Method for quickly measuring topography by using ground laser scanner based on CORS (Continuous Operational Reference System) and ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithms
A laser scanner and scanner technology, which is used in measurement devices, cross-section drawing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low operation efficiency of ground laser scanners, increased time consumption, and influence on the popularization and application of ground laser scanners.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings of the specification.
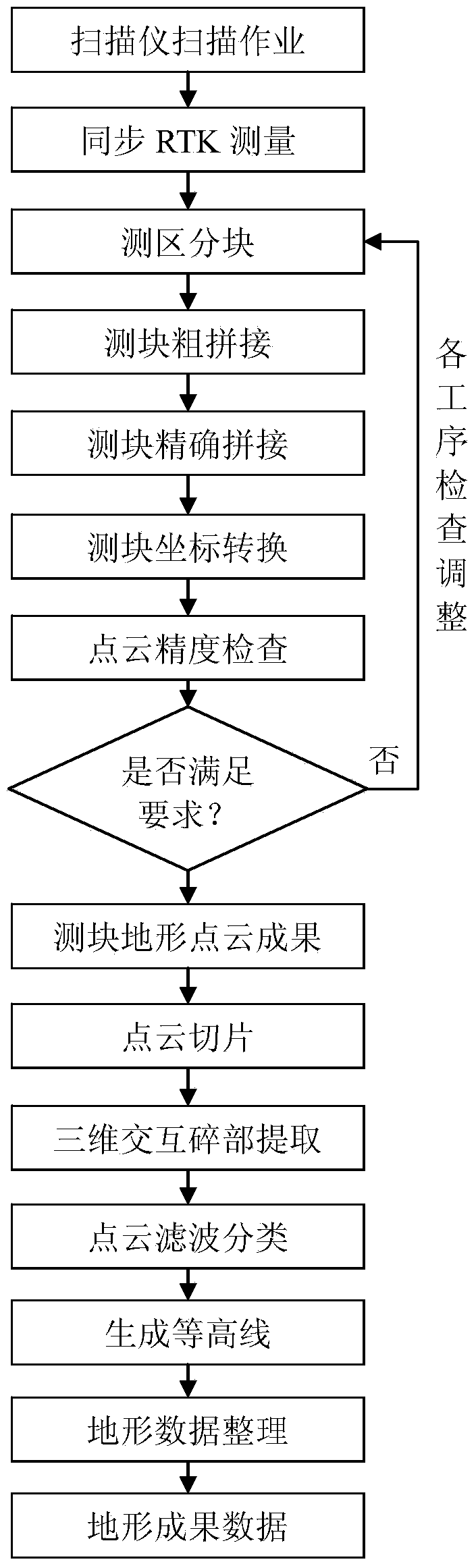
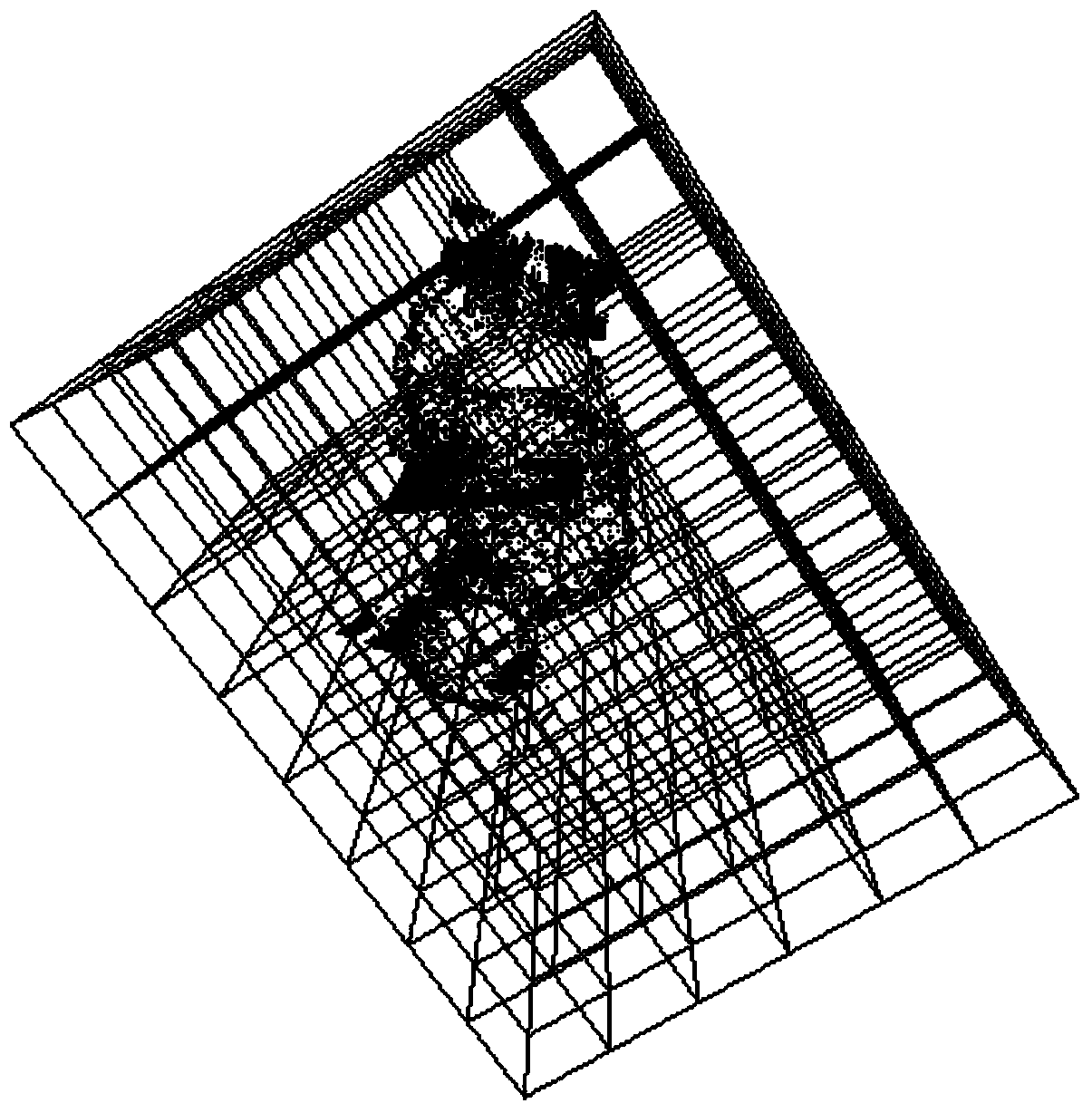
[0062] Such as figure 1 As shown, a ground laser scanner based on CORS and ICP algorithm to quickly measure terrain includes the following steps:
[0063] Step 1: Use RieGL VZ400 ground laser scanner, the scanner comes with an external camera, and the connection device makes the GPS antenna and the scanner (including the camera) coaxially connected; after connection, ensure that the centering deviation of the two instruments is in mm level, because The height difference between the centers of the two instruments is small (usually about 20cm). The horizontal projection deviation of the center of the two instruments caused by the tilt within 5 degrees is less than 2cm, and the height deviation is less than 1cm, then the scanning is not strictly leveled (inclination of 5 degrees). The accuracy has little effect.
[0064] Step 2: Use a small car as a carrie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com