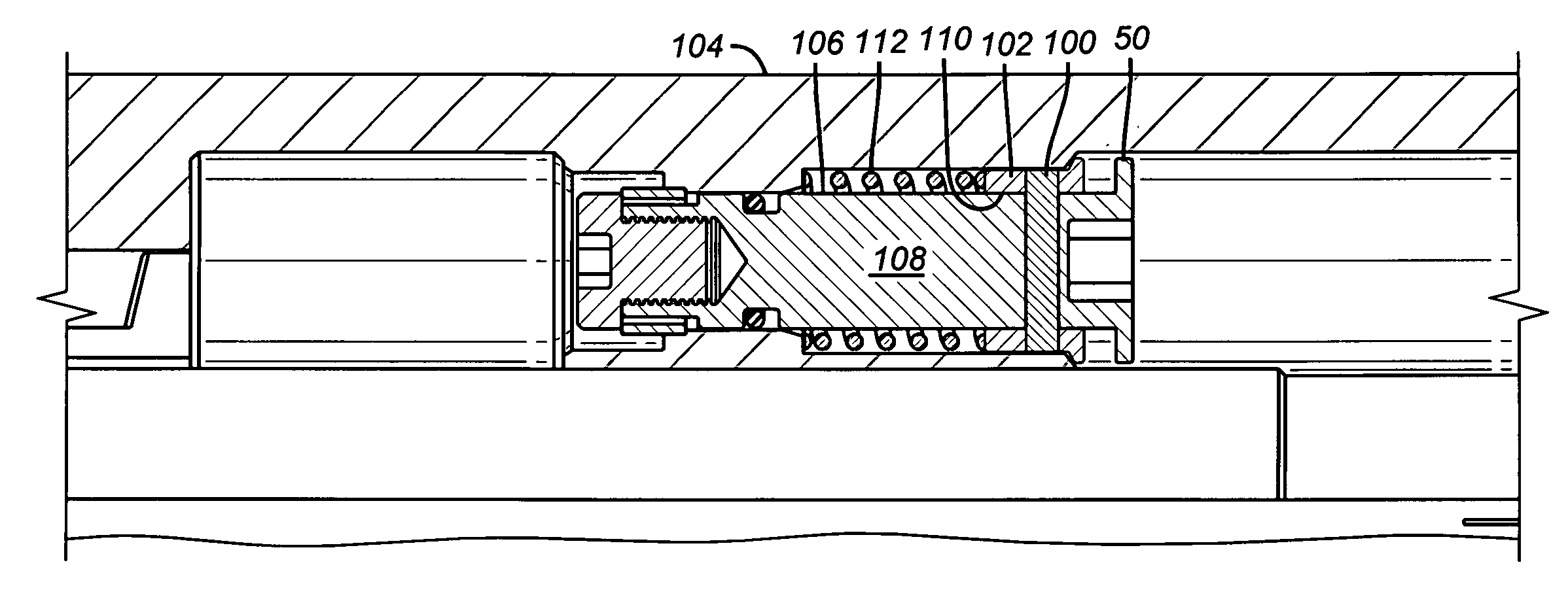
The present invention provides an apparatus for the communication of power or data signals across the rotating gap of two tubular members, such as the stator and rotor of a mud motor, and between said rotating members of a drill string through inductive couplers located axially along the drill string.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
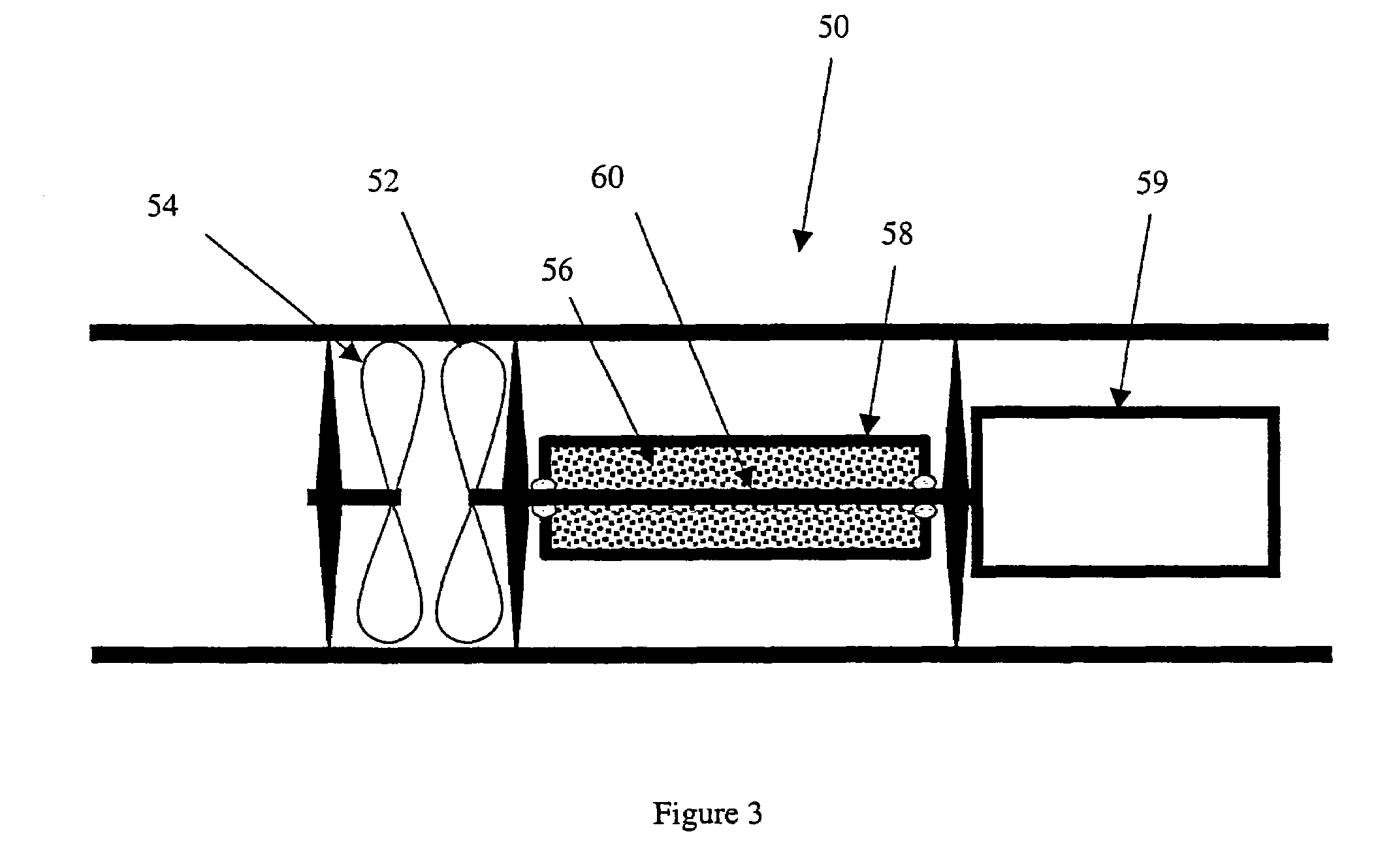
Valve for equalizer sand screens
A series of screens with restrictors to equalize flow through base pipe perforations downstream or upstream of each restrictor features a valve member in the openings so that the screens are closed to flow for run in. Pressure can be developed within the base pipe for operation of downhole equipment below the screens such as a mud motor or in the screen liner such as a packer with no need for an internal string or wash pipe. The openings can be opened selectively when the associated equipment connected to the base pipes has been operated. The valve member can be actuated to open in a variety of ways such as applied pressure, temperature or a change in well fluid condition.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
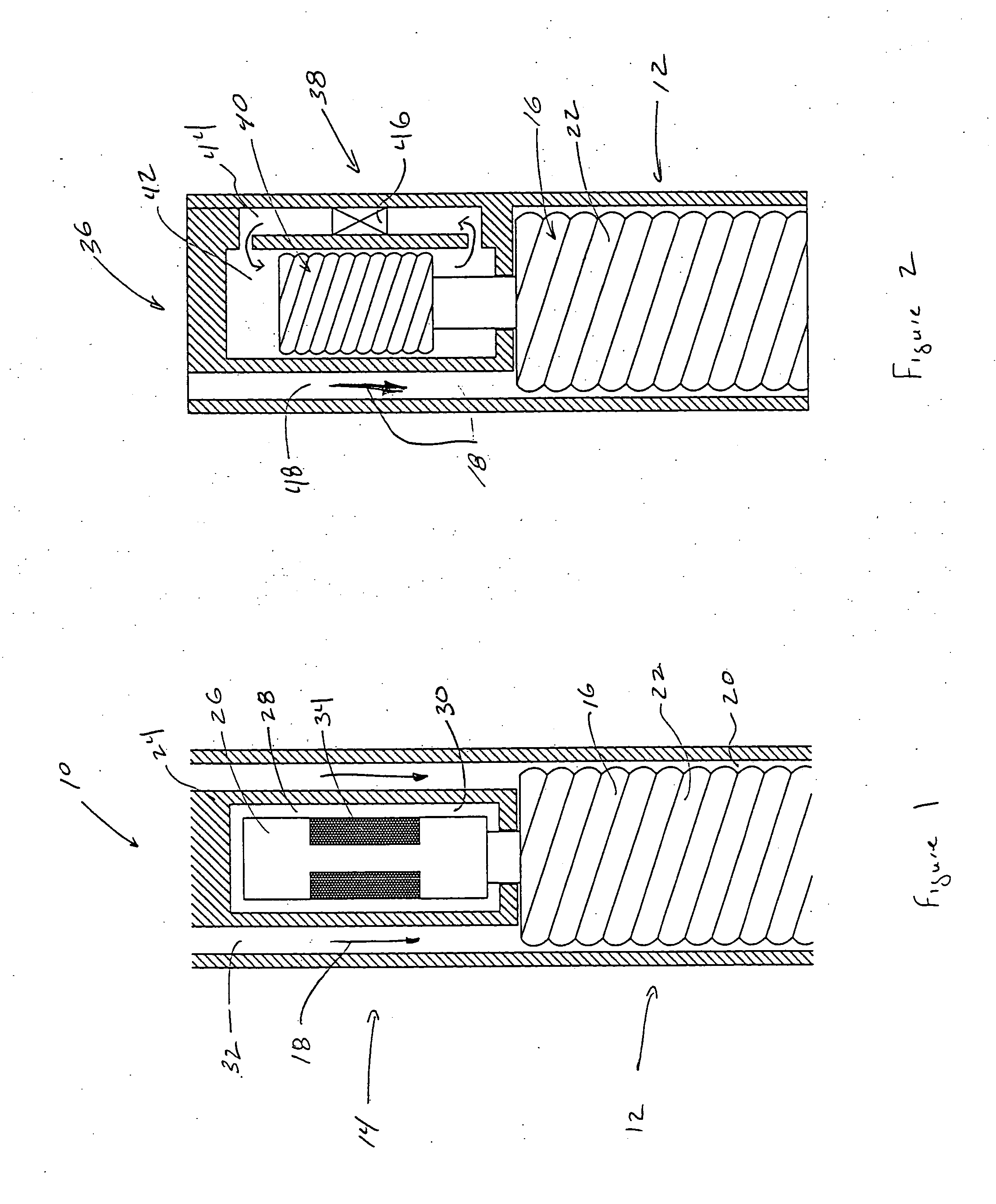
Magnetorheological fluid controlled mud pulser
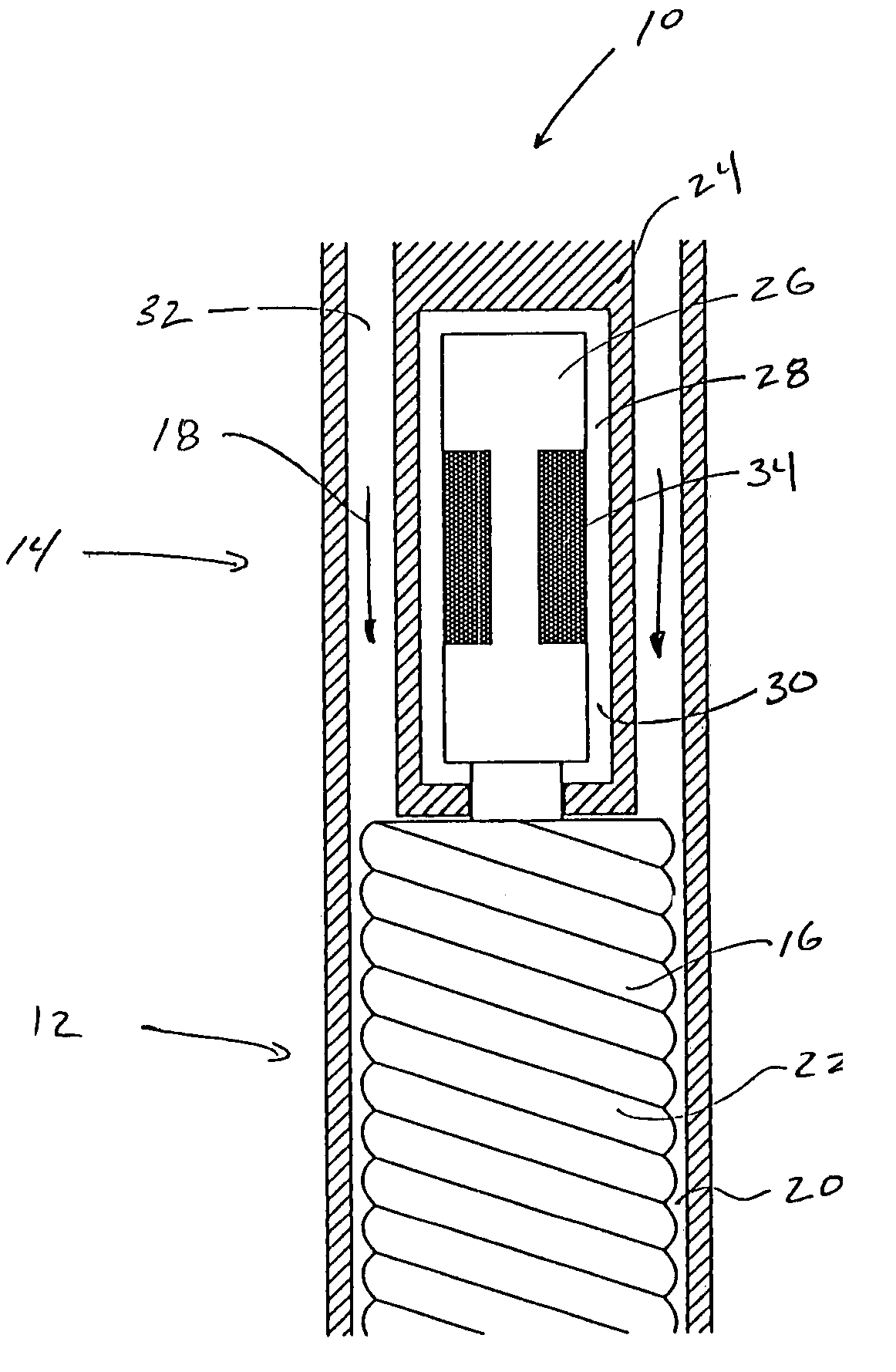
A mud pulser controlled by a field applied to an electroactive fluid. The electroactive fluid is employed to act as a rapid-response brake to slow or interrupt the rotation of a mud motor or mud siren, thus creating pressure pulses in a circulating fluid. In certain embodiments, the electroactive fluid is used as a direct brake acting on a shaft rotating in a volume of electroactive fluid where the shaft is coupled to the mud motor or siren. The application of a field to the electroactive fluid impedes the rotation of the shaft, thus slowing the mud motor and creating a pressure pulse in the circulating fluid. In another embodiment, a Moineau pump circulating an electroactive fluid is coupled to the mud motor. The application of a field to the electroactive fluid slows the rotation of the pump, thus slowing the mud motor and creating a pressure pulse in the circulating fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Flow control valve and method of controlling rotation in a downhole tool
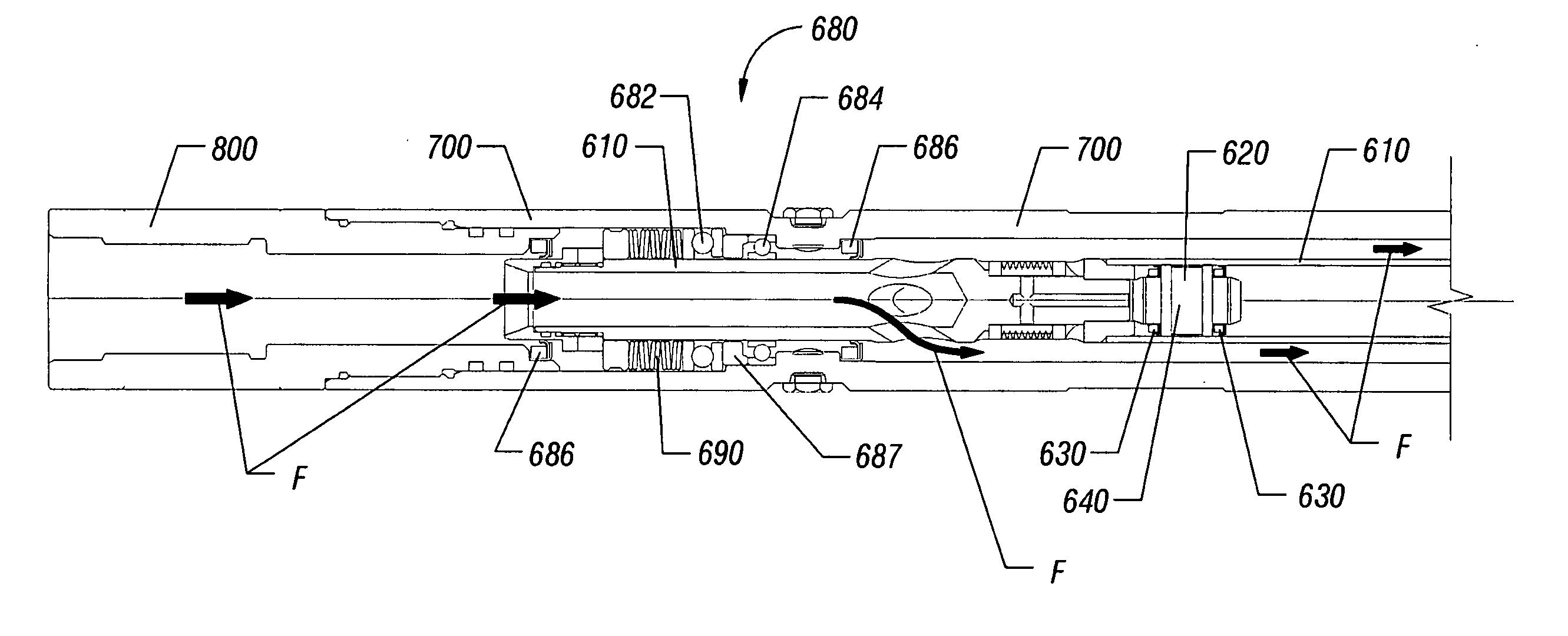
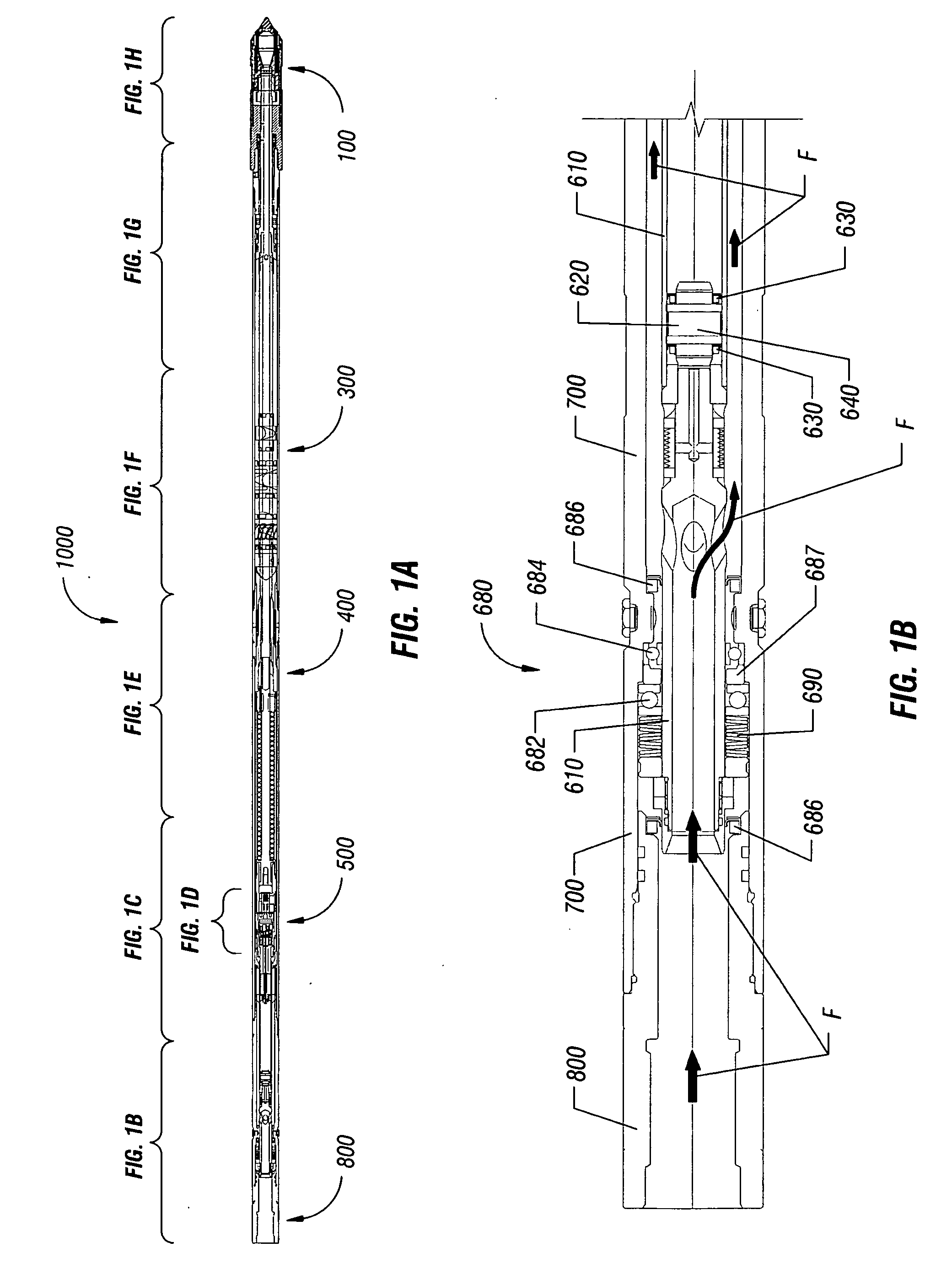
InactiveUS7086486B2Facilitate communicationBypass flowCleaning apparatusFlexible member pumpsHydraulic motorMotor speed
A flow control valve is disclosed for controlling the rotation of a hydraulic motor, such as a turbine, a mud motor, for example, having an element that rotates in response to power fluid. The valve disclosed may include a valve housing and a valve piston, each having a port, moveable relative to one another. When the ports at least partially align, bypass flow is generated which acts to decrease the speed of rotation of the element, such as a turbine shaft. An energizer, such as a pump assembly, is further described which is adapted to move the valve housing or the valve piston in response to the speed of rotation, such that bypass flow is a function of the motor speed (i.e. speed of rotation of the element). A bottom hole assembly including a flow control valve and a method of controlling the rotation of a downhole tool are also described.
Owner:BJ SERVICES CO
Method of drilling lateral wellbores from a slant well without utilizing a whipstock
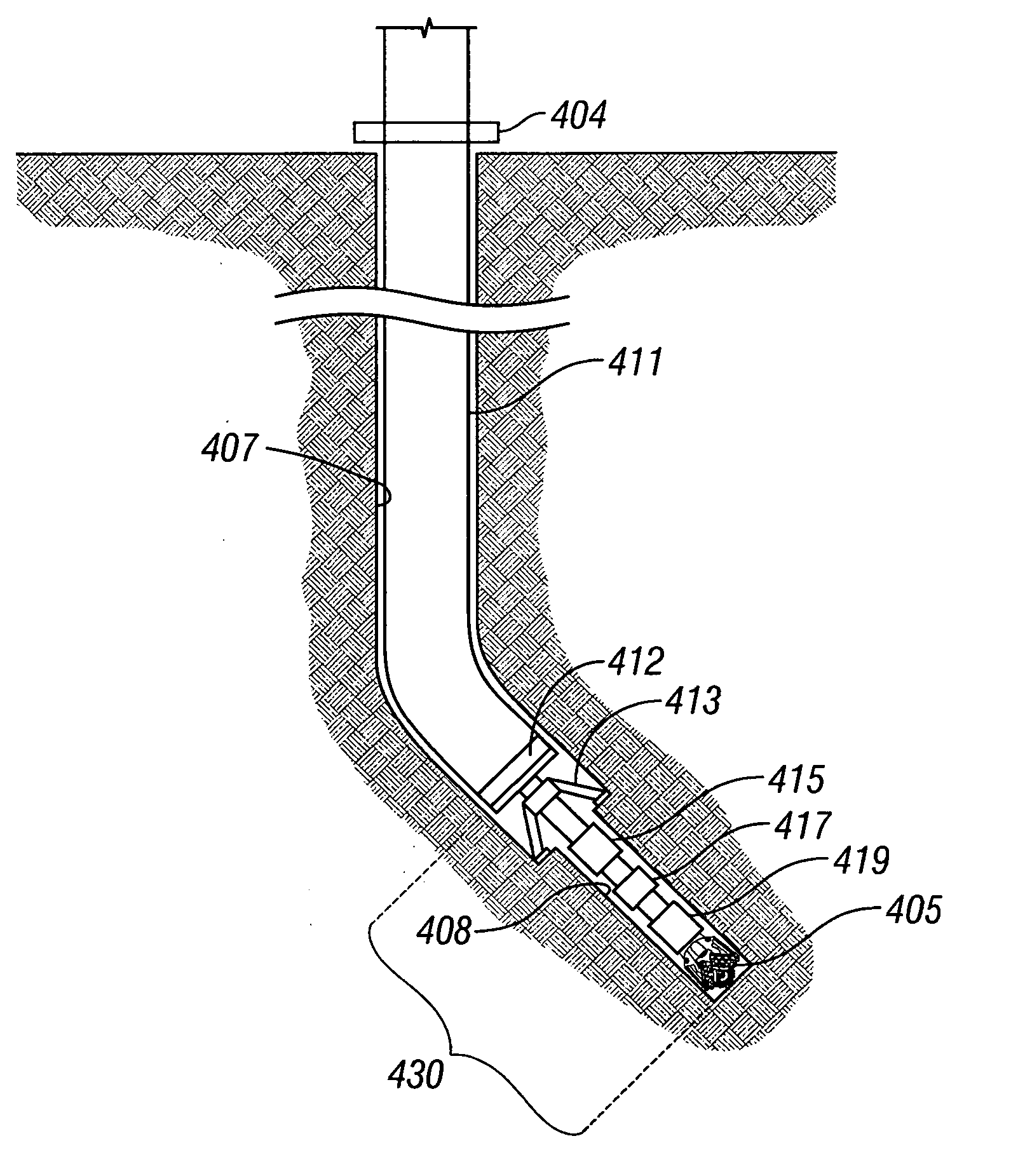
InactiveUS6964308B1Eliminates and reduces disadvantage and problemEfficient productionArtificial islandsDirectional drillingWell drillingMud motor
In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a method for drilling a lateral wellbore from a slant well includes drilling the slant well below the surface of the earth such that the slant well is angled toward a first horizontal direction that coincides with a desired drilling direction for the lateral wellbore. The slant well has a borehole wall that includes a high side portion closest to the surface, a low side portion farthest from the surface, and two side portions between the high side portion and the low side portion. The method further includes disposing a casing string in the slant well, disposing a drill string having a bent sub, a mud motor, and a drill bit coupled at a lower end thereof in the casing string, and positioning the drill bit adjacent either one of the side portions or the low side portion. The method further includes drilling, from either the side portion or the low side portion, an intermediate wellbore with the drill bit, and drilling, from the intermediate wellbore, the lateral wellbore in the desired drilling direction.
Owner:EFFECTIVE EXPLORATION
Autodriller bit protection system and method
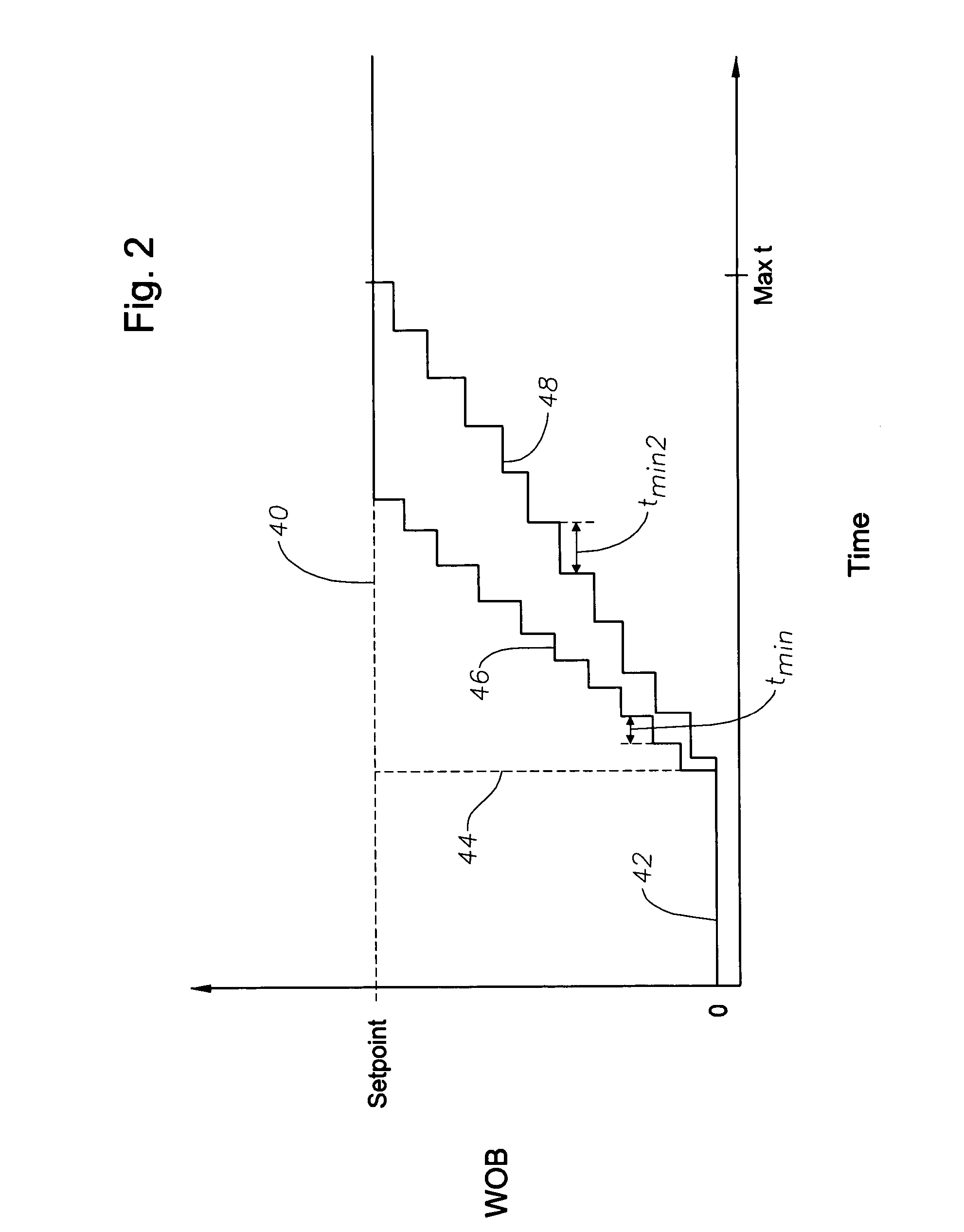
A controller provides an automatic bit protection sequence for an autodriller that can be initiated during the initial stage of set down of the bit within the formation. The automatic protection sequence establishes a setpoint for a parameter of interest (such as weight on bit, ROP, torque) associated with operation of the drilling system and then initiates a gradual increase in that parameter in order to achieve the setpoint. The bit protection sequence may be adjustable so that varying degrees of gradualness may be selected. The controller of the autodriller may also be provided with measured data for torque, rate of penetration (ROP) and / or the differential pressure of the mud motor of the drilling system. Each of these parameters is provided with a predetermined setpoint, and each may be selected as the controlling parameter for operation of the autodriller.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
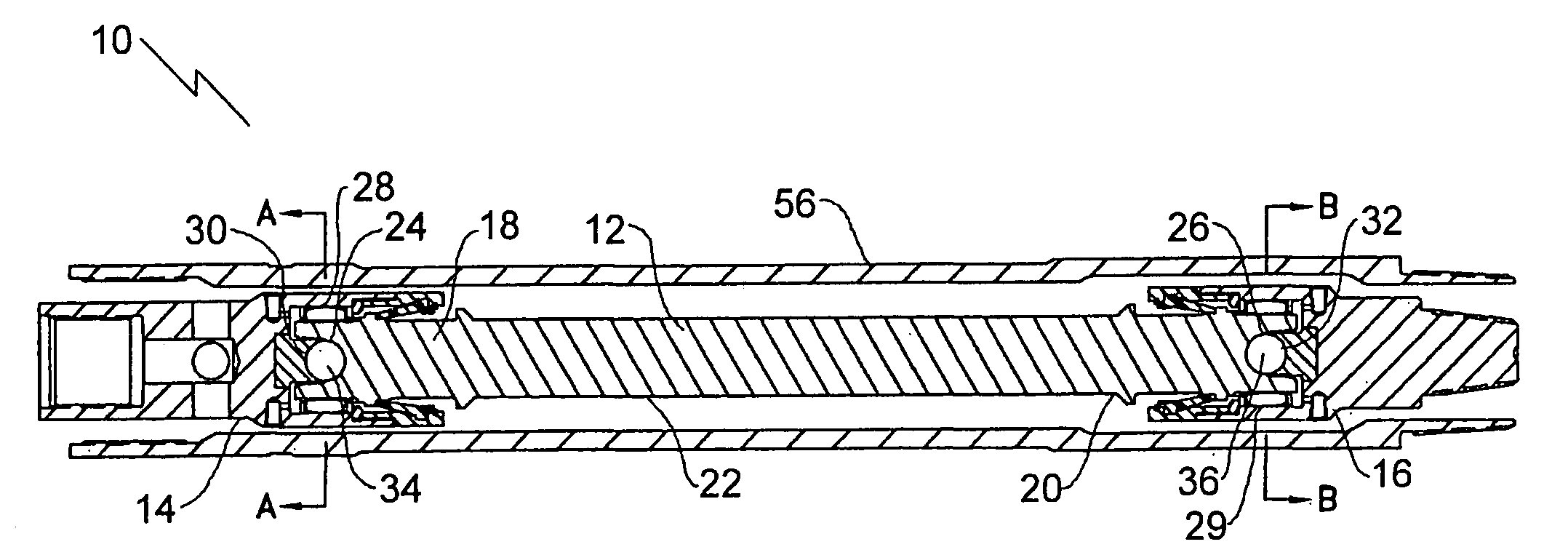
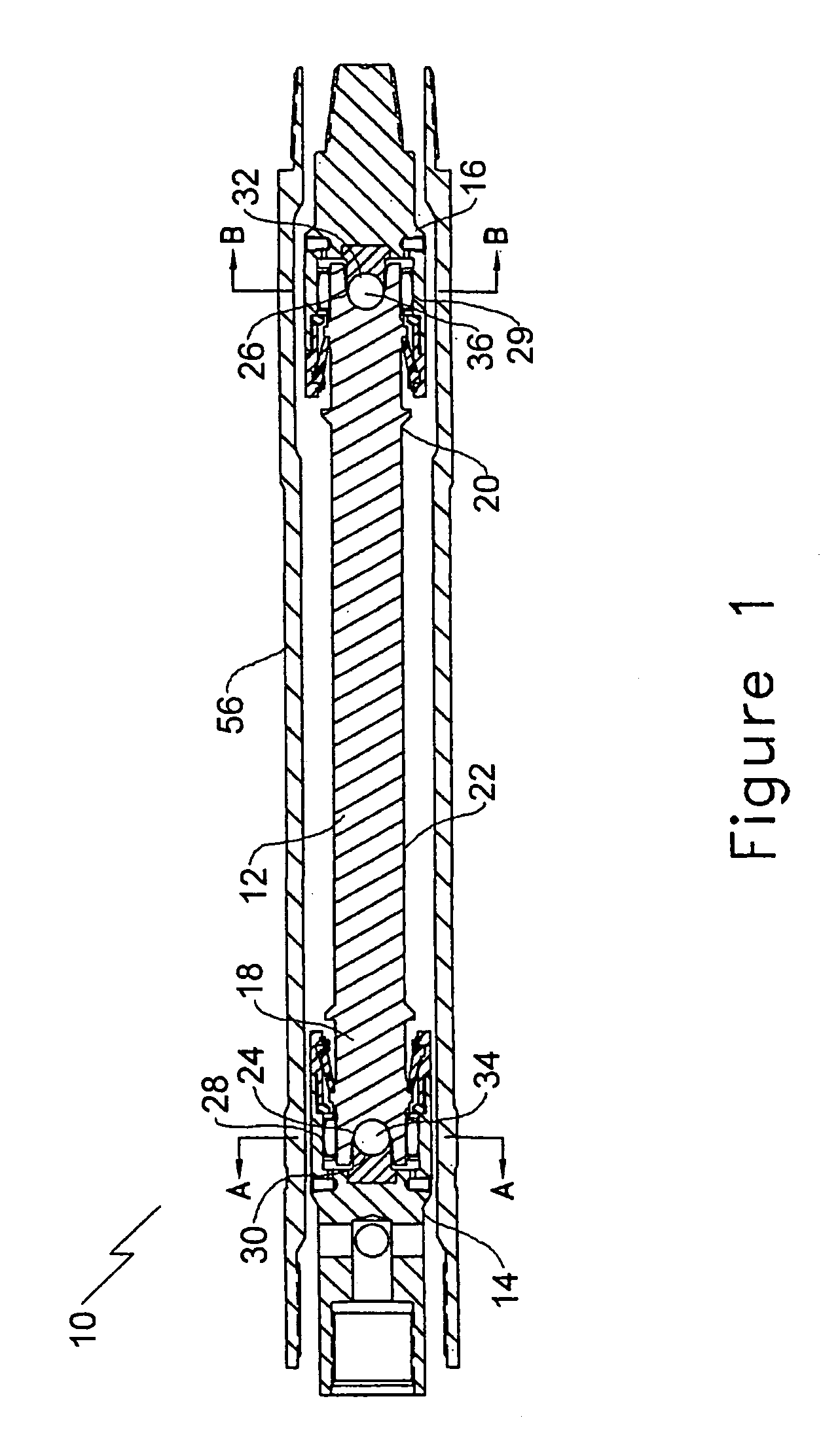
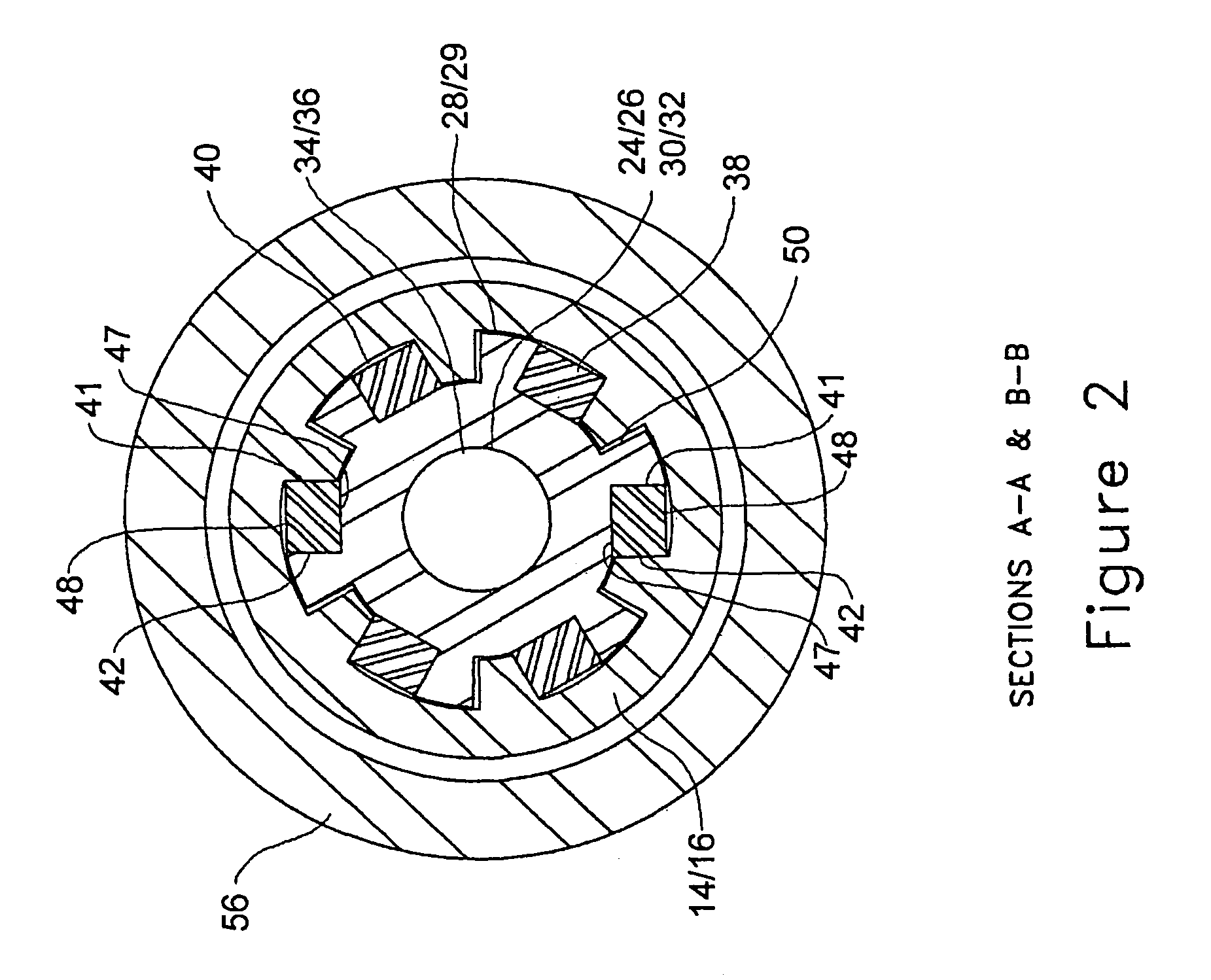
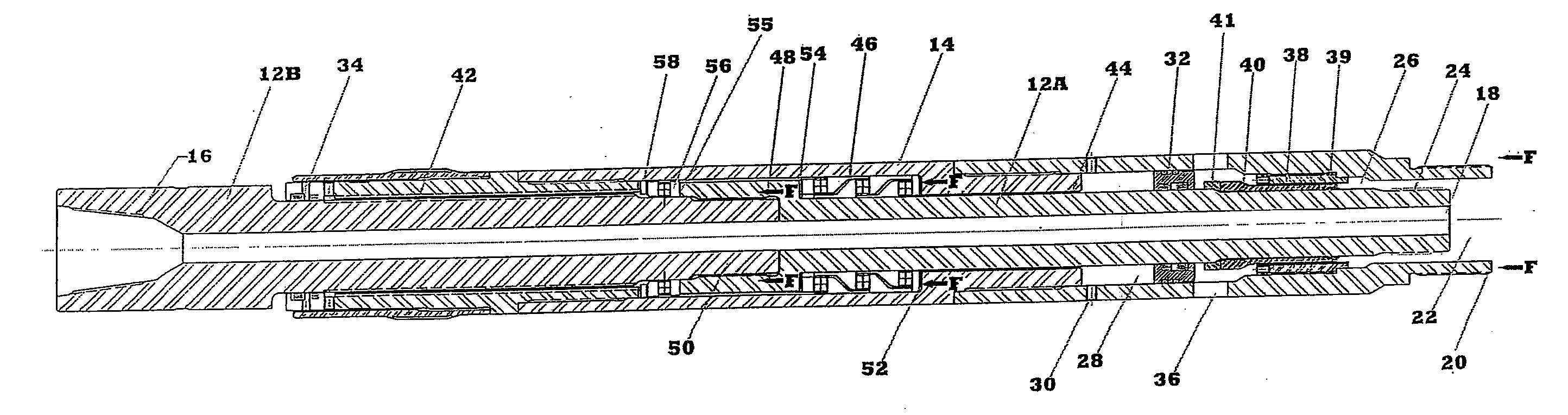
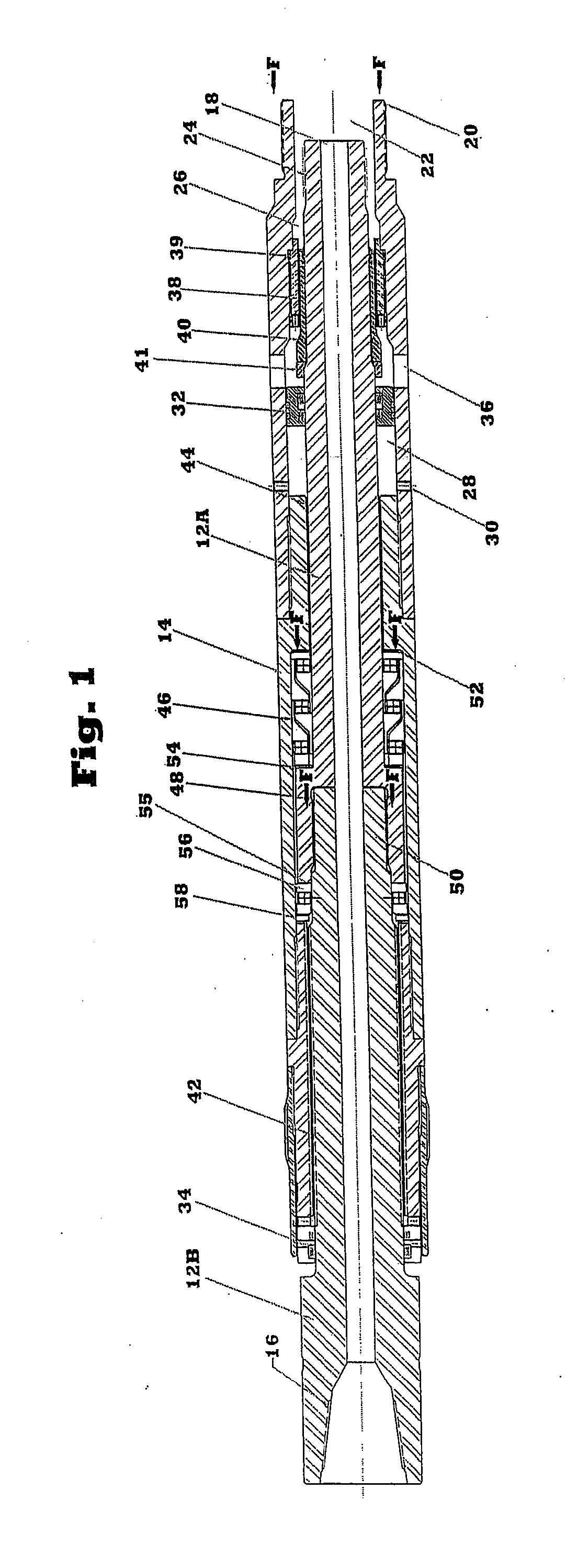
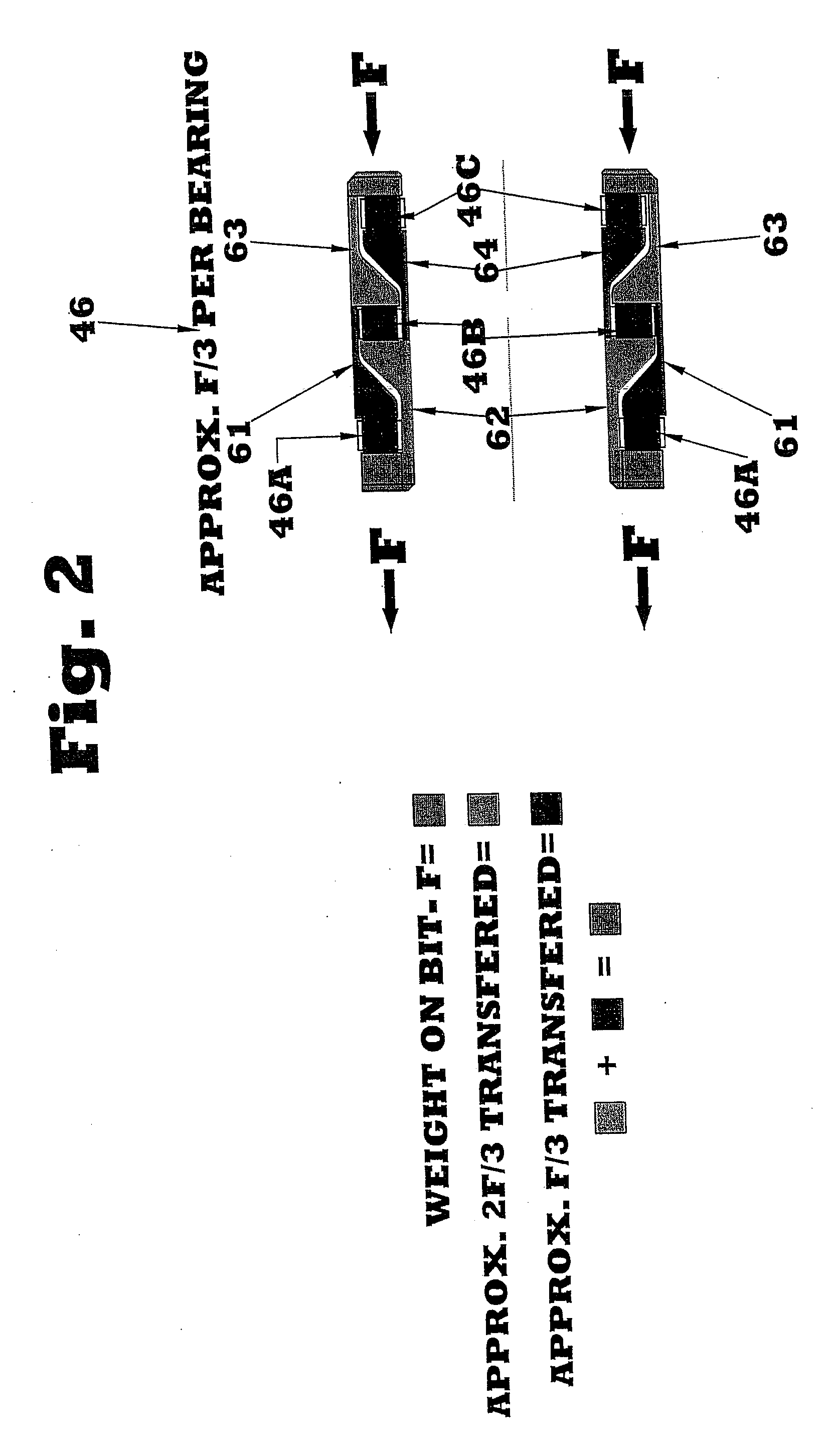
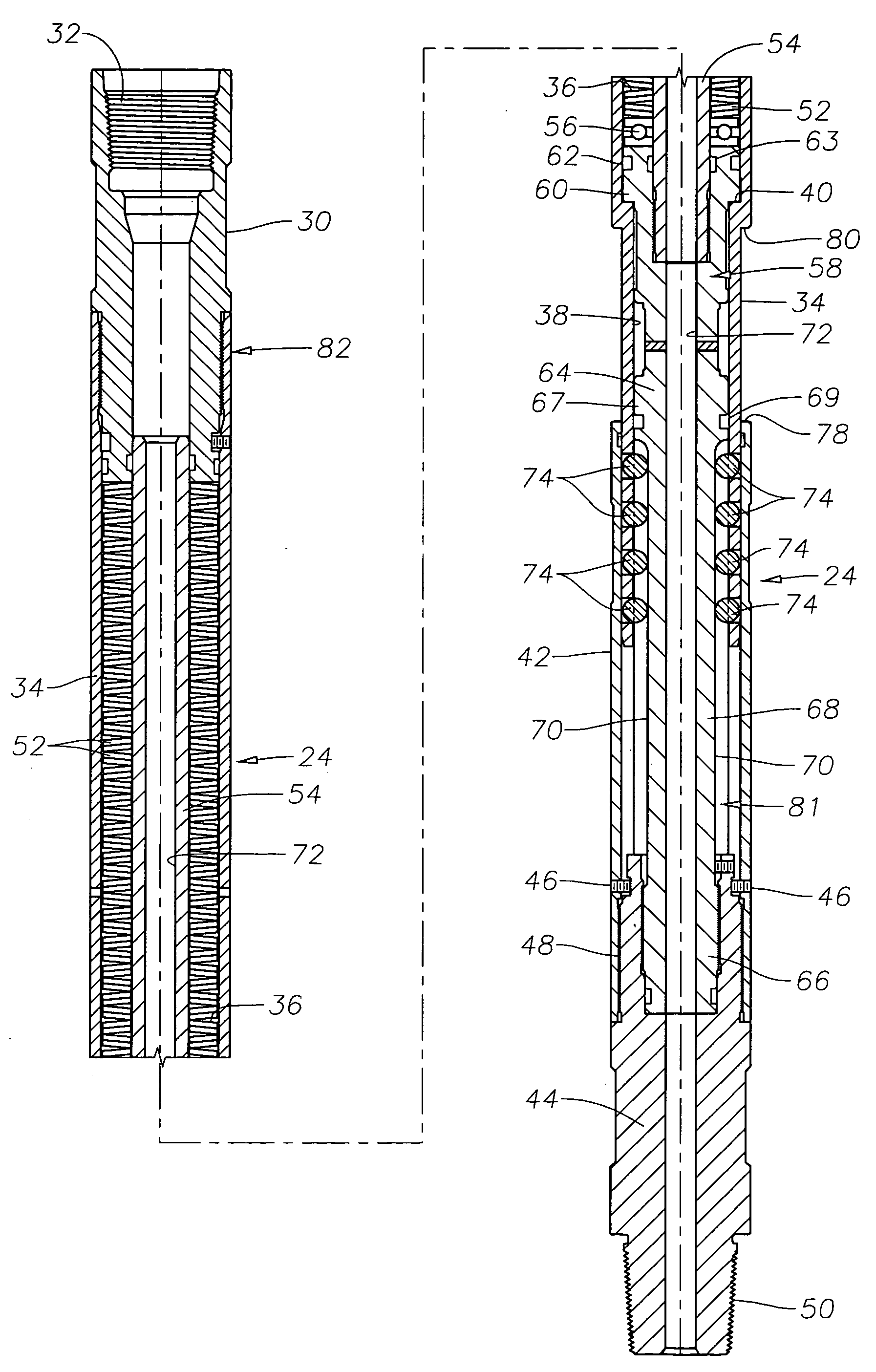
Bearing assembly for downhole mud motor
Owner:CIOCEANU NICU
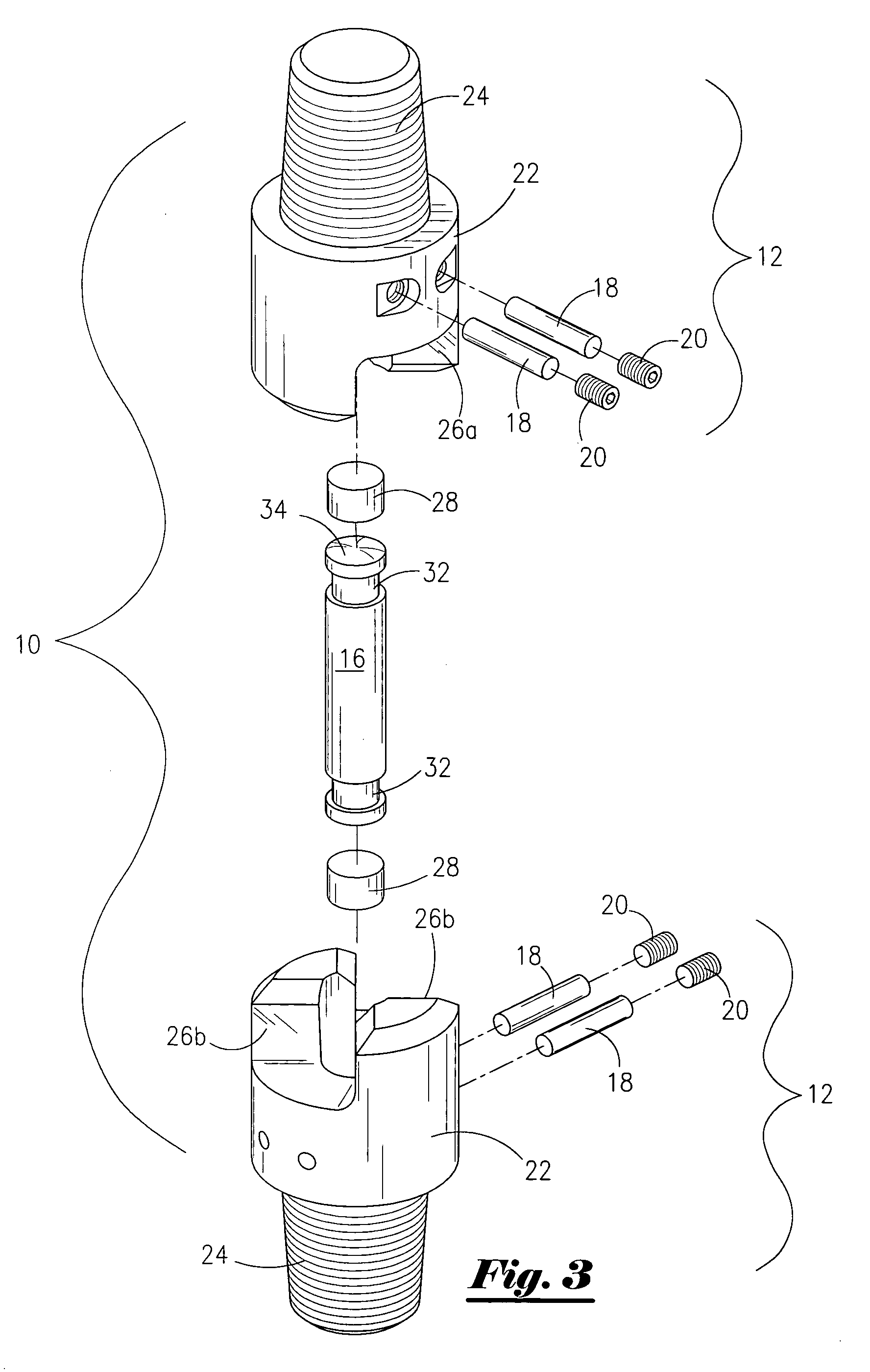
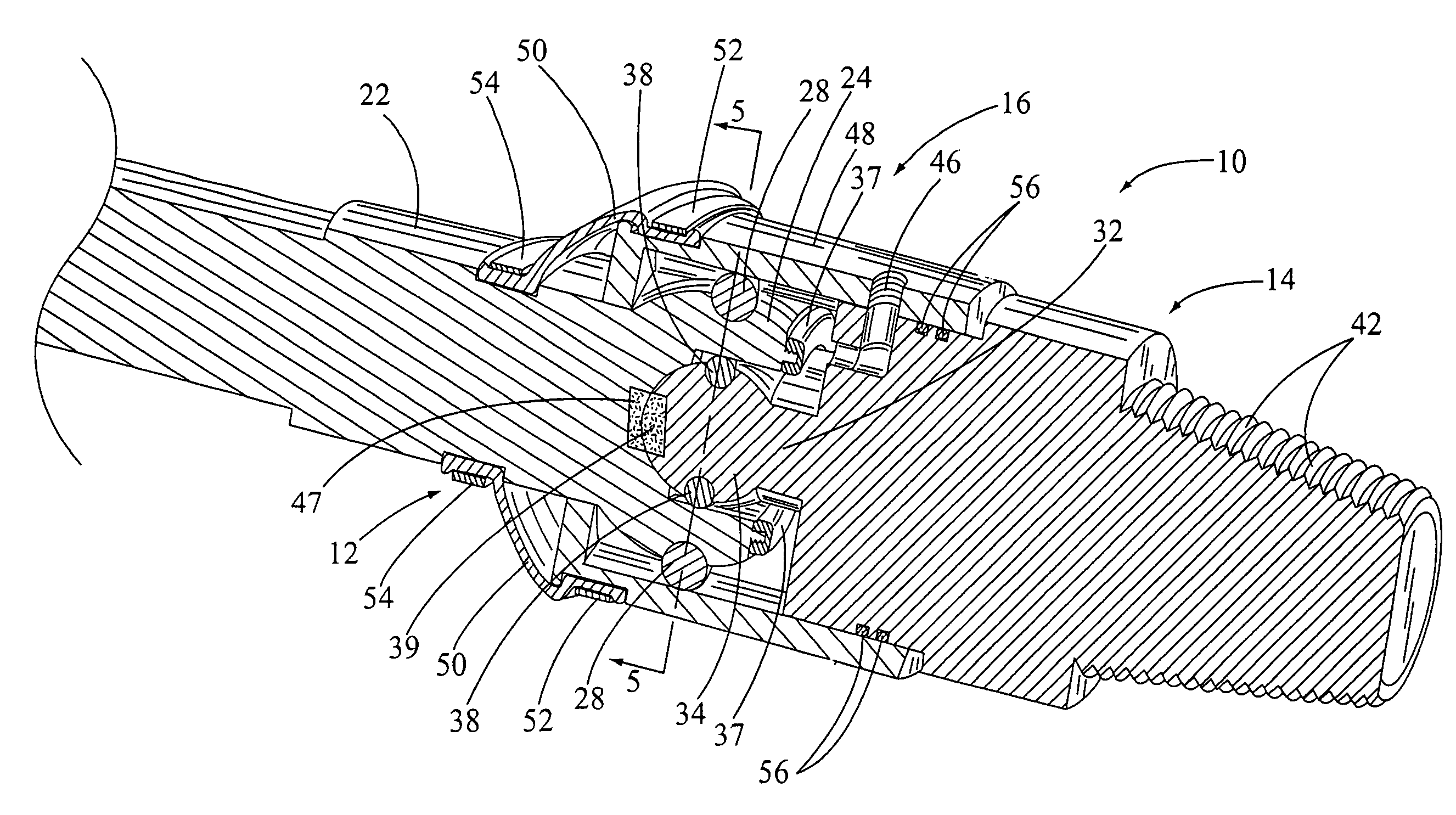
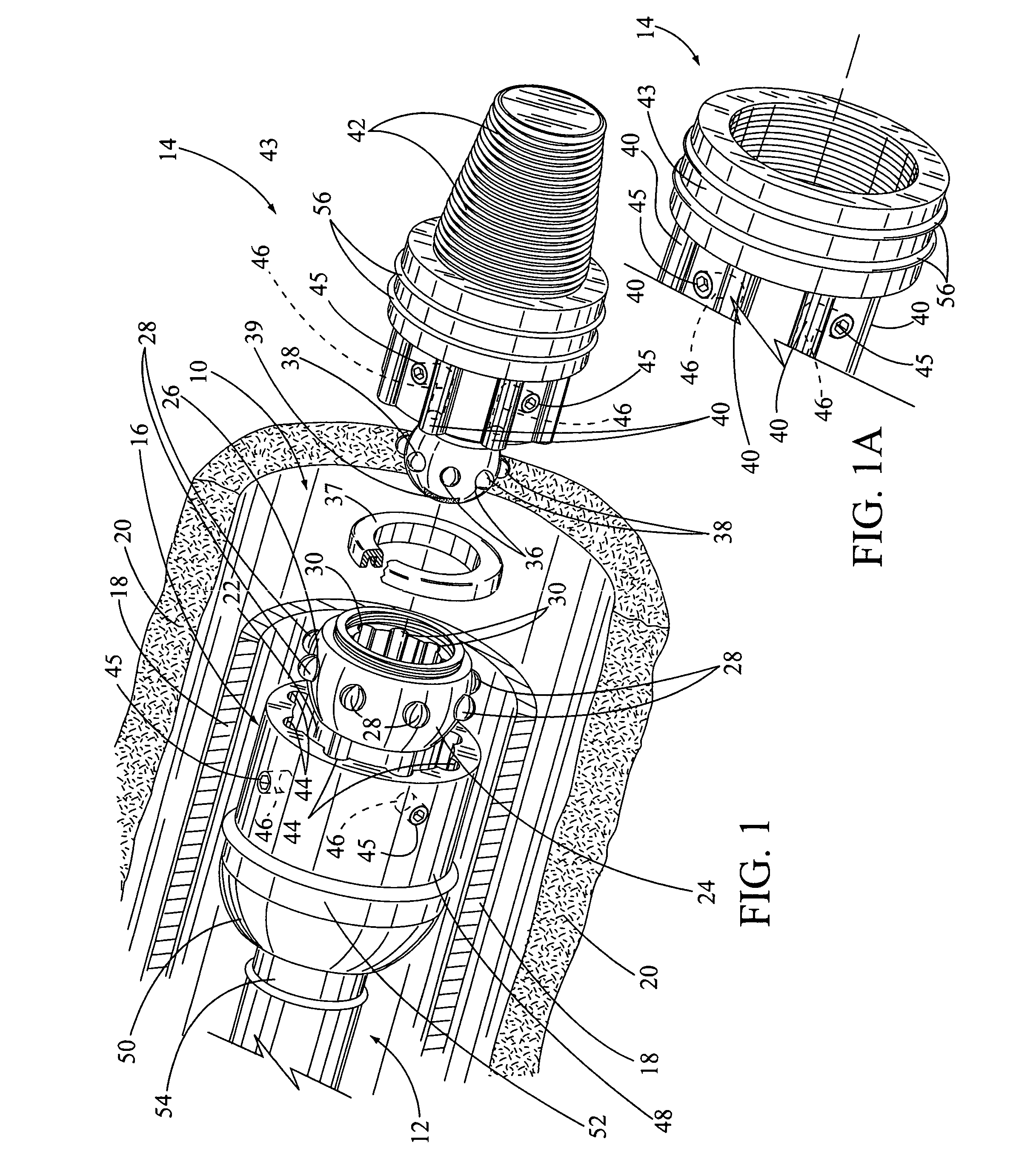
Flexible universal joint sub connection for down hole mud motor method and apparatus
ActiveUS7004843B1For quick replacementNominal costYielding couplingDrilling rodsUniversal jointMud motor
A mud motor universal joint assembly that includes a pair of adjacent cylindrical joints having threaded connection means at one end and interlocking jaws at the other, each cylindrical joint having an internal blind tapered bore within the interlocking jaw portion containing a hard cylindrical load bearing member. The two joints are connected by a hardened cylindrical rod member inserted into the internal blind tapered bore of each joint and retained therein by perpendicular retaining pins. The joints, connecting rod, and bearing members are surface hardened to improve wear. No balls or seals are required and the internal hardened connecting rod and bearing members are easily replaced if necessary at a nominal cost.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Electrical transmission apparatus through rotating tubular members
The present invention provides an apparatus for the communication of power or data signals across the rotating gap of two tubular members, such as the stator and rotor of a mud motor, and between said rotating members of a drill string through inductive couplers located axially along the drill string.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
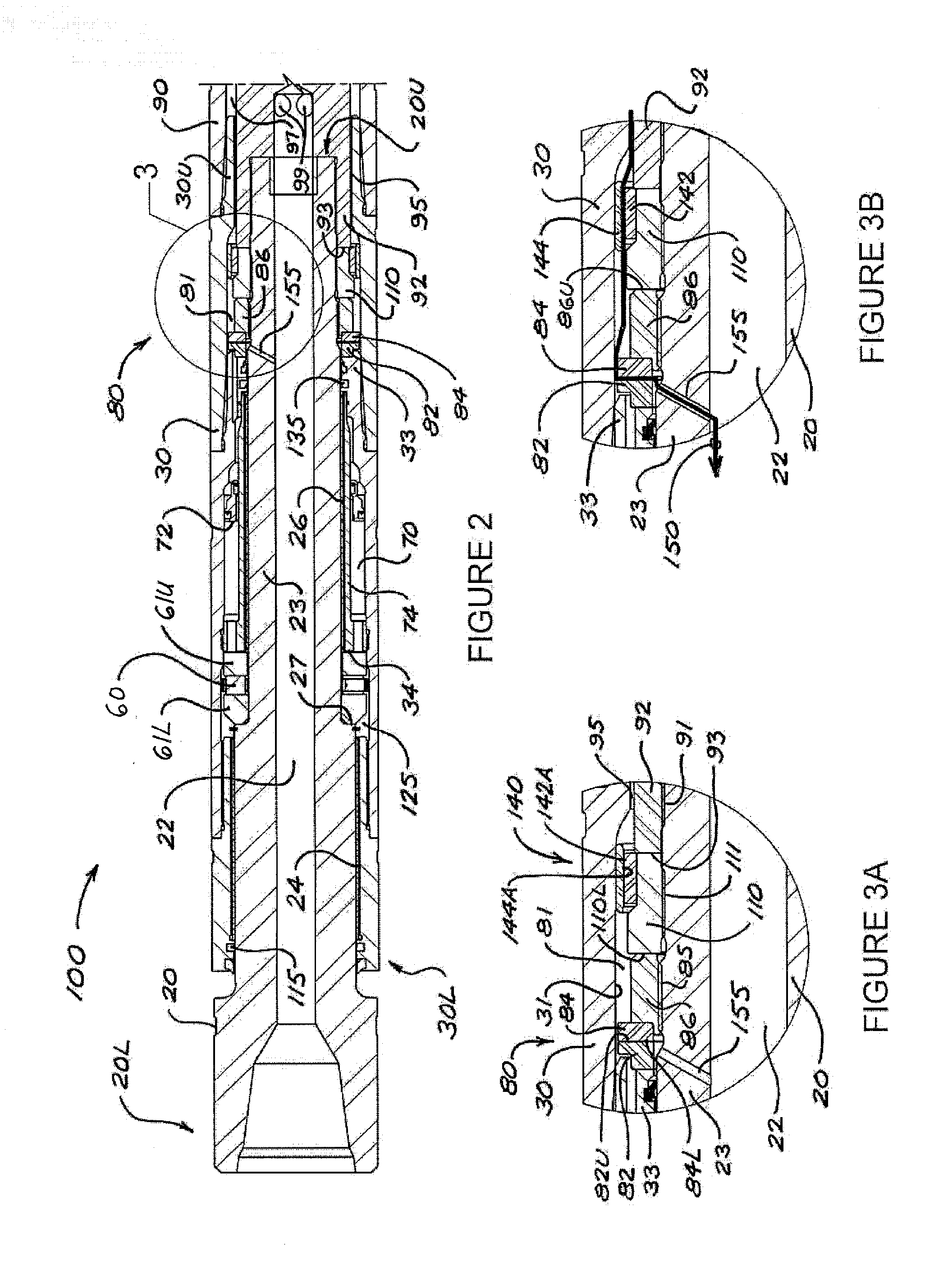
Casing Drilling Bottom Hole Assembly Having Wireless Power And Data Connection
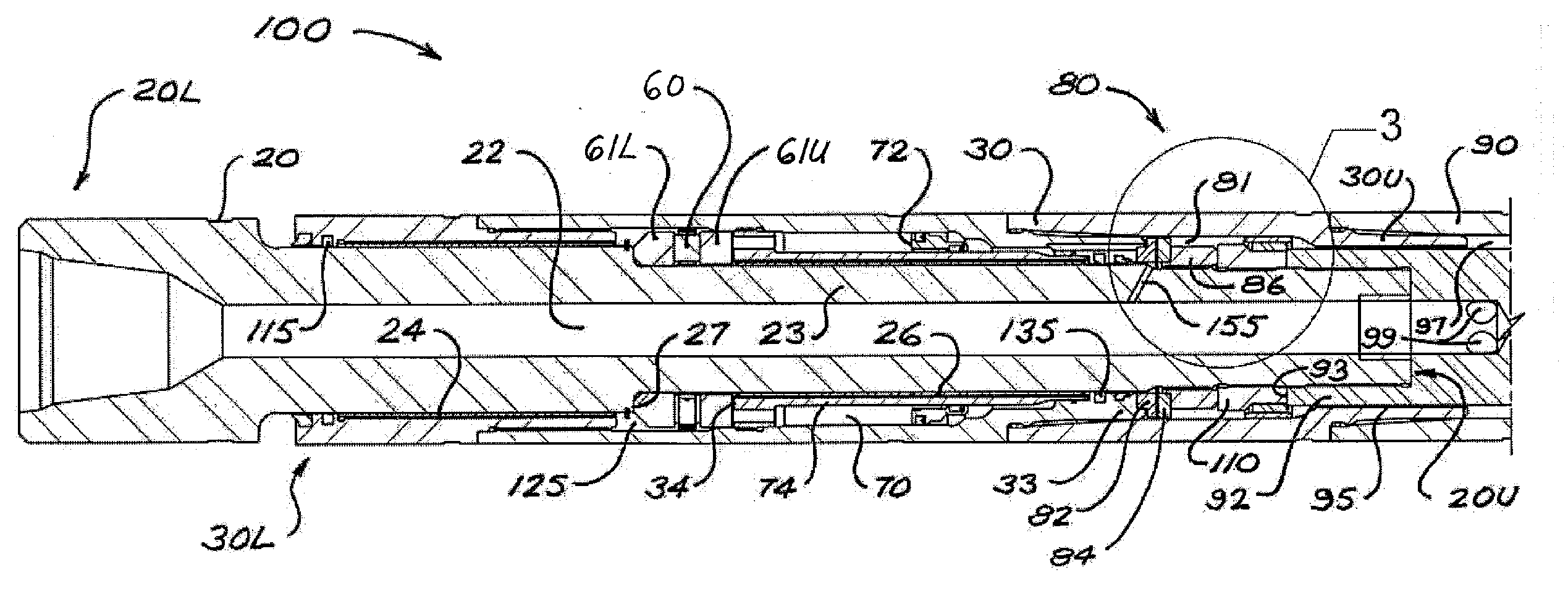
Various embodiments of methods and systems for wireless power and / or data communications transmissions to a sensor subassembly above a mud motor in a bottom hole assembly are disclosed. Power and / or data are supplied by rotary modulator and power generation system positioned above the mud motor. Wires may connect to an annular coil. Power and / or communications are transmitted through the annular coil to an inductively coupled second, mandrel coil that is attached to the rotor. By leveraging resonantly tuned circuits and impedance matching techniques for the coils, power and / or data can be transmitted efficiently from one coil to the other despite relative movement and misalignment of the two coils.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Flow operated orienter
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to a flow operated orienter. In one embodiment, a bottom hole assembly (BHA) for use in drilling a wellbore includes: a first mud motor having a stator and a rotor; a second mud motor having stator and a rotor; a drill bit rotationally coupled to the second rotor and having a tool face and a longitudinal axis inclined relative to a longitudinal axis of the first mud motor; and a clutch. The clutch is operable to: rotationally couple the second stator to the first stator in a first mode at a first orientation of the tool face, rotationally couple the first rotor to the second stator in a second mode, change the first orientation to a second orientation by a predetermined increment, orient the tool face at the second orientation in an orienting mode, and shift among the modes in response a change in flow rate of a fluid injected through the orienter and / or a change in weight exerted on the drill bit.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Magnetorheological fluid controlled mud pulser
A mud pulser controlled by a field applied to an electroactive fluid. The electroactive fluid is employed to act as a rapid-response brake to slow or interrupt the rotation of a mud motor or mud siren, thus creating pressure pulses in a circulating fluid. In certain embodiments, the electroactive fluid is used as a direct brake acting on a shaft rotating in a volume of electroactive fluid where the shaft is coupled to the mud motor or siren. The application of a field to the electroactive fluid impedes the rotation of the shaft, thus slowing the mud motor and creating a pressure pulse in the circulating fluid. In another embodiment, a Moineau pump circulating an electroactive fluid is coupled to the mud motor. The application of a field to the electroactive fluid slows the rotation of the pump, thus slowing the mud motor and creating a pressure pulse in the circulating fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
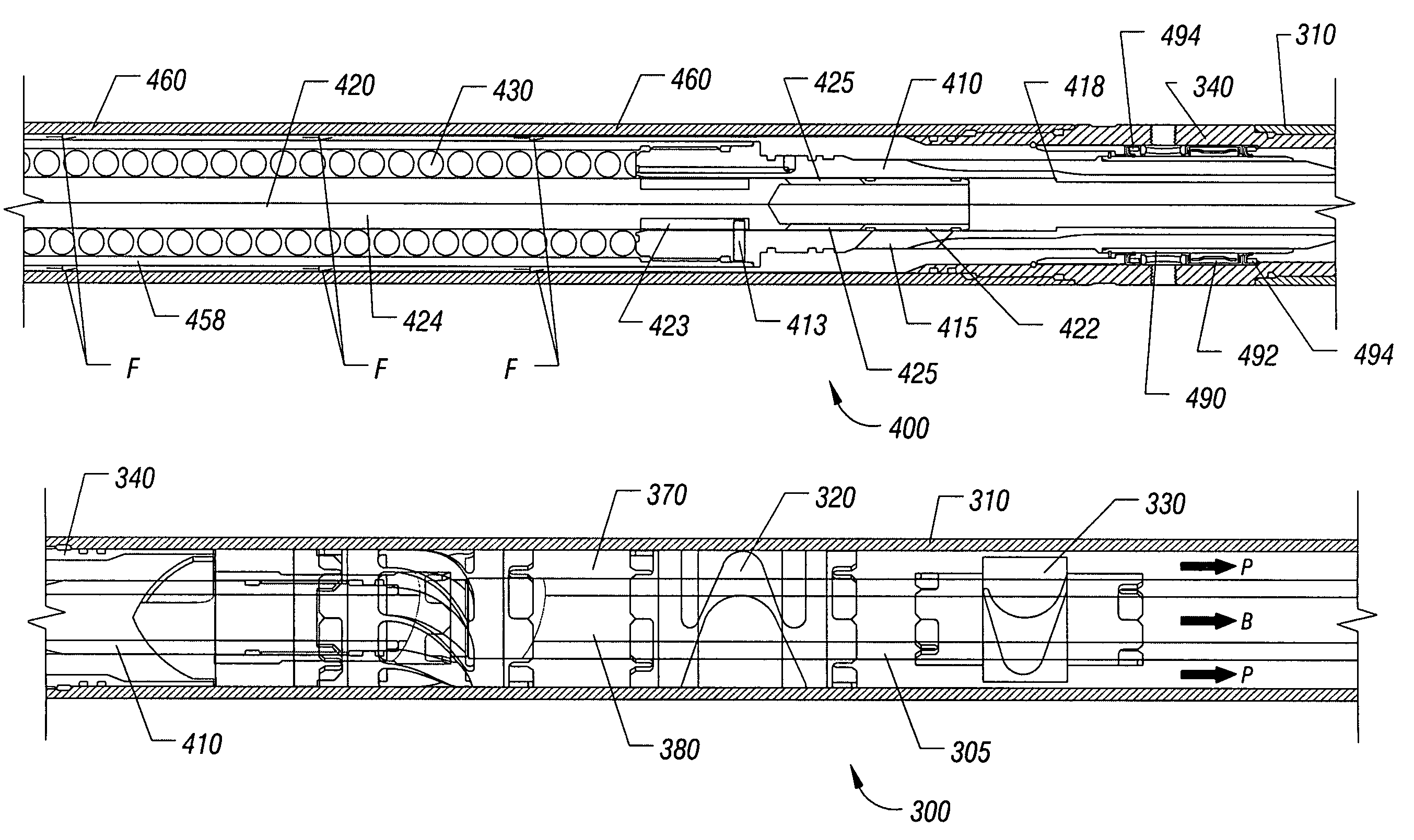
High torque, flexible, dual, constant velocity, ball joint assembly for mud motor used in directional well drilling
A flexible, dual ball joint assembly used for increasing the wear life of a mud motor. The ball joint assembly includes an drive shaft with a drive shaft hollow ball joint. An outer circumference of the hollow ball joint includes a plurality of equally spaced apart drive shaft ball bearings. An inner circumference, inside the hollow ball joint, includes a plurality of equally spaced apart drive shaft grooves. Also, the ball joint assembly includes an annular shaped torque coupler with a torque coupler ball joint. An outer circumference of the torque coupler ball joint includes a plurality of equally spaced apart torque coupler ball bearings. The torque coupler ball bearings are received in the drive shaft grooves for providing lateral movement between the drive shaft and the torque coupler. An outer circumference of the torque coupler next to the torque coupler ball joint includes a plurality of torque coupler lobes equally spaced apart therearound. Further, the ball joint assembly includes a sliding torque sleeve used to secure the drive shaft to the torque coupler during the operation of the ball joint assembly.
Owner:BENSON TODD
Flow control valve
InactiveUS20050173157A1Facilitate communicationBypass flowCleaning apparatusFlexible member pumpsHydraulic motorMotor speed
A flow control valve is disclosed for controlling the rotation of a hydraulic motor, such as a turbine, a mud motor, for example, having an element that rotates in response to power fluid. The valve disclosed may include a valve housing and a valve piston, each having a port, moveable relative to one another. When the ports at least partially align, bypass flow is generated which acts to decrease the speed of rotation of the element, such as a turbine shaft. An energizer, such as a pump assembly, is further described which is adapted to move the valve housing or the valve piston in response to the speed of rotation, such that bypass flow is a function of the motor speed (i.e. speed of rotation of the element). A bottom hole assembly including a flow control valve and a method of controlling the rotation of a downhole tool are also described.
Owner:BJ SERVICES CO
Flow operated orienter
Some embodiments of the present invention generally provide an apparatus that may be used in a coiled tubing drillstring and that can switch between effectively straight drilling and curved drilling without halting drilling. Methods for steering a coiled tubing drillstring are also provided. In one embodiment, an apparatus for use in drilling a wellbore is provided. The apparatus includes a mud motor; a housing; an output shaft; and a clutch actuatable between two positions. The clutch is configured to rotationally couple the mud motor to the output shaft when the clutch is in a first position as a result of fluid being injected through the clutch at a first flow rate, and rotationally couple the output shaft to the housing when the clutch is in a second position as a result of fluid being injected through the clutch at a second flow rate.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
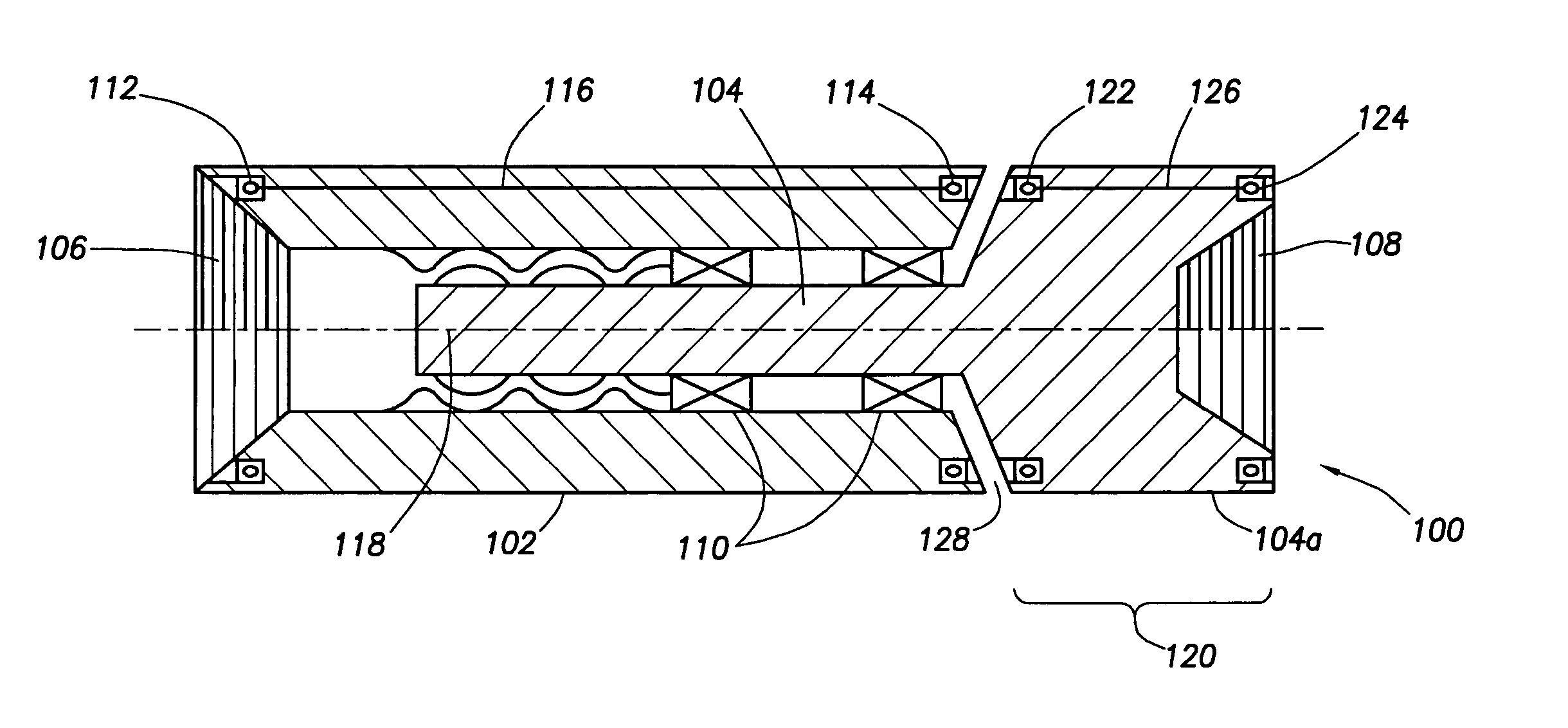
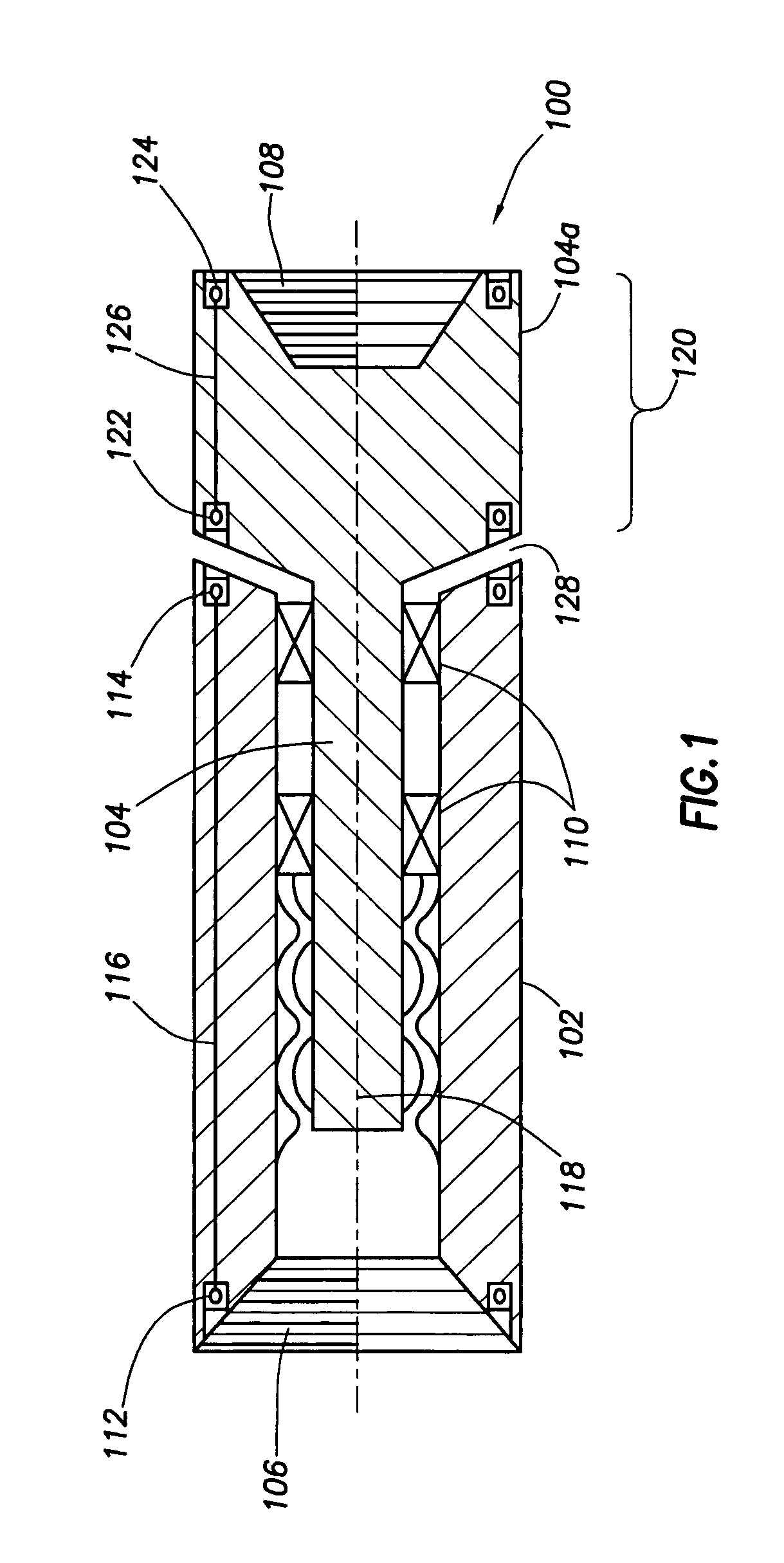
Oil-Sealed Mud Motor Bearing Assembly With Mud-Lubricated Off-Bottom Thrust Bearing
ActiveUS20120195542A1Shorten the lengthControl loadCrankshaftsRoller bearingsDrive shaftThrust bearing
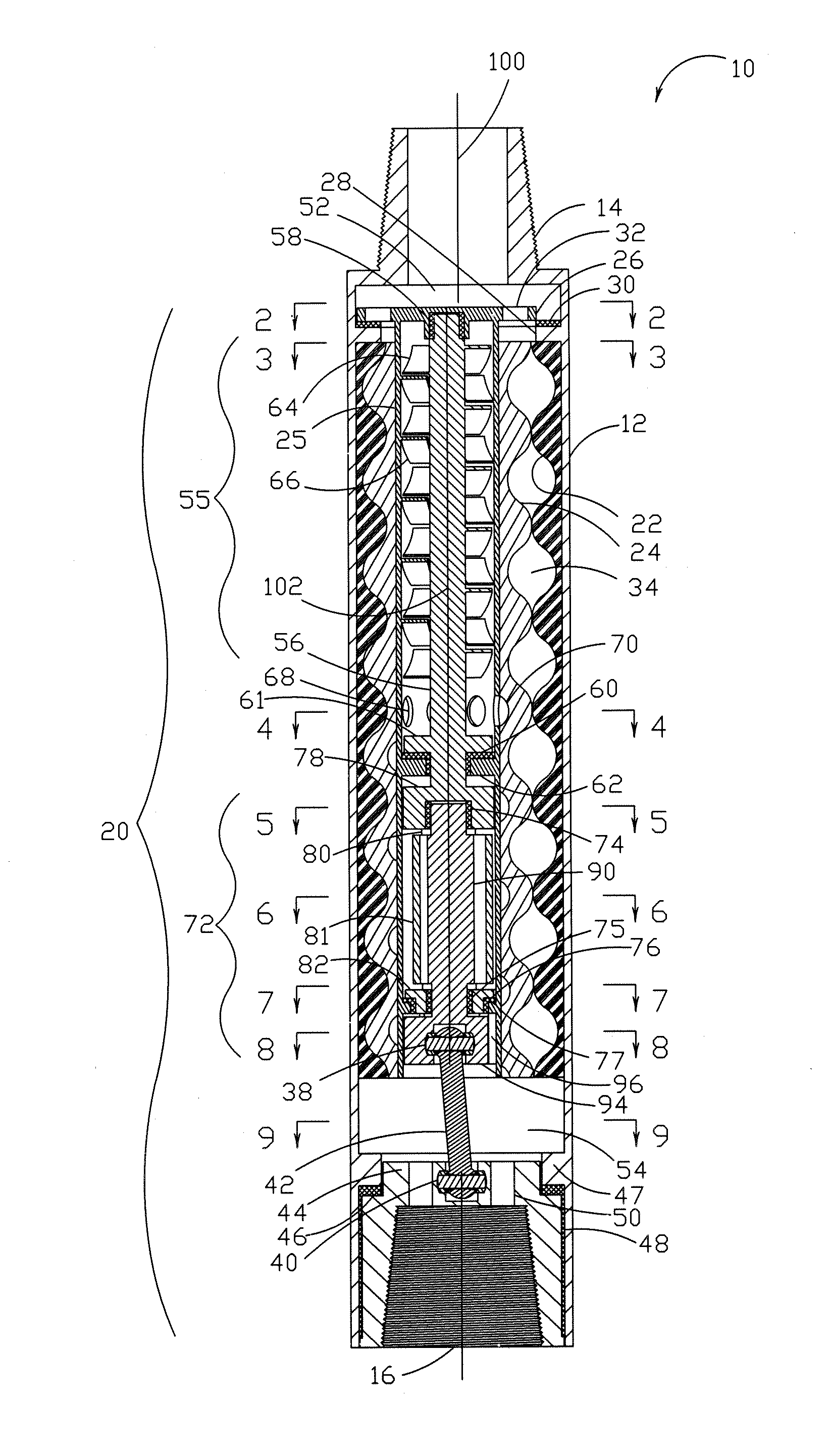
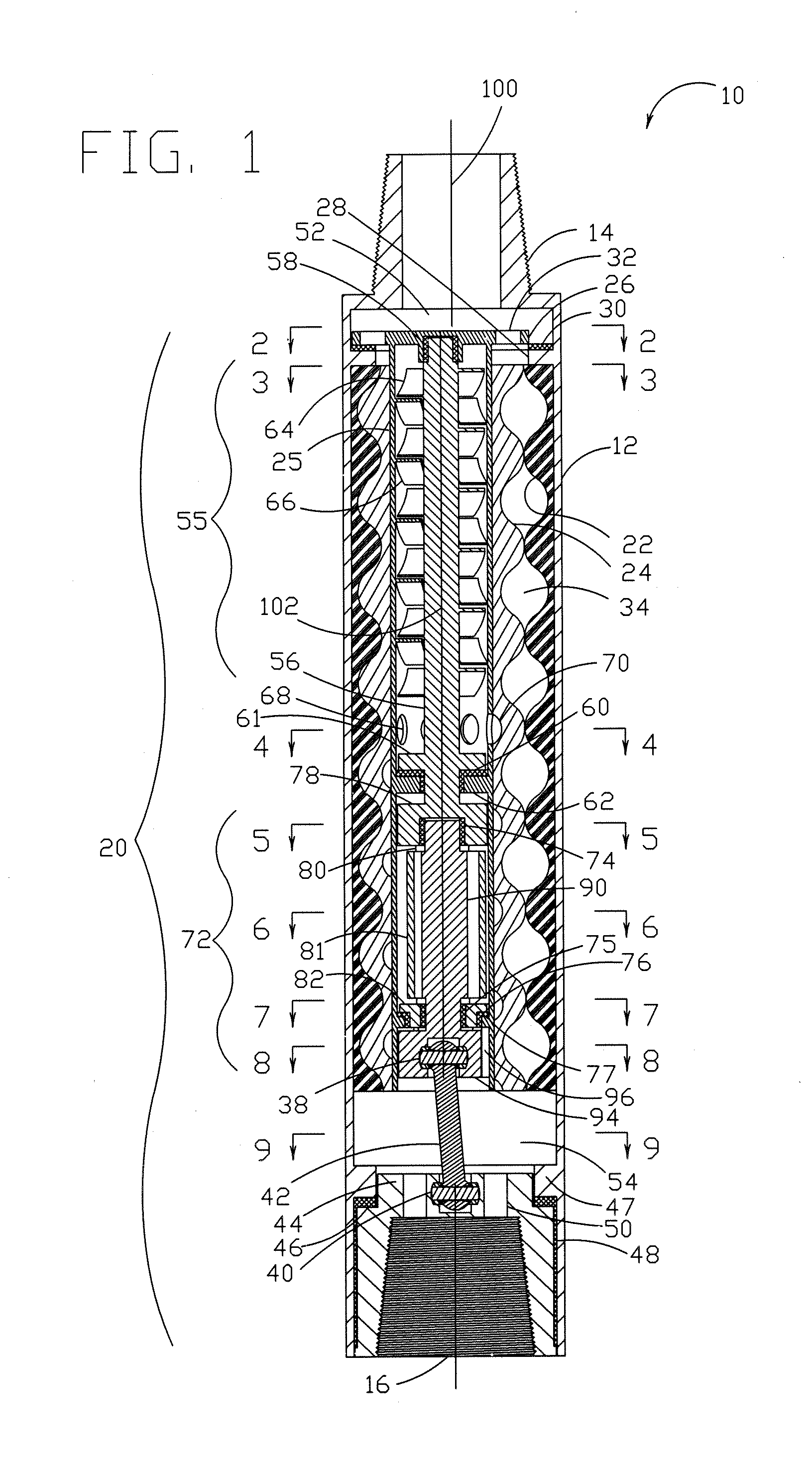
A bearing assembly for a mud motor has a mandrel rotatably disposed within a cylindrical housing, with a rolling-element thrust bearing disposed within an oil-sealed annular chamber between the mandrel and the housing, for resisting on-bottom axial thrust loads. Off-bottom axial thrust loads are resisted by a mud-lubricated thrust bearing assembly located above the oil-sealed chamber. The lower end of a drive shaft adapter coupled to the mandrel is used to provide an upper load-transferring shoulder for the off-bottom thrust bearing, with a lower load-transferring shoulder being provided in association with the housing. The upper and lower shoulders come into mating contact under off-bottom thrust loading, with the upper shoulder rotatable (with the mandrel) relative to the lower shoulder.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Coiled tubing conveyed milling
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Bearing assembly for downhole mud motor
A bearing assembly for use with a mud motor includes a two-piece mandrel and a housing. Two radial bearings and a triple stack axial thrust on-bottom bearing are disposed between the mandrel and housing.
Owner:CIOCEANU NICU
Mud motor force absorption tools
InactiveUS20070000695A1Easy to operateIncreased torque carrying capacityDrilling rodsBorehole drivesMud motorEngineering
A force absorbing tool is attached to a mud motor in a drilling string. The tool includes an outer housing portion that is secured to a drilling string, and an inner mandrel portion that is secured to a mud motor and is moveable axially and rotationally with respect to the outer housing portion between an axially compressed position and an axially extended position. Helical grooves are inscribed on the inner mandrel portion, and a plurality of guide pins are associated with the outer housing and disposed within the helical groove. A compressive spring member to urge the inner mandrel portion toward the axially extended position.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com