Patents
Literature
66 results about "Bond failure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
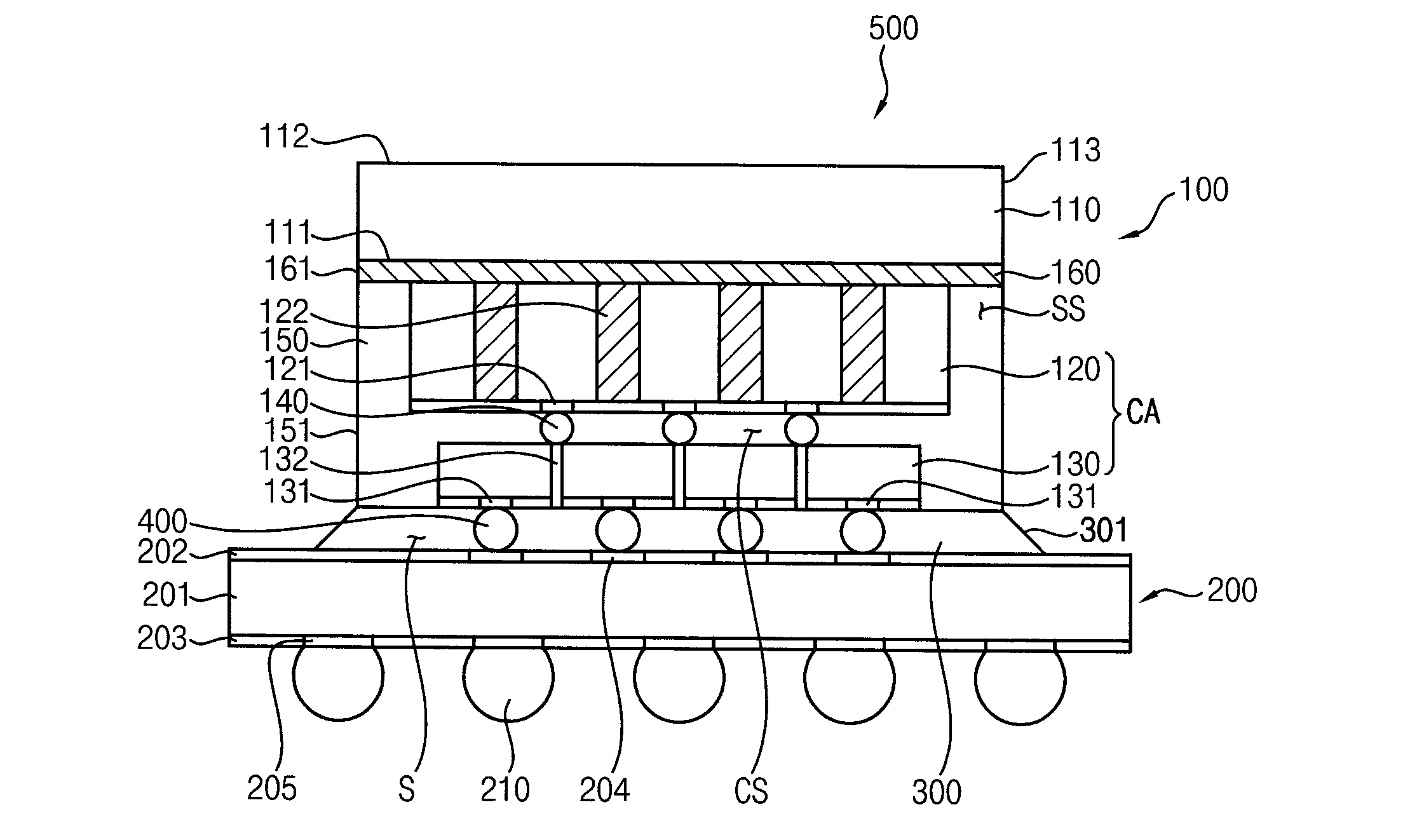
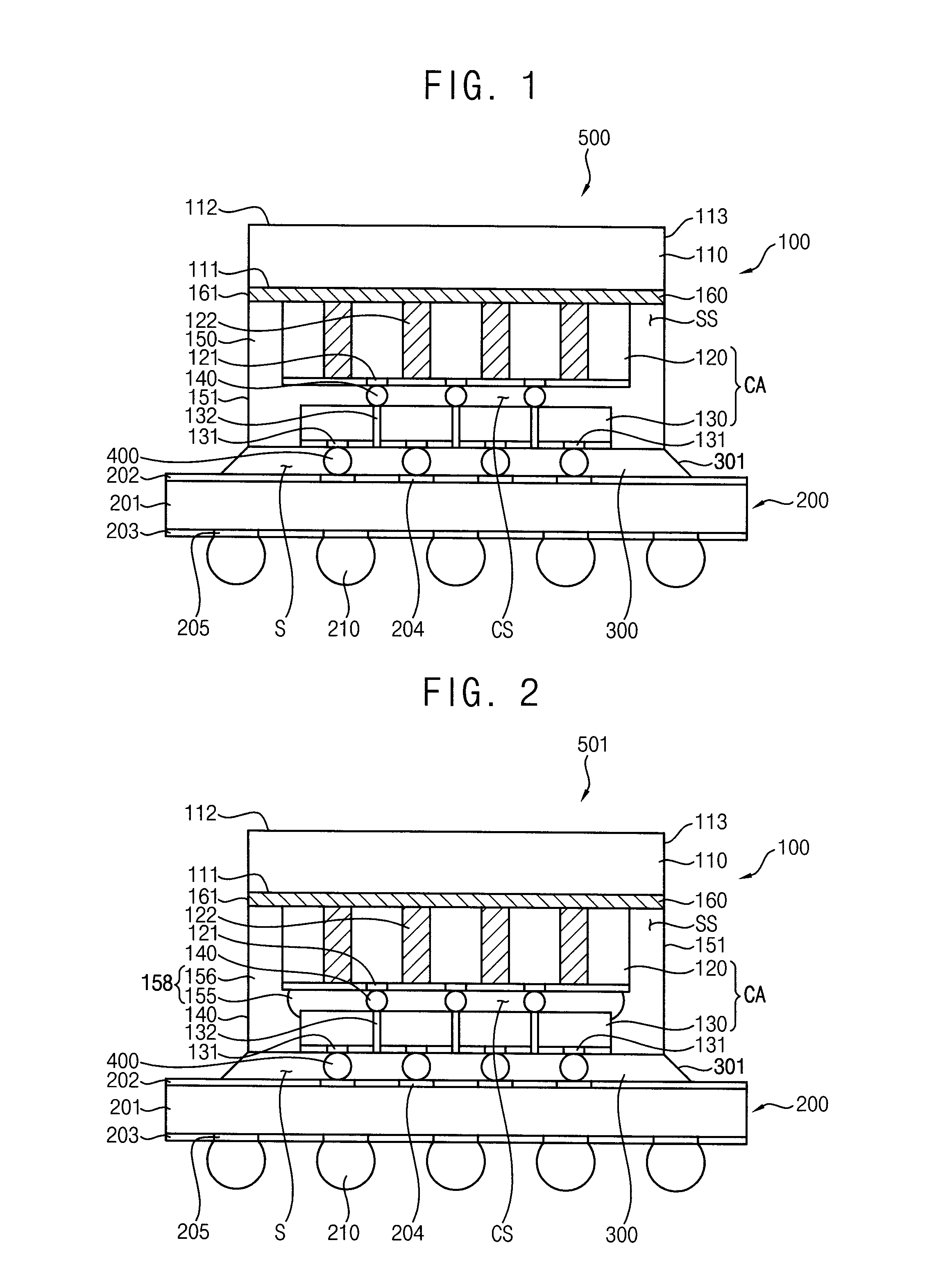
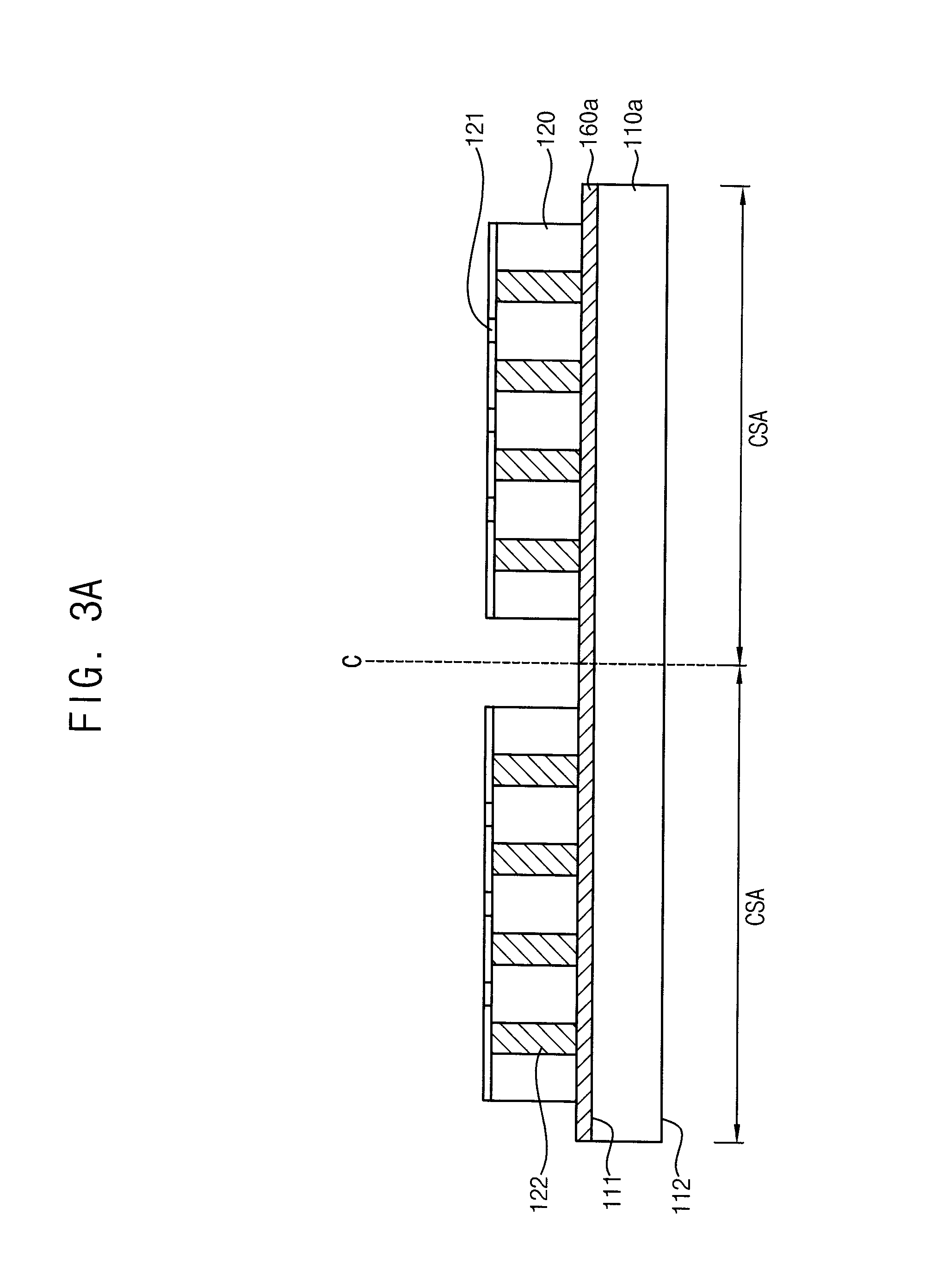
Semiconductor package and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20150228591A1Circuit board warpage is mitigated or prevented in the semiconductor packageGuaranteed uptimeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering
A semiconductor package including a chip stack structure having first and second chips that are secured to a dissipating plate by using a mold layer such that the second chip is combined to the dissipating plate and the first chip is bonded to the second chip, and the first chip has a smaller thickness than the second chip, a circuit board onto which the chip stack structure is mounted in a bonded manner, and an under-fill layer filling a gap space between the circuit board and first chip, a side surface of the under-fill layer being connected to a sidewall of the mold layer may be provided. Due to this bulk mounting structure, the warpage and bonding failures of the semiconductor package may be substantially reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Quartz glass thermal sprayed parts and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20040018361A1Good heat insulationGood adhesivenessLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingQuartzMaterials science
Parts, especially those formed of quartz glass, for film-forming devices, plasma-treating devices and the like have a problem of inner pollution of the devices with particles given by dropping of deposit films from the parts, a problem of hermetical sealing reduction due to bonding failure of the parts to other parts, and a problem of energy efficiency reduction due to the heat insulation failure in the parts. Parts having a thermal sprayed quartz glass film formed on a substrate have an increased ability to hold a deposit thereon, and have an increased ability to hermetically bond to other parts. The parts having a thermal sprayed black quartz glass film have an increased ability of heat insulation property. Even when washed with acid, the abilities of the parts do not lower. The parts can be used for a long period of time and their life is long.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
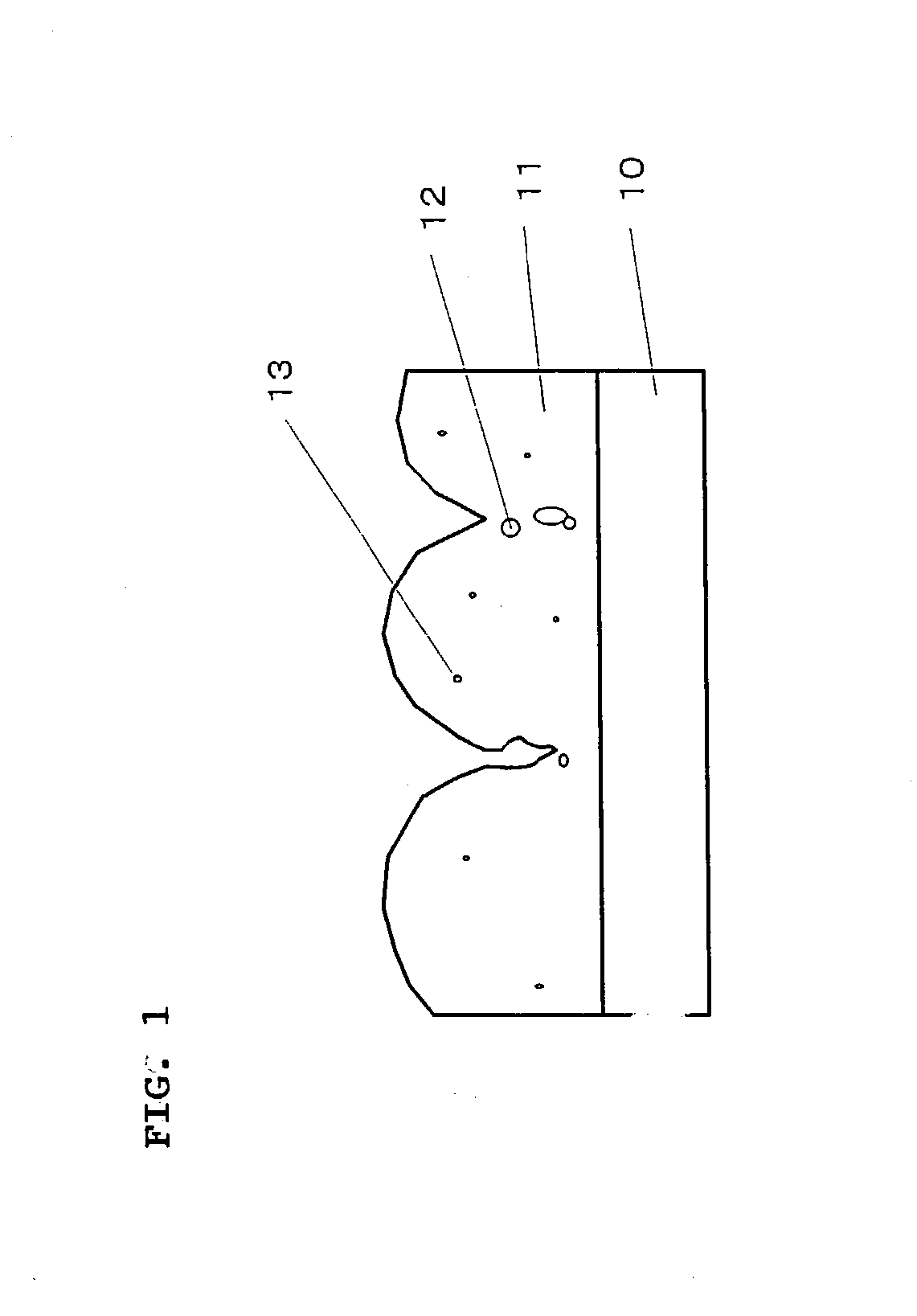
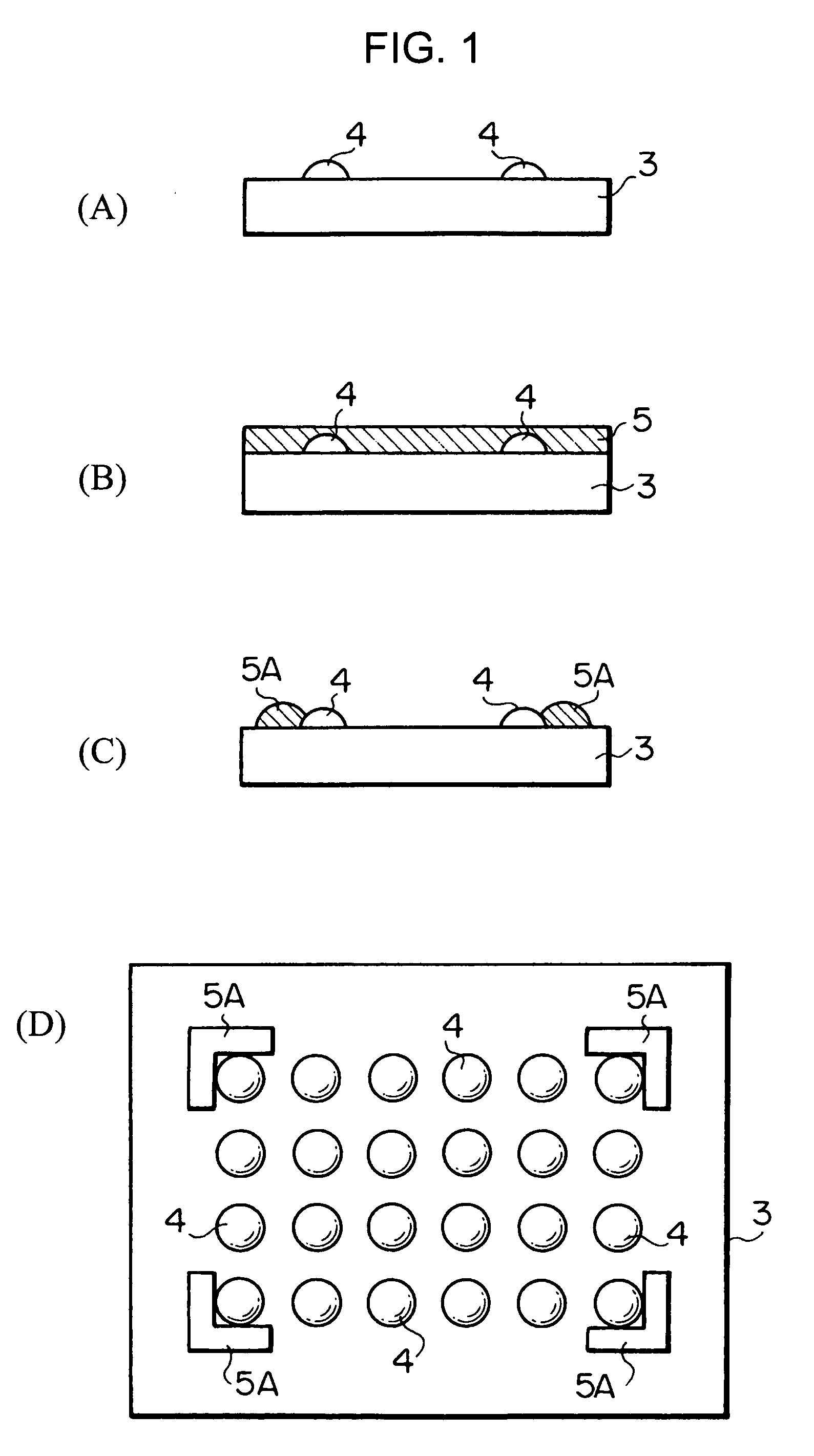
Semiconductor device and process for producing the same
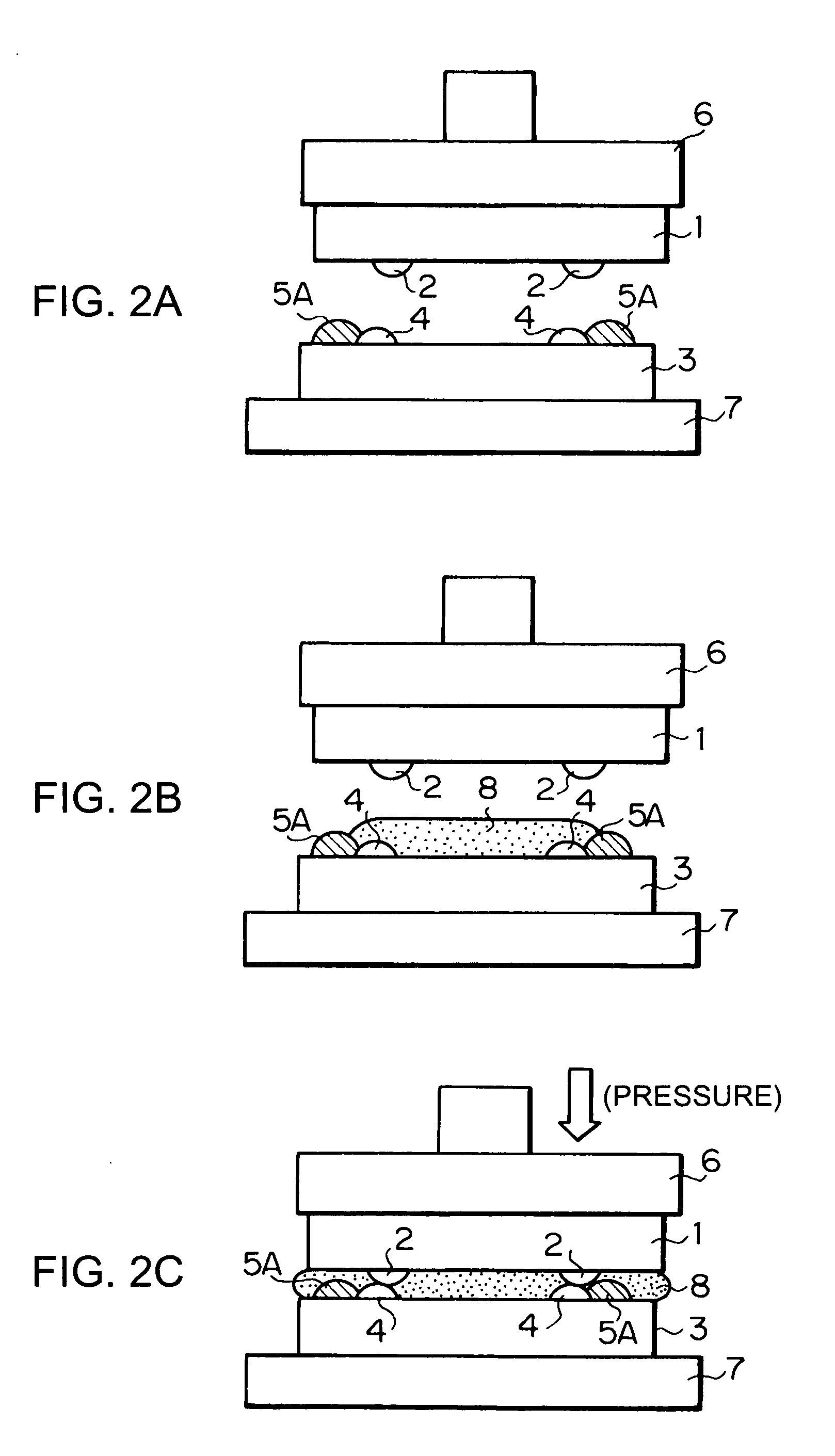
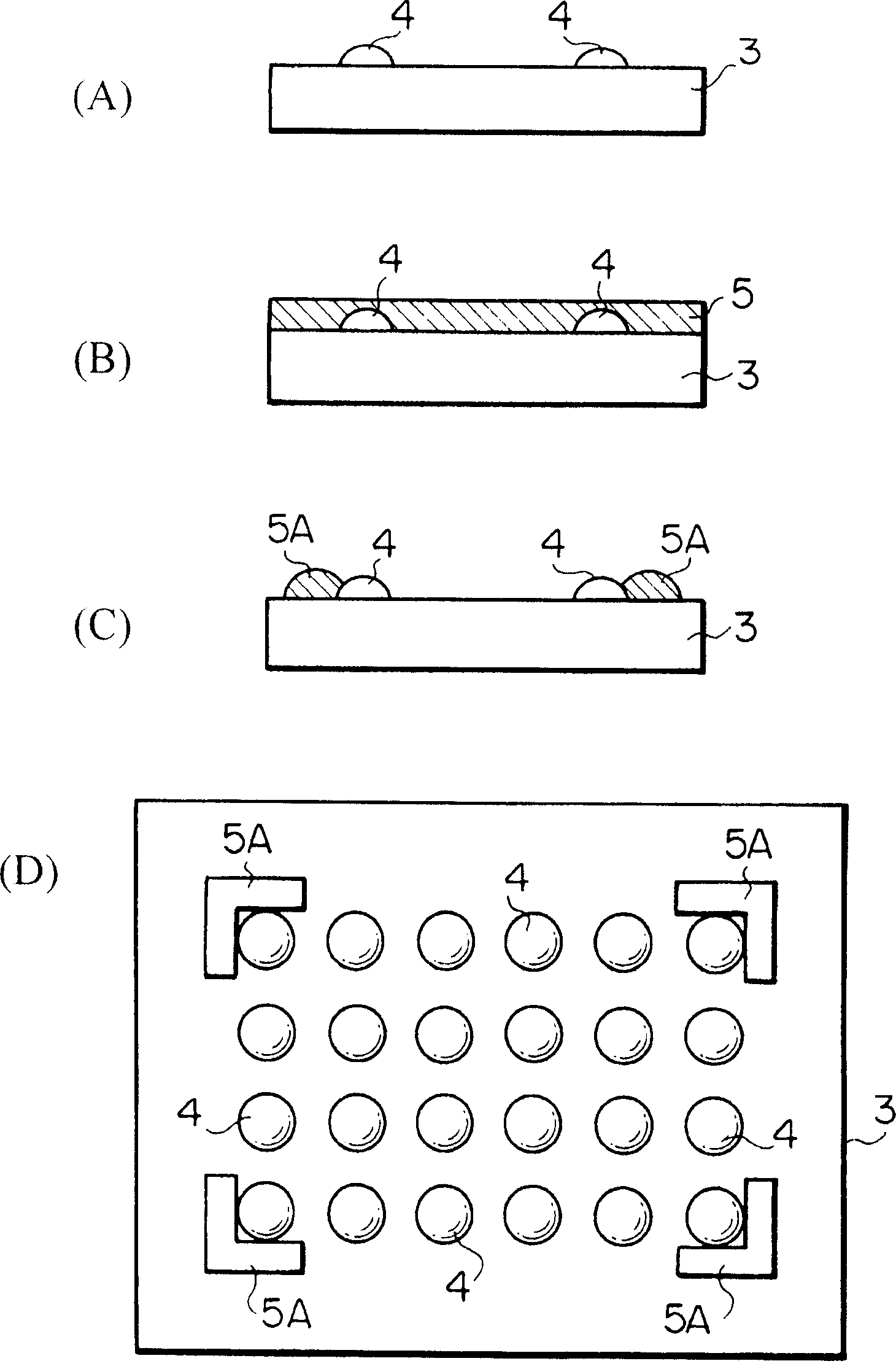
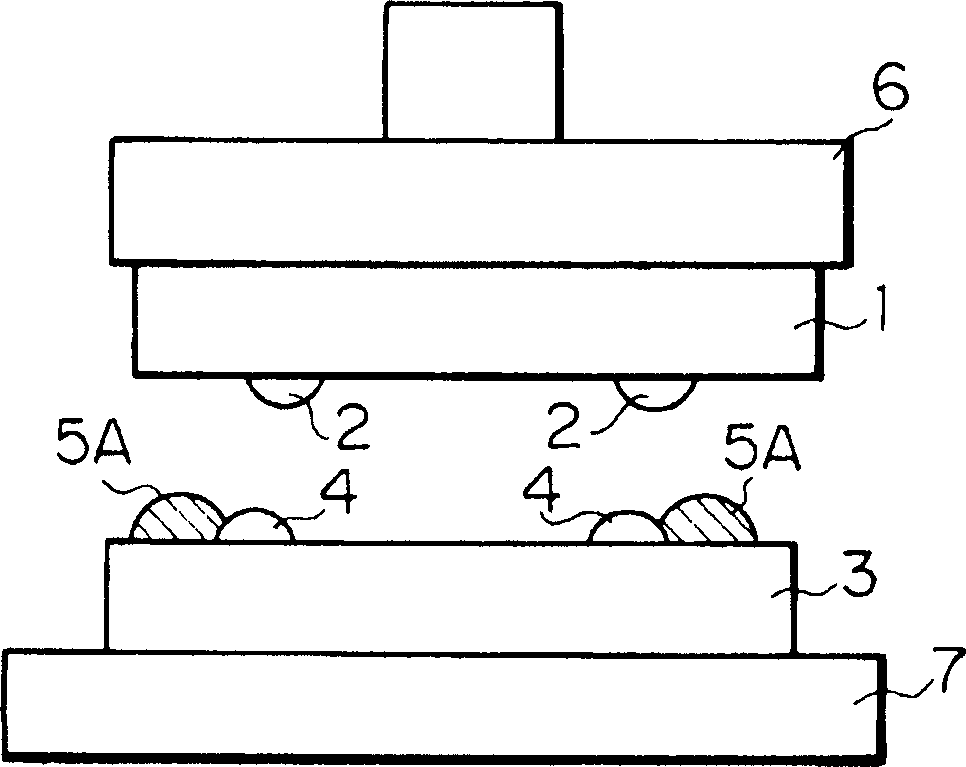
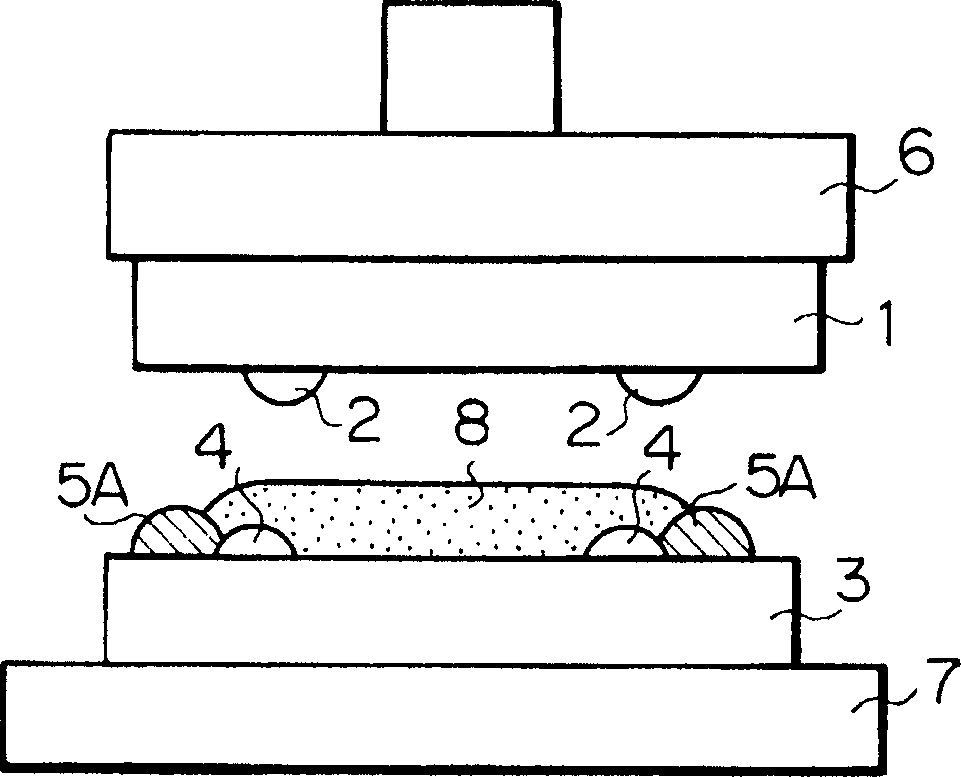
When a semiconductor chip is mounted on a mount substrate by bonding bumps, bonding failure is caused by misalignment between the bumps. Before a semiconductor chip having a plurality of bumps is mounted on a mount substrate (3) having a plurality of bumps (4) by flip chip bonding, a resist layer (5) having a thickness larger than that of the bumps (4) is formed on the mount substrate (3) with the bumps. By patterning the resist layer (5), projecting guides (5A) of semicircular cross section are formed on the mount substrate (3) so as to protrude near the bumps (4) and from a surface on which the bumps (4) are provided, and to have guide faces (curved faces) pointing toward the bumps (4).
Owner:SONY CORP
Hot melt adhesive with high peel and shear strengths for nonwoven applications
A polybutylene based hot melt adhesive composition having a variety of end uses, particularly in construction and elastic attachment applications for nonwoven articles such as disposable diapers. Unlike typical hot melt adhesives, the present composition can withstand high peel and shear loads at elevated temperatures for extended periods of time without experiencing catastrophic bond failure. The composition includes polybutylene polymer or a mixture of polybutylene and polyolefin polymers, and a stabilizer, with the remaining ingredients chosen from one or more of a polyolefin polymer, a tackifier resin, a plasticizer, or a wax. The hot melt adhesive composition can be applied using common application techniques such as extruding or spraying.
Owner:ATO FINDLEY
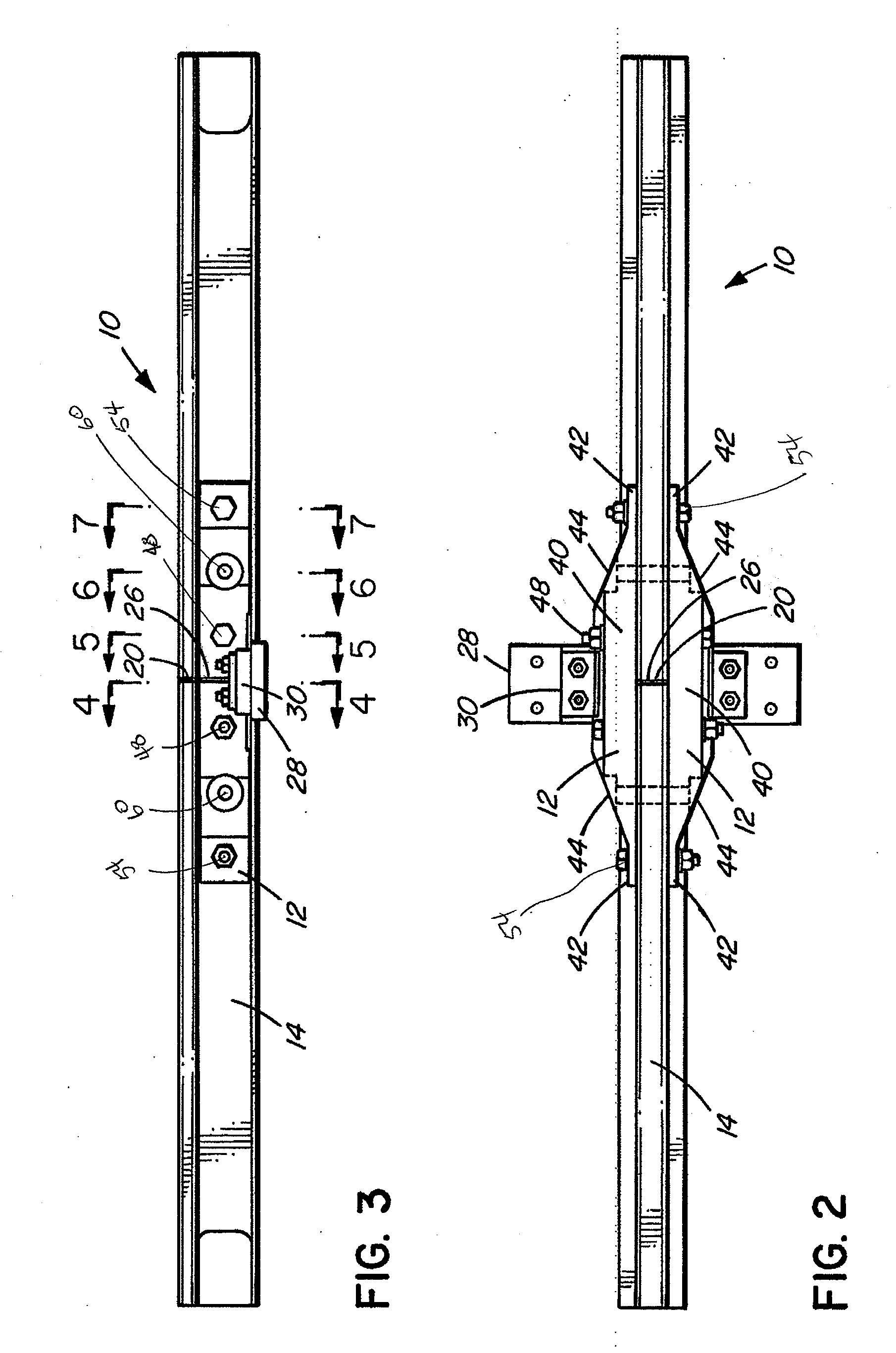
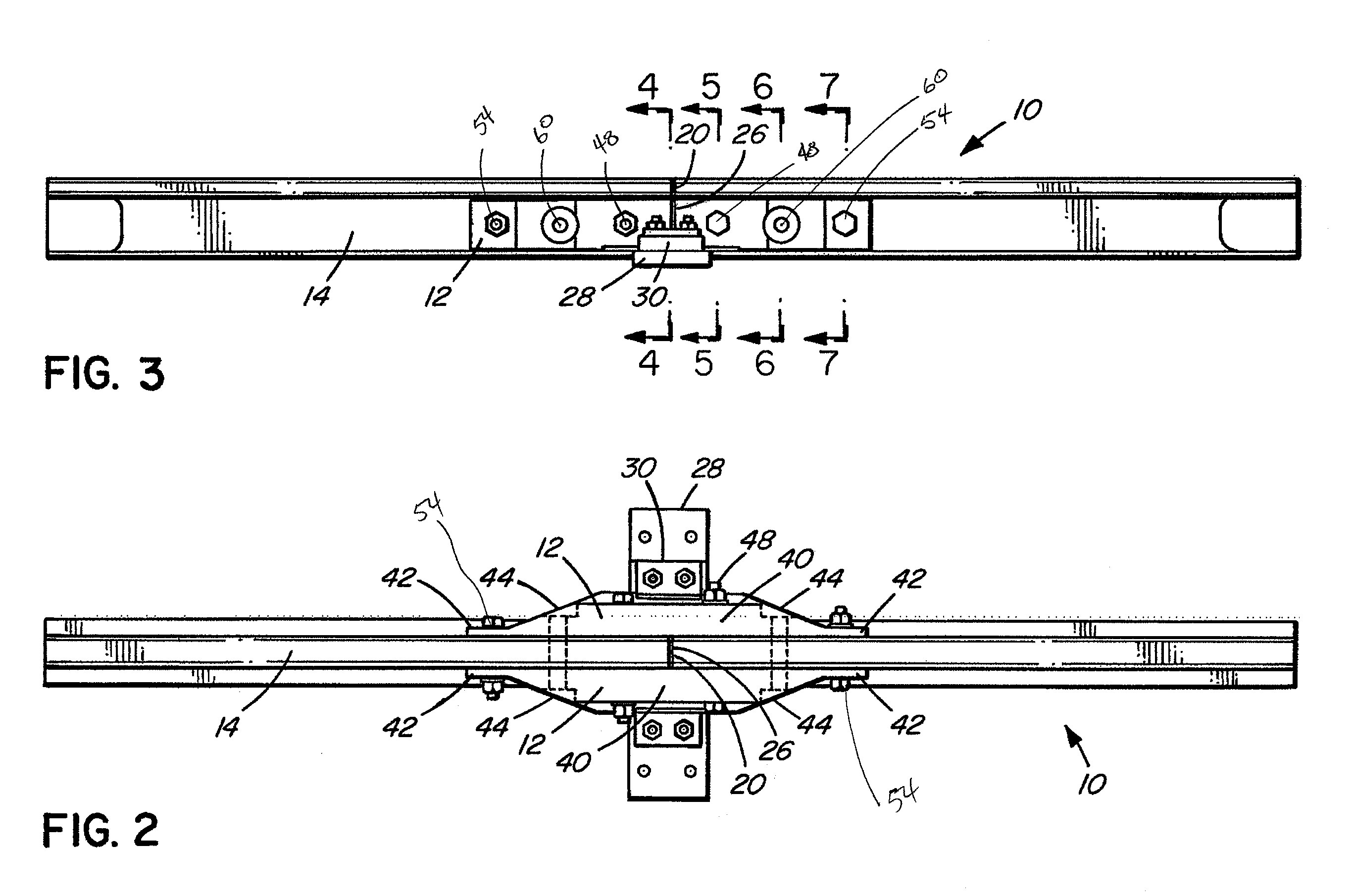
Insulated rail joint assembly
ActiveUS20070272762A1High strengthEasy constructionRail devicesRail jointsCross connectionEngineering
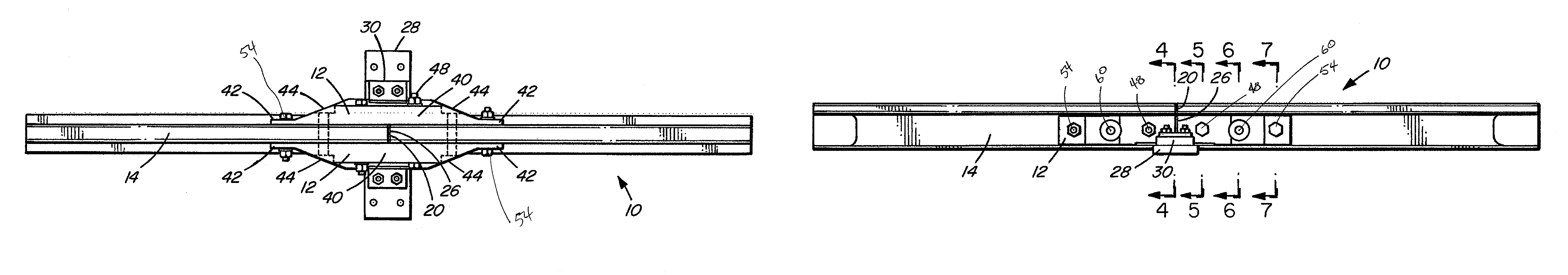
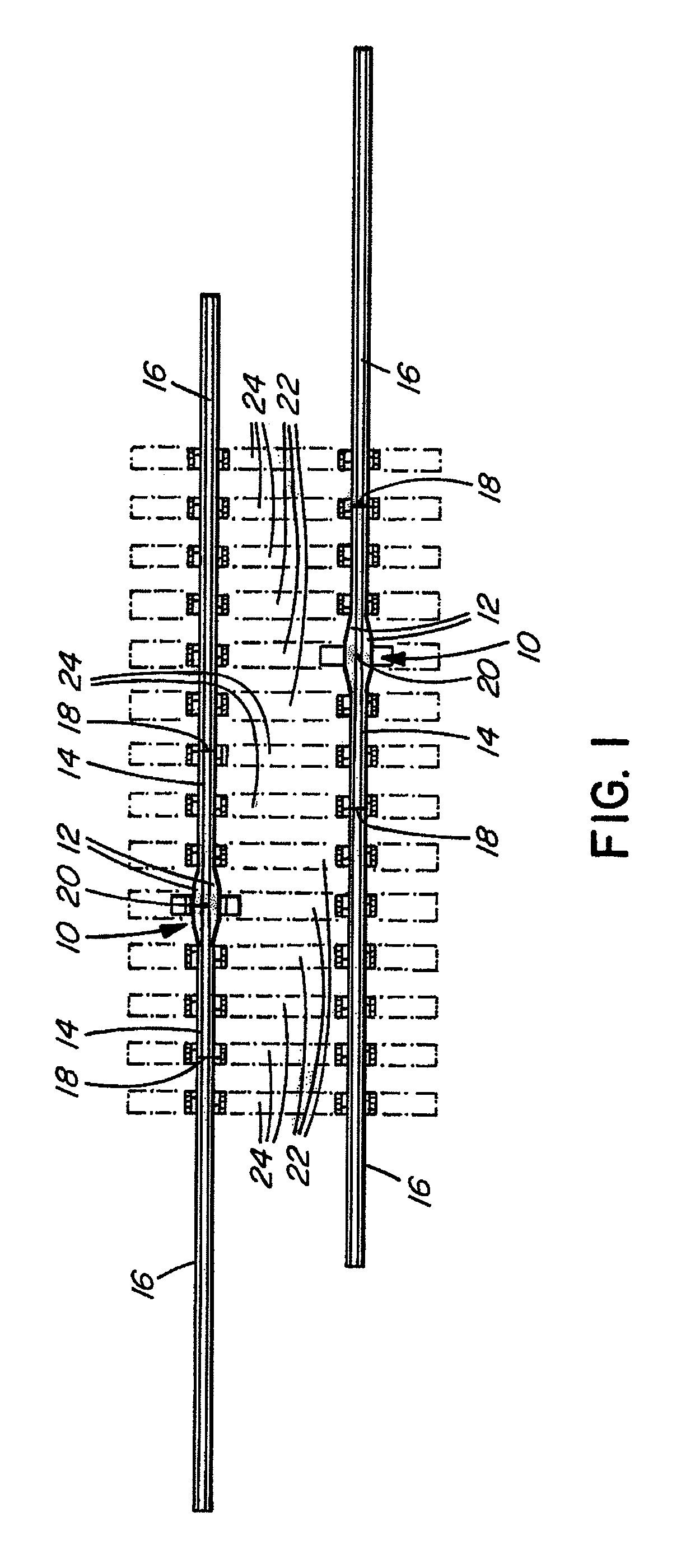
An insulated rail joint assembly comprises a rail with a thick web section, held in place by joint bars and secured with electrically isolated fasteners. The joint bars have non-uniform cross-sections, being shaped with a thicker midsection area and thinner ends. Electrically non-conductive shear pins through the rail and the joint bars provide shear resistance and prevent glue bond failure. High strength cloth between the rail ends and between the rail and the joint bars strengthens the joint, as does an insulating rail clip resiliently fastened to an insulating tie plate, which itself may be supported on a cross tie of increased width.
Owner:VOESTALPINE RAILWAY SYST NORTRAK LLC
Manufacturing method for semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS20060094140A1Prevent stress distributionReduce contact areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesFailure preventionLength wave
A manufacturing method for a semiconductor light emitting device is provided. The method includes preparing a first wafer in which at least one semiconductor layer including the emitter layer is formed; disposing a second wafer transparent to an emission wavelength of the emitter layer on the surface of the first wafer; providing a bonding failure prevention structure to at least either the first wafer or the second wafer for preventing bonding failures of the first wafer and the second wafer; and applying compressive force to a contact face between the first wafer and the second wafer while at the same time, heating the contact face. The first and second wafers can be bonded across their entire surfaces without causing bonding failure.
Owner:SHARP KK
Quartz glass thermal sprayed parts and method for producing the same
InactiveUS7081290B2Good heat insulationImprove abilitiesLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingThermal sprayingQuartz
Parts, especially those formed of quartz glass, for film-forming devices, plasma-treating devices and the like have a problem of inner pollution of the devices with particles given by dropping of deposit films from the parts, a problem of hermetical sealing reduction due to bonding failure of the parts to other parts, and a problem of energy efficiency reduction due to the heat insulation failure in the parts. Parts having a thermal sprayed quartz glass film formed on a substrate have an increased ability to hold a deposit thereon, and have an increased ability to hermetically bond to other parts. The parts having a thermal sprayed black quartz glass film have an increased ability of heat insulation property. Even when washed with acid, the abilities of the parts do not lower. The parts can be used for a long period of time and their life is long.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
Method of detecting wire bonding failures
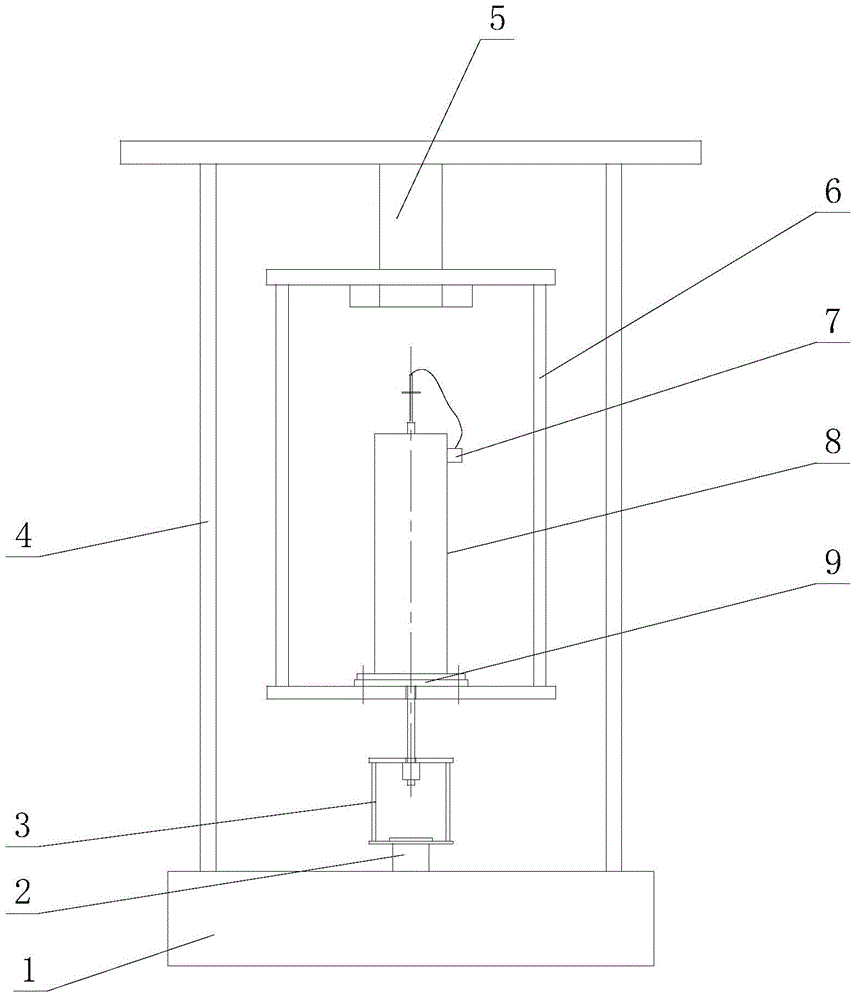
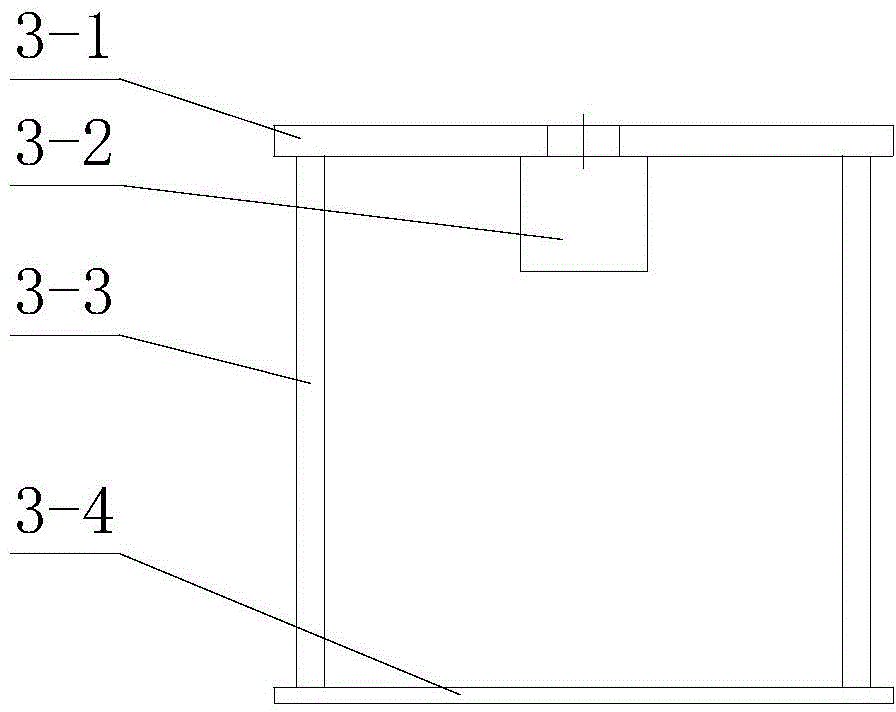
Disclosed is a method of detecting a bonding failure of a wire bonder, which comprises a bonding tool operative to form an electrical connection between a semiconductor die and a substrate using a bonding wire. The method comprises the steps of: forming a first wire bond on a first surface located on the semiconductor die using the bonding tool and the bonding wire; forming a second wire bond on a second surface located on the substrate using the bonding tool and the bonding wire such that a wire loop connects the first and second wire bonds, wherein the first surface is not electrically-conductive; moving the bonding tool in a direction away from the second wire bond to break the bonding wire from the second wire bond; detecting whether the second wire bond remains bonded to the substrate; and determining an occurrence of the bonding failure if the second wire bond is no longer bonded to the substrate.
Owner:ASMPT SINGAPORE PTE LTD
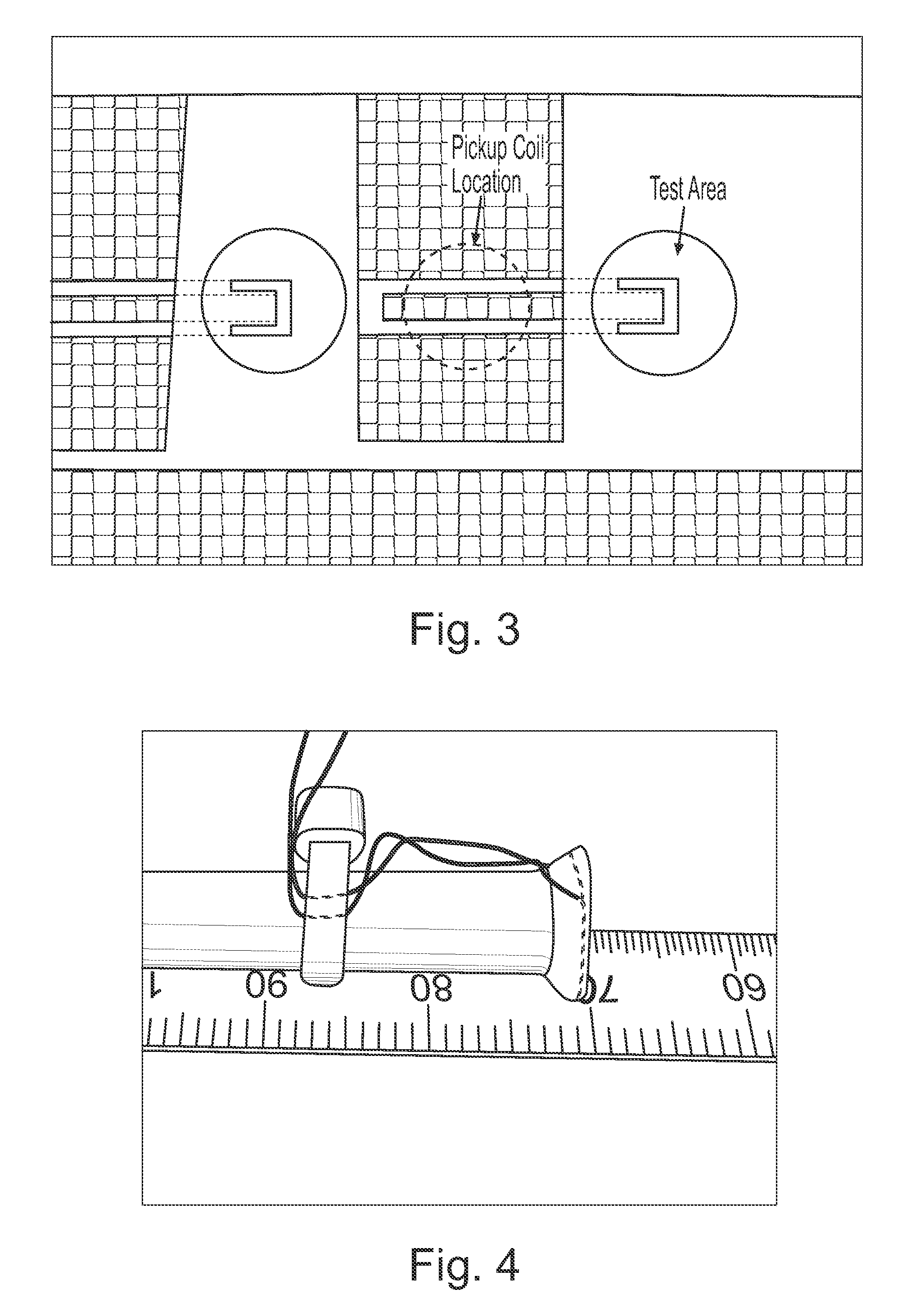
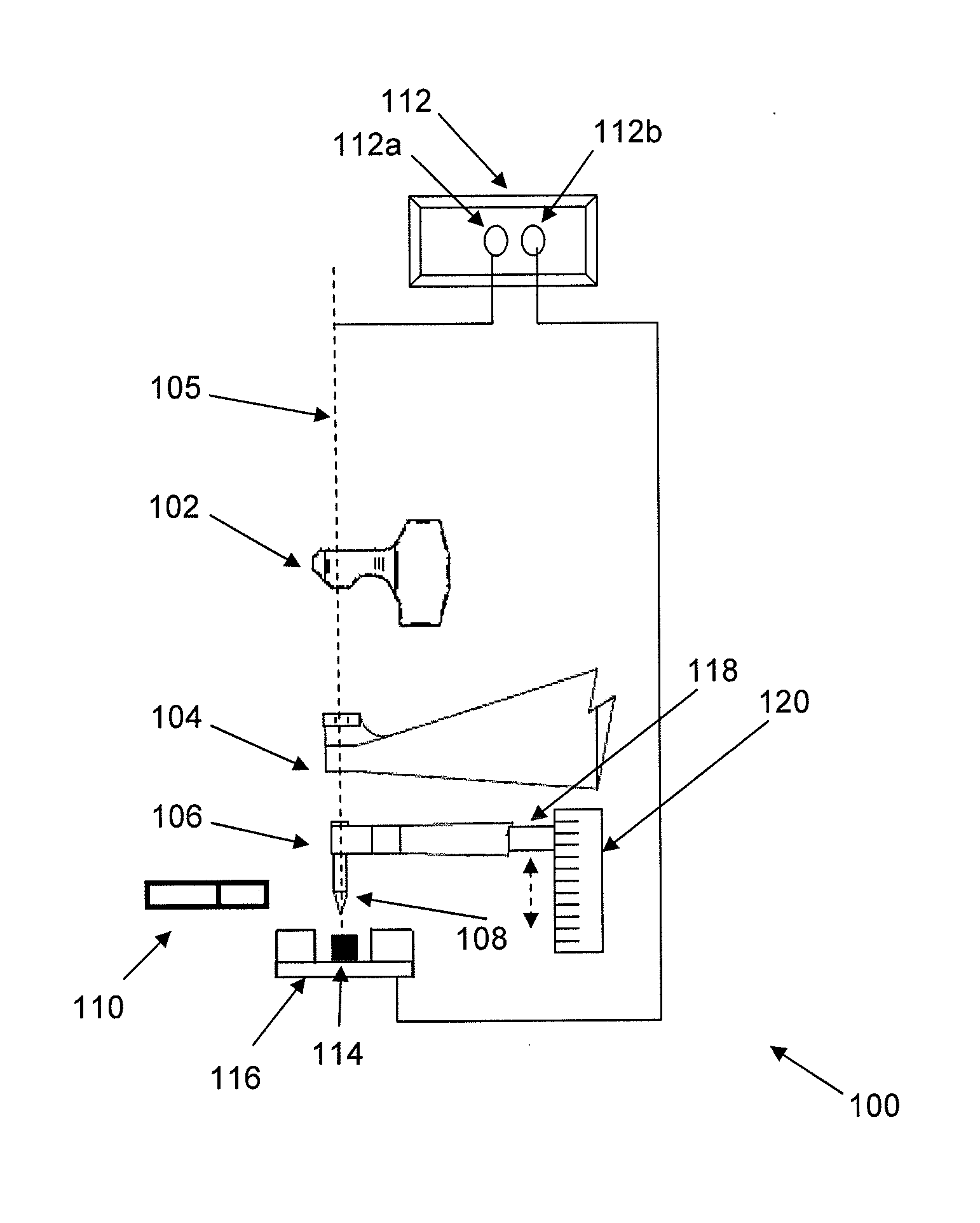
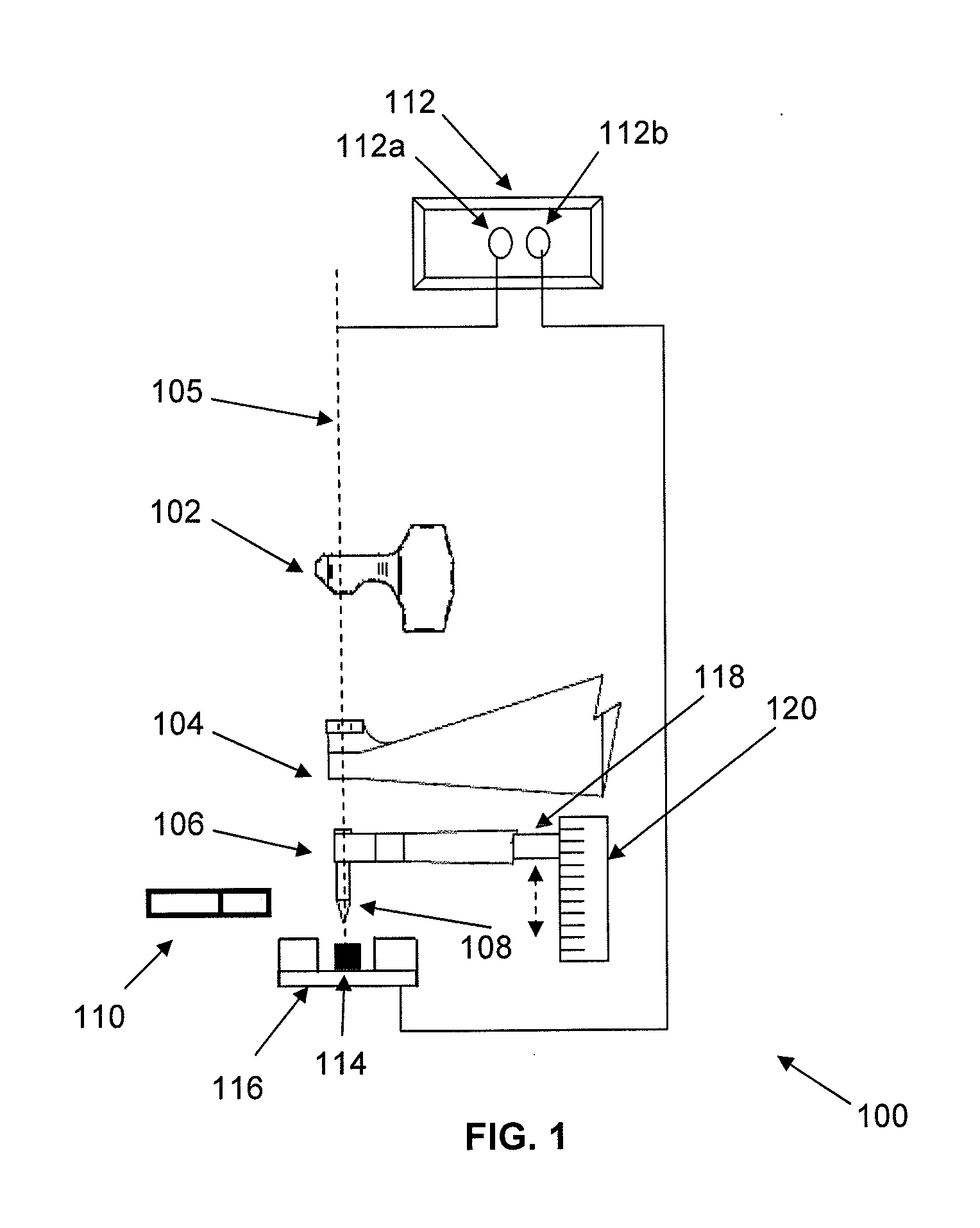
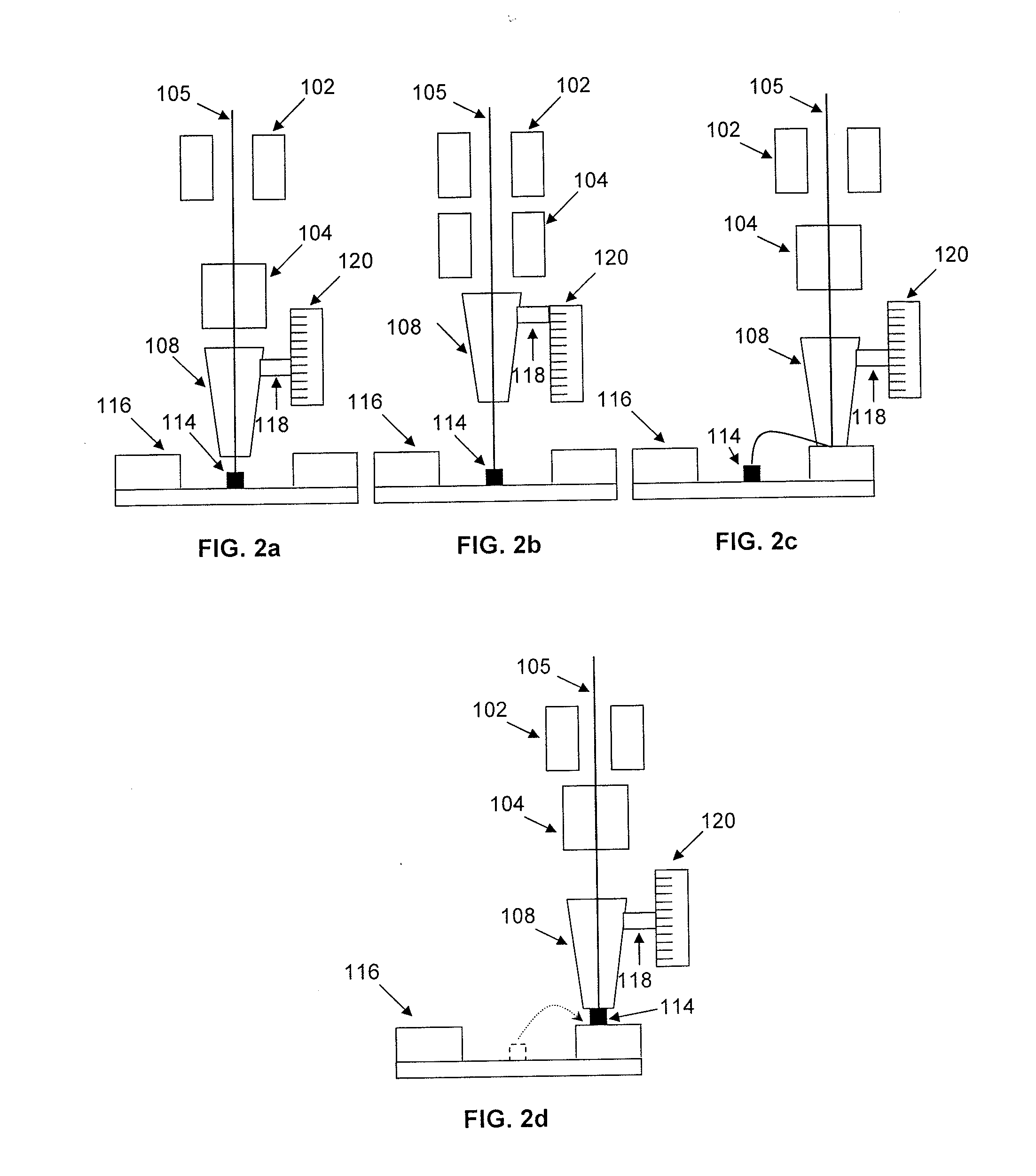
Apparatus and method for non-destructive testing
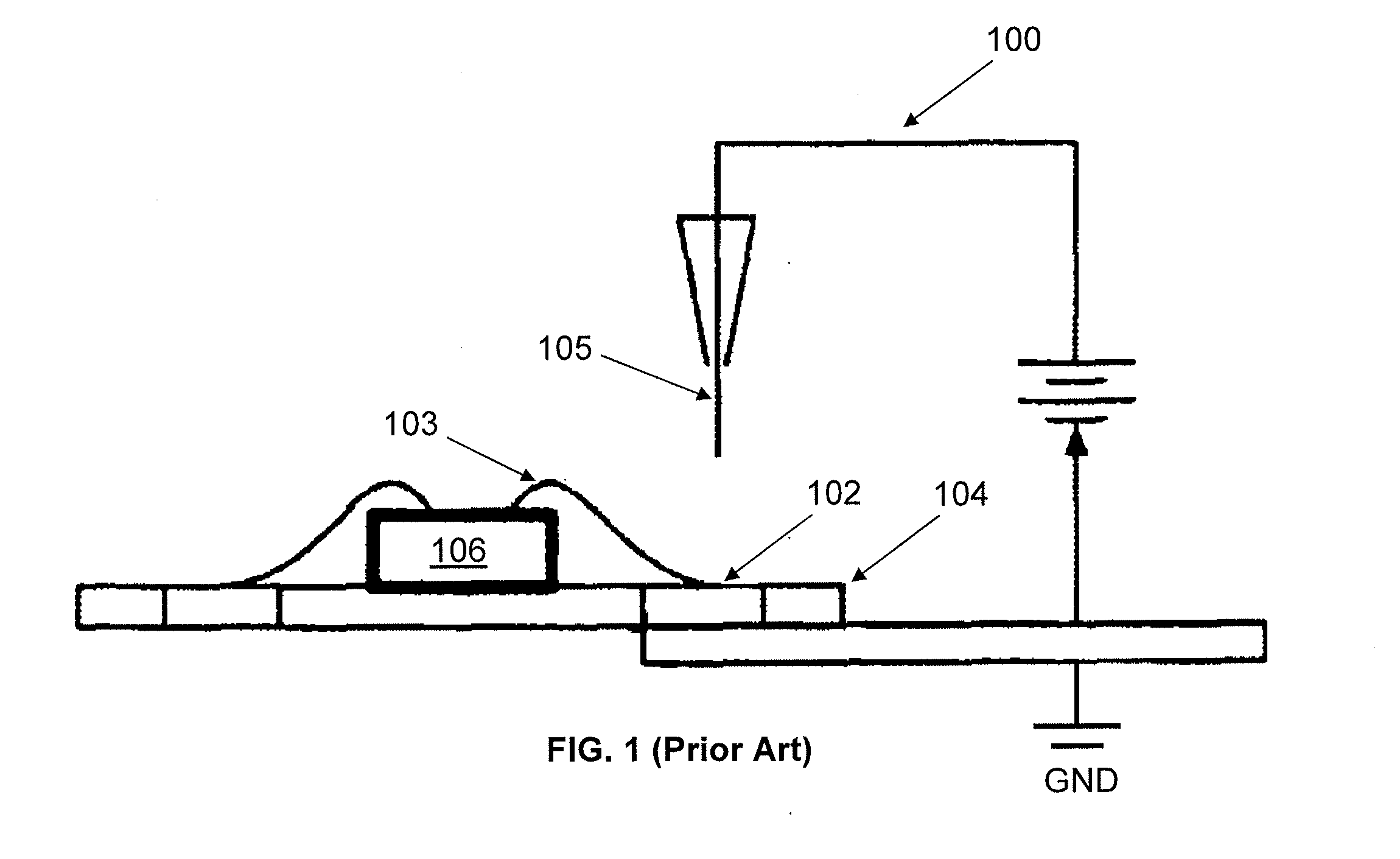
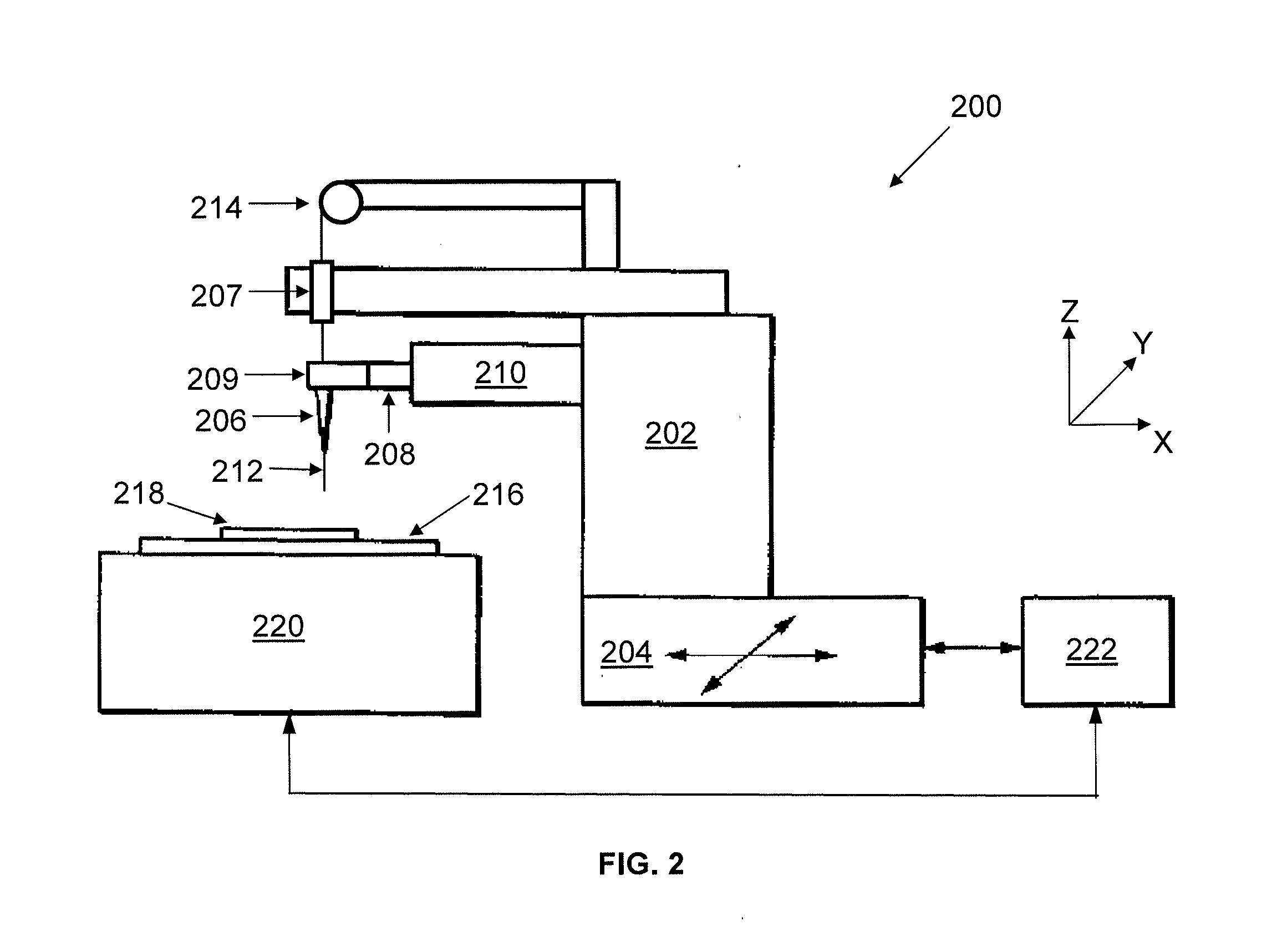
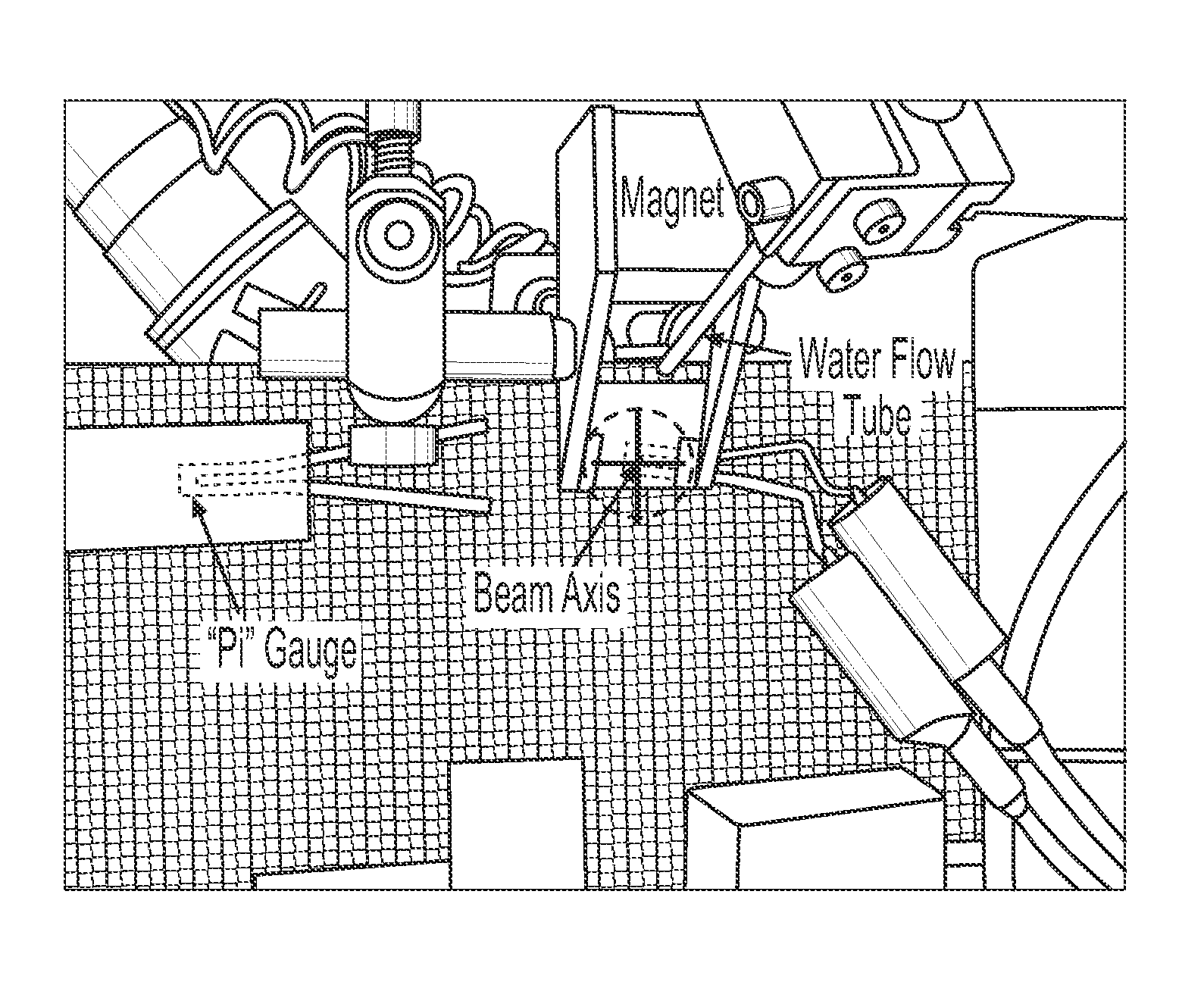
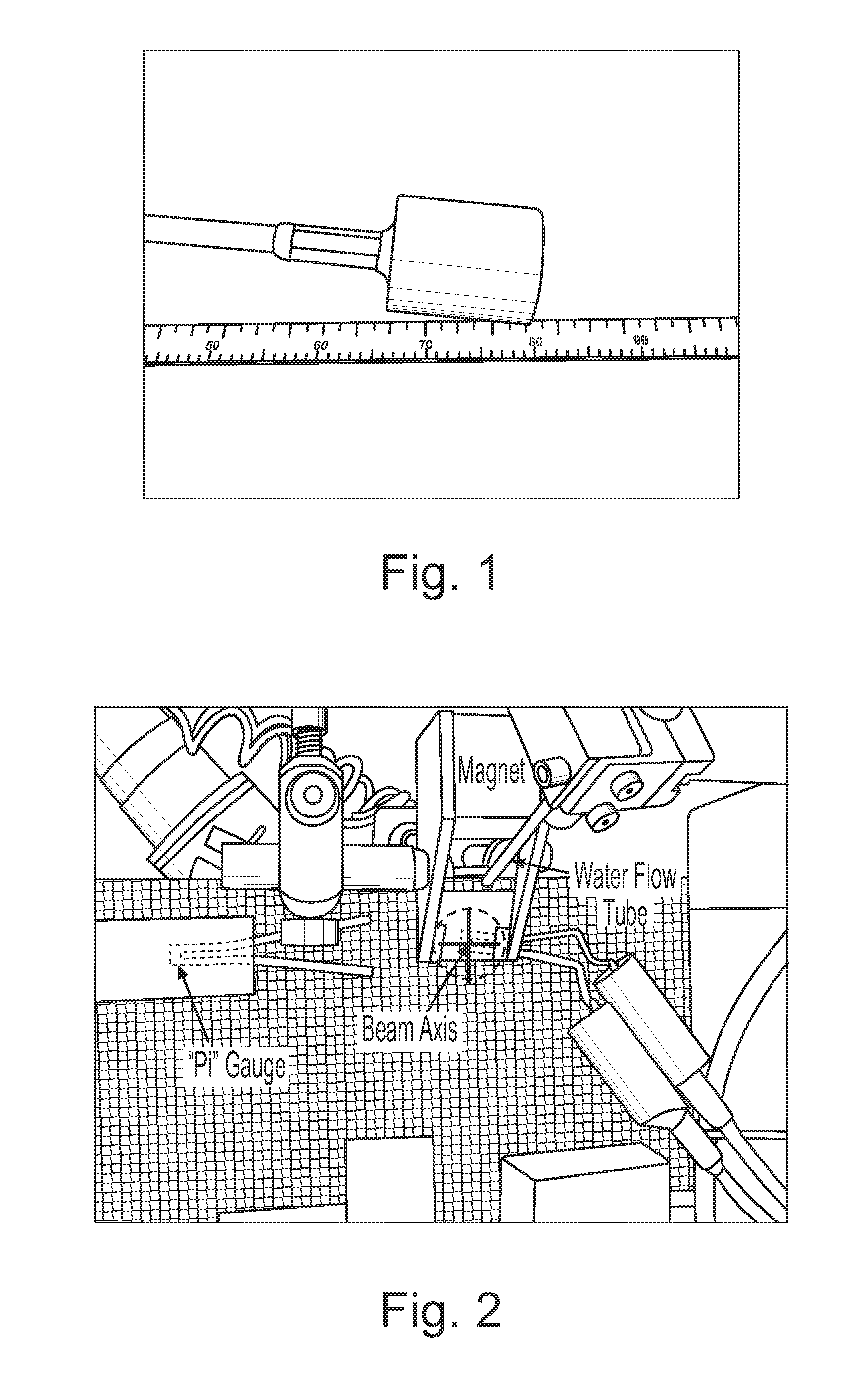
ActiveUS8156811B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveDynamic strength
A diagnostic means to enable real-time inspection of bonded structures. The disclosed apparatus detects bond failure stress waves on-axis from the front side (beam application side). Pi-box and pi-rail EMAT gauges can be used with the disclosed apparatus. An inductively coupled EMAT may also be employed. An improved means to remotely deliver an interrogating laser beam to a surface is provided. The process head may utilize a water column or a water film. The water film process head may include the use of either a single water film or two spaced apart water films. The disclosed apparatus can be used with bonded composite structures, bonded structures using various materials, and to determine the dynamic strength of unbonded solid materials. The apparatus may also be used in other applications that require remote flexible delivery of a localized stress wave to a material and / or diagnosis of the resultant stress waves.
Owner:LSP TECH INC
Large-specification recombination composite structural wood and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103231425AFill in the gapsSolve degummingWood veneer joiningAdhesive application devicesCardboardComposite construction
Owner:ANHUI HONGYU BAMBOO IND TECH
Dynamic fatigue evolution test method for rubber and fiber cord thread bonding
InactiveCN104502276AAccurately reflectEasy to operateUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisElastomerFiber
The invention discloses a dynamic fatigue evolution test method for rubber and fiber cord thread bonding, by means of connecting a fixture with an MTS elastomer test system, the method realizes simulation of continuous evolution process of bonding failure of rubber and a fiber cord thread under various conditions of use in multiple modes such as constant stress, constant strain as well as alternating load and alternating frequency. The beneficial effects of the method are that: the method is simple to operate, the data is reliable, the reproducibility is high, the test process has time continuity, so the method can better simulate the evolution process of bonding fatigue rupture of multiple kinds of rubber and various fiber cord thread composite materials under the condition of real stress, and has important guiding significance for predicting the service life of rubber products,thereby having a broad application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
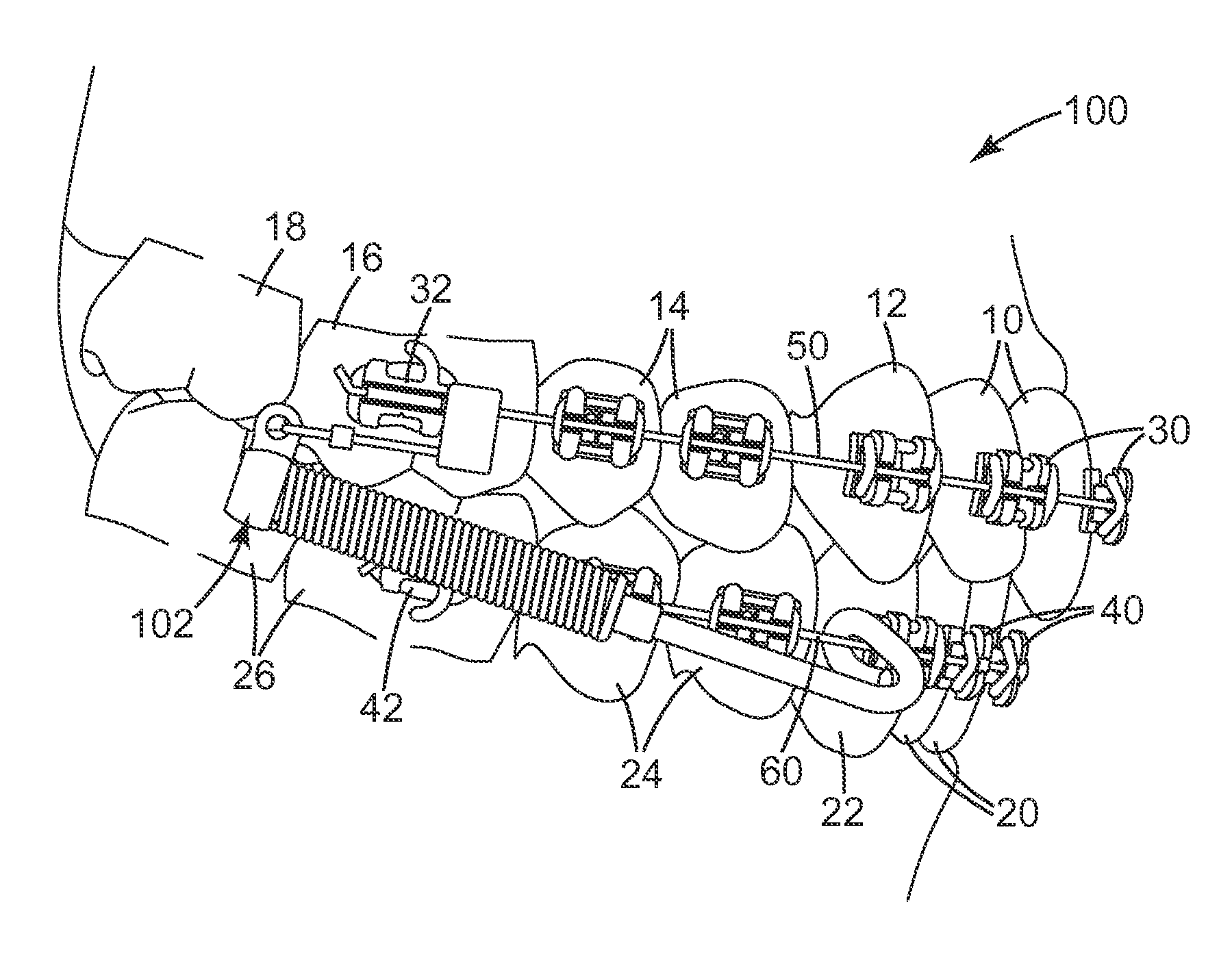
Intraoral orthodontic corrector
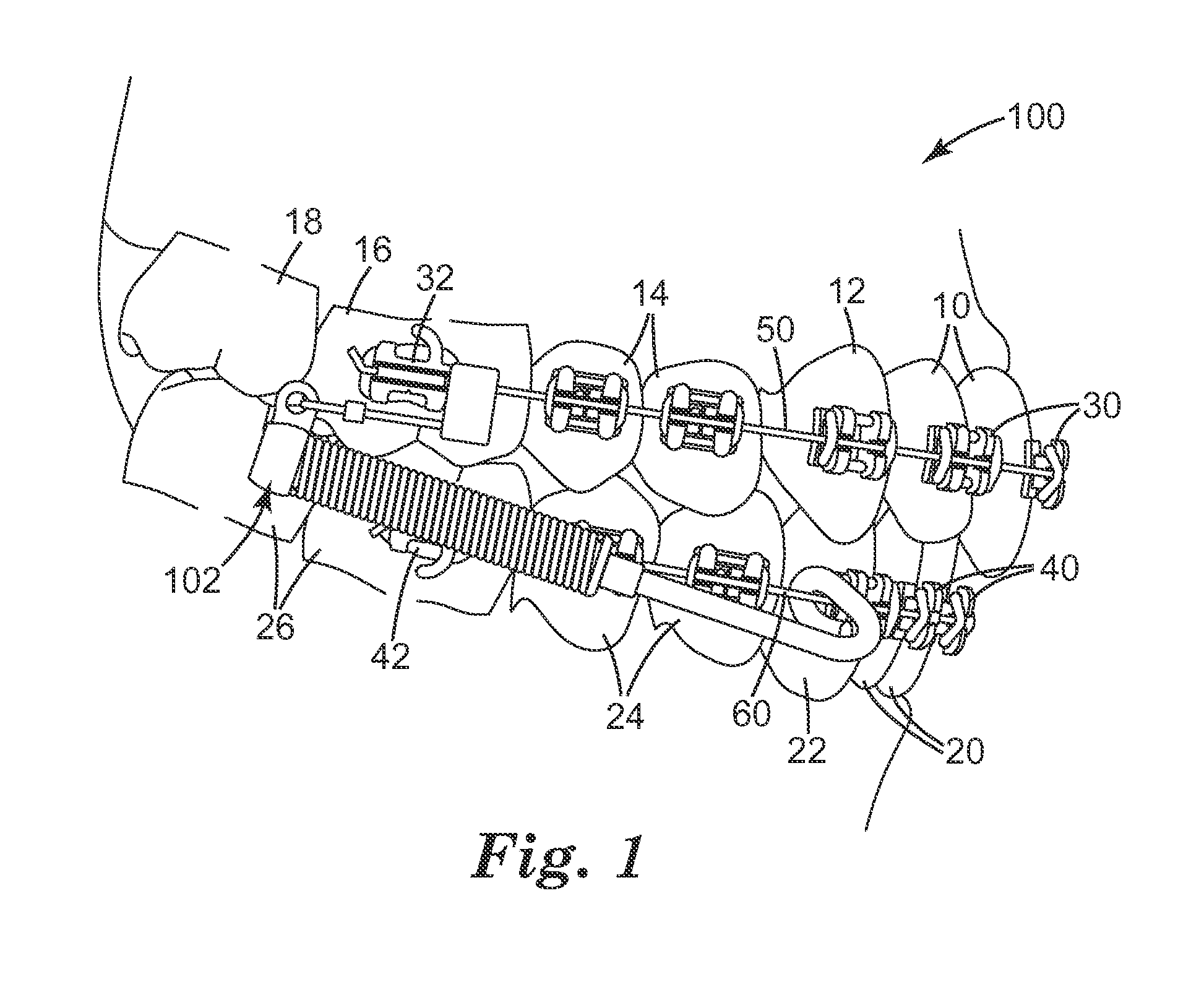
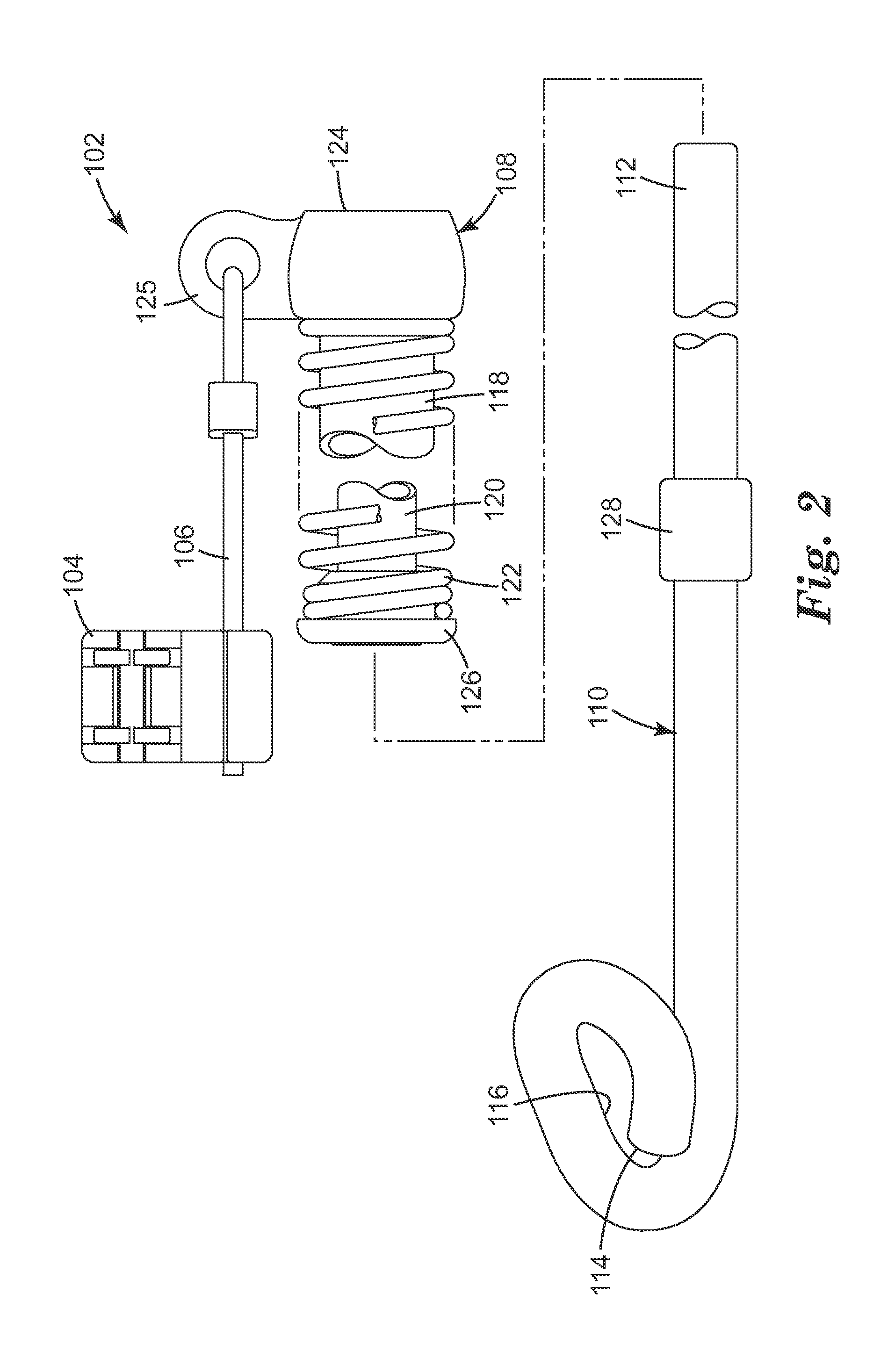
Provided are orthodontic corrector devices, related assemblies and methods which direct forces within the oral cavity. These corrector devices and assemblies include a flexible cantilever which is coupled to both a connector component and a force module. The cantilever acts to isolate adjacent components from mastication forces encountered during treatment. By resiliently deflecting in response to these inadvertent forces, the cantilever reduces the likelihood of device breakage and bond failure. Upon removal of these forces, the cantilever returns to its original orientation thereby maintaining the proper alignment of the corrector. Advantageously, the cantilever also allows the force module to be positioned further in the distal direction thereby enabling a greater range of connection options.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Insulated rail joint assembly
ActiveUS7677466B2High strengthImprove the immunityRail devicesRail jointsCross connectionEngineering
An insulated rail joint assembly comprises a rail with a thick web section, held in place by joint bars and secured with electrically isolated fasteners. The joint bars have non-uniform cross-sections, being shaped with a thicker midsection area and thinner ends. Electrically non-conductive shear pins through the rail and the joint bars provide shear resistance and prevent glue bond failure. High strength cloth between the rail ends and between the rail and the joint bars strengthens the joint, as does an insulating rail clip resiliently fastened to an insulating tie plate, which itself may be supported on a cross tie of increased width.
Owner:VOESTALPINE RAILWAY SYST NORTRAK LLC
Method of recovering a bonding apparatus from a bonding failure
ActiveUS20130180957A1Function increaseEasy constructionSolid-state devicesSoldering apparatusSemiconductor chipEngineering
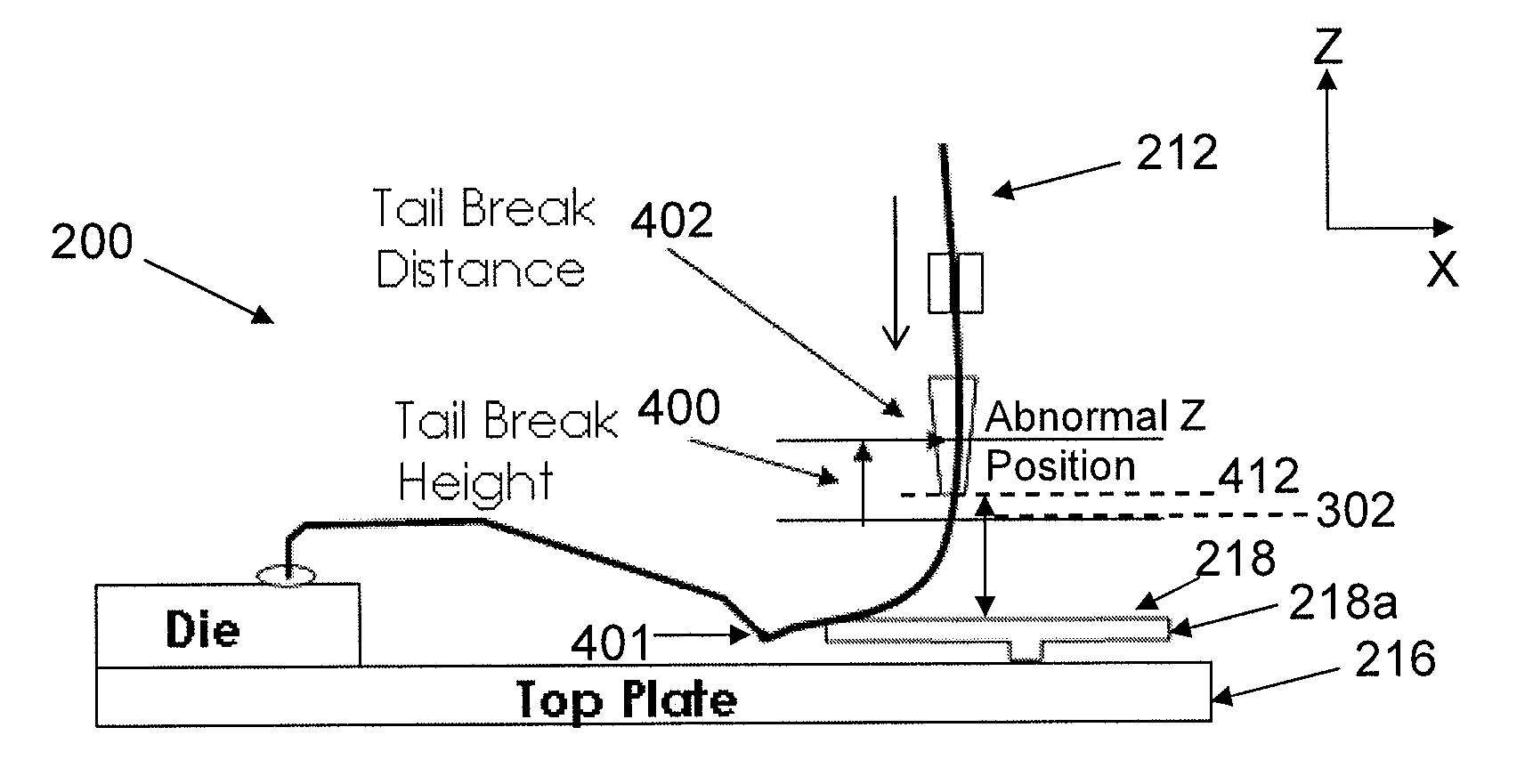
A method of recovering a bonding apparatus from a bonding failure to resume a normal operating state for semiconductor chip fabrication is disclosed. The bonding apparatus comprises: i) a bonding tool for bonding a wire between a semiconductor chip and a substrate; and ii) a position sensor. Specifically, the method comprises the steps of: a) the position sensor determining a position of the bonding tool when the bonding tool contacts a surface to bond the wire to the substrate; b) the bonding apparatus detecting a bonding failure caused by detachment of the semiconductor from the substrate based on the position of the bonding tool; and c) the bonding apparatus detaching the semiconductor chip from the wire.
Owner:ASMPT SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Water distribution valve spool of water jet loom
InactiveCN103696103AGuarantee normal water supply demandAvoid unstable water supplyLoomsInstabilityEngineering
The invention relates to the field of water jet looms, in particular to a water distribution valve spool of a water jet loom. The water distribution valve spool comprises a water distribution shaft and a water distribution sleeve, the water distribution shaft is fixedly arranged in the water distribution sleeve, and holes communicated mutually are formed in the water distribution shaft and the water distribution sleeve respectively. Limiting planes are arranged between the water distribution shaft and the water distribution sleeve, so that the water distribution shaft and the water distribution sleeve are prevented from rotating relatively due to bonding failure, as a result of water supply instability; the water distribution valve spool is reliable and stable in structure, and the requirement on normal water supply of the water jet loom is met.
Owner:ZHENJIANG DONGYI MACHINERY
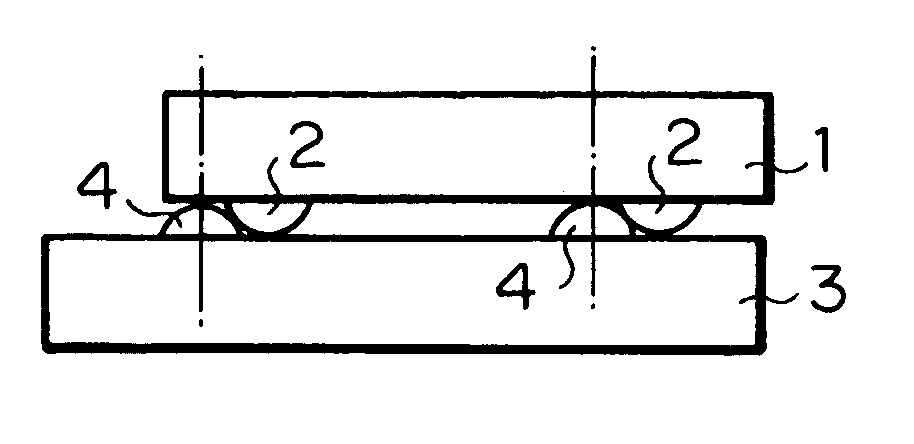
Semiconductor device and process for producing the same
When a semiconductor chip is mounted on a mount substrate by bonding bumps, bonding failure is caused by misalignment between the bumps. <??>Before a semiconductor chip having a plurality of bumps is mounted on a mount substrate (3) having a plurality of bumps (4) by flip chip bonding, a resist layer (5) having a thickness larger than that of the bumps (4) is formed on the mount substrate (3) with the bumps. By patterning the resist layer (5), projecting guides (5A) of semicircular cross section are formed on the mount substrate (3) so as to protrude near the bumps (4) and from a surface on which the bumps (4) are provided, and to have guide faces (curved faces) pointing toward the bumps (4).
Owner:SONY CORP
Integrated circuit having reduced probability of wire-bond failure
InactiveUS6153506ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAsic technologyContact angle
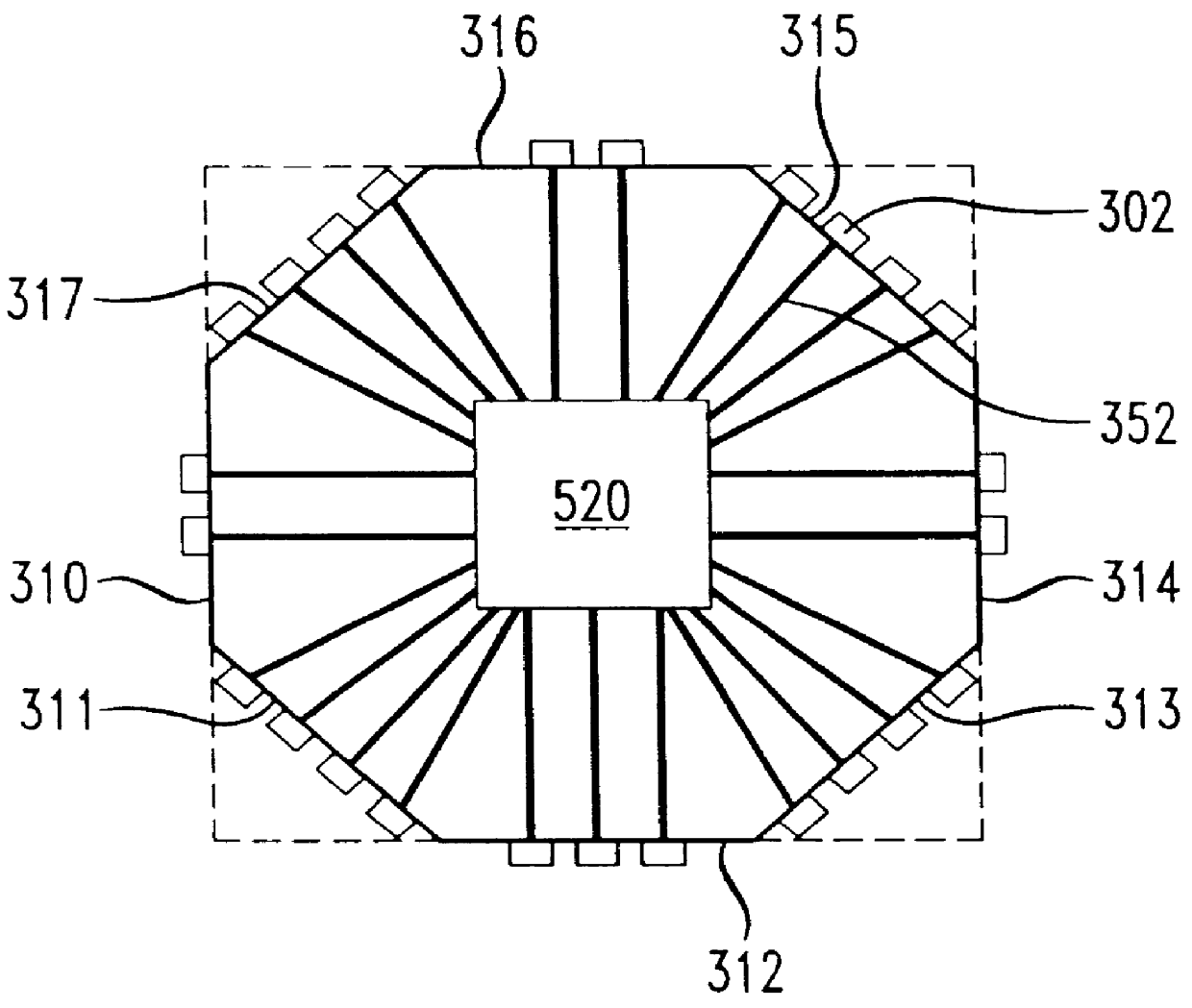
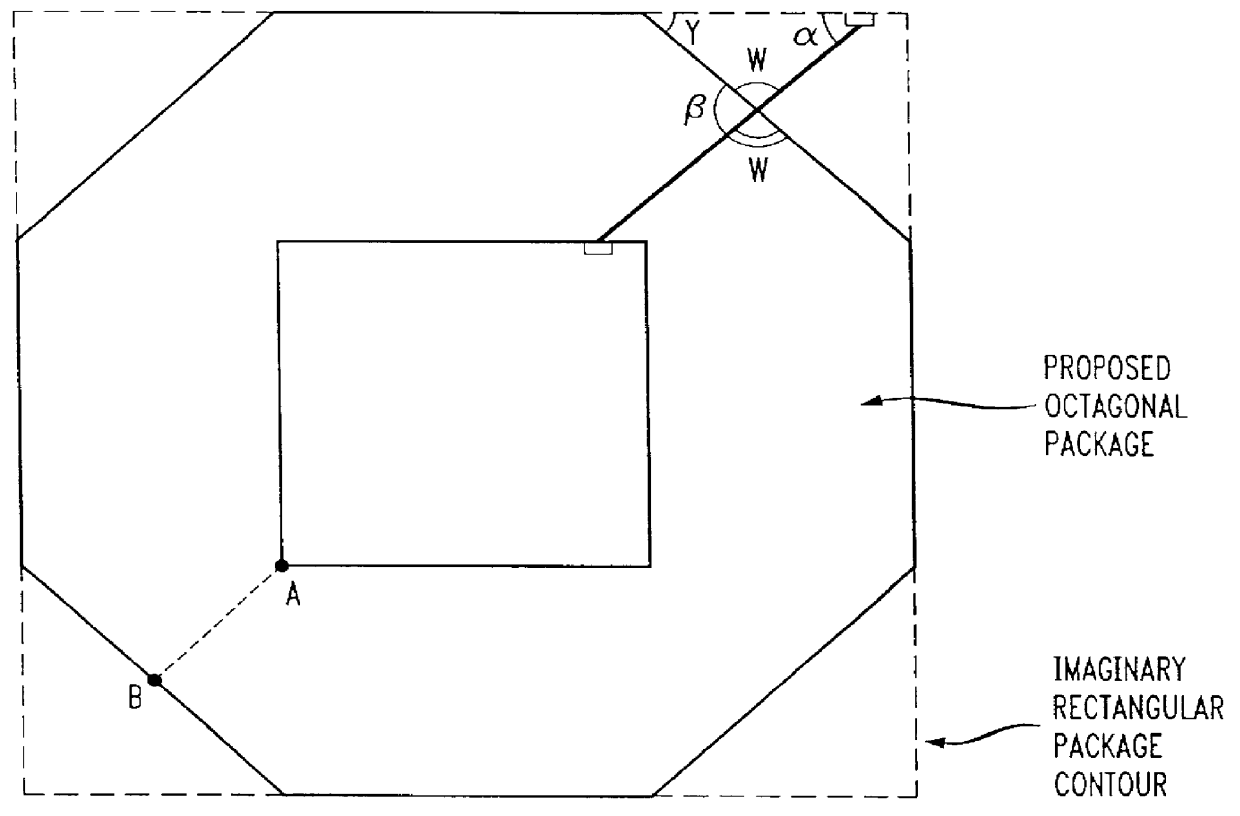
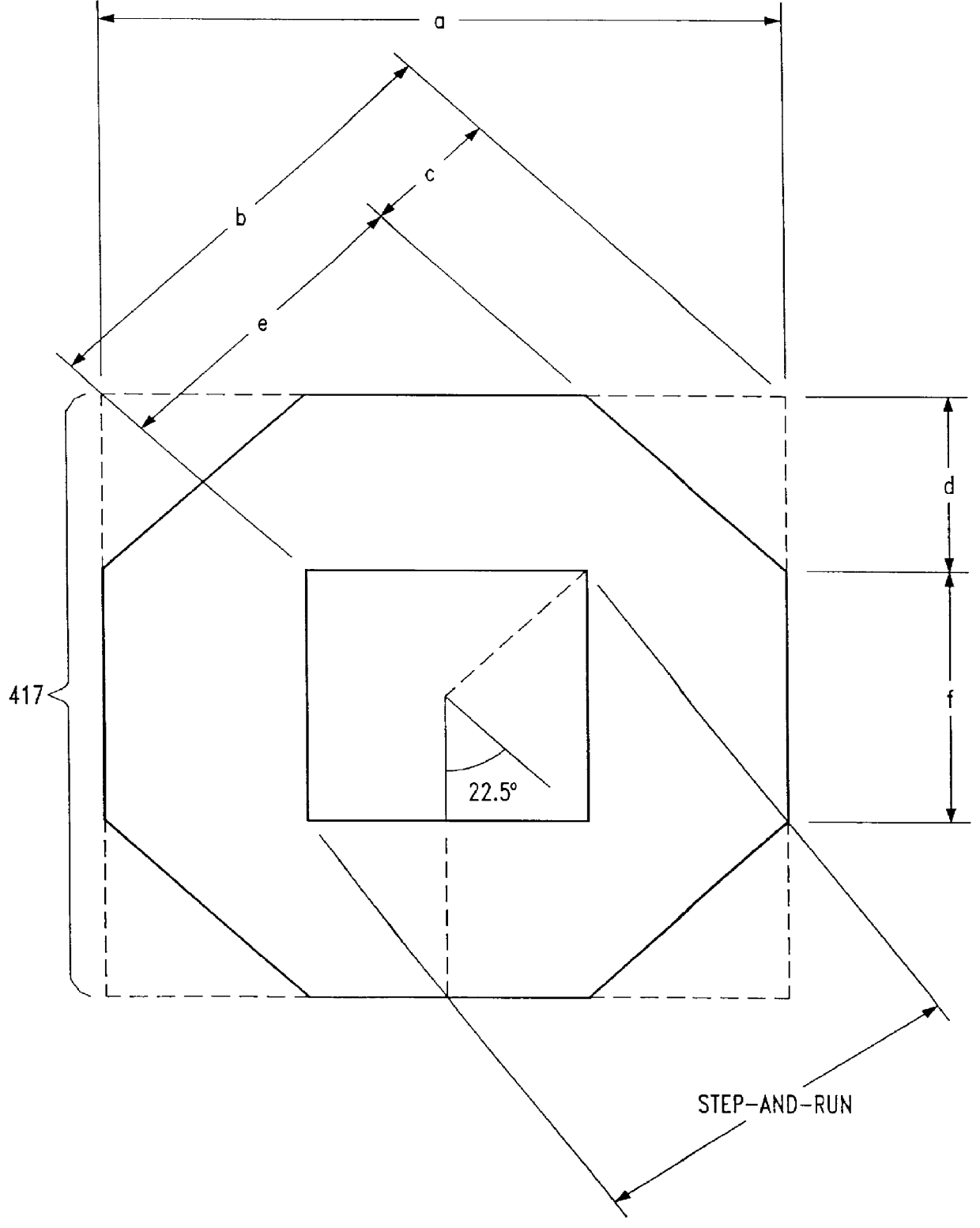
The present invention provides an improved integrated circuit technique for increasing the reliability of wire-bonds in an integrated circuit by increasing the contact angle between certain pins and their respective wire-bonds, particularly those pins otherwise most susceptible to wire-bond failure, i.e., those pins conventionally located toward the corners of a conventional integrated circuit. By doing so, the overall length of the wire-bonds in a chip will be reduced, which in turn can result in further reduction of the probability of wire-bond failures. In a disclosed embodiment, a five or more sided integrated circuit shape is introduced wherein pads on up to four sides of an integrated circuit wafer chip are bonded to pins supported on eight edges of an integrated circuit package. An integrated circuit having at least five pin-supporting edges renders more robust wire-bond angles for any given integrated circuit package size.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC +1
Electronic component package, electronic component mounted apparatus, method of inspecting bonding portion therein, and circuit board
ActiveUS20080266825A1Satisfactory bondabilityReliability of bondabilityLine/current collector detailsElectrically conductive connectionsSolder ballEngineering
An electronic component package includes: an insulating carrier substrate; a connection wiring that is provided on one side of the carrier substrate; an IC chip that is connected to the connection wiring; an external connection land that is disposed on the other side of the carrier substrate and is connected to the connection wiring via a wiring in the carrier substrate; and a solder ball that is disposed on the external connection land. A region of the external connection land that can be bonded to the solder ball has an outer shape that includes at least one arc portion and at least one straight portion. With this configuration, it is possible to provide an electronic component mounted apparatus in which bonding failure of the external connection land and the circuit board-side land with the solder ball can be reduced, and the bonding state can be easily inspected, and a method of inspecting a bonding portion therein.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bonding wire of gold (Au) alloy
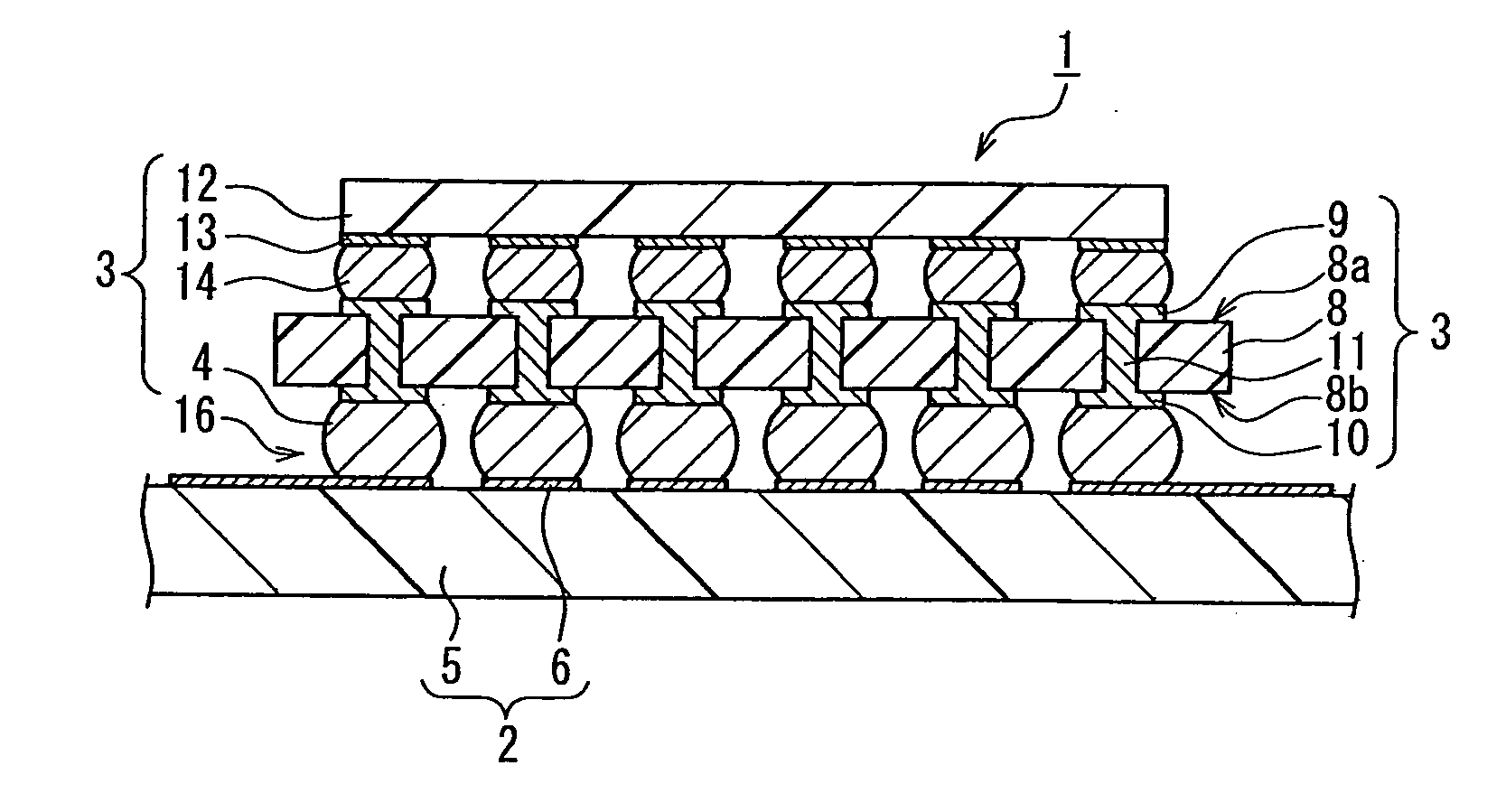
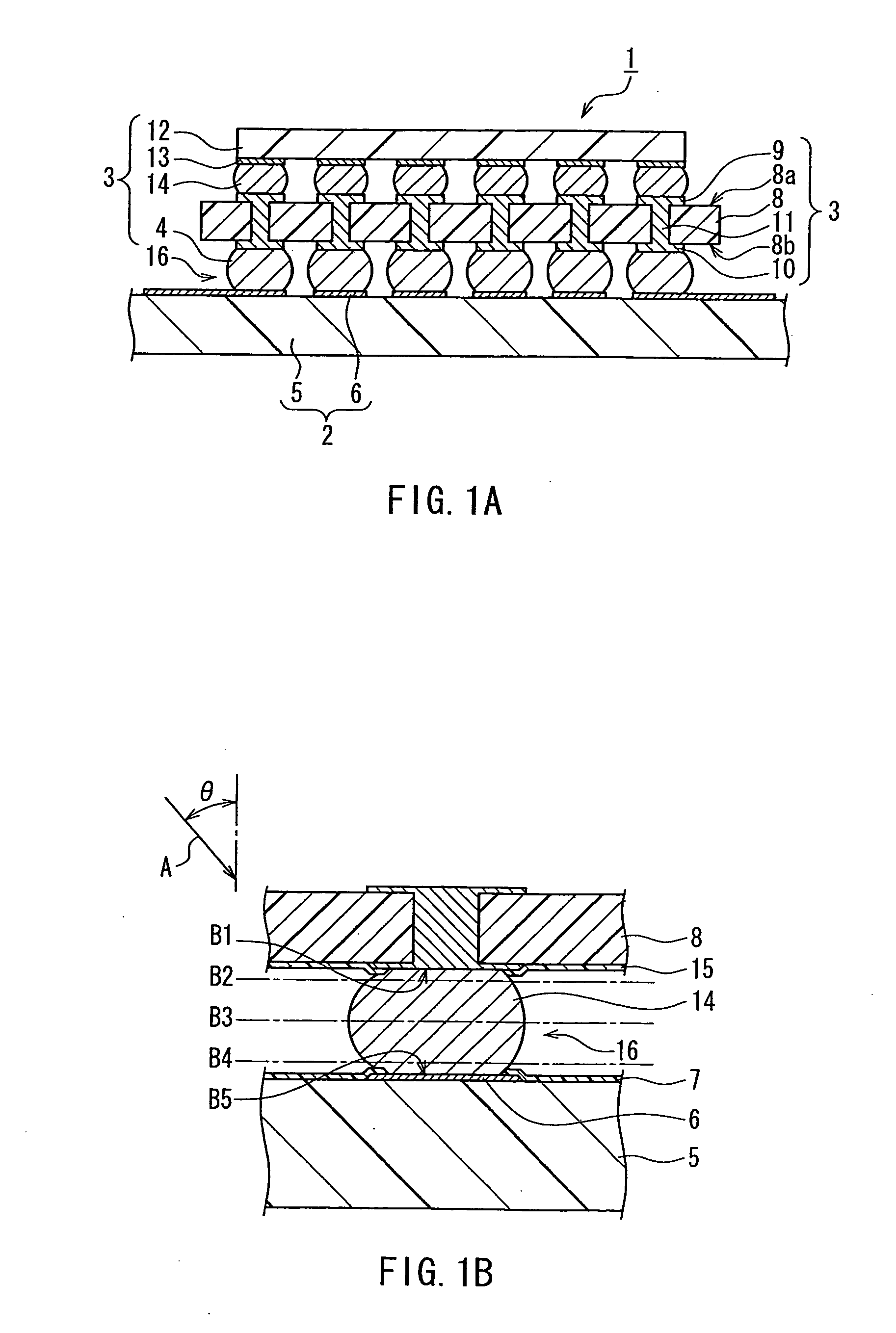
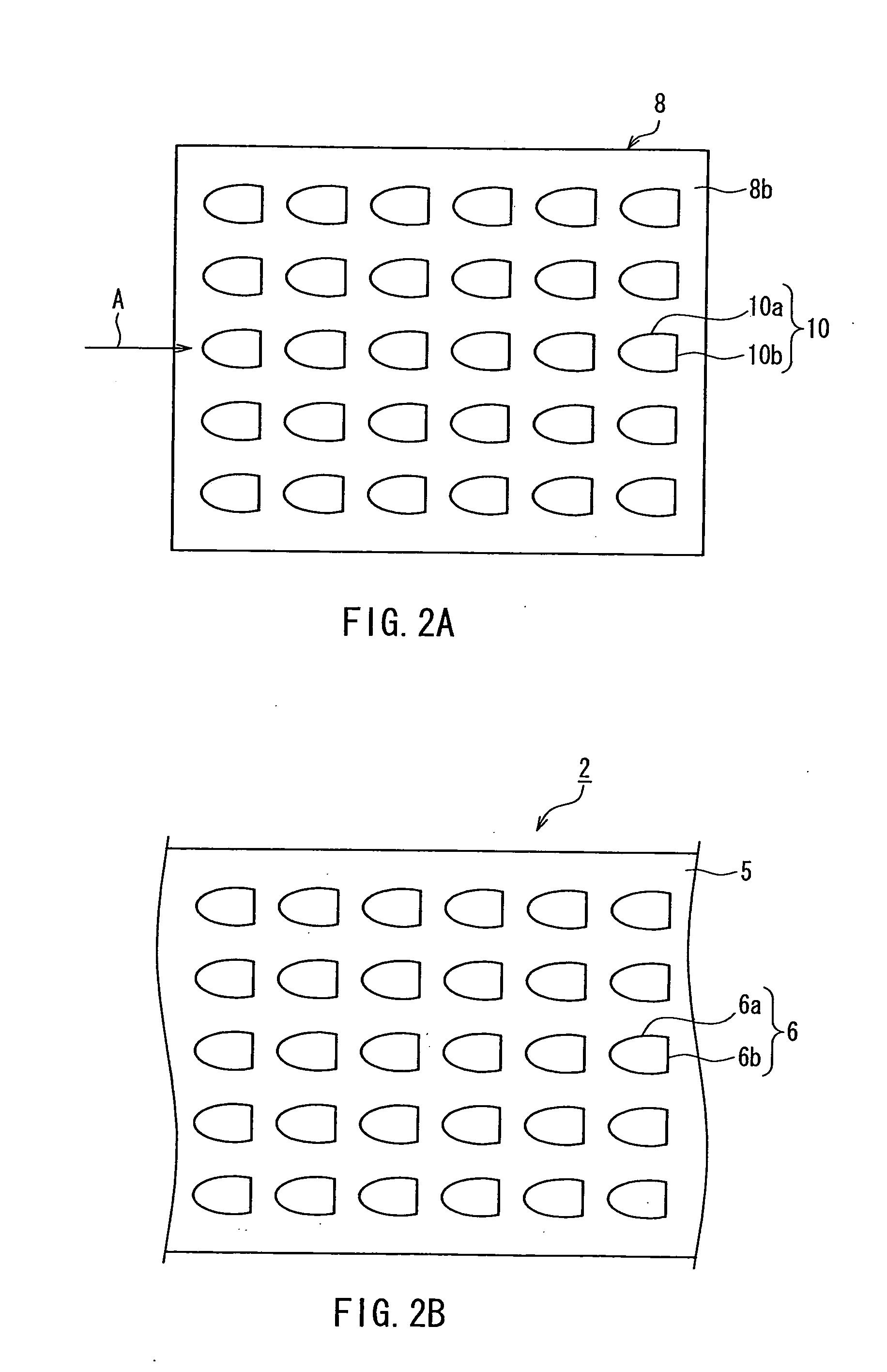
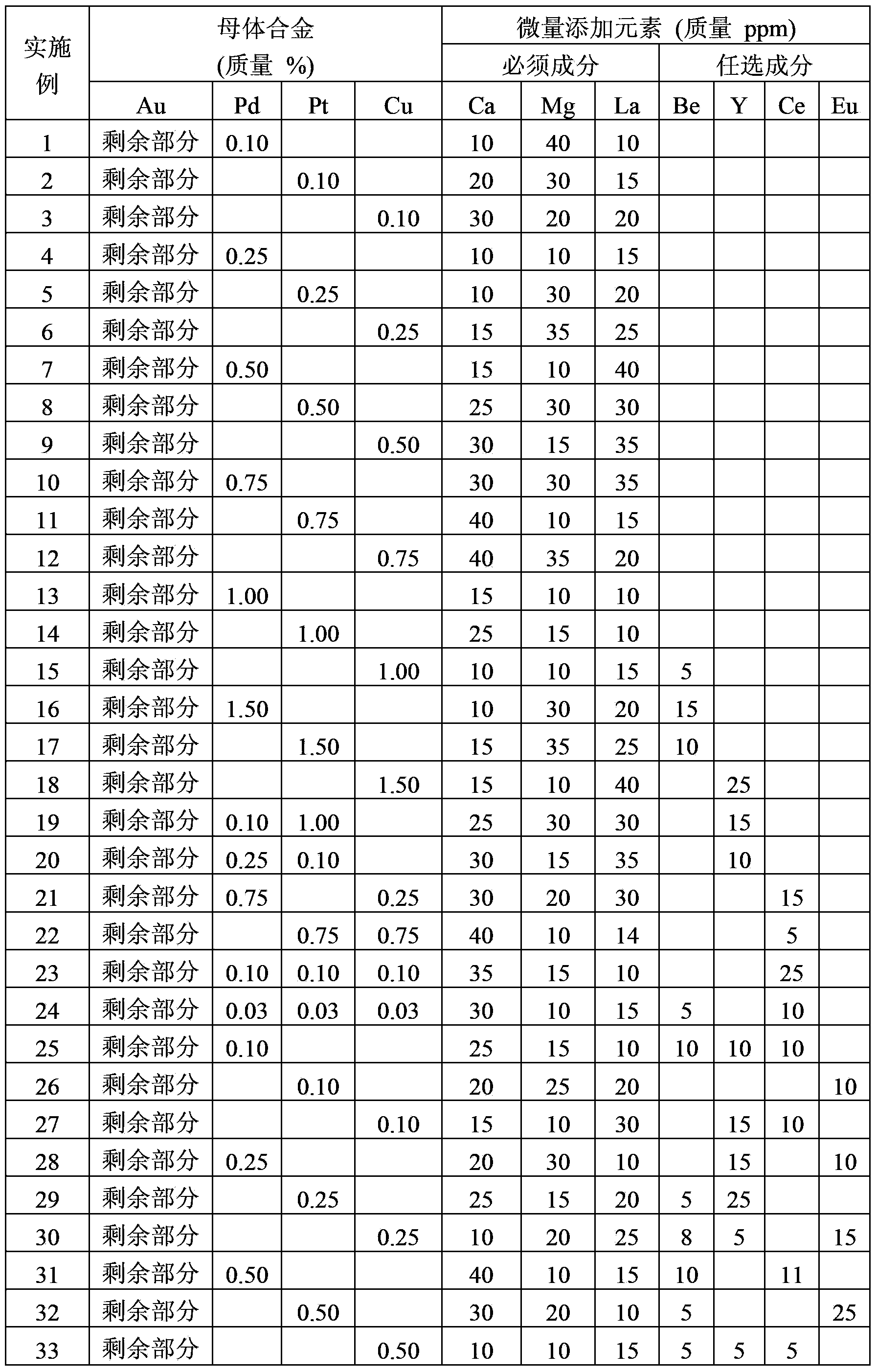
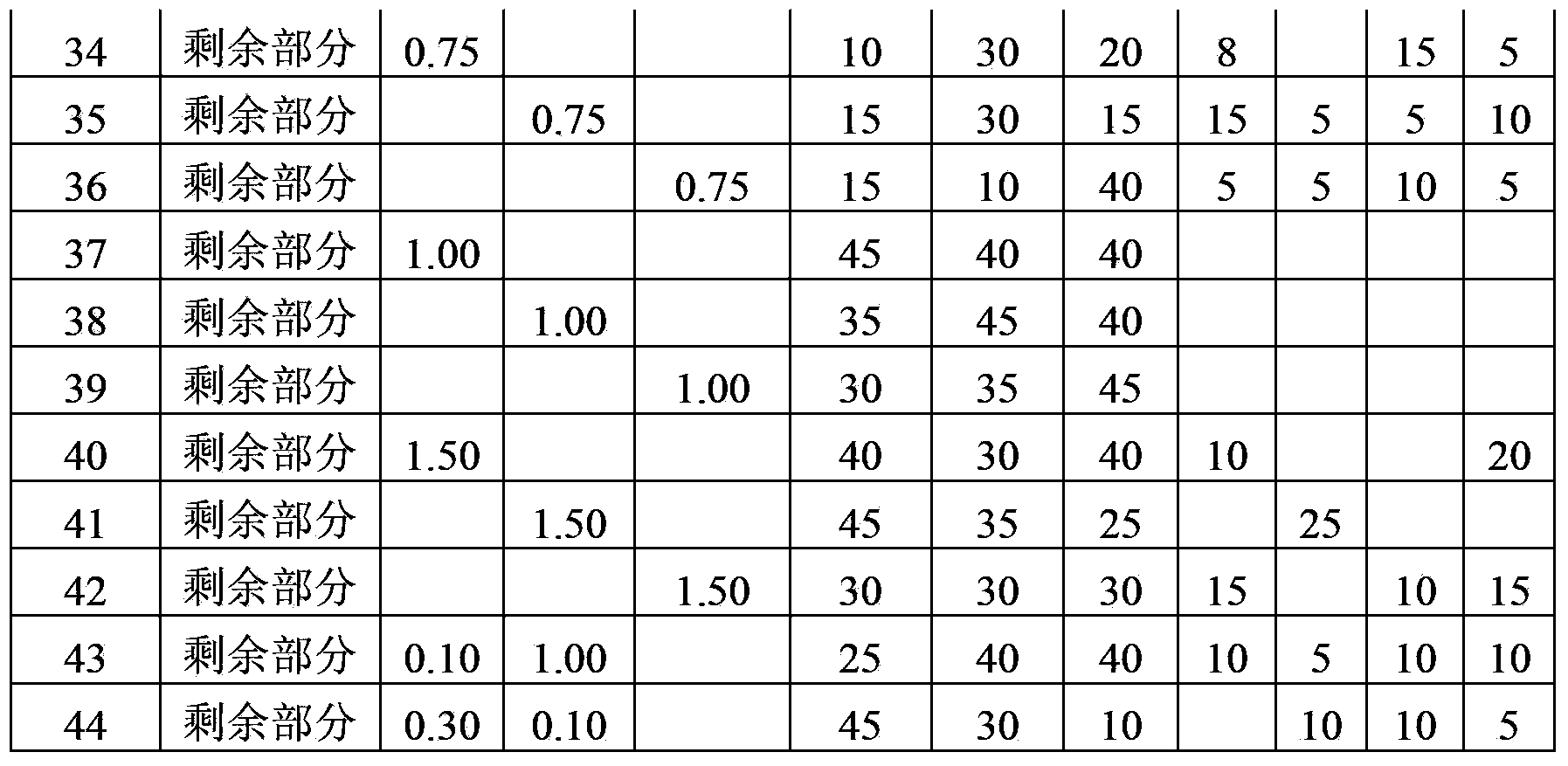
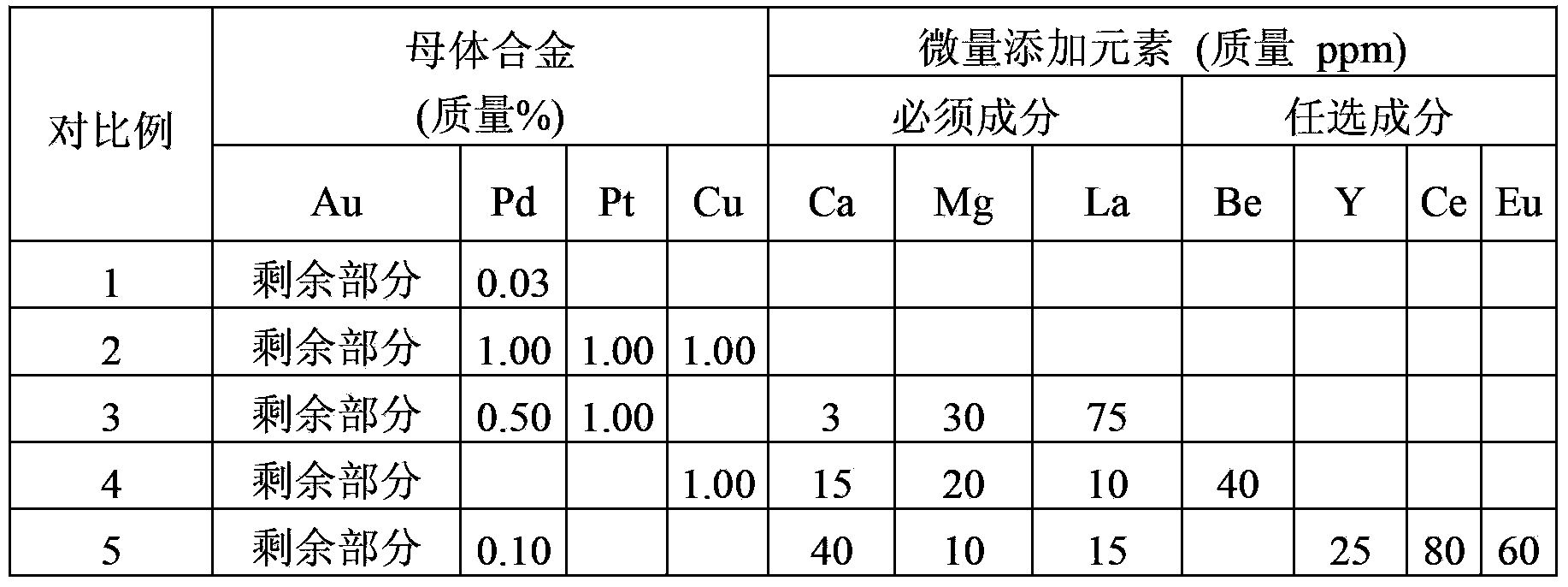
ActiveCN103842529AAvoid damageAvoid flowSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBall bondingBond failure
An ultrafine wire having a diameter of 20 [mu]m or less for ball bonding, with which bonding can be successively conducted hundreds of thousands of times. Ca, Mg, and La are incorporated as minor additive elements in a concentration of 5-50 mass ppm each into an alloy matrix obtained by incorporating one or more of Pd, Pt, and Cu that have a high purity of 3N or above, in a total concentration of 5-2 mass%, into gold that has a high purity of 5N or above. Alternatively, Be is further incorporated in a concentration of 1-20 ppm, and / or one or more of Ce, Y, and Eu are further incorporated in a total concentration of 1-30 mass ppm. Furthermore, the total concentration of these minor additive elements may be regulated to 100 ppm or less. Thus, the additive elements are inhibited from segregating in the surface of the melt ball, and deposits or oxides of the additive elements are inhibited from accumulating on the capillary tip during bonding and thereby increasing the sliding resistance of the wire during loop formation. Since the surface of the capillary tip is kept smooth, bonding failures in the wire bonding, such as neck damage and nonbonding, are inhibited from occurring and long-term continuous bonding is rendered possible.
Owner:TANAKA DENSHI KOGYO KK
Bridge deck reinforcing structure and method
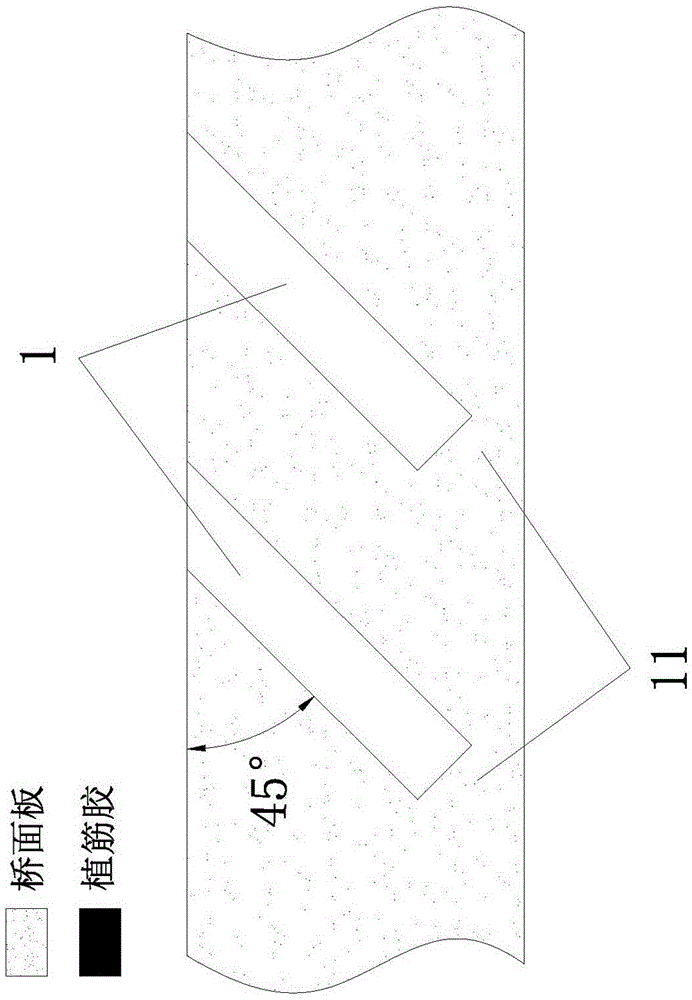
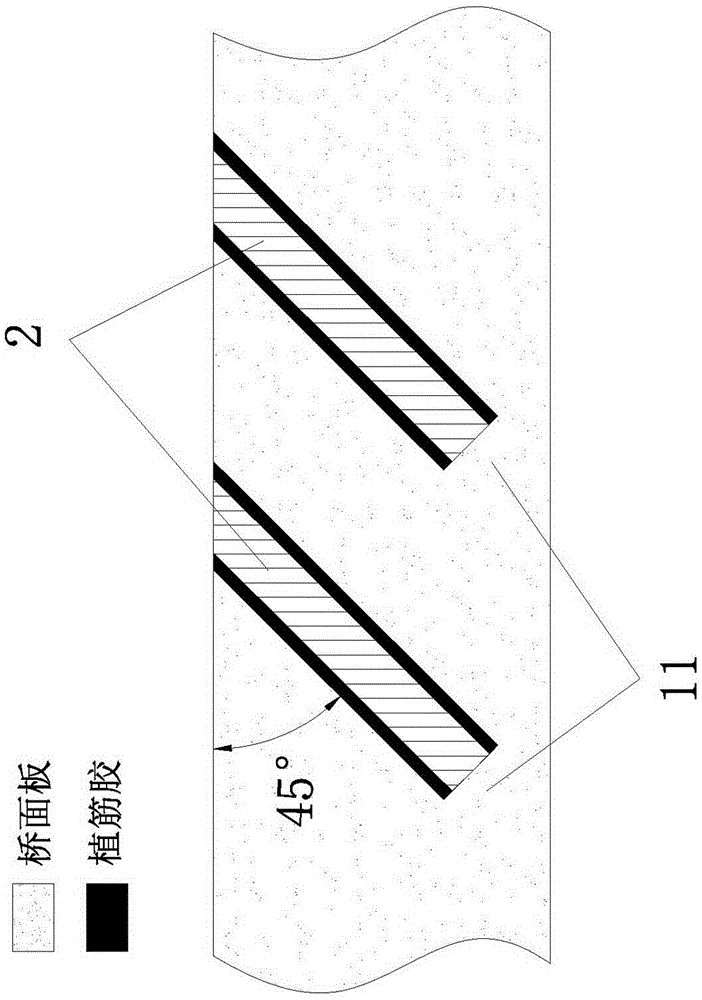
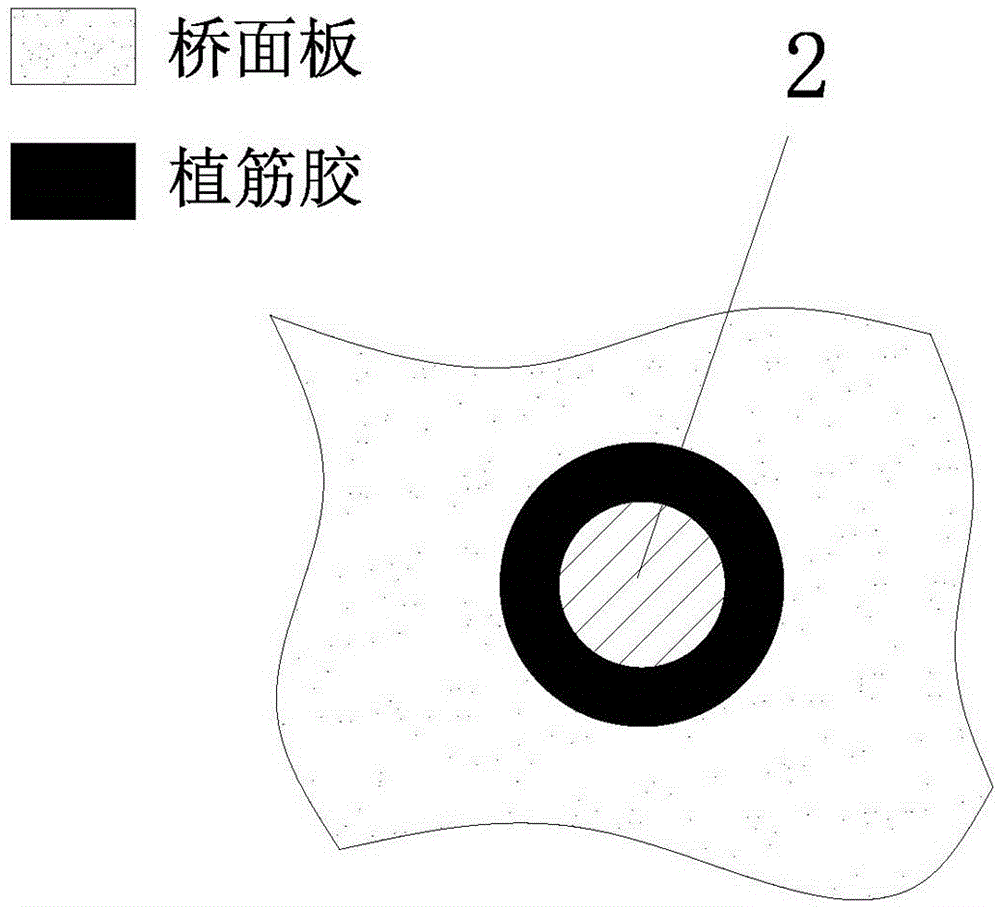
InactiveCN106168016AIncreased shear capacityImprove adhesionBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblySurface layerSurface mounting
The invention provides a bridge deck reinforcing method. The method comprises the steps of drilling, wherein reinforcing holes are drilled in the top surface and / or bottom surface of a bridge deck; glue filling, wherein the reinforcing holes are filled with steel bar embedding glue; steel bar distribution, wherein FRP bars are placed in the reinforcing holes. Compared with a surface bonding method in the prior art, the reinforcing method has the advantages that the FRP bars are protected and limited by a concrete structure of the bridge deck after being placed in the reinforcing holes without being affected by the external environment basically, so that FRP bar and concrete bonding property is improved and bonding failure caused by edge concrete cracking is effectively avoided. Compared with a surface-surface mounting method in the prior art, the reinforcing method has the advantage that reinforcement is conducted by drilling concrete and then placing the FRP bars in the drilled reinforcing holes instead of being conducted on the surface layer of concrete, so that damage to a concrete protection layer is avoided.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
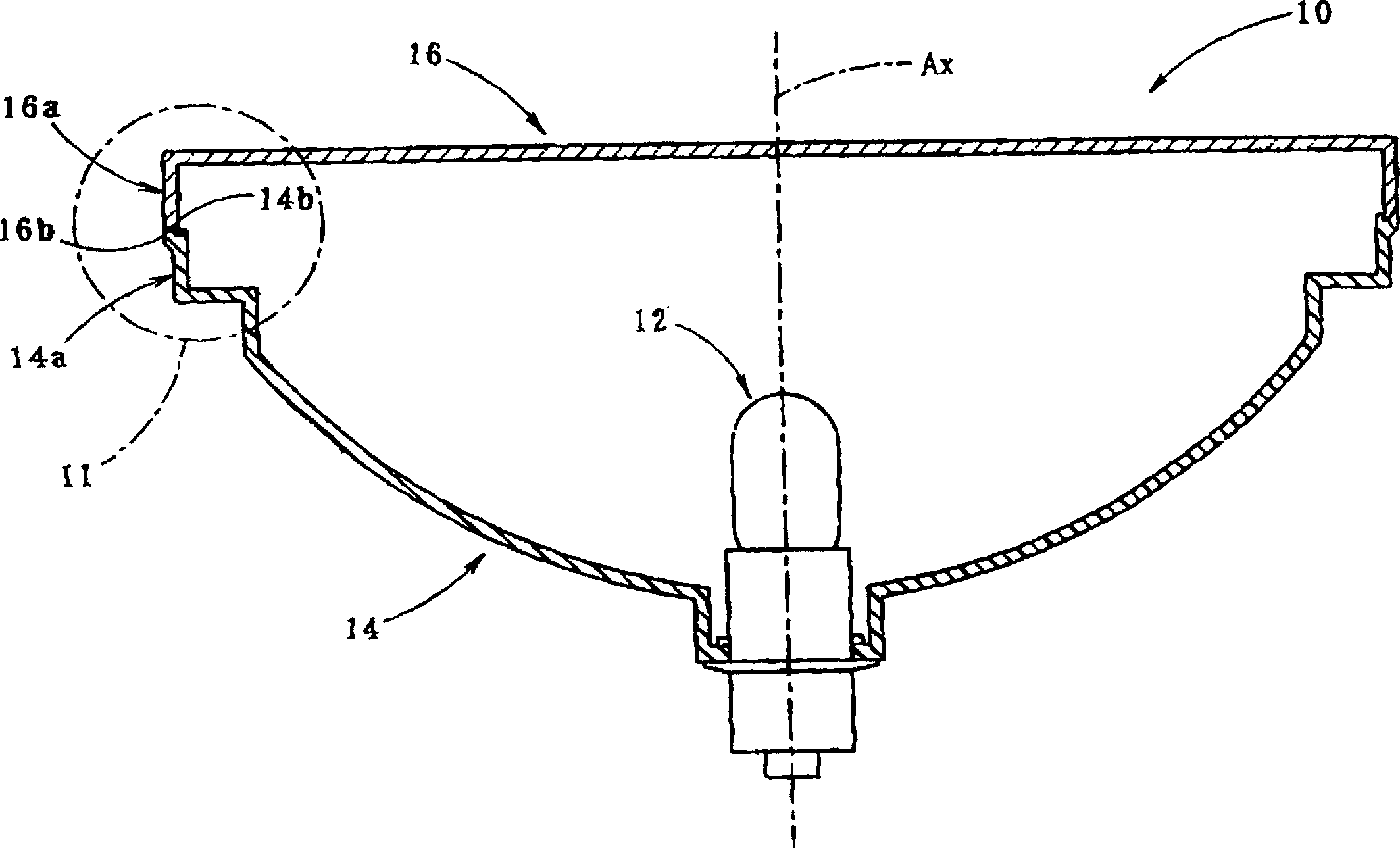
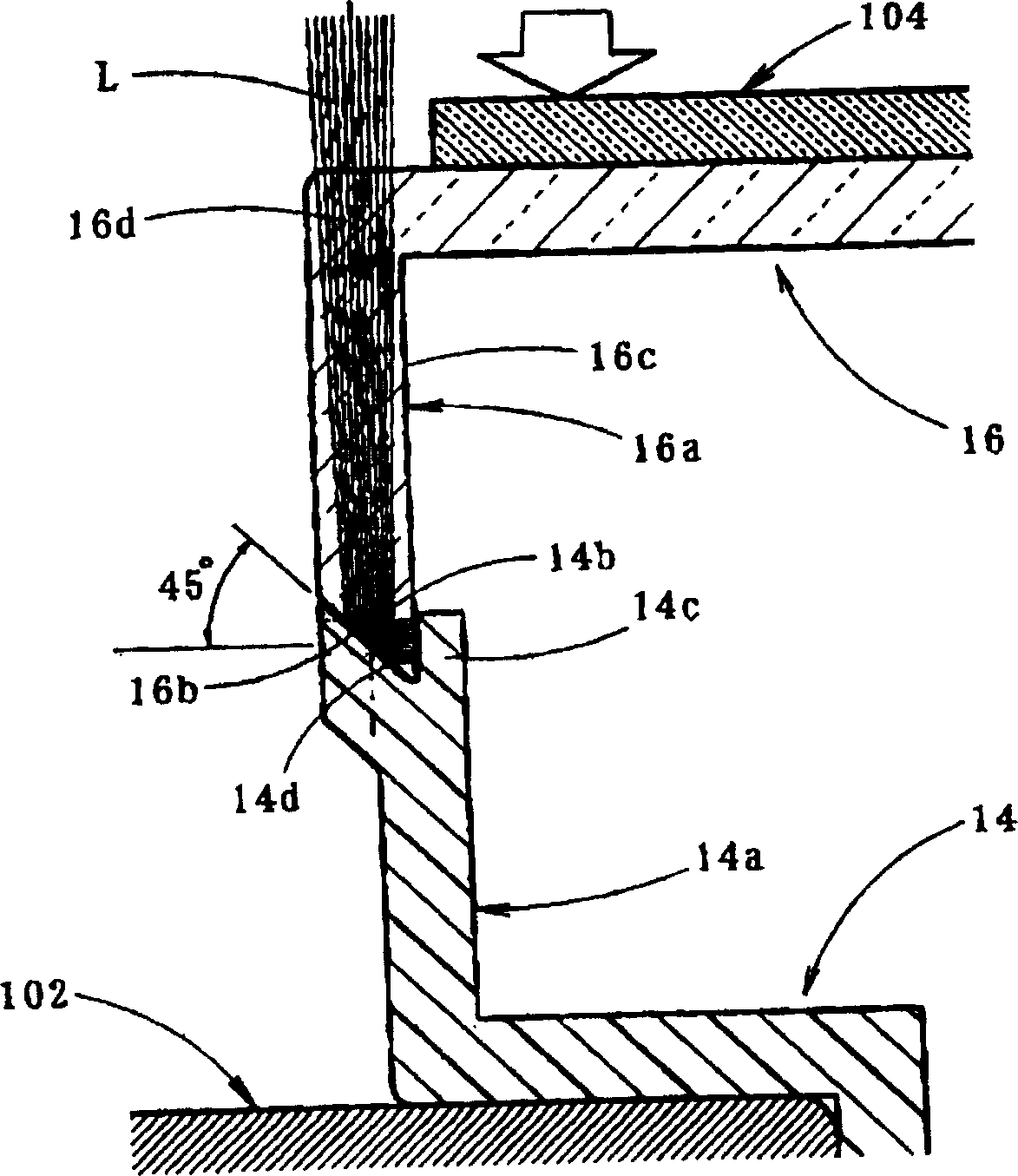
Automotive lamp unit and making method thereof
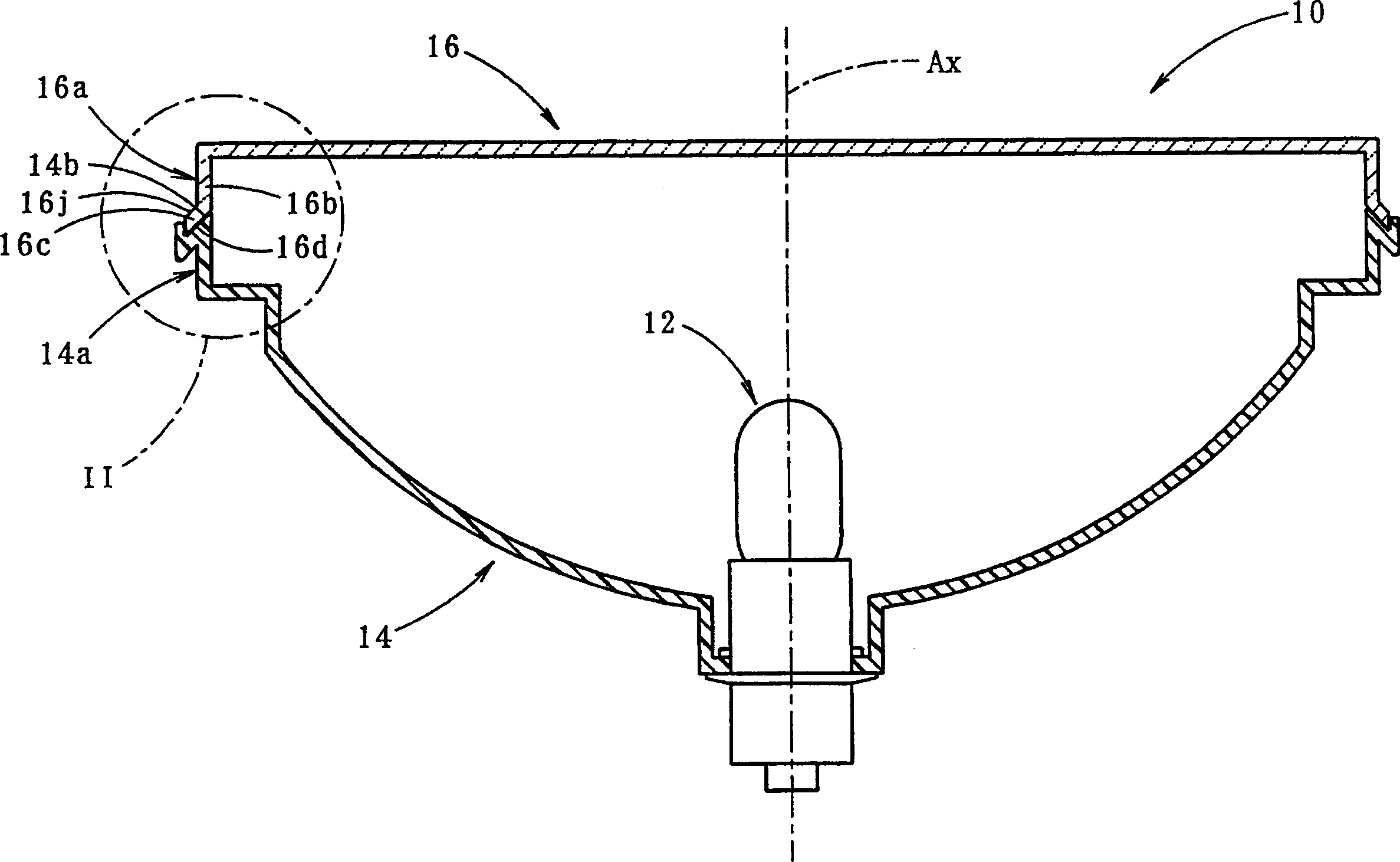
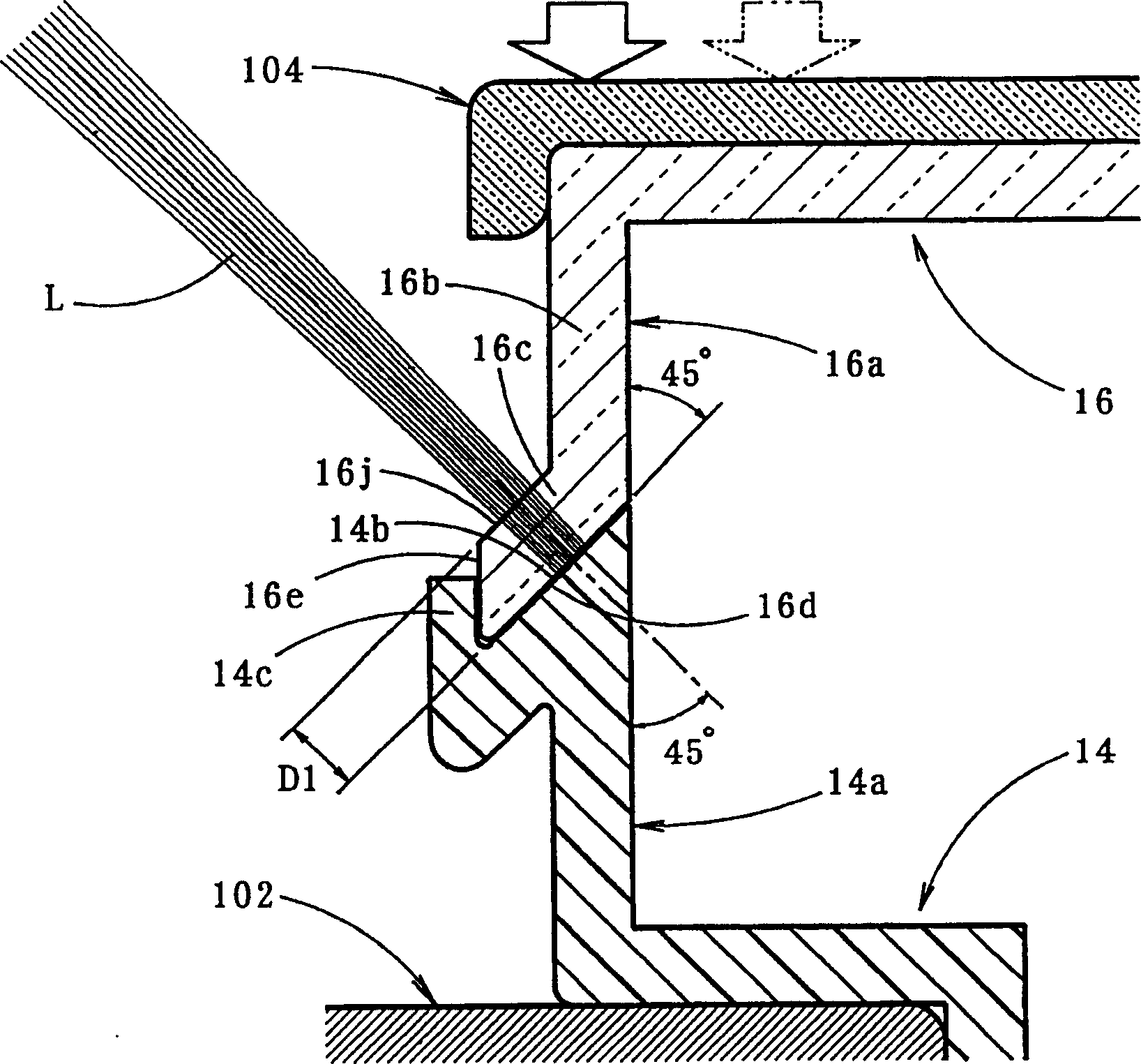
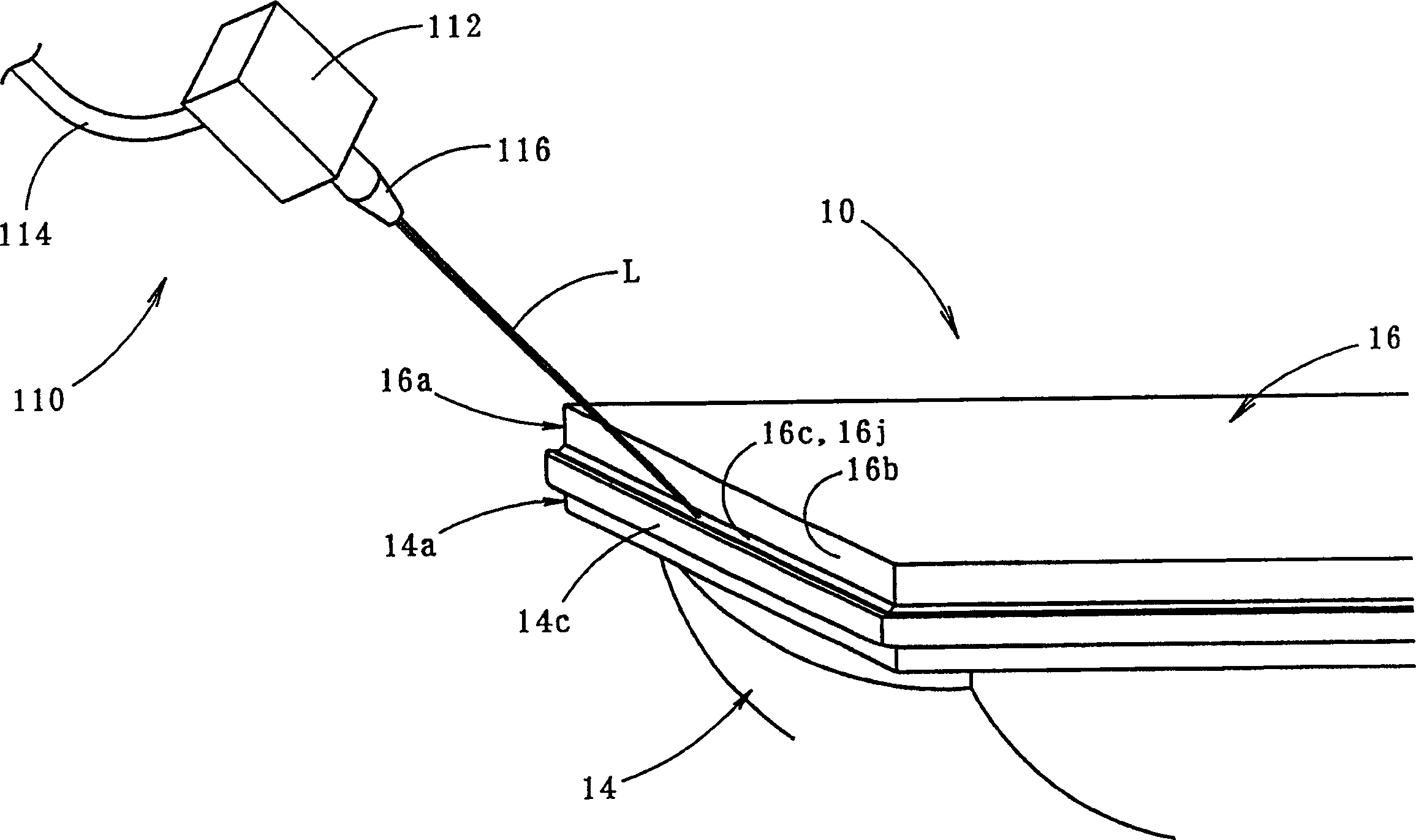
InactiveCN1157553CImprove appearance qualityHigh bonding strengthOptical signallingVehicle lighting systemsLight beamAbutment
A vehicular lamp in which bonding failure between a front lens and a lamp body is prevented while enhancing the bonding strength and improving the quality of the outer appearance around the bonded surface therebetween. An end surface of a seal leg of a front lens and a receiving surface of a lamp body are bonded through laser beam welding so as to improve the outer appearance quality of the area around the bonded surfaces. The end surface is formed on an end portion of the seal leg that is bent and extended outward at a predetermined angle with respect to the bonding direction. The laser beam is irradiated onto the receiving surface through the end portion from a direction substantially orthogonal to the end surface. The resultant permeation distance of the laser beam is made short, resulting in a sufficient amount of irradiation energy. When pressure is applied to the base end portion of the seal leg by pressing on the front lens, the end surface and the receiving surface are brought into abutment in the width direction with uniform pressure.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Testing device and method for bond stress between steel strand and concrete in pre-tensioning-method member
ActiveCN104949913AAvoid influenceThe test data is accurate and reliableUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisObservational errorPull force
The invention relates to a testing device and method for bond stress between a steel strand and concrete in a pre-tensioning-method member. According to the device, a force measuring sensor for detecting the bond stress between the steel strand and the concrete in the pre-tensioning-method member is arranged on the top of a supporting frame; a sleeve placing frame is arranged at the bottom of the force measuring sensor; a sleeve for fixing the pre-tensioning-method member is arranged at the center of the bottom of the sleeve placing frame; the sleeve is fixed by the sleeve placing frame; a downward pull force load is applied to the steel strand in the pre-tensioning-method member by using a force transferring assembly, the load and the displacement of the steel strand are recorded in real time by the force measuring sensor and a displacement sensor, so as to determine the load corresponding to the moment of bonding failure between the steel strand and the concrete, test data are relatively accurate and reliable, the measuring error is greatly reduced, and a reliable evidence for the application and the design of the pre-tensioning-method member is provided.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method of detecting wire bonding failures
Owner:ASMPT SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Method for predicting bonding strength of steel strand under cracking and failures of rotation and protection layer
ActiveCN108830022AGood precisionImprove research deficienciesGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsRadial stressPre stress
The invention discloses a method for predicting the bonding strength of a steel strand under cracking and failures of rotation and a protection layer. The method comprises the steps that a relationalexpression between the limit bonding strength and the radial stress of a bonding failure face is established, the radial stress of the bonding failure face when concrete split bonding fails is determined, the critical radial stress of the bonding failure face when a concrete split failure is turned to a drawing rotation failure is determined, and the minimum thickness of the concrete protection layer under the critical radial pressure stress is determined. Through existing drawing experiment data related to the steel strand, the method is compared and evaluated, and in combination with the twokinds of failure modes, the precision of the method is verified. By considering a twisting spiral structure and a rotation bonding mechanism of the steel strand, the limit bonding strength of the single prestress steel strand under the two kinds of failure modes including the concrete split failure and the drawing rotation failure can be effectively simulated and predicted, and the method has high precision; the defect of research related to a prestress steel strand and concrete theoretical bonding model is overcome.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
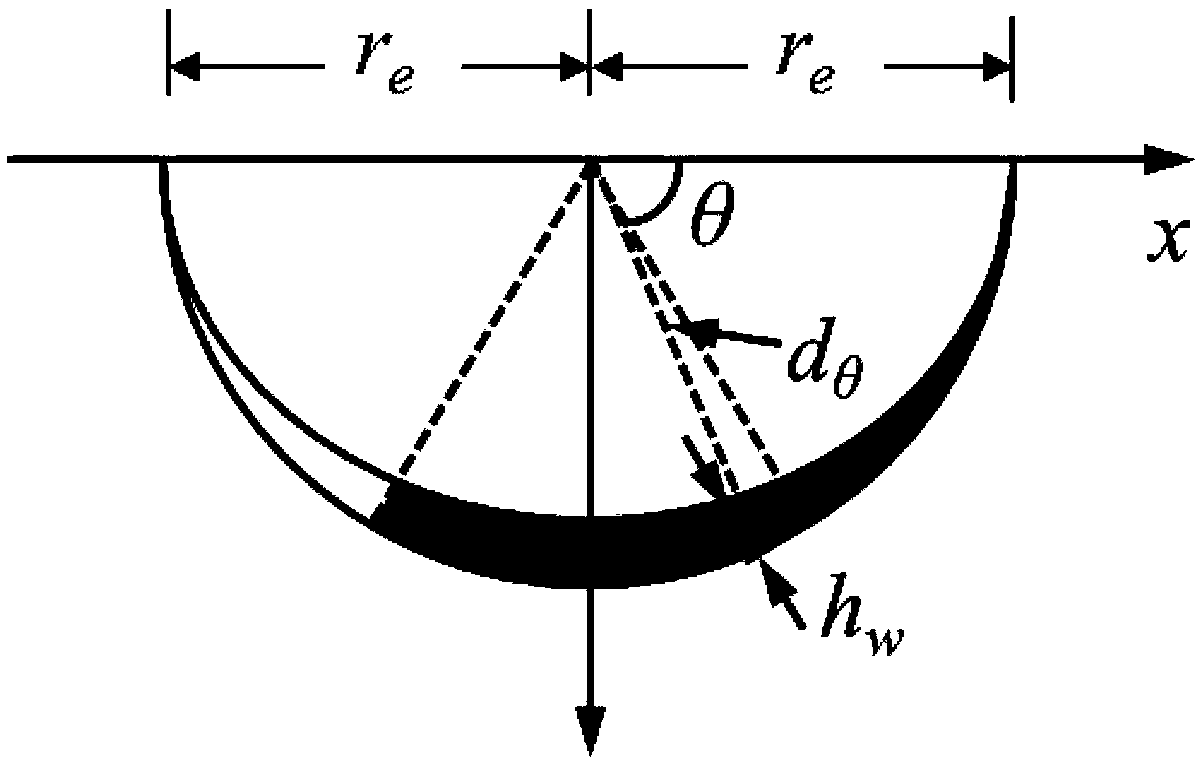
Reverse osmosis membrane element and sealing case thereof
PendingCN109569304AEnsure health and safetyEliminate the risk of internal leakageReverse osmosisReverse osmosisMembrane bodies
The invention discloses a reverse osmosis membrane element and a sealing case thereof. The reverse osmosis membrane element comprises a reverse osmosis membrane body, a water passage adapter connectedwith one end of the reverse osmosis membrane body, and the sealing case connected in a sleeve mode to the outer surface of the reverse osmosis membrane body, wherein the sealing case comprises a sealing case body in a hollow cylindrical shape; the outer circumference of the upper portion of the sealing case body is provided with an O-type sealing ring, and the sealing case body and the O-type sealing ring are integrally made of high-molecular food-grade materials. According to the reverse osmosis membrane element, the sealing case saves glue applied onto the back surface and tightly seals upthe surface of the reverse osmosis membrane body through elasticity, thereby effectively ensuring sanitary safety of the reverse osmosis membrane element; besides, with the O-type sealing ring, the sealing case saves auxiliary sealing by white tapes, simplifies assembling processes and meanwhile avoids the risk of internal leakage of a reverse osmosis filter element due to bonding failure betweenthe white tapes and concentrated water sealing rings as well as external tapes.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANGEL DRINKING WATER IND GRP
Corner longitudinal reinforcement centralized and profiled bar built-in reinforcing structure of RC (Reinforced Concrete) rectangular column and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103452241AImprove gripImprove restraintStrutsPillarsEarthquake resistanceReinforced concrete column
The invention relates to a corner longitudinal reinforcement centralized and profiled bar built-in reinforcing structure of an RC (Reinforced Concrete) rectangular column and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of earthquake resistance strengthening of RC columns. According to the corner longitudinal reinforcement centralized and profiled bar built-in reinforcing structure and the preparation method thereof, longitudinal reinforcements at the four corners of a cross section of an original rectangular column are centralized based on the form that reinforcements are distributed on the cross section of the original rectangular column, so as to form an isosceles-right-triangle delta-shaped longitudinal reinforcement distributed form, and reinforcing inequilateral angle irons of the four corners of the cross section of the rectangular column are fixed at the outer sides of the two ends of an initially-reinforced reinforcement cage through steel reinforcing rods. Due to the form, a good binding effect can be provided for concrete, and the concrete can be prevented from shedding too early under the action of oblique earthquakes. The method comprises the following specific operating steps: forming the reinforcement cage, mounting the angle irons and forming the reinforcing structure. The corner longitudinal reinforcement centralized and profiled bar built-in reinforcing structure and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the condition that the RC square column is not subjected to bond failure under the action of the oblique earthquakes can be guaranteed on the premise that the condition that the structure is designed according to X and Y principal-axis directions is basically not changed, and the oblique bearing capacity, ductility and earthquake resistance of the column are improved greatly.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
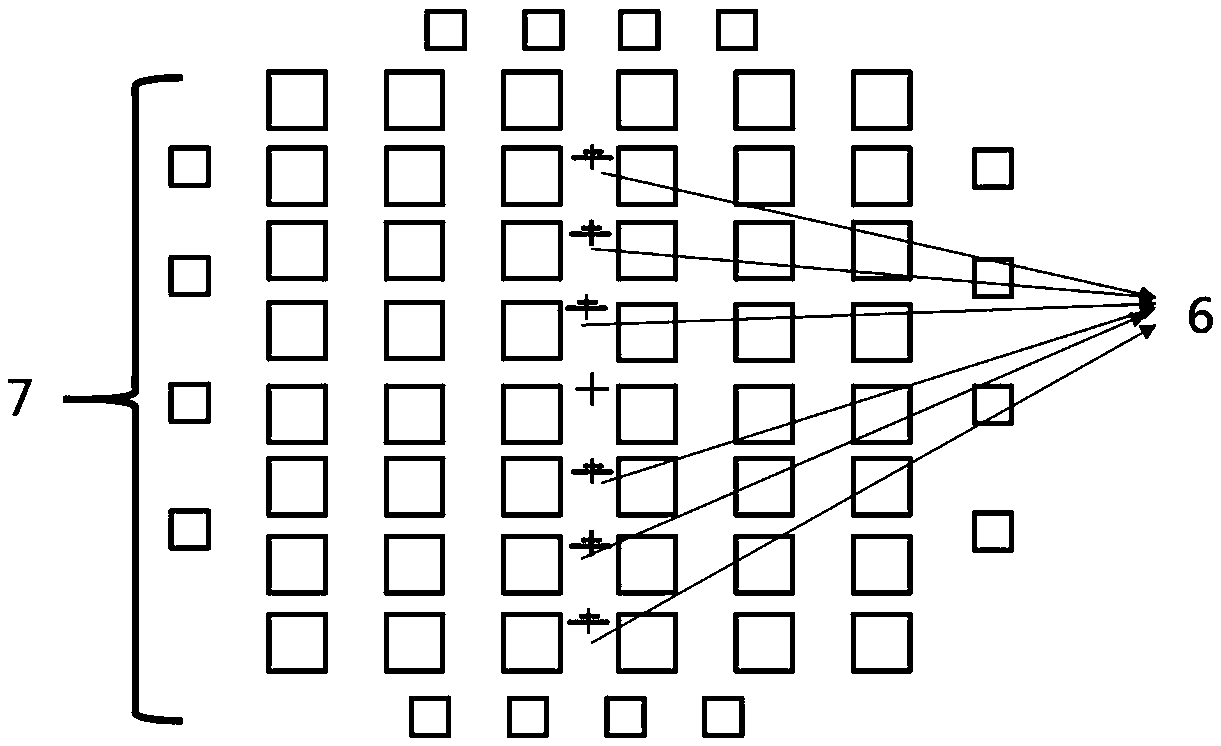
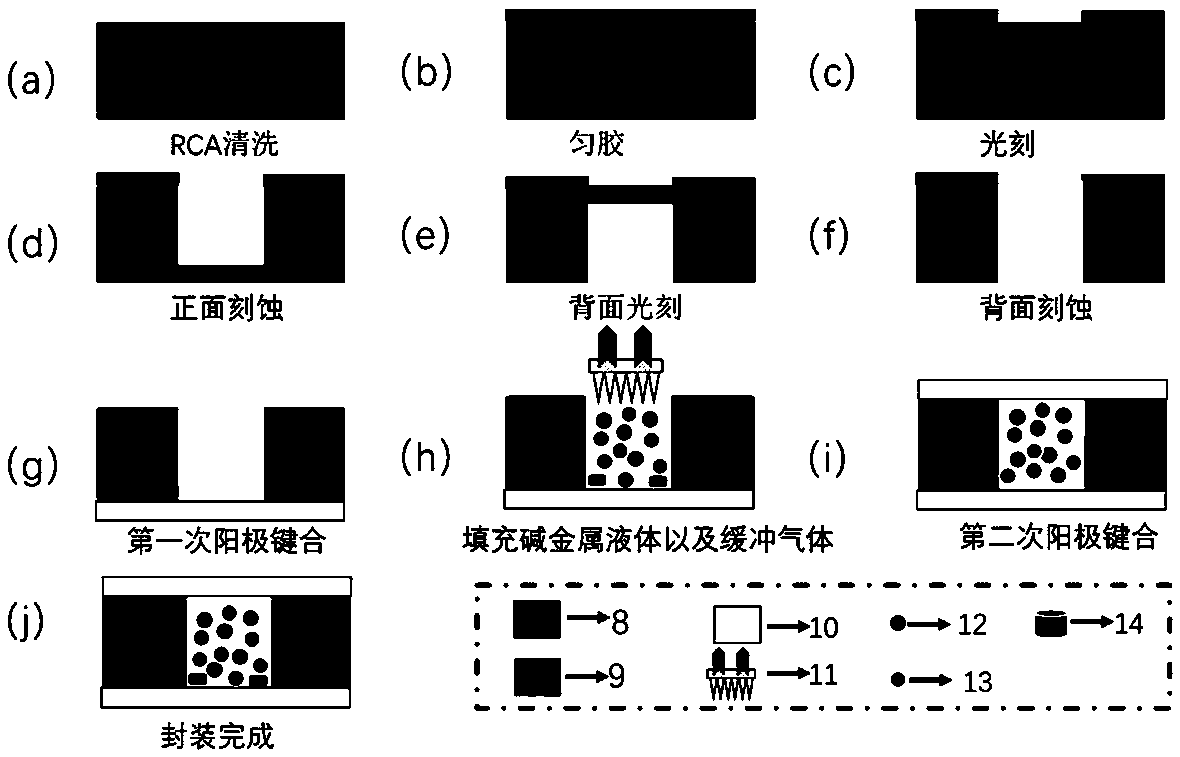
Preparation method of alkali metal atom micro air chamber based on MEMS process
PendingCN110759314AReduce volumeAvoid poor light transmissionDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingAdhesiveAnodic bonding
The invention discloses a preparation method of a soda ash metal atom micro air chamber based on an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) process. The preparation method comprises the steps of RCA (Reactive Clear Adhesive) cleaning, photoetching, etching low-temperature anodic bonding and scribing. The high-precision, low-stress and high-purity MEMS atomic air chamber can be manufactured, and (1)the noise problem caused by atomic depolarization relaxation due to the fact that a conventional glass-silicon-glass atomic air chamber is different in quality is avoided; (2) the problem of poor airtightness caused by weak atom bonding force of different bonding layers is solved by anodic bonding; (3) the problem of bonding failure or low air tightness caused by poor surface flatness is solved;(4) the problem of low density caused by overflow of alkali metal is solved; (5) attenuation or damage of device performance can be avoided through low-temperature bonding, and residual stress and buckling deformation introduced by high-temperature bonding are reduced or eliminated; and (6) the problem that residual reactants are easily left during preparation of the single-chamber atomic gas chamber to influence subsequent light transmission is solved, and the volume size of the single-chamber atomic gas chamber is smaller than that of a double-chamber atomic gas chamber.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Vehicle light assembly
InactiveCN1134605CPrevent bond failureIncreased binding widthVehicle headlampsOptical articlesEdge surfaceLight beam
A vehicular lamp in which bonding failure between a front lens and a lamp body is prevented while enhancing the bonding strength and improving the quality of the outer appearance around the bonded surface therebetween. An edge surface of a seal leg of the front lens and a receiving surface of a lamp body are bonded together by laser beam welding so as to improve the quality of the outer appearance of the portion around the bonded surfaces. The bonded surface is inclined at a predetermined angle with respect to a plane perpendicular to the bonding direction. Even if the edge surface of the seal leg or the receiving surface has a wave-like irregularity such that gaps are created in areas therebetween, the pressure in the bonding direction acting on the members to be bonded causes slippage between them, resulting in sealing the gaps. The beam spot diameter of a laser beam irradiated onto the receiving surface is increased in an amount corresponding to the angle of inclination of the bonded surface, thus increasing the bonding width and enhancing the bonding strength.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Detection device and detection method for second bonding points
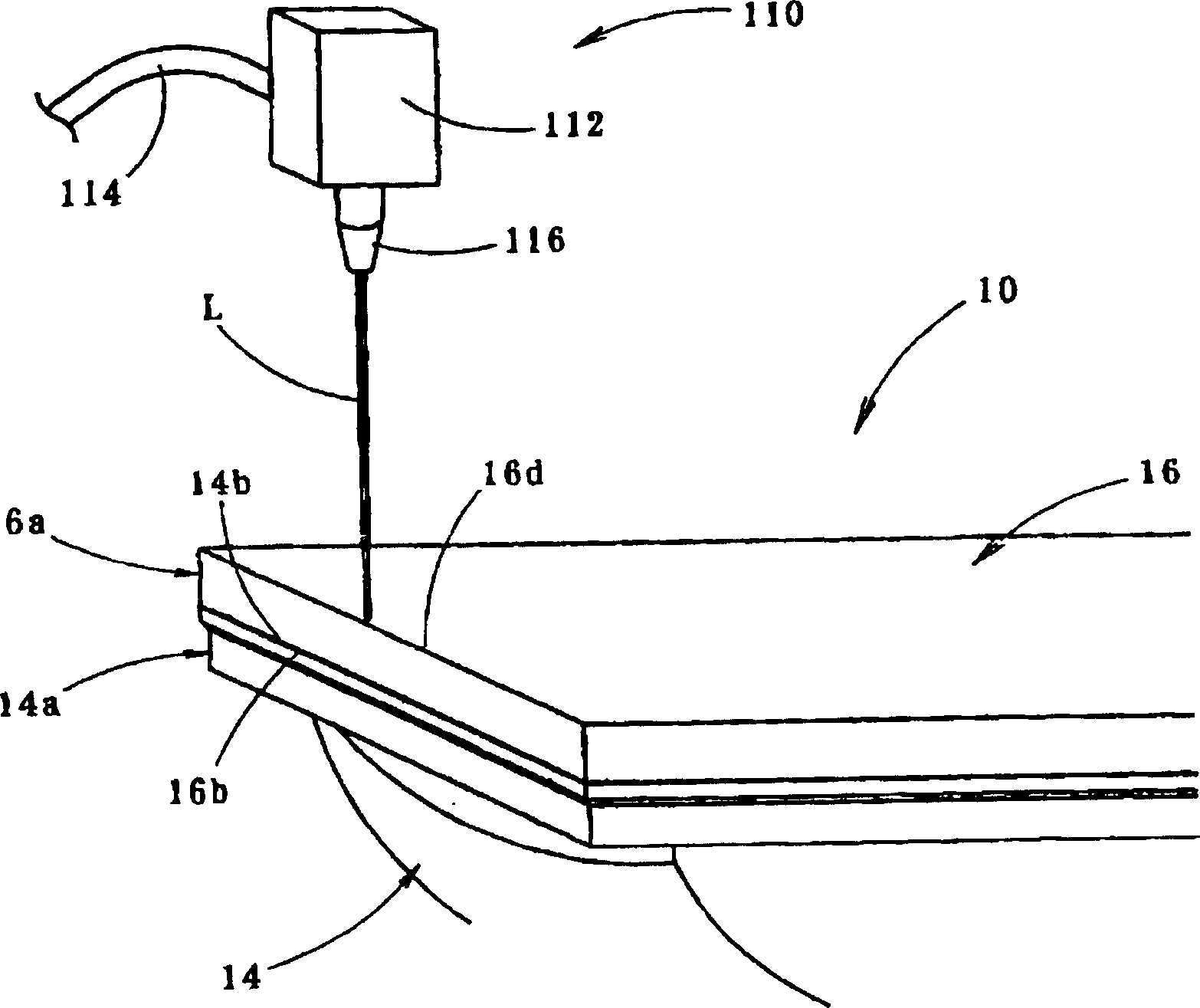
InactiveCN110935656AReduce manufacturing costElectronic circuit testingSortingStructural engineeringElectrical performance
The invention discloses a detection device and a detection method for second bonding points. The detection device for the second bonding points comprises a machine body, a transfer station fixedly installed on the machine body, a detection mechanism arranged at one side of the transfer station, and a sorting mechanism arranged on the machine body, wherein the detection mechanism comprises an installation frame fixedly connected to the machine body, an optical detection component installed on the installation frame, and an electrical performance detection device installed at one side of the transfer station. According to the detection device and the detection method for the second bonding points, optical detection and electric detection are carried out on the second bonding points of bondedchips, bonding failure points and the layering condition or the pollution condition of the bonding points are inspected, the welding firmness degrees of the second bonding points are evaluated, and the chips with unstable second bonding points are screened, so that the production cost is reduced.
Owner:南京微毫科技有限公司
MEMS device, preparation method and electronic device
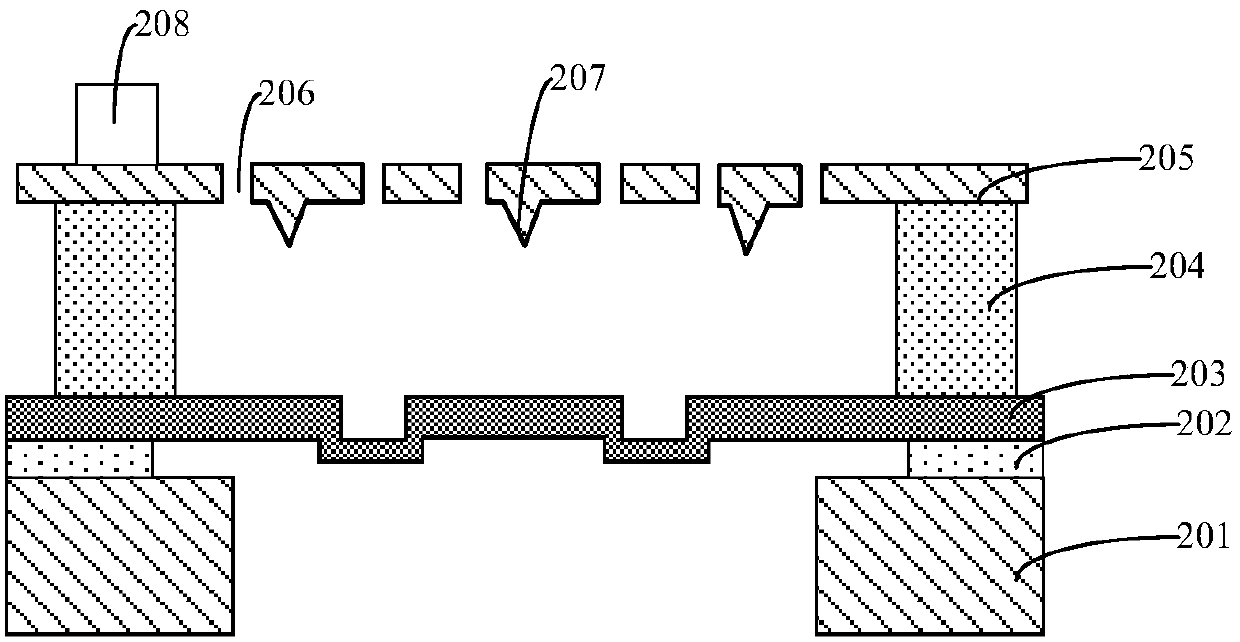
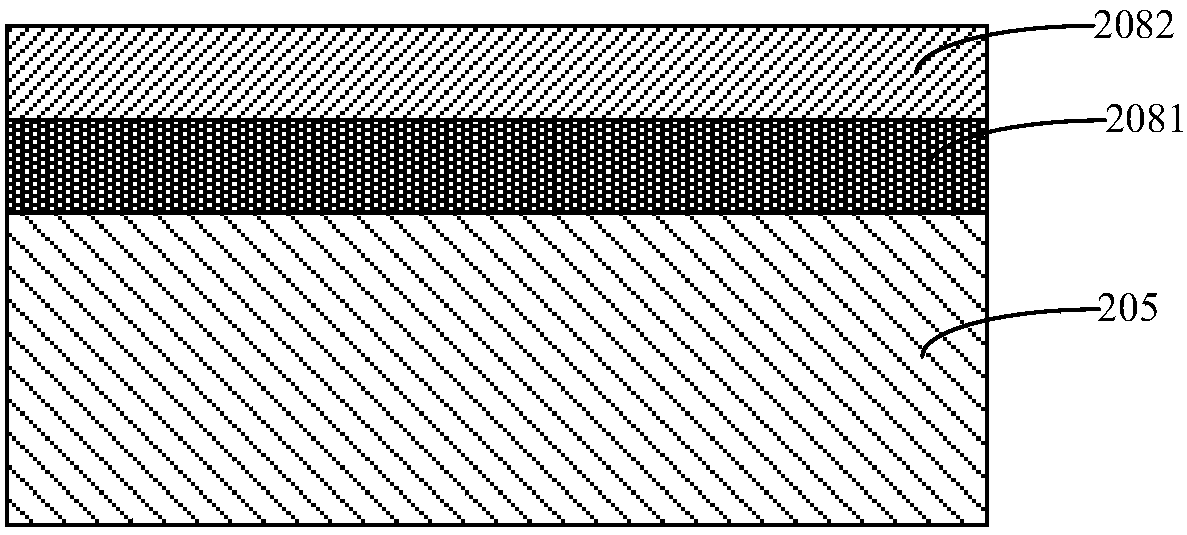
InactiveCN109704269AImprove performanceImprove yieldElectrical transducersDecorative surface effectsDiffusionEngineering
The invention provides an MEMS device, a preparation method and an electronic device. The MEMS device includes: a back plate; The interconnection layer positioned on the back plate; Wherein the interconnection layer comprises a first conductive layer and a second conductive layer which are sequentially stacked, the interconnection layer further comprises a diffusion barrier layer, and the diffusion barrier layer is arranged between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer and used for preventing mutual diffusion between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer. According to the invention, the diffusion barrier layer is arranged to prevent mutual diffusion between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer, so that the problem of bonding failure of the interconnection layer is solved, and the performance and the yield of the MEMS device are further improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com