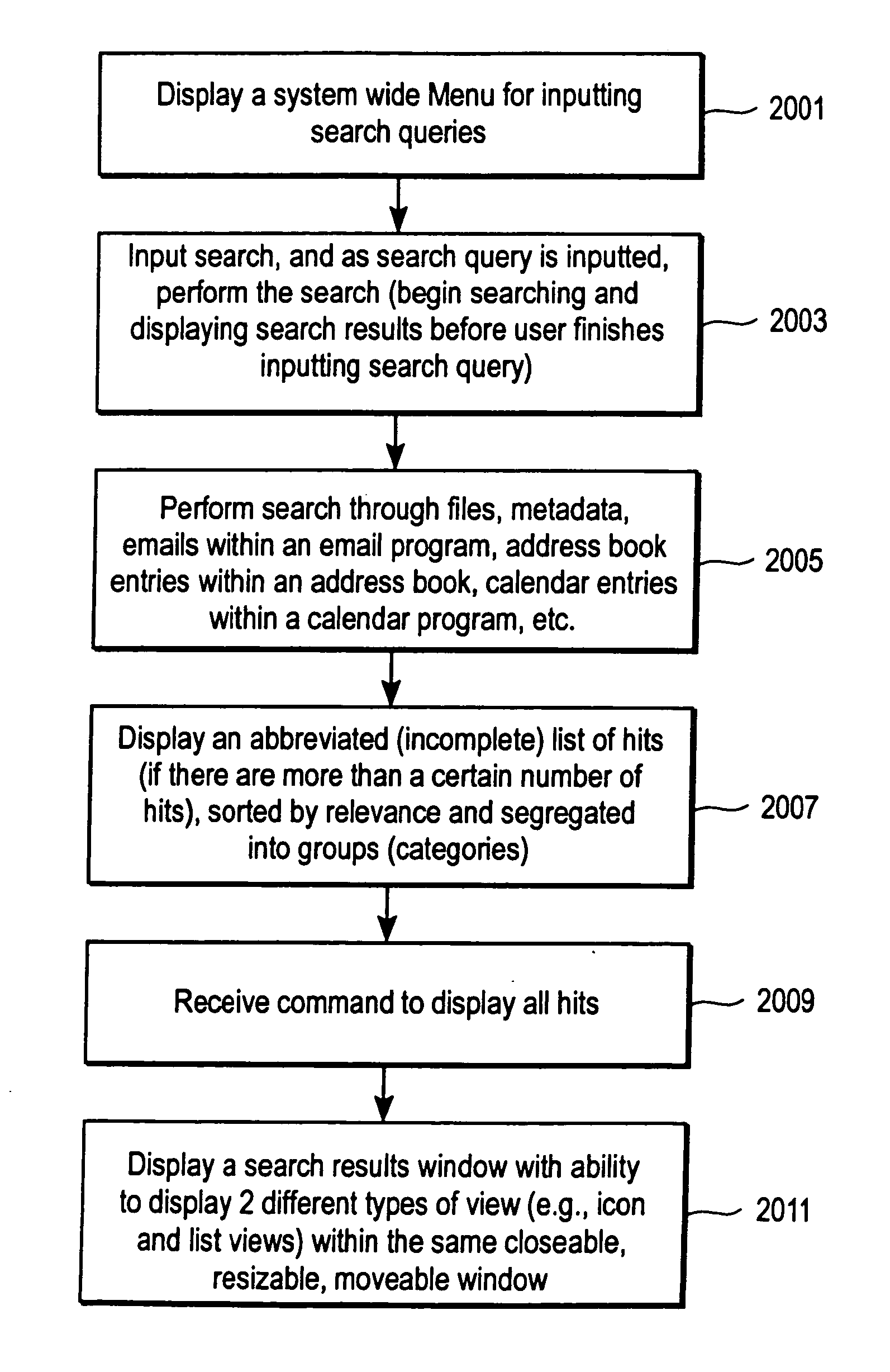
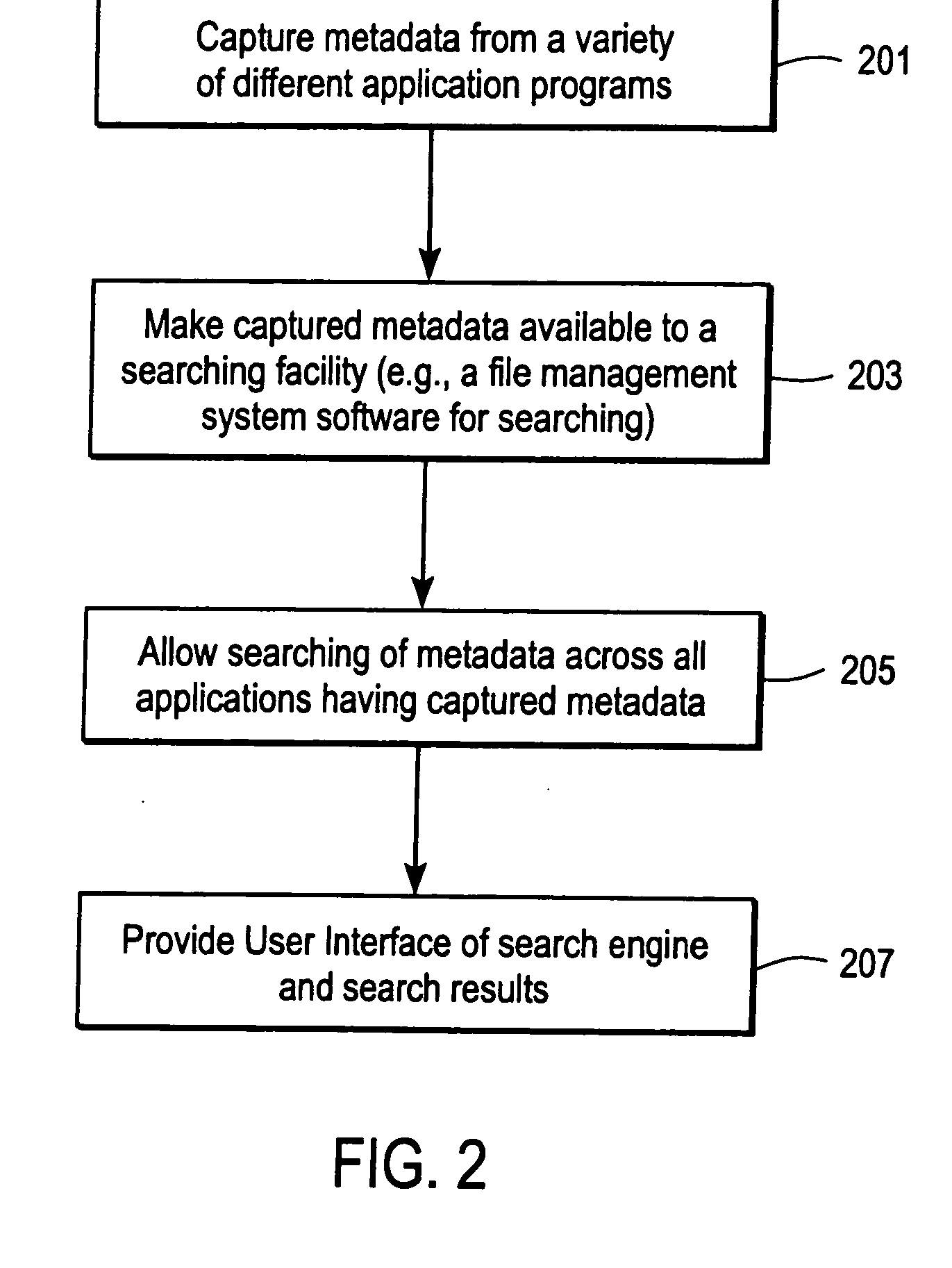
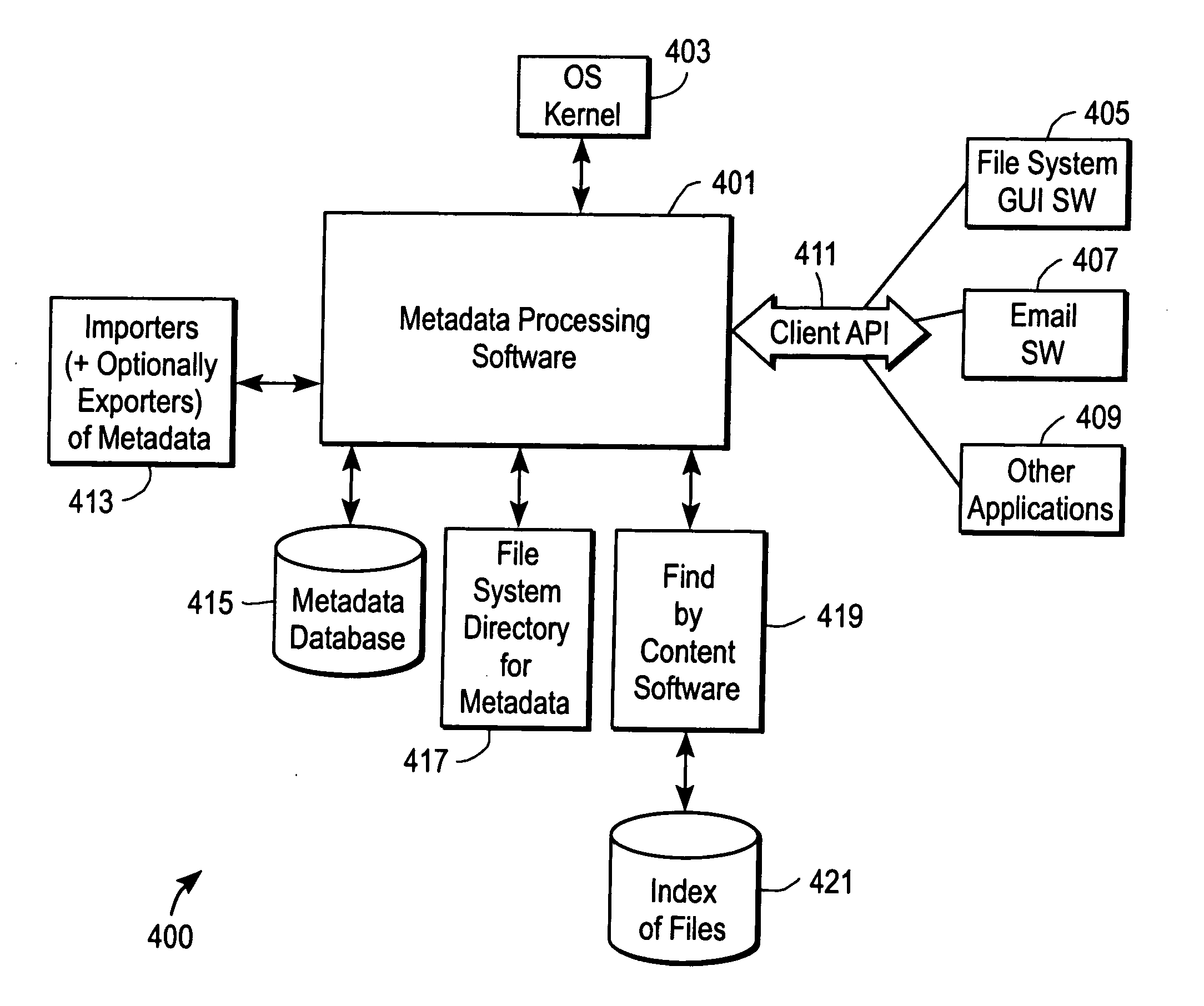
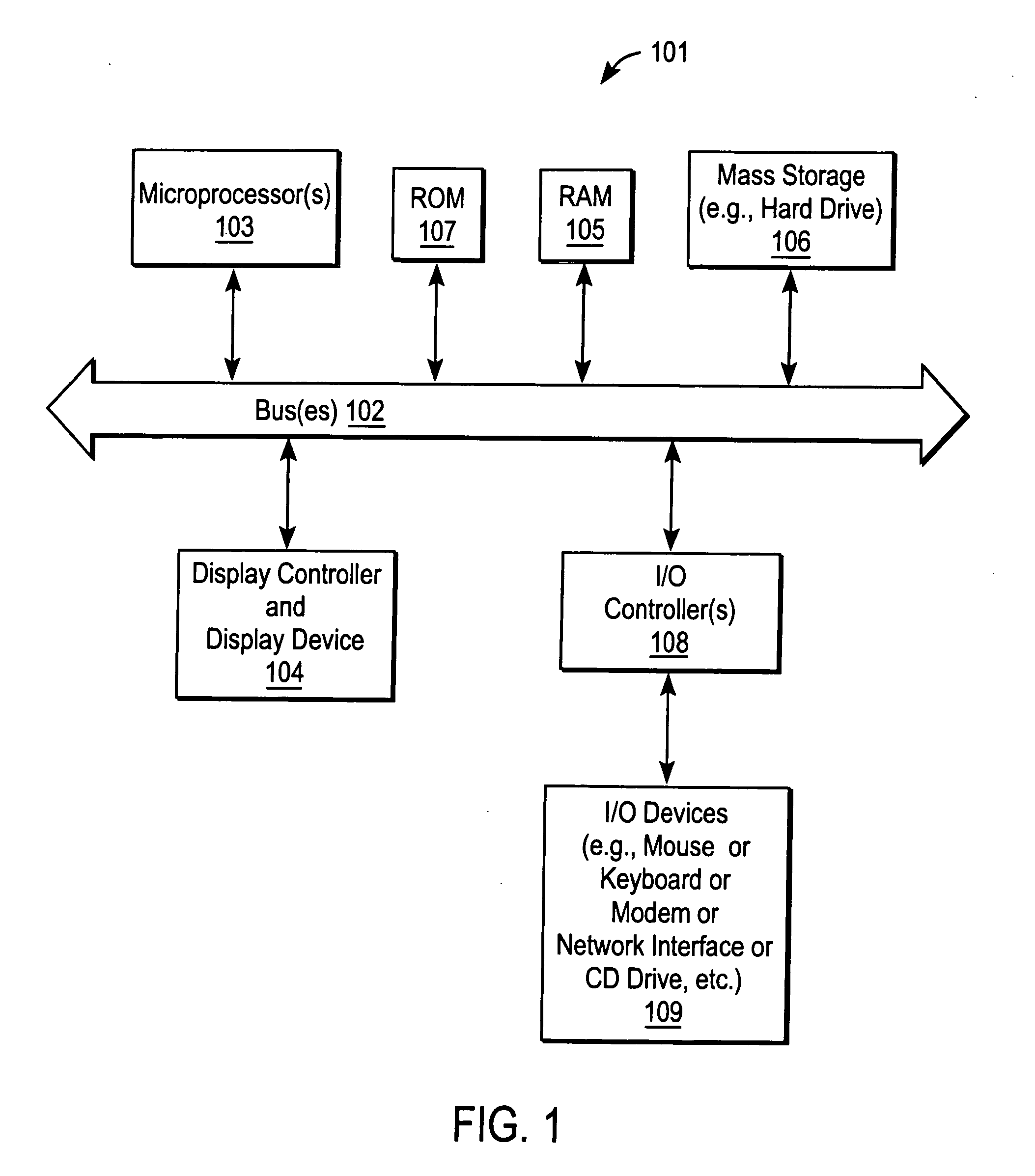
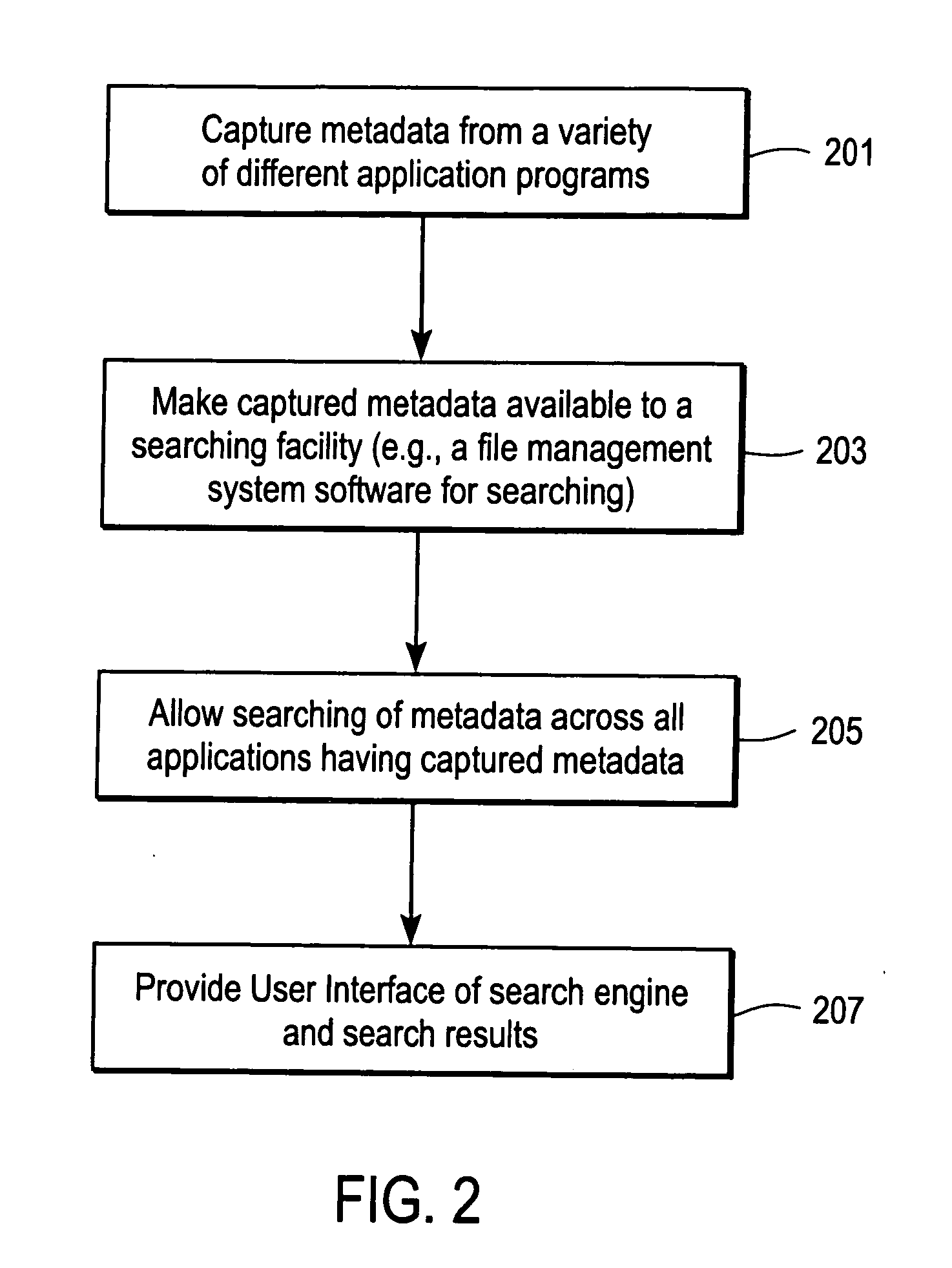
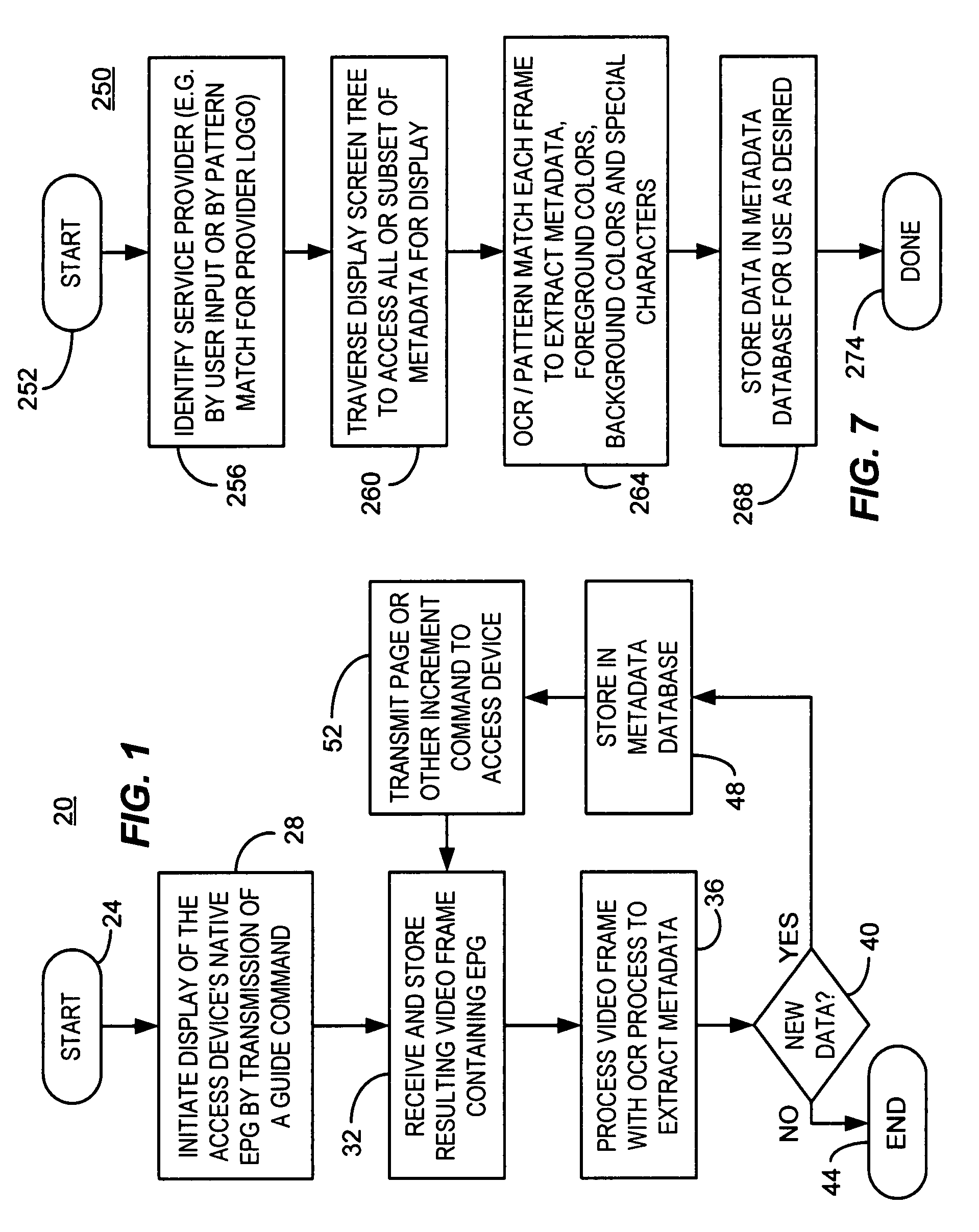
Patents
Literature
288 results about "Metadatabase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
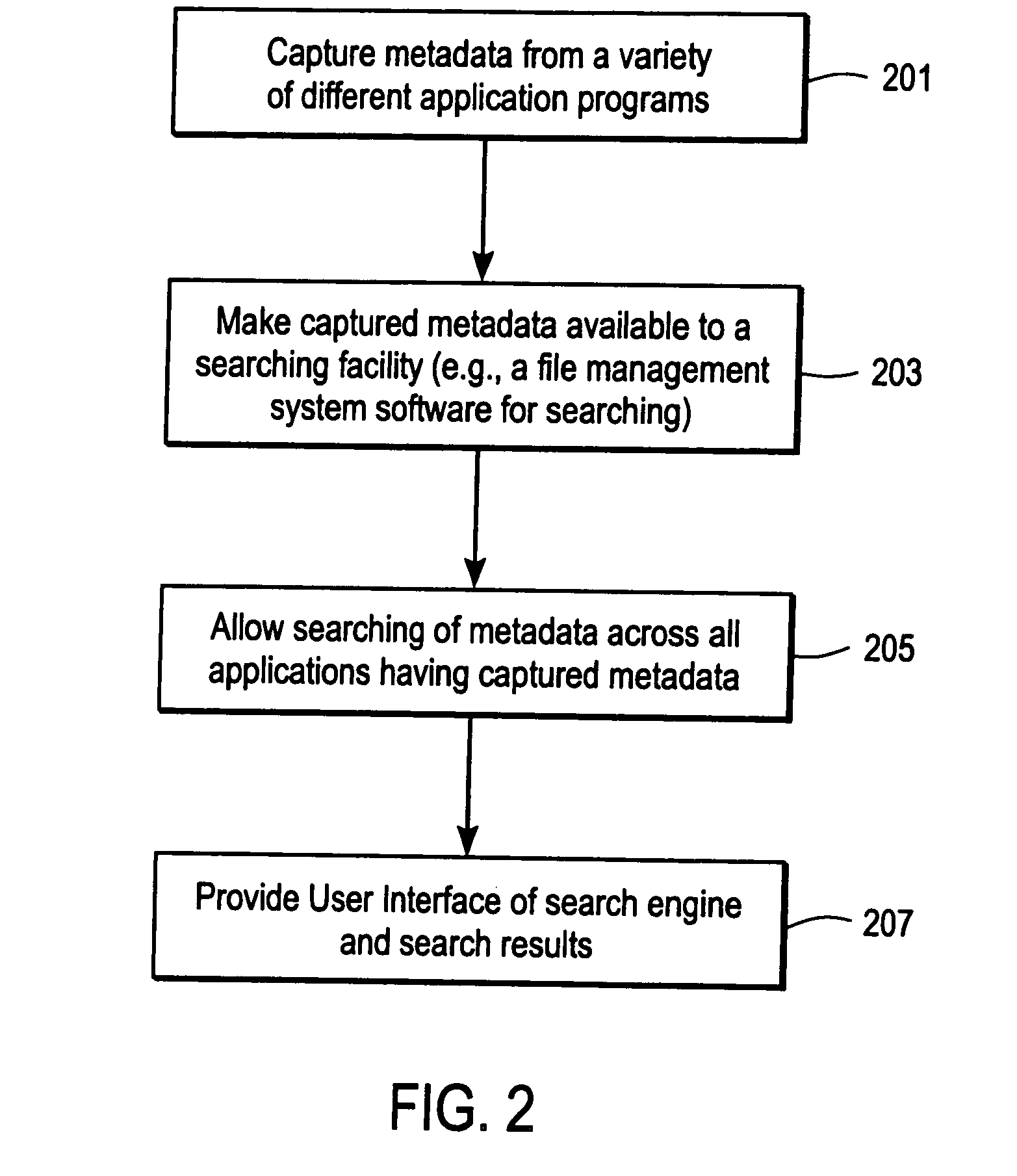
Metadatabase is a database model for (1) metadata management, (2) global query of independent databases, and (3) distributed data processing. The word metadatabase is an addition to the dictionary. Originally, metadata was only a common term referring simply to "data about data", such as tags, keywords, and markup headers. However, in this technology, the concept of metadata is extended to also include such data and knowledge representation as information models (e.g., relations, entities-relationships, and objects), application logic (e.g., production rules), and analytic models (e.g., simulation, optimization, and mathematical algorithms). In the case of analytic models, it is also referred to as a Modelbase.
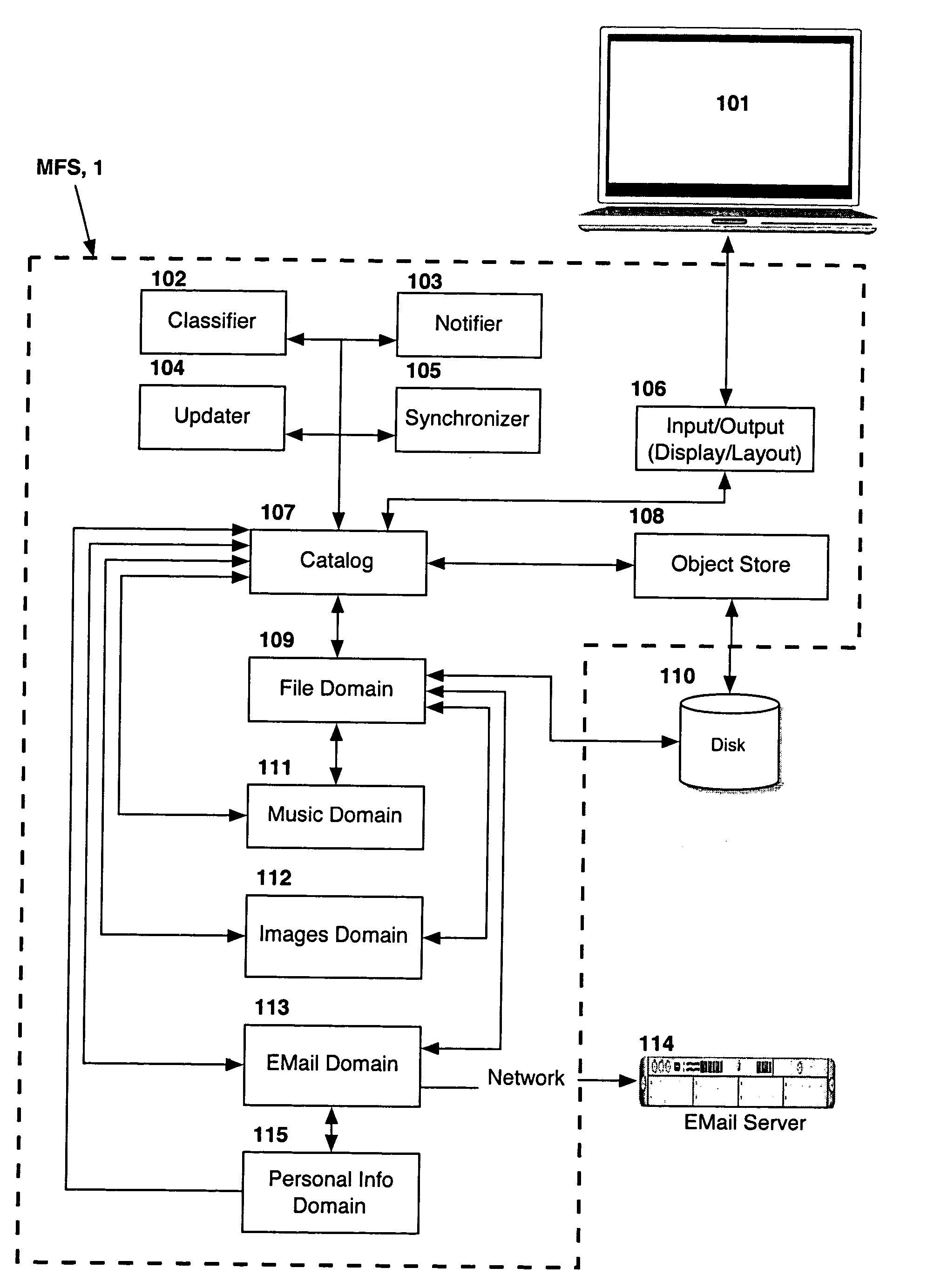
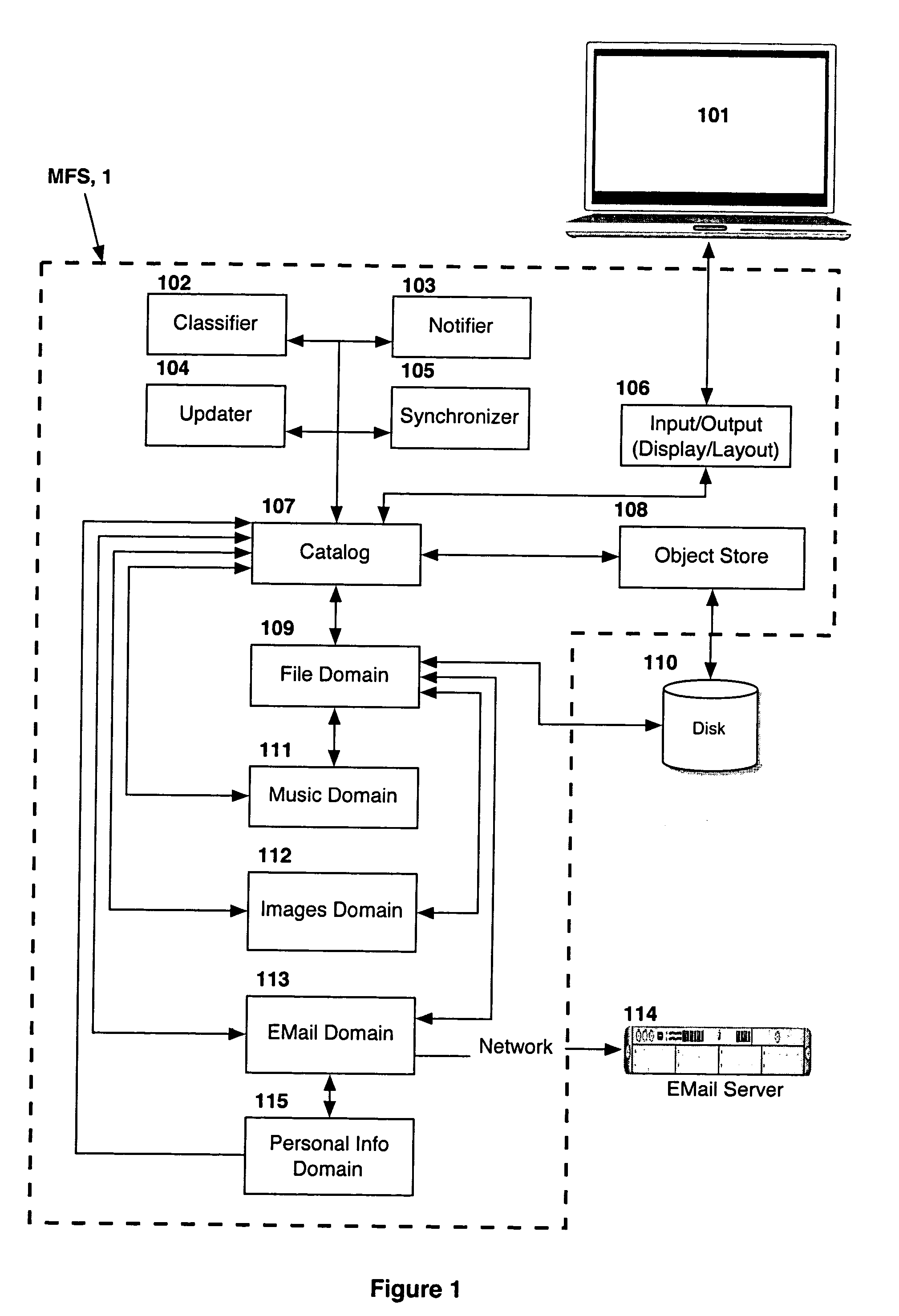
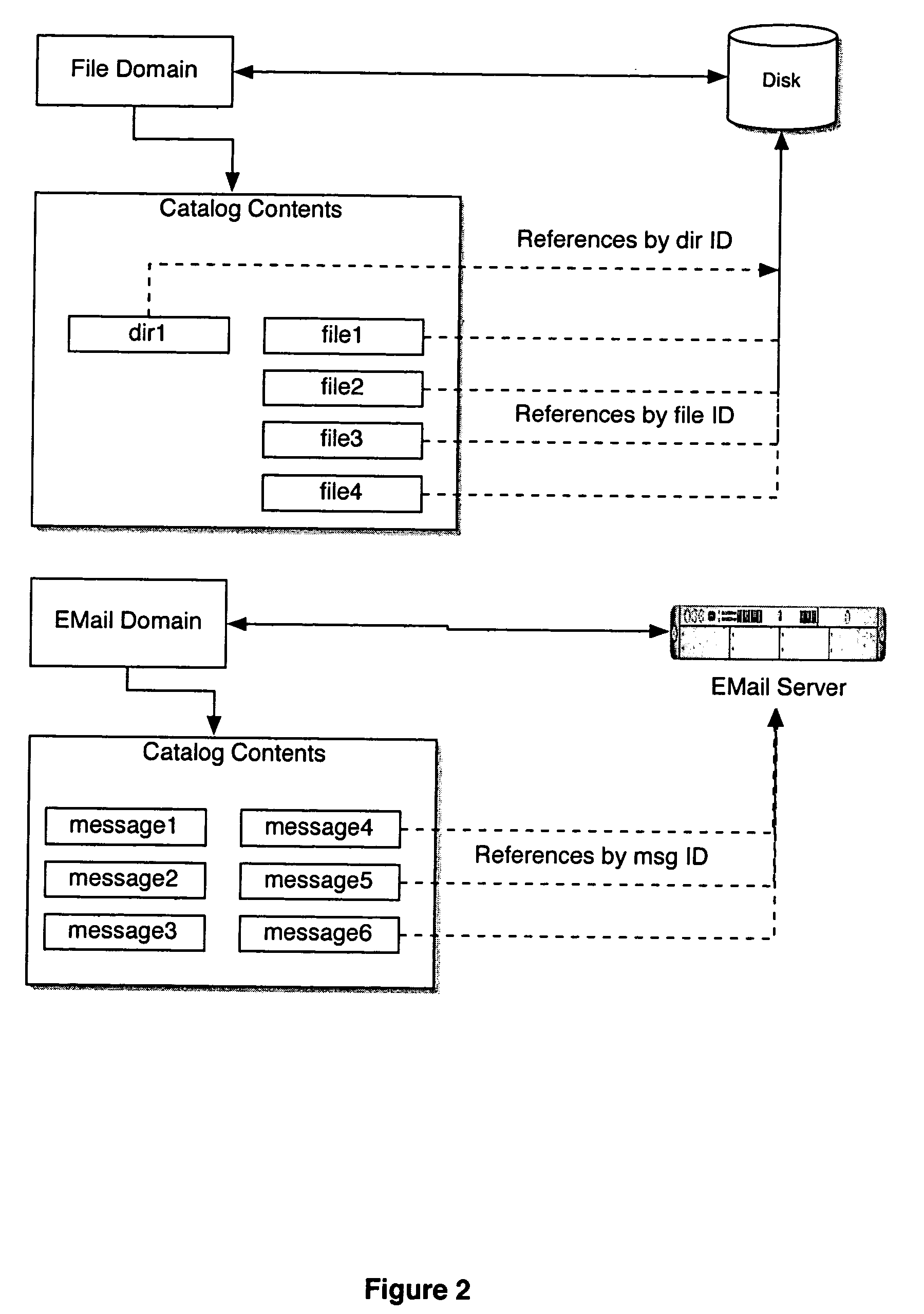
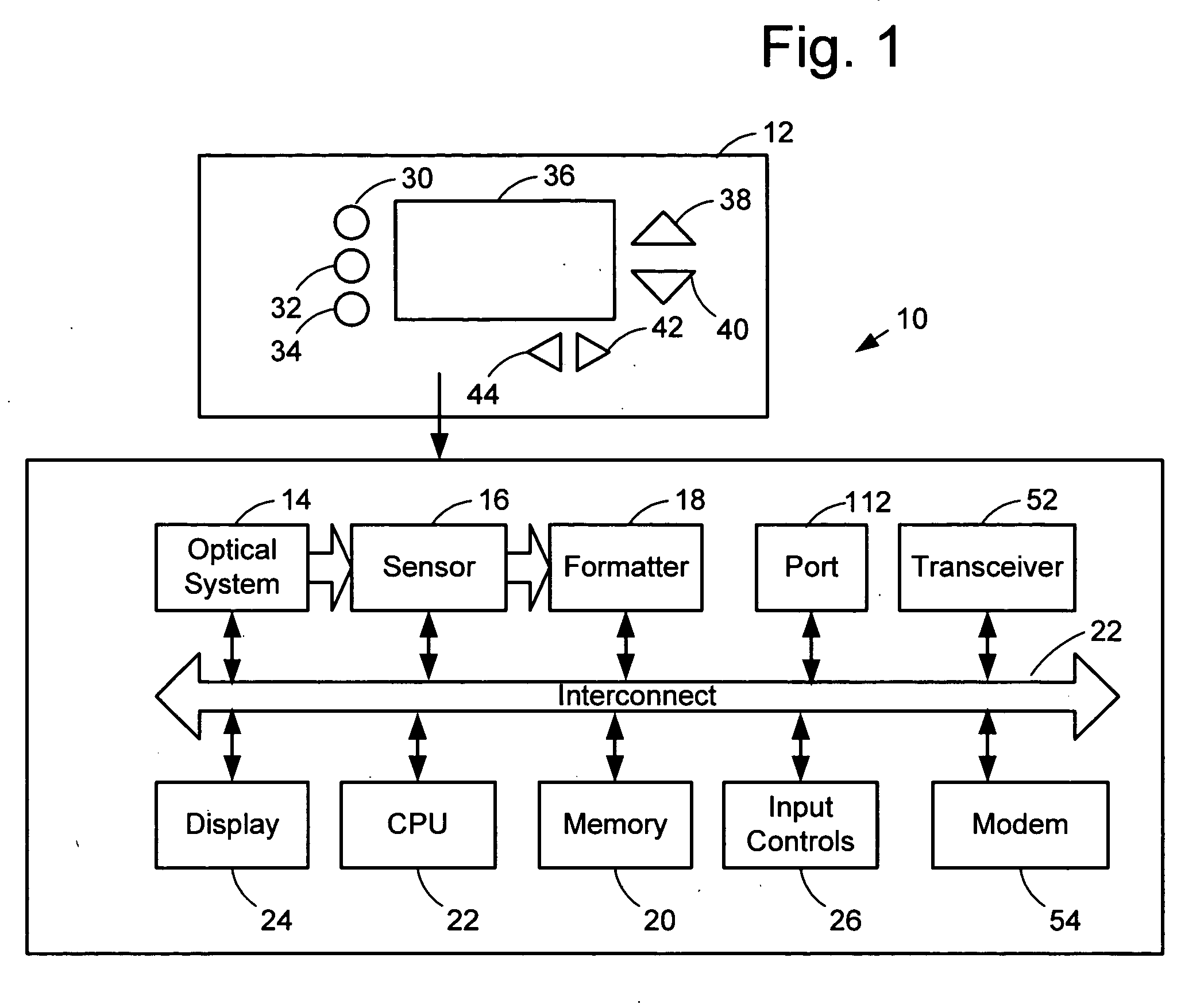
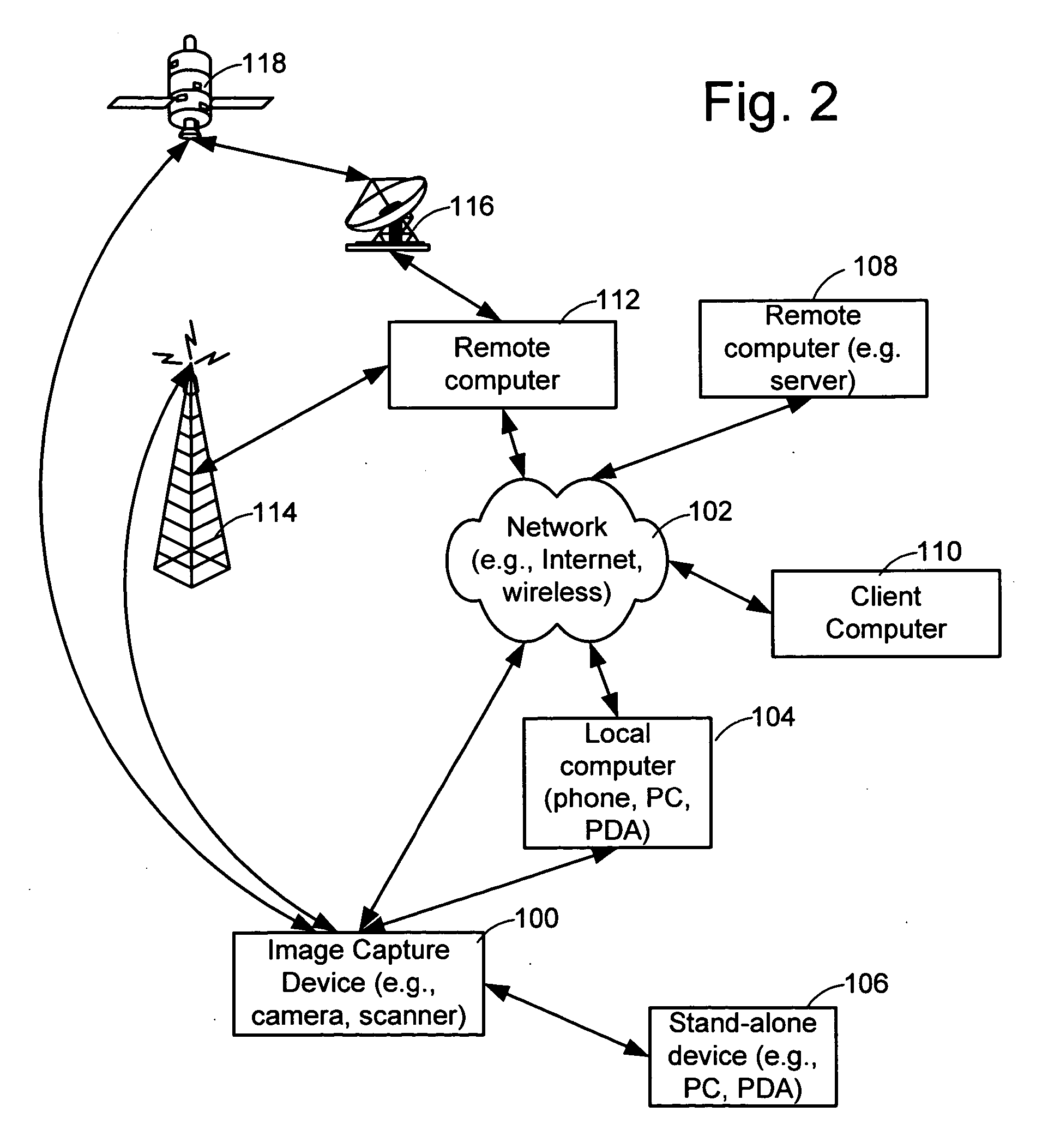
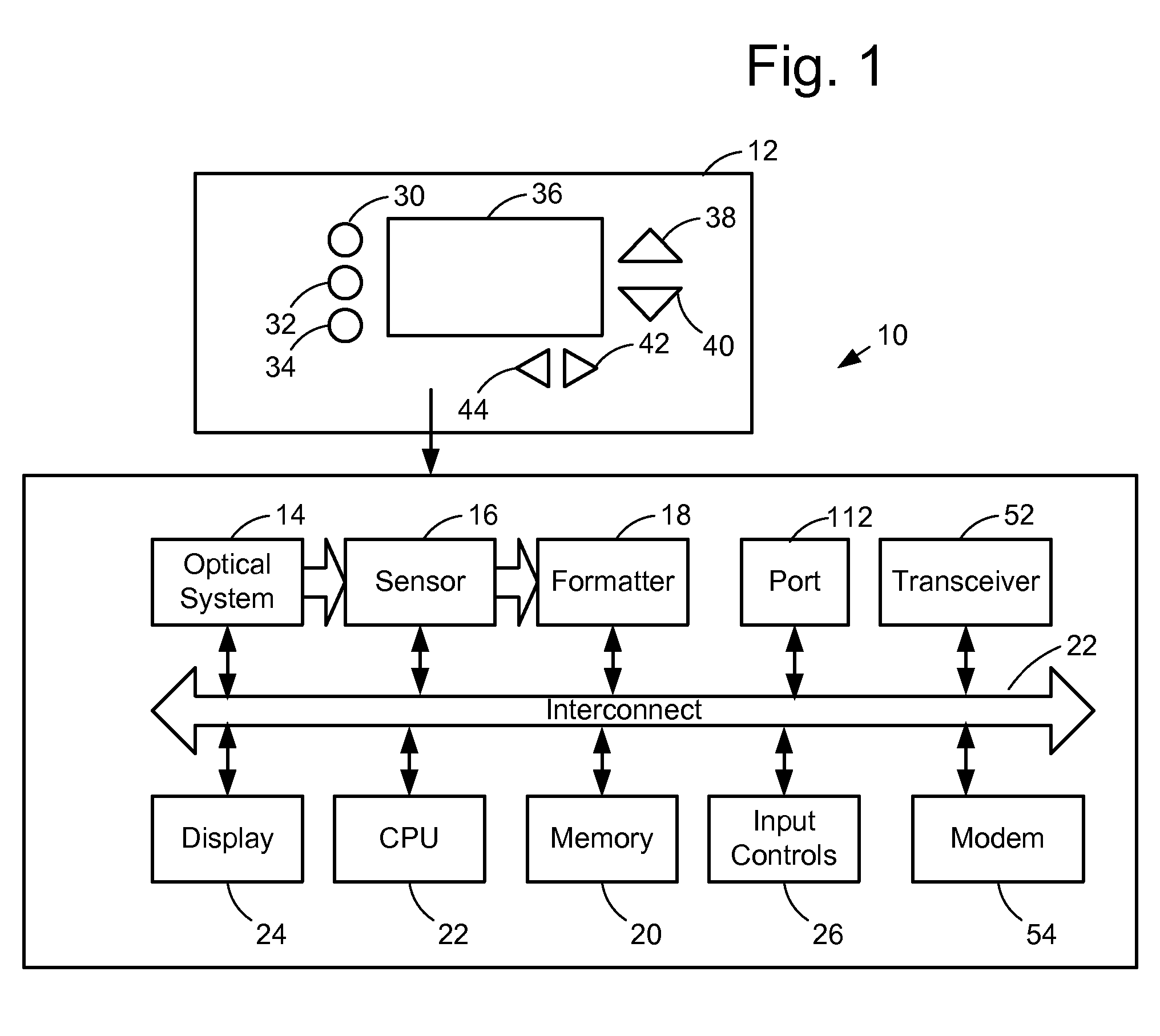
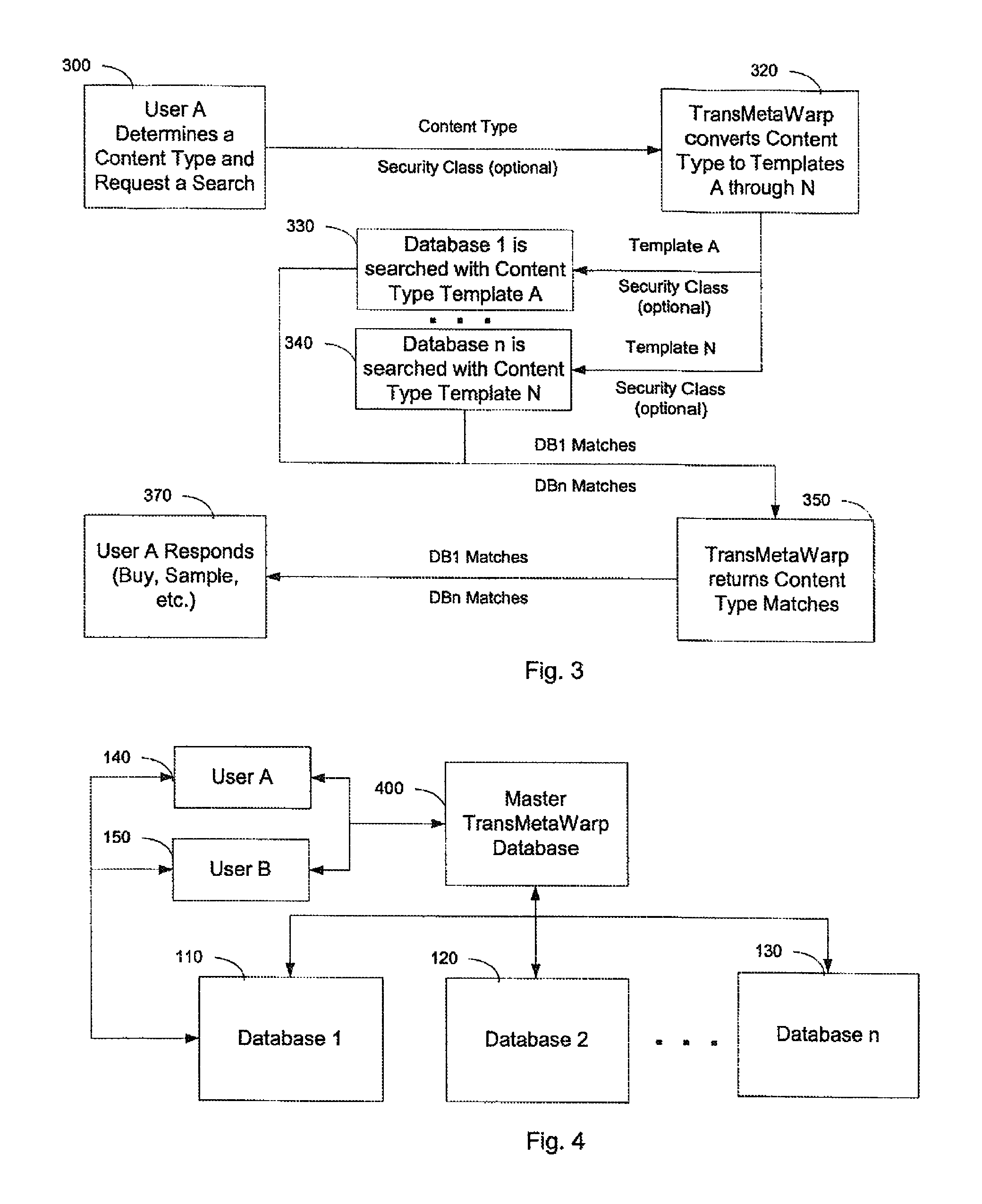
Computer system for automatic organization, indexing and viewing of information from multiple sources
ActiveUS7275063B2Facilitate communicationMultimedia data indexingFile access structuresPathPingSoftware system
Owner:EHIERARCHY LLC
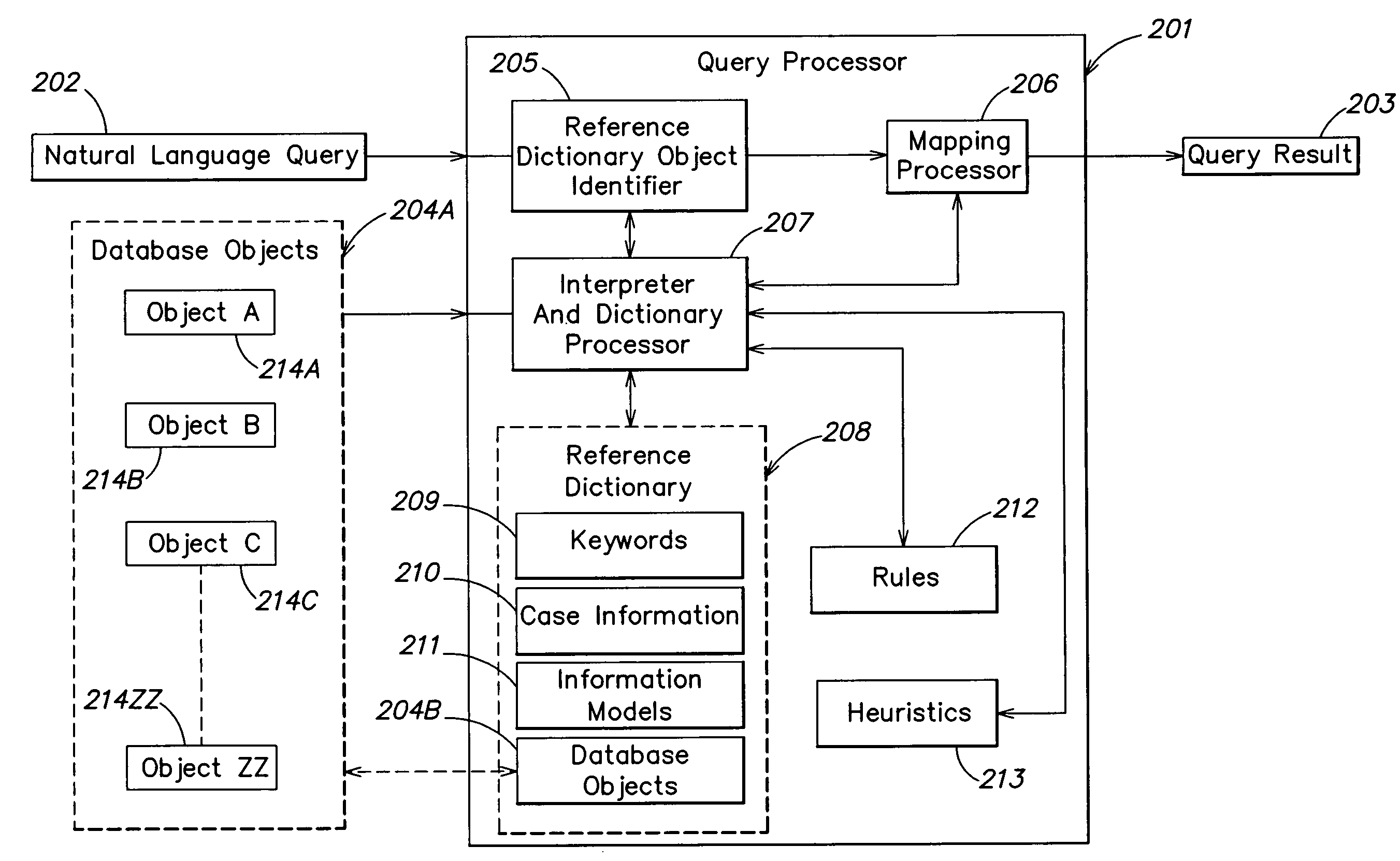
Natural language interface using constrained intermediate dictionary of results
InactiveUS7177798B2Not assureSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsR languageInformation type
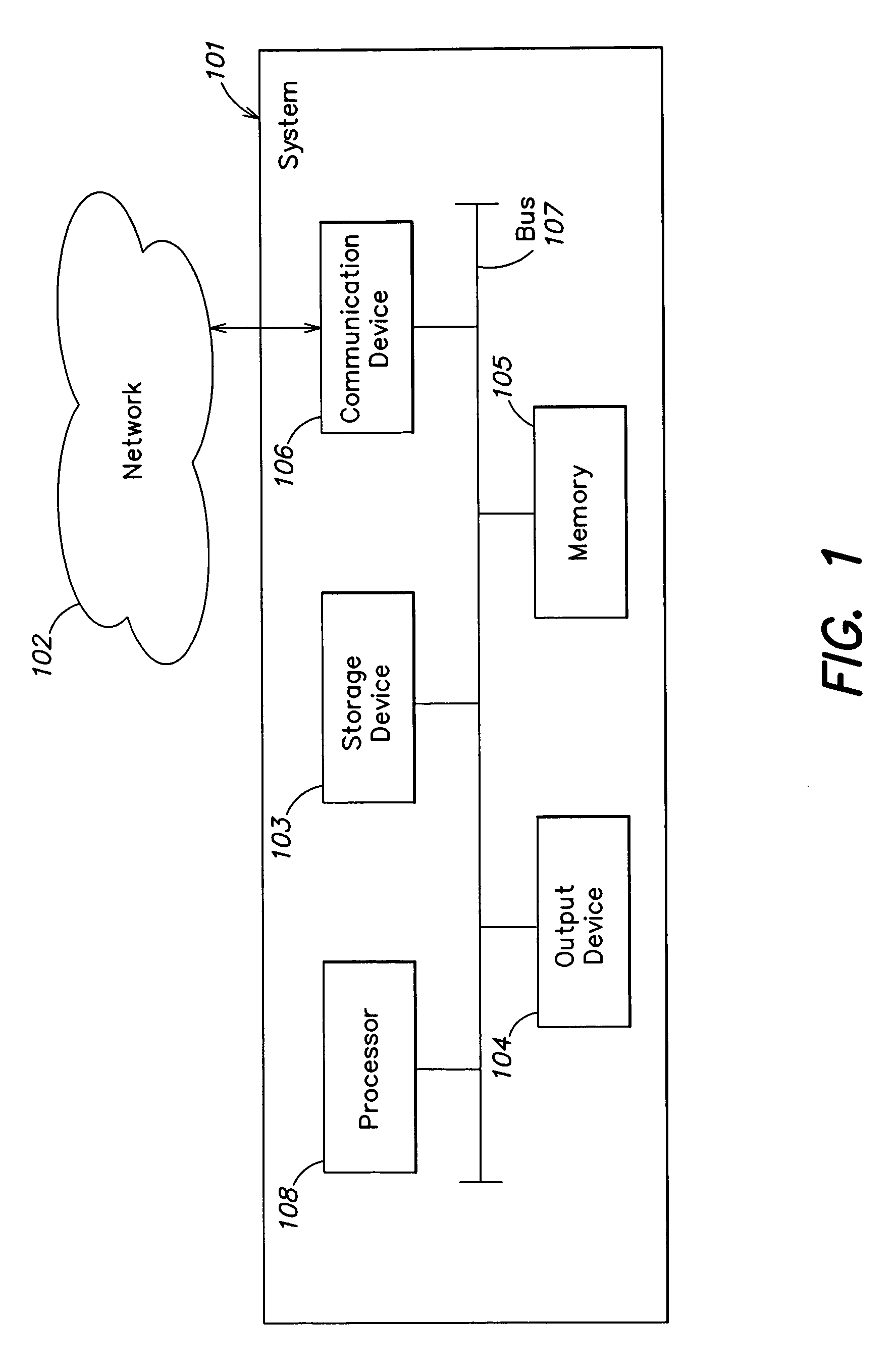
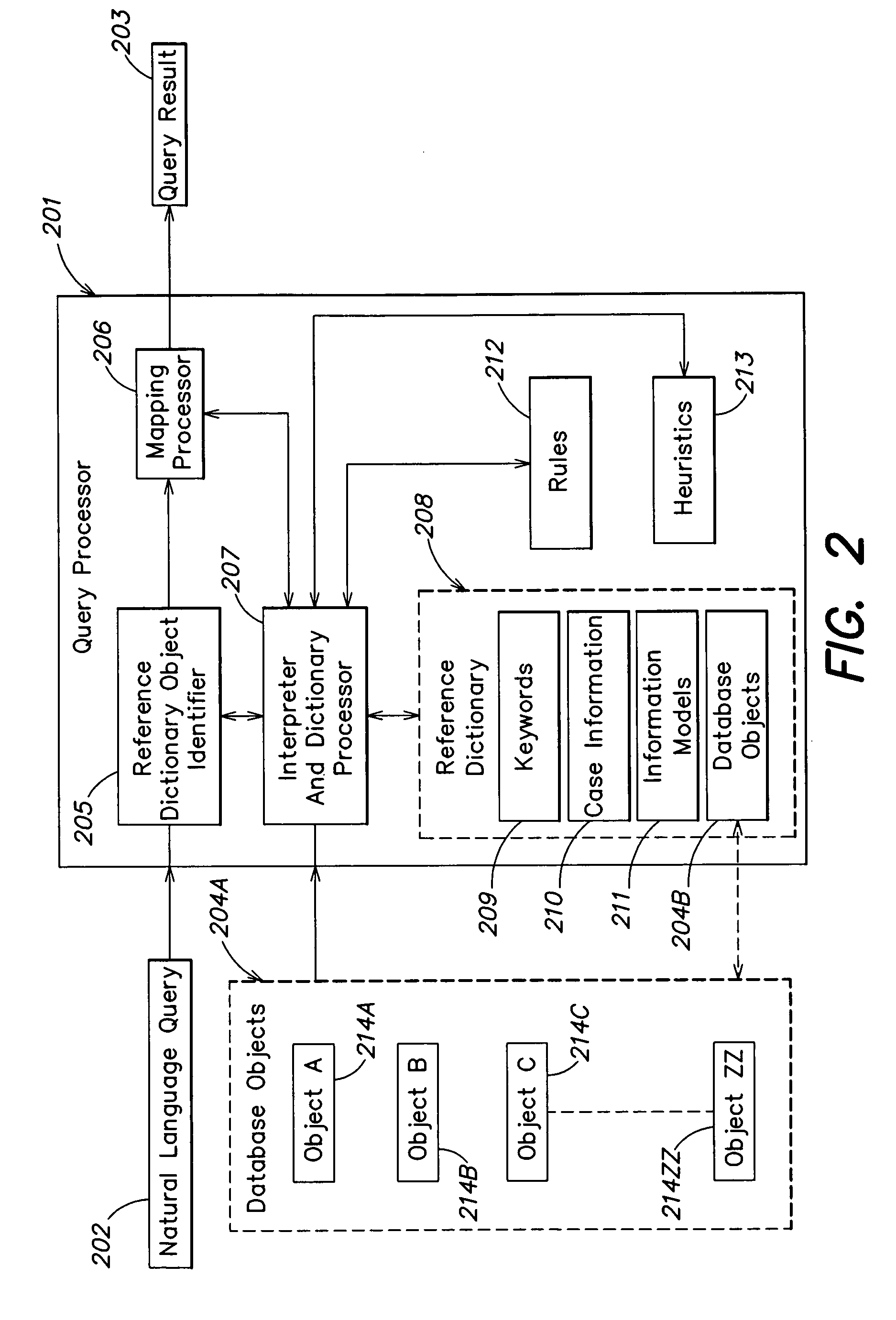
A method for processing a natural language input provided by a user includes: providing a natural language query input to the user; performing, based on the input, a search of one or more language-based databases; providing, through a user interface, a result of the search to the user; identifying, for the one or more language-based databases, a finite number of database objects; and determining a plurality of combinations of the finite number of database objects. The one or more language-based databases include at least one metadata database including at least one of a group of information types including case information, keywords, information models, and database values.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Auto playlist generator
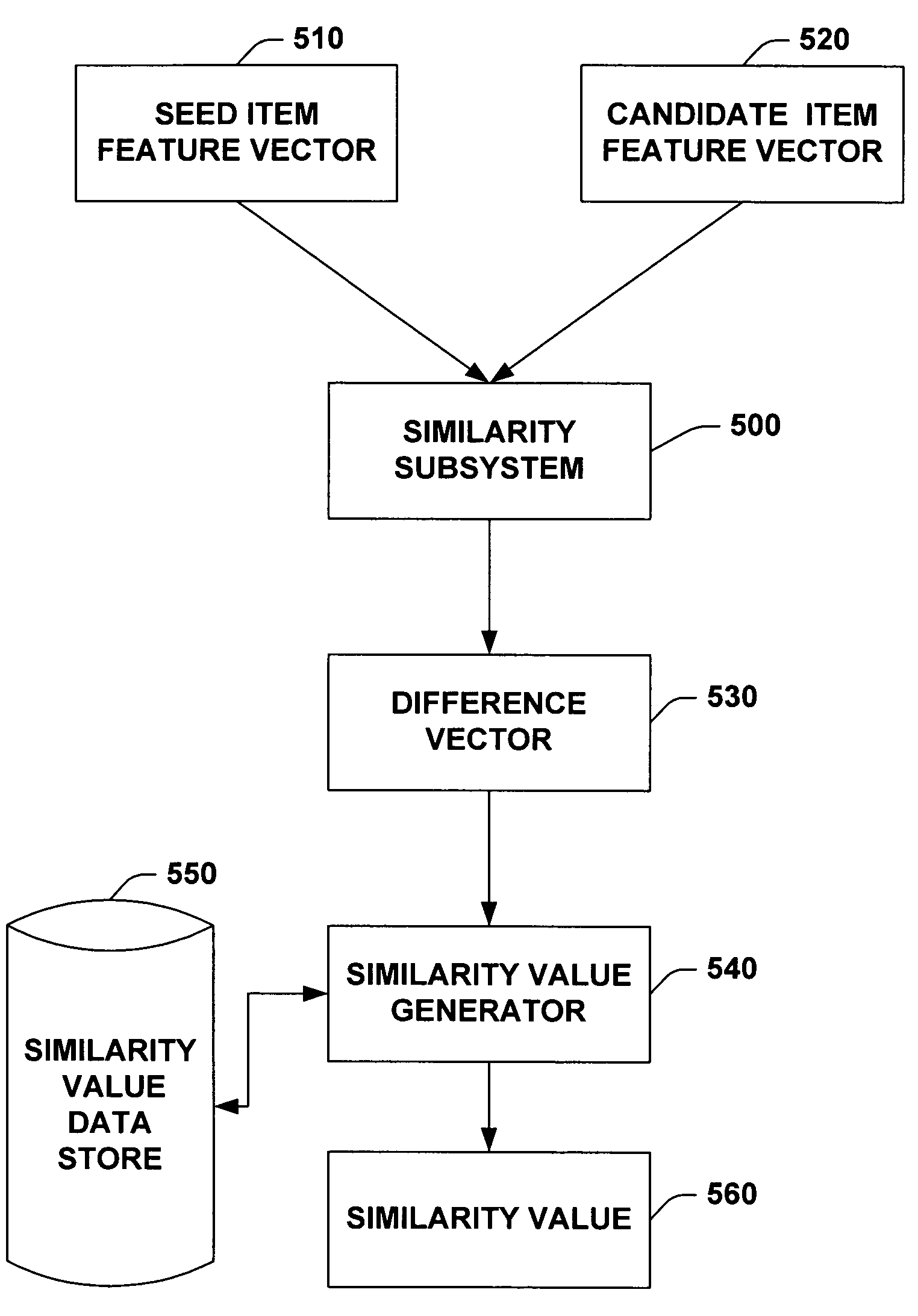
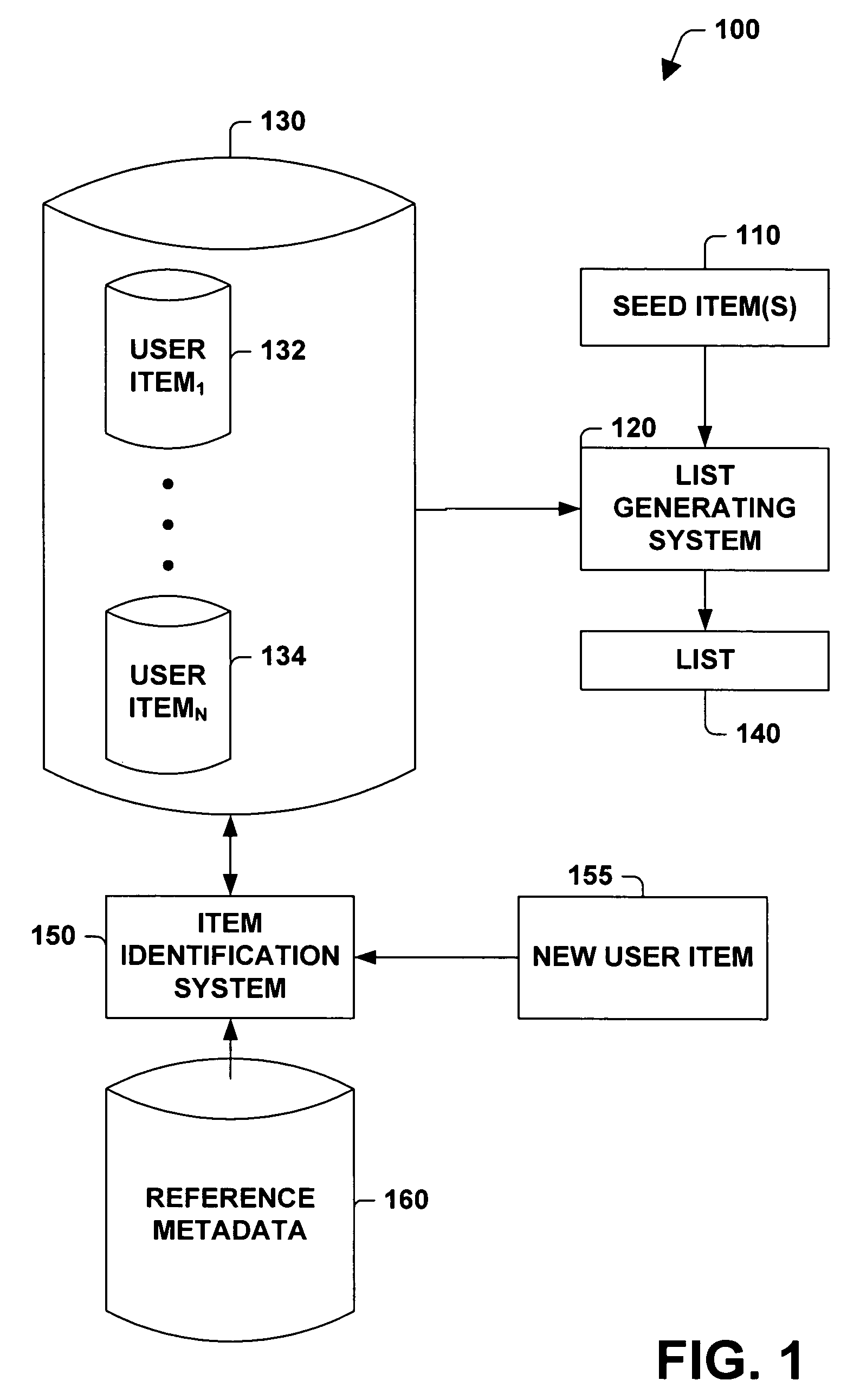
ActiveUS6993532B1Simplifies list generationEfficient use ofGearworksMetadata audio data retrievalInformation retrievalMetadatabase
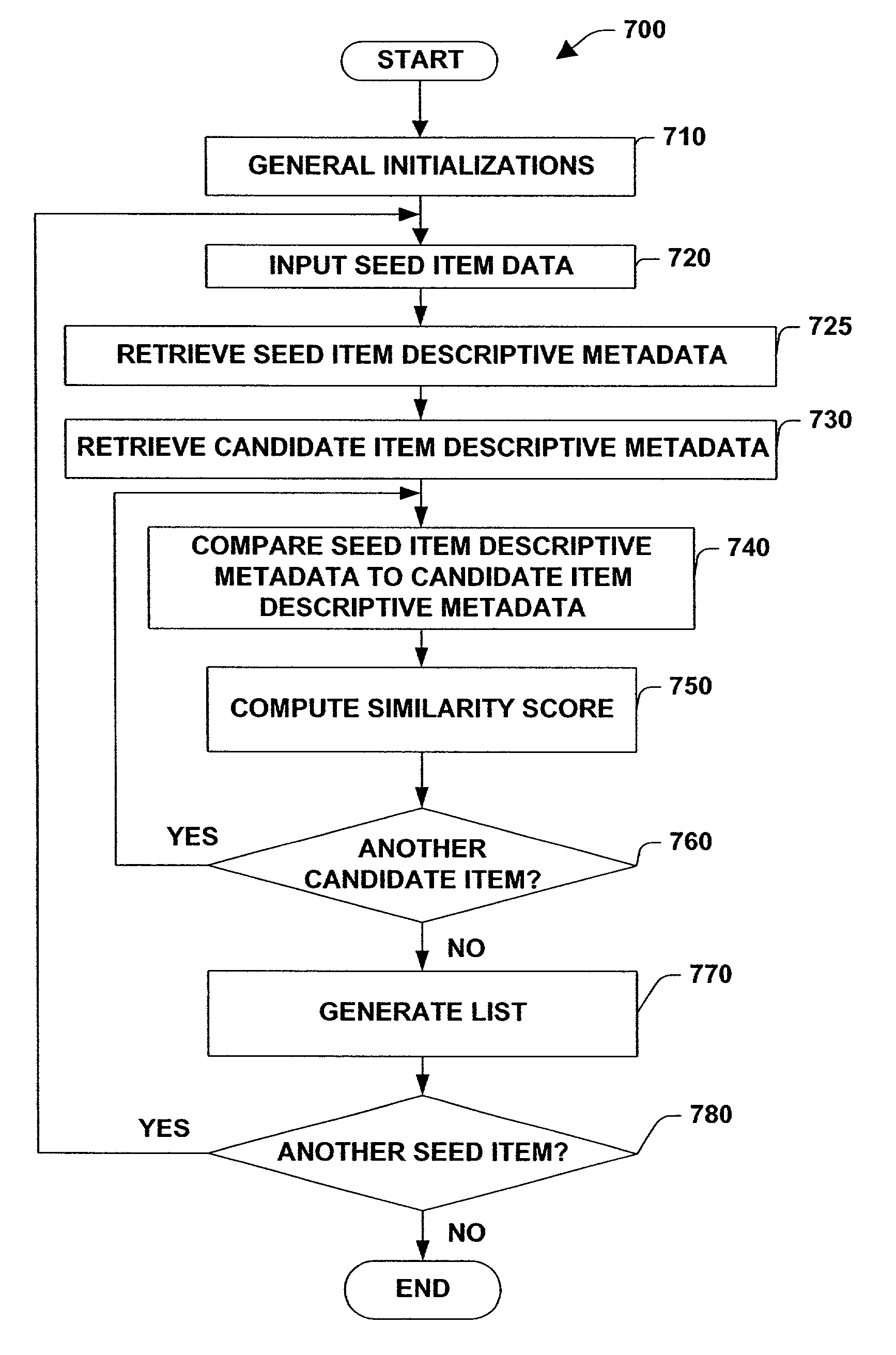
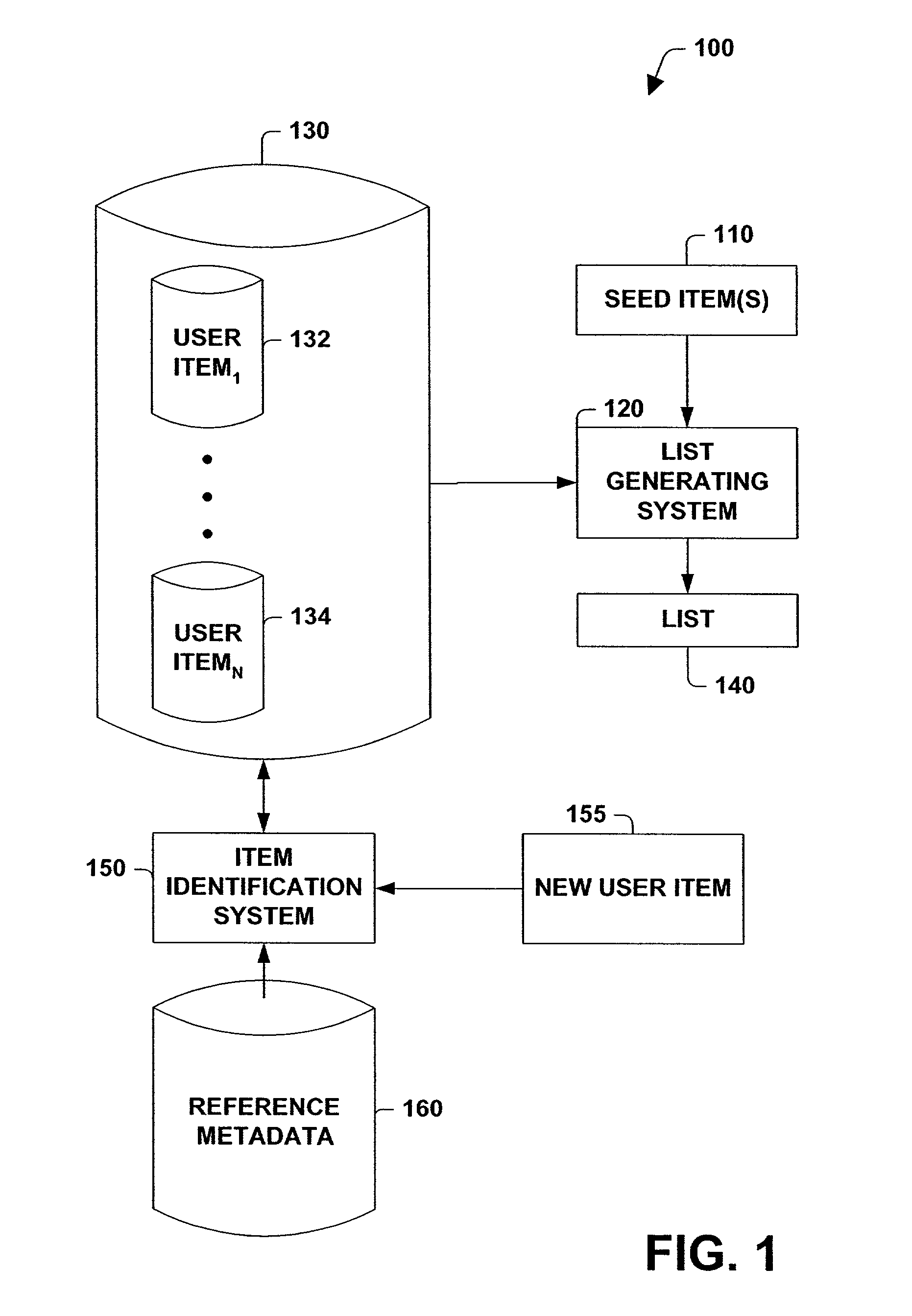
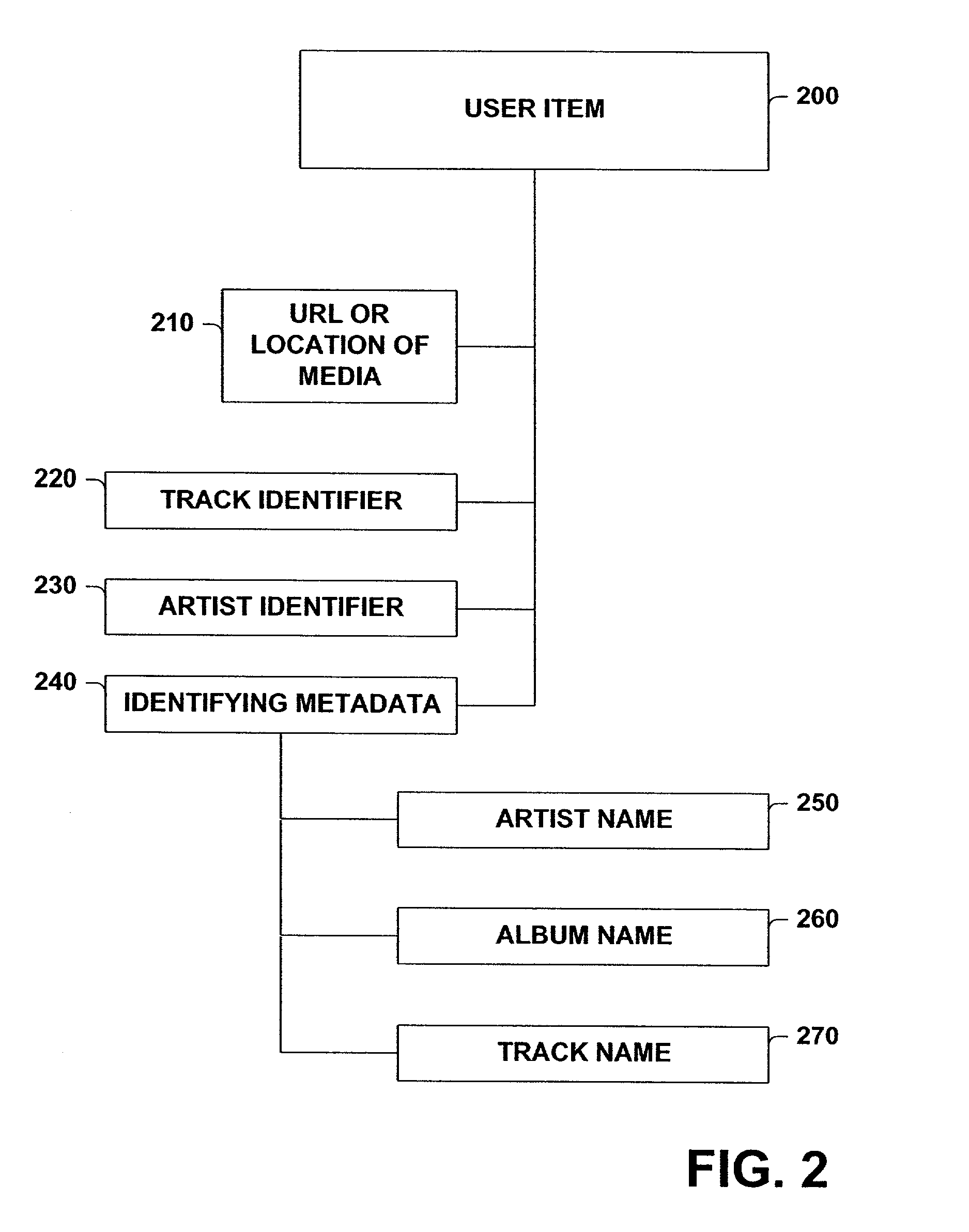
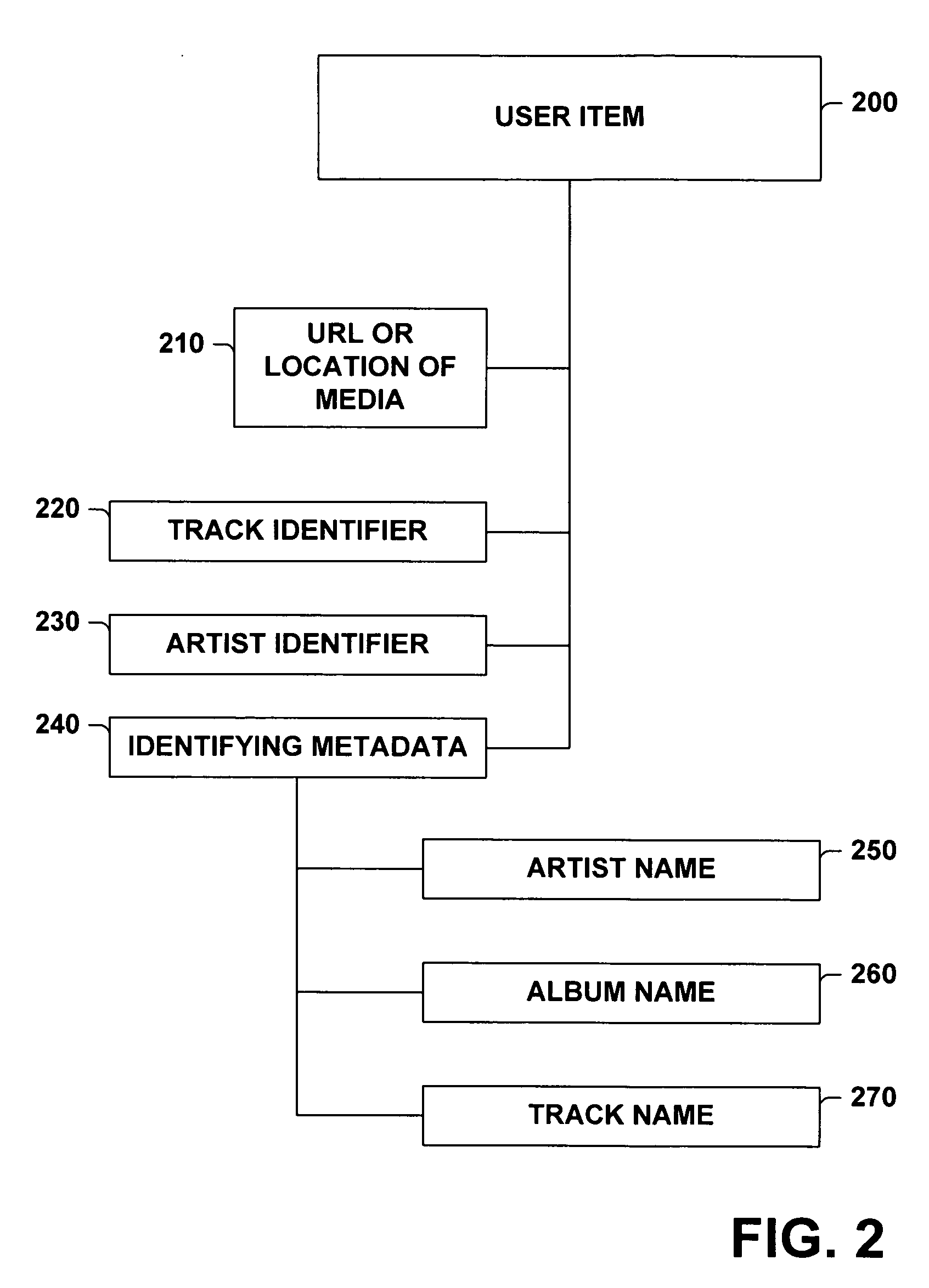
A system and method for generating a list is provided. The system includes a seed item input subsystem, an item identifying subsystem, a descriptive metadata similarity determining subsystem and a list generating subsystem that builds a list based, at least in part, on similarity processing performed on seed item descriptive metadata and user item descriptive metadata and user selected thresholds applied to such similarity processing. The method includes inexact matching between identifying metadata associated with new user items and identifying metadata stored in a reference metadata database. The method further includes subjecting candidate user items to similarity processing, where the degree to which the candidate user items are similar to the seed item is determined, and placing user items in a list of items based on user selected preferences for (dis)similarity between items in the list and the seed item.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
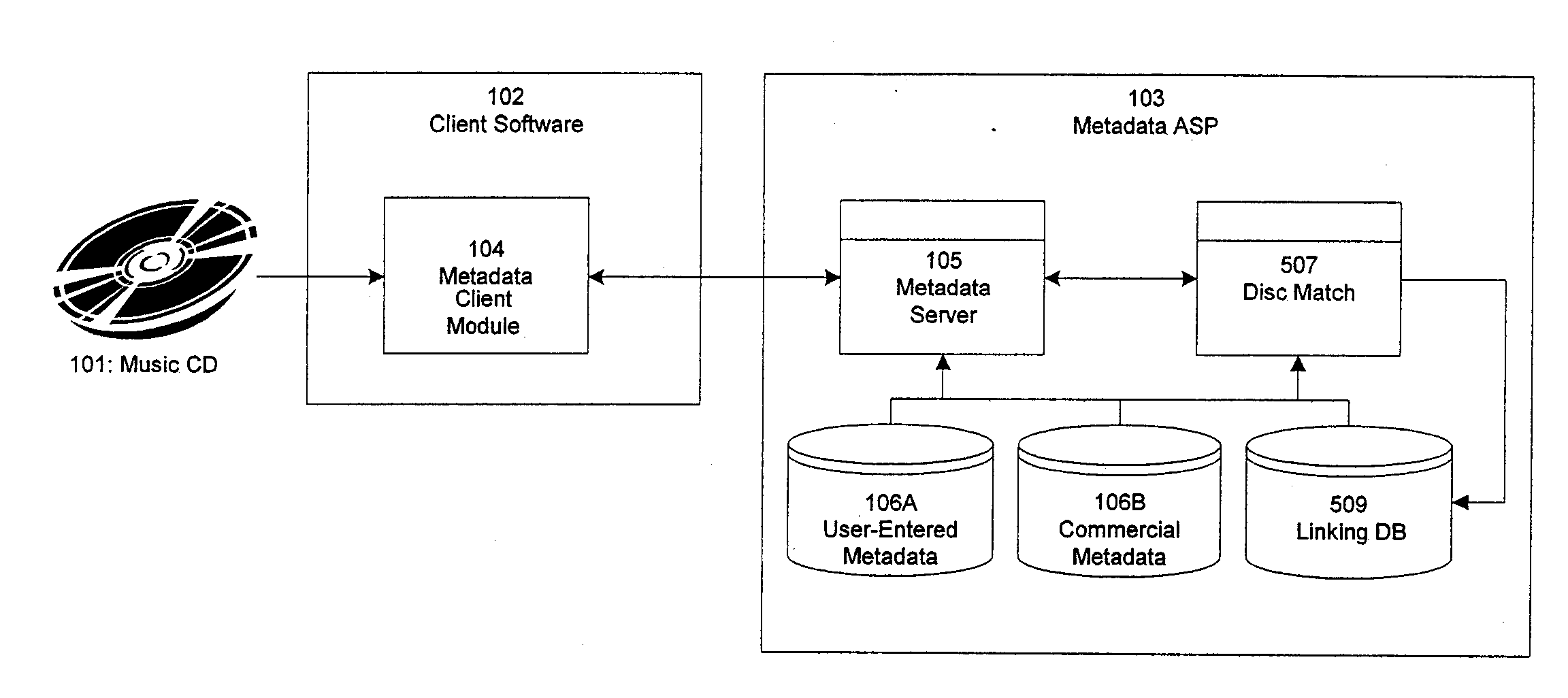
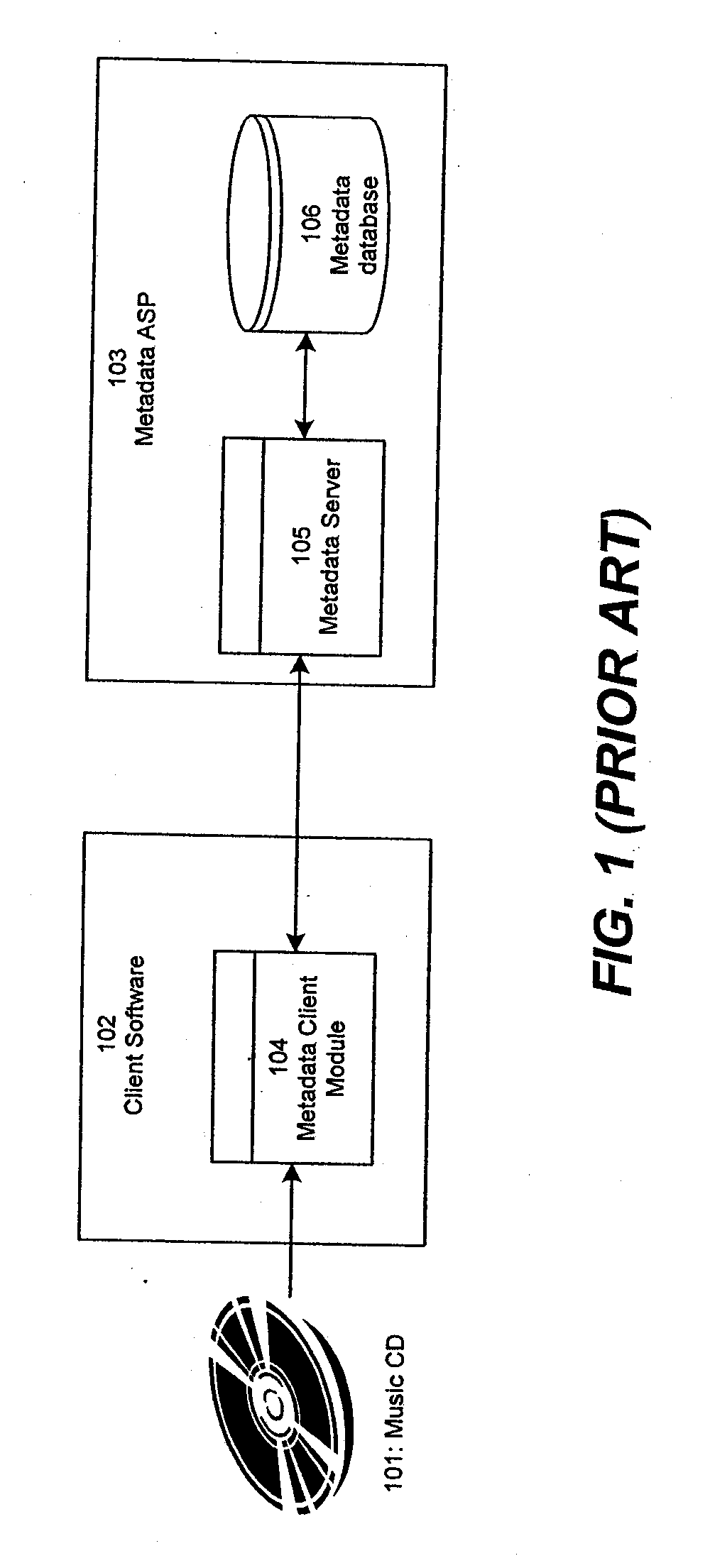
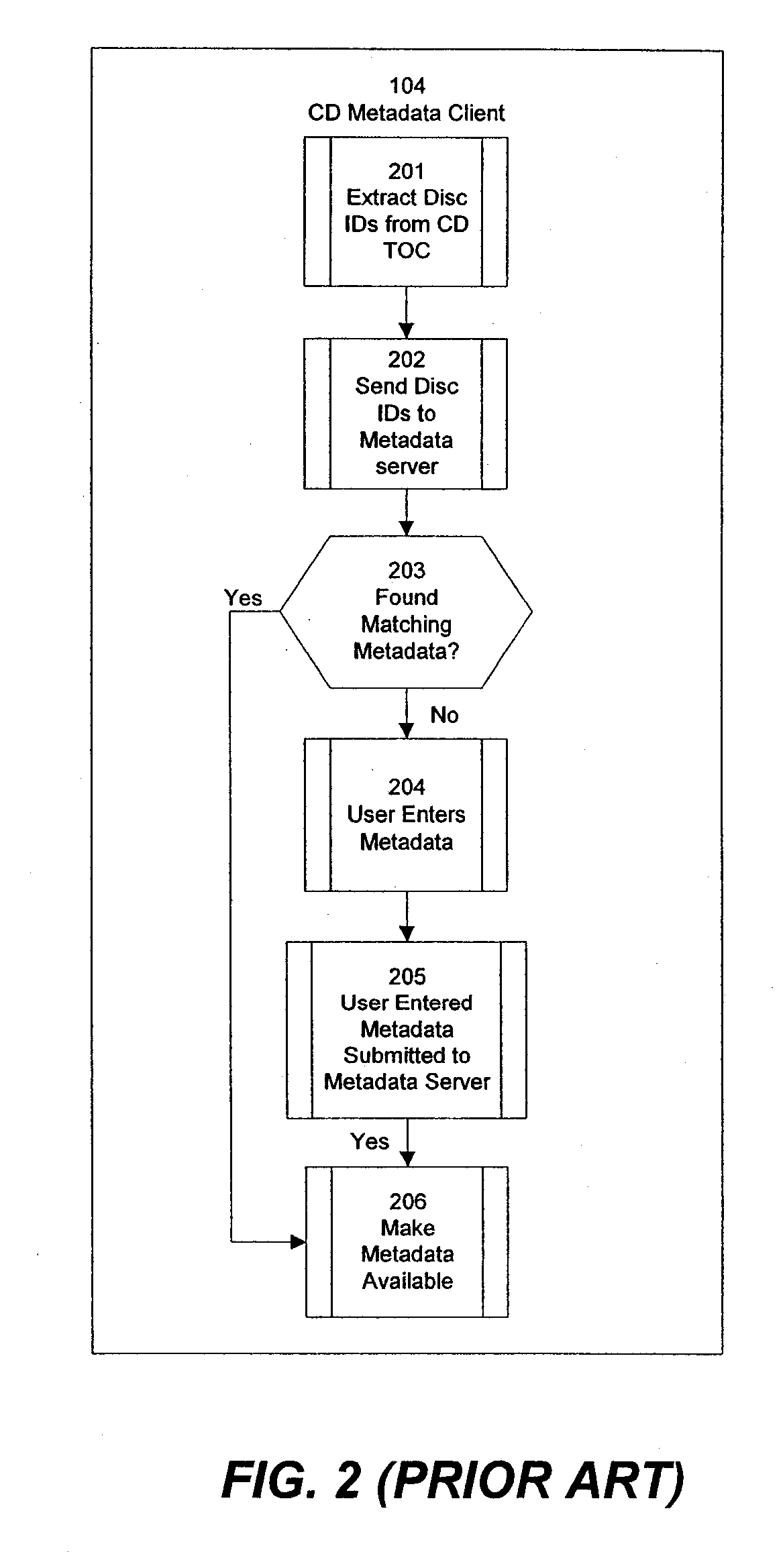
Associating and linking compact disc metadata
InactiveUS7707221B1Improve accuracyQuality improvementMetadata audio data retrievalDigital data processing detailsCompact discUser input
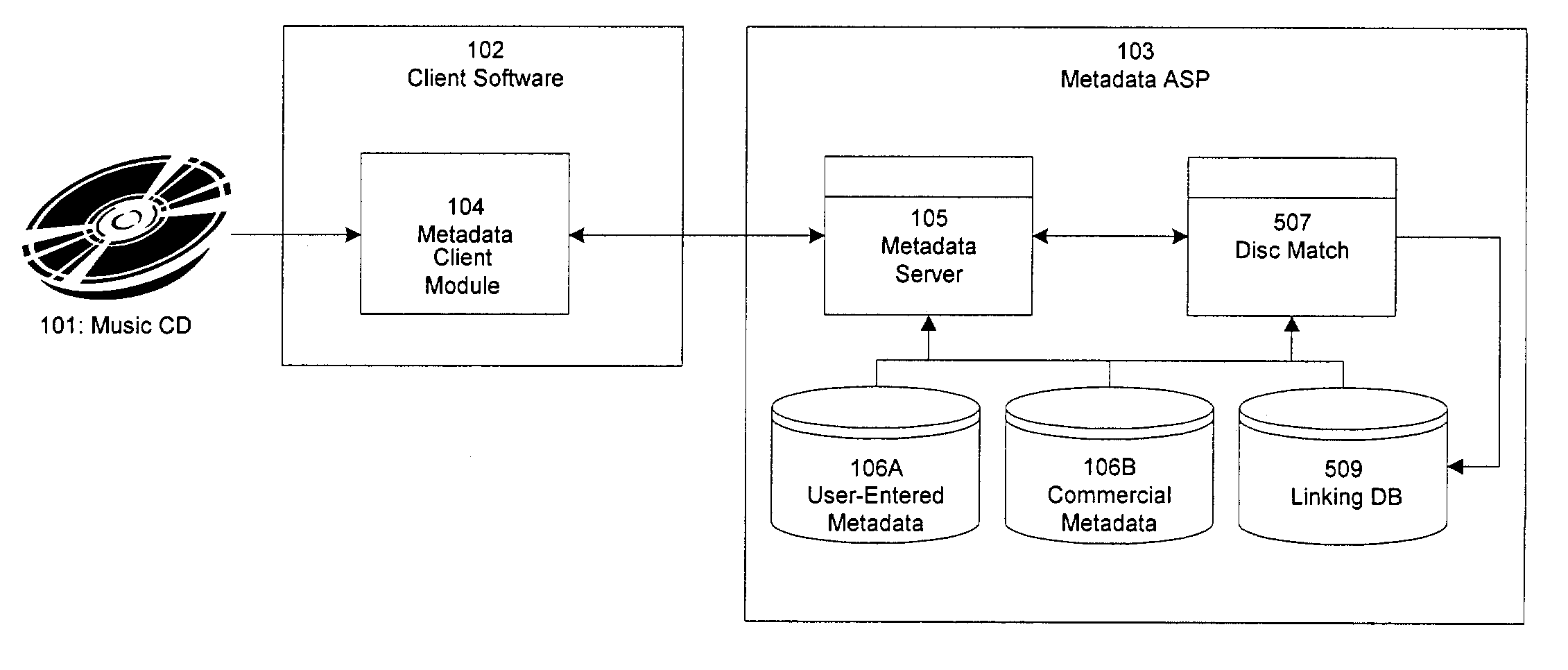
Improved techniques for enhancing, associating, and linking various sources of metadata for music files, to allow integration of commercially generated metadata with user-entered metadata, and to ensure that metadata provided to the user is of the highest quality and accuracy available, even when the metadata comes from disparate sources having different levels of credibility. The invention further provides improved techniques for identifying approximate matches when querying metadata databases, and also provides improved techniques for accepting user submissions of metadata, for categorizing user submissions according to relative credibility, and for integrating user submissions with existing metadata.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Associating and linking compact disc metadata
InactiveUS20090307201A1Improve accuracyQuality improvementMetadata audio data retrievalDigital data processing detailsCompact discUser input
Improved techniques for enhancing, associating, and linking various sources of metadata for music files, to allow integration of commercially generated metadata with user-entered metadata, and to ensure that metadata provided to the user is of the highest quality and accuracy available, even when the metadata comes from disparate sources having different levels of credibility. The invention further provides improved techniques for identifying approximate matches when querying metadata databases, and also provides improved techniques for accepting user submissions of metadata, for categorizing user submissions according to relative credibility, and for integrating user submissions with existing metadata.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Associating data with images in imaging systems
InactiveUS20060041591A1Readily apparentDigital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalDatabaseManagement system
A reference to auxiliary data is steganographically encoded within a media signal. The auxiliary data is stored in a metadata database that maps the reference encoded in the media signal to its corresponding metadata. Various application programs and devices can access the metadata by extracting the reference from the media signal, and querying the database for metadata corresponding to the reference. The metadata database may be implemented in a network server to make metadata readily available to devices and applications distributed throughout a network. This steganographic link to metadata may be used to retrieve metadata across media management systems. In one configuration, for example, media management systems have metadata servers that maintain metadata for a collection of media signals. The metadata server is responsible for responding to requests for metadata associated with media titles in its collection. In the event that a metadata server does not have metadata associated with a particular media title, it forwards the reference extracted from the media signal to a metadata router, which in turn, re-directs the request to the appropriate metadata server.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP +1
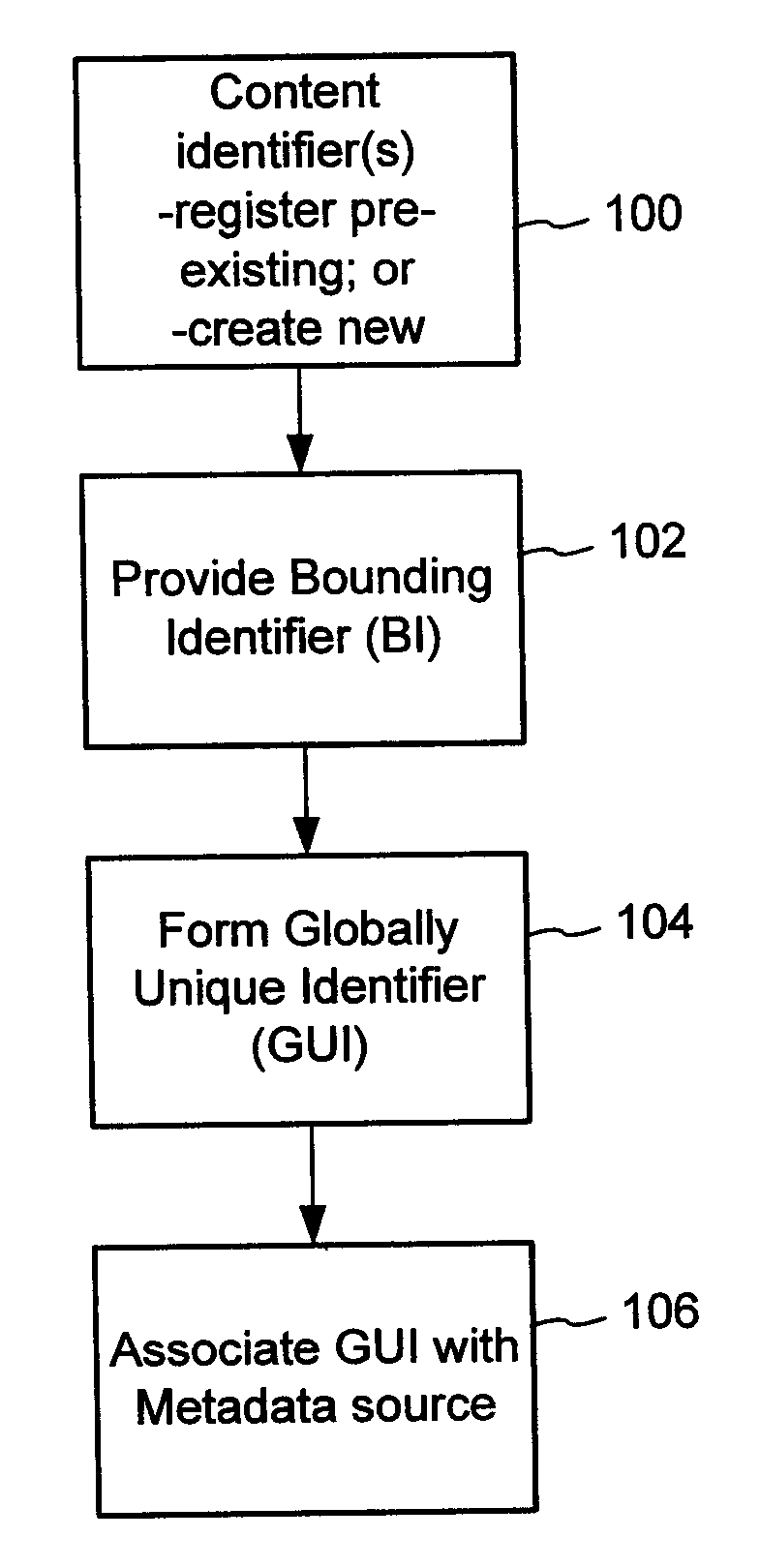
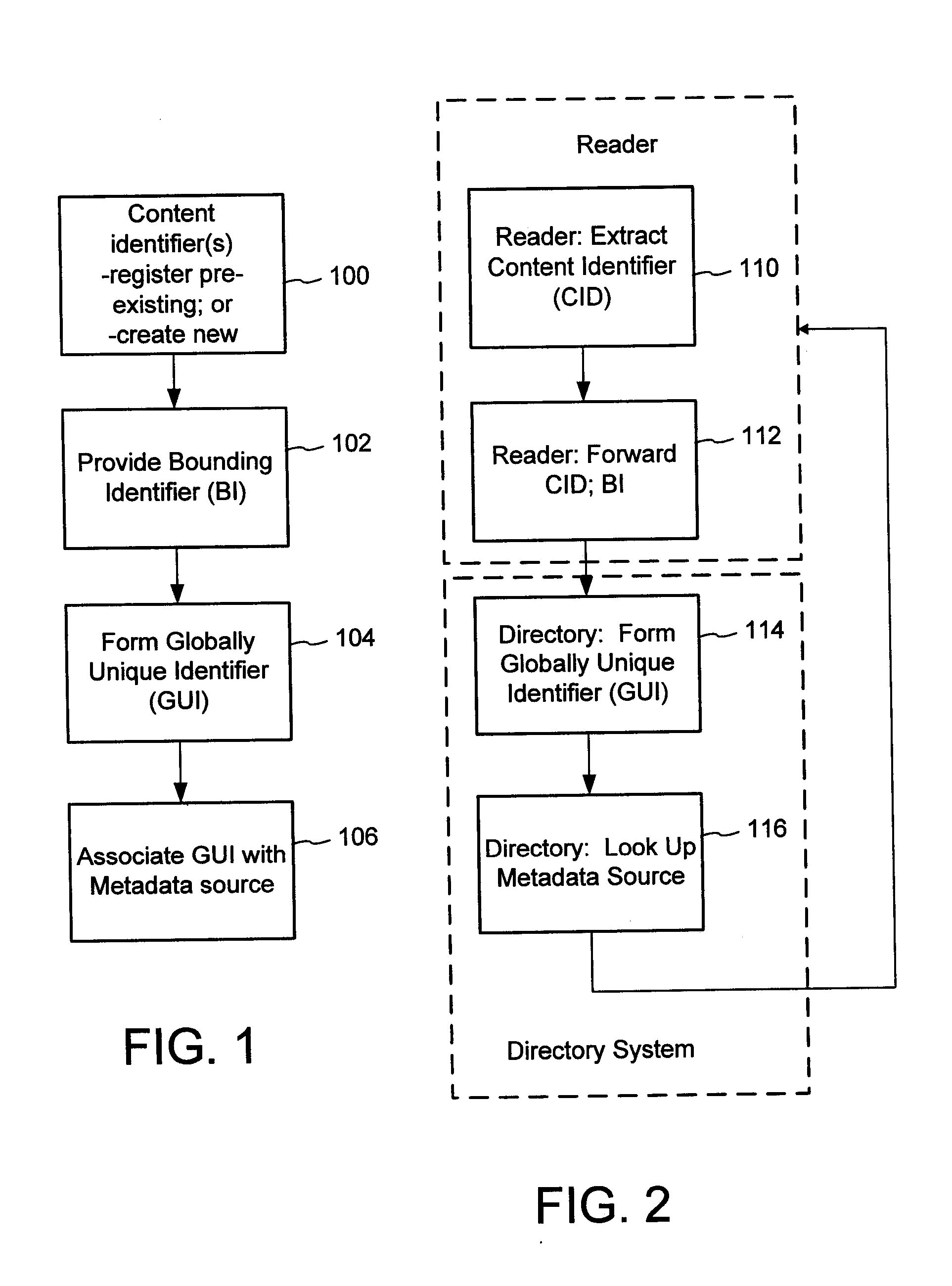
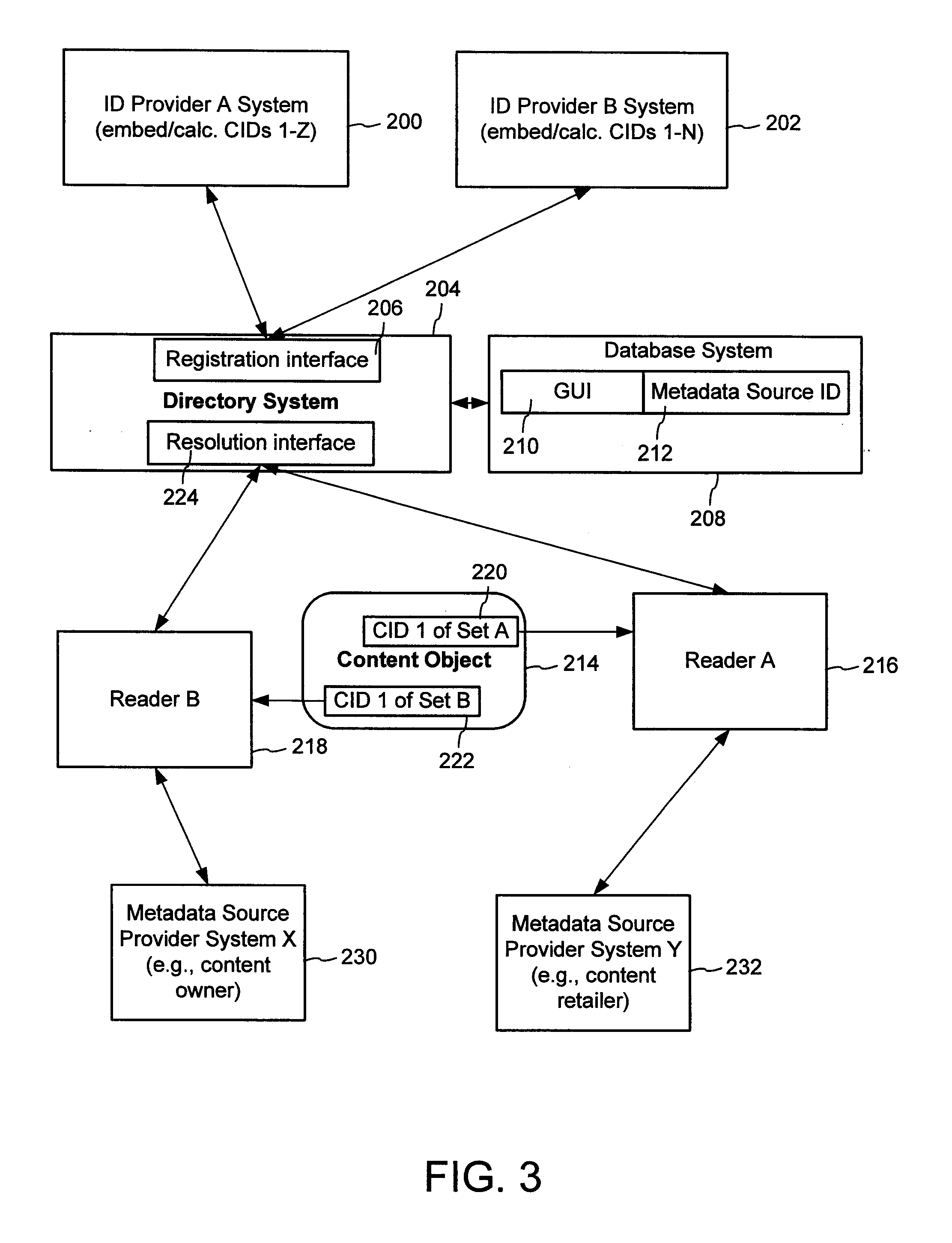
Content Metadata Directory Services
ActiveUS20070192352A1Increase the number ofComplicate to identifyMultimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierWeb site
A method of associating a content object with metadata uses a combination of a content identifier and a bounding identifier to enable handling of disparate sets of content identifiers for content objects with potentially conflicting content identifiers. The method receives a content identifier for a content object from among a set of content identifiers. It provides a unique bounding identifier for the set of content identifiers. This unique bounding identifier is used in combination with the content identifier to form a globally unique identifier for the content object. This globally unique identifier is associated with a metadata source, which enables routing of a user to the metadata source. Another novel method addresses content objects with two or more content identifiers, potentially referencing different metadata sources. This method registers different globally unique identifiers for a content object. These globally unique identifiers each comprise a content identifier provided with the content object and a bounding identifier identifying a set of content identifiers of which the content identifier is a member. For each of the globally unique identifiers, information is maintained about a metadata source. The method receives a first content identifier for the content object, and uses a bounding identifier associated with the set of the first content identifier to determine the globally unique identifier for the first content identifier. The user is routed to the metadata source associated with globally unique identifier. This document describes a novel system that enables multiple identity providers (ID Providers) to register and use the system. The ID Provider registers with a metadata directory system, receives a unique bounding identifier, and uses this bounding ID (e.g., an ID provider ID) with subsequent interactions with the metadata directory system. Separately, metadata source providers register metadata sources with the metadata directory system. This enables many different participants to associate content objects with metadata sources using one or more identify providers. Examples of metadata source providers include content providers, like content owners or retailers that have the flexibility of working with different ID providers to associate content objects with metadata. Both content providers and ID providers can register and use the system. The metadata source is the system or device that provides the metadata, like a web site. The directory system uses an identifier for the metadata source, which enables it to maintain an association between a content object and its corresponding metadata source. For example, in some embodiments, a URL serves to identify the location of the source. The Content Metadata Directory Services (CMDS) is a global trusted directory service that connects consumers of identified content to content-provider authorized and managed metadata databases and other digital resources. It includes mostly links to metadata, forms globally unique IDs based upon overlapping content identifiers and unique bounding identifiers, enables multiple content identifiers within a content object, and enables multiple content identity technology providers, even when they are using different technology.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Methods and systems for managing data
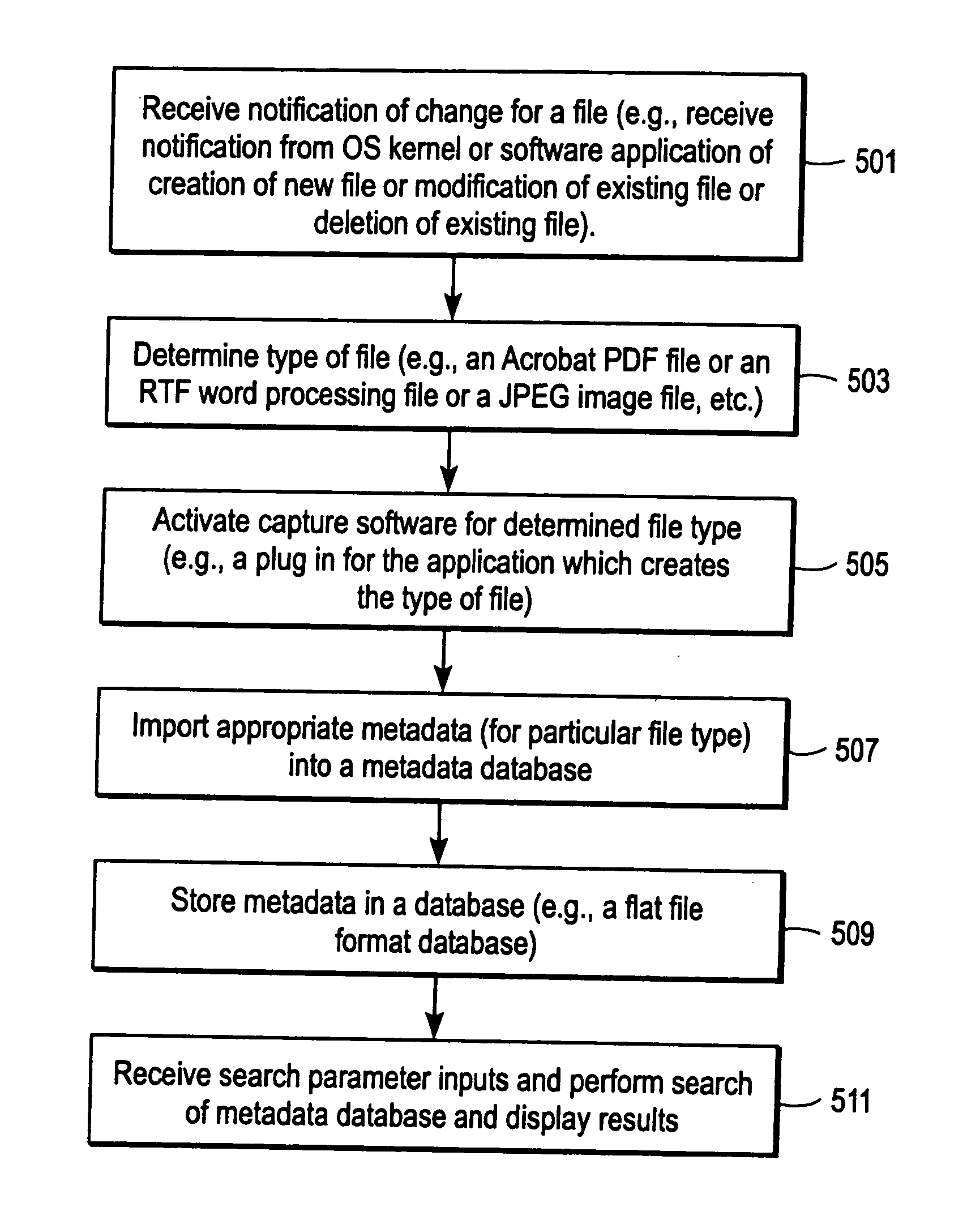
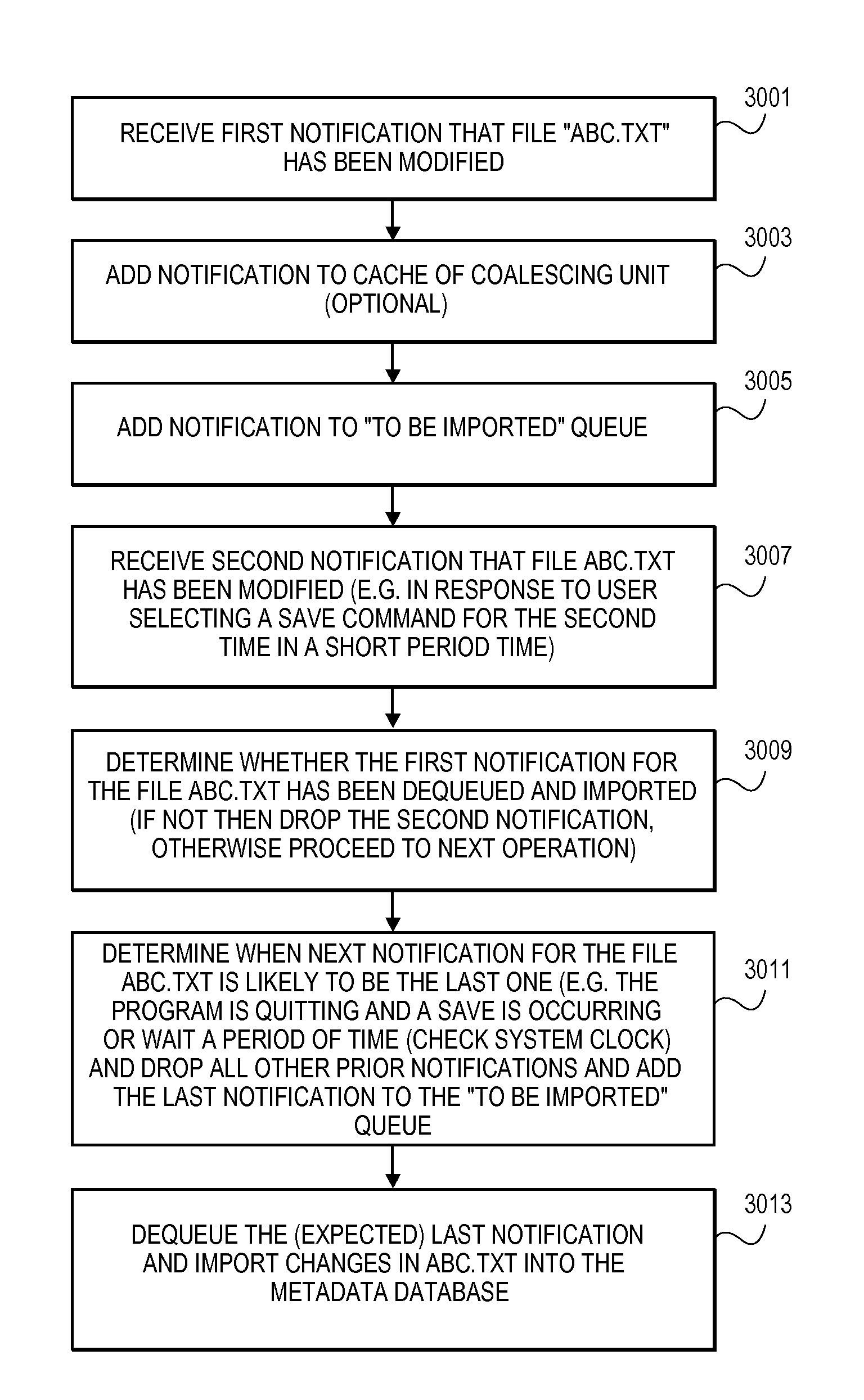
InactiveUS20060031263A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData systemMetadatabase
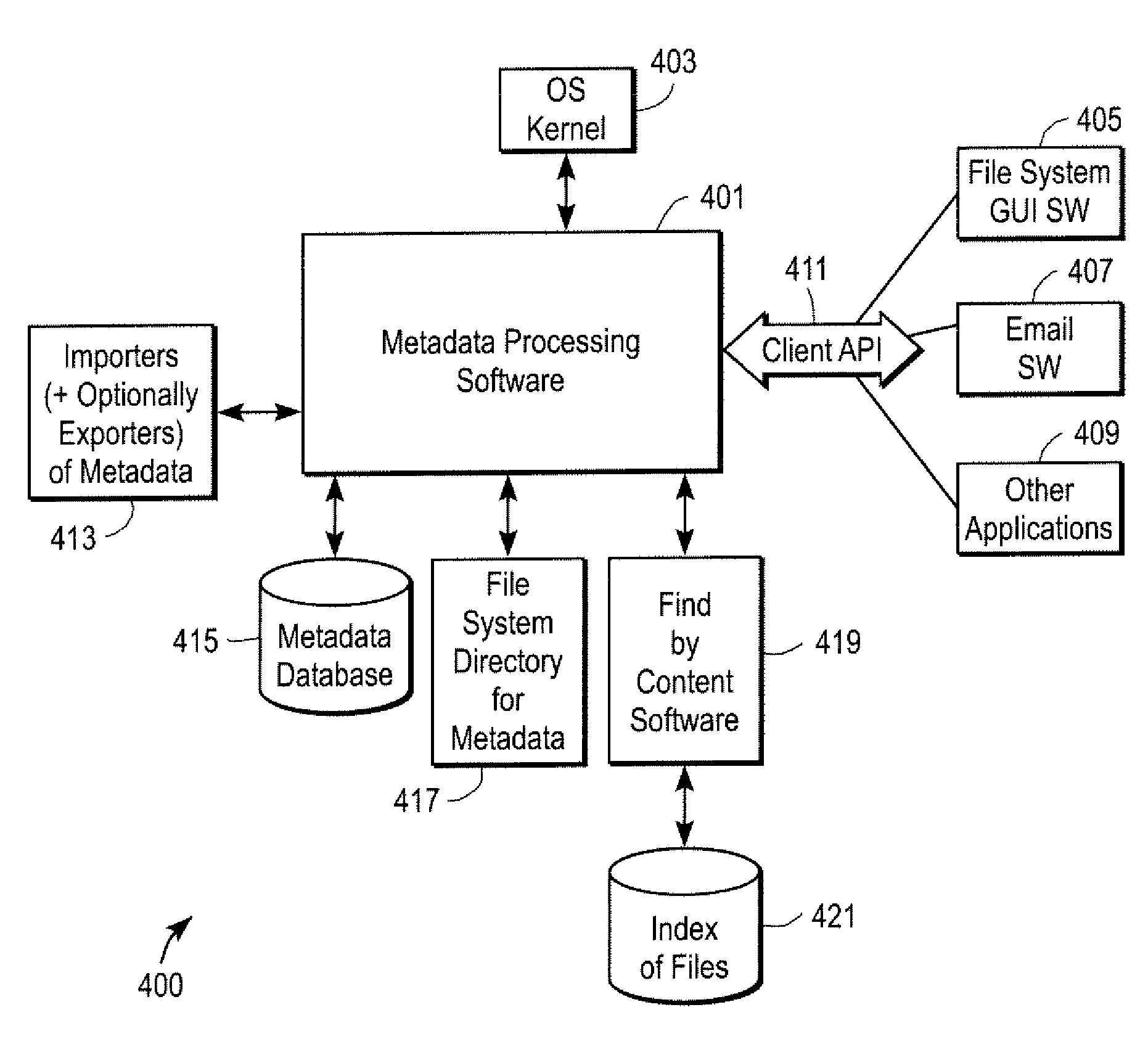
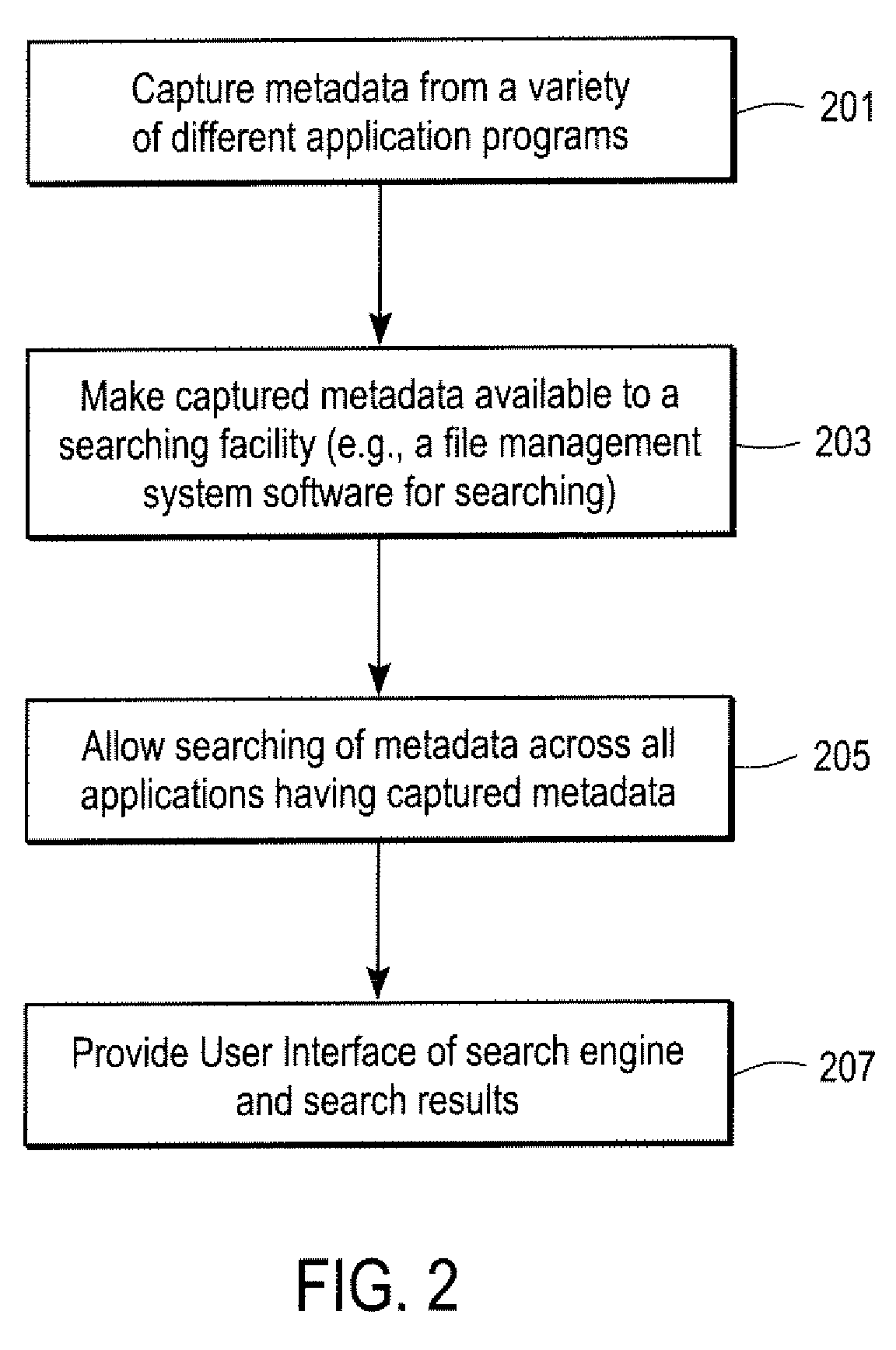
Systems and methods for managing data, such as metadata or indexes of content of files. In one exemplary method, notifications to update a metadata database or an index database are combined into a combined notification. According to other aspects, an order among logical locations on a storage device is determined in order to specify a sequence for scanning for files to be indexed. According to another aspect, a method includes determining whether to index a file based on a path name of the file relative to a plurality of predetermined path names.
Owner:APPLE INC
Integration of visualizations, reports, and data
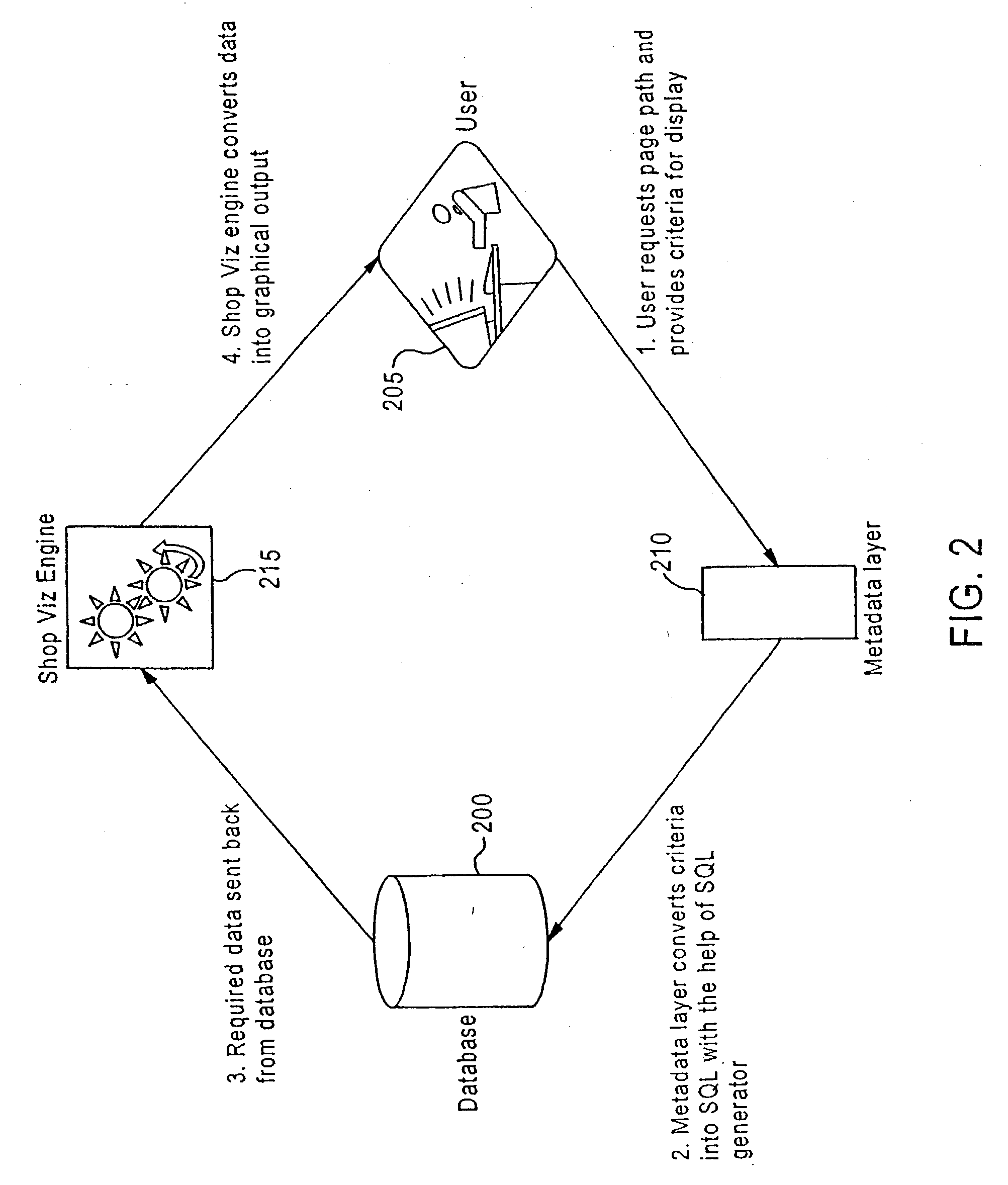
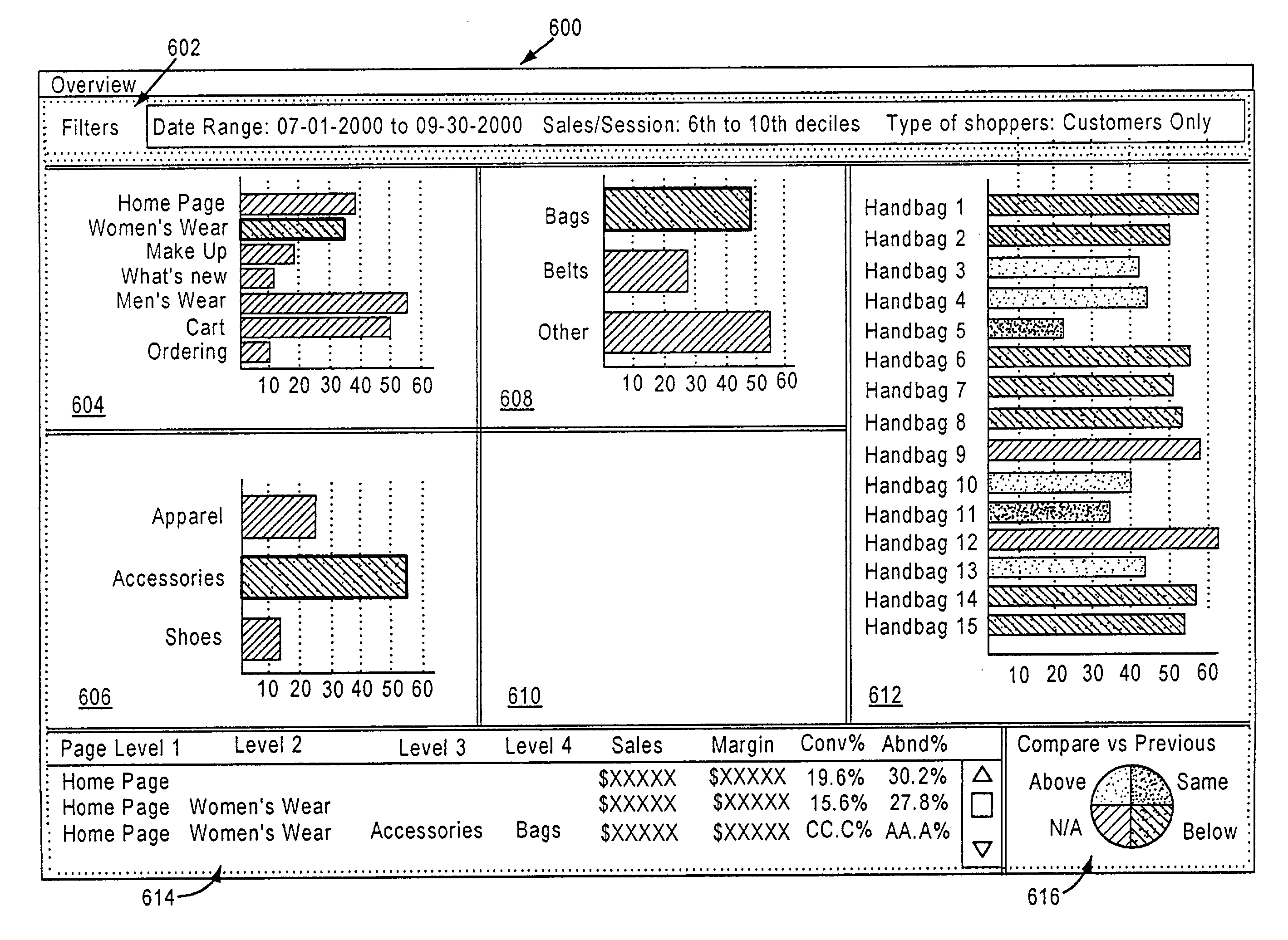
ActiveUS20040174397A1Shorten the timeDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWeb siteGraphics
A method of graphically displaying the path of a customer traversing a web site and related business data is described. The method includes receiving a user request for a visualization. The user request may include data filters and exclusions. Responsive to the user request, traffic data is selected for analysis. The selected traffic data is analyzed and displayed to the user. The display may be in the form of a visualization including a graph and related business data. The graph may be of an overview, referral, path, page-to-page path, and animation type. A system for visualizing traffic patterns and the path of a customer at a site is described in conjunction with the above method. The system includes a logical data model, a dimensional data model, a report specification, a graphical interface, metadata database and an analysis report. The graphical interface is used for viewing visualization information.
Owner:TERADATA US
System and method for multimedia playlist
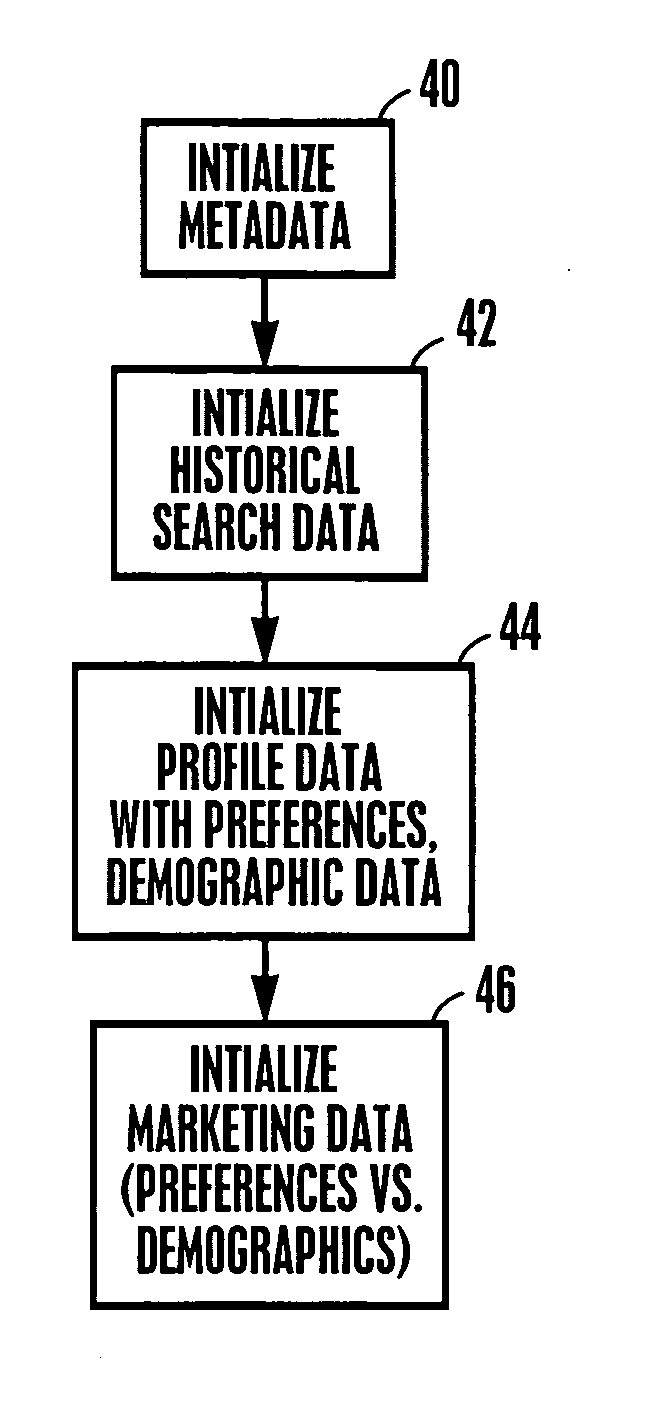
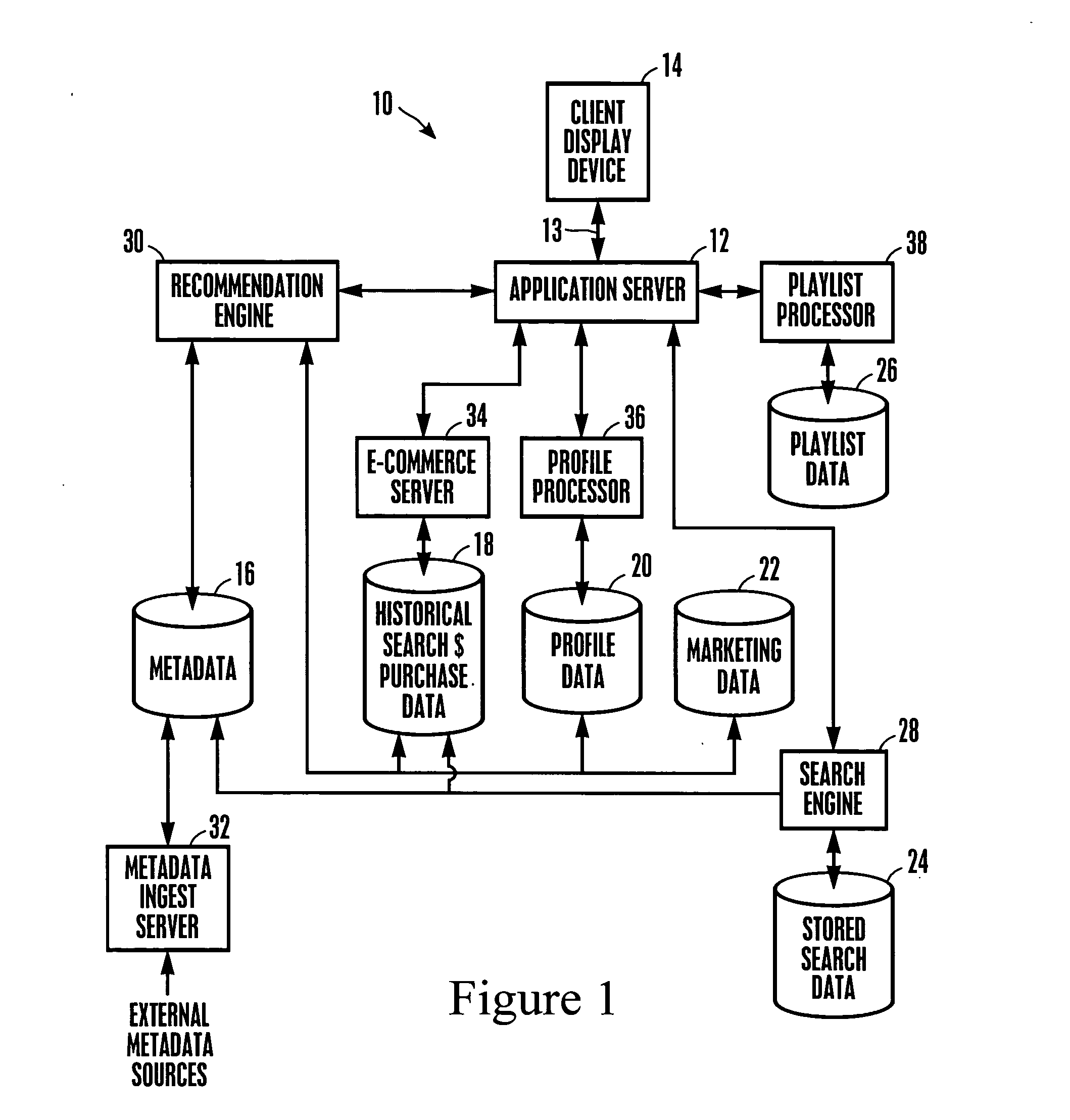
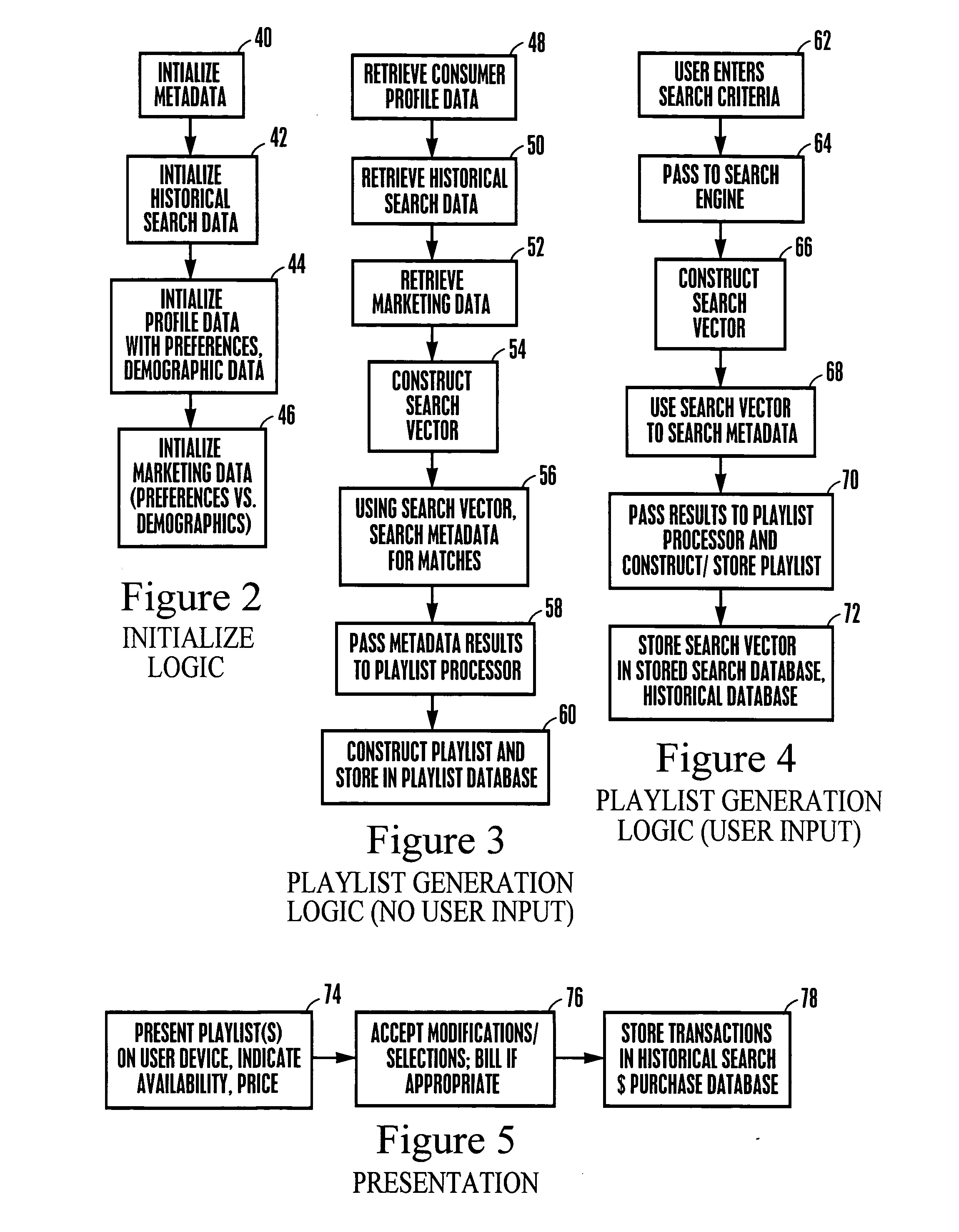
InactiveUS20050210507A1Television system detailsDigital data information retrievalDemographic dataA* search algorithm
A playlist of multimedia content is generated based on the results of a search algorithm operating on a metadata database connected to a network. The search algorithm utilizes a search vector that is generated using demographic data and consumer profile data, and / or based on a consumer search request. The playlist, which can list heterogeneous titles of multimedia content, may be accessed anywhere on the network by any suitable authorized device.
Owner:SONY CORP +2
Apparatus, system, and method for data access management
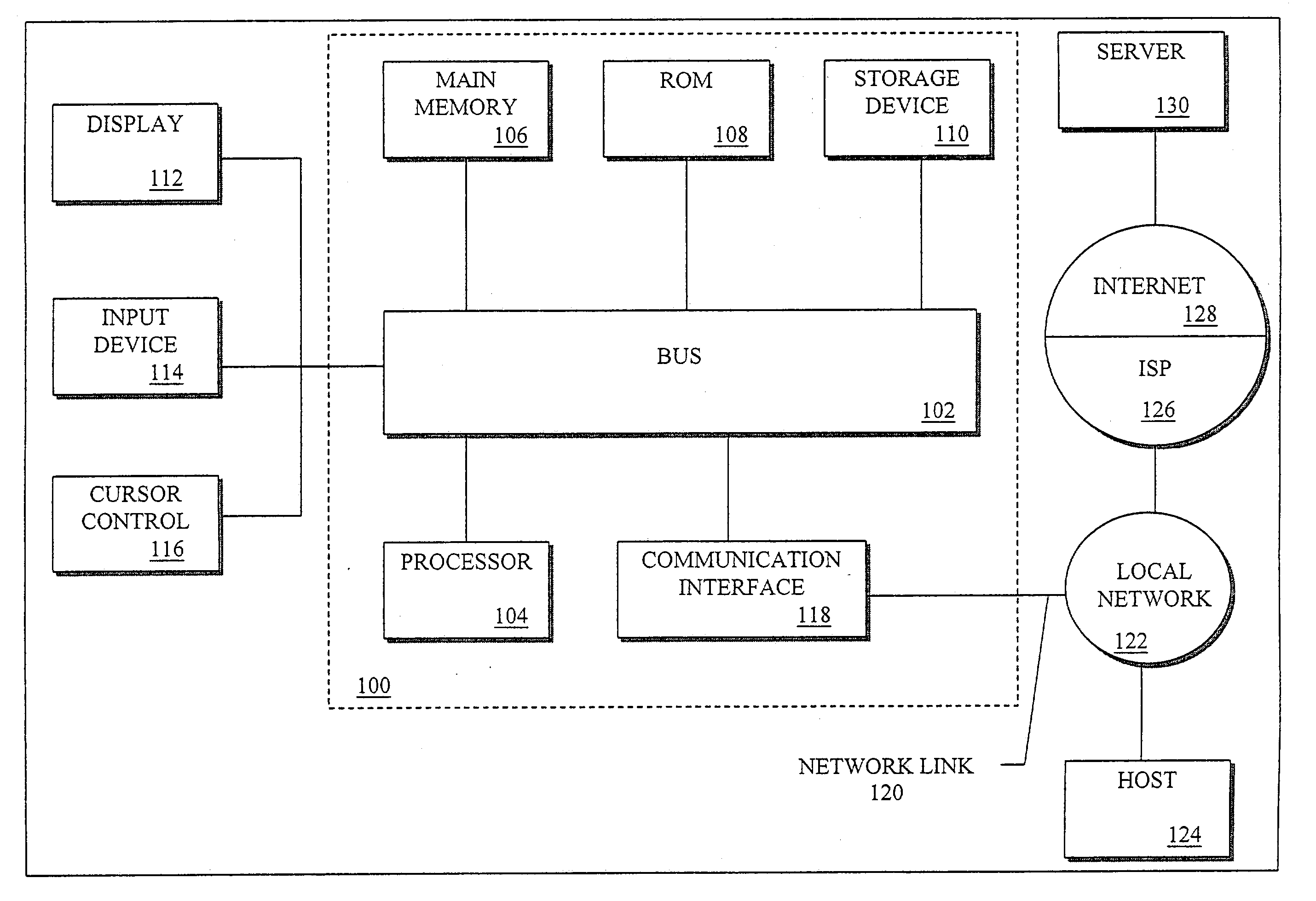
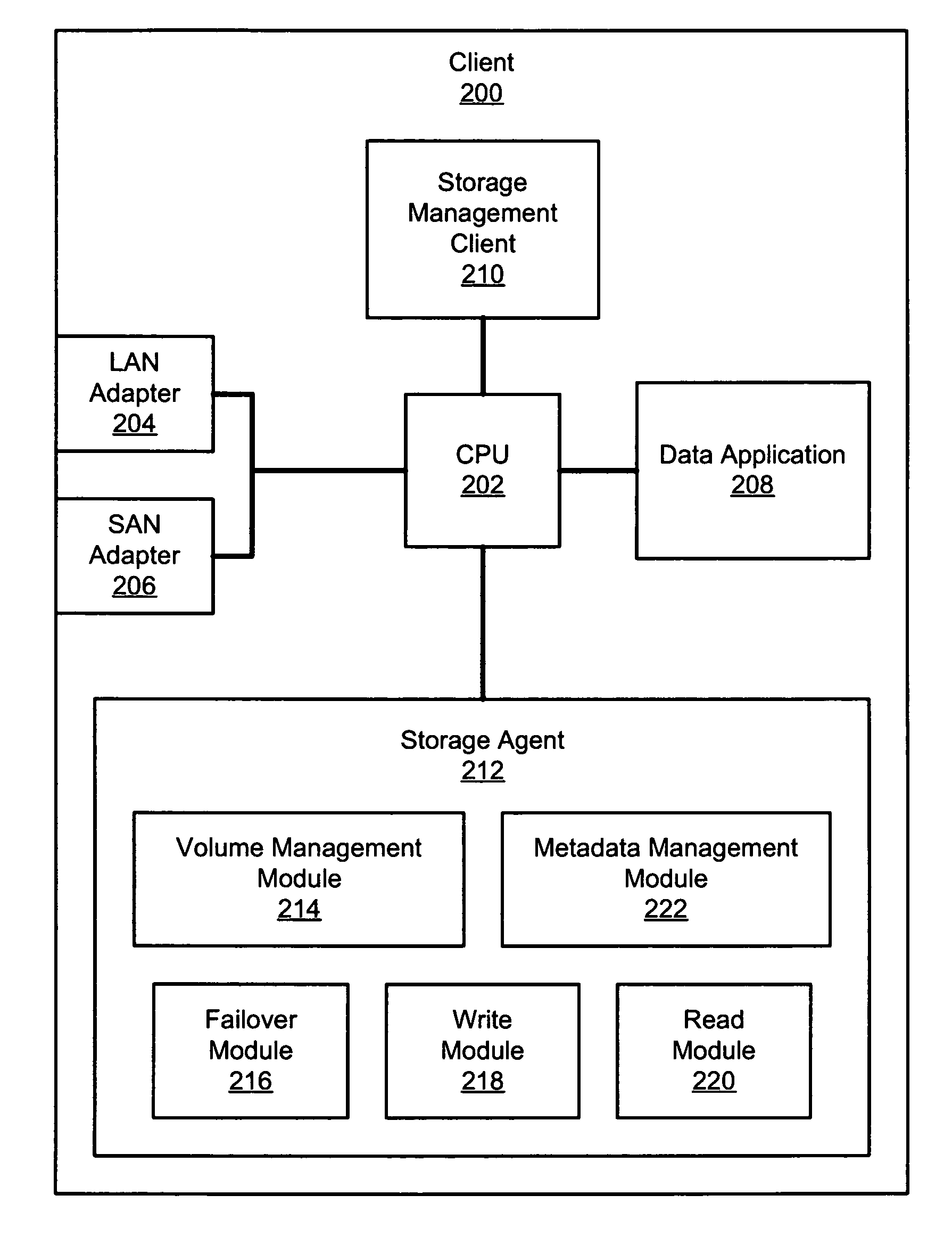
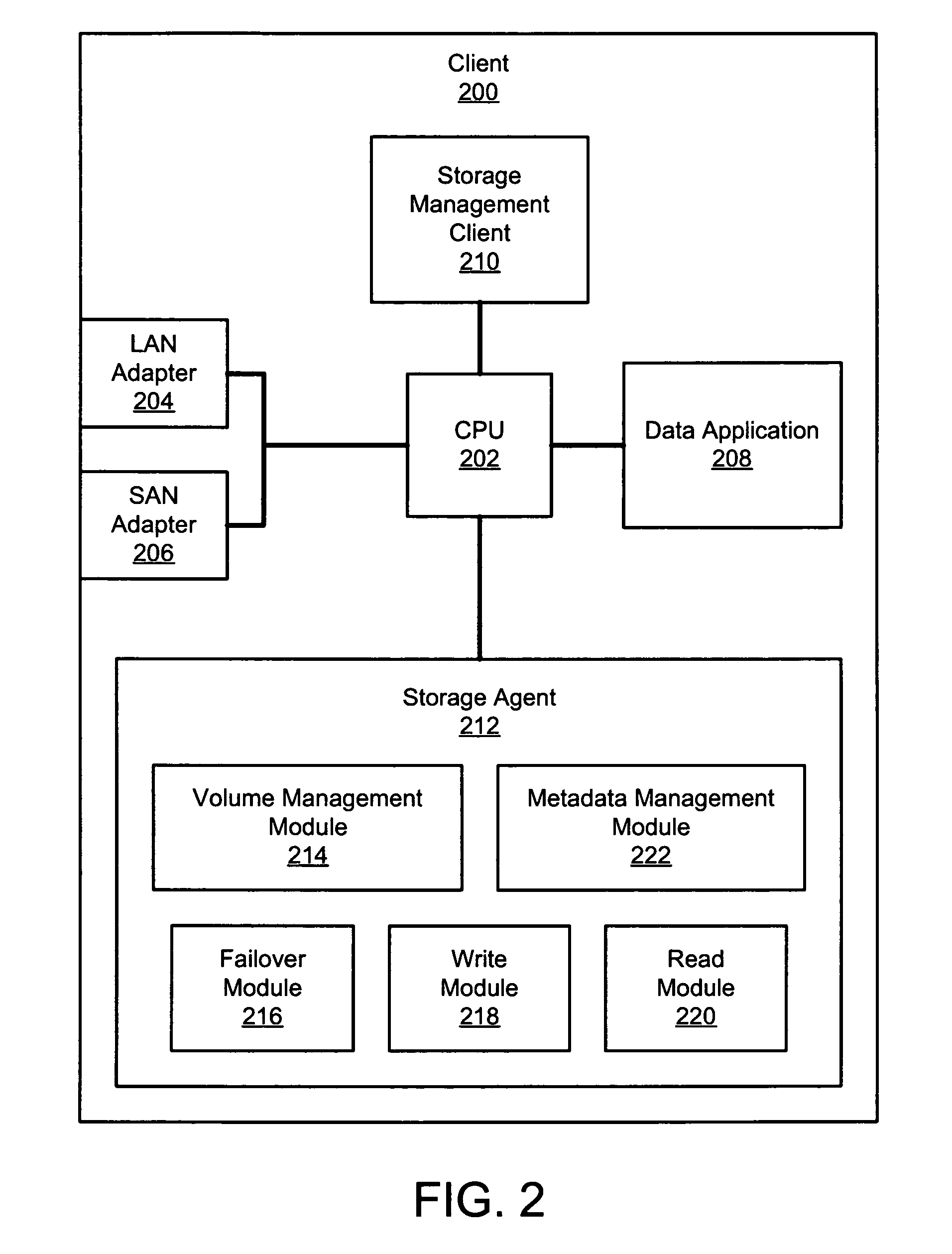
InactiveUS7533181B2Occur more quicklyProduce quicklyInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionStorage area network
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for data access management on a storage device connected to a storage area network. A client includes network connections to a first and second network, where the second network comprises a storage area network (SAN). The client also includes a storage management client and a storage agent. The storage agent is configured to minimize the amount of metadata processing that occurs on the client by sending the metadata or a copy thereof to a storage server to be stored in a centralized metadata database. The storage server also includes a storage manager that is configured to manage data access by the storage agent to the requested storage device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and systems for managing data
InactiveUS20070112809A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData systemMetadatabase
Systems and methods for managing data, such as metadata or indexes of content of files. In one exemplary method, notifications to update a metadata database or an index database are combined into a combined notification. According to other aspects, an order among logical locations on a storage device is determined in order to specify a sequence for scanning for files to be indexed. According to another aspect, a method includes determining whether to index a file based on a path name of the file relative to a plurality of predetermined path names.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and systems for managing data
Methods and systems for processing data, including metadata and an index database. In one exemplary method, a first folder, representing a first search query, is stored, and a second folder, representing a second search query wherein the second folder has a predetermined hierarchical relationship to the first folder, is stored, and the search queries are used to search one or both of an index database and a metadata database. In the metadata database, the type of metadata for one file type differs from the type of metadata for another file type.
Owner:APPLE INC
Authenticating Metadata and Embedding Metadata in Watermarks of Media Signals
InactiveUS20070266252A1Television system detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer scienceDatabase
A method of associating metadata with a media signal receives an identifier for the media signal, uses the identifier to look up metadata in a metadata database, validates the metadata by checking attributes of the media signal relative to at least a portion of the metadata to provide validated metadata; and provides the validated metadata to a requesting application. Related methods enable searching of metadata across metadata databases, routing metadata requests to the metadata databases, controlling access to and validating metadata for media content, and re-associating valid metadata with media content.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Auto playlist generator
InactiveUS7024424B1Wide applicationSimplifies list generationGearworksMusical toysInformation retrievalMetadatabase
A system and method for generating a list is provided. The system includes a seed item input subsystem, an item identifying subsystem, a descriptive metadata similarity determining subsystem and a list generating subsystem that builds a list based, at least in part, on similarity processing performed on seed item descriptive metadata and user item descriptive metadata and user selected thresholds applied to such similarity processing. The method includes inexact matching between identifying metadata associated with new user items and identifying metadata stored in a reference metadata database. The method further includes subjecting candidate user items to similarity processing, where the degree to which the candidate user items are similar to the seed item is determined, and placing user items in a list of items based on user selected preferences for (dis)similarity between items in the list and the seed item.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and systems for managing data
Methods and systems for processing data, including metadata and an index database. In one exemplary method, a first folder, representing a first search query, is stored, and a second folder, representing a second search query wherein the second folder has a predetermined hierarchical relationship to the first folder, is stored, and the search queries are used to search one or both of an index database and a metadata database. In the metadata database, the type of metadata for one file type differs from the type of metadata for another file type.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and systems for managing data
ActiveUS20070112743A1Increase speedAvoid accessDigital data processing detailsFile metadata searchingInformation typeData system
Systems and methods for managing data, such as metadata. In one exemplary method, a search is performed based on a search query of at least metadata of a first plurality of files and a set of a permissions is determined for a first user, wherein the set of permissions defines at least a right to view information. Results of the search are displayed based upon the set of permissions. In the metadata database, there is metadata from a number of files of different types. The type of information in metadata for a first type of file differs from a type of information in metadata for a second type of file.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and systems for managing data
InactiveUS20050289127A1Increase speedAvoid accessDigital data processing detailsFile metadata searchingInformation typeData system
Systems and methods for managing data, such as metadata. In one exemplary method, a search is performed based on a search query of at least metadata of a first plurality of files and a set of a permissions is determined for a first user, wherein the set of permissions defines at least a right to view information. Results of the search are displayed based upon the set of permissions. In the metadata database, there is metadata from a number of files of different types. The type of information in metadata for a first type of file differs from a type of information in metadata for a second type of file.
Owner:APPLE INC
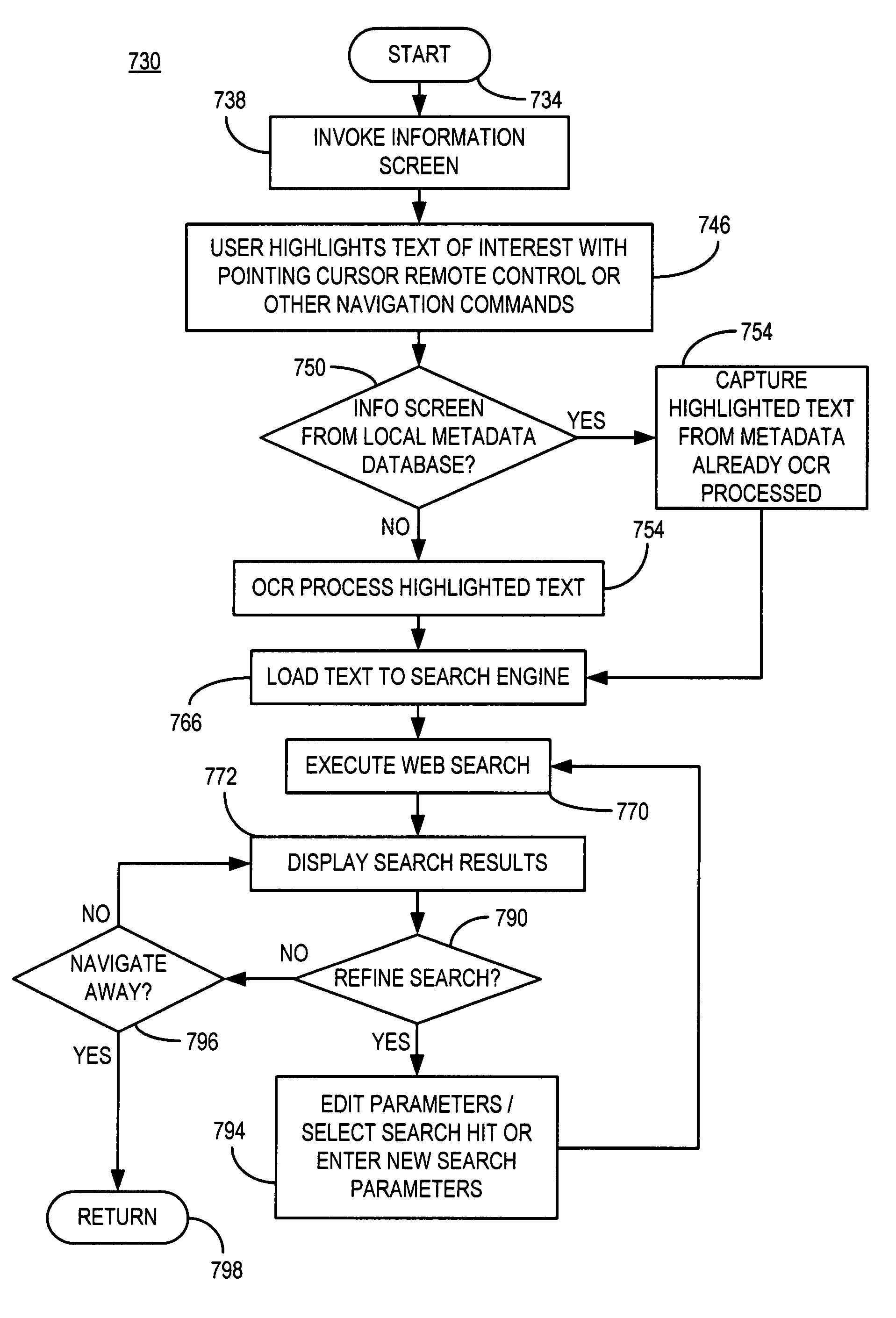
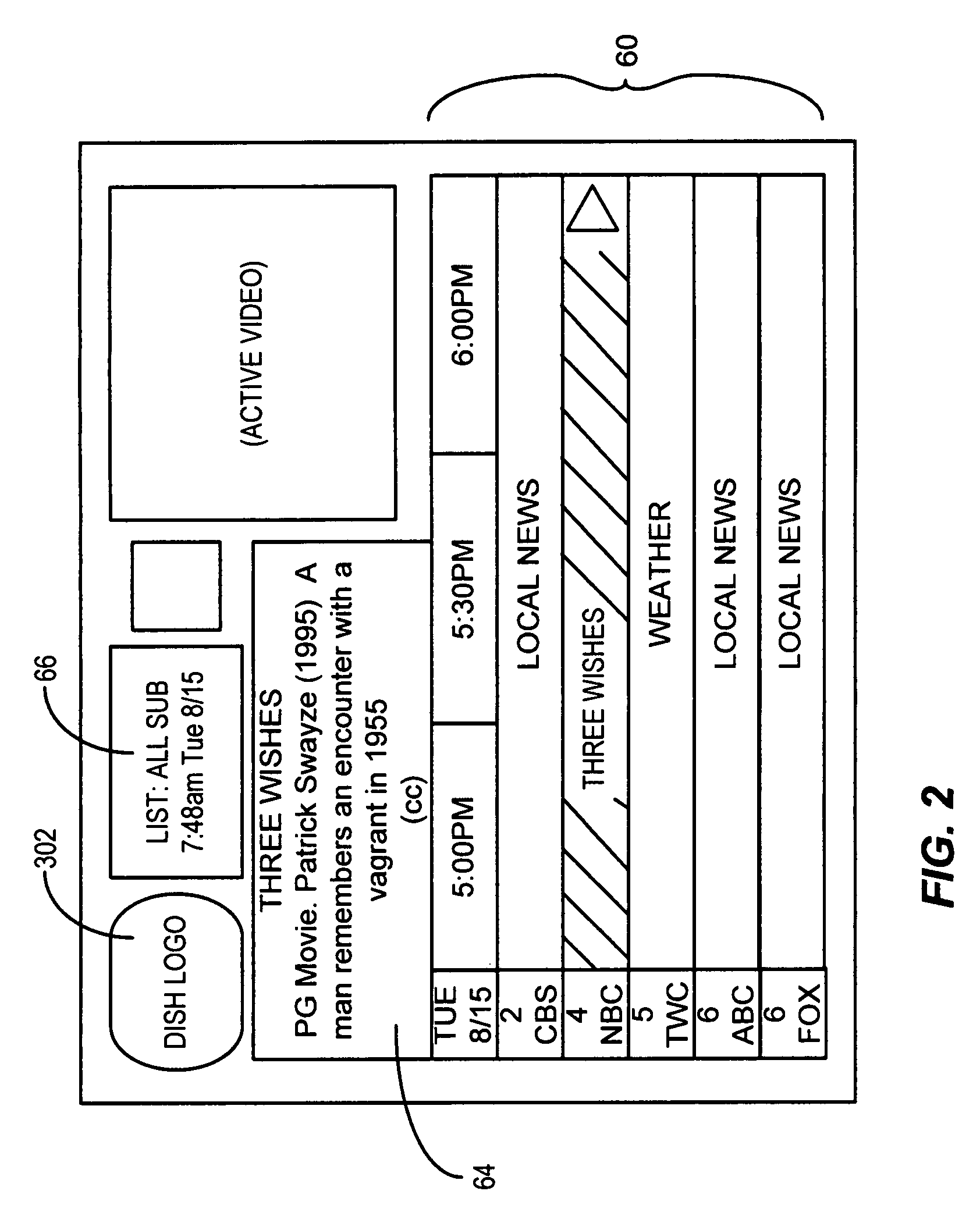
Metadata from image recognition
A method of acquiring data associated with a television program consistent with certain embodiments involves acquiring information that identifies a currently playing television program; receiving a command from a user interface that selects an image forming a portion of a frame of video displayed on the television, wherein said frame of video is a portion of the television program; accessing a specified web site that contains a database of metadata associated with television programs via the Internet; querying the specified web site for metadata associated with the image by providing the image along with the information that identifies the currently playing television program; receiving a response from the specified web site that provides metadata associated with the image; and displaying at least a portion of the metadata. This abstract is not to be considered limiting, since other embodiments may deviate from the features described in this abstract.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Methods and systems for managing data
InactiveUS7672962B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData systemMetadatabase
Systems and methods for managing data, such as metadata or indexes of content of files. In one exemplary method, notifications to update a metadata database or an index database are combined into a combined notification. According to other aspects, an order among logical locations on a storage device is determined in order to specify a sequence for scanning for files to be indexed. According to another aspect, a method includes determining whether to index a file based on a path name of the file relative to a plurality of predetermined path names.
Owner:APPLE INC
Virtual file system integrating multiple cloud storage services and operating method of the same
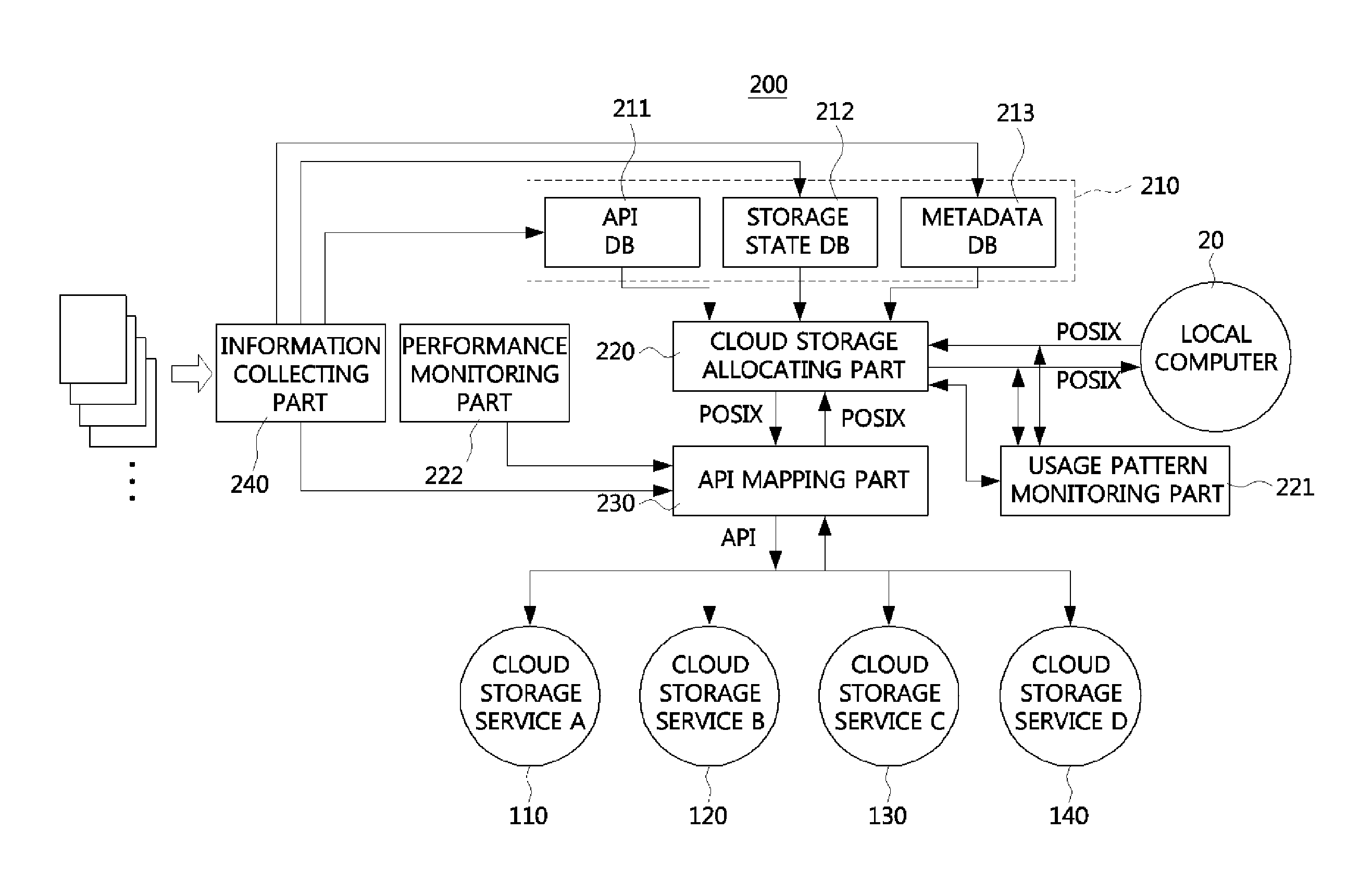
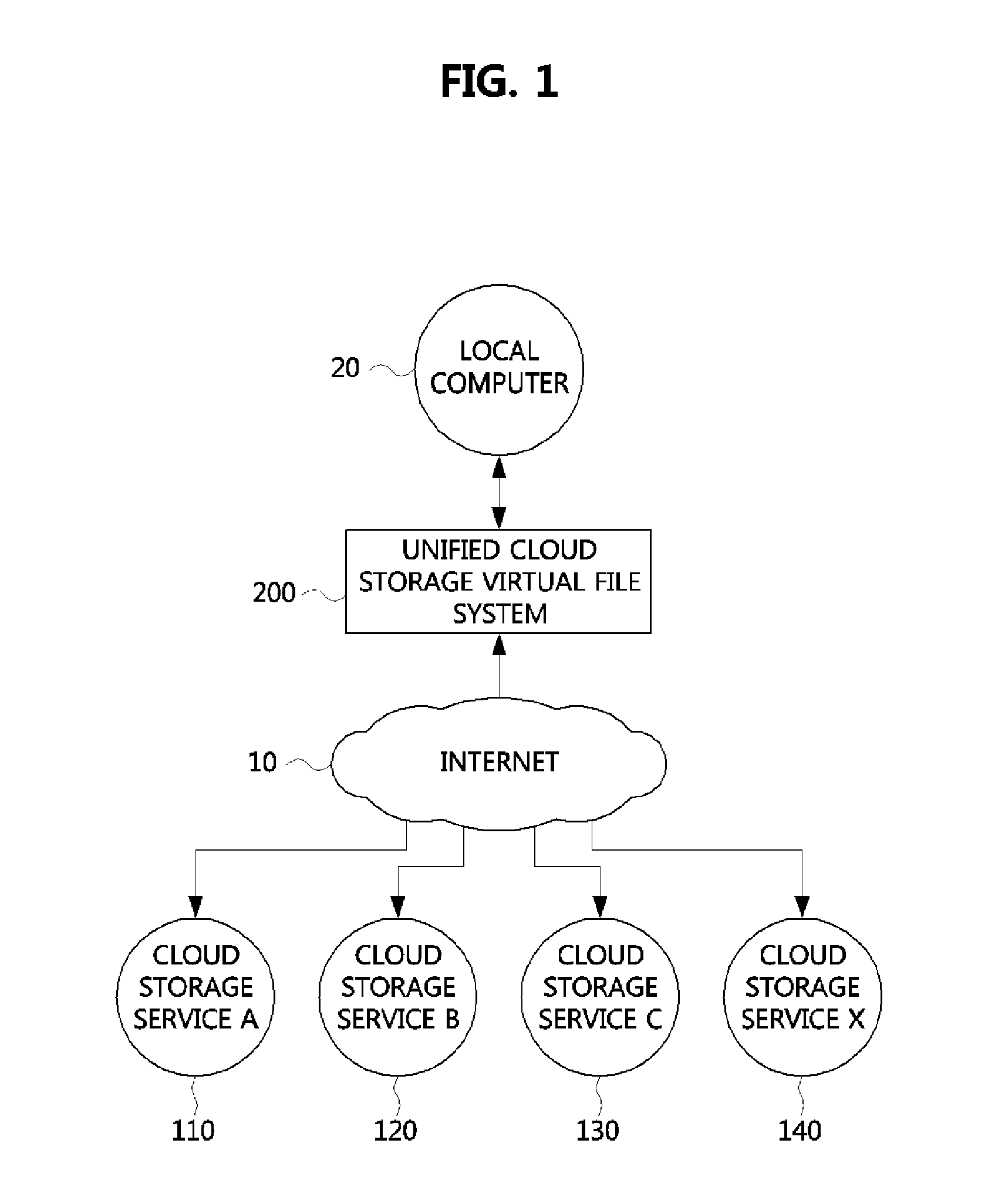
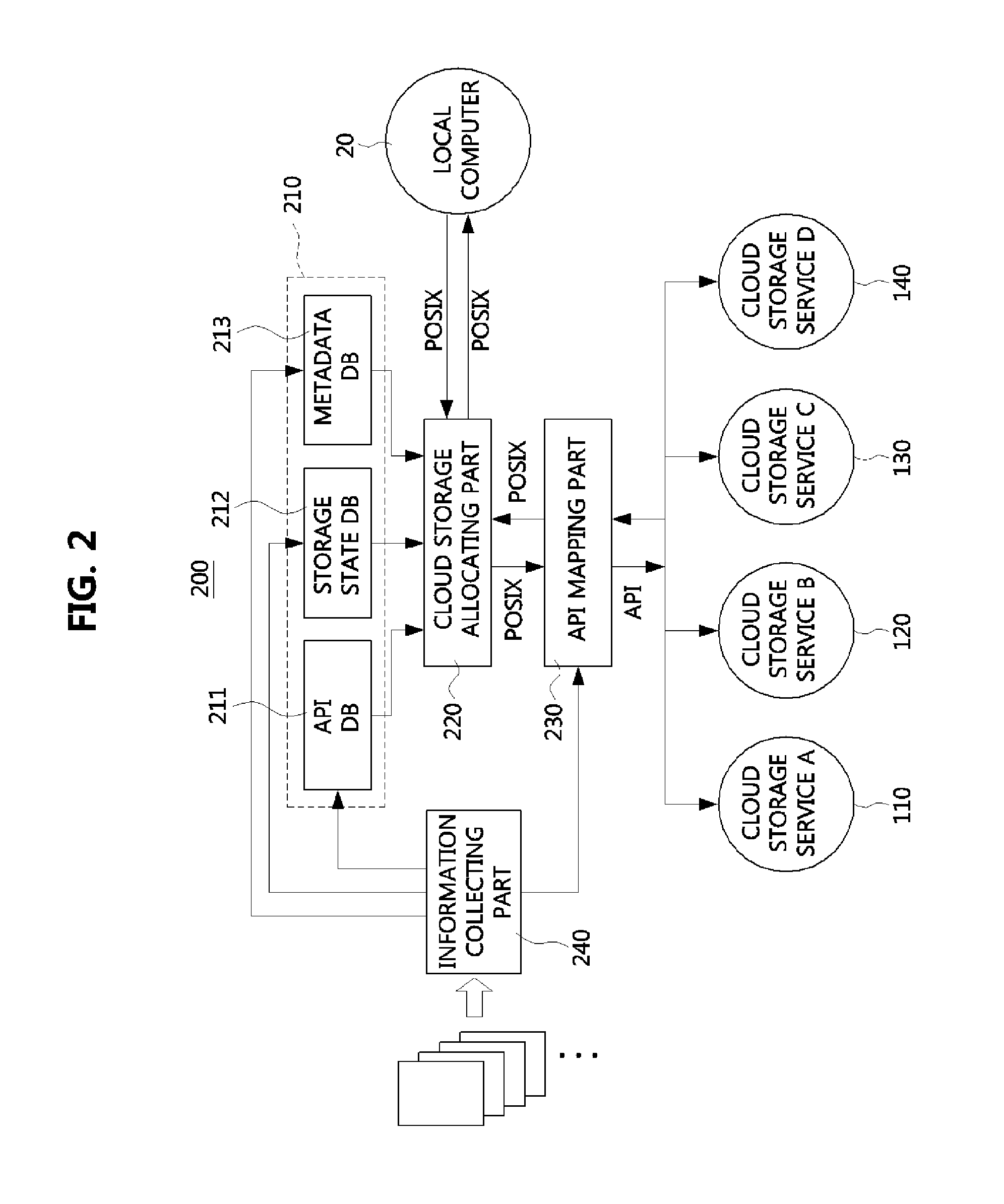
InactiveUS20140164449A1Digital data information retrievalProgram control using stored programsVirtual file systemCloud storage
Disclosed is a virtual file system integrating and managing multiple cloud storages. A virtual file system may comprise an API database storing information on open API of the cloud storages, a storage state database storing state information of the cloud storages, a metadata database storing metadata of the cloud storages, a cloud storage allocation part receiving an user request and selecting a cloud storage appropriate for the user request among the cloud storages by referring to the storage state database and the metadata database, and an API mapping part reading out open API information of the cloud storage selected by the cloud storage allocation part from the API database, converting the user request to an open API of the selected cloud storage, and transferring the converted open API to the selected cloud storage.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Method and system for implementing application server load balancing
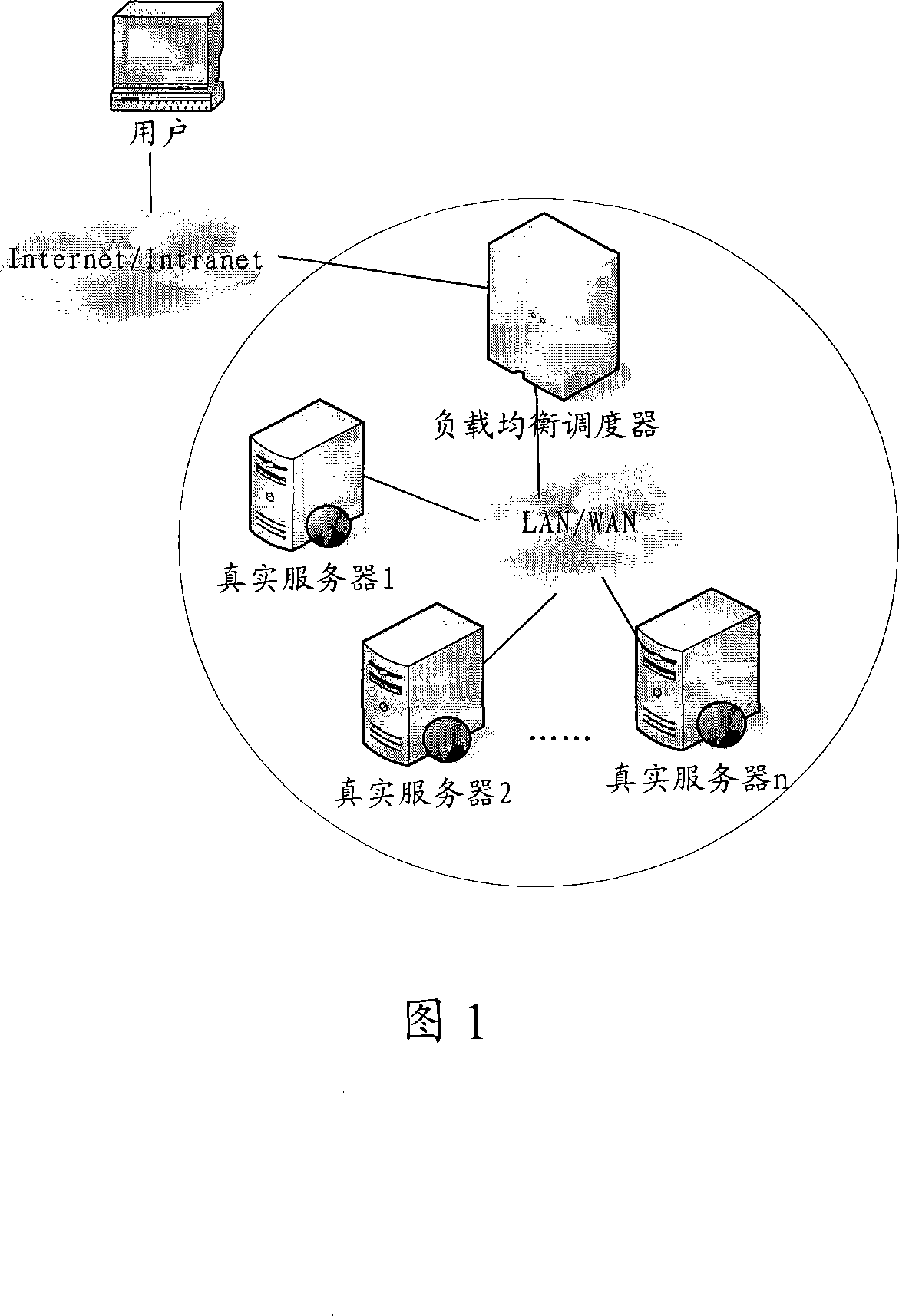
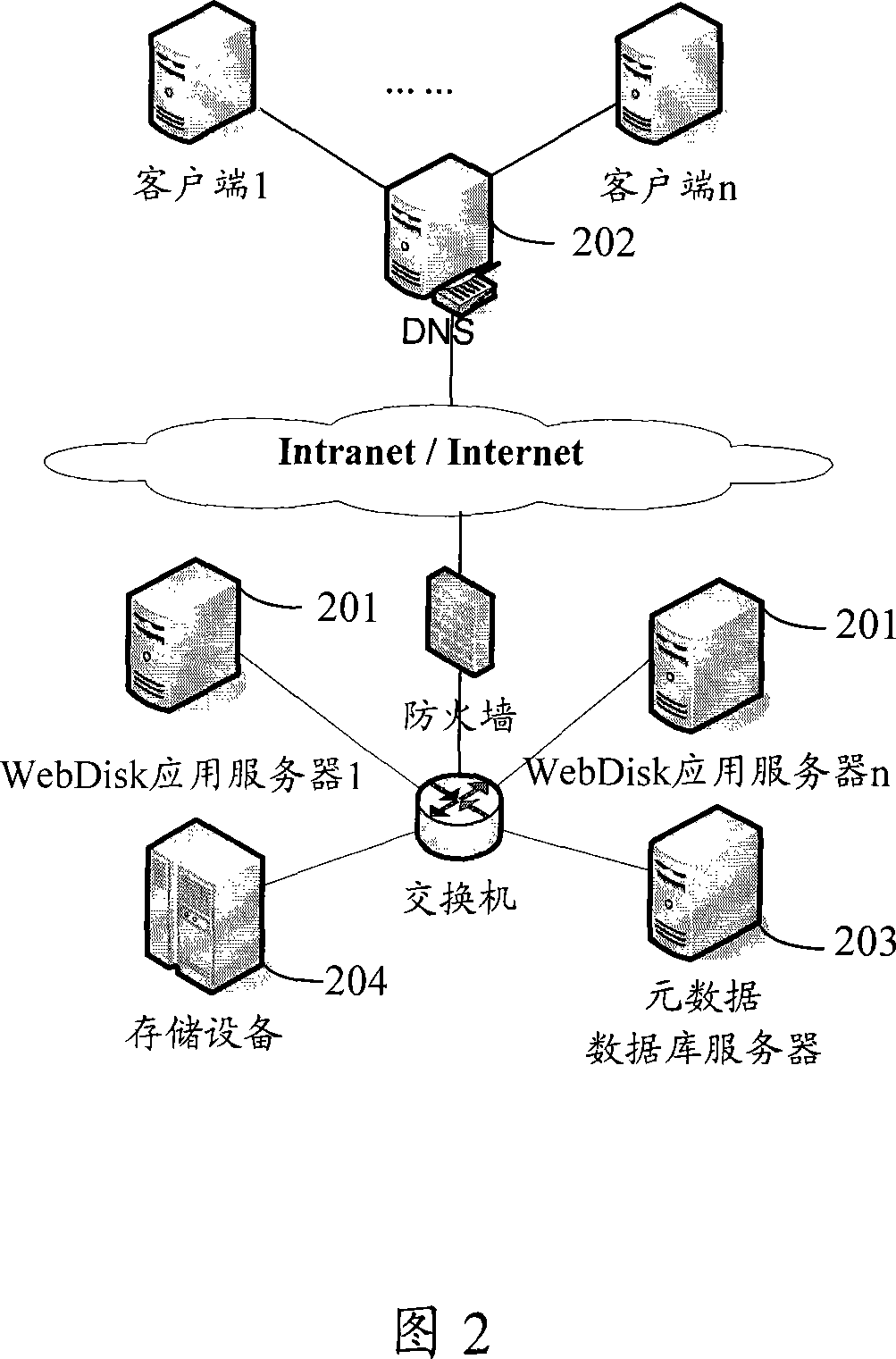
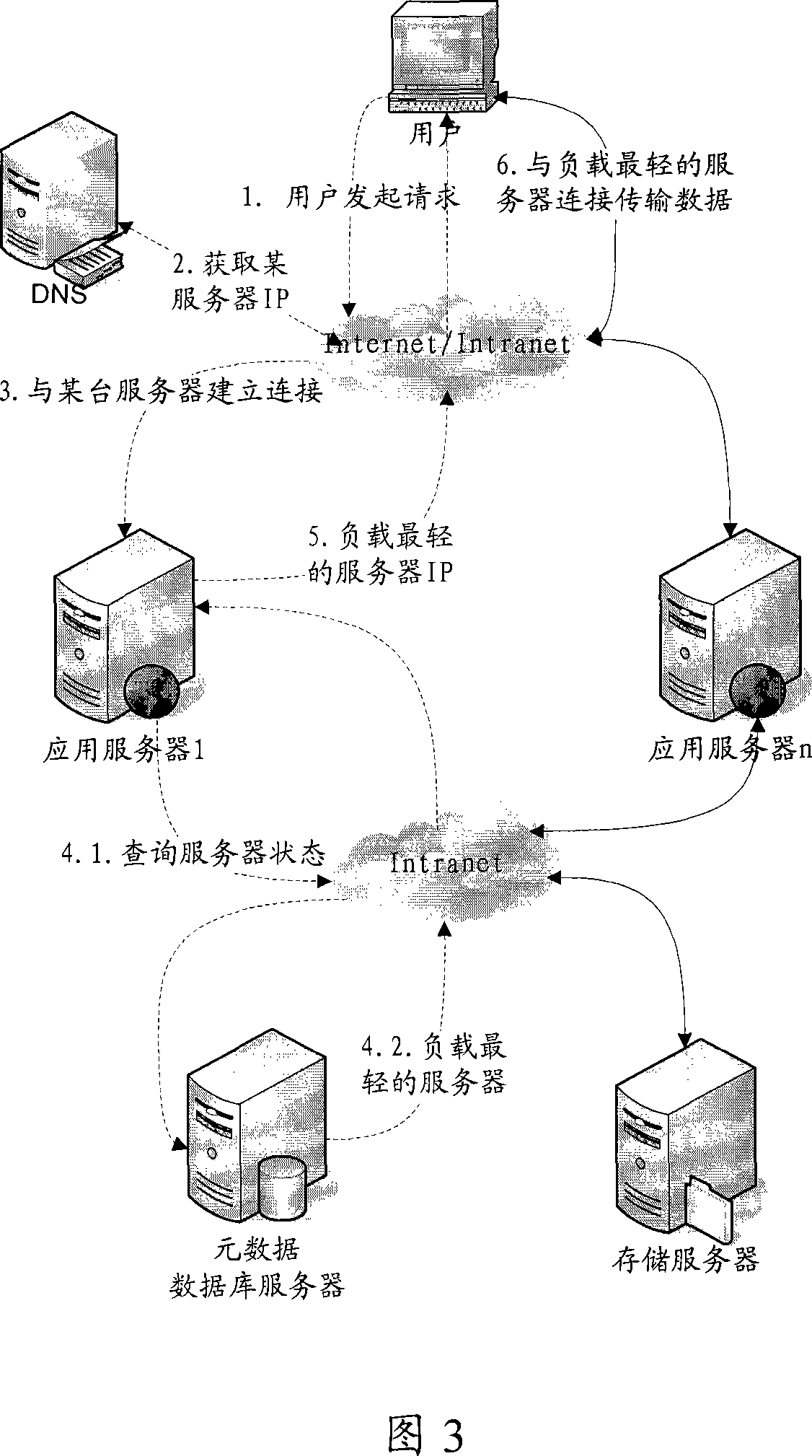
ActiveCN101115016AEliminate bottlenecksEvenly distribute workData switching networksDomain nameApplication server
The invention discloses a method to realize application server, comprising the following steps: a domain name analyzing server receives a request with application server cluster domain name sent by a user, and assigns an application server with an IP address mark to the user from the pre-stored application server IP address list corresponding to the domain name; the application server assigned to the user locates an application server for the user according to the current load information of each application server in the application server cluster stored in a meta-data base server, and feedbacks the application server information to the user. The located server stores the file data uploaded by the user in the storage device at the network side during the communication with the user. The invention can realize direct P2P data transmission, balance distribution operations, and make full use of every application server resource in the application server cluster.
Owner:UNITED INFORMATION TECH H K COMPANY
Data delivery system and sending station therefor
InactiveUS7155504B1Reliable dataNot slow down responseData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsGuidelineSummary data
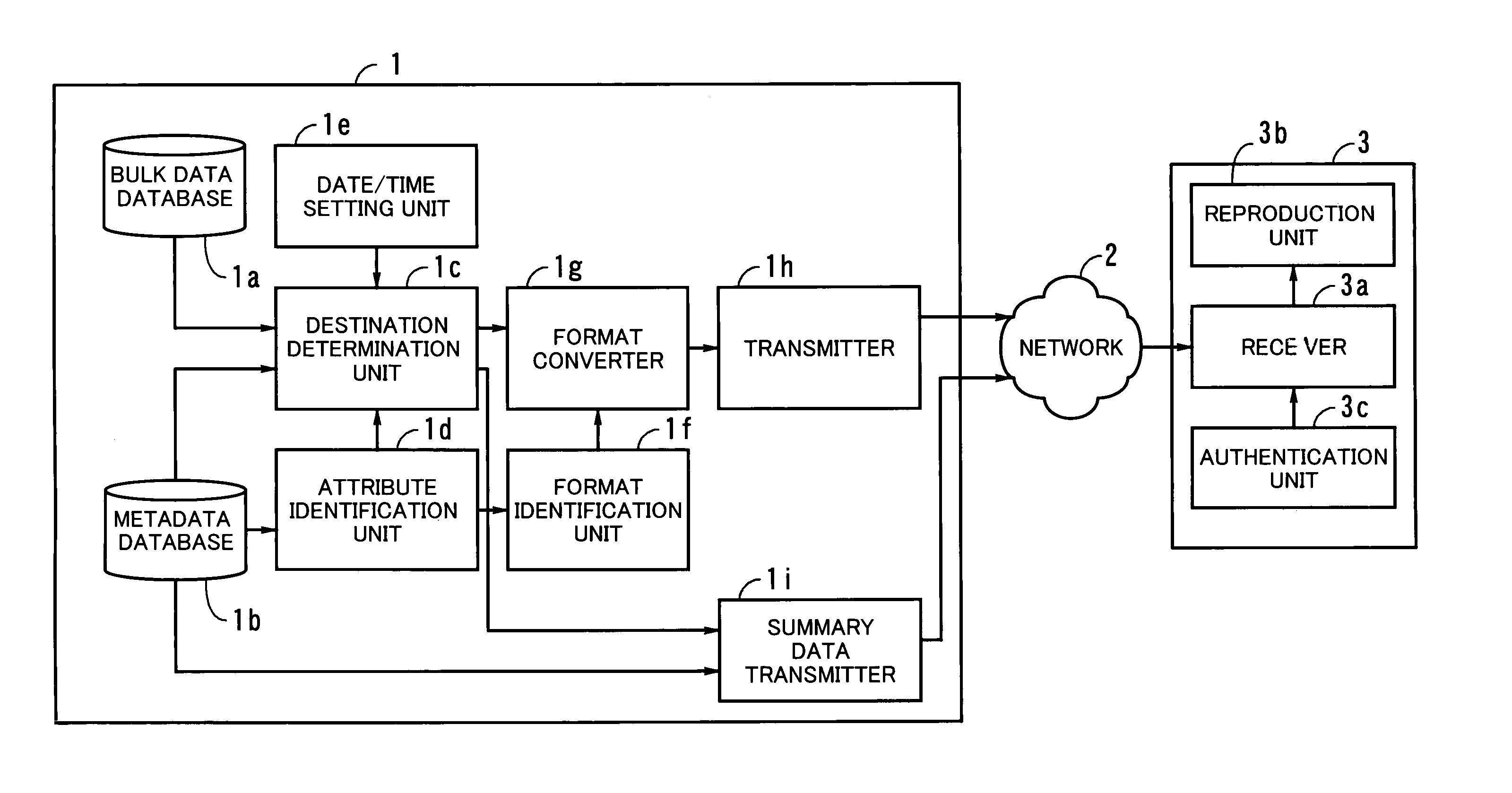
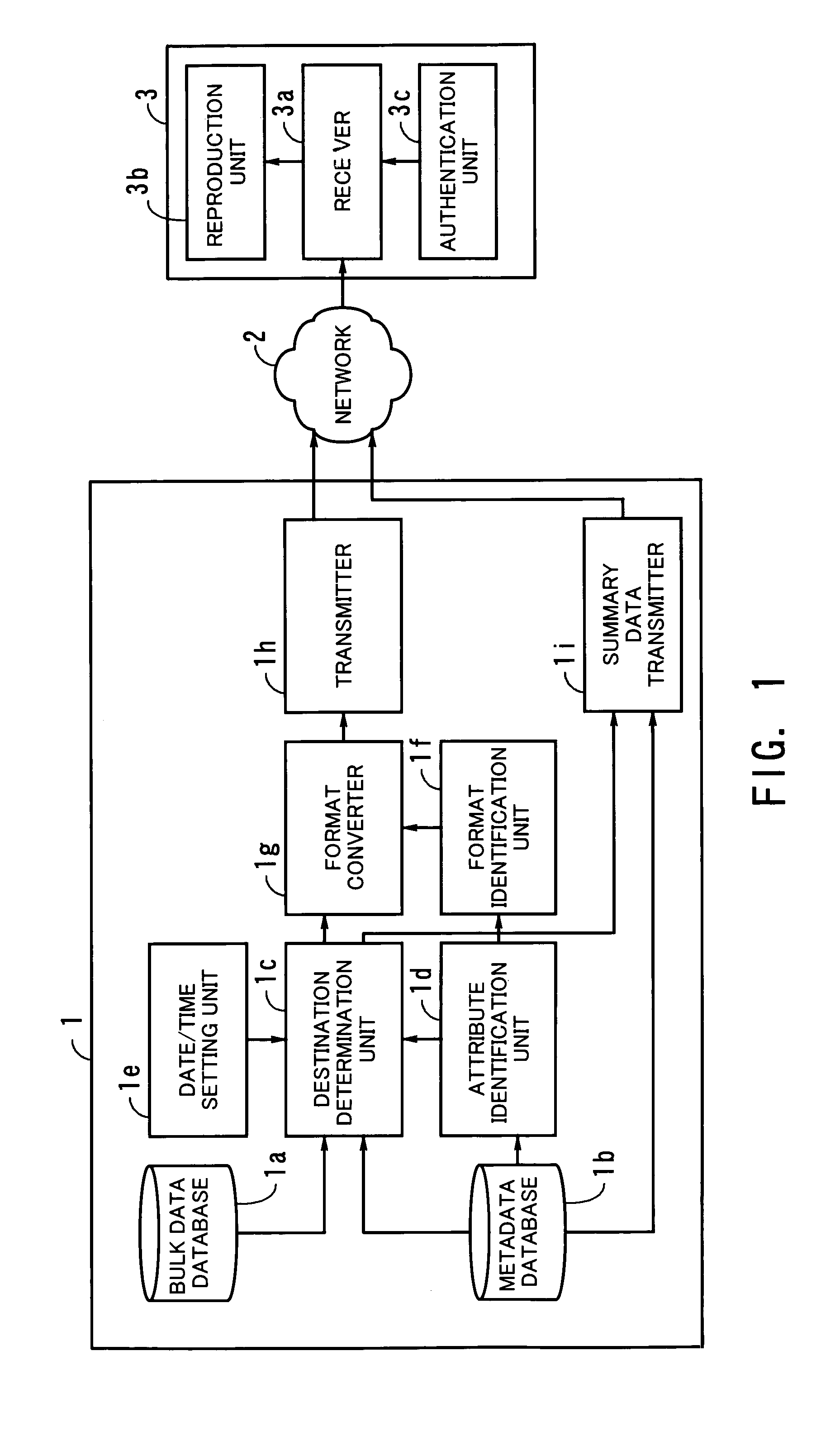
A data delivery system which delivers created data to all the parties that need it. Documents such as engineering drawings are stored as bulk data files in a bulk data database. Metadata files containing attribute information of bulk data are stored in a metadata database. When the date and time of a data distribution session is given to a date / time setting unit, an attribute identification unit makes access to a relevant metadata file to identify the attributes of the bulk data to be transmitted. Based on this result, a destination determination unit determines the destinations of each bulk data file. A format identification unit then identifies which data formats the receiving stations can handle. If necessary, the data format is changed by a format converter, so as to meet the requirements of each destination. Summary data briefly describes what kinds of bulk data files are to be distributed. A summary data transmitter compiles such summary data and sends it to the receiving stations. Each receiving station now returns a downloading request, and in response to this, a transmitter sends out the requested bulk data files, which meets the destination's format guideline. A receiver in the receiving station accepts those bulk data files and a reproduction unit restores the received data to its original form.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for managing multimedia files
InactiveUS20110161174A1Increase capacityMultimedia data indexingAdvertisementsDeep linkingDatabase manager
A system for locating, segmenting, annotating and retrieving multimedia files, provides a database of metadata (68) relating to multimedia files (70), a database manager (64), and a database client (66) for accessing the data contained within the database. The database client (66), together with the metadata database (68) and database manager (64) provide a variety of different functionalities, namely a deep linking functionality, a segmentation functionality, a metadata annotation functionality, a retrieval functionality, and an access functionality. The user, through database client (68) annotates the multimedia file or segment of multimedia file with metadata which is saved in the database (68). When the user desires to locate a multimedia file, the metadata is searched or browsed to locate the database entry associated with the multimedia file in question. The system further provides the ability for the user to load, open and start the playing of a multimedia file from a point intermediate to its start and end point, and without the user having to experience the portion between the start point and the intermediate point, break down larger files into shorter segments or individual frames (or still images) or regions within frames (or still images) without creating additional copies of the selected segments of the multimedia files of interest, thereby avoiding copyright issues from arising.
Owner:TAGMOTION
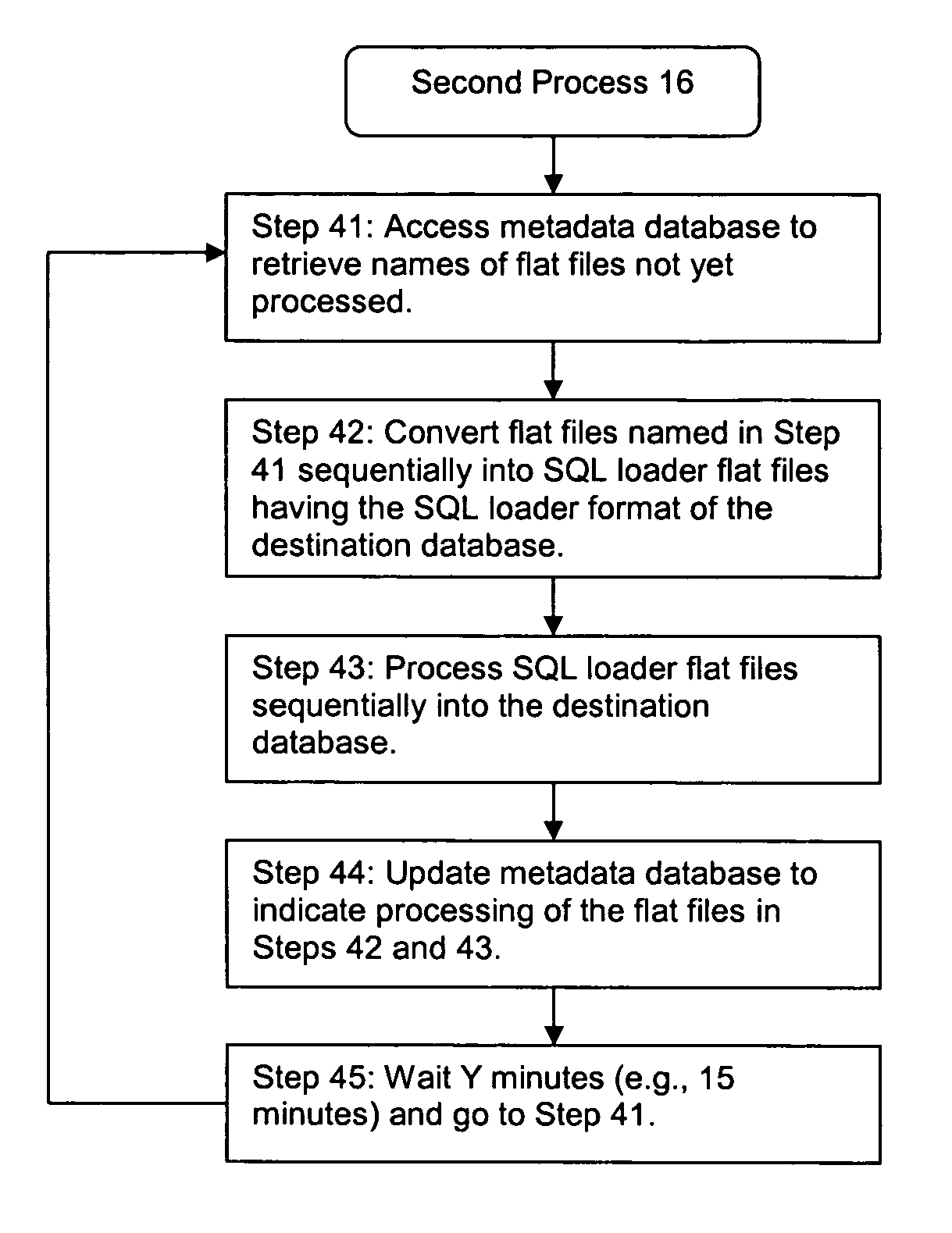
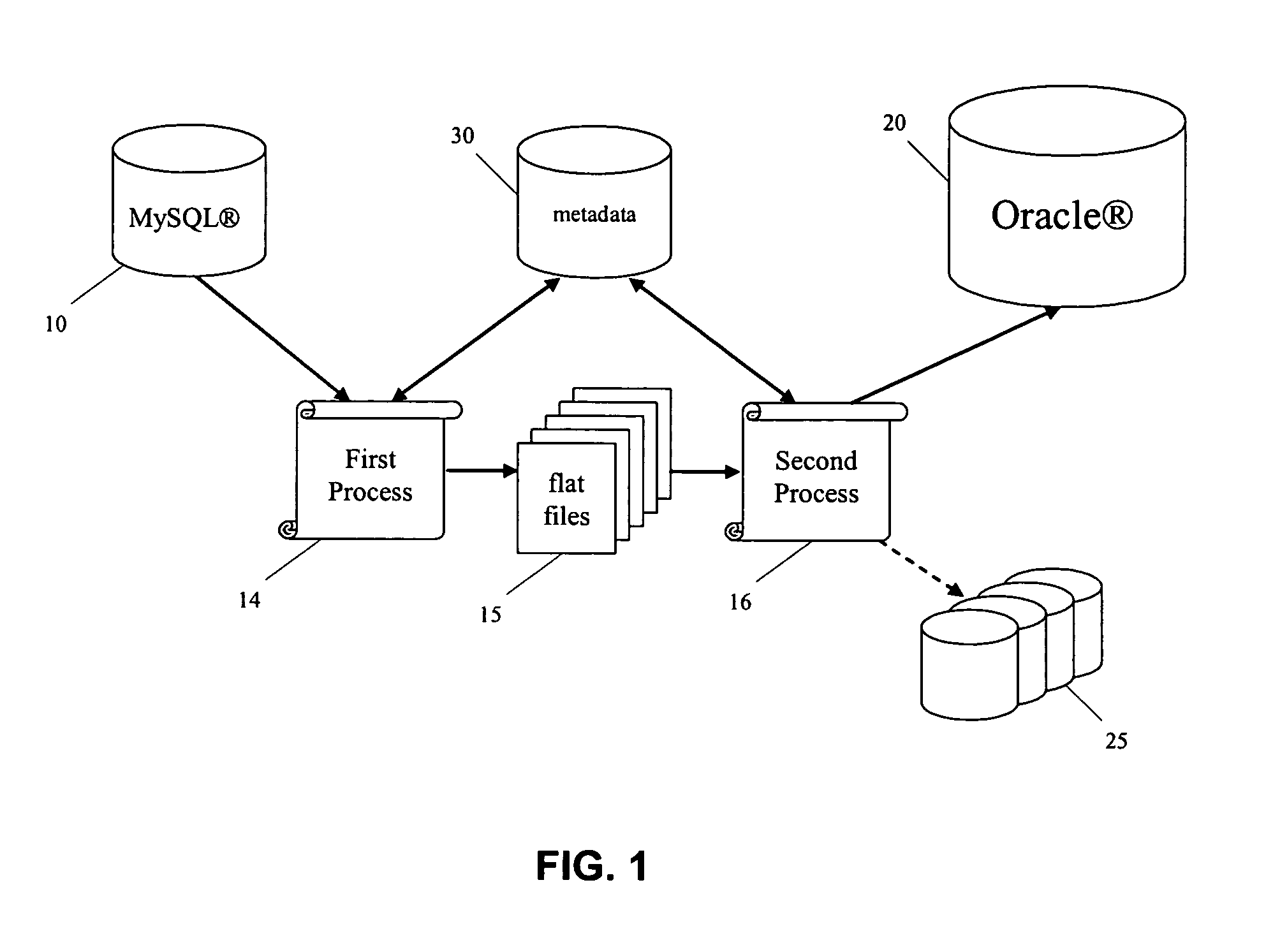
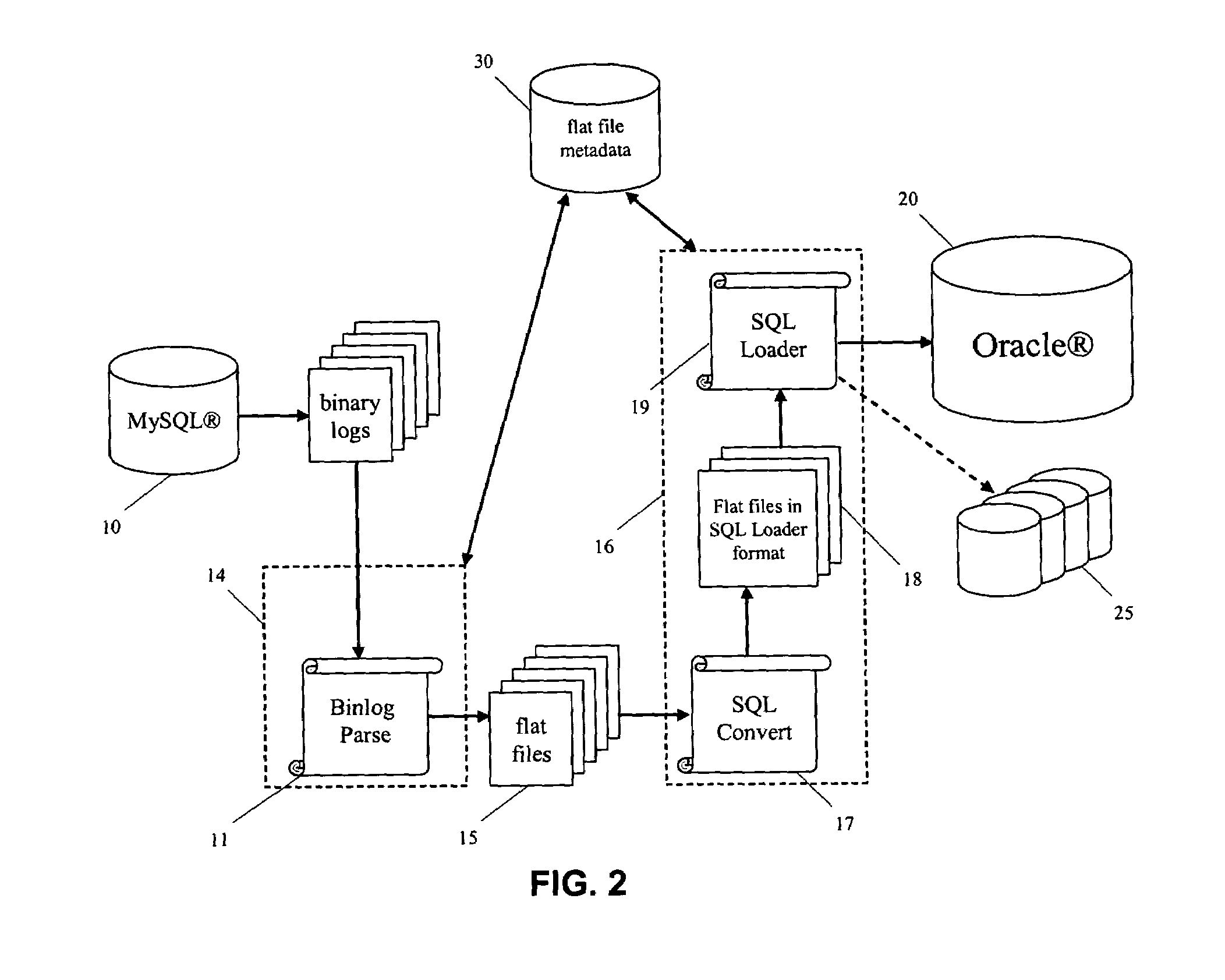
Database replication across different database platforms
InactiveUS7702698B1Increase the amount of dataEasy to handleDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSQLMetadatabase
Database replication across different database platforms is carried out by transforming a binary log of database updates made to a first database into an SQL loader format of a second database and then processing the transformed log of updates into the second database. The transformation of the binary log includes the step of parsing the binary log into SQL statements, storing the SQL statements as a flat file, and transforming the flat file into an input file having the SQL loader format of the second database. The metadata of the flat files is stored in a separate database. As the flat files are transformed into input files of the second database, the status of the flat files is updated in the metadata database.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Digital content inventory management system supporting automatic mass data processing and the method thereof
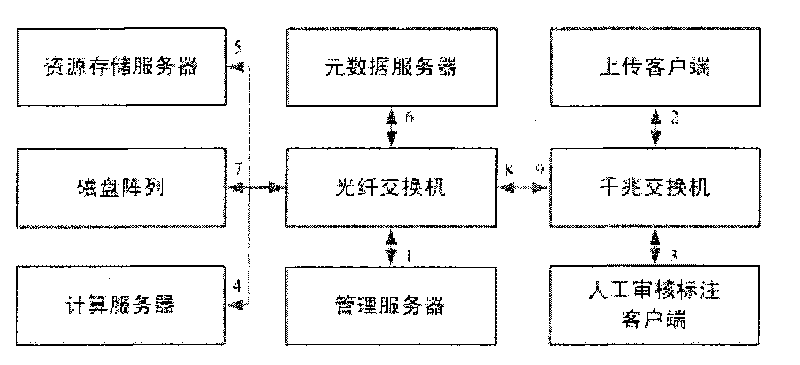
InactiveCN101754056AQuick calculationEfficient managementMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionInteraction interfaceWork flow
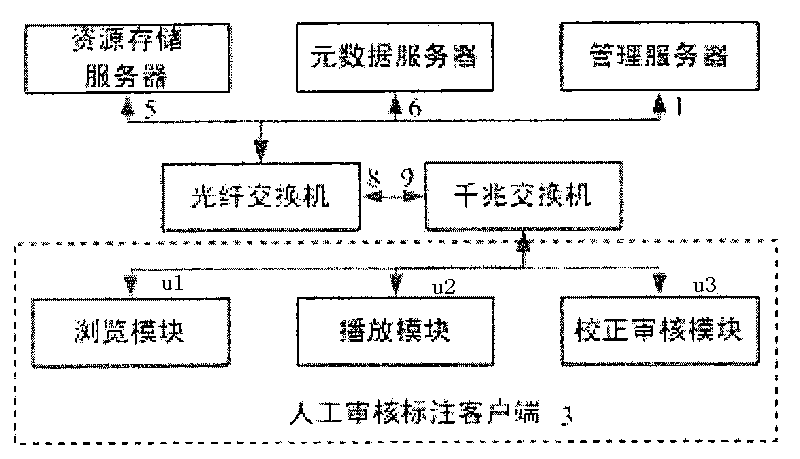
The invention relates to a digital content inventory management system supporting automatic mass data processing and the method thereof, which comprise a management server responsible for exchanging messages with and responding messages to other modules, determining the position where resources are stored, allocating computing servers for computation tasks and controlling the work flow, an uploading client responsible for uploading external multimedia resources, a artificial auditing and annotating client for providing an interaction interface for artificial audition and annotation of metadata results, computing servers responsible for managing and starting up an computing engine to acquire metadata results of media resources, a resource storage server responsible for managing media resource information, a metadata server responsible for managing metadata information, a disk array responsible for storing physical files of media resources, a resource database and a metadata database. The digital content inventory management system supporting automatic mass data processing and the method thereof can automatically process mass media data, automatically acquire the contents of multimedia data and perform automatic inventory of the contents, thus achieving the effective management of the contents of mass multimedia data.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrating and enhancing searching of media content and biometric databases
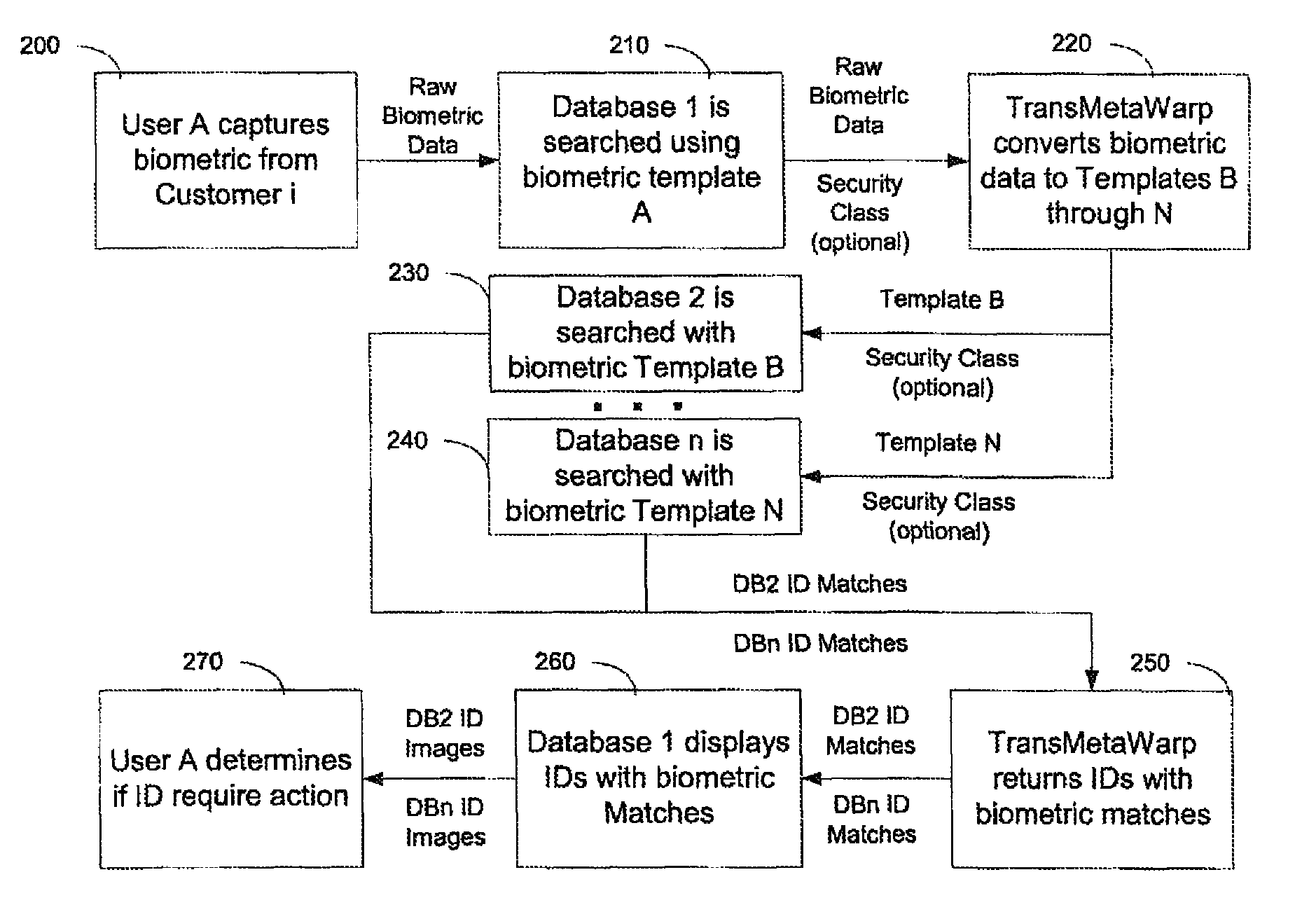
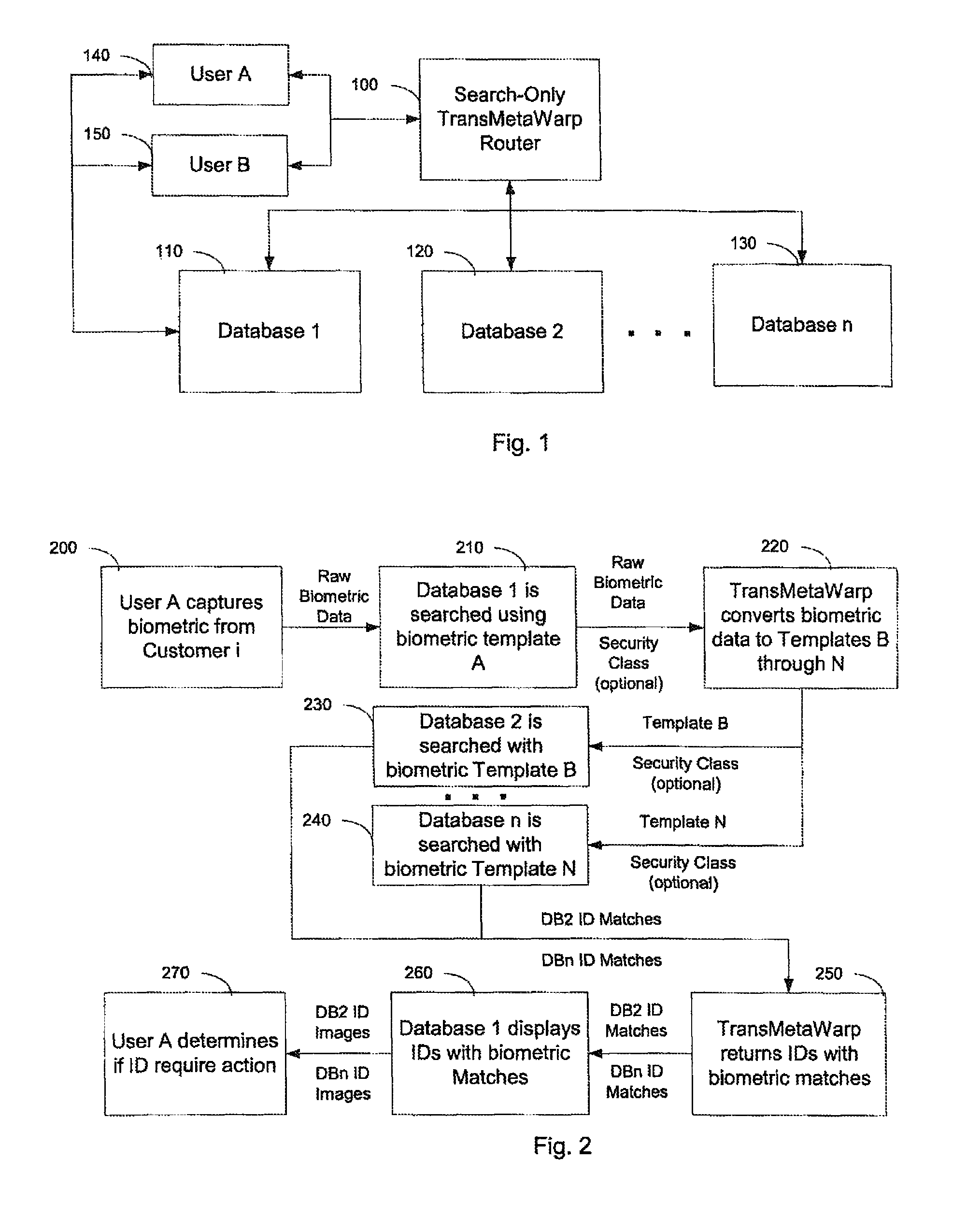
InactiveUS8055667B2Increase incomeReduce identityDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsInformation retrievalMetadatabase
Metadata for a content signal is searched by transforming the content signal into different hash formats, each being used to retrieve identifying information from corresponding databases. The identifying information enables retrieval of metadata from metadata databases. These systems and methods enable devices to access a wide array of dynamic metadata from disparate sources through queries that are derived from intrinsic content attributes.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
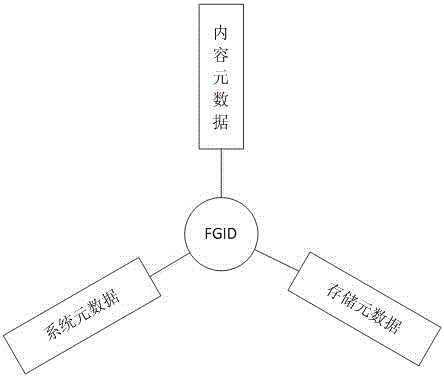
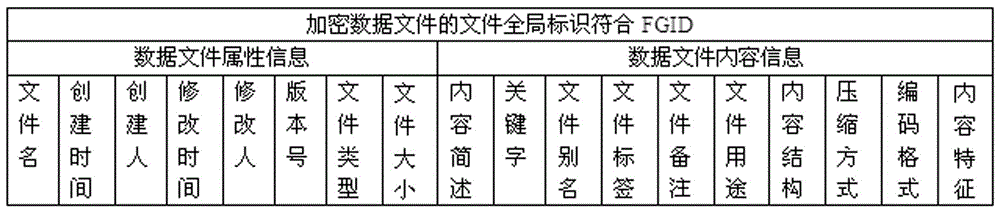
Encrypted data file storage and retrieval system and method
ActiveCN105678189ASearch guaranteeEnsure safetyDigital data protectionSpecial data processing applicationsData fileCloud storage system
The invention discloses an encrypted data file storage and retrieval method. The method comprises the steps that after content metadata is extracted from a data file, the data file is encrypted to generate an encrypted data file to be stored in storage equipment of a cloud storage system; the content metadata is added with a file global identifier of the data file in an encrypted state and then stored in a content metadatabase of the cloud storage system; when the encrypted data file stored in the cloud storage system is retrieved, the content metadatabase is retrieved through an inverted index method to acquire the file global identifier matched with a retrieval keyword, and attribute information and content information of the encrypted data file corresponding to the file global identifier are listed to serve as a retrieval result. According to the method, the content metadata is extracted before the data file is encrypted, the file global identifier of the file in the encrypted state is added into the content metadata, the encrypted data file stored in the cloud storage system is retrieved through the file global identifier, and the retrieval convenience of the data file is guaranteed while the safety and the privacy of the data file in a cloud storage environment are guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Integration of visualizations, reports, and data
A method of graphically displaying the path of a customer traversing a web site and related business data is described. The method includes receiving a user request for a visualization. The user request may include data filters and exclusions. Responsive to the user request, traffic data is selected for analysis. The selected traffic data is analyzed and displayed to the user. The display may be in the form of a visualization including a graph and related business data. The graph may be of an overview, referral, path, page-to-page path, and animation type. A system for visualizing traffic patterns and the path of a customer at a site is described in conjunction with the above method. The system includes a logical data model, a dimensional data model, a report specification, a graphical interface, metadata database and an analysis report. The graphical interface is used for viewing visualization information.
Owner:TERADATA US
Systems and methods for accessing content using an internet content guide
InactiveUS20110276585A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsInternet contentMarine navigation
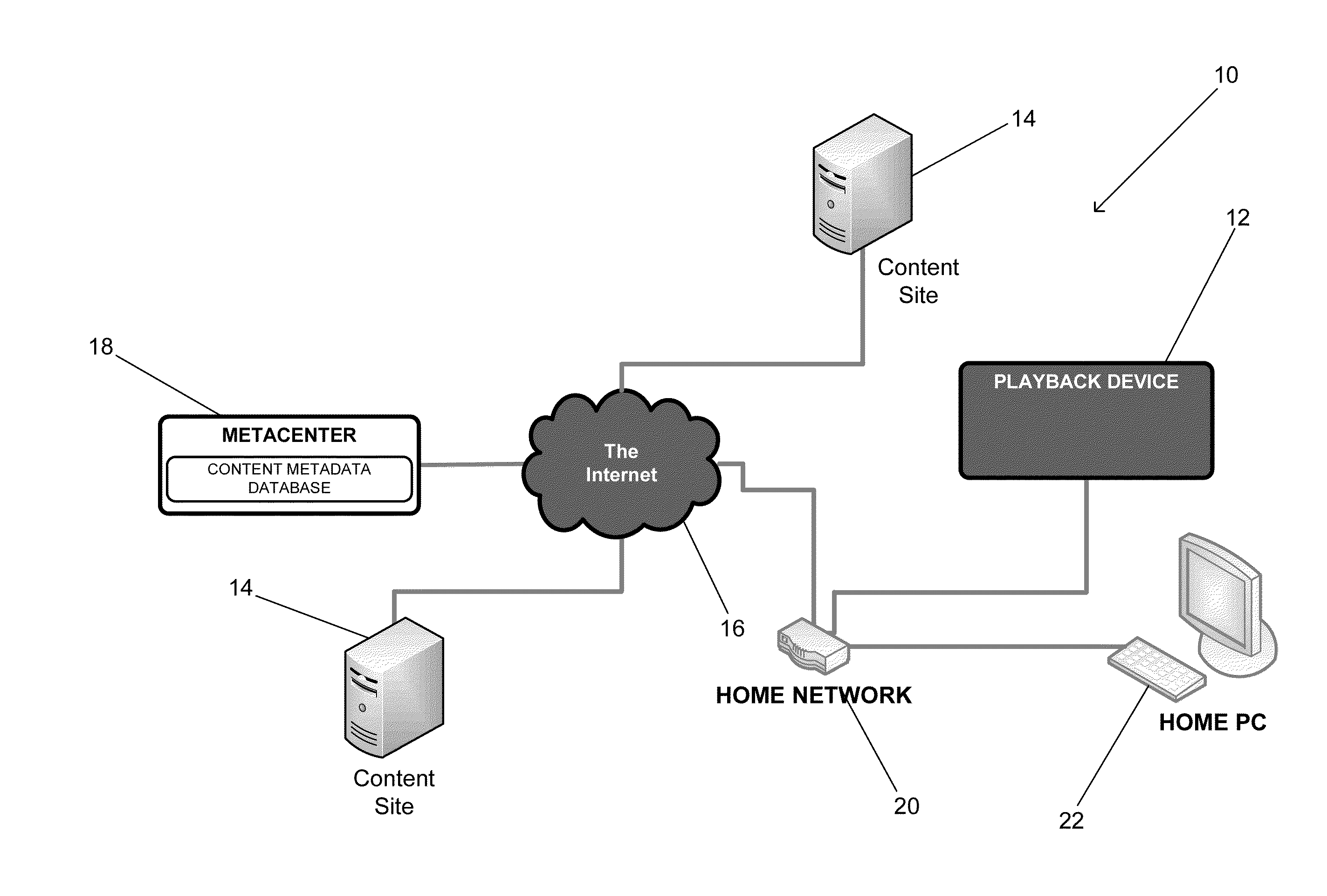
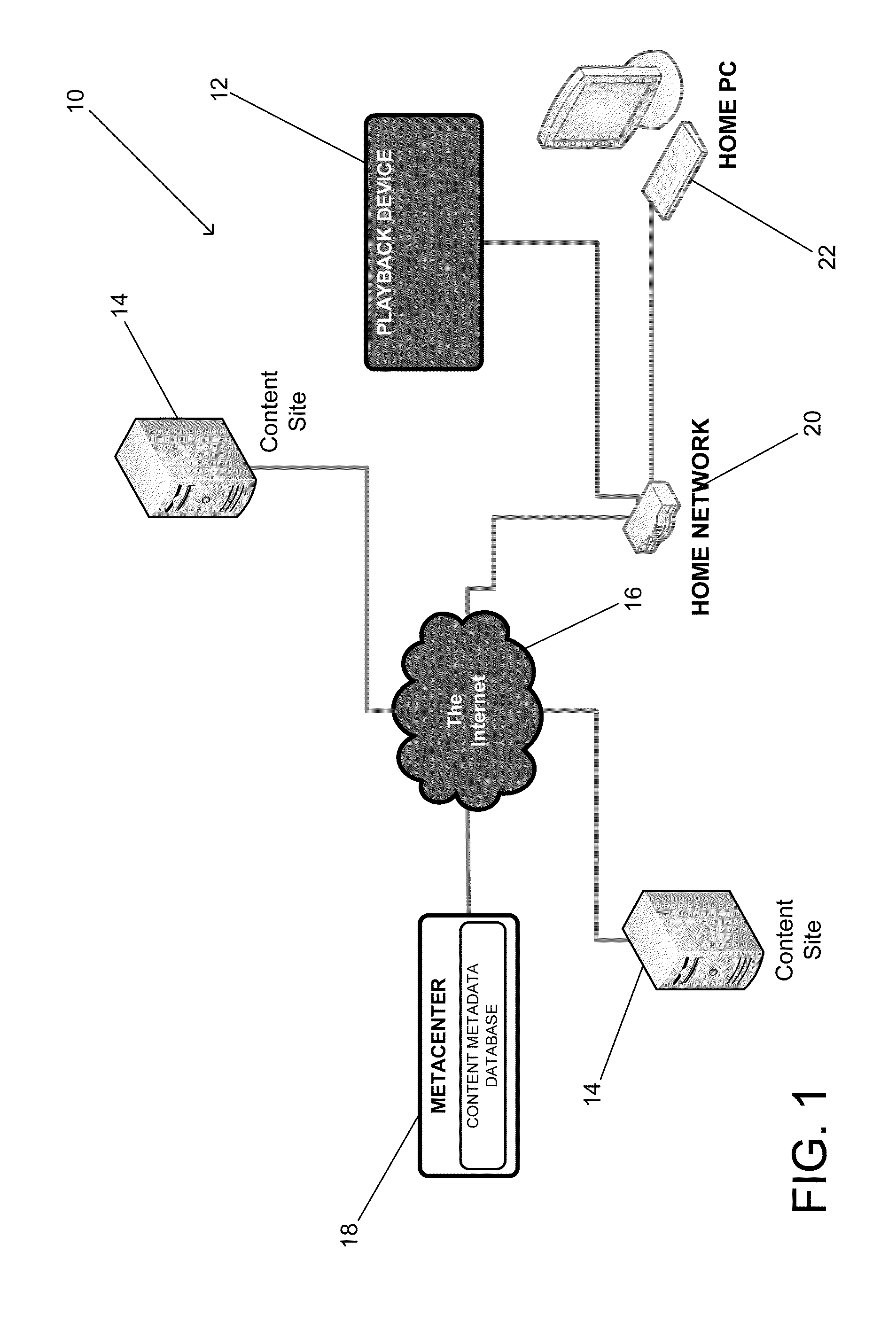
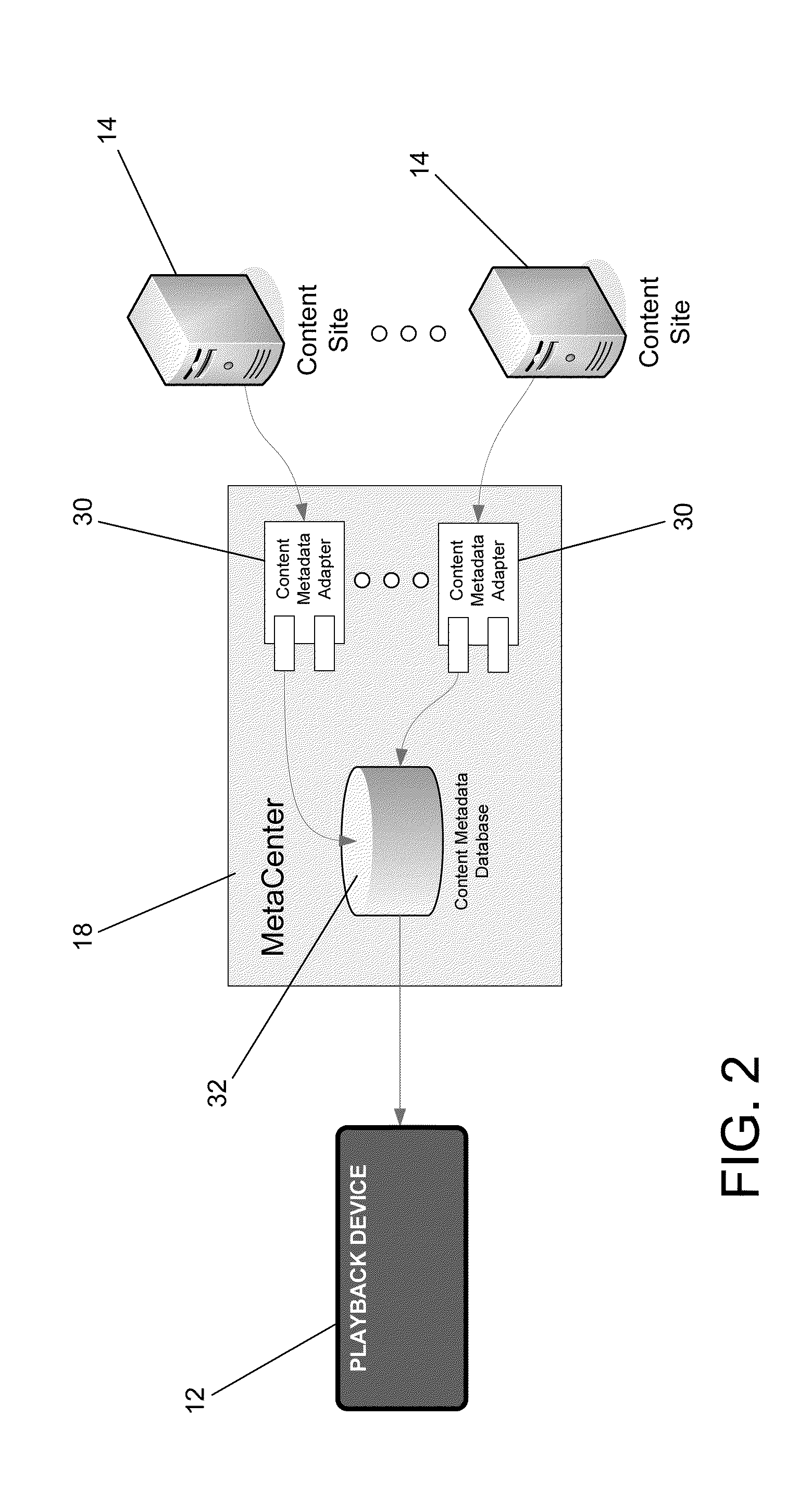
Systems and methods for providing Internet Content Guides (ICG) on playback devices that can be used to access content via the Internet from a plurality of sources using a remote database containing navigation hierarchy definitions for specific device models and / or device instances are described, where content metadata included in the remote database is collected by a remote server from the plurality of sources. One embodiment of the invention includes a metacenter configured to retrieve content metadata from feeds on a plurality of remote servers describing content accessible via the remote servers and to use the content metadata retrieved from the feeds to update a content metadata database, and a plurality of playback devices configured to communicate with the metacenter and access content via the Internet. In addition, the content metadata database defines a plurality of navigation hierarchies for different playback devices, where each navigation hierarchy includes category information and content information, each playback device is configured to obtain a navigation hierarchy appropriate to the playback device from the metacenter, where the navigation hierarchy obtained by the playback device only includes category and content information that the playback device is authorized to access and is capable of playing back, and the playback devices are configured to generate an Internet content guide using the navigation hierarchy obtained from the metacenter.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com