Methods to increase the capacity of high content cell-based screening assays
a cell-based screening and high-content technology, applied in the field of drug discovery, cell biology, molecular biology, can solve the problems of consuming hundreds of millions of dollars per drug created, significantly affecting the capacity requirements of such high-content cell-based screening assays, and slow and costly process of drug discovery, so as to increase the capacity to provide high-content information, maintain the “hit” rate, and reduce the cost and time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
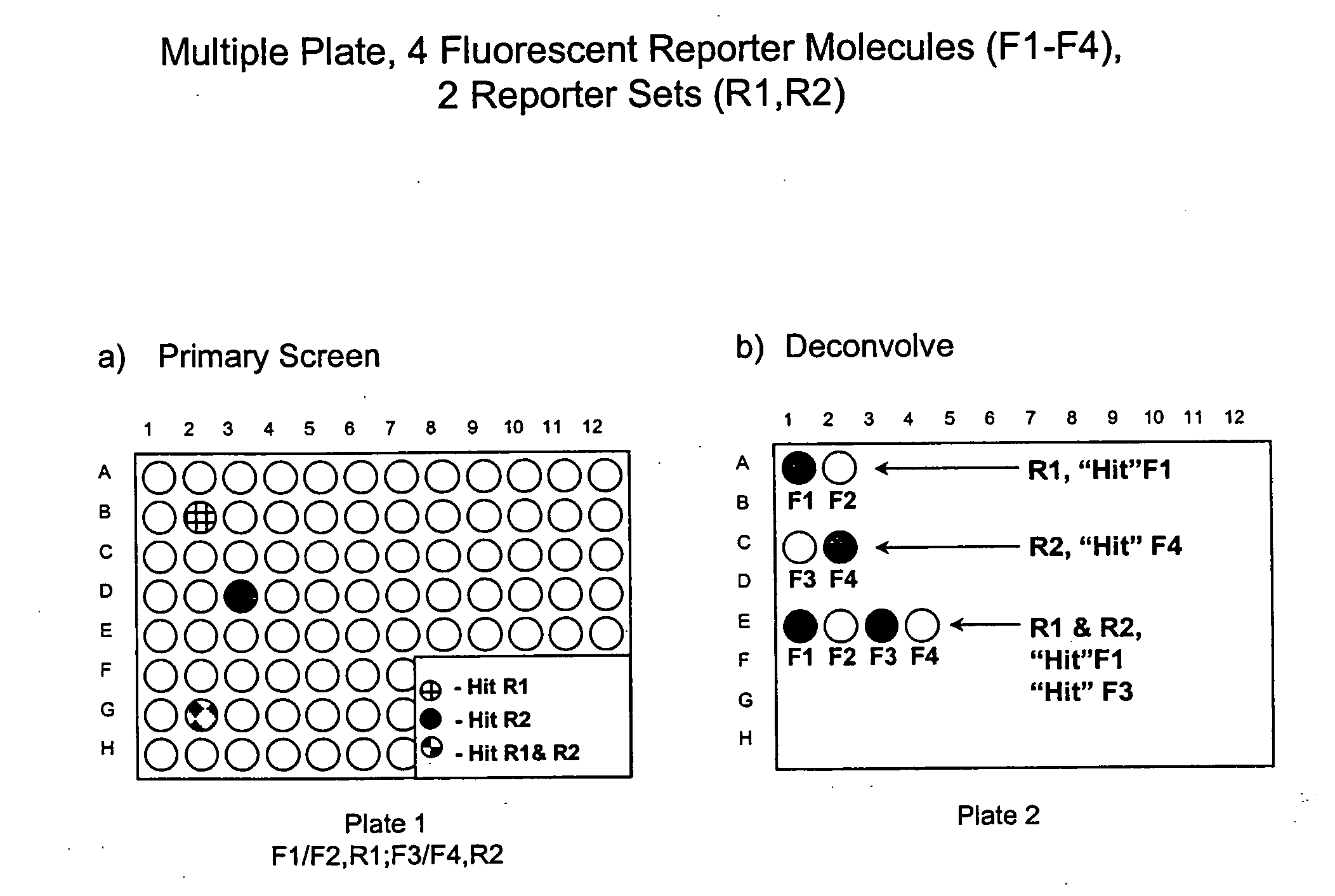
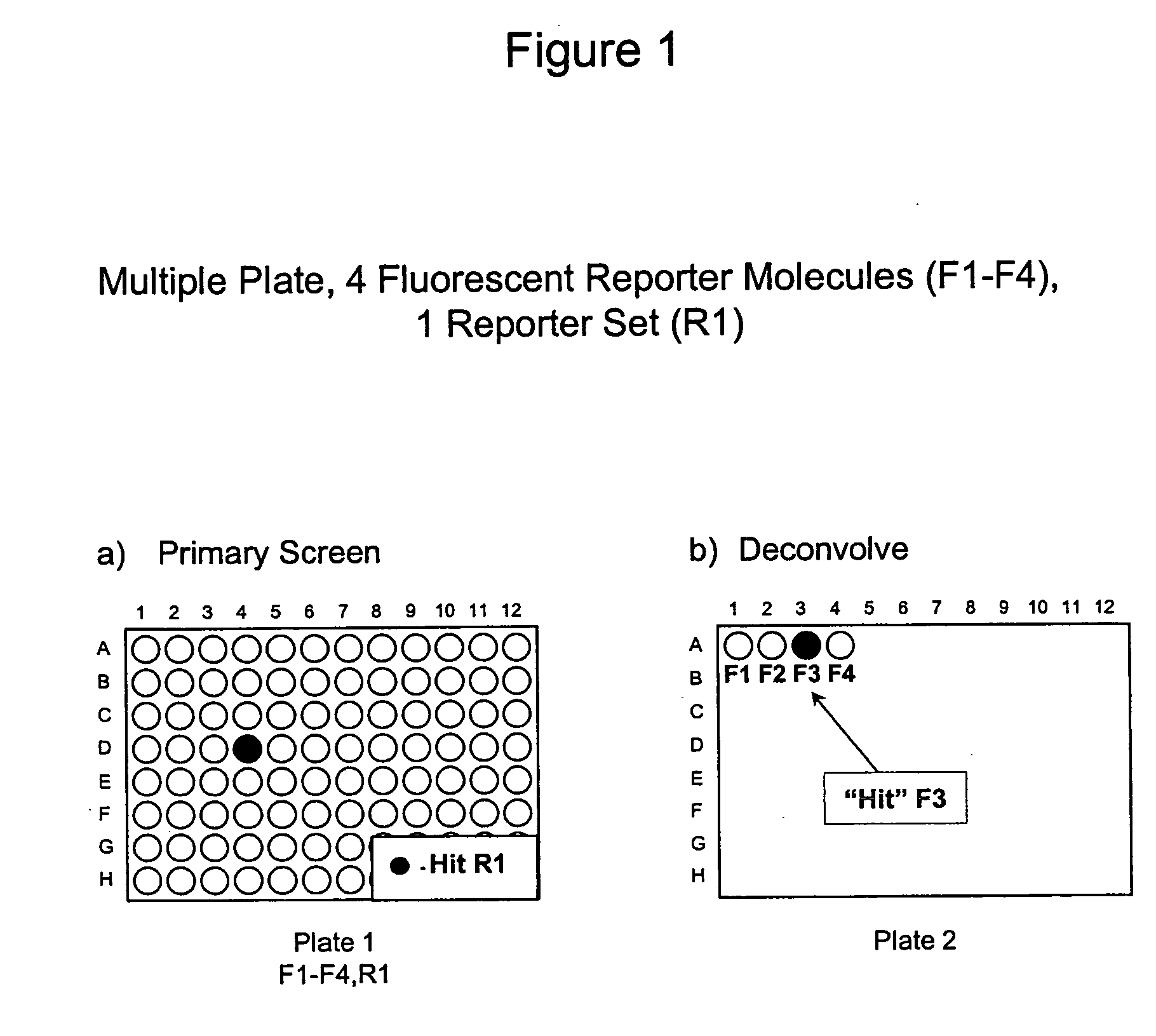
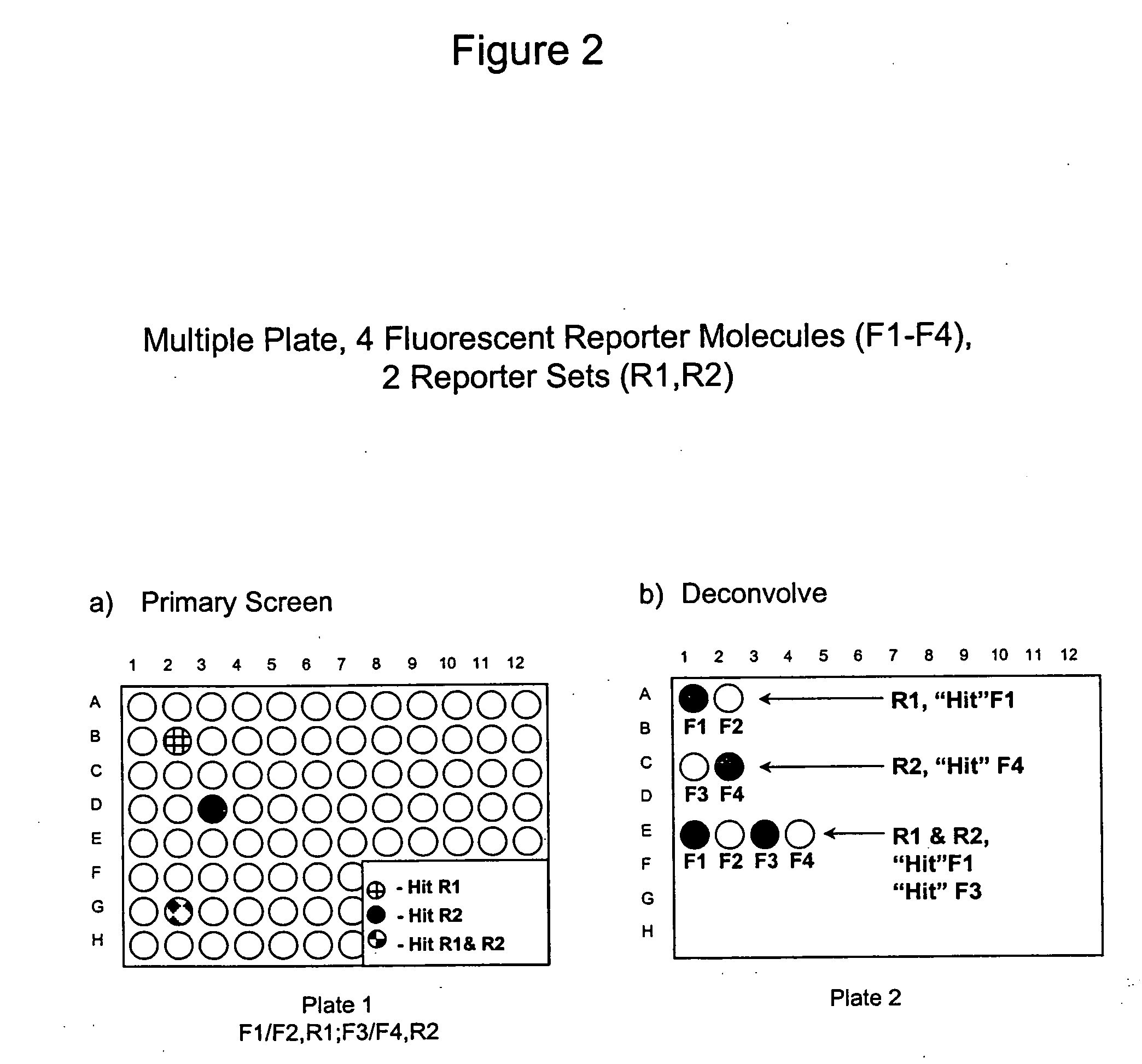
1. Reporter Sets and Relevant Image Analysis Methods
[0135] Non-limiting examples of reporter set types, and cellular events reported on by them: [0136] a. Multiple transcription factor translocations to a common cell compartment, such as from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, using transcription factor-fluorescent protein chimeras, antibodies, or combinations thereof. Fluorescent signals from this reporter set are measured using any method for measuring translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, such as those disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,989,835, WO 98 / 38490, and WO 00 / 17643, and those described below. [0137] b. Multiple receptor internalizations from the cell surface to the cell interior using receptor-fluorescent protein chimeras, fluorescent ligands for the receptors, antibody tags, or any combination thereof. Fluorescent signals from this reporter set would be measured using any method for measuring translocation from the cell surface to the inside of the cell, such as those ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| processing time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com