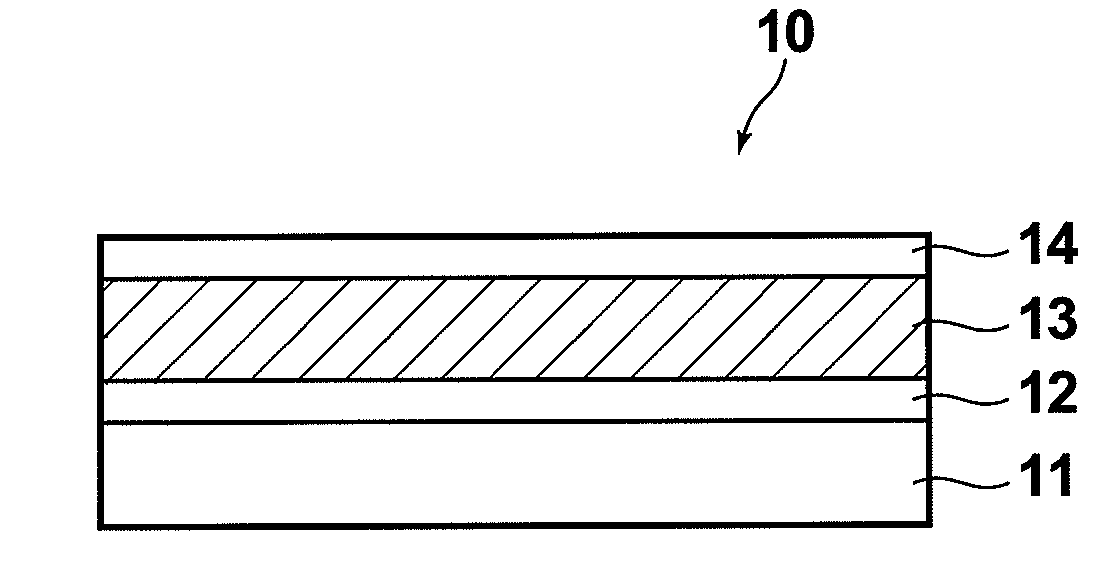
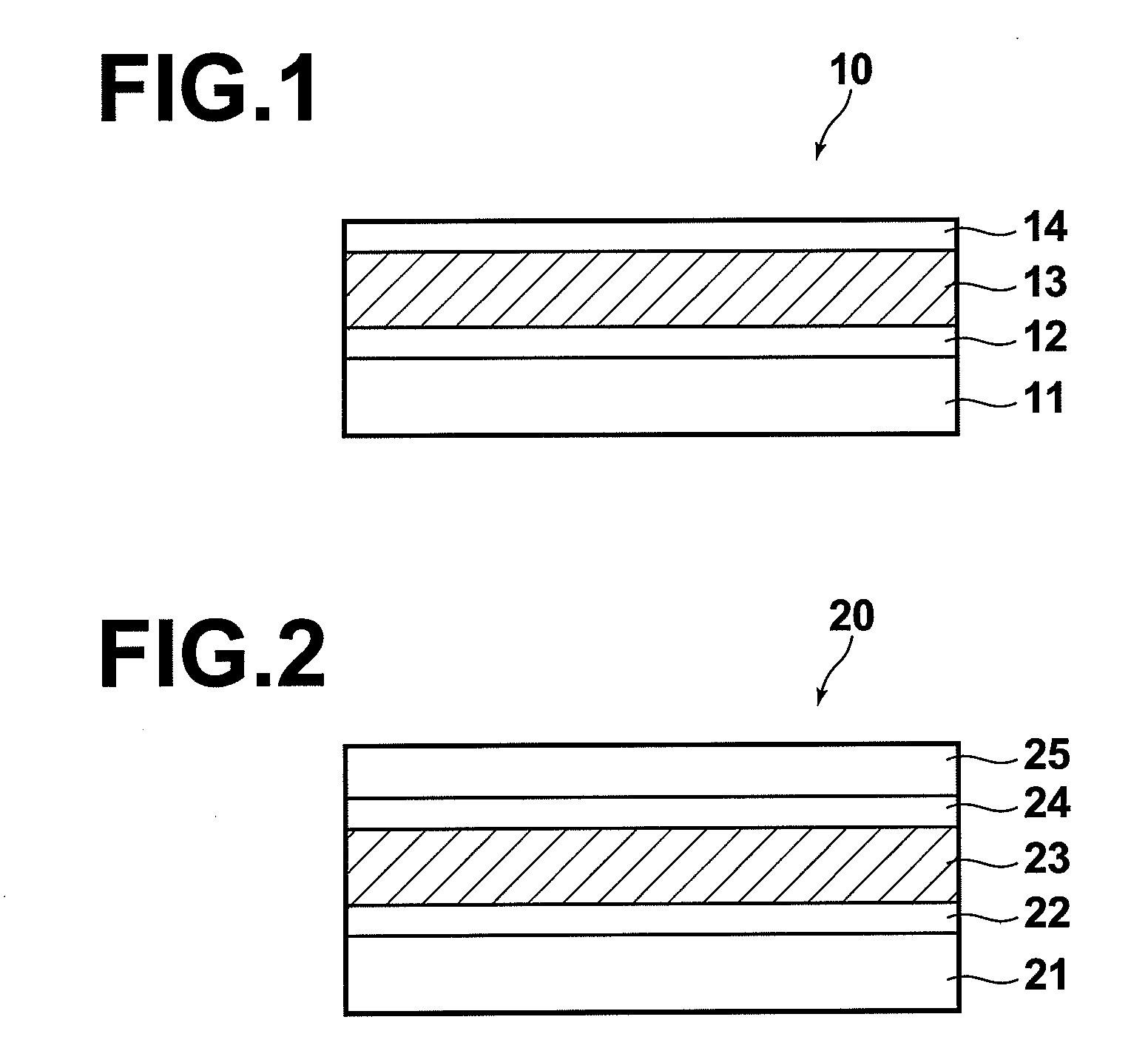
Patents
Literature
60 results about "Amorphous selenium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
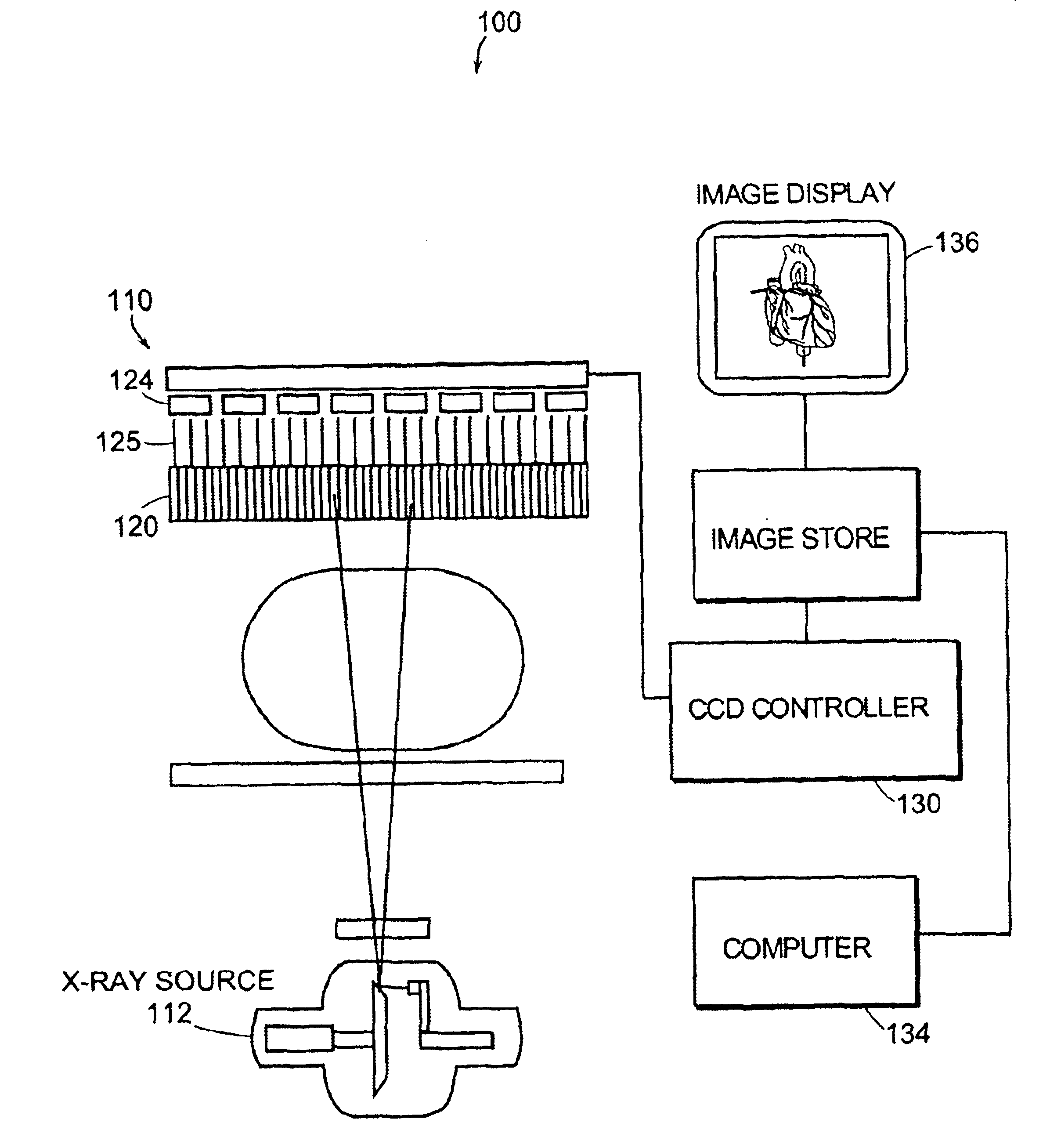
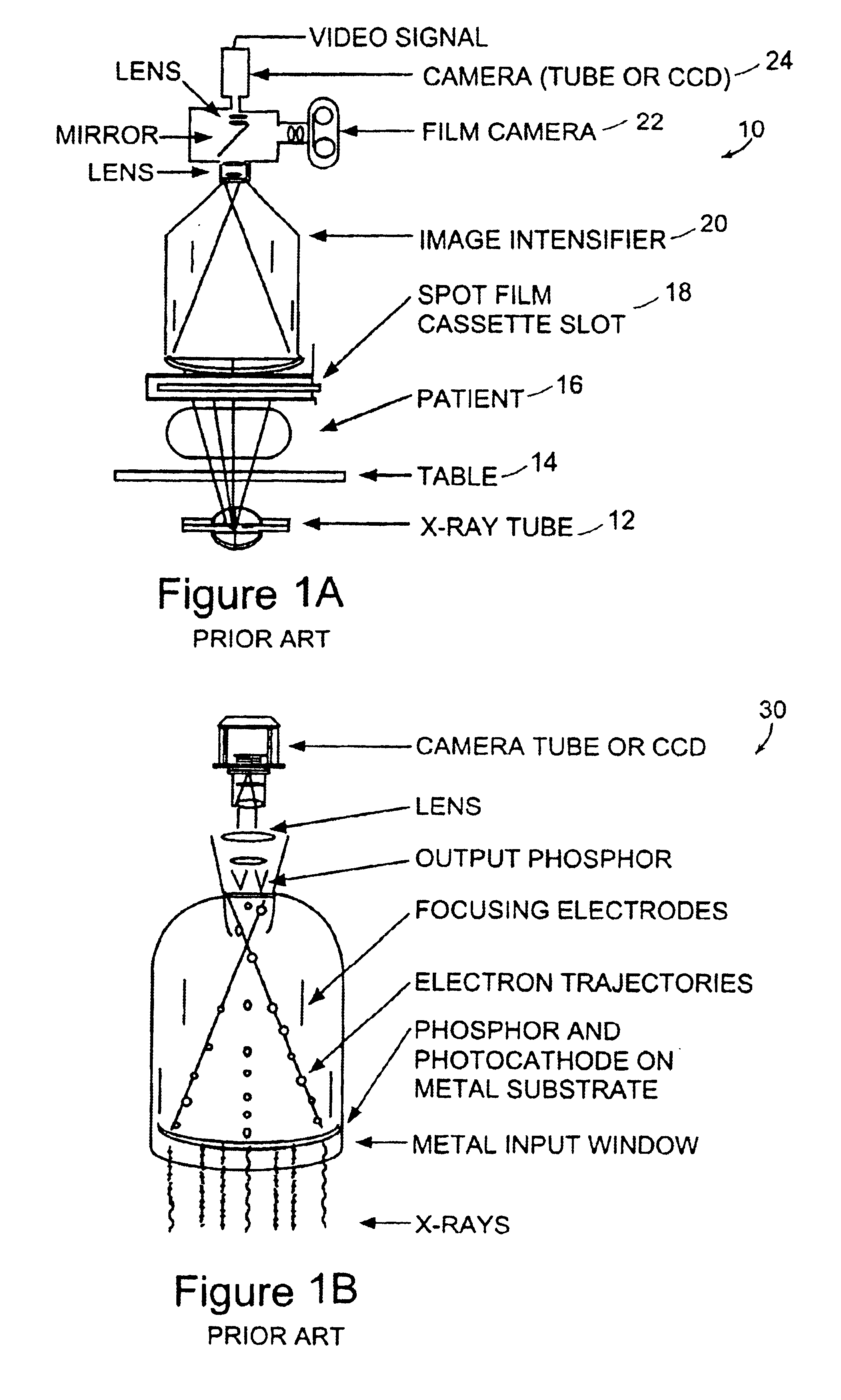
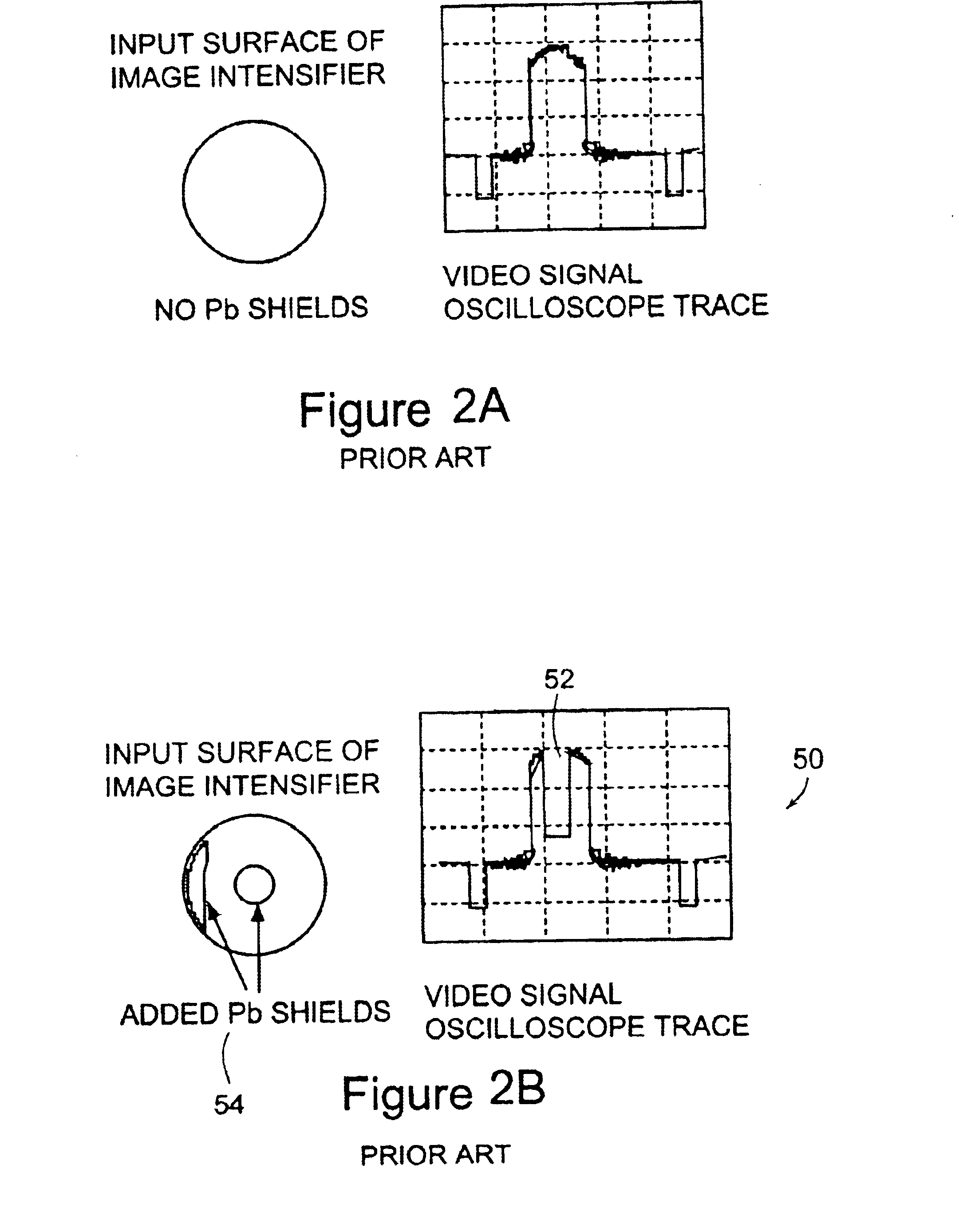
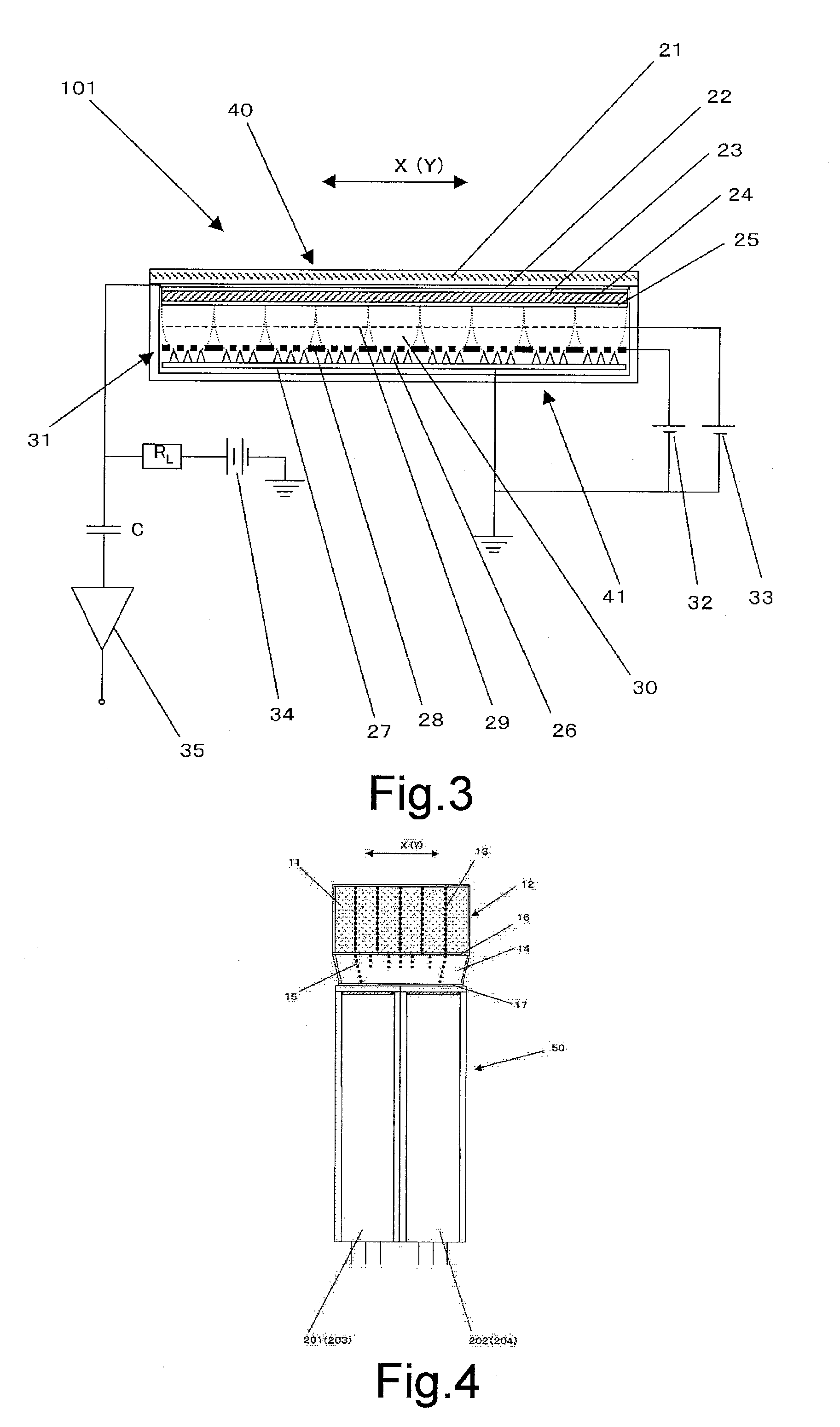
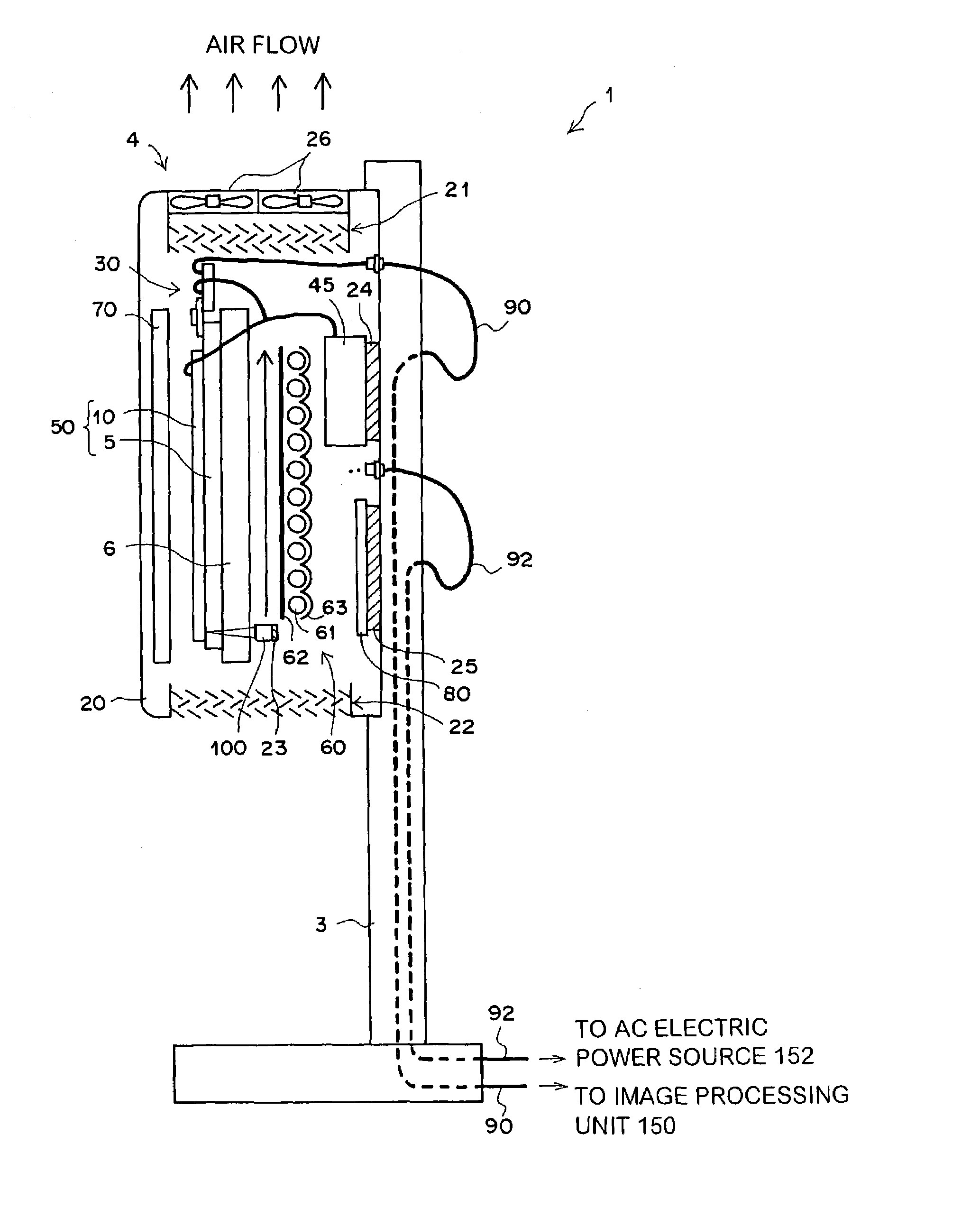
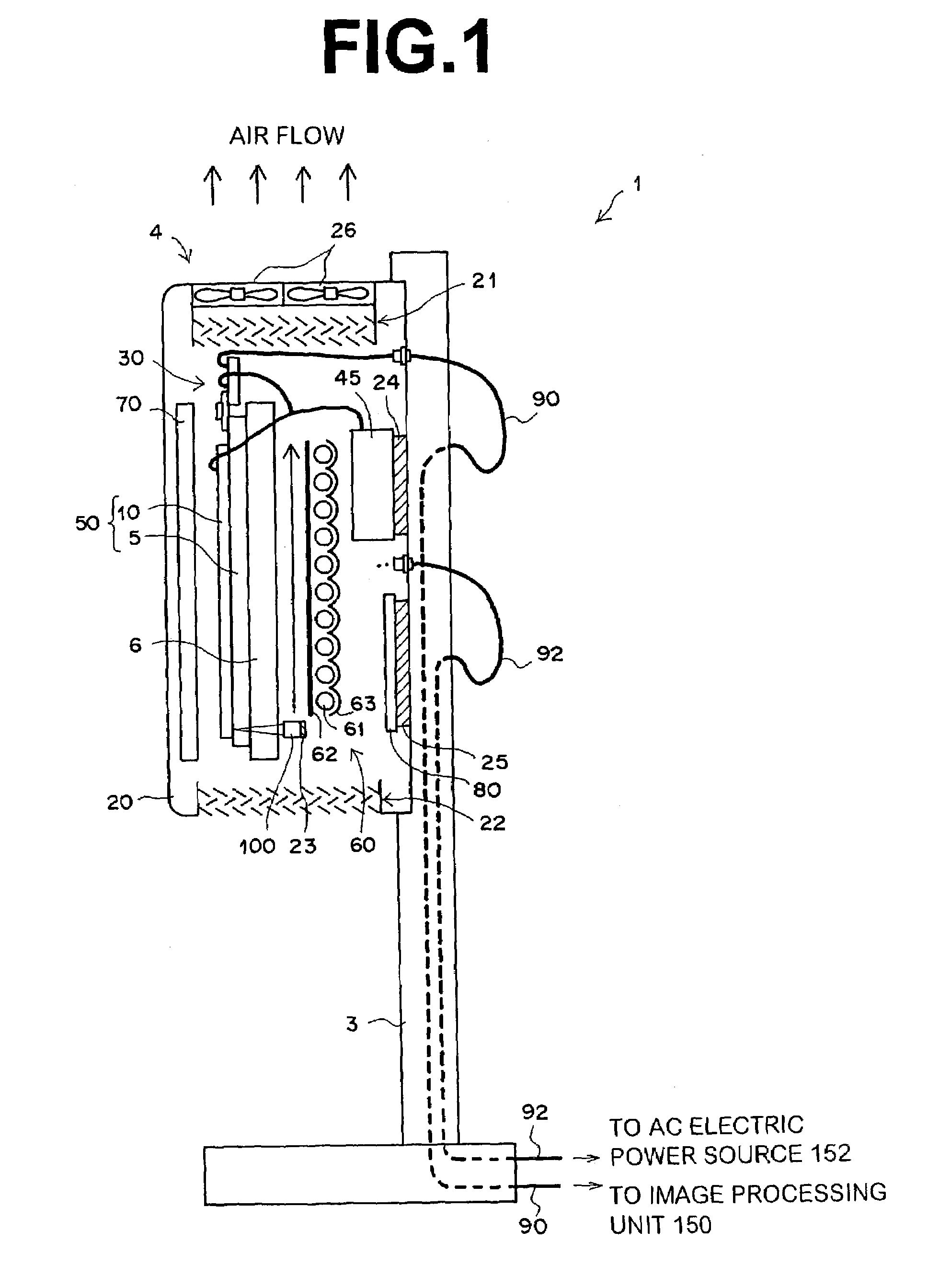
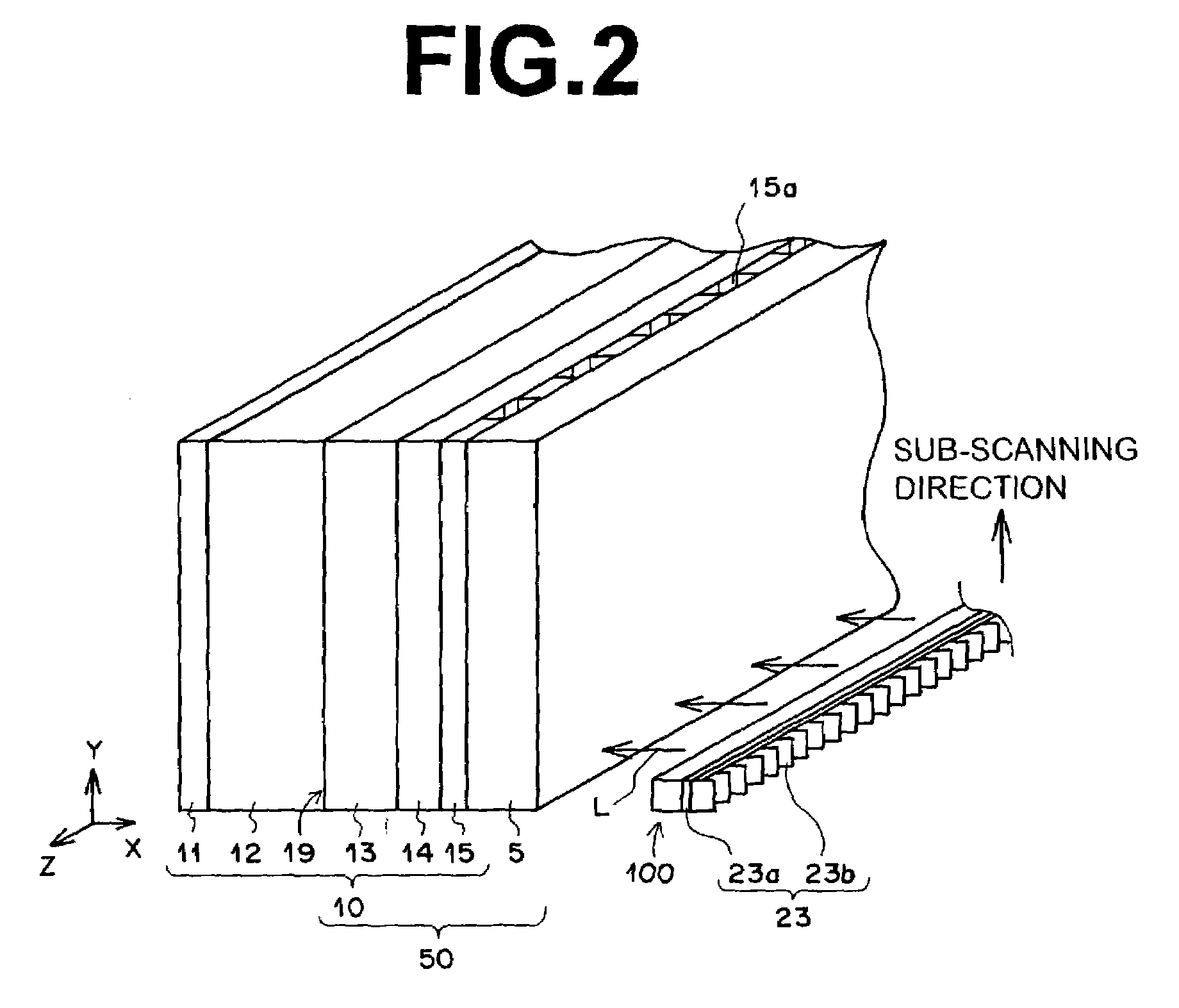
System and method for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging
InactiveUS6895077B2Increase frame rateAccurate imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesFluorescenceX-ray
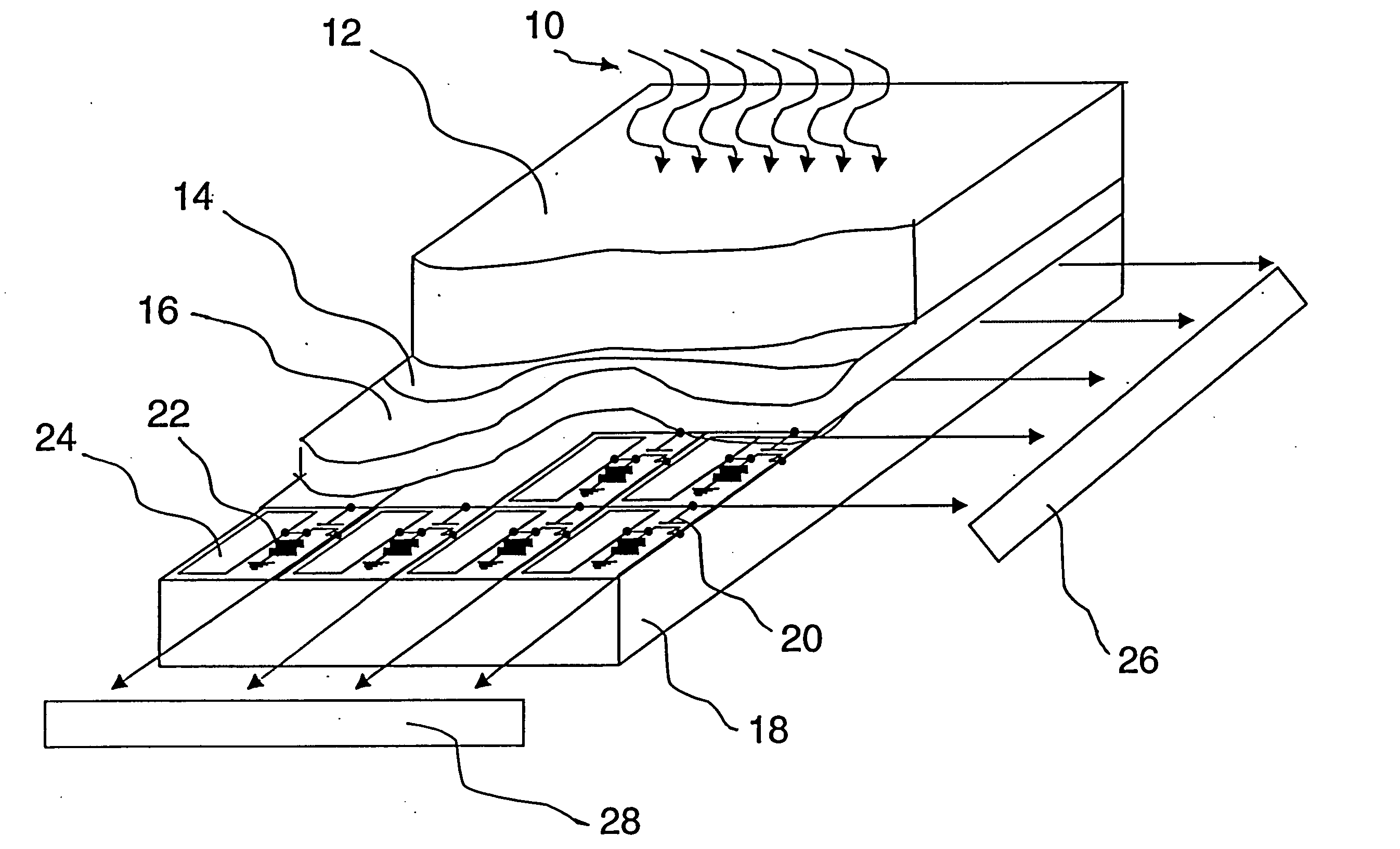
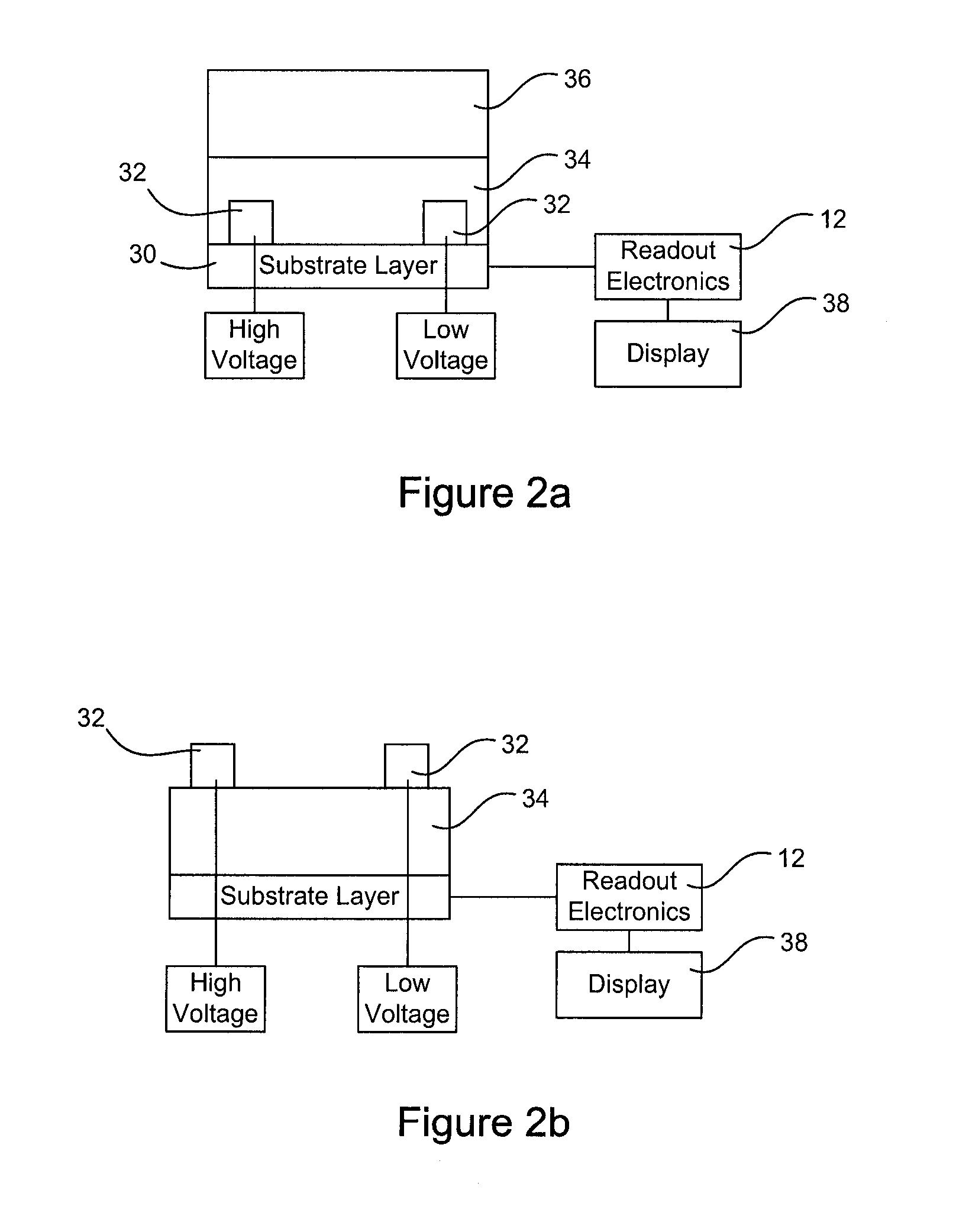
A system for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charge coupled device (CCD) is used to accurately image selected tissue. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen re-radiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by the CCD sensor. In a preferred embodiment the imager uses four 8×8-cm three-side buttable CCDs coupled to a CsI:T1 scintillator by straight (non-tapering) fiberoptics and tiled to achieve a field of view (FOV) of 16×16-cm at the image plane. Larger FOVs can be achieved by tiling more CCDs in a similar manner. The imaging system can be operated in a plurality of pixel pitch modes such as 78, 156 or 234-μm pixel pitch modes. The CCD sensor may also provide multi-resolution imaging. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. Other preferred embodiments may include each image being directed on flat panel imagers made from but not limited to, amorphous silicon and / or amorphous selenium to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images used for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
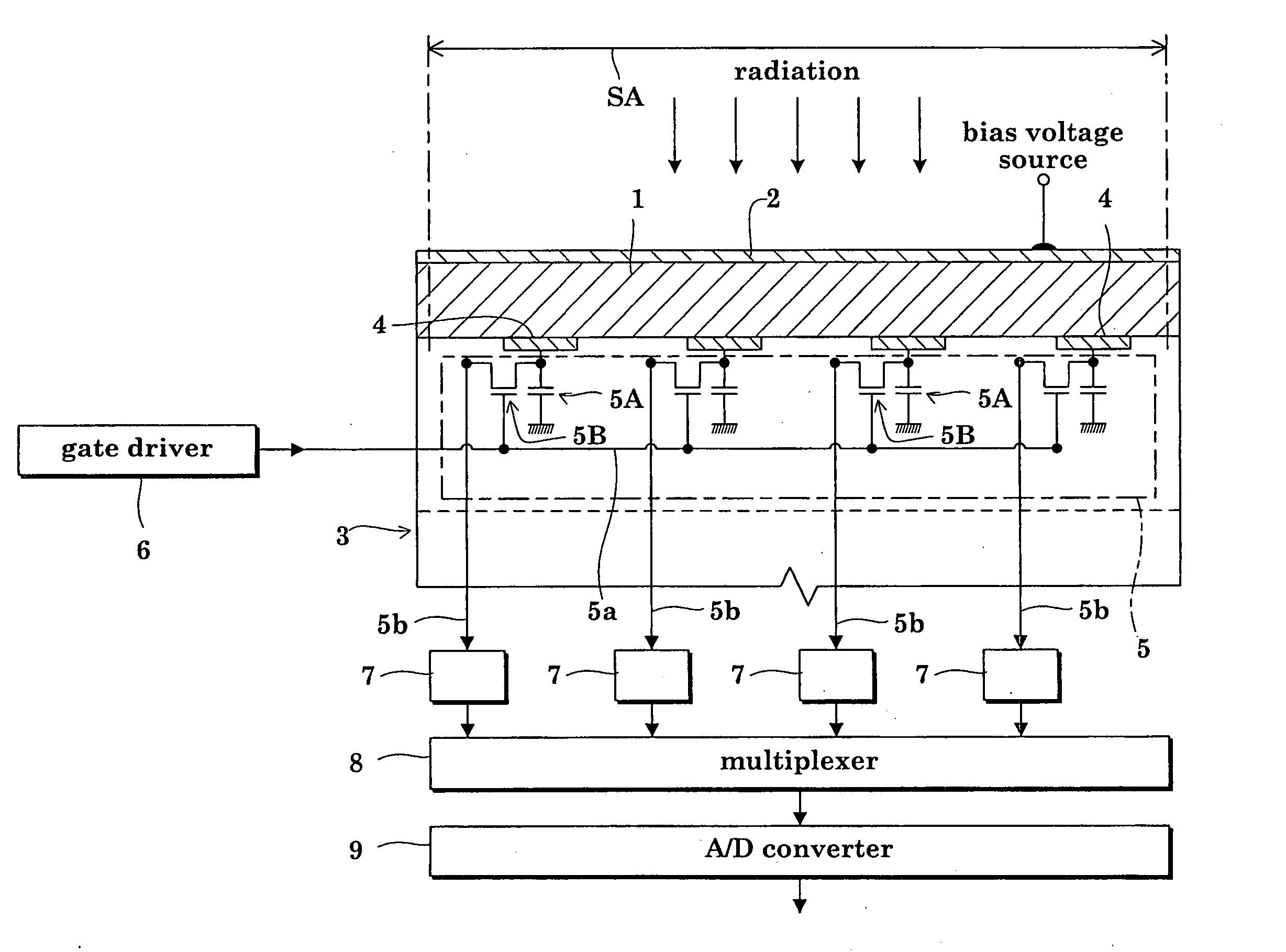
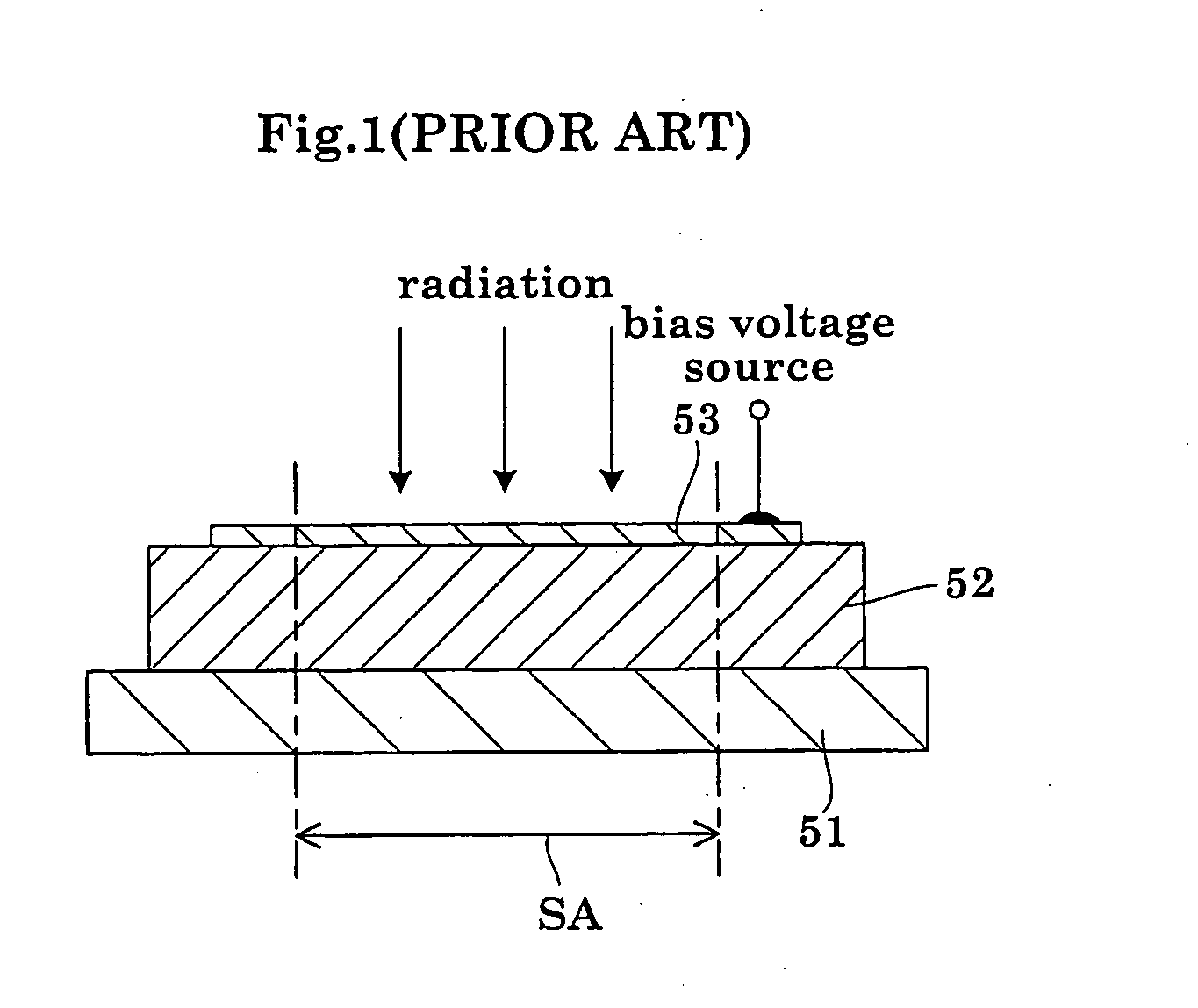
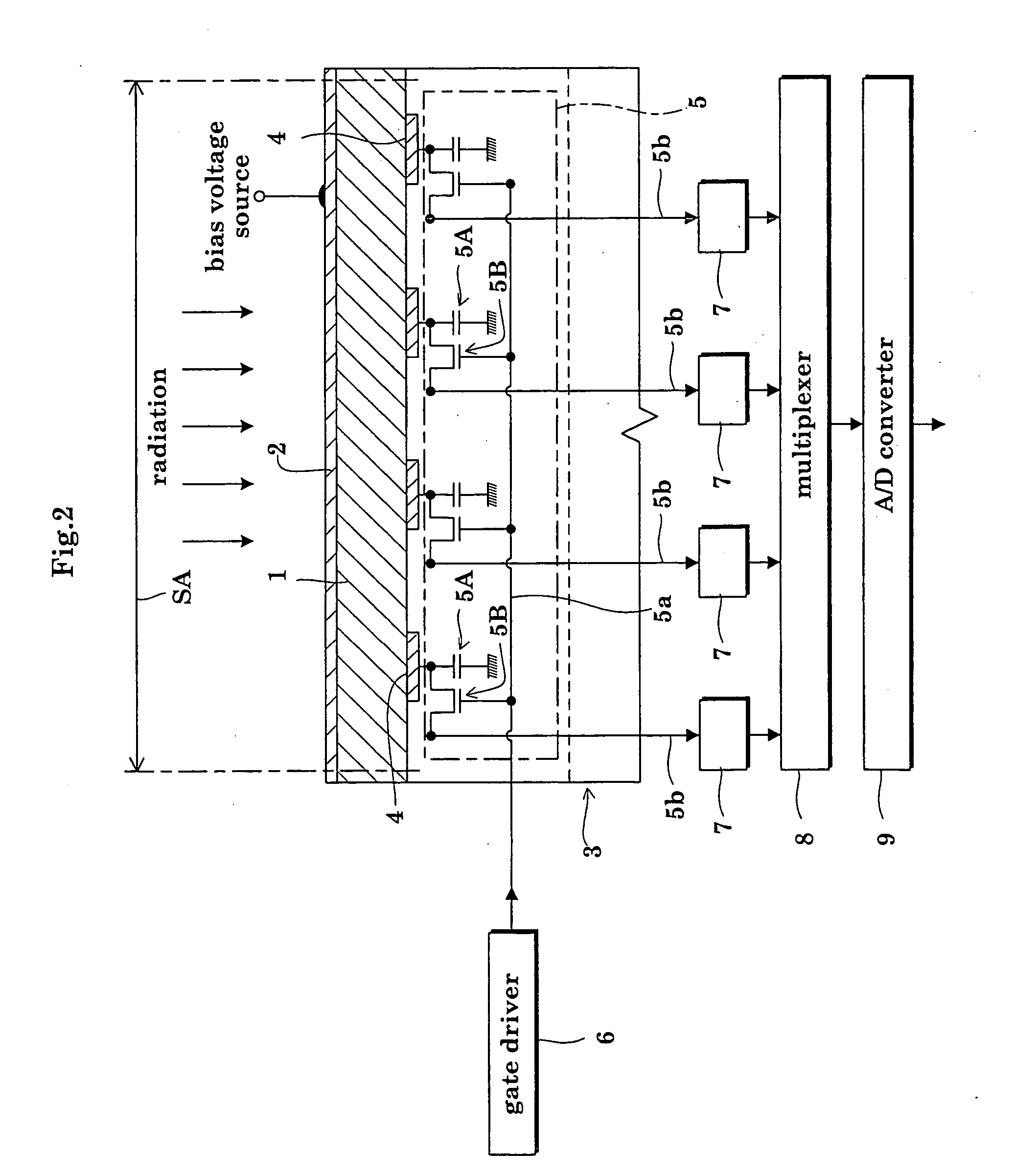
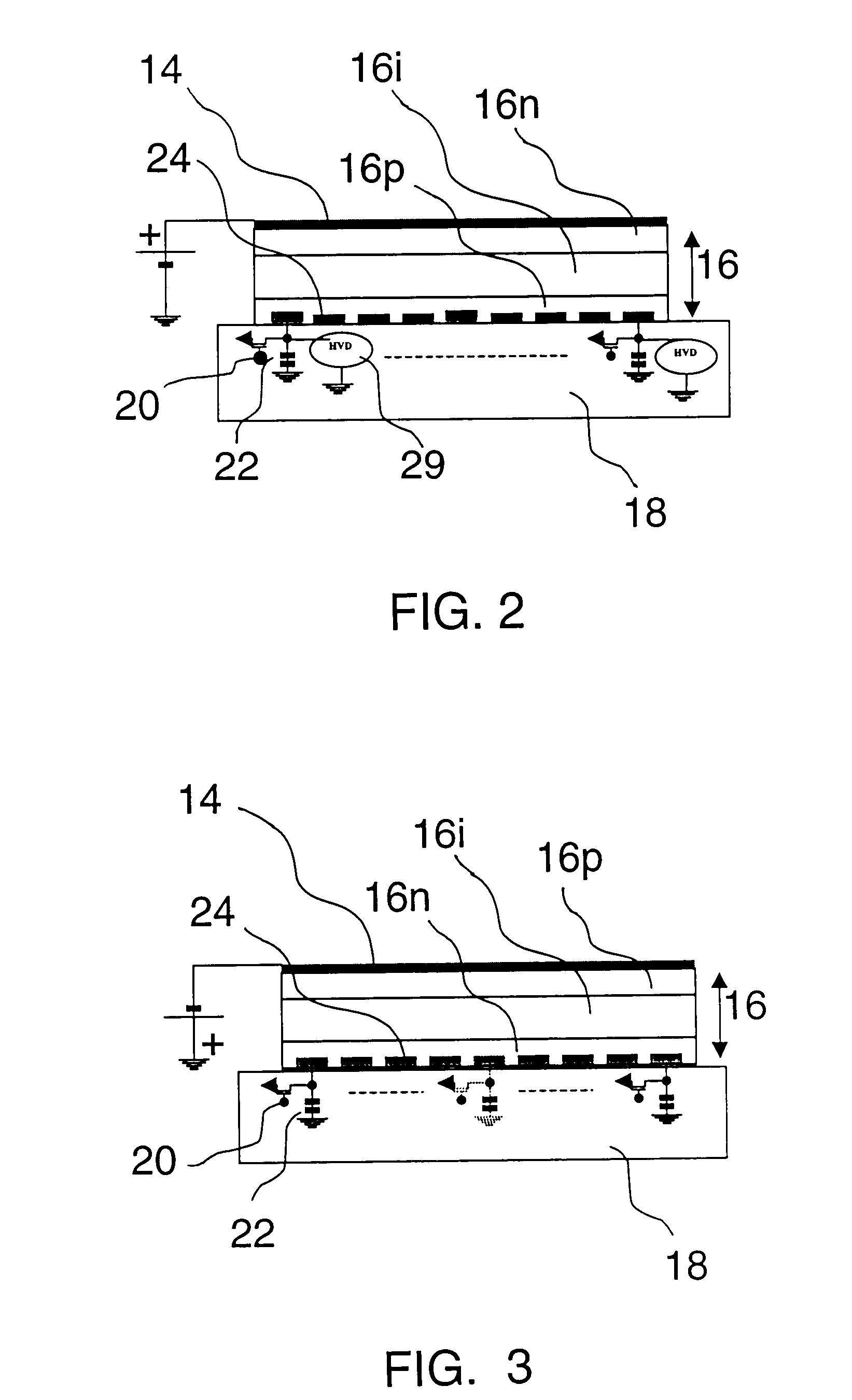
Radiation detector
InactiveUS20050061987A1Improve adhesionSuppress generationPhotometrySolid-state devicesDeposition temperatureAmorphous selenium
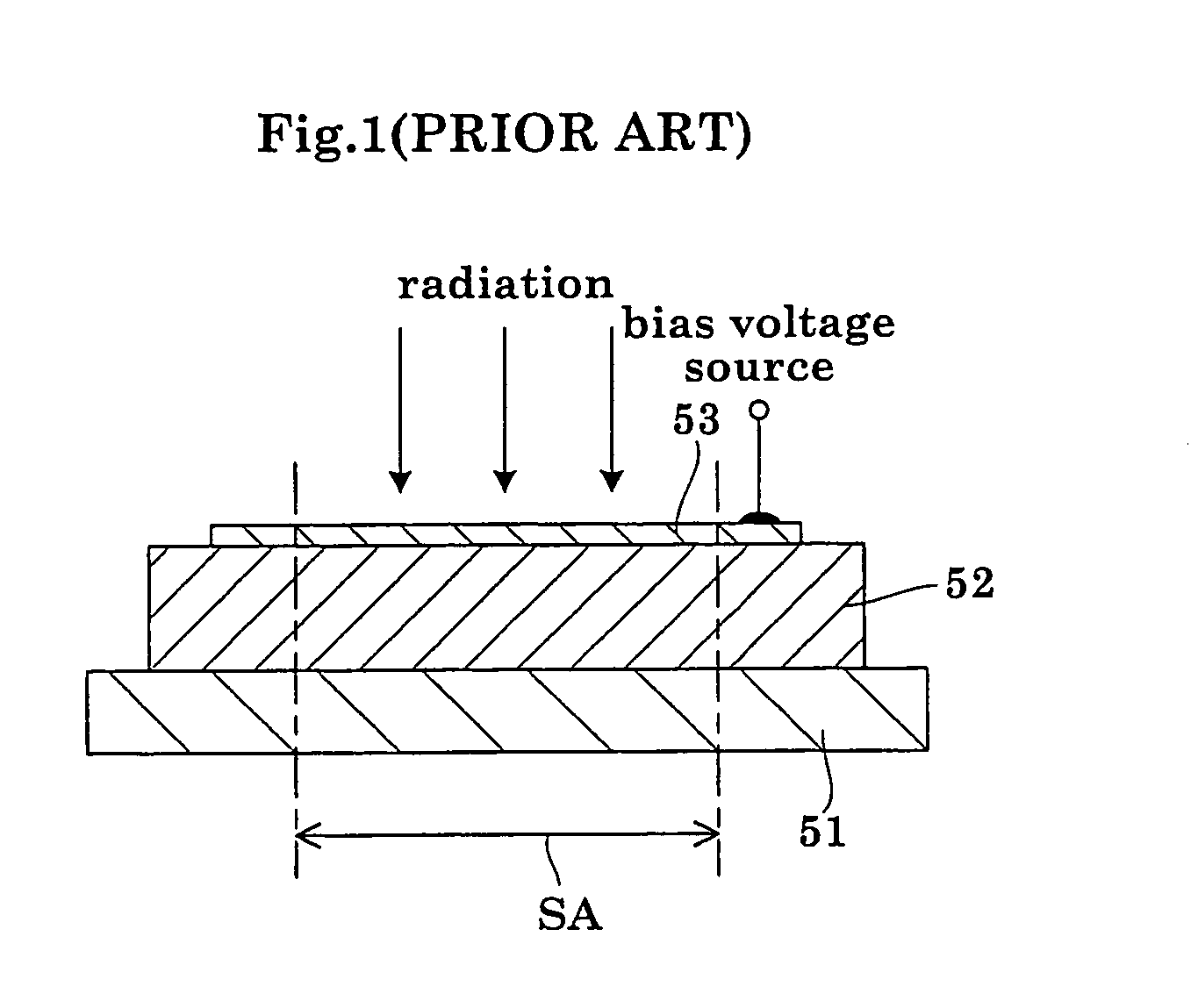
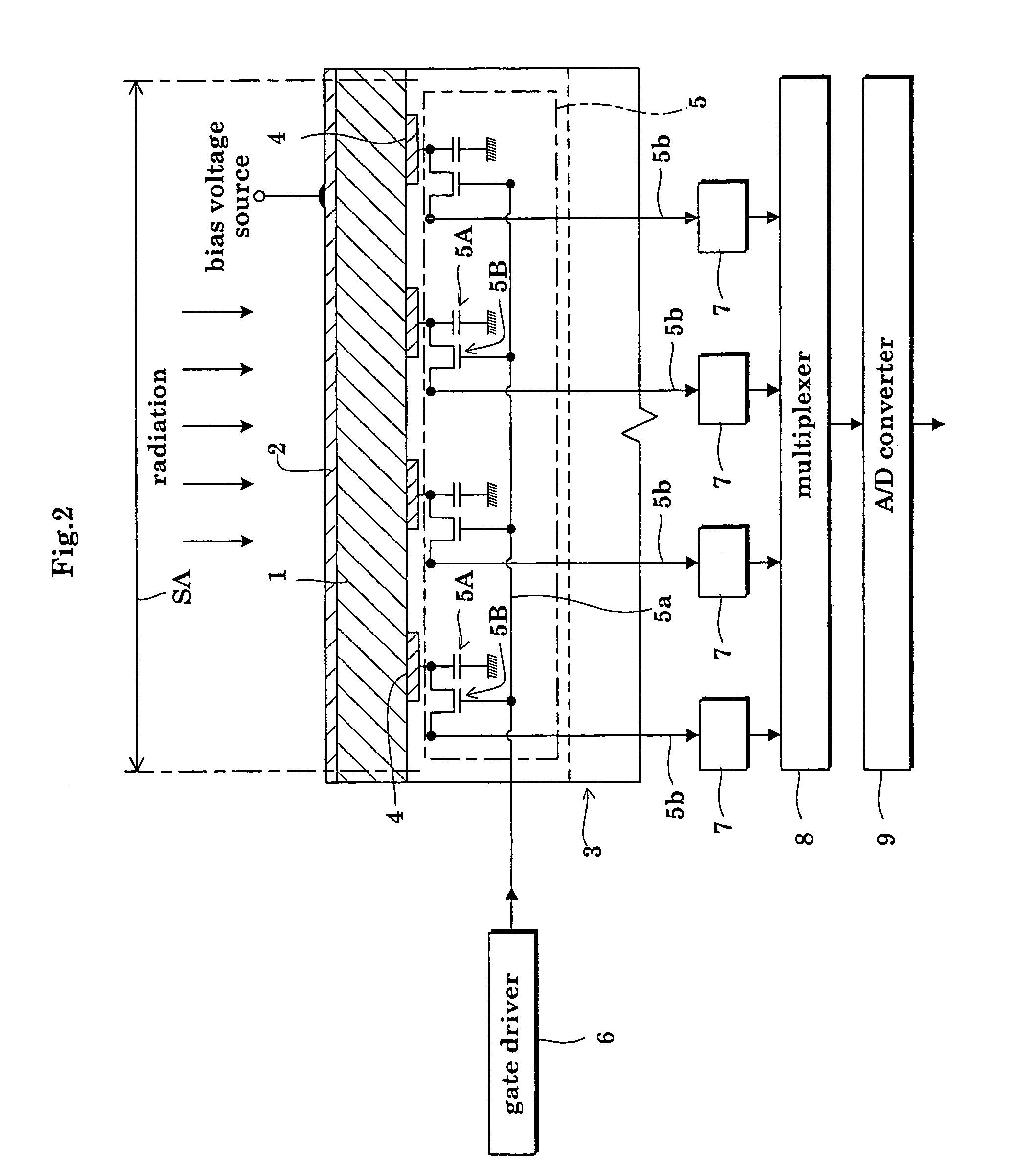
The radiation detector according to this invention has a common electrode for bias voltage application formed on a surface of an amorphous selenium semiconductor film (a-Se semiconductor film) sensitive to radiation. The common electrode is a gold thin film having a thickness in a range of 100 to 1,000 Å. The gold thin film acting as the common electrode may be formed on the surface of the a-Se semiconductor film at a relatively low vapor deposition temperature and in a reduced vapor deposition time. This feature suppresses a generation of defects in the a-Se semiconductor film due to formation of the common electrode. The gold thin film for the common electrode is not so thick as in the prior art, but is 1,000 Å or less. With the reduced thickness, the common electrode has improved boding property with respect to the a-Se semiconductor film.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
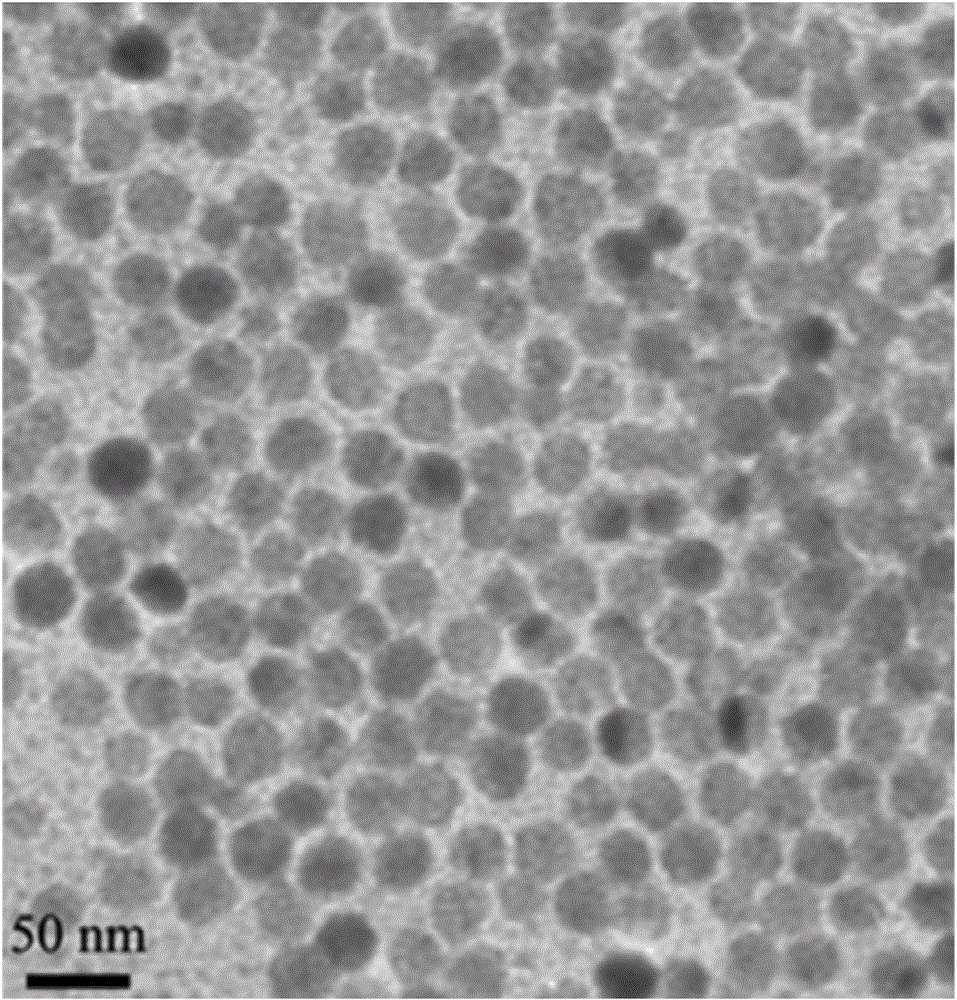
Selenium nano-particles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106219501AImprove stabilityImprove bioavailabilityMaterial nanotechnologySulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsCelluloseAmorphous selenium
The invention relates to selenium nano-particles and a preparation method thereof, in particular to amorphous selenium nano-particles with the grain diameter being 1-300 nm and a preparation method of the selenium nano-particles. The preparation method of the selenium nano-particles includes the steps that selenium combined macromolecules, a selenium source and a reducing agent or an oxidizing agent are subjected to a mixed reaction in a water phase medium, and nano-particles with the grain diameter being 1-300 nm are prepared; the selenium combined macromolecules are selected from water-soluble protein, water-soluble cellulose and water-soluble pectin and a combination of water-soluble protein, water-soluble cellulose and water-soluble pectin. According to the technical scheme, the nano selenium particles can be well stabilized, the nano selenium particles are not easily gathered into micron fine particles or larger selenium particles, and it is guaranteed that the nano selenium particles have good bioavailability and a good biological effect.
Owner:温彩珑
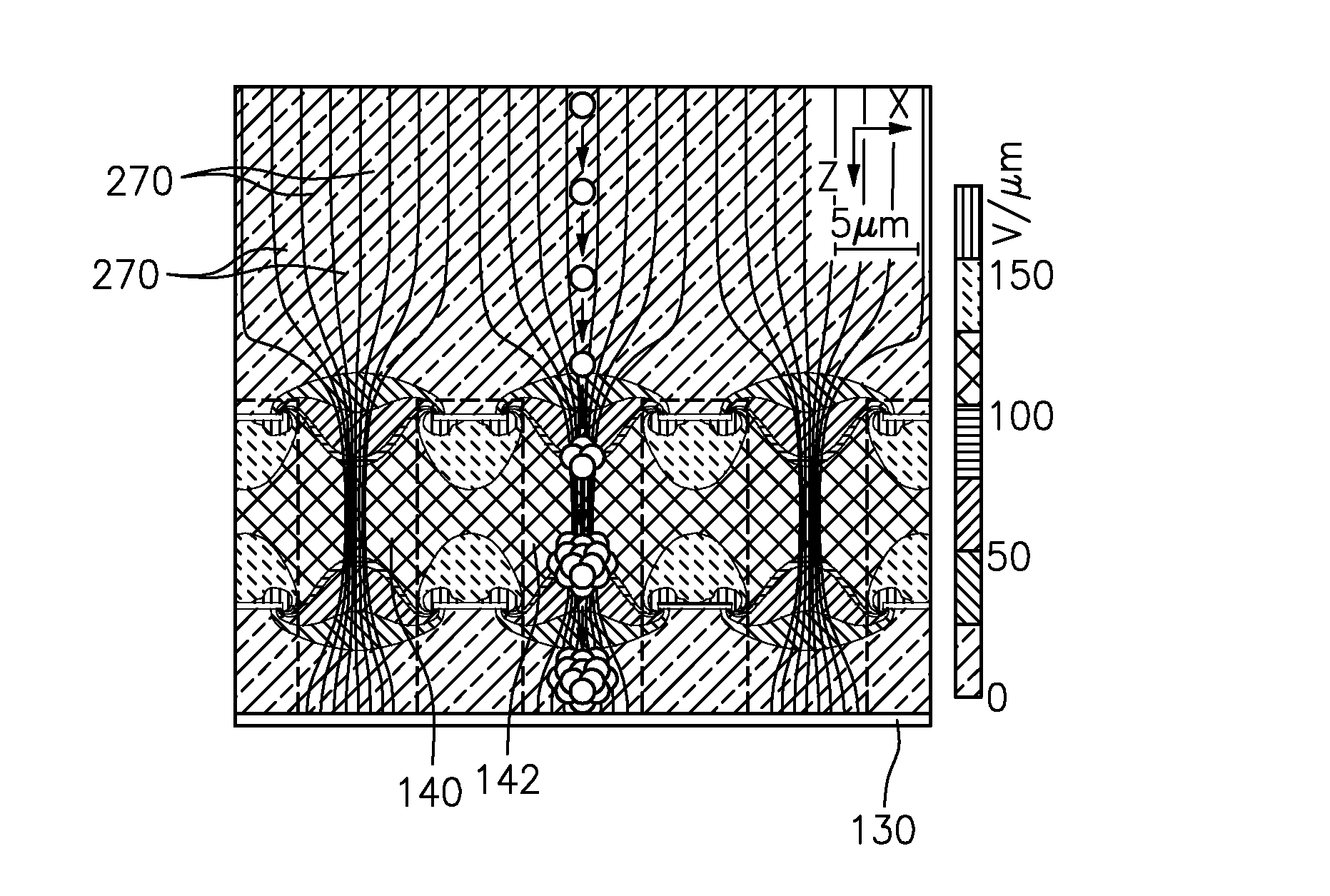
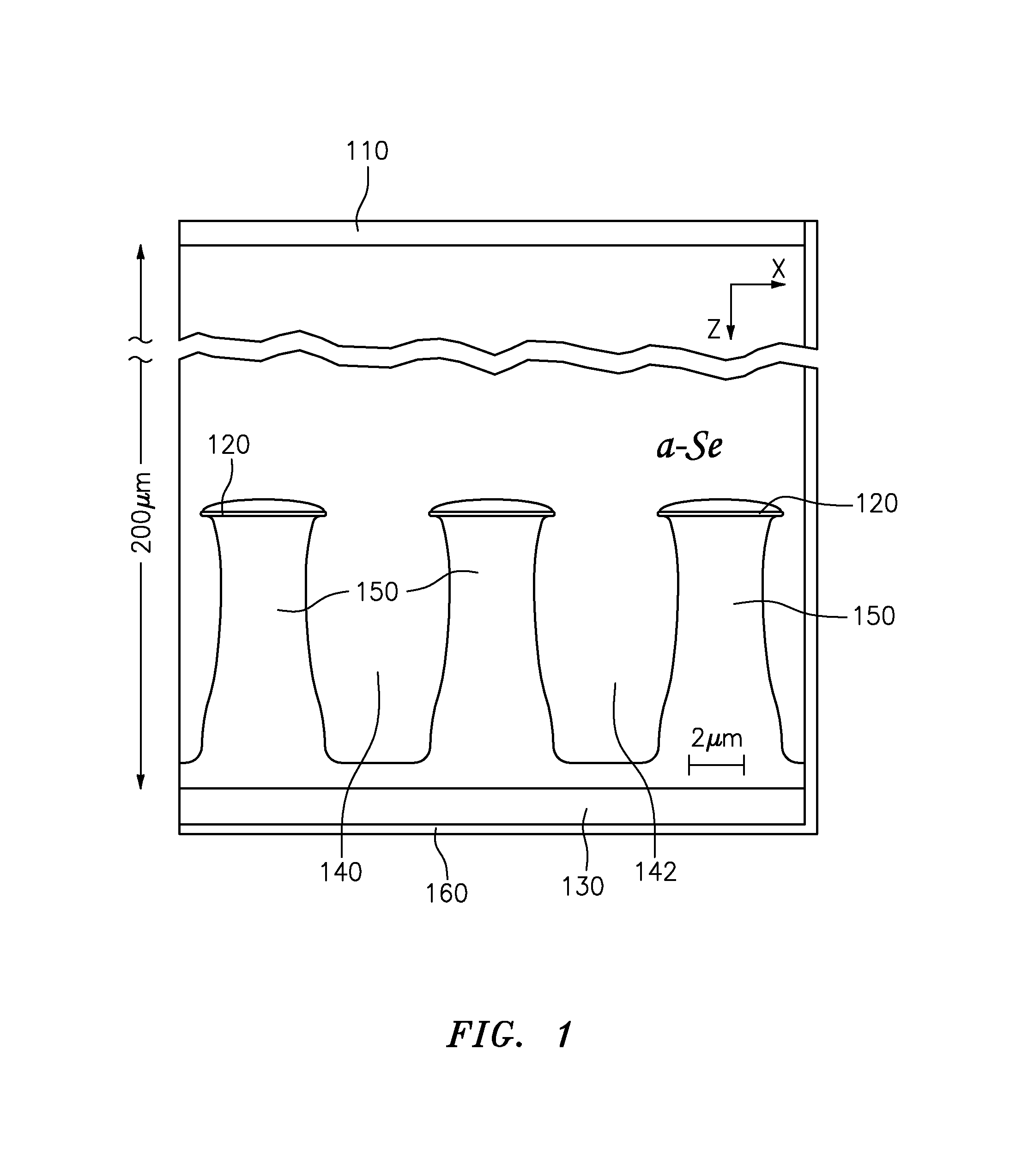
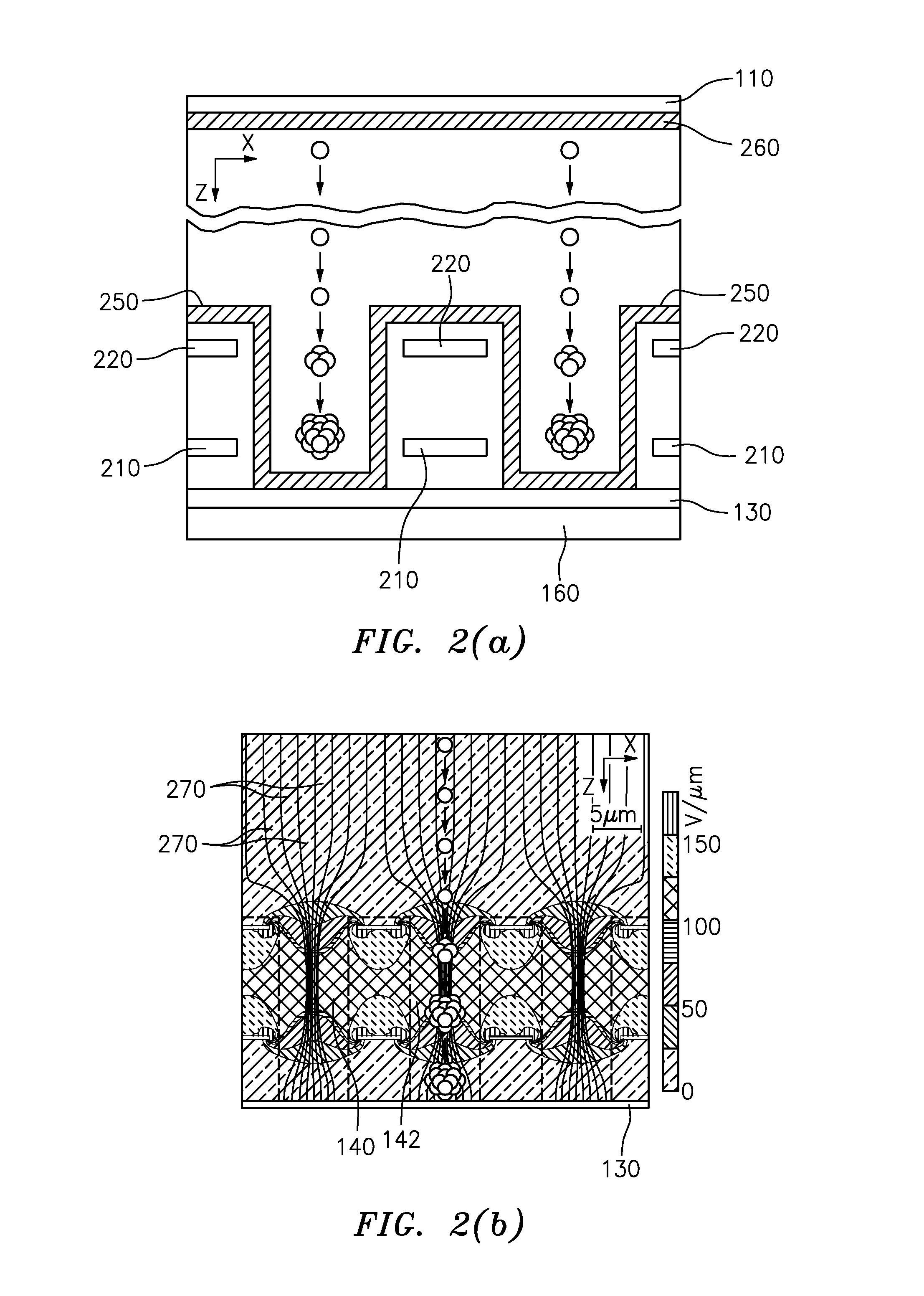
Field-shaping multi-well avalanche detector for direct conversion amorphous selenium
ActiveUS20150171232A1Stable multiplication gainSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous seleniumHigh density
A field shaping multi-well avalanche detector and method for fabrication thereof are disclosed. The field shaping multi-well avalanche detector provides stable avalanche multiplication gain in direct conversion amorphous selenium radiation detectors. The detector provides stable avalanche multiplication gain by eliminating field hot-spots using high-density avalanche wells with insulated wells and field-shaping within each well.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Radiation detector
InactiveUS20100237251A1Simple structureLow costTelevision system detailsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesAmorphous seleniumQuantum efficiency
A thin radiation detector with a high sensitivity is described. The radiation detector has light receiving elements receiving lights emitted by scintillators, performs a photoelectric conversion by using an avalanche multiplication film formed by amorphous selenium, and reads signals by using electron beams constantly discharged from a plurality of electron beam emitting sources called as a field emission array. The avalanche multiplication film formed by amorphous selenium is quite thin and has a simple structure, so it can be formed compactly and realized at a low cost. In addition, a signal amplification degree is approximately 1000 times, so an expensive low noise amplifier or a dedicated temperature adjusting mechanism is not required, and a quantum efficiency is sufficient for a wavelength of 300˜400 nm.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Indirect x-ray image detector for radiology
InactiveUS6982425B1Increase dose rateSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous seleniumCapacitance
An x-ray image detector suitable for radiology has an active matrix substrate with scanning and read-out circuits. Over this active matrix substrate, which can be a two dimensional array of TFTs associated with a storage capacitance, there is deposited a photoreceptor made of a thin layer of amorphous selenium based multilayer structure. The photoreceptor is covered with a light-transparent electrode on top of which there is provided a scintillator. The indices of refraction of the scintillator and of the selenium based multilayer may be matched with the use of the biasing electrode.
Owner:ANALOGIC CANADA
Indirect x-ray image detector for radiology
InactiveUS20060027760A1Increase dose rateSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCapacitanceAmorphous selenium
Owner:ANALOGIC CANADA
Radiation detector and method for producing photoconductive layer for recording thereof
InactiveUS20080230710A1Enhanced electron transport capabilitiesHole-transportability can be greatly improvedSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingAmorphous seleniumOpto electronic
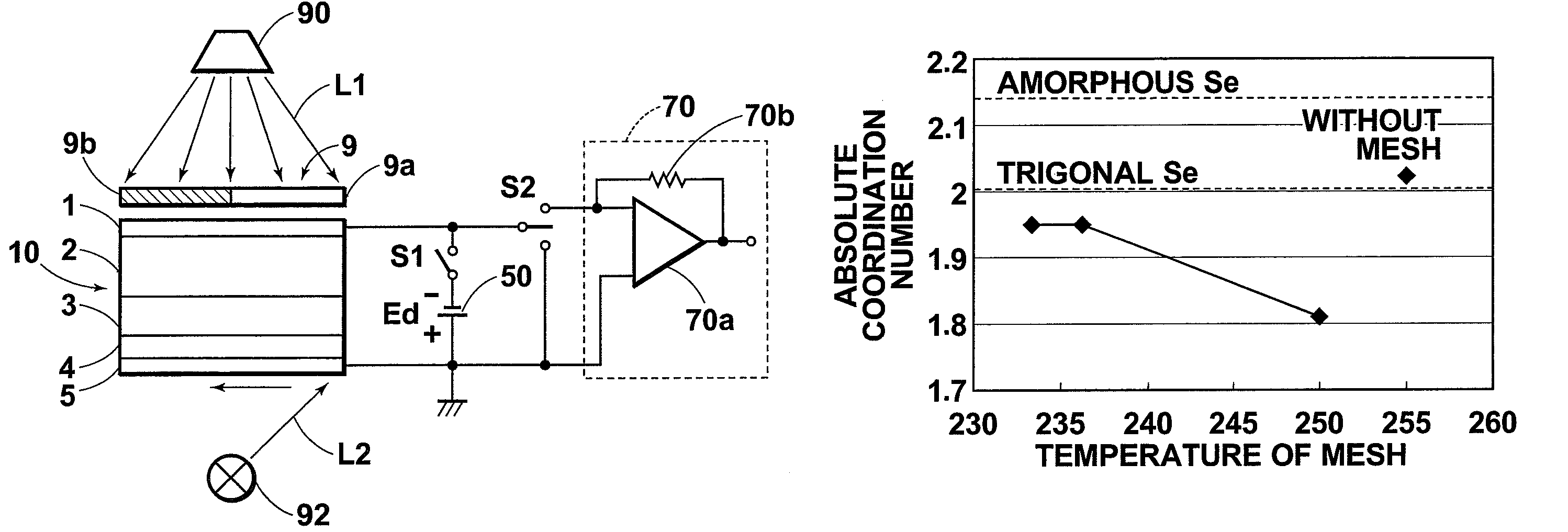
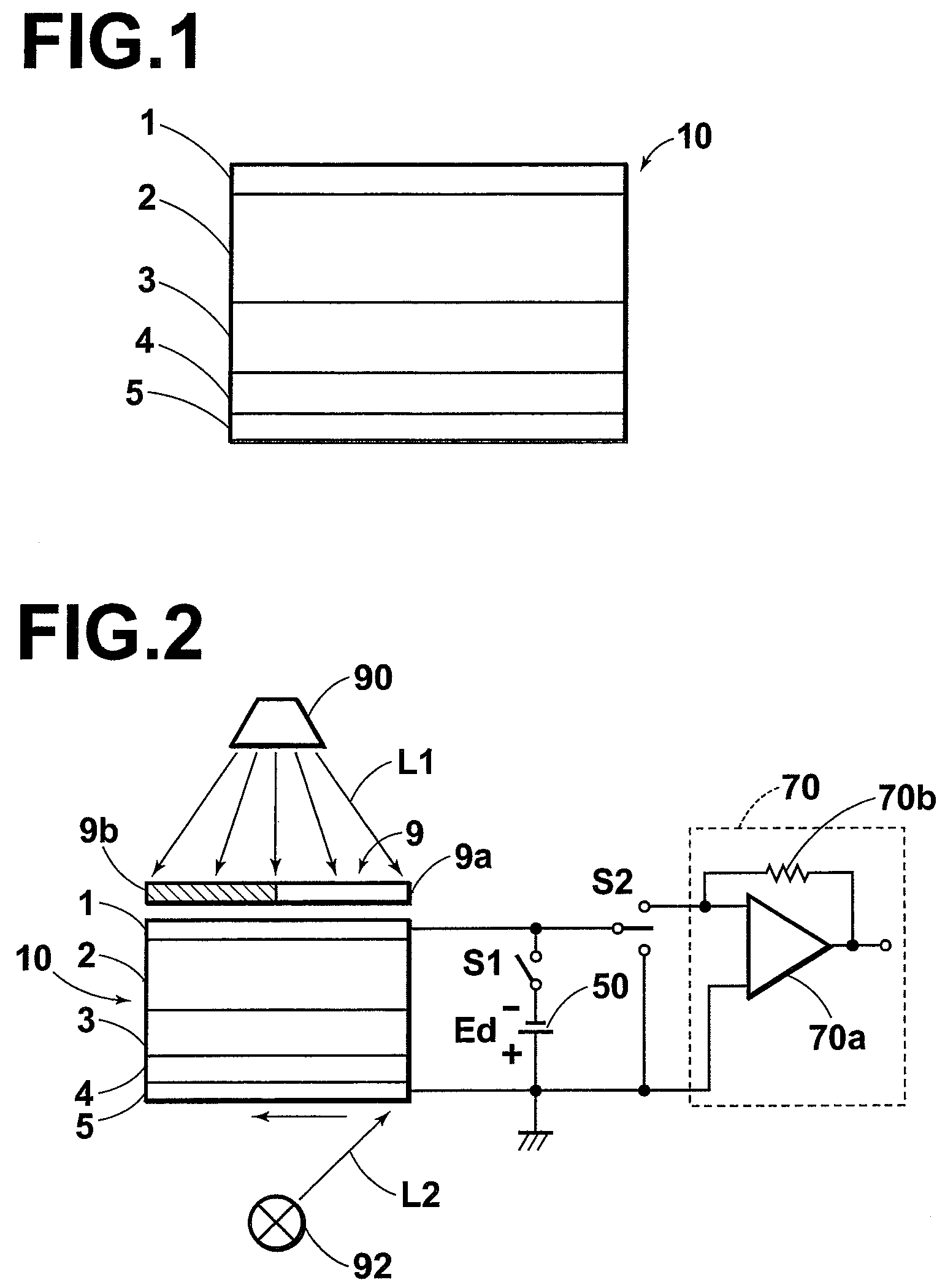
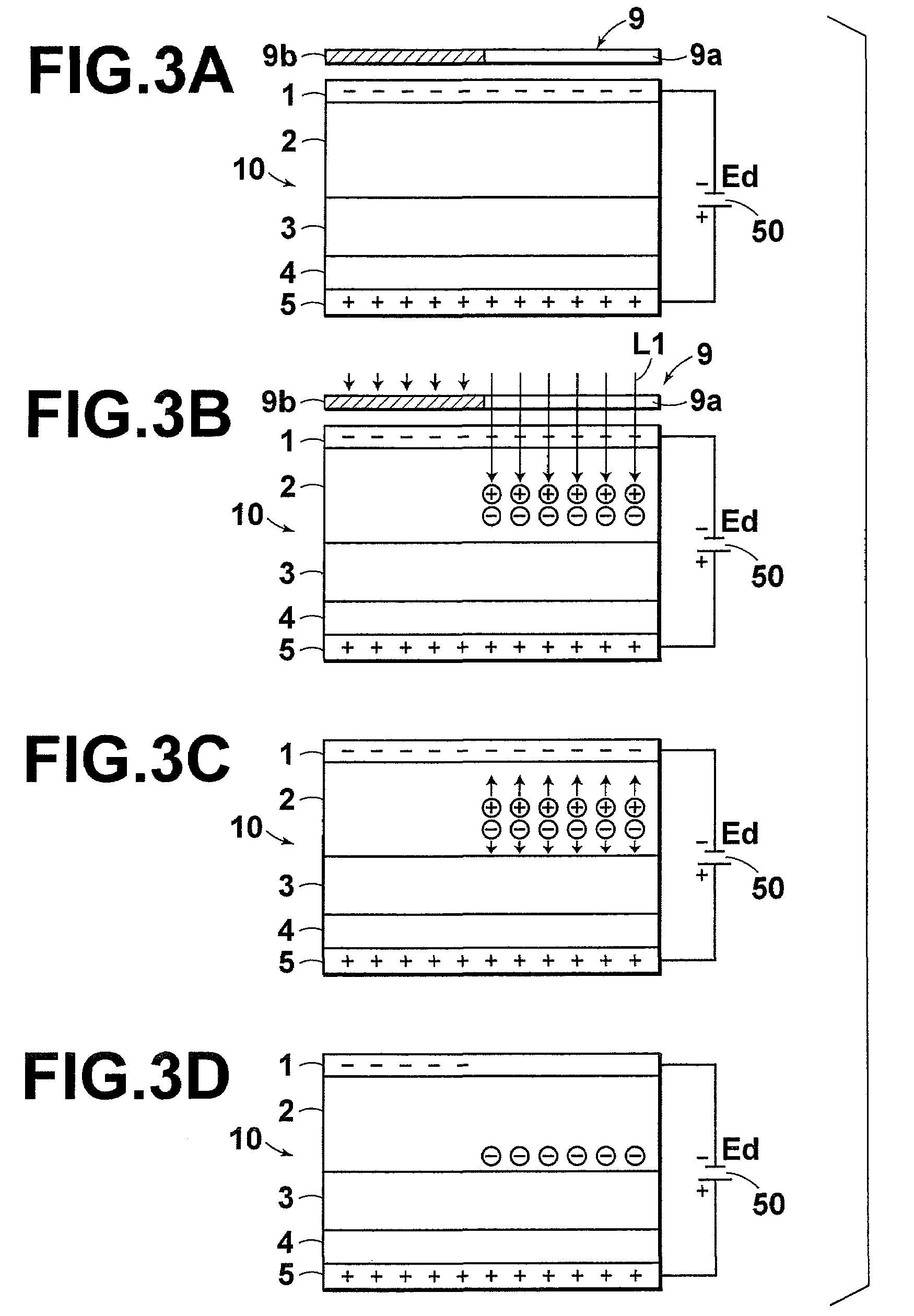
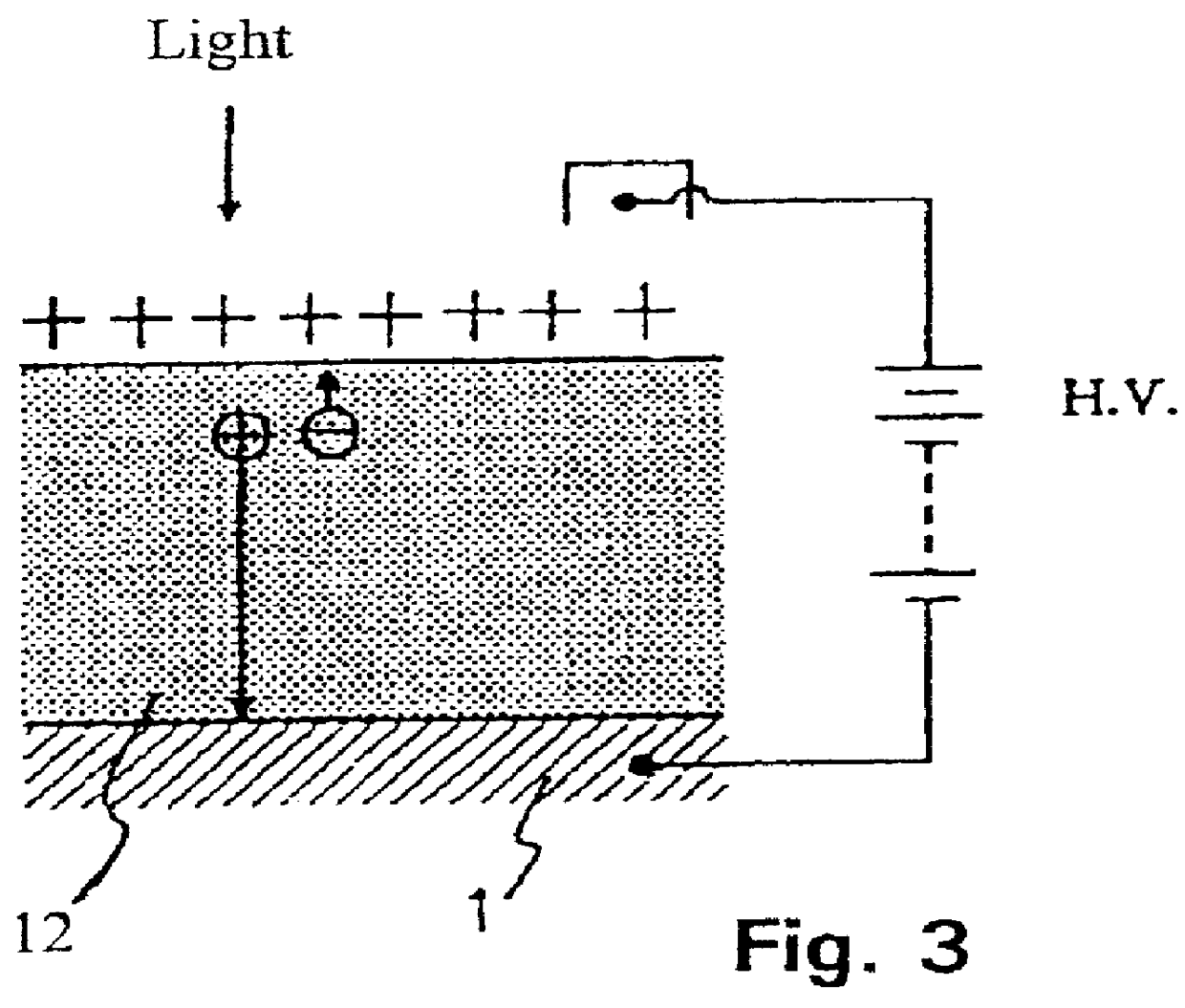
In a radiation detector, electrodes are provided on both sides of a photoconductive layer for recording. When the photoconductive layer for recording is irradiated with radiation during application of a predetermined bias voltage between the electrodes, electric charges are generated within the photoconductive layer for recording. Then, the generated electric charges are detected as an electric signal by the radiation detector. As the material for the photoconductive layer for recording, amorphous selenium having a coordination number of 1.95±0.02 is used.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Application of amorphous selenium
ActiveCN106115635AWith spectral tunabilitySimple preparation processNon-linear opticsElemental selenium/telluriumAmorphous seleniumHarmonic
The invention discloses an application of amorphous selenium, and in particular, relates to the application of the amorphous selenium as an optical second harmonic material. Amorphous selenium particles with different particle sizes are prepared by using femtosecond laser liquid ablation of a selenium solid target material, single amorphous selenium particle with the particle size of more than 300 nm has the function of generating near infrared optical second harmonic waves, and an amorphous selenium particle dimer with the diameter of about 200 nm also has the optical second harmonic wave function. The amorphous selenium is presented to have the wide-spectral optical second harmonic wave function for the first time, and the field that traditional optical second harmonic materials are all crystals is broken. The preparation process is simple, the repeatability is good, the stability is high and the cost is low. The amorphous selenium is used as a novel optical second harmonic material, and can replace the traditional materials to be applied in biological detection, medical diagnosis, surface detection and other fields.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
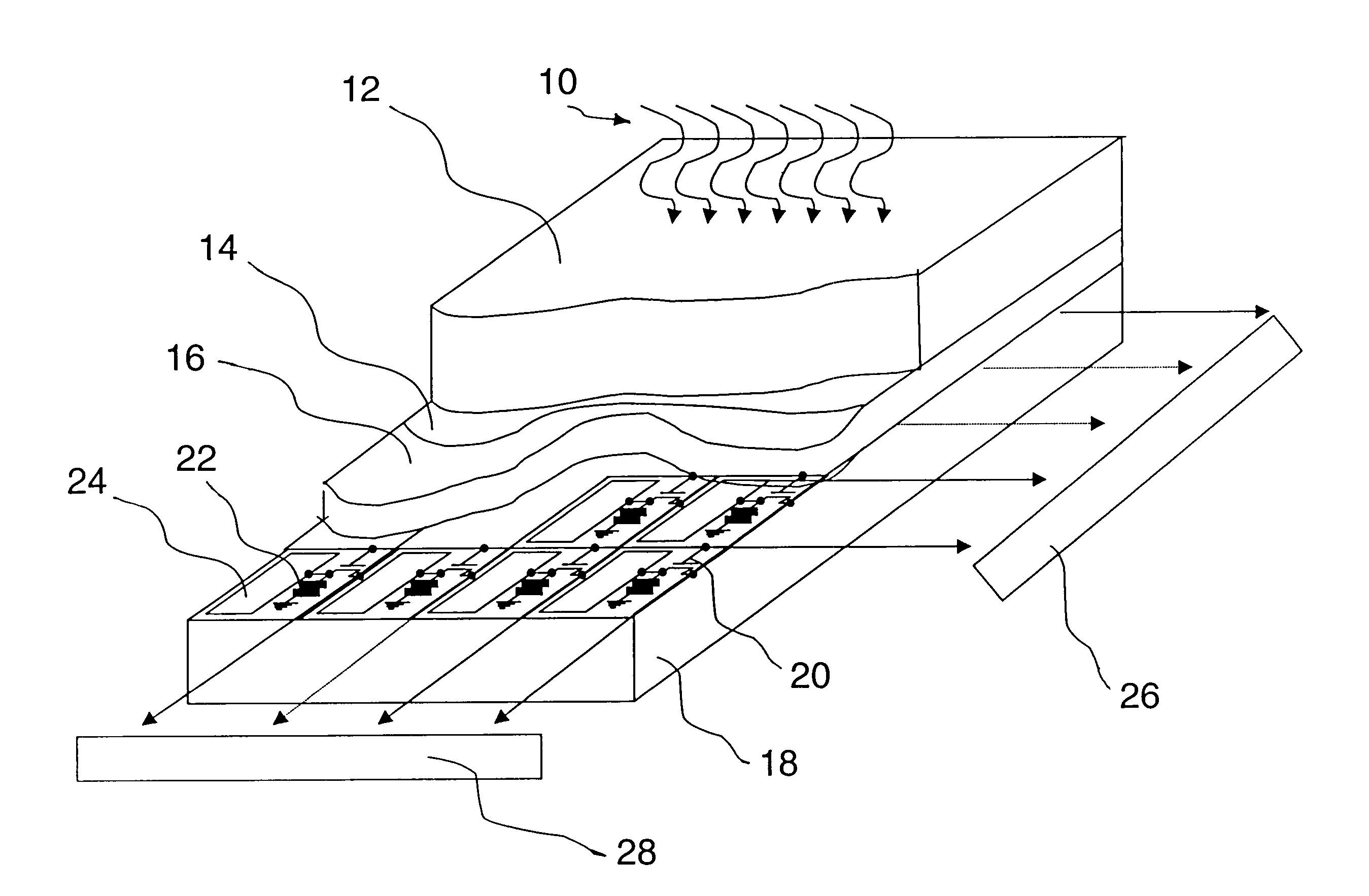
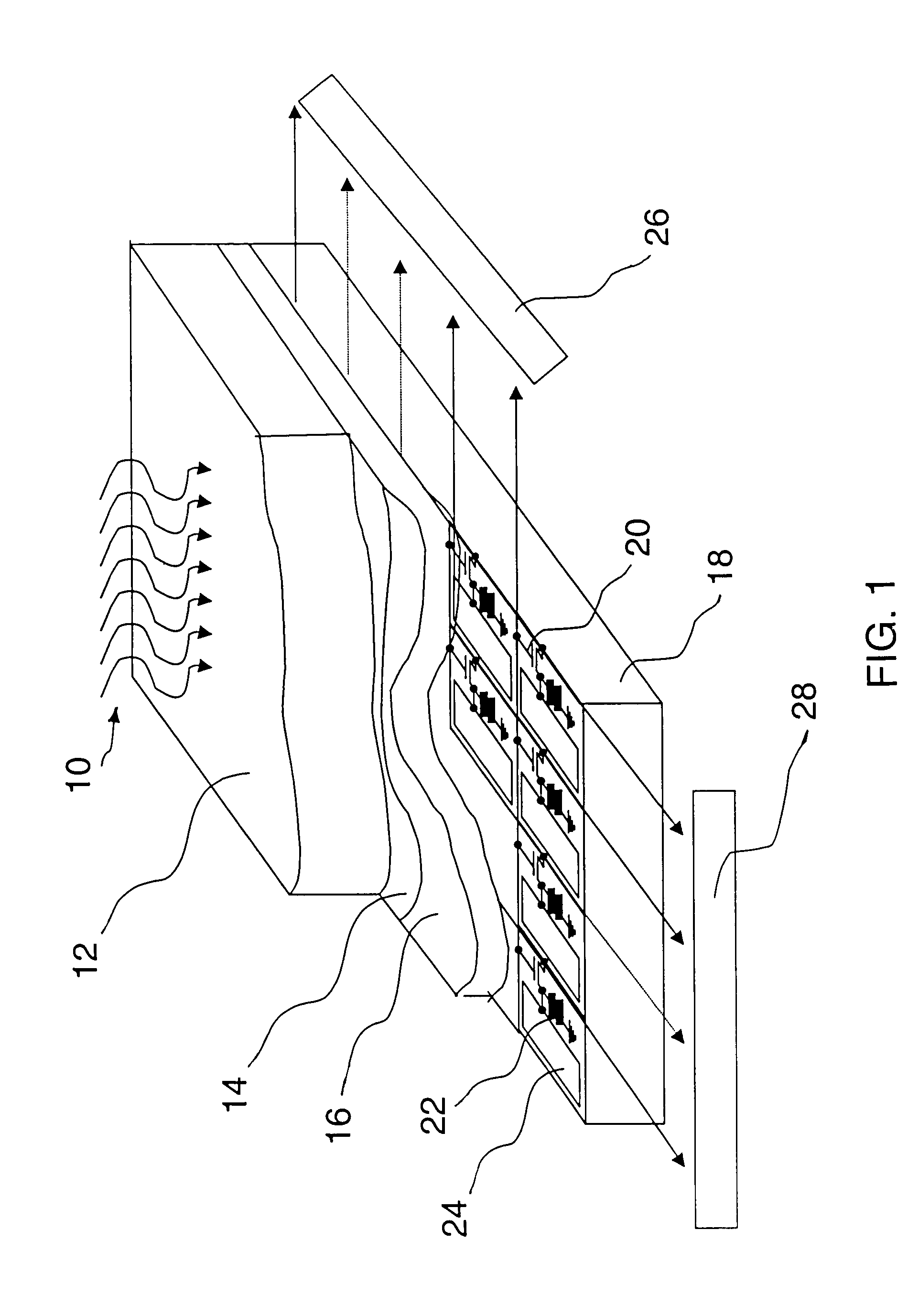
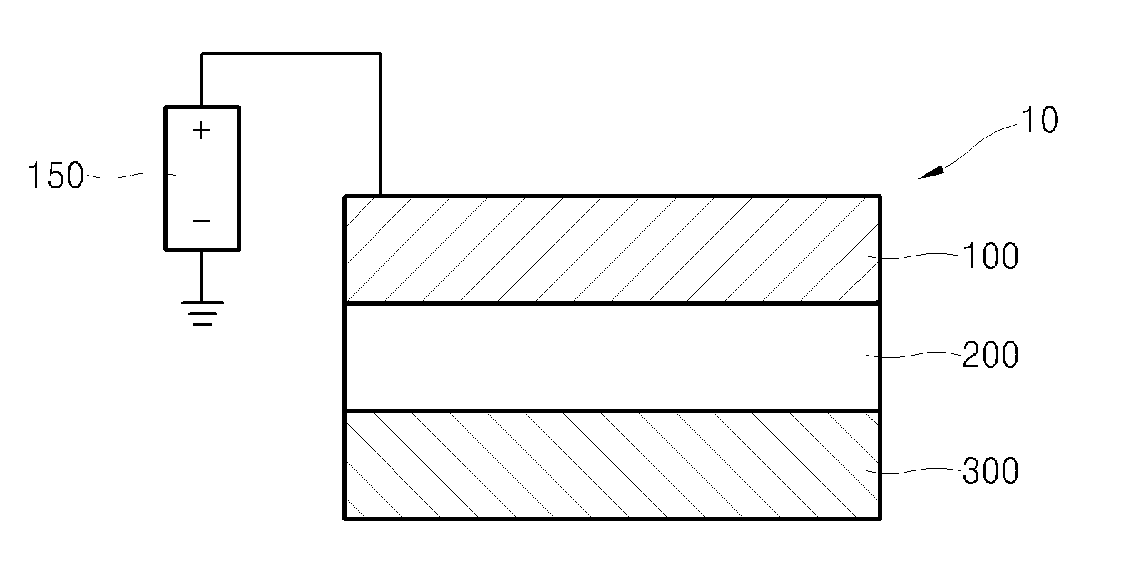
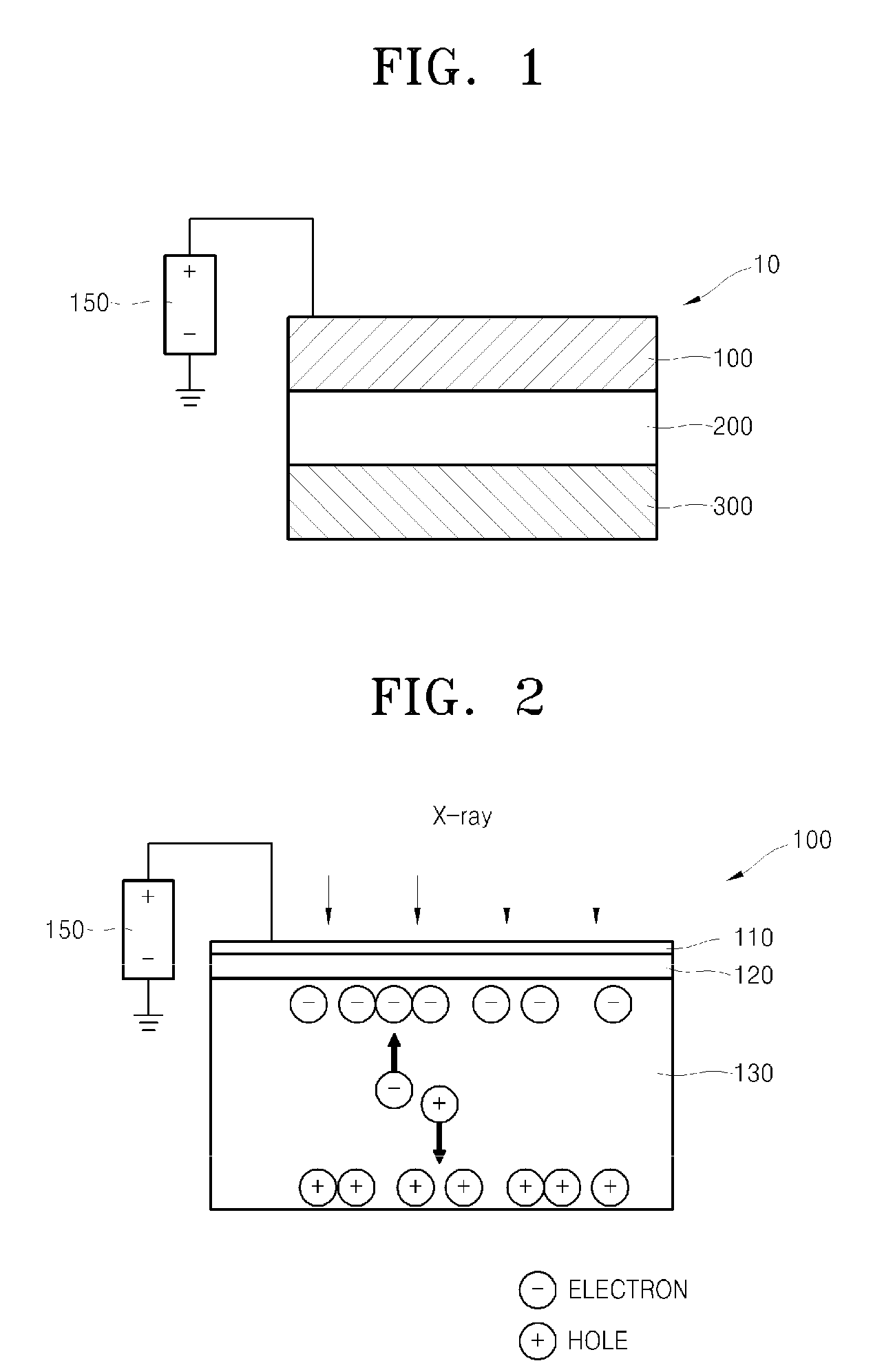
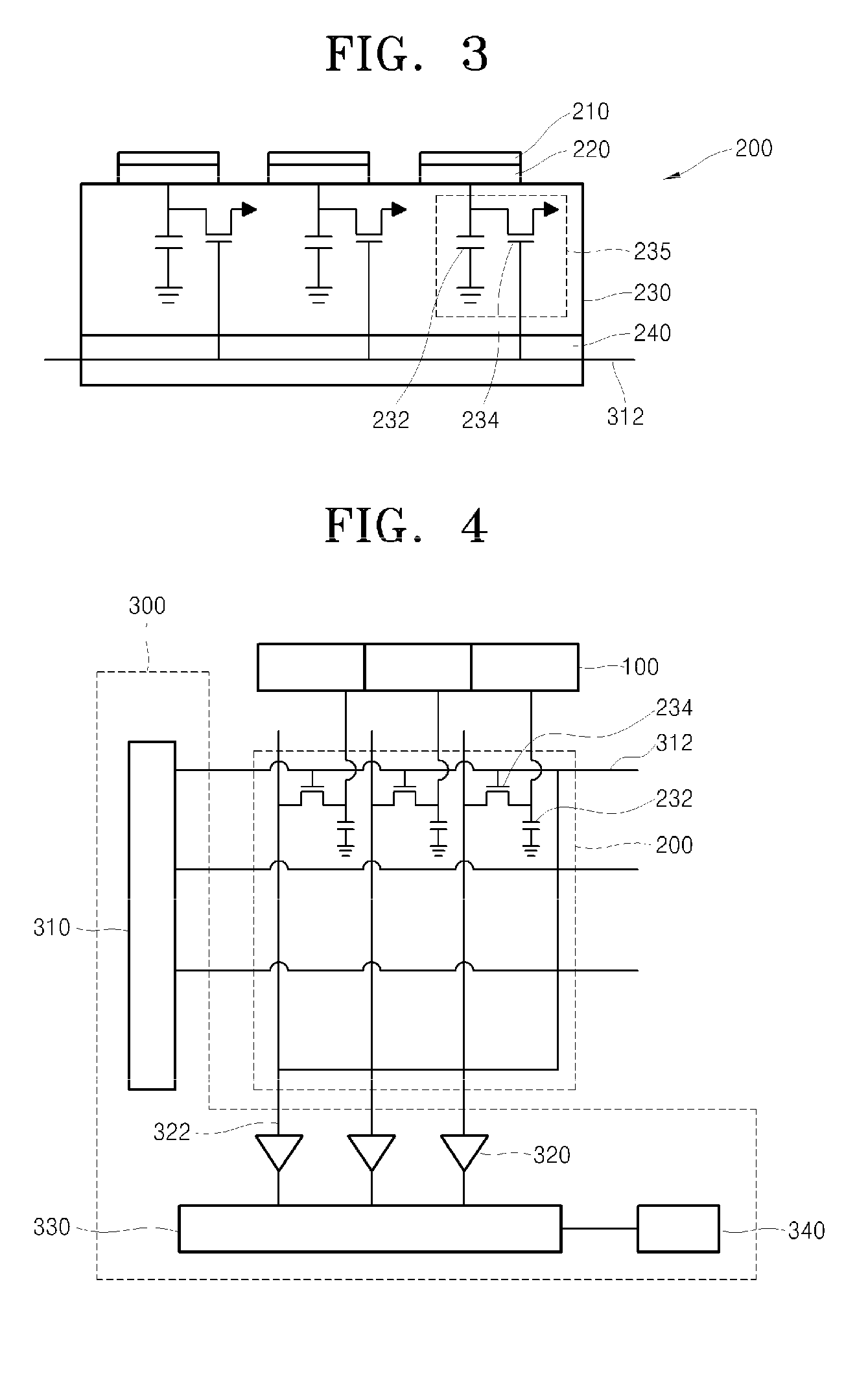
Electro-medical imaging apparatus having chalcogen-thin film transistor array
InactiveUS20080217547A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl signalX-ray
Provided is an electro-medical imaging apparatus manufactured using a thin film transistor (TFT) array including chalcogen-based semiconductor elements that can generate and store an electric signal from an X-ray signal so as to be able to replace a traditional film type X-ray reader. The electro-medical imaging apparatus includes: a signal generating unit where electron-hole pairs are formed by absorbing an optical energy irradiated from outside; a power source connected to a surface of the signal generating unit and applies an electric signal so as to separate the electron-hole pairs to be accumulated each in opposite sides of the signal generating unit according to their polarities; a signal storage unit that is in contact with the signal generating unit and receives and stores one of the separated charges; and a signal converter that is in contact with the signal storage unit and applies a control signal to the signal storage unit in order to convert an electric signal, which generated by the charges stored in the signal storage unit, into an image signal. The signal generating unit may use amorphous selenium (a-Se), which is one of chalcogen materials, or CdTe or CdZnTe which is a compound material using chalcogen. Also, the signal storage unit may include a TFT array including Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST) or a TFT array including CuInSe2 (CIS).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
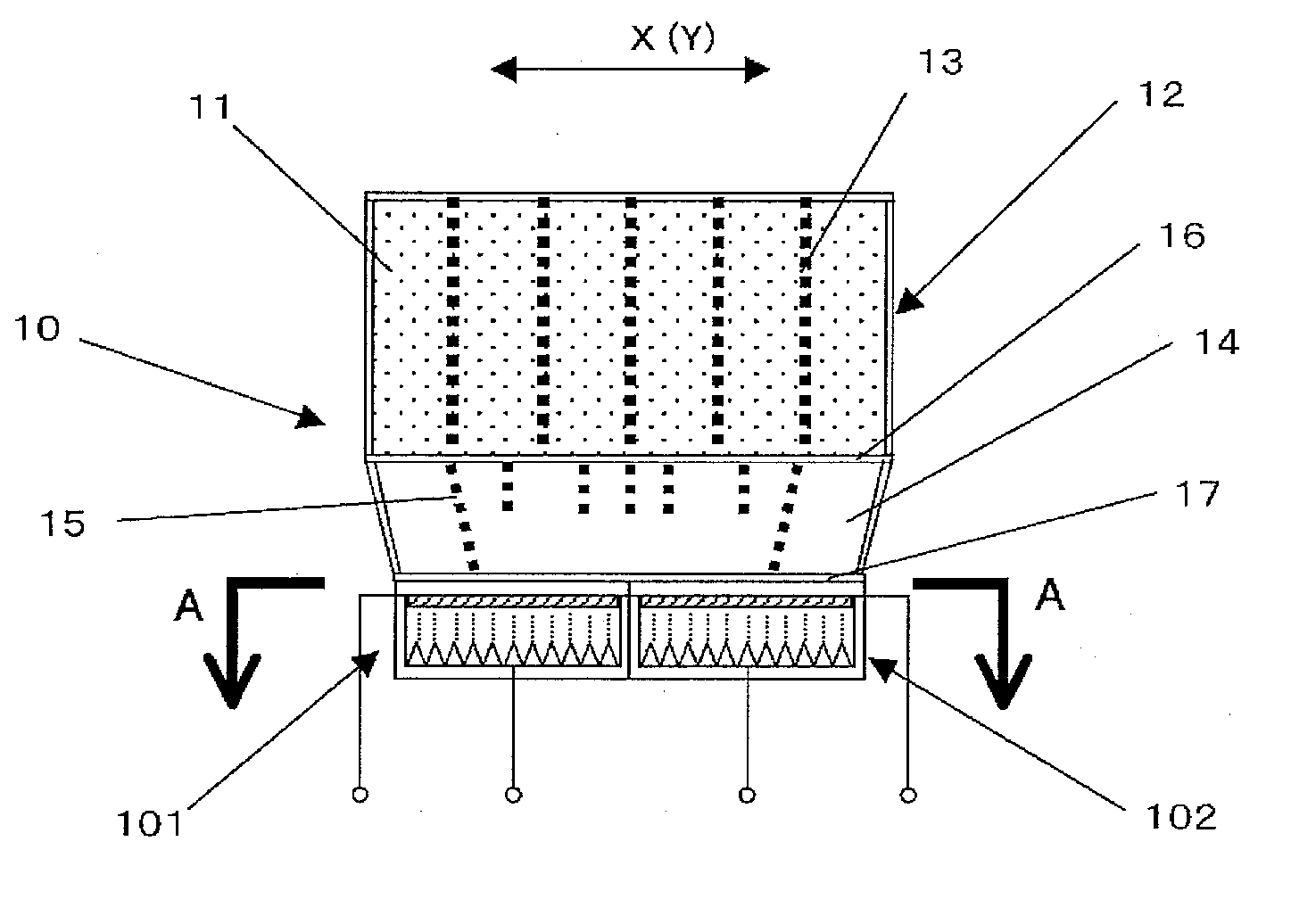
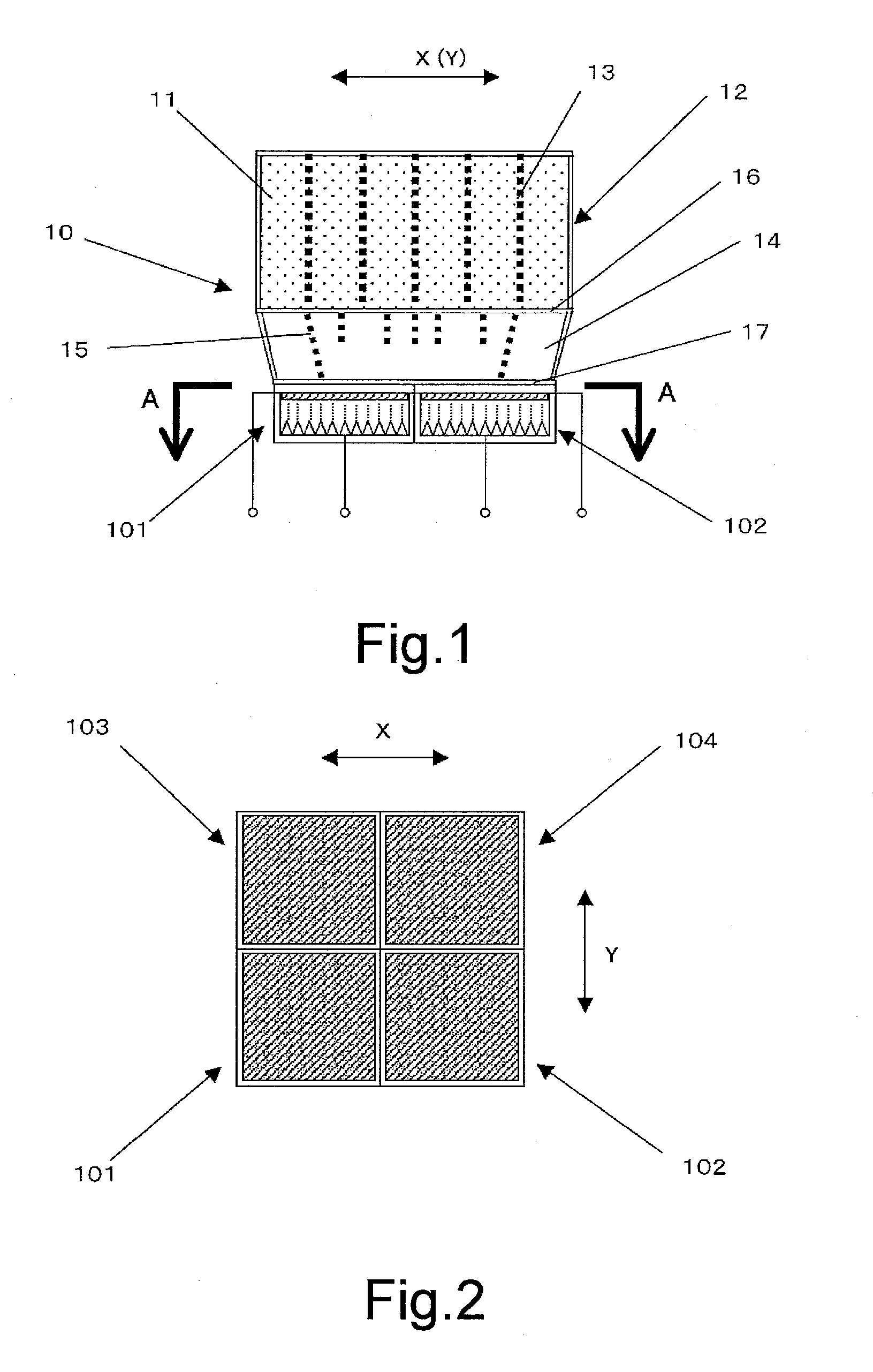
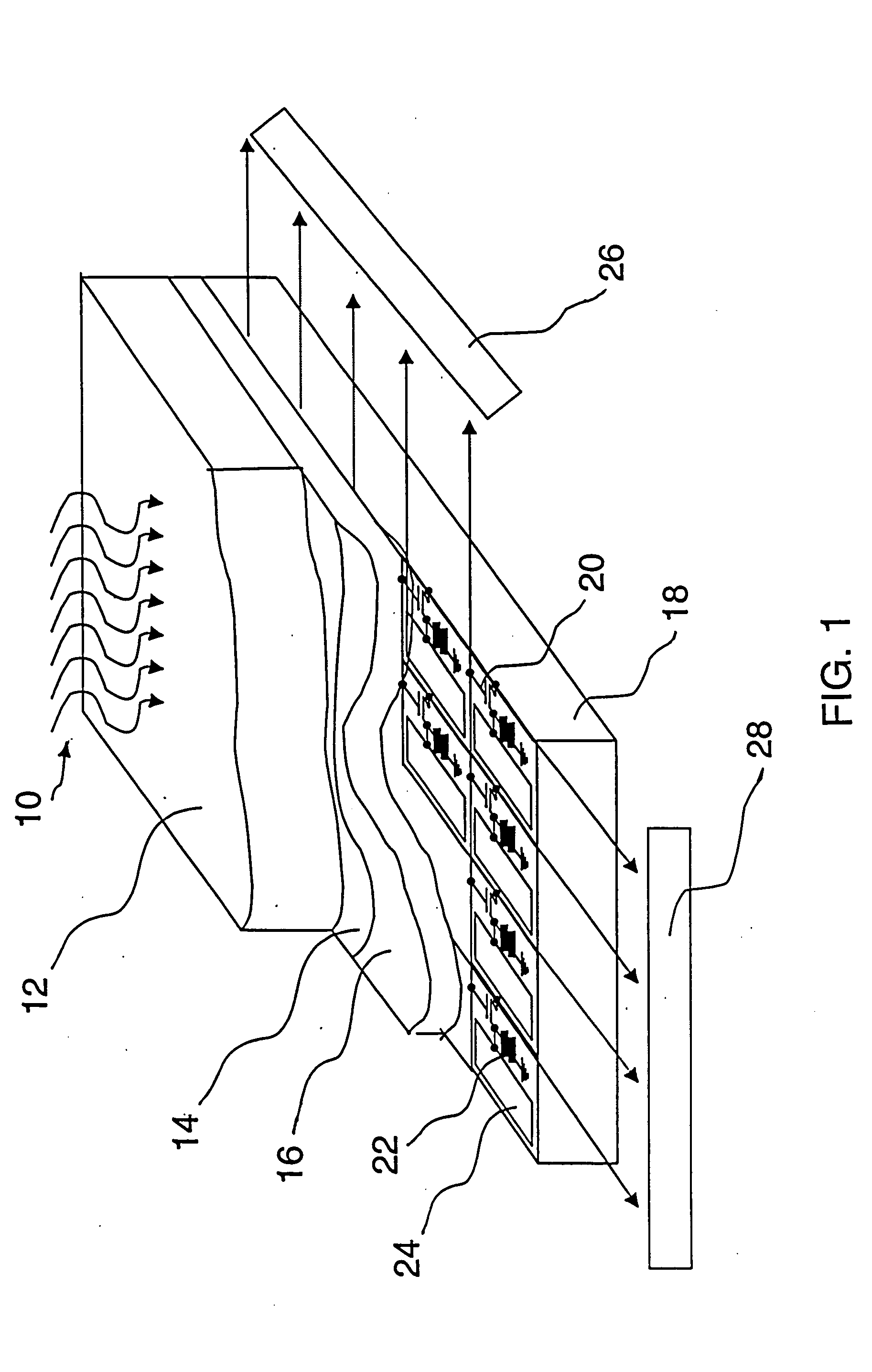
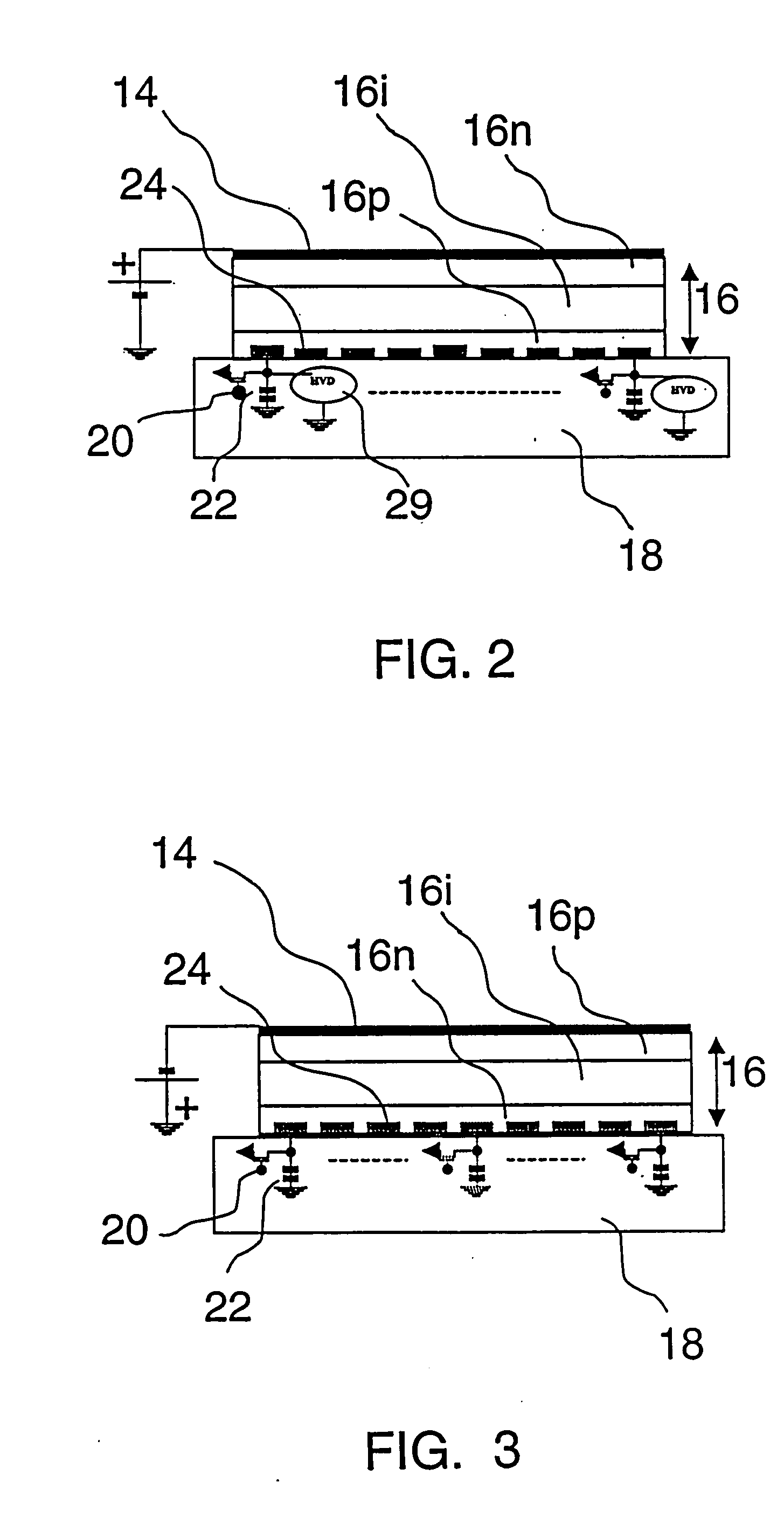
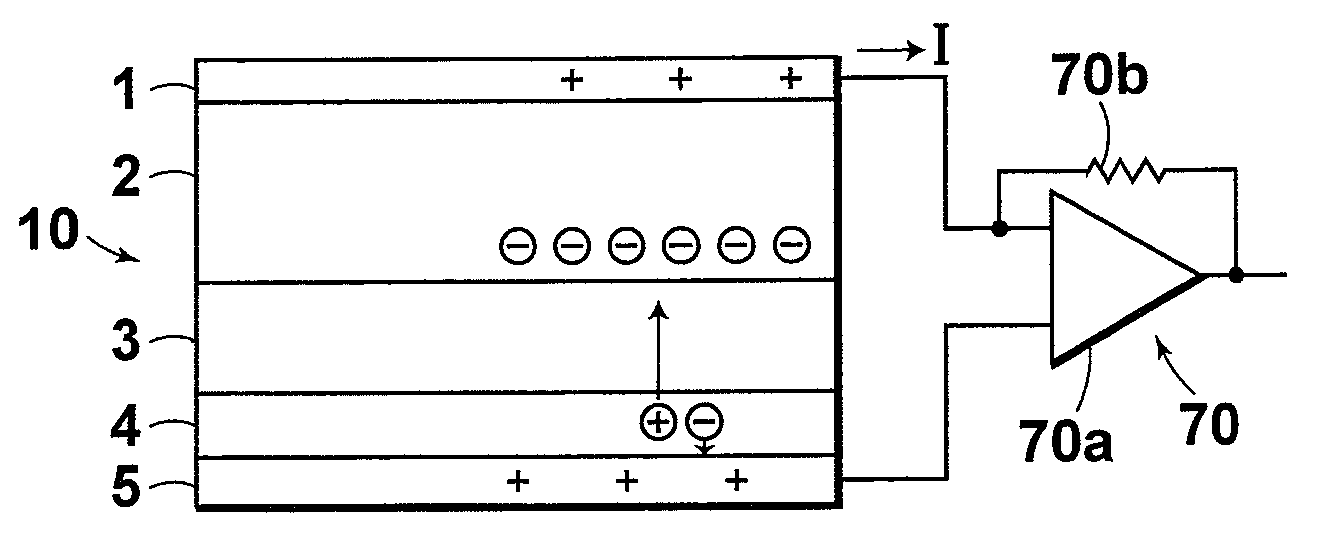
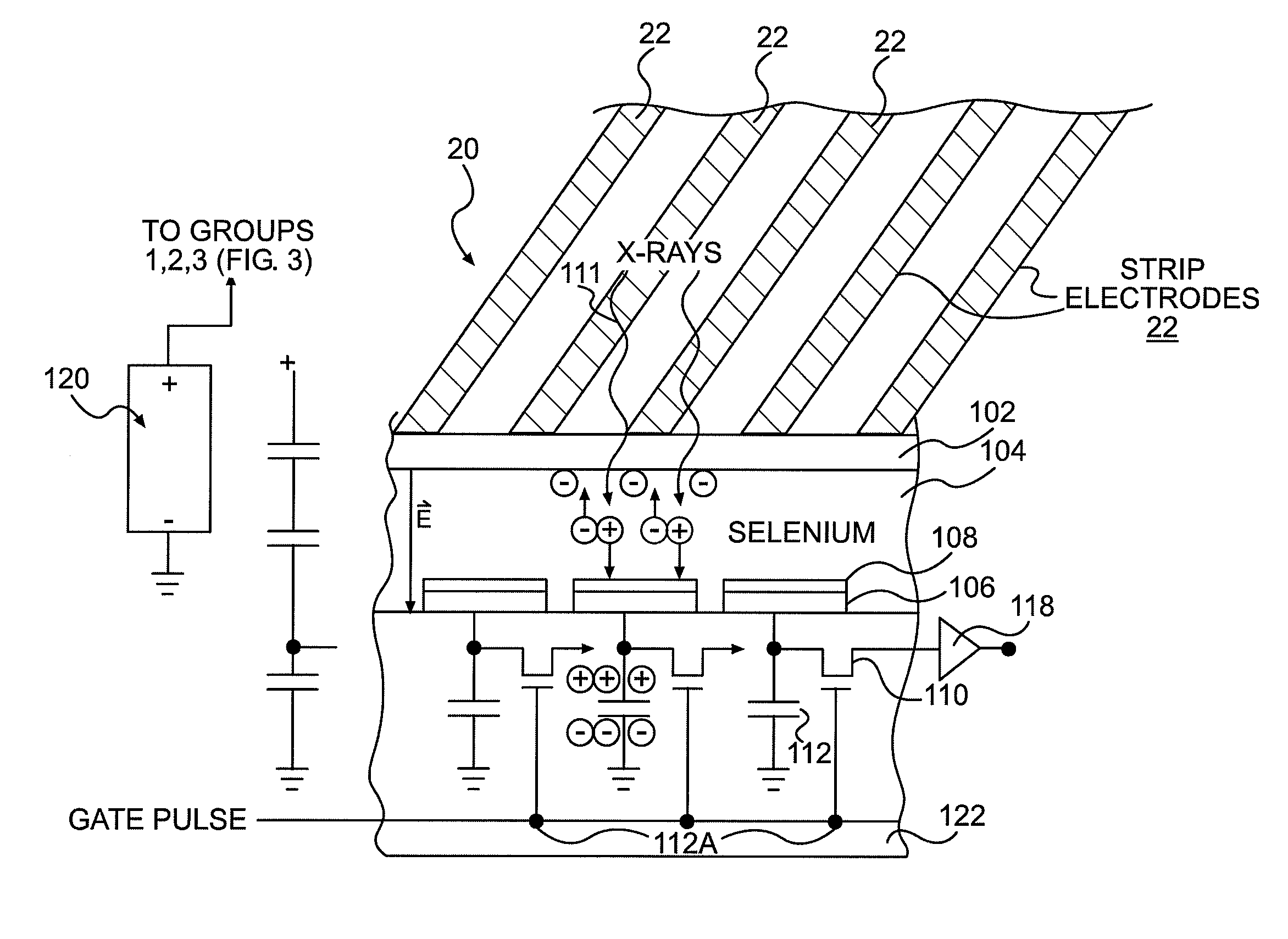
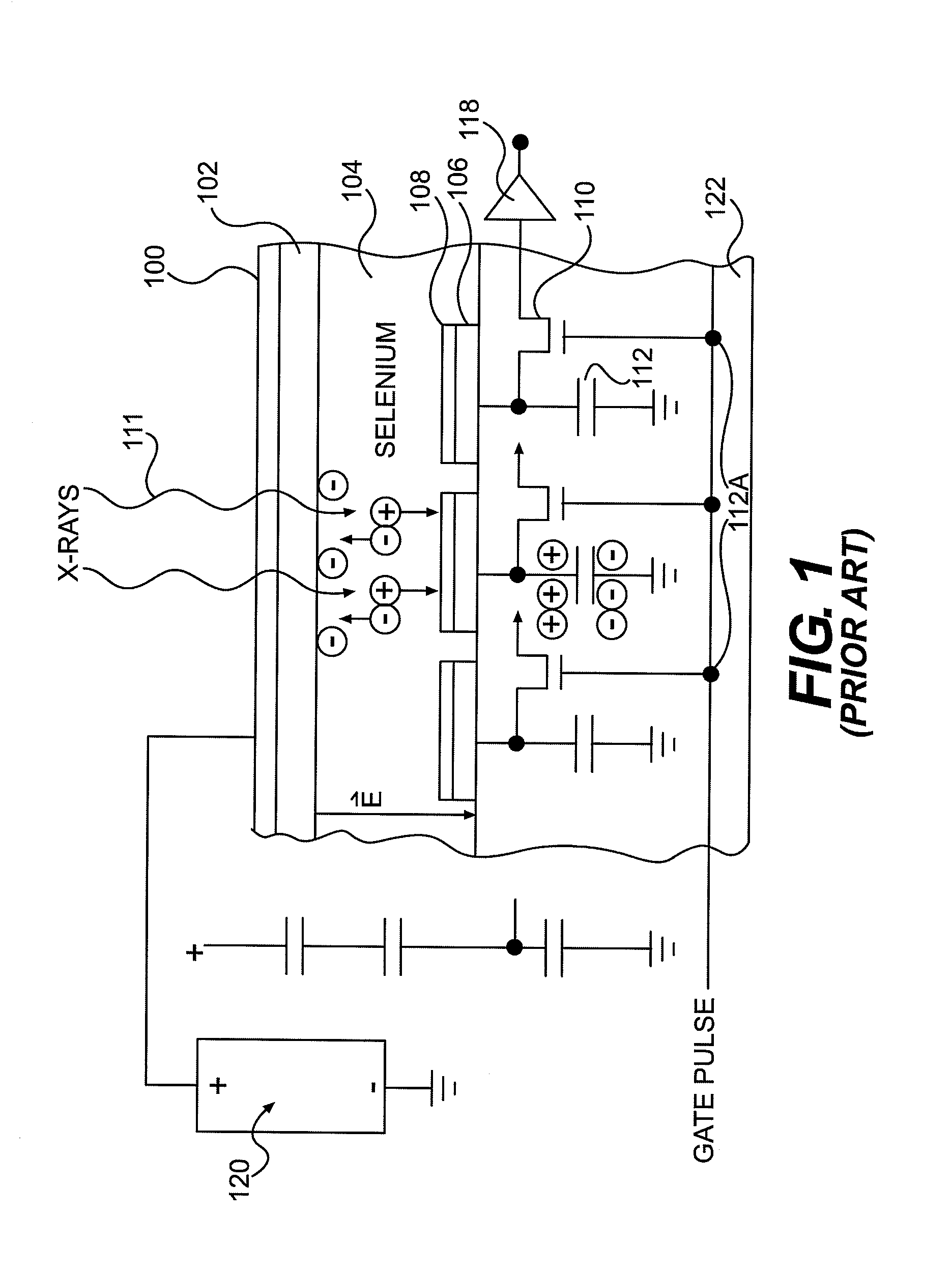
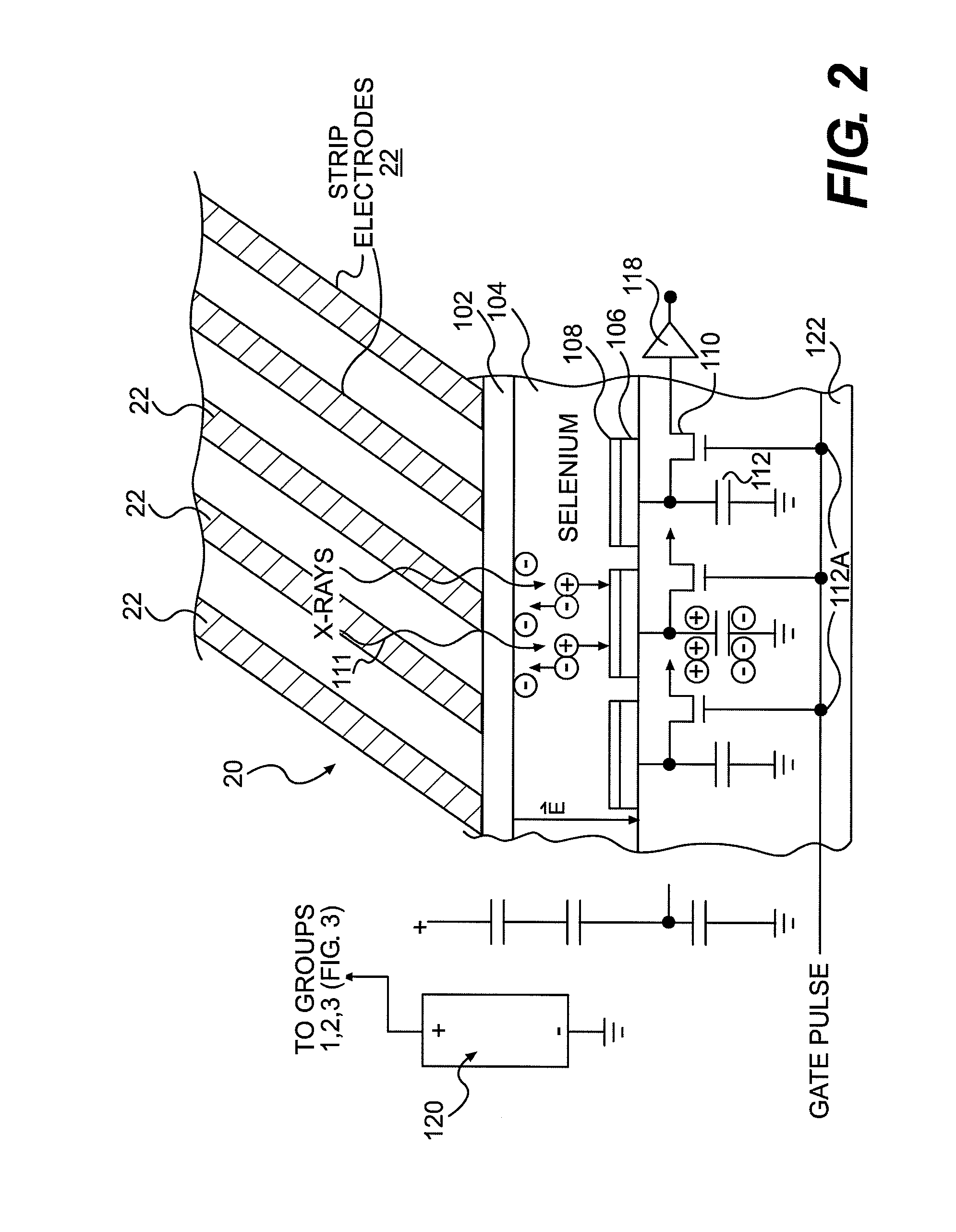
Direct Conversion X-Ray Imaging Device With Strip Electrodes
A flat panel X-ray imager using an amorphous selenium detector which uses a dielectric layer within the X-ray conversion layer to form an interface between the X-ray conversion layer and the high voltage bias electrode. To accomplish the removal of trapped counter charges at the dielectric / selenium layer, a plurality of discrete or strip electrodes are provided in contact with the dielectric layer and which are electrically coupled into distinct groups. During X-ray exposure, a high bias voltage is applied to all groups of strip electrodes. Following X-ray exposure and image readout, the groups of strip electrodes are energized using a plurality of differently-phased energization signals to drive trapped counter charges toward “gutter” strip electrodes at the sides of the detector. A second embodiment of the flat panel X-ray imager includes sandwiching the discrete electrodes in a dielectric layer applied against the selenium layer and including a continuous electrode on the opposite side of the dielectric layer. Application of a high voltage bias to the continuous electrode results in an electric field in the selenium layer that is smoothed during X-ray acquisition. Discrete electrode energization to drive trapped counter charges to the gutter electrodes occurs while the high voltage bias is present.
Owner:DIRECTXRAY DIGITAL IMAGING TECH
Flat panel detector and lag data sheet generation method and lag compensation correction method thereof
ActiveCN108172659ASolve complex afterimage problemsImage enhancementFinal product manufactureSilicon detectorCorrection method
The invention provides a compensation correction method of a flat panel detector image lag. The compensation correction method comprises the following steps of generating a lag data sheet and storingthe data sheet in a flat panel detector or detector software; obtaining a current bright field image and a dark filed image; enabling a lag signal of each pixel in the dark field image to be corresponding to the lag data sheet, and finding out a lag value of the lag signal of each pixel corresponding to the lag data sheet, and a moment corresponding to the lag value; enabling the moment corresponding to the lag value to be added with the time interval of the collection time between the current bright field image and the dark field image to obtain a new moment, finding a lag value correspondingto the new moment from the lag data sheet, and generating a current image evaluation lag template matrix; and enabling the lag template matrix to be subtracted from the current bright field image toperform lag compensation correction. The compensation correction method of the flat panel detector image lag disclosed in the invention can be used for solving the complex lag problems, and is wide inapplicable range, and suitable for a noncrystalline silicon detector and amorphous selenium, CMOS and other semiconductor detectors.
Owner:SHANGHAI IRAY TECH
Planar radiation detector using radiation-induced-charge conversion film of amorphous selenium
ActiveUS20080224049A1Confirm effect of suppressionReduce probabilitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous seleniumAlloy
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Two-dimensional selenium nanosheet as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108793098AEnable mass manufacturingExcellent peelabilityNanotechnologyElemental selenium/telluriumAmorphous seleniumSe element
The invention provides a two-dimensional selenium nanosheet. The two-dimensional selenium nanosheet is an amorphous structure. The two-dimensional selenium nanosheet is narrower in band gap, wider inresponse spectrum, better in stability and excellent in optical detection performance at the same time. The invention also provides a preparation method of the two-dimensional selenium nanosheet. Themethod comprises the following steps: providing an amorphous selenium raw material, peeling the selenium raw material by using a liquid-phase peeling method to obtain the two-dimensional selenium nanosheet. The liquid-phase peeling method is firstly used for preparing the two-dimensional selenium nanosheet from the non-layered selenium raw material; the peeling effect is good; the two-dimensionalselenium nanosheet can be prepared in large scale; the cost is lower; the preparation method is simple and is easy to operate. The invention also provides application of the two-dimensional selenium nanosheet to optical detectors.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7045790B2Reduce signal to noise ratioAvoid problemsSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous seleniumSolid state detector
A solid-state detector is accommodated within a case housing. The solid-state detector is provided with a layer containing amorphous selenium as a principal constituent and operates such that the solid-state detector records image information as an electrostatic latent image, and such that the solid-state detector generates electric currents in accordance with the electrostatic latent image when the solid-state detector is scanned with reading light. A heat discharging device discharges heat within the case housing to the exterior of the case housing, such that a temperature of the layer containing the amorphous selenium as the principal constituent is kept at a temperature lower than 40° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Carbon-selenium composite material, positive pole of lithium-selenium battery, and application of positive pole
InactiveCN108502844AIncrease pressure differenceEnhanced capillary actionMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode carriers/collectorsAmorphous seleniumElectrochemical response
The invention belongs to the field of energy storage, and particularly relates to a carbon-selenium composite material, a positive pole of a lithium-selenium battery, and an application of the positive pole. The carbon-selenium composite material is of an amorphous crystal phase, has a uniform structure, and consists of hollow porous nano carbon spheres and amorphous selenium distributed in the inner pore channels of the hollow porous nano carbon spheres. In the carbon-selenium composite material provided by the invention, selenium can enter the porous channels of the porous carbon as much aspossible, so that selenium cannot run off from the positive pole in an electrode reaction, so that higher utilization rate and reversibility can be achieved in an electrochemical reaction.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Radiation detector and method for producing photoconductive layer for recording thereof
InactiveUS7488966B2Hole-transportability can be greatly improvedEnhanced electron transport capabilitiesVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesAmorphous seleniumOpto electronic
In a radiation detector, electrodes are provided on both sides of a photoconductive layer for recording. When the photoconductive layer for recording is irradiated with radiation during application of a predetermined bias voltage between the electrodes, electric charges are generated within the photoconductive layer for recording. Then, the generated electric charges are detected as an electric signal by the radiation detector. As the material for the photoconductive layer for recording, amorphous selenium having a coordination number of 1.95±0.02 is used.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
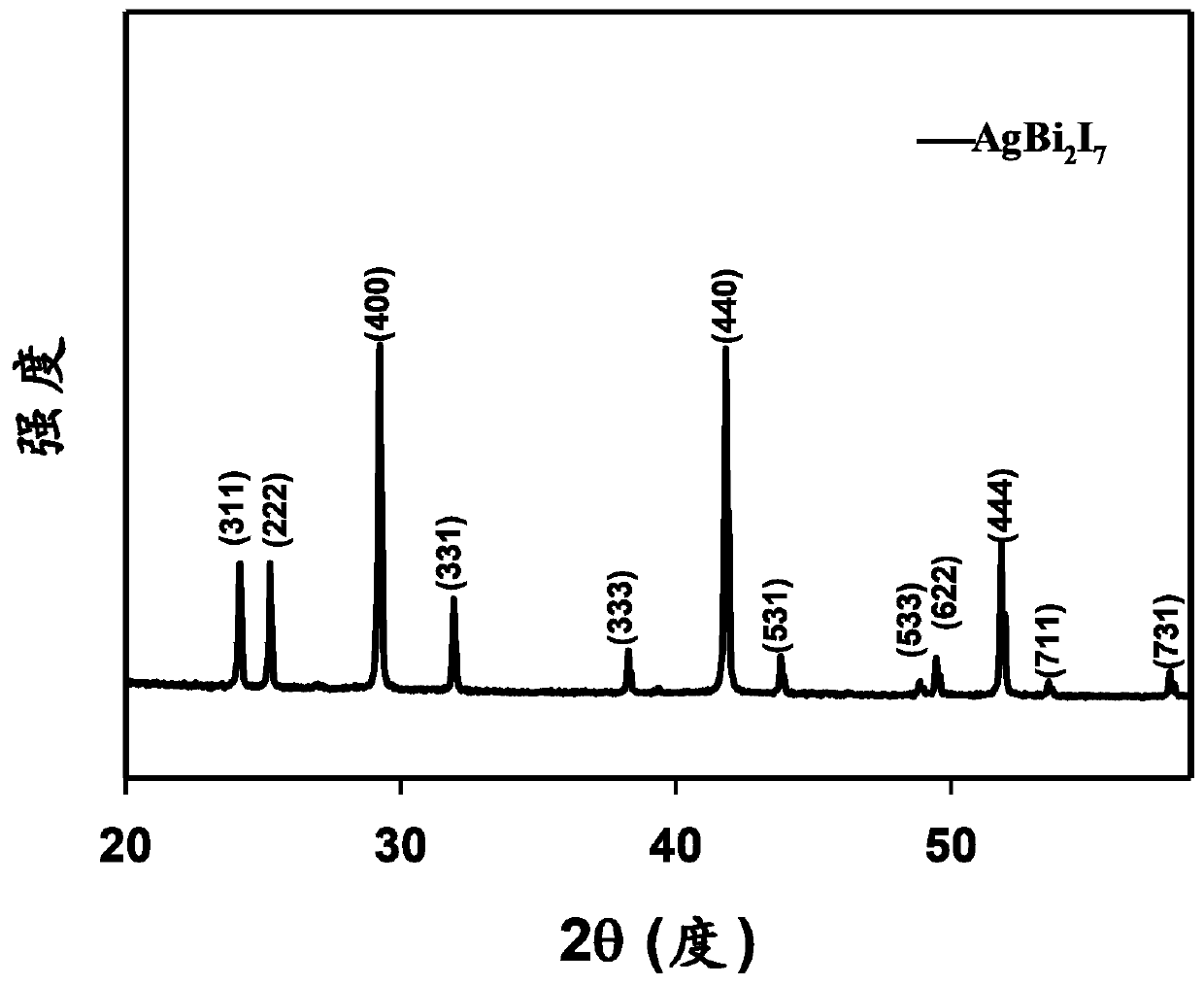
Silver bismuth iodine single crystal, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN110644051AHigh detection sensitivityPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsAmorphous seleniumOctahedron
The invention discloses a silver bismuth iodine single crystal. According to the silver bismuth iodine single crystal, the chemical formula is AgBi2I7, and the crystal has a face-centered cubic structure; the cell parameters comprise that a, b and c are the same and equal to 12.22 angstrom, and alpha, beta and gamma are the same and equal to 90 DEG; and each Bi<3+> and the surrounding eight I<-> form a regular hexahedron, and each Ag<+> and the surrounding six I<-> form a regular octahedron. According to the invention, the crystal is a novel radiation detection material, and is environmentallyfriendly; the X-ray detection sensitivity of the detector prepared from the crystal is 364.7 [mu]CGy[air]<-1>cm<-2>, is equivalent to the sensitivity (318 [mu]CGy[air]<-1>cm<-2>) of the traditional tellurium-zinc-cadmium X-ray detector, and is higher than the sensitivity (20 [mu]CGy[air]<-1>cm<-2>) of the amorphous selenium X-ray detector; and the novel Bi-based halide single crystal material canfurther be used for X-ray imaging and preparation of gamma-ray detectors.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
High-definition digital X-ray flat panel detector
InactiveCN103698799AImprove image qualityLayered productsRadiation intensity measurementX-rayOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a high-definition digital X-ray flat panel detector which comprises a protective layer, an electrode layer, an insulating layer, an X-ray semiconductor layer, an electronic closing layer, an amorphous selenium layer, a thin film transistor layer, a storage capacitor, a charge amplifier, a gate control circuit, a digital converter and a glass substrate. With the adoption of the mode, the high-definition digital X-ray flat panel detector eliminates image blurring caused by photoelectric scattering, ensures the quality of an image, and can be very reliable in a high-humidity and completely-exposed environment.
Owner:江苏龙信电子科技有限公司
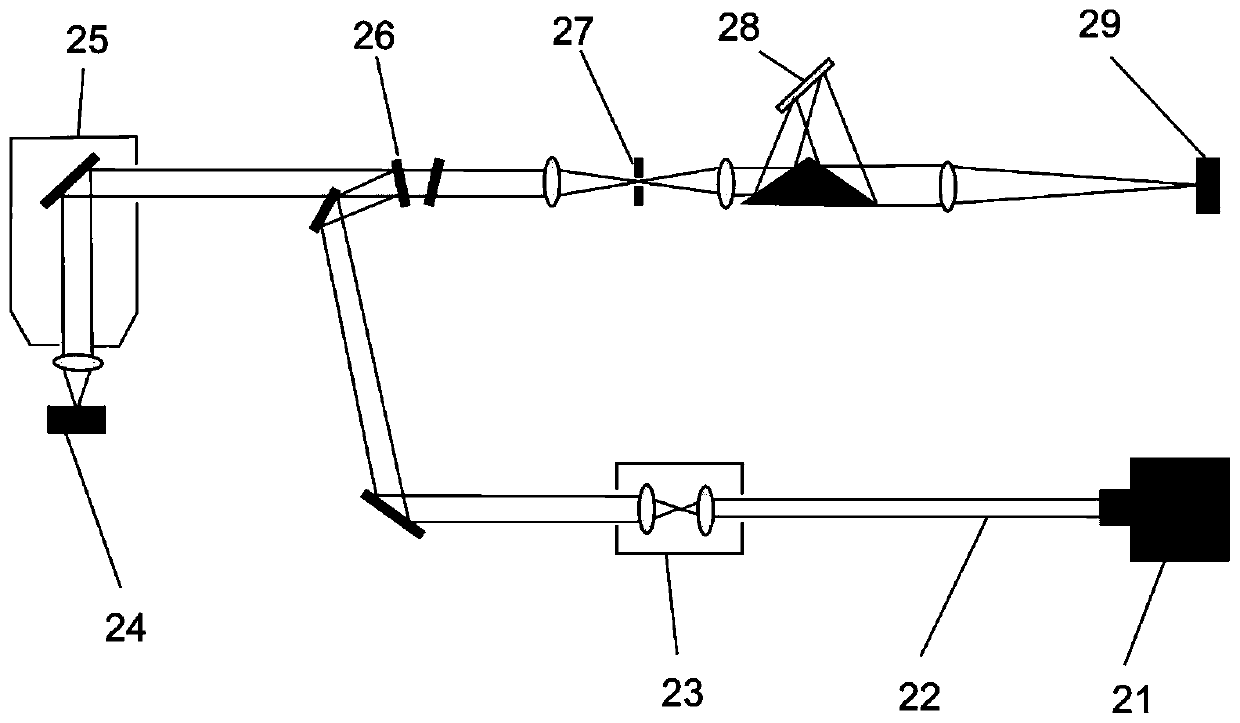
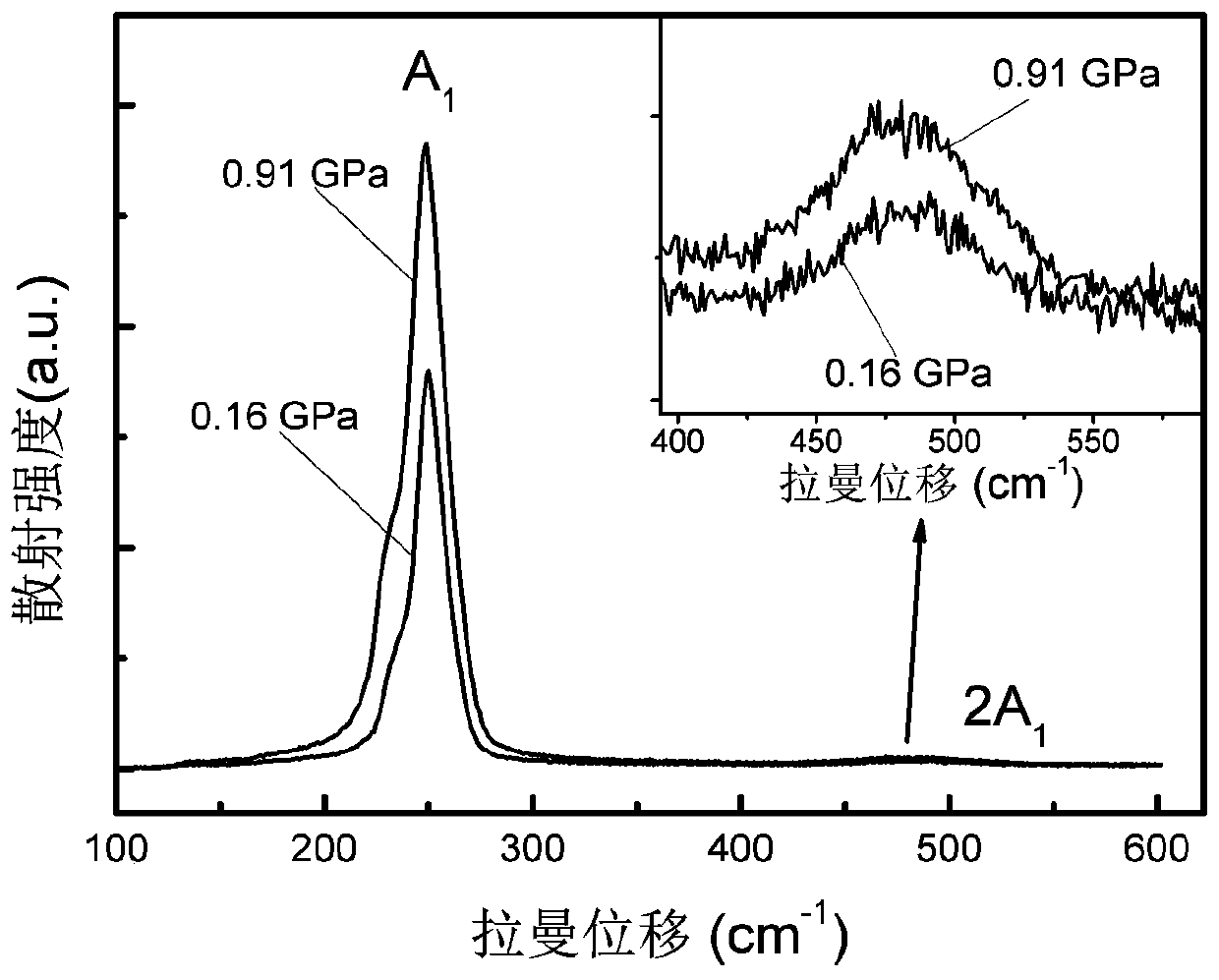
Method for detecting electroneutral defect state of amorphous selenium
InactiveCN111239098AHigh feasibilityEfficient detectionRaman scatteringAmorphous seleniumSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to a method for detecting the electroneutral defect state of amorphous selenium, which belongs to the field of physical property detection of semiconductor materials, and particularly comprises the following steps: S1, loading an amorphous selenium sample into a diamond anvil cell pressing cavity, and applying pressure to the sample; S2, measuring Raman scattering signals ofamorphous selenium under different pressures; and S3, determining the defect state energy level by analyzing the change of the Raman scattering intensity along with the pressure. The method provided by the invention is high in feasibility, simple and feasible, can effectively detect the electrically neutral defect state of the amorphous selenium caused by dihedral angle distortion, and can accurately determine the defect state energy level and the change relationship of the defect state energy level with the pressure.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method and apparatus for a lateral radiation detector
ActiveUS8836069B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous seleniumPhotovoltaic detectors
A lateral Metal-Semiconductor-Metal (MSM) Photodetector (PD) is based on amorphous selenium (a-Se). It has low dark current, high photoconductive gain towards short wavelengths, and high speed of operation up to several KHz. From processing point of view, a lateral structure is more attractive due to ease of fabrication as well as compatibility with conventional thin-film transistor (TFT) processes. The lateral a-Se MSM PD therefore has potentials in a variety of optical sensing applications particularly in indirect X-ray imaging utilizing scintillators and ultraviolet (UV) imaging for life sciences.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
Photoconductor for electrophotography
InactiveUS6045958AHigh sensitivityDegrading preservabilityElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeAmorphous seleniumElectrical conductor
A first selenium-arsenic layer of a photoconductor, deposited on a conductive substrate, has a thickness and arsenic concentration effective to preserve an electrically charged surface potential in darkness and to transport carriers generated on exposure to light. The first layer is between 20 to 70 mu m thick. A second amorphous selenium-arsenic alloy layer, formed on the first layer, generates carriers on exposure to light. The surface roughness, Rmax., of the conductive substrate is less than or equal to 0.5 mu m. The first layer, or both of the photoconductive layers, are doped with iodine. When both layers contain iodine, the iodine content of the second layer is equal to or less than that of the first layer. The thickness of the second layer is between 5 to 30 mu m. The arsenic content of the amorphous selenium-arsenic alloy of the second layer is equal to or greater than that in the first layer. After deposition of the first and second layers, the photoconductor is heat treated at between 100 DEG to 200 DEG for 30 to 80 minutes. In a further embodiment the first layer of the photoconductor has an arsenic content in the range of 10 to 45 wt %. The second layer arsenic content is in the range of 25 to 45 wt %.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Preparation method of selenium selenide thin film with certain forbidden band width
ActiveCN110349836AFast heating rateImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationAmorphous seleniumOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a preparation method of a selenium selenide thin film with a certain forbidden band width. The forbidden band width of the selenium selenide thin film is 1.14-1.79 eV. The method adopts a near-space sublimation method, and comprises two steps of preparing an amorphous selenium selenide thin film and annealing the amorphous selenium selenide thin film. The selenium selenidefilm can be used for constructing a laminated selenide thin film solar cell so as to improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the selenium selenide thin film solar cell.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
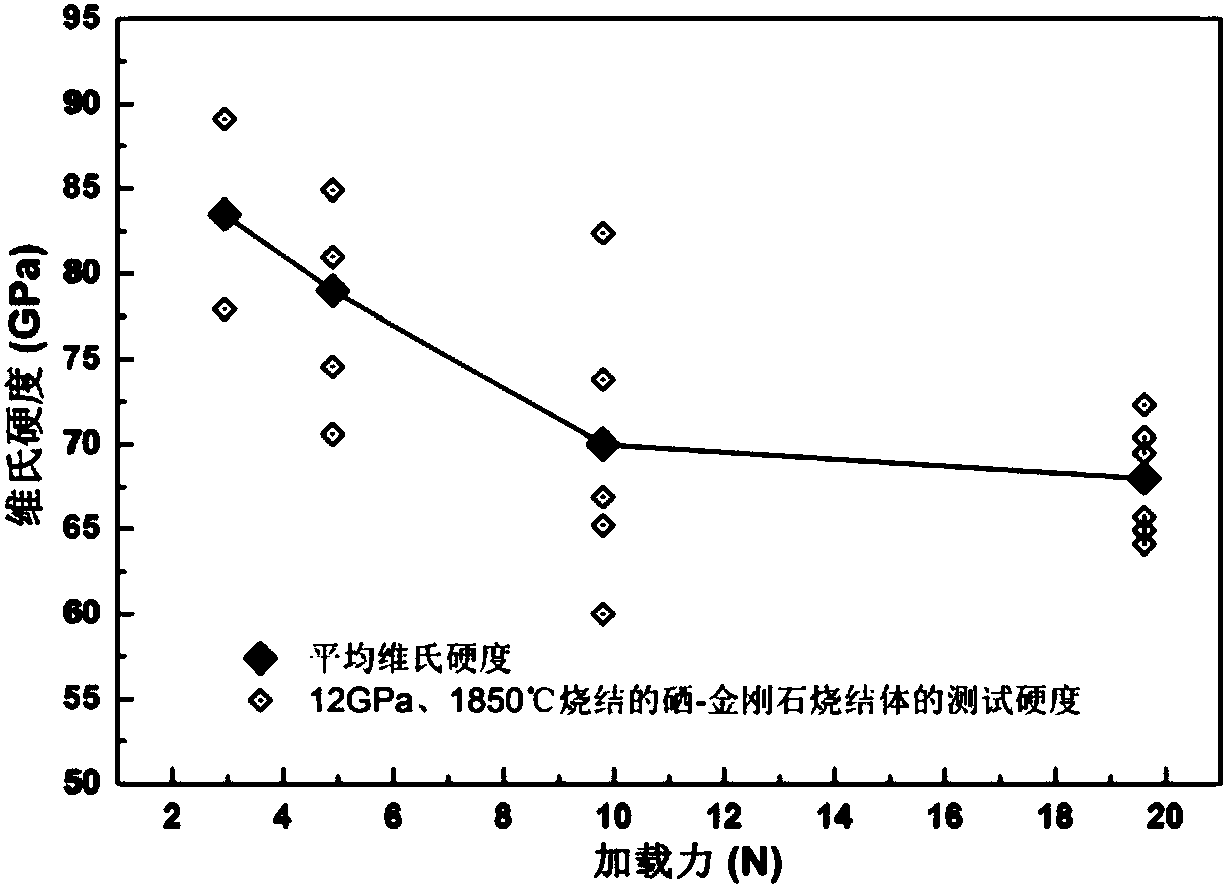
Polycrystalline diamond sintering body of selenium catalyst and preparation method thereof
A polycrystalline diamond sintering body of selenium catalyst and a preparation method thereof relates to the technical field of ultra-hard materials. The preparation method includes the steps of: mixing 31.59-34.047 weight parts of micron diamond powder and 1.473-4.79 weight parts of micron selenium powder, grinding the mixed powder until the selenium powder becomes amorphous selenium powder; placing the mixed powder in a mold, and shaping the powder at room temperature under pressure of 5-20 MPa to form a green body; sintering and curing the green body under 6.5-12.5 GPa at sintering temperature of 1500-1900 DEG C. The preparation method is simple and can be used for preparing the high-hardness polycrystalline diamond sintering body.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Light-shielding detector flat plate
InactiveCN103743418AShadingPhenomenon that prevents exposureConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyAmorphous seleniumOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a light-shielding detector flat plate comprising a light-shielding layer and a raw material layer. The light-shielding layer is formed by light-shielding glass. The upper layer of the raw material layer is an electrode plate for arranging a bias voltage; the next layer is an amorphous selenium material plate; the following layer is a charge collection electrode plate; and the lowest layer is a charge reading circuit board. The light-shielding layer is installed on the upper and lower surfaces of the raw material layer through glass cement. Through the above method, the light-shielding detector flat plate is capable of effectively shielding light from irradiating on the plane, preventing exposure phenomenon, which leads to non-accuracy of a device and even damage to the device, from happening to the plane.
Owner:江苏龙信电子科技有限公司
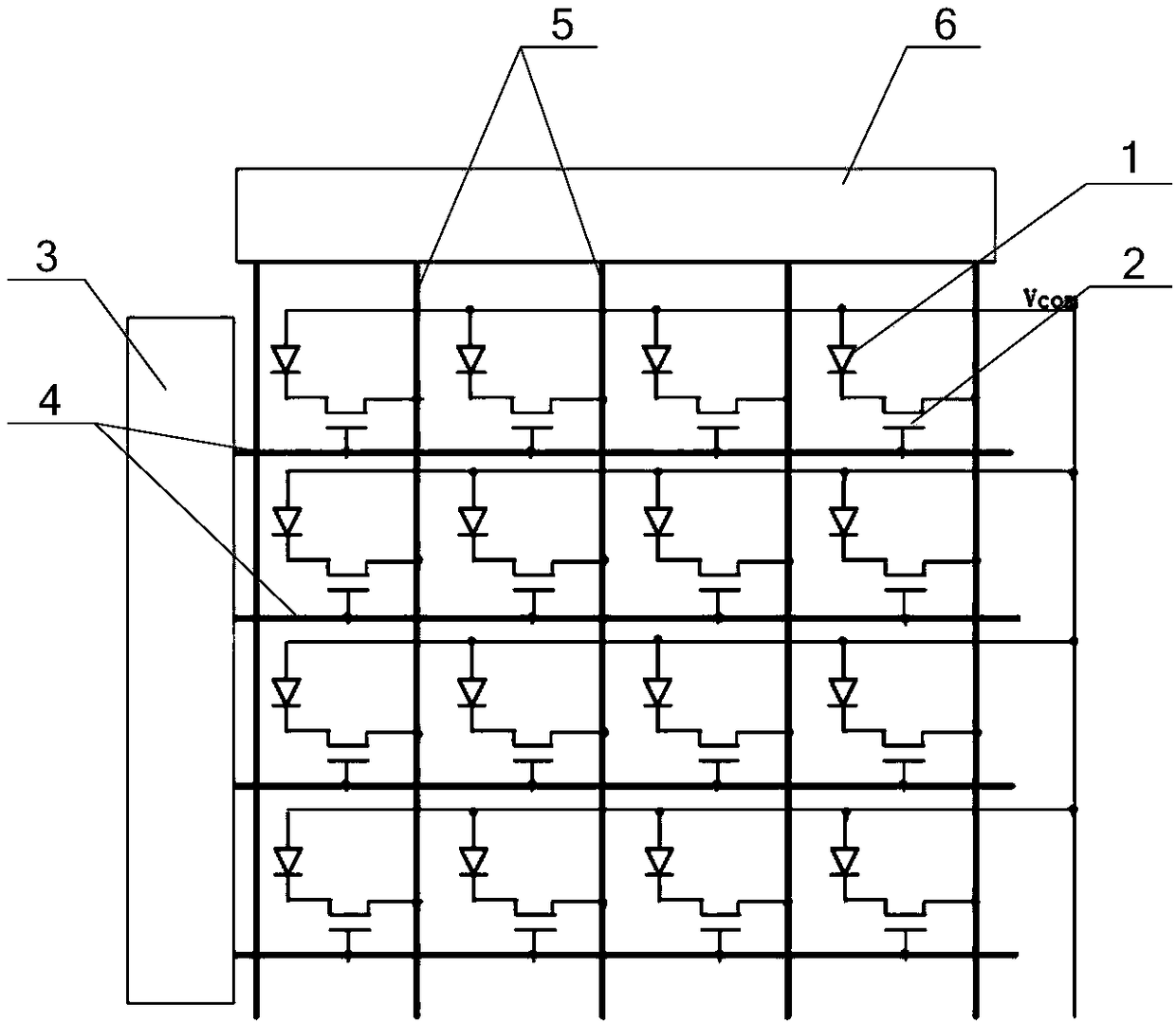
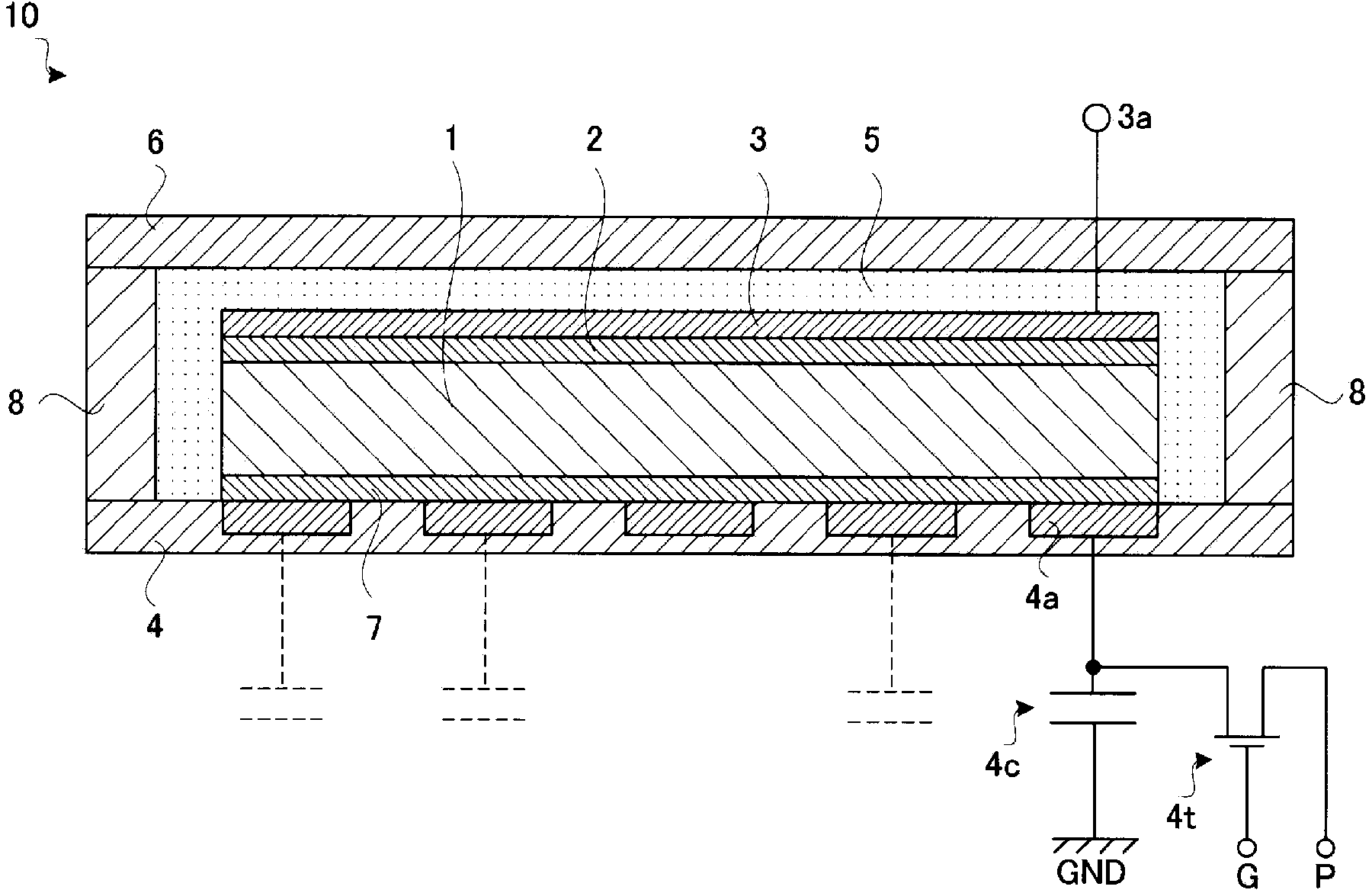
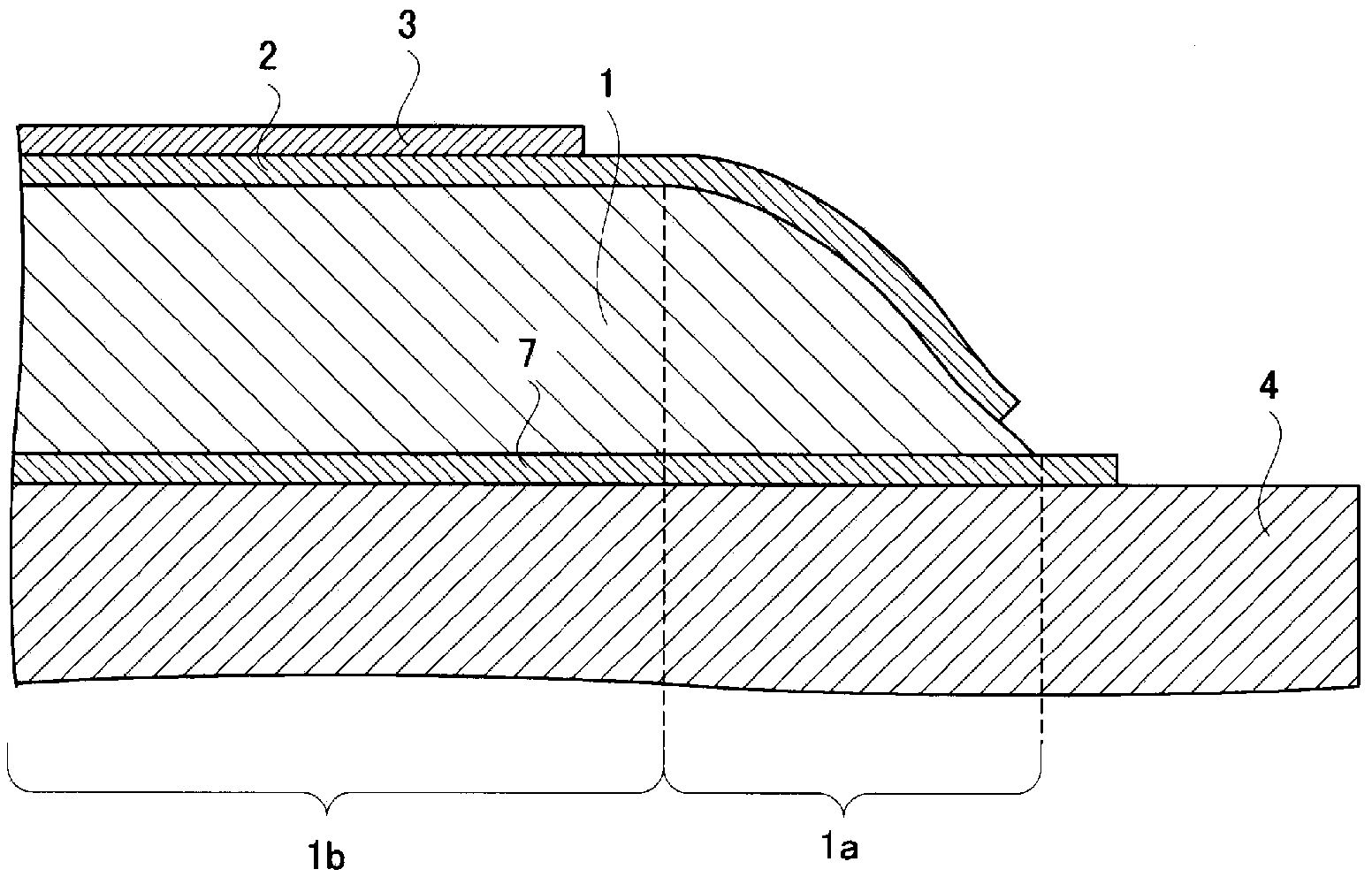
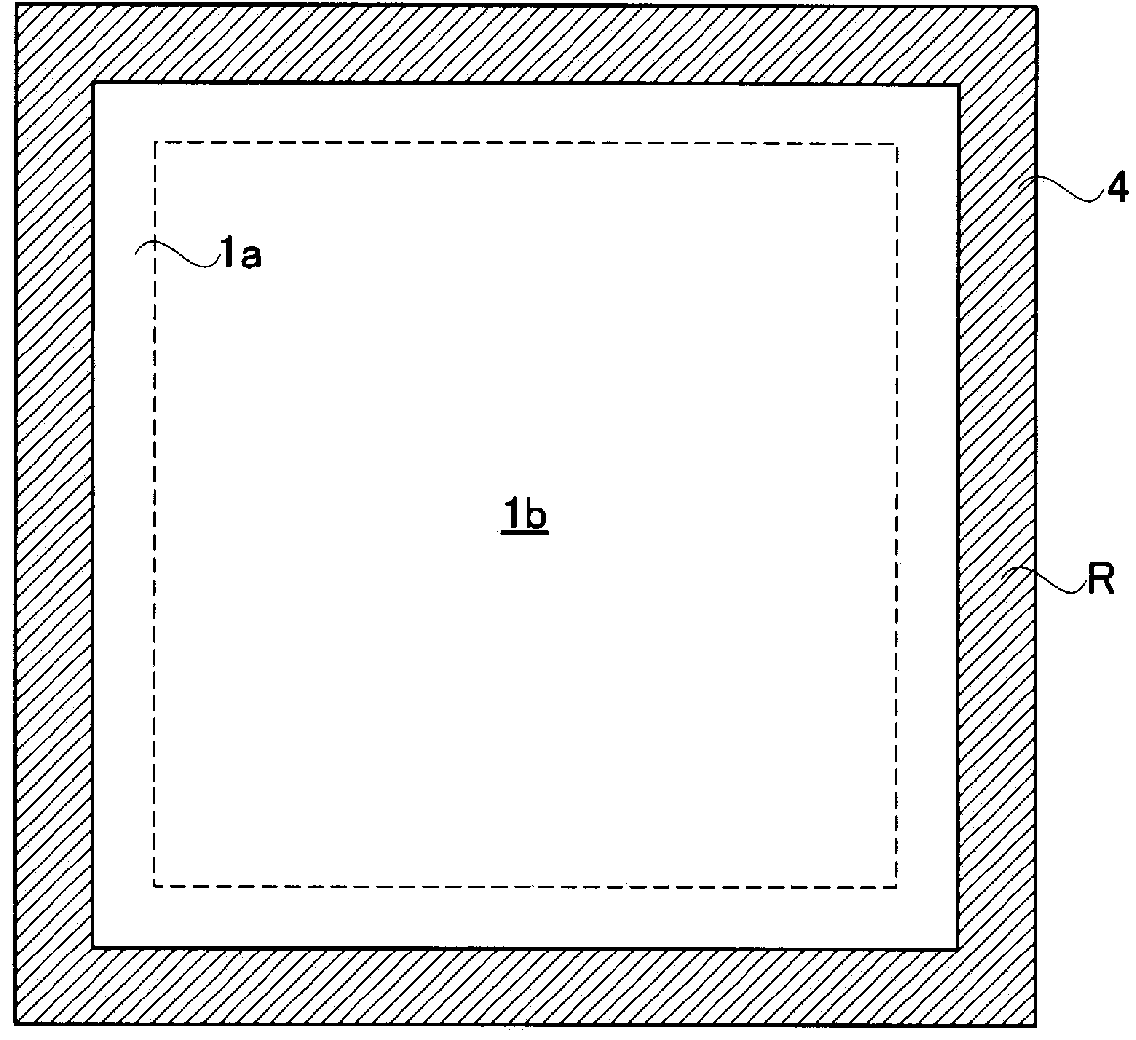
Radiation detector
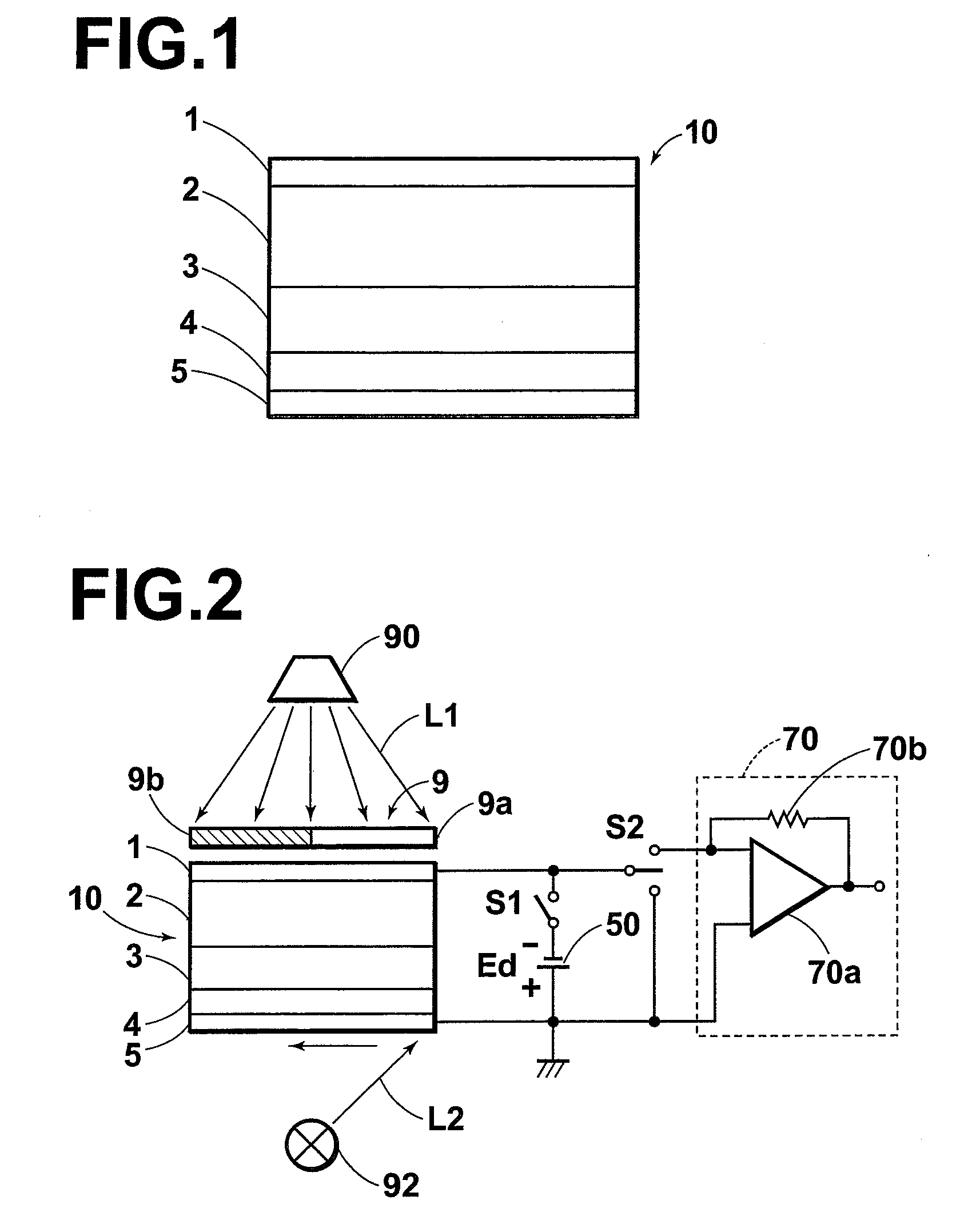
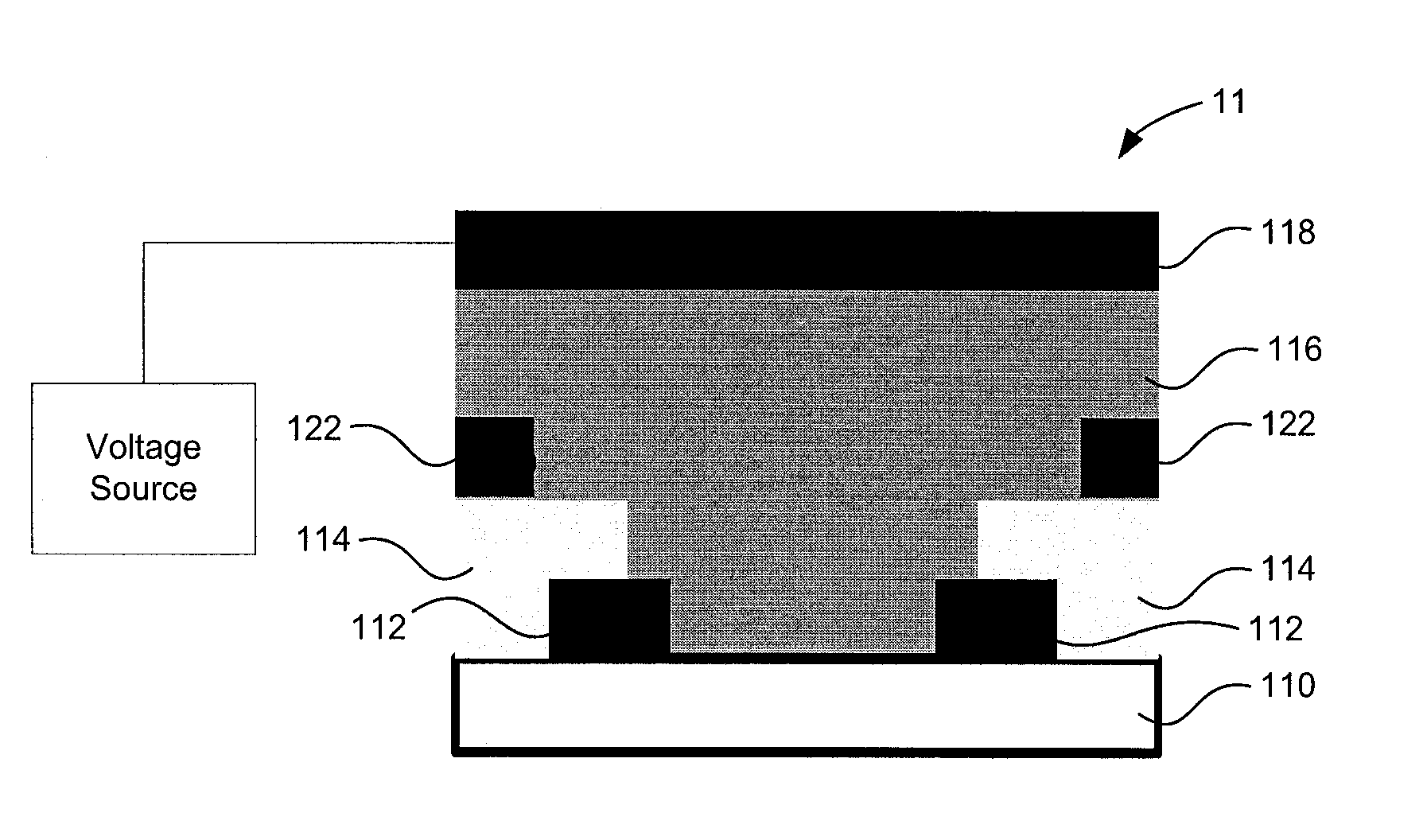
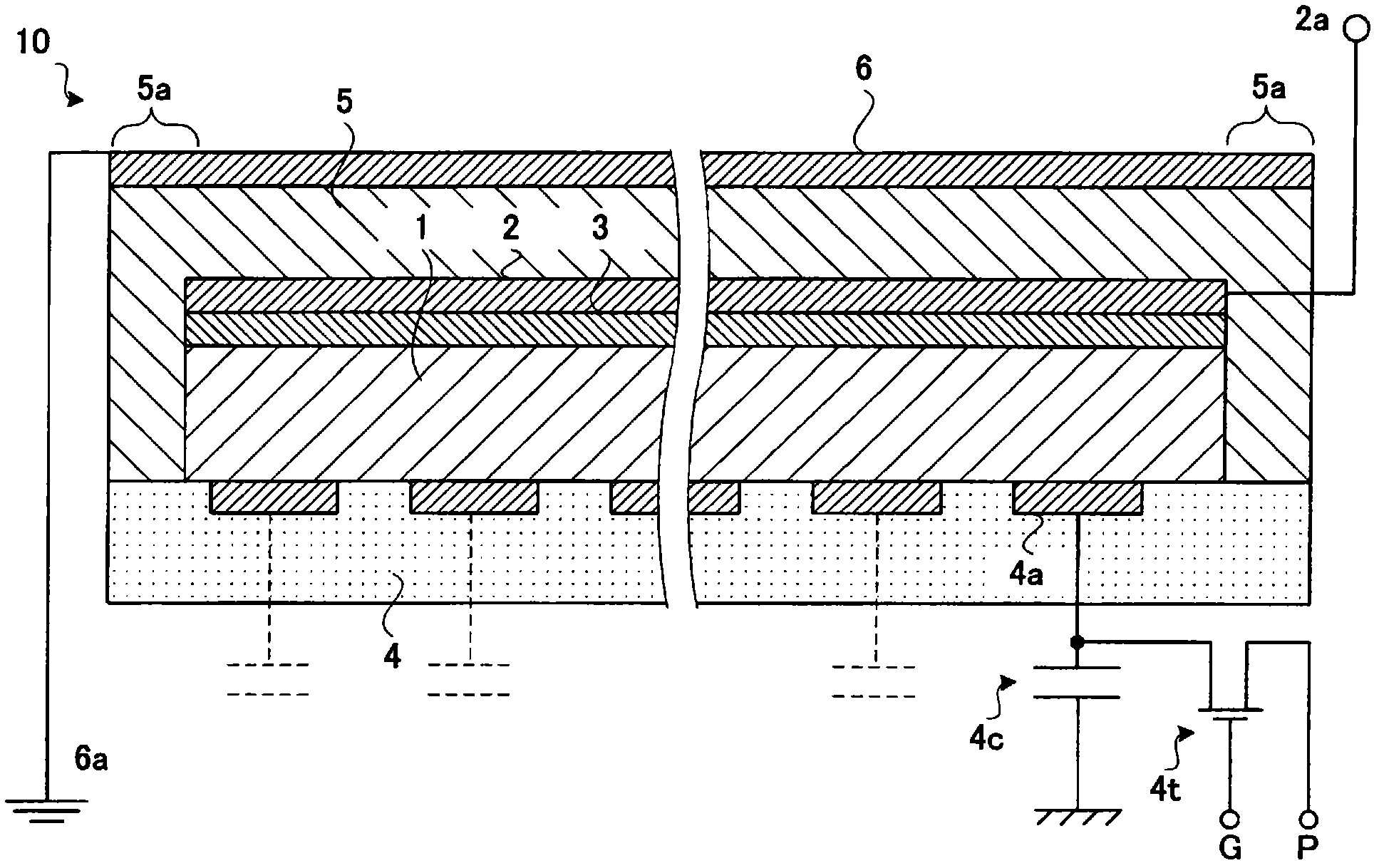
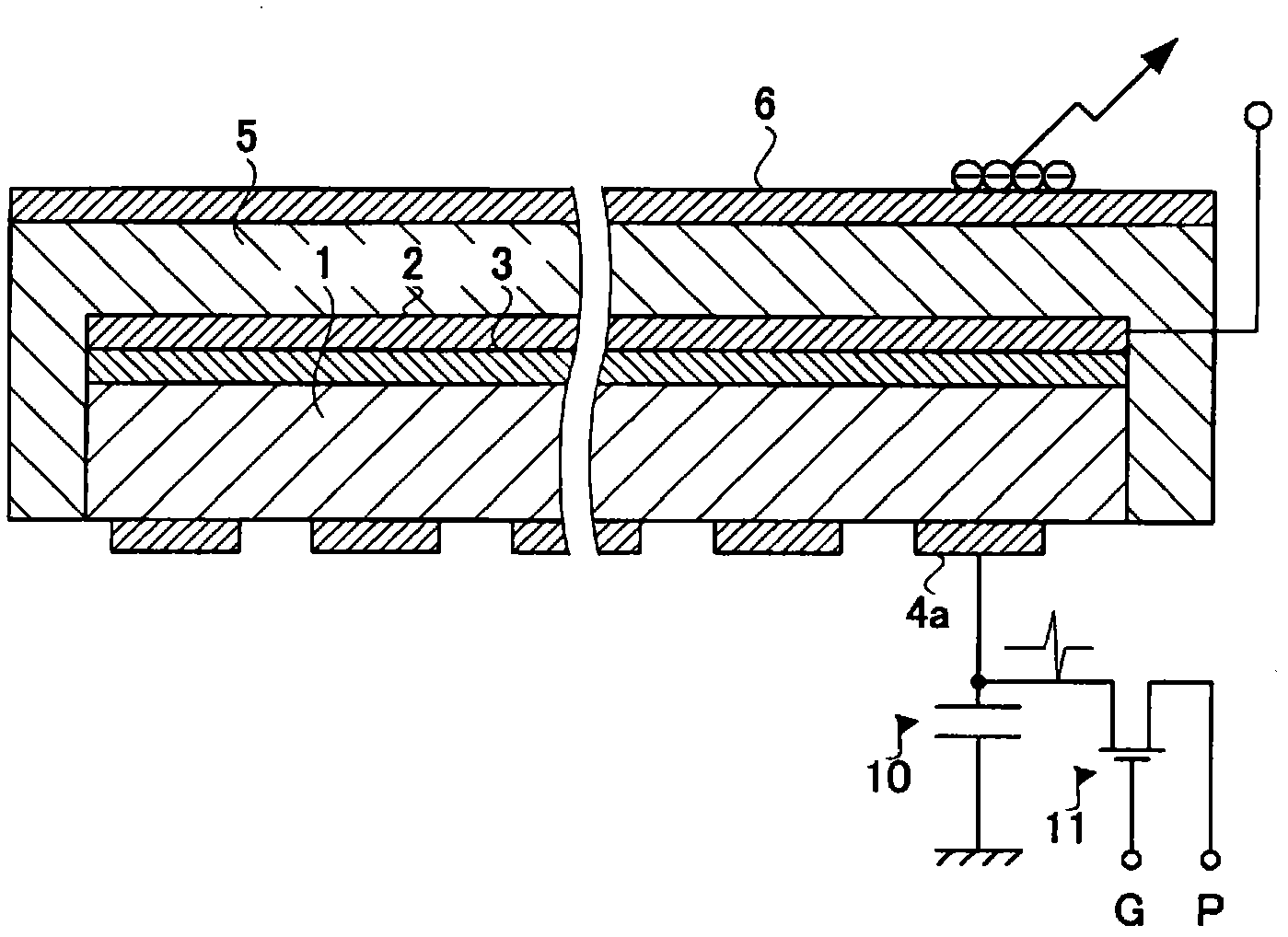
InactiveCN103534808AAvoid defectsShort circuit will notSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesElectricityAmorphous selenium
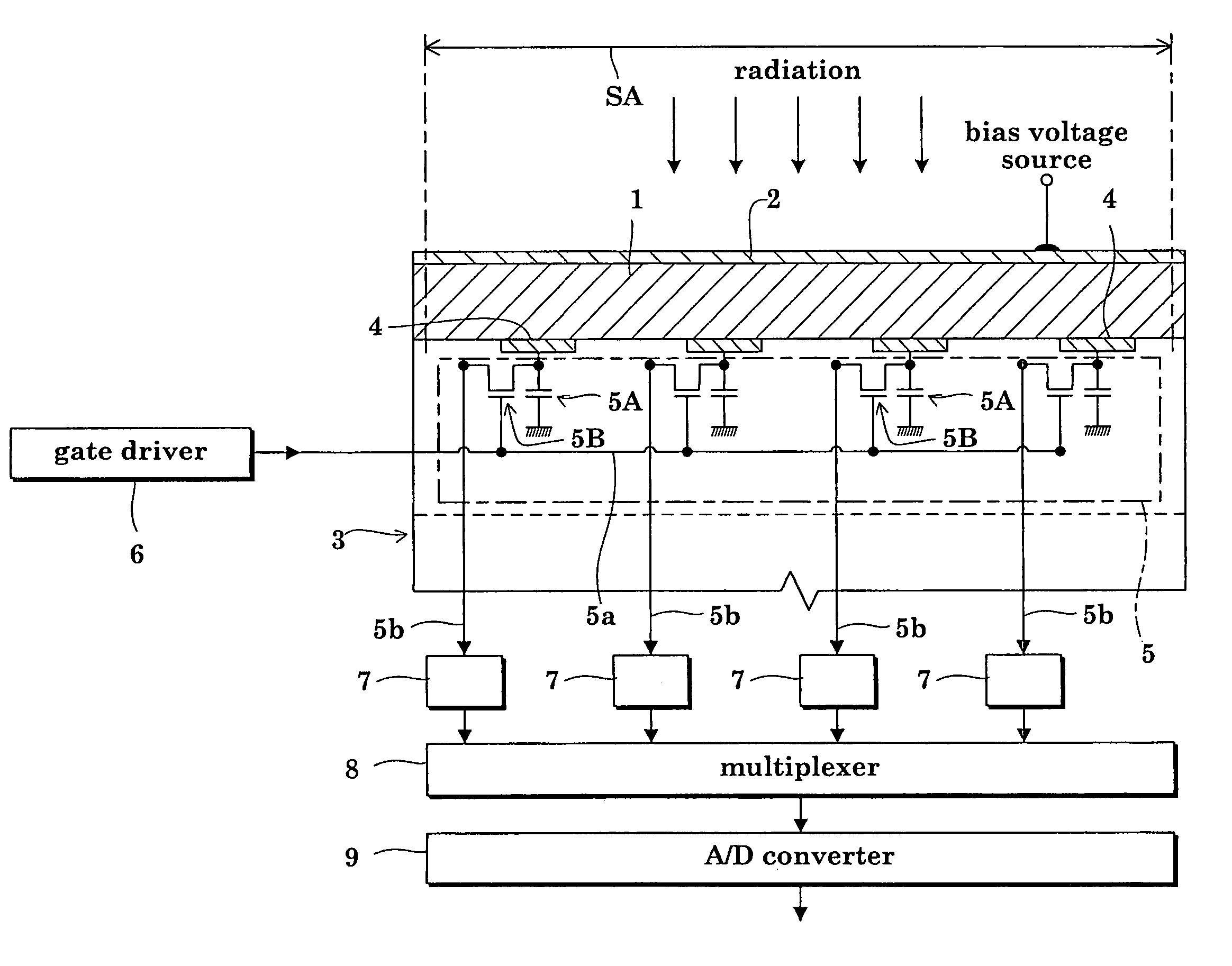
Provided is a radiation detector that prevents shorting of electrical wirings that intersect with an inter-layer insulating layer there between, and wherein the occurrence of detector element failure is suppressed. By means of the present configuration, an amorphous selenium layer (1) and the electrical wiring of an active matrix substrate (4) are contrived in a manner so as to not short. Namely, the electrical wiring is provided to the position at which the layer thickness of the amorphous selenium layer (1) is covered by a thick central portion. As a result, the electrical wiring is reliably isolated from an electrode layer, and so it is possible to provide a radiation detector that can withstand long-term use.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Radiation detector, and radiation imaging device provided with same
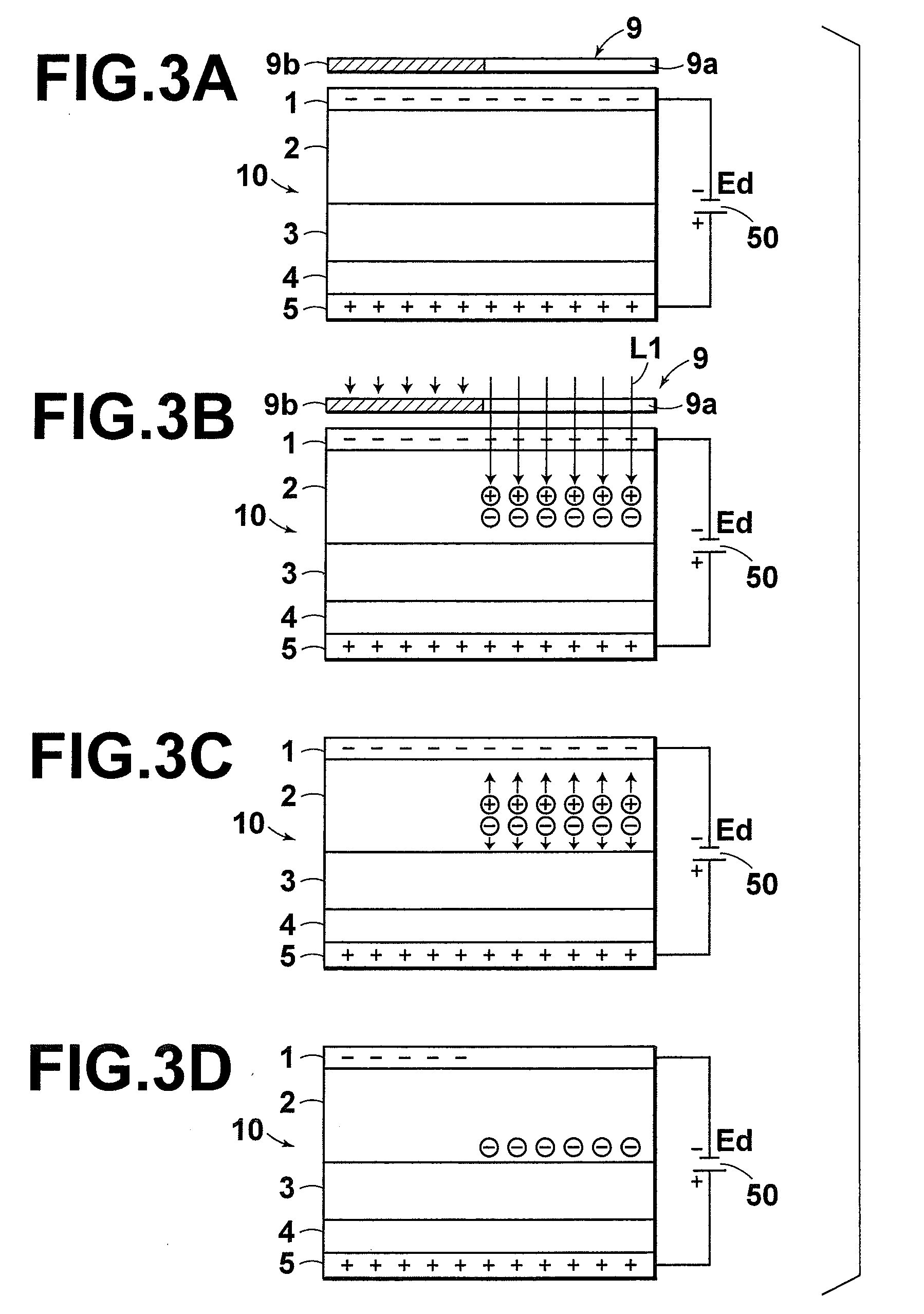
InactiveCN102369458AReduce failureSolid-state devicesRadiation intensity measurementHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a radiation detector and a radiation imaging device provided with the same. The disclosed configuration comprises an active matrix substrate (4), an amorphous selenium layer (1), a high resistance layer (3), a gold electrode layer (2), an insulating layer (5), and an auxiliary plate (6), layered in the given order. In order to provide a radiation detector wherein an electric load does not accumulate at the auxiliary plate (6), and the formation of voids and pinholes in an amorphous semiconducting layer or a carrier-selective high resistance film (3) is prevented, in embodiment 1, an inorganic anion exchange body is added to the insulating layer (5). As the inorganic anion exchange body adsorbs chloride ions that are within the insulating layer (5), it is possible to prevent failure of an X-ray detector (10) caused by chloride ions being drawn to the gold electrode layer (2).
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
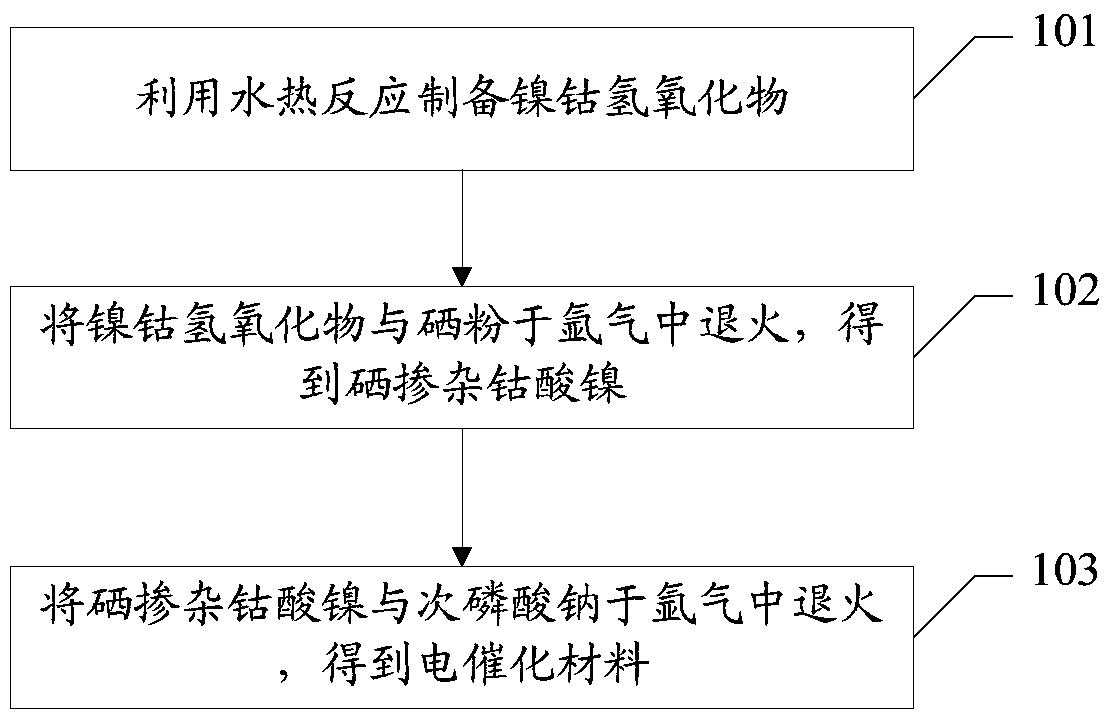
Preparation method of electro-catalytic material, electro-catalytic material and application of electro-catalytic material
PendingCN110732333AHigh activityIncrease exposurePhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesElectrolytic agentPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of an electrocatalytic material, the electrocatalytic material and application of the electrocatalytic material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing nickel-cobalt hydroxide by utilizing a hydrothermal reaction; annealing the nickel-cobalt hydroxide and selenium powder in argon to obtain selenium-doped nickel cobaltate; annealing the selenium-doped nickel cobaltate and sodium hypophosphite in argon to obtain the electro-catalytic material; an amorphous selenium and phosphorus double-doped nickel cobaltate material is prepared by the preparation method; the material has a three-dimensional amorphous structure; the active sites are greatly increased, exposure of the active sites is facilitated, the electrocatalytic material has good activity in HER and OER reactions of electrolyzing water in an alkaline electrolyte, and meanwhile, the electrocatalytic material is used as a cathode catalyst and an anode catalyst to fully decompose water, and only 1.54 V voltage is needed for driving an electrolytic cell to generate 10mA / cm < 2 > current density.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Radiation detector
ActiveUS7947970B2High charge transport performanceImprove hole transport abilityX-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous seleniumOptoelectronics
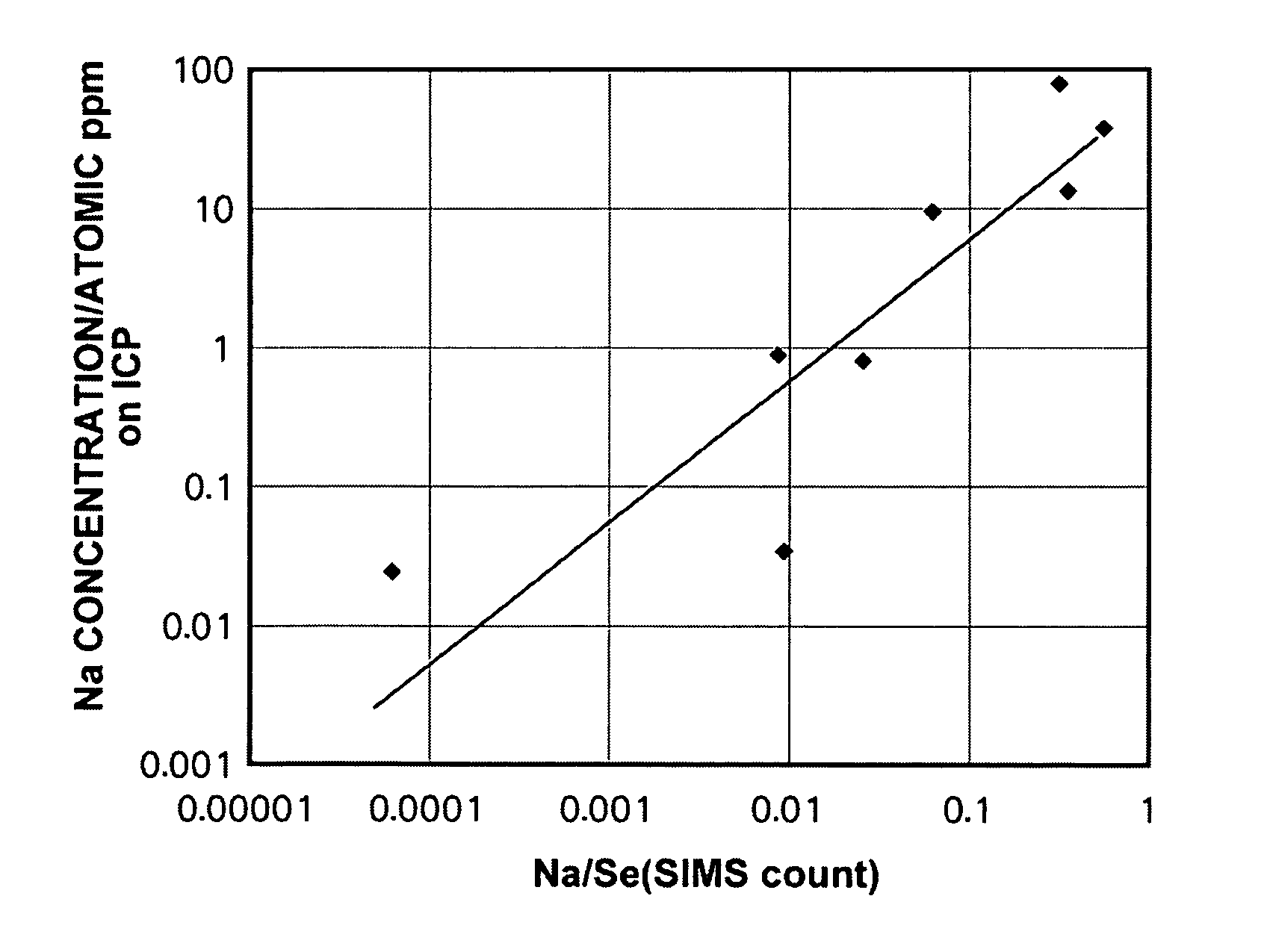
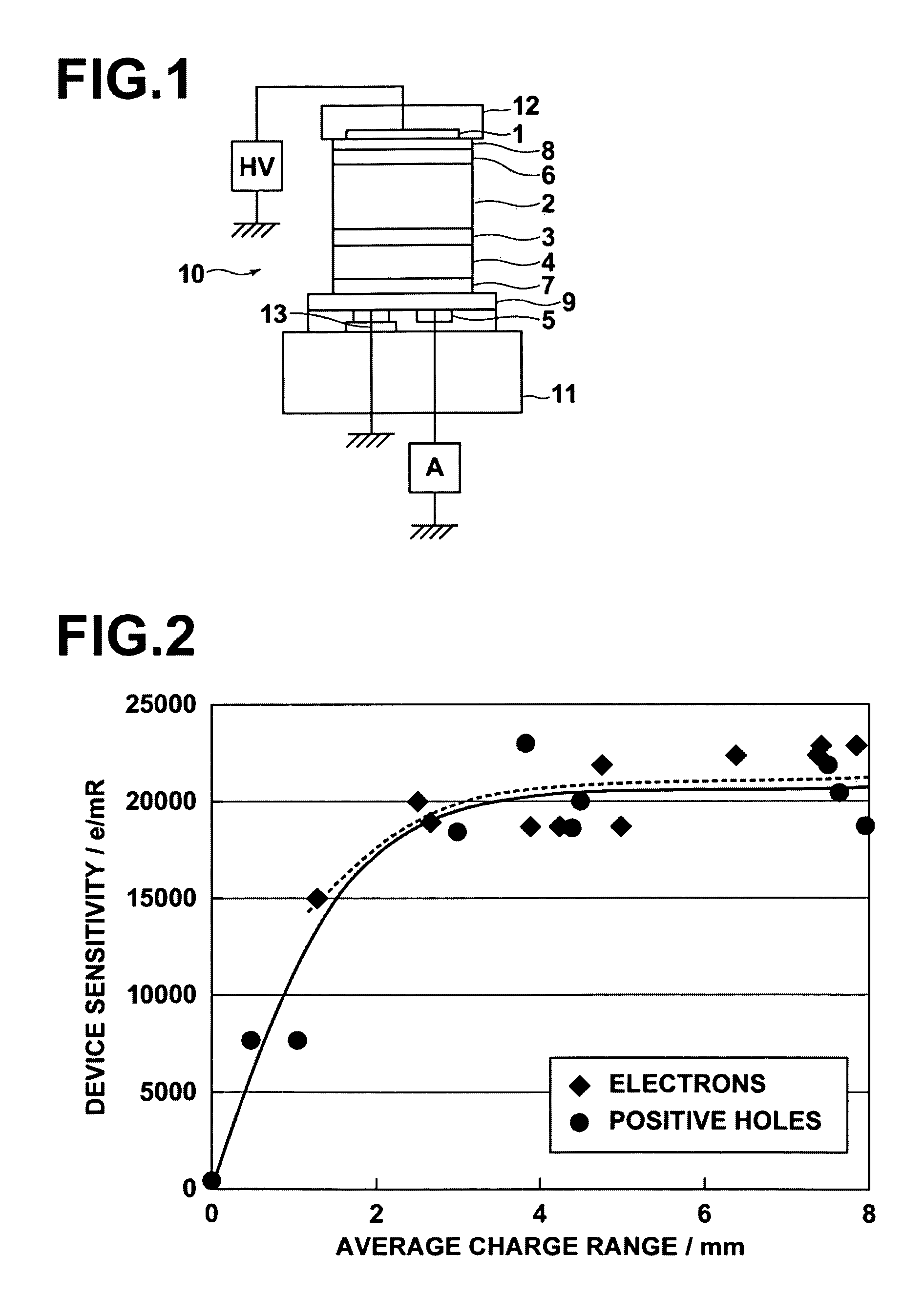
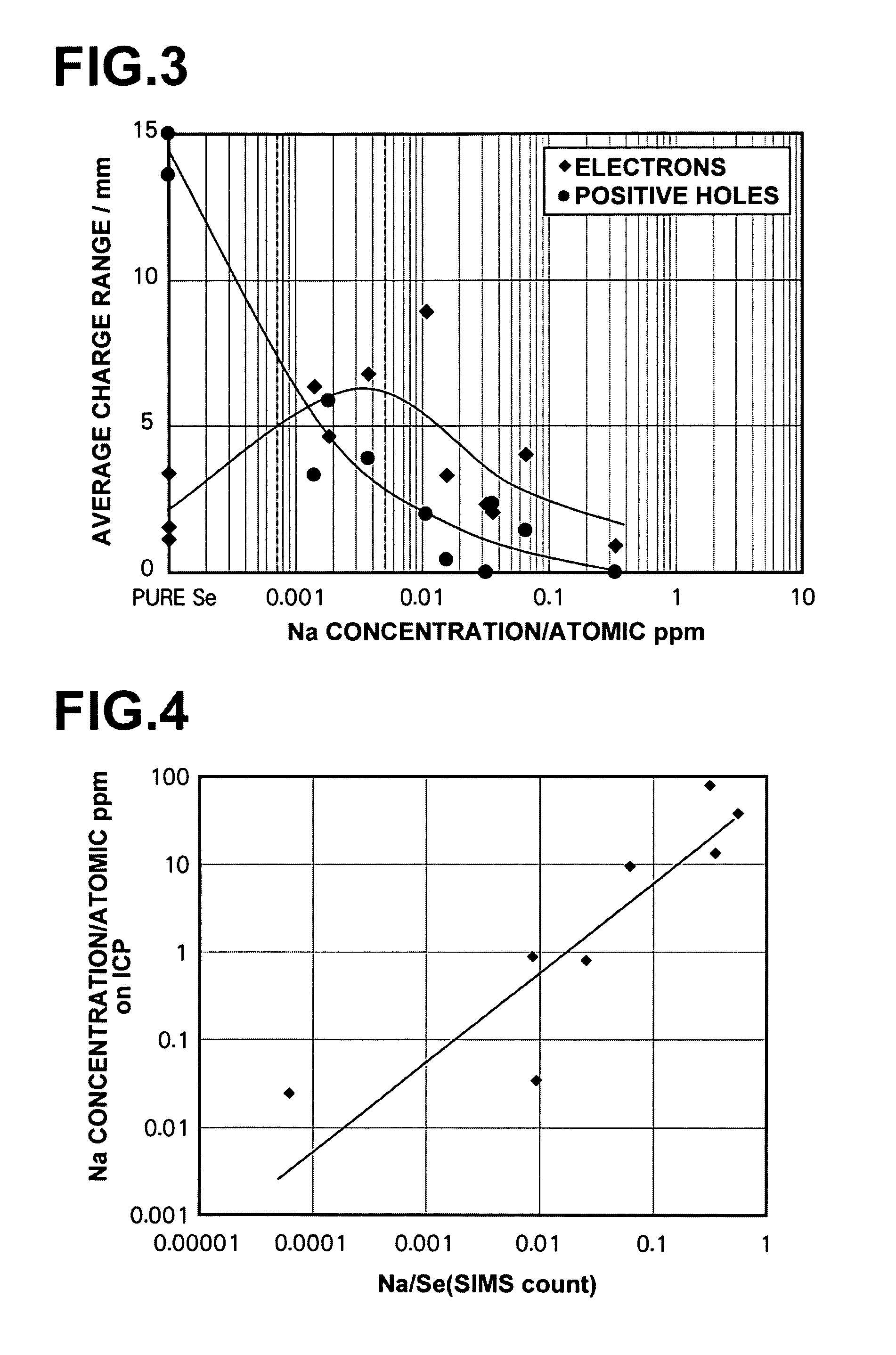
A radiation detector is constituted by: a recording photoconductive layer; and electrodes provided on both sides of the photoconductive layer. Electric charges, which are generated within the recording photoconductive layer when radiation is irradiated thereon while a predetermined biasing voltage is being applied between the electrodes, are read out as electric signals. The recording photoconductive layer is formed by amorphous selenium that contains alkali metal elements within a range from 0.0007 atomic ppm to 0.0035 atomic ppm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiation detector
InactiveUS7233003B2Improve adhesionSuppress generationMeasurement with semiconductor devicesPhotometryAmorphous seleniumDeposition temperature
The radiation detector according to this invention has a common electrode for bias voltage application formed on a surface of an amorphous selenium semiconductor film (a-Se semiconductor film) sensitive to radiation. The common electrode is a gold thin film having a thickness in a range of 100 to 1,000 Å. The gold thin film acting as the common electrode may be formed on the surface of the a-Se semiconductor film at a relatively low vapor deposition temperature and in a reduced vapor deposition time. This feature suppresses a generation of defects in the a-Se semiconductor film due to formation of the common electrode. The gold thin film for the common electrode is not so thick as in the prior art, but is 1,000 Å or less. With the reduced thickness, the common electrode has improved boding property with respect to the a-Se semiconductor film.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com