Sintering method of neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A sintering method, NdFeB technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inorganic materials, etc., can solve the problems affecting magnetic properties, grain growth, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform grain size and increased coercive force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
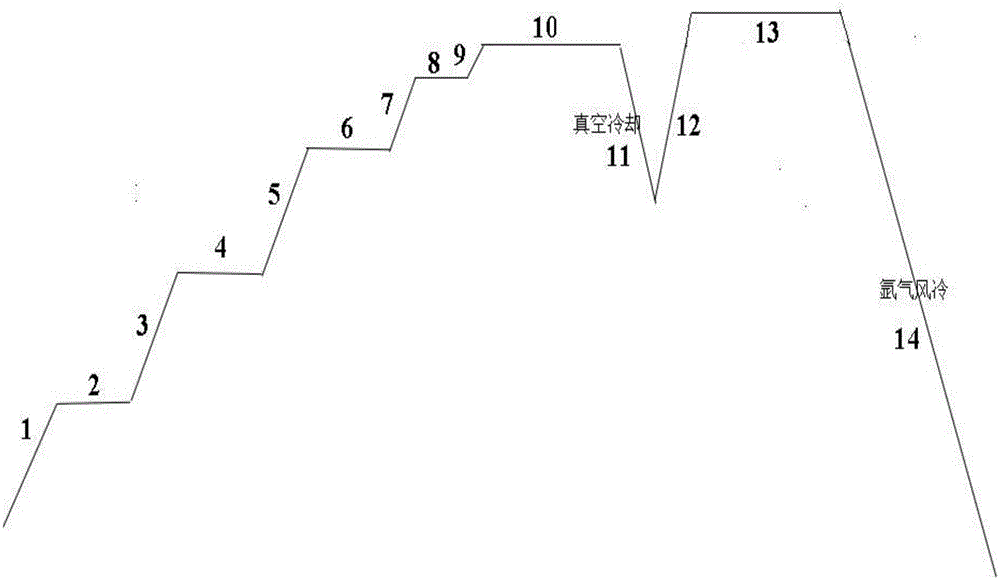
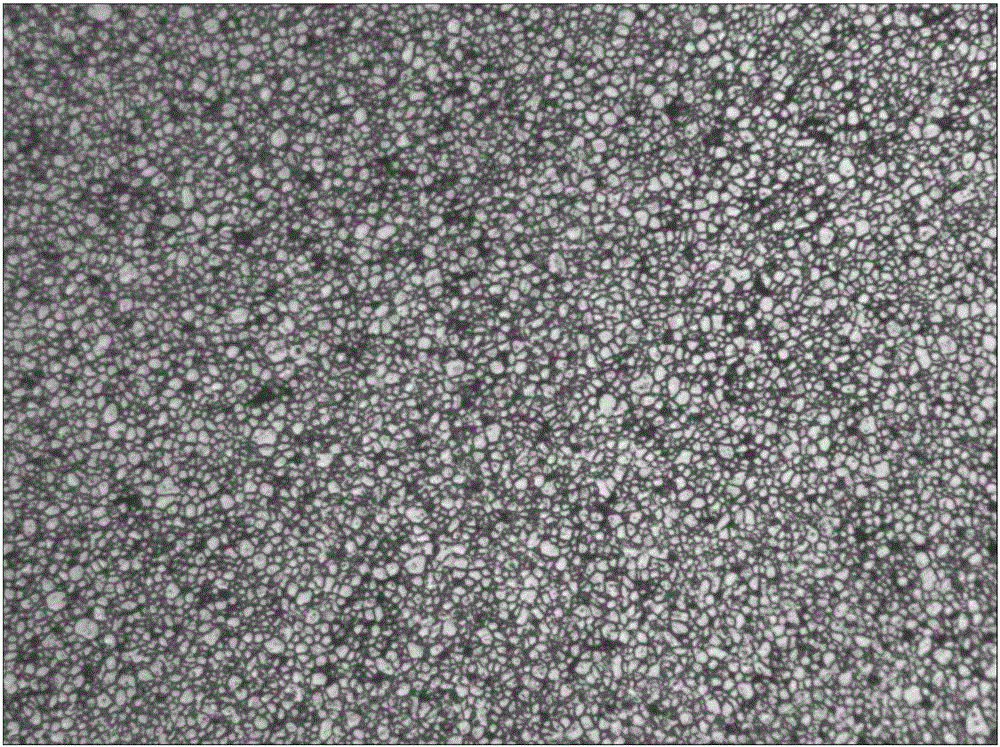
[0083] This embodiment adopts the design composition as (PrNd) 32.5 B 0.88 Al 0.66 Cu 0.15 co 1.2 Ga 0.5 Zr 0.2 Fe 其余 The formula is equipped with raw materials, using flake flakes, hydrogen explosion, and jet milling techniques, using a fully automatic sealed press to press, isostatic pressing, and then sintering according to the sintering method of the present invention, and then performing primary and secondary tempering to obtain the blank Test properties and microstructure metallography.
[0084] Firstly, raw materials are prepared according to the ratio of 32.5% NdPr, 0.88% Boron, 0.66% Aluminum, 0.15% Copper, 1.2% Cobalt, 0.5% Gallium, 0.2% Zirconium, and the rest iron.
[0085] Then, the raw materials are smelted by using the strip-spinning process, and the strips are prepared into strips, and the thickness of the strips is controlled between 0.25-0.3mm.
[0086] Then use the hydrogen explosion + jet mill process to grind the flakes into fine powder, and the pa...
Embodiment 2
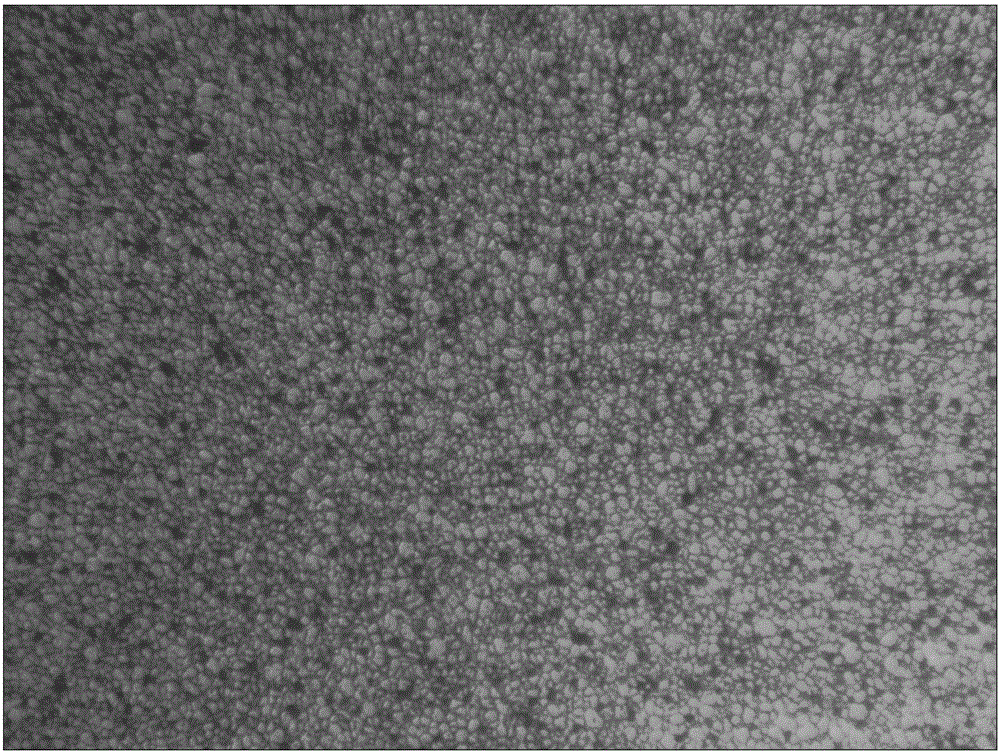
[0097] This embodiment adopts the design composition as (PrNd) 32.5 B 0.88 Al 0.66 Cu 0.15 co 1.2 Ga 0.5 Zr 0.2 Fe 其余 The formula is equipped with raw materials, using flake flakes, hydrogen explosion, and jet milling techniques, using a fully automatic sealed press to press, isostatic pressing, and then sintering according to the sintering method of the present invention, and then performing primary and secondary tempering to obtain the blank Test properties and microstructure metallography.
[0098] Firstly, raw materials are prepared according to the ratio of 32.5% NdPr, 0.88% Boron, 0.66% Aluminum, 0.15% Copper, 1.2% Cobalt, 0.5% Gallium, 0.2% Zirconium, and the rest iron.
[0099] Then, the raw materials are smelted by using the strip-spinning process, and the strips are prepared into strips, and the thickness of the strips is controlled between 0.25-0.3mm.
[0100] Then use the hydrogen explosion + jet mill process to grind the flakes into fine powder, and the pa...
Embodiment 3
[0110] This embodiment adopts the design composition as (PrNd) 30.6 Dy 1.2 B 0.88 Al 0.5 Cu 0.15 co 1.2 Ga 0.32 Zr 0.17 Fe 其余 The formula is equipped with raw materials, using flake flakes, hydrogen explosion, and jet milling techniques, using a fully automatic sealed press to press, isostatic pressing, and then sintering according to the sintering method of the present invention, and then performing primary and secondary tempering to obtain the blank Test properties and microstructure metallography.
[0111] Firstly, the raw materials are prepared according to the ratio of 30.6% NdPr, 1.2% Dysprosium, 0.88% Boron, 0.5% Aluminum, 0.15% Copper, 1.2% Cobalt, 0.32% Gallium, 0.17% Zirconium, and the rest iron.
[0112] Then, the raw materials are smelted by using the strip-spinning process, and the strips are prepared into strips, and the thickness of the strips is controlled between 0.25-0.3mm.
[0113] Then use the hydrogen explosion + jet mill process to grind the flak...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com