Method and system for uncorrectable error detection
a technology of error detection and error correction, applied in the field of error correction codes, can solve problems such as unresolved problems, multi-bit errors, and inability to correct, and achieve the effects of improving the accuracy of error detection, and increasing the difficulty of ue detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
)
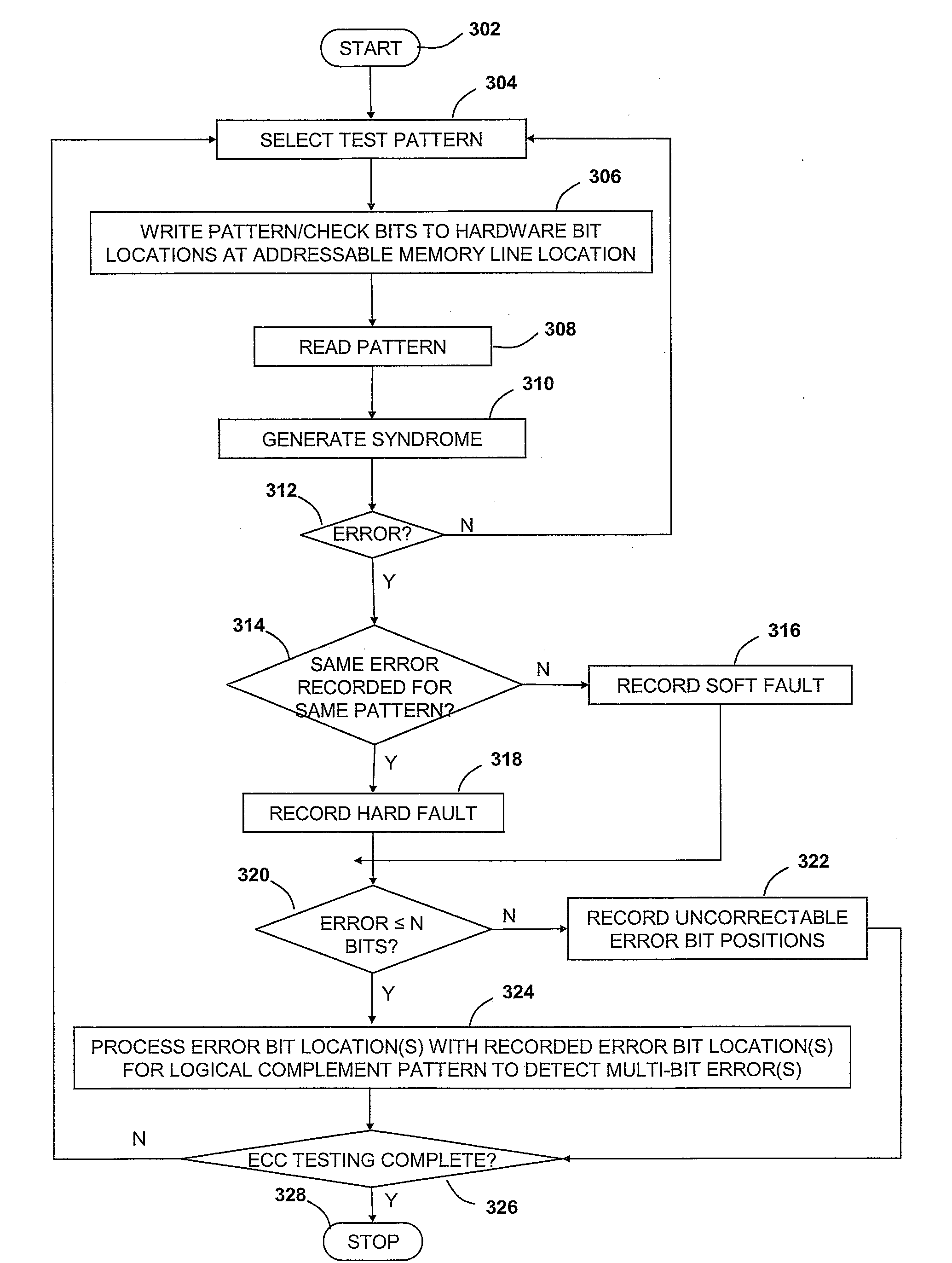
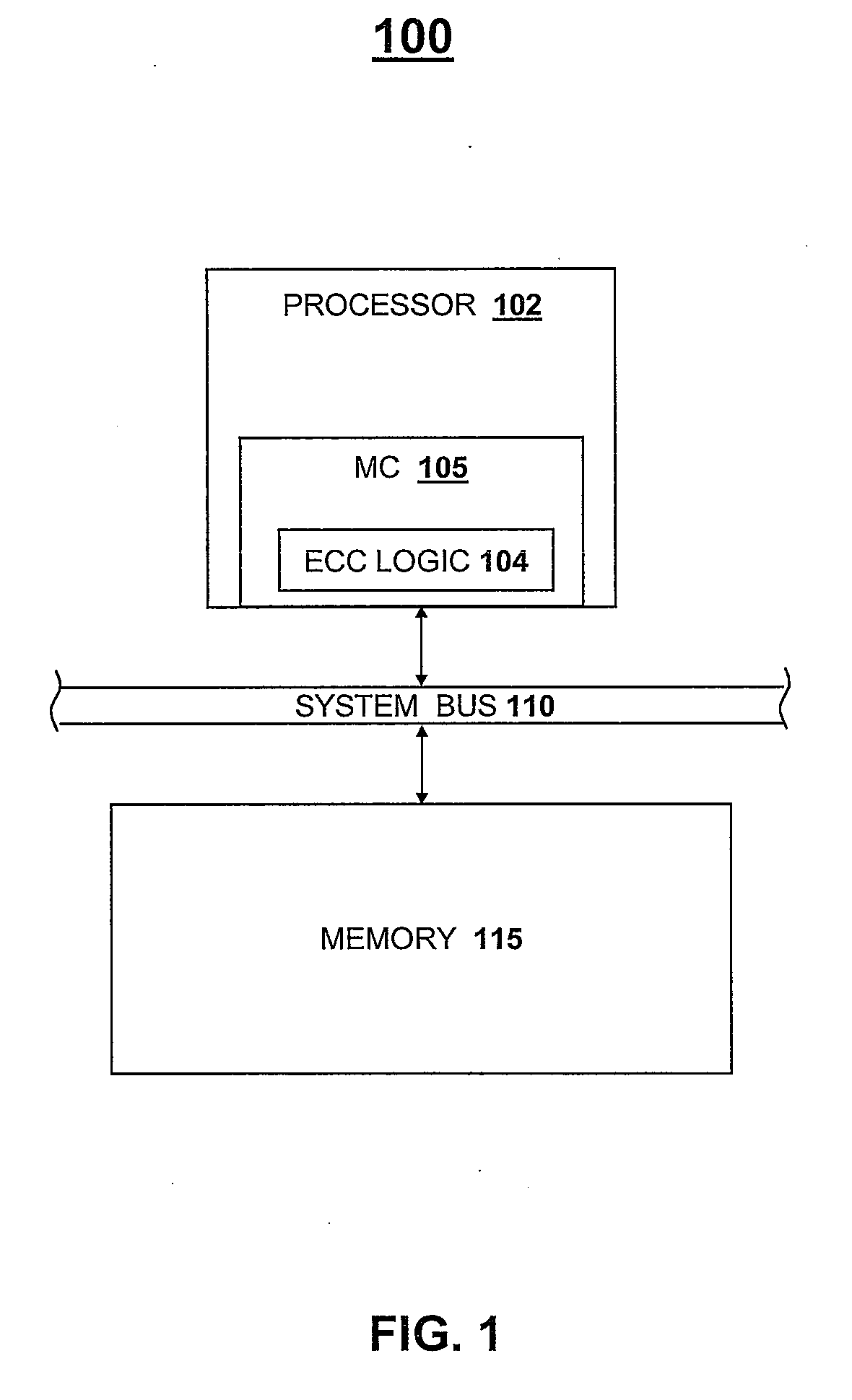
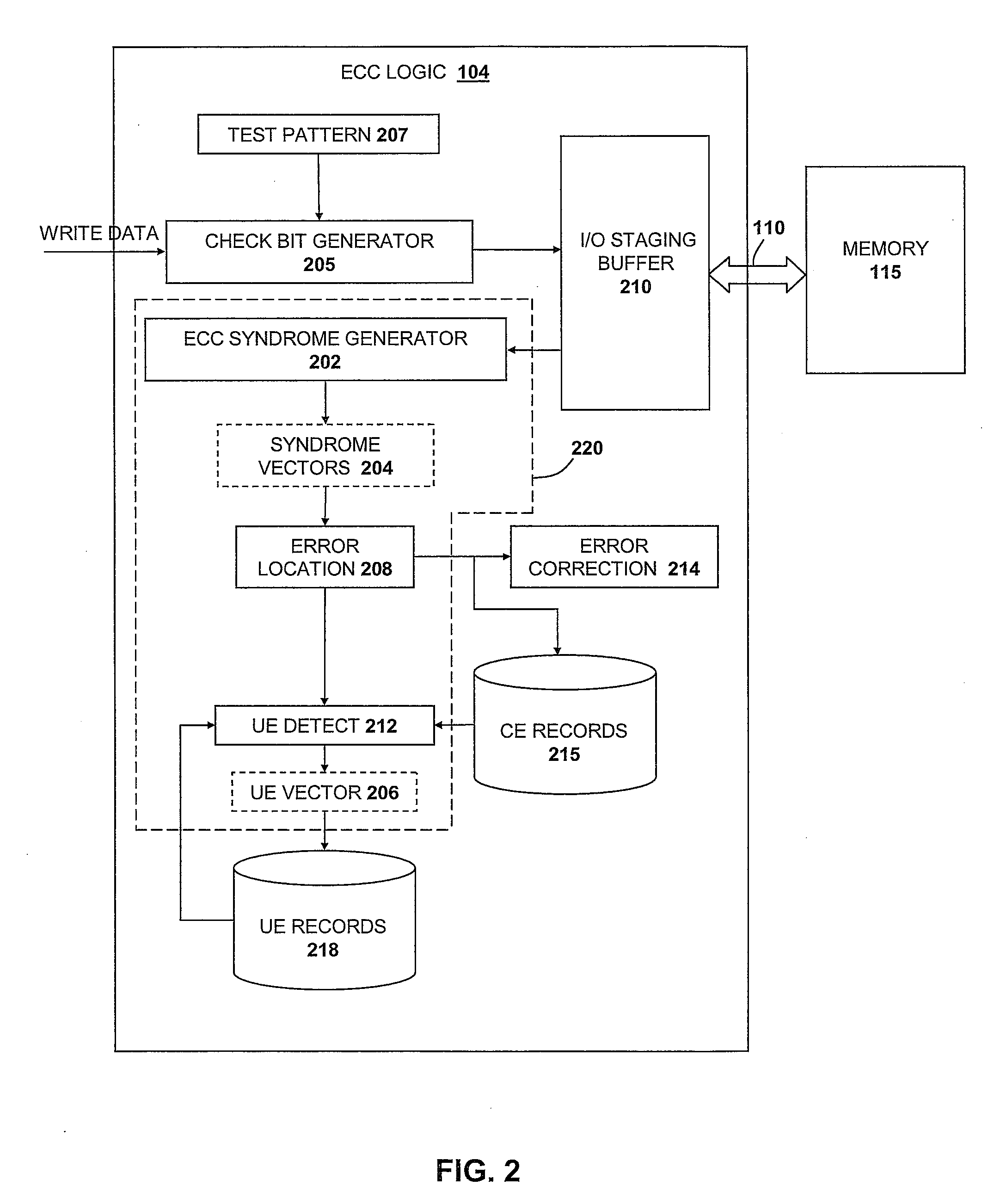
[0019]The present invention is directed to a method and system for utilizing correctable error (CE) analysis to identify otherwise undetected multi-bit errors. Specifically, and as depicted and described below with reference to the figures, the present invention utilizes CE and uncorrectable error (UE) logging mechanisms in combination with error detection mechanisms native to conventional error correction code (ECC) logic to detect multi-bit errors falling outside the scope of errors defined by the ECC logic as being correctable. In the depicted embodiments, the multi-bit error detection method and system are implemented within a memory system in which ECC logic is utilized to detect and correct errors within memory devices. It should be noted that the invention may be more widely applicable to other devices in which data is stored in and / or transported to and from designated hardware bit storage or transport devices such as in registers, buffers, bitlines, etc. that may be includ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com