Patents
Literature
44 results about "Statistical static timing analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
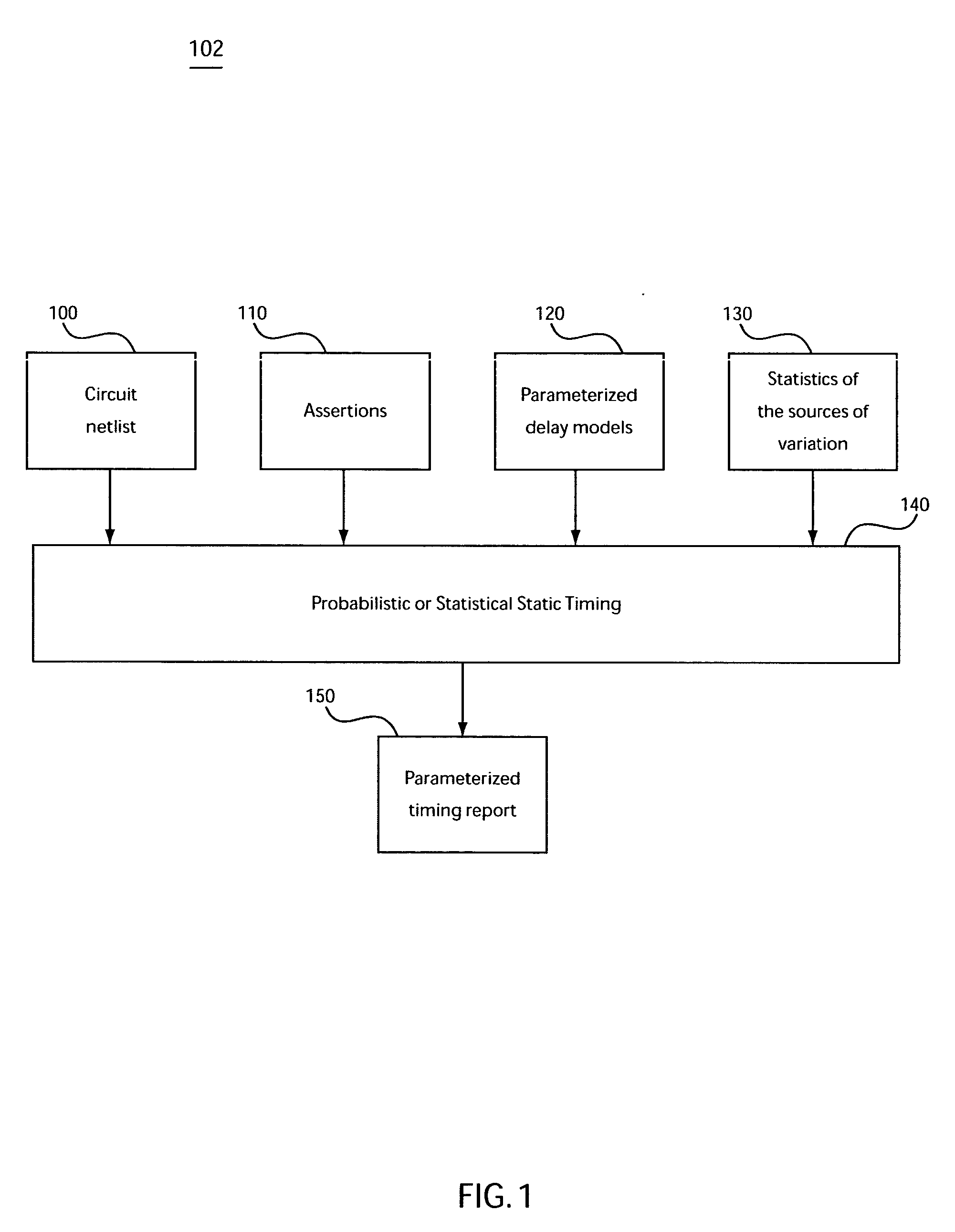
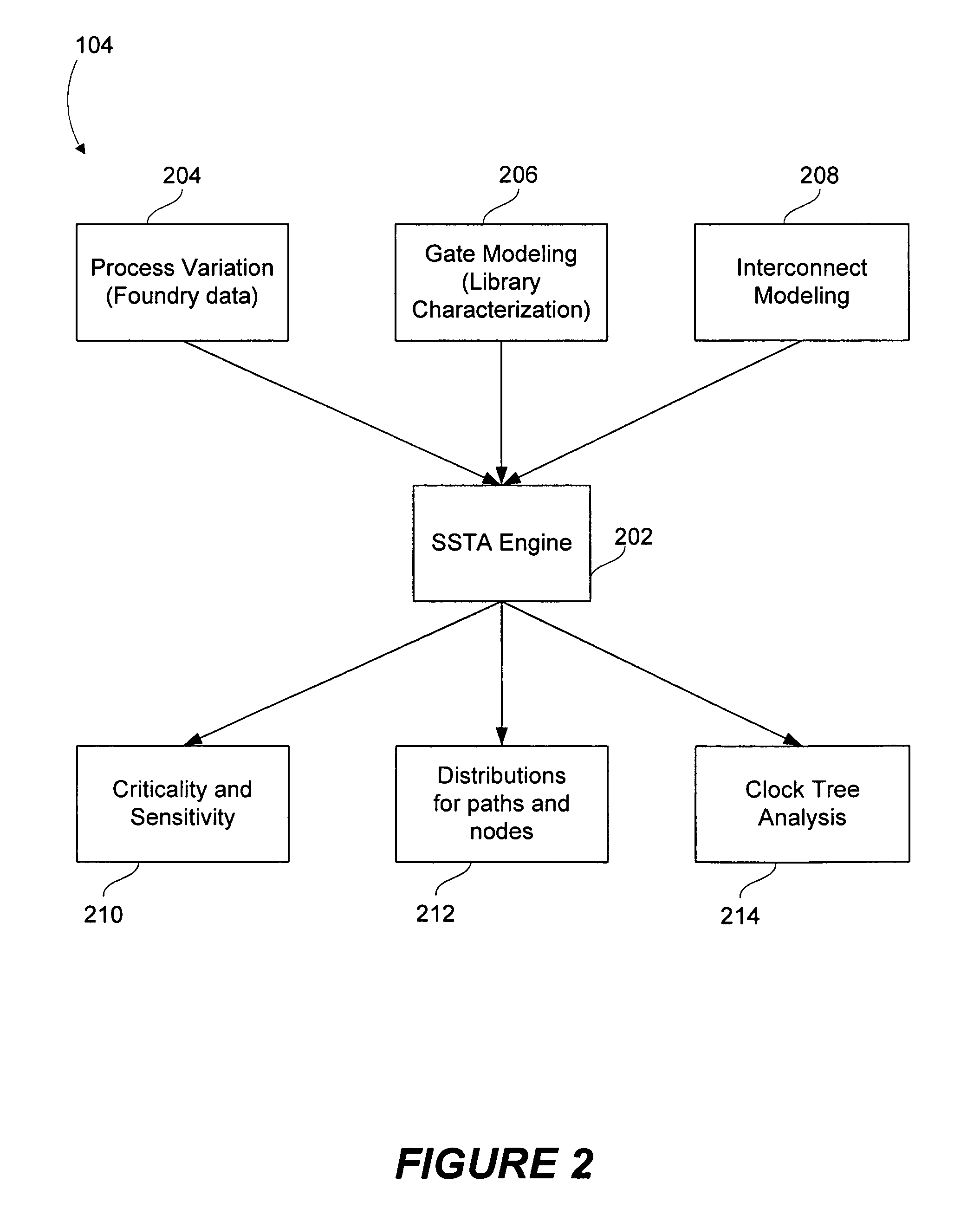
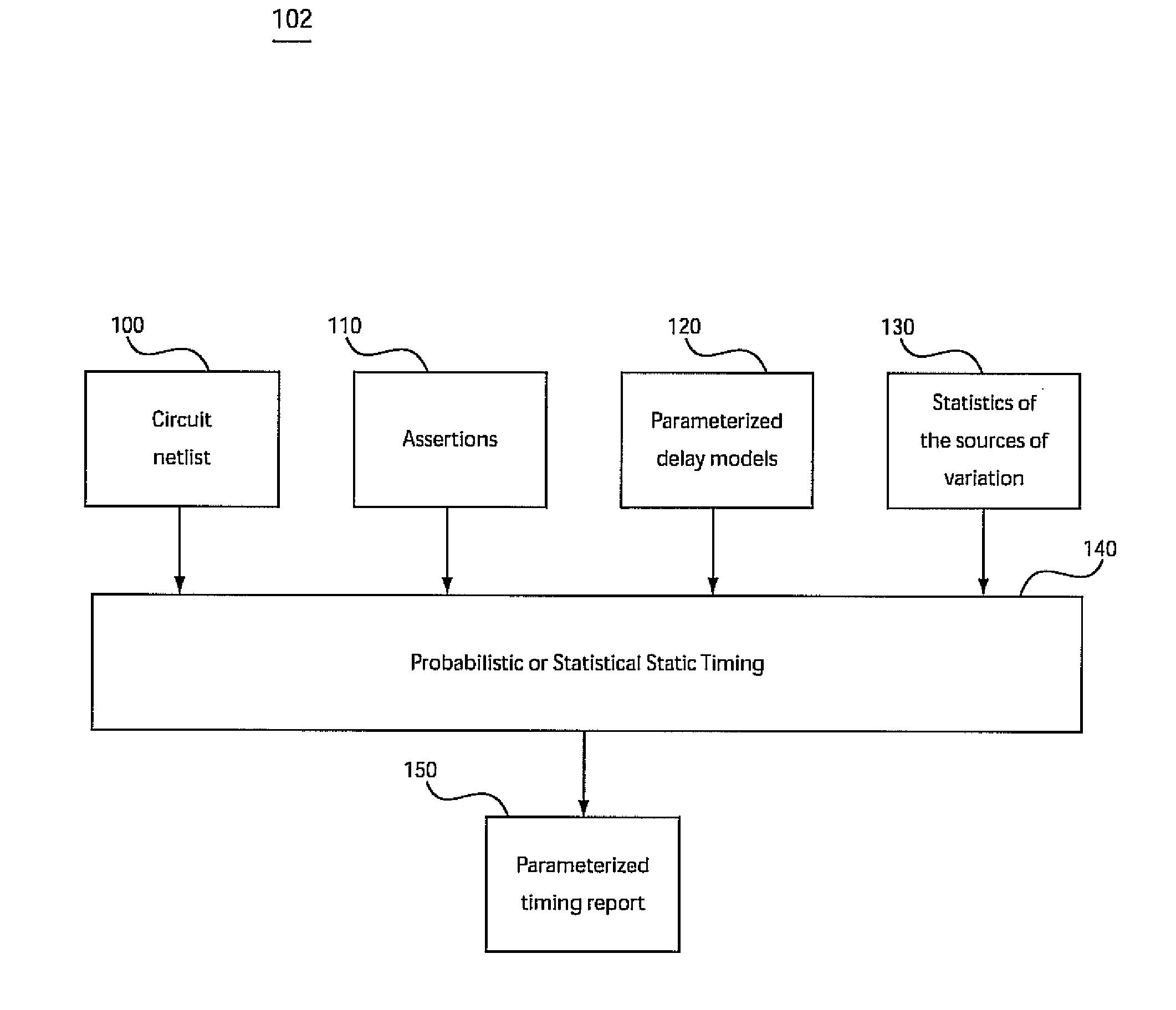
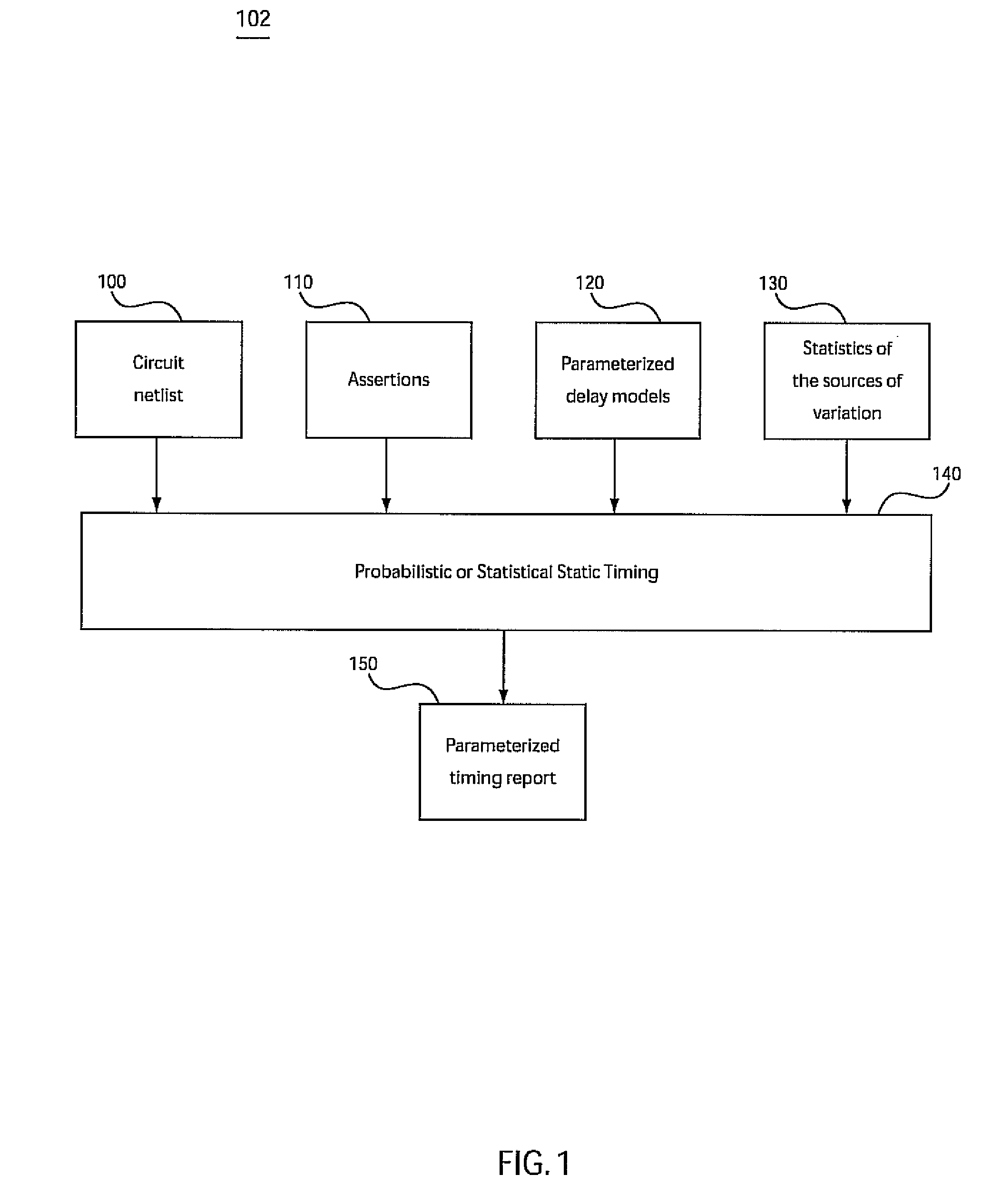
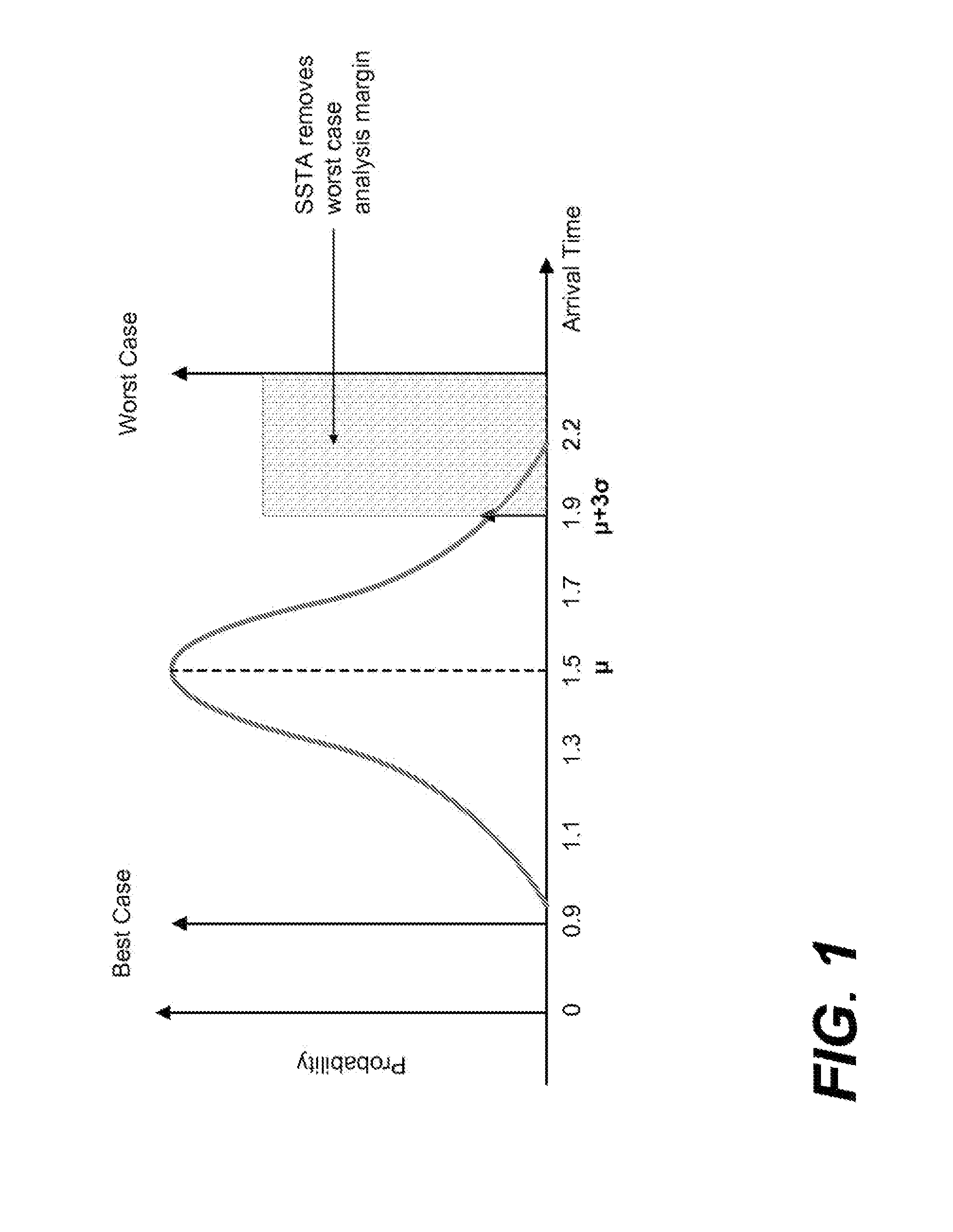
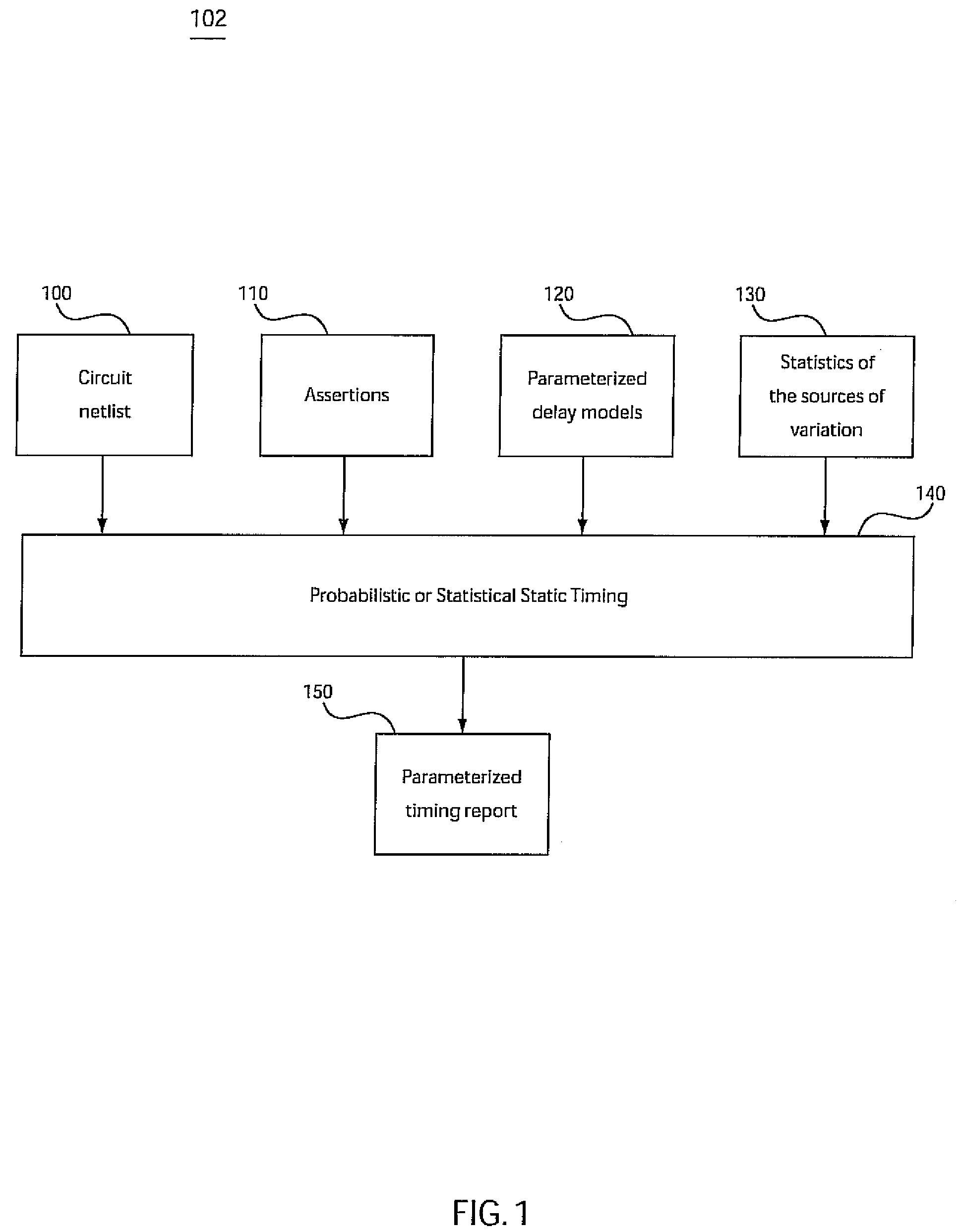
Conventional static timing analysis (STA) has been a stock analysis algorithm for the design of digital circuits over the last 30 years. However, in recent years the increased variation in semiconductor devices and interconnect has introduced a number of issues that cannot be handled by traditional (deterministic) STA. This has led to considerable research into statistical static timing analysis, which replaces the normal deterministic timing of gates and interconnects with probability distributions, and gives a distribution of possible circuit outcomes rather than a single outcome.
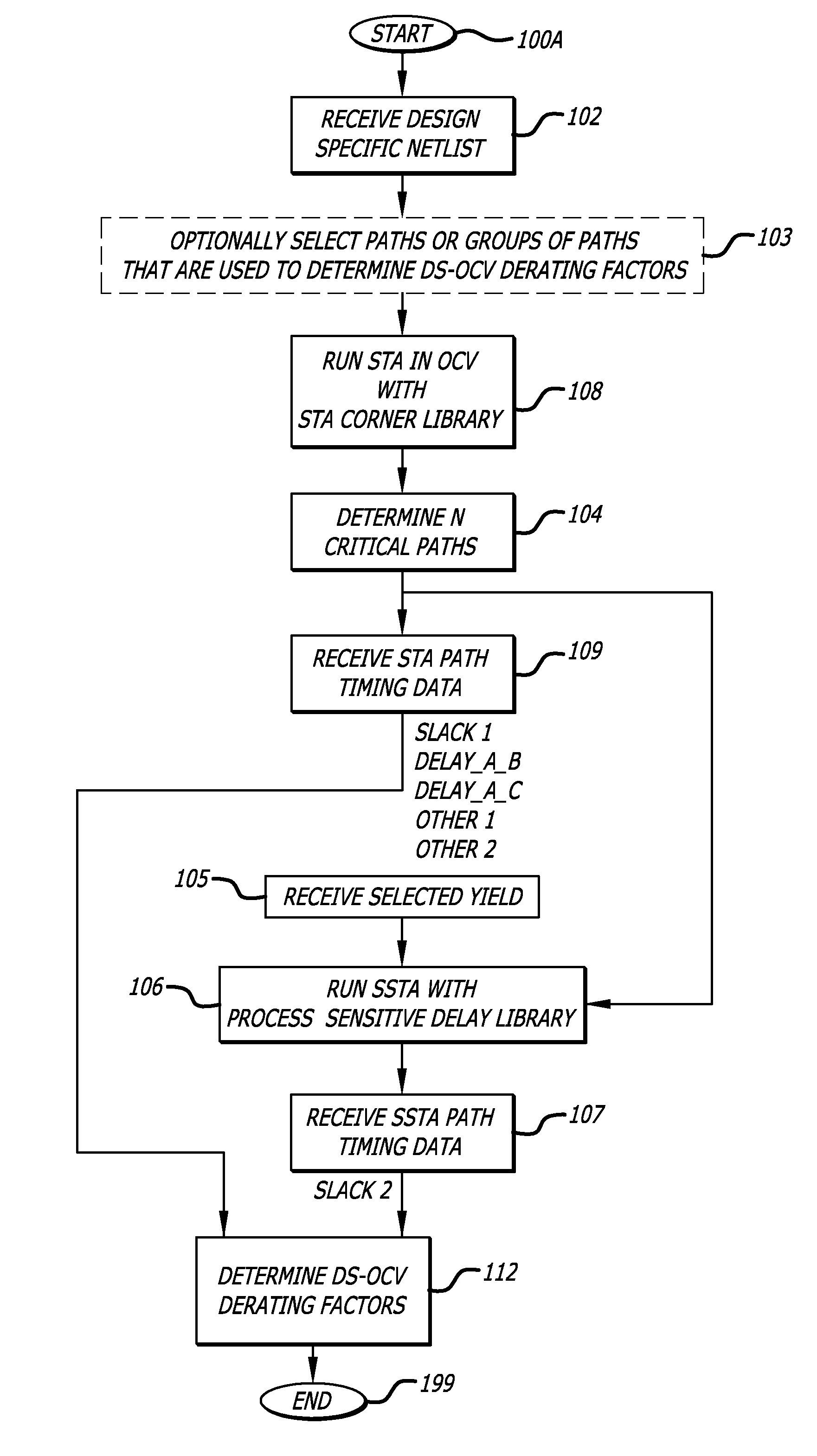
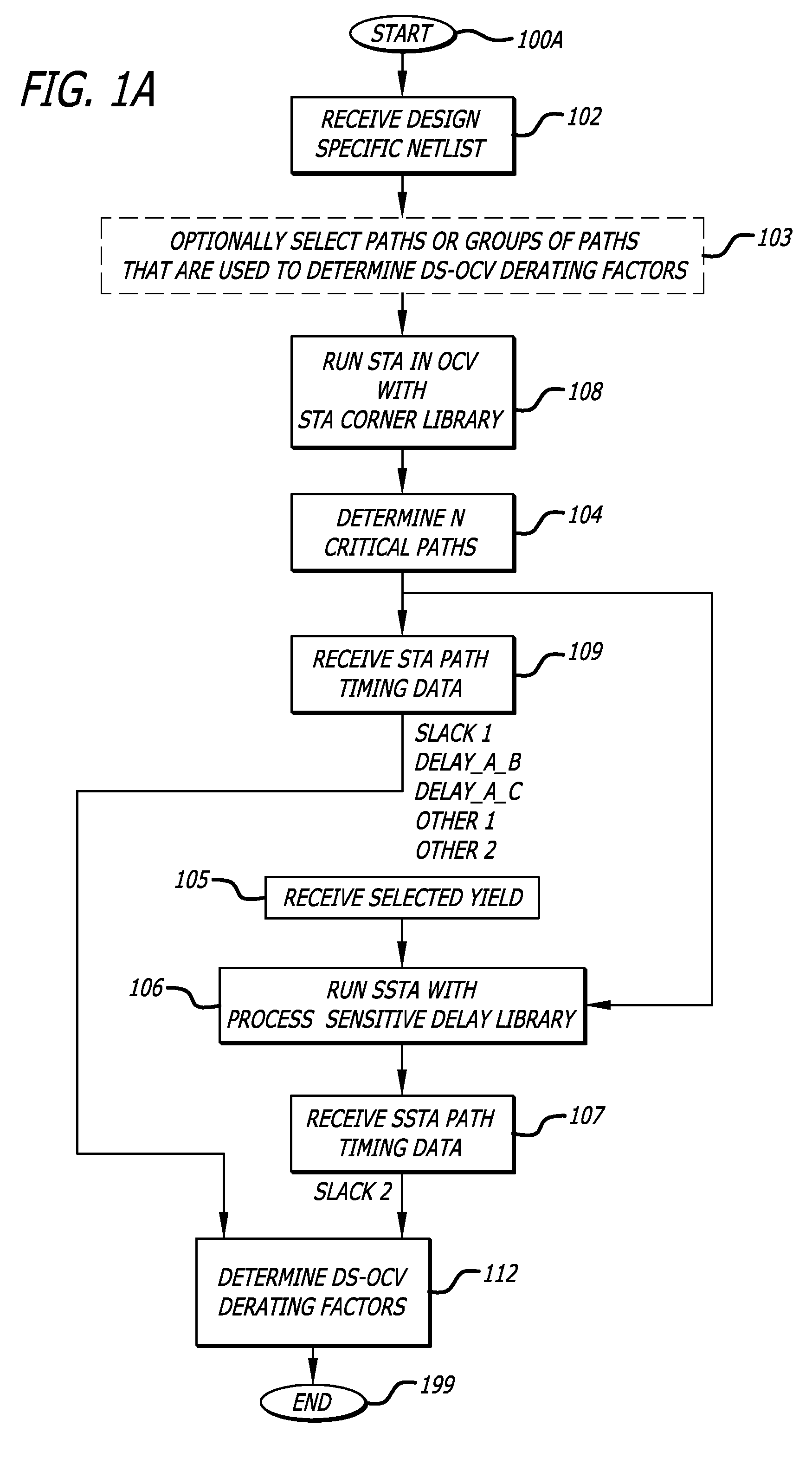
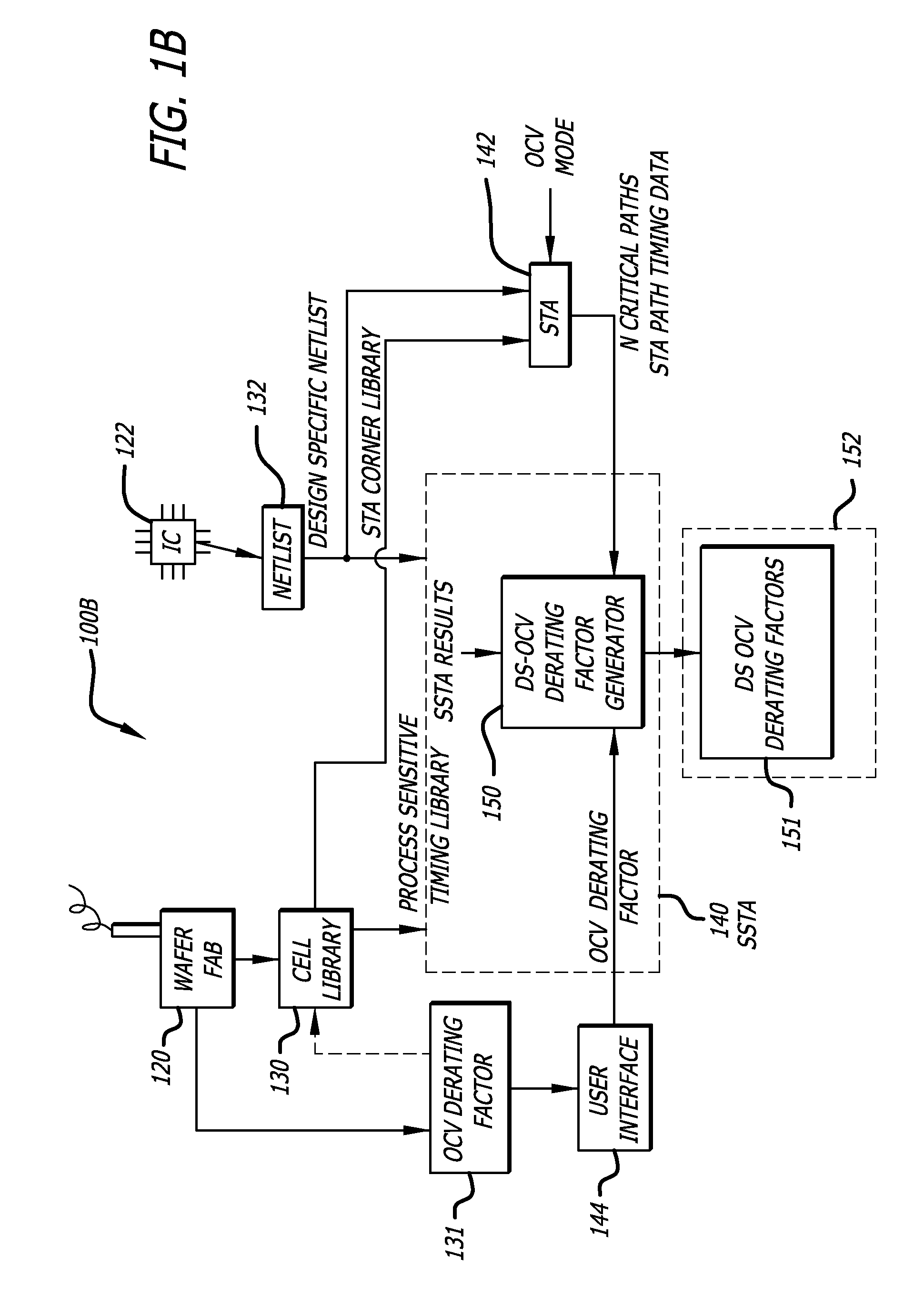
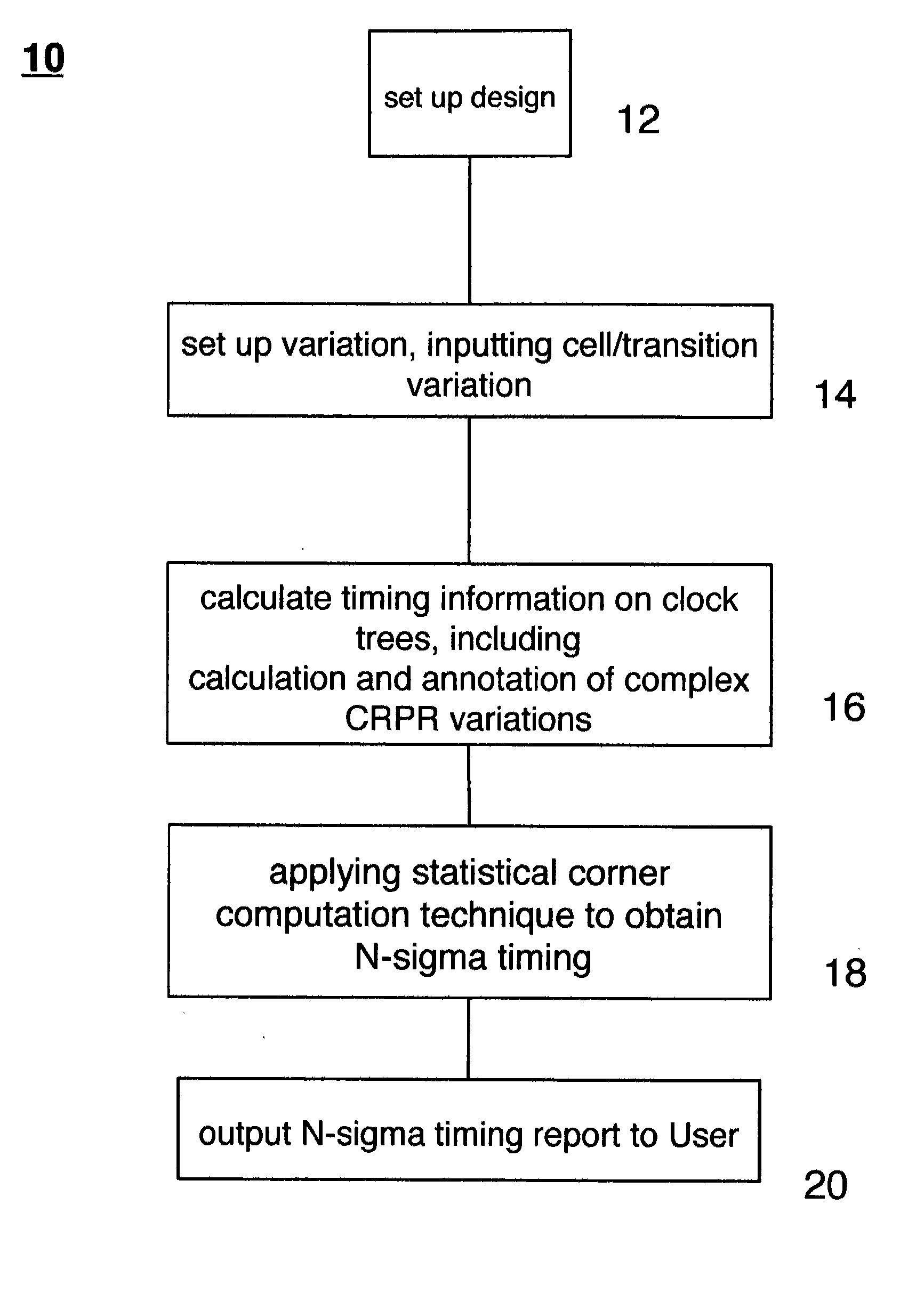
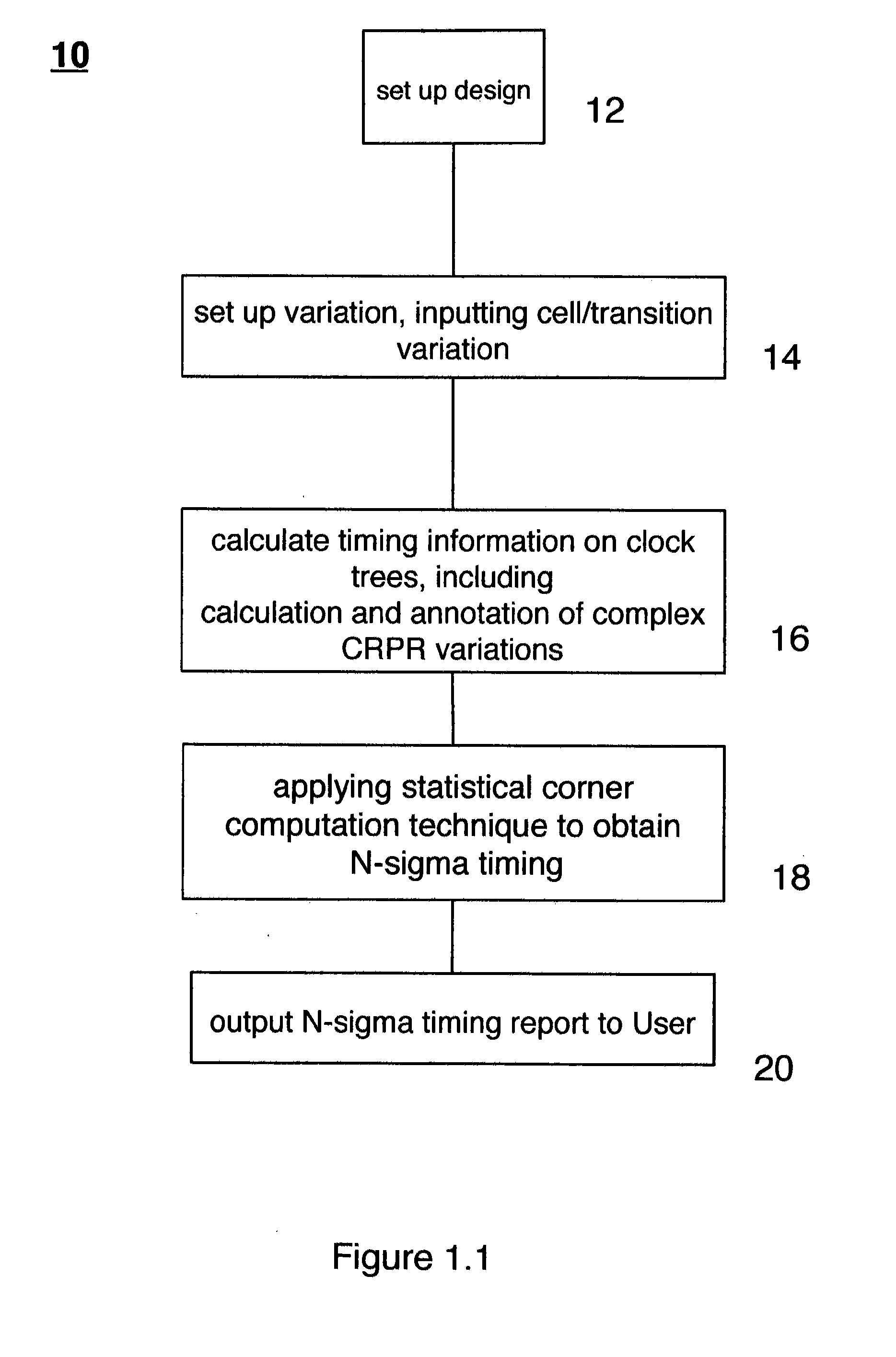
Design-specific on chip variation de-rating factors for static timing analysis of integrated circuits
InactiveUS8336010B1Reduce running timeDesign specificationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime informationDying processes
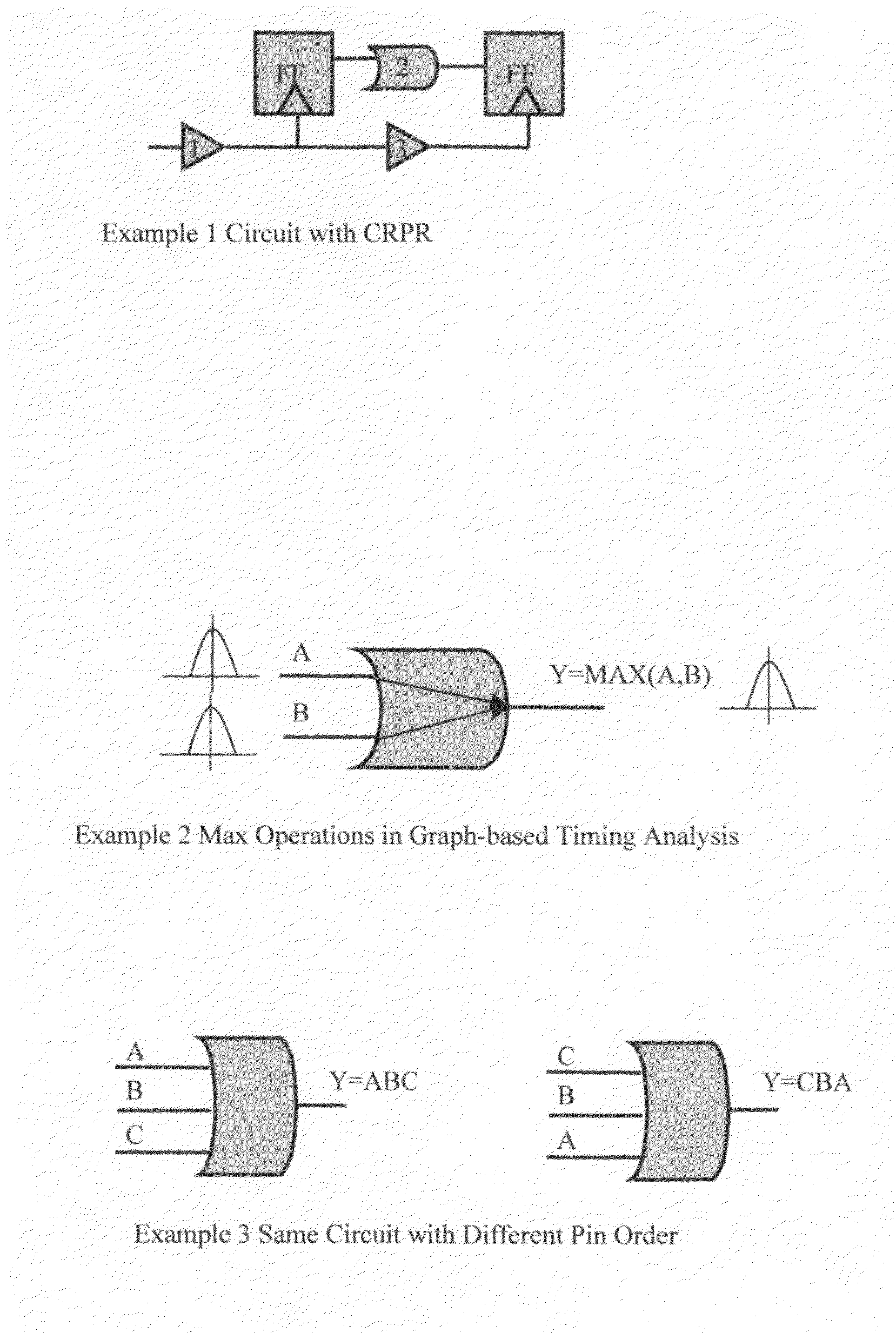
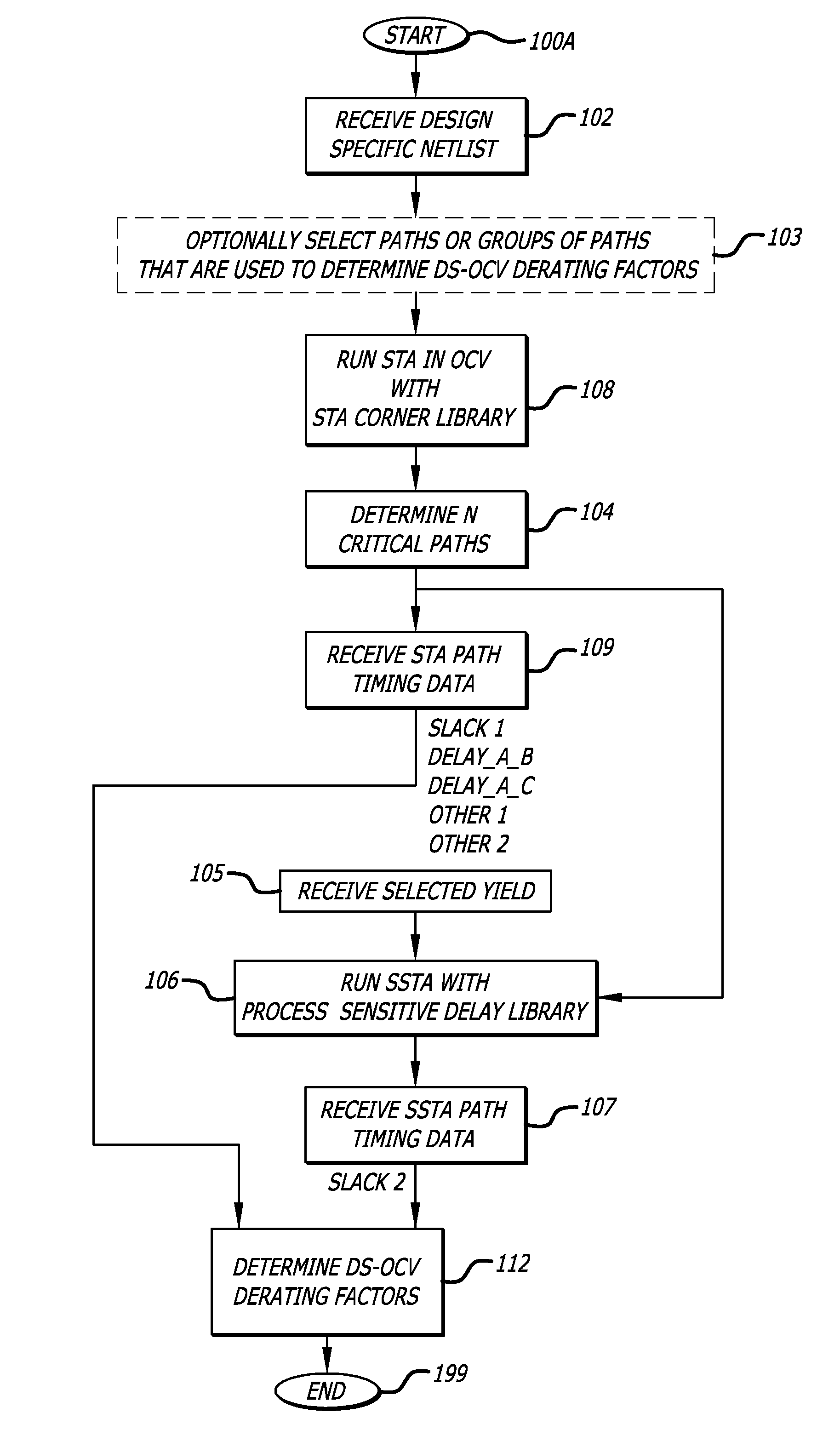
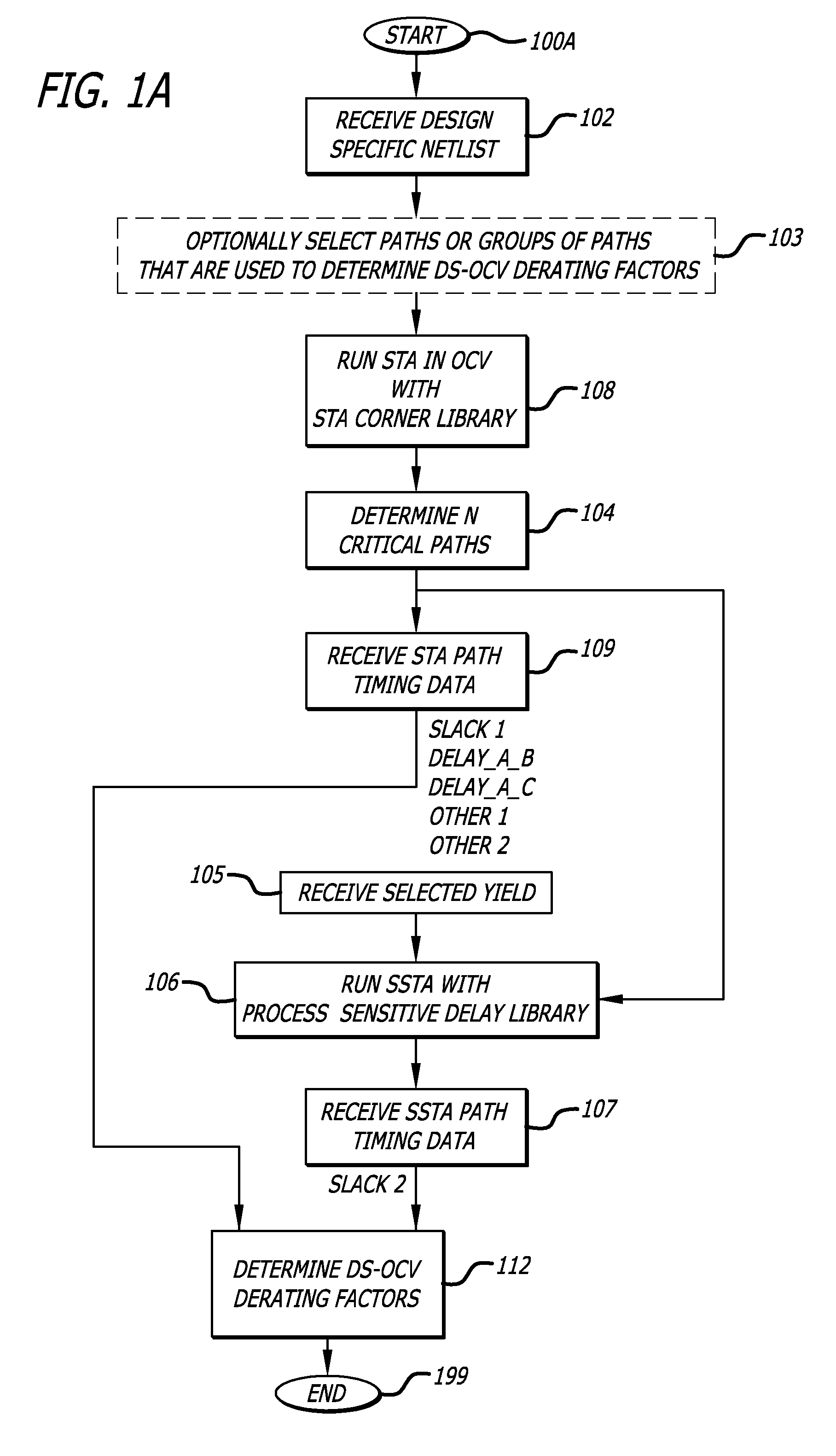
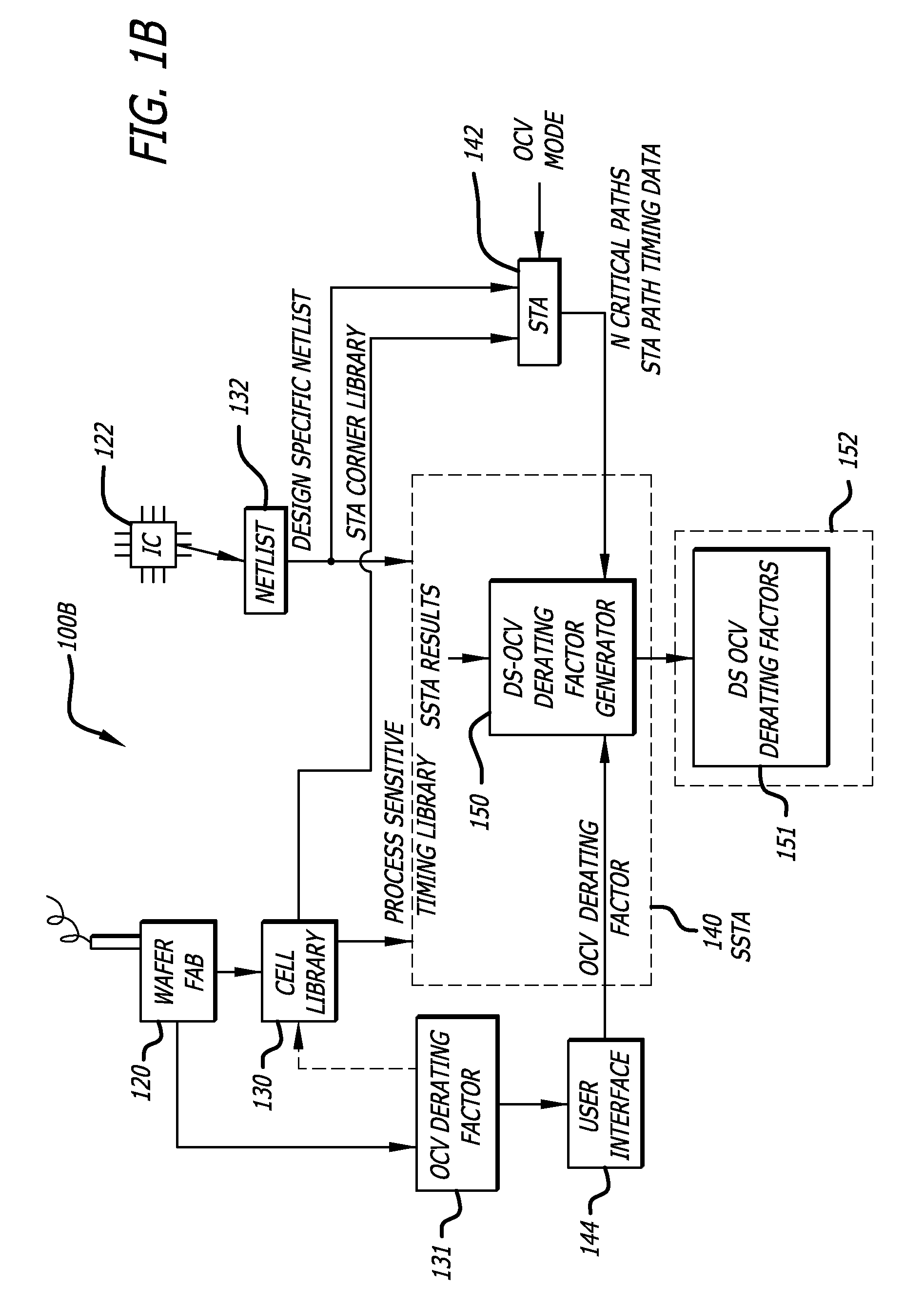
In one embodiment of the invention, a method of analysis of a circuit design with respect to within-die process variation is disclosed to generate a design-specific on chip variation (DS-OCV) de-rating factor. The method includes executing a static timing analysis (STA) in an on-chip variation mode using a process corner library. Collecting timing information of the top N critical timing paths. Executing a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) on the N critical timing paths using timing models characterized for SSTA with sensitivities of delays to process variables. Compare the two timing results and deriving DS-OCV de-rating factors for the clock / data paths to be used in a STA OCV timing analysis to correctly account for the effects of process variations. A user may select to specify DS-OCV de-rating factors for paths or groups of paths and achieve an accurate timing analysis report in a reduced amount of run-time.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
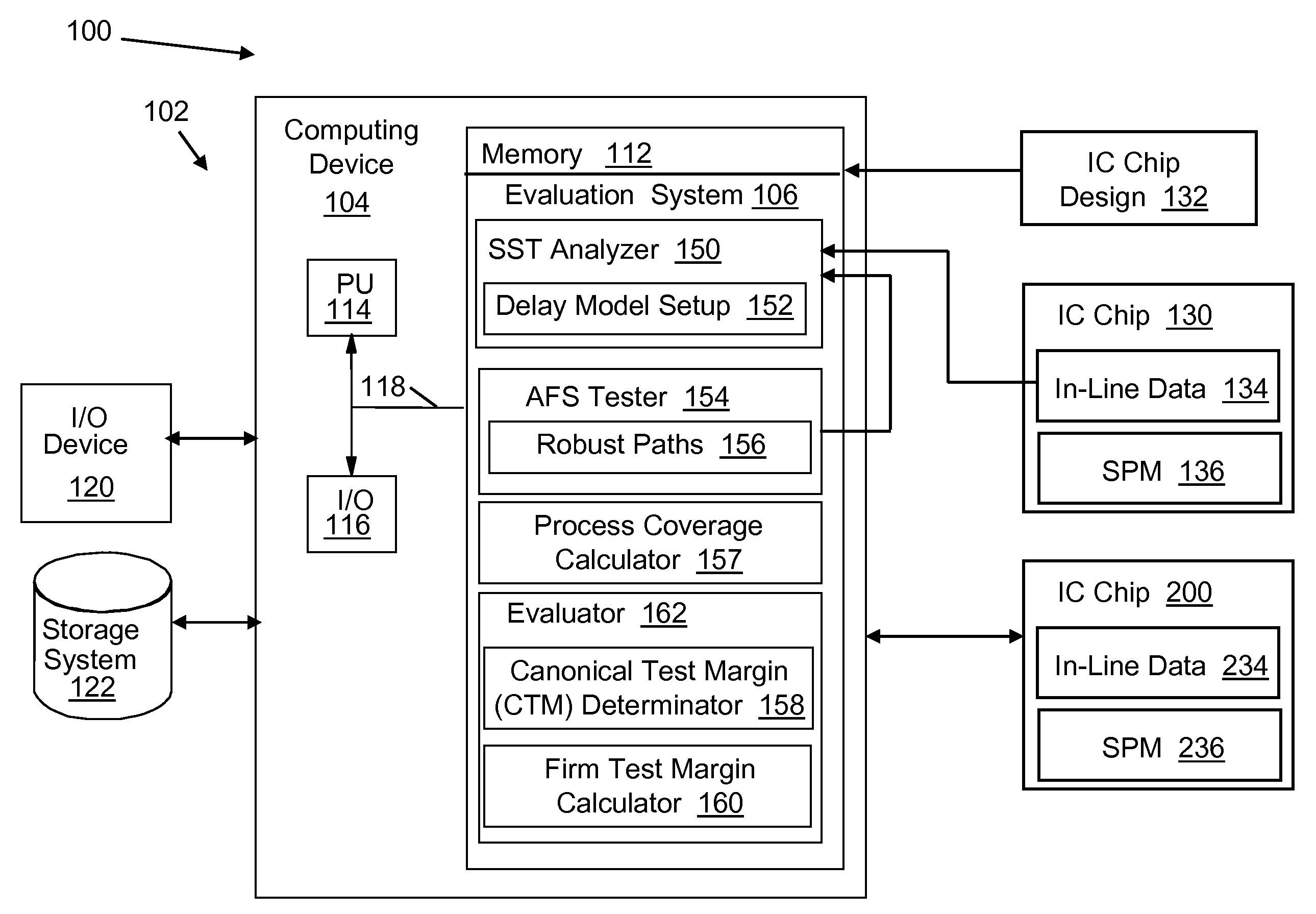
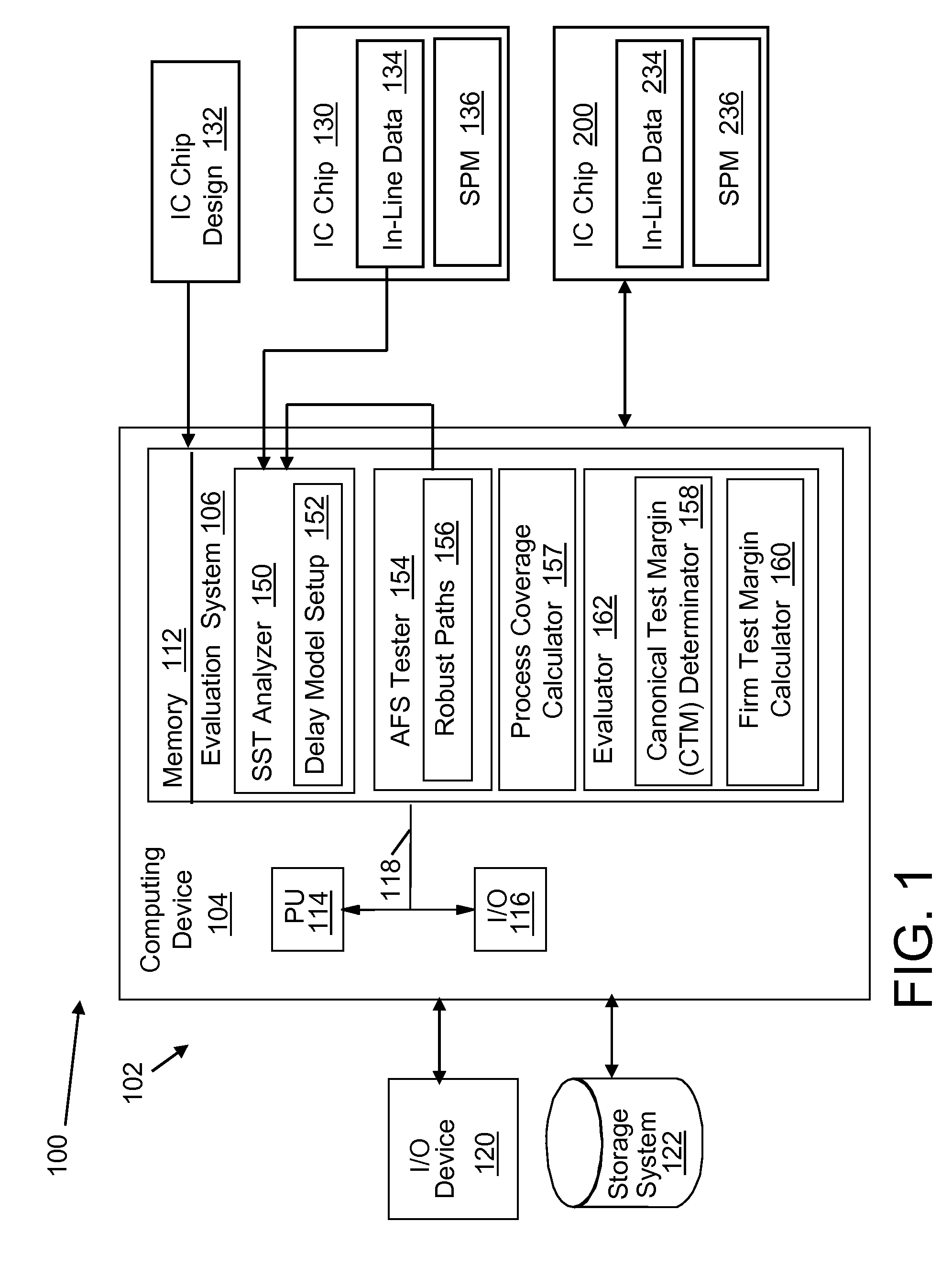
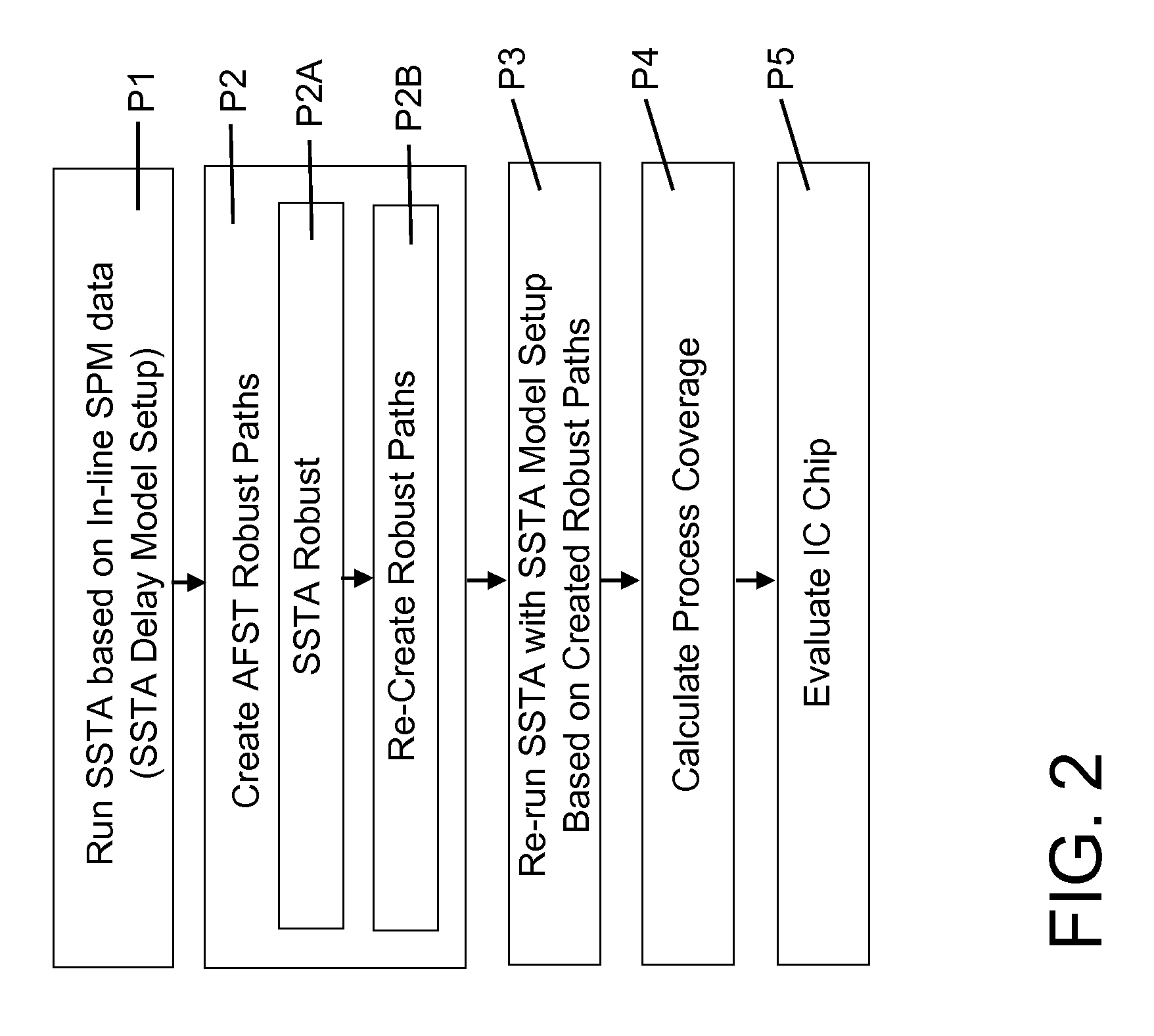
IC chip at-functional-speed testing with process coverage evaluation
ActiveUS7620921B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementProbabilistic CADSpeed testComputation process
Methods, systems and program products for evaluating an IC chip are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes running a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) of a full IC chip design; creating at-functional-speed test (AFST) robust paths for an IC chip, the created robust paths representing a non-comprehensive list of AFST robust paths for the IC chip; and re-running the SSTA with the SSTA delay model setup based on the created robust paths. A process coverage is calculated for evaluation from the SSTA runnings; and a particular IC chip is evaluated based on the process coverage.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
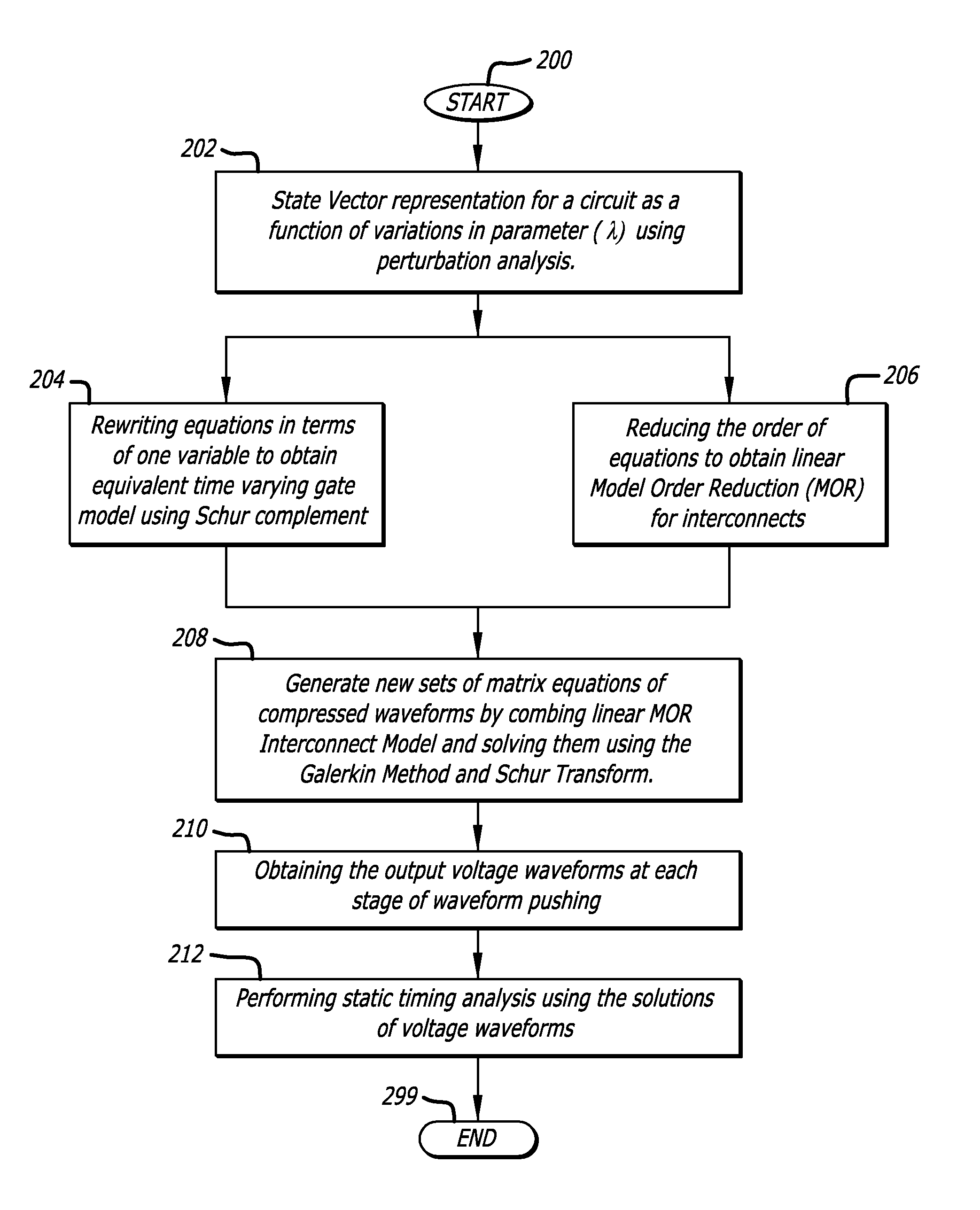
Methods and apparatus for waveform based variational static timing analysis
ActiveUS8245165B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic networkPhases of clinical research
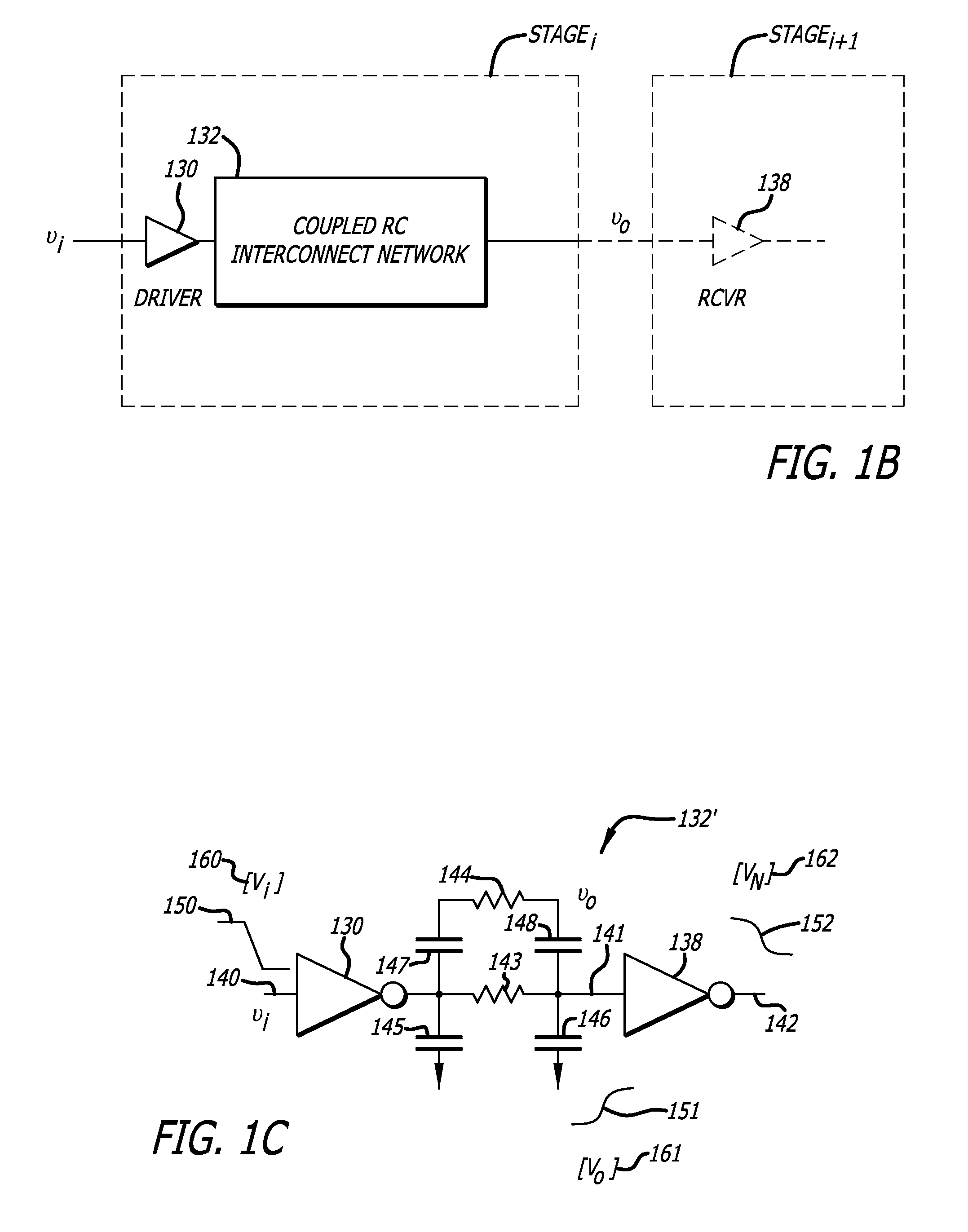
A system and method are disclosed for waveform based variational static timing analysis. A circuit is divided into its linear circuit parts and non-linear circuit parts and modeled together, by a combination of linear modeling techniques, into linear equations that may be represented by matrices. The linear equations in matrix form may be readily solved by a computer such that an input waveform to an input pin of the circuit can be sequentially “pushed” through the various interconnects and logic networks of the circuit to an output pin. Output voltage waveforms are obtained at each stage of the waveform pushing and may be used to perform static timing analysis.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Statistics static state sequential analysis method applied to near/sub threshold digital circuit
ActiveCN106066919AResolve inaccuraciesSolve efficiency problemsSpecial data processing applicationsTime delaysSimulation
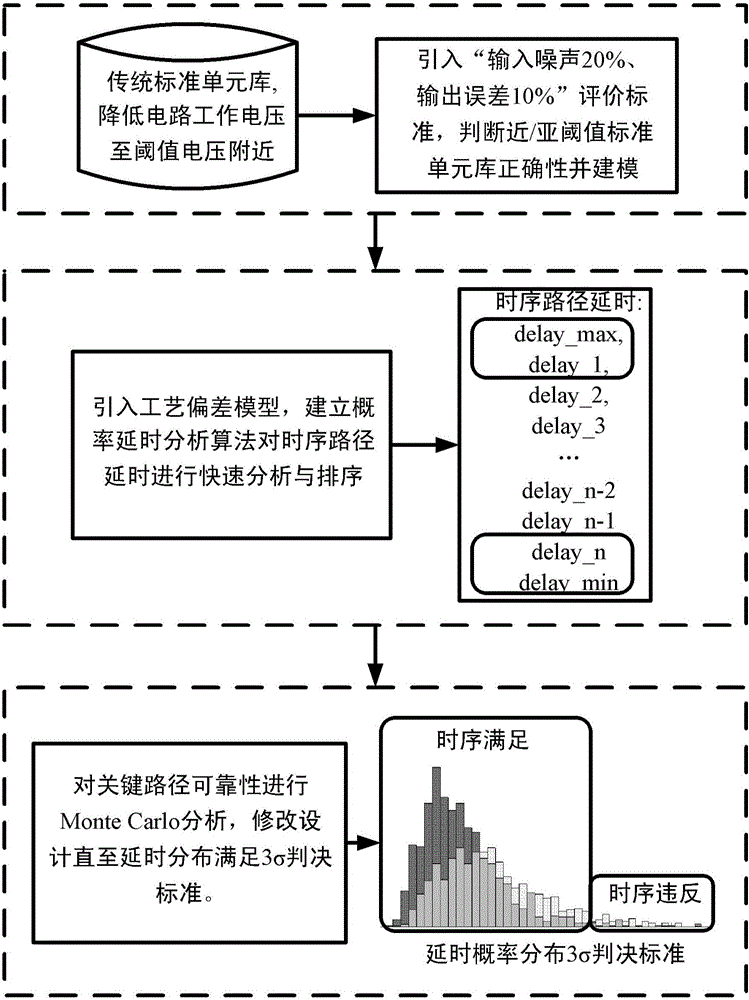
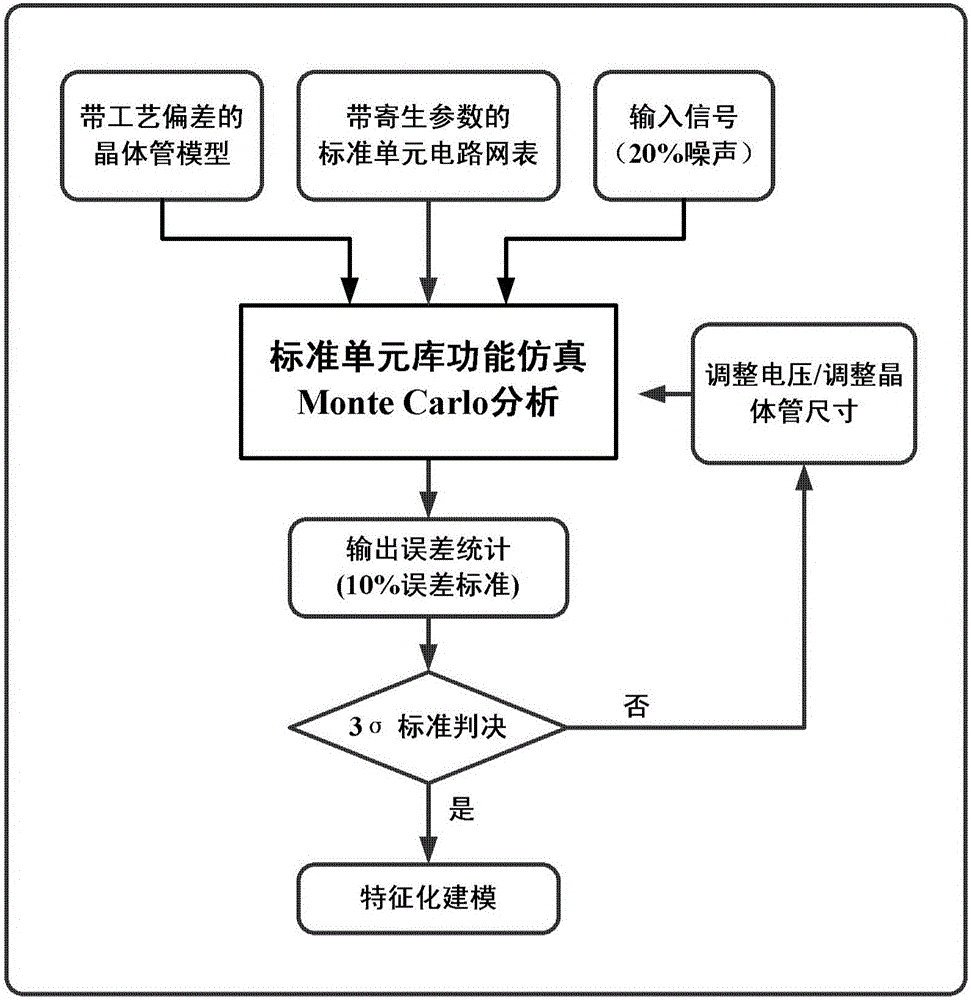
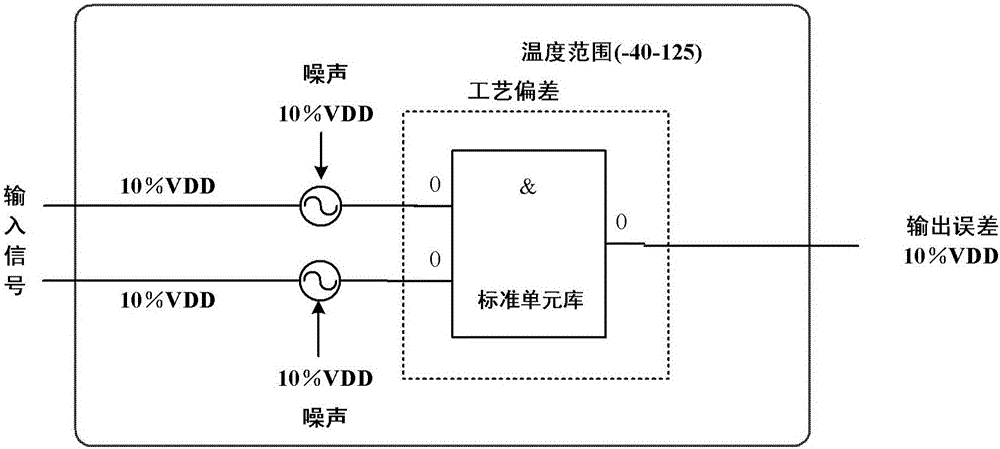
The invention discloses a statistics static state sequential analysis method applied to a near / sub threshold digital circuit; the method comprises the following steps: reducing the standard cell library work voltage to near the threshold-voltage, and carrying out function simulation and characterization modeling for a near / sub threshold standard cell library; using a probability time-delay analysis algorithm to fast parse and rank path time-delays; using a Monte Carlo parse strategy and 3 [sigma] decision standard to concisely parse a suspected path, thus further improving sequential reliability. The provided accurate, reliable and fast statistics static state sequential analysis method can solve near / sub threshold digital circuit sequential analysis reliability problems, fully considers technology deviation influences on the path sequence, thus solving the near / sub threshold digital circuit sequential analysis reliability problems; compared with a conventional static state sequential analysis method and a Hspice-based sequential simulation method, the statistics static state sequential analysis method has obvious advantages on sequential analysis accuracy and efficiency.
Owner:SOI MICRO CO LTD
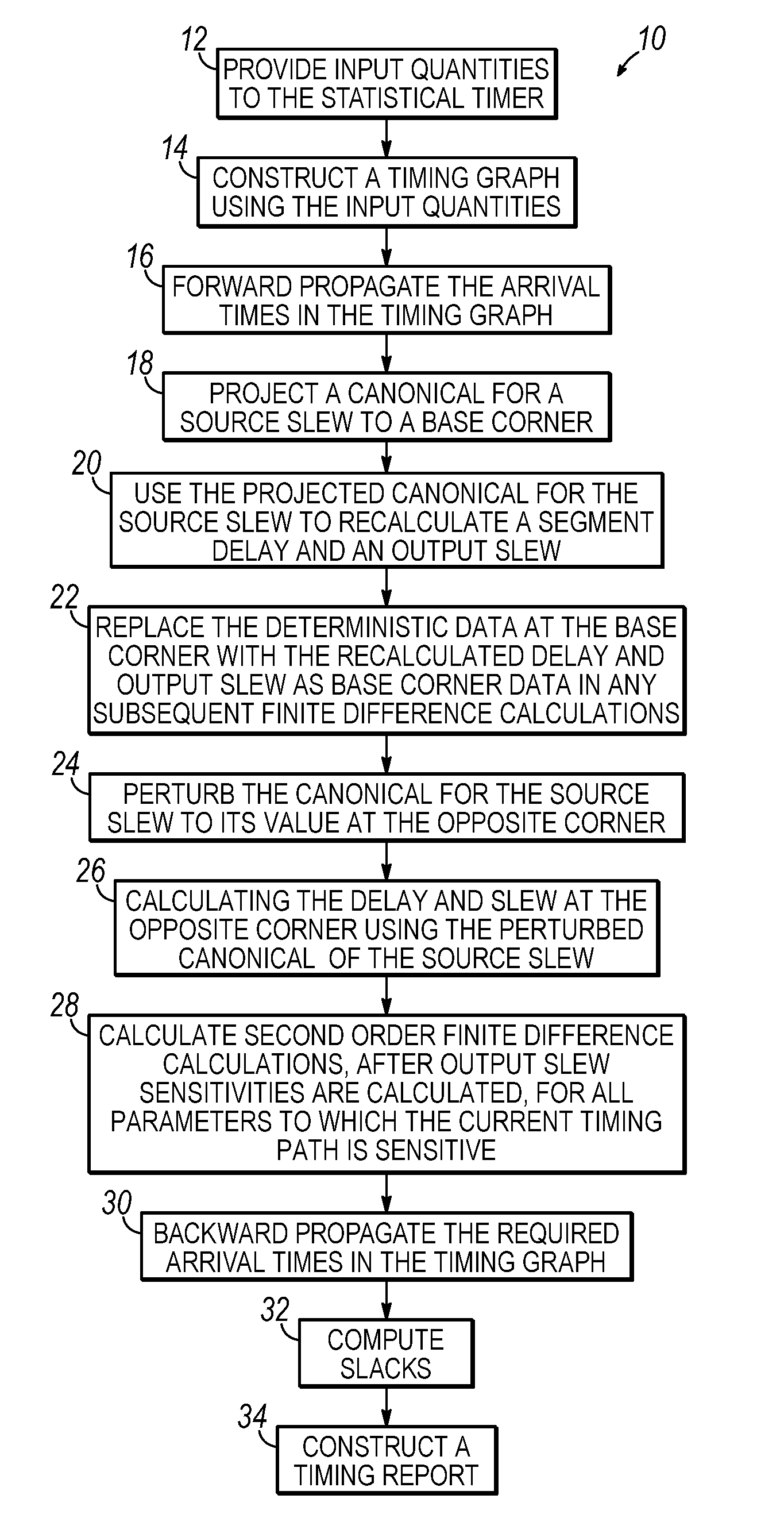
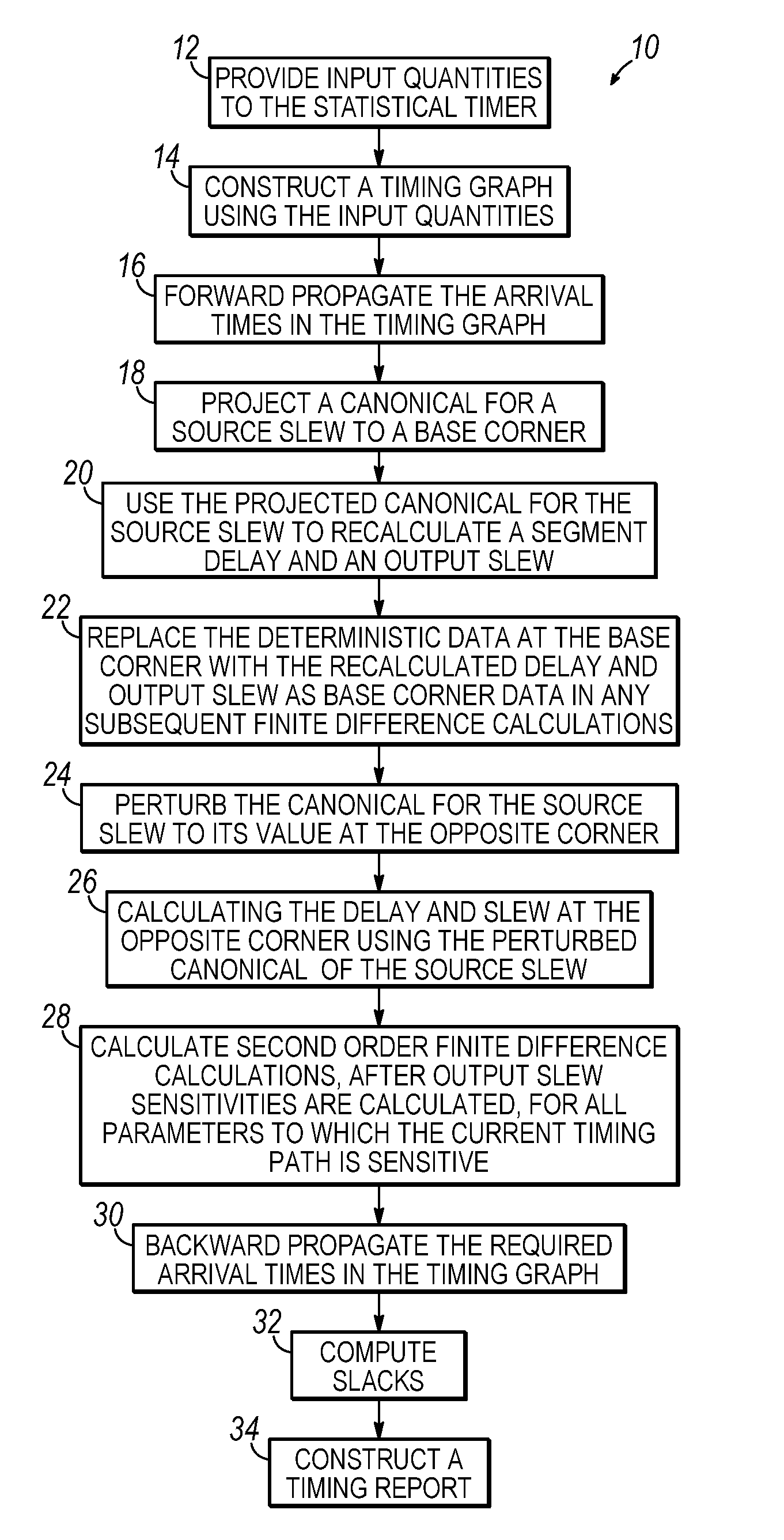
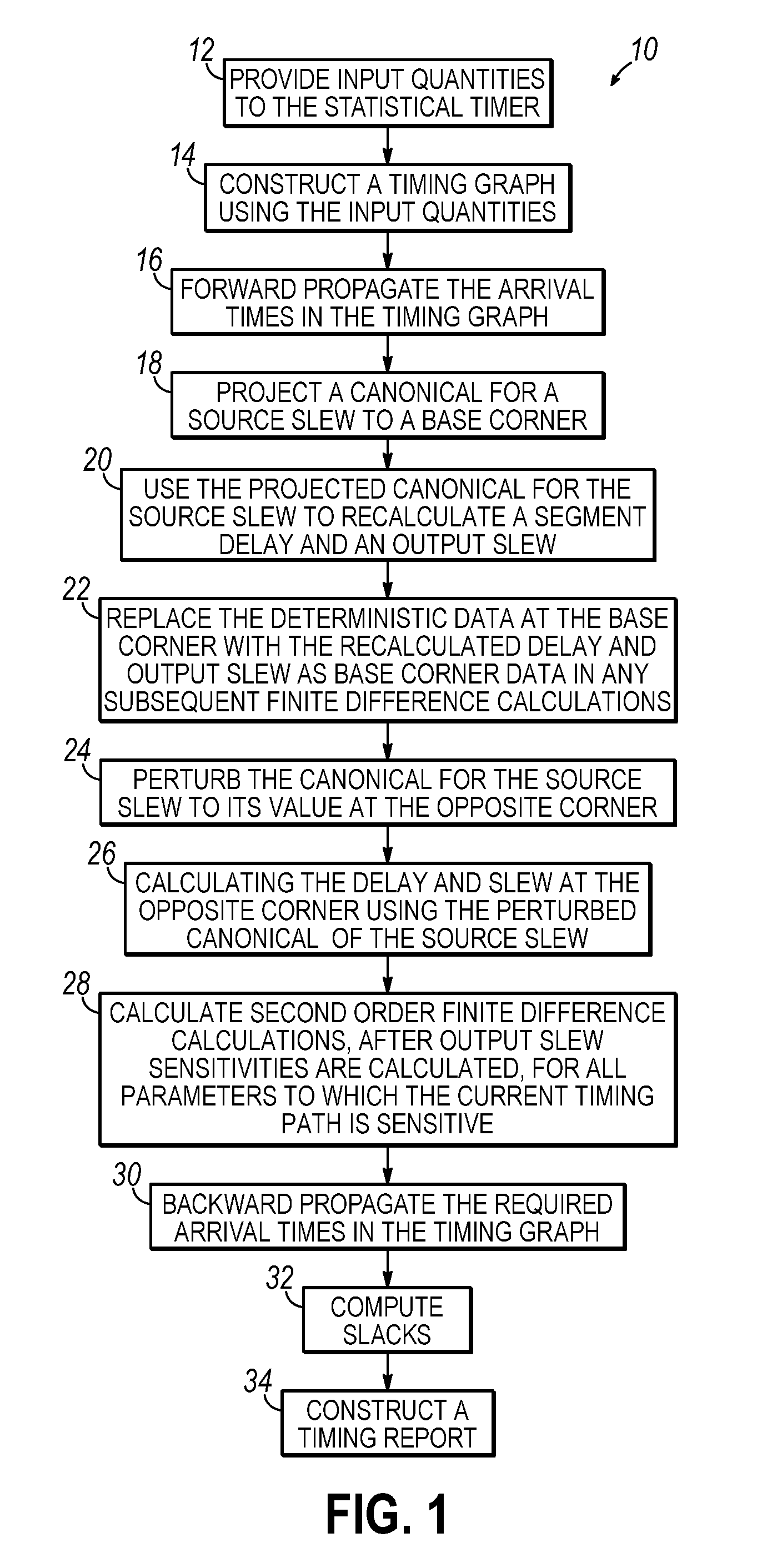
Methods for statistical slew propagation during block-based statistical static timing analysis
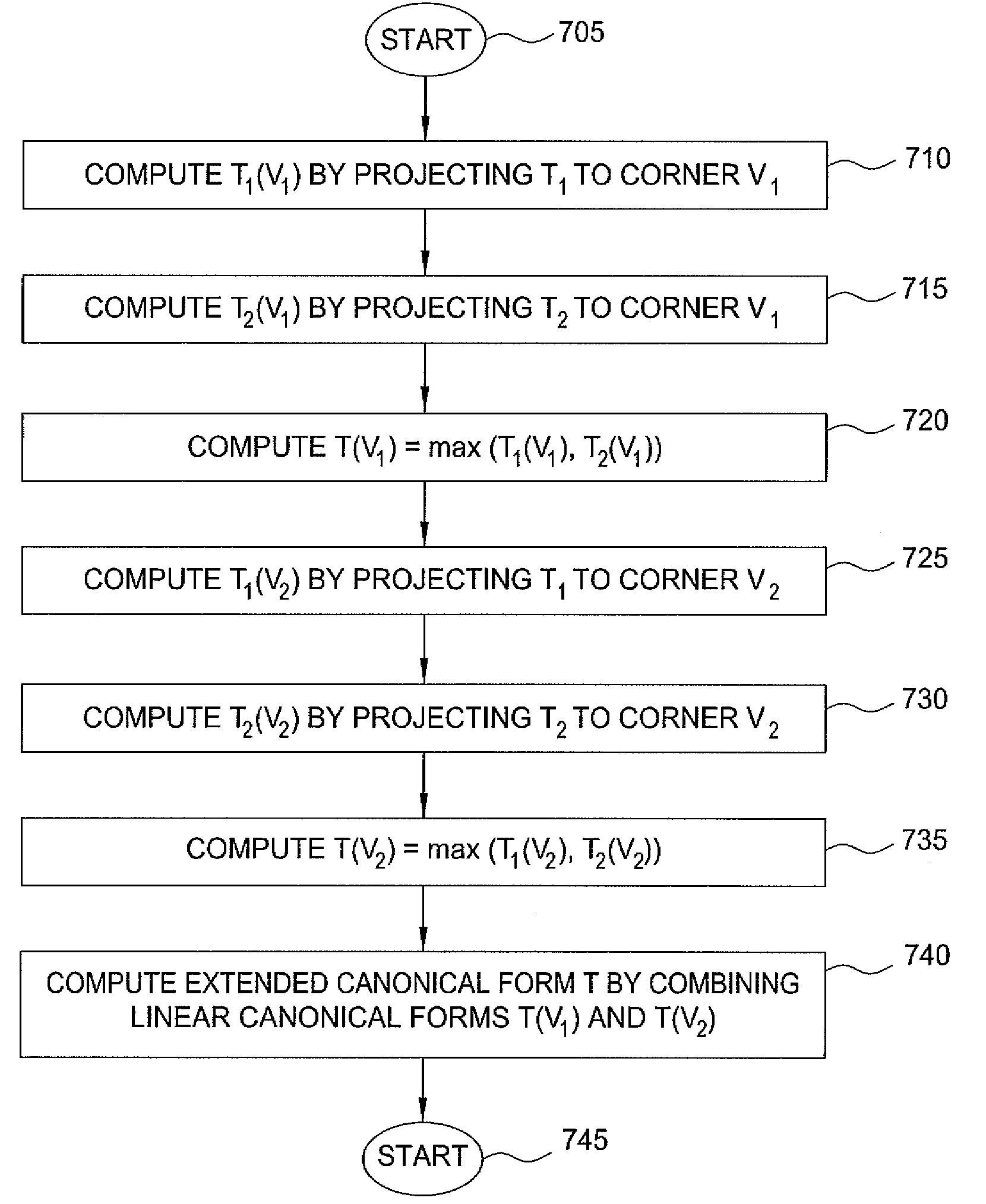
ActiveUS20090288051A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
Methods for statistical slew propagation in static statistical timing analysis. The method includes projecting a canonical approximation of an input slew over a timing path to a first corner and using the projected input slew to calculate a delay and an output slew at the first corner. The method further includes perturbing the canonical approximation of the input slew to a different corner, calculating a delay and an output slew at the different corner using the perturbed input slew canonical, and determining a sensitivity of the delay and the output slew to a plurality of parameters, simultaneous with implicit sensitivity calculations to the input slew, with finite difference calculations between the first corner and perturbed data.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
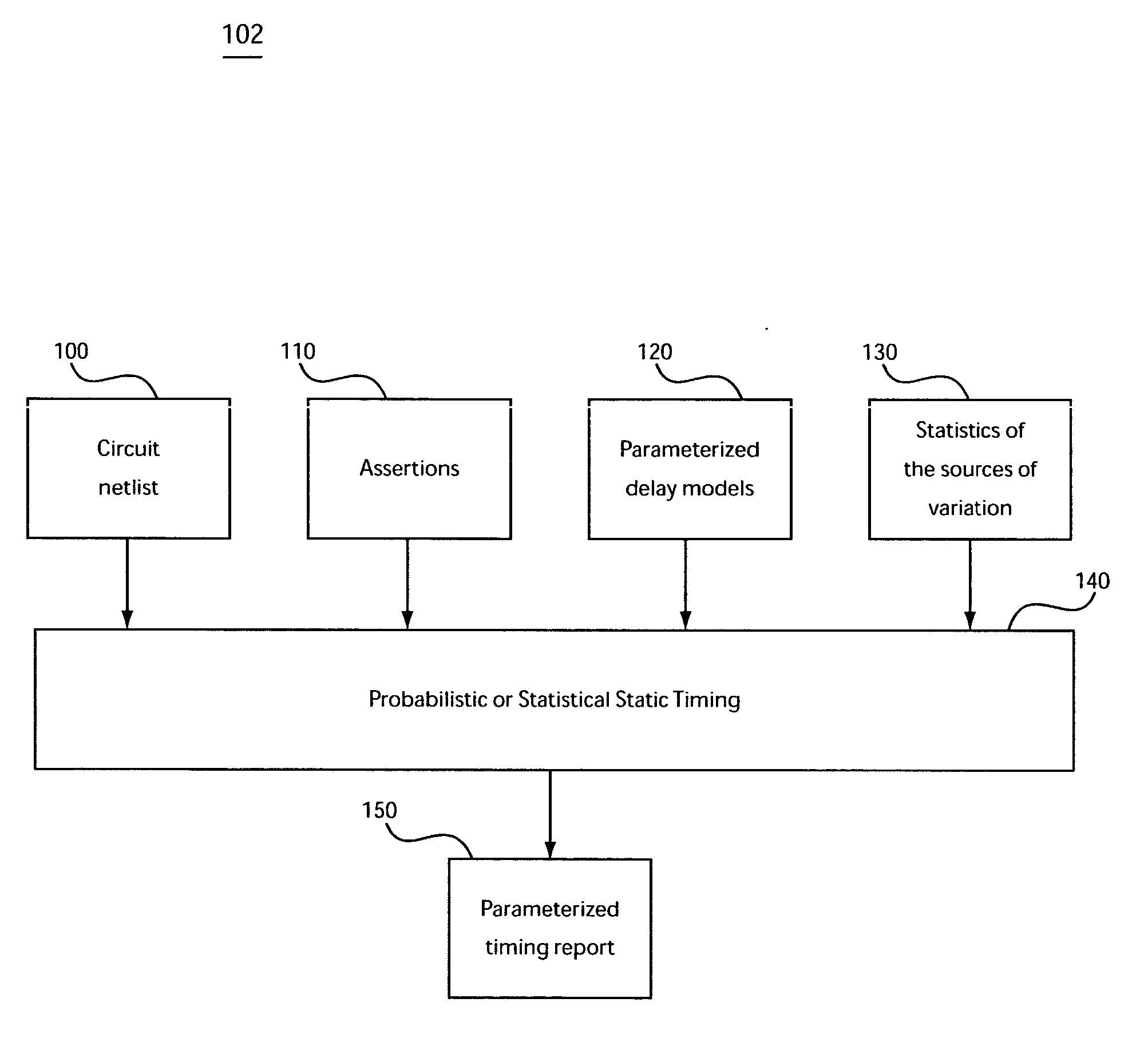
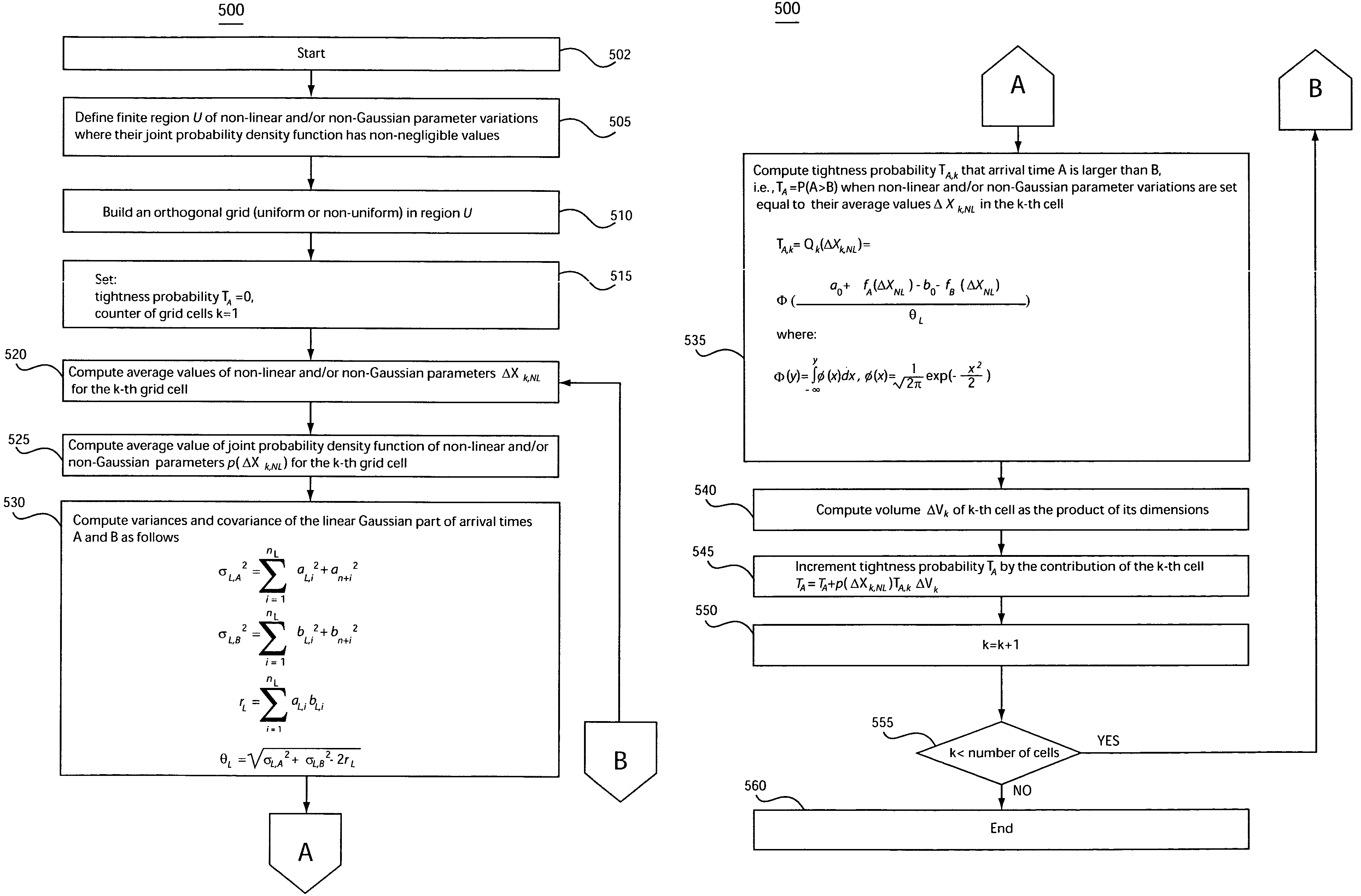
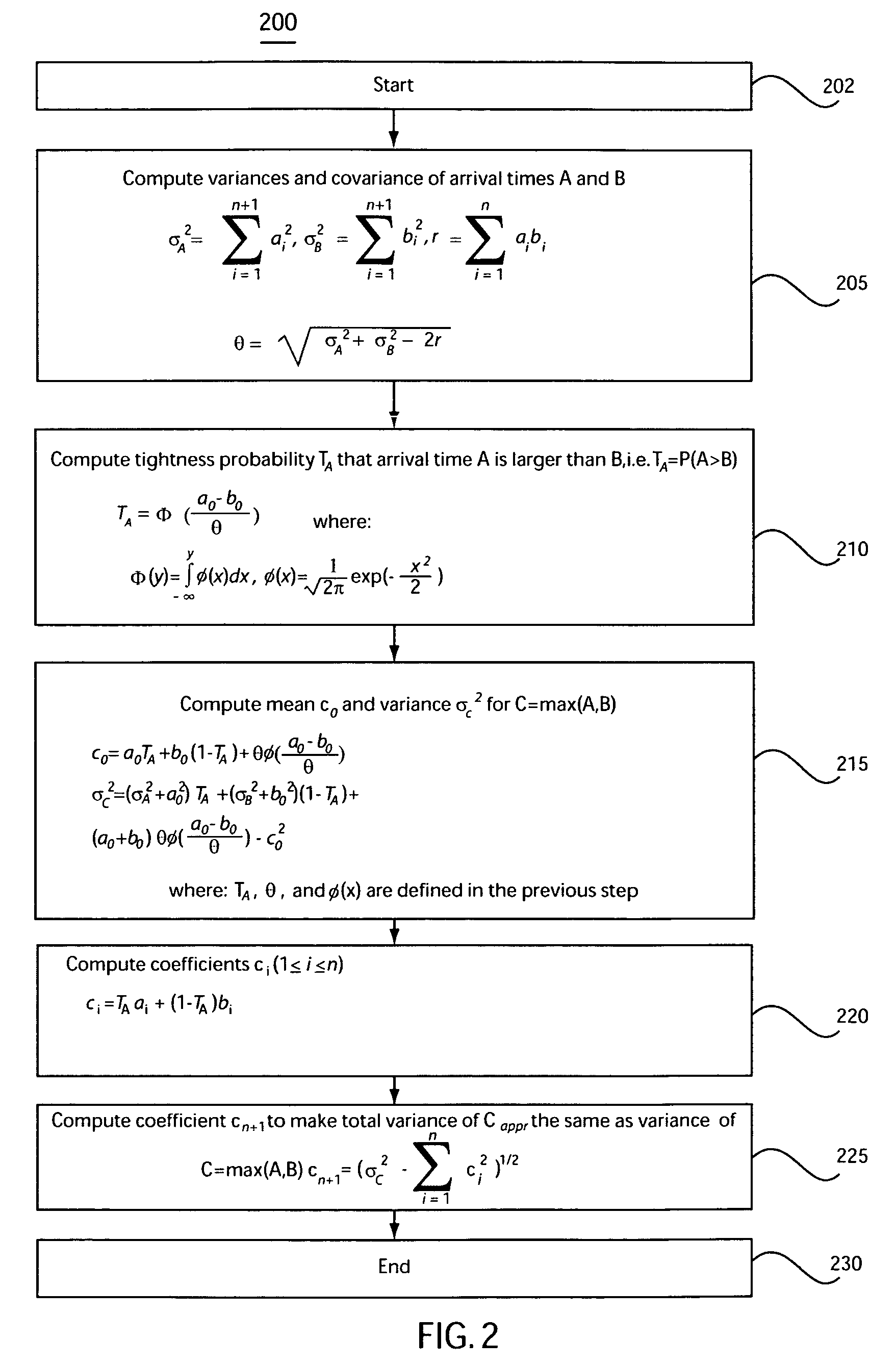
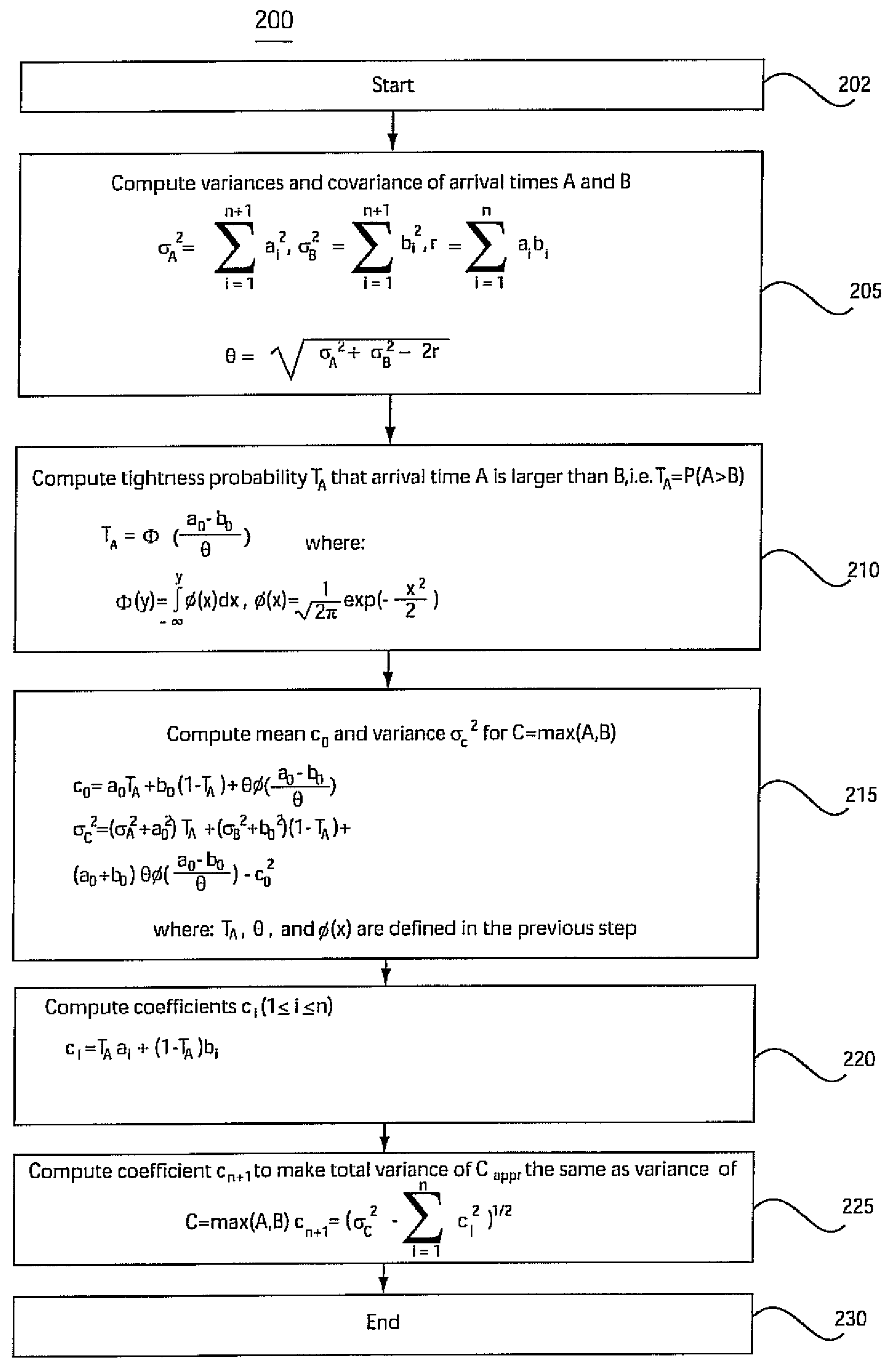
System and method for accommodating non-gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS20060085775A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer scienceStatistical static timing analysis
There is provided a system and method for statistical timing analysis of an electrical circuit. The system includes at least one parameter input, a statistical static timing analyzer, and at least one output. The at least one parameter input is for receiving parameters of the electrical circuit. At least one of the parameters has at least one of a non-Gaussian probability distribution and a non-linear delay effect. The statistical static timing analyzer is for calculating at least one of a signal arrival time and a signal required time for the electrical circuit using the at least one parameter. The at least one output is for outputting the at least one of the signal arrival time and the signal required time.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
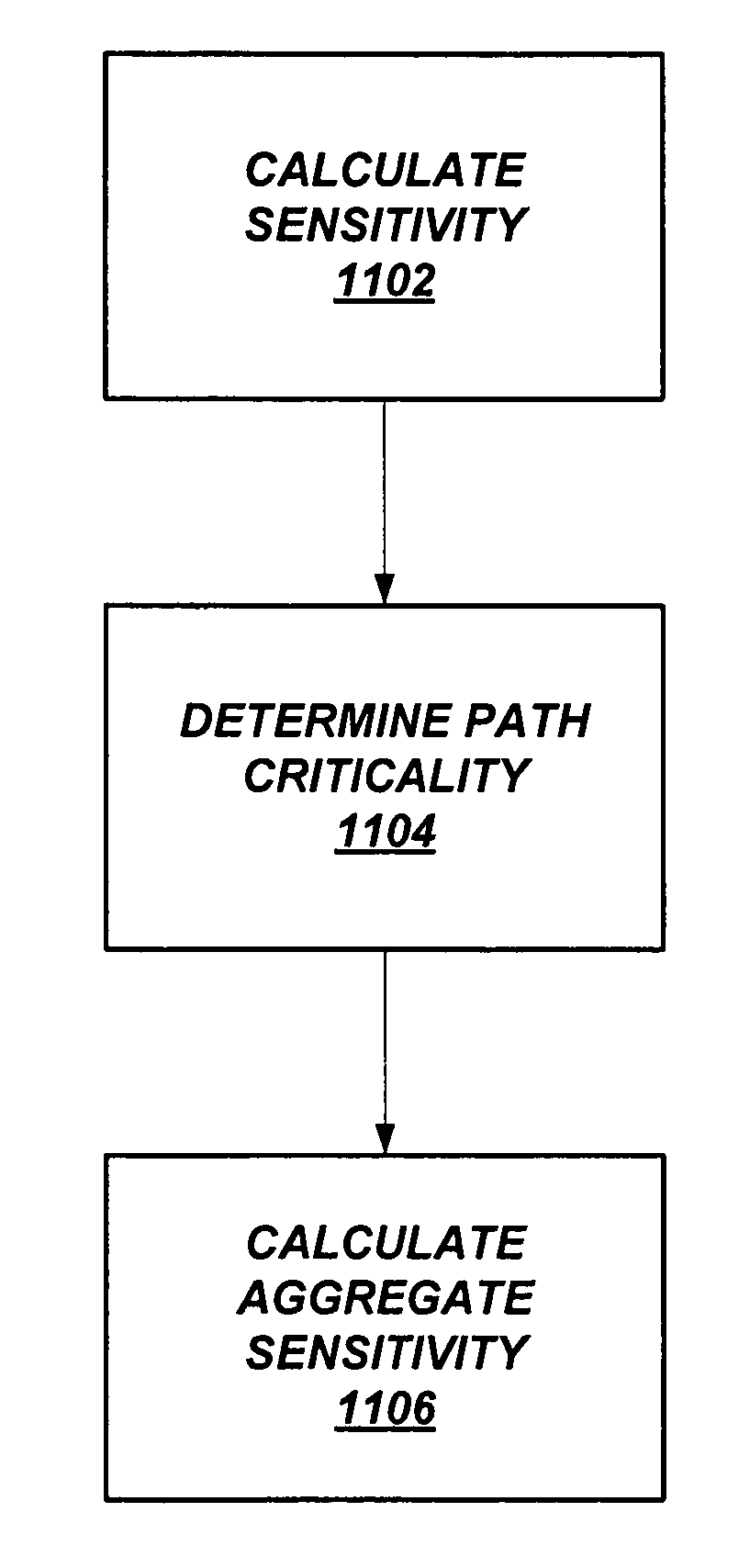
Aggregate sensitivity for statistical static timing analysis
ActiveUS7458049B1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationCircuit modelingTime distribution
A system and a method are disclosed for circuit analysis. A circuit modeling system calculates sensitivities of gates for statistical static timing analysis of a circuit. Timing distribution sensitivities of gates and correlations between the sensitivities are determined. A Monte Carlo simulation is run using the sensitivities to determine timing distribution of paths and determine probabilities of paths being the critical path. Aggregate sensitivities for cells are also determined.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and method for accommodating non-Gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS7293248B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationArrival timeComputer science
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Clock deviation arrangement method driven by production yield under technique parametric variation
InactiveCN101038602AClear and precise constraintsImprove yieldSpecial data processing applicationsArrival timeStatistical static timing analysis
The invention belongs to the IC technique field, particularly to a yield-driven clock skewing arrangement method, which comprises the steps of: setting up a statistic timing sequence restriction diagram according to the statistic result of static time series analysis, searching the key ring on the restriction diagram, redistributing the safety allowance, compacting the key ring into a over-point, updating the weight mean of the correspondent edge, inserting the relation between the key points and the compacted over-points in to a relation tree, repeating till only one over-point is left or the number of the edge is 0, traversing the tree, computing the true clock arrival time of all the leaf nodes for representing the trigger to obtain the clock skewing between the timing sequence adjacent trigger. The method takes into account of the uncertainty of the signal delay, thereby the yield of the chip will be improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Sensitivity-based complex statistical modeling for random on-chip variation
ActiveUS8407640B2Accurate calculationEasy to handleCAD circuit designProbabilistic CADGraphicsCommon path
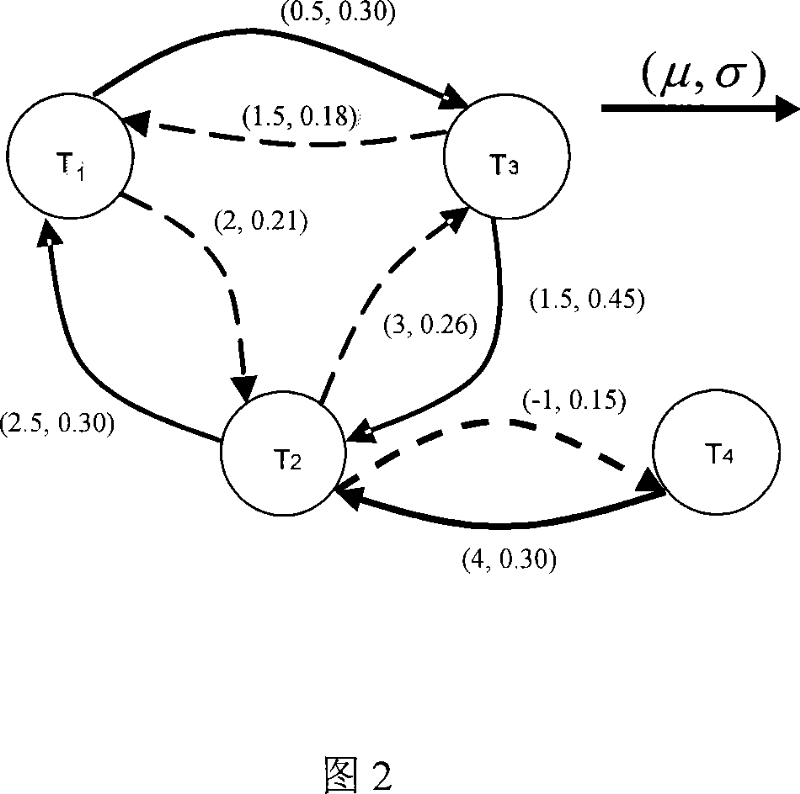
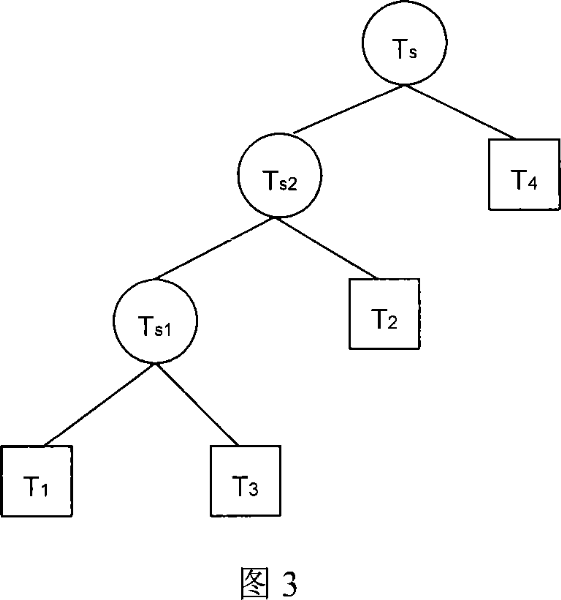
The invention provides a method for performing statistical static timing analysis using a novel on-chip variation model, referred to as Sensitivity-based Complex Statistical On-Chip Variation (SCS-OCV). SCS-OCV introduces complex variation concept to resolve the blocking technical issue of combining local random variations, enabling accurate calculation of statistical variations with correlations, such as common-path pessimism removal (CPPR). SCS-OCV proposes practical statistical min / max operations for random variations that can guarantee pessimism at nominal and targeted N-sigma corner, and extends the method to handle complex variations, enabling graph-based full arrival / required time propagation under variable compaction. SCS-OCV provides a statistical corner evaluation method for complex random variables that can transform vector-based parametric timing information to the single-value corner-based timing report, and based on the method derives equations to bridge POCV / SSTA with LOCV. This significantly reduces the learning curve and increases the usage of the technology, being more easily adopted by the industry.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
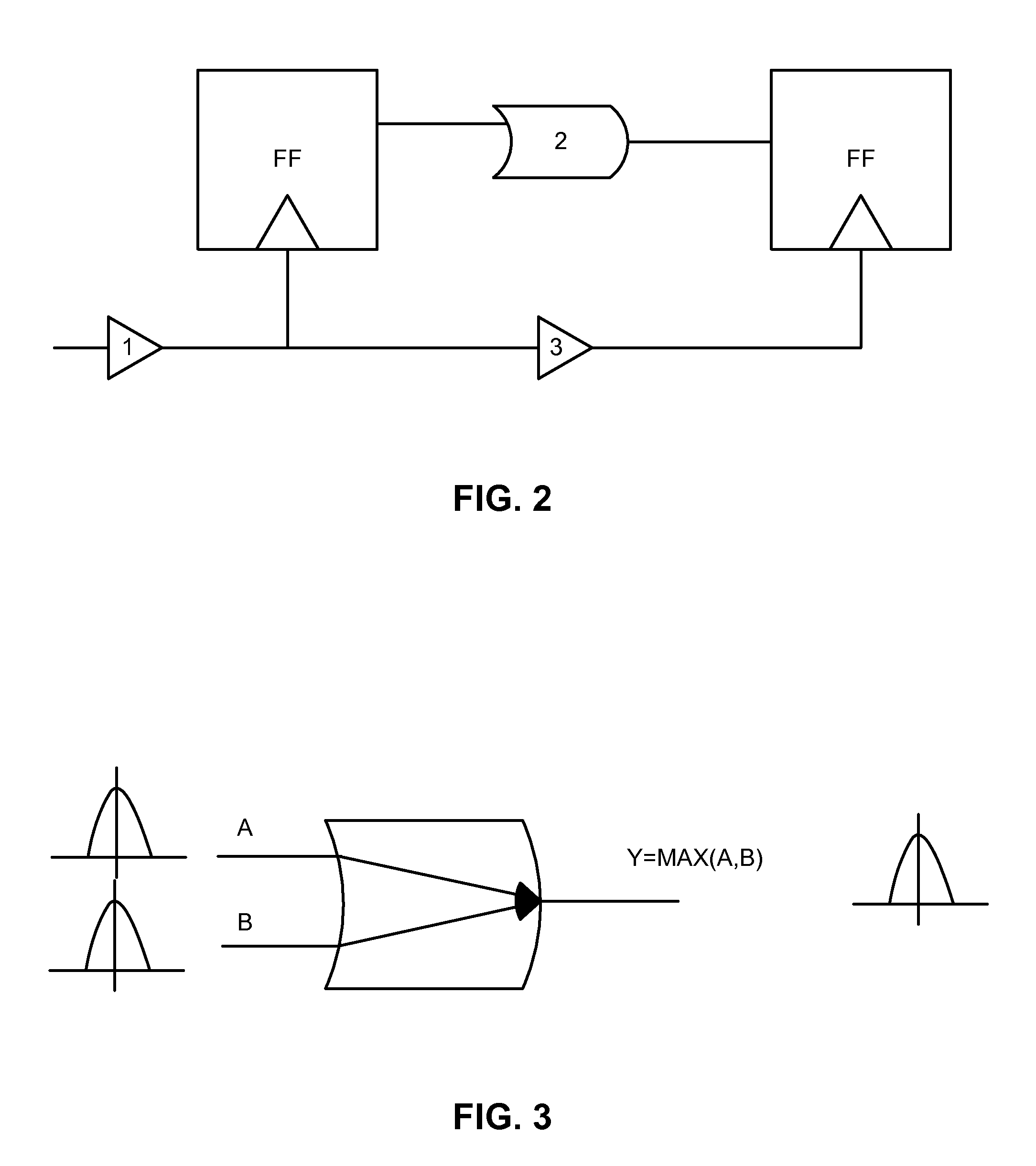
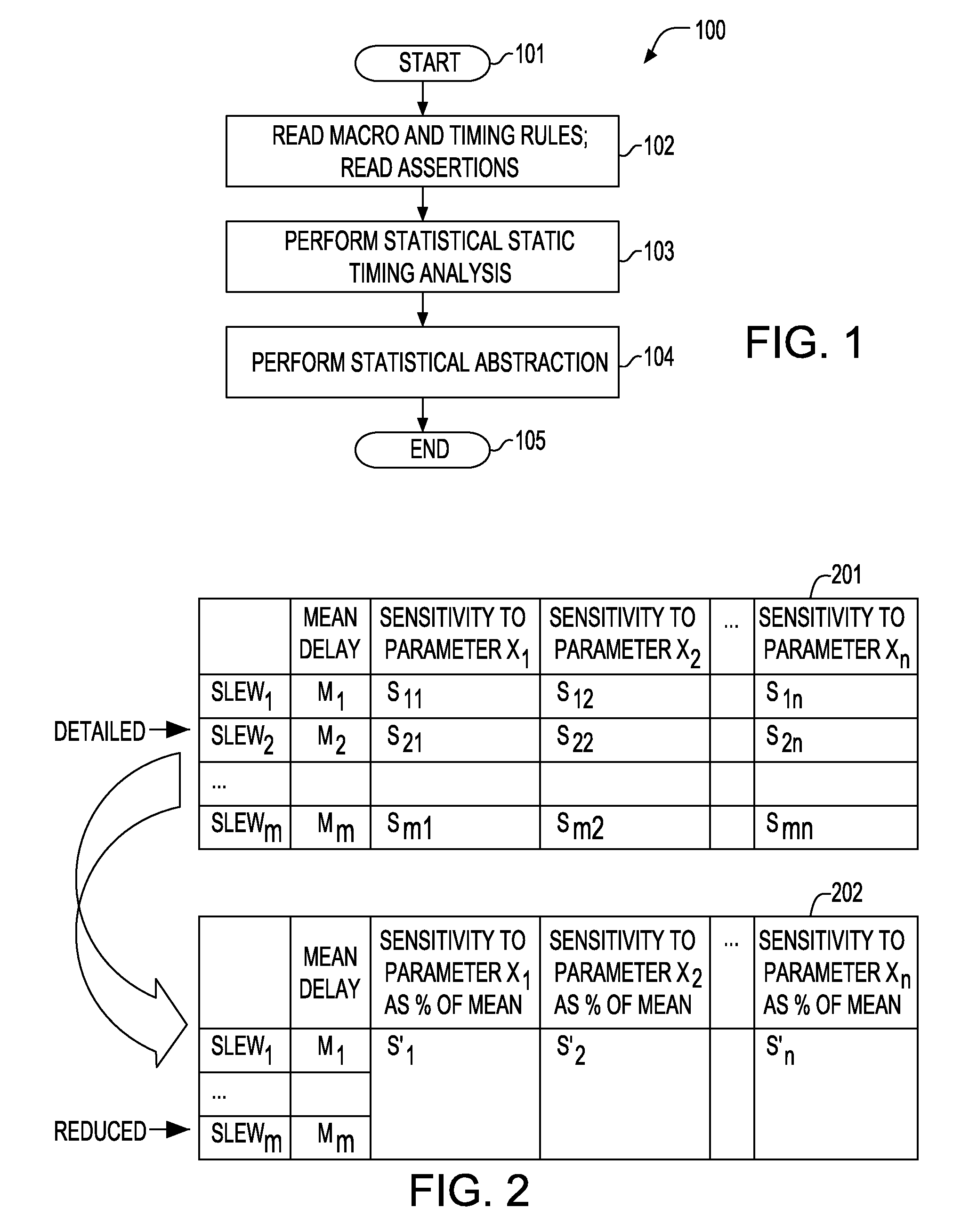
Method of Performing Statistical Timing Abstraction for Hierarchical Timing Analysis of VLSI circuits
ActiveUS20100211922A1Simpler statistical timing modelFaster yet accurate analysisComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
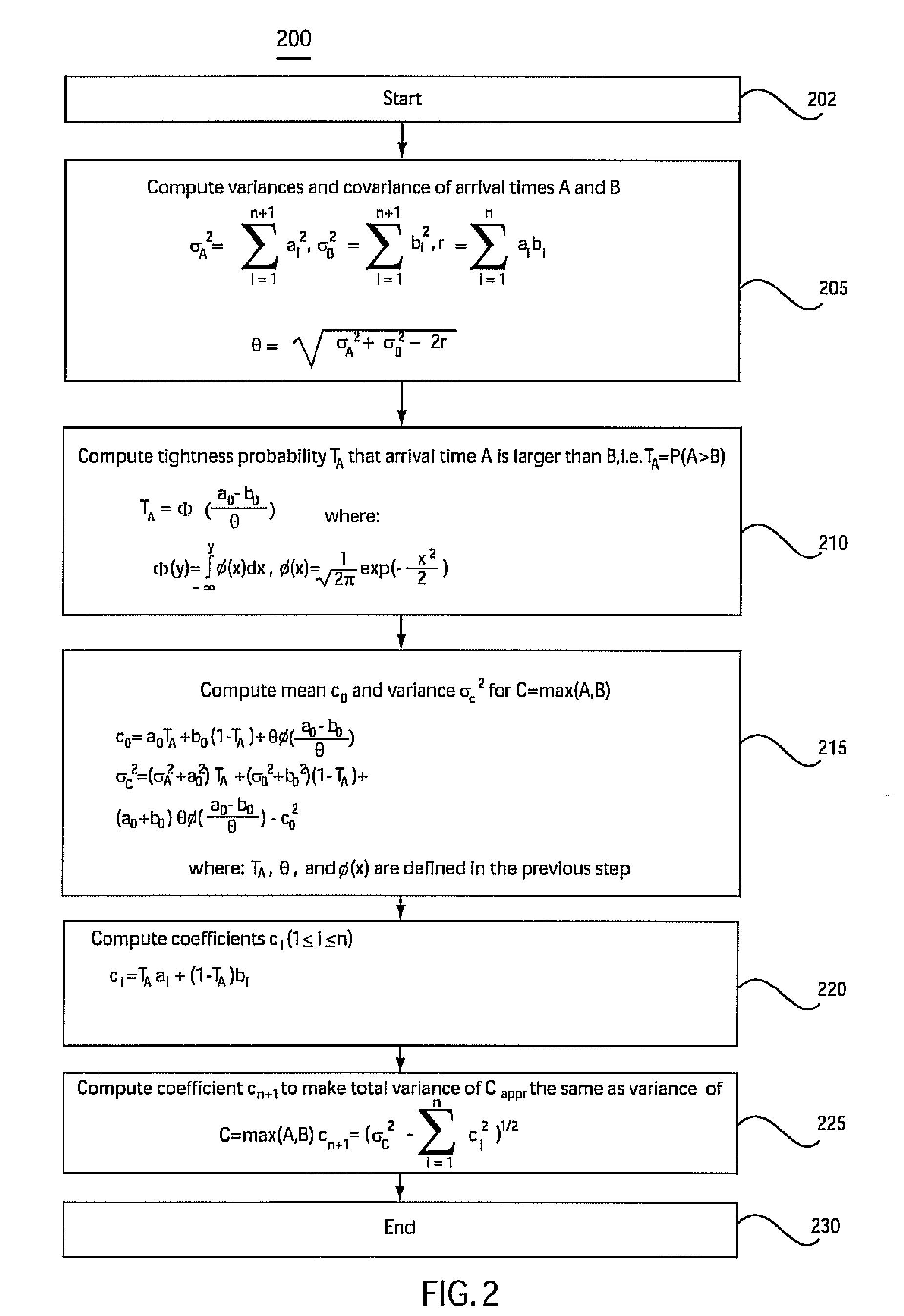
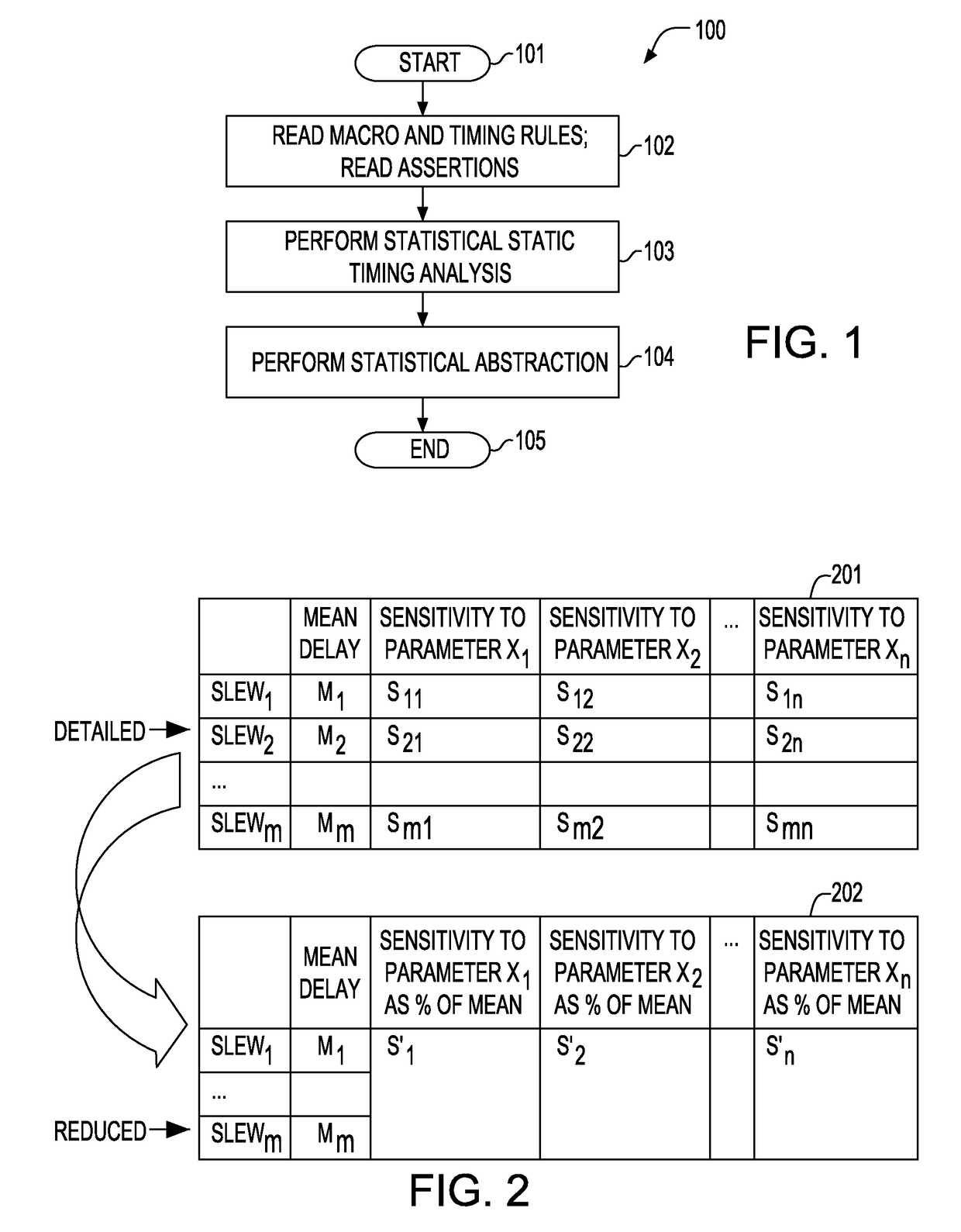
A method for performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of an integrated circuit (IC) chip design by abstracting one or more macros of the design. The method includes performing a statistical static timing analysis of at least one macro; performing a statistical abstraction of the macro to obtain a statistical abstract model of the macro timing characteristics; applying the statistical abstract model as the timing model for each occurrence of the macro leading to a simplified IC chip design; and performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of the simplified chip design. The method achieves a context aware statistical abstraction, where a generated statistical abstract model is instantiated for each macro of the chip during statistical static timing analysis at the chip level, providing a compressed and pruned statistical timing abstraction and reducing the model-size during the statistical abstraction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Sensitivity-based complex statistical modeling for random on-chip variation
ActiveUS20120072880A1Accurate calculationEasy to handleCAD circuit designProbabilistic CADGraphicsCommon path
The invention provides a method for performing statistical static timing analysis using a novel on-chip variation model, referred to as Sensitivity-based Complex Statistical On-Chip Variation (SCS-OCV).SCS-OCV introduces complex variation concept to resolve the blocking technical issue of combining local random variations, enabling accurate calculation of statistical variations with correlations, such as common-path pessimism removal (CPPR).SCS-OCV proposes practical statistical min / max operations for random variations that can guarantee pessimism at nominal and targeted N-sigma corner, and extends the method to handle complex variations, enabling graph-based full arrival / required time propagation under variable compaction.SCS-OCV provides a statistical corner evaluation method for complex random variables that can transform vector-based parametric timing information to the single-value corner-based timing report, and based on the method derives equations to bridge POCV / SSTA with LOCV. This significantly reduces the learning curve and increases the usage of the technology, being more easily adopted by the industry.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and method for accommodating non-gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS20070234256A1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designArrival timeTHD analyzer
There is provided a system and method for statistical timing analysis and optimization of an electrical circuit having two or more digital elements. The system includes at least one parameter input and a statistical static timing analyzer and electrical circuit optimizer. The at least one parameter input is for receiving parameters of the electrical circuit. At least one of the parameters has at least one of a non-Gaussian probability distribution and a non-linear delay effect. The statistical static timing analyzer and electrical circuit optimizer is for calculating at least one of a signal arrival time and a signal required time for the electrical circuit using the at least one parameter and for modifying a component size of the electrical circuit to alter gate timing characteristics of the electrical circuit based upon the at least one of the signal arrival time and the signal required time.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Performing a statistical timing abstraction for a hierarchical timing analysis of VLSI circuits
ActiveUS8122404B2Simpler statistical timing modelReducing size and complexityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
A method for performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of an integrated circuit (IC) chip design by abstracting one or more macros of the design. The method includes performing a statistical static timing analysis of at least one macro; performing a statistical abstraction of the macro to obtain a statistical abstract model of the macro timing characteristics; applying the statistical abstract model as the timing model for each occurrence of the macro leading to a simplified IC chip design; and performing a hierarchical statistical timing analysis of the simplified chip design. The method achieves a context aware statistical abstraction, where a generated statistical abstract model is instantiated for each macro of the chip during statistical static timing analysis at the chip level, providing a compressed and pruned statistical timing abstraction and reducing the model-size during the statistical abstraction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
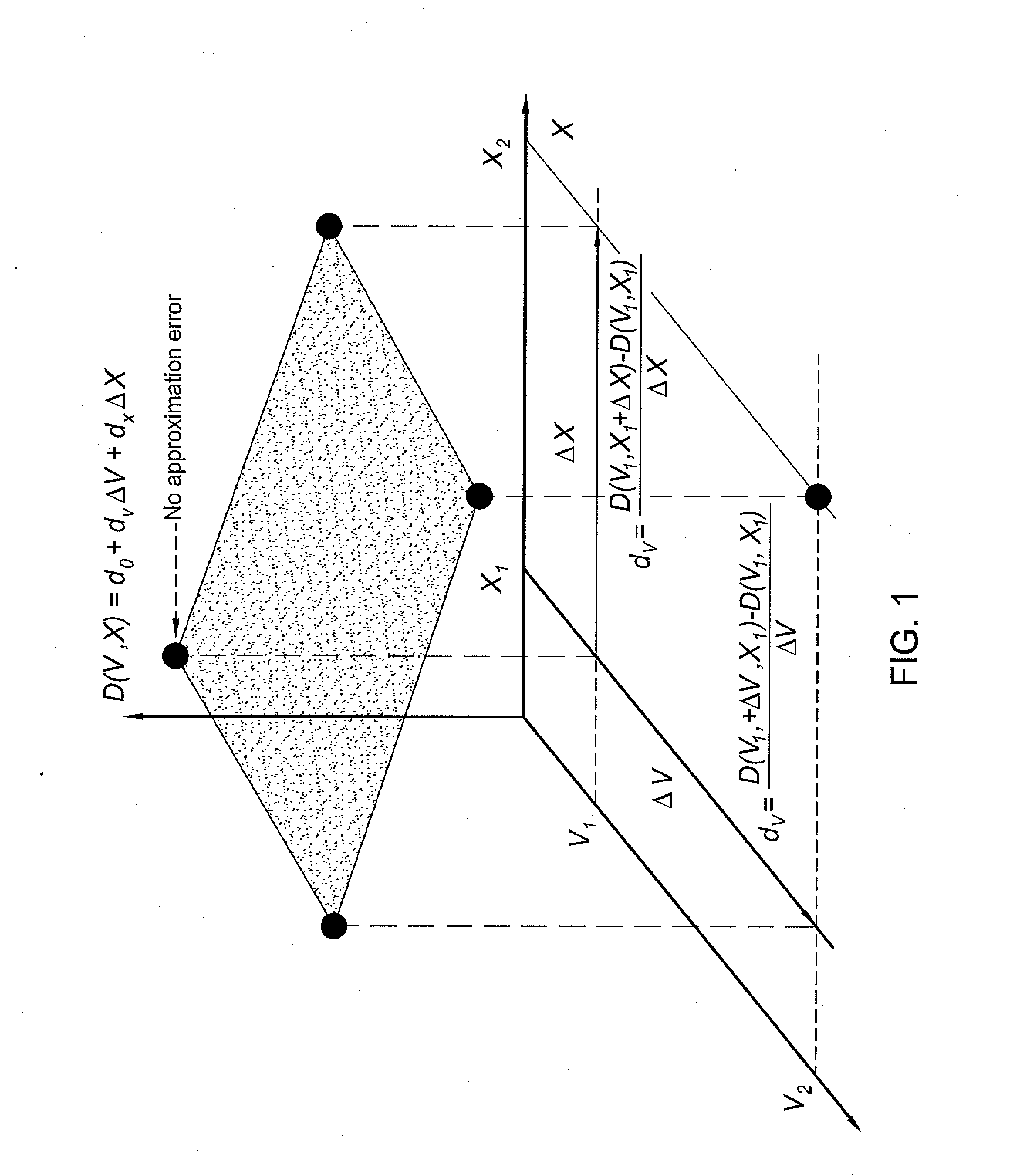
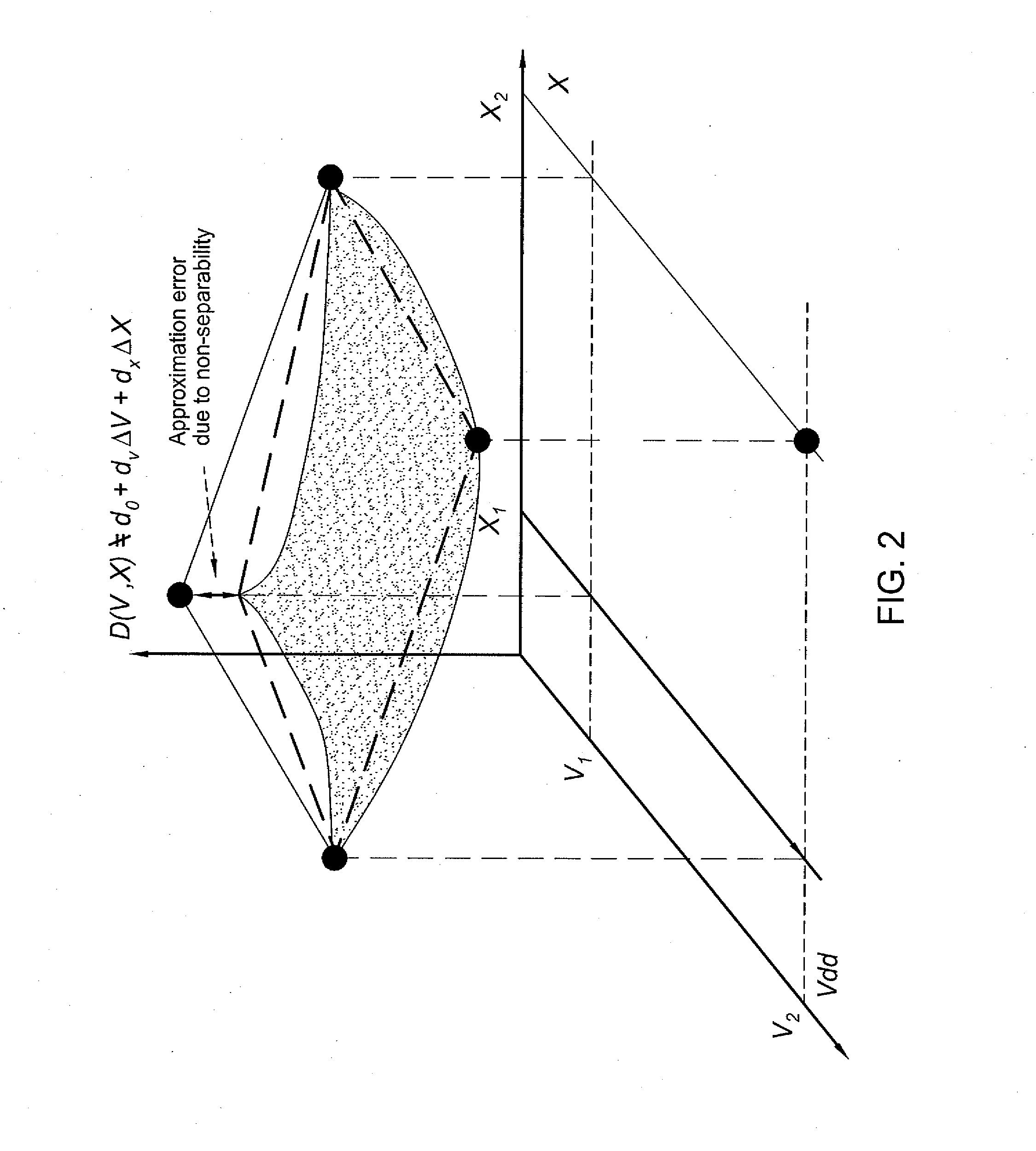
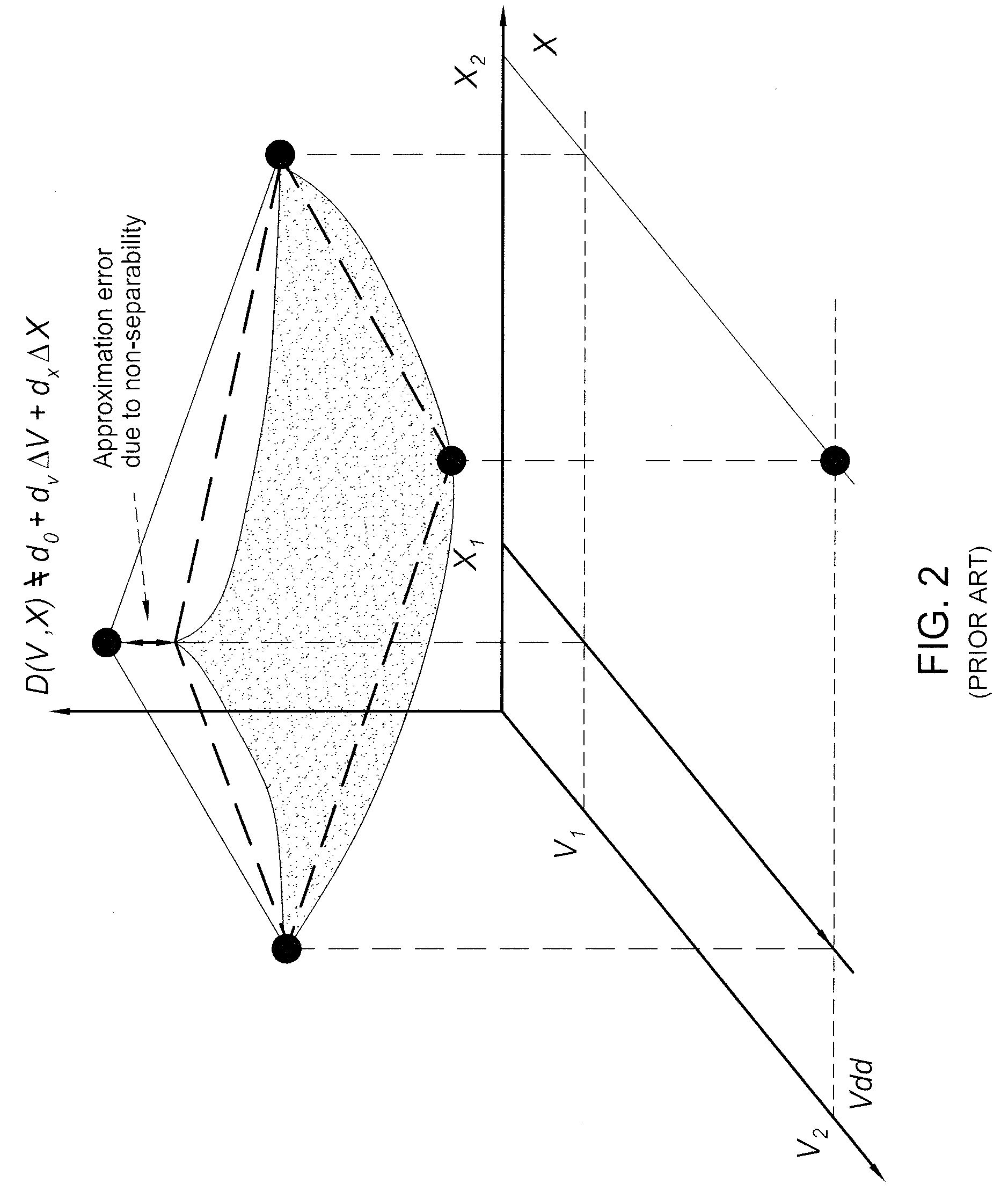
Performing statistical timing analysis with non-separable statistical and deterministic variations
InactiveUS20120117527A1Probabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationArrival timeTiming/quantity
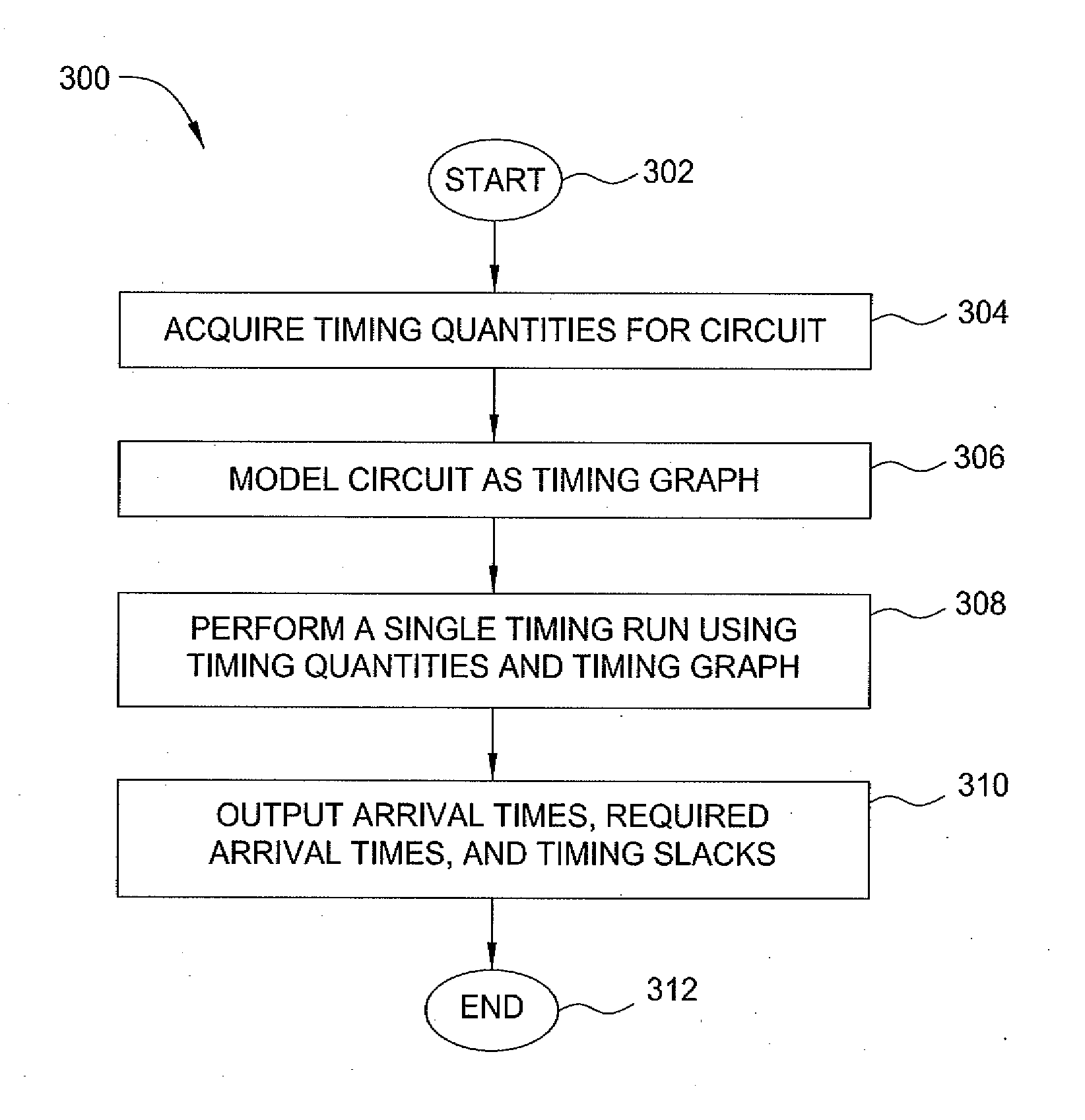
In one embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for performing statistical timing analysis with non-separable statistical and deterministic variations. One embodiment of a method for performing timing analysis of an integrated circuit chip includes computing delays and slews of chip gates and wires, wherein the delays and slews depend on at least a first process parameter that is deterministic and corner-based and a second process parameter that is statistical and non-separable with the first process parameter, and performing a single timing run using the timing quantity, wherein the single timing run produces arrival times, required arrival times, and timing slacks at outputs, latches, and circuit nodes of the integrated circuit chip. The computed arrival times, required arrival times, and timing slacks can be projected to a corner value of deterministic variations in order to obtain a statistical model of the delays and stews at the corresponding corner.
Owner:IBM CORP
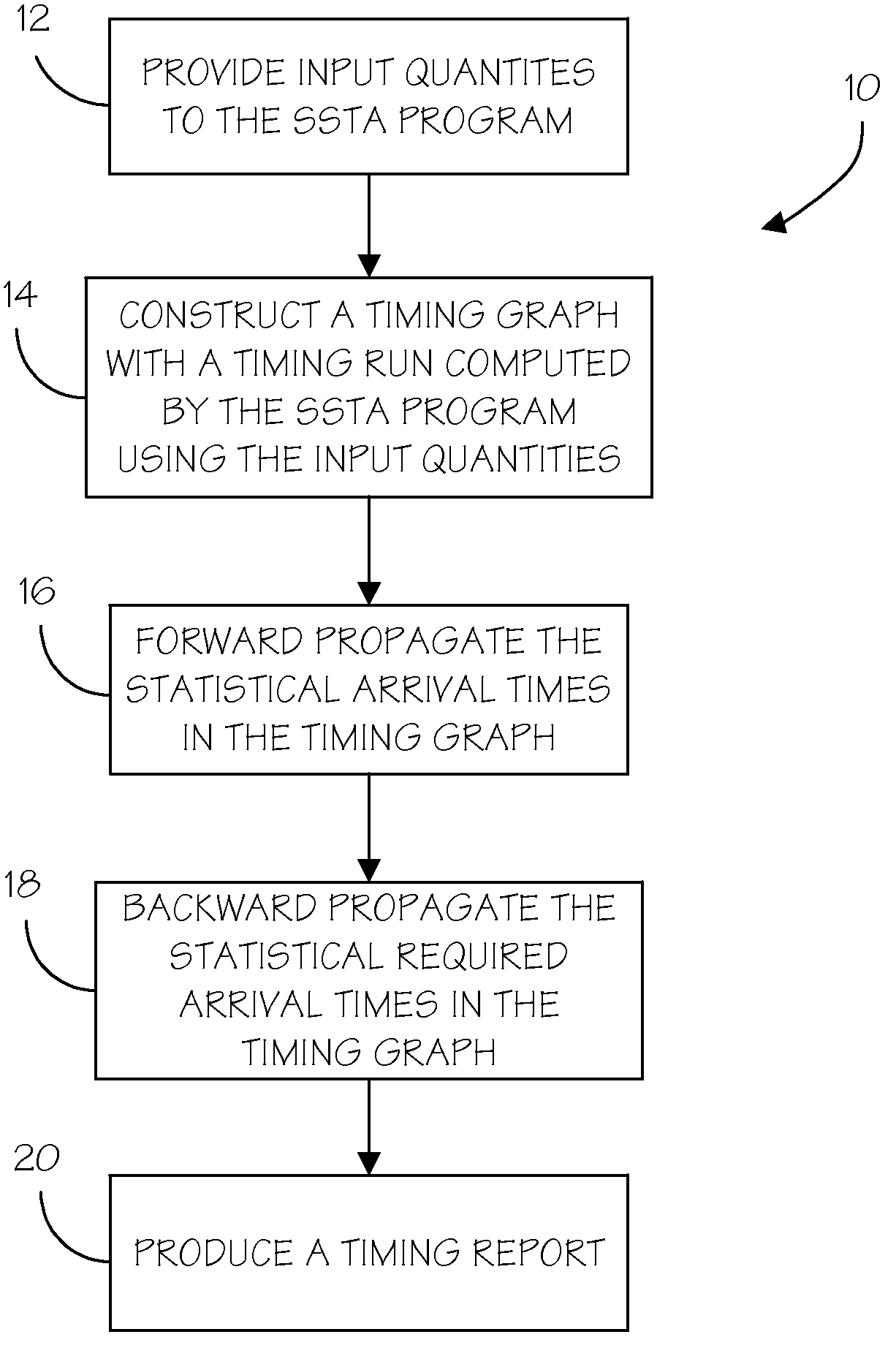
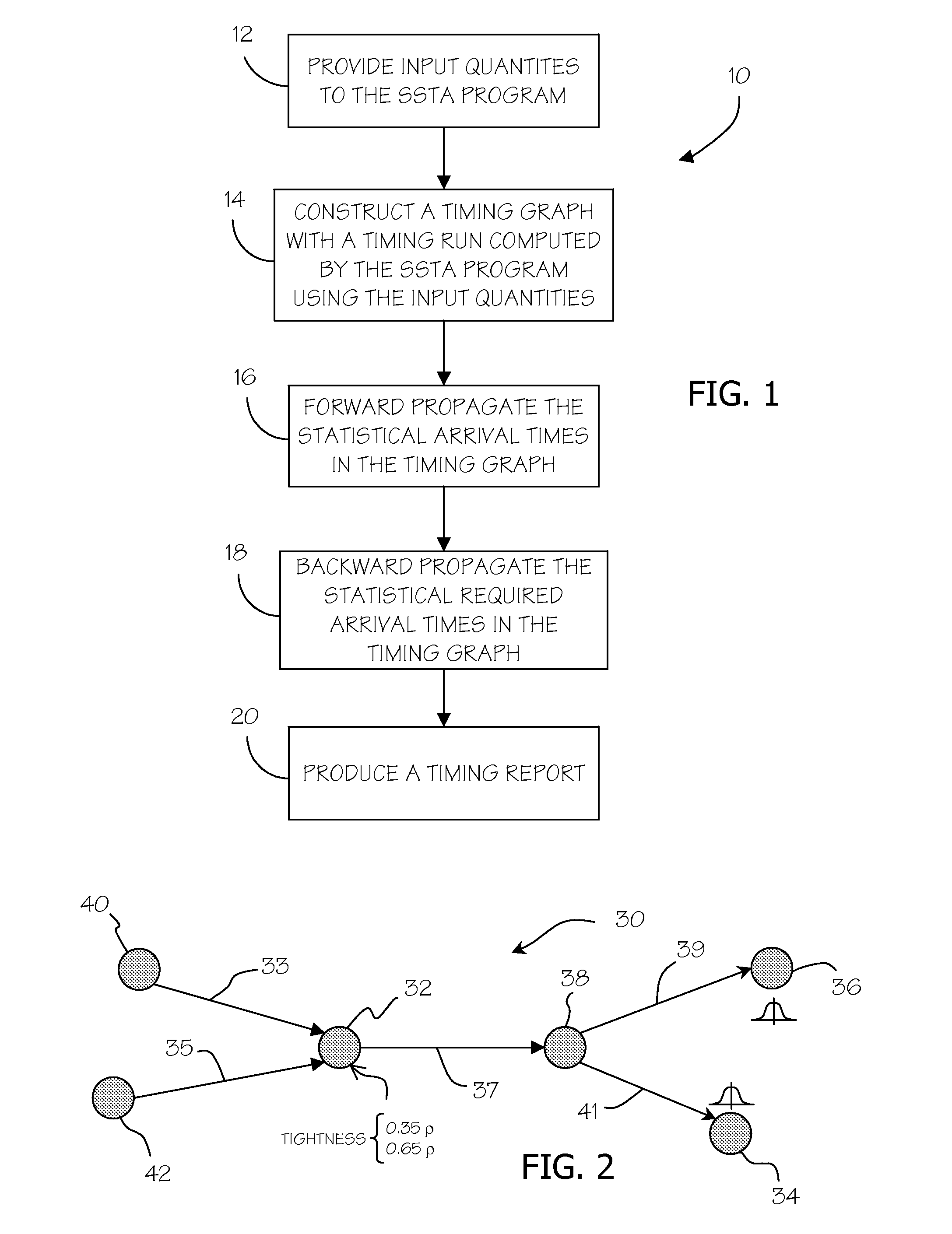
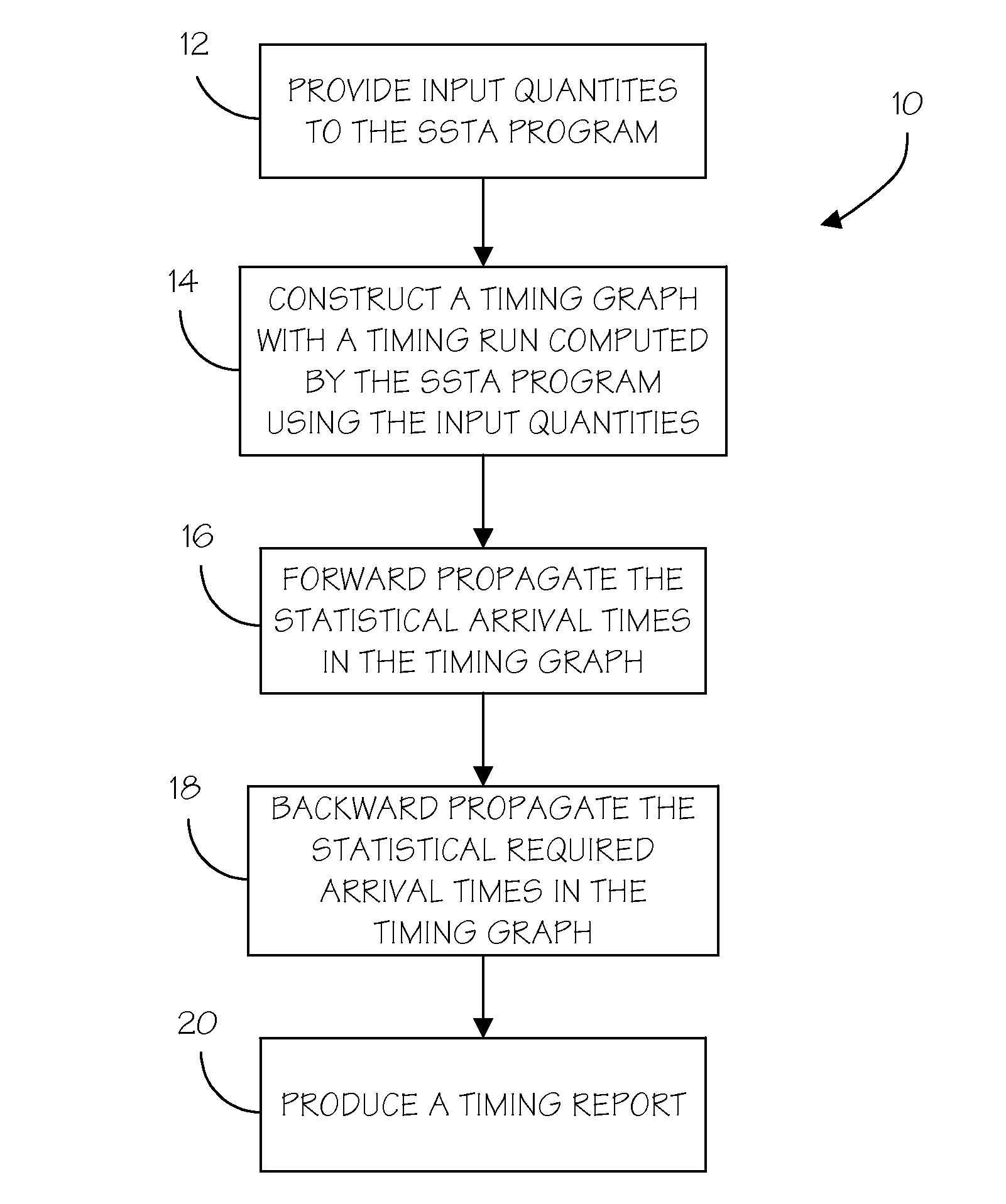
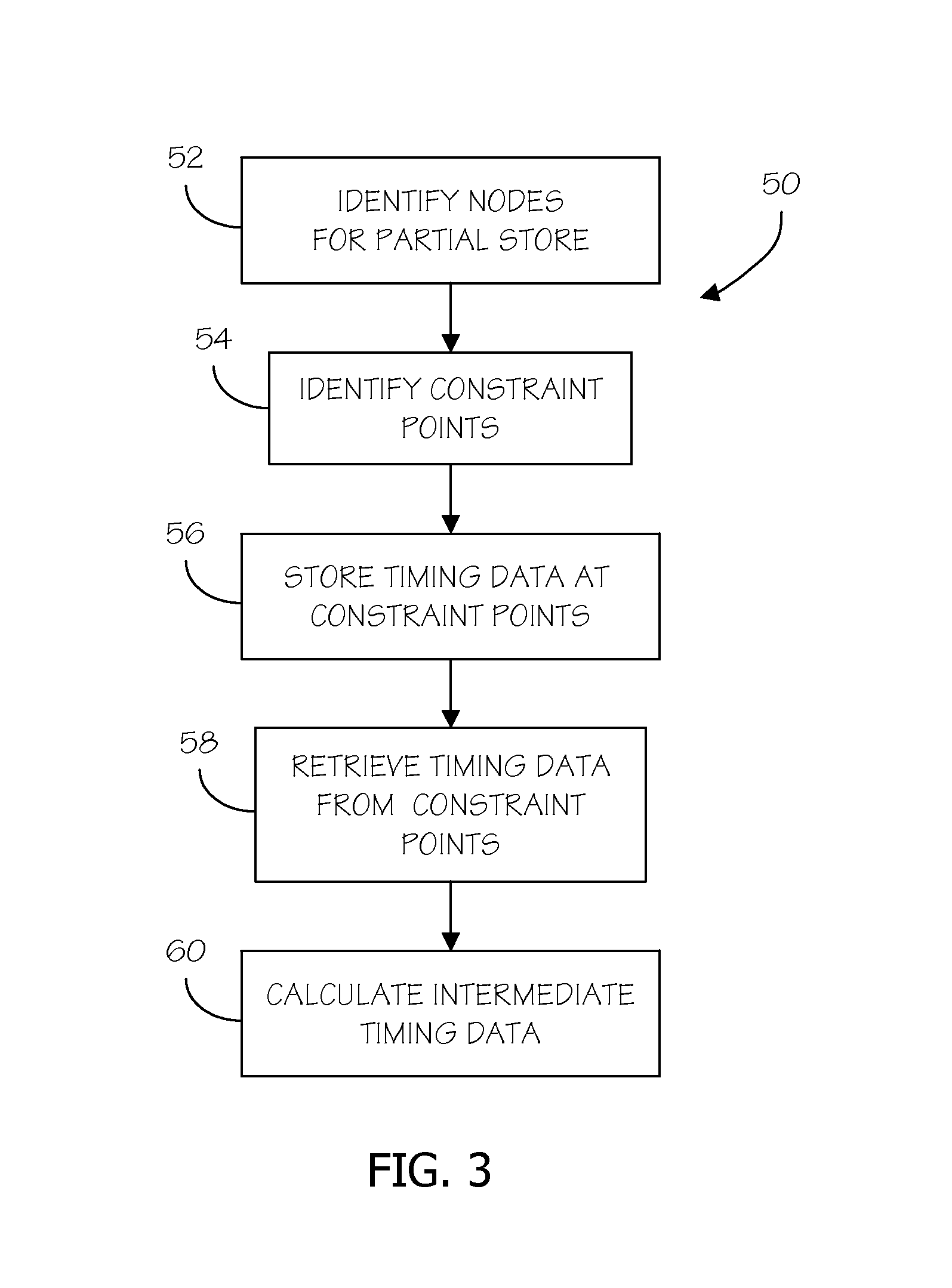
Methods for conserving memory in statistical static timing analysis
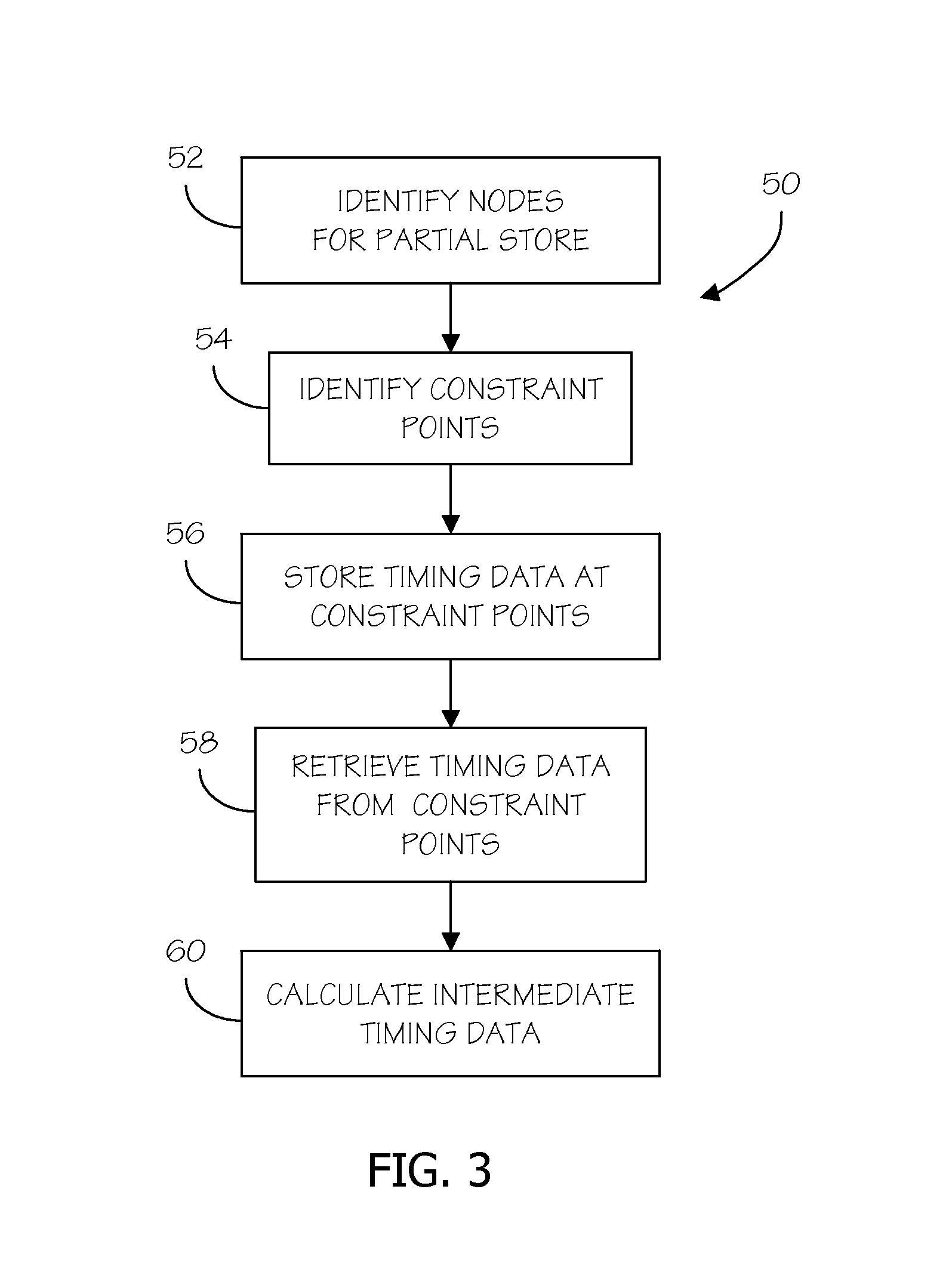
ActiveUS7849429B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisReal-time computing
A method is provided for memory conservation in statistical static timing analysis. A timing graph is created with a timing run in a statistical static timing analysis program. A plurality of nodes in the timing graph that are candidates for a partial store and constraint points are identified. Timing data is persistently stored at constraint points. The persistent timing data is retrieved from the constraint points and used to calculate intermediate timing data at the plurality of nodes during timing analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Methods for practical worst test definition and debug during block based statistical static timing analysis
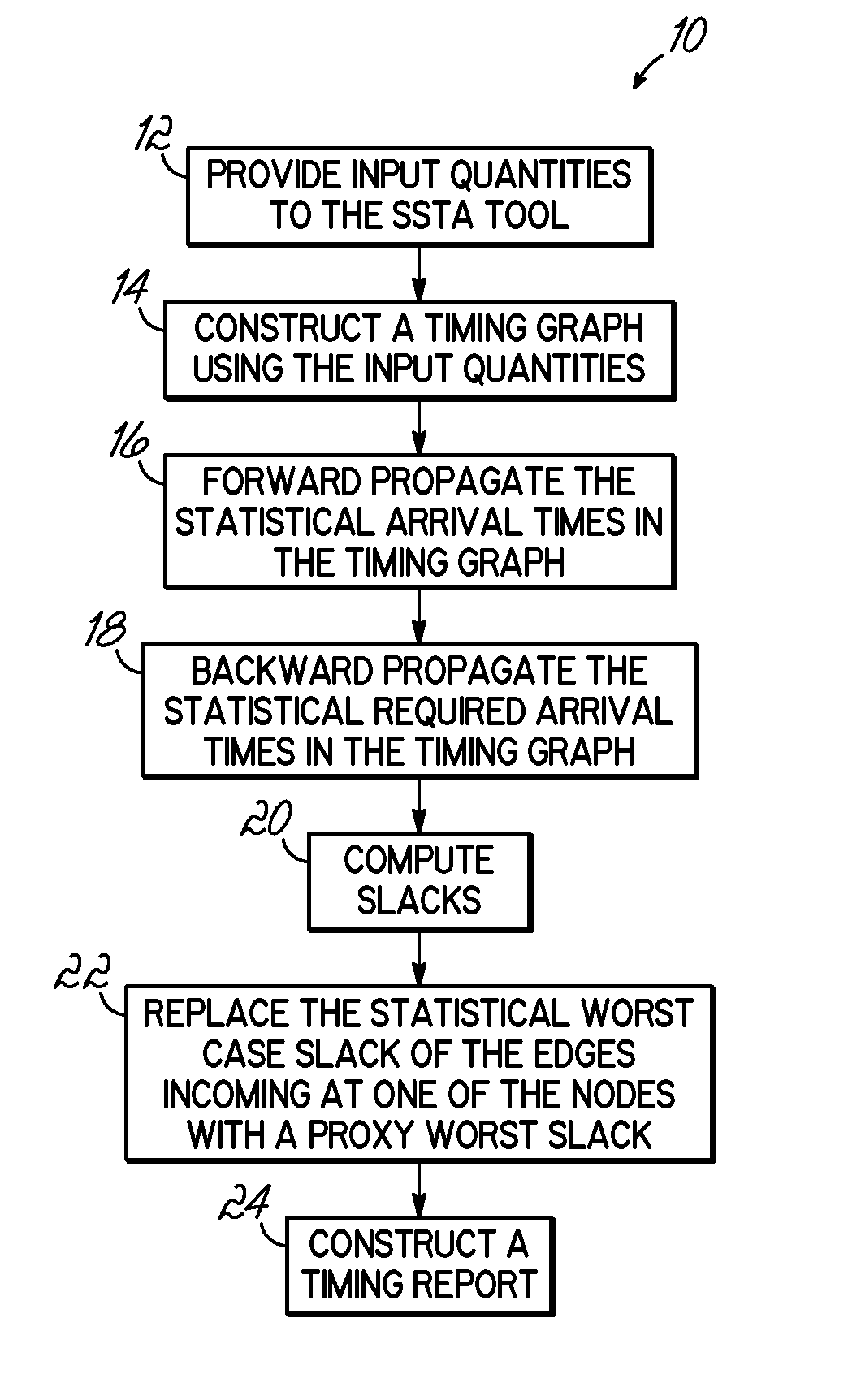
ActiveUS7873926B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
Methods for analyzing timing of an integrated circuit using block-based static statistical timing analysis and for practical worst test definition and debug. The method includes building a timing graph, determining a slack for each of the nodes in the timing graph, and identifying a statistically worst slack for at least one of the nodes. The method further includes replacing this statistically worst slack with a proxy worst slack.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Performing statistical timing analysis with non-separable statistical and deterministic variations
InactiveUS8418107B2Probabilistic CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationArrival timeTiming/quantity
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
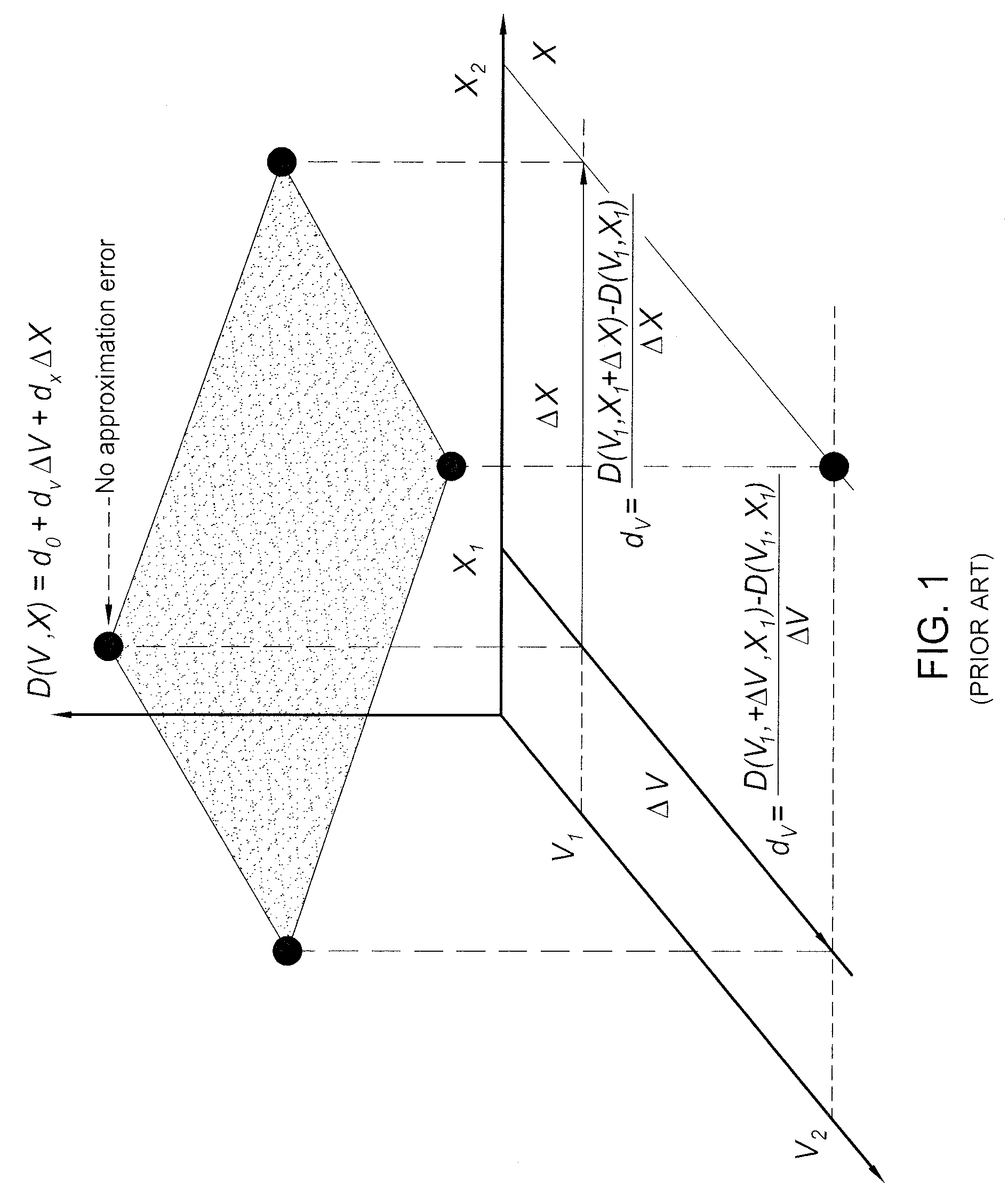
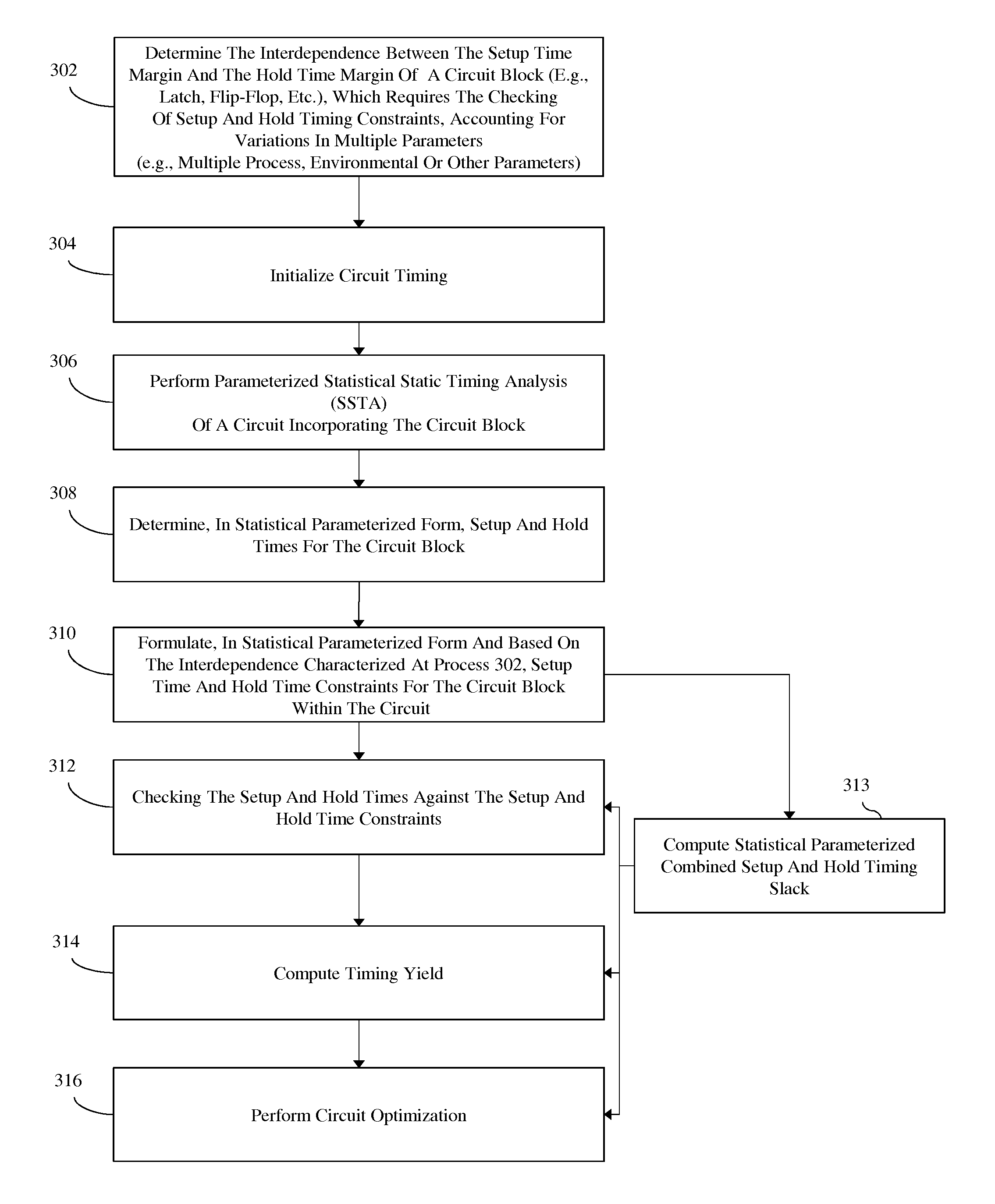
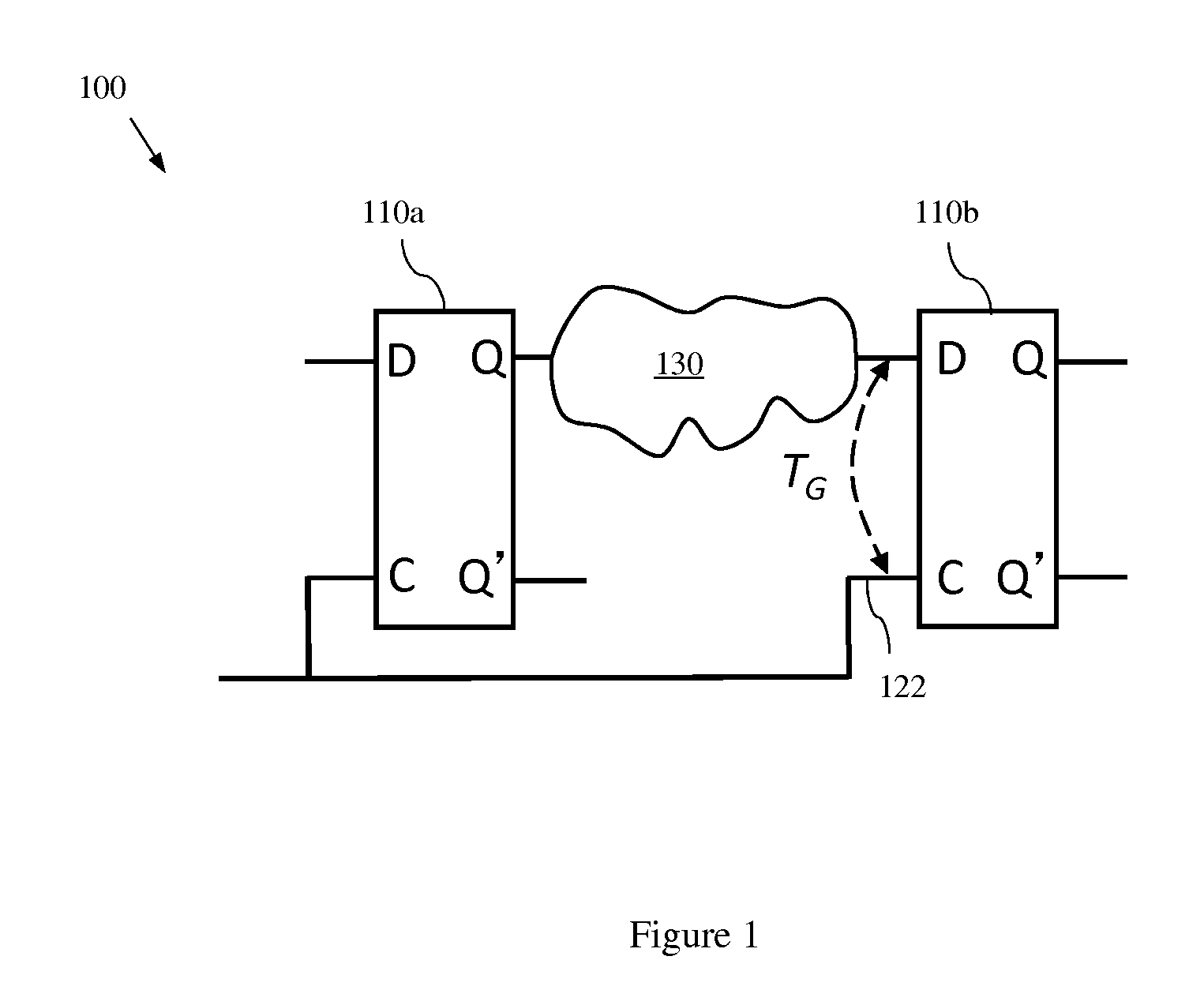
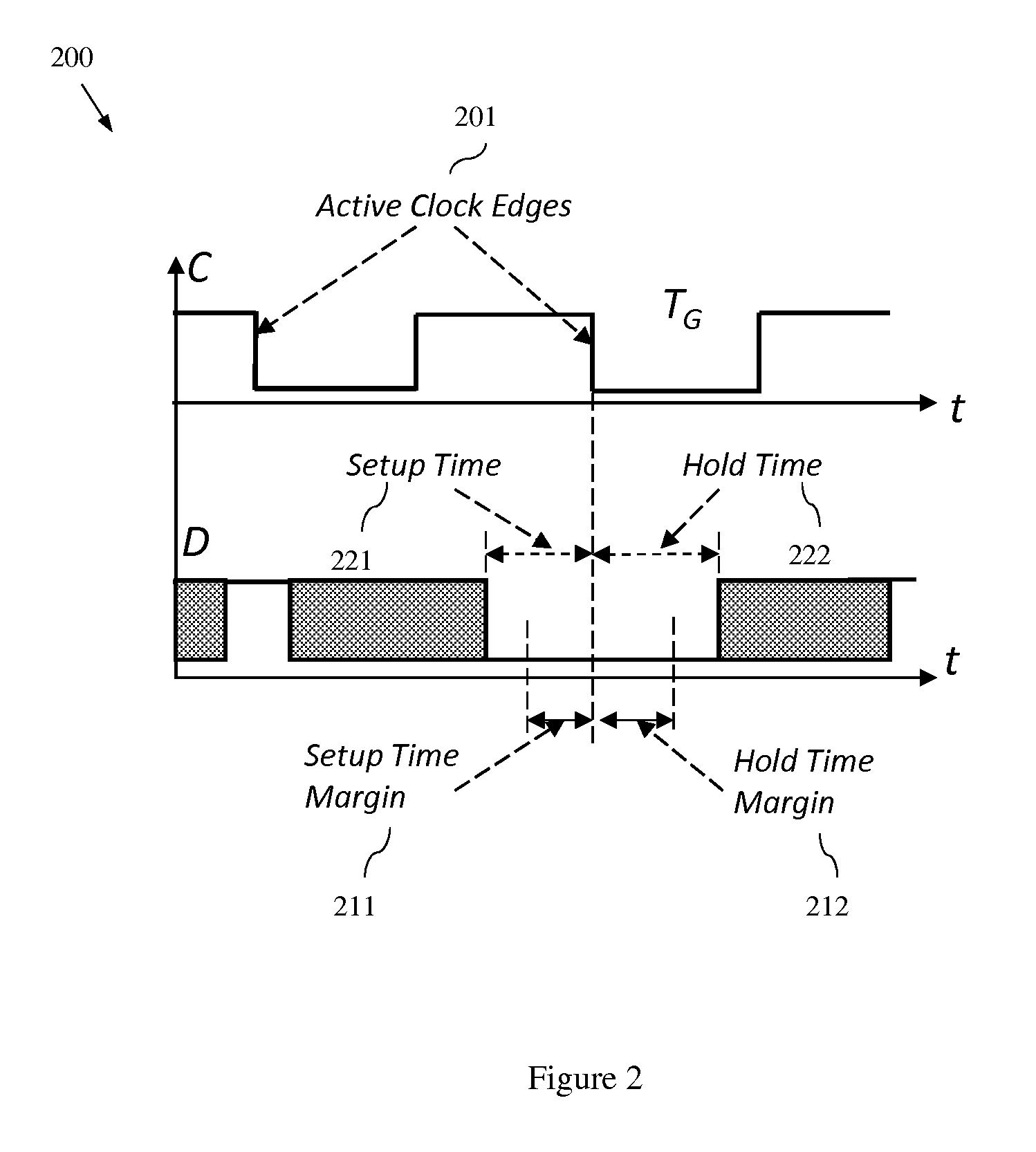
Method, system and program storage device for performing a parameterized statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) of an integrated circuit taking into account setup and hold margin interdependence
InactiveUS8468483B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectricityAlgorithm
In embodiments of a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) method, system and program storage device, the interdependence between the setup time and hold time margins of a circuit block (e.g., a latch, flip-flop, etc., which requires the checking of setup and hold timing constraints) is determined, taking into account possible variations in multiple parameters (e.g., using a variation-aware characterizing technique). A parameterized statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) of a circuit incorporating the circuit block is performed in order to determine, in statistical parameterized form, setup and hold times for the circuit block. Based on the interdependence between the setup and hold time margins, setup and hold time constraints can be determined in statistical parameterized form. Finally, the setup and hold times determined during the SSTA can be checked against the setup and hold time constraints to determine, if the time constraints are violated or not and to what degree.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Methods for conserving memory in statistical static timing analysis
ActiveUS20090241078A1Balance costComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
A method is provided for memory conservation in statistical static timing analysis. A timing graph is created with a timing run in a statistical static timing analysis program. A plurality of nodes in the timing graph that are candidates for a partial store and constraint points are identified. Timing data is persistently stored at constraint points. The persistent timing data is retrieved from the constraint points and used to calculate intermediate timing data at the plurality of nodes during timing analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method, system and program storage device for performing a parameterized statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) of an integrated circuit taking into account setup and hold margin interdependence
InactiveUS20130104092A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectricityAlgorithm
In embodiments of a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) method, system and program storage device, the interdependence between the setup time and hold time margins of a circuit block (e.g., a latch, flip-flop, etc., which requires the checking of setup and hold timing constraints) is determined, taking into account possible variations in multiple parameters (e.g., using a variation-aware characterizing technique). A parameterized statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) of a circuit incorporating the circuit block is performed in order to determine, in statistical parameterized form, setup and hold times for the circuit block. Based on the interdependence between the setup and hold time margins, setup and hold time constraints can be determined in statistical parameterized form. Finally, the setup and hold times determined during the SSTA can be checked against the setup and hold time constraints to determine, if the time constraints are violated or not and to what degree.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
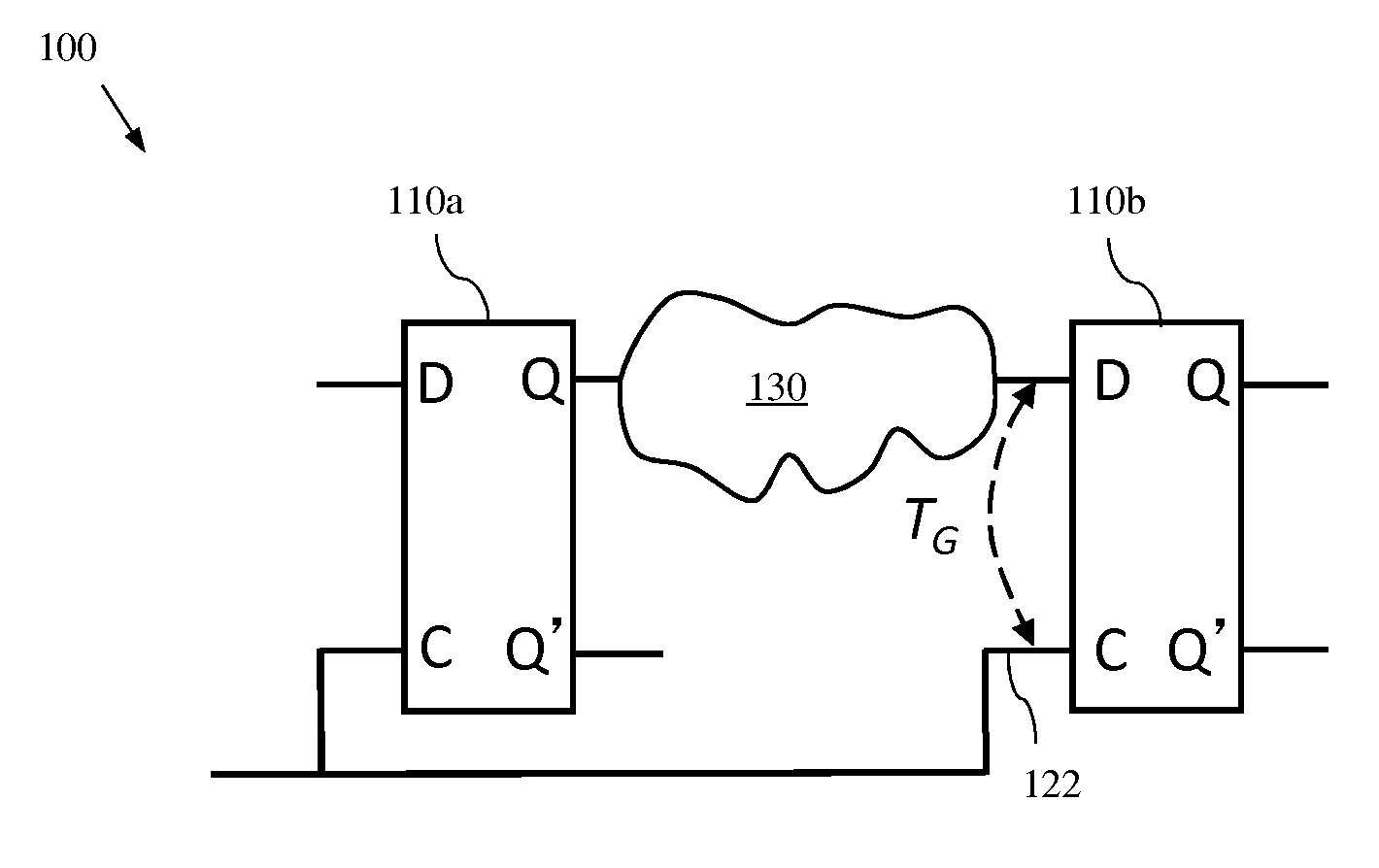
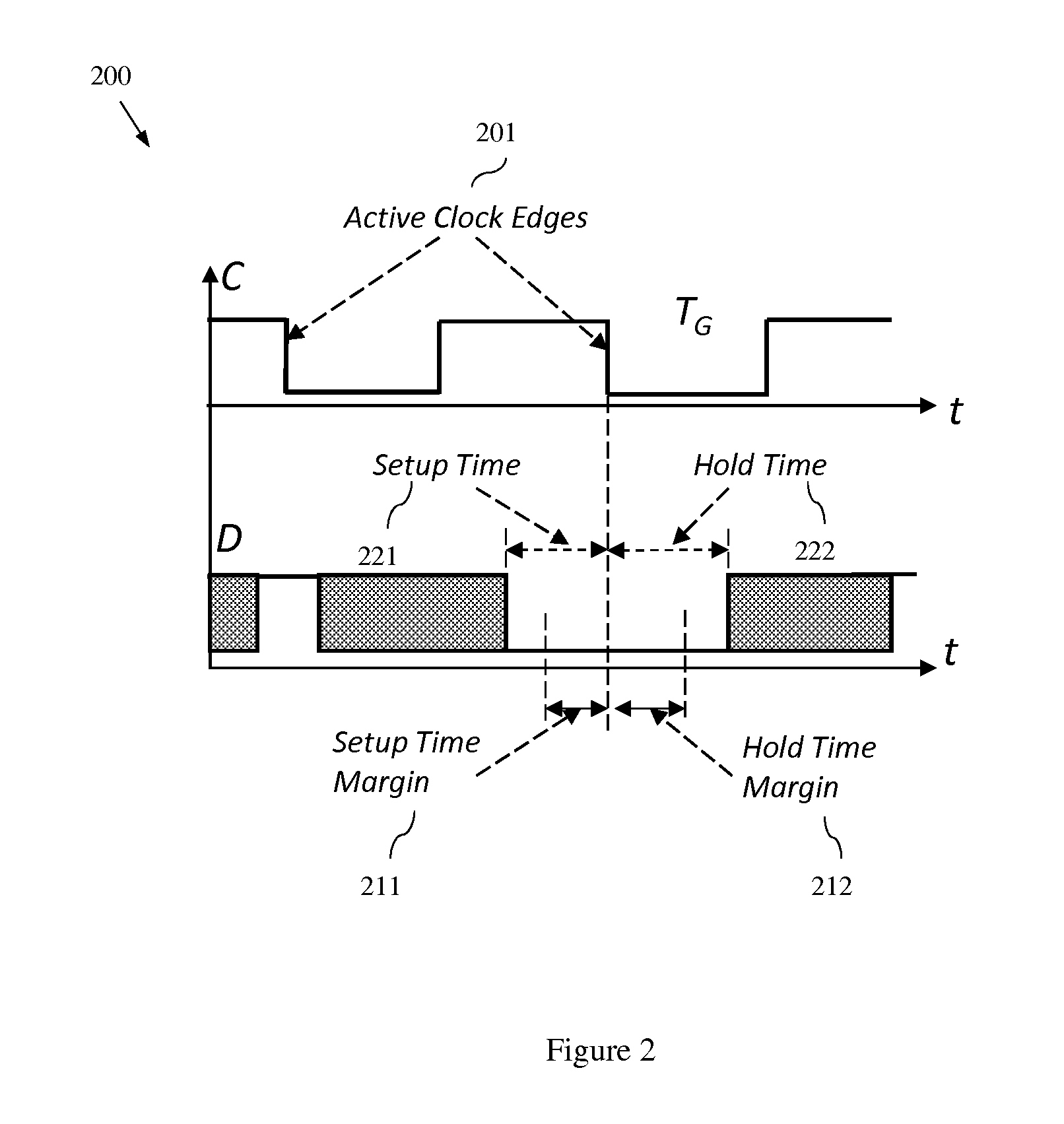
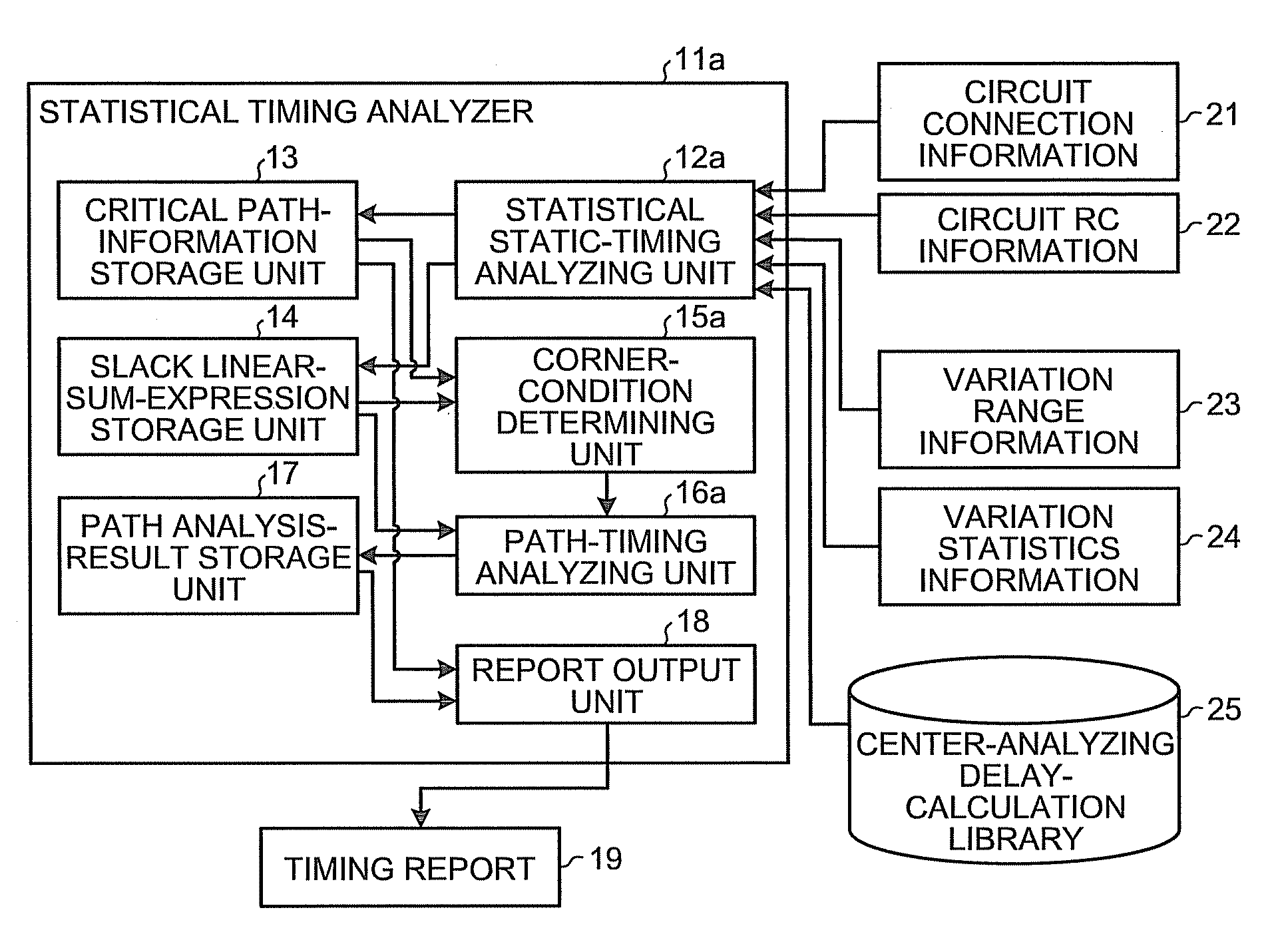
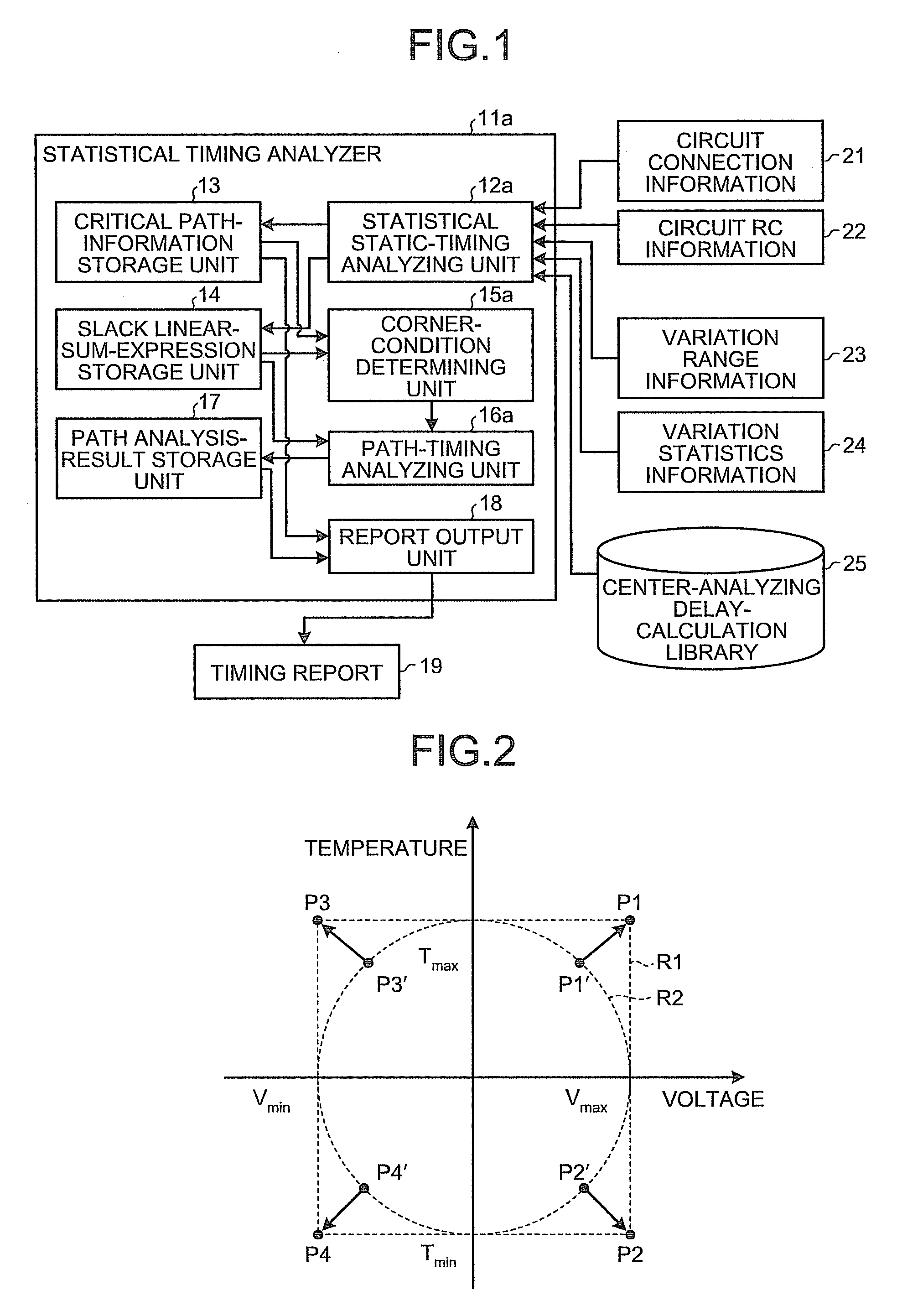
Statistical timing analyzer and statistical timing analysis method
InactiveUS20090249272A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationAnalysis methodStatistical static timing analysis
A statistical timing analyzer comprises a statistical static-timing analyzing unit that performs a statistical static timing analysis of a semiconductor integrated circuit; a corner-condition determining unit that determines corner conditions of the semiconductor integrated circuit based on a result of the statistical static timing analysis; and a path-timing analyzing unit that performs a static timing analysis of the semiconductor integrated circuit based on the corner conditions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Methods for statistical slew propagation during block-based statistical static timing analysis
ActiveUS8086976B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatistical static timing analysisComputer science
Methods for statistical slew propagation in static statistical timing analysis. The method includes projecting a canonical approximation of an input slew over a timing path to a first corner and using the projected input slew to calculate a delay and an output slew at the first corner. The method further includes perturbing the canonical approximation of the input slew to a different corner, calculating a delay and an output slew at the different corner using the perturbed input slew canonical, and determining a sensitivity of the delay and the output slew to a plurality of parameters, simultaneous with implicit sensitivity calculations to the input slew, with finite difference calculations between the first corner and perturbed data.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Statistical static timing analysis of signal with crosstalk induced delay change in integrated circuit
ActiveUS8244491B1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDigital variable/waveform displayNormal densityArrival time
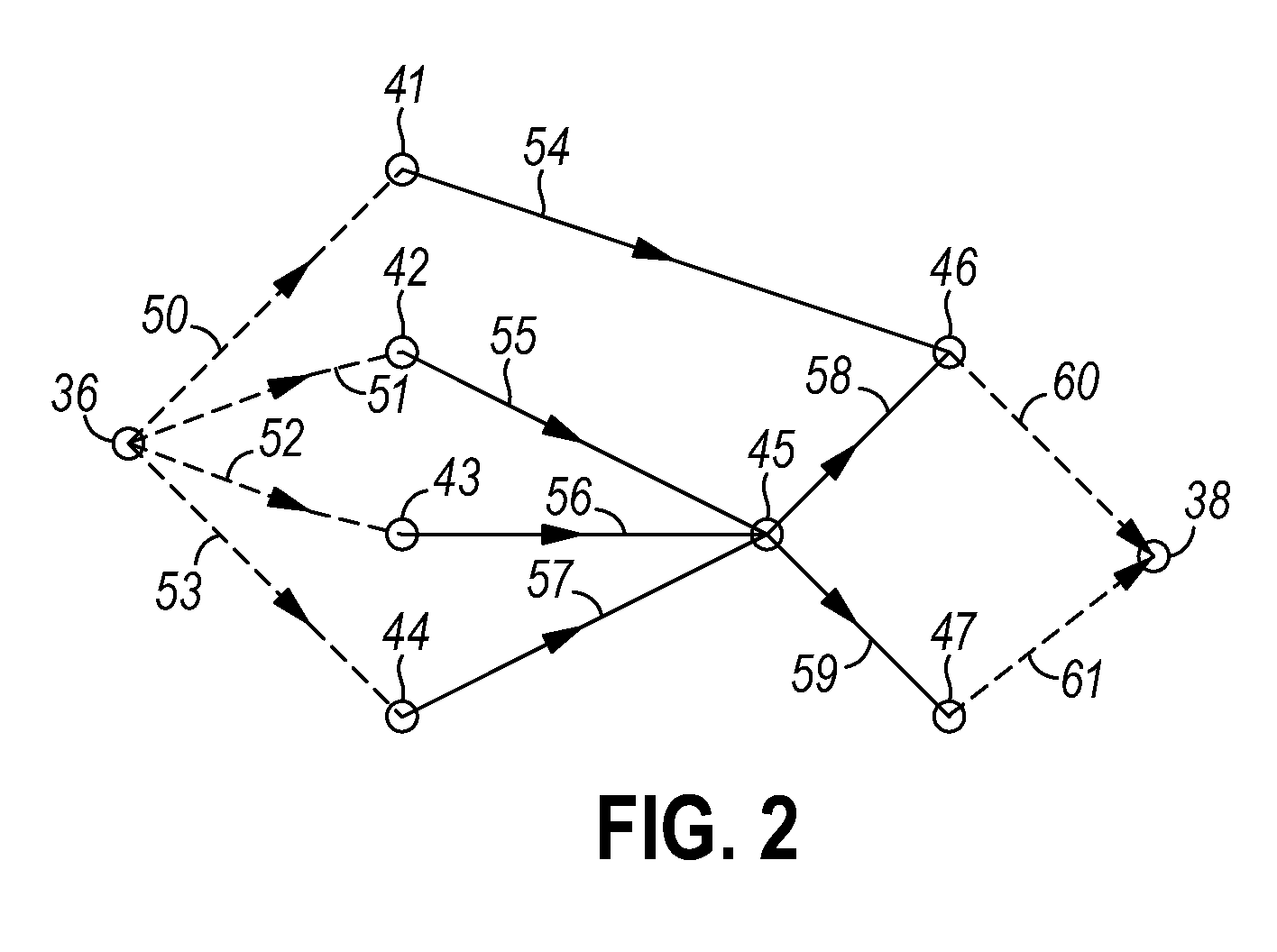
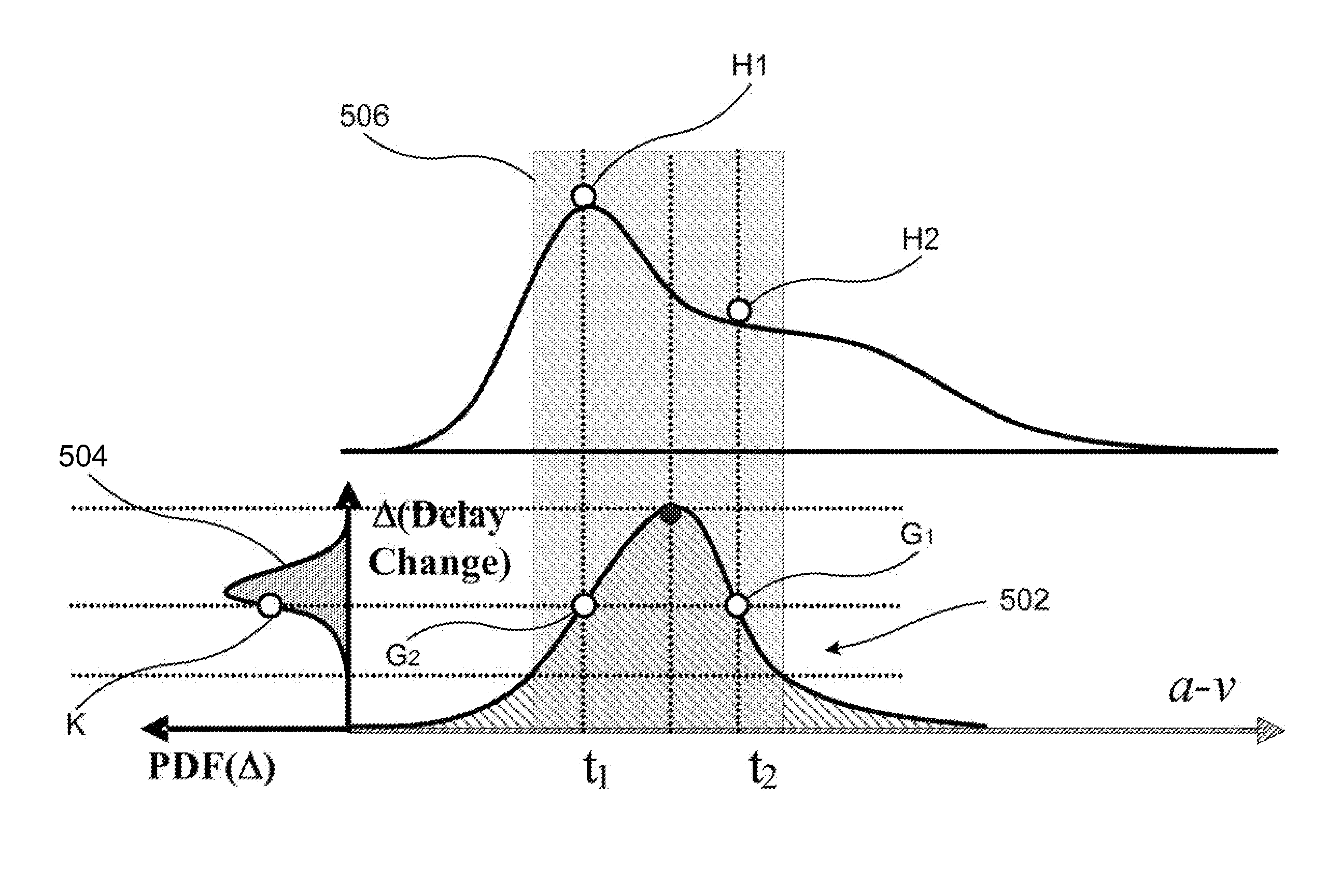
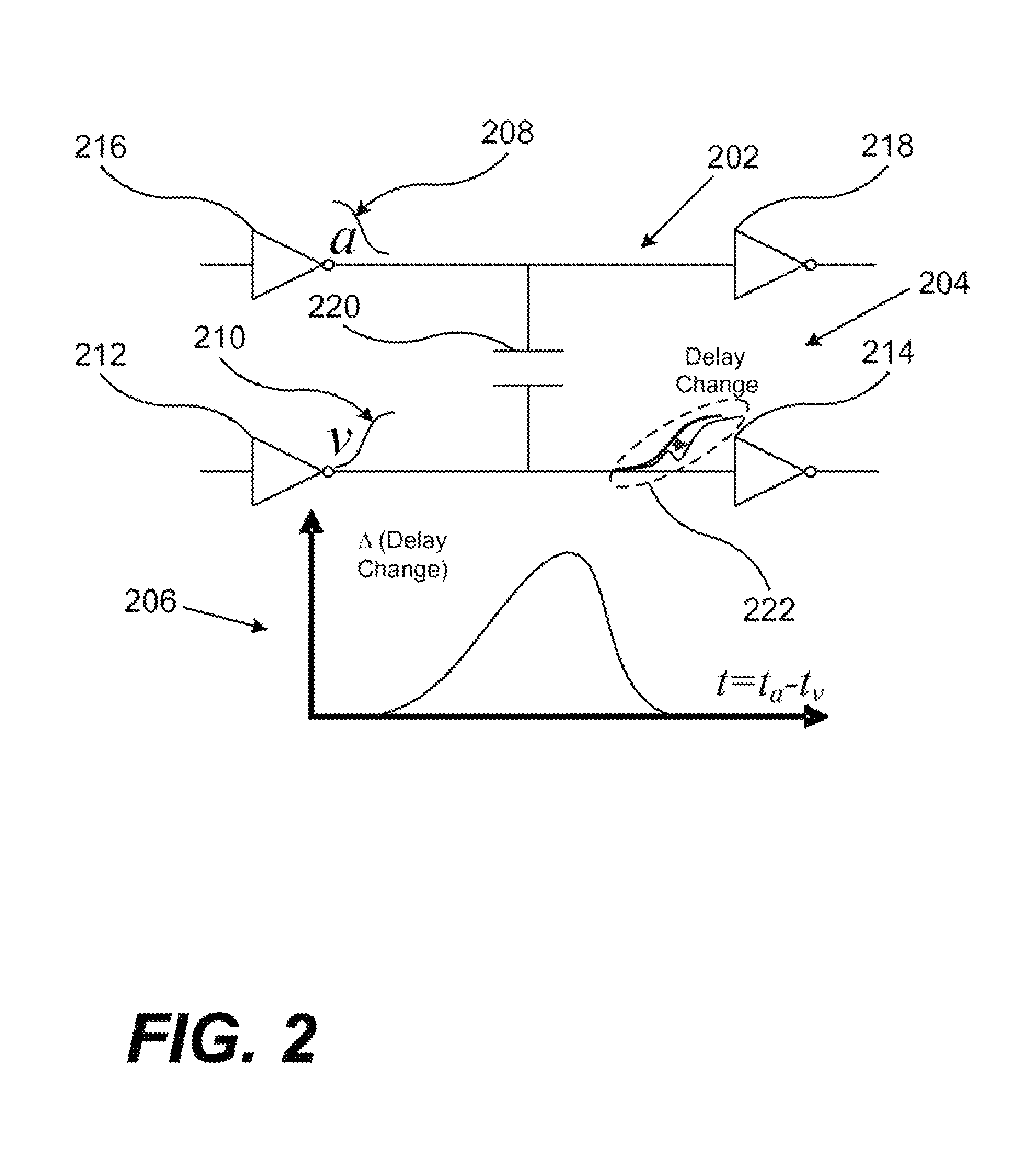
A method is provided to evaluate crosstalk effect of aggressor switching upon victim net signal transition time within an integrated circuit comprising: combining a first probability density function (PDF) of first aggressor switching time in response to a first input signal to an aggressor net driver and a second aggressor switching time in response to a second input signal to the aggressor net driver; determining a delay change curve that represents a relationship between delay change of arrival time of a victim net signal transition and relative alignment of the aggressor net driver switching time and a victim net driver switching time; and determining a third PDF of delay change of a transition of the victim net signal based upon the combination and the delay change curve.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
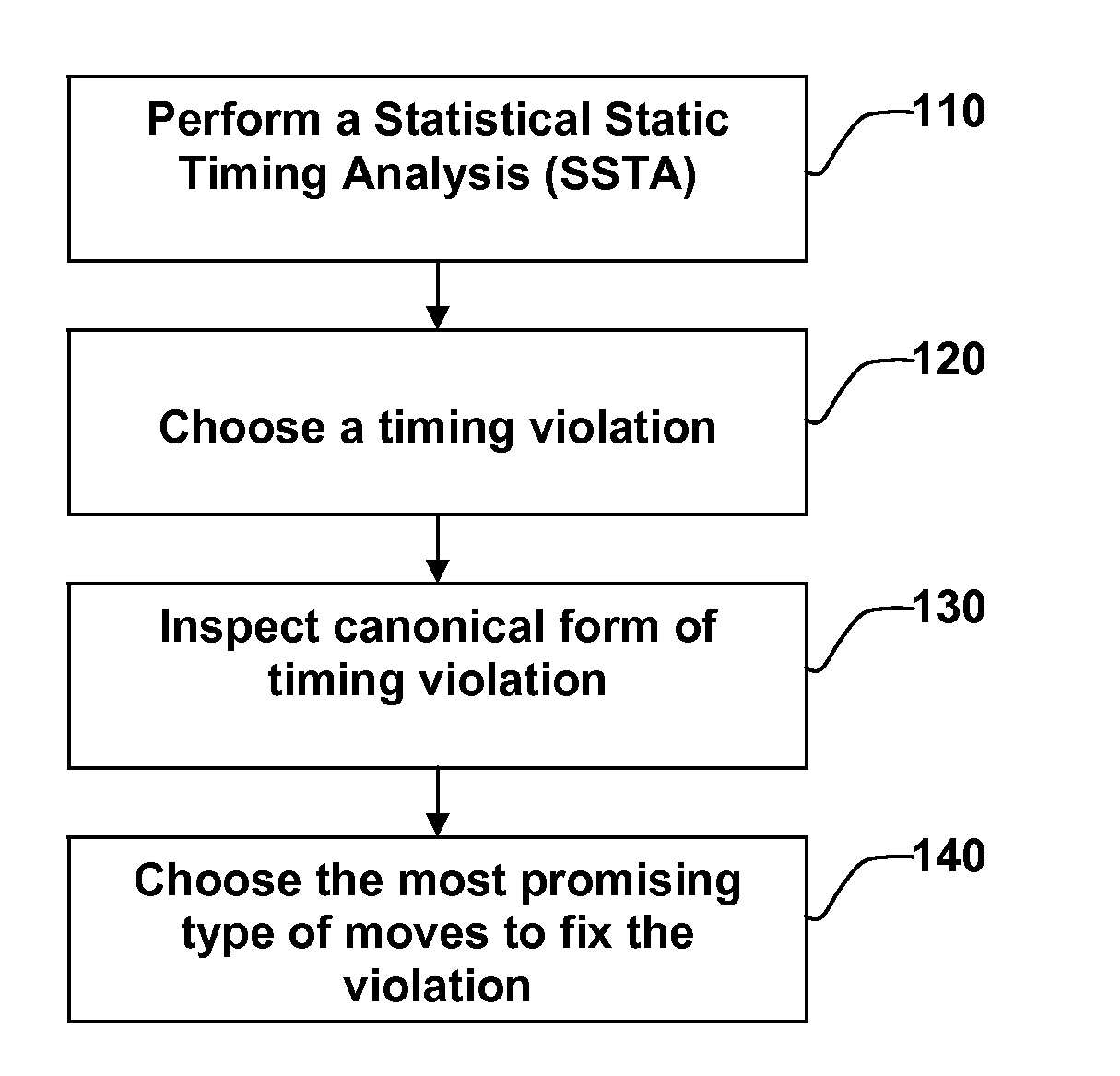
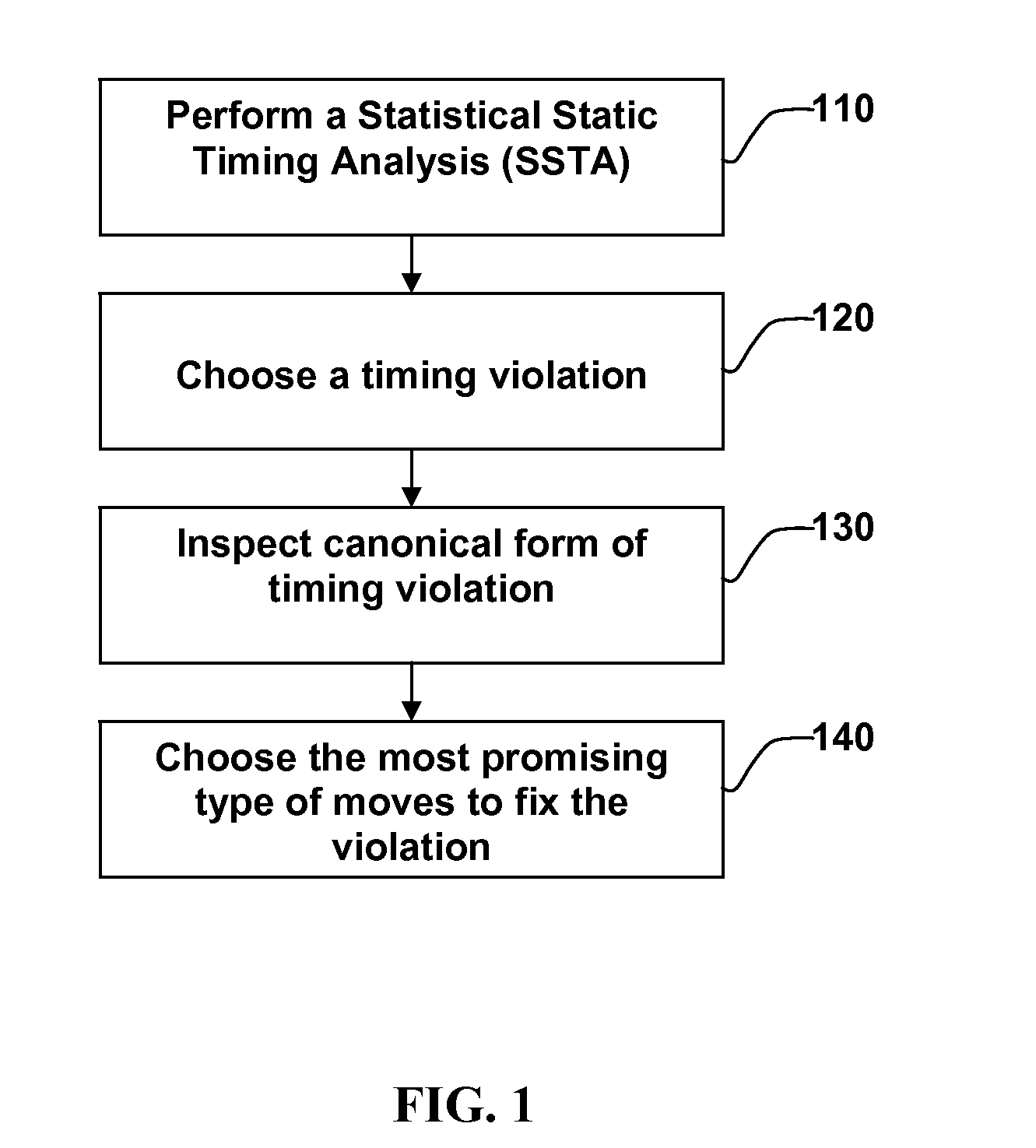
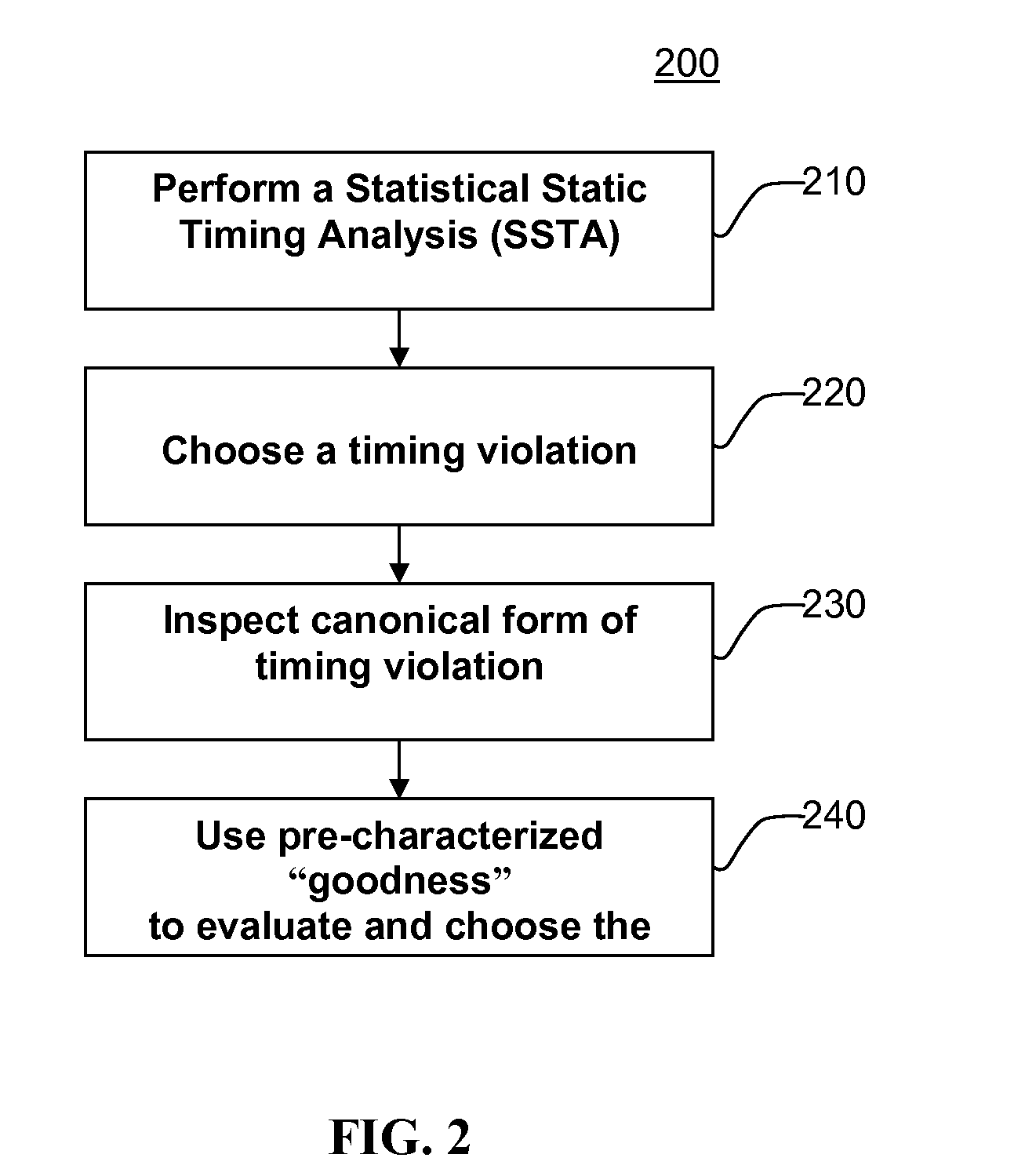
Method for Achieving An Efficient Statistical Optimization of Integrated Circuits
InactiveUS20140040844A1Increase percentageReduce iterative processSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringTiming closure
Method for performing timing closure of integrated circuits in the presence of manufacturing and environmental variations. The starting design is analyzed using statistical static timing analysis to determine timing violations. Each timing violation in its statistical canonical form is examined. In a first aspect of the invention, the canonical failing slack is inspected to determine what type of move is most likely to fix the timing violation taking into account all relevant manufacturing and environmental variations. In a second aspect of the invention, pre-characterized moves such as insertion of delay pad cells are evaluated for their ability to fix the timing violation without triggering timing, and the best move or set of moves is selected.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
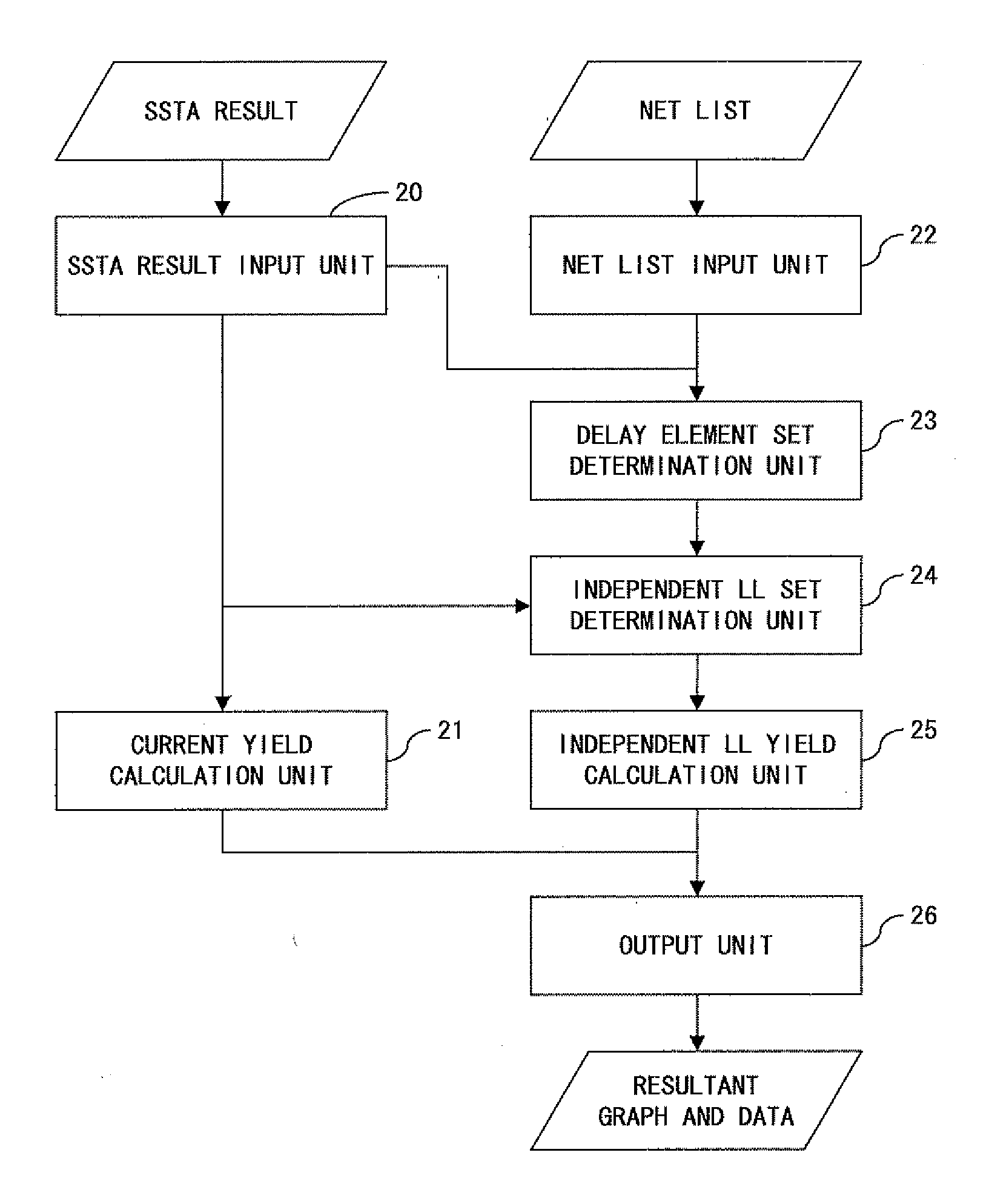
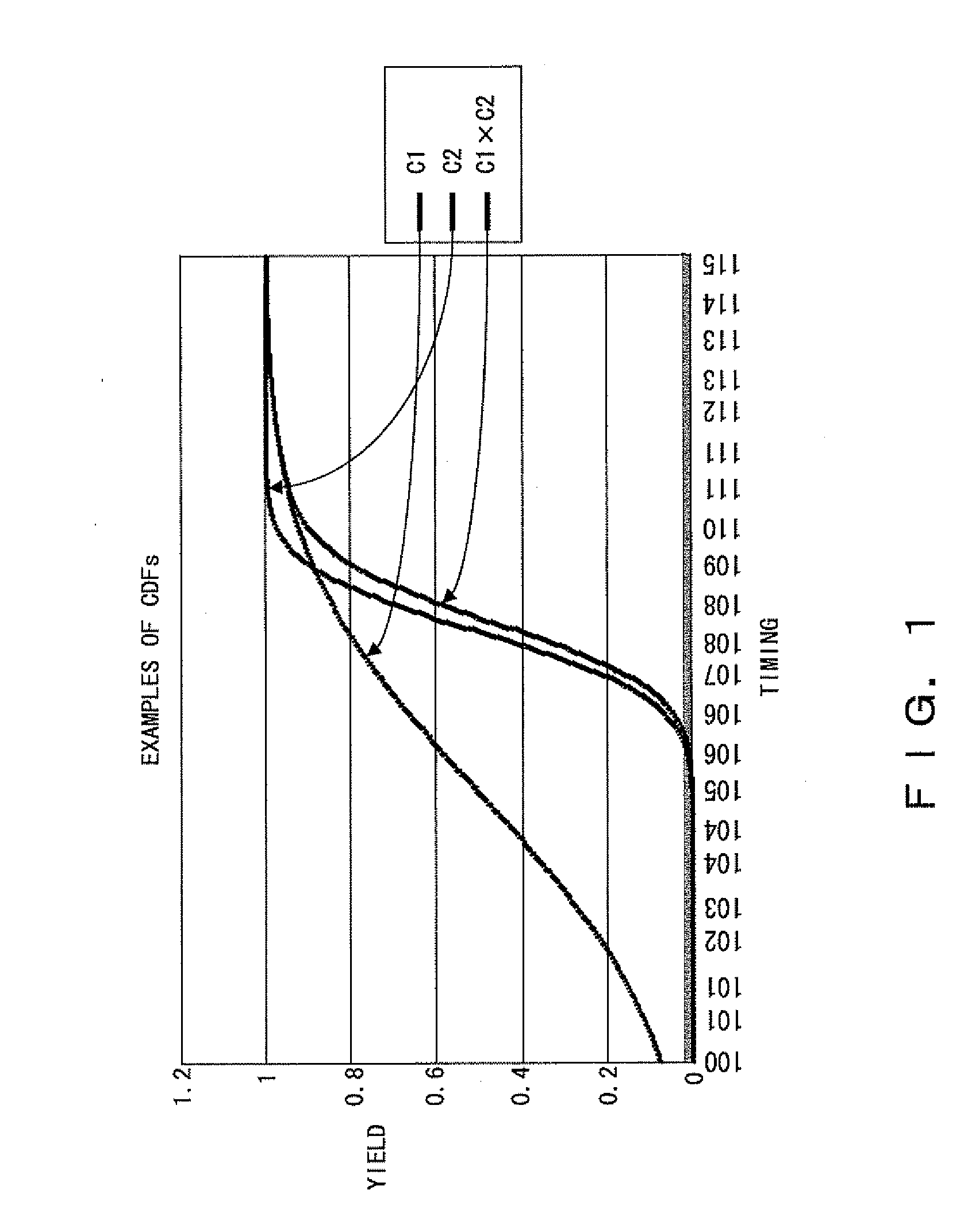
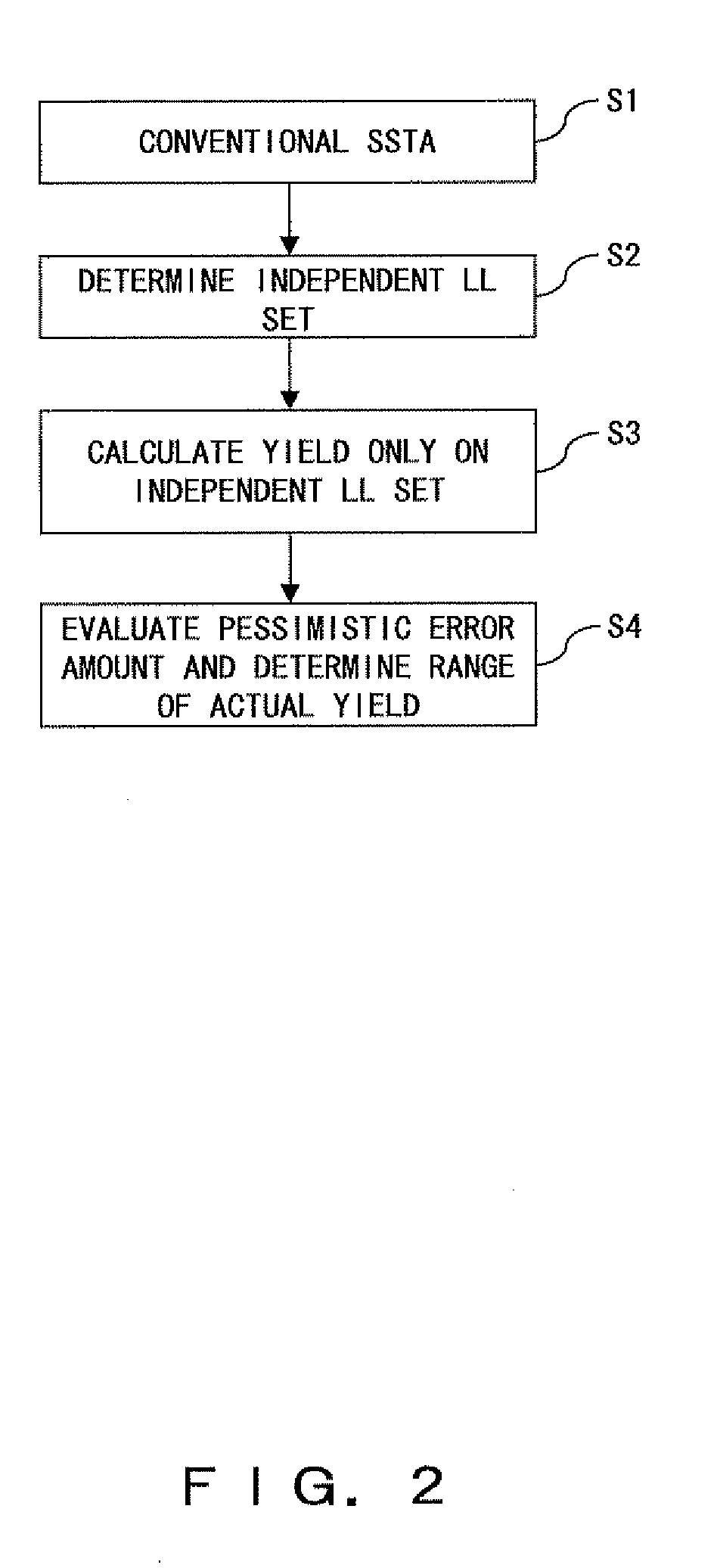
Method of evaluating pessimistic error in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS20080010558A1Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer scienceStatistical static timing analysis
First, a yield is calculated by employing conventional SSTA. Next, an independent LL set is determined, the independent LL set being a subset having sets of delay element sets that only include gates and nets not being shared by two or more paths. Next, a yield is calculated by employing SSTA while using only the independent LL set. Thereby, it is understood that the actual yield is between the yield obtained by employing the conventional SSTA and the yield obtained by employing the SSTA using only the independent LL set.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
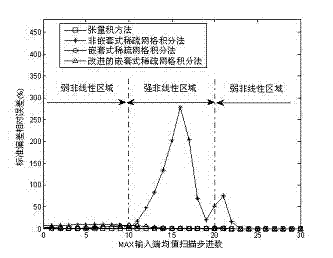
Statistical timing analysis method and device based on improved adaptive random configuration method
InactiveCN102054090AReduce calculation precisionImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsIntegration pointTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a statistical static timing analysis method. In the method, the MAX approximation problem in the statistical static timing analysis method is solved through an adaptive random configuration method (MASCM) based on an improved nested sparse grid integration method. In the MASCM, the MAX approximation is divided into two classes according to input end conditions, namely a linear input condition and a nonlinear input condition, wherein under the linear input condition, an input end with the maximum mean value is selected as output of the MAX; and under the nonlinear input condition, the orthogonal multinomial expansion coefficient is calculated by the improved nested sparse grid integration method. The improved nested sparse grid integration method improves the utilization rate of integration points in the random configuration method, guarantees the integration accuracy, reduces the number of configuration points and reduces the calculation time for statistical static timing analysis. Compared with the conventional methods, the provided MASCM has the equivalent calculation accuracy, while the needed number of integration points and calculation time are greatly reduced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Static timing analysis with design-specific on chip variation de-rating factors
InactiveUS8762908B1Reduce running timeDesign specificationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTime informationDying processes
In one embodiment of the invention, a method of analysis of a circuit design with respect to within-die process variation is disclosed to generate a design-specific on chip variation (DS-OCV) de-rating factor. The method includes executing a static timing analysis (STA) in an on-chip variation mode using a process corner library. Collecting timing information of the top N critical timing paths. Executing a statistical static timing analysis (SSTA) on the N critical timing paths using timing models characterized for SSTA with sensitivities of delays to process variables. Compare the two timing results and deriving DS-OCV de-rating factors for the clock / data paths to be used in a STA OCV timing analysis to correctly account for the effects of process variations. A user may select to specify DS-OCV de-rating factors for paths or groups of paths and achieve an accurate timing analysis report in a reduced amount of run-time.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Circuit reliability analysis method
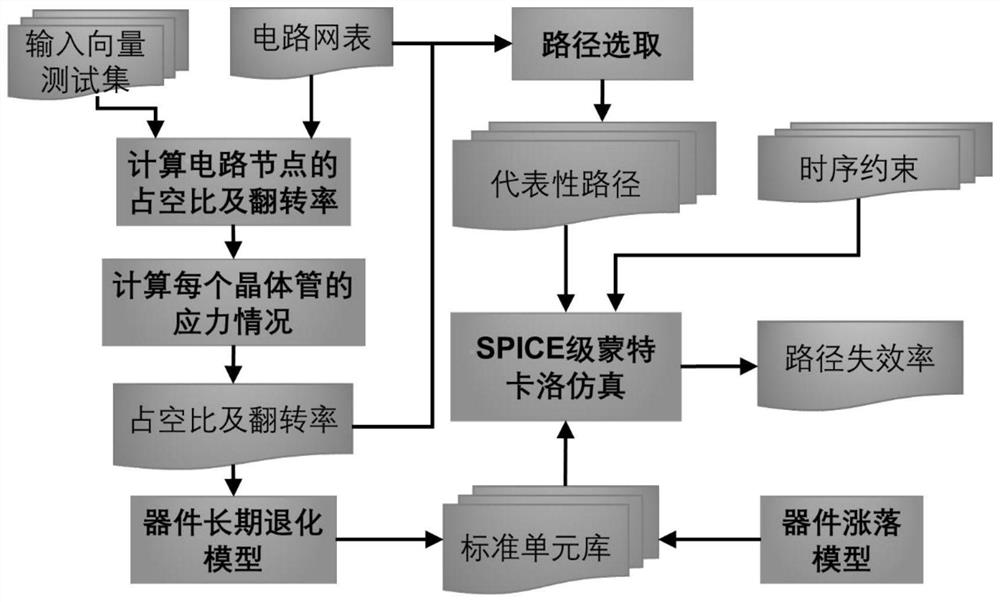
ActiveCN111898335AIncrease application speedFlexible balanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsCircuit reliabilityHemt circuits
The invention discloses a circuit reliability analysis method, which relates to an integrated circuit reliability design technology, and comprises the following steps of: firstly, synthesizing a circuit, performing path analysis and calculating a workload, and obtaining an input condition, a load condition and a degradation degree of each logic gate on a critical path; and then transistor-level Monte Carlo simulation is carried out, transistor-level simulation degradation information is utilized, and a circuit degradation perception standard cell library does not need to be established, so that a simulation result is more accurate, application of nodes in a circuit is accelerated, and statistical static timing analysis is supported.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System and method for accommodating non-gaussian and non-linear sources of variation in statistical static timing analysis
InactiveUS20080201676A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designArrival timeStatistical static timing analysis
There is provided a system and method for statistical timing analysis and optimization of an electrical circuit having two or more digital elements. The system includes at least one parameter input and a statistical static timing analyzer and electrical circuit optimizer. The at least one parameter input is for receiving parameters of the electrical circuit. At least one of the parameters has at least one of a non-Gaussian probability distribution and a non-linear delay effect. The statistical static timing analyzer and electrical circuit optimizer is for calculating at least one of a signal arrival time and a signal required time for the electrical circuit using the at least one parameter and for modifying a component size of the electrical circuit to alter gate timing characteristics of the electrical circuit based upon the at least one of the signal arrival time and the signal required time.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com