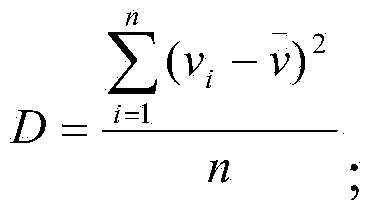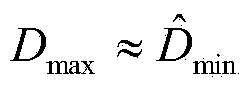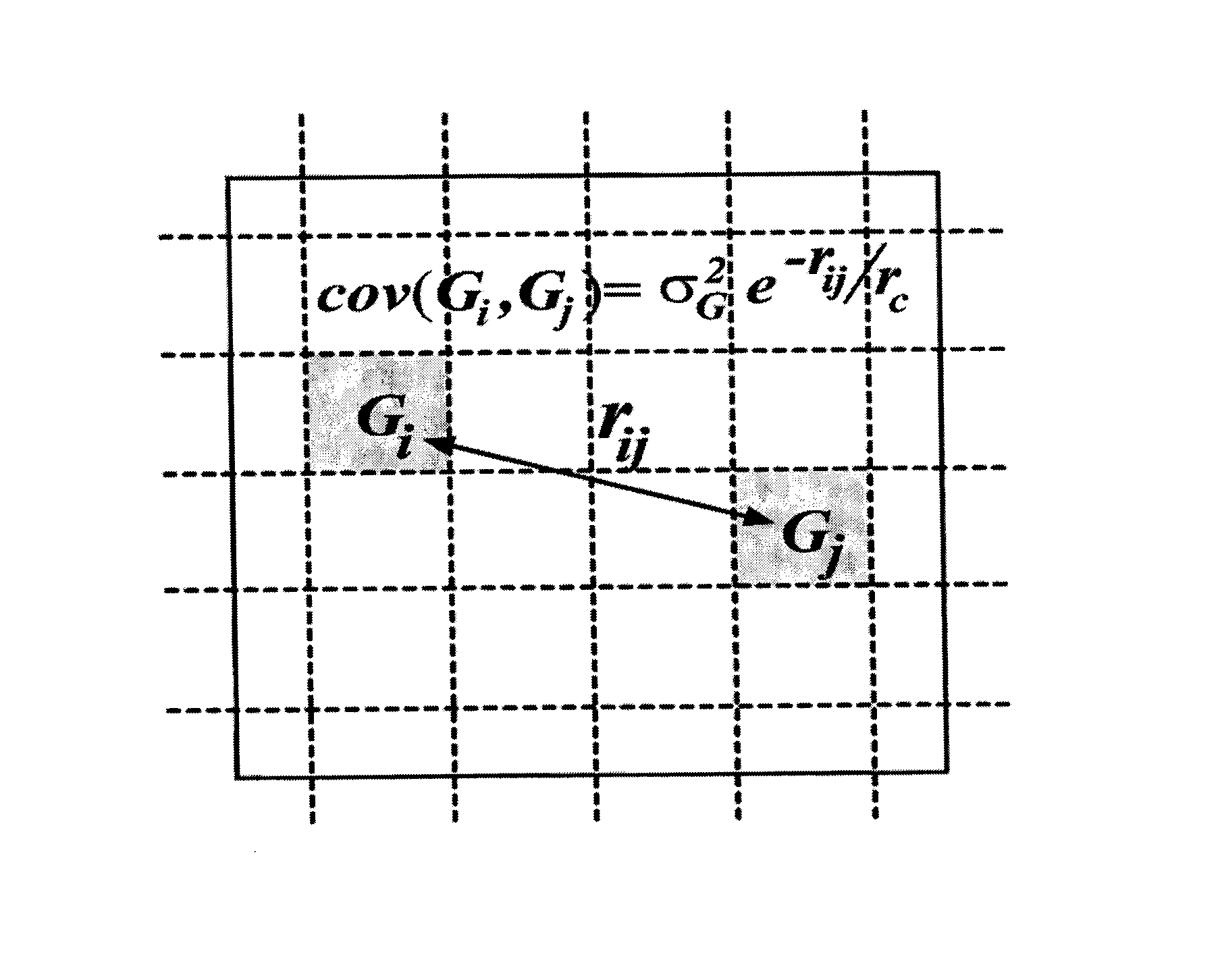Patents
Literature
124 results about "Statistical timing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
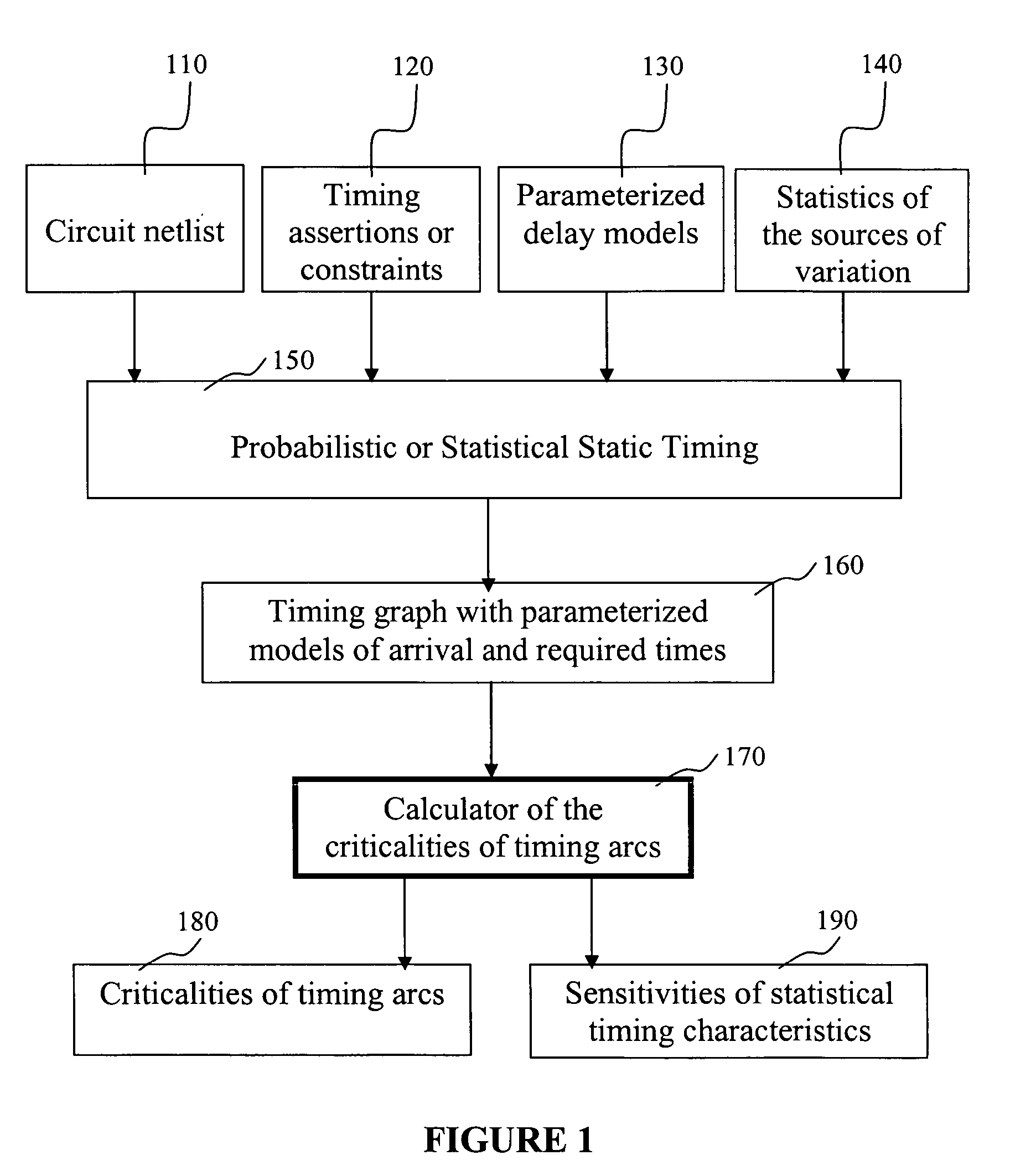
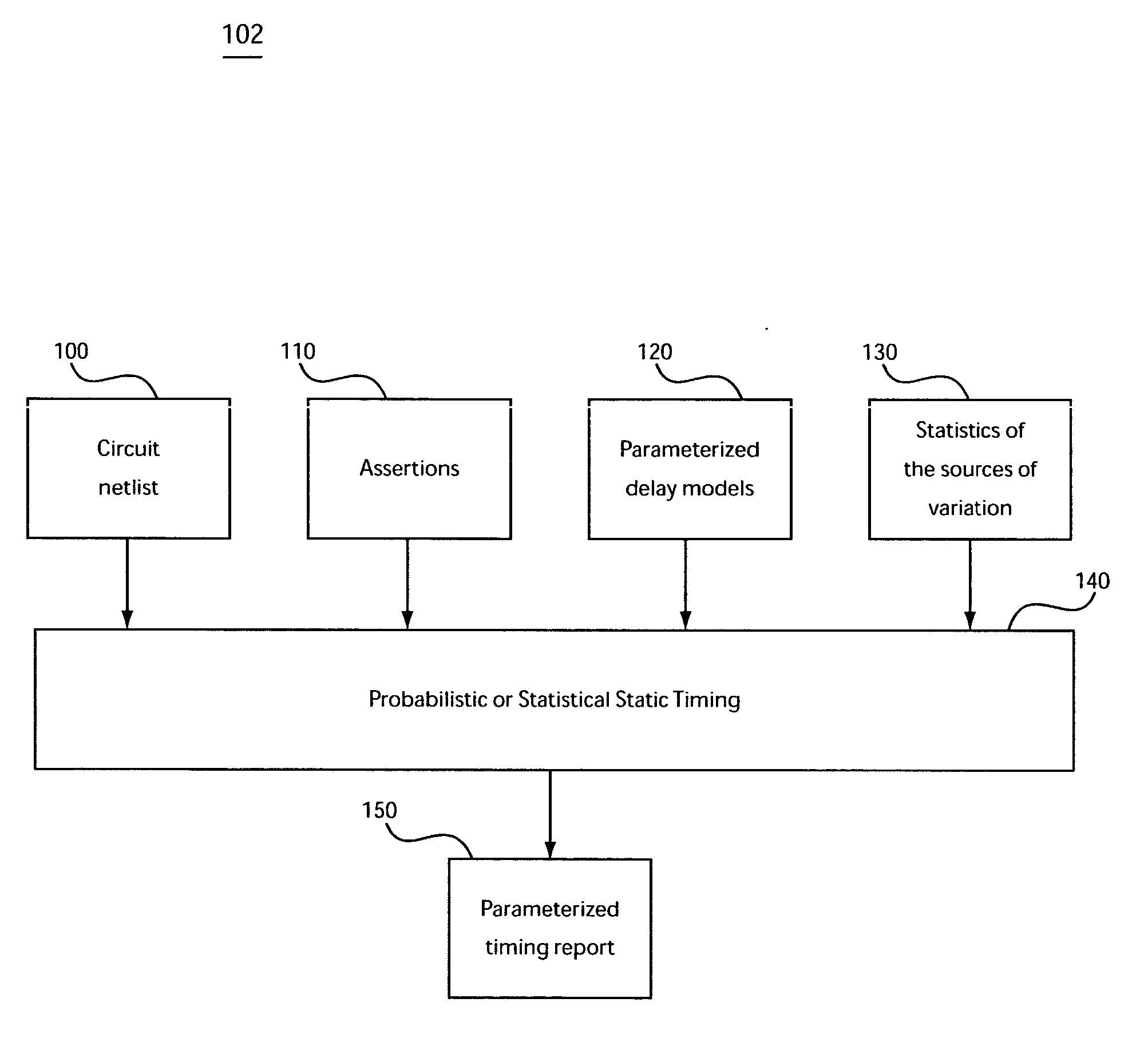
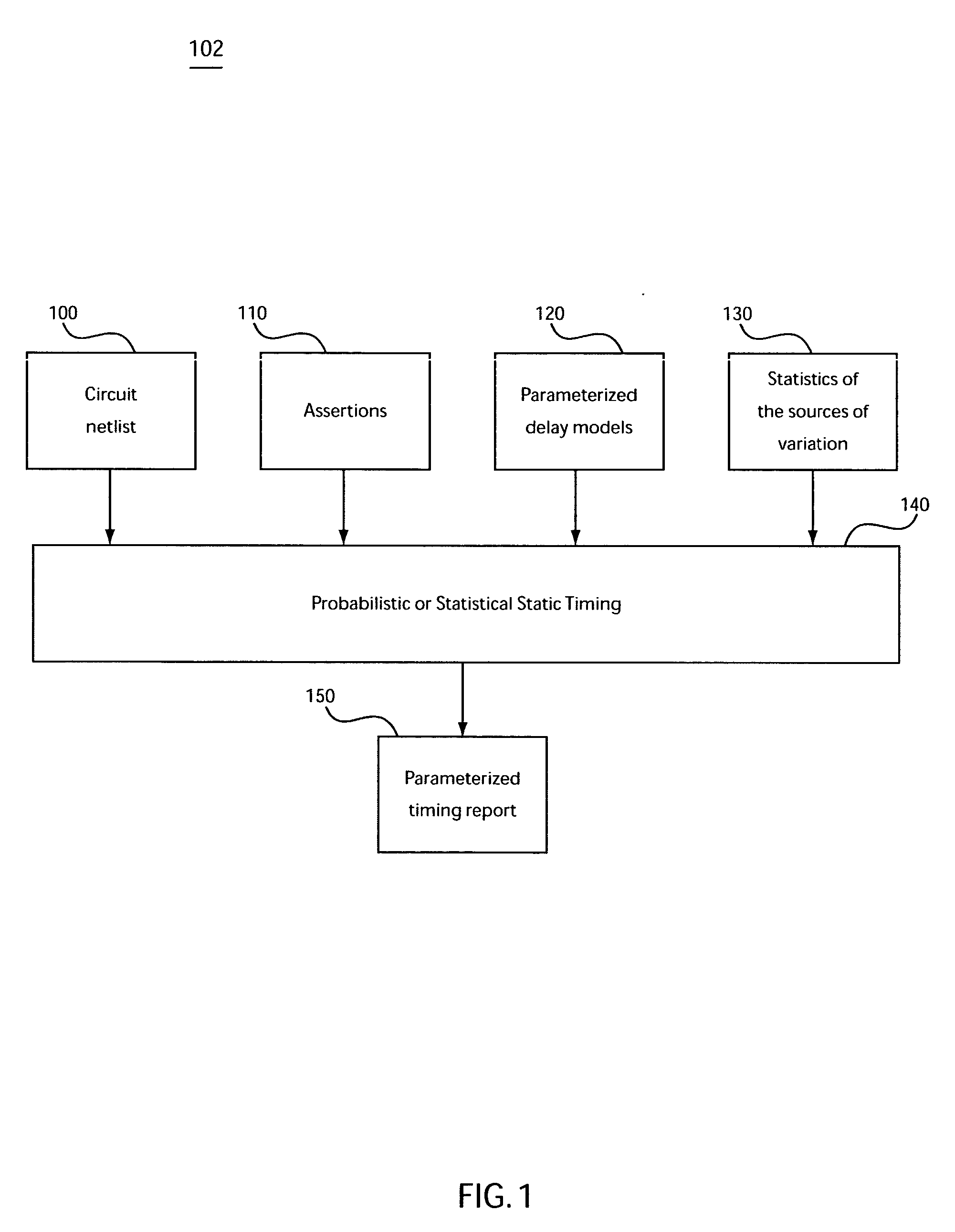
Method, system, and program product for computing a yield gradient from statistical timing
InactiveUS7480880B2Geometric CADComputation using non-denominational number representationCircuit delayComputer science
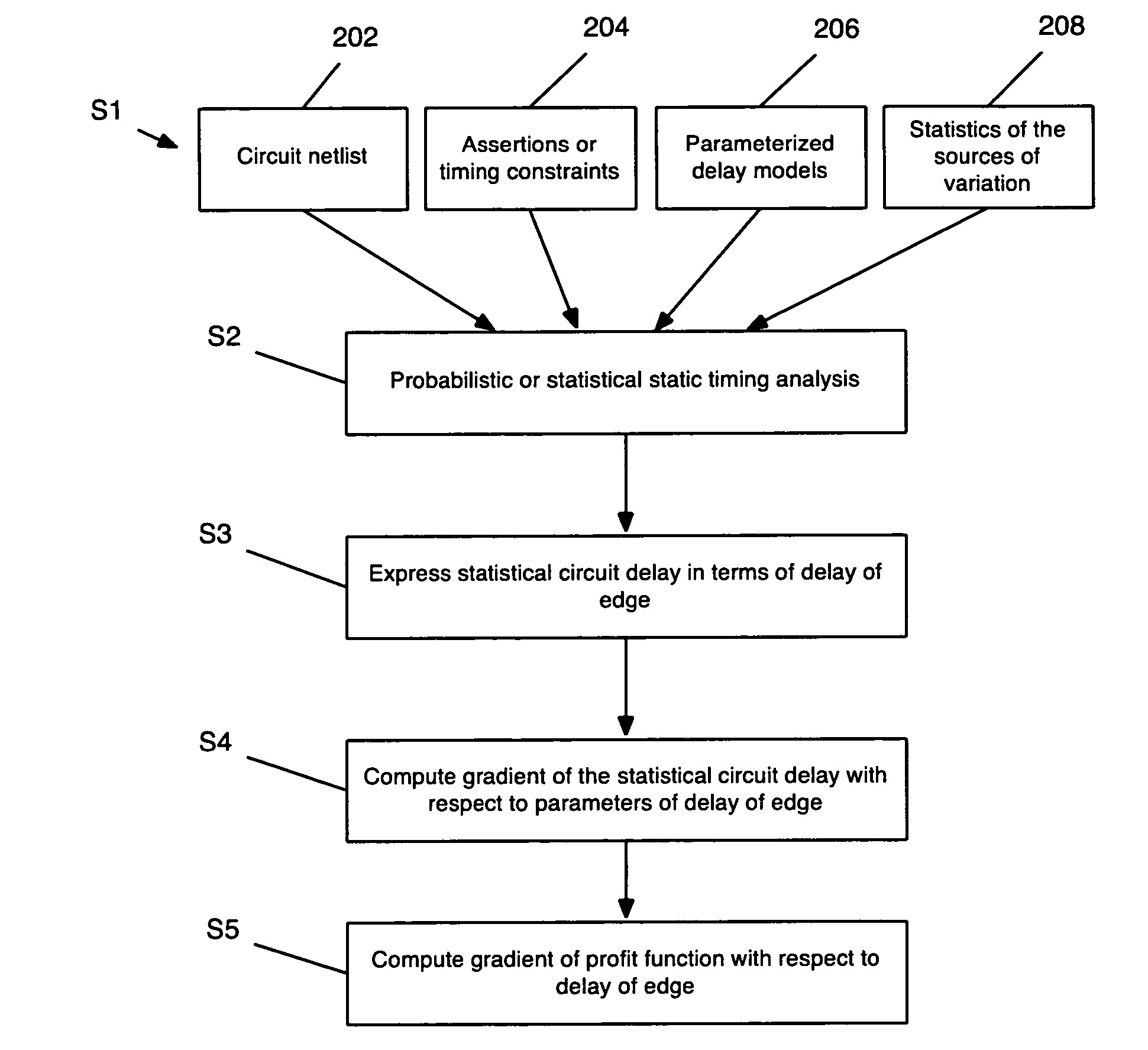
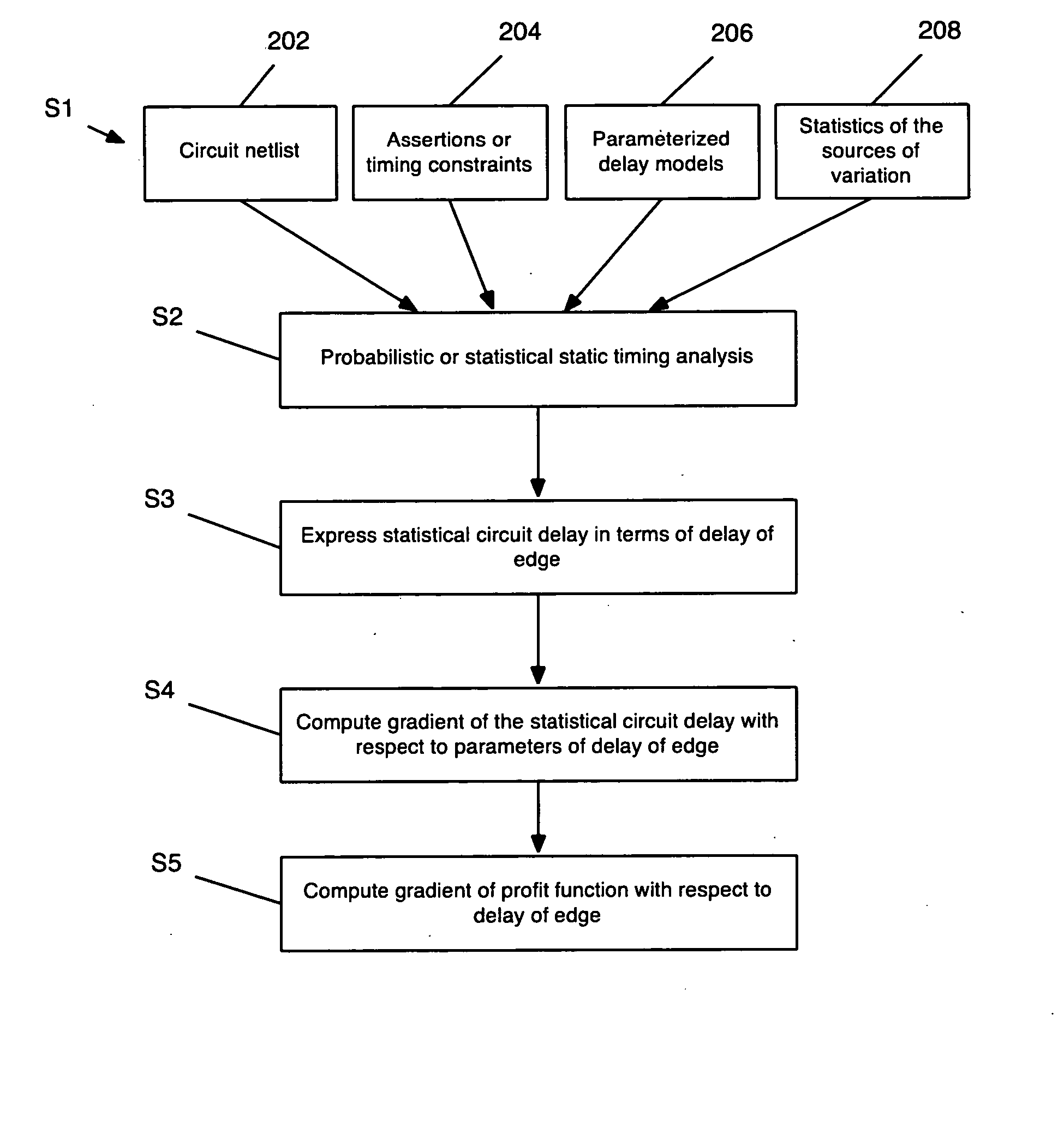
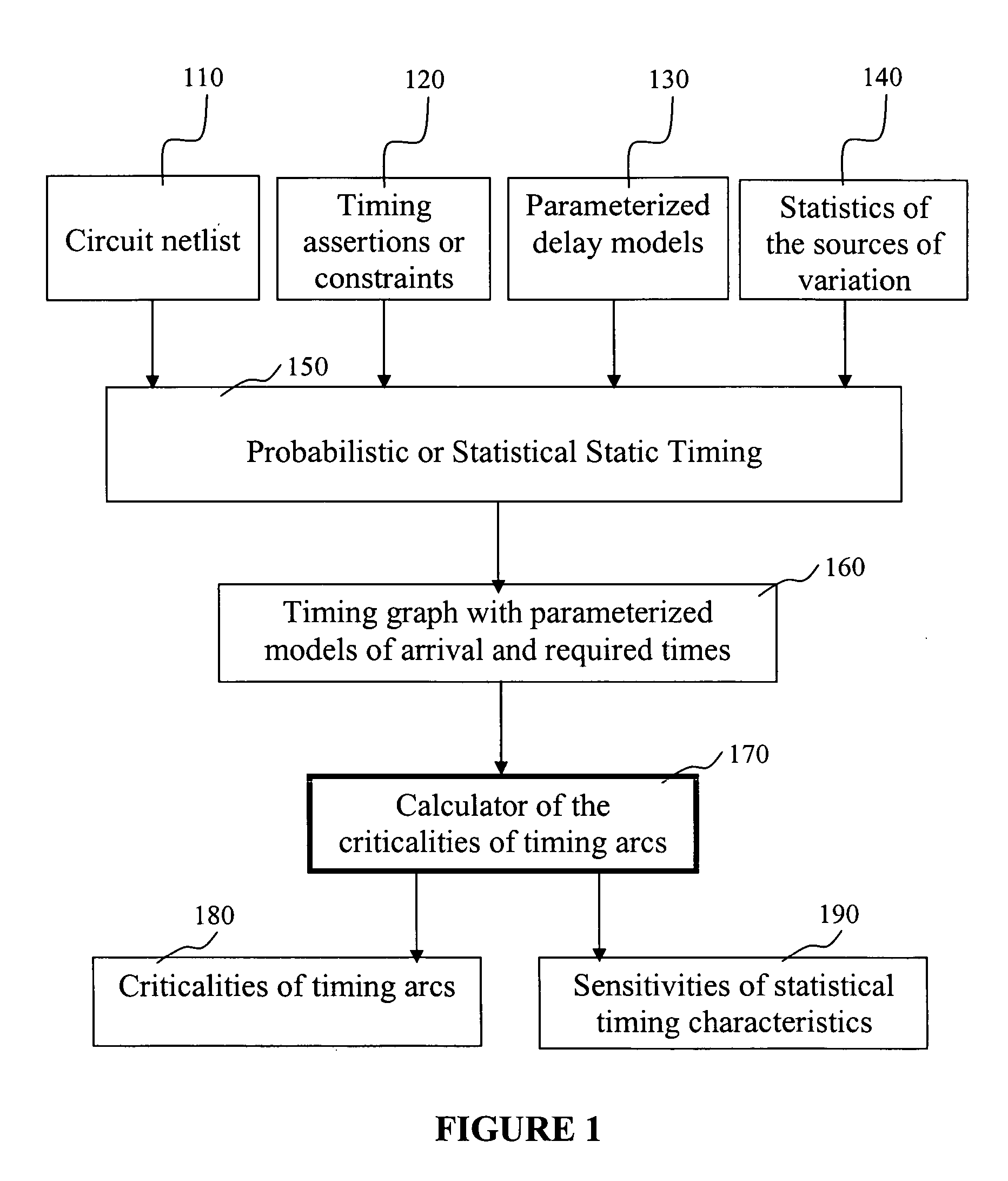
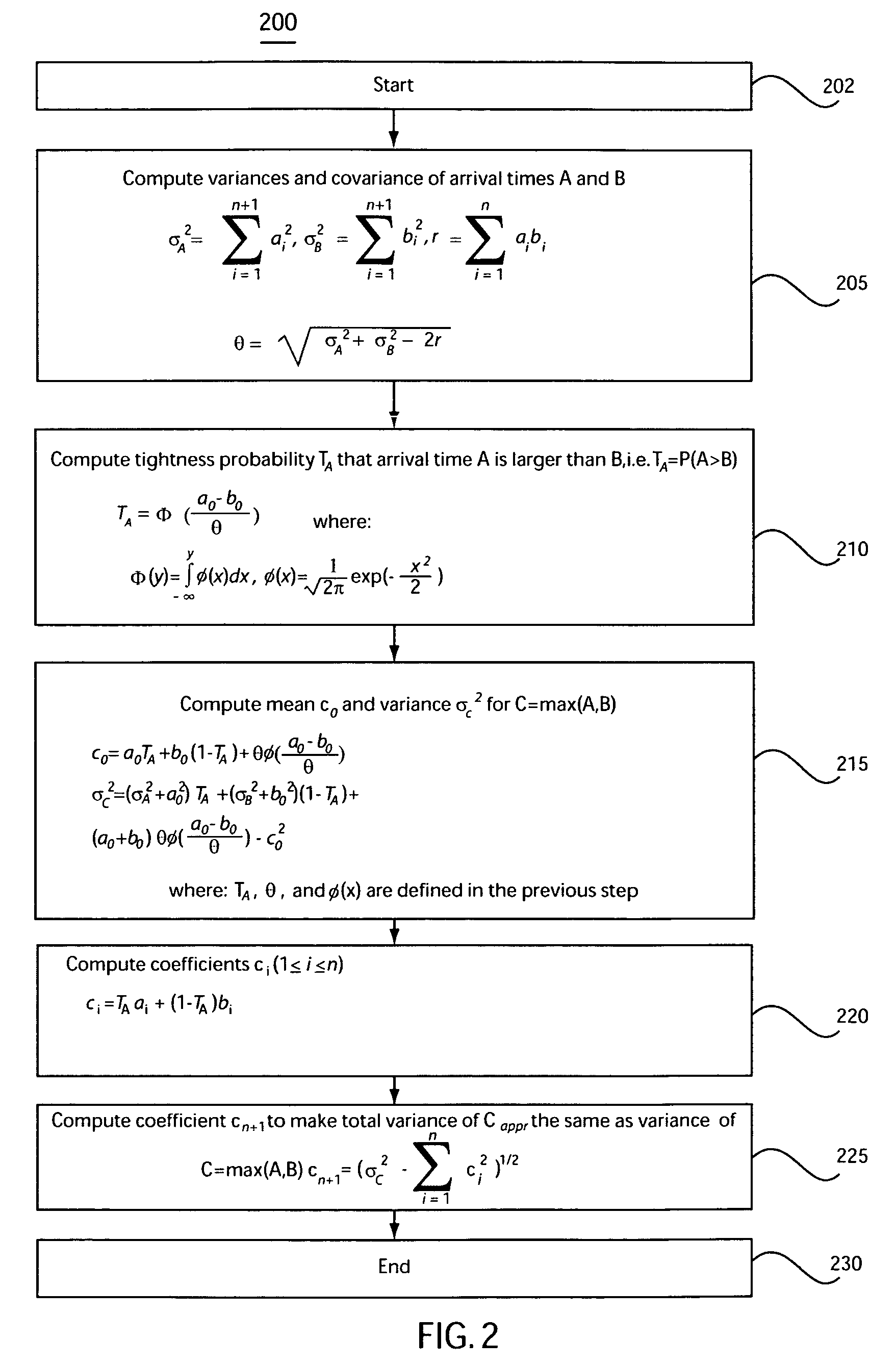
The invention provides a method, system, and program product for determining a gradient of a parametric yield of an integrated circuit with respect to parameters of a delay of an edge of a timing graph of the circuit. A first aspect of the invention provides a method for determining a gradient of a parametric yield of an integrated circuit with respect to parameters of a delay of an edge of a timing graph of the circuit, the method comprising: conducting a statistical timing analysis; expressing a statistical circuit delay in terms of a delay of the edge; and computing a gradient of the statistical circuit delay with respect to parameters of the delay of the edge.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method, system, and program product for computing a yield gradient from statistical timing
The invention provides a method, system, and program product for determining a gradient of a parametric yield of an integrated circuit with respect to parameters of a delay of an edge of a timing graph of the circuit. A first aspect of the invention provides a method for determining a gradient of a parametric yield of an integrated circuit with respect to parameters of a delay of an edge of a timing graph of the circuit, the method comprising: conducting a statistical timing analysis; expressing a statistical circuit delay in terms of a delay of the edge; and computing a gradient of the statistical circuit delay with respect to parameters of the delay of the edge.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
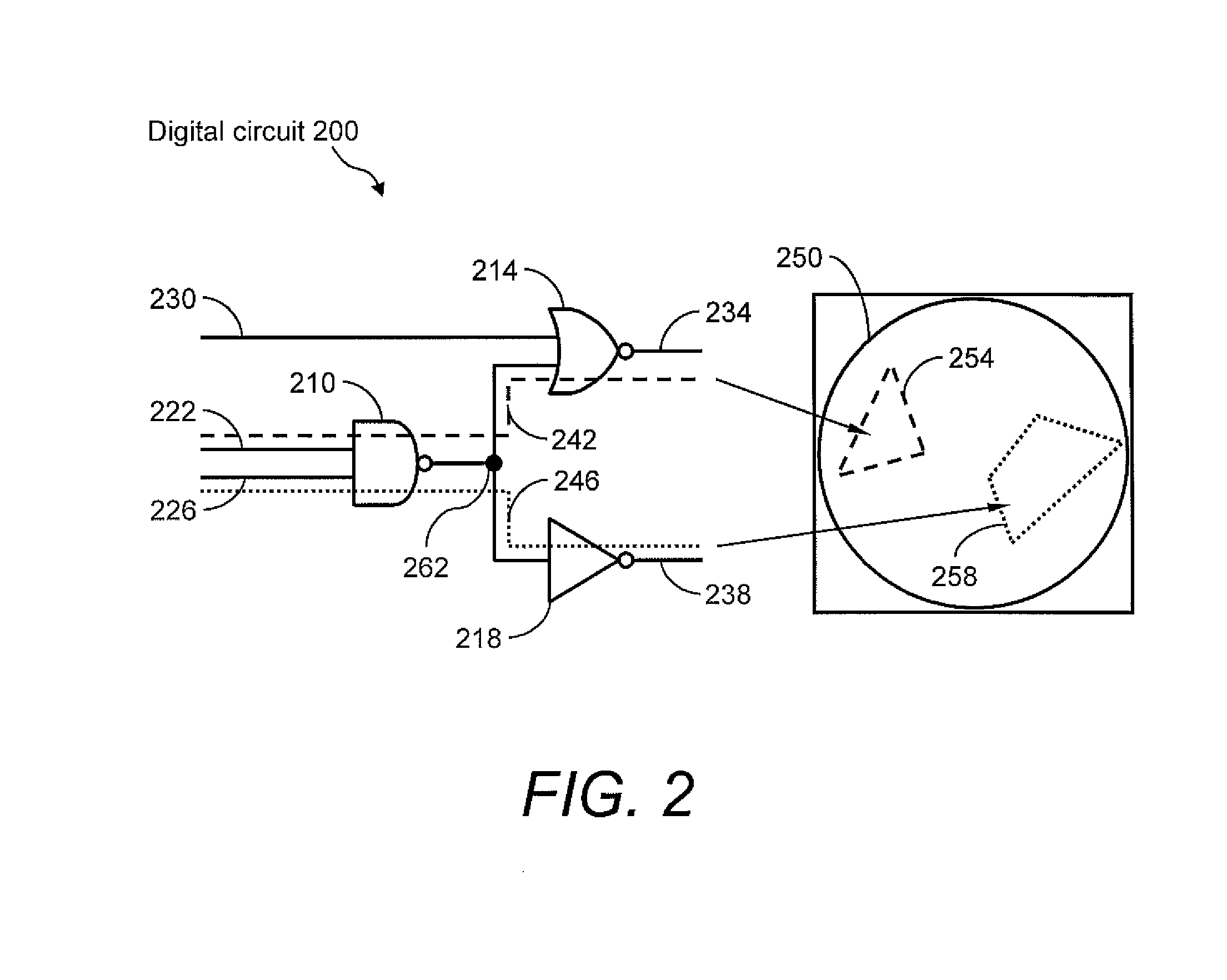
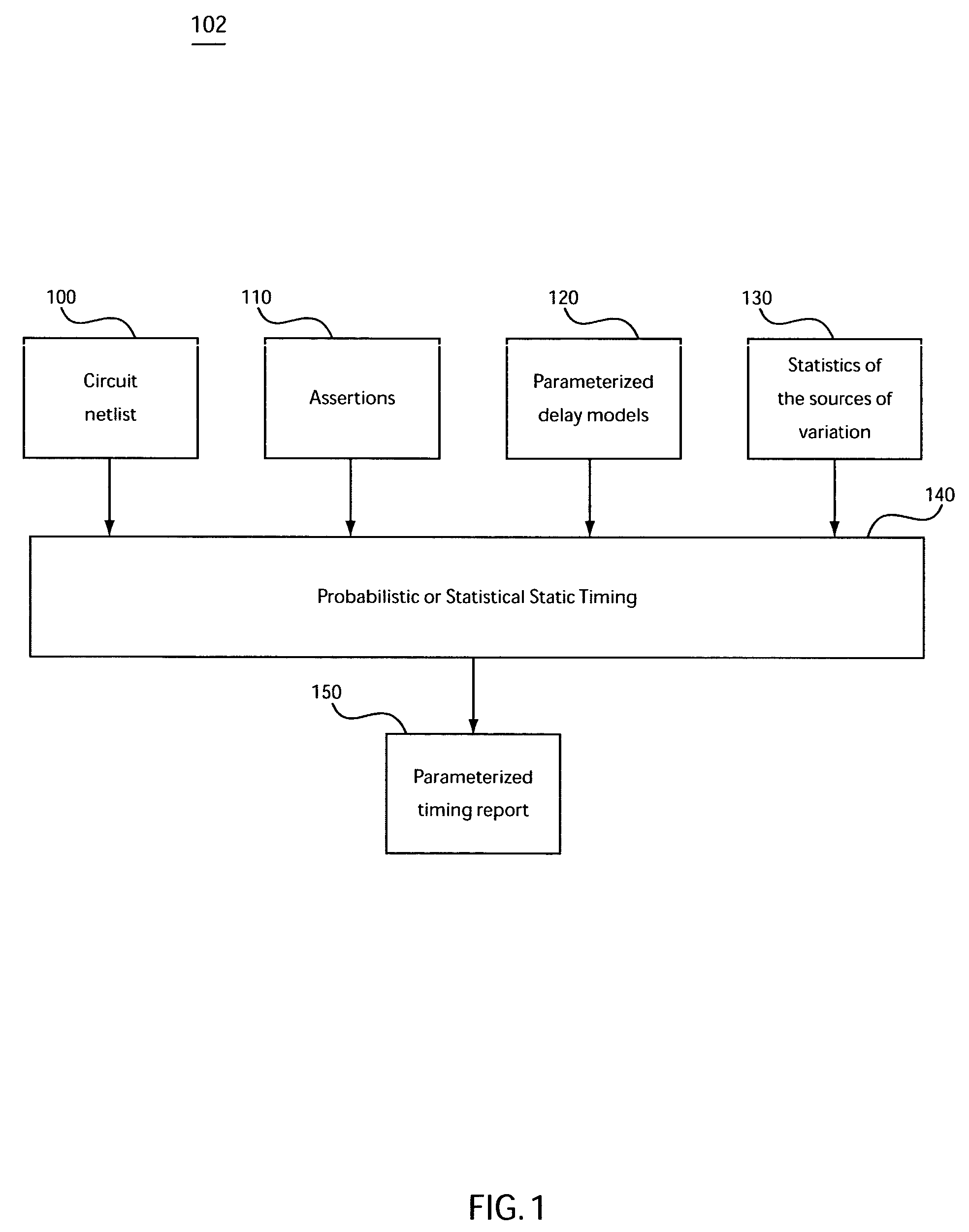
System and method for statistical timing analysis of digital circuits
ActiveUS20050065765A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputation using non-denominational number representationCMOSTheoretical computer science
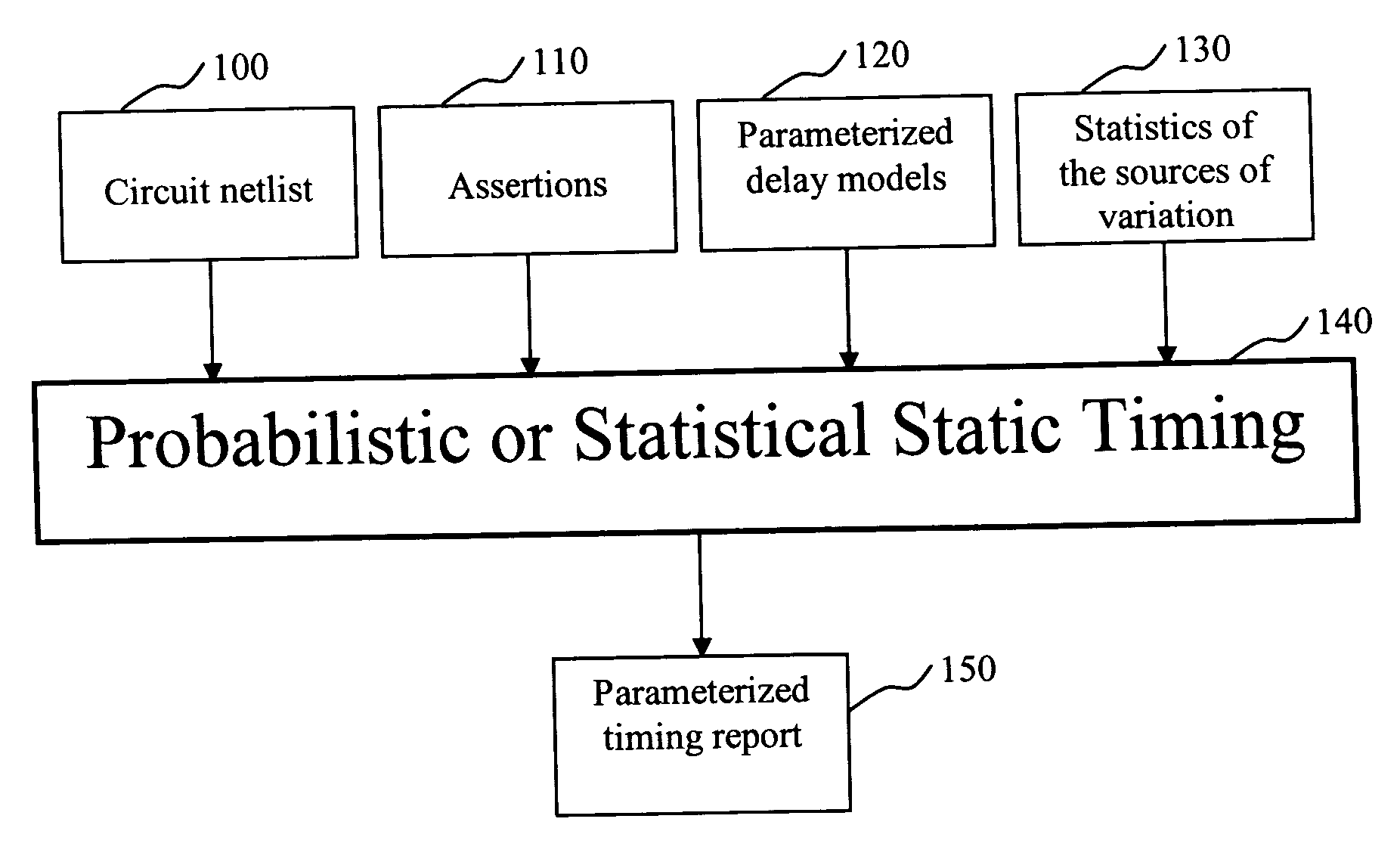
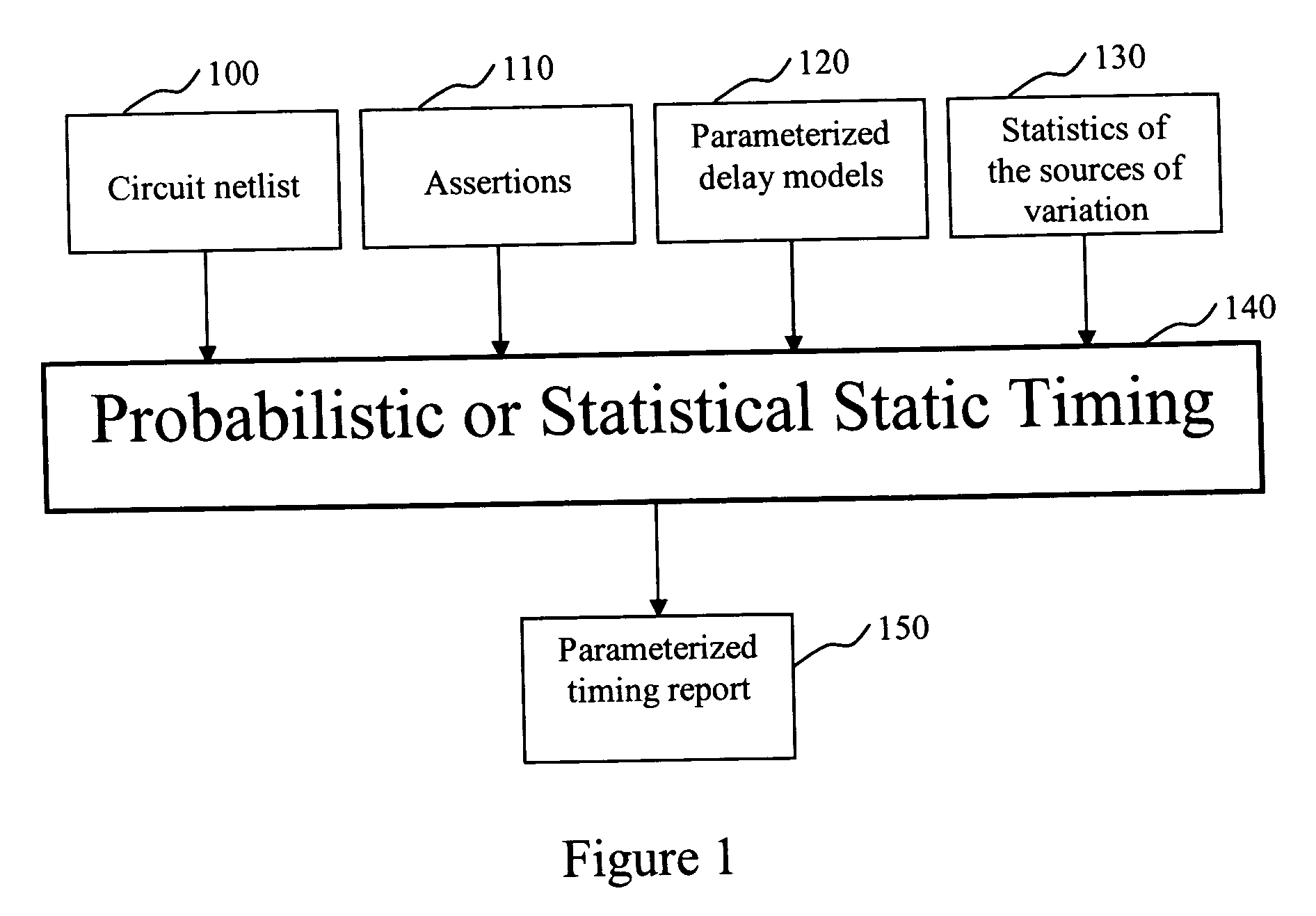
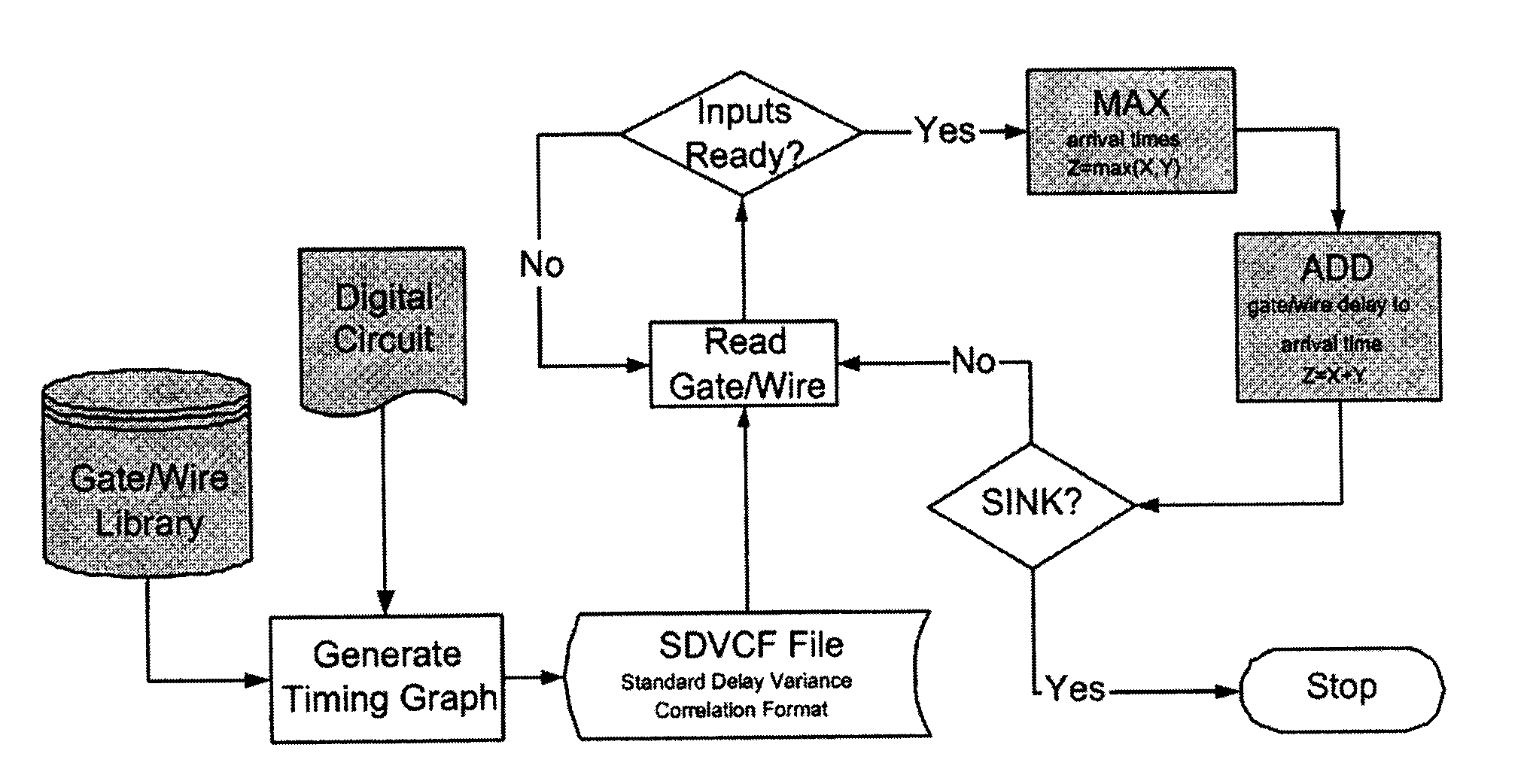
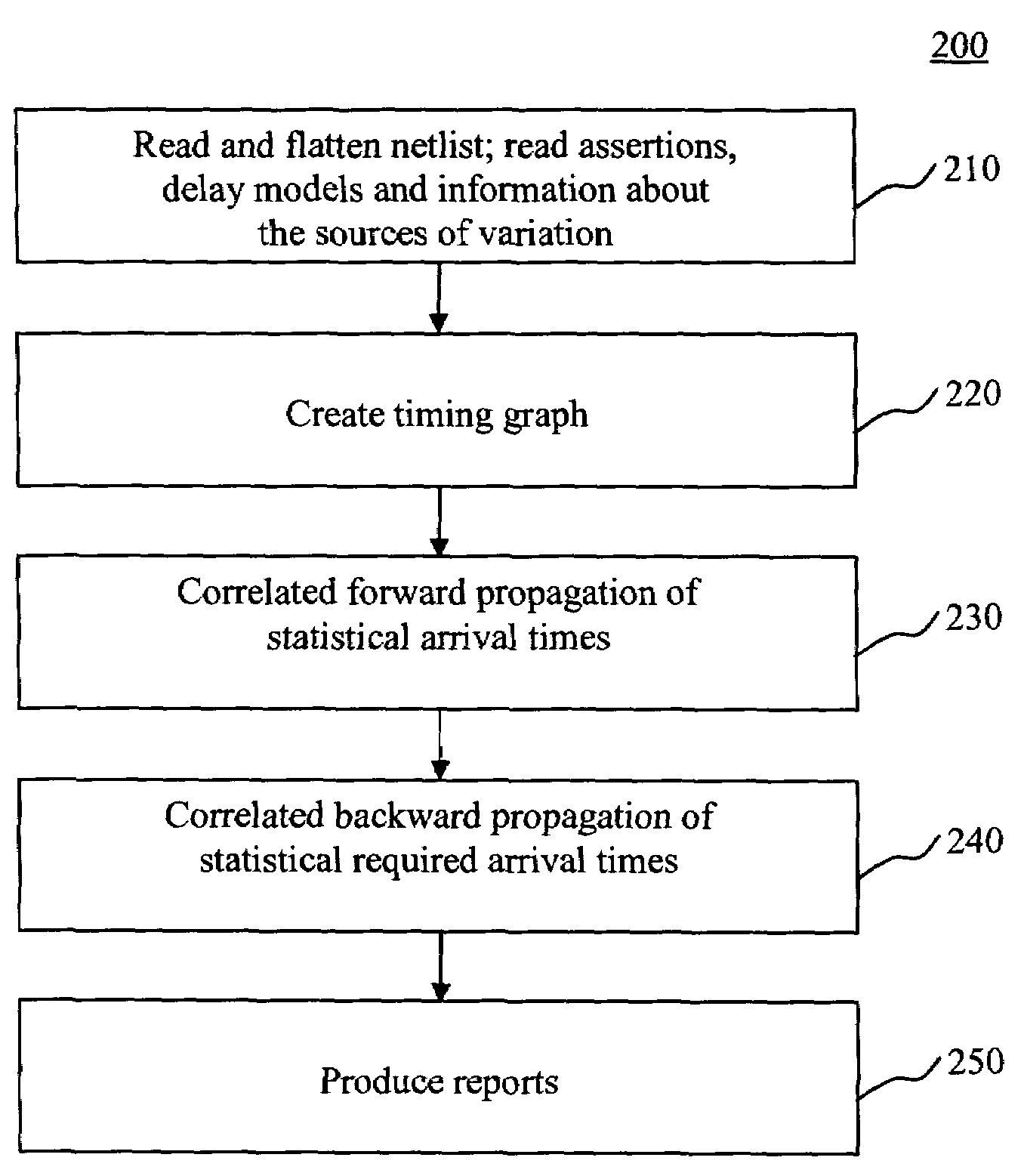
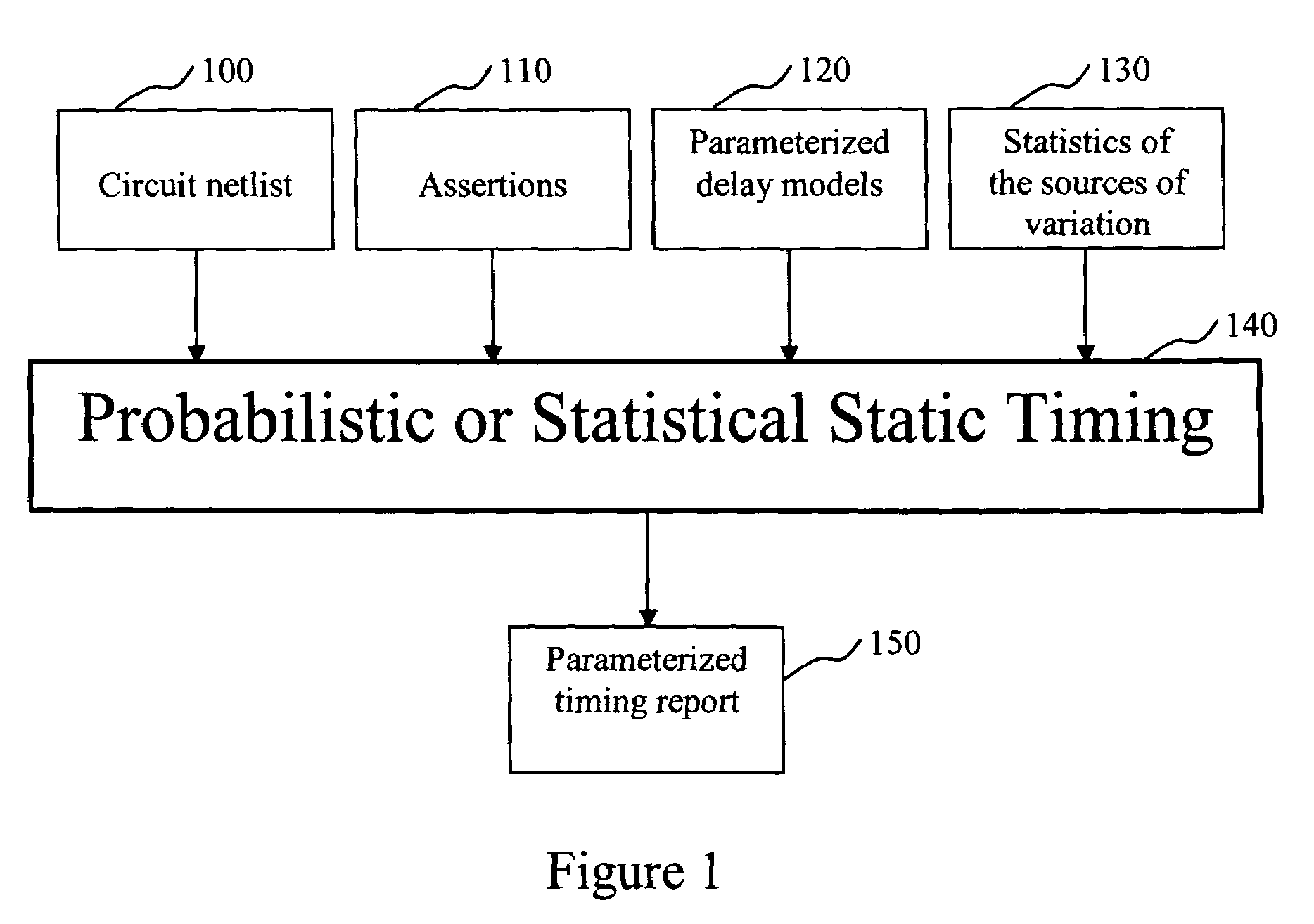
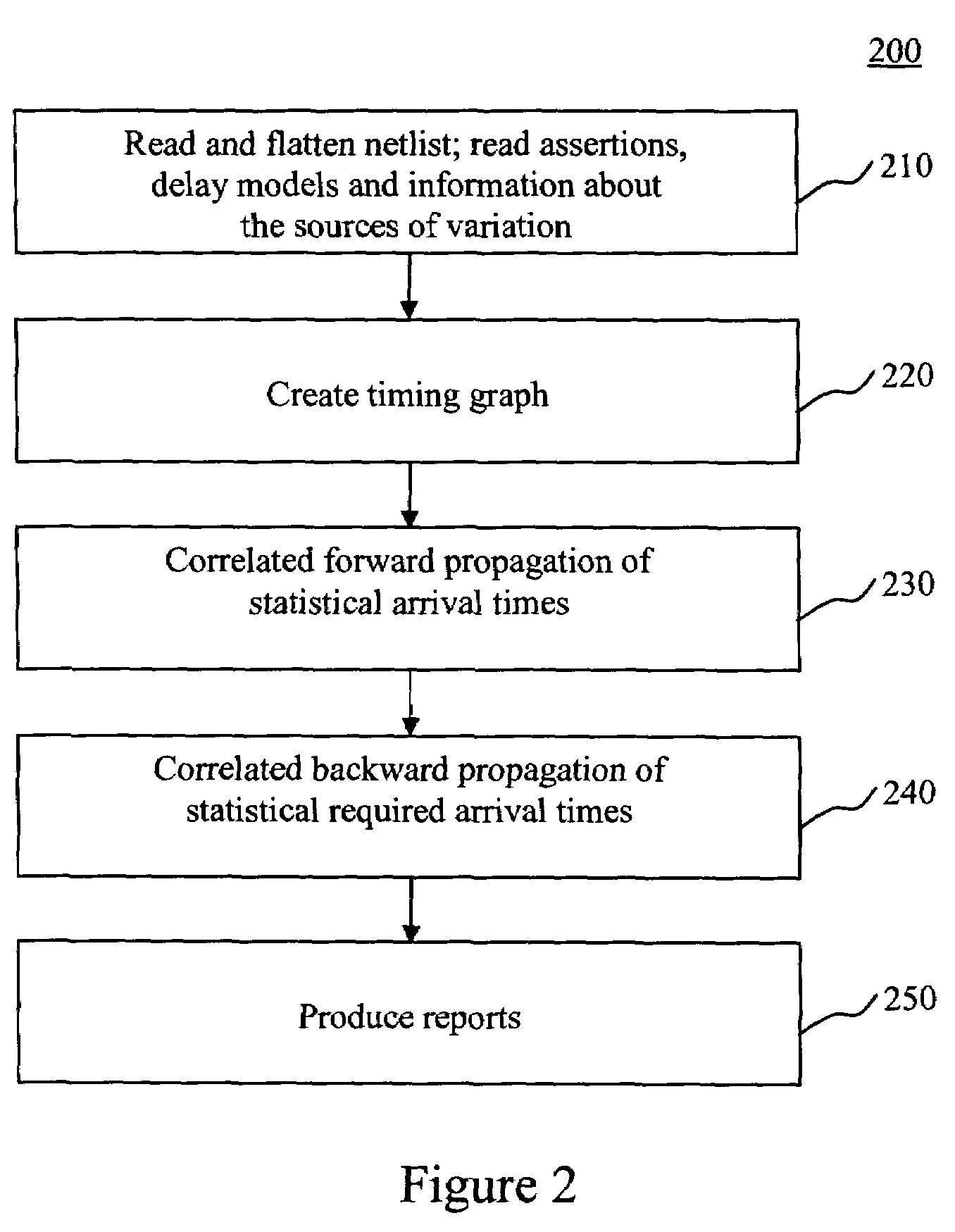
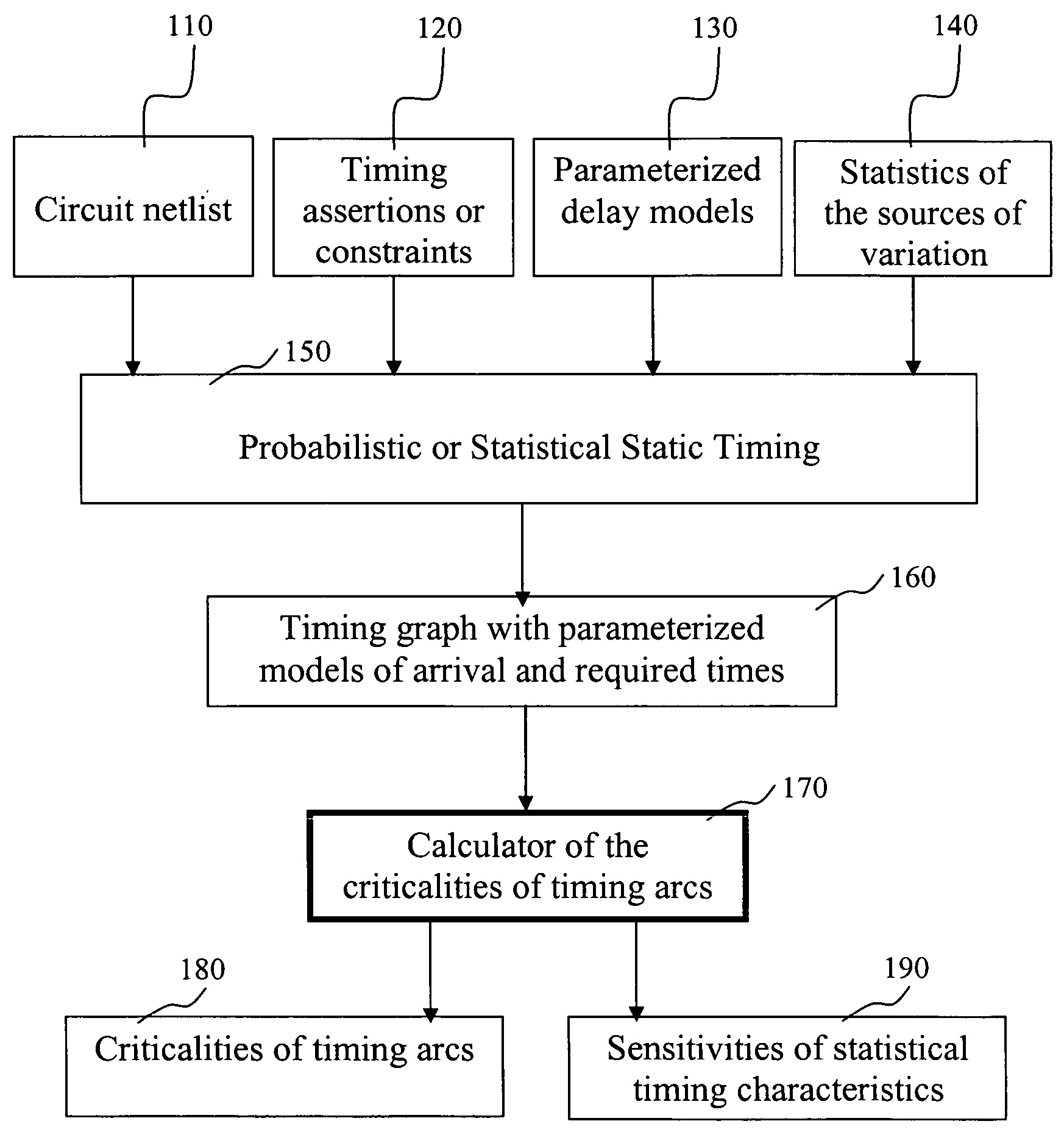
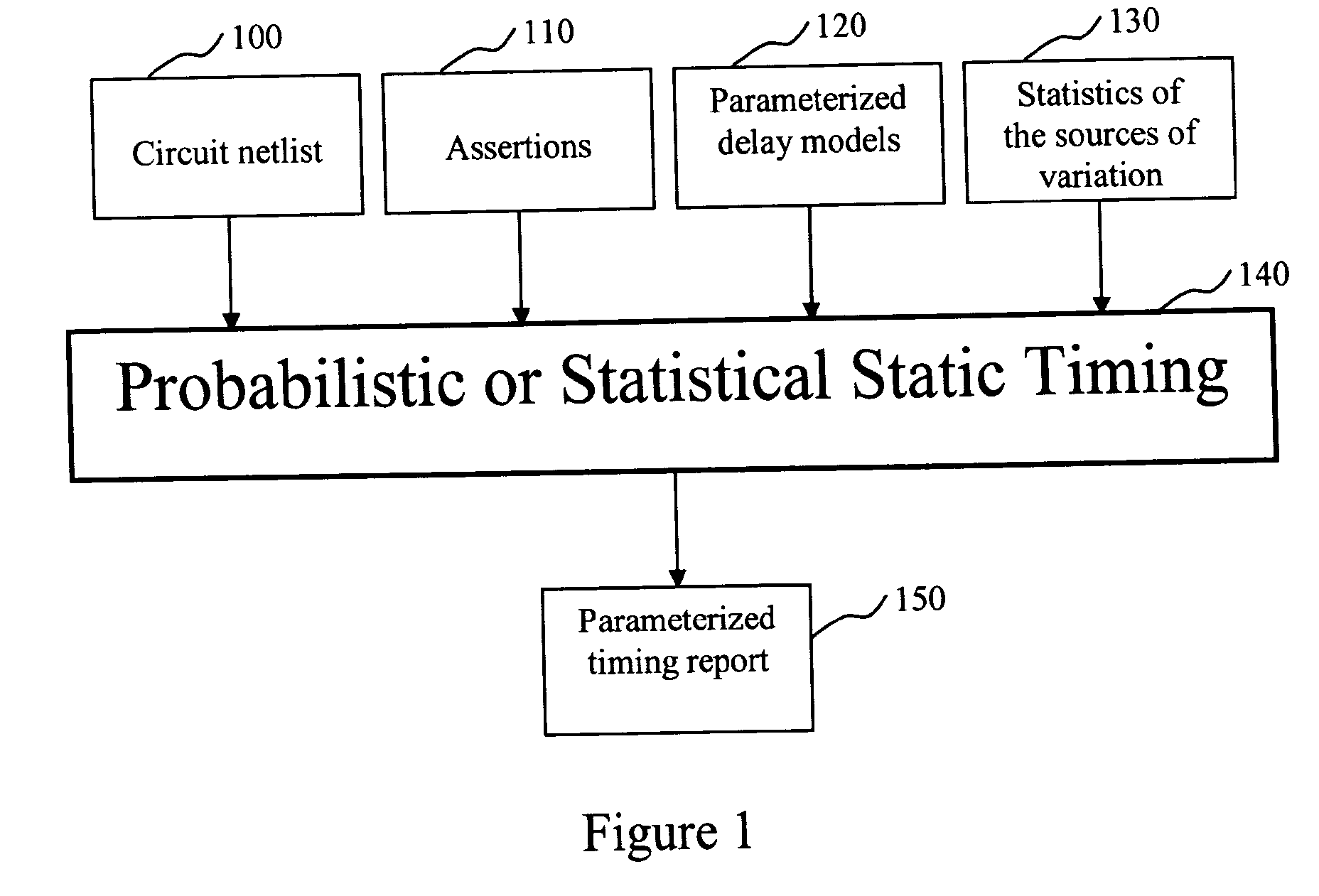
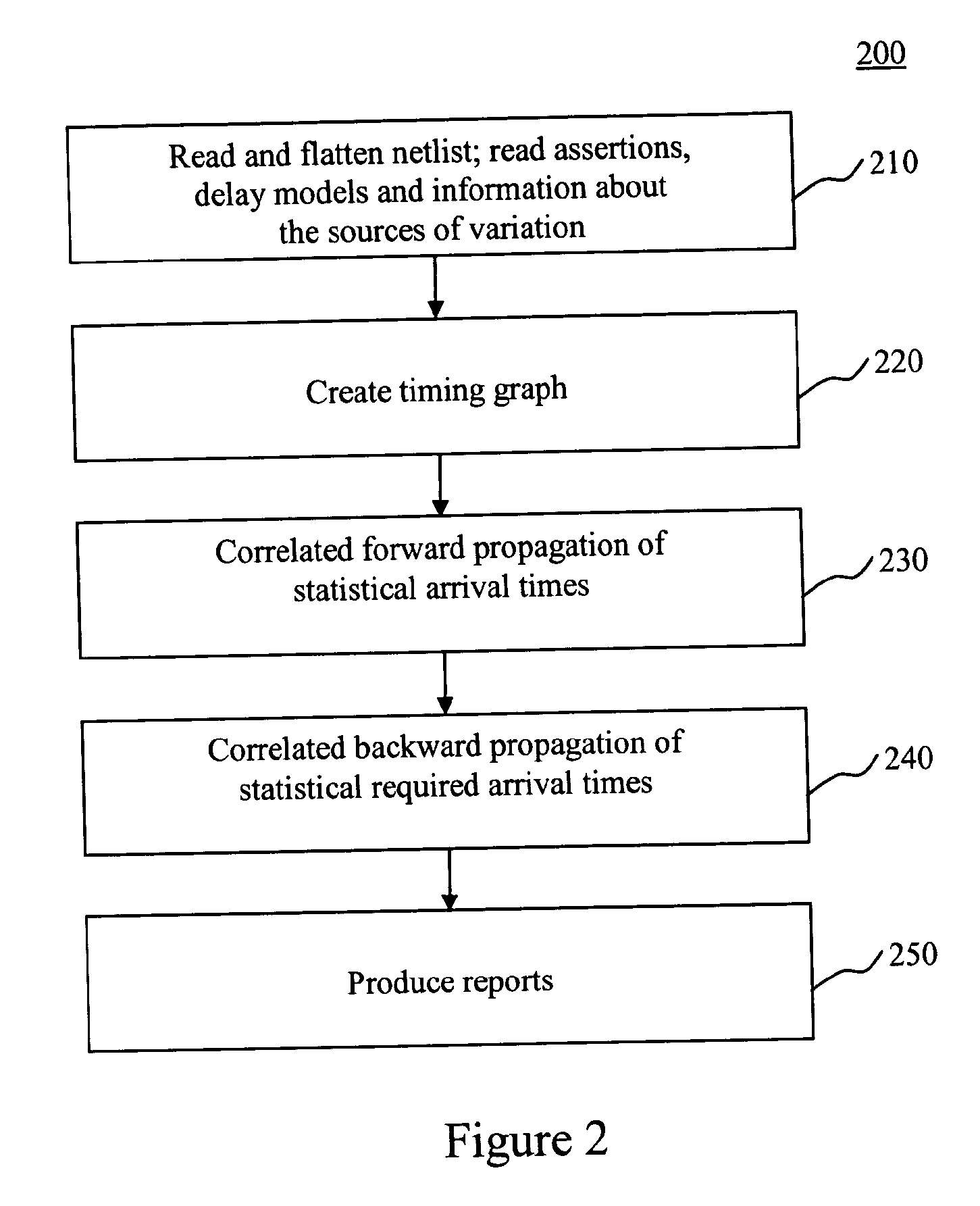
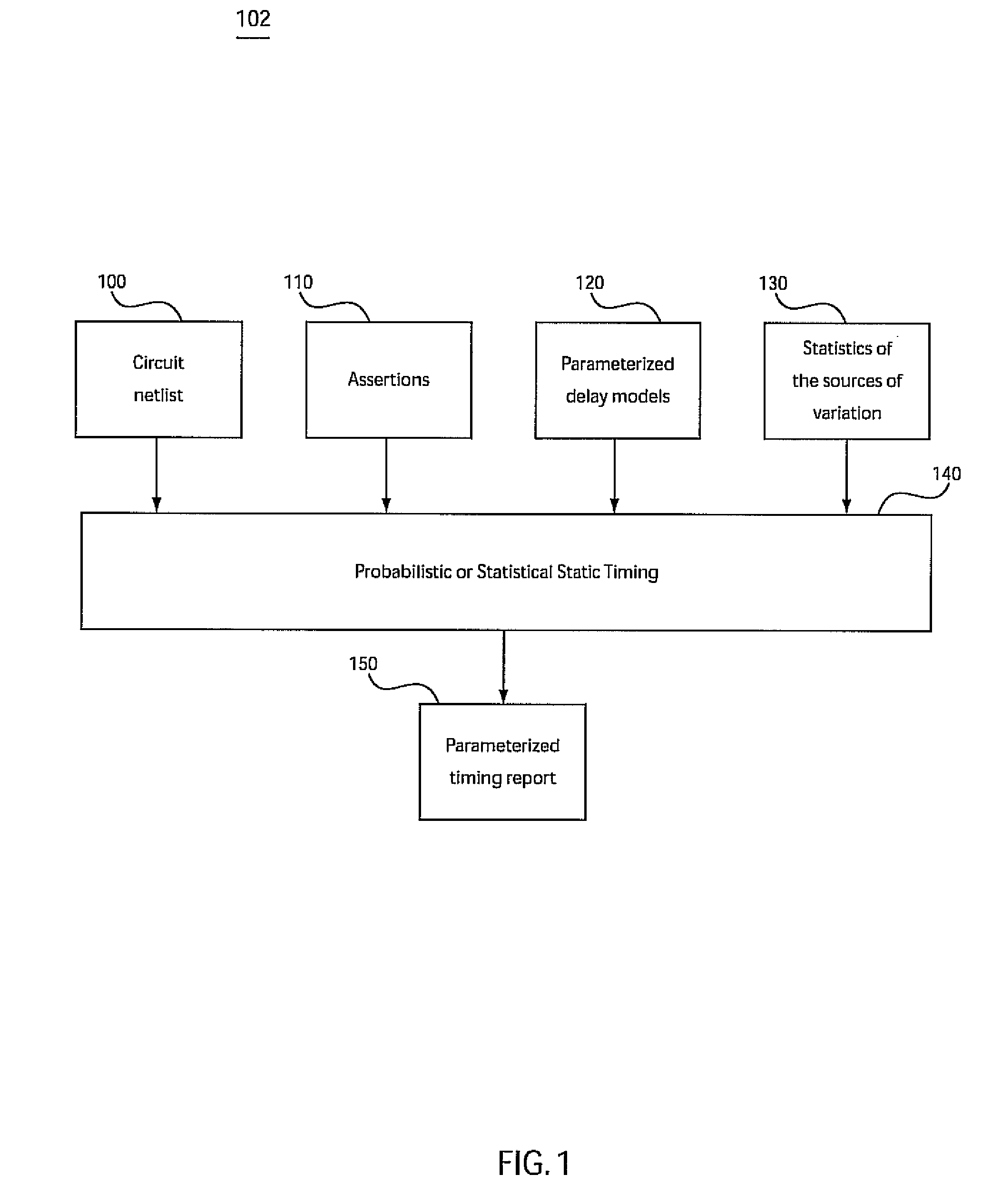
The present invention is a system and method for statistical or probabilistic static timing analysis of digital circuits, taking into account statistical delay variations. The delay of each gate or wire is assumed to consist of a nominal portion, a correlated random portion that is parameterized by each of the sources of variation and an independent random portion. Arrival times and required arrival times are propagated as parameterized random variables while taking correlations into account. Both early mode and late mode timing are included; both combinational and sequential circuits are handled; static CMOS as well as dynamic logic families are accommodated. The timing analysis complexity is linear in the size of the graph and the number of sources of variation. The result is a timing report in which all timing quantities such as arrival times and slacks are reported as probability distributions in a parameterized form.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
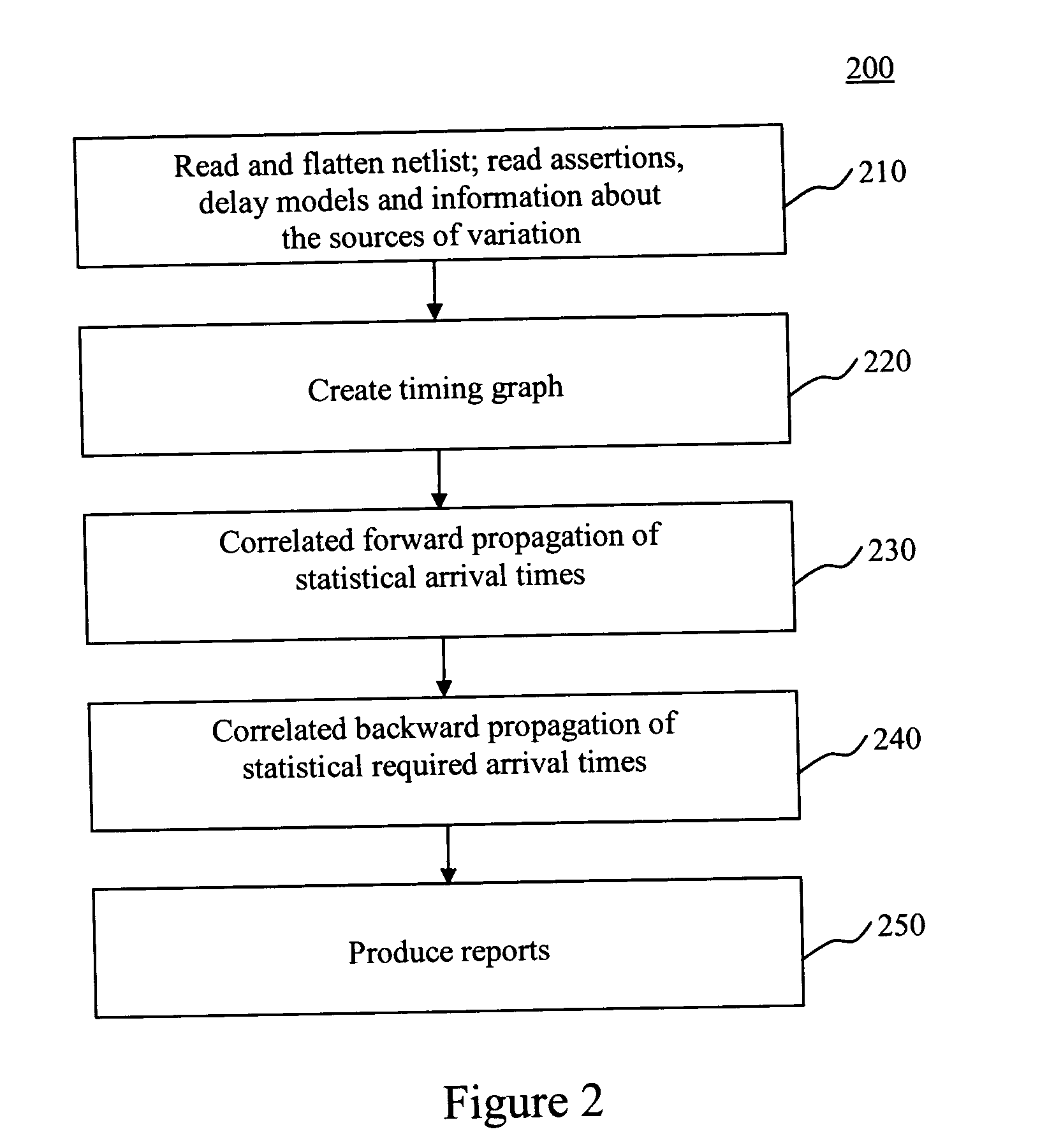
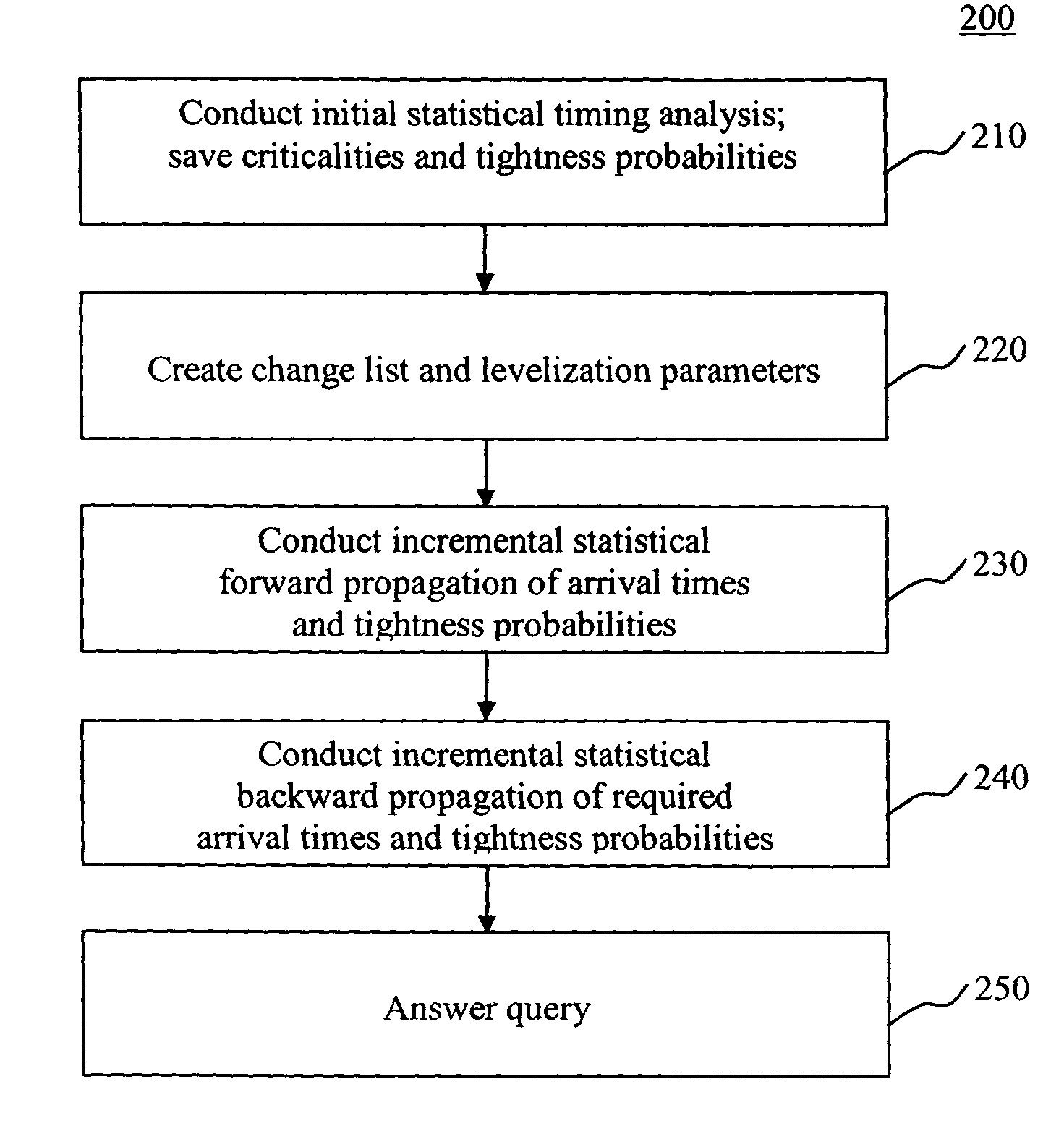
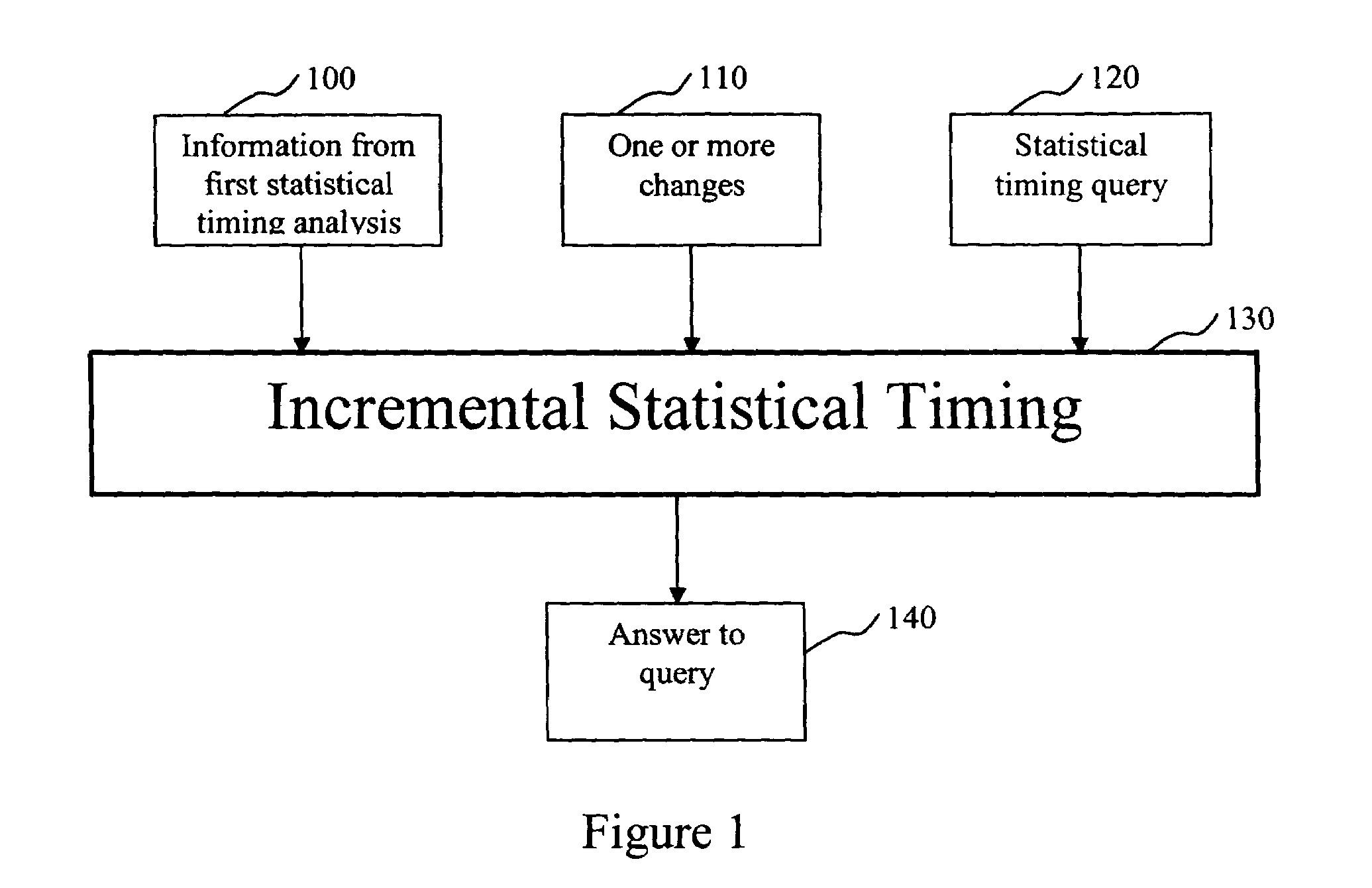
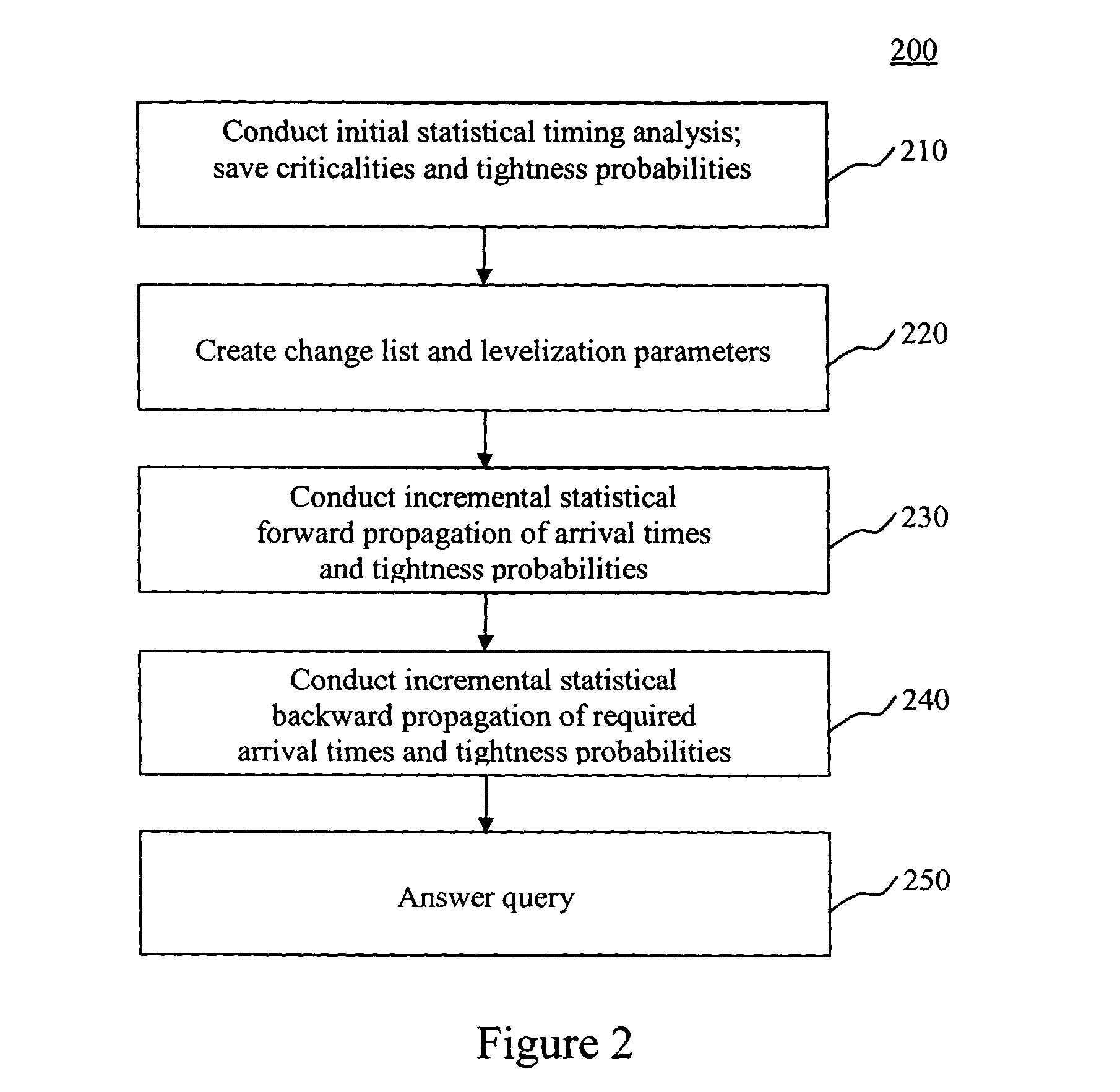
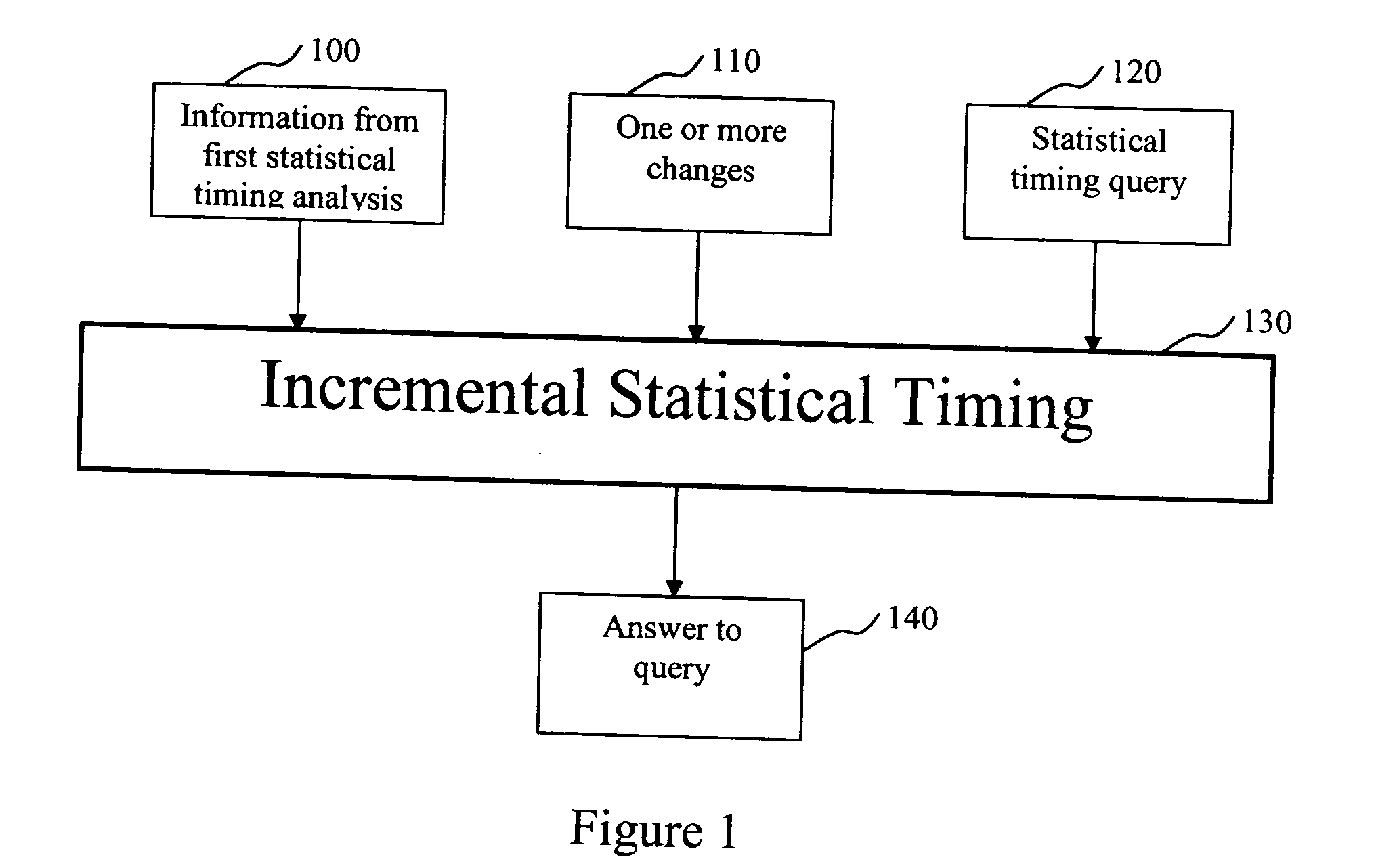
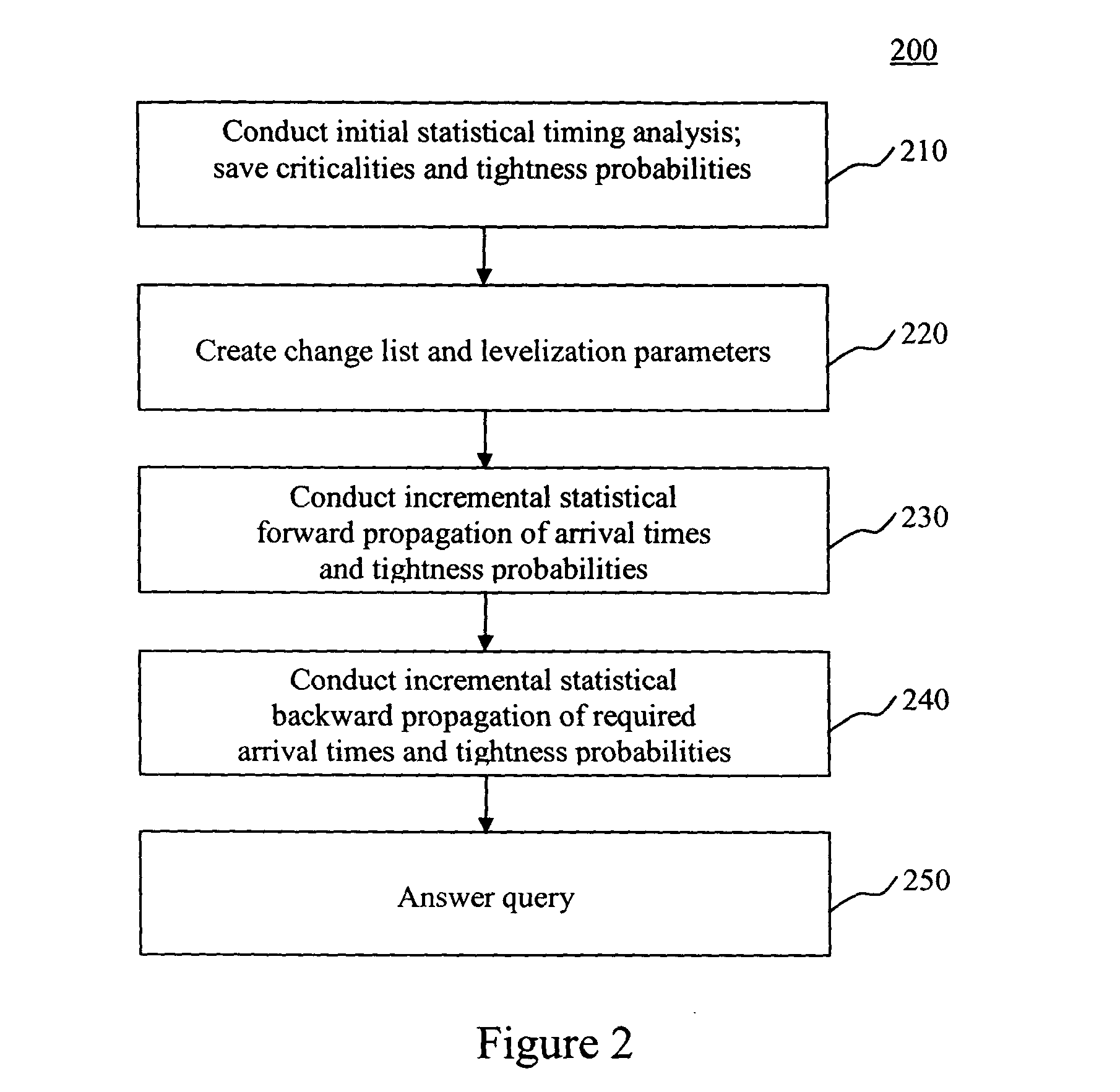
System and method for incremental statistical timing analysis of digital circuits
InactiveUS7111260B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCMOSComputer Aided Design
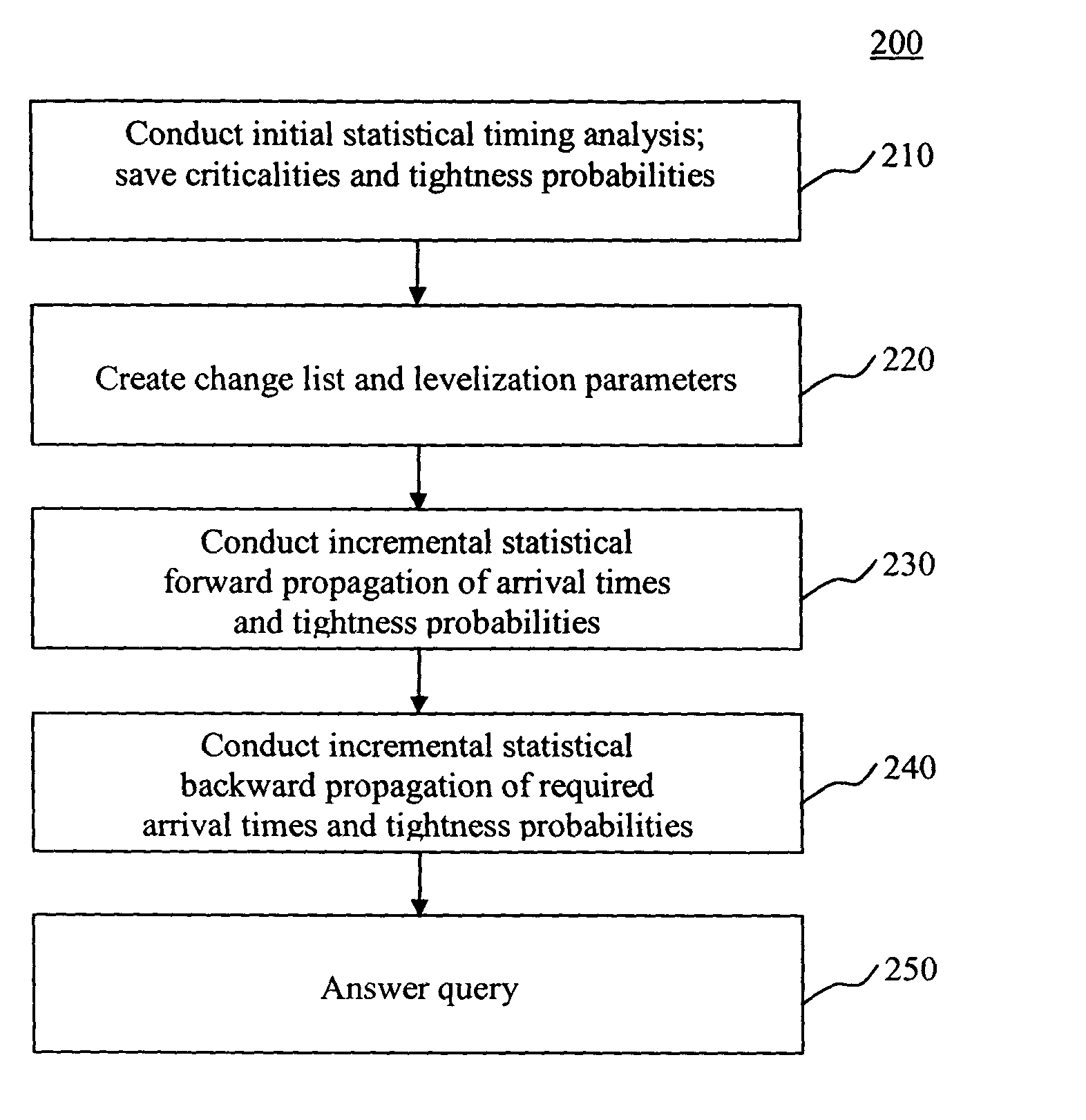
The present invention is a system and method for efficiently and incrementally updating the statistical timing of a digital circuit after a change has been made in the circuit. One or more changes in the circuit is / are followed by timing queries that are answered efficiently, constituting a mode of timing that is most useful in the inner loop of an automatic computer-aided design (CAD) synthesis or optimization tool. In the statistical re-timing, the delay of each gate or wire is assumed to consist of a nominal portion, a correlated random portion that is parameterized by each of the sources of variation and an independent random portion. Correlations are taken into account. Both early mode and late mode timing are included; both combinational and sequential circuits are handled; static CMOS as well as dynamic logic families are accommodated.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Efficient statistical timing analysis of circuits
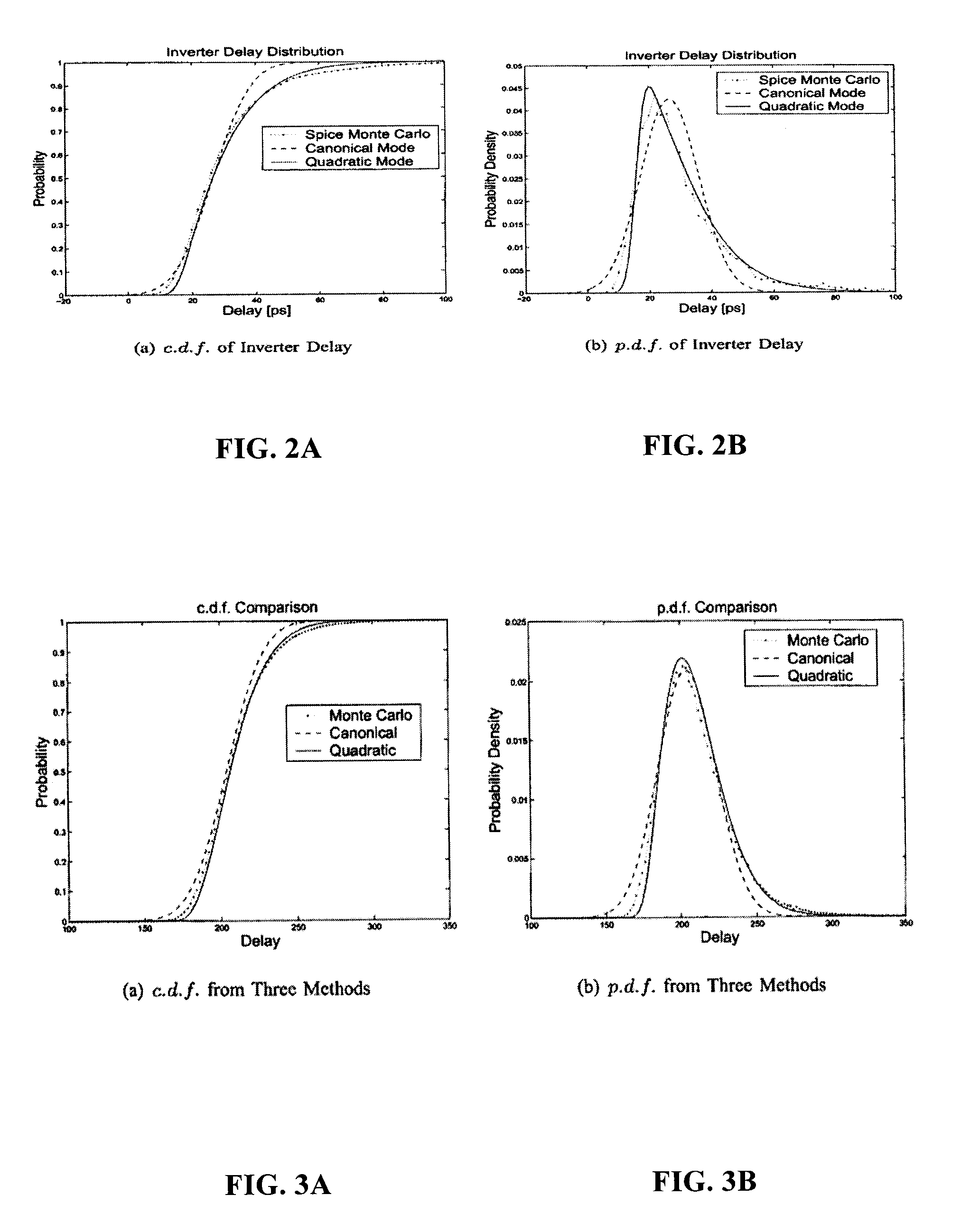
ActiveUS20070277134A1Lighten the computational burdenSmall sizeProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAnalysis methodComputer science
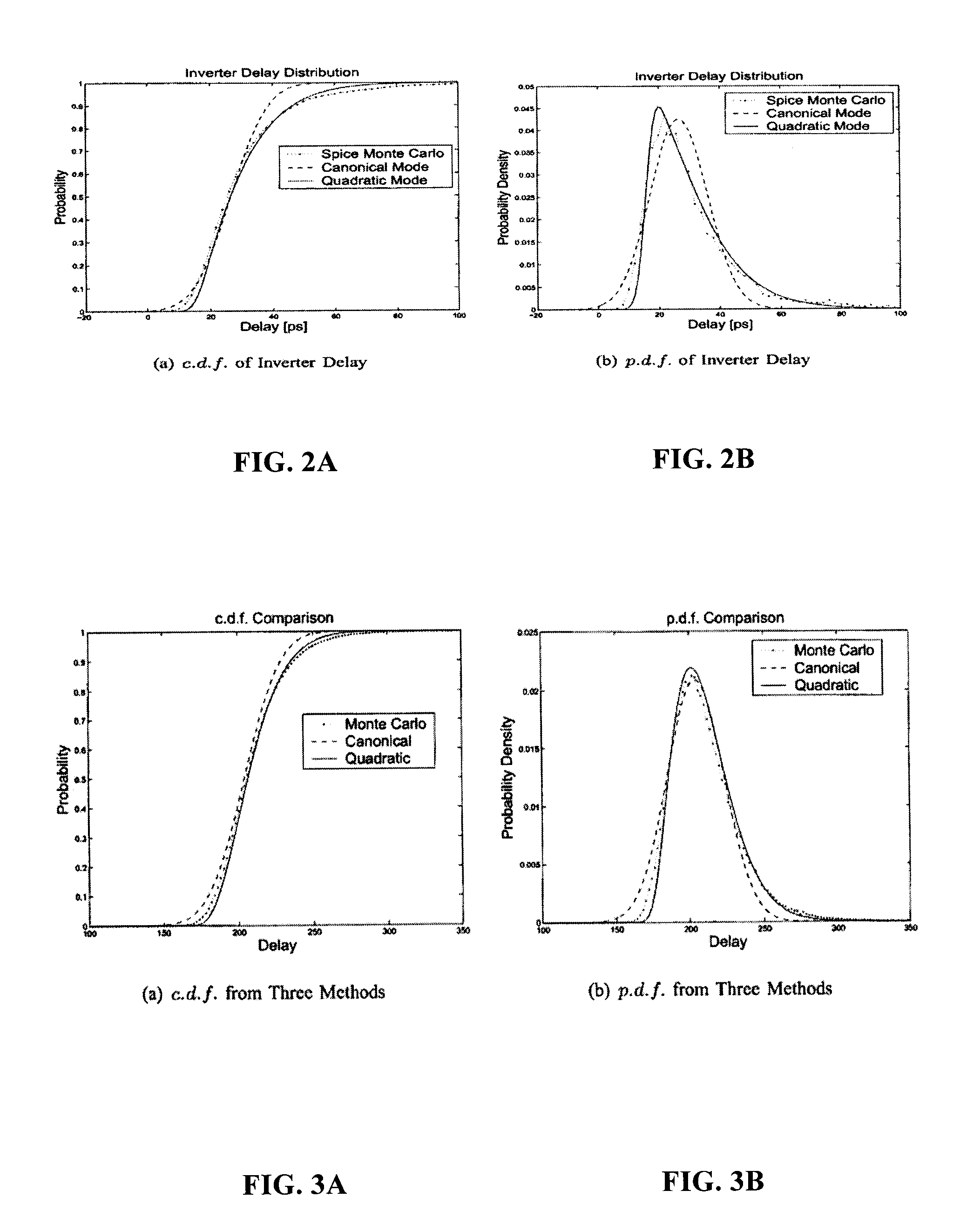
Statistical timing analysis methods for circuits are described which compensate for circuit elements having correlated timing delays with a high degree of computational efficiency. An quadratic timing model is used to represent each delay element along a circuit path, wherein each element's delay has a first-order relationship to local variations and a second-order relationship to global variations. Propagation of the modeled delays through the circuit is efficiently done via straightforward ADD operations where an input propagates through another element in a circuit path, and via a MAX operation (or an approximation thereof) where two or more inputs merge at an intersection. The inputs to the MAX operator can be tested for gaussianity, and can be processed by the MAX operation (or its approximation) if they are substantially gaussian. Otherwise, they may be stored in a tuple for processing at later points along the circuit path.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System and method for incremental statistical timing analysis of digital circuits
InactiveUS20050066296A1Efficiently and incrementally updatingAnswered efficientlyComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCMOSComputer Aided Design
The present invention is a system and method for efficiently and incrementally updating the statistical timing of a digital circuit after a change has been made in the circuit. One or more changes in the circuit is / are followed by timing queries that are answered efficiently, constituting a mode of timing that is most useful in the inner loop of an automatic computer-aided design (CAD) synthesis or optimization tool. In the statistical re-timing, the delay of each gate or wire is assumed to consist of a nominal portion, a correlated random portion that is parameterized by each of the sources of variation and an independent random portion. Correlations are taken into account. Both early mode and late mode timing are included; both combinational and sequential circuits are handled; static CMOS as well as dynamic logic families are accommodated.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
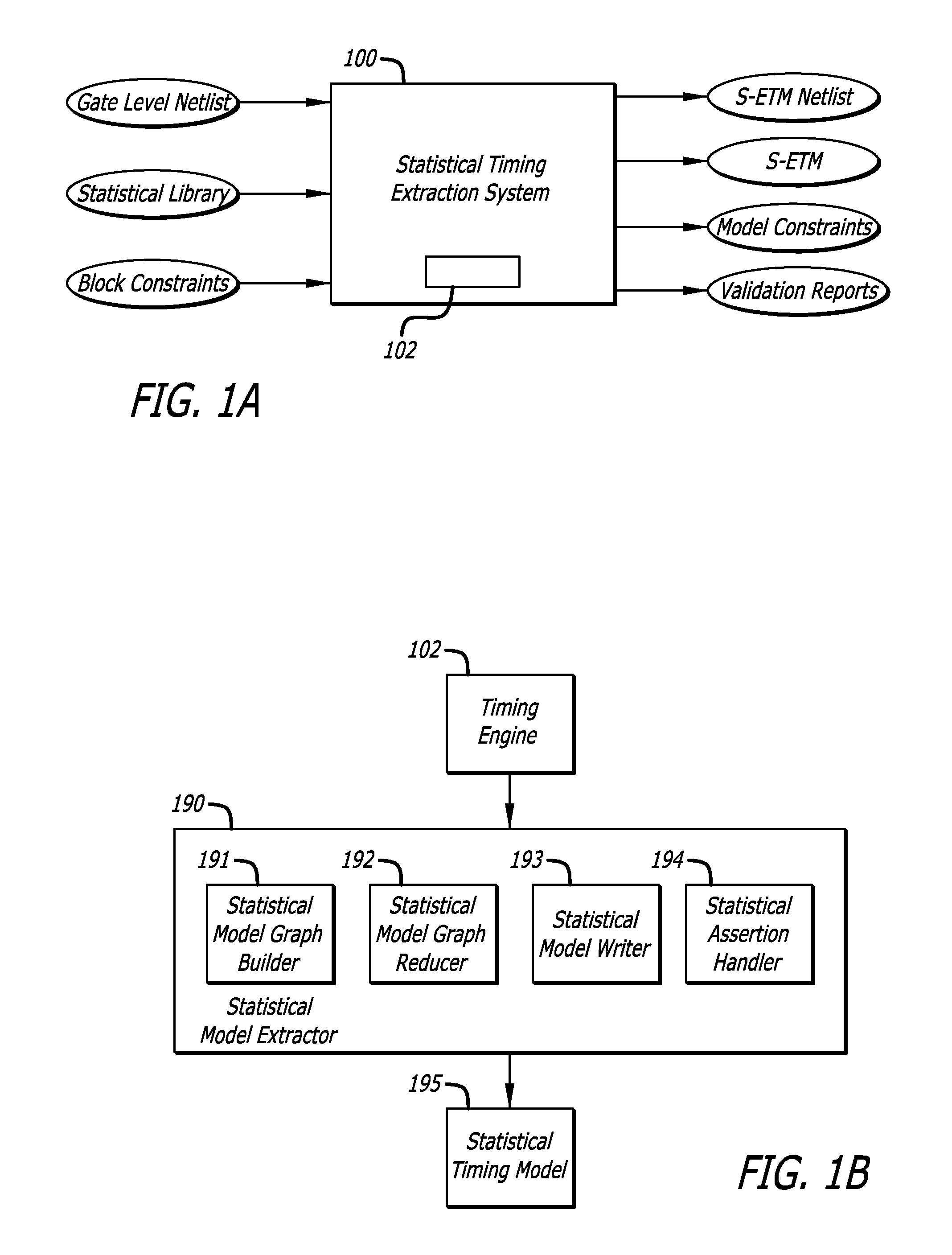
Methods, systems, and apparatus for variation aware extracted timing models
ActiveUS8239798B1Reduce timing graphReduce analysisComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringArrival time
In one embodiment of the invention, a method of analysis of a circuit design is disclosed to generate a statistical timing model. The method includes receiving a timing graph of a circuit including arcs with a statistical function of delay, slew, or arrival time; determining primary input ports and output ports of the circuit; identifying timing pins between the input ports and the output ports of the circuit; and evaluating the timing pins from input ports to output ports to reduce the timing graph to ease analysis of the reduced timing graph with a processor.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method, apparatus, and program for block-based static timing analysis with uncertainty
InactiveUS7000205B2Easy to handleComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationArrival timeComputer science
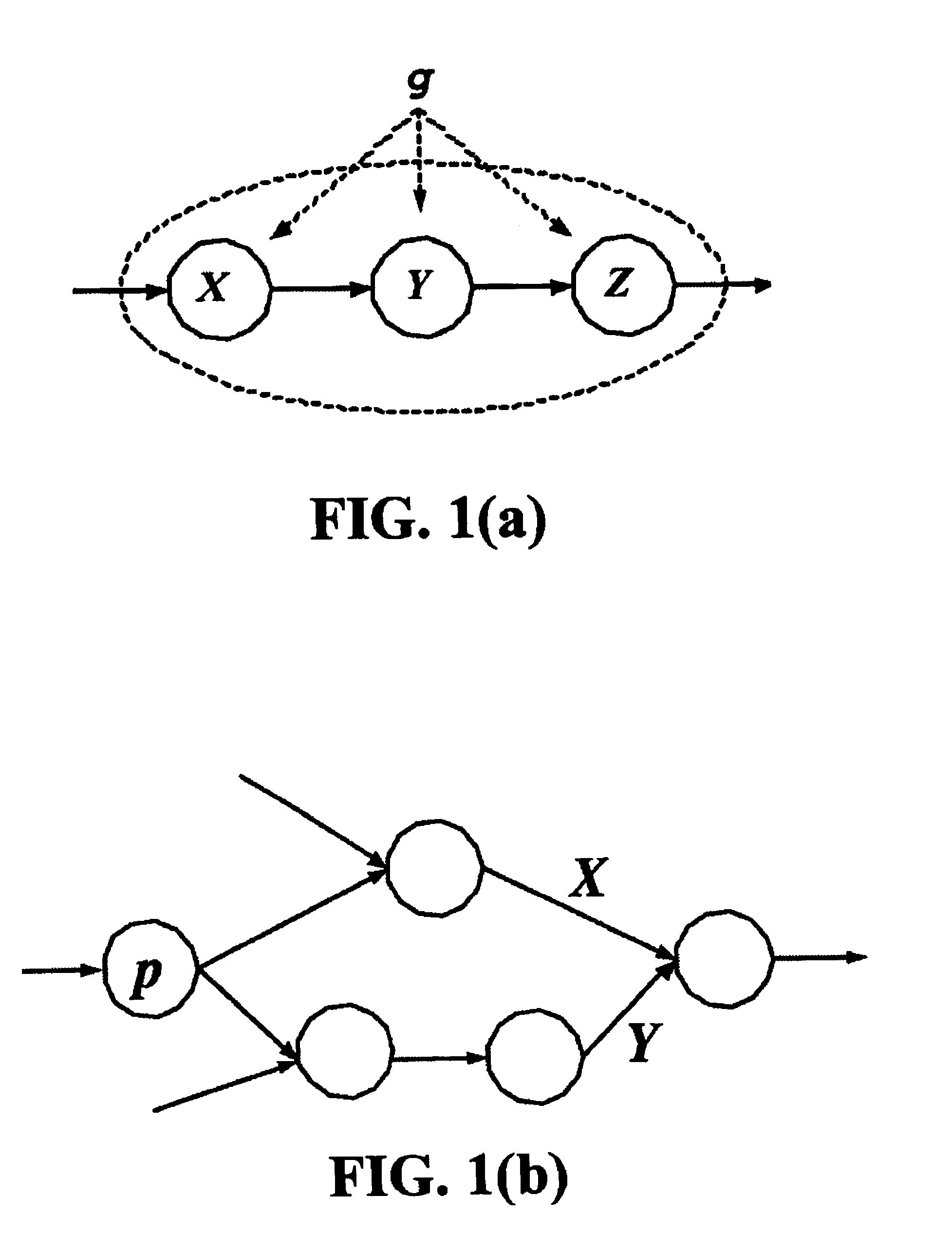
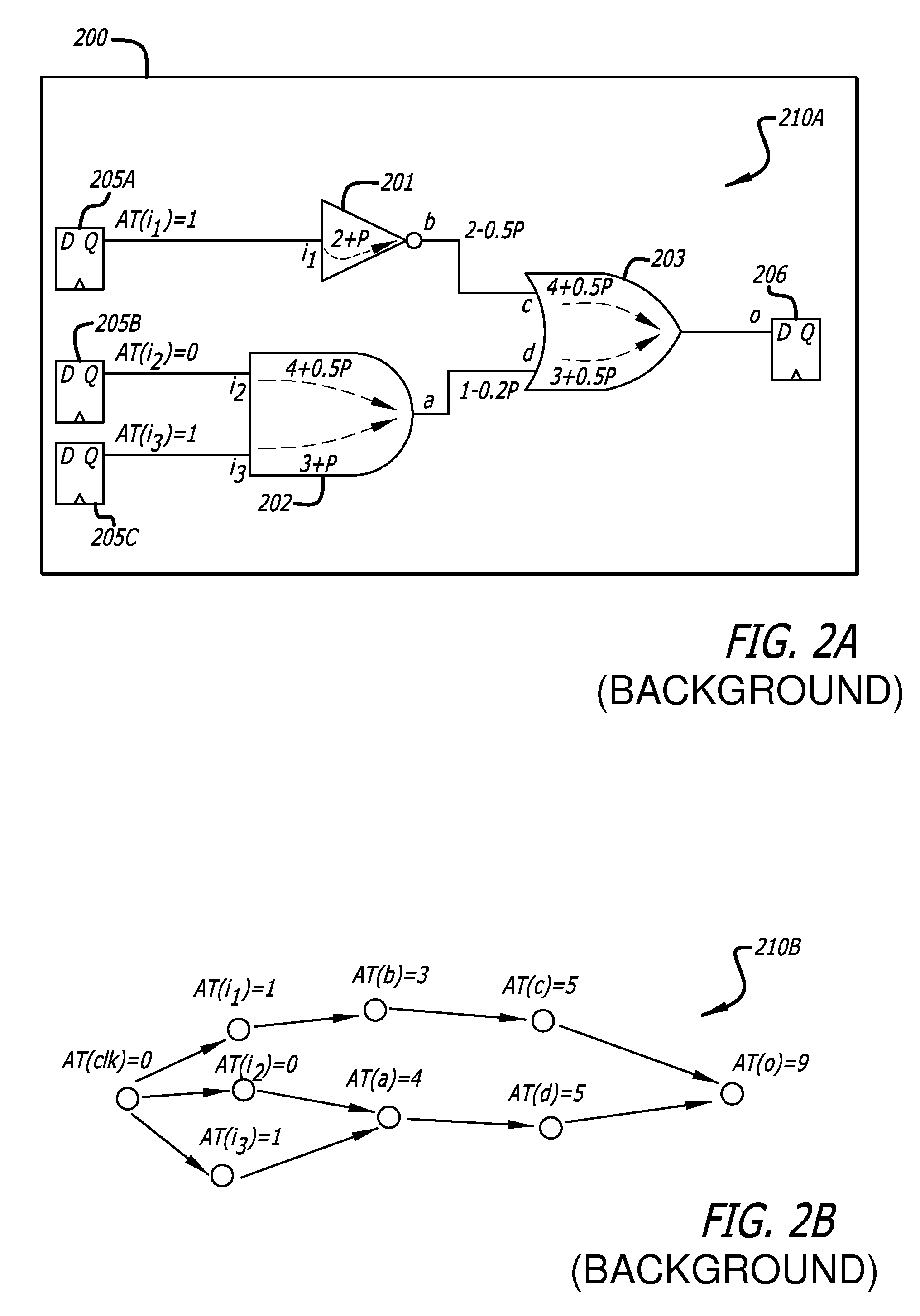
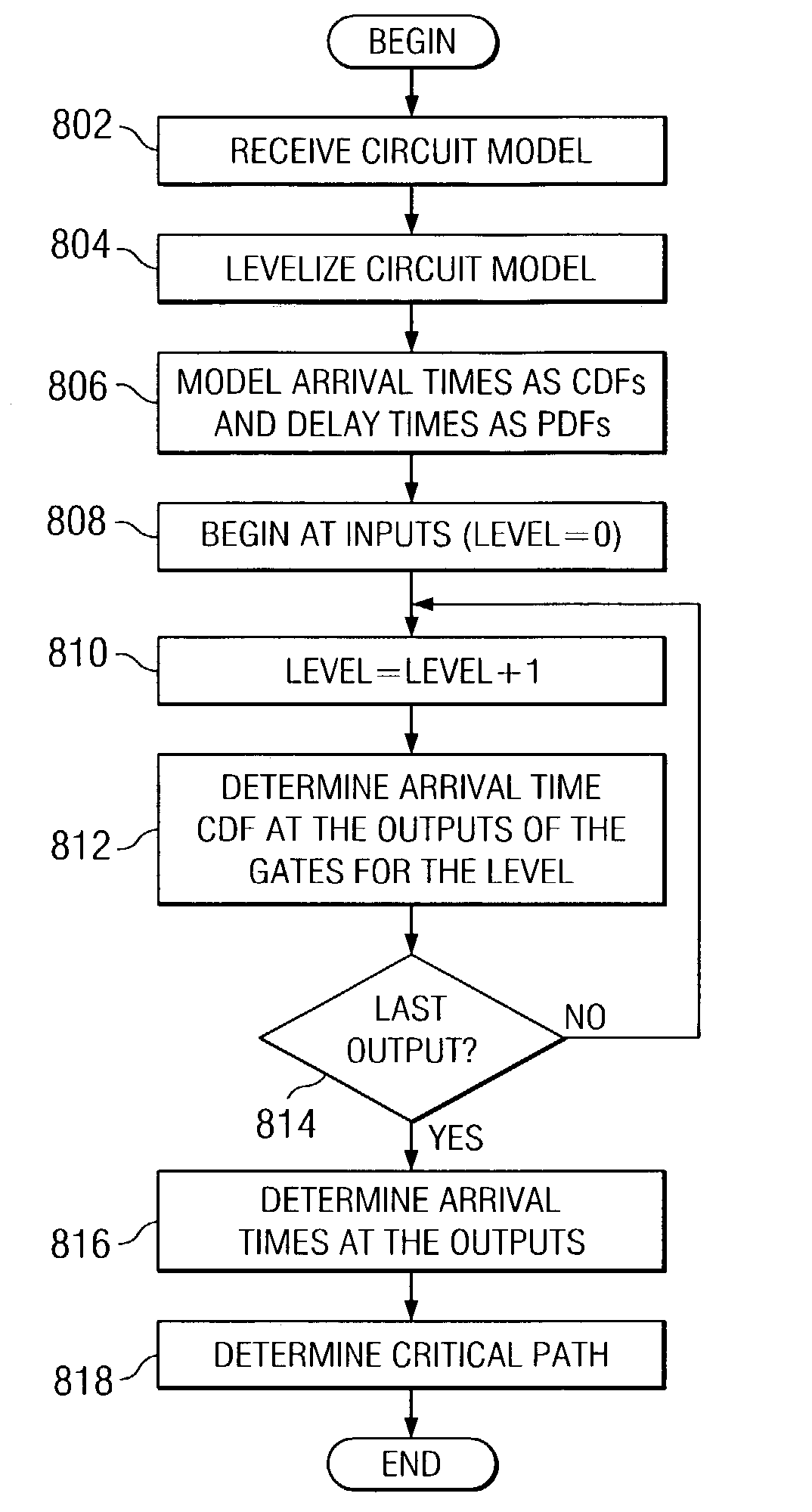
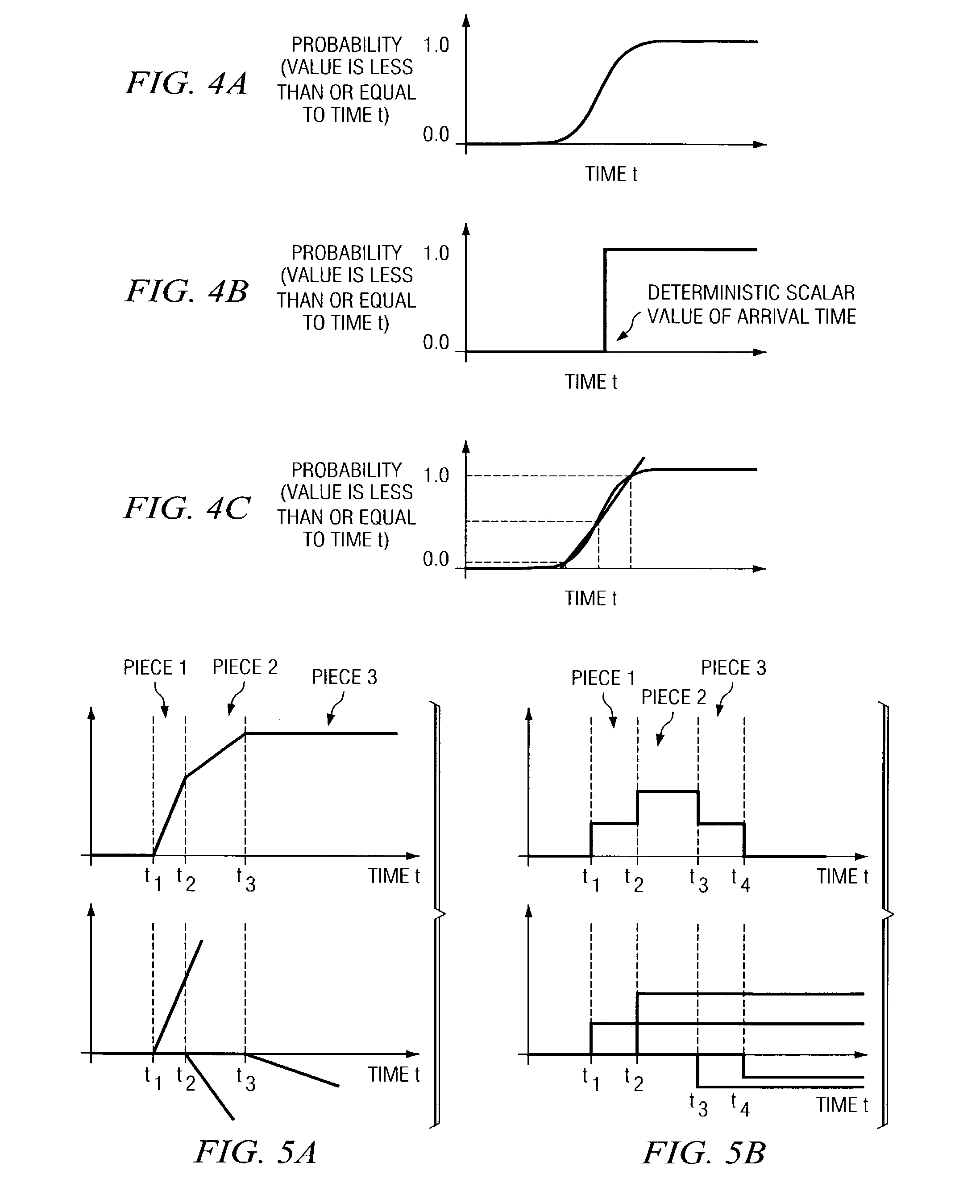
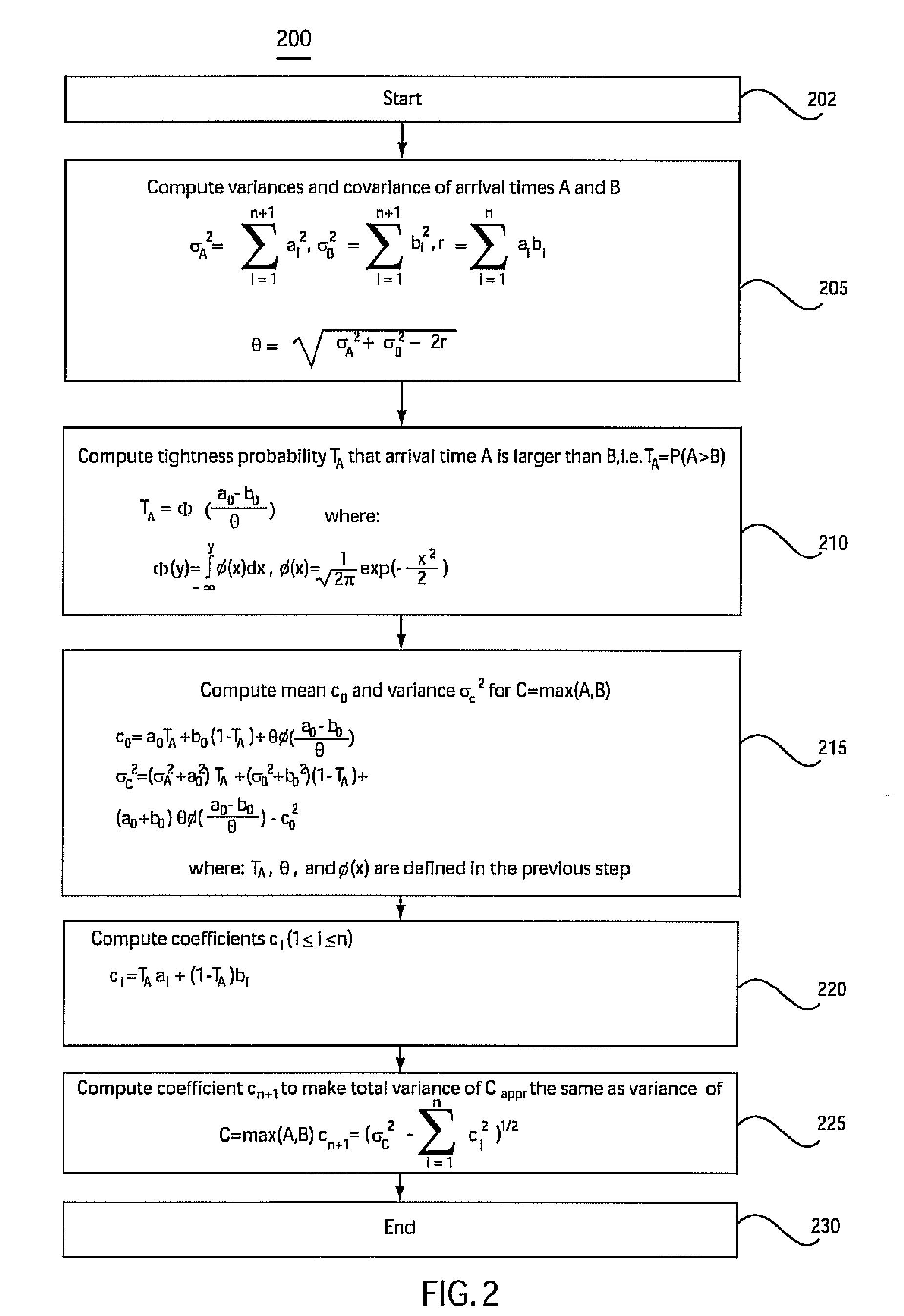
A block-based statistical timing analysis technique is provided in which the delay and arrival times in the circuit are modeled as random variables. The arrival times are modeled as Cumulative Probability Distribution Functions (CDFs) and the gate delays are modeled as Probability Density Functions (PDFs). This leads to efficient expressions for both max and addition operations, the two key functions in both regular and statistical timing analysis. Although the proposed approach can handle any form of the CDF, the CDFs may also be modeled as piecewise linear for computational efficiency. The dependency caused by reconvergent fanout is addressed, which is a necessary first step in a statistical STA framework. Reconvergent fanouts are efficiently handled by a common mode removal approach using statistical “subtraction.”
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for statistical timing analysis of digital circuits
ActiveUS7428716B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputation using non-denominational number representationCMOSTheoretical computer science
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
System and method of criticality prediction in statistical timing analysis
InactiveUS20070143722A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAlgorithmStatistical timing
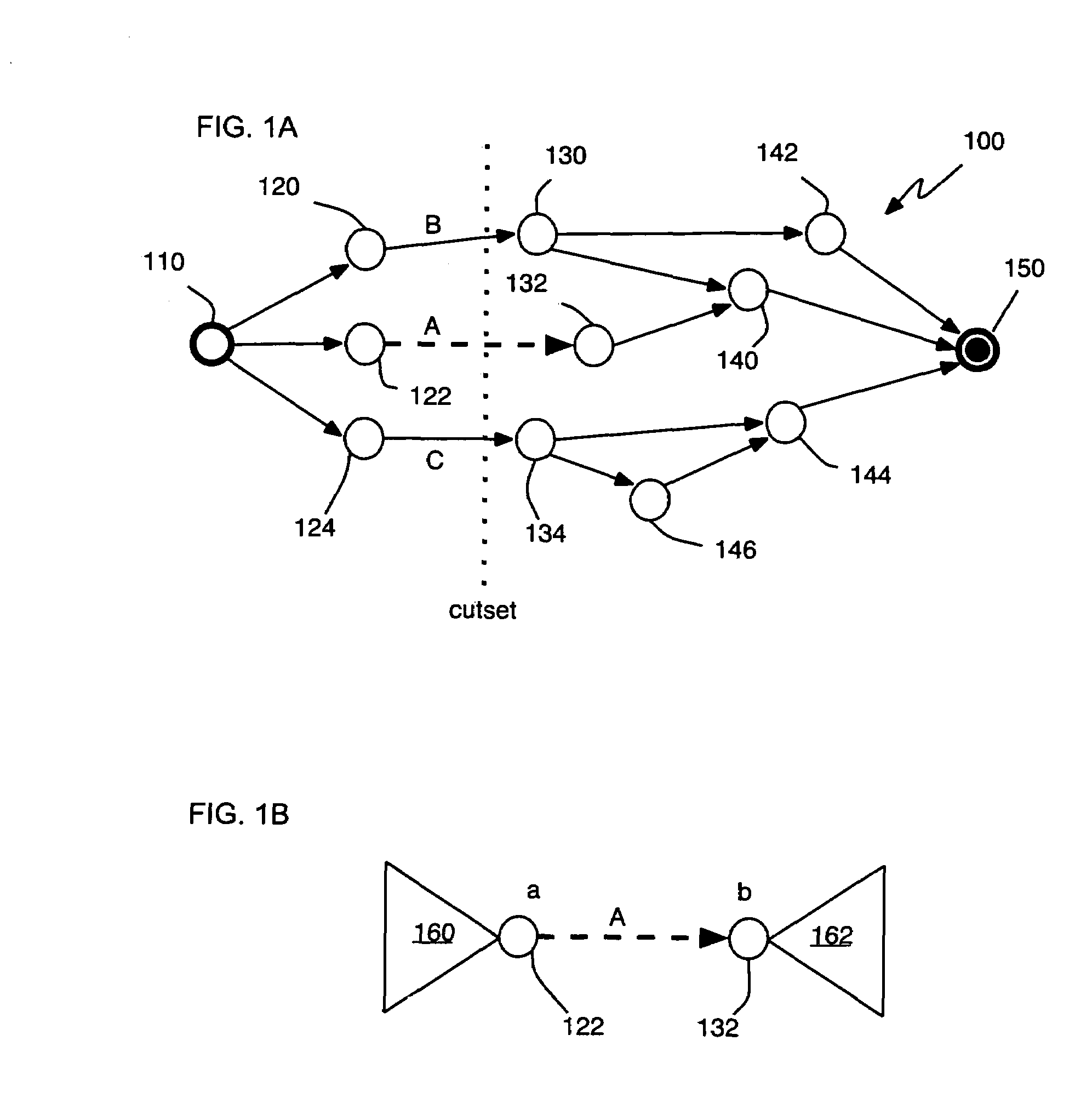
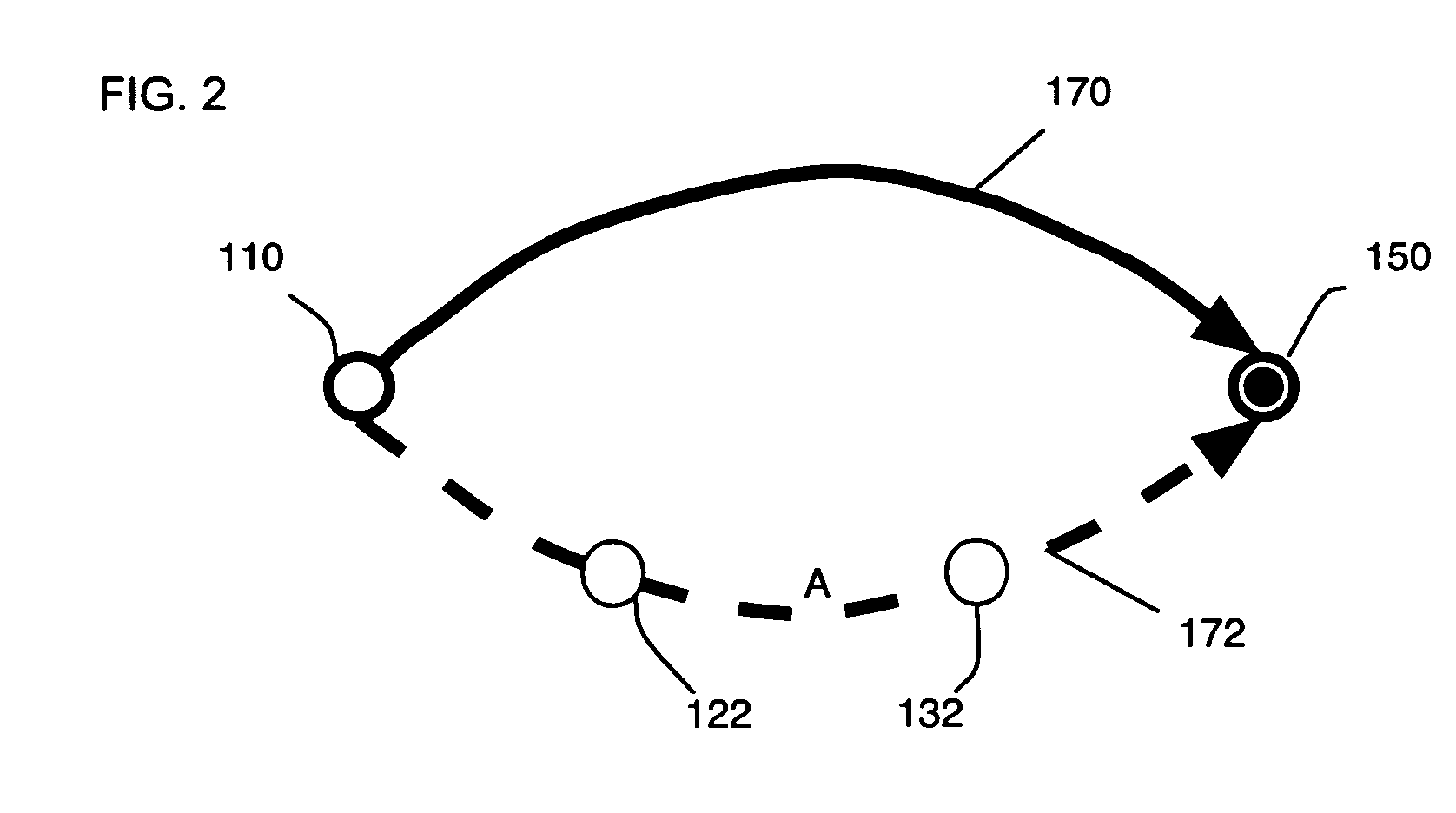
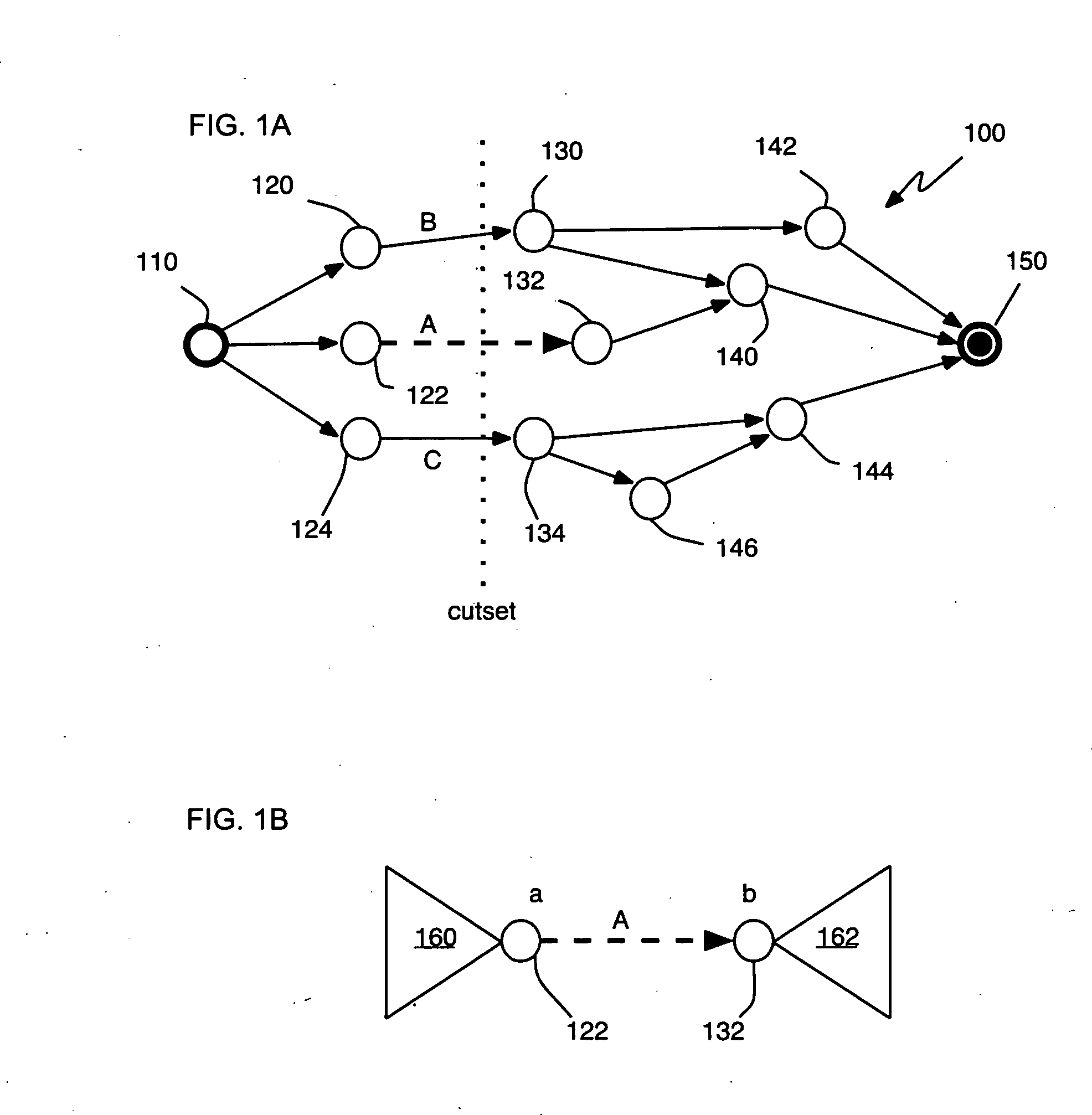
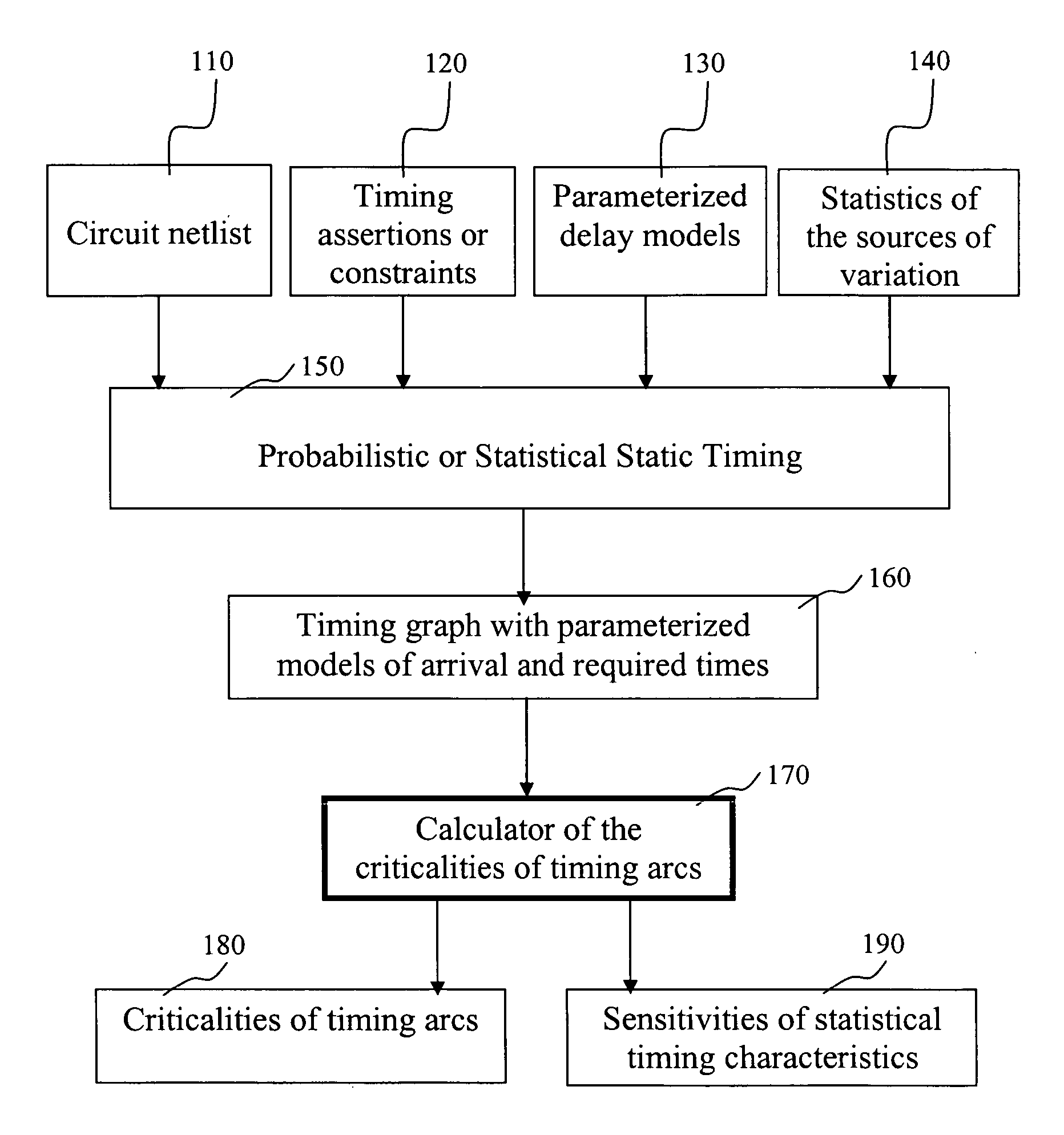
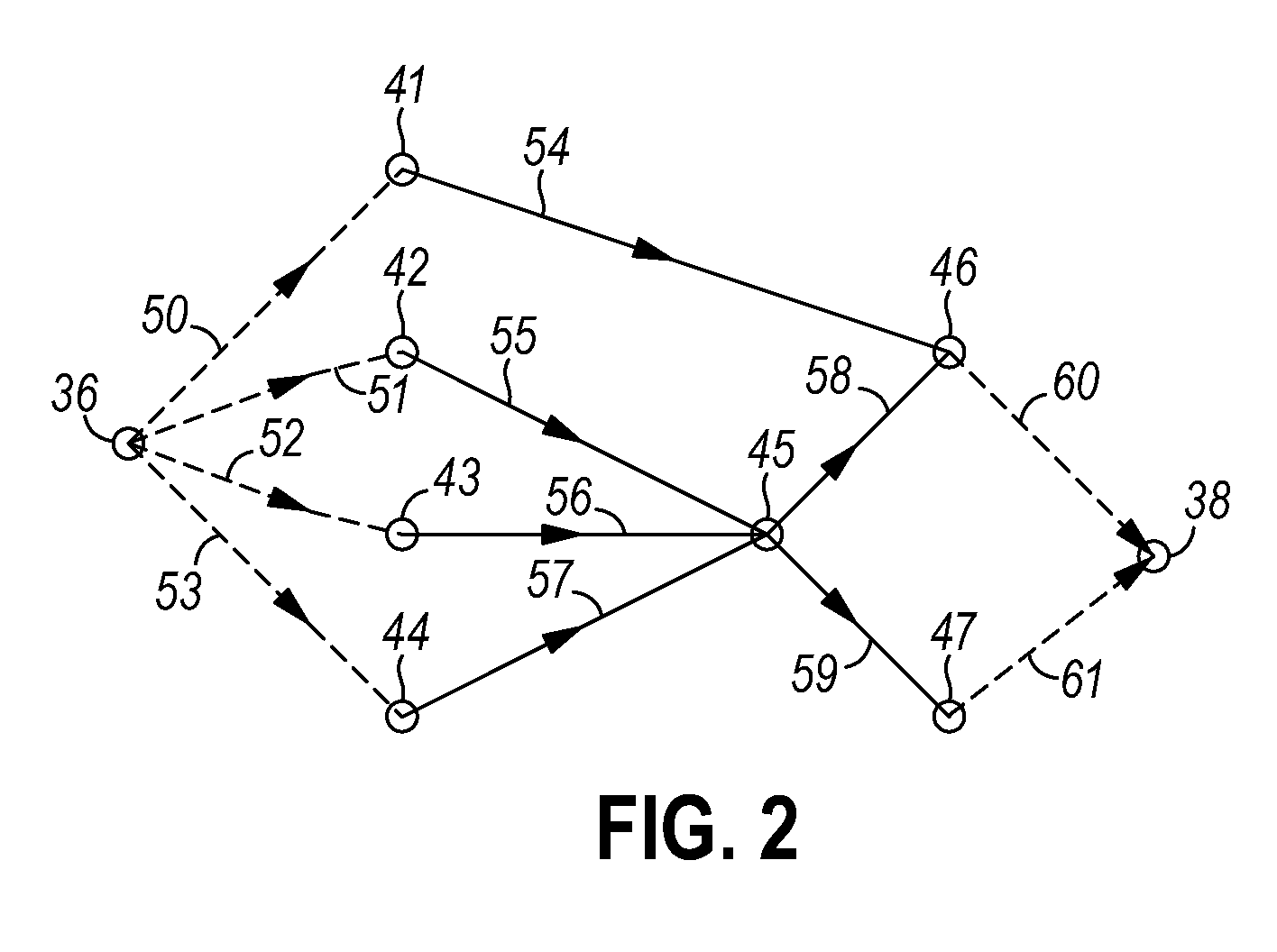
A method for determining criticality probability of an edge of a timing graph of a circuit is described. The method includes forming a directed acyclic timing graph corresponding to a circuit being timed, performing statistical timing of the circuit, for each edge of interest, defining a cutset that divides the timing graph into a plurality of parts, determining an edge slack for each edge in the cutset, computing a statistical maximum of all edge slacks in the cutset, and inferring edge criticality probabilities of each edge from the statistical maximum. A system for determining criticality probability of an edge of a timing graph of a circuit is also described.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and system for collating application programs
InactiveCN103034498AImprove experienceSpecific program execution arrangementsInput/output processes for data processingApplication softwareOperating system
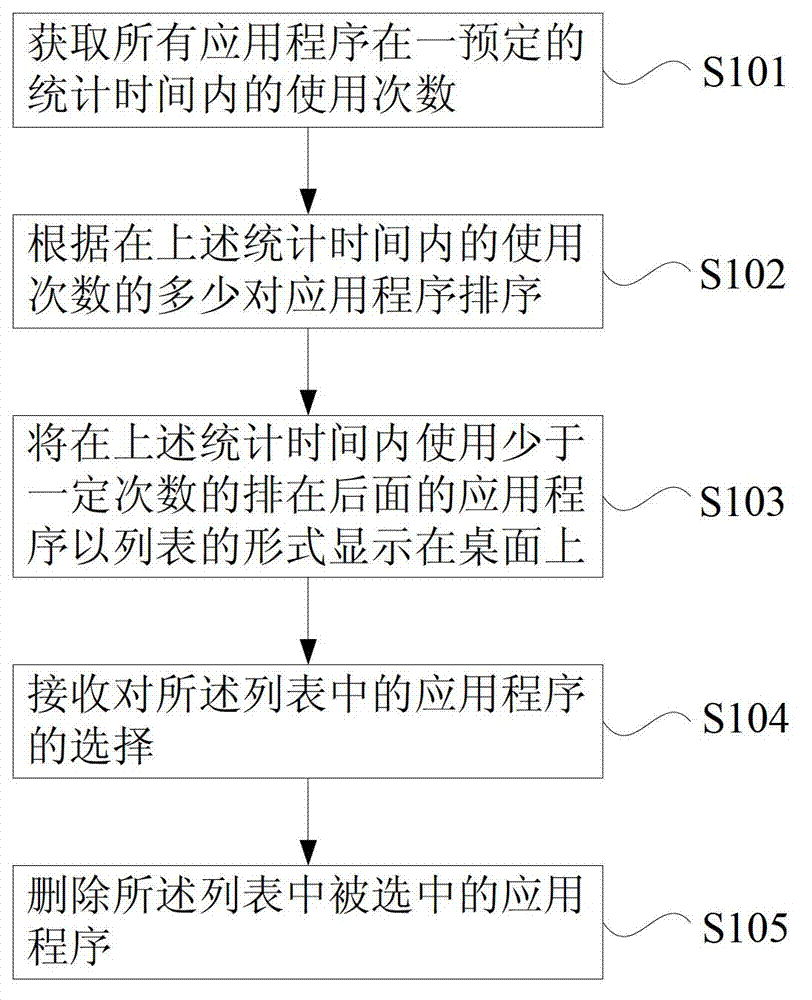
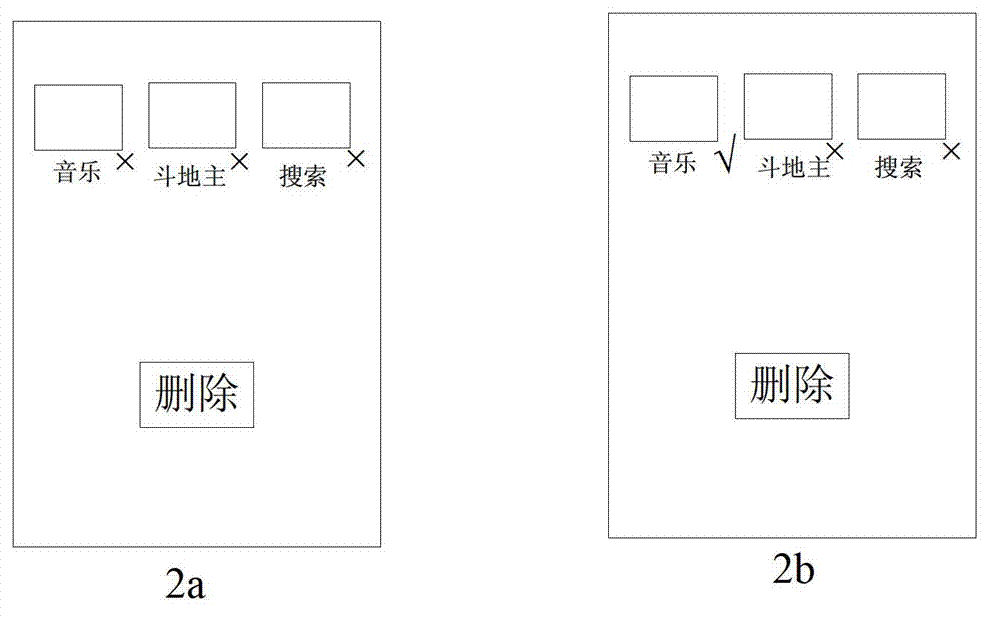
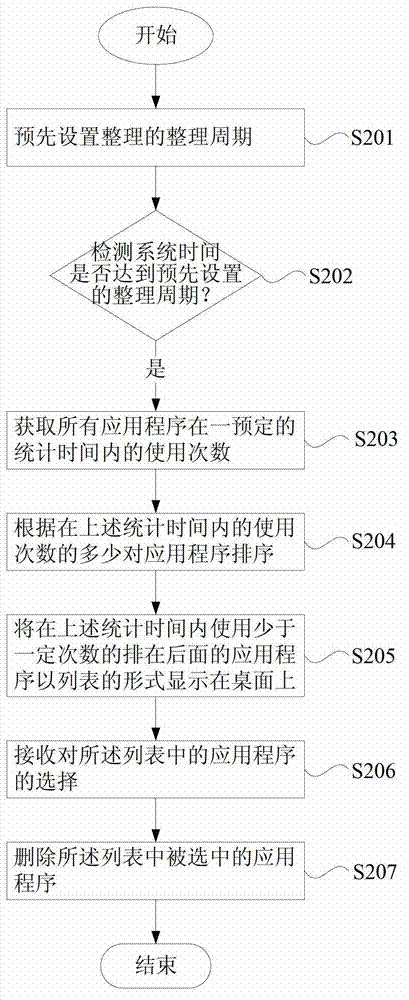
The invention discloses a method and a system for collating application programs, wherein the method comprises the following steps of A1, acquiring the number of use of the all application programs in a preset statistical time; A2, sequencing the application programs according to the number of use in the preset statistical time; A3, displaying the rear application programs of which the number of use is fewer than a certain number on a desktop in a list way in the statistical time; A4, receiving a choice of the application programs in the list; and A5, deleting the chosen application programs in the list. According to the invention, the application programs are automatically compared and sequenced according to the acquired number of use of the application programs; the application programs which are used by a user for fewer times are displayed on the desktop in the list way, then the application programs are deleted according the choice of the user; and the aims that the user is automatically reminded of cleaning the application programs which are not commonly used in a mobile terminal at a fixed period and a disk space is defragged are realized, and the experience satisfaction degree of the user is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
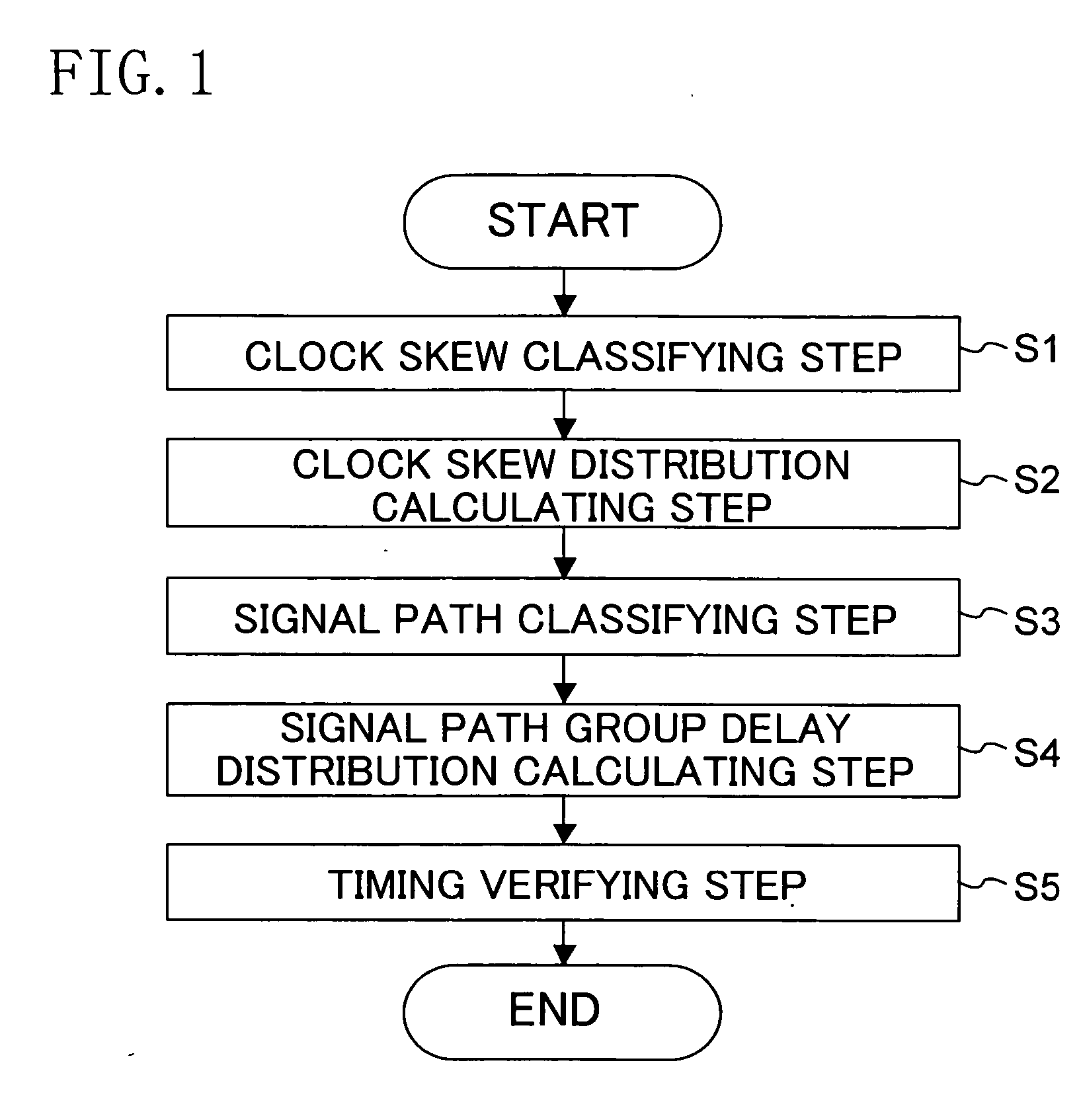
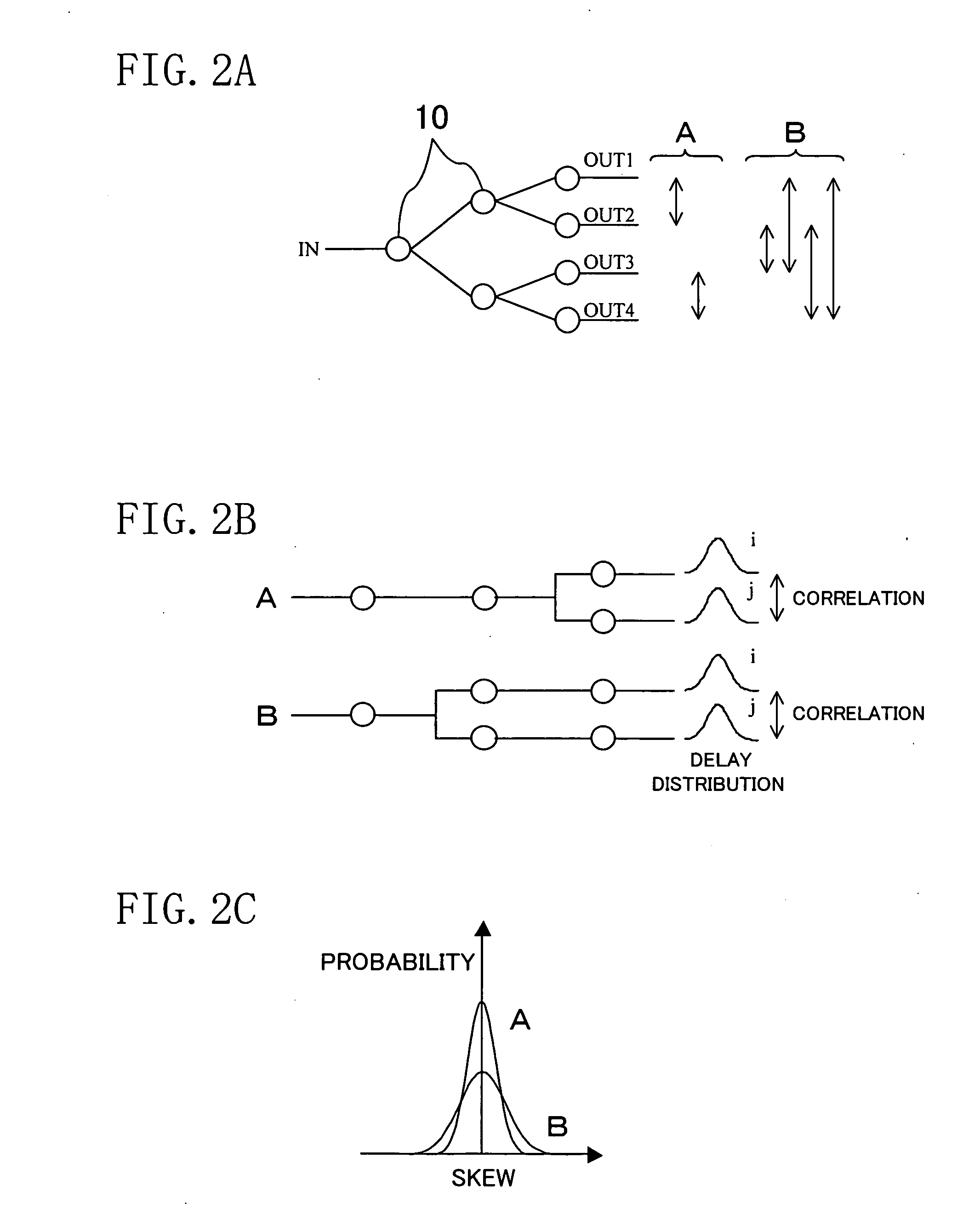
Timing analysis method and device
InactiveUS20080034338A1Improving timing convergenceReduce data volumeComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAnalysis methodComputer science
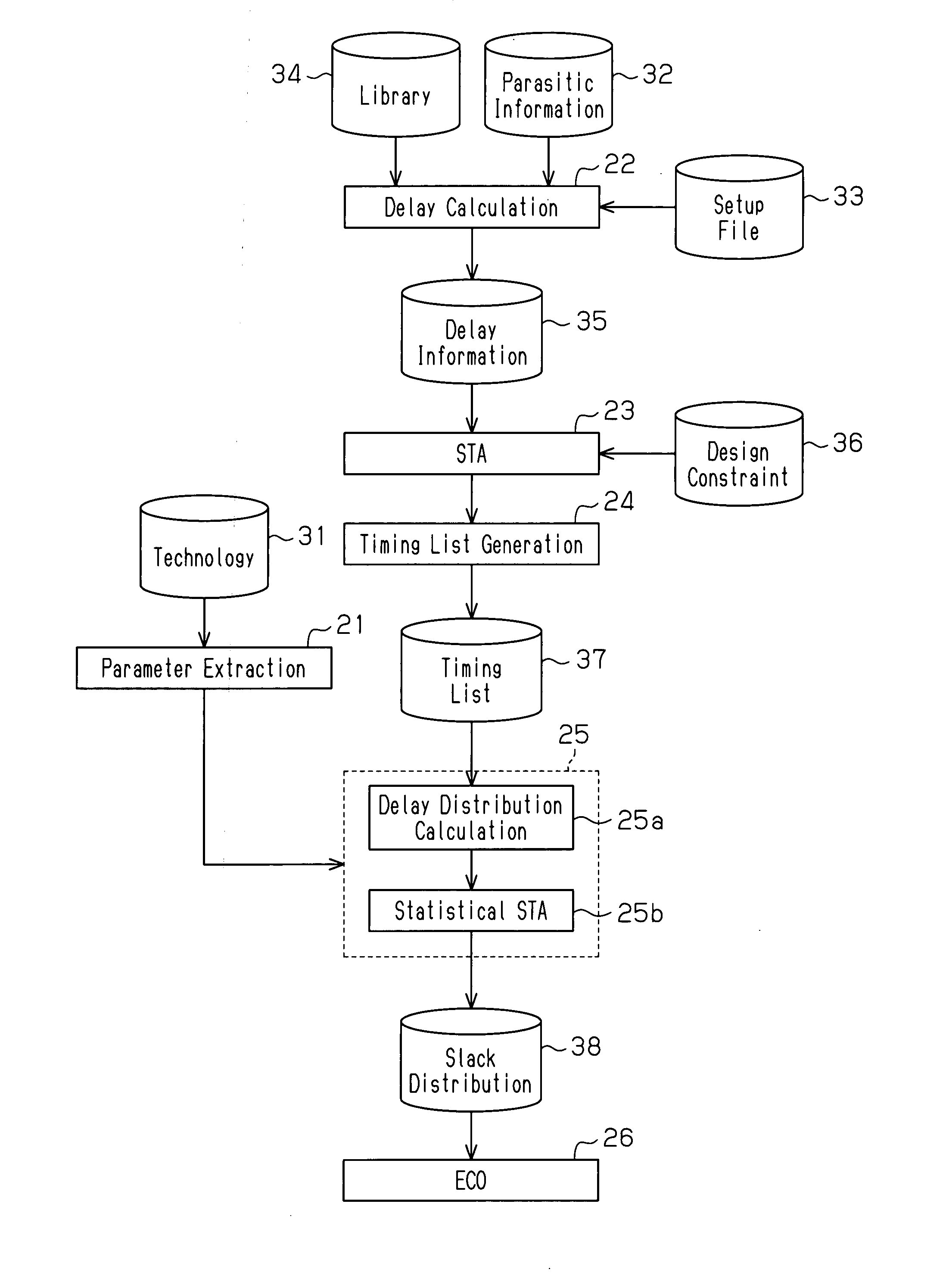
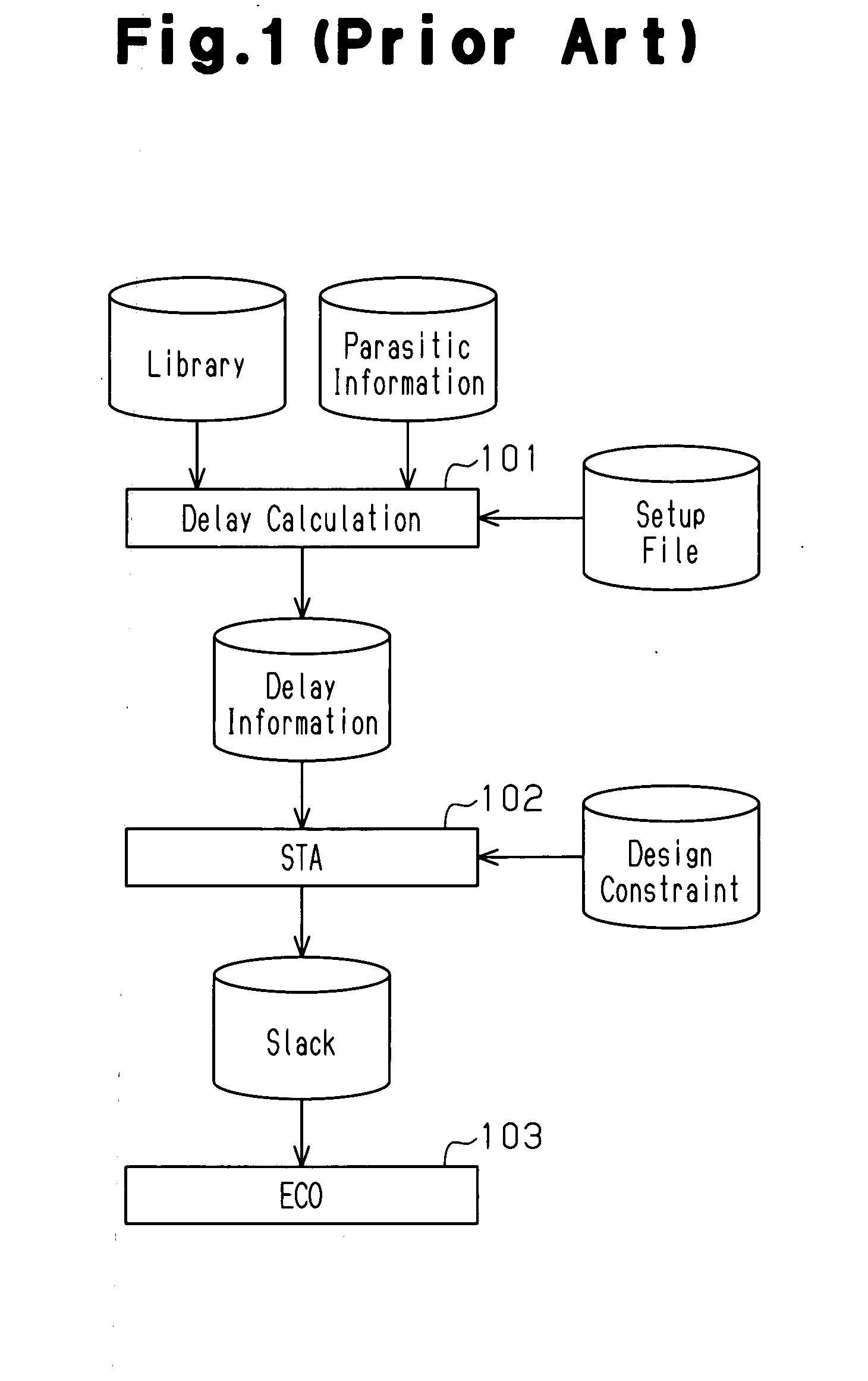
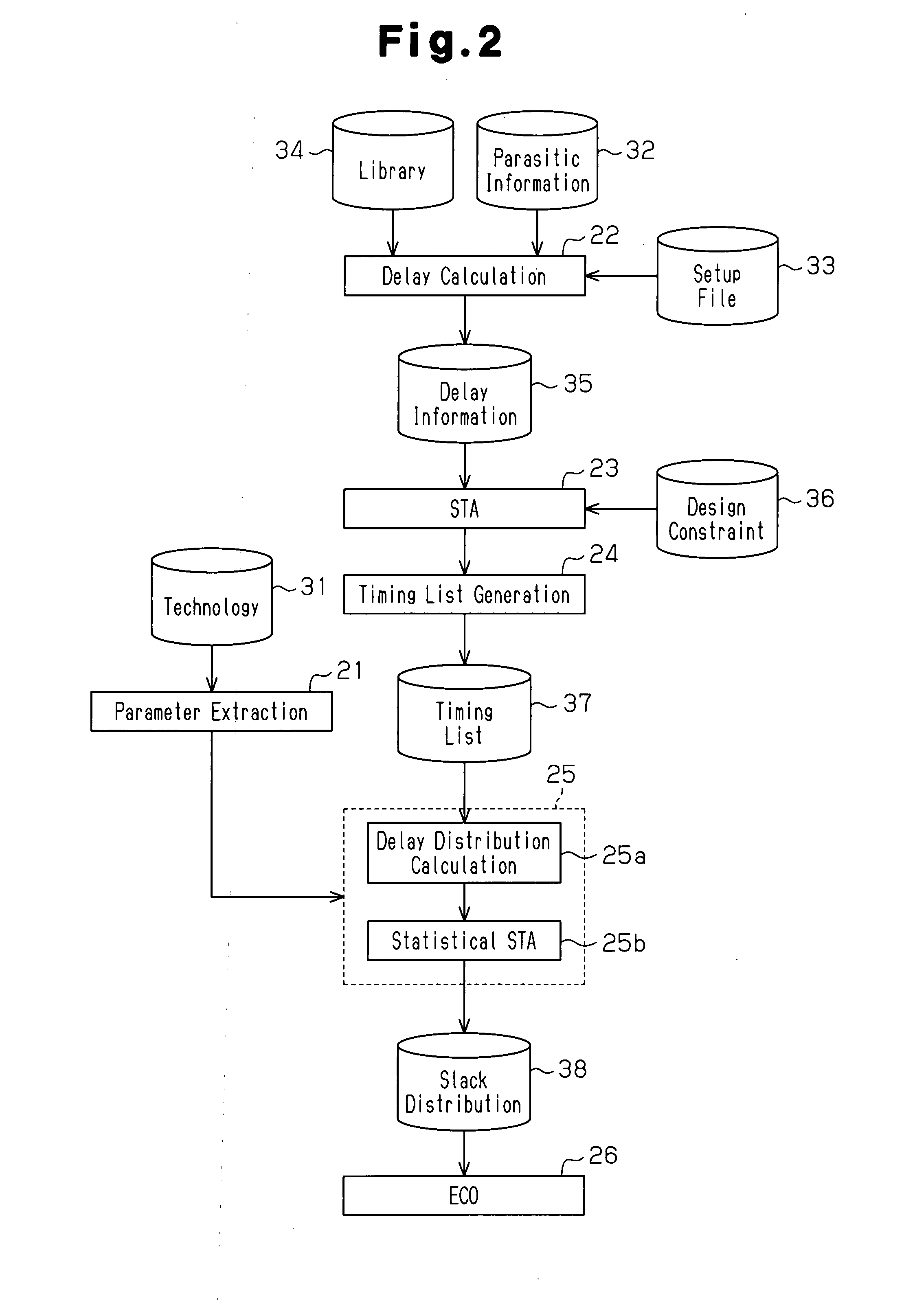
A timing analysis device for preventing the amount of data and the number of analysis operations from increasing in a statistical analysis, while improving the timing convergence in a path included in a net under relatively strict timing conditions. The timing analysis device performs a static timing analysis to extract a net under relatively strict timing conditions from the analysis result and generate a timing list. The device further performs delay distribution calculation for the extracted net to analyze the delay variation in each of one or more instances included in the net. The device retrieves the timing list and sets a unique delay variation for each instance to calculate a delay distribution. The device further performs a statistical timing analysis based on the calculated delay distribution.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Methods for statistical slew propagation during block-based statistical static timing analysis
ActiveUS20090288051A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
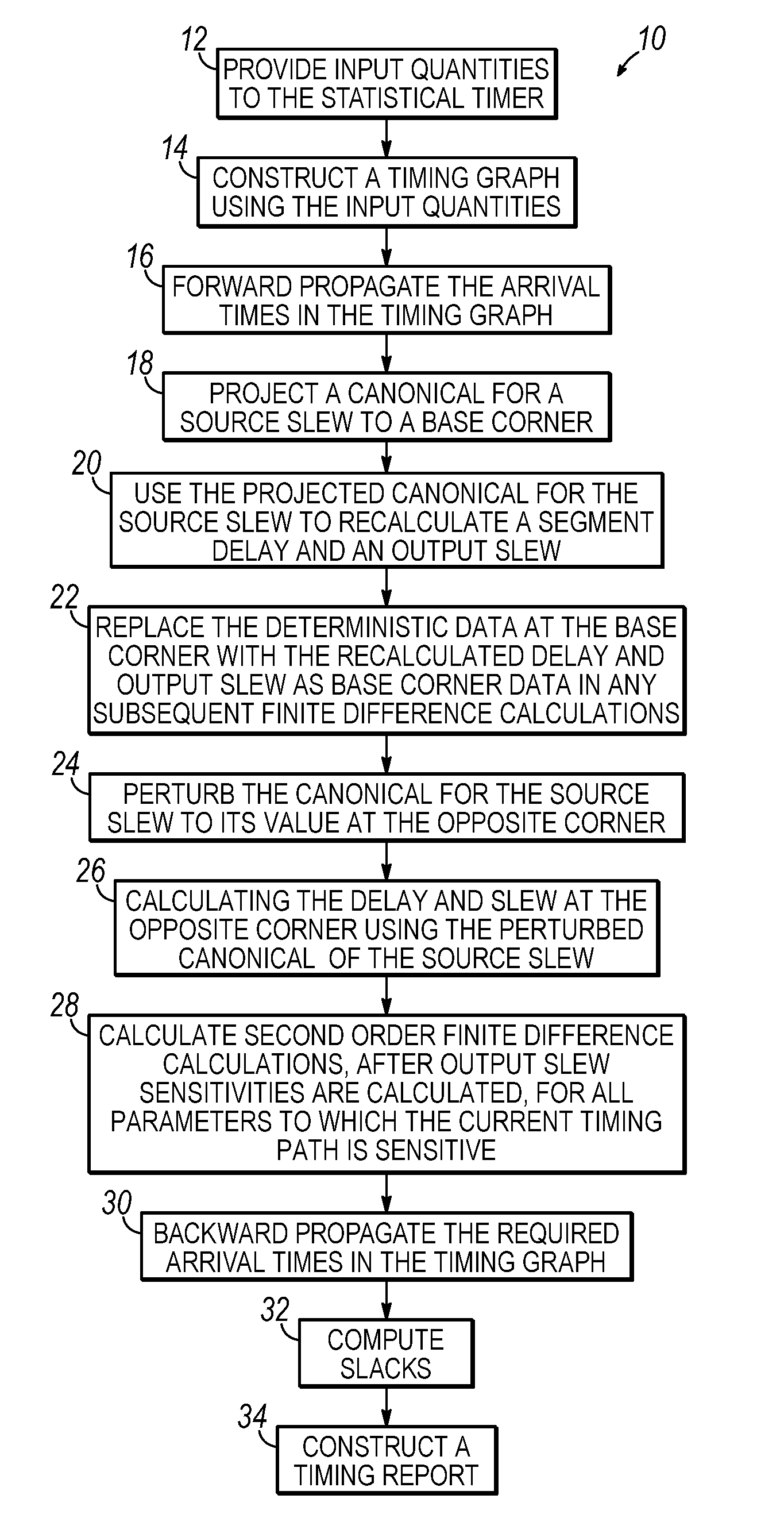
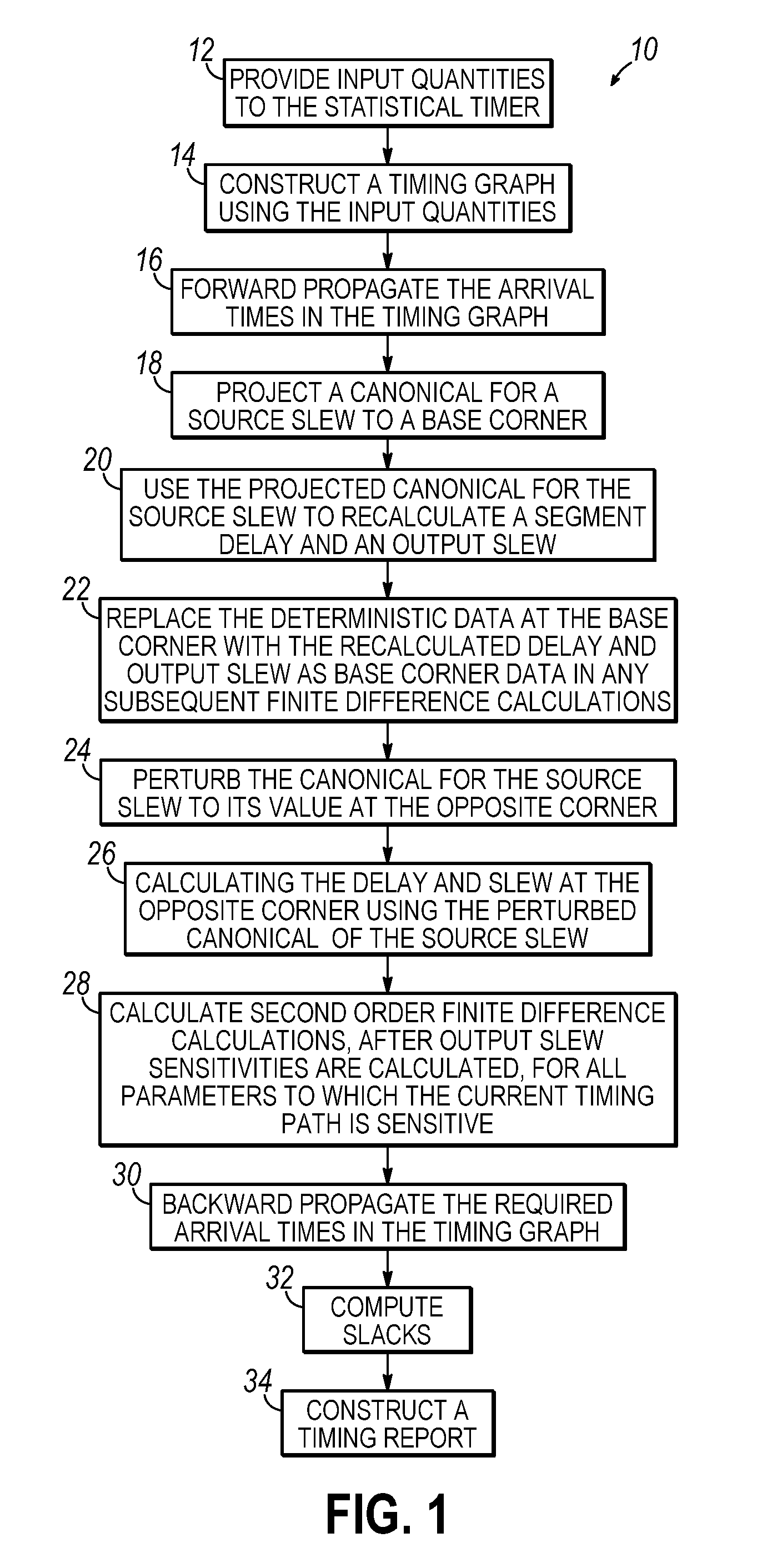
Methods for statistical slew propagation in static statistical timing analysis. The method includes projecting a canonical approximation of an input slew over a timing path to a first corner and using the projected input slew to calculate a delay and an output slew at the first corner. The method further includes perturbing the canonical approximation of the input slew to a different corner, calculating a delay and an output slew at the different corner using the perturbed input slew canonical, and determining a sensitivity of the delay and the output slew to a plurality of parameters, simultaneous with implicit sensitivity calculations to the input slew, with finite difference calculations between the first corner and perturbed data.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
System and method of criticality prediction in statistical timing analysis
InactiveUS7437697B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAlgorithmStatistical timing
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
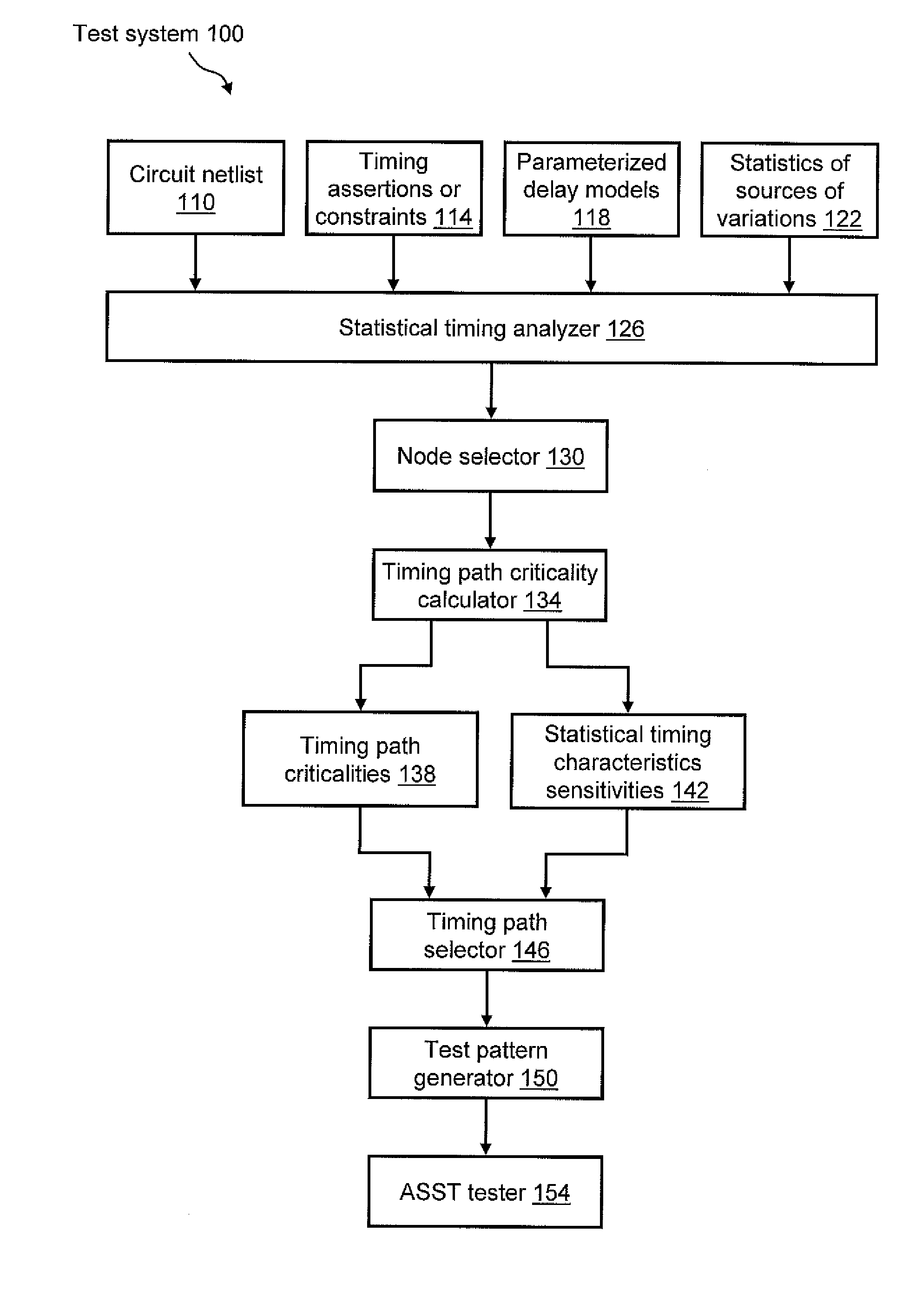
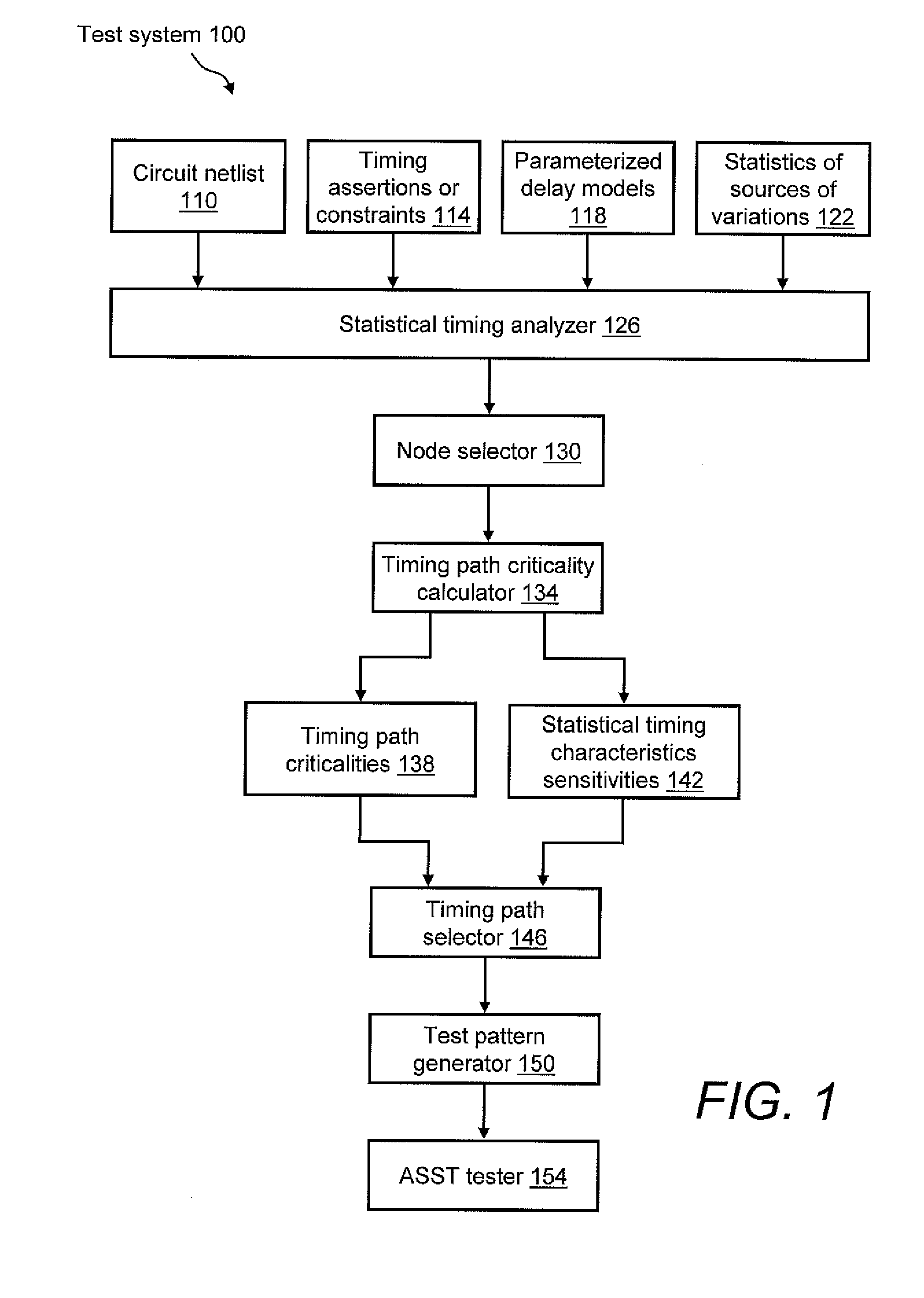
System and method for generating at-speed structural tests to improve process and environmental parameter space coverage
A system for enhancing the practicability of at-speed structural testing (ASST). In one embodiment, the system includes first means for performing statistical timing analysis on a design of logic circuitry. A second means performs a criticality analysis on the logic circuitry as a function of the statistical timing analysis so as to determine a criticality probability for each node of the logic circuitry. A third means selects nodes of the logic circuitry as a function of the criticality analysis. A fourth means selects timing paths as a function of the criticality probabilities of the selected nodes. A fifth means generates an ASST pattern for each of the selected timing paths. A sixth mean is provided to perform ASST on a fabricated instantiation of the design at functional speed using the generated ASST pattern.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
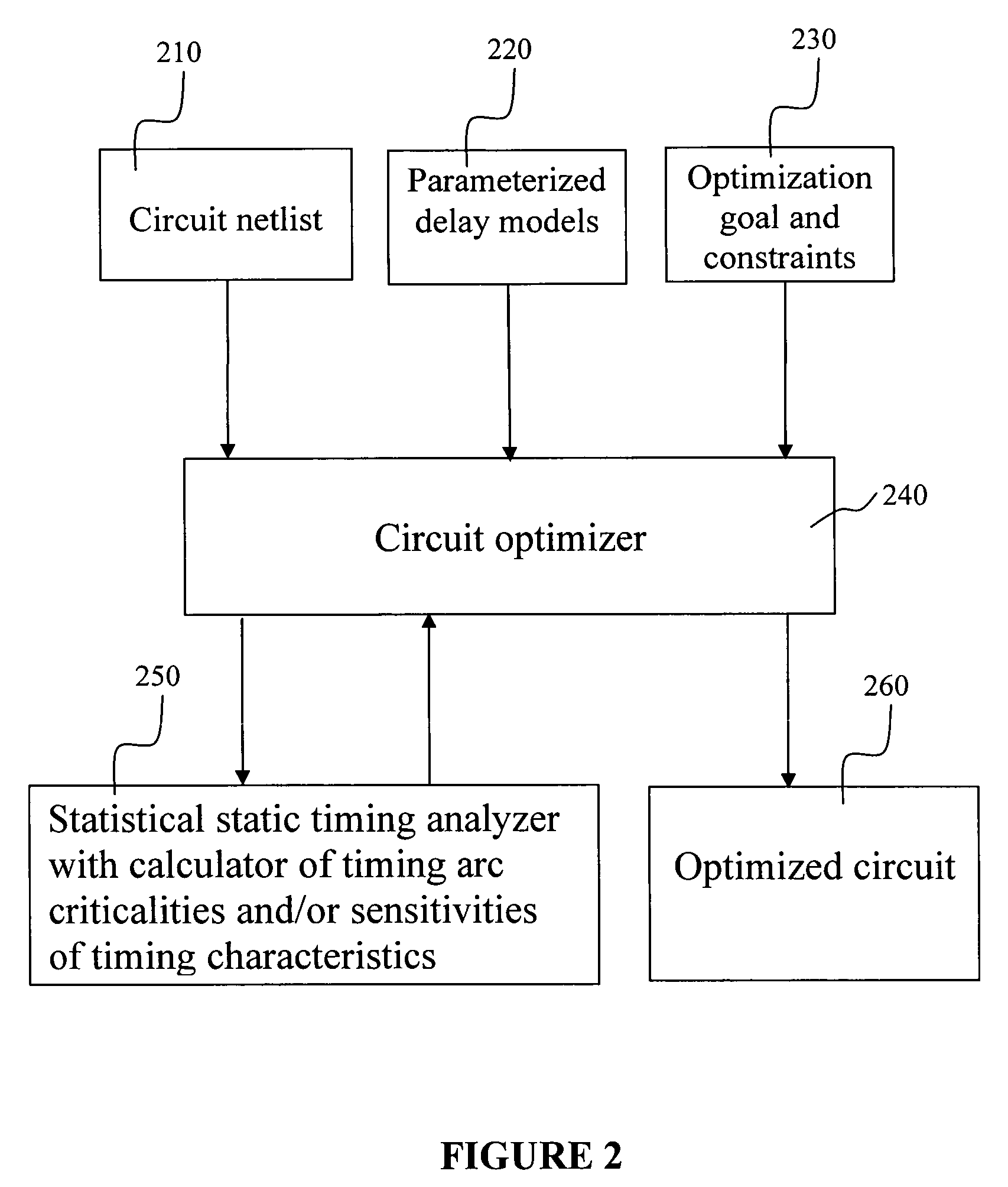
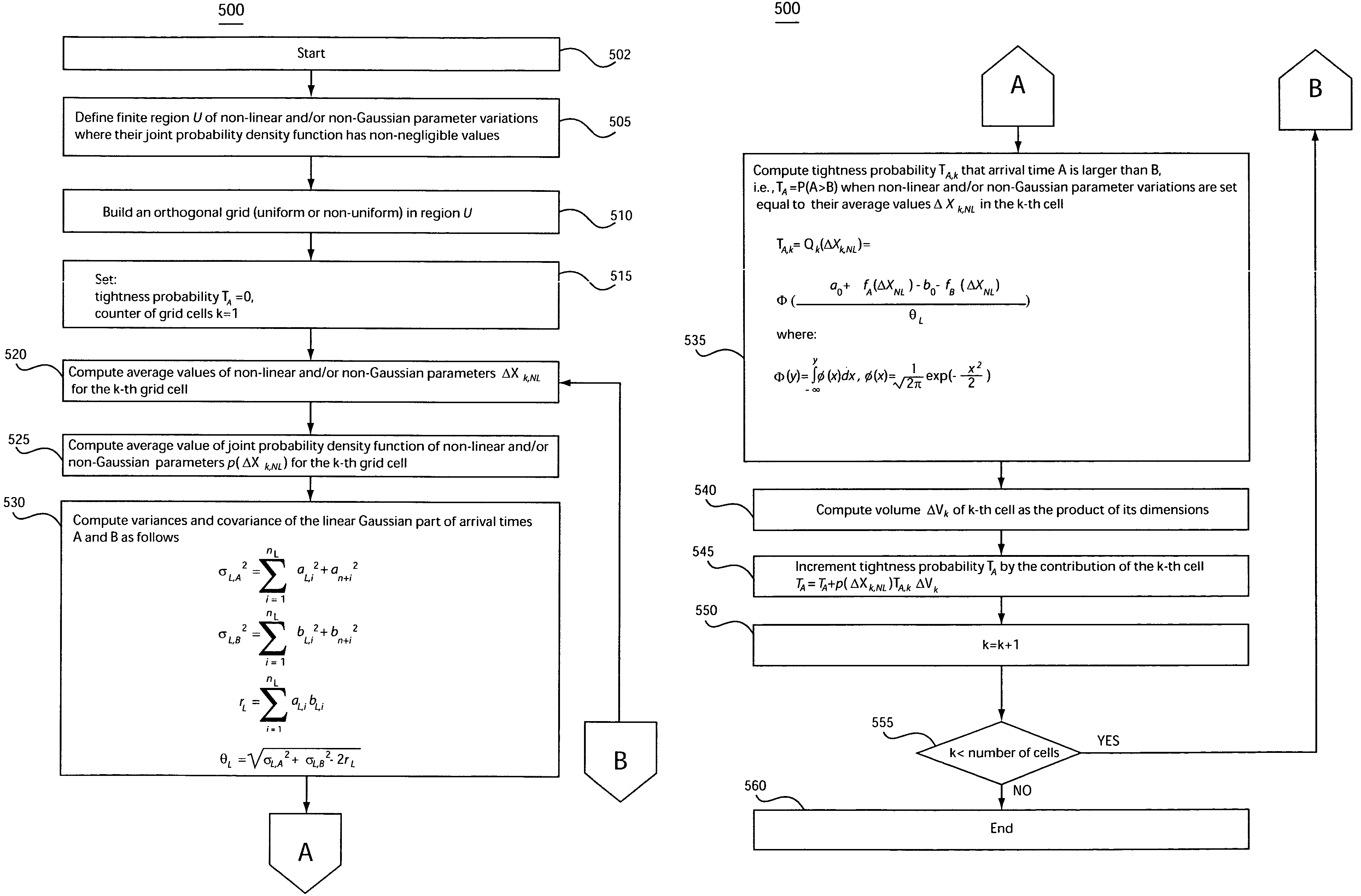
System and method for accommodating non-gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS20060085775A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer scienceStatistical static timing analysis
There is provided a system and method for statistical timing analysis of an electrical circuit. The system includes at least one parameter input, a statistical static timing analyzer, and at least one output. The at least one parameter input is for receiving parameters of the electrical circuit. At least one of the parameters has at least one of a non-Gaussian probability distribution and a non-linear delay effect. The statistical static timing analyzer is for calculating at least one of a signal arrival time and a signal required time for the electrical circuit using the at least one parameter. The at least one output is for outputting the at least one of the signal arrival time and the signal required time.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
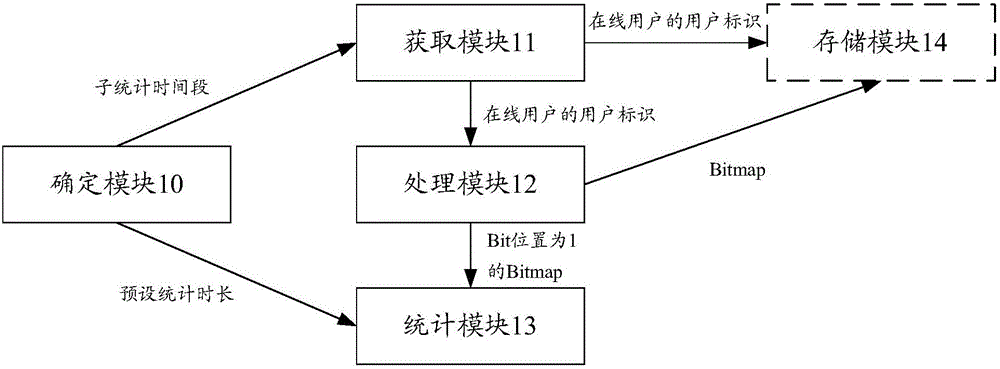
Device and method for processing data
ActiveCN105824952AImprove statistics performanceImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsData miningBitmap
The invention discloses a device and method for processing data. The device comprises a determination module, an acquisition module, a processing module and a counting module, wherein the determination module is used for determining each sub-counting time period according to preset counting duration; the acquisition module is used for acquiring user identities of online users in each sub-counting time period; the processing module is used for creating a bitmap corresponding to each sub-counting time period and setting bit sites corresponding to the acquired user identities to 1 in the created bitmaps; the counting module is used for counting the active user volume in the preset counting duration. According to the embodiments of the invention, the performance and efficiency of counting of the active user volume are improved, and the storage space is saved.
Owner:宁夏众志好活网络科技有限公司
System and method for accommodating non-Gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS7293248B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationArrival timeComputer science
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Urban traffic jam distinguishing method based on RFID technology
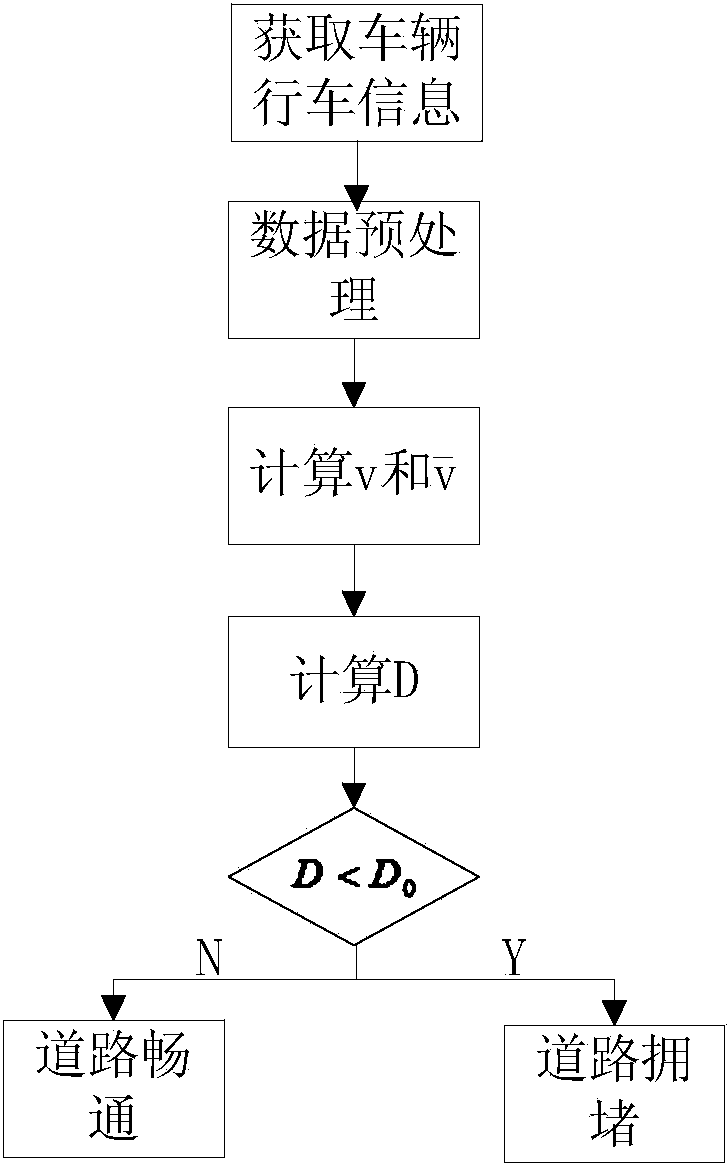
ActiveCN103473928ALarge amount of informationReduce operational overheadDetection of traffic movementSimulationTraffic flow
The invention relates to the technical field of traffic information and provides an urban traffic jam distinguishing method based on an RFID technology. The urban traffic jam distinguishing method comprises the steps of reading data of RFID tags installed on passing automobiles through RFID readers arranged at urban intersections, and obtaining driving information; setting a statistics time interval as T, performing matching on the driving information obtained through two RFID readers, and obtaining the number of automobiles passing through a road segment between the two RFID readers within the T time period and the driving information; performing data preprocessing to remove abnormal data; calculating the stroke speed and the average stroke speed of every automobile; obtaining a traffic flow state characteristic value; and distinguishing traffic jams according to the traffic flow state characteristic value D. Compared with other jam distinguishing methods, the urban traffic jam distinguishing method is simple in algorithm, small in operation spending, quick in operating speed and low in achieving difficulty, and more accurate judgment results can be obtained.
Owner:重庆科知源科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for static timing analysis in the presence of a coupling event and process variation
InactiveUS7739640B2Improve accuracyReduce pessimismComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCouplingAlgorithm
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for statistical timing analysis of digital circuits
InactiveUS20090013294A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer aided designCMOSHemt circuits
The present invention is a system and method for statistical or probabilistic static timing analysis of digital circuits, taking into account statistical delay variations. The delay of each gate or wire is assumed to consist of a nominal portion, a correlated random portion that is parameterized by each of the sources of variation and an independent random portion. Arrival times and required arrival times are propagated as parameterized random variables while taking correlations into account. Both early mode and late mode timing are included; both combinational and sequential circuits are handled; static CMOS as well as dynamic logic families are accommodated. The timing analysis complexity is linear in the size of the graph and the number of sources of variation. The result is a timing report in which all timing quantities such as arrival times and slacks are reported as probability distributions in a parameterized form.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
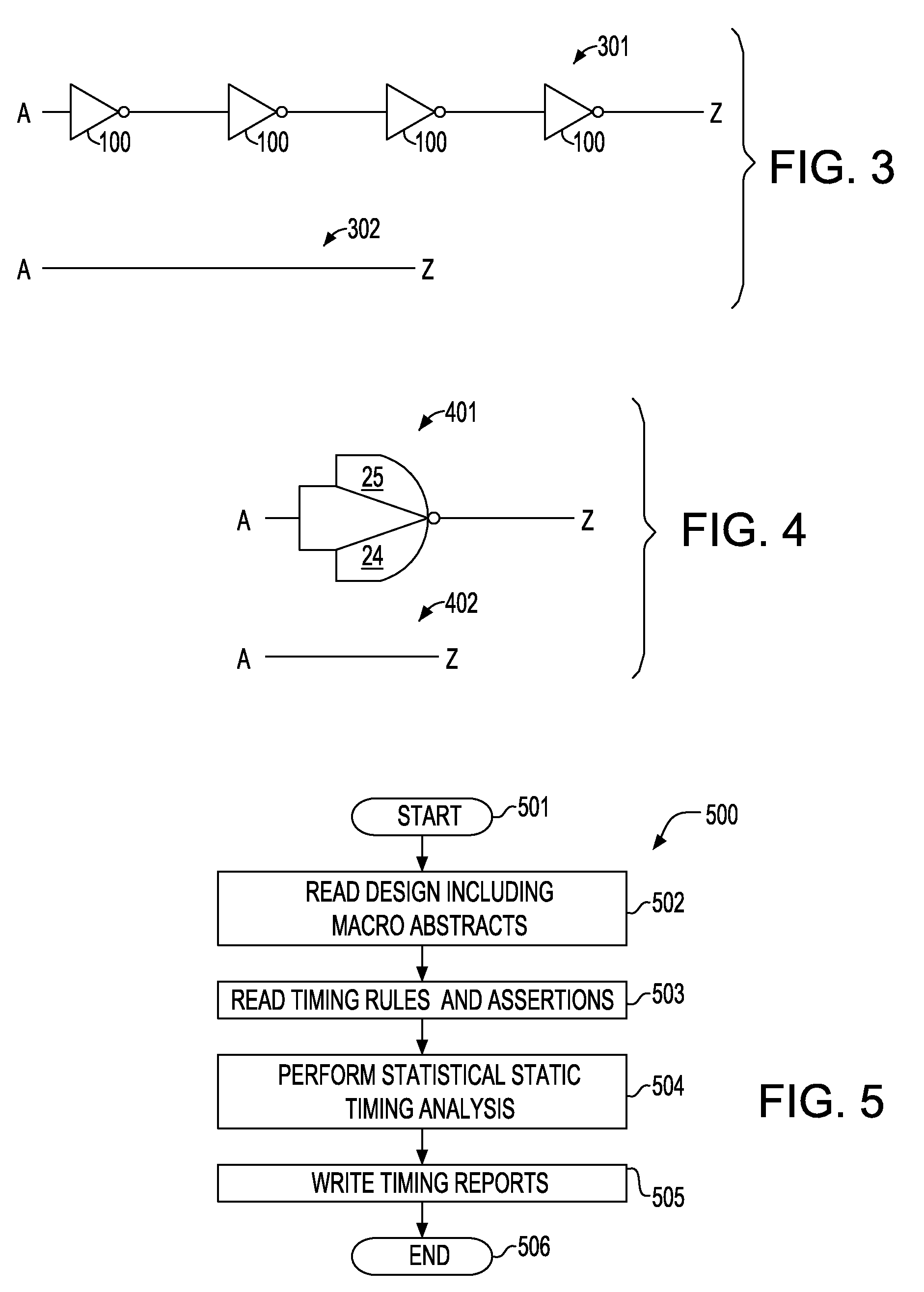
Method of Performing Statistical Timing Abstraction for Hierarchical Timing Analysis of VLSI circuits
ActiveUS20100211922A1Simpler statistical timing modelFaster yet accurate analysisComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
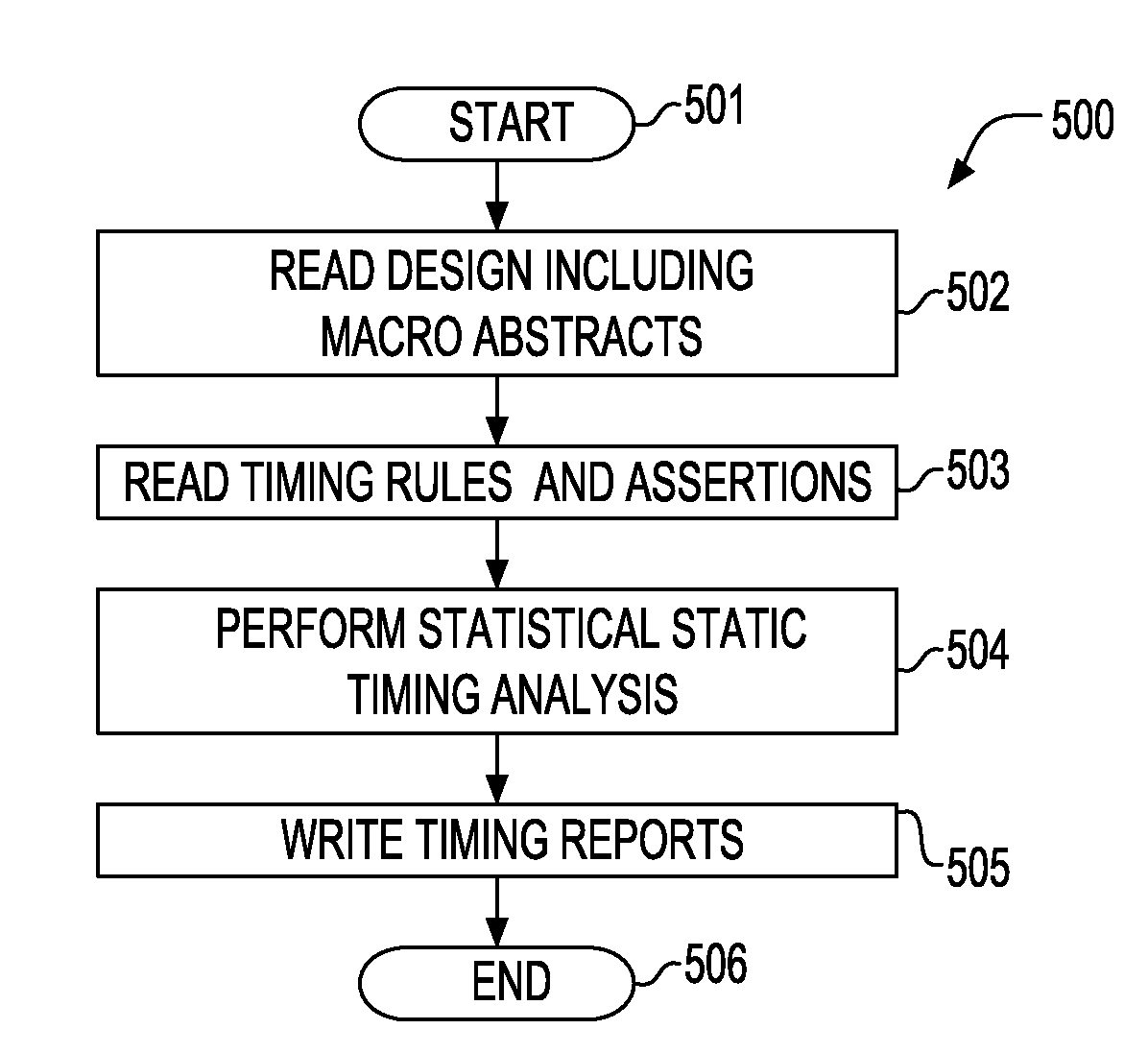
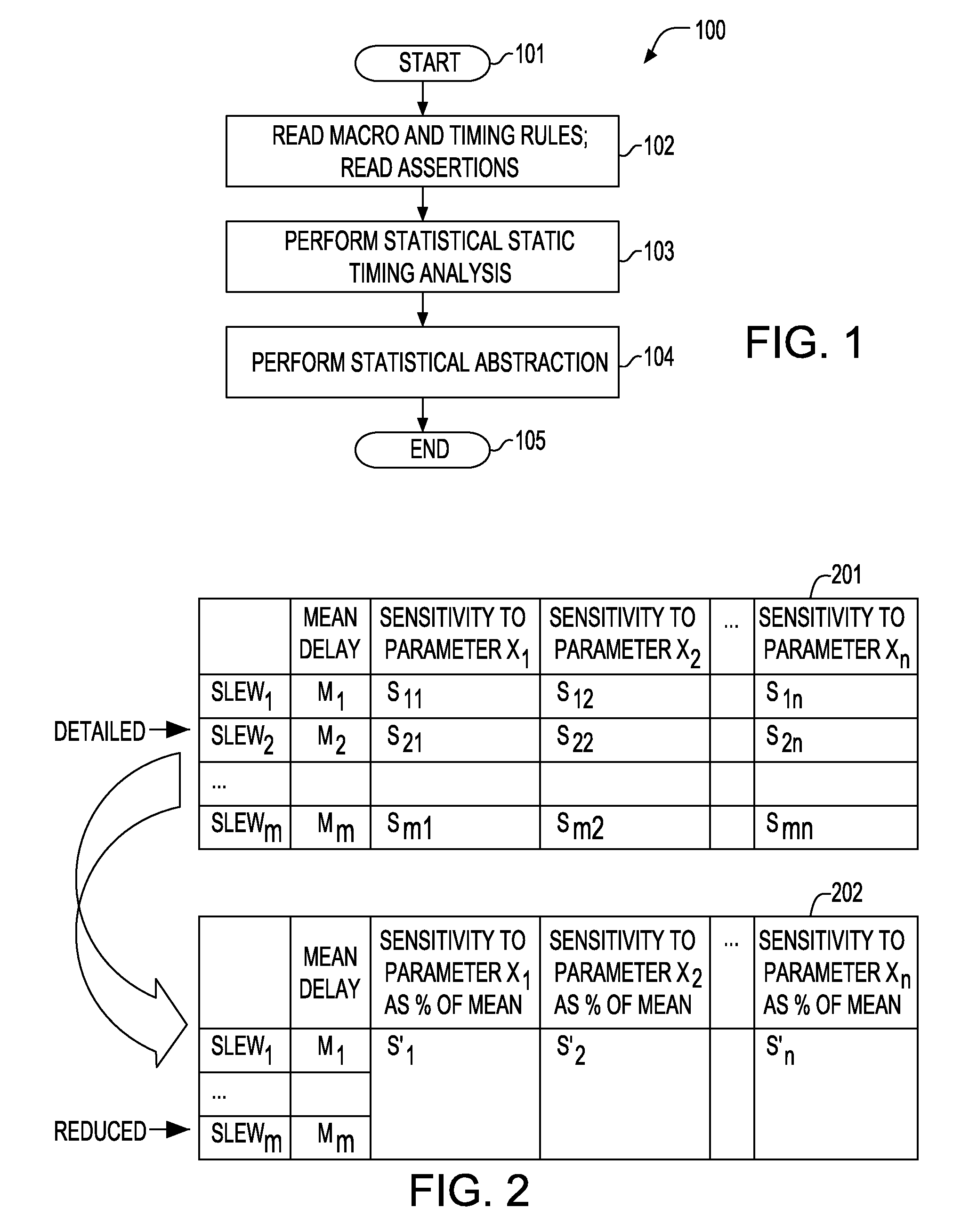
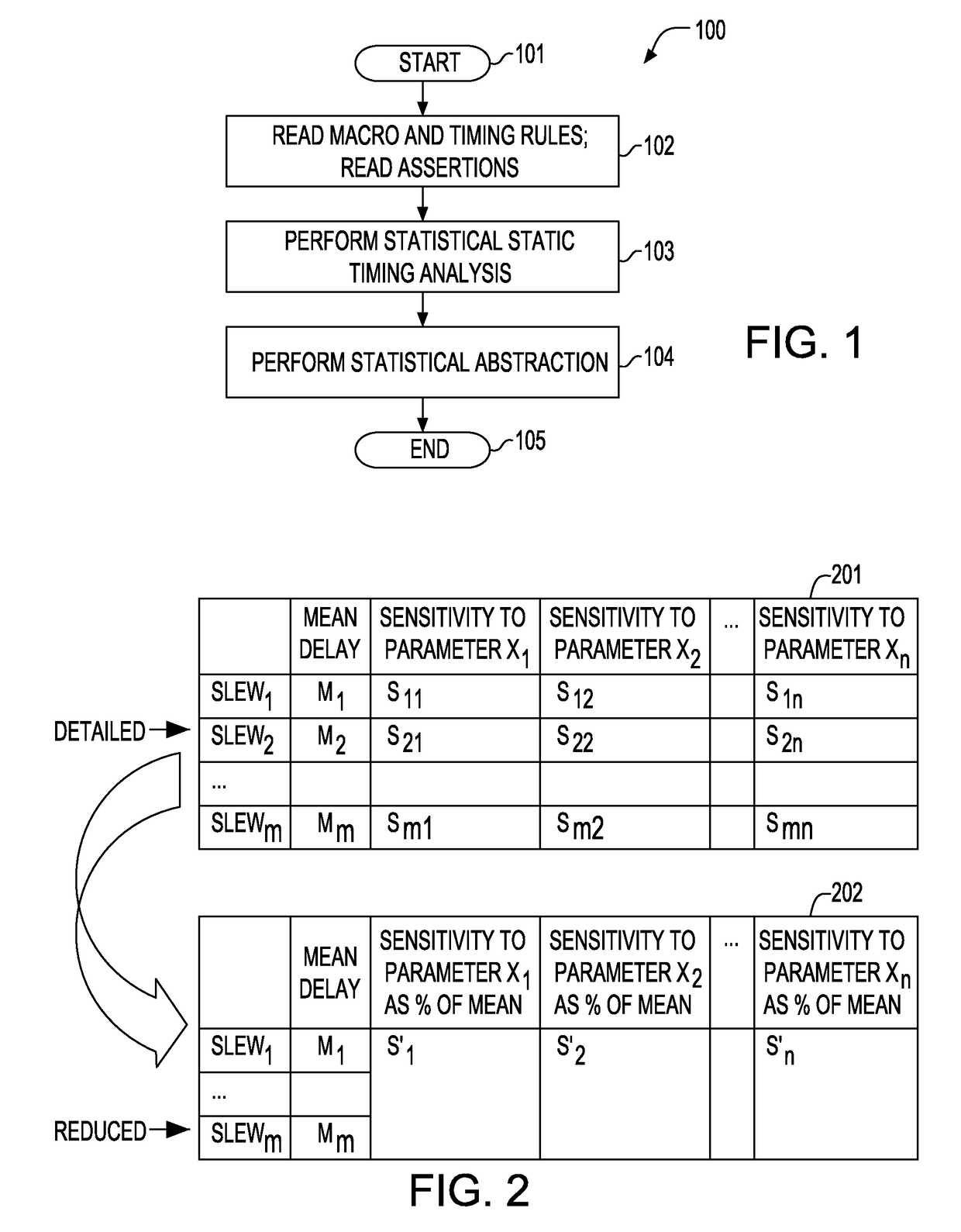
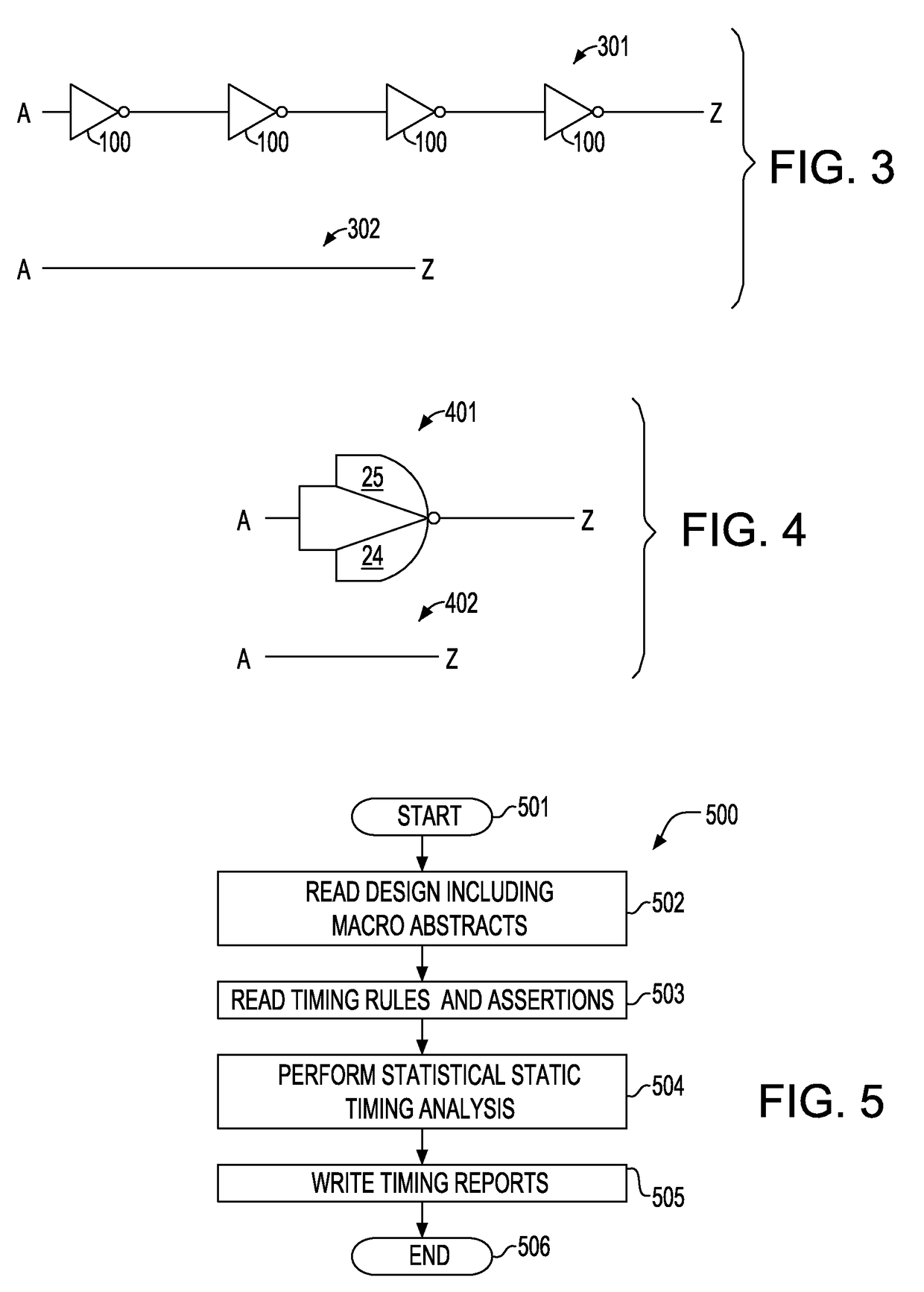
A method for performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of an integrated circuit (IC) chip design by abstracting one or more macros of the design. The method includes performing a statistical static timing analysis of at least one macro; performing a statistical abstraction of the macro to obtain a statistical abstract model of the macro timing characteristics; applying the statistical abstract model as the timing model for each occurrence of the macro leading to a simplified IC chip design; and performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of the simplified chip design. The method achieves a context aware statistical abstraction, where a generated statistical abstract model is instantiated for each macro of the chip during statistical static timing analysis at the chip level, providing a compressed and pruned statistical timing abstraction and reducing the model-size during the statistical abstraction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Efficient statistical timing analysis of circuits
ActiveUS7689954B2Improve accuracyExtension of timeProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAnalysis methodComputer science
Statistical timing analysis methods for circuits are described which compensate for circuit elements having correlated timing delays with a high degree of computational efficiency. An quadratic timing model is used to represent each delay element along a circuit path, wherein each element's delay has a first-order relationship to local variations and a second-order relationship to global variations. Propagation of the modeled delays through the circuit is efficiently done via straightforward ADD operations where an input propagates through another element in a circuit path, and via a MAX operation (or an approximation thereof) where two or more inputs merge at an intersection. The inputs to the MAX operator can be tested for gaussianity, and can be processed by the MAX operation (or its approximation) if they are substantially gaussian. Otherwise, they may be stored in a tuple for processing at later points along the circuit path.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Data statistics method and device
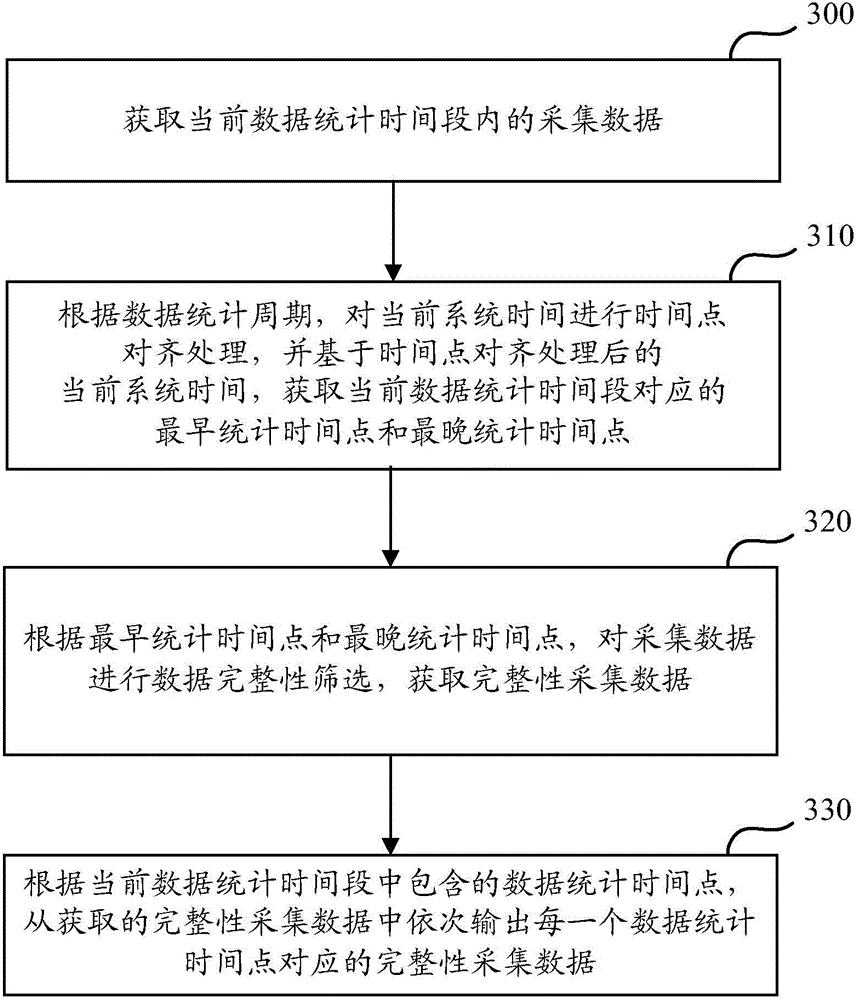
ActiveCN104598551AGuaranteed accuracyTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsData integrityTime segment
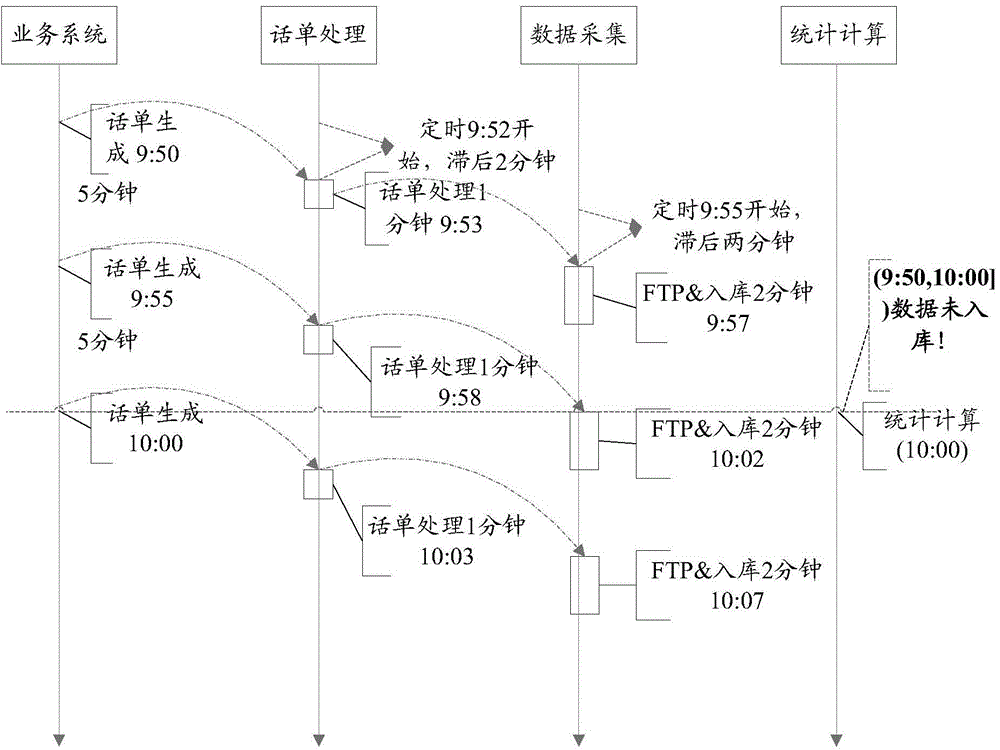
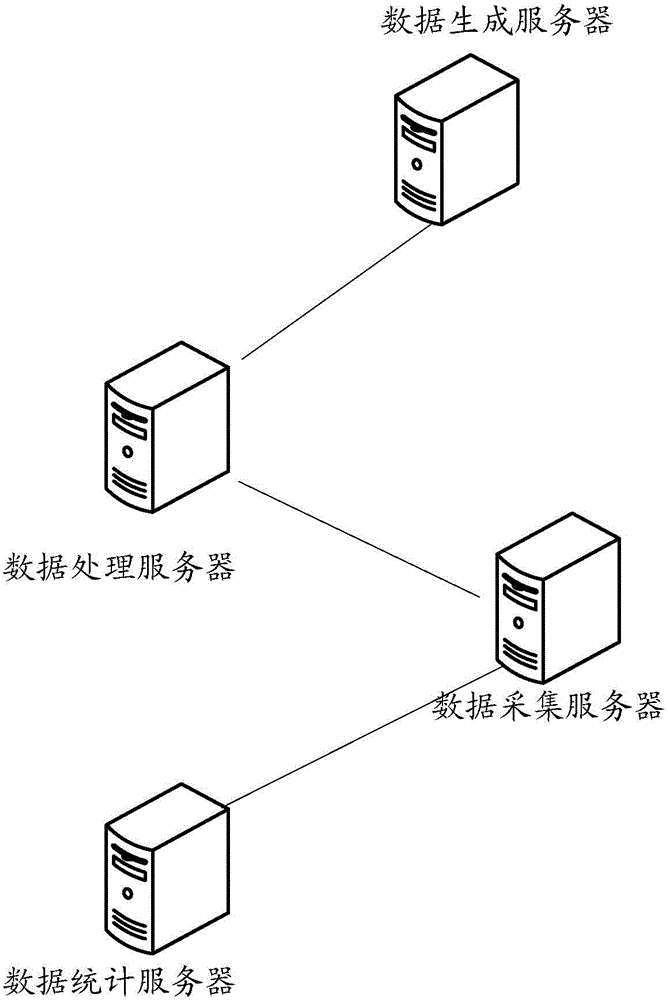
The invention discloses a data statistics method and device. The method comprises the following steps that when the current system time reaches the time point for data statistics, collection data in the current data statistics time period is obtained; the current system time is subjected to time point alignment processing to obtain the earliest statistics time point and the latest statistics time point corresponding to the current data statistics time period; all collection data is screened according to the earliest statistics time point, the latest statistics time point and the generating time point corresponding to each collection datum, the completeness collection data is obtained, and the completeness collection data is output. When the technical scheme is adopted, the preset of the delay time is not needed, when the current system time reaches the data statistics time point, a service system only carries out data completeness screening on the obtained collection data, and the data completeness statistics result of the current data in the statistics time period can be obtained, so that the accuracy of the statistics result can be ensured.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
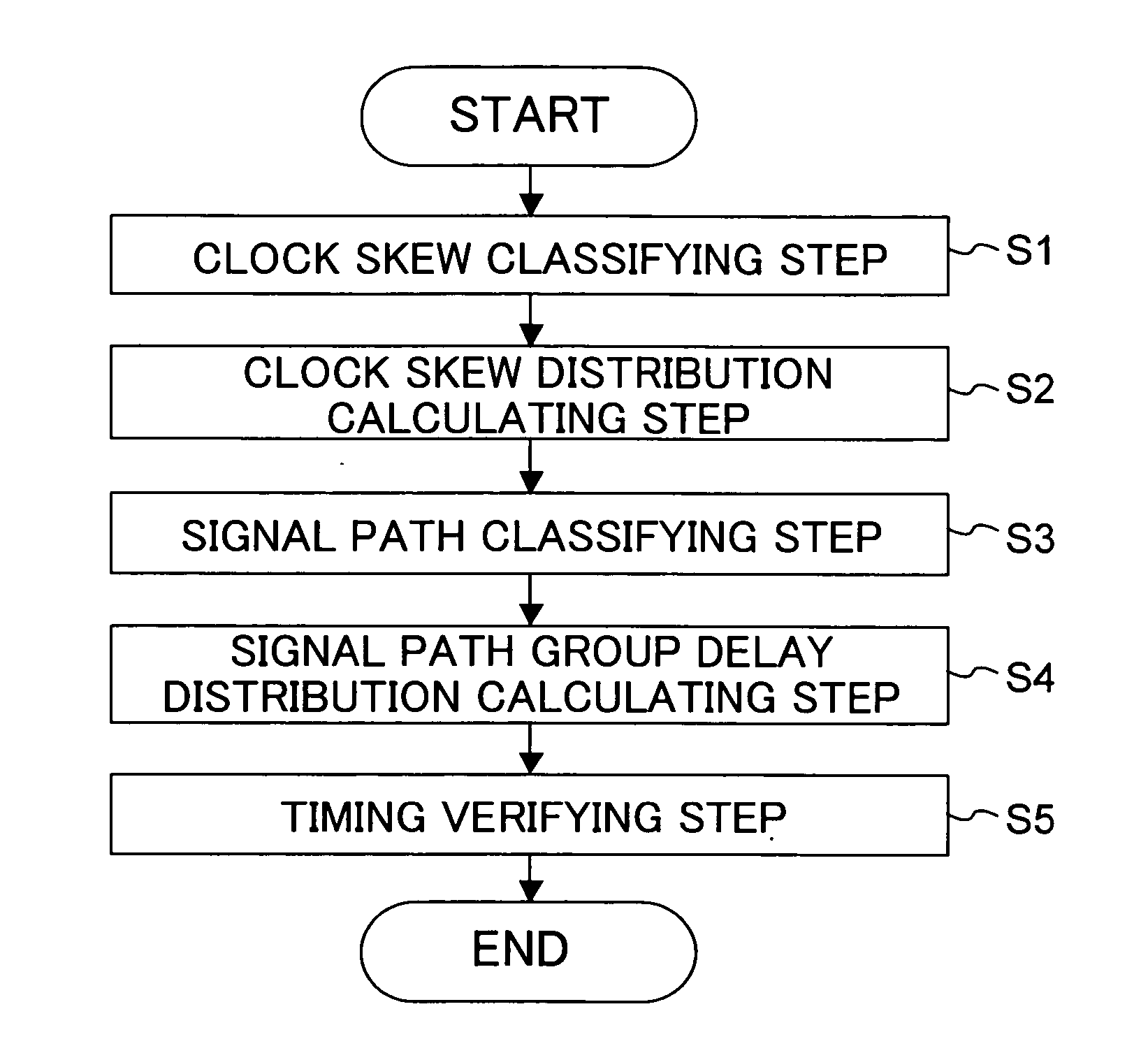
Timing verification method for semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20070050742A1Improve reliabilityNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectronic circuit testingComputer scienceSemiconductor
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
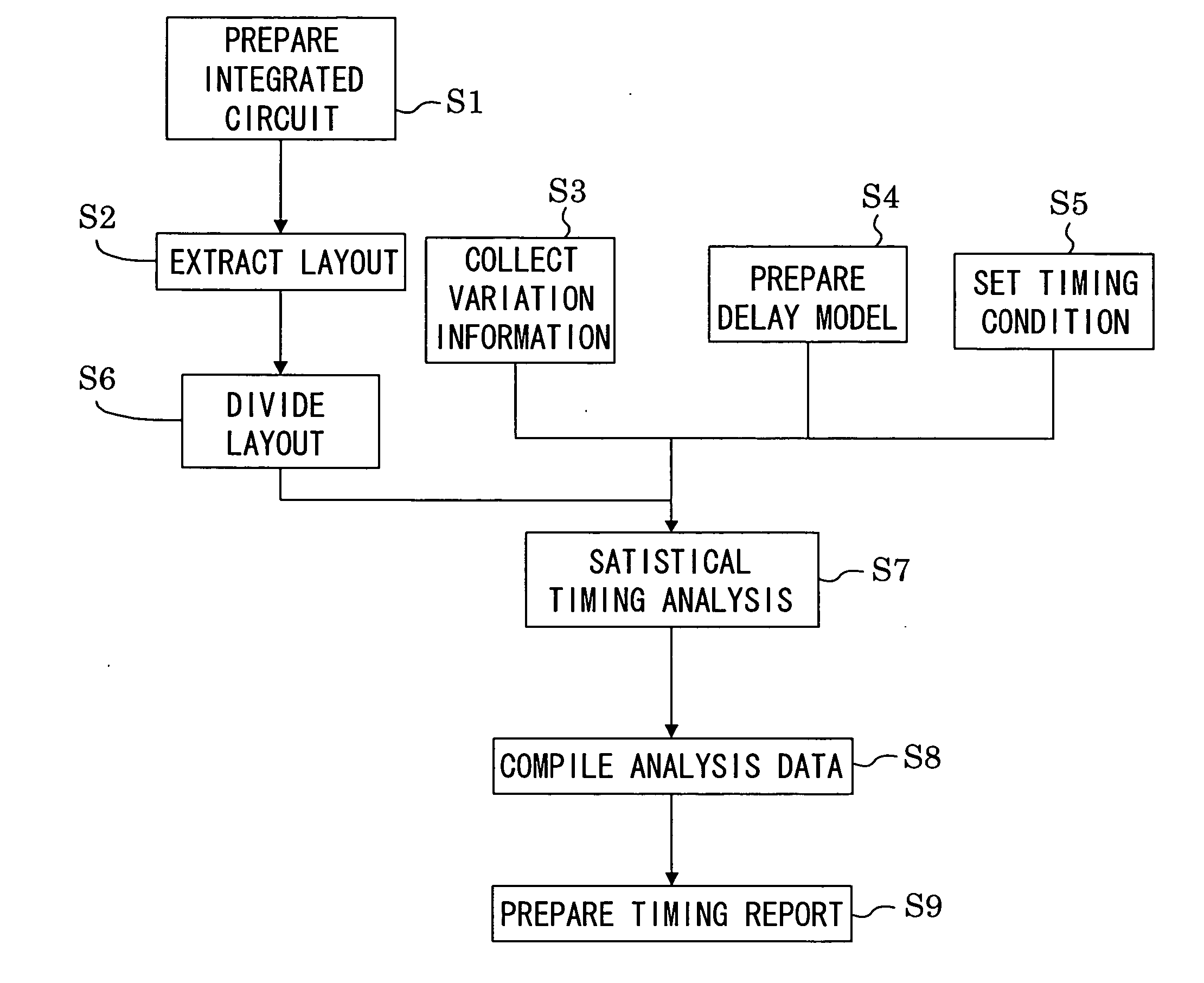
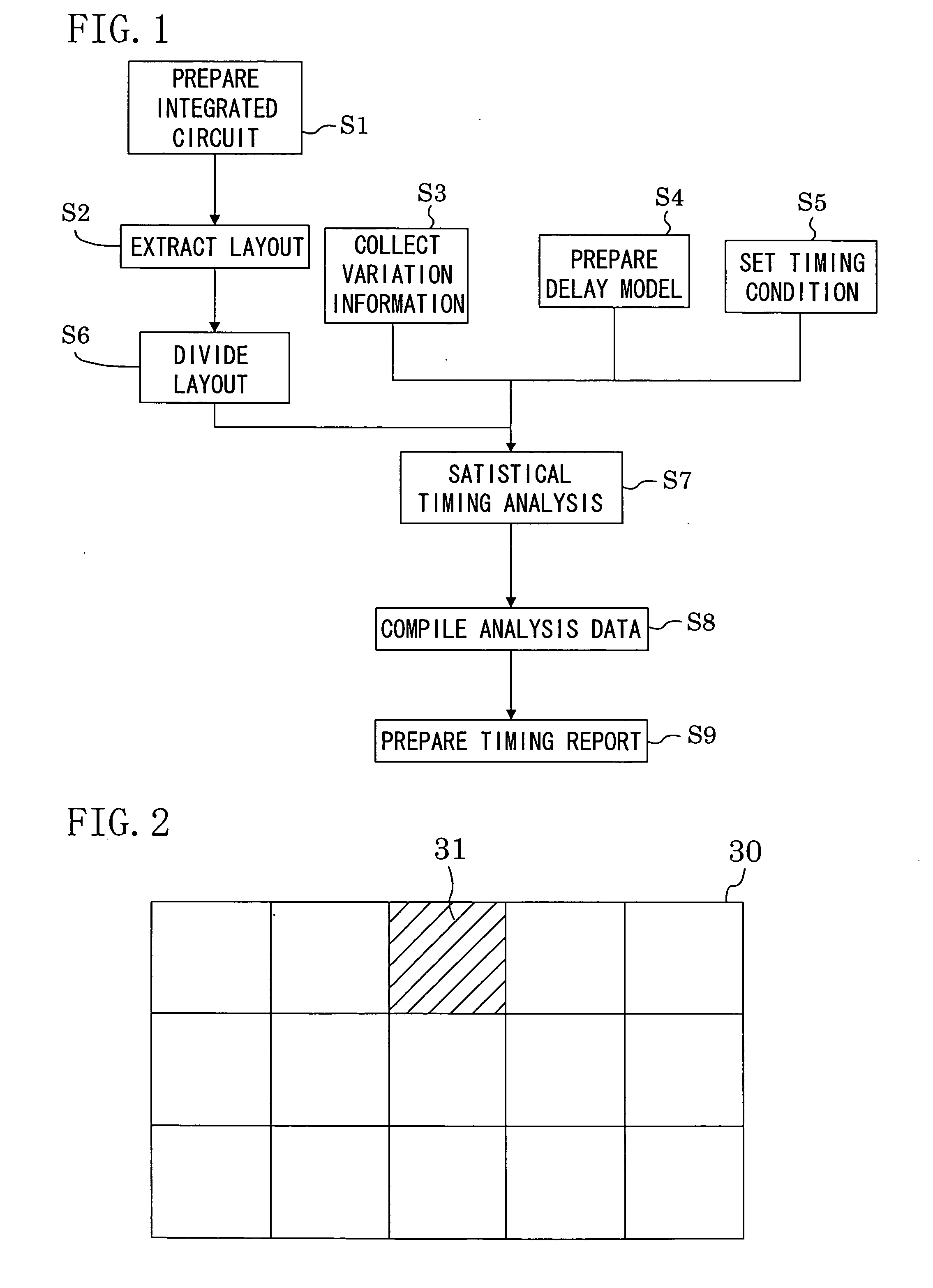
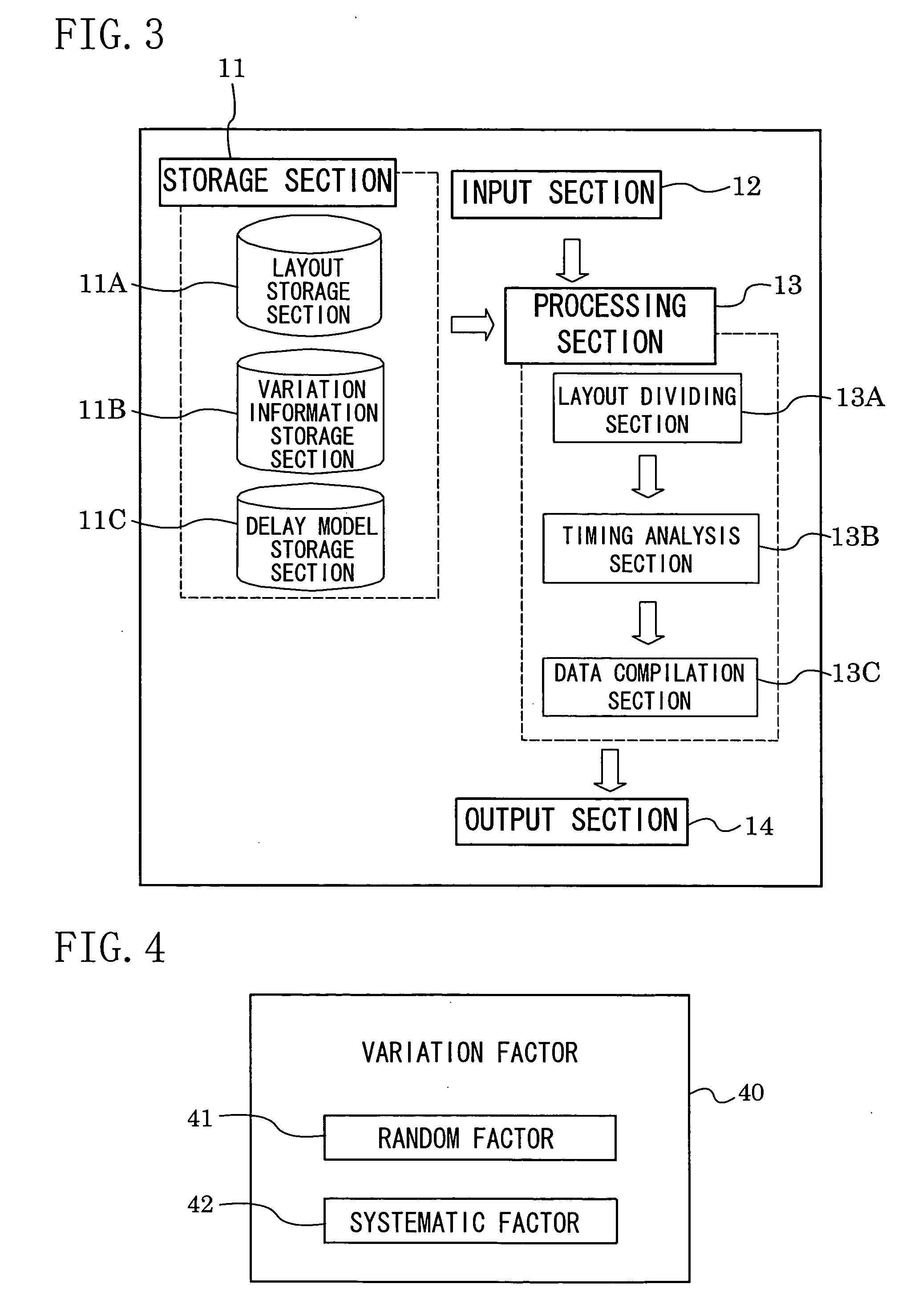
System and method for integrated circuit timing analysis
InactiveUS20070089077A1High-speed analysisImprove accuracyComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAnalysis dataComputer science
An integrated circuit timing analysis system includes: a first storage section for storing a layout of an integrated circuit including a plurality of transistors; and a processing section for processing the layout stored in the first storage section. The processing section includes a layout dividing section for dividing the layout stored in the first storage section into a plurality of sublayouts, a timing analysis section for performing statistical timing analysis on each of the sublayouts and a data compilation section for compiling the analysis data of the sublayouts to determine a timing of the integrated circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
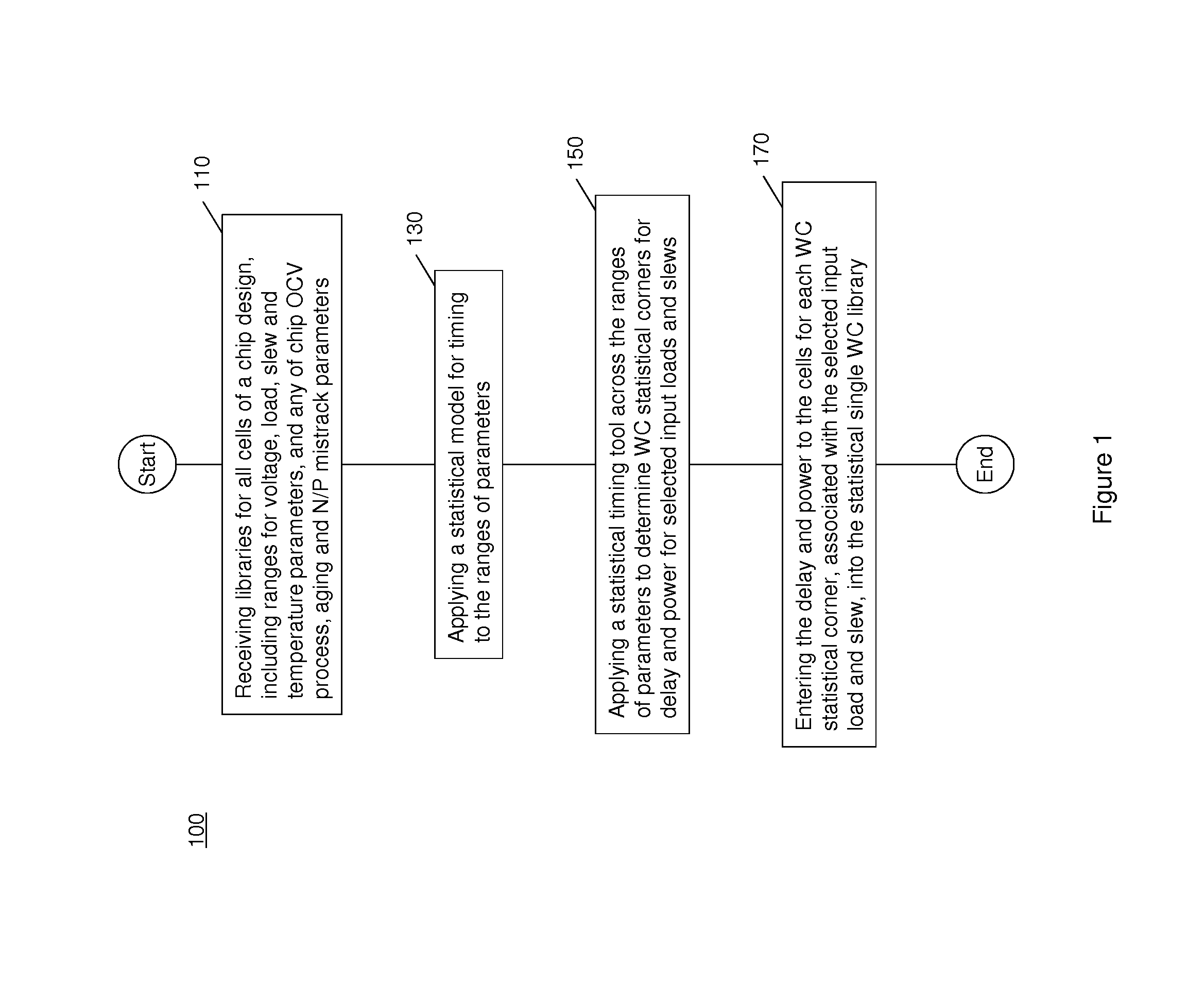
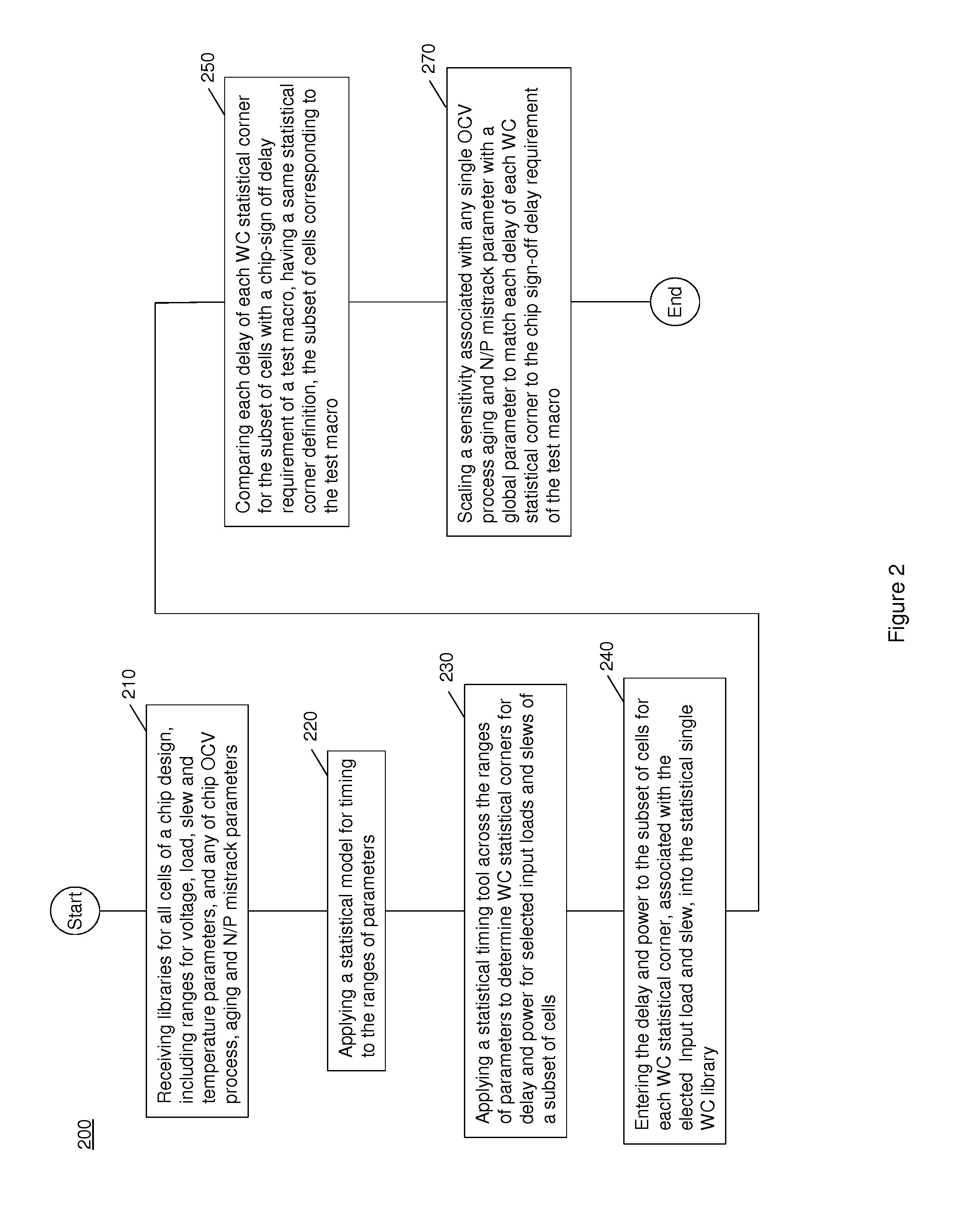
Statistical single library including on chip variation for rapid timing and power analysis
InactiveUS8413095B1Improve performanceProbabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPower analysisComputer science
A statistical single library that includes on-chip variation (OCV) is created for timing and power analysis of a digital chip design. Initially, library values for all cells of a digital chip design, including ranges for environmental and process parameters, are subject to a statistical model to create statistical timing for the ranges of the parameters. A statistical timing tool is applied across the ranges of the parameters to determine statistical corners for delay and input power to a subset of cells. The statistically determined delay and input power to the subset of cells is entered into the statistical single library. Each delay of each statistical corner for the subset of cells is compared with a chip sign-off statistical delay requirement of a test macro.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
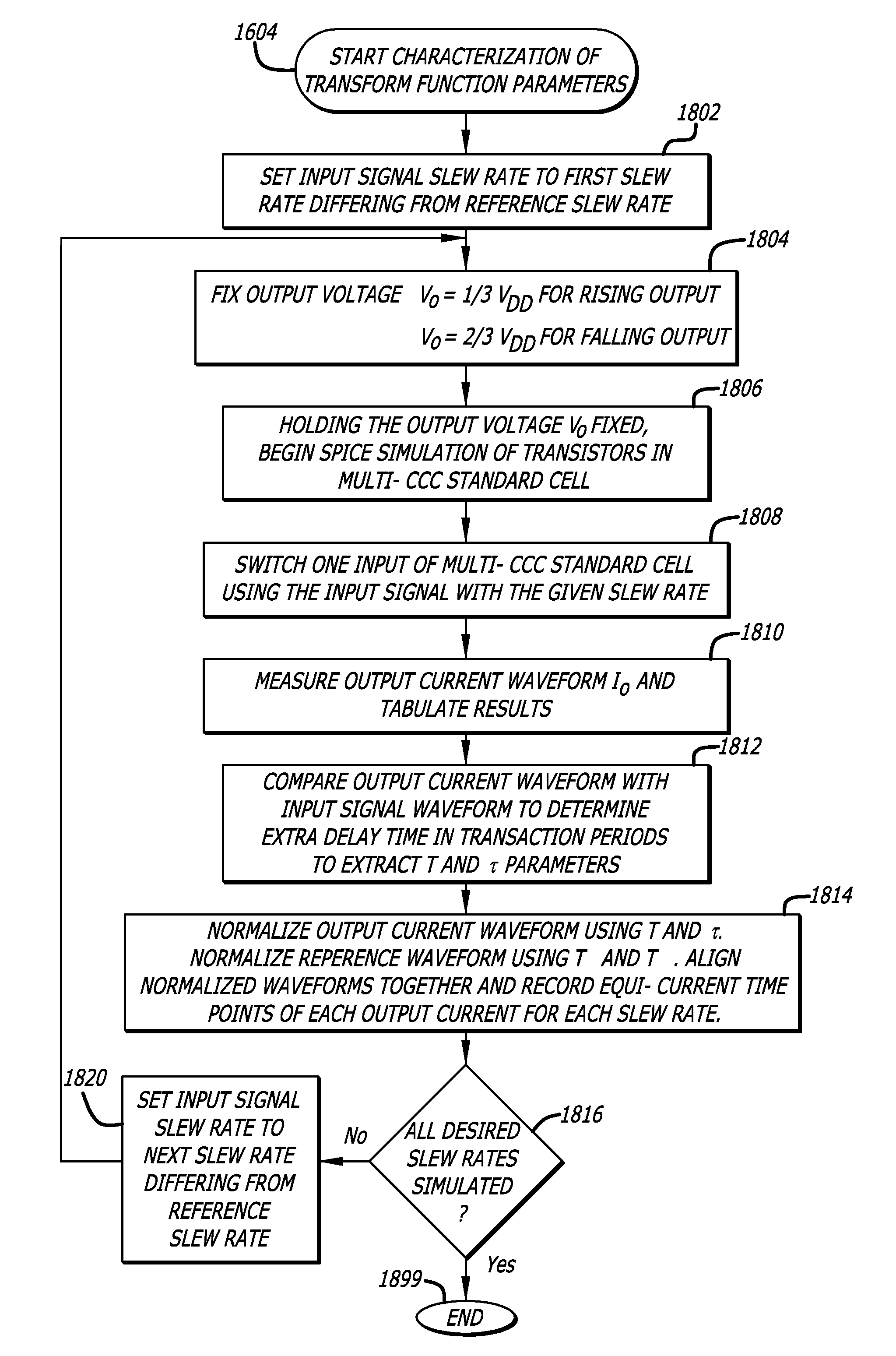
Sensitivity and static timing analysis for integrated circuit designs using a multi-CCC current source model
InactiveUS8516420B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringCapacitor
In one embodiment of the invention, a multi-CCC current source model is disclosed to perform statistical timing analysis of an integrated circuit design. The multi-CCC current source model includes a voltage waveform transfer function, a voltage dependent current source, and an output capacitor. The voltage waveform transfer function receives an input voltage waveform and transforms it into an intermediate voltage waveform. The voltage dependent current source generates an output current in response to the intermediate voltage waveform. The output capacitor is coupled in parallel to the voltage dependent current source to generate an output voltage waveform for computation of a timing delay.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
System and method for accommodating non-gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS20070234256A1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designArrival timeTHD analyzer
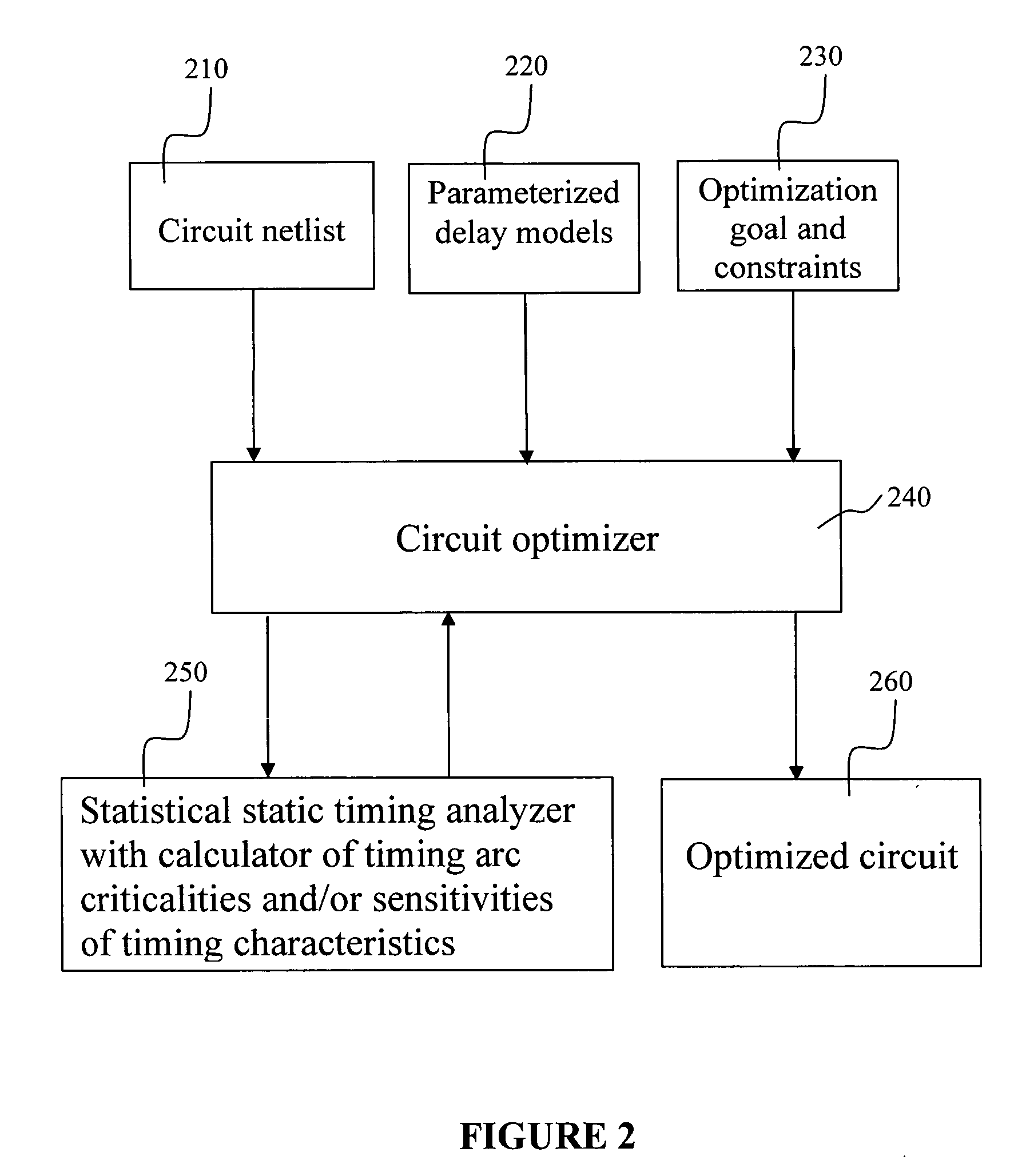
There is provided a system and method for statistical timing analysis and optimization of an electrical circuit having two or more digital elements. The system includes at least one parameter input and a statistical static timing analyzer and electrical circuit optimizer. The at least one parameter input is for receiving parameters of the electrical circuit. At least one of the parameters has at least one of a non-Gaussian probability distribution and a non-linear delay effect. The statistical static timing analyzer and electrical circuit optimizer is for calculating at least one of a signal arrival time and a signal required time for the electrical circuit using the at least one parameter and for modifying a component size of the electrical circuit to alter gate timing characteristics of the electrical circuit based upon the at least one of the signal arrival time and the signal required time.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Performing a statistical timing abstraction for a hierarchical timing analysis of VLSI circuits
ActiveUS8122404B2Simpler statistical timing modelReducing size and complexityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
A method for performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of an integrated circuit (IC) chip design by abstracting one or more macros of the design. The method includes performing a statistical static timing analysis of at least one macro; performing a statistical abstraction of the macro to obtain a statistical abstract model of the macro timing characteristics; applying the statistical abstract model as the timing model for each occurrence of the macro leading to a simplified IC chip design; and performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of the simplified chip design. The method achieves a context aware statistical abstraction, where a generated statistical abstract model is instantiated for each macro of the chip during statistical static timing analysis at the chip level, providing a compressed and pruned statistical timing abstraction and reducing the model-size during the statistical abstraction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com