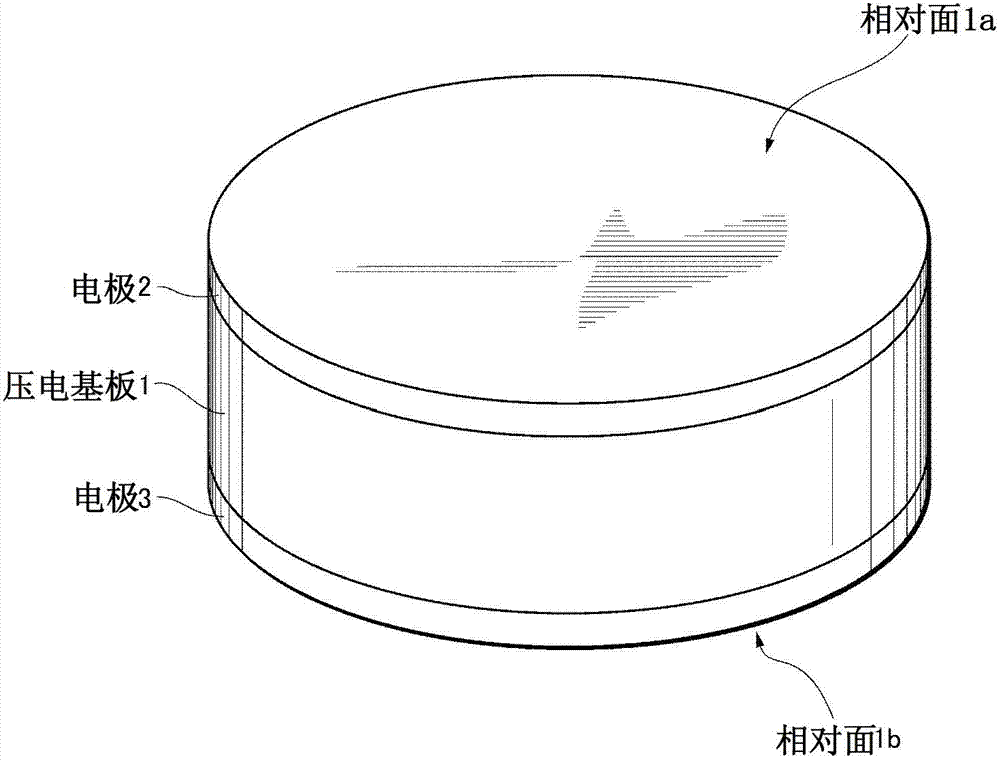
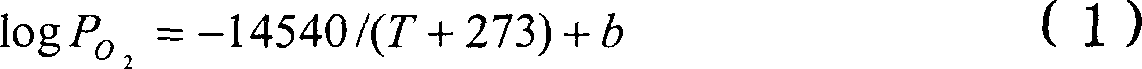Patents
Literature
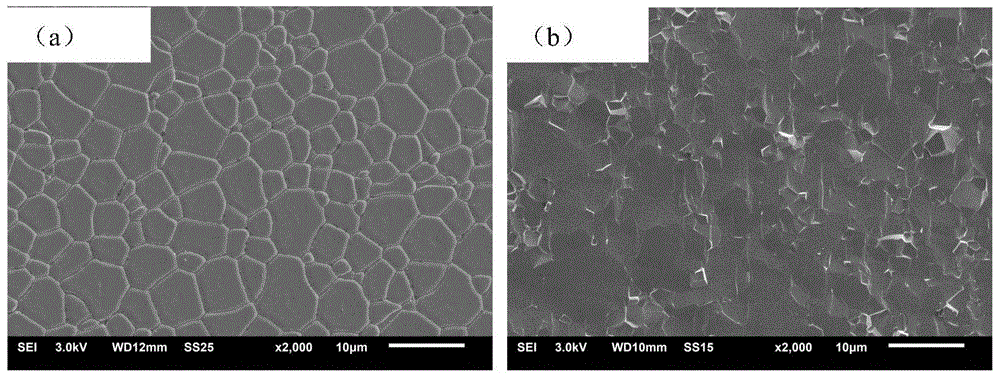
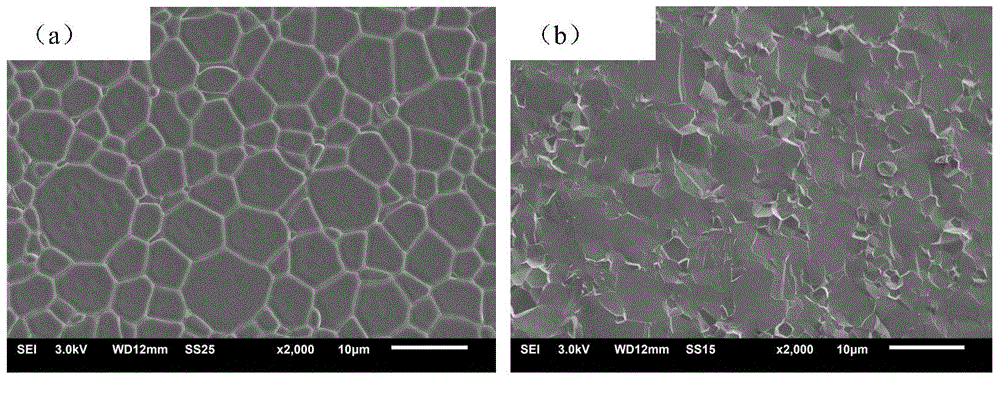
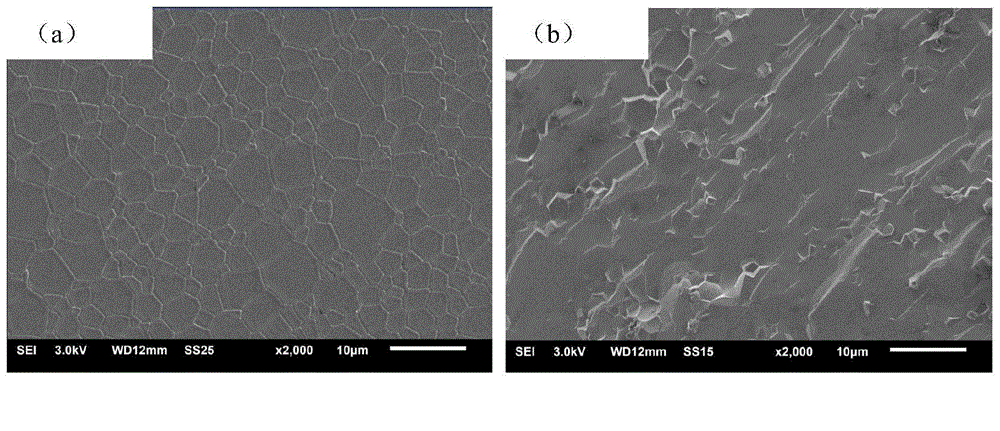
98 results about "Abnormal grain growth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
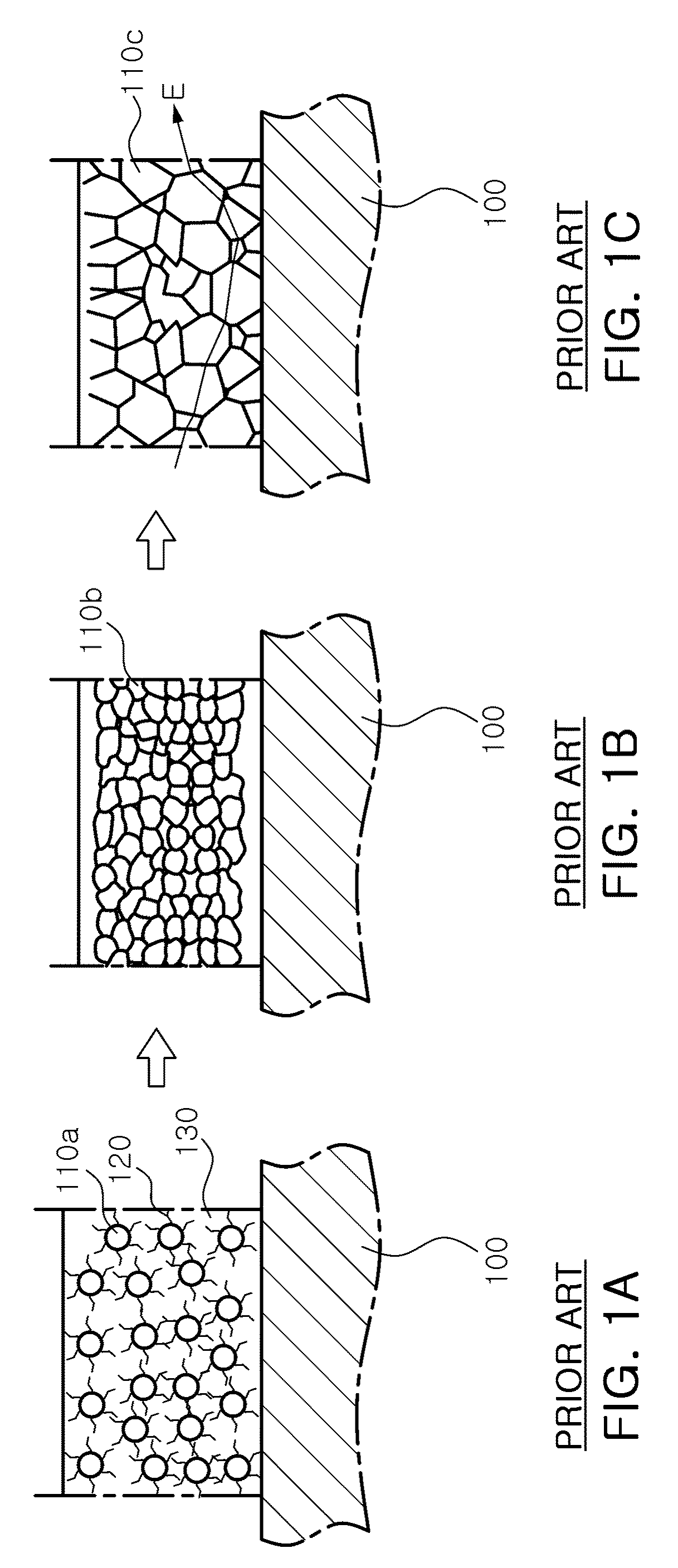
Abnormal or discontinuous grain growth, also referred to as exaggerated or secondary recrystallisation grain growth, is a grain growth phenomenon through which certain energetically favorable grains (crystallites) grow rapidly in a matrix of finer grains resulting in a bimodal grain size distribution.
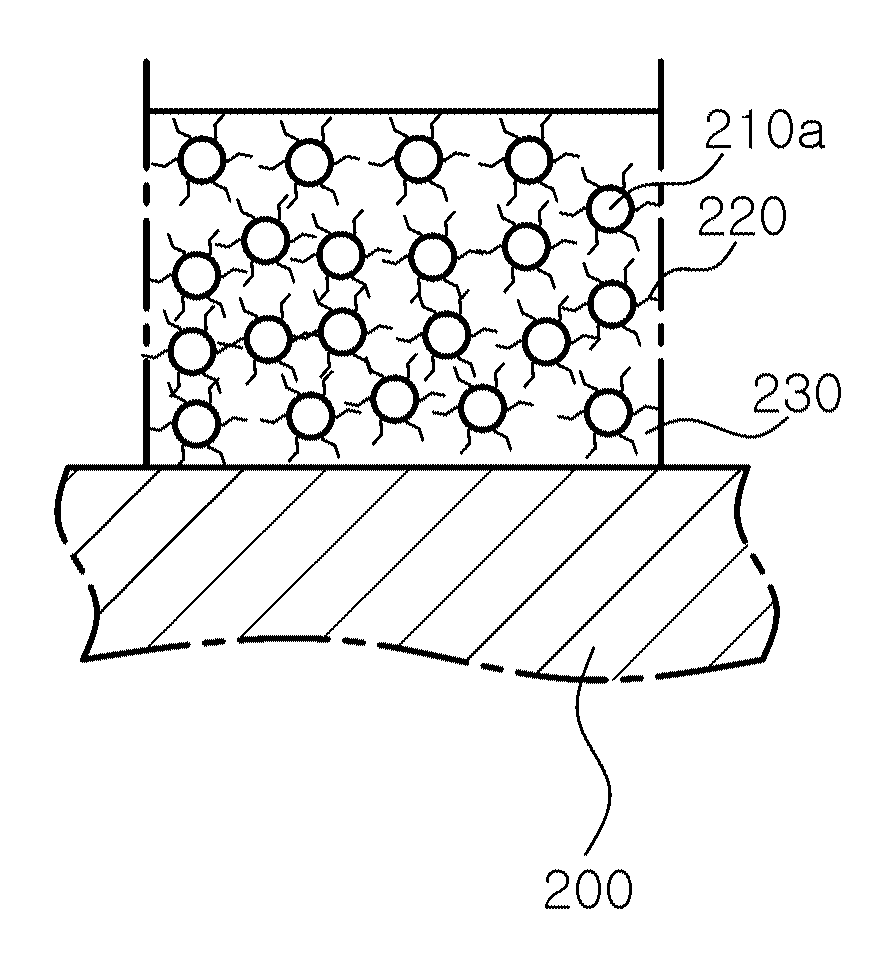
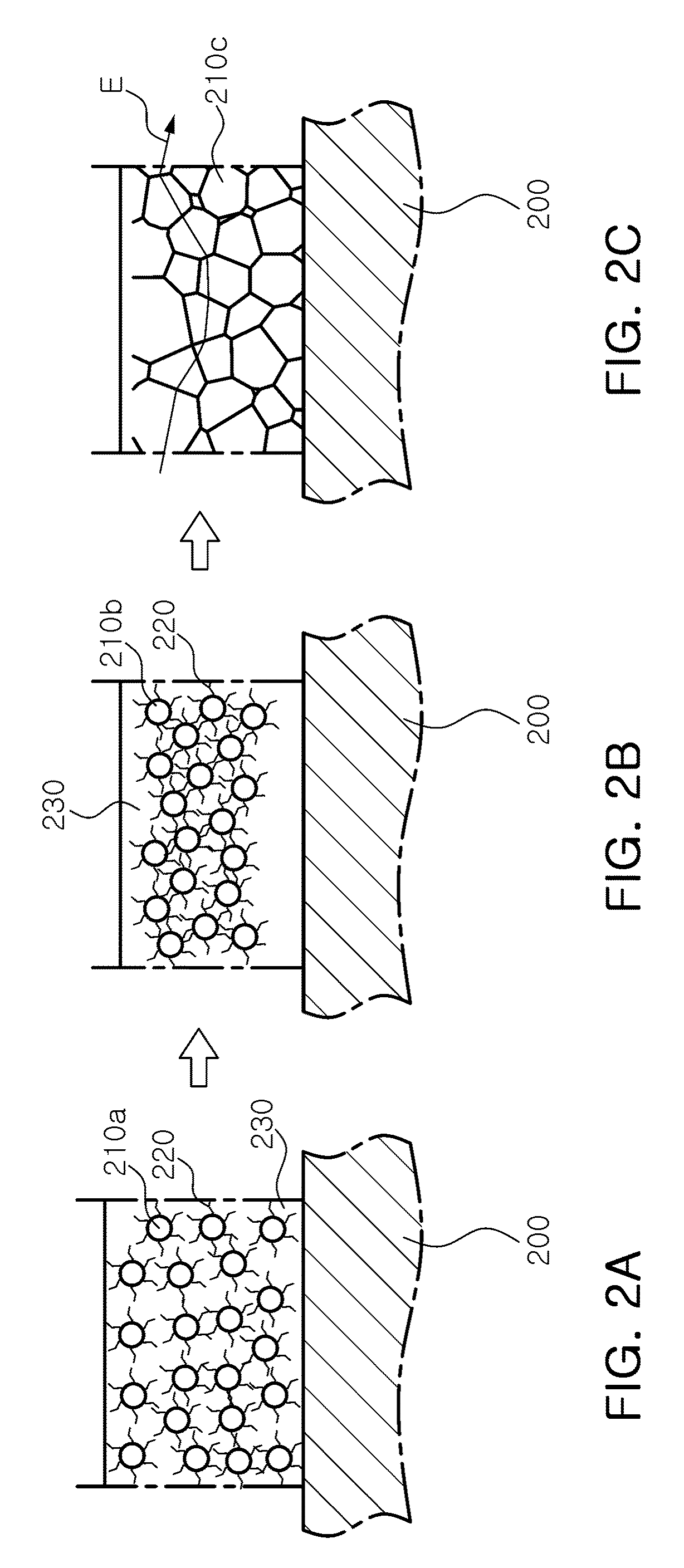
Solid electrolyte ceramic material and production method therefor
Provided is a solid electrolyte ceramic material which exhibits high density, high strength, and lithium ion conductivity, and with which defects such as uneven calcination, crack formation and pores, and the occurrence of abnormal grain growth are inhibited or avoided. This ceramic material is an oxide sintered body having a garnet or garnet-like crystal structure configured from at least Li, La, Zr, and O. The oxide sintered body further includes Al and Mg as additional elements.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
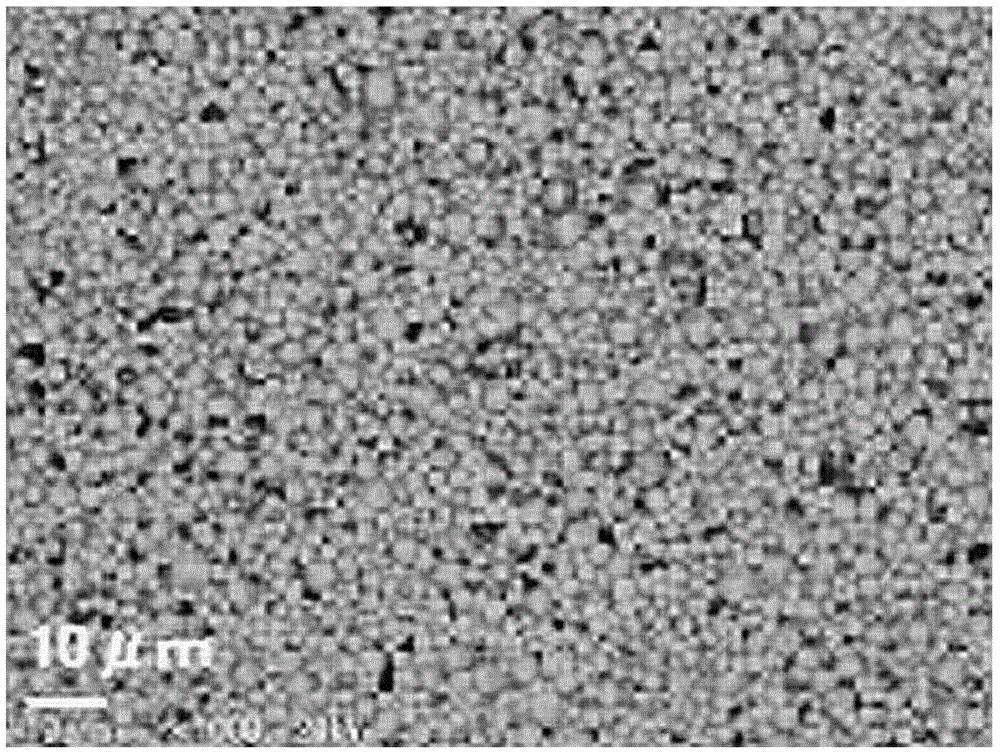
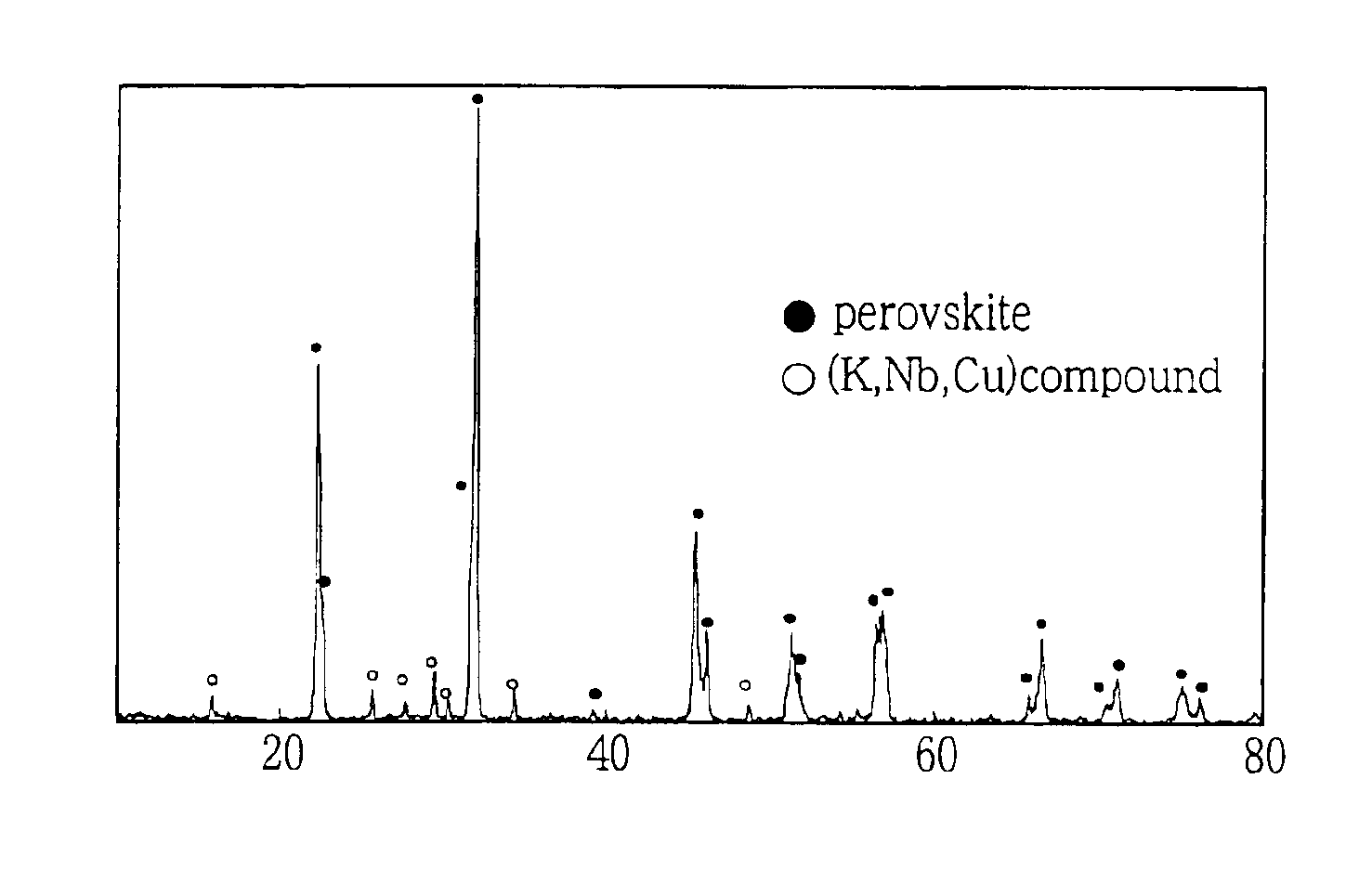
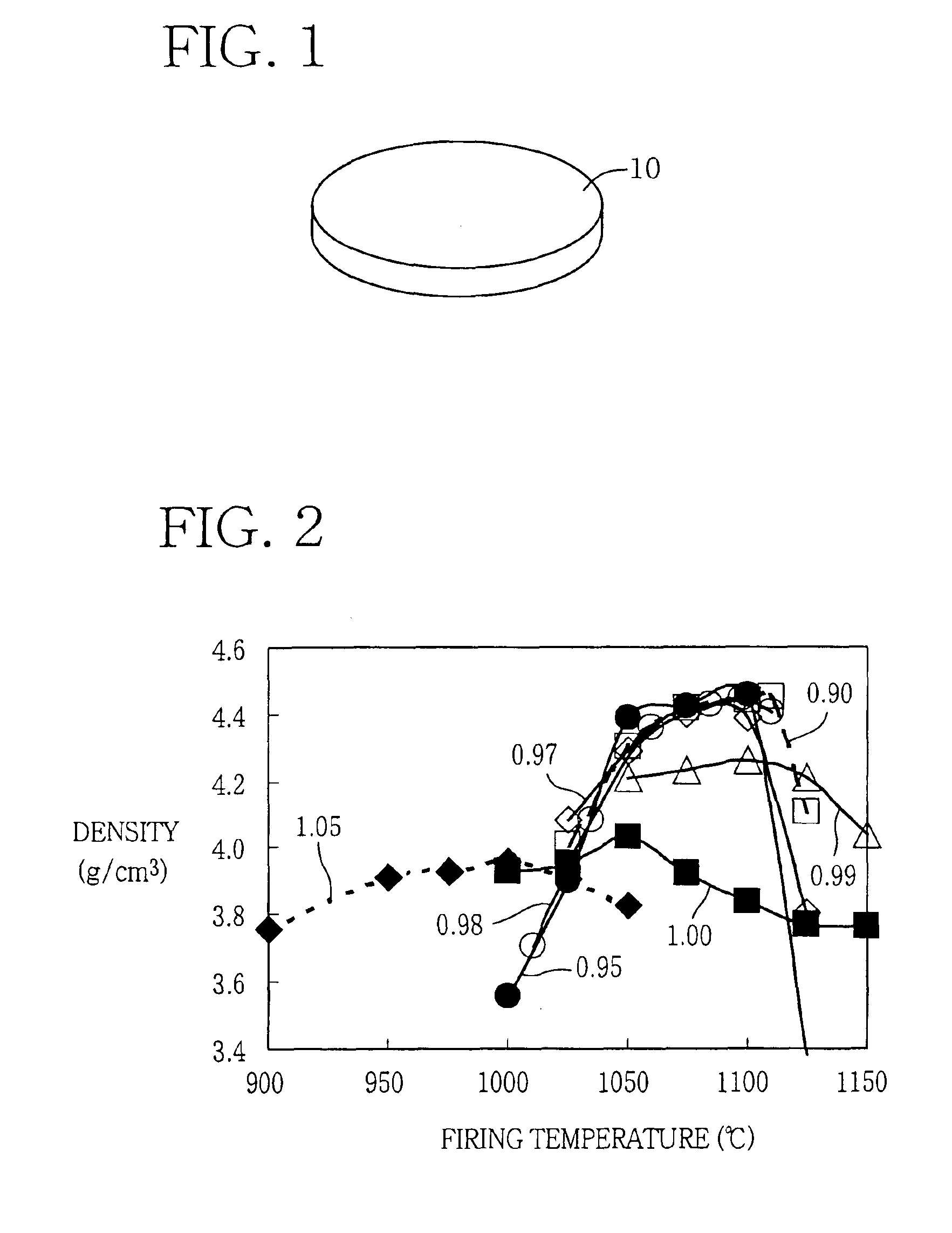
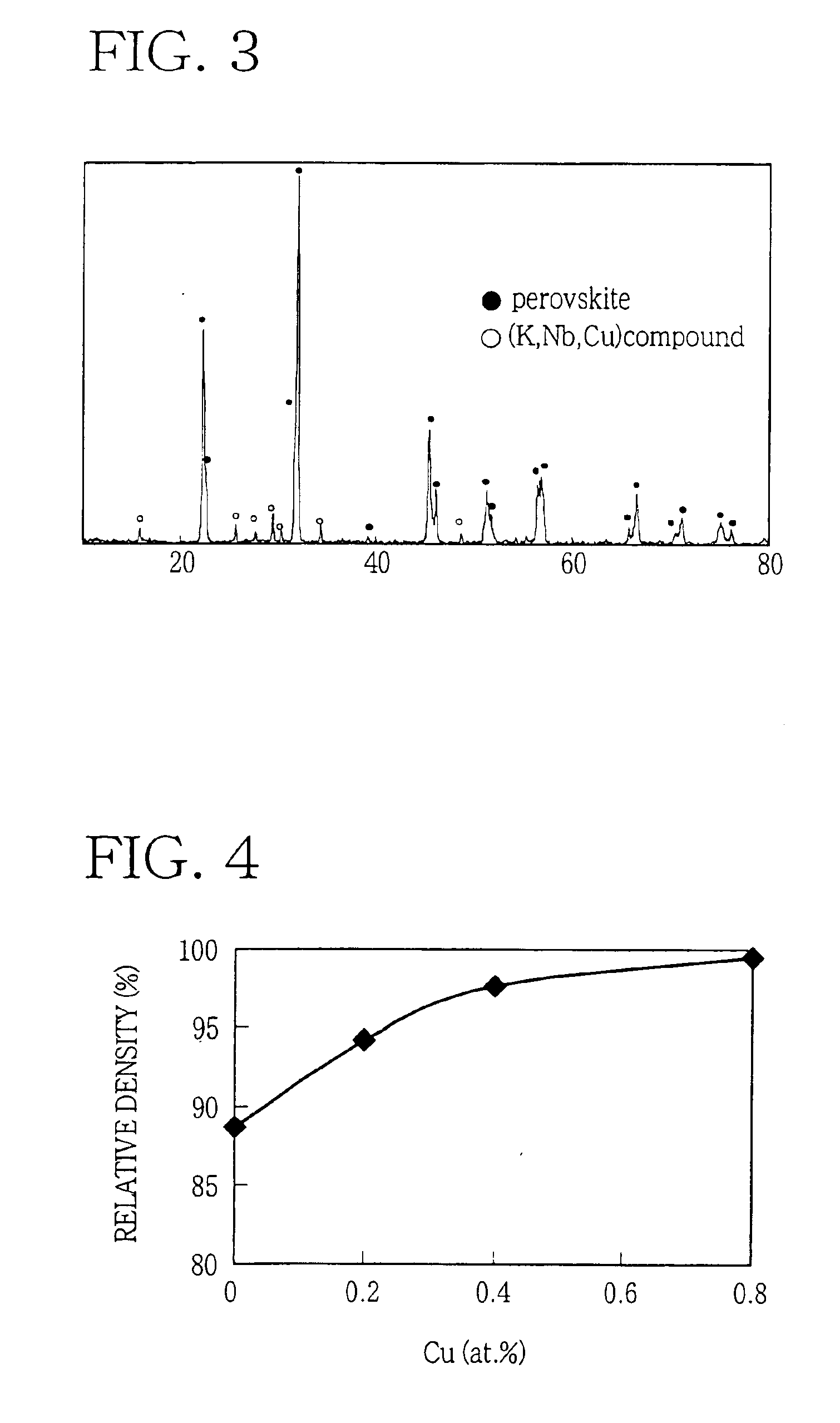
Lead-free piezoelectric ceramic composition wherin Cu is contained in (KxA1-x)y(Nb1-zBz)O3perovskite compound, and process of preparing the same
InactiveUS6884364B2Improve sintering performanceImprove sinterabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionAbnormal grain growthSecondary component
A lead-free piezoelectric ceramic composition wherein a suitable amount of Cu is contained in a perovskite compound of a non-stoichiometric composition represented by a formula (KxA1-x)y(Nb1-zBz)O3, wherein “A” represents at least one of Na and Bi, while “B” represents at least one of Ta and Ti, and wherein 0<x≦1, 0<y<1, and 0≦z≦1, so that by-products such as KaCubNbcOd and KaCubTacOd are produced as a result of reaction of (Nb1-zBz) with Cu in the process of calcination of a starting material, and the by-products restrict melting and abnormal grain growth of (KxNa1-x)(Nb1-zTaz) O3 during firing of a calcined body, thereby improving sinterability of the fired body, while restricting volatilization of alkali components and melting of KNbO3, thereby increasing the density and improving the piezoelectric properties of the fired body. The ceramic composition is prepared by firing a starting composition including the perovskite composition as a primary component, and a secondary component in the form of at least one of compounds KaCubNbcOd, KeCufTagOh and KiCujTikOl.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD +1
Method for developing fine grained, thermally stable metallic material
InactiveUS20110076419A1Radiation applicationsPretreated surfacesAbnormal grain growthMetallic materials
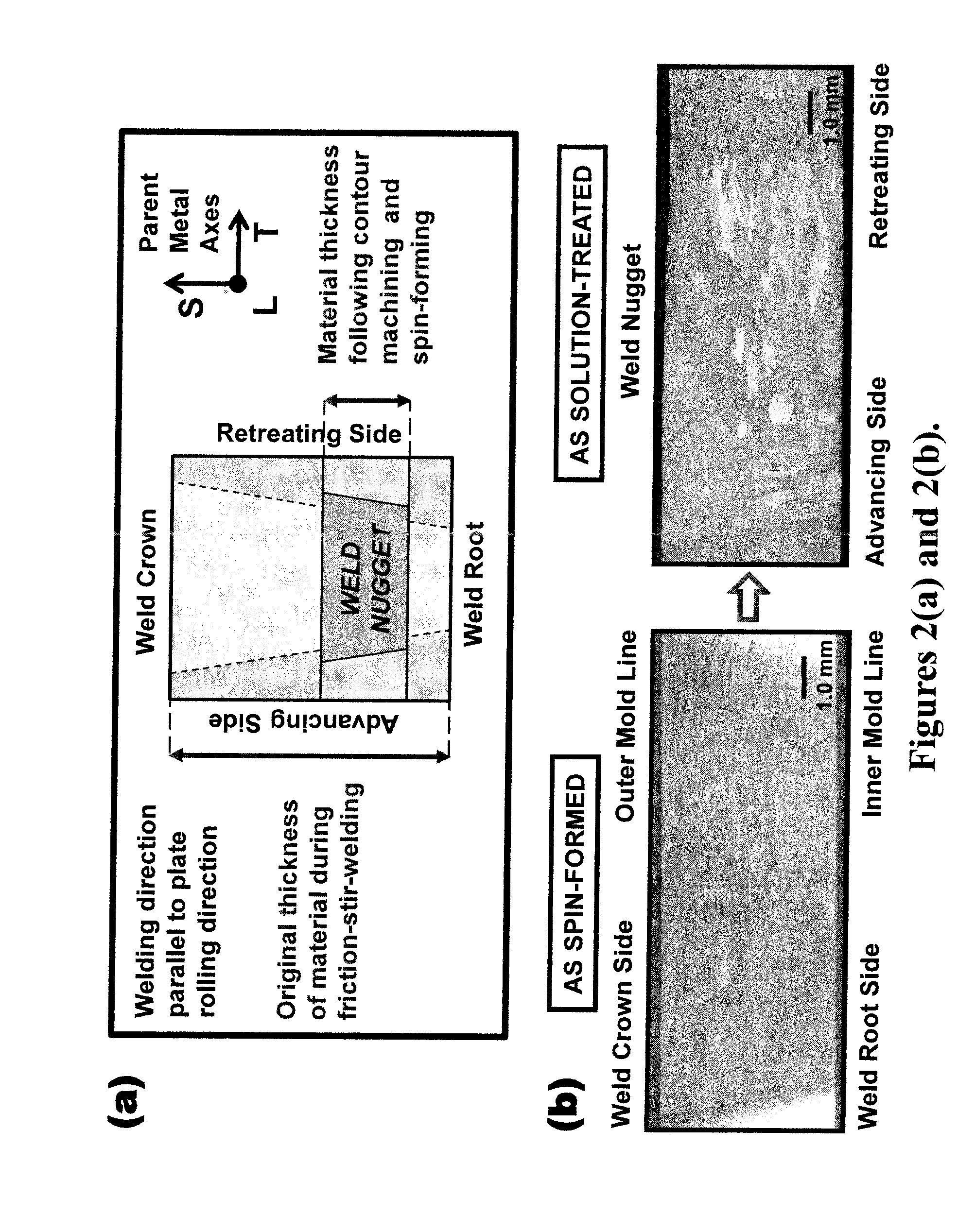
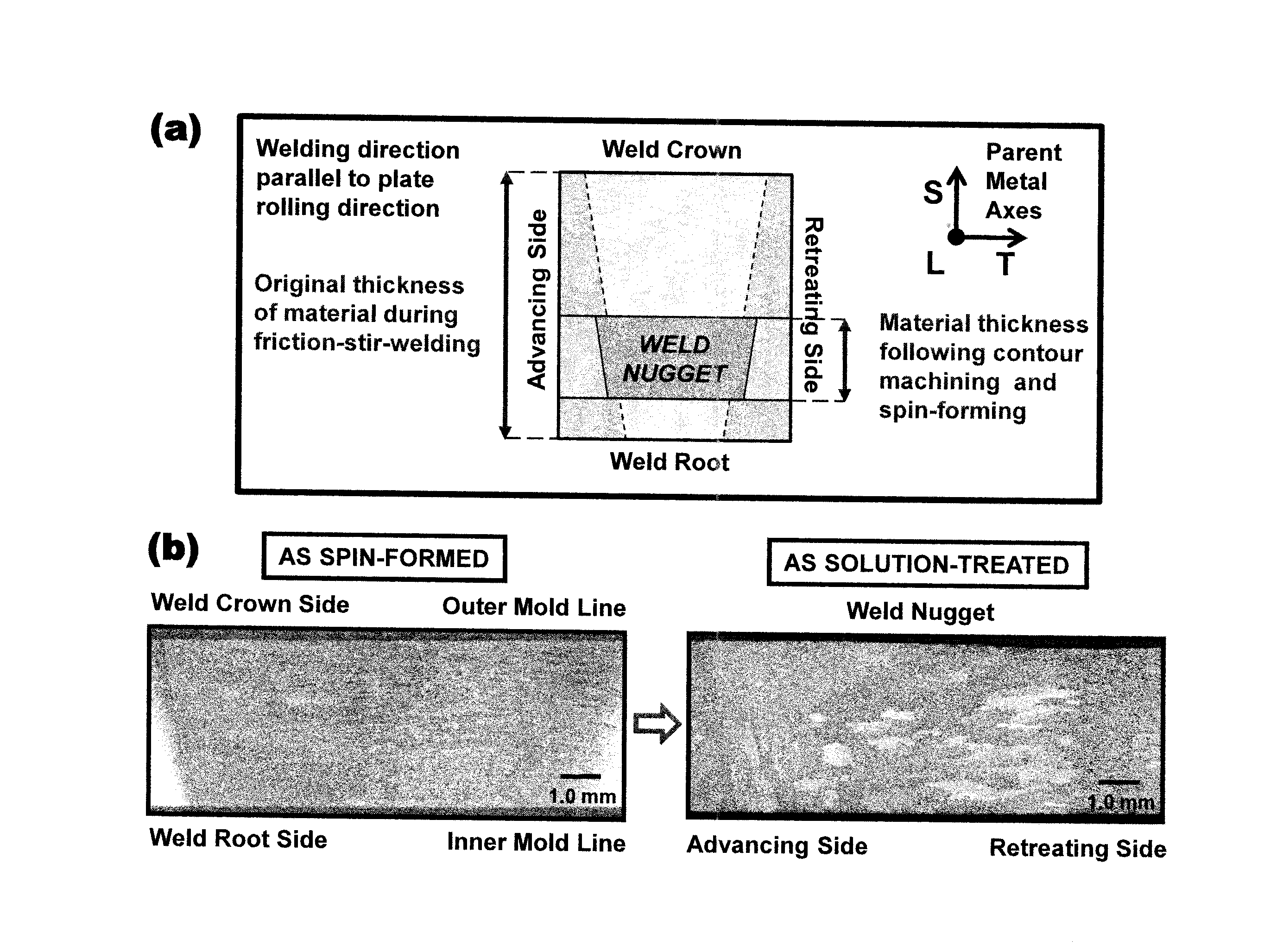
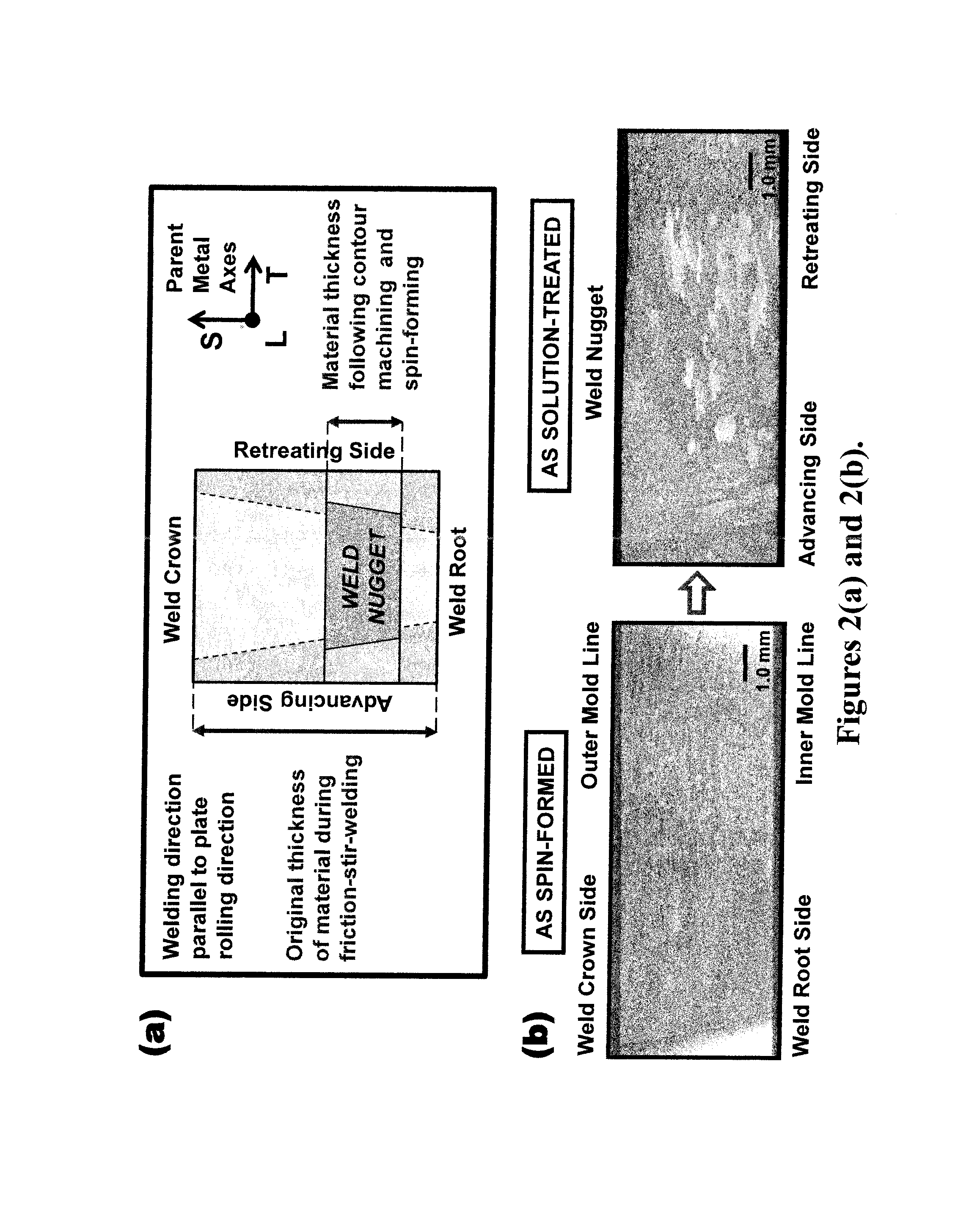
A method for developing fine grained, thermally stable metallic material in which friction stir welding or friction stir processing is performed along at least a portion of the material. Thereafter, a thin layer is removed from either side, or both sides of the material to eliminate the origin of abnormal grain growth occurring when the friction stir welded or friction stir processed material is subjected to subsequent hot forming processes. A sheet of extraneous material is optionally attached to either side, or both sides of the material prior to the friction stir welding or friction stir processing, and this extraneous material is removed after the friction stir welding or friction stir processing. A layer containing pinning particles or a sheet of extraneous material containing pinning particles is further optionally introduced on either side, or both sides of the material prior to the friction stir processing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method to improve properties of aluminum alloys processed by solid state joining
ActiveUS20060054252A1Restored mechanical strengthDecrease in original ductilityNon-electric welding apparatusAbnormal grain growthStored energy
A method for forming an aluminum alloy article having improved mechanical properties using a solid-state joining process in which the problem of ductility reduction is minimized by conducting a thermal exposure treatment prior to solution heat treatment. This thermal exposure treatment, done at a temperature below the solution heat treatment temperature, releases stored energy in the aluminum-alloy material. The aluminum-alloy material then does not have sufficient energy to cause recrystallization and abnormal grain growth during the subsequent solution heat treatment process. The resultant aluminum-alloy material has a restored mechanical strength with only a minor, but acceptable, decrease in original ductility.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
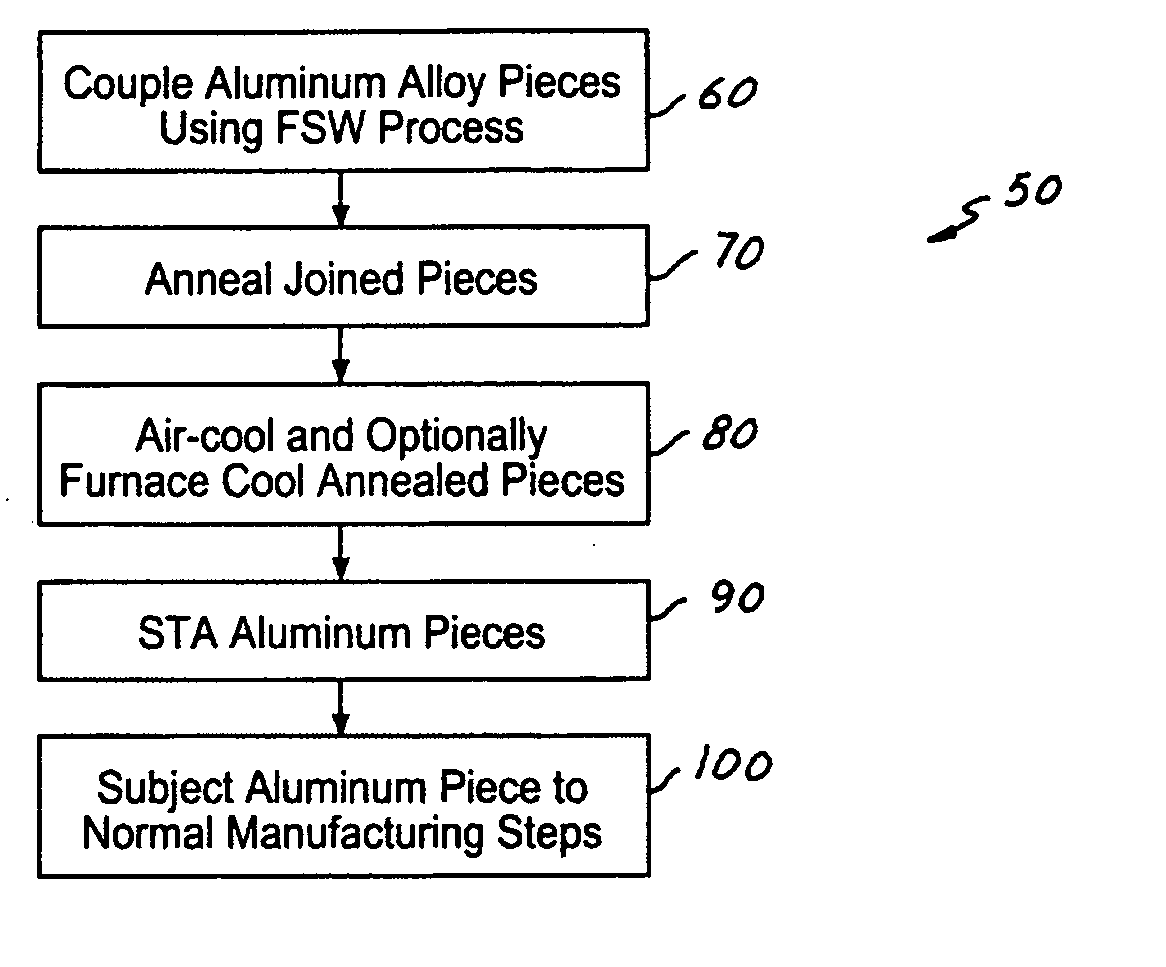
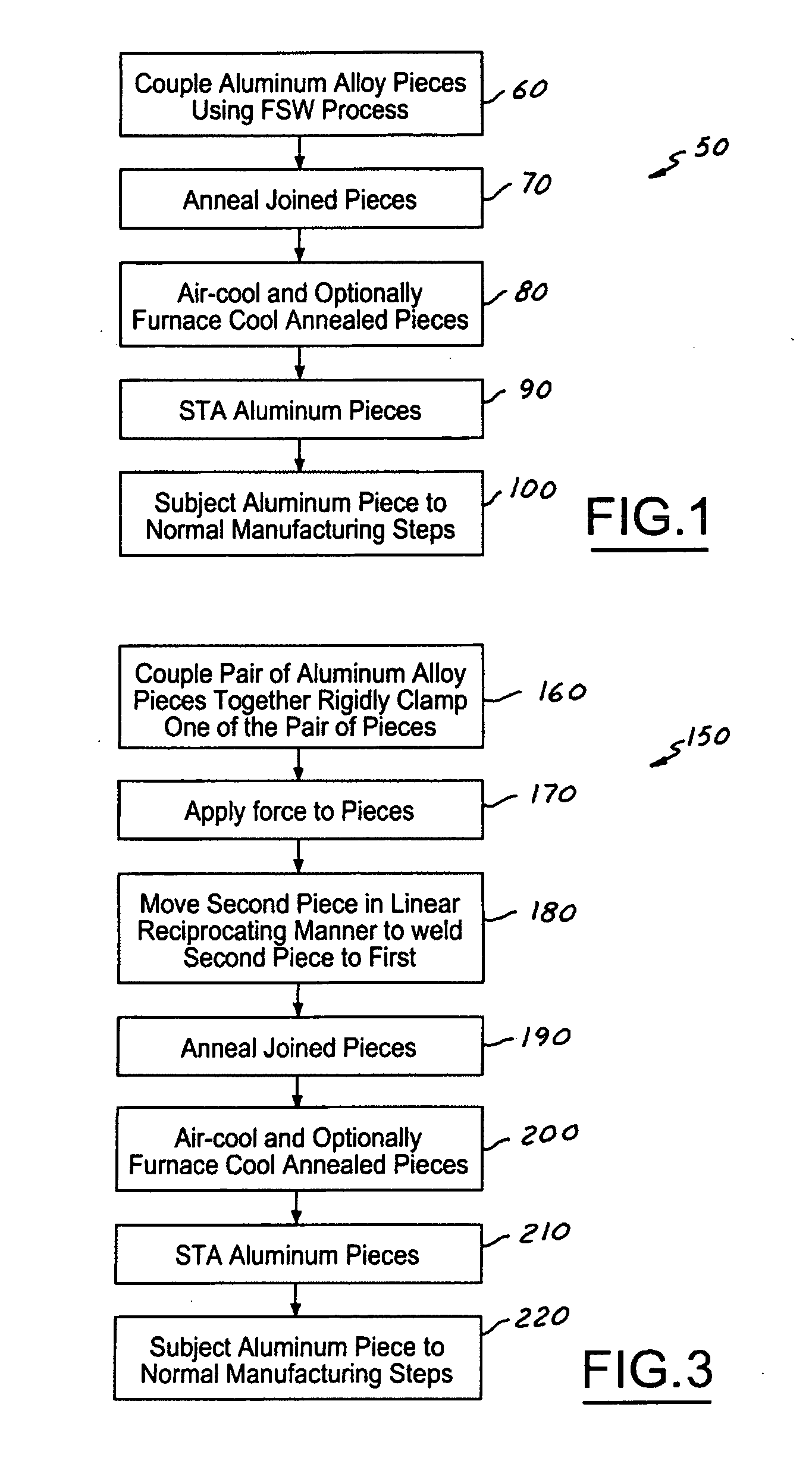
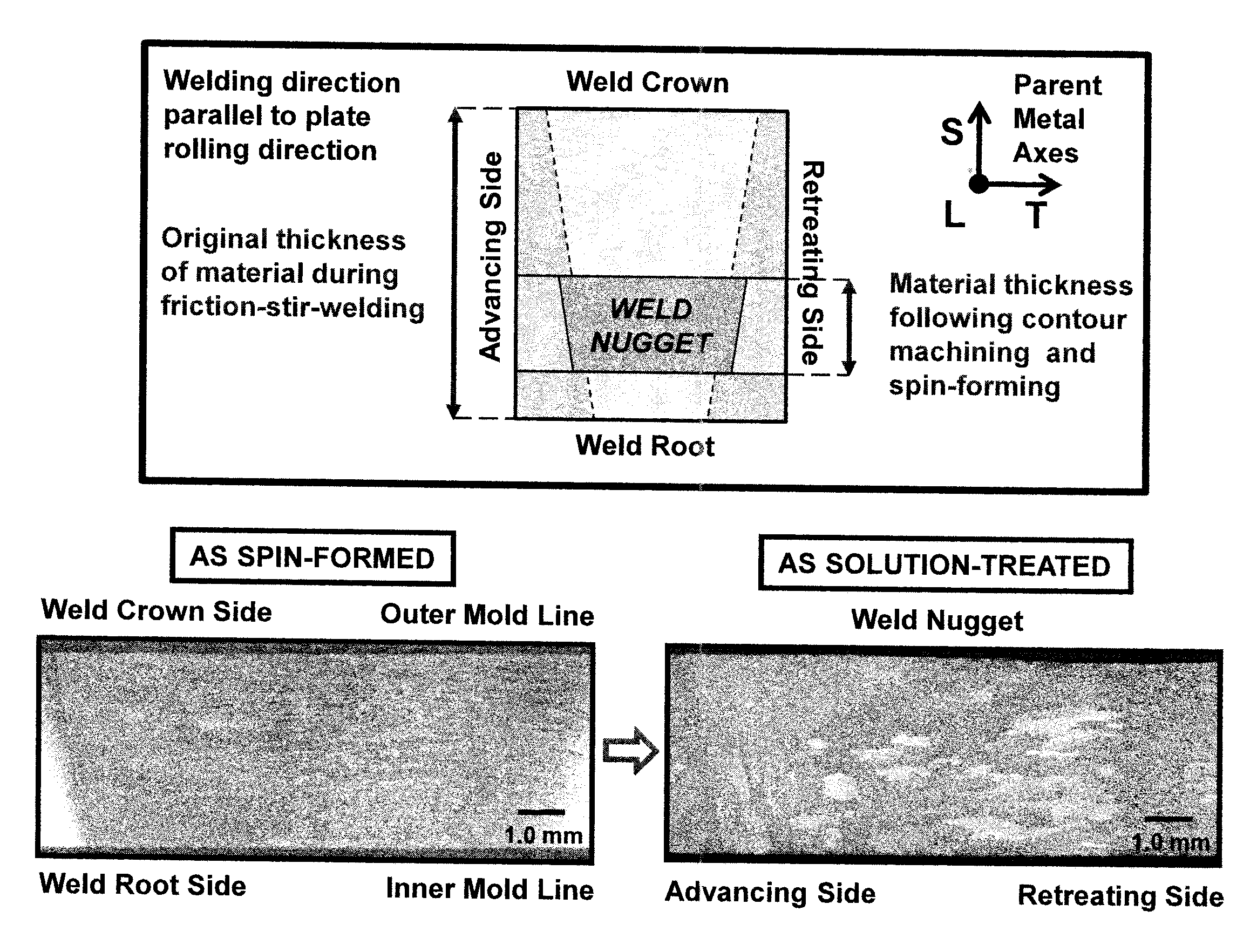
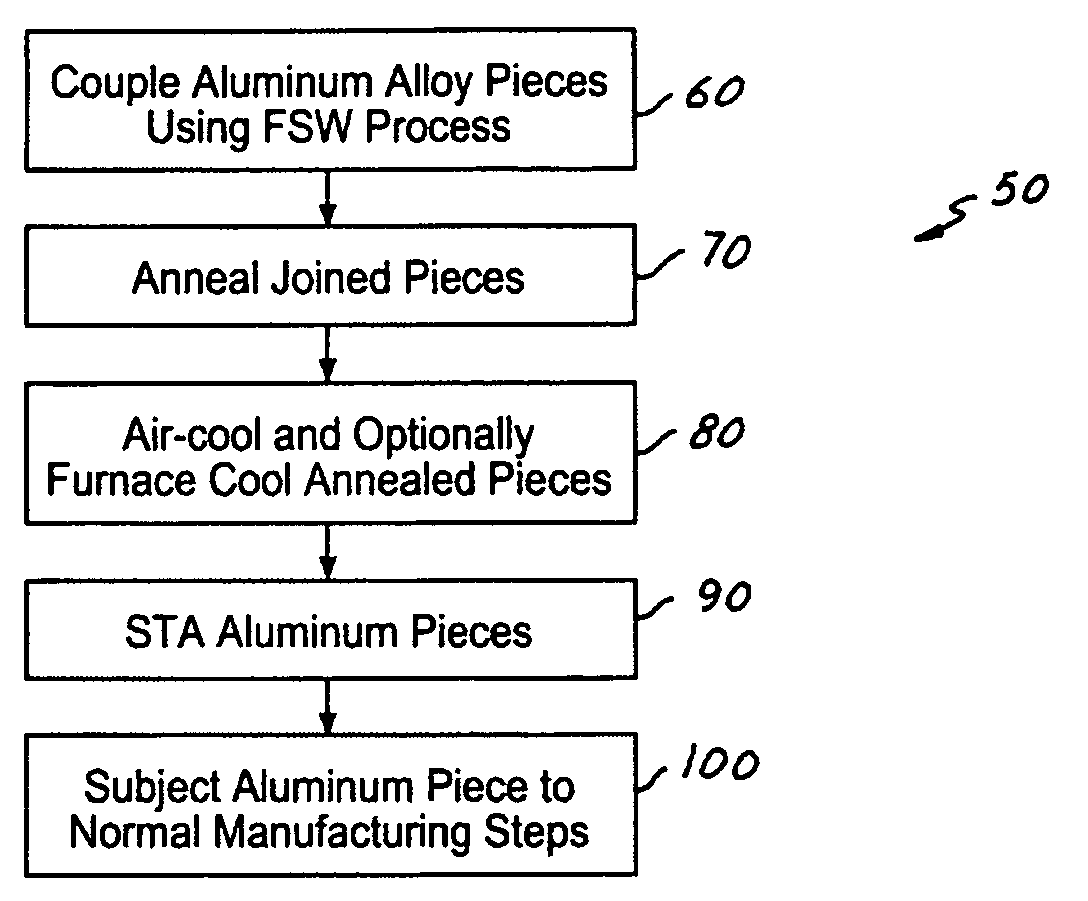
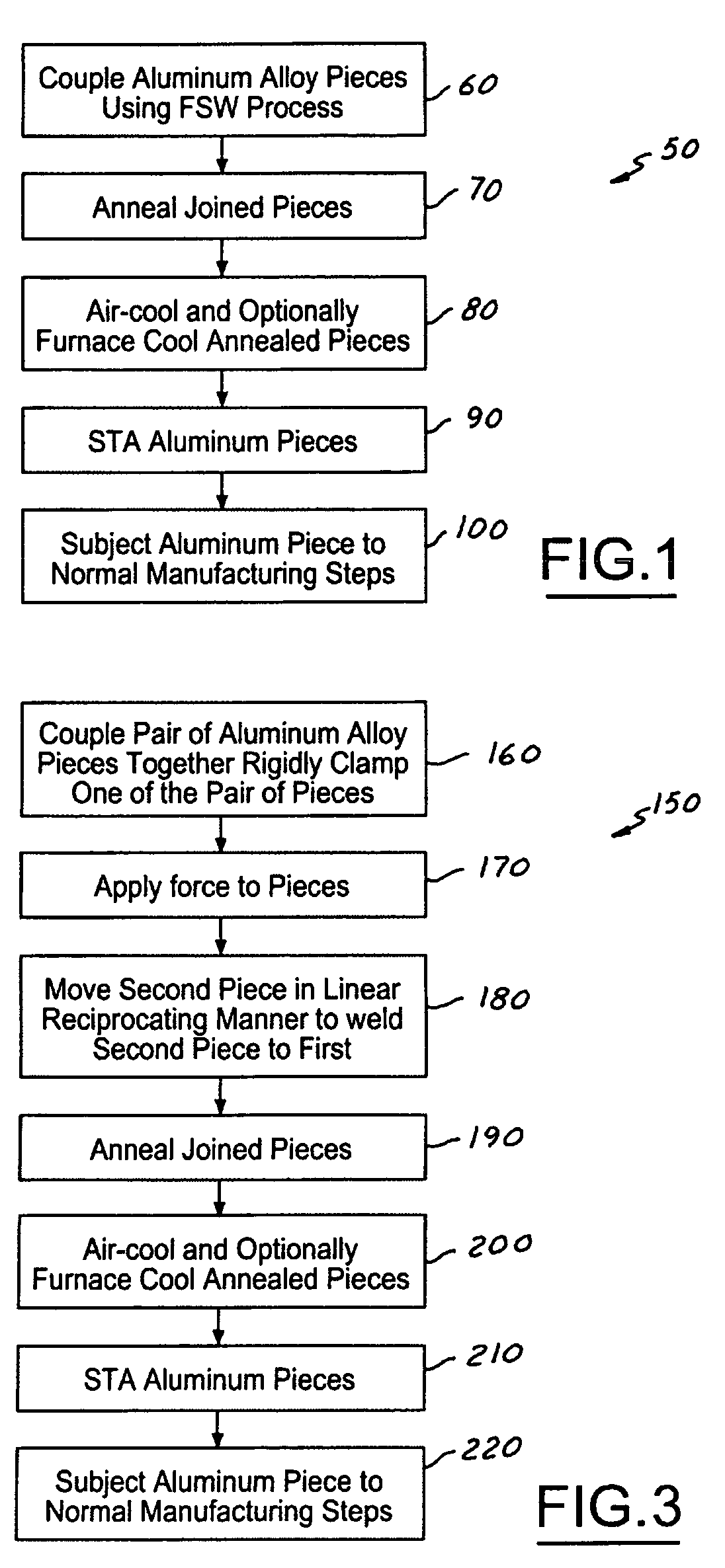
Abnormal Grain Growth Suppression in Aluminum Alloys
ActiveUS20120090738A1High strengthImprove ductilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAbnormal grain growthSpins
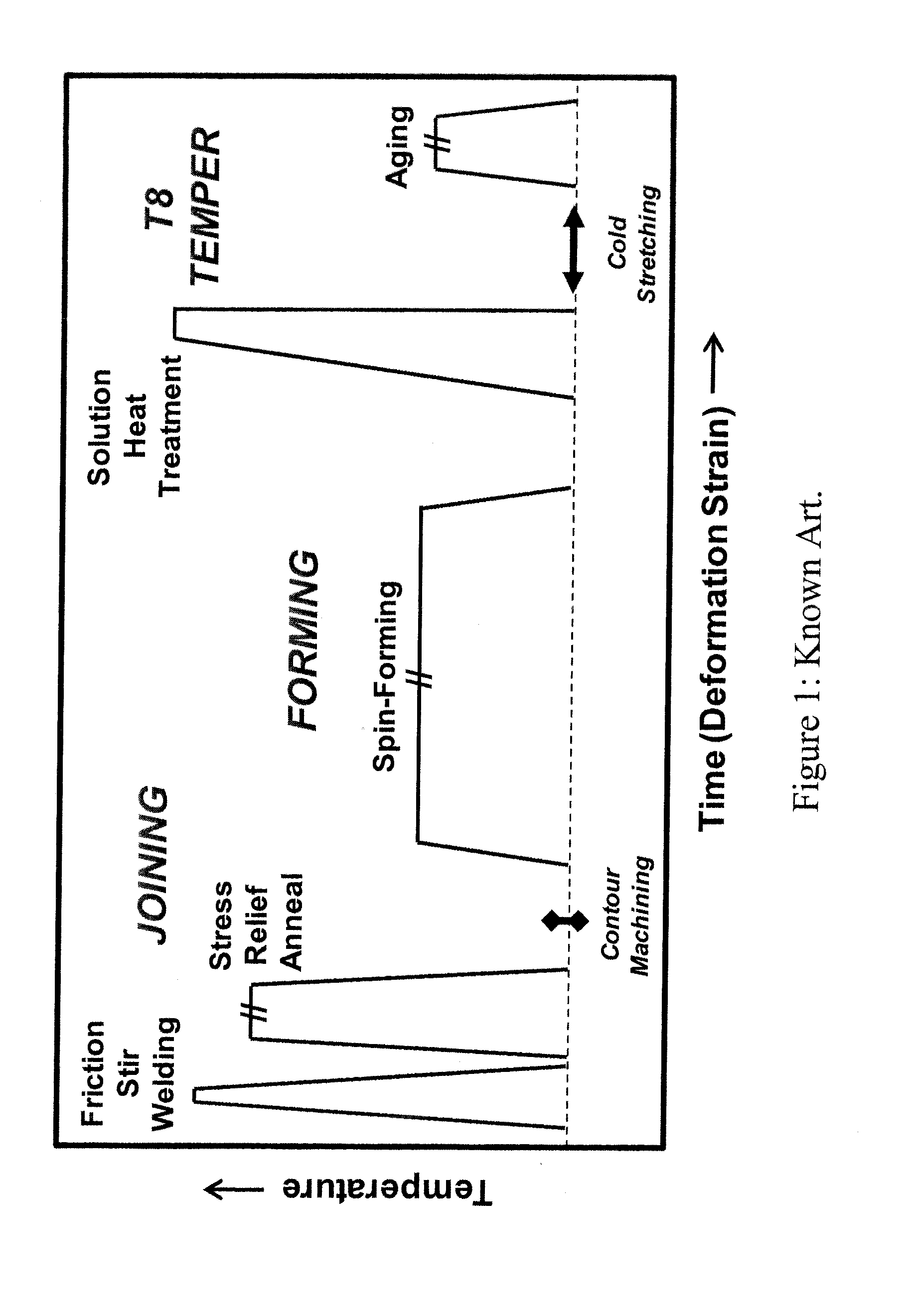
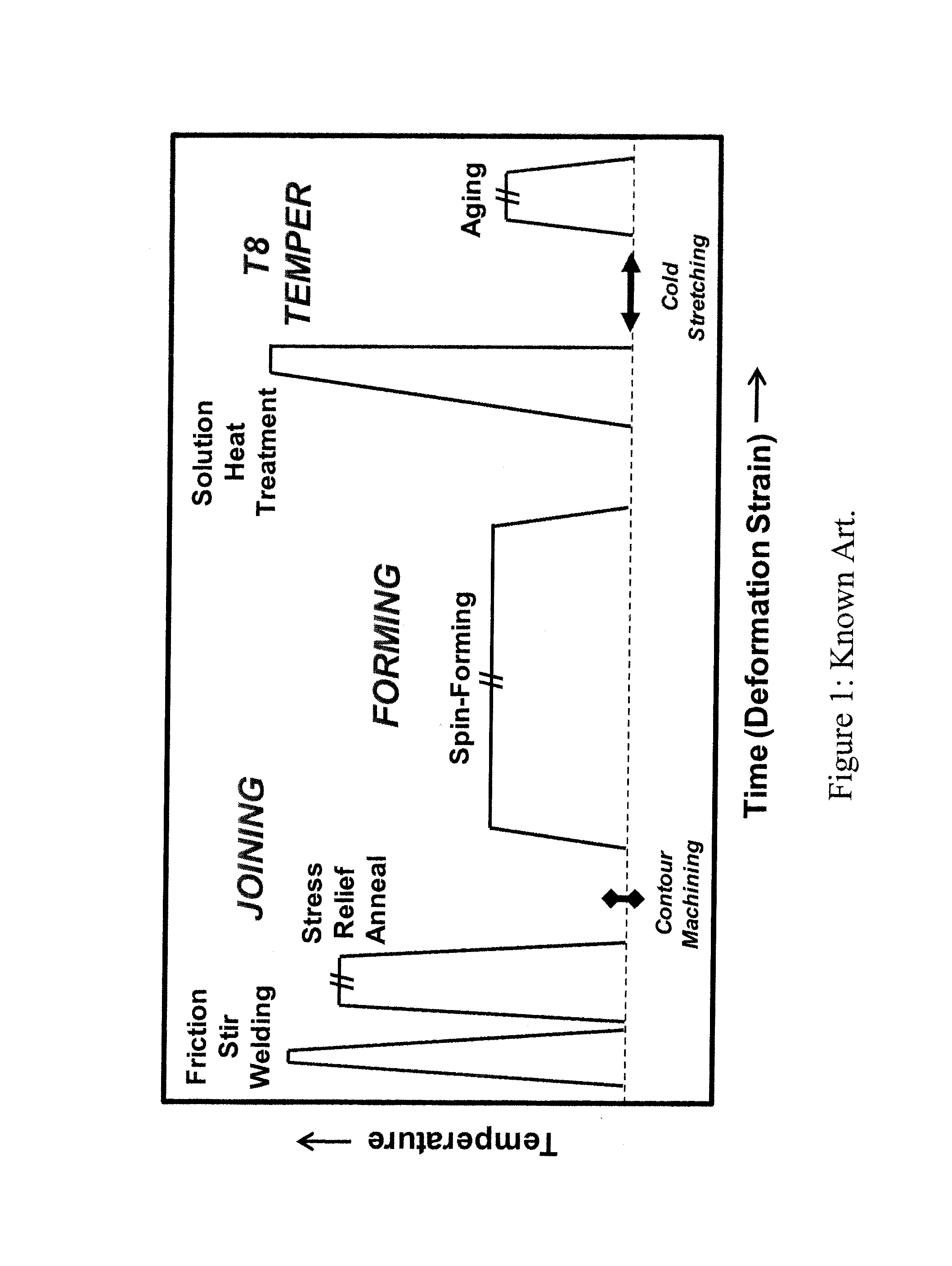
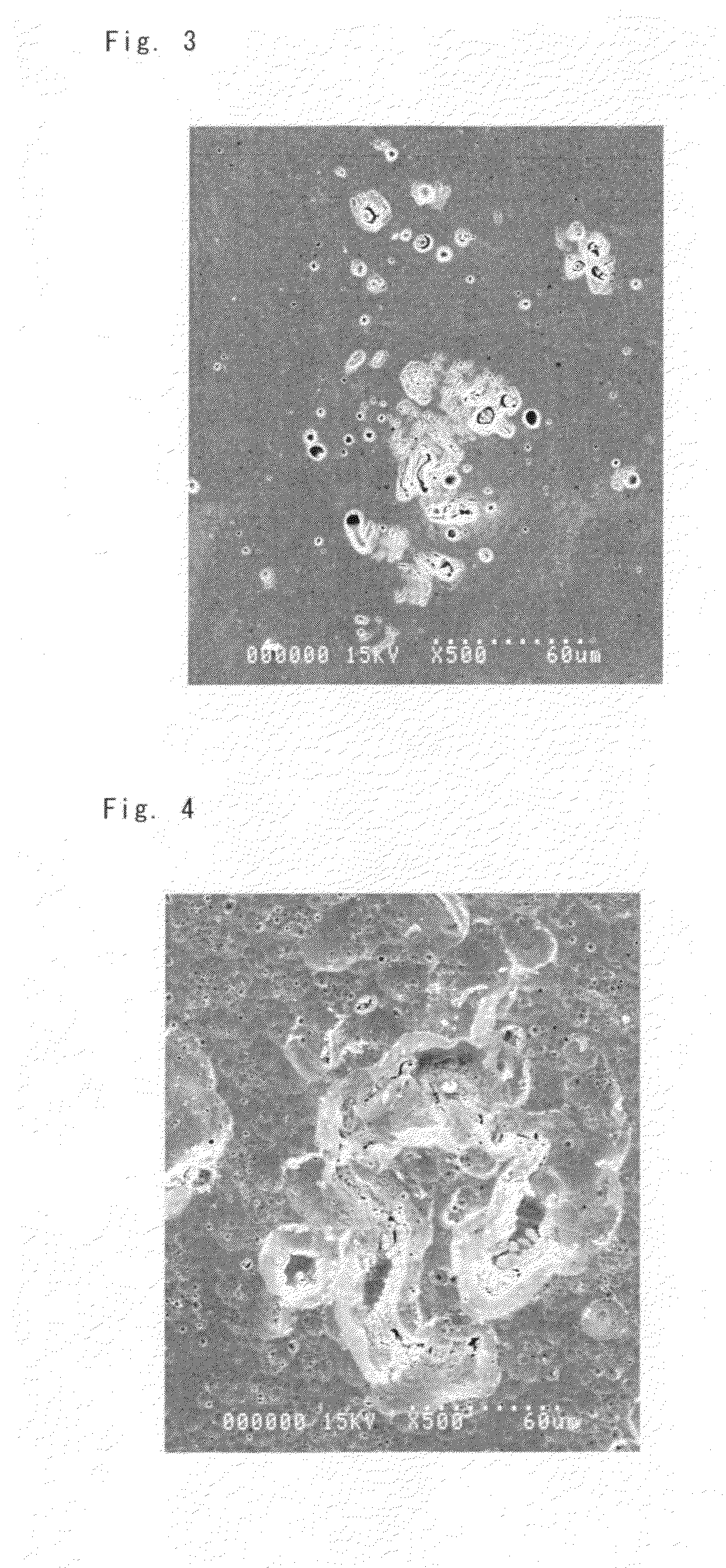
The present invention provides a process for suppressing abnormal grain growth in friction stir welded aluminum alloys by inserting an intermediate annealing treatment (“IAT”) after the welding step on the article. The IAT may be followed by a solution heat treatment (SHT) on the article under effectively high solution heat treatment conditions. In at least some embodiments, a deformation step is conducted on the article under effective spin-forming deformation conditions or under effective superplastic deformation conditions. The invention further provides a welded article having suppressed abnormal grain growth, prepared by the process above. Preferably the article is characterized with greater than about 90% reduction in area fraction abnormal grain growth in any friction-stir-welded nugget.
Owner:NASA
Apparatus for and method of heat-treating thin film on surface of substrate
ActiveUS20120093492A1Avoid abnormal grain growthAvoid it happening againDrying solid materials with heatMaintainance of heating chambersAbnormal grain growthHalogen
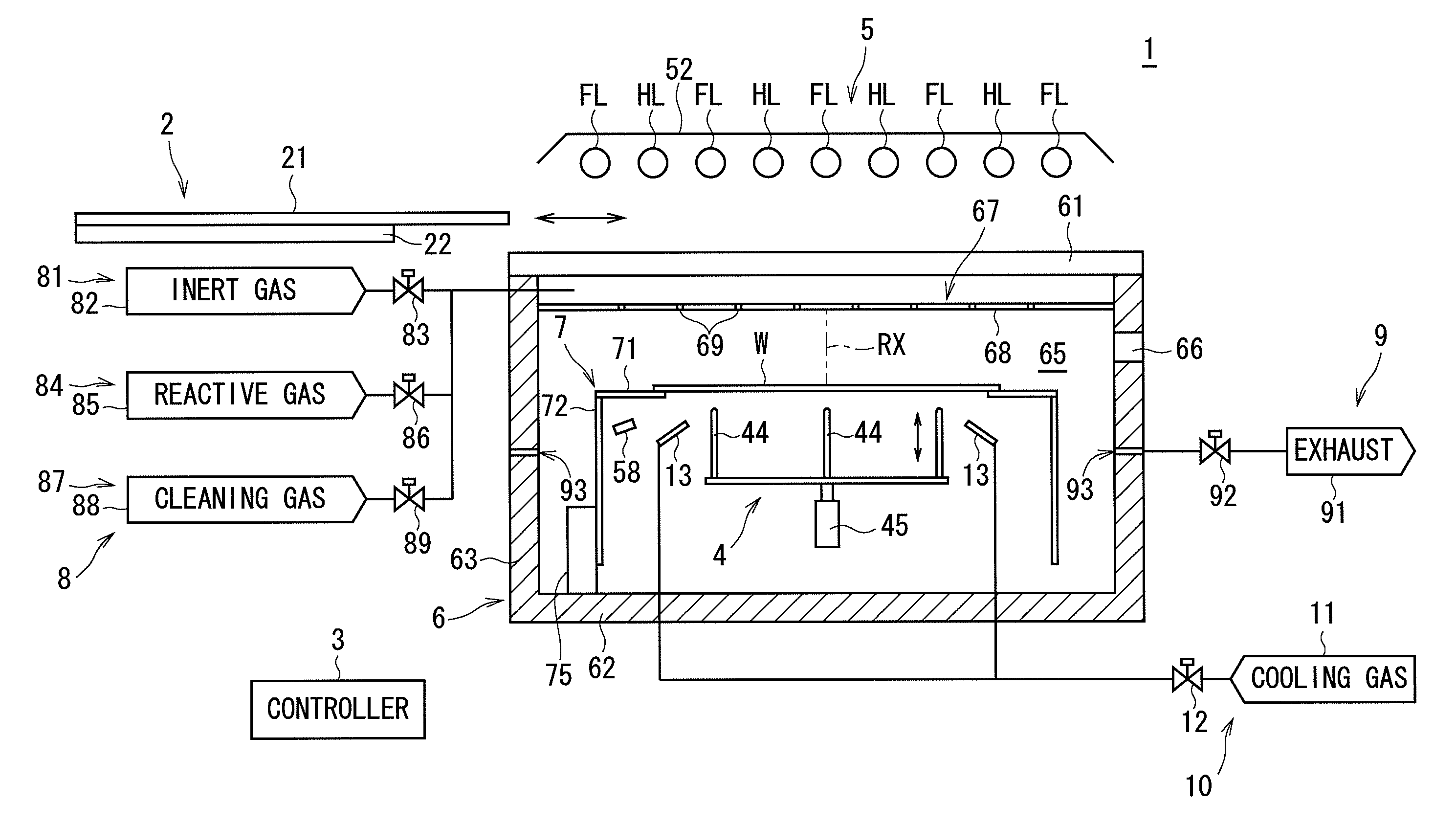
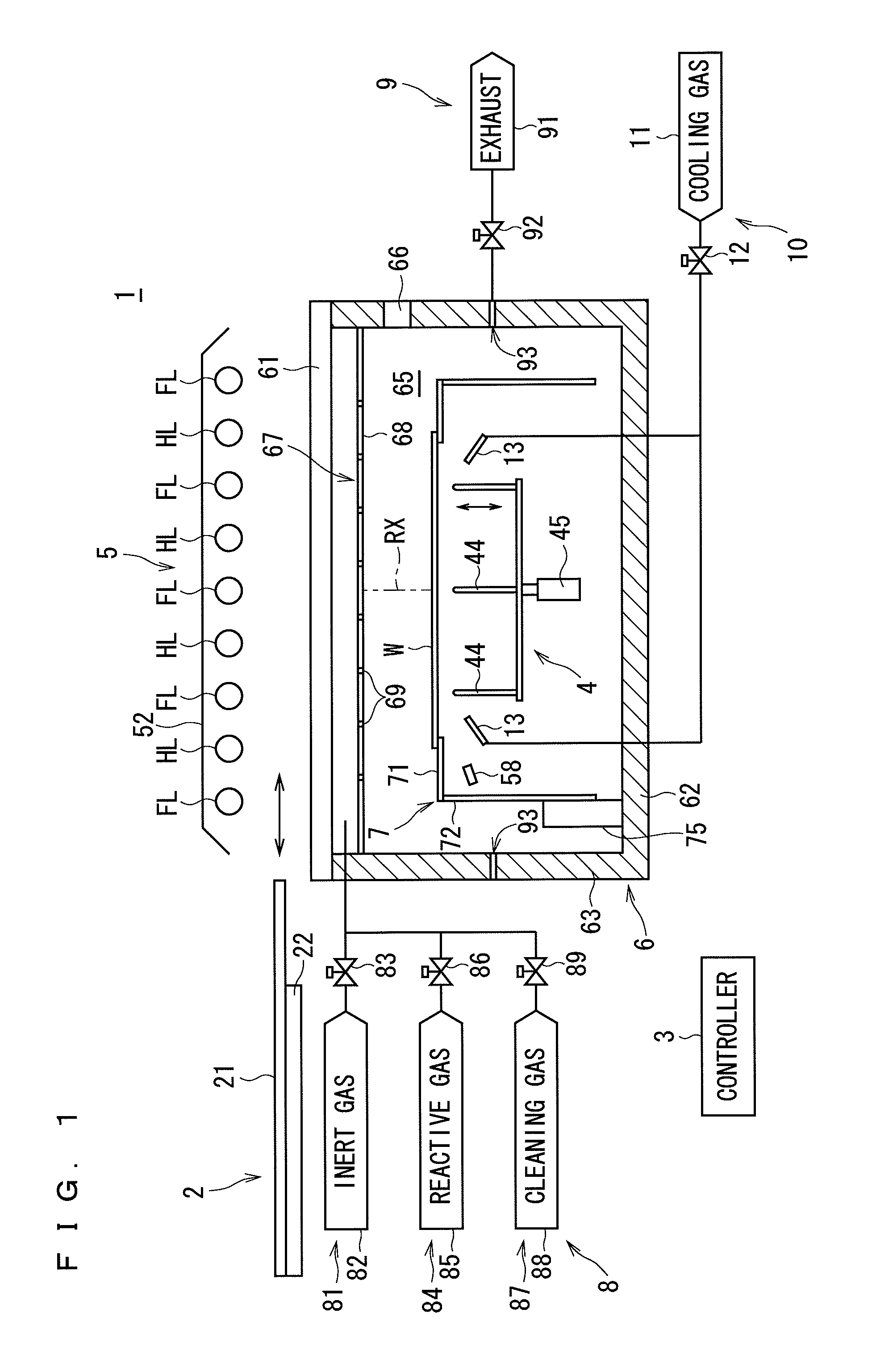
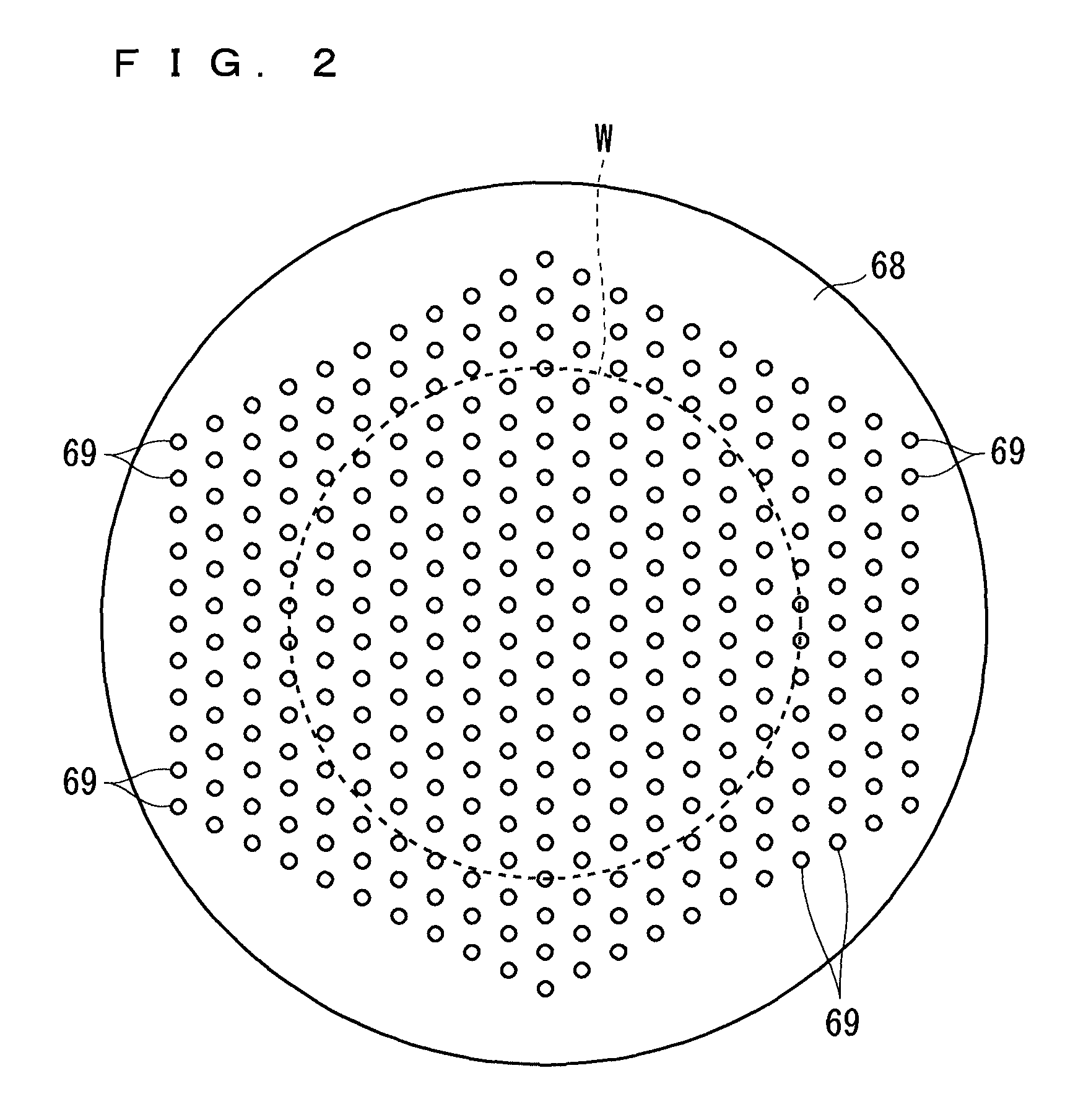
A semiconductor wafer having a surface with a thin film formed thereon is transported into a chamber and held by a holder. After an atmosphere provided in the chamber is replaced, flashes of light are directed from flash lamps in a light irradiation part toward the semiconductor wafer to perform a baking process on the thin film. The irradiation of the semiconductor wafer with light from halogen lamps in the light irradiation part also starts at the same time as the irradiation thereof with the flashes of light. The flashes of light emitted for an extremely short period of time and having a high intensity allow the surface temperature of the thin film to rise momentarily. This prevents the occurrence of abnormal grain growth resulting from prolonged baking in the film.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Preparation method of transparent tetravalent chromium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet ceramics
The invention relates to a preparation method of transparent tetravalent chromium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet ceramics. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing raw material powder according to a stoichiometric ratio of a to-be-prepared ceramic component structural formula (Al1-xCrx)5CayY3-yO12 (x is not smaller than 0.001 and not larger than 0.01, and y is not smaller than 10x and not larger than 40x); adding a sintering aid and a charge compensating agent; mixing by ball-milling to obtain a slurry material; drying and sieving the slurry material and then molding to obtain a biscuit; calcining to remove volatile impurities; sintering the biscuit in vacuum at the temperature of 1730 to 1850 DEG C for 4 to 30 hours; subsequently annealing in air at the temperature of 1300 to 1550 DEG C for 10 to 25 hours to obtain compact Cr<4+>:YAG transparent ceramics. The Cr<4+>:YAG transparent ceramics prepared by the method disclosed by the invention are high in compactness, good in uniformity, free of segregation, reasonable in grain graduation distribution, free of abnormal grain growth, free of grain interior and intergranular pores and high in penetration rate, and have the conditions for being a laser gain medium.
Owner:河南和光光电有限公司
Apparatus for and method of heat-treating thin film on surface of substrate
ActiveUS8963050B2Avoid it happening againAvoid abnormal grain growthElectric discharge heatingDrying solid materials with heatAbnormal grain growthLight irradiation
A semiconductor wafer having a surface with a thin film formed thereon is transported into a chamber and held by a holder. After an atmosphere provided in the chamber is replaced, flashes of light are directed from flash lamps in a light irradiation part toward the semiconductor wafer to perform a baking process on the thin film. The irradiation of the semiconductor wafer with light from halogen lamps in the light irradiation part also starts at the same time as the irradiation thereof with the flashes of light. The flashes of light emitted for an extremely short period of time and having a high intensity allow the surface temperature of the thin film to rise momentarily. This prevents the occurrence of abnormal grain growth resulting from prolonged baking in the film.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Sintering method of neodymium-iron-boron magnet
ActiveCN106252012AUniform sizeShape improvementInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAbnormal grain growthSquare degree
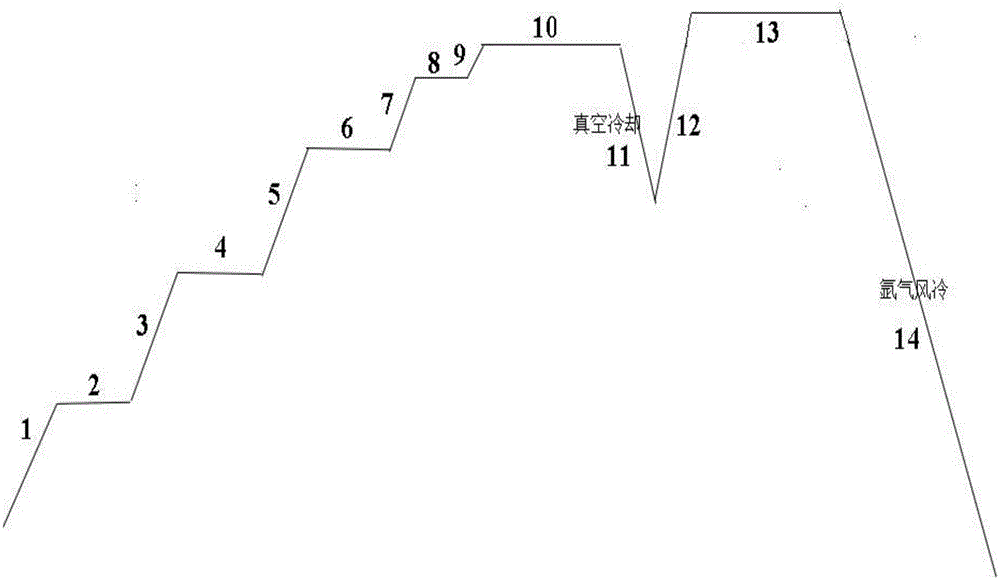
The invention provides a sintering method of a neodymium-iron-boron magnet. A plurality of steps in a preparation process of the neodymium-iron-boron magnet are analyzed; grain growth can be significantly prevented by use of a segmented sintering method from a neodymium-iron-boron sintering process; and the magnet with fine grains and uniform density is obtained, so that the magnetic property of the magnet is significantly improved; especially for the neodymium-iron-boron magnet with low rare earth content, the problems that grains abnormally grow and the residual magnetism and the square degree of the magnet cannot reach the requirements due to the fact that the granularity of neodymium-iron-boron magnet powder and the oxygen content in the process are reduced are solved when heavy rare earth content is reduced within the industry. By the method provided by the invention, the neodymium-iron-boron magnet which is free of abnormal grain growth and has better residual magnetism and square degree can be obtained.
Owner:京磁材料科技股份有限公司
Tungsten Sintered Sputtering Target
InactiveUS20110094879A1Avoid abnormal grain growthImprove production yieldCellsElectric discharge tubesAbnormal grain growthImpurity
Provided is a tungsten sintered sputtering target, wherein the phosphorus content is 1 wtppm or less and the remainder is other unavoidable impurities and tungsten. The inclusion of phosphorus heavily affects the abnormal grain growth of tungsten and the deterioration in the target strength. In particular, if phosphorus is contained in an amount exceeding 1 ppm, crystal grains subject to abnormal grain growth will exist in the tungsten target. Thus, the object is to prevent the abnormal grain growth of tungsten and improve the product yield of the target by strongly recognizing the phosphorus contained in the tungsten as a harmful impurity and controlling the inclusion thereof to be as low as possible.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
Method of converting PCA to sapphire and converted article
InactiveUS8157912B2Speed up the conversion processFully convertedFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthAbnormal grain growthBoric acid
Polycrystalline alumina (PCA) that has been doped with magnesium oxide is converted to sapphire by additionally doping the PCA with boron oxide and sintering to induce abnormal grain growth. The boron oxide may be added to an already formed green PCA ceramic shape by applying an aqueous boric acid solution to the green ceramic and heating the green ceramic in air to convert the boric acid to boron oxide.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Alloy powder for rare-earth magnet, methods for manufacturing alloy powder and rare-earth magnet and powder manufacturing device
ActiveCN103817335ALow coercivityImprove coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsAbnormal grain growthMicrometer
The invention discloses alloy powder for a rare-earth magnet, methods for manufacturing the alloy powder and the rare-earth magnet and a powder manufacturing device. The method for manufacturing the alloy powder includes acquiring all powder with the grain size smaller than 50 micrometers in working procedures for finely crushing at least one type of alloy for the rare-earth magnet and at least one type of alloy coarse powder for the rare-earth magnet by the aid of high-speed inert gas flow with the oxygen content lower than 1000ppm. By the aid of the alloy powder, the methods and the powder manufacturing device, ultrafine powder with the grain size smaller than 1 micrometer does not need to be separated from crushed powder which is transmitted from a crushing device and has a low oxygen content, the oxygen content of atmosphere of the crushing device is reduced and is lower than 1000ppm when the crushing device is used for crushing, and accordingly abnormal grain growth (AGG) can be prevented in a follow-up sintering procedure for acquiring a sintered magnet with a low oxygen content. The alloy powder, the methods and the powder manufacturing device have the advantages that working procedures can be simplified, and the manufacturing cost can be reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet manufacturing method and device
ActiveCN102842419ALess prone to growthSave rare earthPermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAbnormal grain growthRare earth
The invention discloses a sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet manufacturing method and device. The method comprises the following steps: in the manufacturing procedure of Nd-Fe-B system sintered magnet in which the oxygen content is below 2,500 ppm and in the crushing procedure under the condition that the oxygen content in inert gas is below 1,000 ppm, after the grading step, a mixing step is added to re-mix the originally separated ultrafine powder into finished crushed powder, and the originally separated ultrafine powder enters the follow-up processing procedure together with the finished crushed powder. By adopting the method, in the follow-up sintering procedure, AGG (Abnormal Grain Growth) can not be easily caused in the follow-up sintering procedure, besides, precious rare earth can be saved and extremely high pricing competitiveness is achieved through material conservation.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet manufacturing method and device
ActiveCN102842418ALess prone to abnormal grain growthImprove coercive forcePermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAbnormal grain growthSintered magnets
The invention discloses a sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet manufacturing method and device. The method comprises the following steps: in the manufacturing procedure of Nd-Fe-B system sintered magnet in which the oxygen content is below 2,500 ppm and in the crushing procedure under the condition that the oxygen content in inert gas is below 1,000 ppm, and the grading step is omitted, so that ultrafine powder which is originally separated is continually mixed in finished crushed powder and enters the follow-up processing procedure together with the finished crushed powder. By adopting the method, in the follow-up sintering procedure, AGG (Abnormal Grain Growth) can not be easily caused in the follow-up sintering procedure, and the characteristics such as simplifying the procedure and lowering the production cost, are achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Method for solid-state single crystal growth
InactiveUS20050150446A1High reproduction possibilitySuppress abnormal grain growthPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthAbnormal grain growthNumber density
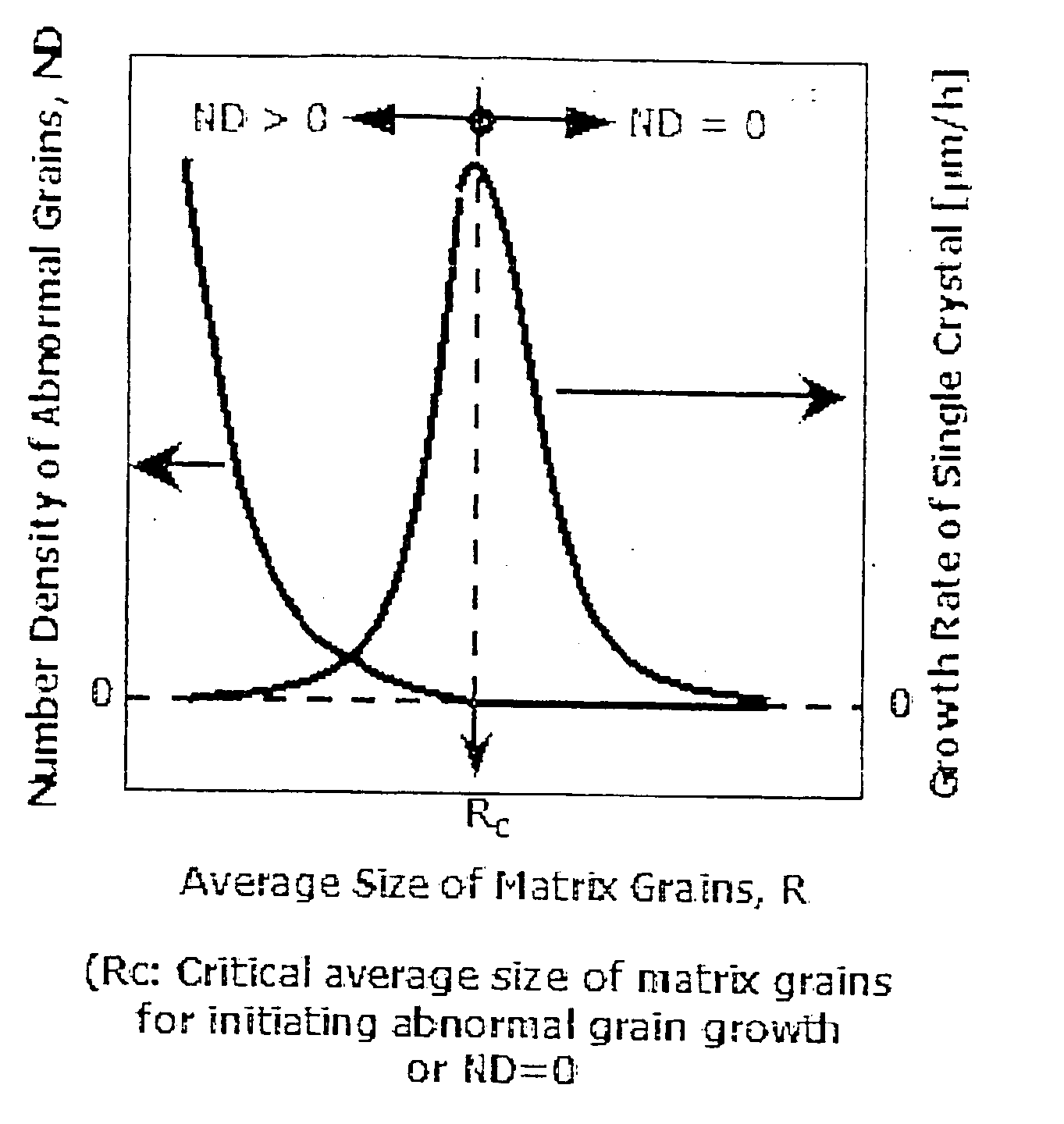
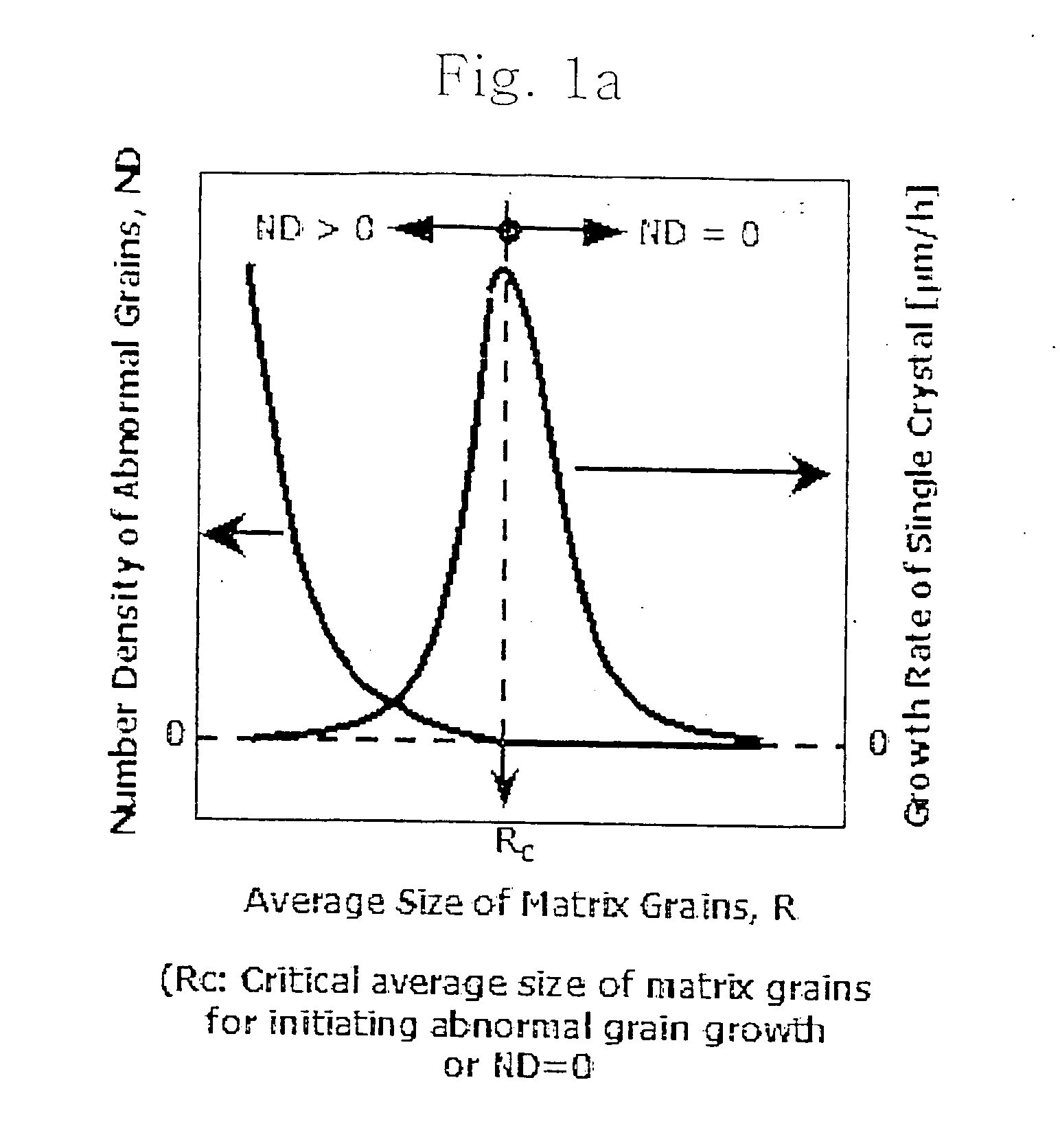
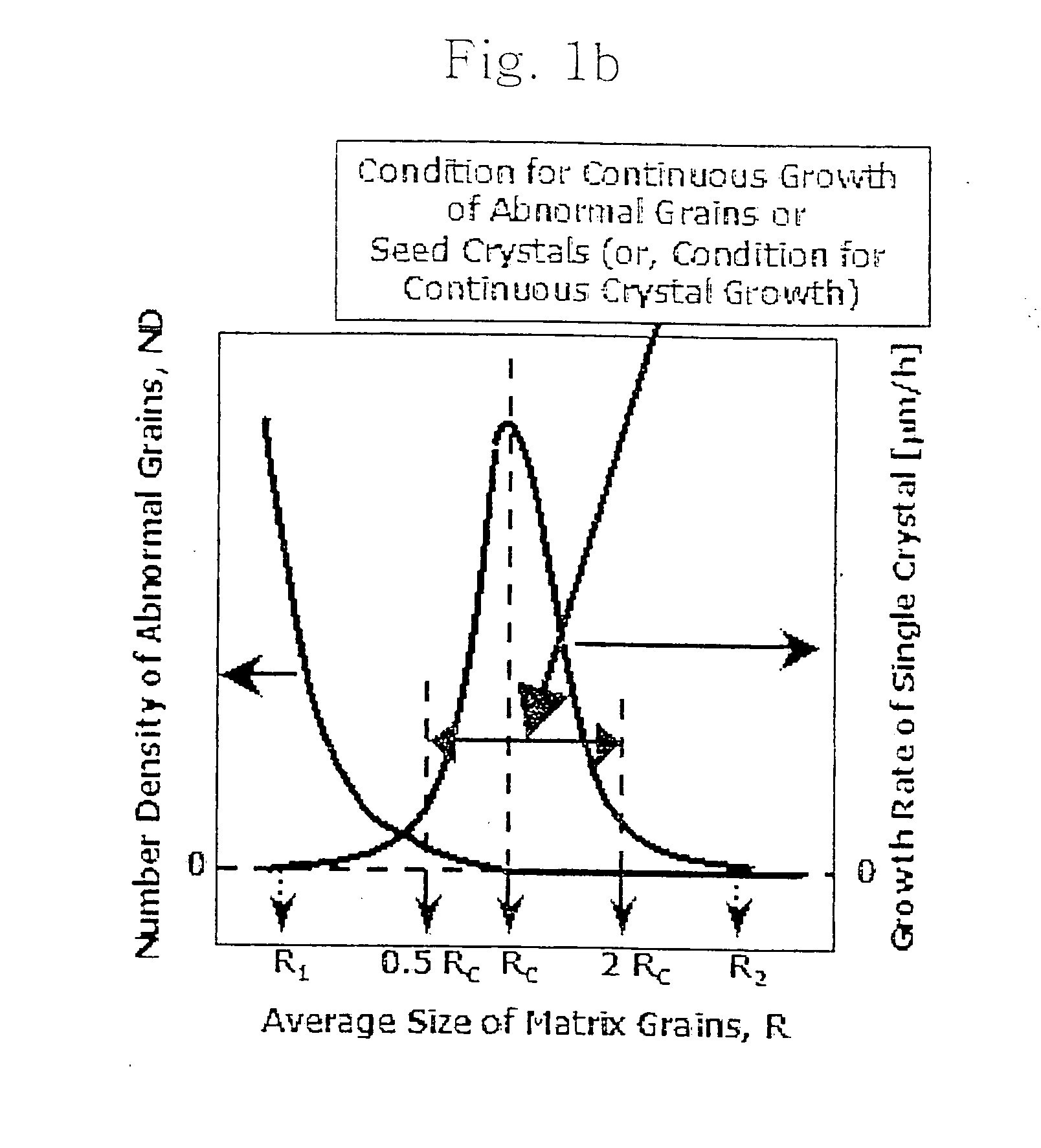
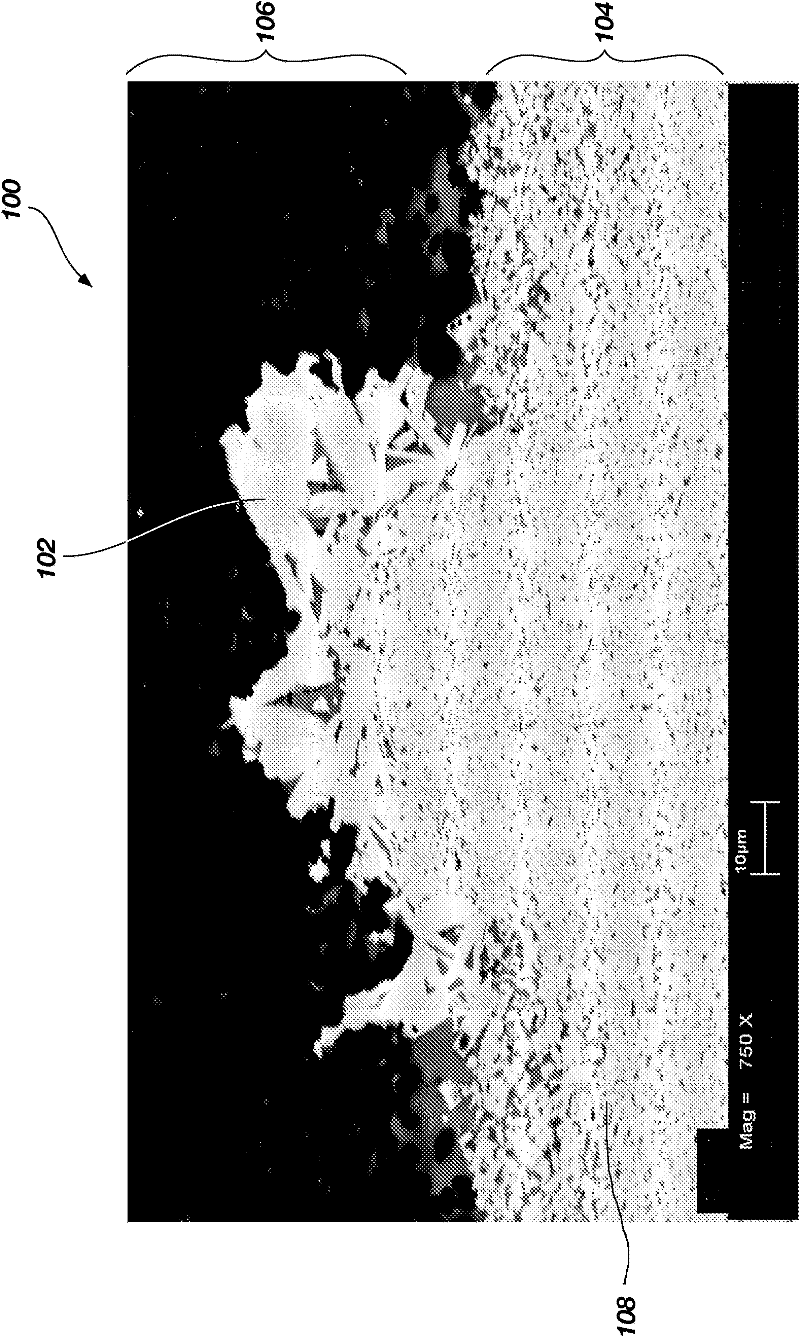
The invention relates to a method for growing single crystals in polycrystalline bodies in which abnormal grain growth occurs. The method is characterized by controlling the average size of matrix grains of polycrystalline bodies in which abnormal grain growth occurs, whereby reducing the number density (number of abnormal grains / unit volume) of abnormal grains to generate only a extremely limited number of abnormal grains or inhibit the generation of abnormal grains within the extent of guaranteeing the driving force of abnormal grain growth. Therefore, the invention grows continuously only the extremely limited number of abnormal grains or only the seed single crystal into the polycrystalline body to obtain a large single crystal having a size larger than 50 mm.
Owner:CERACOMP
Polycrystalline diamond compact including a cemented tungsten carbide substrate that is substantially free of tungsten carbide grains exhibiting abnormal grain growth and applications therefor
Embodiments relate to polycrystalline diamond compacts ("PDCs") including a polycrystalline diamond ("PCD") table that is substantially free of defects formed due to abnormal grain growth of tungsten carbide grains, and methods of fabricating such PDCs. In an embodiment, a PDC comprises a cemented tungsten carbide substrate including an interfacial surface that is substantially free of tungsten carbide grains exhibiting abnormal grain growth, and a PCD table bonded to the interfacial surface of the cemented tungsten carbide substrate. The PCD table includes a plurality of bonded diamond grains defining a plurality of interstitial regions. At least a portion of the interstitial regions includes a metal-solvent catalyst disposed therein. The PCD table may be substantially free of chromium or the PCD table and the cemented tungsten carbide substrate may each include chromium.
Owner:US SYNTHETIC CORP
Process for manufacturing an article made of an oxide-dispersion-strengthened alloy
InactiveUS6042662AHigh strengthIncrease pressureGlass making apparatusMetal-working apparatusAbnormal grain growthOxide dispersion-strengthened alloy
This process makes it possible to manufacture articles of any shape by stamping, in which articles the matrix of the alloy has to have a coarse-grained structure. According to the invention, a partial hot-forming operation is carried out by stamping a blank made of an oxide-dispersion-strengthened alloy, especially a nickel-based alloy, having an initial ultrafine-grained structure, in order to form a shaped component, this shaped component is subjected to a secondary recrystallization heat treatment so as to develop an abnormal grain growth, and then a new hot-forming operation is carried out by stamping in order to give the recrystallized shaped component the final shape of the article.
Owner:SEVA
Method to improve properties of aluminum alloys processed by solid state joining
A method for forming an aluminum alloy article having improved mechanical properties using a solid-state joining process in which the problem of ductility reduction is minimized by conducting a thermal exposure treatment prior to solution heat treatment. This thermal exposure treatment, done at a temperature below the solution heat treatment temperature, releases stored energy in the aluminum-alloy material. The aluminum-alloy material then does not have sufficient energy to cause recrystallization and abnormal grain growth during the subsequent solution heat treatment process. The resultant aluminum-alloy material has a restored mechanical strength with only a minor, but acceptable, decrease in original ductility.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Polycrystal silicon preparation method
InactiveCN105529249AInhibition of abnormal growthImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAbnormal grain growthDeposition process
The invention discloses a polycrystal silicon preparation method, which comprises the steps of: introducing a small amount of N2O into a reaction chamber body as a doping gas when carrying out a polycrystal silicon deposition process, so that the N2O reacts with SiH4 serving as a process gas to generate SiO2; and doping polycrystal silicon, wherein excessive part of the SiH4 continues to decompose to generate polycrystal silicon. The presence of the SiO2 inhibits abnormal grain growth in the polycrystal silicon deposition process, thus size of polycrystal silicon grains can be reduced, grain uniformity can be increased and surface evenness can be improved, thereby eliminating the problem of polycrystal silicon particle production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
W-containing r-fe-b-cu sintered magnet and quenching alloy
ActiveUS20160300648A1Reduce dilution effectHigh melting pointInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsAbnormal grain growthRare-earth element
The present invention discloses a W-containing R—Fe—B—Cu serial sintered magnet and quenching alloy. The sintered magnet contains an R2Fe14B-type main phase, the R being at least one rare earth element comprising Nd or Pr; the crystal grain boundary of the rare earth magnet contains a W-rich area above 0.004 at % and below 0.26 at %, and the W-rich area accounts for 5.0 vol %˜11.0 vol % of the sintered magnet. The sintered magnet uses a minor amount of W pinning crystal to segregate the migration of the pinned grain boundary in the crystal grain boundary to effectively prevent abnormal grain growth and obtain significant improvement. The crystal grain boundary of the quenching alloy contains a W-rich area above 0.004 at % and below 0.26 at %, and the W-rich area accounts for at least 50 vol % of the crystal grain boundary.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Method of forming metal wiring and metal wiring formed using the same
InactiveUS20100196681A1Improve featuresStable structureMaterial nanotechnologyPretreated surfacesAbnormal grain growthNanoparticle
Disclosed are a method of forming metal wiring and metal wiring formed using the same. The method includes printing wiring using an ink composition including metallic nanoparticles and dispersants maintaining dispersion of the metallic nanoparticles, performing a first firing process of firing the wiring under vacuum or in an inert atmosphere to suppress grain growth, and performing a second firing process of firing the wiring with the vacuum or inert atmosphere released, to accelerate grain growth. The method of forming metal wiring induces abnormal grain growth by rapidly removing dispersants, capable of inducing the growth of metallic nanoparticles, at a temperature at which the growth force of the metallic nanoparticles is high, in the process of firing the metallic nanoparticles. Accordingly, the metal wiring has a coarse-grained structure containing metallic particles with a large average particle size, and the electrical and mechanical characteristics thereof can be enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for non-pressure spark plasma sintering of ceramics
InactiveCN109081700AVarious shapesImproved characteristics for applying axial pressureAbnormal grain growthAxial pressure
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic nonmetal ceramic preparation and discloses a method for non-pressure spark plasma sintering of ceramics. The method includes: according to a shape of arequired ceramic sample, adopting a direct coagulation casting method for forming a ceramic biscuit; placing the ceramic biscuit in a graphite mould, and sintering by means of non-pressure spark plasma sintering to obtain the required ceramic sample. The graphite mould comprises upper and lower pressure heads and a hollow forming cavity, the upper and lower pressure heads are matched with the forming cavity, the forming cavity is internally in a non-pressure state when axial pressure is applied to the pressure heads in a sintering process, spark plasma sintering is not only available for powder forming but also available for forming of the ceramic biscuit, obtained ceramic samples are diversified in shape, and aeolotropism of the required ceramic samples is improved. By the method, problems of long sintering period, high sintering temperature, abnormal grain growth, pressure unloading and the like of a traditional sintering process are solved, and high-performance ceramic samples can be obtained.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Piezoelectric ceramic and piezoelectric device
ActiveCN103172374AExcellent piezoelectric propertiesExcellent relative permittivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyAbnormal grain growthElectromechanical coupling coefficient
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Mn-zn ferrite containing less than 50 mol% fe2o3
An Mn-Zn ferrite includes base components of 44.0 to 49.8 mol % Fe 2 O 3 , 4.0 to 26.5 mol % ZnO, at least one of 0.1 to 4.0 mol % TiO 2 and SnO 2 , 0.5 mol % or less Mn 2 O 3 , and the remainder consisting of MnO, and contains 0.20 (0.20 excluded) to 1.00 mass % CaO as additive. Since the Mn-Zn ferrite contains less than 50 mol % Fe 2 O 3 and a limited amount (0.5 mol % or less) of Mn 2 O 3 , an abnormal grain growth does not occur even if CaO content is more than 0.20 mass %, and a high electrical resistance can be gained. And, since an appropriate amount of TiO 2 and / or SnO 2 is contained, an initial permeability is kept adequately high, whereby an excellent soft magnetism can be achieved in a high frequency band such as 1 MHz.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Piezoelectric ceramic composition and the method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070200084A1Improve sintering performanceImprove piezoelectric performancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionAbnormal grain growthCeramic
The present invention provides a piezoelectric ceramic composition, especially a lead-free piezoelectric ceramic composition, with a suitable amount of CeO2 or CeO2-containing complex additives, which is represented by the following formula: (Na0.475K0.475Li0.05)(Nb1-xAx)O3+yCeO2+zBO2 wherein “A” represents Sb or Sb+Ta, “B” represents a tetravalent transition metal, 0≦x≦0.2, 0.2 wt % <y<1.2 wt % and 0≦z 1 wt %. Addition of CeO2 or CeO2-containing complex additives suppresses melting and abnormal grain growth of (Na0.475K0.475Li0.05)(Nb1-xAx)O3 during sintering, thereby improving sinterability and increasing the density of the composition. As a result, the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of the ceramics are enhanced. Furthermore, the represented compositions have a wide sintering temperature range so that the process for preparing such a lead-free piezoelectric ceramic composition has high degree efficiency.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Soft magnetic steel having excellent forging characteristic soft magnetic part and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveCN105886893AOptimizing Forging PerformanceImprove addMagnetic materialsCrystalliteAbnormal grain growth
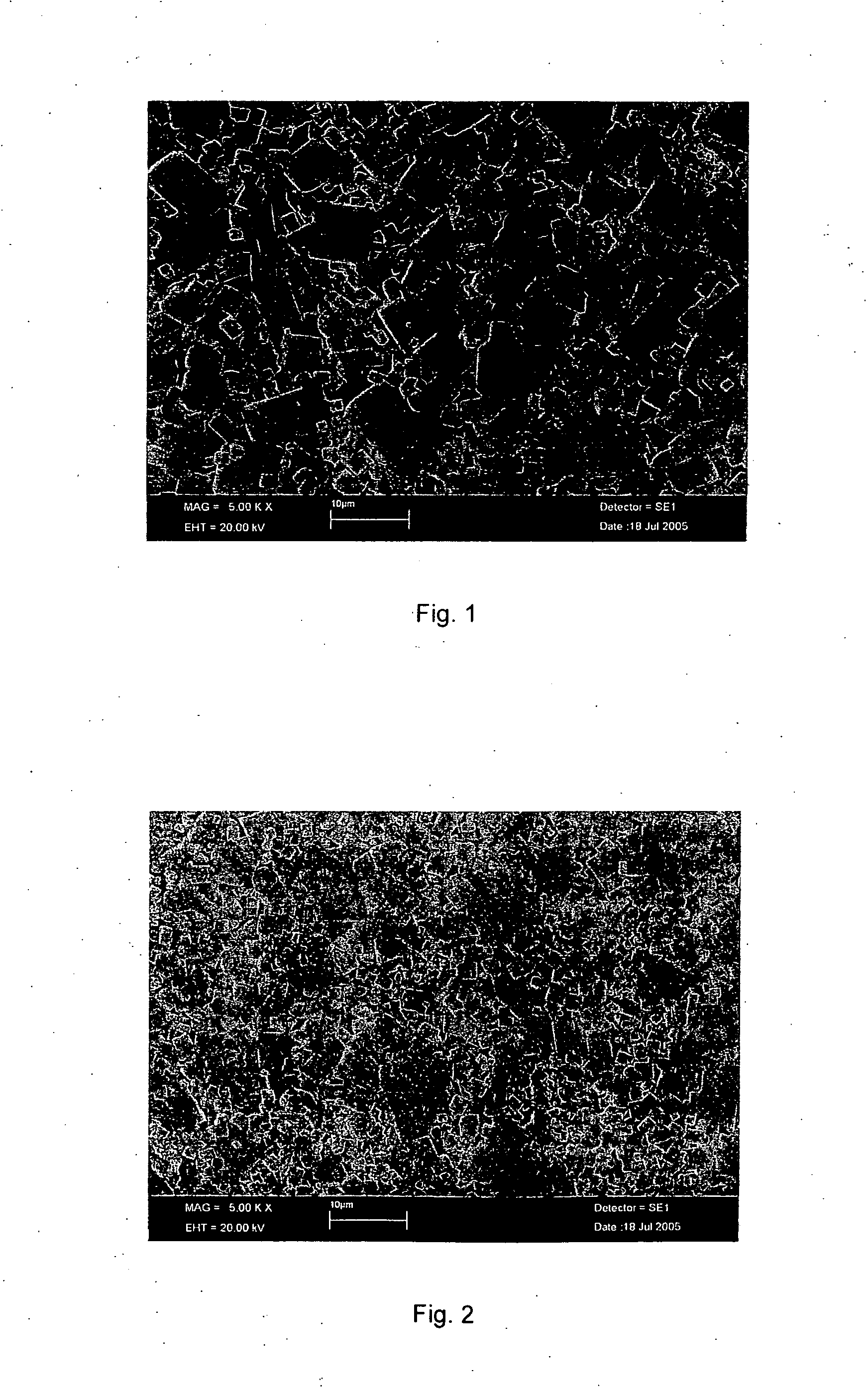
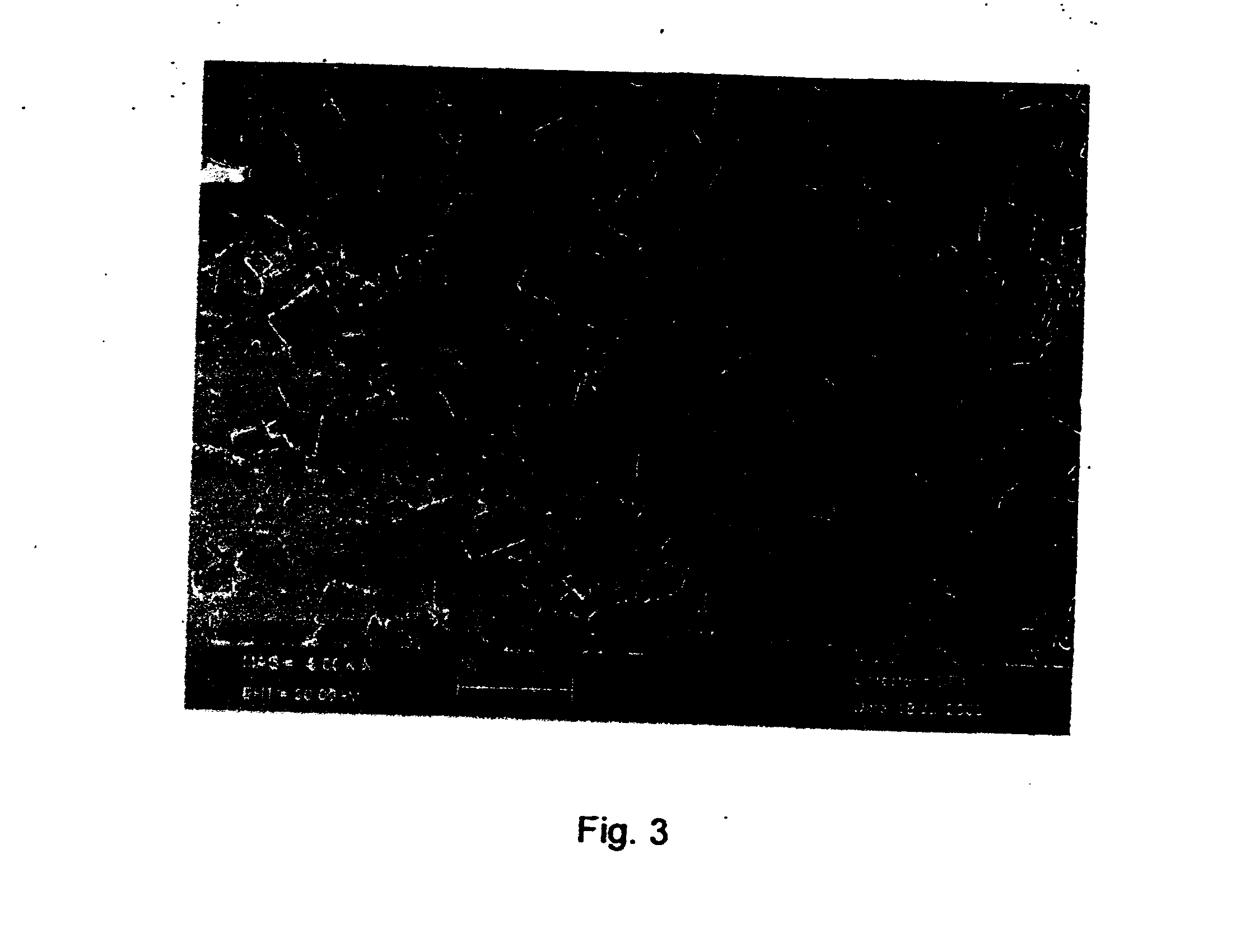
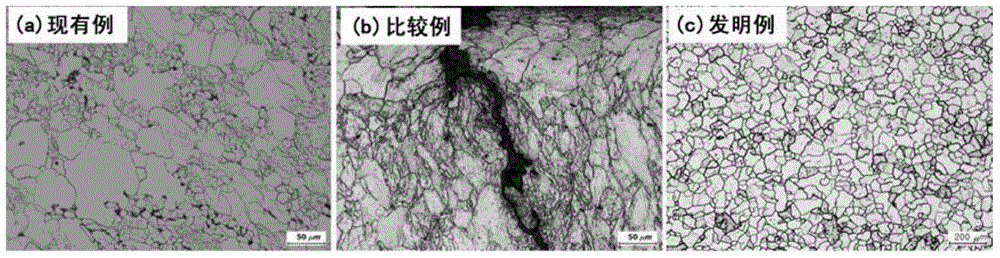
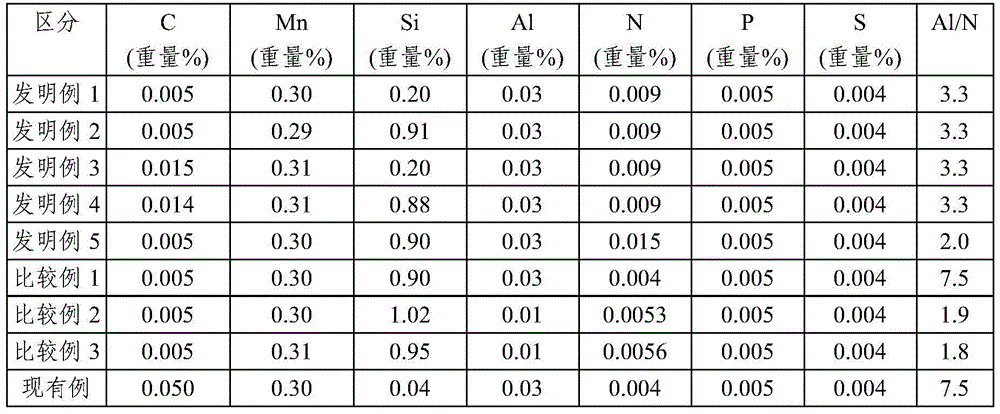
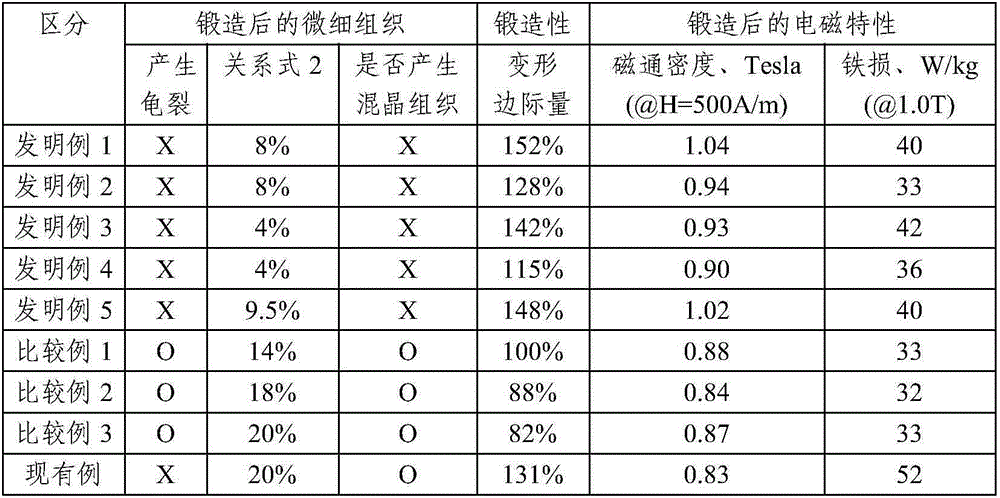
The present invention relates to soft magnetic steel materials and a soft magnetic steel member excellent in forgeability and excellent in electromagnetic characteristics, and a method of manufacturing the same, which uses AlN in a microstructure to suppress the possibility of abnormal grain growth during hot forging or after cold forging. The soft rolled steel materials excellent in forgeability according to one aspect of the present invention comprise, in % by weight, C: 0.001 to 0.02%, Mn: 0.1 to 1.2%, Si: 0.2 to 1.2%, Al:0.01 to 0.1%, N:0.005 to 0.015%, P:0.02% or less, S: 0.02% or less, and the unavoidable impurities, and satisfy the following relational expression 1, the microstructure is single-phase ferrite, and in[Relation1]: Al / N>= 2, wherein Al and N are contents indicating the content of each element (weight%).
Owner:浦项控股股份有限公司
Ceramic circuit board, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing ceramic circuit board
InactiveCN104781928AHigh positioning accuracyNormal composite structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAbnormal grain growthElectrical resistance and conductance
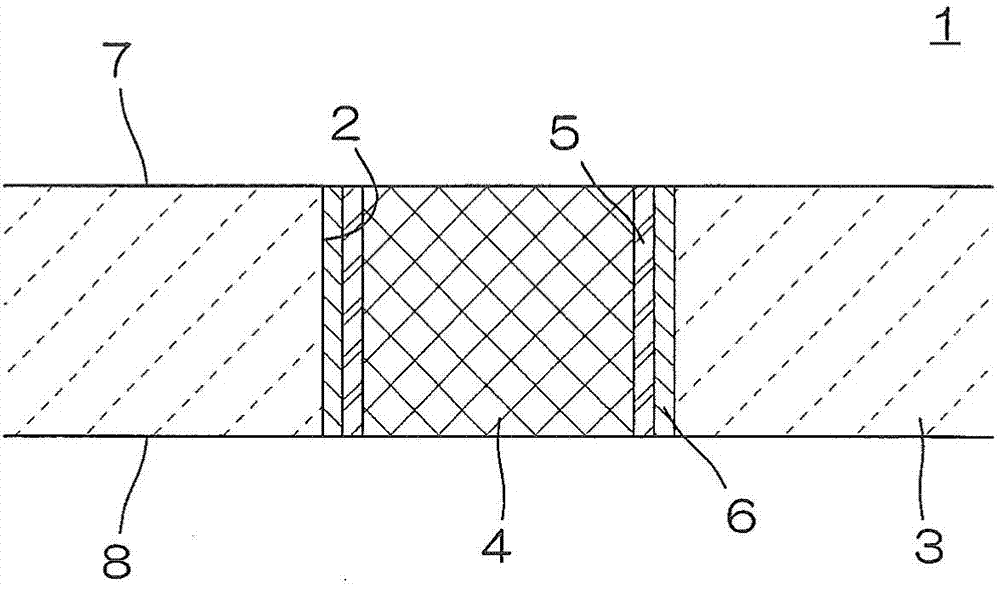
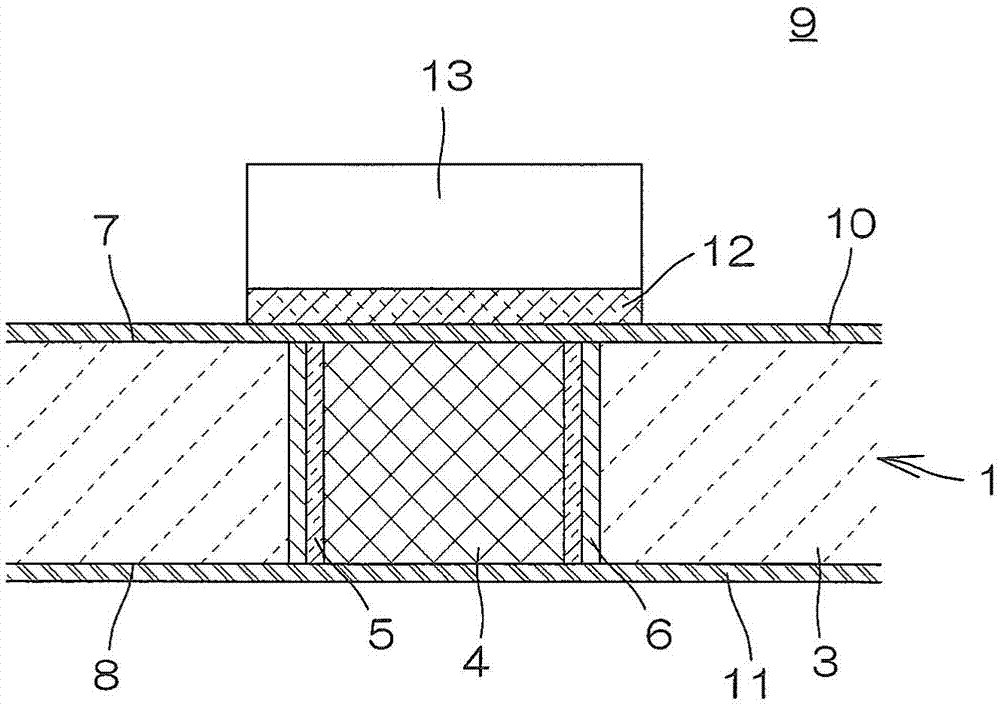
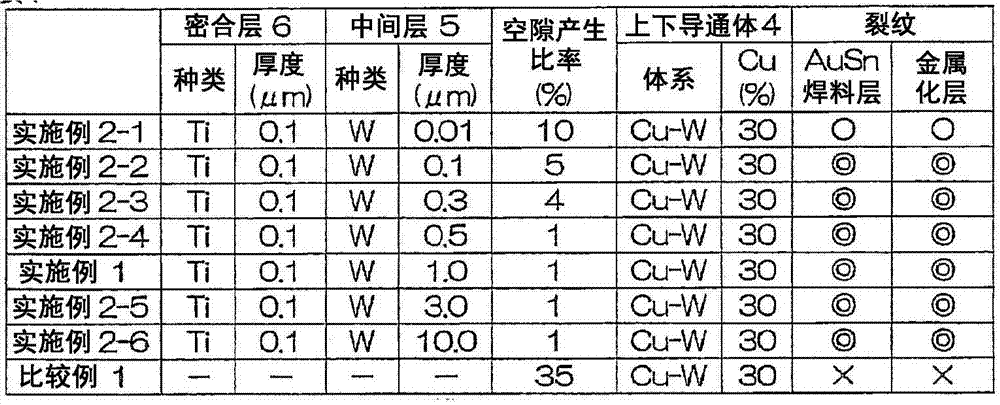
Provided is a ceramic wiring substrate comprising a vertical conducting body which is formed by forming a vertical conducting hole in a substrate after the substrate is formed in a plate shape by sintering a ceramic precursor, forming a porous structure made of a metal with a high melting point in the vertical conducting hole, and infiltrating a low-resistance metal into the hole. The vertical conducting body has a normal composite structure with no abnormal grain growth, voids, cracks, or the like, and has no possibility of sloughing from the substrate. Also provided are a method for manufacturing the ceramic wiring substrate, and a semiconductor device configured using the ceramic wiring substrate. On the inner surface of the vertical conducting hole (2) of the substrate (3) before the vertical conducting body (4) having the composite structure is formed, an intermediate layer (5) comprising at least one from among the group consisting of Mo, W, Co, Fe, Zr, Re, Os, Ta, Nb, Ir, Ru, and Hf is formed.
Owner:ALLIED MATERIAL
Abnormal grain growth suppression in aluminum alloys
InactiveUS9090950B2High strengthImprove ductilityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAbnormal grain growthHeat treated
The present invention provides a process for suppressing abnormal grain growth in friction stir welded aluminum alloys by inserting an intermediate annealing treatment (“IAT”) after the welding step on the article. The IAT may be followed by a solution heat treatment (SHT) on the article under effectively high solution heat treatment conditions. In at least some embodiments, a deformation step is conducted on the article under effective spin-forming deformation conditions or under effective superplastic deformation conditions. The invention further provides a welded article having suppressed abnormal grain growth, prepared by the process above. Preferably the article is characterized with greater than about 90% reduction in area fraction abnormal grain growth in any friction-stir-welded nugget.
Owner:NASA
Ceramic member and corrosion-resisting member
InactiveUS20080176735A1Improve plasma resistanceReduce the amount requiredSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine structureAbnormal grain growth
A ceramic member having a high density, small grain diameter, and excellent plasma resistance is provided. The ceramic member is constituted of a fine structure composed of fine grains, which is a ceramic member comprising an yttria as a main component and obtained through firing, wherein the ceramic member has an open porosity, as determined through a measurement by the Archimedes method, of less than 0.5%. By diminishing open voids, sites which is an origin of plasma erosion can be diminished. Thus, a ceramic member having excellent plasma resistance can be provided. By inhibiting abnormal grain growth to form a ceramic member constituted of stall grains, particle contamination by dusting can be reduced. Thus, plasma resistance and preventing particulate contamination can be improved.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Silicon-based thin film solar cell with quantum well structures and manufacturing method thereof
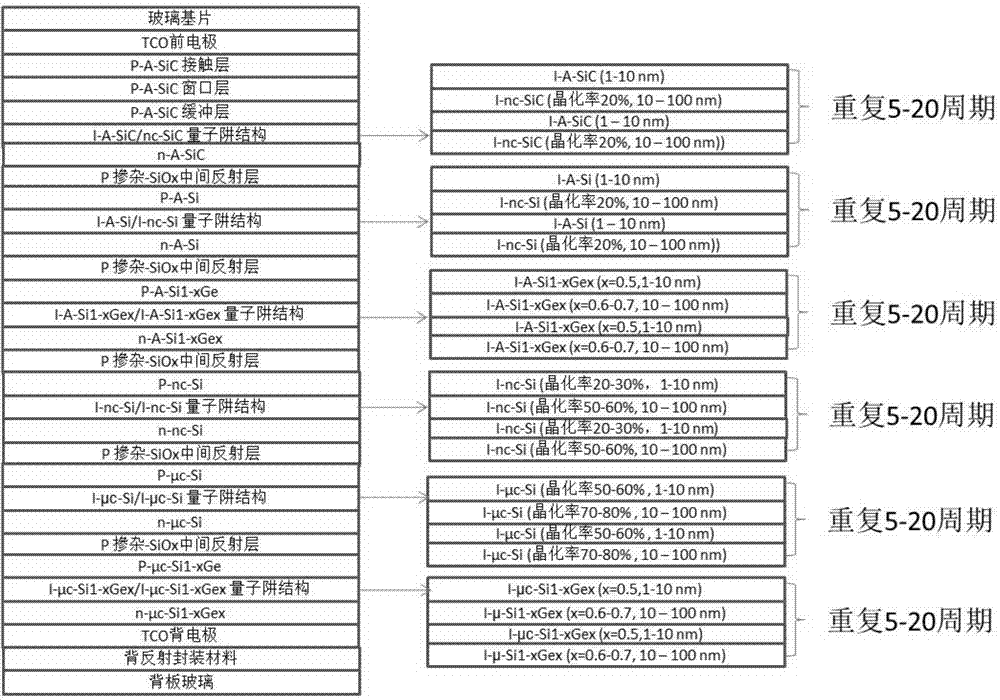
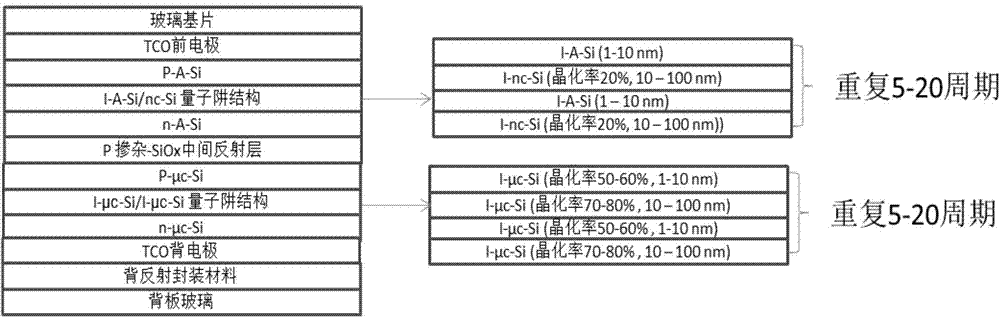
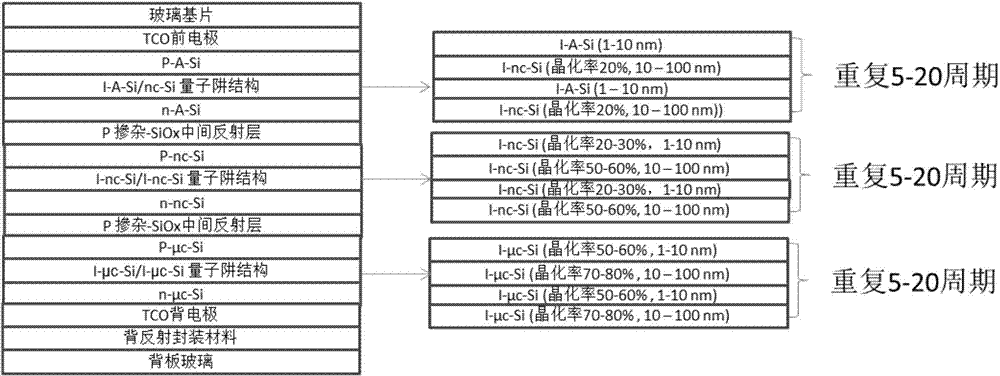
ActiveCN104733548AImprove efficiencyUniform sizeFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationAbnormal grain growthPower flow
The invention discloses a silicon-based thin film solar cell with quantum well structures and a manufacturing method thereof. In the multi-junction thin film solar cell, for an i layer of a pin structure of each junction, materials which are identical in crystal structure but different in energy gap are adopted for forming one quantum well structure. The quantum wells can separate and capture free electrons, large current is formed under the excitation of sunlight, and then the efficiency of the thin film solar cell is improved. The barrier heights of the quantum wells can be adjusted through the energy gaps of the matched materials, and the barrier widths of the quantum wells can be adjusted through the thicknesses of the matched materials. Meanwhile, the quantum well structure of the i layer of the pin structure of each junction avoids abnormal grain growth and hole or crack formation, high-quality thin films which are compact, uniform in grain size and matched in energy gap are manufactured, and the quantum well structures are beneficial for sufficient absorption of sunlight. Thus, the efficiency of the silicon-based thin film solar cell is further improved.
Owner:湖南共创光伏科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com