Logic circuit utilizing pass transistors and logic gate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
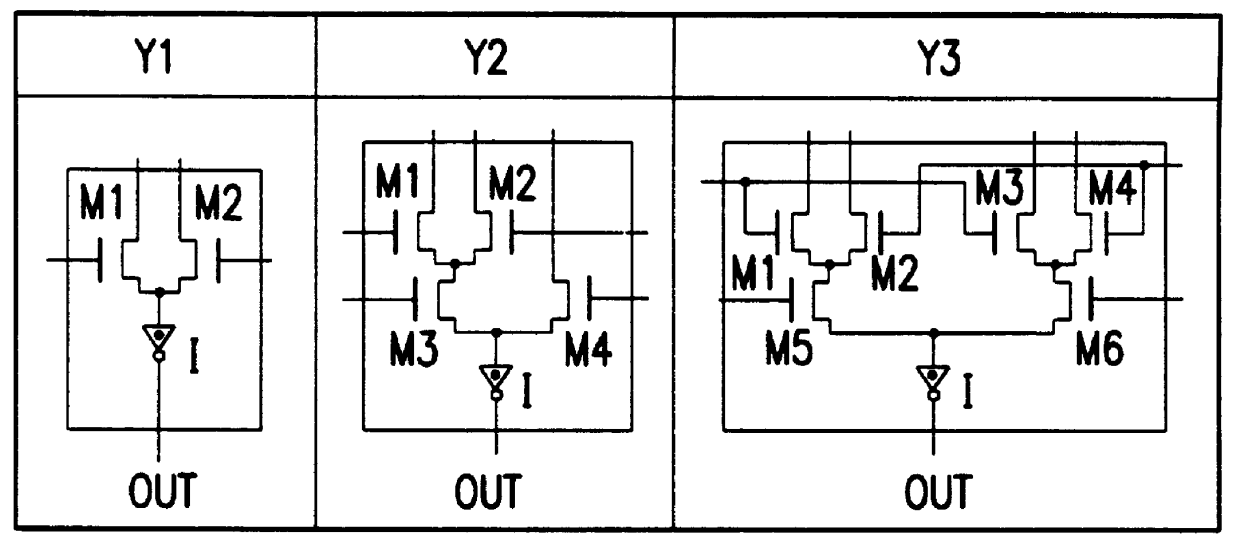
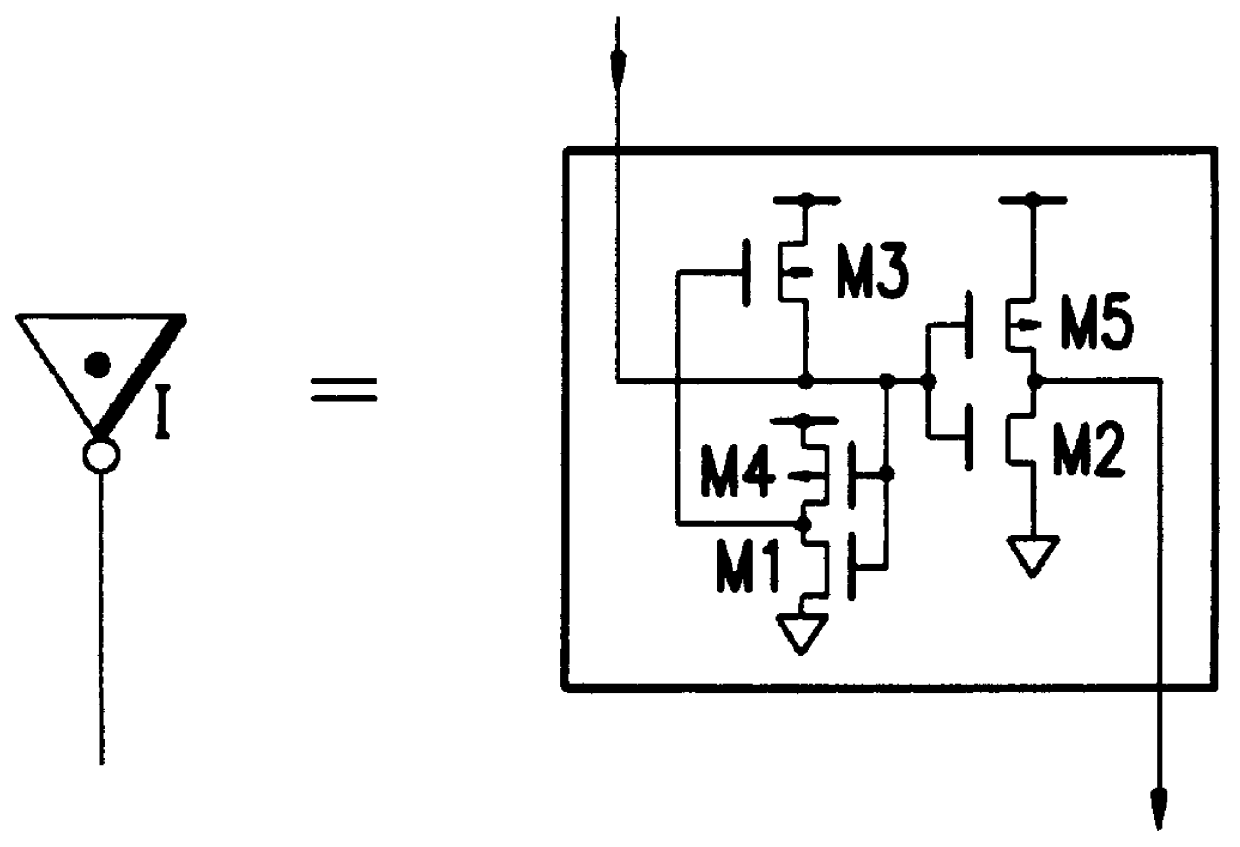
FIG. 12 is a circuit diagram of a logic circuit of the present invention. This logic circuit includes two single-stage pass-transistor logic trees. N-channel MOS transistors and P-channel MOS transistors employed are enhancement mode MOS transistors whose threshold voltages are on a level with those of MOS transistors employed in a conventional CMOS logic circuit. For example, when a supply voltage (=power supply potential-reference potential) is 3.3 V, the threshold voltages of the N-channel MOS transistors and P-channel MOS transistors are typically 0.55 V and -0.55 V, respectively.
N-channel MOS transistors M1 and M2 constitute a first pass-transistor logic tree. In the first pass-transistor logic tree, the sources and gates of the transistors M1 and M2 act as input nodes and receive logic signals a, b, c, and c. The drains of the transistors M1 and M2 are coupled, thus forming an intermediate output node. The logic signals a and b can be mutually independent, while the logic sign...
second embodiment
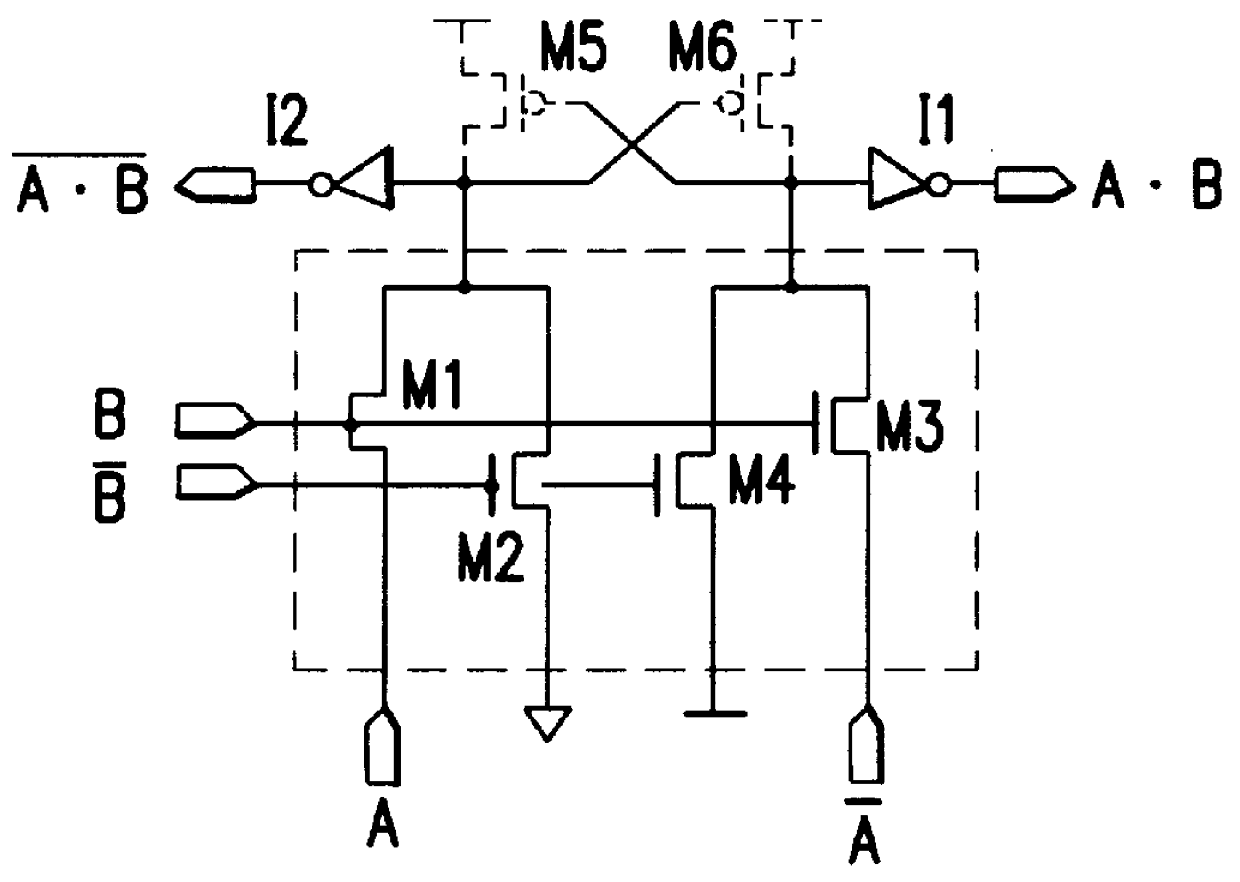
FIG. 16 is a circuit diagram of a logic circuit of the present invention having two single-stage pass-transistor logic trees.
Each of T1 and T2 in the drawing denotes a circuit (hereinafter, a pair pass transistor element) enclosed in a square drawn with a dot-dash line in FIG. 17. Here, an N-channel MOS transistor M1A and P-channel MOS transistor M1B are connected in parallel with their sources and drains coupled, thus forming a first unit pass transistor. An N-channel MOS transistor M2 A and P-channel MOS transistor M2B are connected in parallel with their sources and drains coupled, thus forming a second unit pass transistor. The output terminals (drains) of the first and second unit pass transistors are coupled. A pair pass transistor element T is thus configured. The N-channel MOS transistor and P-channel MOS transistor constituting each unit pass transistor are connected so that they can receive two input signals P and Q, which are mutually complementary, through the gates ther...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com