Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) triple-frequency motion-to-motion positioning method
A positioning method and frequency-moving technology, applied in the field of satellite navigation and positioning, can solve problems such as the failure of the ambiguity value of the whole circle, achieve high-precision and high-efficiency motion-to-motion positioning, improve calculation accuracy, and improve calculation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The technical scheme of the present invention is described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment:
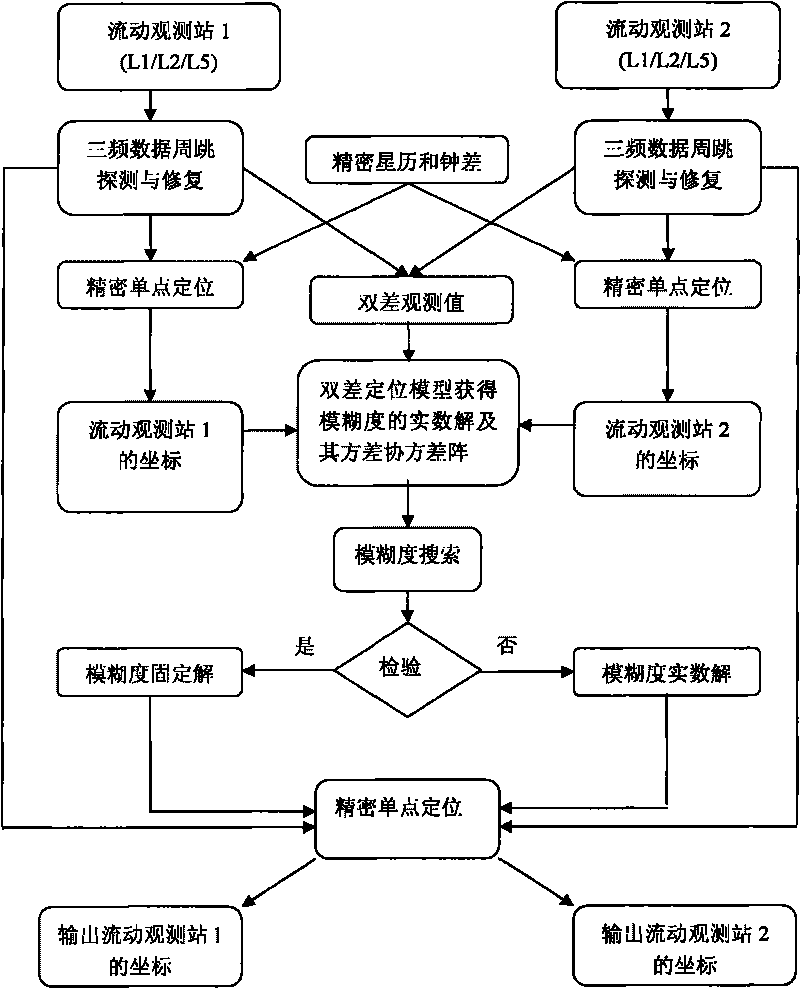
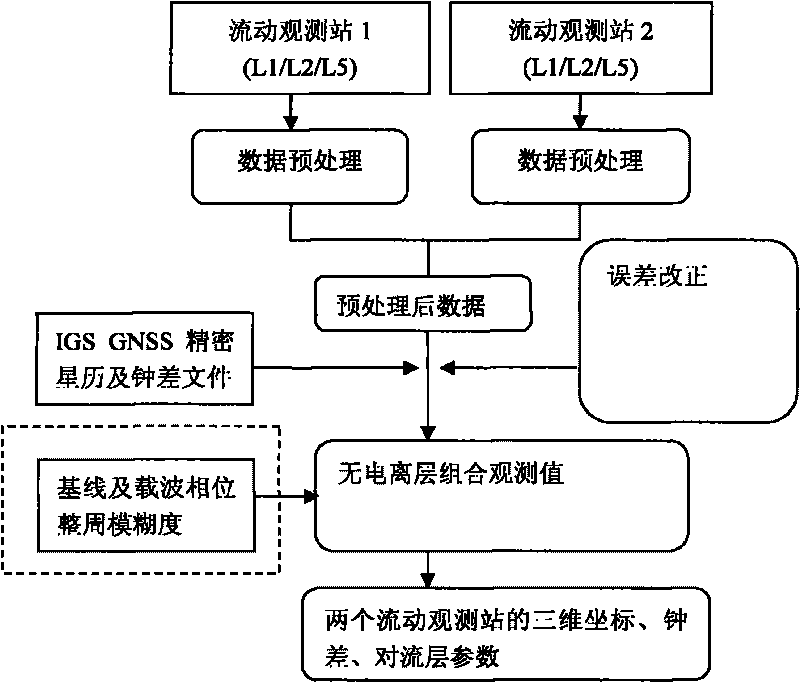
[0023] The three frequency bands involved in the embodiment are three frequency bands, respectively identified as L1 / L2 / L5. The GNSS mobile-to-mobile positioning process provided by the embodiment of the present invention is as follows: figure 2 Shown:
[0024] In the starting epoch, perform the following three steps,
[0025] Step 1. The two moving carriers are respectively used as mobile observation station 1 and mobile observation station 2, and the original observation tri-frequency GNSS data is provided under the precise ephemeris and clock error, and then the original tri-frequency GNSS data is preprocessed, including Tri-frequency data cycle slip detection and repair.
[0026] Step 2: According to the preprocessed tri-frequency GNSS data obtained from mobile observation station 1, perform tri-frequency precise point positioning on mobile...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com