Patents
Literature
101 results about "Silicon detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silicon Detectors. Through the photovoltaic effect, detectors provide a means of transforming light energy to an electrical current. The root of the theory behind this phenomenon is a small energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the detector.
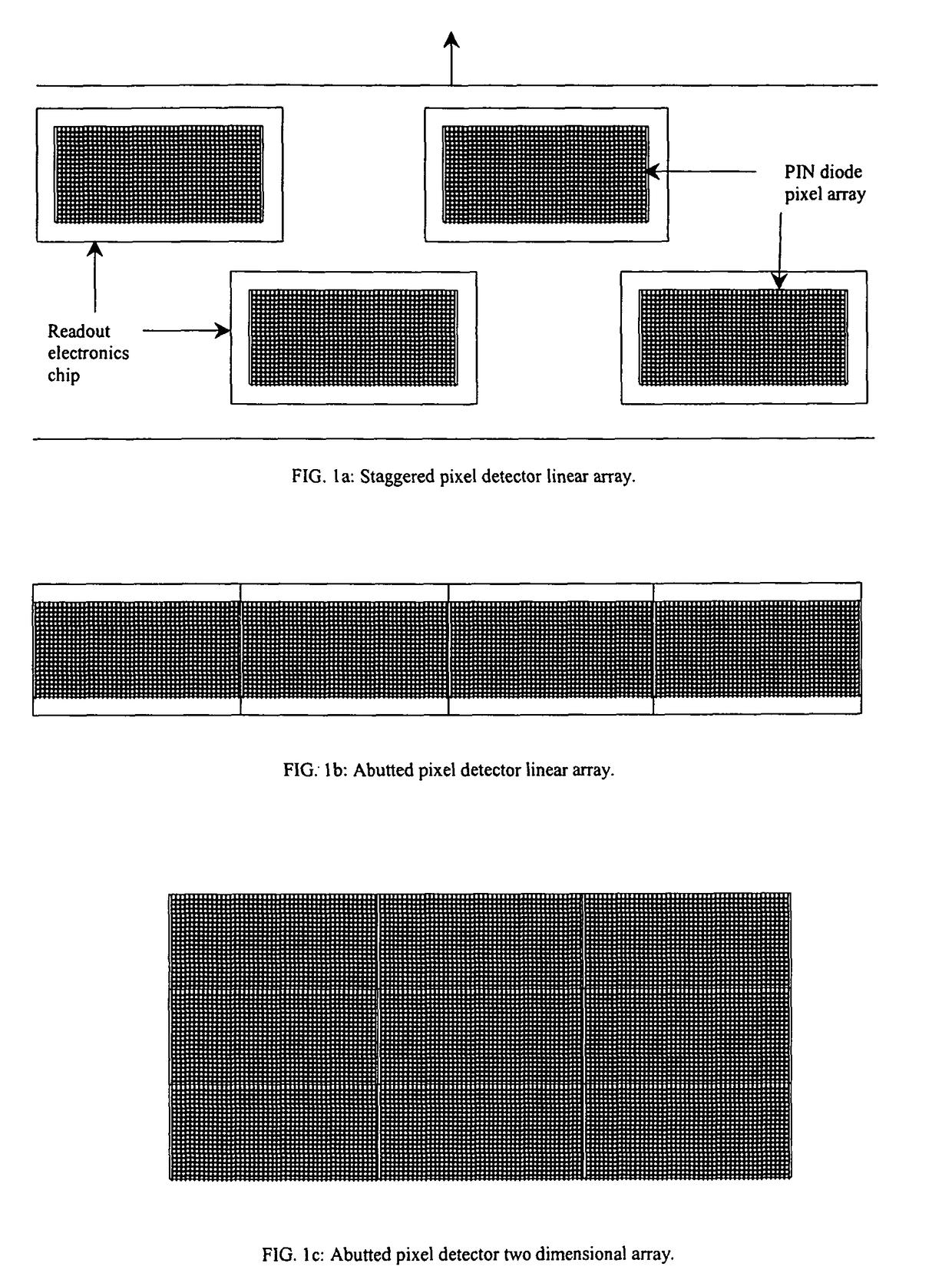
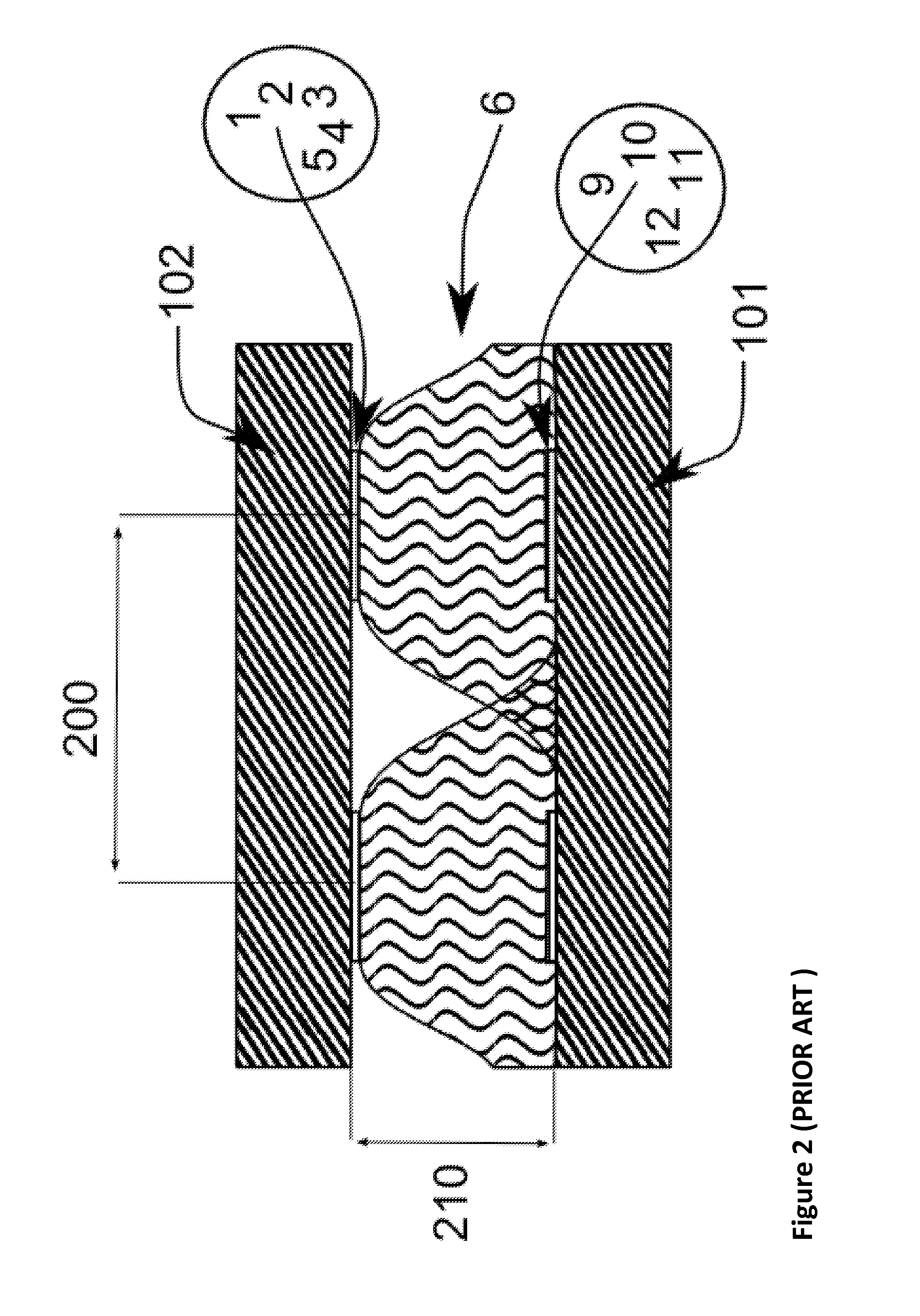
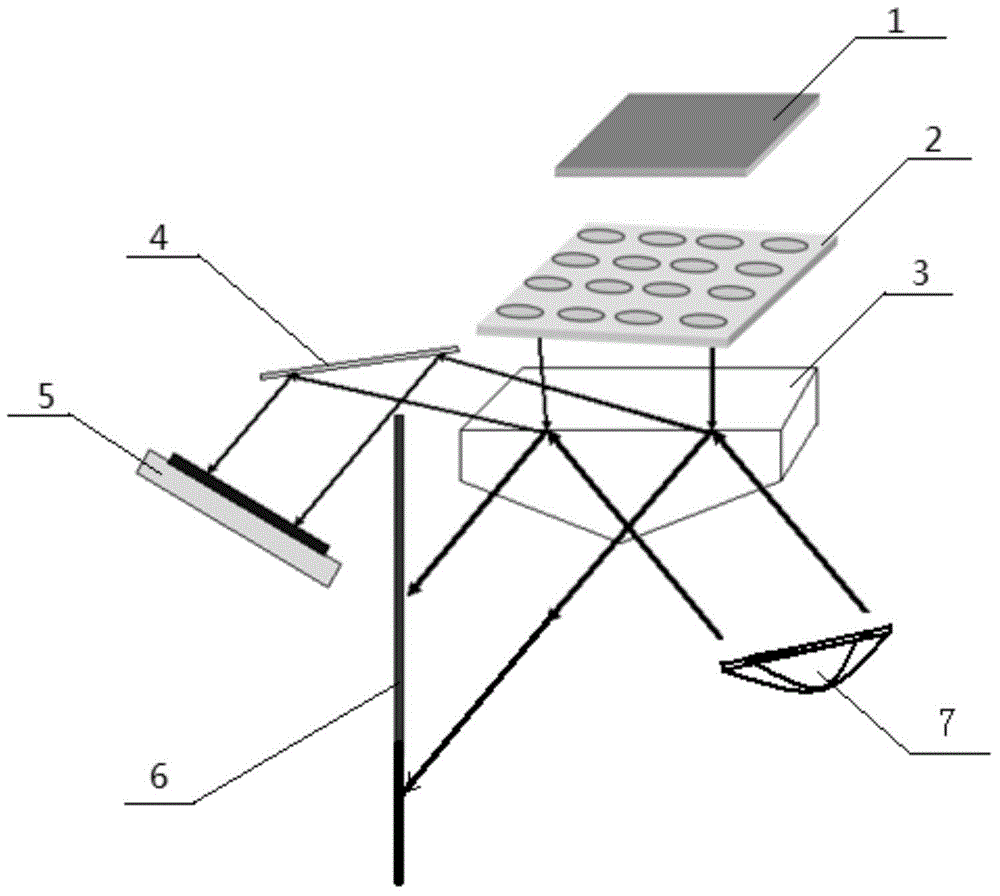
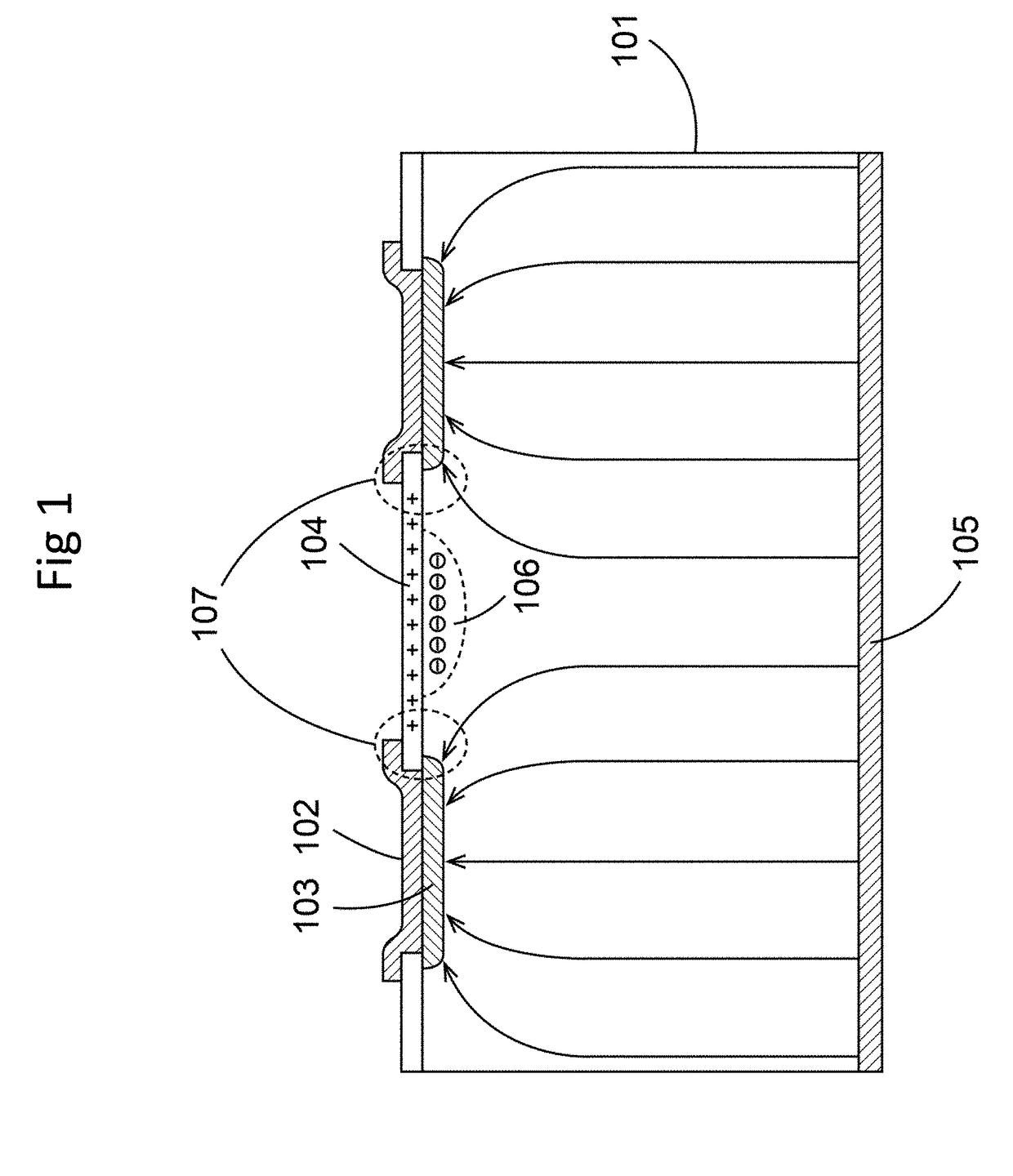
Silicon detector assembly for x-ray imaging
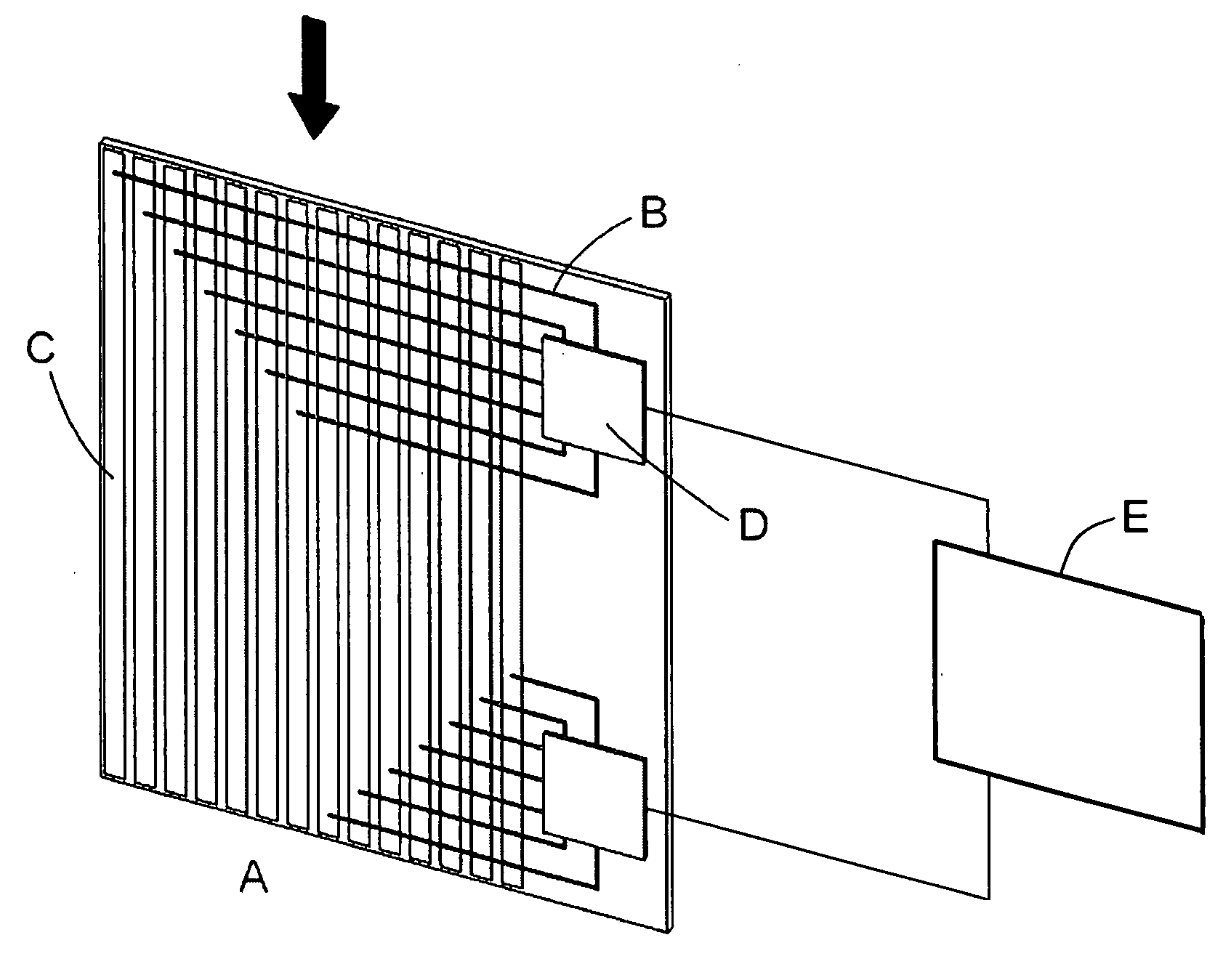
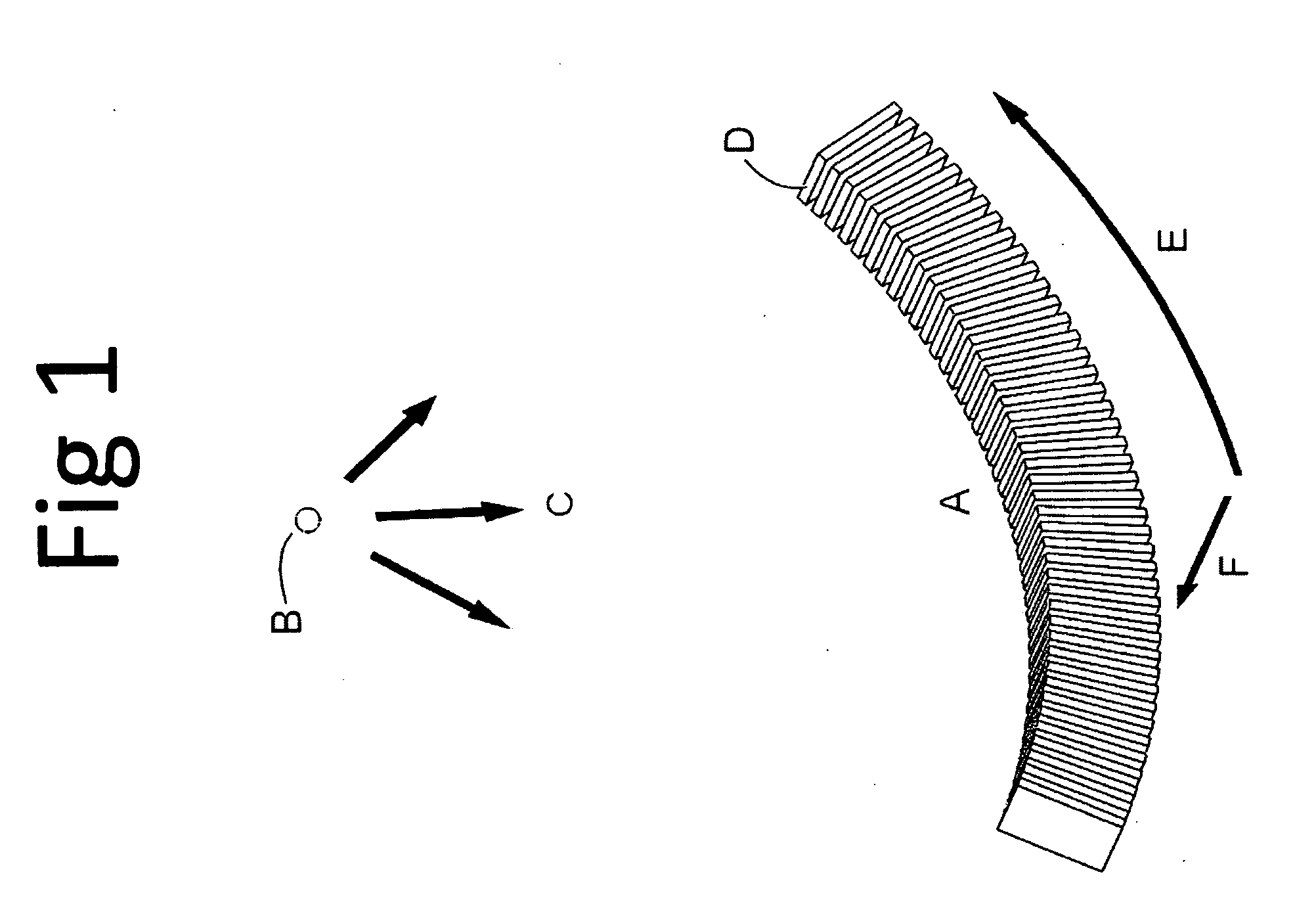
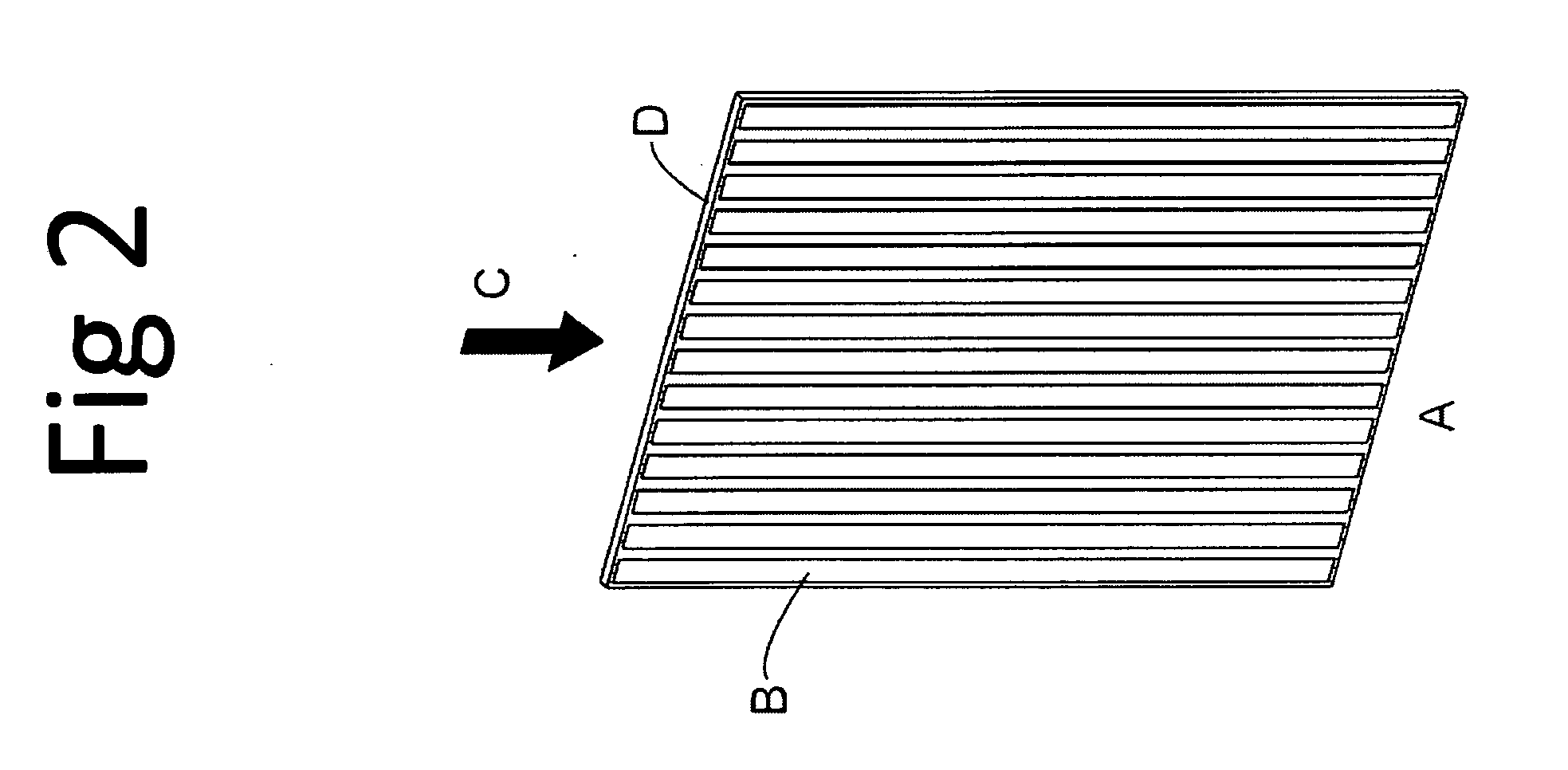
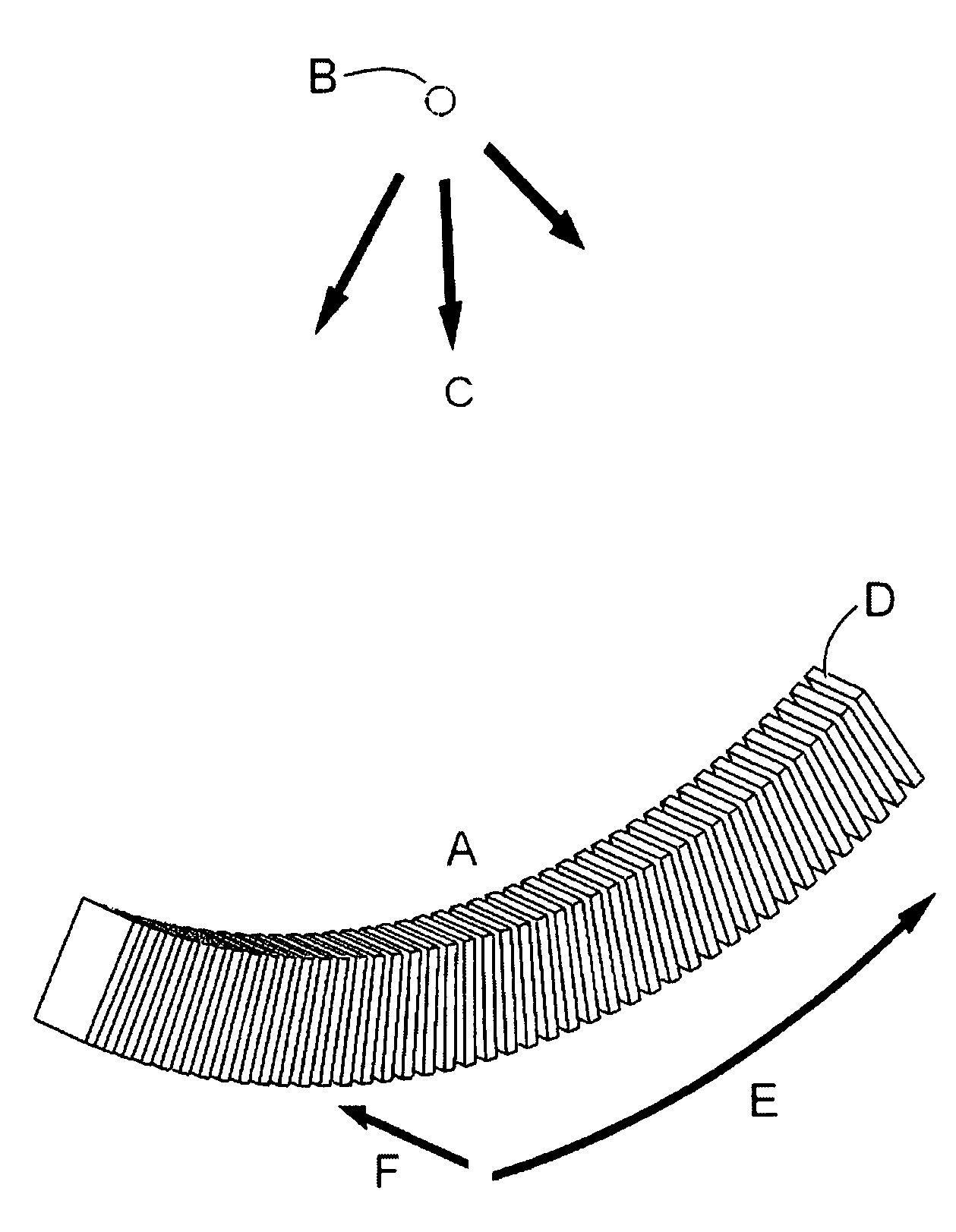
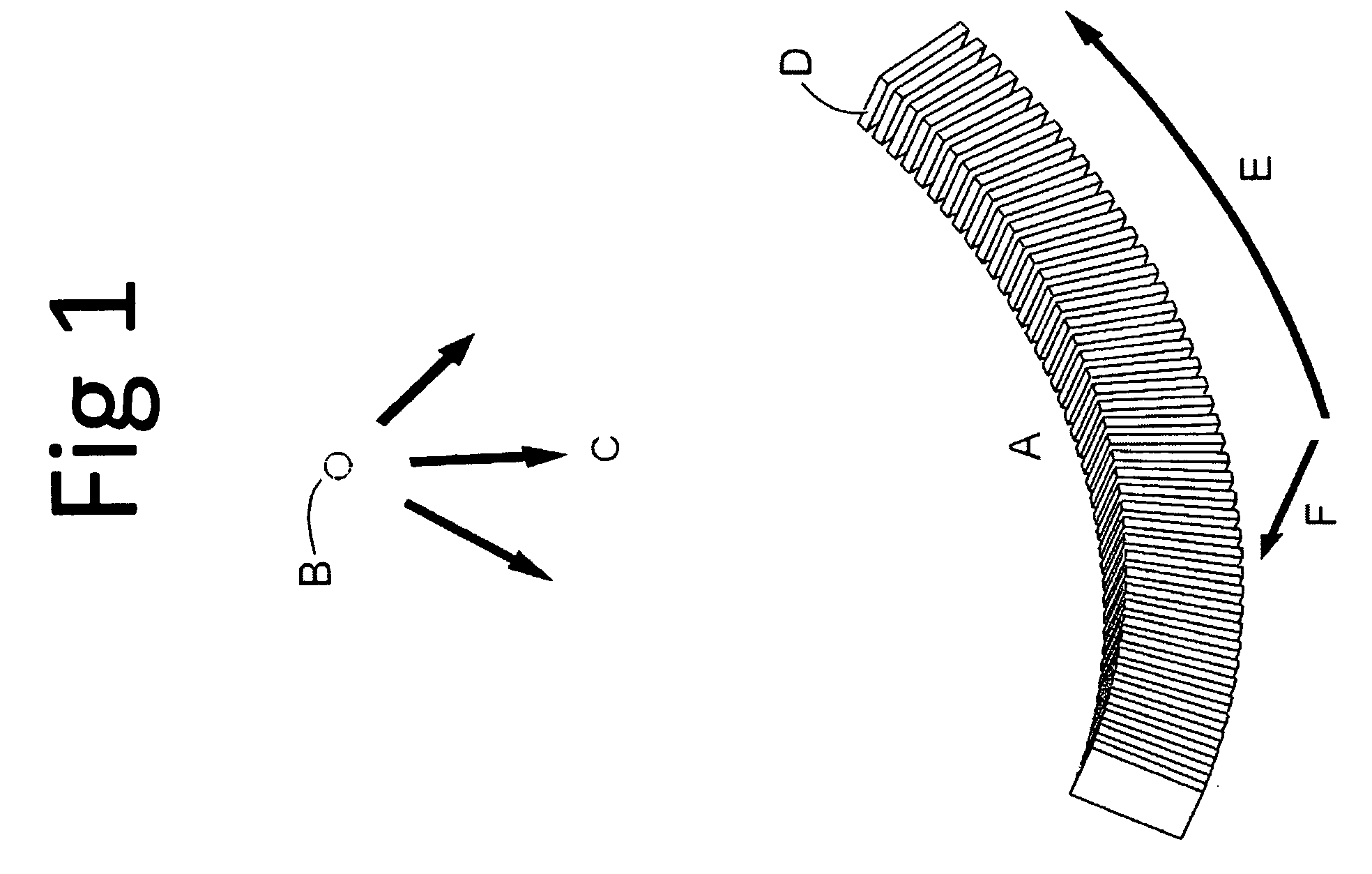
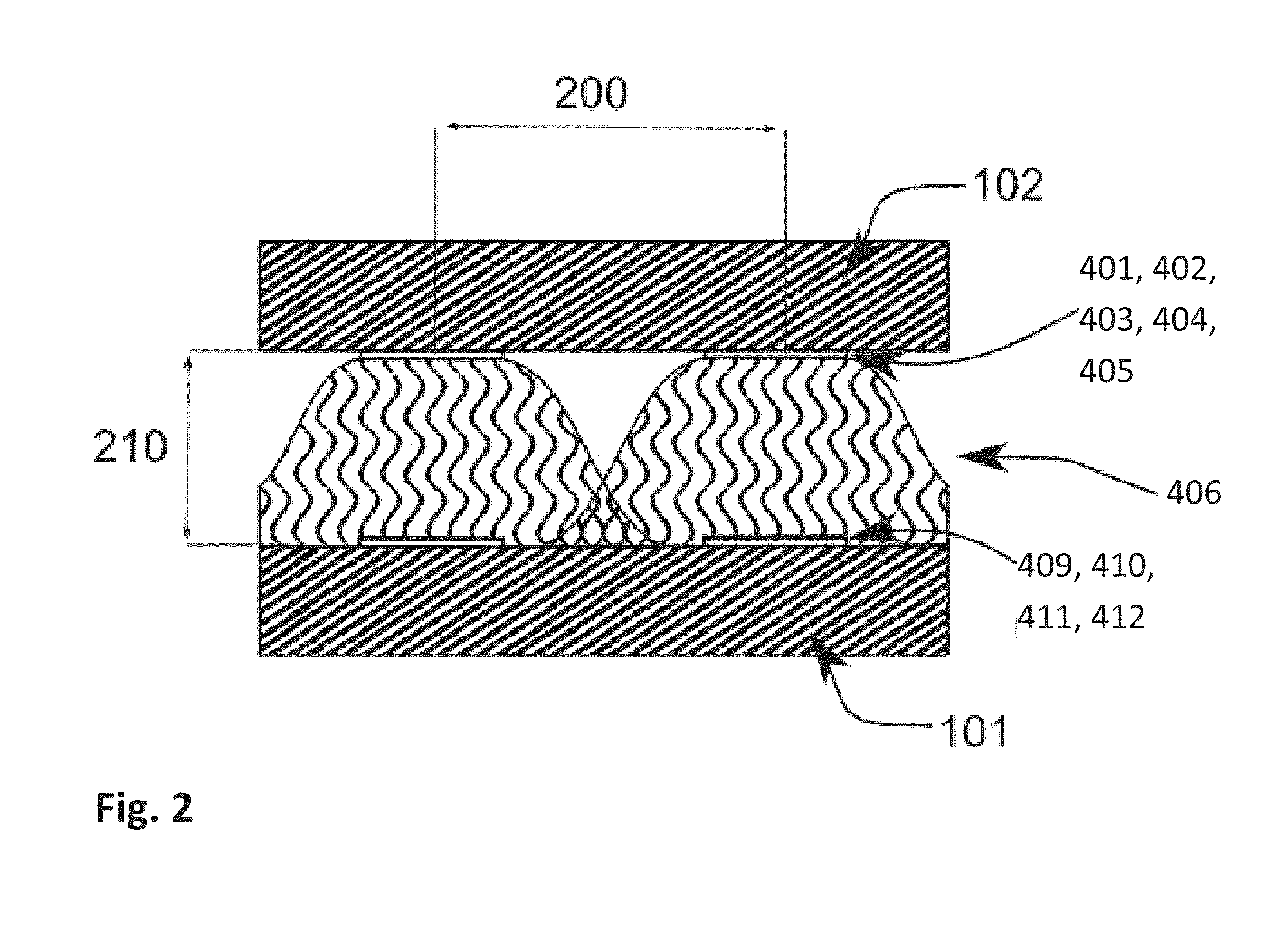
A Silicon detector for x-ray imaging is based on multiple semiconductor detector modules (A) arranged together to form an overall detector area, where each semiconductor detector module includes an x-ray sensor of crystalline Silicon oriented edge-on to incoming x-rays and connected to integrated circuitry for registration of x-rays interacting in the x-ray sensor through the photoelectric effect and through Compton scattering and for an incident x-ray energy between 40 keV and 250 keV to provide the spatial and energy information from these interactions to enable an image of an object. Further, anti-scatter modules (B) are interfolded between at least a subset of the semiconductor detector modules to at least partly absorb Compton scattered x-rays.
Owner:PRISMATIC SENSORS
Silicon detector assembly for X-ray imaging
A Silicon detector for x-ray imaging is based on multiple semiconductor detector modules (A) arranged together to form an overall detector area, where each semiconductor detector module includes an x-ray sensor of crystalline Silicon oriented edge-on to incoming x-rays and connected to integrated circuitry for registration of x-rays interacting in the x-ray sensor through the photoelectric effect and through Compton scattering and for an incident x-ray energy between 40 keV and 250 keV to provide the spatial and energy information from these interactions to enable an image of an object. Further, anti-scatter modules (B) are interfolded between at least a subset of the semiconductor detector modules to at least partly absorb Compton scattered x-rays.
Owner:PRISMATIC SENSORS
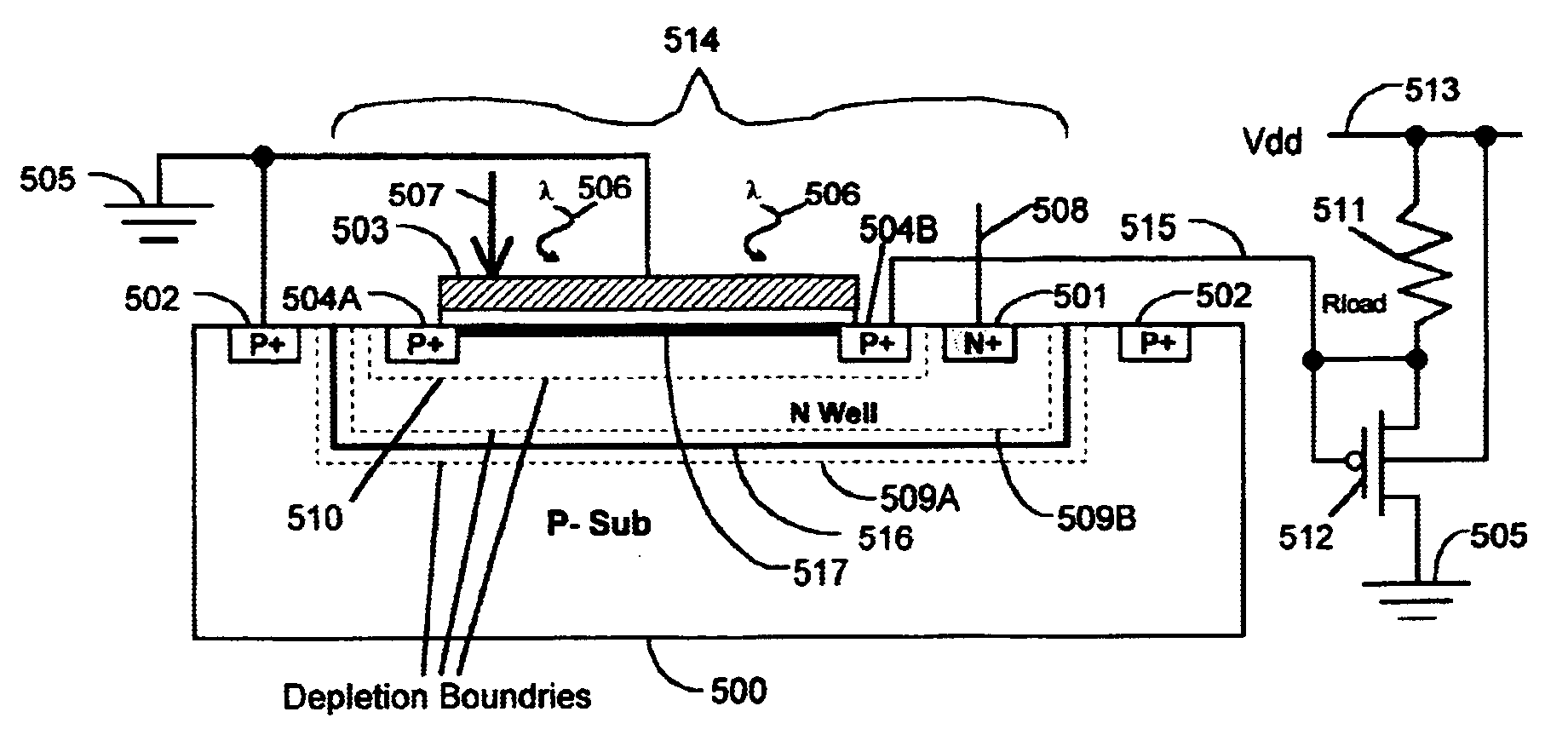
Low-resistivity photon-transparent window attached to photo-sensitive silicon detector
InactiveUS6025585ALow resistivityHigh resistivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOS sensorX-ray
The invention comprises a combination of a low resistivity, or electrically conducting, silicon layer that is transparent to long or short wavelength photons and is attached to the backside of a photon-sensitive layer of silicon, such as a silicon wafer or chip. The window is applied to photon sensitive silicon devices such as photodiodes, charge-coupled devices, active pixel sensors, low-energy x-ray sensors and other radiation detectors. The silicon window is applied to the back side of a photosensitive silicon wafer or chip so that photons can illuminate the device from the backside without interference from the circuit printed on the frontside. A voltage sufficient to fully deplete the high-resistivity photosensitive silicon volume of charge carriers is applied between the low-resistivity back window and the front, patterned, side of the device. This allows photon-induced charge created at the backside to reach the front side of the device and to be processed by any circuitry attached to the front side. Using the inventive combination, the photon sensitive silicon layer does not need to be thinned beyond standard fabrication methods in order to achieve full charge-depletion in the silicon volume. In one embodiment, the inventive backside window is applied to high resistivity silicon to allow backside illumination while maintaining charge isolation in CCD pixels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
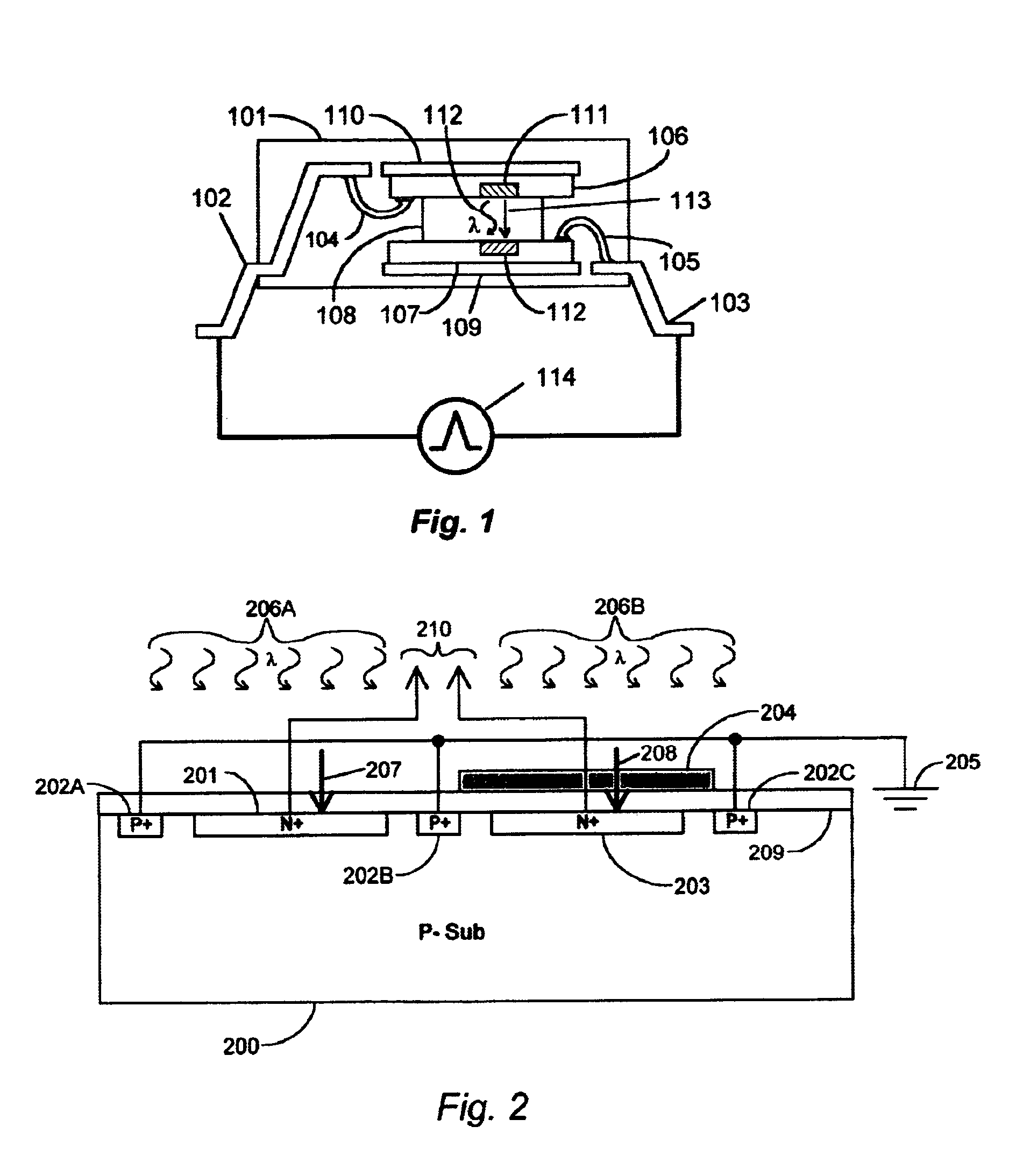
Radiation sensor with photo-thermal gain
InactiveUS6888141B2Increase temperatureImprove the overall coefficientRadiation pyrometryPhotometryTransmittanceRadiation sensor
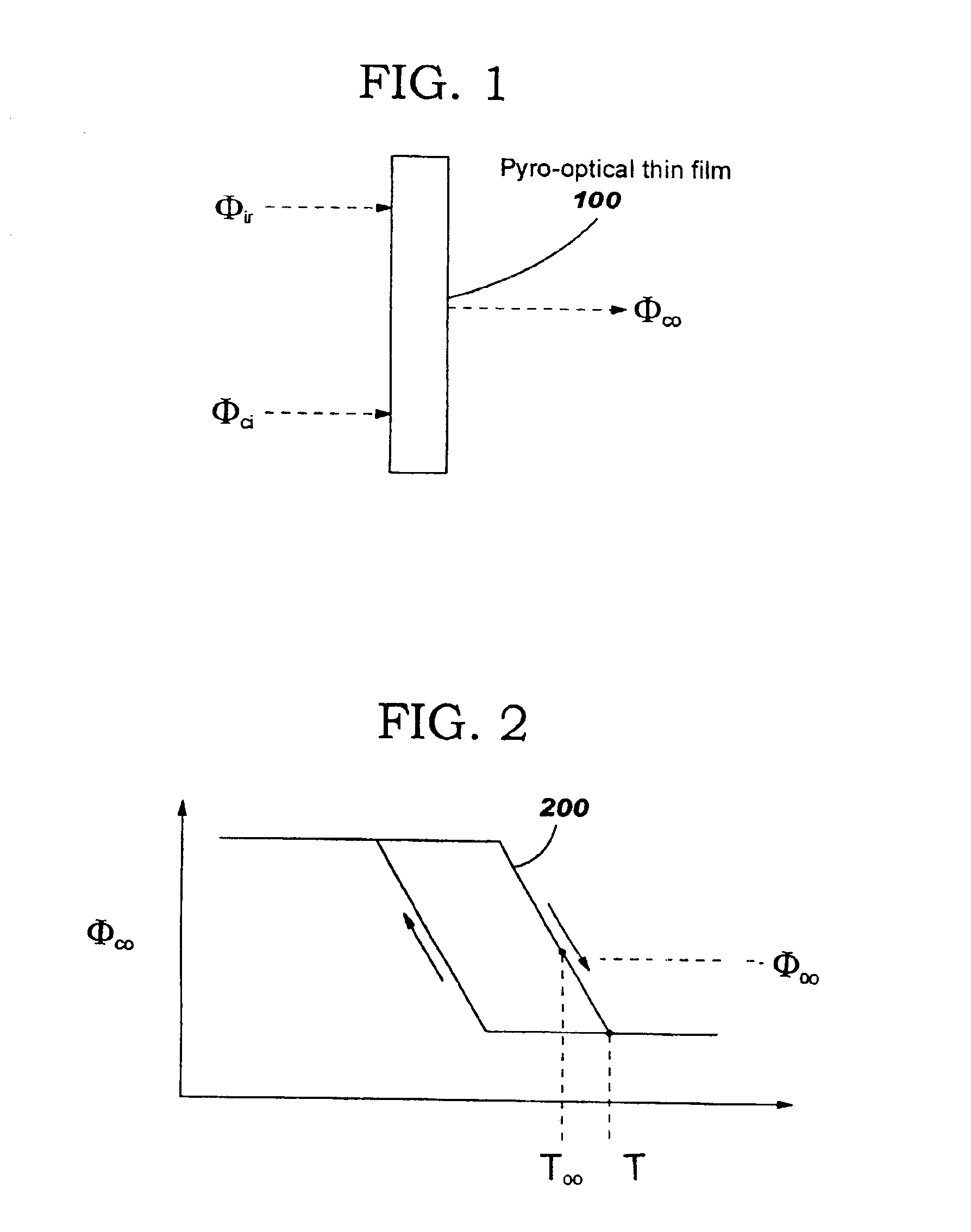
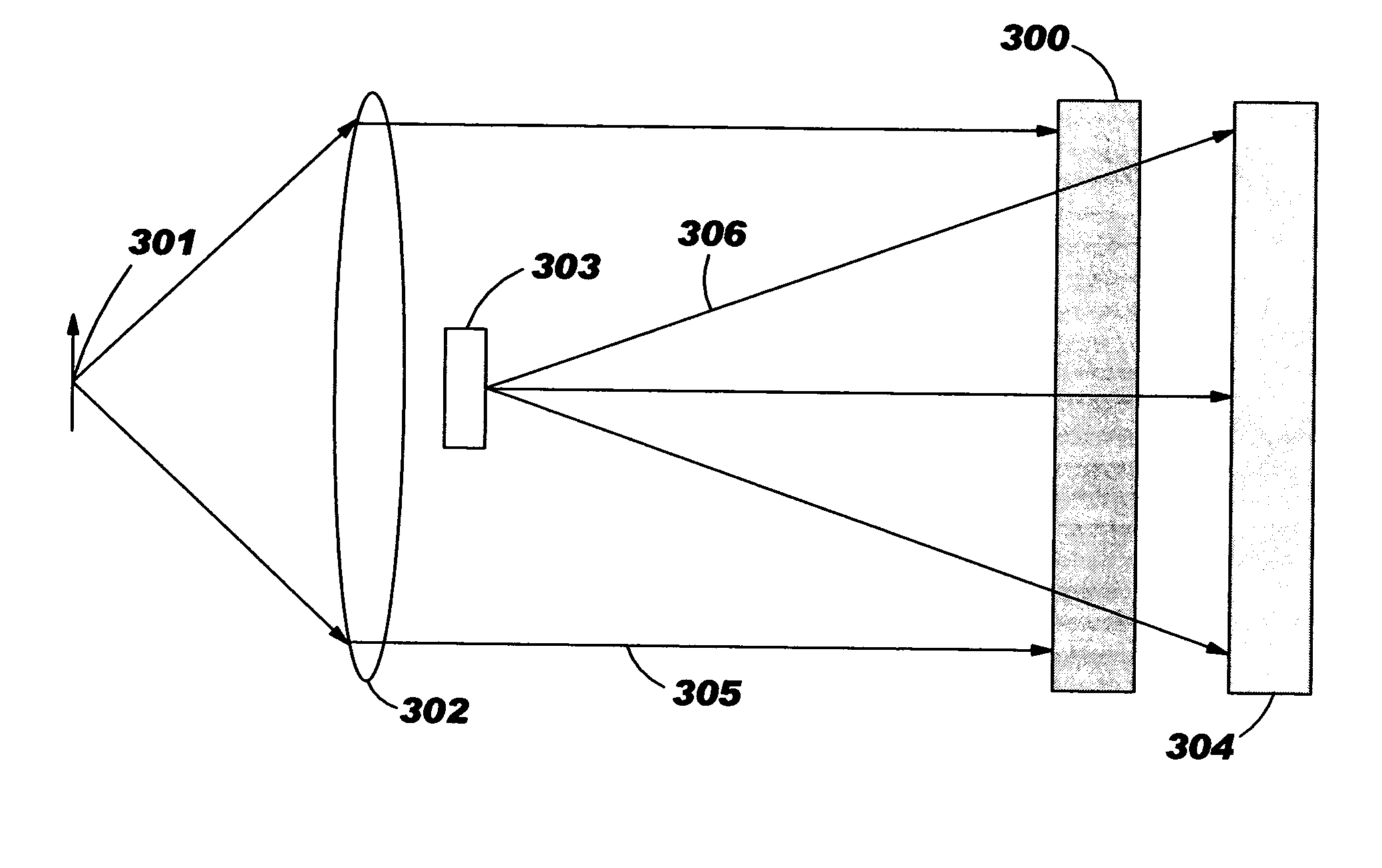
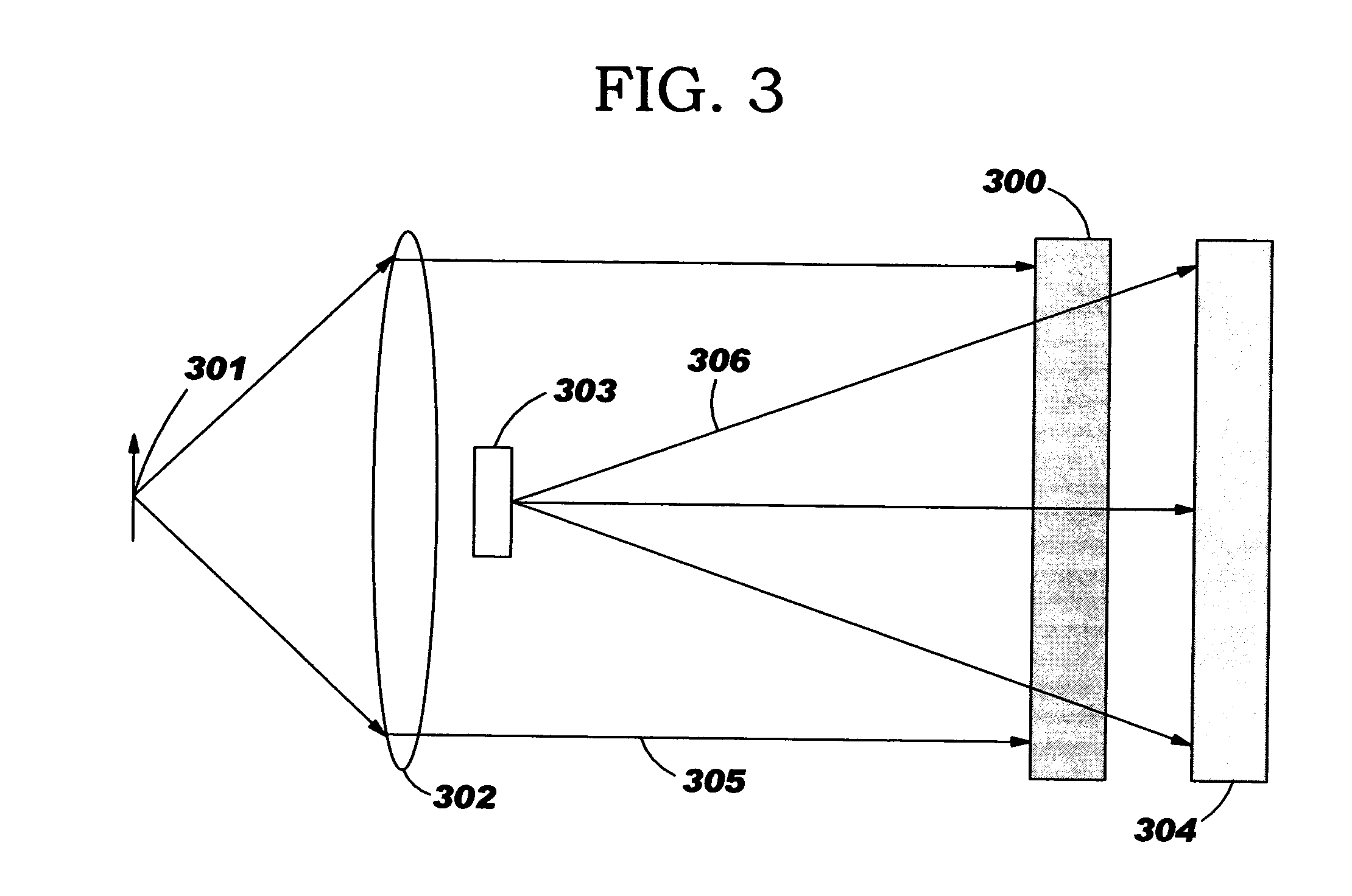
A thermal sensor for low level radiation with built-in photo-thermal gain utilizing a thin film of pyro-optical material to modulate the reflectivity and / or transmission of a photonic carrier beam. The photonic carrier beam is modulated by the temperature of the pyro-optical film and detected by typically a silicon detector. A slight temperature increase of the pyro-optical film due to absorption of low level radiation increases the coefficient of absorption of the photonic carrier beam which in turn causes a further increase in temperature of the pyro-optical film. The photonic carrier beam provides power to increase the temperature of the pyro-optical film beyond the heating caused by the absorption of low level radiation alone. This thermal amplification effect provides a radiation sensor with photo-thermal gain.
Owner:MULTISPECTRAL IMAGING
High resoultion digital imaging apparatus
InactiveUS8120683B1Improve quantum efficiencyImprove the immunityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital imagingData acquisition
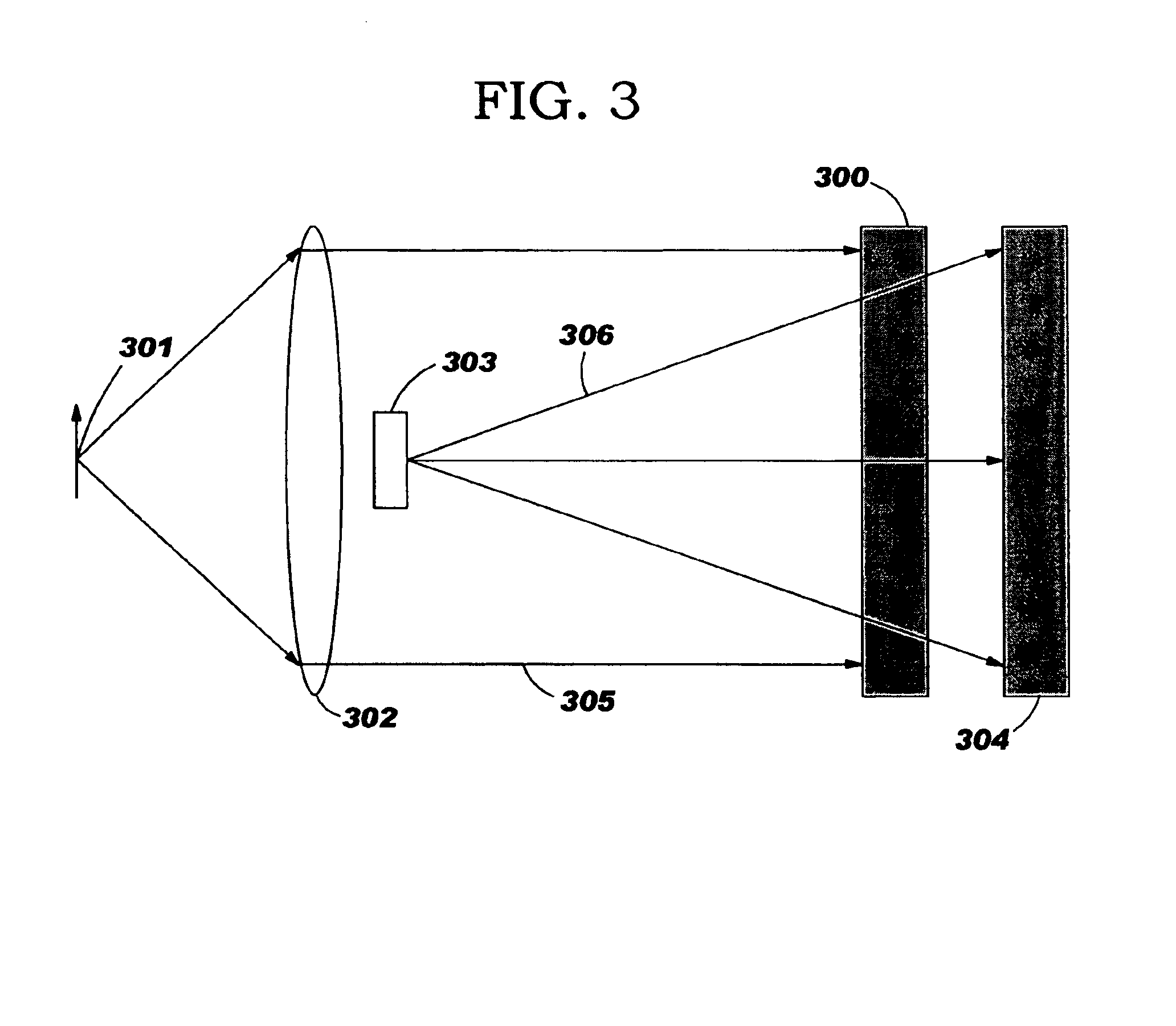
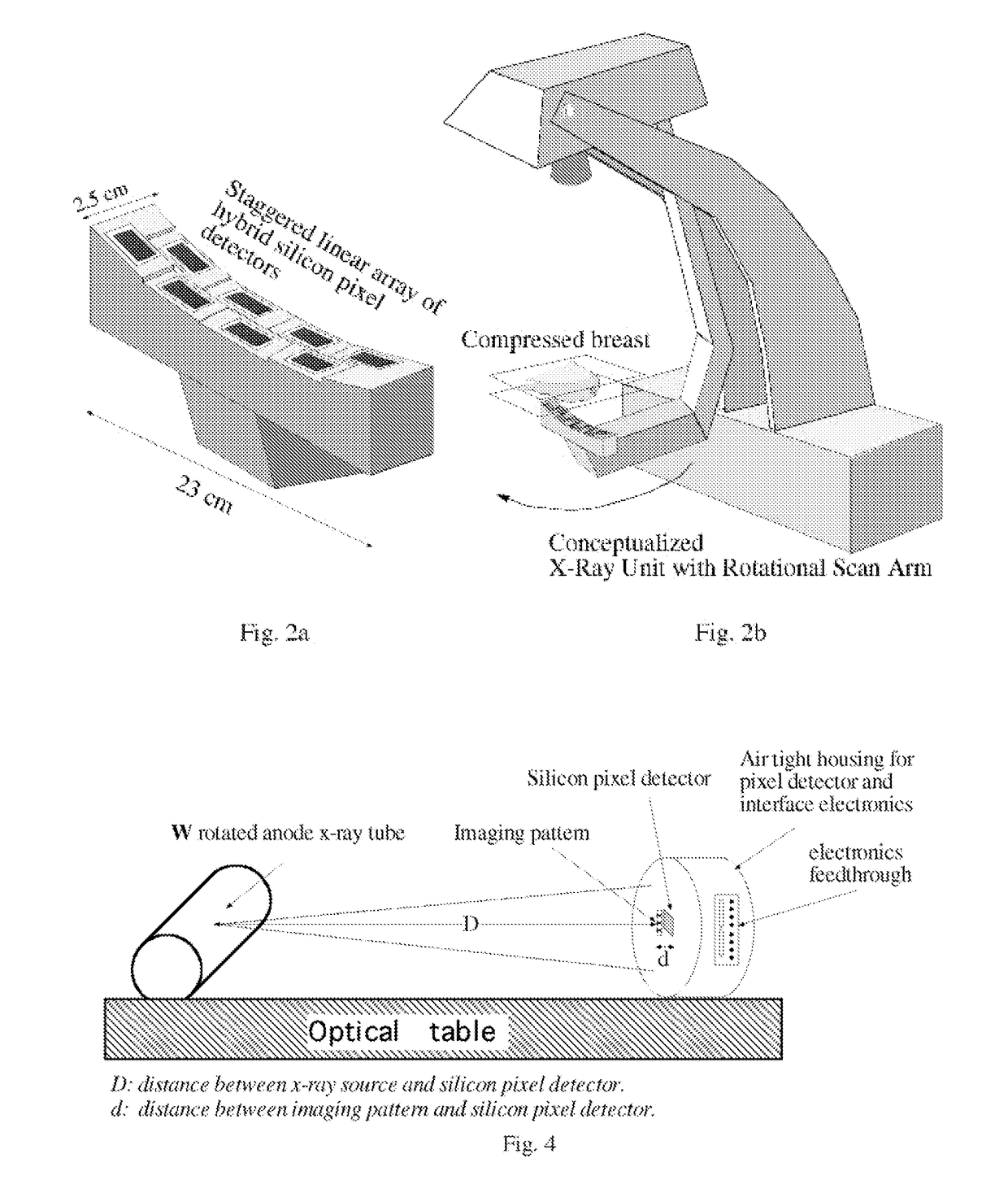
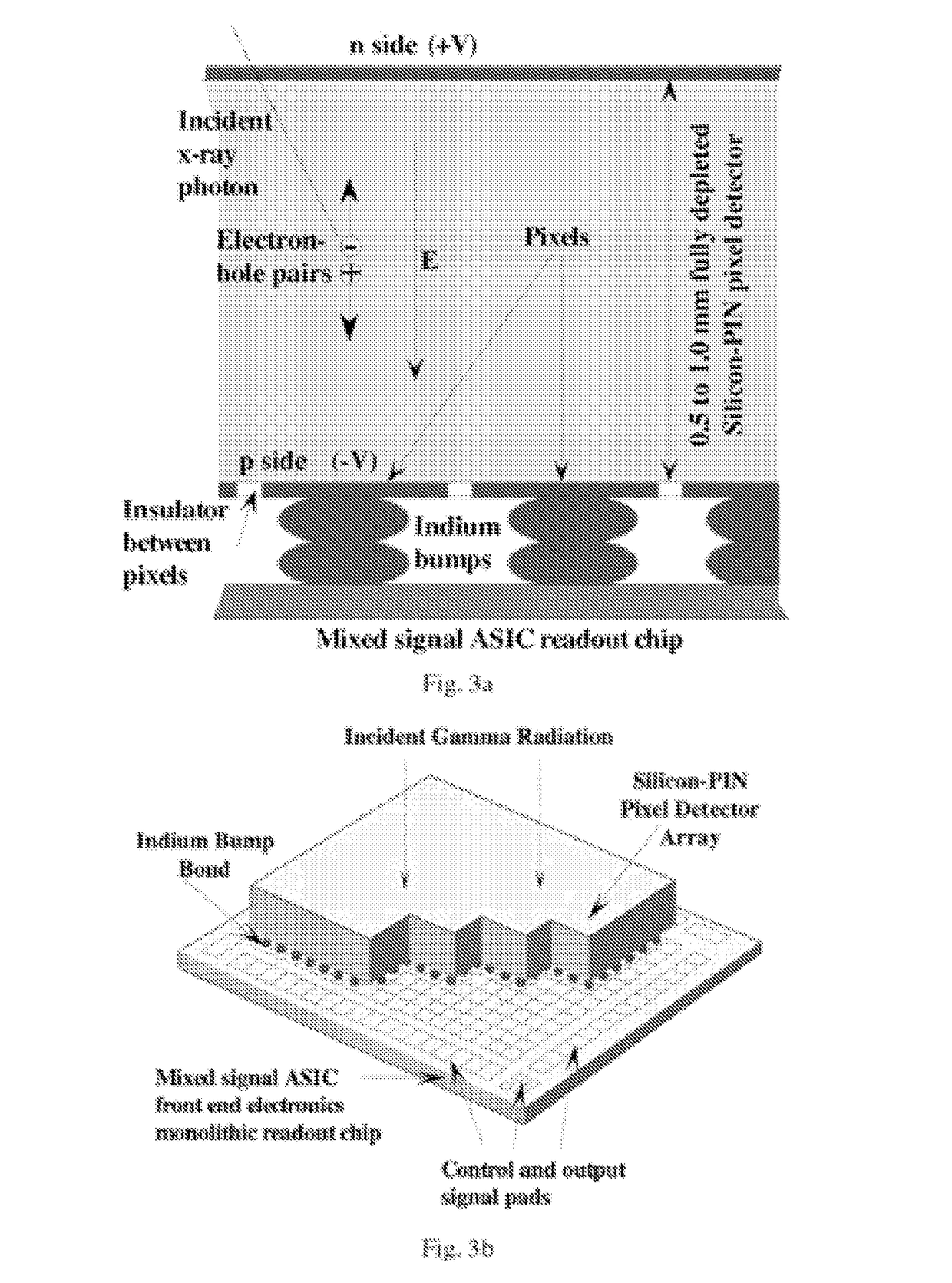
An integrated application specific integrated circuit having a detection layer, a time delayed integration capability, data acquisition electronics, and a readout function is provided for detecting breast cancer in women. The detection layer receives x-ray radiation and converts the received energy to electron pairs, one of which is received by pixels. The time delay integration is on the chip and a part of the readout architecture. The detector may be a hybrid silicon detector (SiPD), a CdZnTe detector, or a GaAs detector.
Owner:NOVA R&D
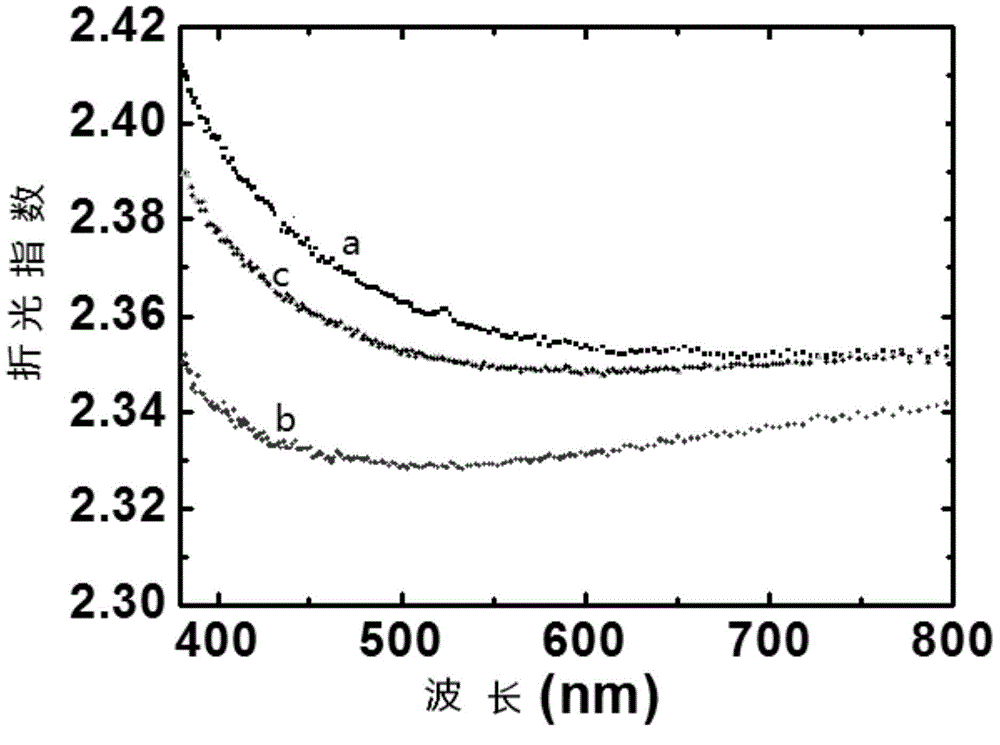
Silicon detector structure with broad spectral response and method of making same
InactiveCN102290481AWide spectral response rangeImprove absorption rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSpectral responseSilicon detector
The invention relates to a silicon detector structure with a wide spectral response range, which comprises an n-type silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide medium masking layer, a p-type doping layer, a front surface contact electrode, an antireflection film layer, a broad-spectrum absorbing black silicon layer, a medium passivating layer and a back surface contact electrode, wherein a circular groove is arranged on the surface of the n-type silicon substrate; the silicon dioxide medium masking layer is formed around the circular groove on the surface of the n-type silicon substrate, and the middle of the silicon dioxide medium masking layer is an annular structure; the p-type doping layer is arranged in the circular groove of the n-type silicon substrate; the front surface contact electrode is produced on the inner wall of the annular structure of the silicon dioxide medium masking layer and covers the partial edge of the surface of the annular structure to form an annular structure; the antireflection film layer is produced in the annular structure of the front surface contact electrode and covers the surface of the p-type doping layer; the broad-spectrum absorbing black silicon layer is produced on the back surface of the n-type silicon substrate; the medium passivating layer is point-type and is formed on the surface of the broad-spectrum absorbing black silicon layer; and the back surface contact electrode is produced on the surface of the broad-spectrum absorbing black silicon layer and covers the point-type medium passivating layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-sensitivity radioactive aerosol continuous monitor
InactiveCN104360371AMeet the requirements of continuous monitoringX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentParticle injectionReciprocating motion
The invention belongs to the technical field of designing and improving of environmental radiation monitoring equipment, and particularly relates to a high-sensitivity radioactive aerosol continuous monitor which comprises a sampling module and a measuring module. The upper halves of the sampling module and the measuring module are mounted in an upper-portion supporting module, a sampling module moving unit and a vacuumizing measuring module moving unit can be in up-down reciprocating motion and are mounted in a lower-portion supporting module, a U-019-300-100 particle injection type silicon detector and a vacuum adapter are mounted in a right-side vacuum chamber of the upper-portion supporting module, an annular silica sealing gasket is mounted above the sampling module moving unit and the vacuumizing measuring module moving unit and used for sealing, and a spring sleeves the outer side of each of the sampling module moving unit and the vacuumizing measuring module moving unit. The high-sensitivity radioactive aerosol continuous monitor is mainly used for the field of environmental monitoring.
Owner:63653 FORCES PLA
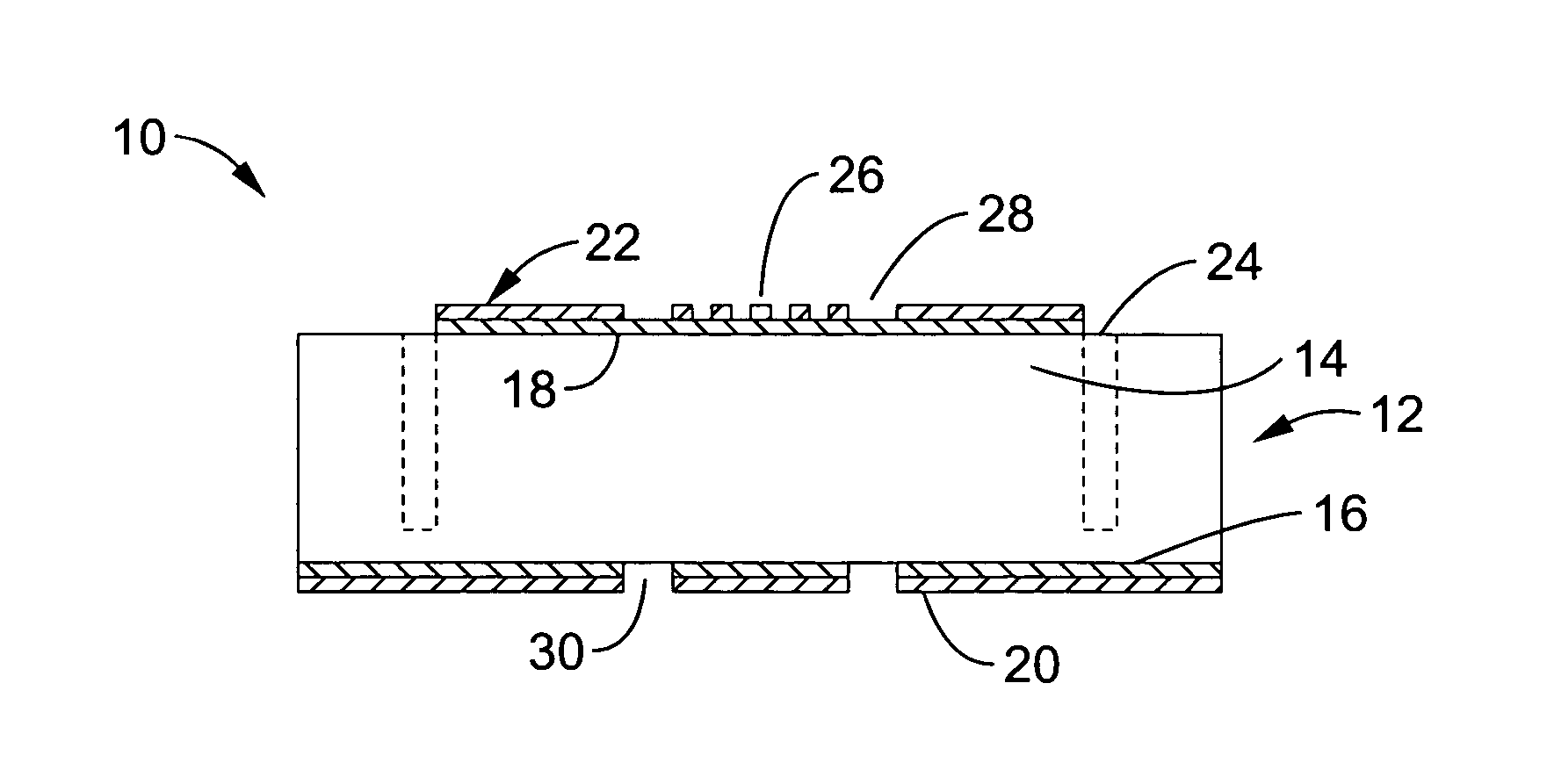
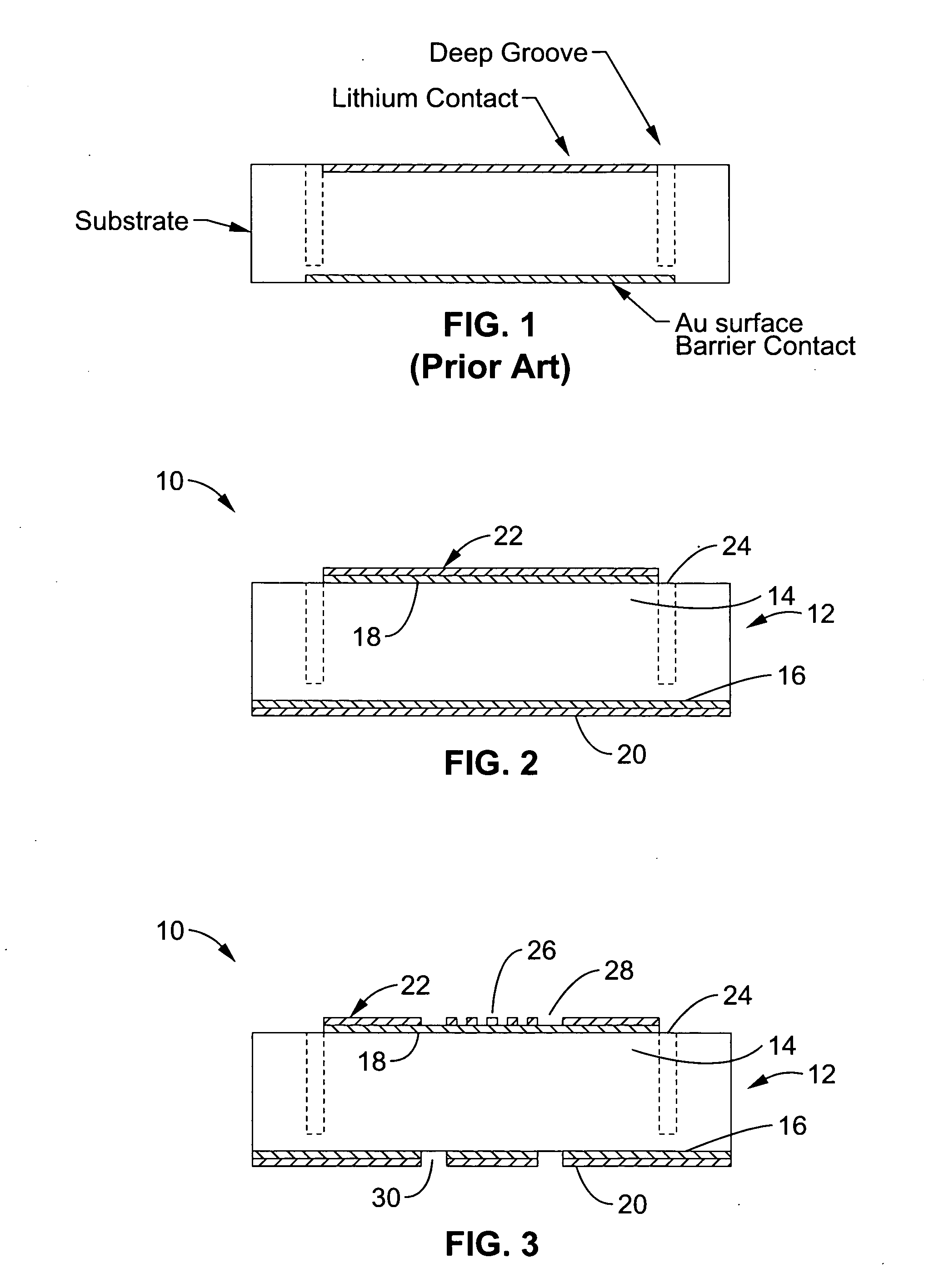
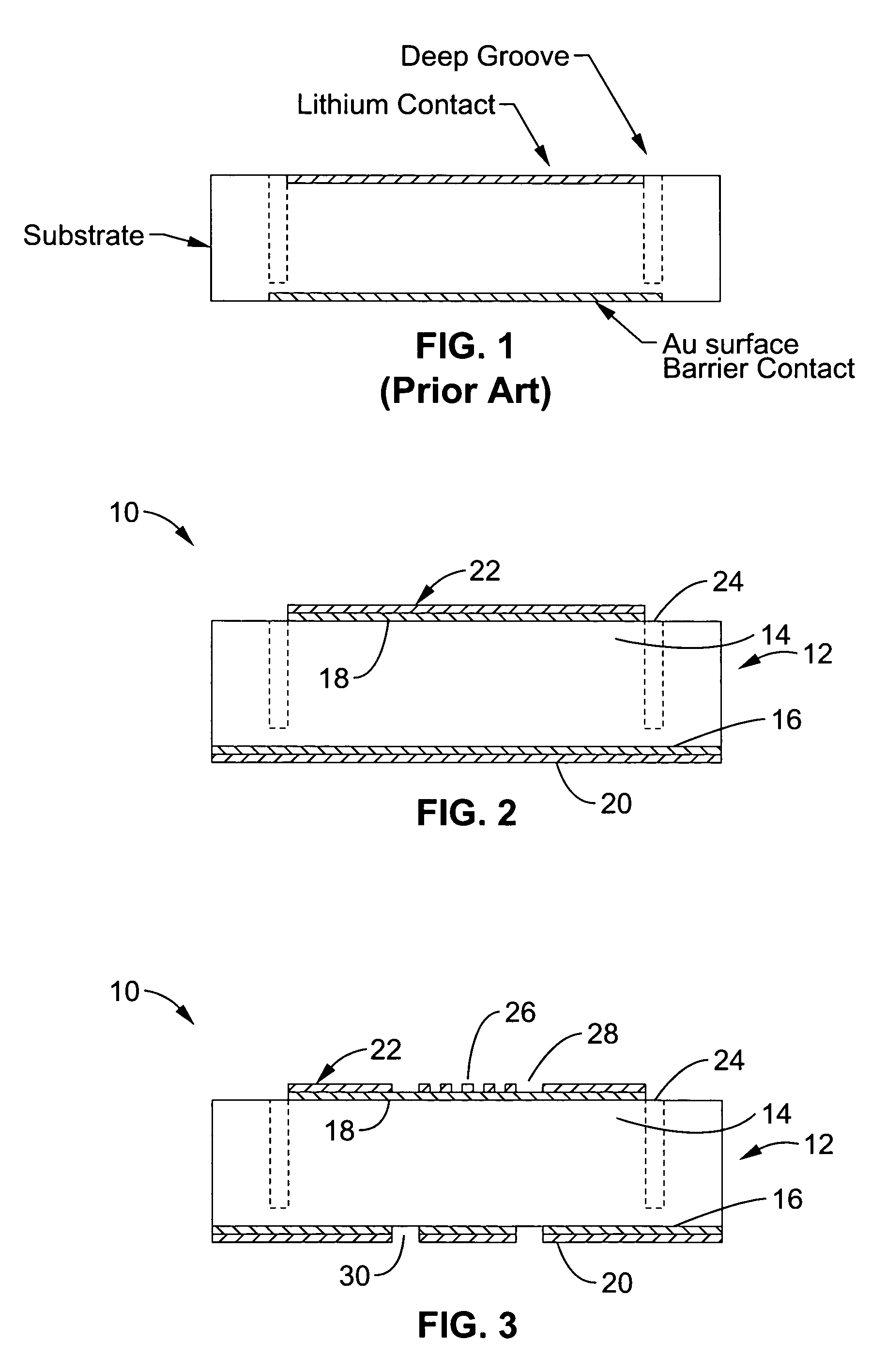
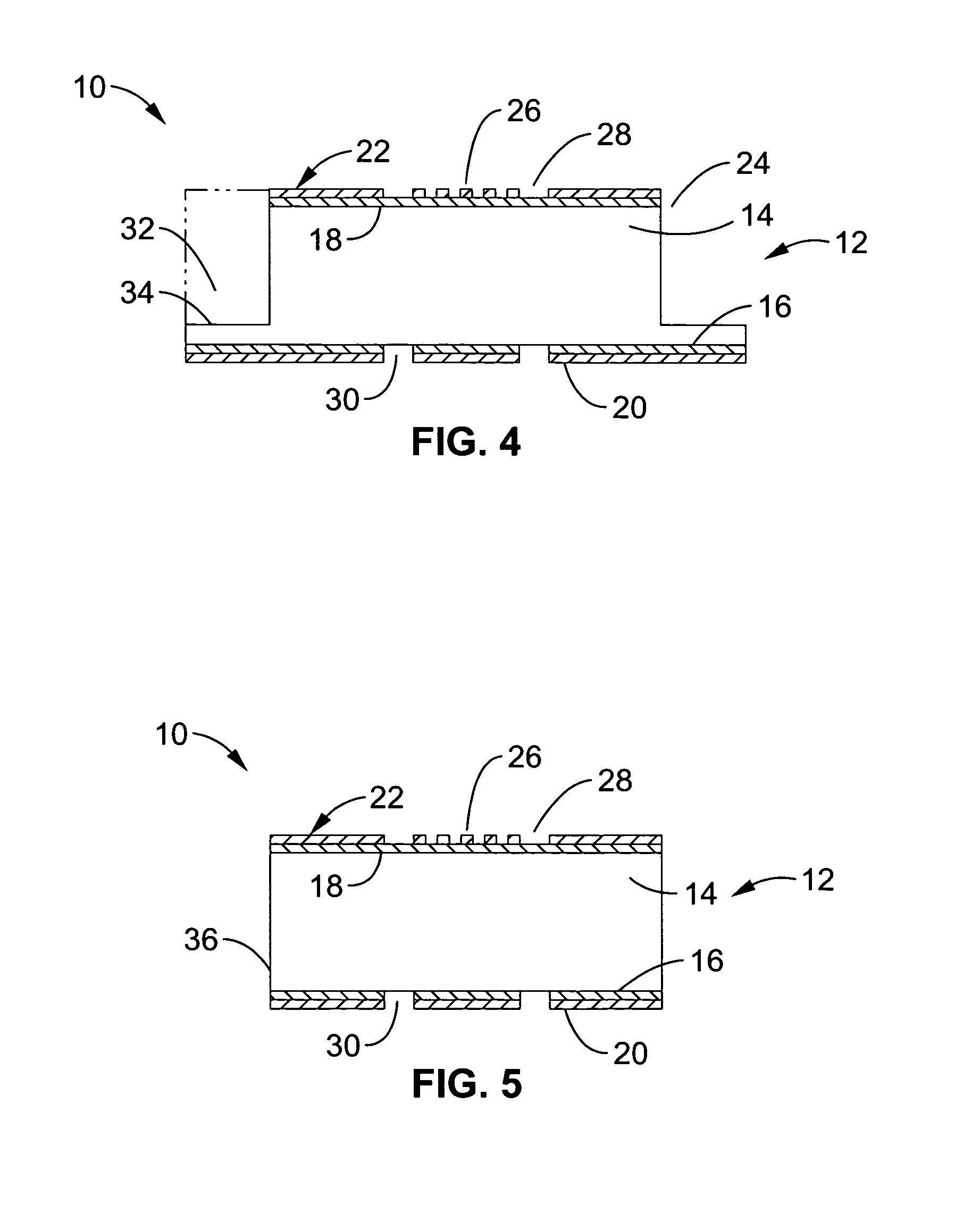
Lithium-drifted silicon detector with segmented contacts
InactiveUS20050001213A1Reduce leakage currentIncreasing achievable signal-to-noise ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectroscopyContact layer
A method and apparatus for creating both segmented and unsegmented radiation detectors which can operate at room temperature. The devices include a metal contact layer, and an n-type blocking contact formed from a thin layer of amorphous semiconductor. In one embodiment the material beneath the n-type contact is n-type material, such as lithium compensated silicon that forms the active region of the device. The active layer has been compensated to a degree at which the device may be fully depleted at low bias voltages. A p-type blocking contact layer, or a p-type donor material can be formed beneath a second metal contact layer to complete the device structure. When the contacts to the device are segmented, the device is capable of position sensitive detection and spectroscopy of ionizing radiation, such as photons, electrons, and ions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fourier transform spectrometer on silicon substrate and method for obtaining reconstructed spectrum of light source
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
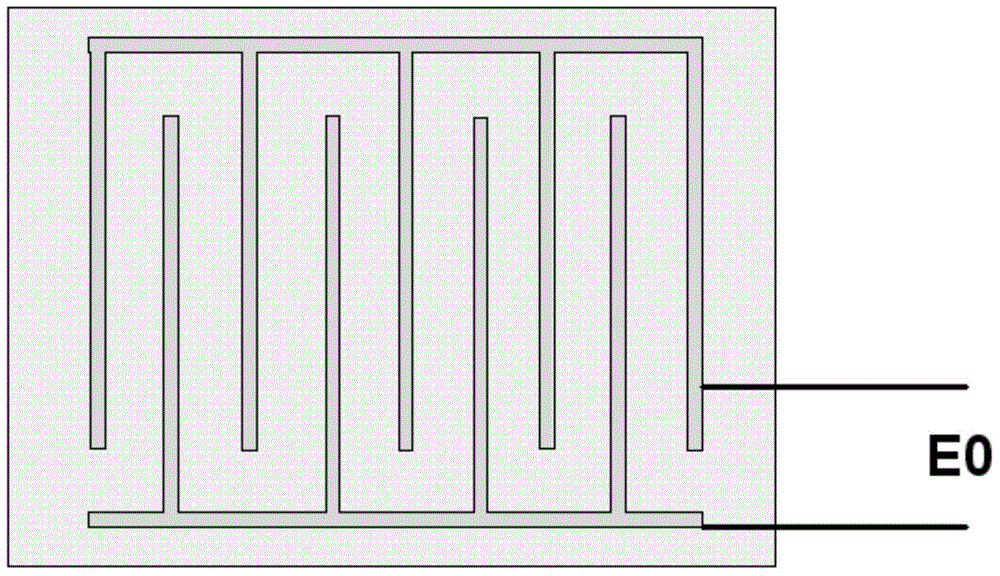
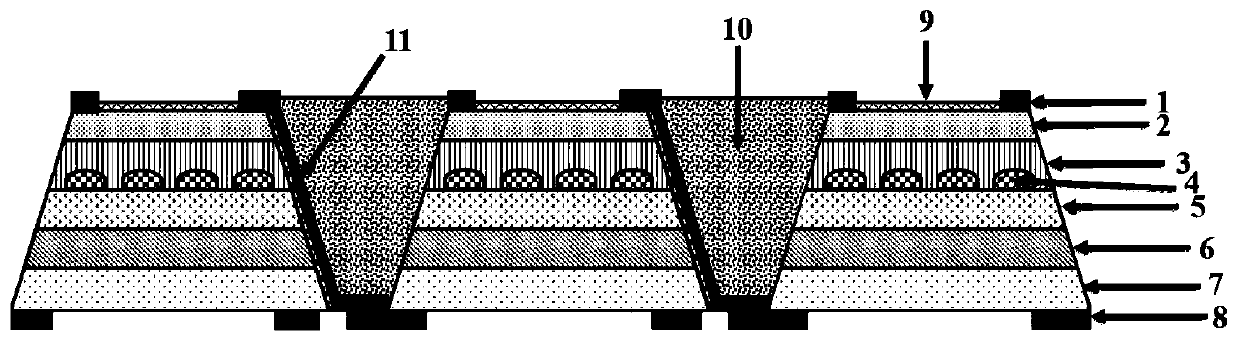
Open-and-close type three-dimensional trench electrode silicon detector
ActiveCN106449801ASimple manufacturing processImprove detection efficiencySemiconductor devicesSilicon detectorSilicon dioxide
The invention discloses an open-and-close type three-dimensional trench electrode silicon detector. An open-and-close type groove electrode and a central electrode are formed after etching on the silicon through diffusion and doping, the open-and-close type groove electrode surrounds the central electrode, the central electrode is connected with the negative electrode, the open-and-close type groove electrode is connected with the positive electrode, and the open-and-close type groove electrode is an open and discontinuous cylindrical structure. The bottom of the detector has a silicon dioxide protective layer. The area of the dead zone is smallest, particles can enter from both sides during working, and reaction is more flexible. The problem that in the prior art, the three-dimensional silicon detector can only be single-sided etched, the particles can only be incident on one side, and there is a dead zone, so that the detection performance of the detector is affected.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
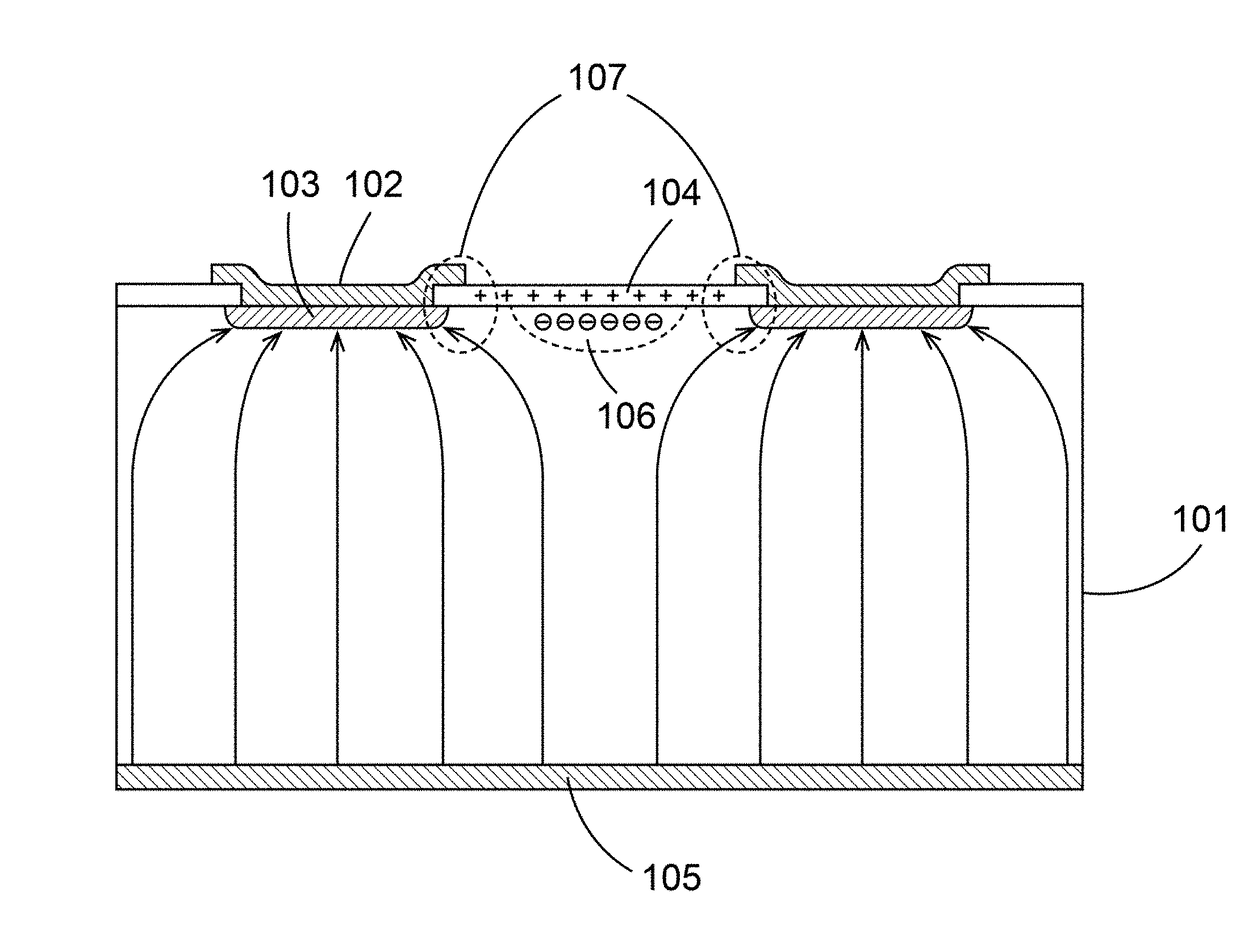
Surface passivation by quantum exclusion using multiple layers
ActiveUS20130181312A1Reduce degradationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesLength waveSilicon detector
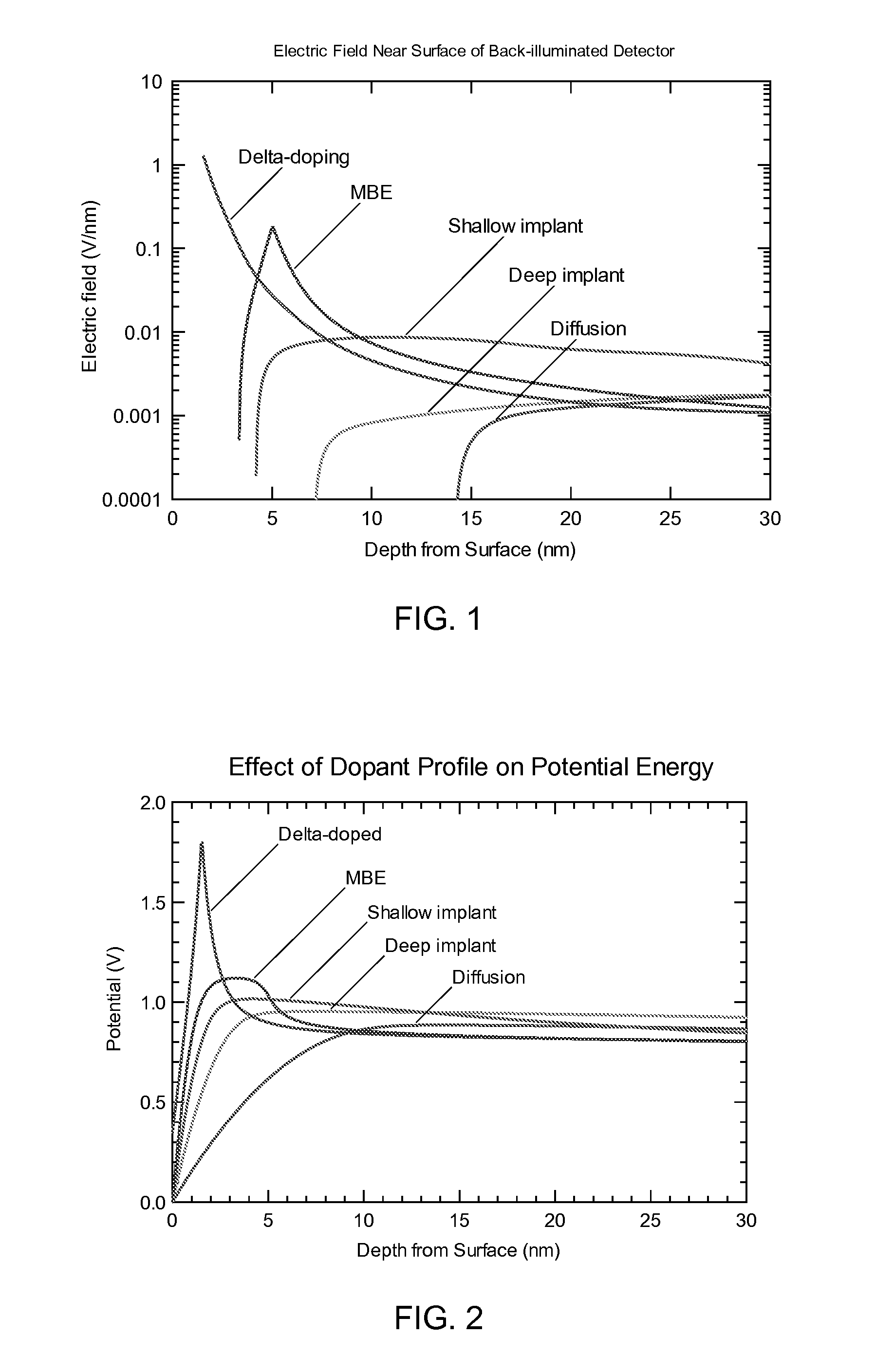
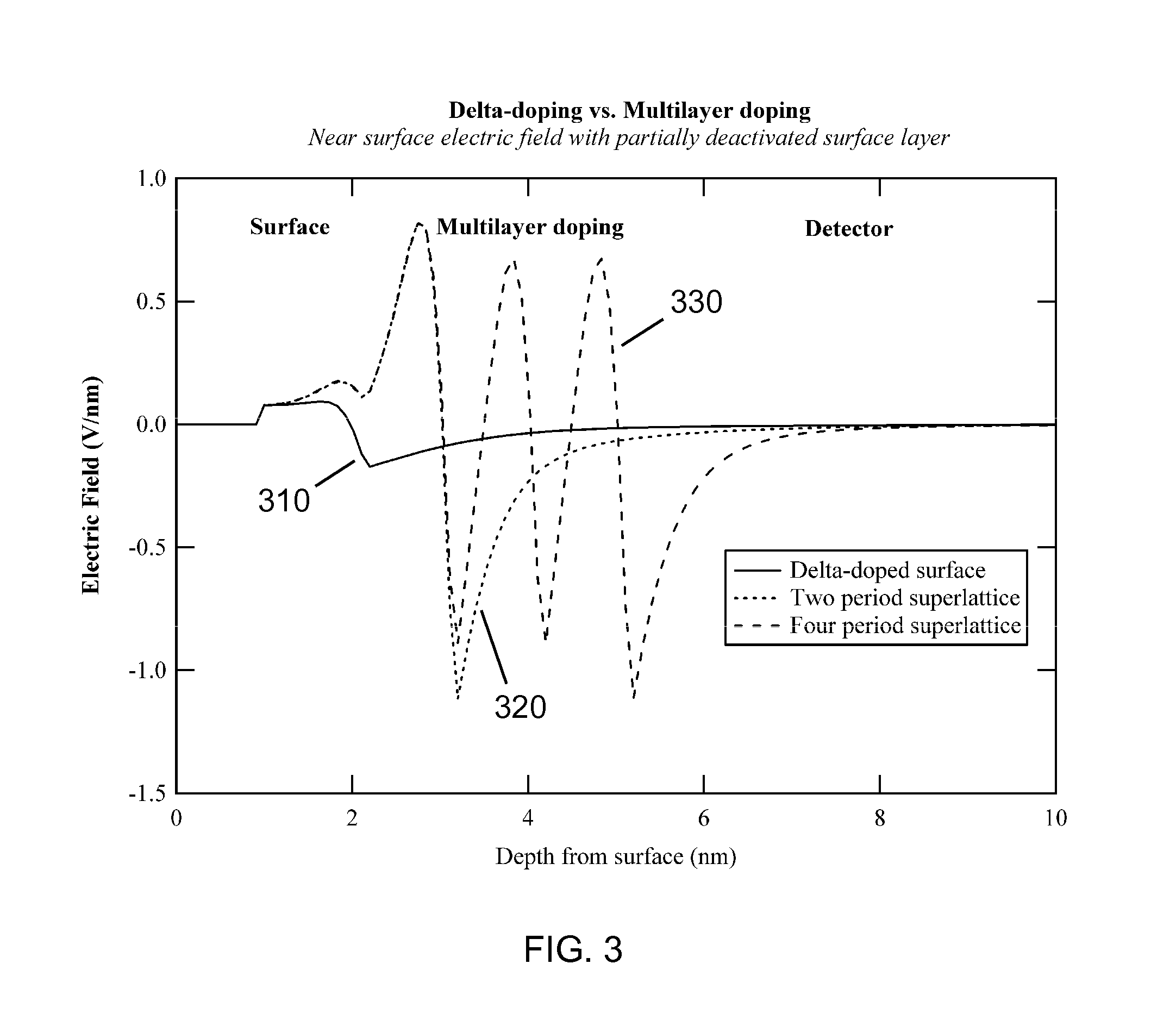
A semiconductor device has a multilayer doping to provide improved passivation by quantum exclusion. The multilayer doping includes at least two doped layers fabricated using MBE methods. The dopant sheet densities in the doped layers need not be the same, but in principle can be selected to be the same sheet densities or to be different sheet densities. The electrically active dopant sheet densities are quite high, reaching more than 1×1014 cm−2, and locally exceeding 1022 per cubic centimeter. It has been found that silicon detector devices that have two or more such dopant layers exhibit improved resistance to degradation by UV radiation, at least at wavelengths of 193 nm, as compared to conventional silicon p-on-n devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
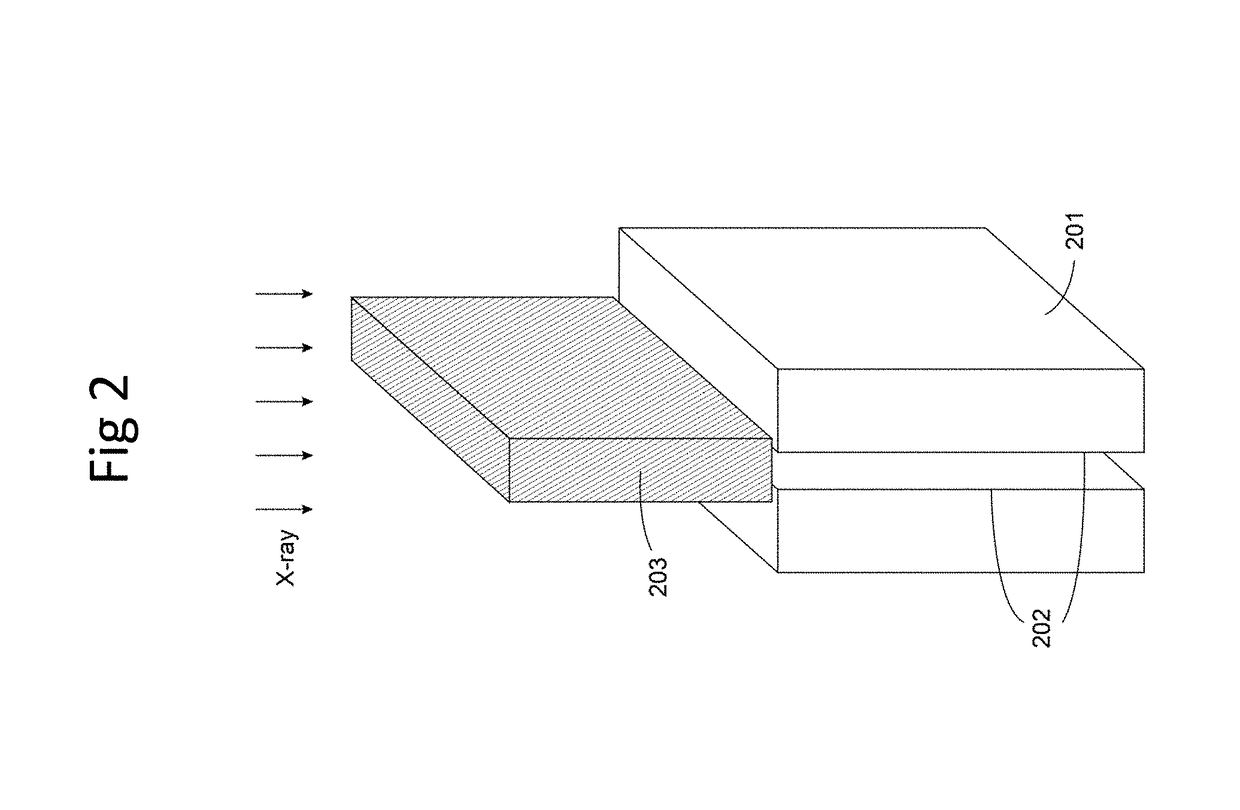
Semiconductor bump-bonded x-ray imaging device
InactiveUS20150276945A1Reliable manufacturingSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSPixel density
A high pixel density intraoral x-ray imaging sensor includes a direct conversion, fully depleted silicon detector bump bonded to a readout CMOS substrate by capillary bump bonds.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
Solar-blind ultraviolet irradiation calibrating device
InactiveCN104075883ASimple structureEasy to operateTesting optical propertiesUltraviolet lightsEnergy flux
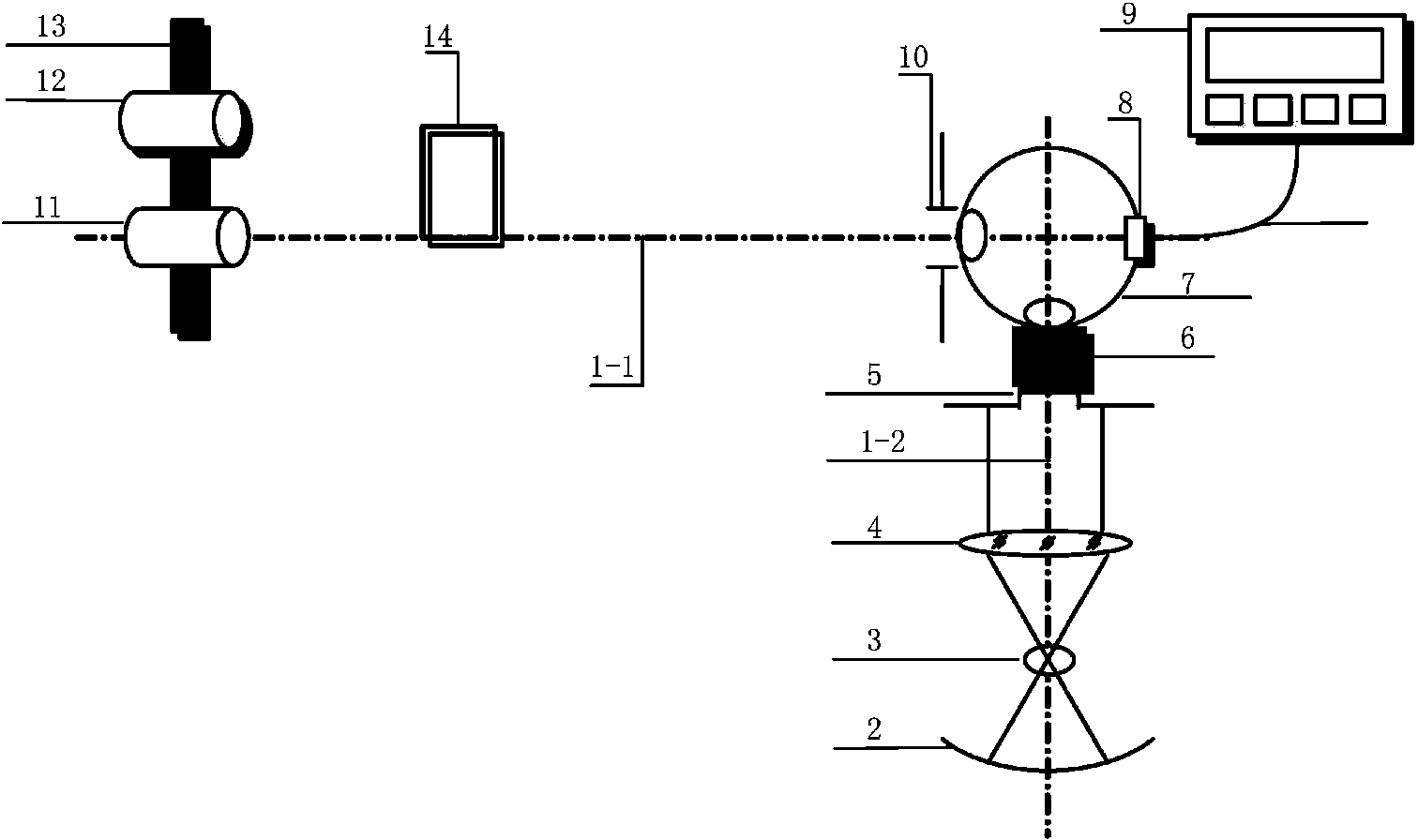
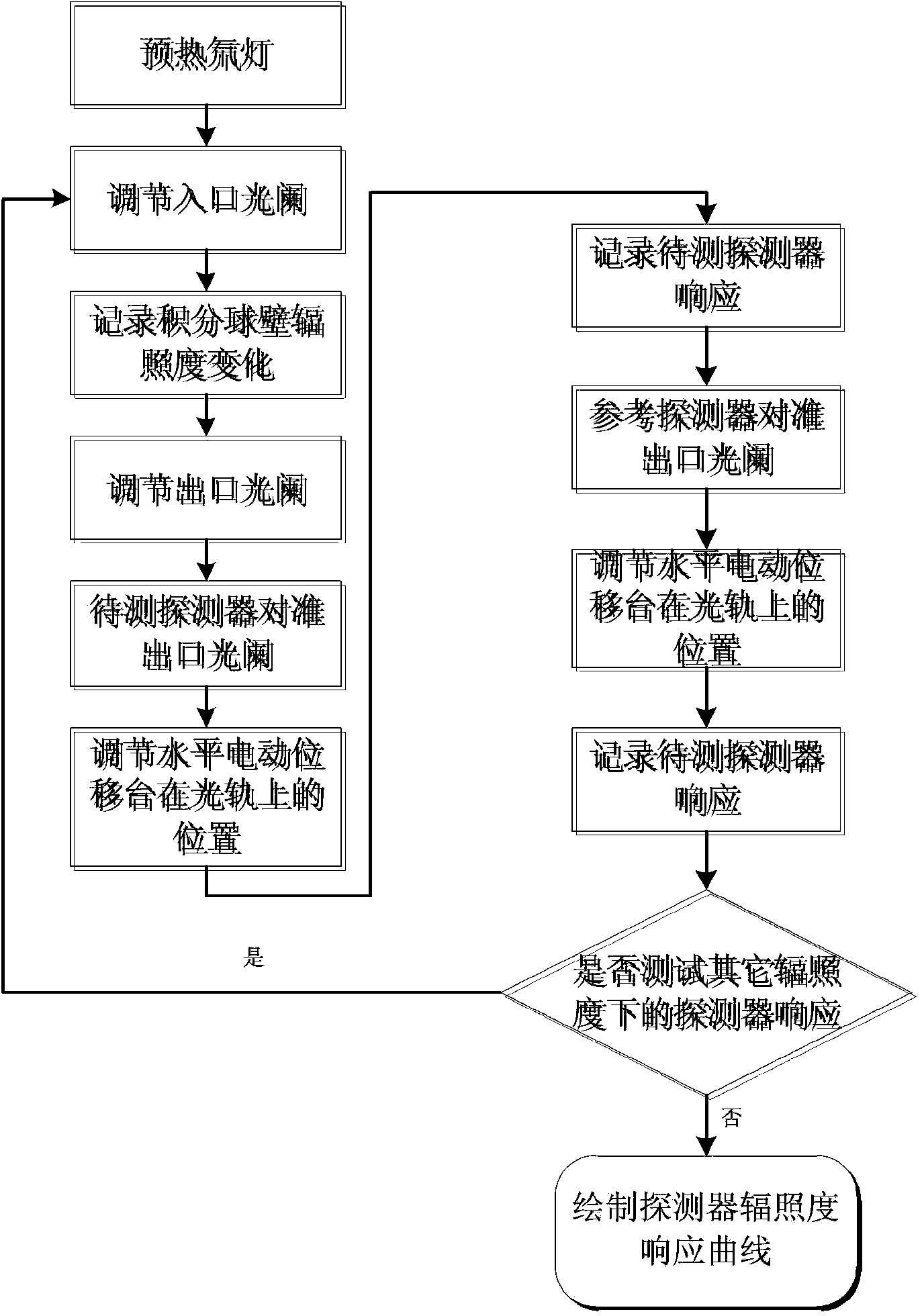
A solar-blind ultraviolet irradiation calibrating device relates to the field of ultraviolet irradiation calibration and solves the problems that existing solar-blind ultraviolet detection is narrow in dynamic range and low in accurate. The device comprises an L-shaped light track, an ultraviolet light source, an inlet diaphragm, a shielding cover, an integrating sphere, an outlet diaphragm, a silicon detector, a reference detector and a horizontal electric displacement bench, wherein the inlet diaphragm is used for controlling the radiation energy flux entering the integrating sphere, the shielding cover is used for shielding environmental stray light around the light source from entering the integrating sphere, the outlet diaphragm is tightly attached to an outlet of the integrating sphere and used for controlling the radiation energy flux of the outlet of the integrating sphere, the silicon detector is used for monitoring the irradiation change situation on the wall of the integrating sphere, the reference detector is used for measuring the irradiation at some position, and the horizontal electric displacement bench enables the reference detector and a detector to be detected to be arranged at the center of a light path in turns. The solar-blind ultraviolet irradiation calibrating device is simple in structure, strong in operability, high in accuracy and capable of achieving solar-blind ultraviolet detector irradiation calibration in a large dynamic range of 10-7 to 10-13W / cm<2>.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lithium-drifted silicon detector with segmented contacts
InactiveUS7060523B2Easy to makeReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectroscopyContact layer
A method and apparatus for creating both segmented and unsegmented radiation detectors which can operate at room temperature. The devices include a metal contact layer, and an n-type blocking contact formed from a thin layer of amorphous semiconductor. In one embodiment the material beneath the n-type contact is n-type material, such as lithium compensated silicon that forms the active region of the device. The active layer has been compensated to a degree at which the device may be fully depleted at low bias voltages. A p-type blocking contact layer, or a p-type donor material can be formed beneath a second metal contact layer to complete the device structure. When the contacts to the device are segmented, the device is capable of position sensitive detection and spectroscopy of ionizing radiation, such as photons, electrons, and ions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
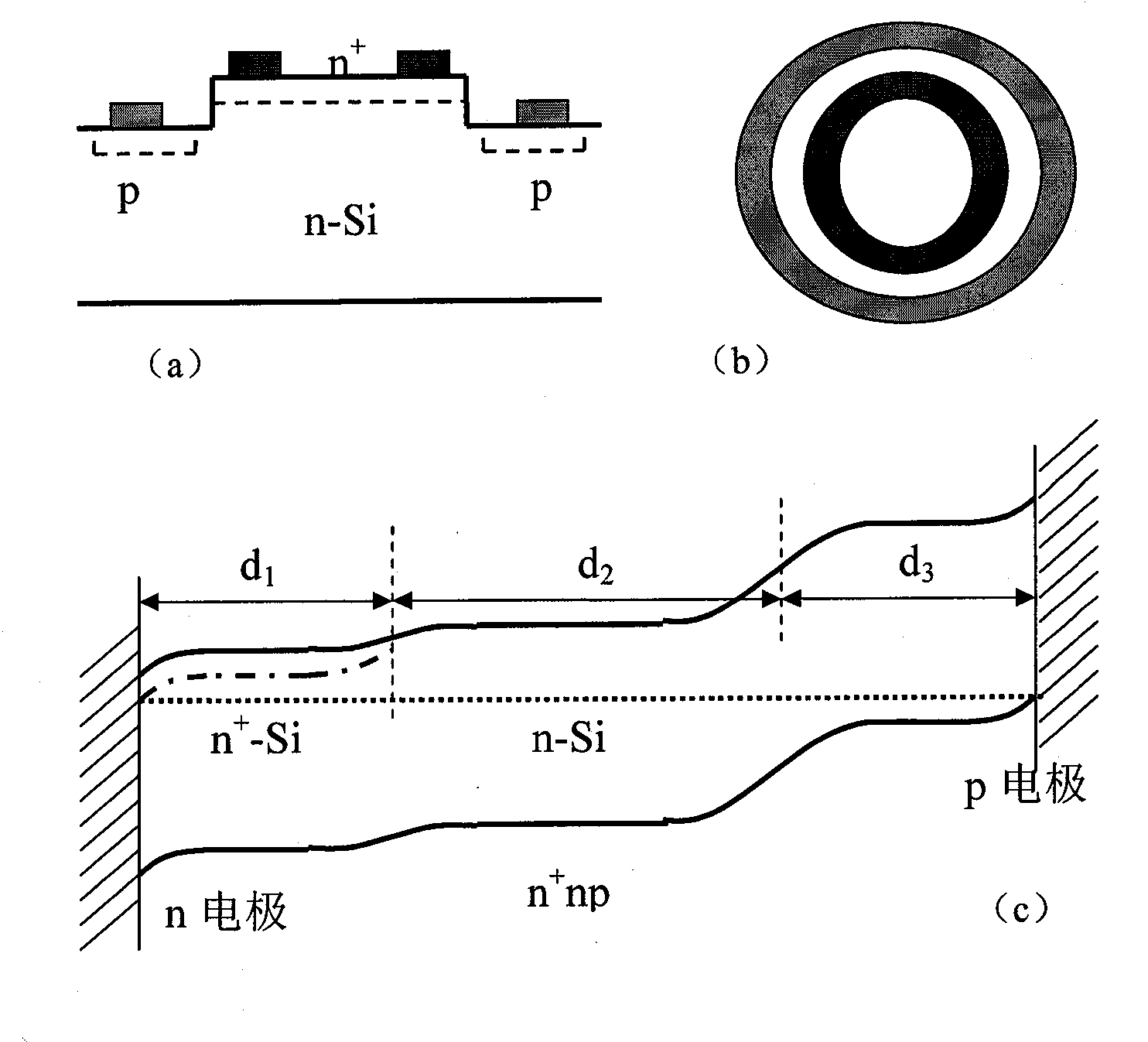
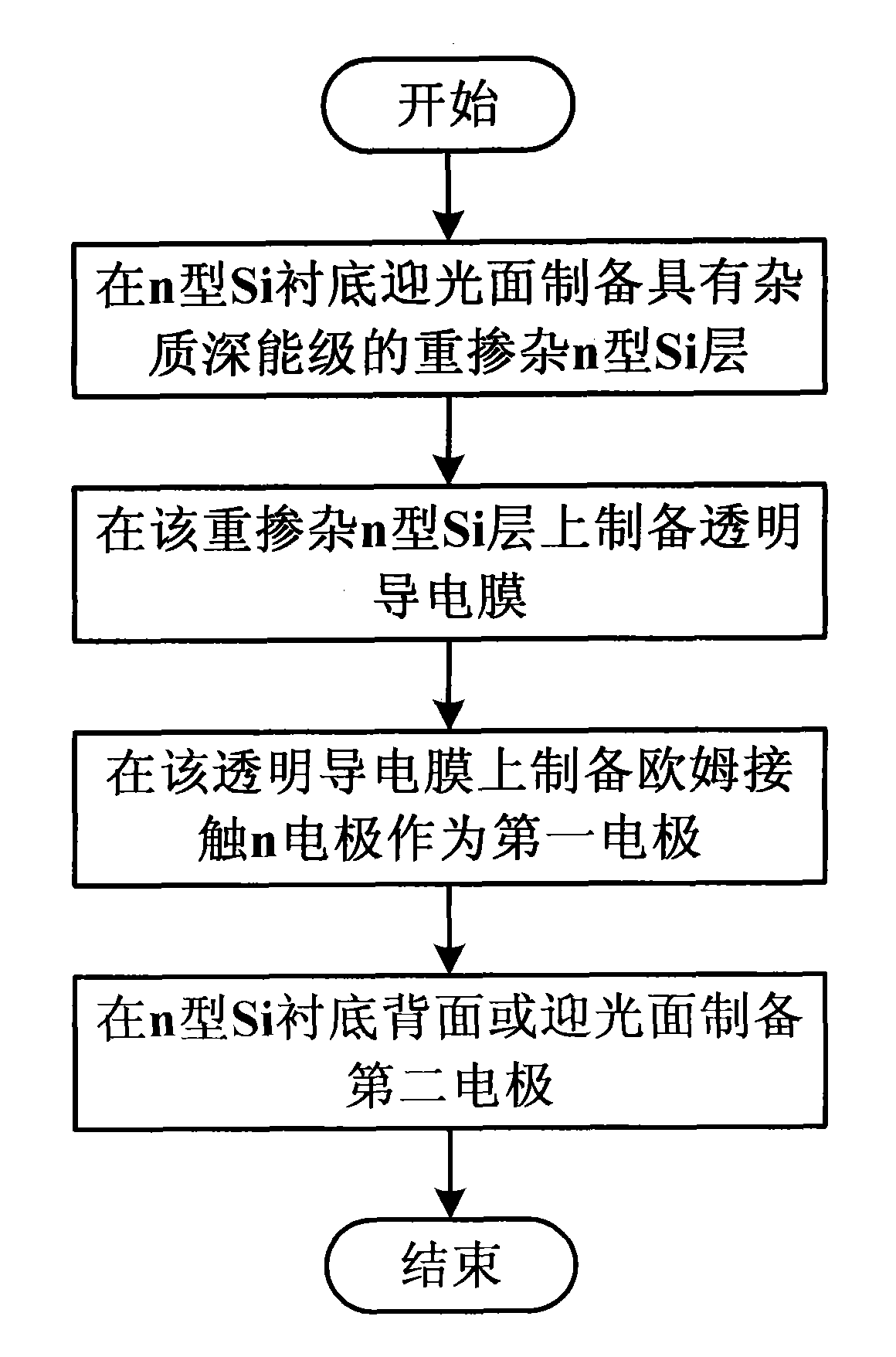
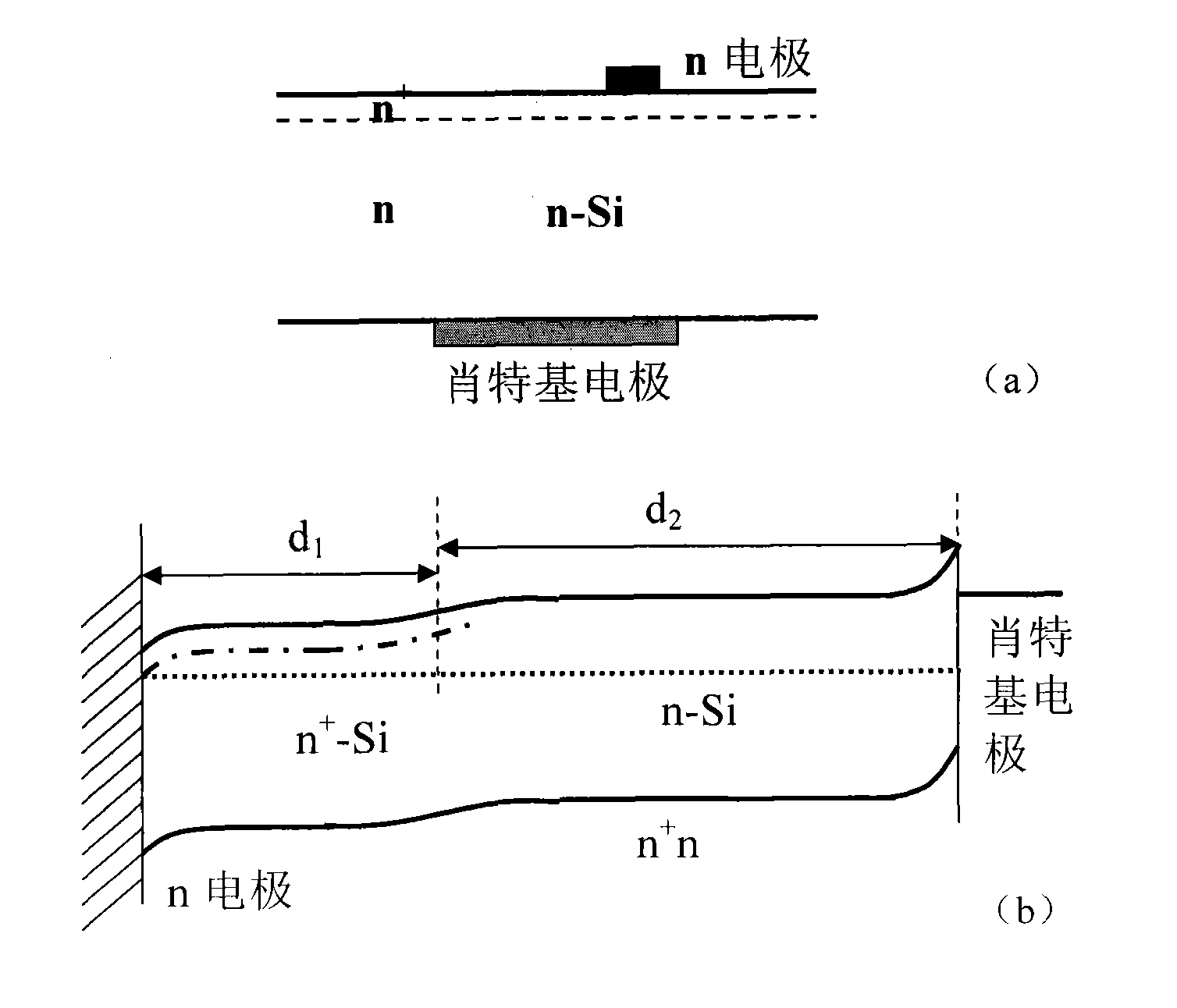
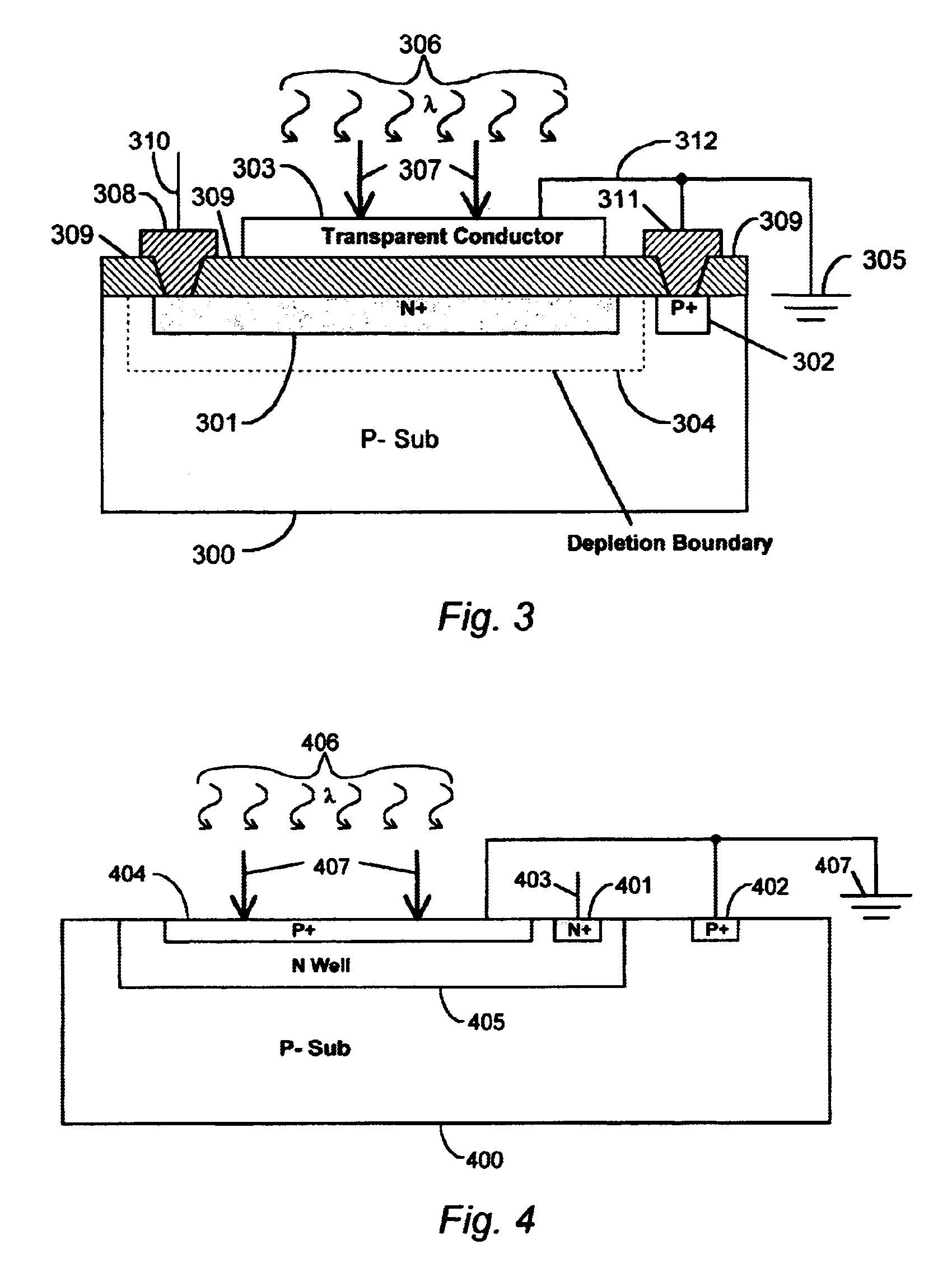
Method for preparing silicon detector with high photoelectric response at room temperature
InactiveCN101887930AHigh sensitivityIncrease the scope of applicationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactTransparent conducting film
The invention discloses a method for preparing a silicon detector with high photoelectric response at the room temperature. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a heavily doped n-type silicon (Si) layer with an impurity deep energy level on a light receiving surface of an n-type Si substrate, preparing a transparent conductive film on the heavily doped n-type Si layer, and preparing an ohmic contact n electrode on the transparent conductive film serving as a first electrode; and preparing a Schottky electrode on a back surface or the light receiving surface of the n-type Si substrate serving as a second electrode, or forming a p-type Si region on the back surface or the light receiving surface of the n-type Si substrate, and preparing an ohmic contact p electrode on the p-type Si region serving as the second electrode. By using the method, the photoelectric response of the silicon detector can be greatly improved, namely the flexibility is improved and the detection range is expanded to an infrared light region.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aerosol continuous radiation monitoring device for nuclear power plant
PendingCN109254316AEnsure safetyRadiation intensity measurementNuclear energy generationNuclear powerGamma ray
The invention provides an aerosol continuous radiation monitoring device for a nuclear power plant. The device comprises a shielding body, a detecting component disposed inside the shielding body, a filtering component disposed inside the shielding body and under the detecting component, and a circuit board and an ARM processing board disposed at the detecting component, wherein the detecting component comprises a PIPS semiconductor detector and a plastic scintillator detector, the filtering component comprises a filter housing, and the filter housing is provided with an inlet chamber, an exhaust chamber, a roll cassette, a cam, a paper pressing mechanism and a paper feeding motor. The aerosol continuous radiation monitoring device provided by the invention utilizes a PIPS semiconductor detector (passivated injection surface silicon detector) to detect alpha and beta radiations in the aerosol, and detects the background gamma rays presented in the environment through a large plastic scintillator detector.
Owner:SHAANXI WEIFENG NUCLEAR ELECTRONICS +1
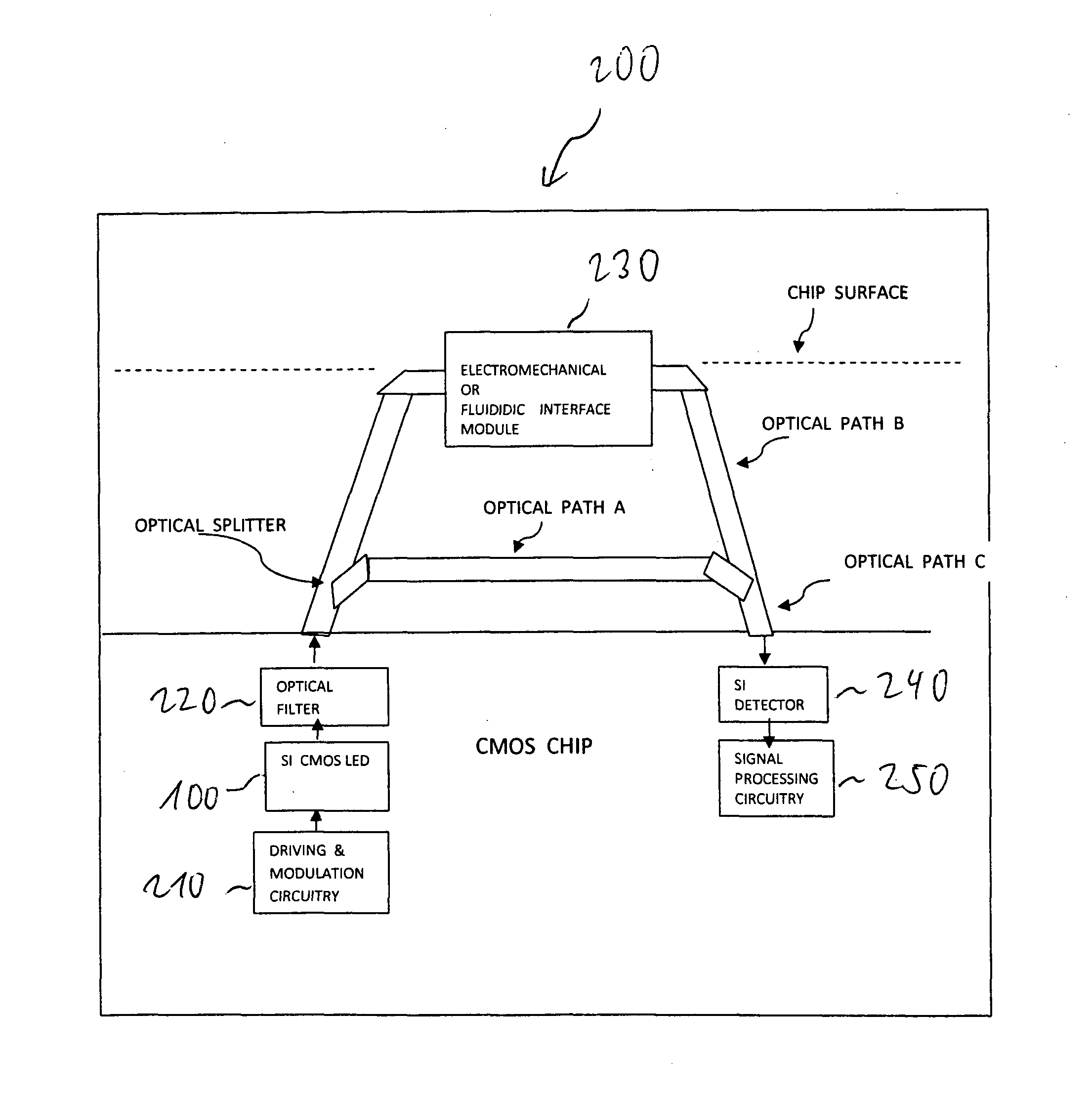
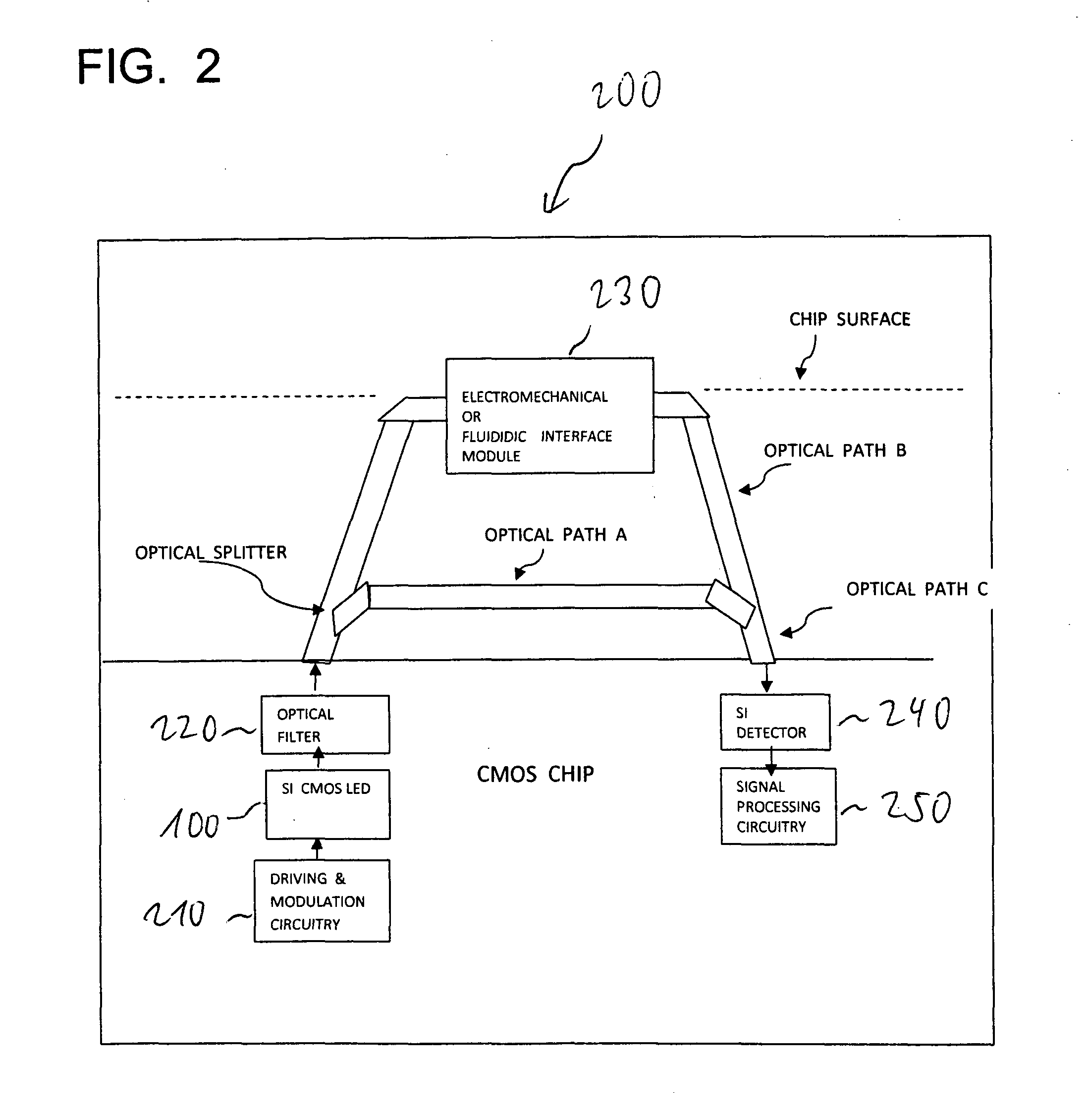
CMOS moems sensor device
InactiveUS20120154812A1Overcome disadvantagesHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSilicon detector
The present invention relates to a sensor device. More particularly, the invention relates to a CMOS-based micro-optical-electromechanical-sensor (MOEMS) device with silicon light emitting devices, silicon waveguides and silicon detectors being fabricated using current Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) technology or Silicon on Insulator (SOI) technology. According to the invention there is provided a sensor comprising: a Silicon-based light emitting structure; an integrated electro-optical mechanical interface structure that is capable to sense mechanical deflections; an integrated electronic driving and processing circuitry so as to detect physical parameters such as vibration, motion, rotation, acceleration.
Owner:TSHWANE UNIV OF TECH
Flat panel detector and lag data sheet generation method and lag compensation correction method thereof
ActiveCN108172659ASolve complex afterimage problemsImage enhancementFinal product manufactureSilicon detectorCorrection method
The invention provides a compensation correction method of a flat panel detector image lag. The compensation correction method comprises the following steps of generating a lag data sheet and storingthe data sheet in a flat panel detector or detector software; obtaining a current bright field image and a dark filed image; enabling a lag signal of each pixel in the dark field image to be corresponding to the lag data sheet, and finding out a lag value of the lag signal of each pixel corresponding to the lag data sheet, and a moment corresponding to the lag value; enabling the moment corresponding to the lag value to be added with the time interval of the collection time between the current bright field image and the dark field image to obtain a new moment, finding a lag value correspondingto the new moment from the lag data sheet, and generating a current image evaluation lag template matrix; and enabling the lag template matrix to be subtracted from the current bright field image toperform lag compensation correction. The compensation correction method of the flat panel detector image lag disclosed in the invention can be used for solving the complex lag problems, and is wide inapplicable range, and suitable for a noncrystalline silicon detector and amorphous selenium, CMOS and other semiconductor detectors.
Owner:SHANGHAI IRAY TECH
High-temperature sensor for metal tubular black body hollow cavity
ActiveCN103162840AImprove accuracyCompact structureRadiation pyrometryData processing systemBlack body
The invention relates to a high-temperature sensor for a metal tubular black body hollow cavity and belongs to the technical field of temperature sensors for measurement of high temperatures. The high-temperature sensor for the metal tubular black body hollow cavity comprises the black body hollow cavity, a shielding cover, a coupler, transmission optical fibers, a light splitting detection system and a data processing system, wherein the head portion of the outer surface of the black body hollow cavity is arranged to be in a rib-piece type structure according to the design, and the black body hollow cavity is arranged to be in a blind hole form according to the design. The black body hollow cavity made of high-temperature resistant metal materials is used as a to-be-sensed portion of the high-temperature sensor, the silica optical fibers are used for transmitting signals, a double silicon detector is used for splitting light and conducting photoelectric conversion, and therefore the high-temperature sensor for the metal tubular black body hollow cavity is compact in structure and reliable in performance. In addition, the shielding cover is arranged outside the black body hollow cavity according to the design; and combined with the special-shaped structure of the black body hollow cavity and through theoretical analysis and numerical calculation, the high-temperature sensor for the metal tubular black body hollow cavity has the advantages of being good in high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistant, high in accuracy and the like, and can solve the high-temperature measuring problem which cannot be solved at present.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Semiconductor bump-bonded x-ray imaging device
ActiveUS20150279890A1Reliable manufacturingSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCMOSPixel density
A high pixel density intraoral x-ray imaging sensor includes a direct conversion, fully depleted silicon detector bump bonded to a readout CMOS substrate by cu-pillar bump bonds.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
Radiation sensor with electro-thermal gain
InactiveUS20050061977A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSensor arrayRadiation sensor
A thermal sensor or sensor array for detecting including imaging of low level radiation. The sensor utilizes a thin film of pyro-optical material to modulate the reflectivity and / or transmission of a photonic carrier beam. The photonic carrier beam is modulated by the temperature of the pyro-optical film and detected by typically a silicon detector. A slight increase in the temperature of the pyro-optical film due to absorbed low level radiation causes a corresponding change in the electrical resistance of heaters within each pixel of the thermal sensor array. An external fixed amplitude voltage or current source provides power to increase the temperature of the pyro-optical film beyond the heating caused by the absorption of low level radiation alone. This thermal amplification effect provides a radiation sensor with electro-thermal signal gain.
Owner:MULTISPECTRAL IMAGING
Photo detector methods to reduce the disabling effects of displacement current in opto-couplers
InactiveUS6864555B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitancePhotovoltaic detectors
This invention discloses the several means by which transient noise due to capacitance related displacement current can be excluded from the optical signal coming from a silicon detector used in opto-couplers. The exclusion of such noise permits a high degree of detector sensitivity which permits the use of low efficiency silicon based LEDs for opto-coupler applications.
Owner:WORLEY EUGENE ROBERT
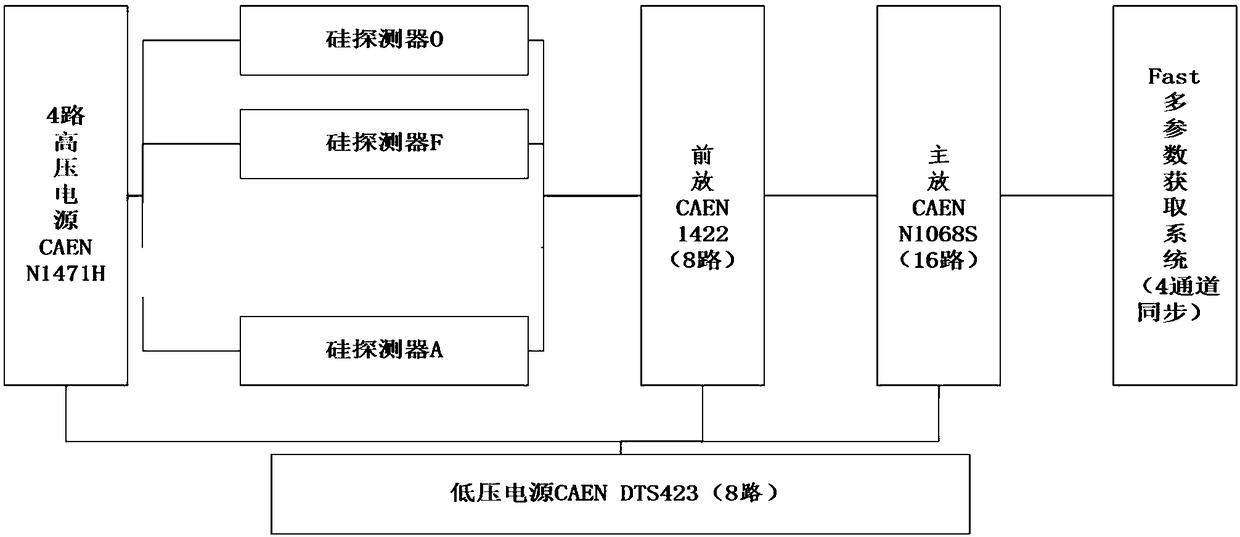
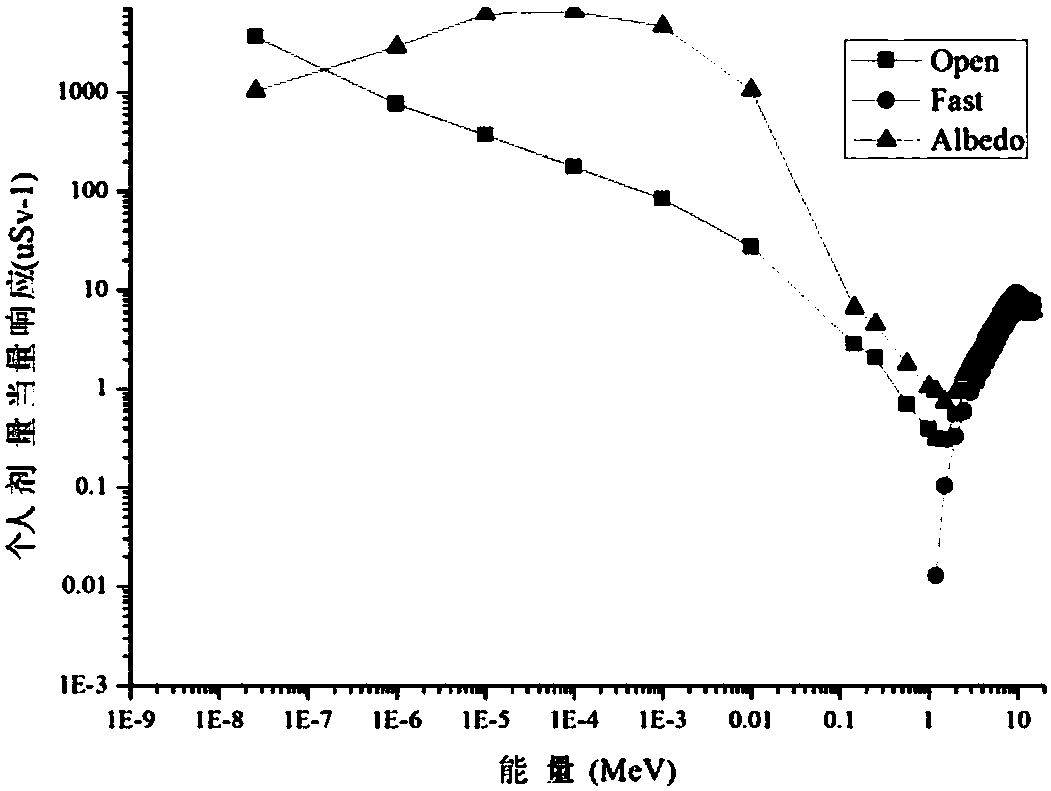
Active neutron personal dosimeter based on three silicon detectors, and measurement method of active neutron personal dosimeter
ActiveCN108445529AGive exactLow detection limitNeutron radiation measurementDosimeterSilicon detector
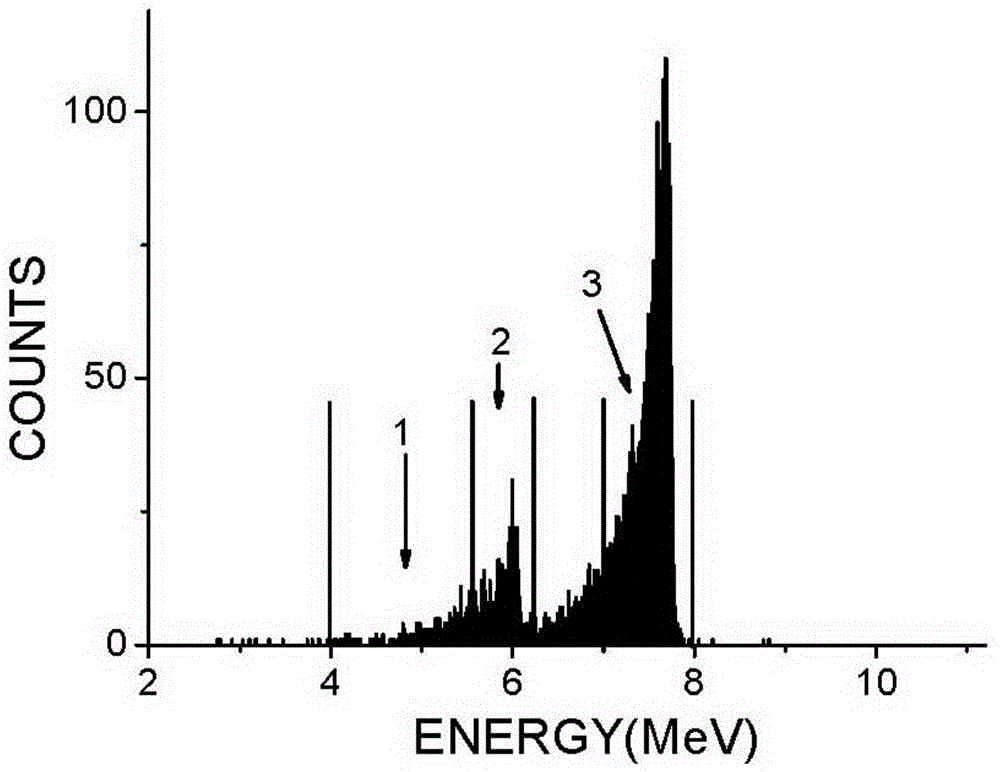
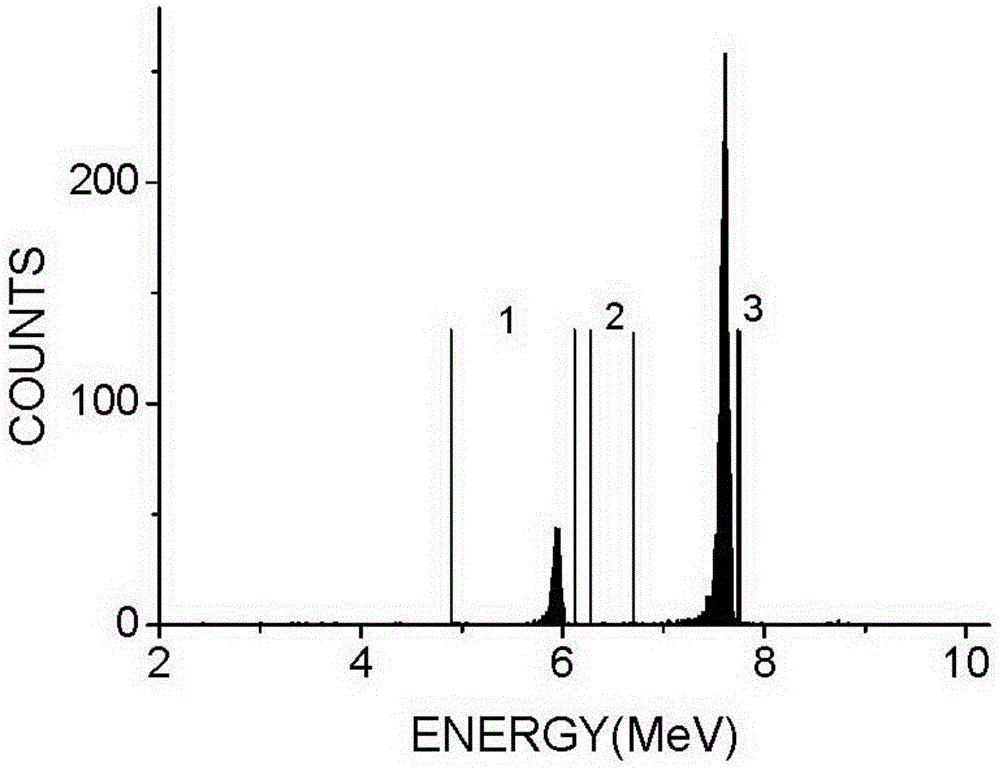
The invention relates to an active neutron personal dosimeter based on three silicon detectors, and a measurement method of the active neutron personal dosimeter. The personal dosimeter comprises a main detector, an outer transformant module, and a nuclear electronics system. The main detector and the outer transformant module comprise three passivation injection planar silicon detectors which aresequentially an Open detector, a Fast detector and an Albedo detector from the top to the bottom. A polyethylene layer and a 6LiF coating layer are disposed in front of the Open detector, a polyethylene layer is arranged in front of the Fast detector, and a boron-containing polyethylene layer, a polyethylene layer and a 6LiF coating layer are arranged in front of the Albedo detector. The nuclearelectronics system provides high voltages for all detectors, and obtains detection signals for multichannel analysis. The personal dosimeter provides two measurement modes. A direct reading mode can present the neutron fluence and personal dose equivalent information in real time, and a spectrum unfolding mode can give a more precise neutron field power spectrum. The personal dosimeter is wide inenergy measurement range, has the energy resolution capability, and can be used in an n-gamma mixed field.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
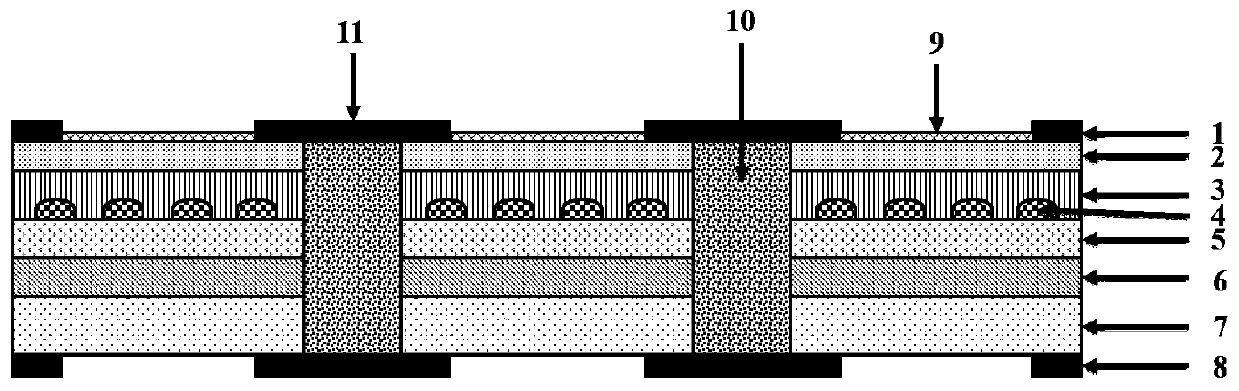
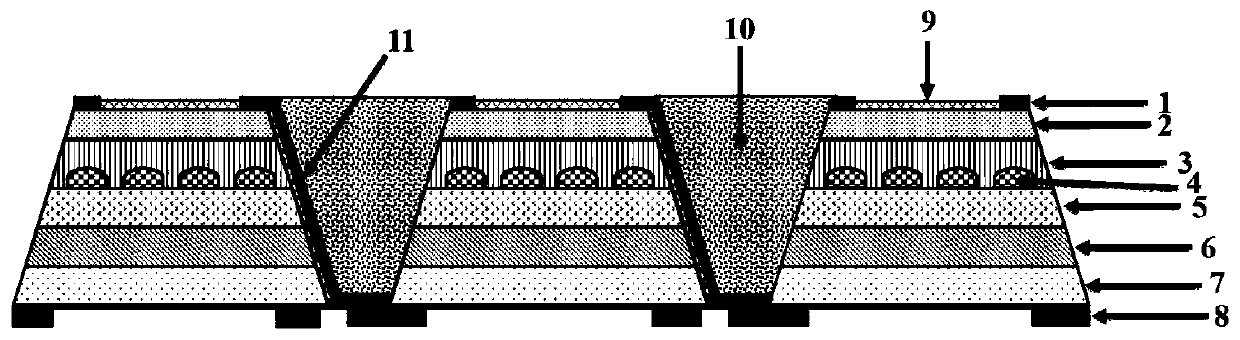
Integrated biosensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106940298AEasy Array SensingReduce lossPhase-affecting property measurementsOptical power meterPhotodetector
The invention discloses an integrated biosensor and a preparation method thereof, wherein an incident waveguide is arranged on the input end of a body, the input end of a waver filter is positioned on the input end of the body, the output end of the wave filter is positioned on the output end of the body, a thermal tuning micro ring is arranged on the output end of the wave filter, the input end of a power splitter is positioned on the download end of the thermal tuning micro ring, a sensing micro ring is arranged on the other output end of the power splitter, a germanium-silicon detector is arranged on the output port of the download end of the sensing micro ring, a heating electrode is arranged on the thermal tuning micro ring, and the sensing micro ring is positioned in a sensing window. According to the present invention, the photodetector and the sensing passive device are monolithically integrated so as to easily perform the array sensing; the input light source is the broad spectrum light source, and the external optical power meter is not required, such that the loss and the complexity of the system are reduced; and the expensive tunable laser and the high-precision spectrometer are not required so as to substantially reduce the whole system cost.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Alpha, beta and gamma radioactive aerosol continuous sampling and measuring device
InactiveCN104216002AAccurate measurementConvenient and efficient controlRadiation intensity measurementSodium iodideReducer
The invention relates to an alpha, beta and gamma radioactive aerosol continuous sampling and measuring device which comprises a frame, a sampling chamber, a measuring chamber, a boosting motor, a tape conveying motor, a tape collection plate, a tape feeding plate, a filter paper tape, a passivated ion implantation plane silicon detector and a sodium iodide detector. The sampling chamber comprises an upper air chamber and a lower air chamber, and the upper air chamber and the lower air chamber are communicated with each other; the top of the upper air chamber is provided with an air inlet, and the bottom of the lower air chamber is provided with an air outlet; the measuring chamber comprises an upper measuring chamber and a lower measuring chamber, and the upper measuring chamber and the lower measuring chamber are communicated with each other; an output end of the boosting motor is connected with an eccentric shaft through a speed reducer, and the eccentric shaft is connected with both the upper air chamber and the upper measuring chamber through a connecting rod; the tape conveying motor is arranged on one side, close to the measuring chamber, of the frame; the tape collection plate is connected with the tape conveying motor through a speed reducer; the tape feeding plate is arranged on the other side of the frame; one end of the filter paper tape is wound on the tape feeding plate, and the other end of the filter paper tape sequentially penetrates between the upper air chamber and the lower air chamber and between the upper measuring chamber and the lower measuring chamber and then are wound on the tape collection plate; the passivated ion implantation plane silicon detector is arranged at the bottom of the upper measuring chamber; the sodium iodide detector is arranged in the lower measuring chamber.
Owner:BEIJING RADIATION APPL RES CENT
Near-infrared polarization interferometer spectrometer
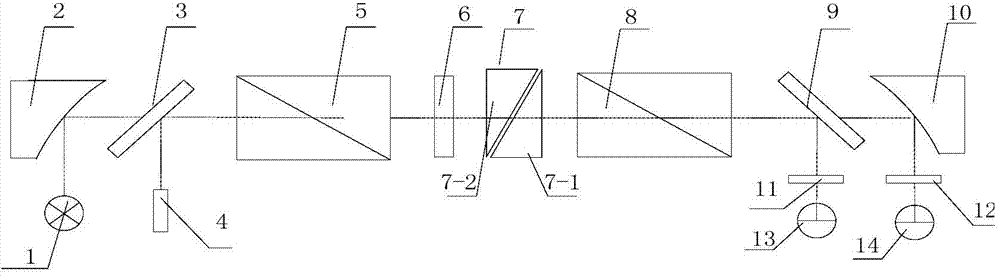
ActiveCN103900694ASimple structureMiniaturizationRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryDirect couplingPrism
The invention relates to a near-infrared polarization interferometer spectrometer. The near-infrared polarization interferometer spectrometer comprises a light source group, a collimation off-axis parabolic mirror, a first cold light mirror, a polarizing prism, a compensation crystal, a scanning optical wedge component, an analyzing prism, a second cold light mirror, a convergence off-axis parabolic mirror and a detector which are arranged in sequence in the light-path direction. The light source group comprises a halogen tungsten lamp which carries out direct coupling output through a single mode fiber and a He-Ne laser device for sending a calibration light source. The detector comprises a silicon detector and an InGaAs detector. The near-infrared polarization interferometer spectrometer is simple in structure.
Owner:重庆中科摇橹船信息科技有限公司
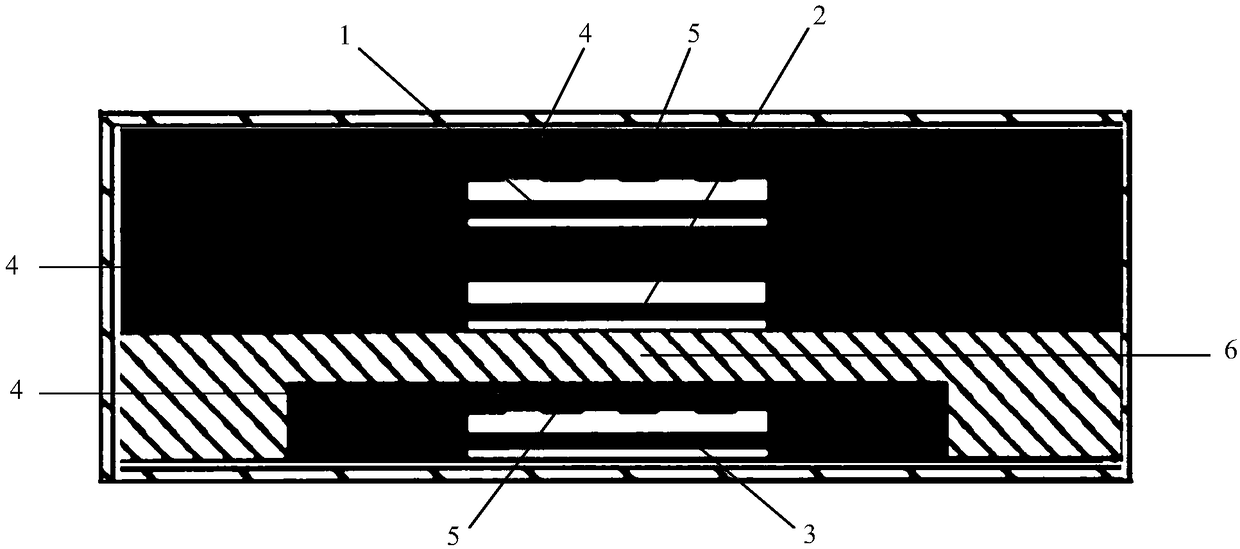
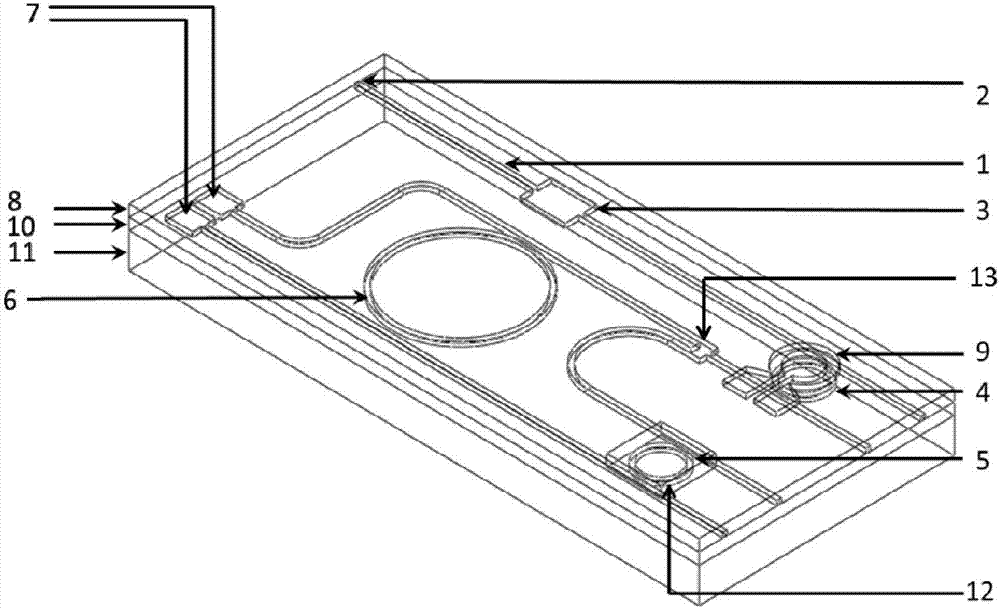
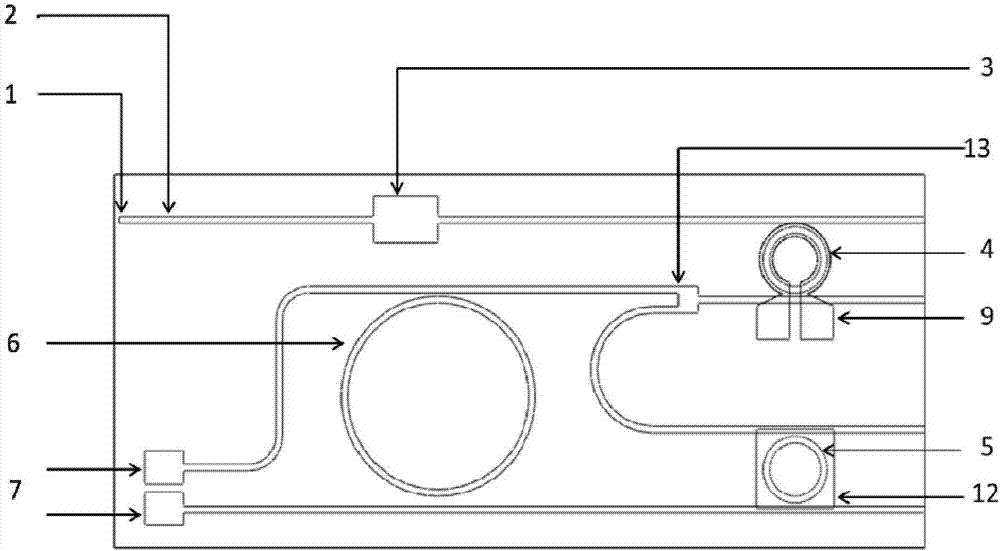
Three-dimensional groove electrode silicon detector with variable center collecting electrodes
ActiveCN106449802AIncrease in structural volumeSolve the problem of inconvenient structure size adjustmentSemiconductor devicesState of artP type silicon
The invention discloses a three-dimensional groove electrode silicon detector with variable center collecting electrodes. A peripheral electrode comprises a first linear portion, a second linear portion and a bent portion, wherein the first linear portion is parallel to the second linear portion, and the end of the first linear portion is hermetically connected with the end of the second linear portion through the bent portion. A long center electrode is positioned in the middle of the peripheral electrode and parallel to the first linear portion and the second linear portion, and the length of the first linear portion is as same as that of the second linear portion. Isolation silicon is arranged between the peripheral electrode and the long center electrode, a p type silicon substrate is arranged below the long center electrode, and the bottom of the p type silicon substrate is plated with a silicon dioxide protective layer. The three-dimensional groove electrode silicon detector is simple and reasonable in structure and strong in radiation resistance, and solves the problems that electric fields between a positive electrode and a negative electrode are non-uniform, a weak electric field area exists, the size of a single detector unit structure has a great influence on the radiation resistance, and consequently, the size is inconveniently adjusted in the prior art.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Ultraviolet detection converter and methods for preparing and using same
ActiveCN104965318ALow priceImprove signal-to-noise ratioPrismsNon-linear opticsTotal internal reflectionUltraviolet detectors
The invention relates to an ultraviolet detection converter and methods for preparing and using same, and relates to an ultraviolet detection and imaging method. The invention aims to solve the problems that a reading circuit of a present ultraviolet detector is difficult in technology and high in cost. An ultraviolet detection converter is an optical isosceles prism formed by cutting transparent relaxor ferroelectric ceramic material, and the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is 150 to 165 degrees. The method for preparing the ultraviolet detection converter comprises cutting a relaxor ferroelectric ceramic block into an isosceles prism, grinding and polishing to obtain the ultraviolet detection converter. Ultraviolet light emitted from an ultraviolet lens array irradiates on the bottom of the ultraviolet detection converter, near infrared parallel light emitted from an infrared light source irradiates on the bottom of the ultraviolet detection converter in the way that incident angle is less than a total internal reflection angle, and a silicon detector array receives the light. The spatial distribution of the near infrared light is the same as that of the ultraviolet light emitted from the ultraviolet lens array, a reading circuit and array processing are needless.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Radiation hard silicon detectors for x-ray imaging
ActiveUS20180321394A1Improve robustnessImprove efficiencyHandling using diaphragms/collimetersRadiation intensity measurementSoft x rayX-ray
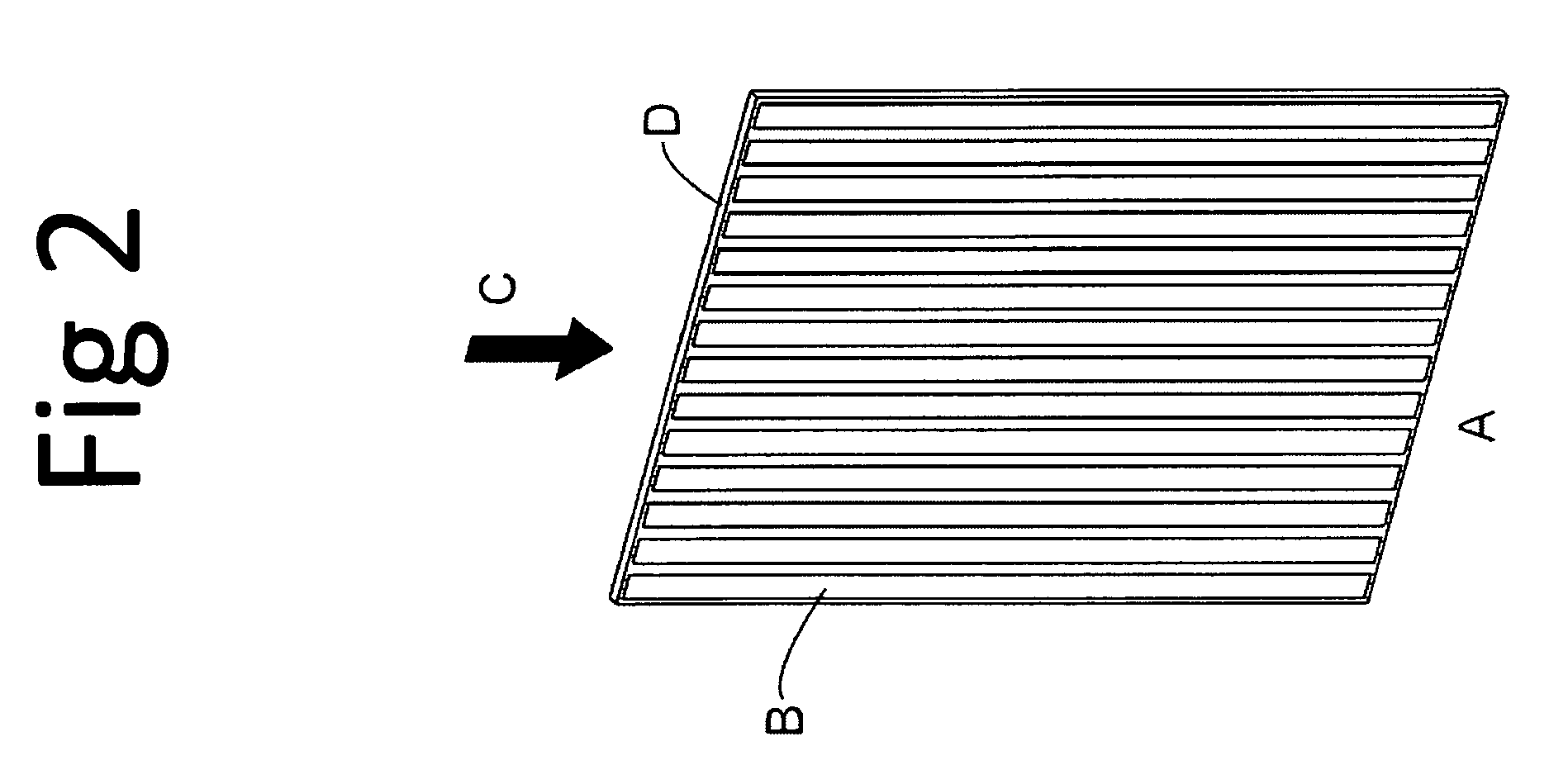
Disclosed is a detector system for x-ray imaging. The detector system includes a detector having a plurality of edge-on detector modules. Each of the edge-on detector modules includes a first edge that is adapted to be oriented towards an x-ray source and a front-side running essentially parallel to the direction of incoming x-rays. The front-side includes at least one charge collecting electrode. At least a subset of the plurality of edge-on detector modules being pairwise arranged, front-side to front-side, whereby a front-side to front-side gap is defined between the front-sides of the pairwise arranged edge-on detector modules. The pairwise arranged edge-on detector modules are associated with an anti-scatter collimator arranged in the x-ray path between the x-ray source and the edge-on detector modules and overlapping the front-side to front-side gap.
Owner:PRISMATIC SENSORS
Manufacturing method of silicon detector array device for enhancing blue light efficiency
ActiveCN109698248AReduce reflectionImprove acceptance rateSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyControl layer
A manufacturing method of a silicon detector array device for enhancing the blue light efficiency belongs to the field of photoelectric technology. The problem on how to provide a manufacturing methodof a silicon detector array device with high blue light sensitivity, high gain and high integration is solved. The preparation method of the invention includes the following steps: depositing an avalanche layer on a cleaned substrate material; depositing a field control layer on the upper surface of the avalanche layer; depositing an absorption layer on the upper surface of the field control layer and preparing doping junctions by ion implantation; depositing a non-depletion layer on the upper surface of the absorption layer; preparing isolation regions; preparing anodes and anode electrode leads; preparing a transparent layer on the non-depletion layer or on the non-depletion layer and the anodes; thinning the substrate; and finally, preparing cathodes and cathode electrode leads, removing the hard substrate, and completing packaging to obtain an array device. The array device manufactured by the method has high blue light responsiveness and high quantum efficiency.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com