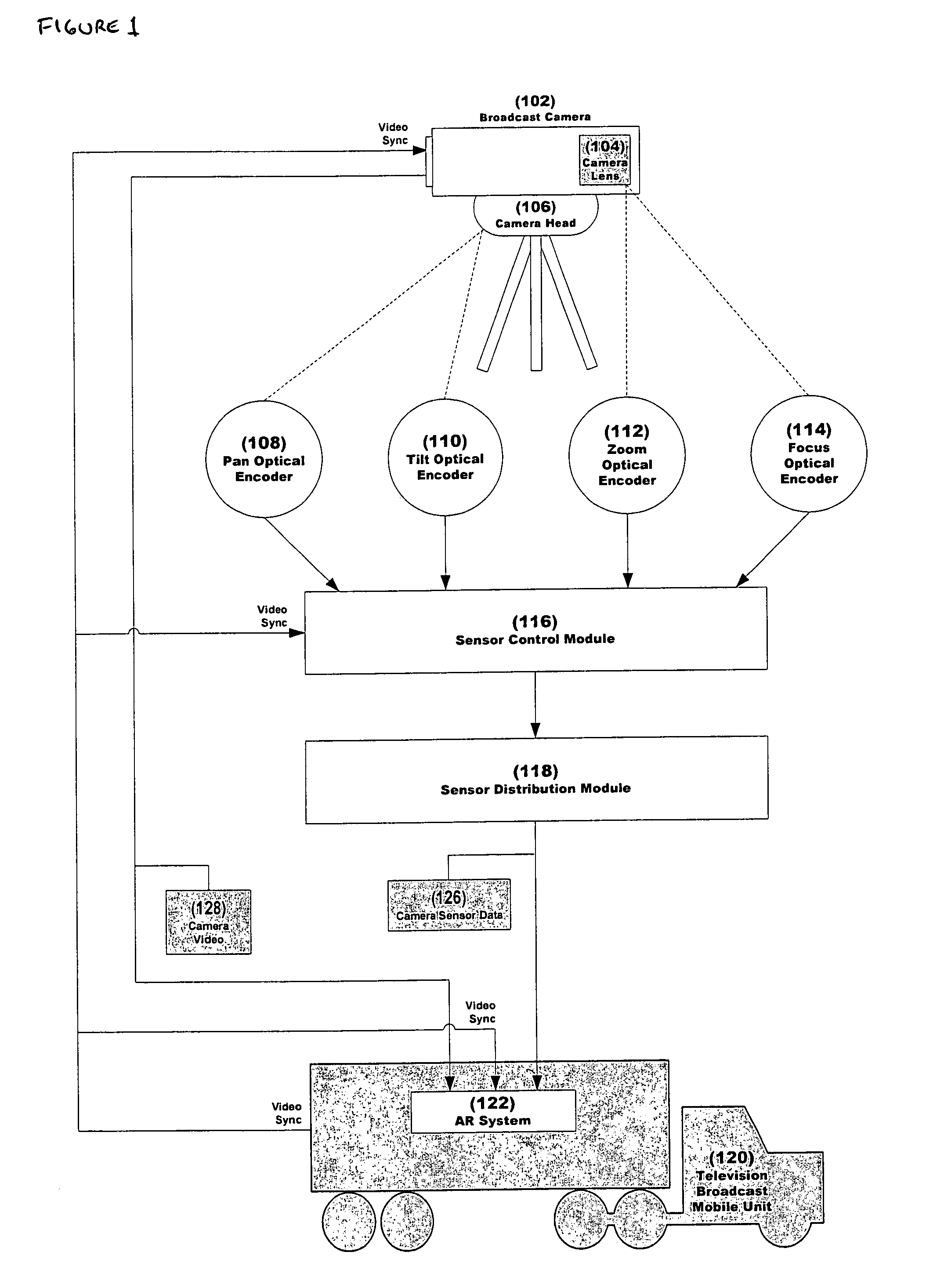
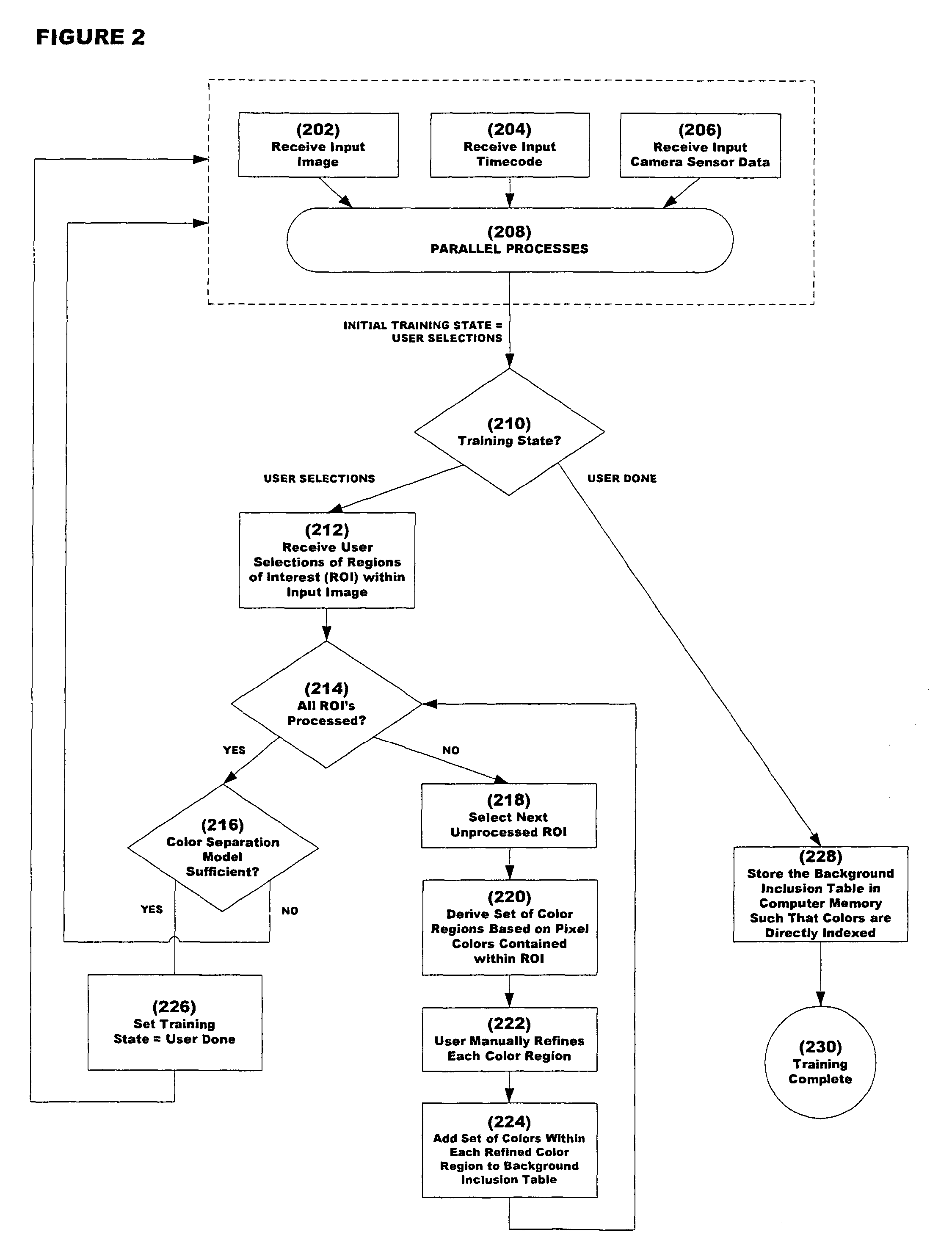
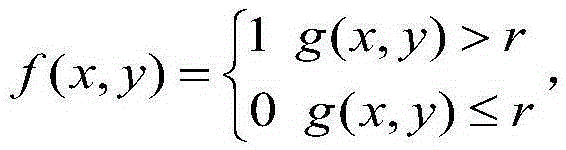Patents
Literature
139 results about "World space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
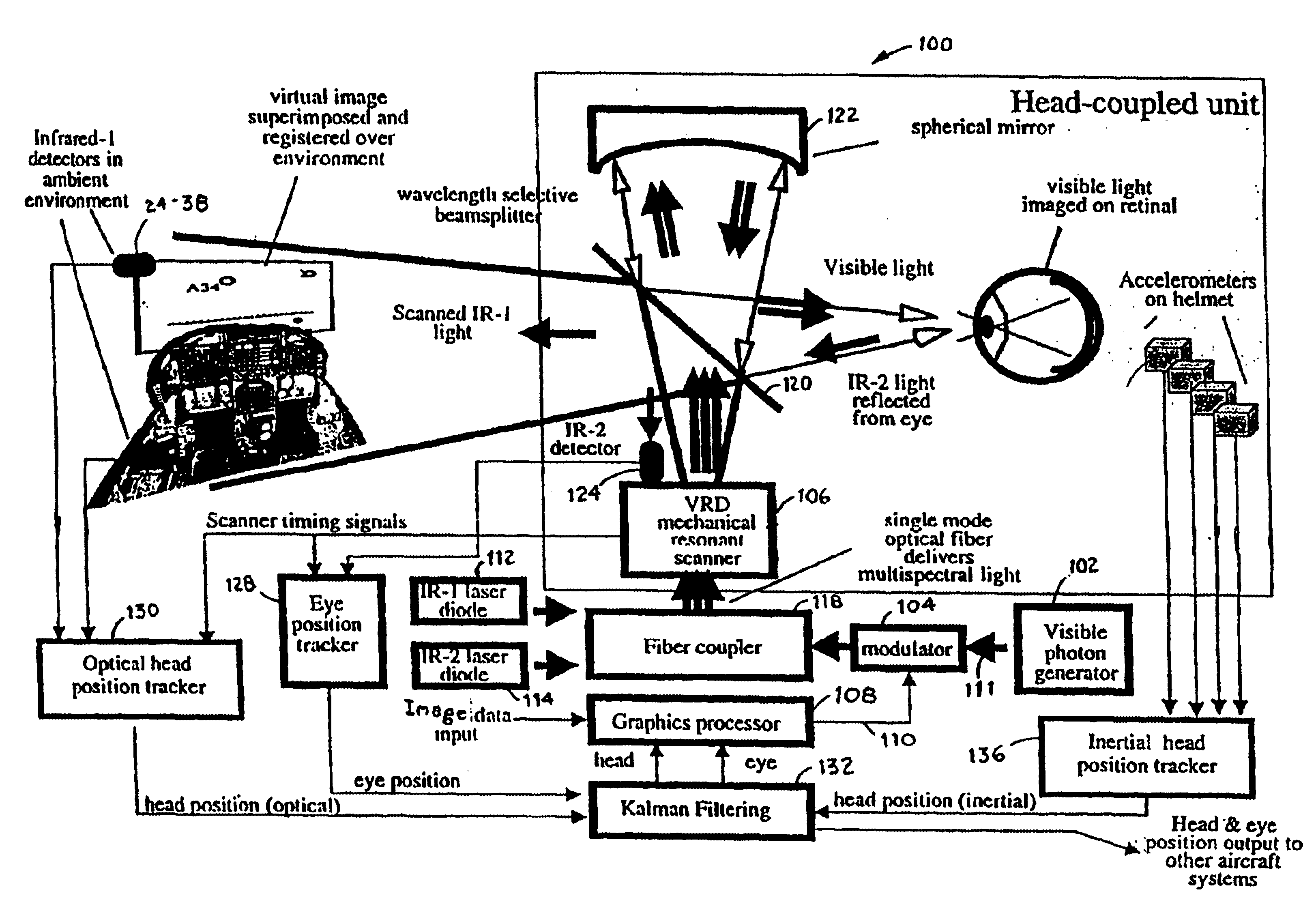
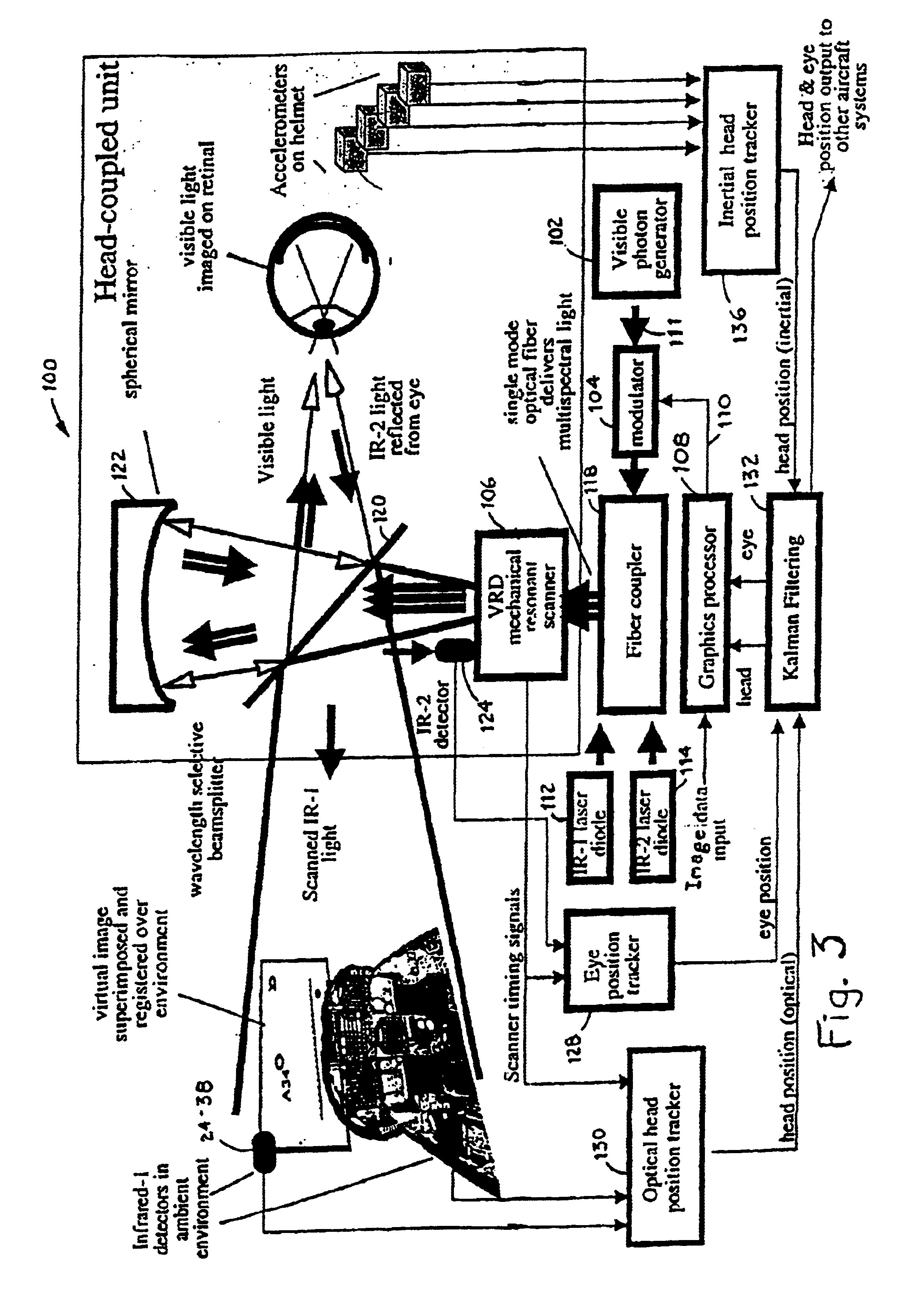
Virtual image registration in augmented display field
InactiveUS6867753B2Accurate locationAccurate predictionInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainTemporal resolution
A virtual image is registered among a perceived real world background. Tracking light is scanned into the real world environment, which includes at least one detector pair. A first time and a second time at which the tracking light impinges on the first detector is detected, in which the first time and second time occurs within adjacent scan lines. A time at which a horizontal scan line edge (e.g., beginning of scan line or end of scan line) is encountered is derived as occurring one half way between the first time and the second time. The horizontal location of the first detector then is determined within a specific scan line inferring the scan line edge time. The vertical location of the detector is determined within a scan frame by measuring time duration using the beginning of the frame. By determining a location independently from the temporal resolution of the augmented imaging system, the temporal location of the detector is identified to a sub-pixel / sub-line precision. The augmented image is registered either to a 3D real world spatial coordinate system or to a time domain coordinate system based upon tracked position and orientation of the user.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
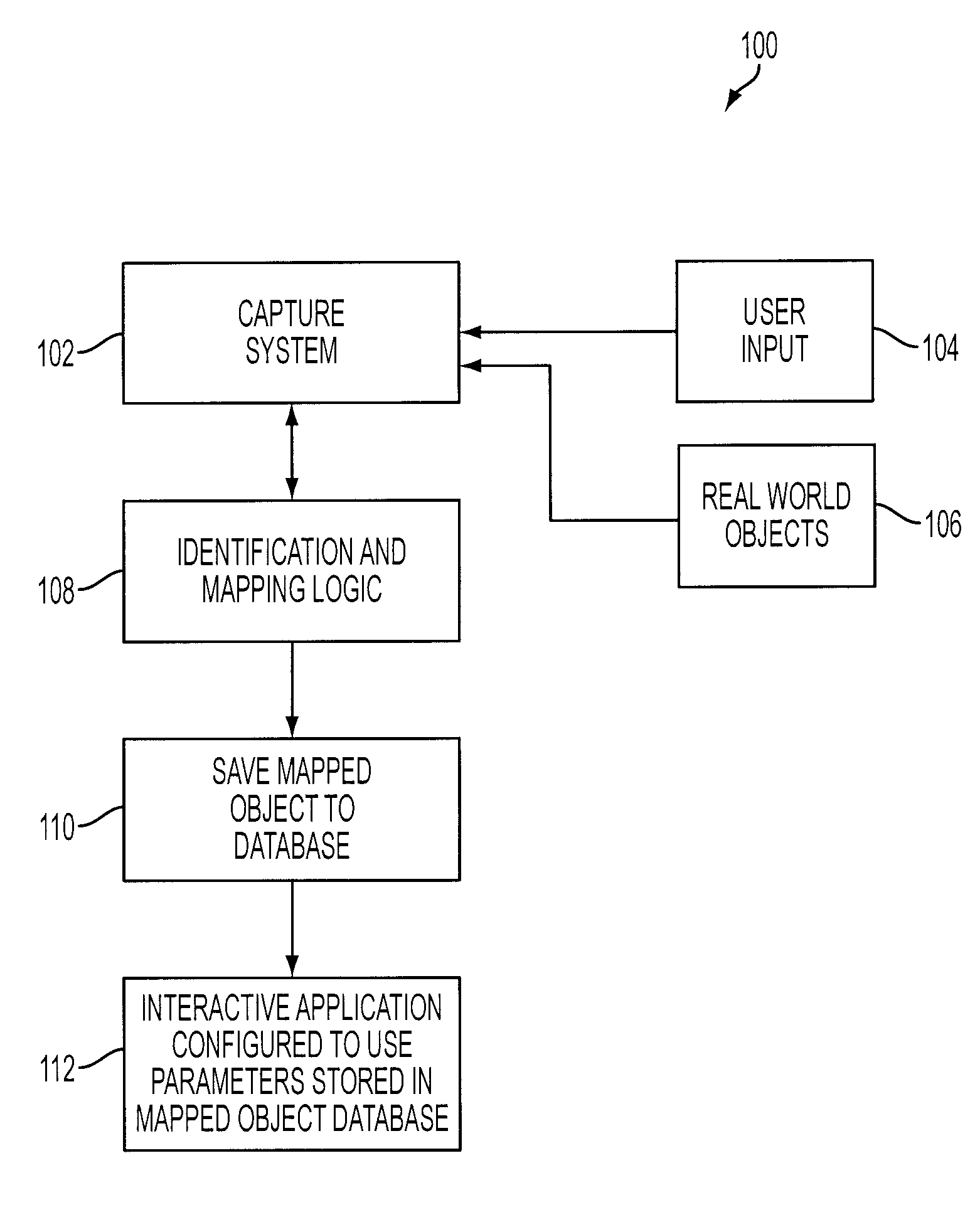
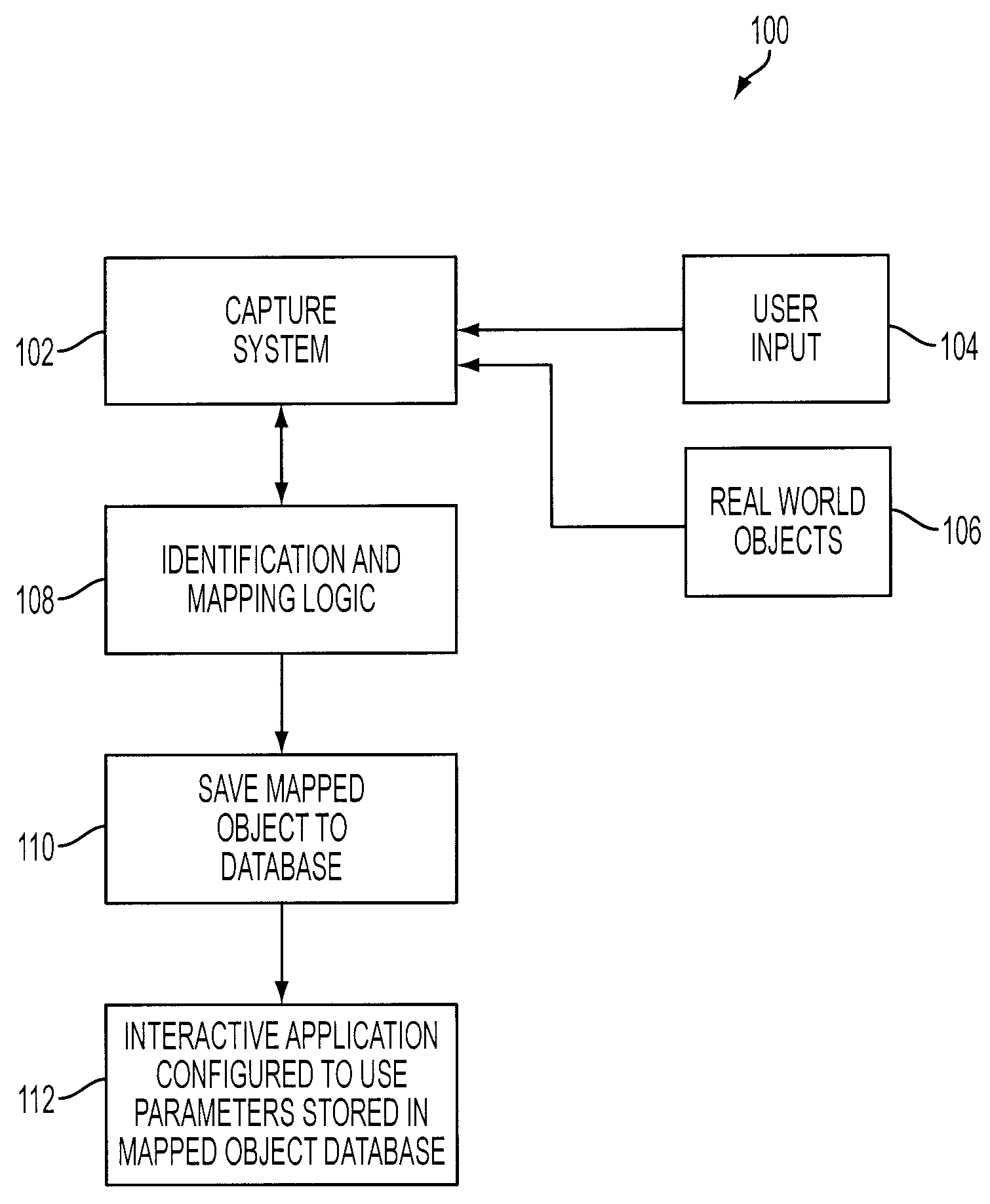
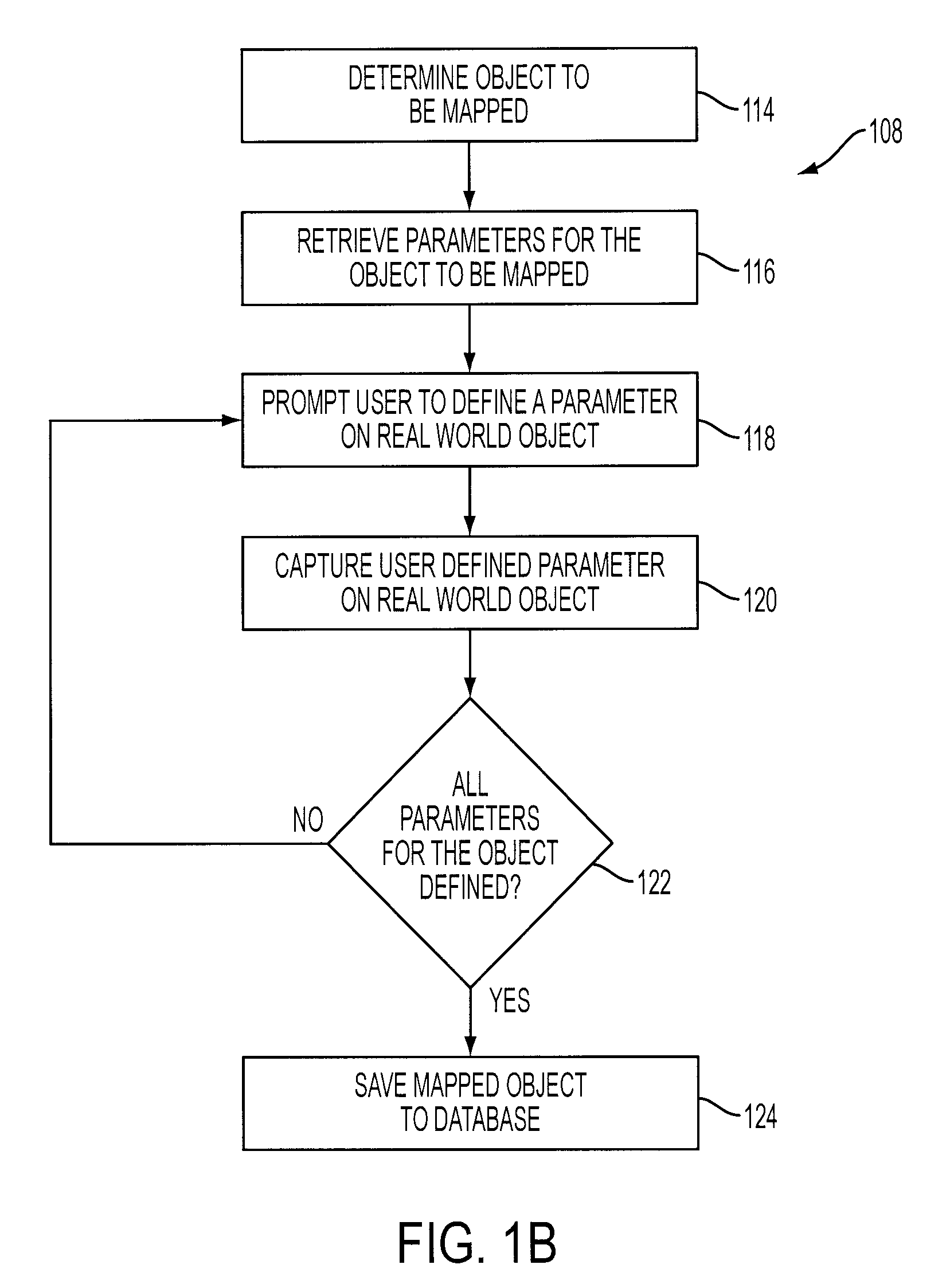
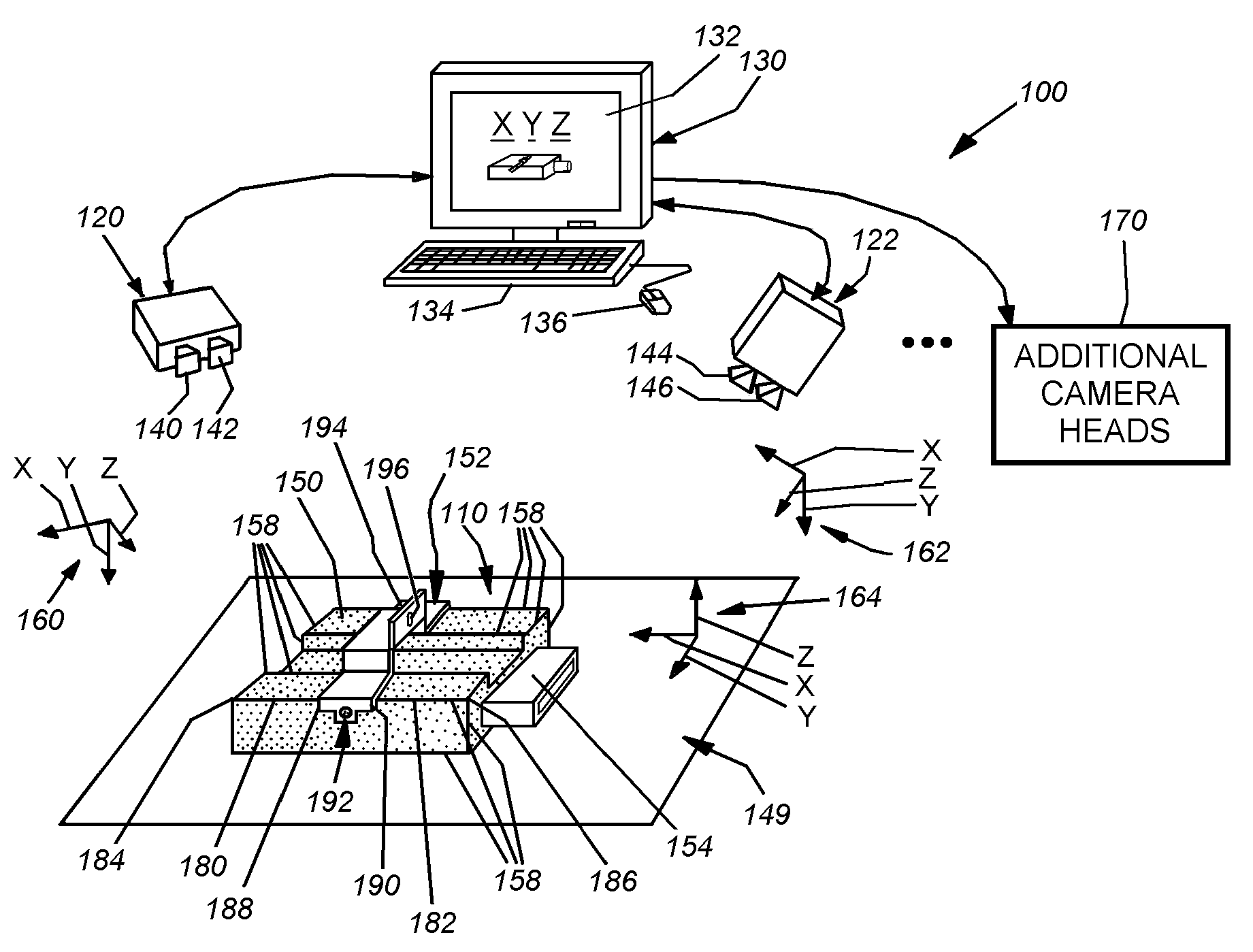
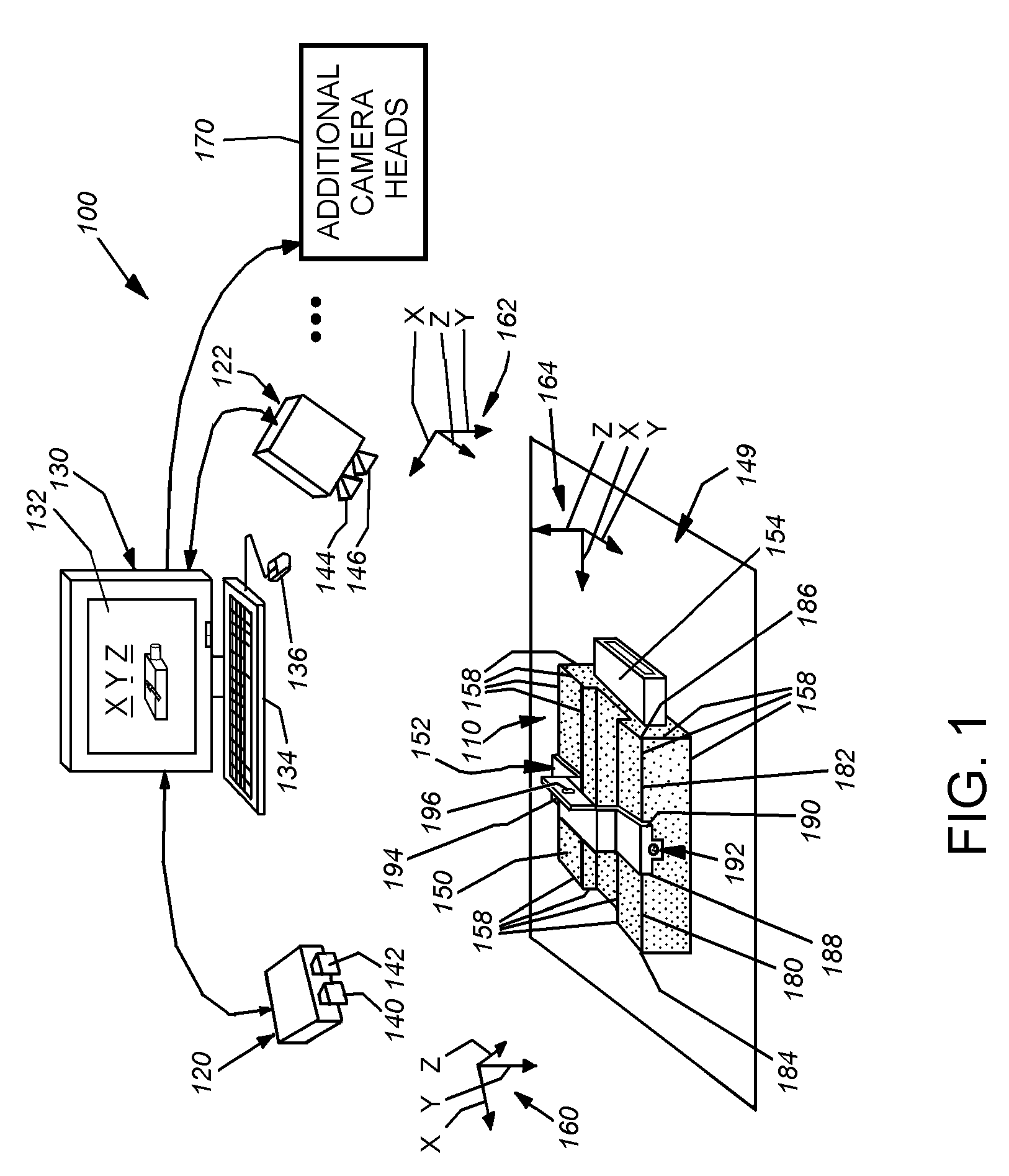
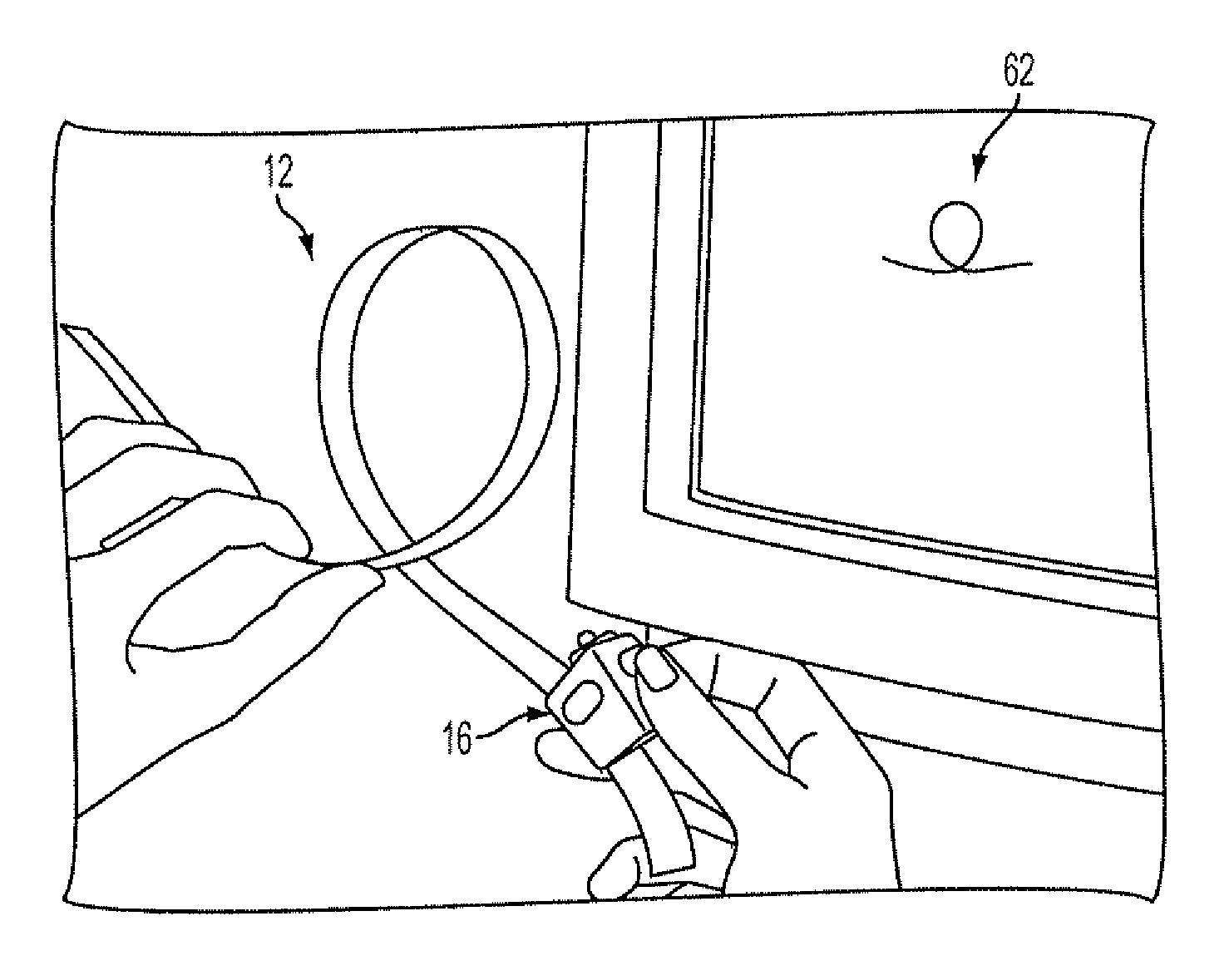
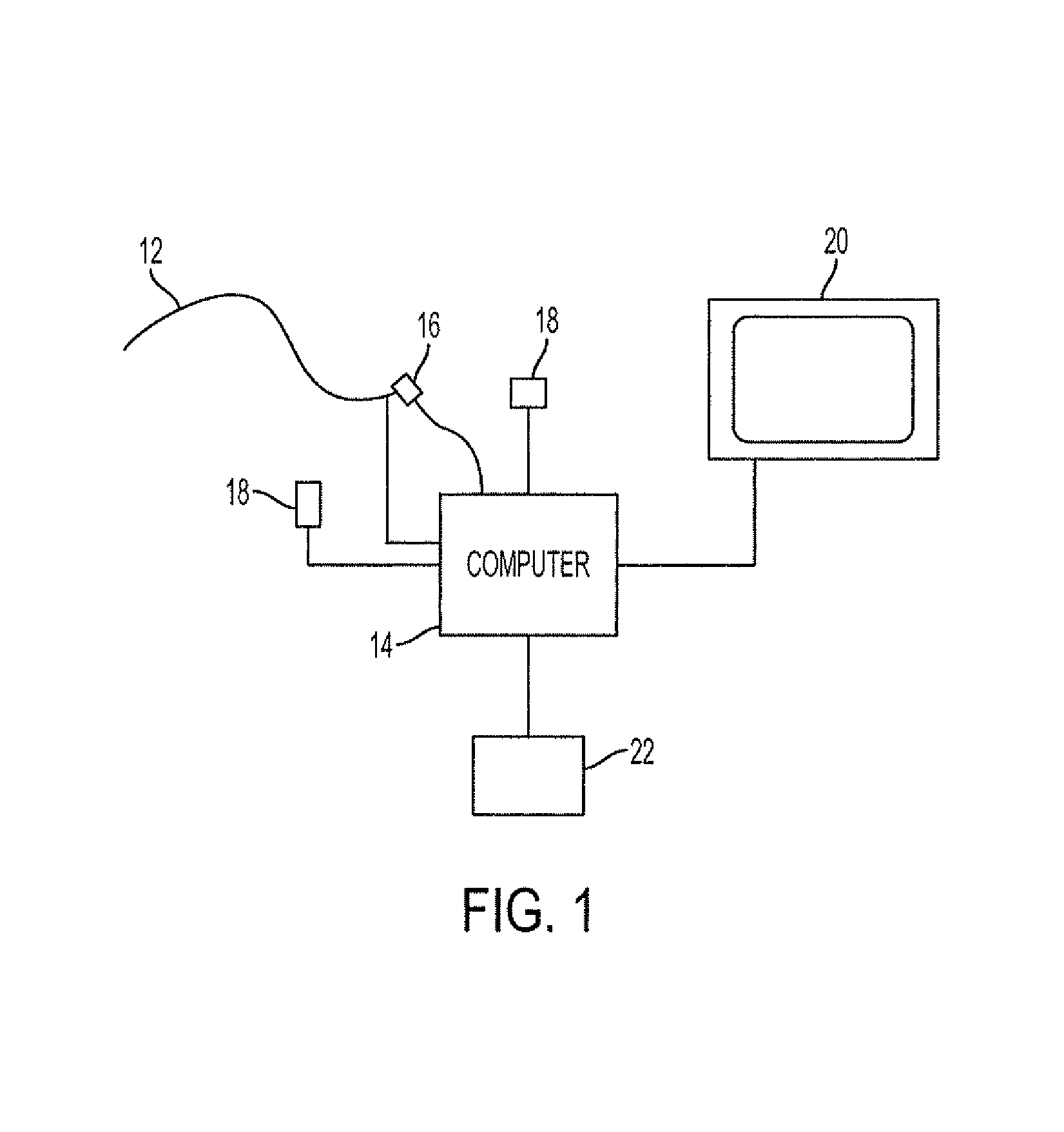
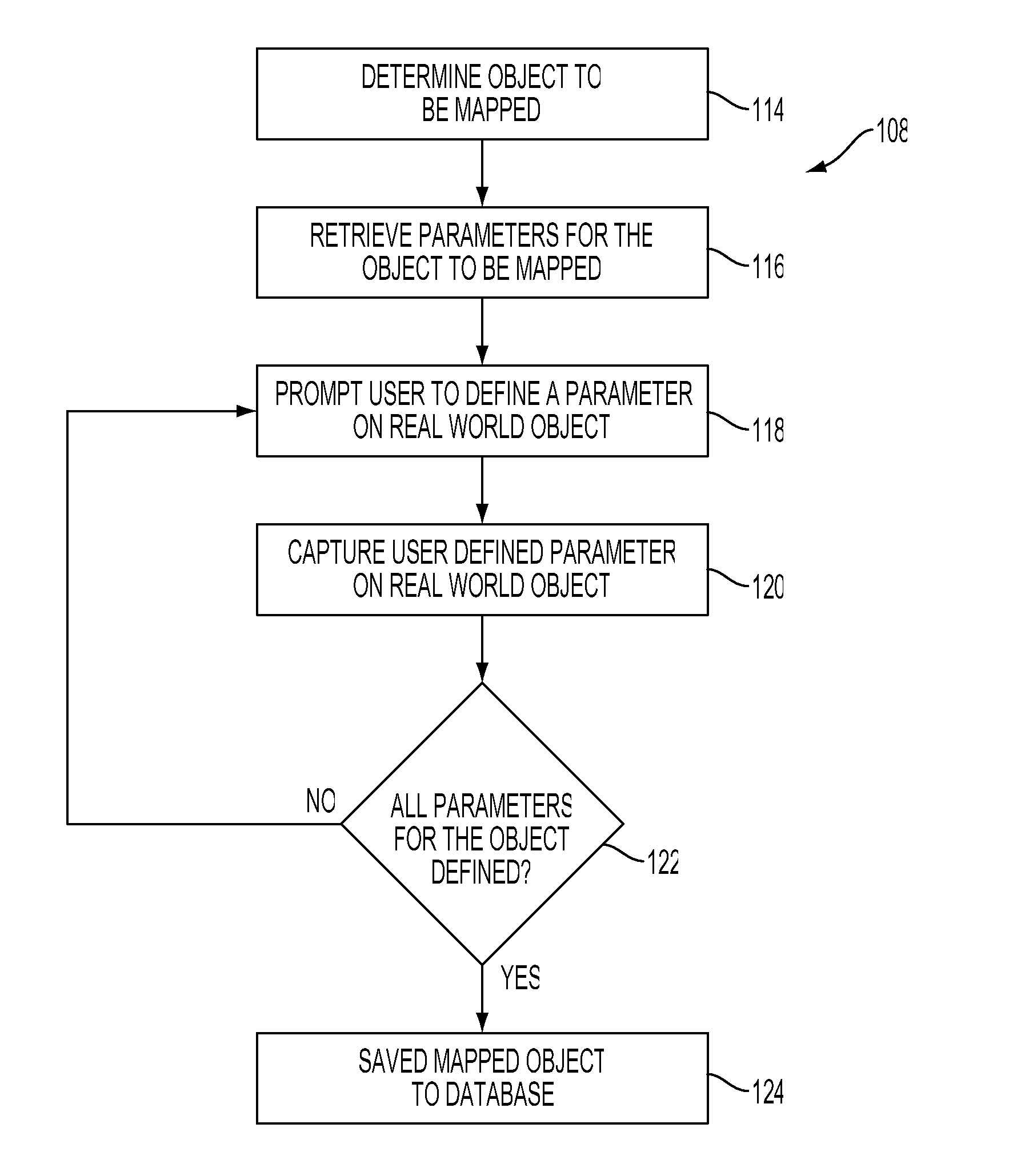
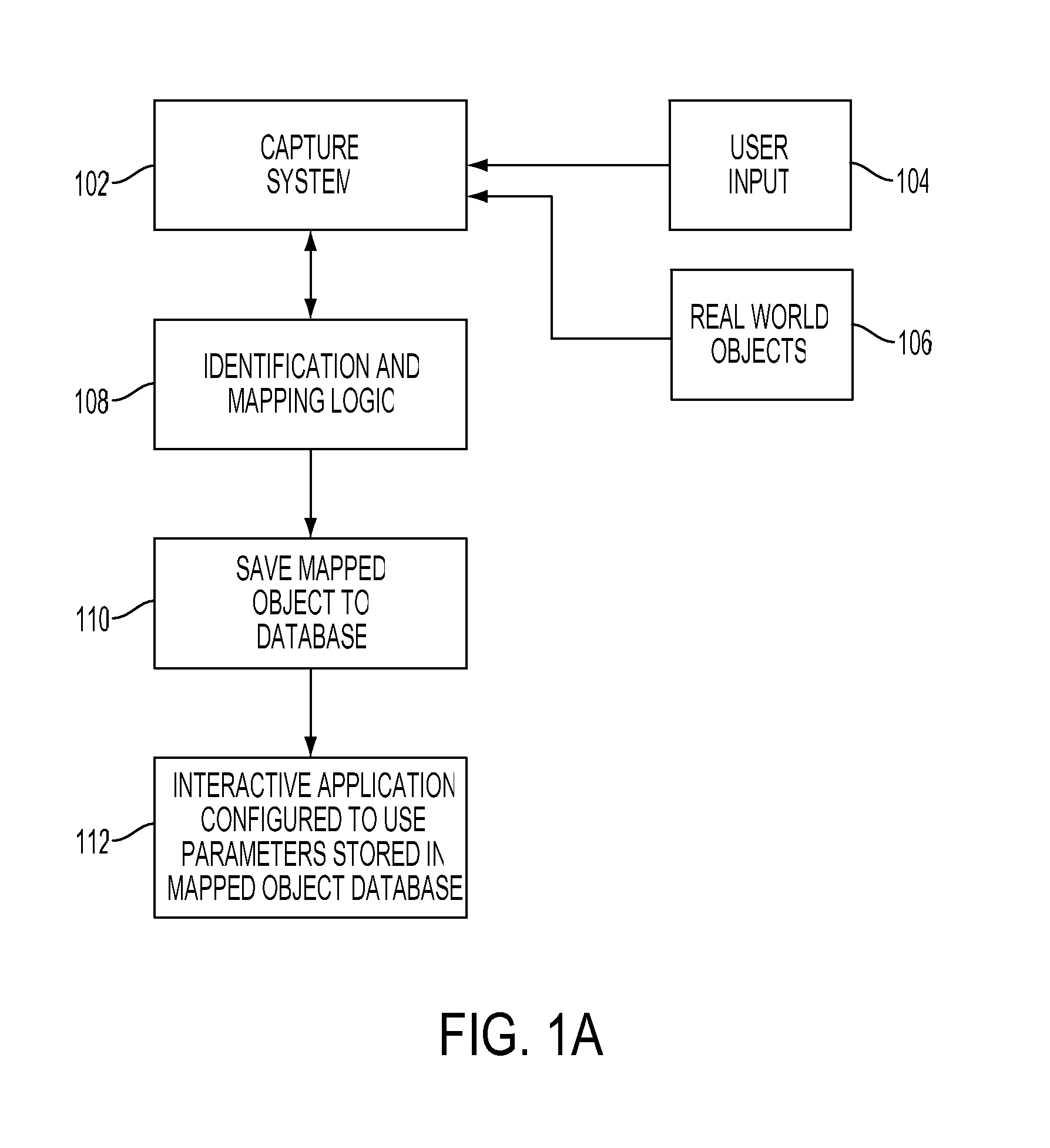
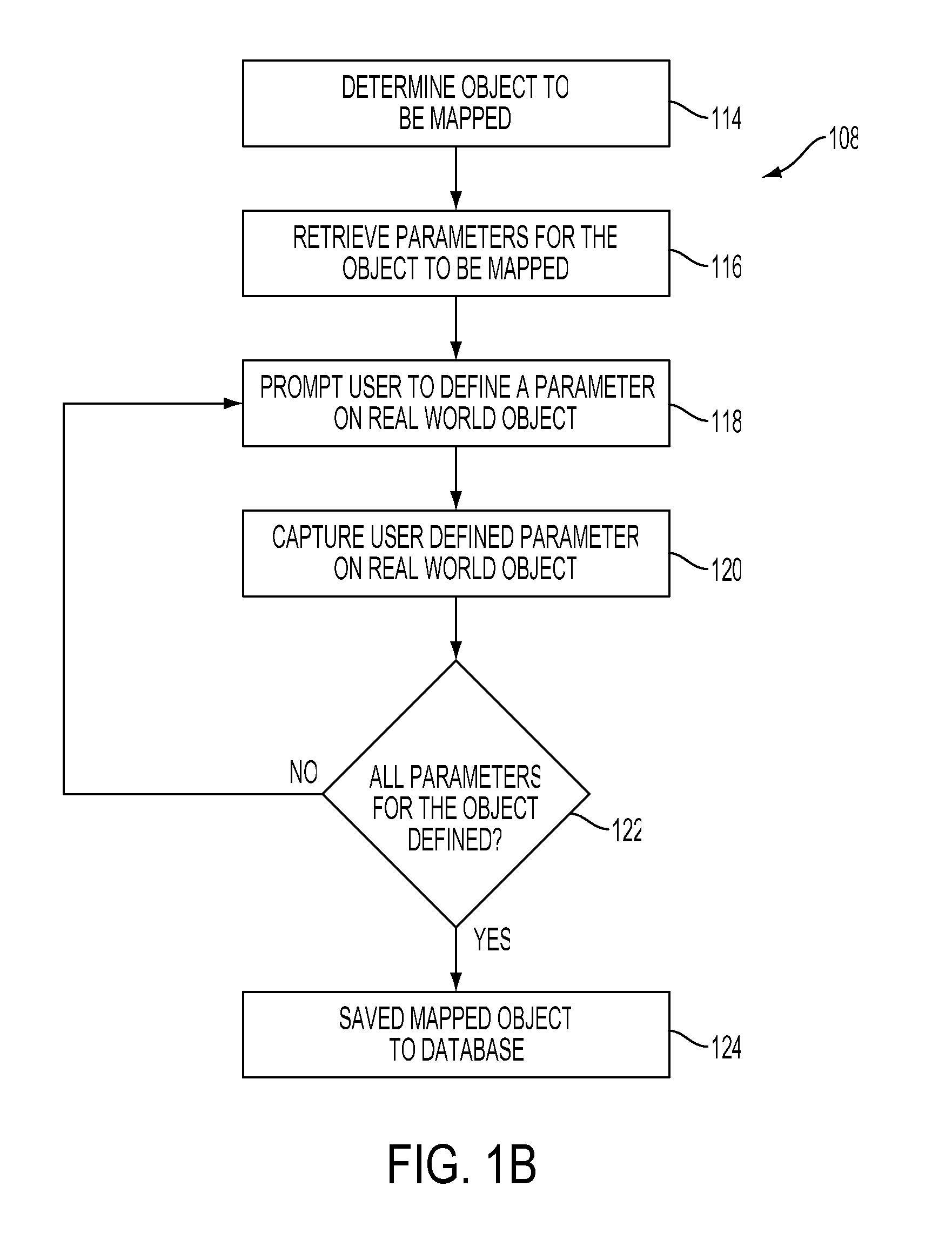
Selective interactive mapping of real-world objects to create interactive virtual-world objects
A method for interactively defining a virtual-world space based on real-world objects in a real-world space is disclosed. In one operation, one or more real-world objects in the real-world space is captured to define the virtual-world space. In another operation, one of the real-world objects is identified, the identified object is to be characterized into a virtual-world object. In yet another operation, a user is prompted for user identification of one or more object locations to enable extraction of parameters for real-world object, and the object locations are identified relative to an identifiable reference plane in the real-world space. In another operation, the extracted parameters of the real-world object may be stored in memory. The virtual-world object can then be generated in the virtual world space from the stored extracted parameters of the real-world object.
Owner:SONY COMP ENTERTAINMENT EURO +1
System and method for three-dimensional alignment of objects using machine vision
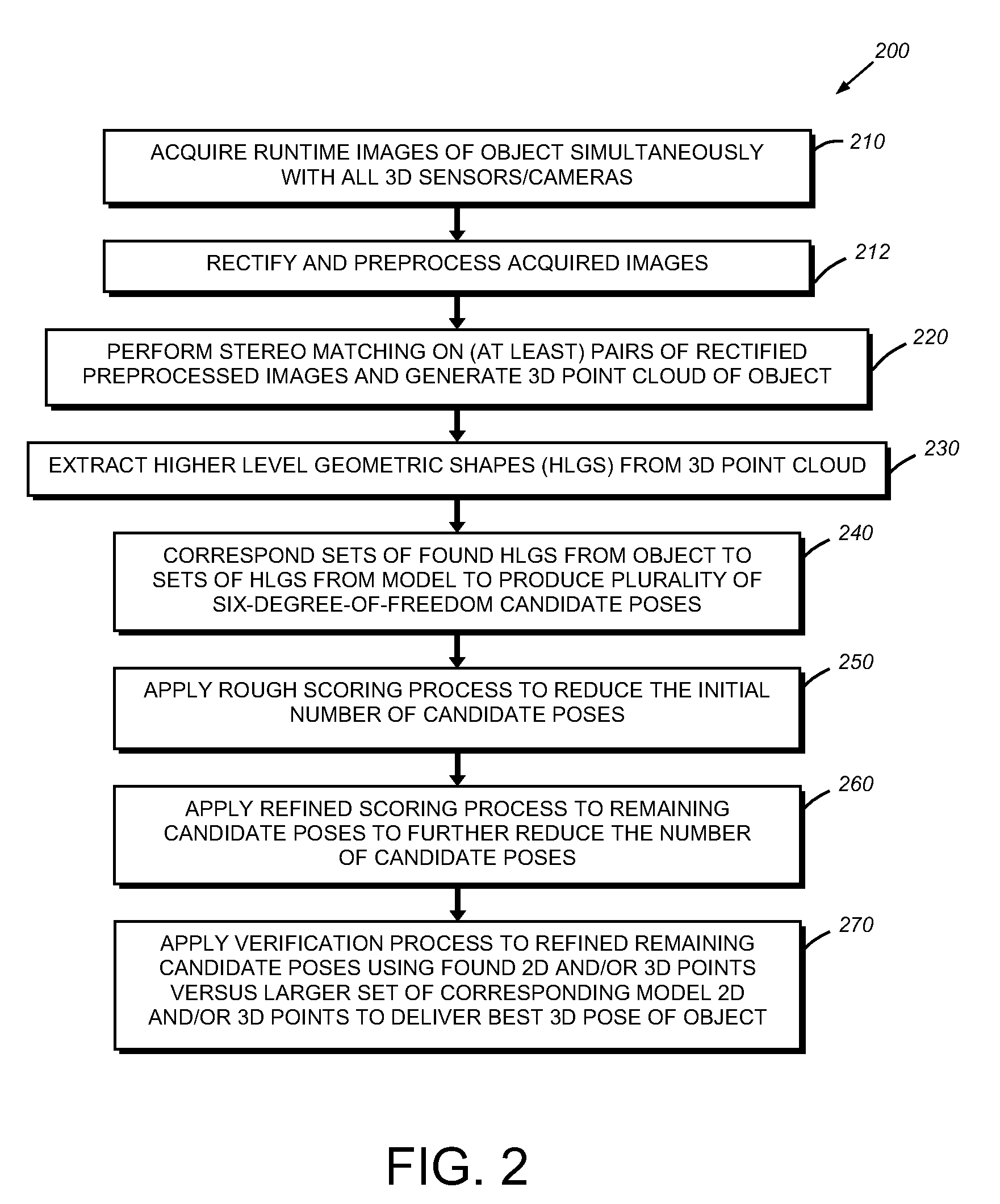
This invention provides a system and method for determining the three-dimensional alignment of a modeledobject or scene. After calibration, a 3D (stereo) sensor system views the object to derive a runtime 3D representation of the scene containing the object. Rectified images from each stereo head are preprocessed to enhance their edge features. A stereo matching process is then performed on at least two (a pair) of the rectified preprocessed images at a time by locating a predetermined feature on a first image and then locating the same feature in the other image. 3D points are computed for each pair of cameras to derive a 3D point cloud. The 3D point cloud is generated by transforming the 3D points of each camera pair into the world 3D space from the world calibration. The amount of 3D data from the point cloud is reduced by extracting higher-level geometric shapes (HLGS), such as line segments. Found HLGS from runtime are corresponded to HLGS on the model to produce candidate 3D poses. A coarse scoring process prunes the number of poses. The remaining candidate poses are then subjected to a further more-refined scoring process. These surviving candidate poses are then verified by, for example, fitting found 3D or 2D points of the candidate poses to a larger set of corresponding three-dimensional or two-dimensional model points, whereby the closest match is the best refined three-dimensional pose.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Controlling unmanned aerial vehicles to avoid obstacle collision
ActiveUS20170193830A1Simple and efficientObstacle collisionScene recognitionRemote controlled aircraftApparent SizeDistance sensors
A method, device, framework, and system provide the ability to control an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to avoid obstacle collision. Range data of a real-world scene is acquired using range sensors (that provide depth data to visible objects). The range data is combined into an egospace representation (consisting of pixels in egospace). An apparent size of each of the visible objects is expanded based on a dimension of the UAV. An assigned destination in the real world scene based on world space is received and transformed into egospace coordinates in egospace. A trackable path from the UAV to the assigned destination through egospace that avoids collision with the visible objects (based on the expanded apparent sizes of each of the visible objects) is generated. Inputs that control the UAV to follow the trackable path are identified.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
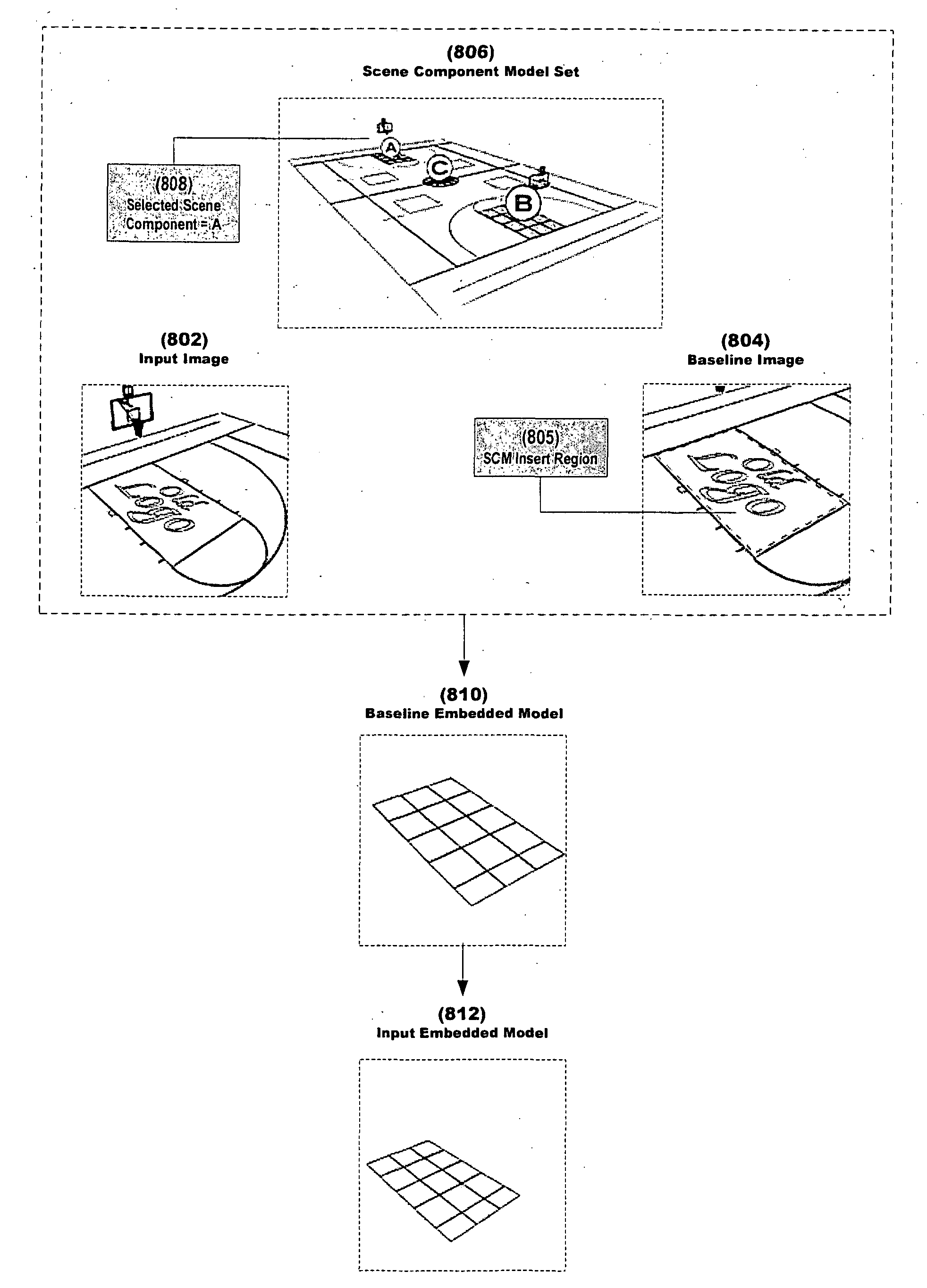
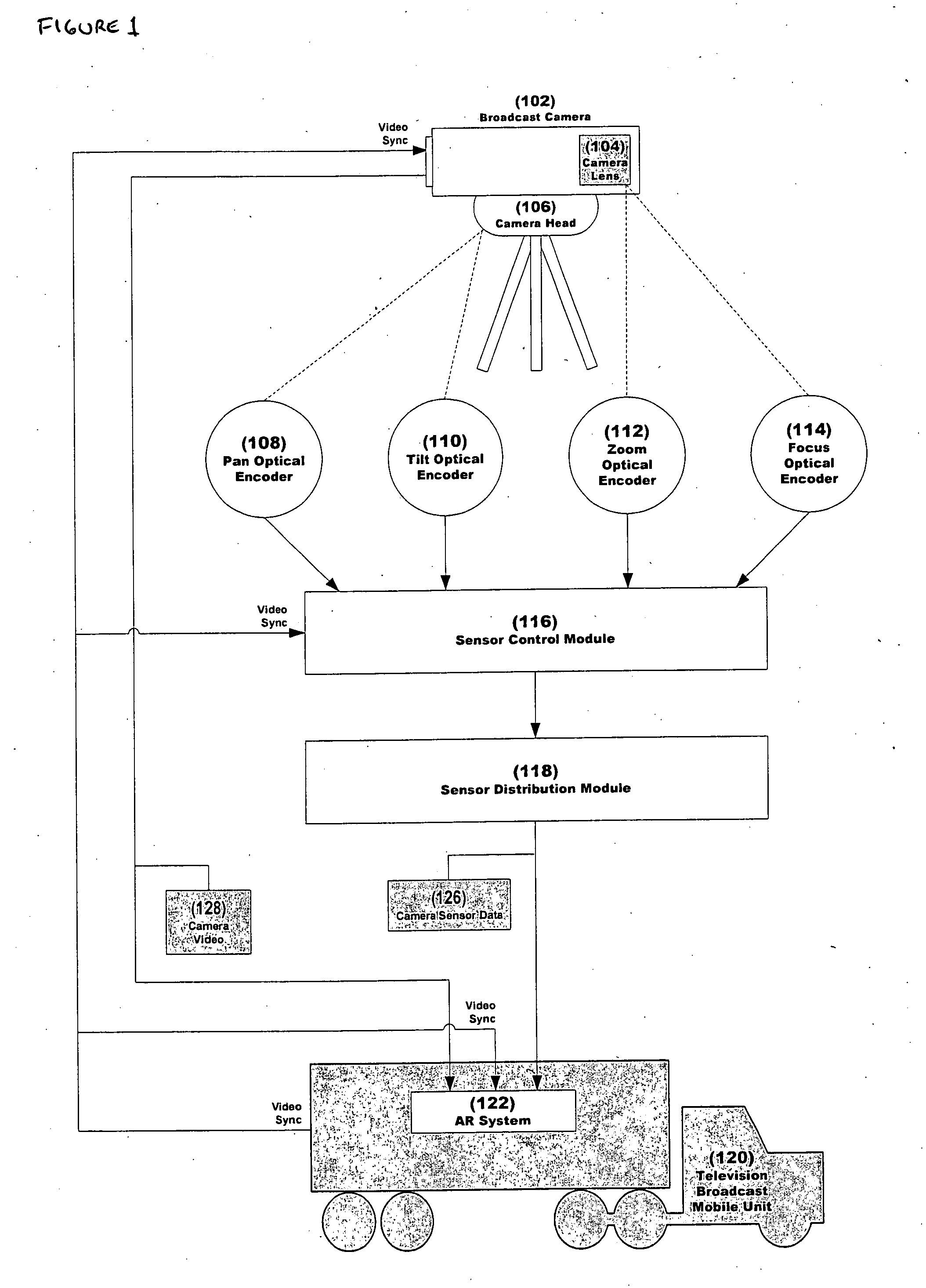
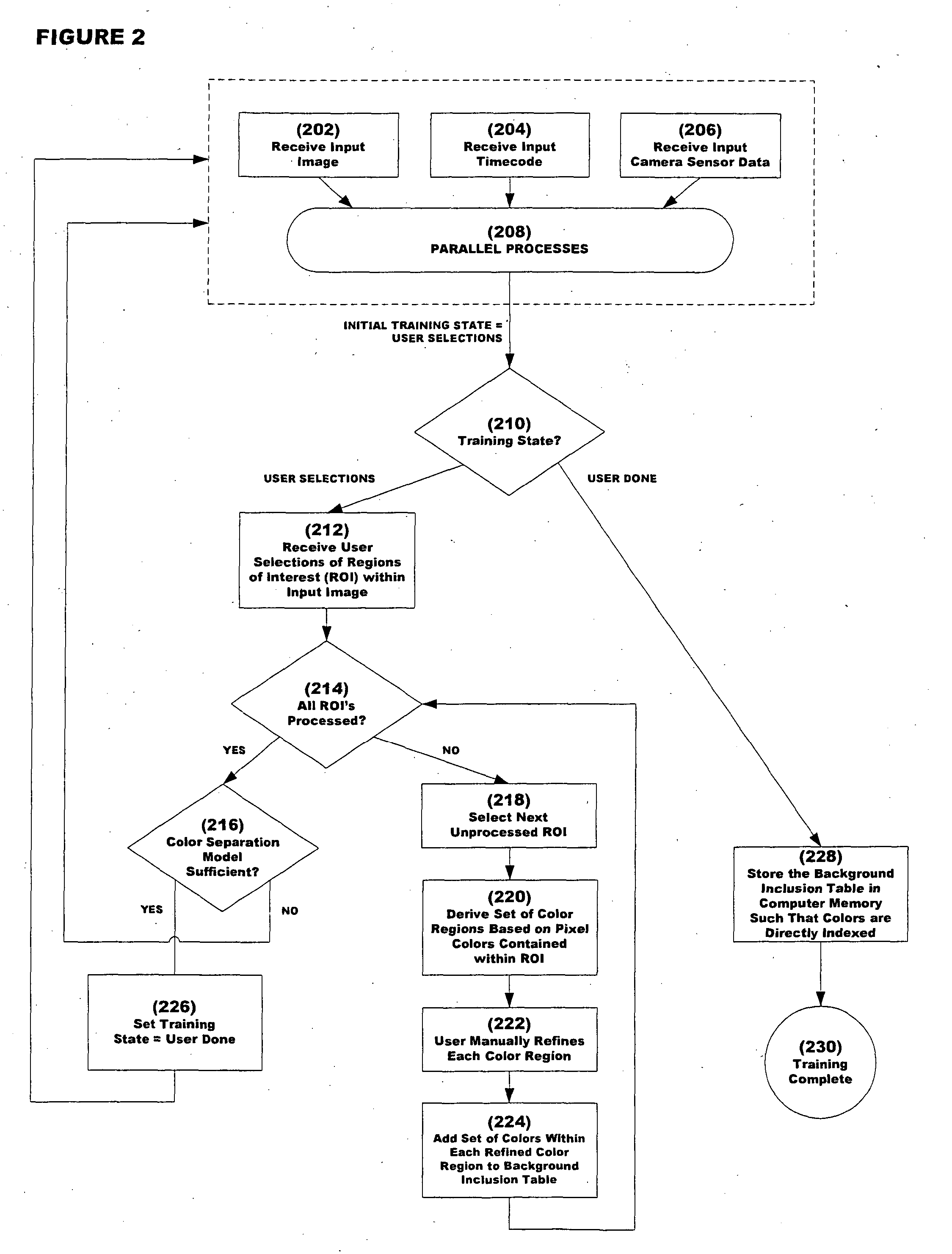
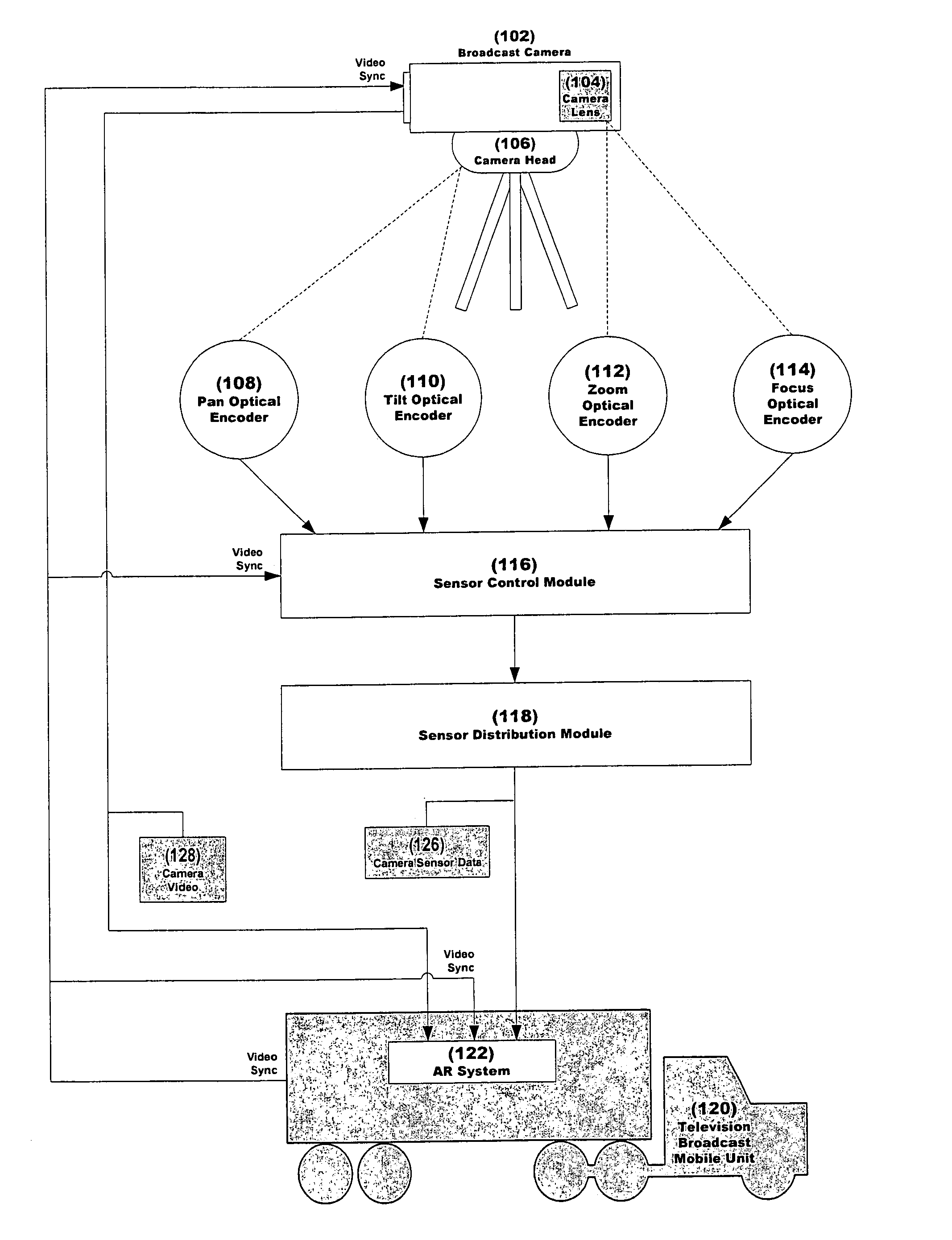
System and method for inserting content into an image sequence
ActiveUS20050001852A1Effect flexibilityEffect utilityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Time system
A real-time system and method for inserting perspective correct content into an image sequence are presented. The invention inserts the content with the location, size, orientation, shape and occlusion properties that are appropriate for the camera view represented by the image sequence. Both static and dynamic content insert positions are supported. The location, size, orientation and shape of the inserted content are determined independently of the image sequence content. Furthermore, no knowledge of three dimensional real world space locations or real world measurements, as related to the content of the image sequence, is used during the content insert process.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
System and method for inserting content into an image sequence
ActiveUS7116342B2Unique and effectiveRobust systemTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer graphics (images)Time system
A real-time system and method for inserting perspective correct content into an image sequence are presented. The invention inserts the content with the location, size, orientation, shape and occlusion properties that are appropriate for the camera view represented by the image sequence. Both static and dynamic content insert positions are supported. The location, size, orientation and shape of the inserted content are determined independently of the image sequence content. Furthermore, no knowledge of three dimensional real world space locations or real world measurements, as related to the content of the image sequence, is used during the content insert process.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for efficient animation and collision detection using local coordinate systems
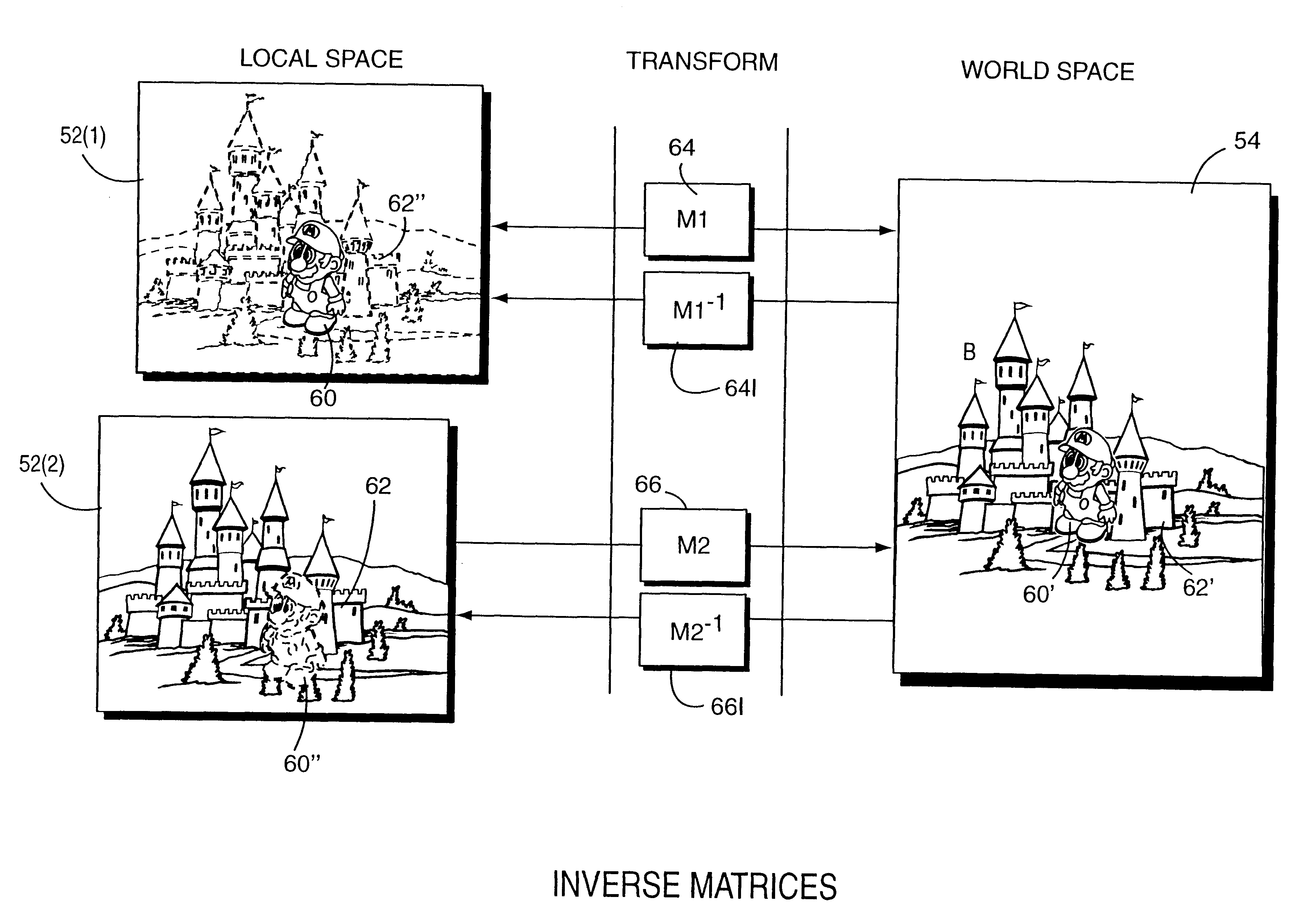
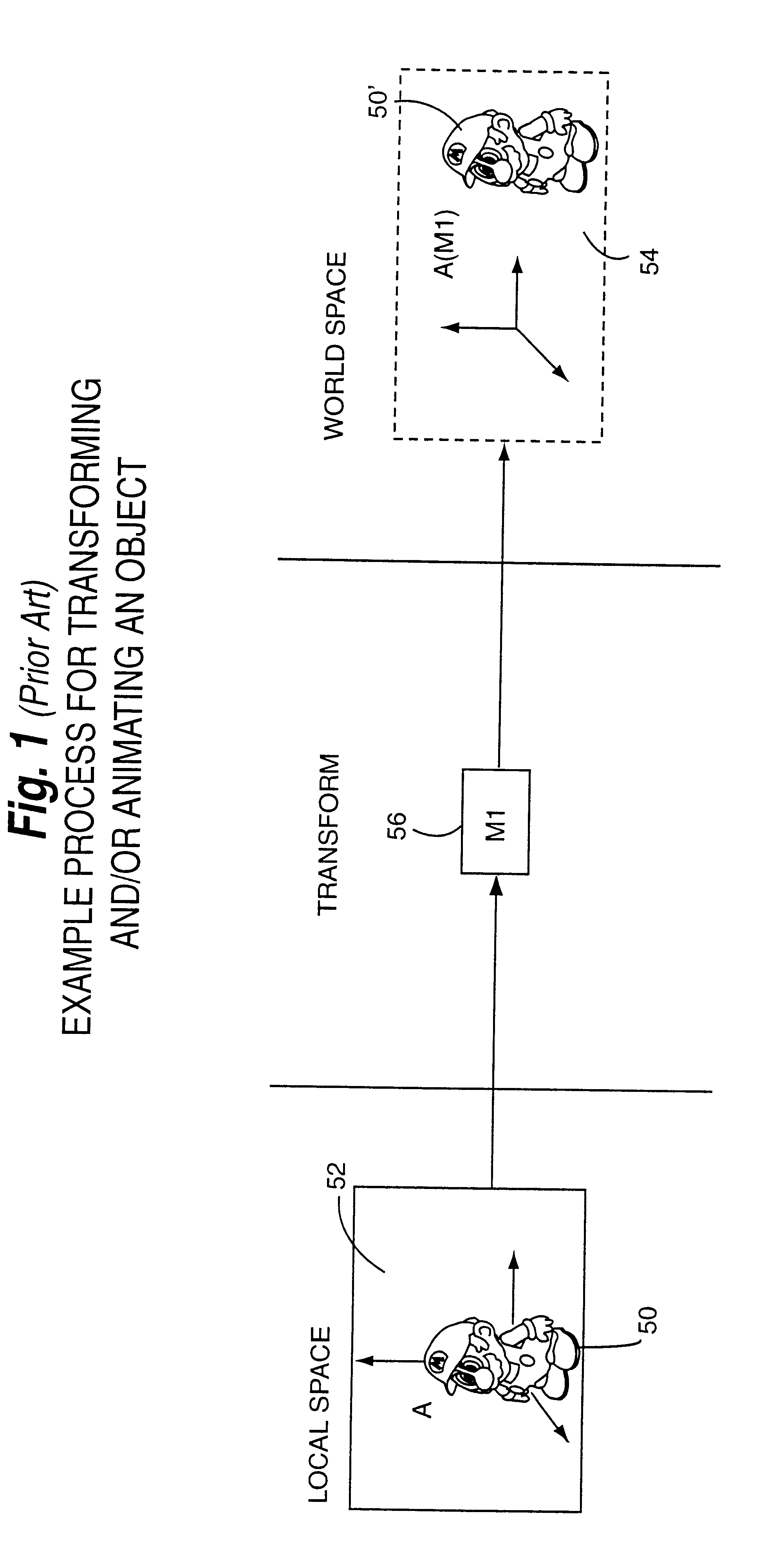
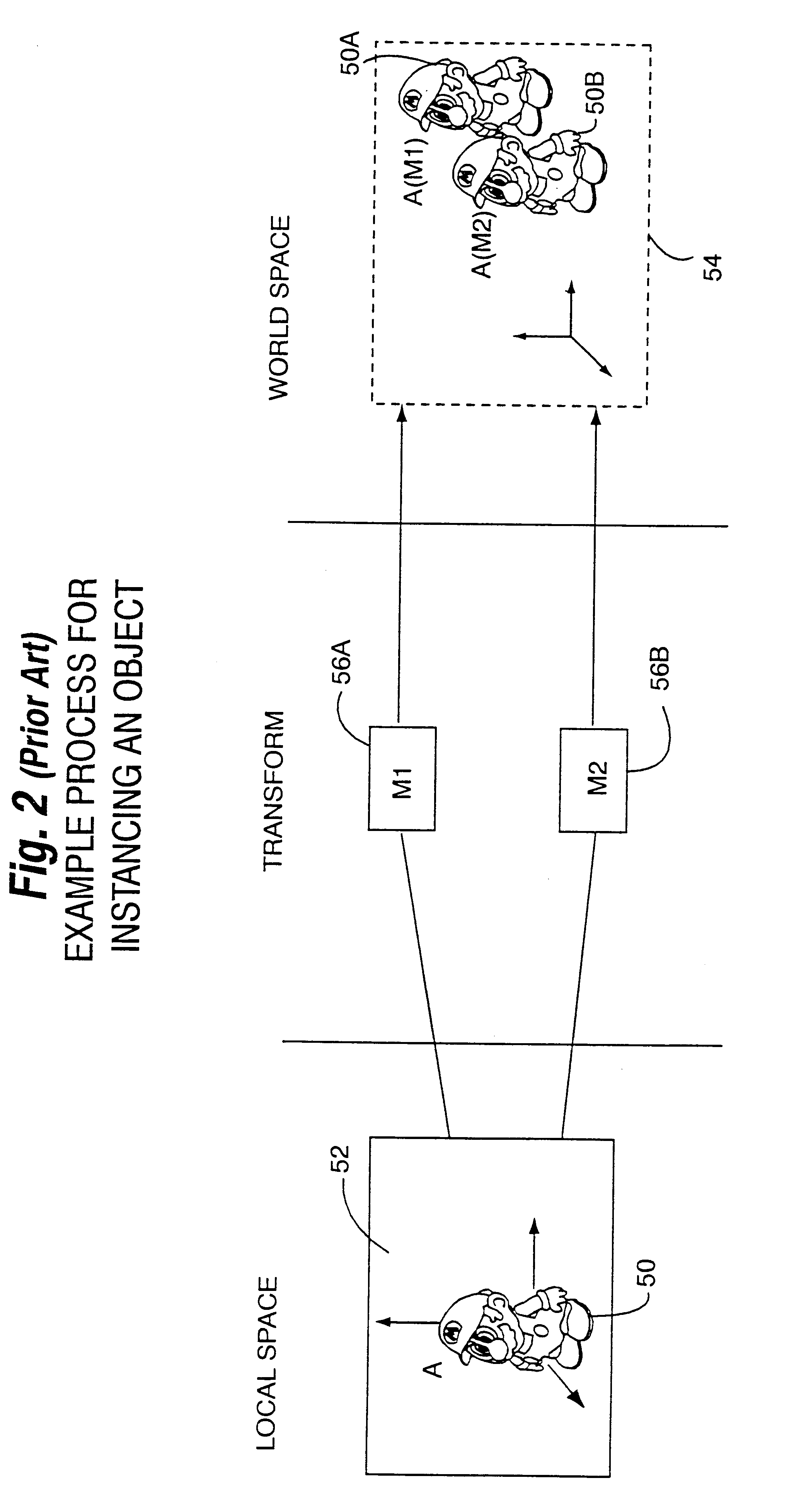
Performance gains are realized by transforming less complex objects to the local space of a more complex object for collision detection against the more complex object. An inverse transformation stack may be used to efficiently enable transformation from world coordinate space to local coordinate space for collision detection. Avoiding the need to transform complex objects to world space for collision detection provides performance improvements by conserving processing resources and reducing the number of operations involved in collision detection. Advantages include: the ability to perform collision detection with animation objects, the ability to allow inheritance of motion in a complex hierarchy, and the ability to use instancing. Using the local coordinate space to perform collision detection with animated, instanced, hierarchical objects provides significant performance improvements over the world coordinates-based approach widely used in the past.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Measurments using a single image
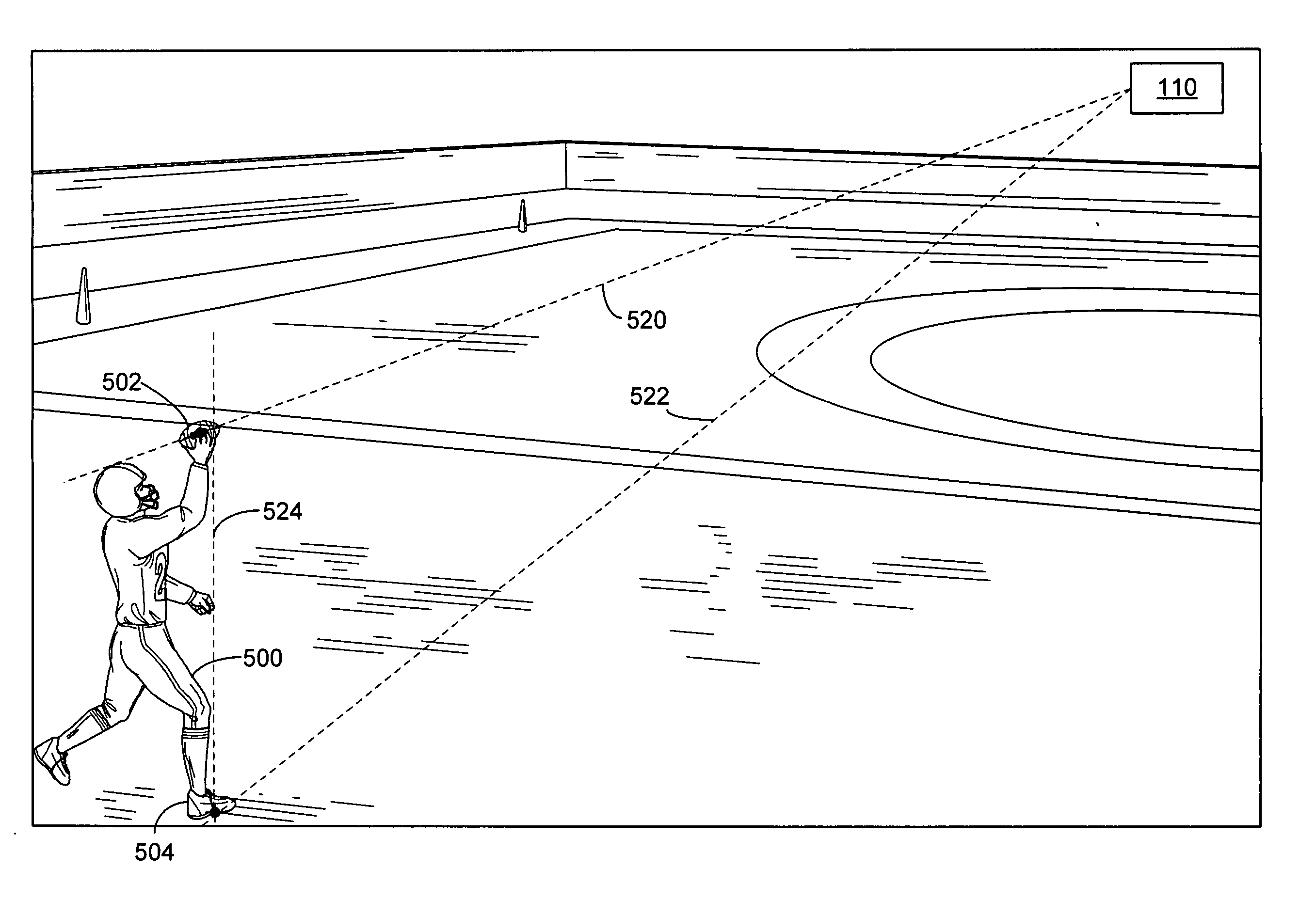
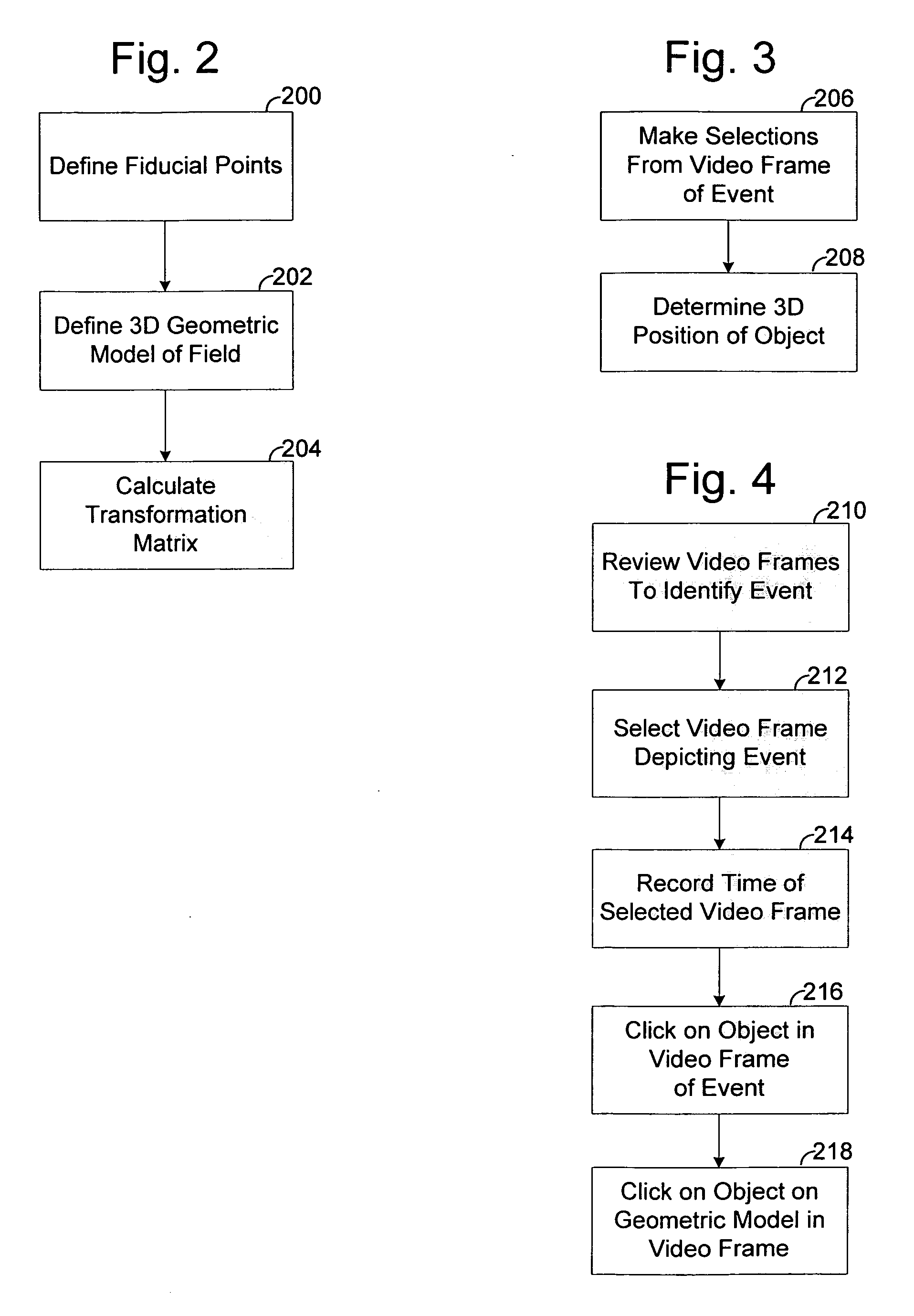
A method used in broadcasts of events is disclosed for identifying the coordinates of an object in world space from a video frame, where the object is not on the geometric model of the environment. Once the world coordinates of the object are identified, a graphic may be added to a video replay showing the object. The method may also be expanded in a further embodiment to identify a trajectory of an object over time moving through world space from video images of the start and end of the trajectory, where the object is not on the geometric model of the environment. Once the trajectory of the object in world space is identified, a graphic may be added to a video replay showing the trajectory.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
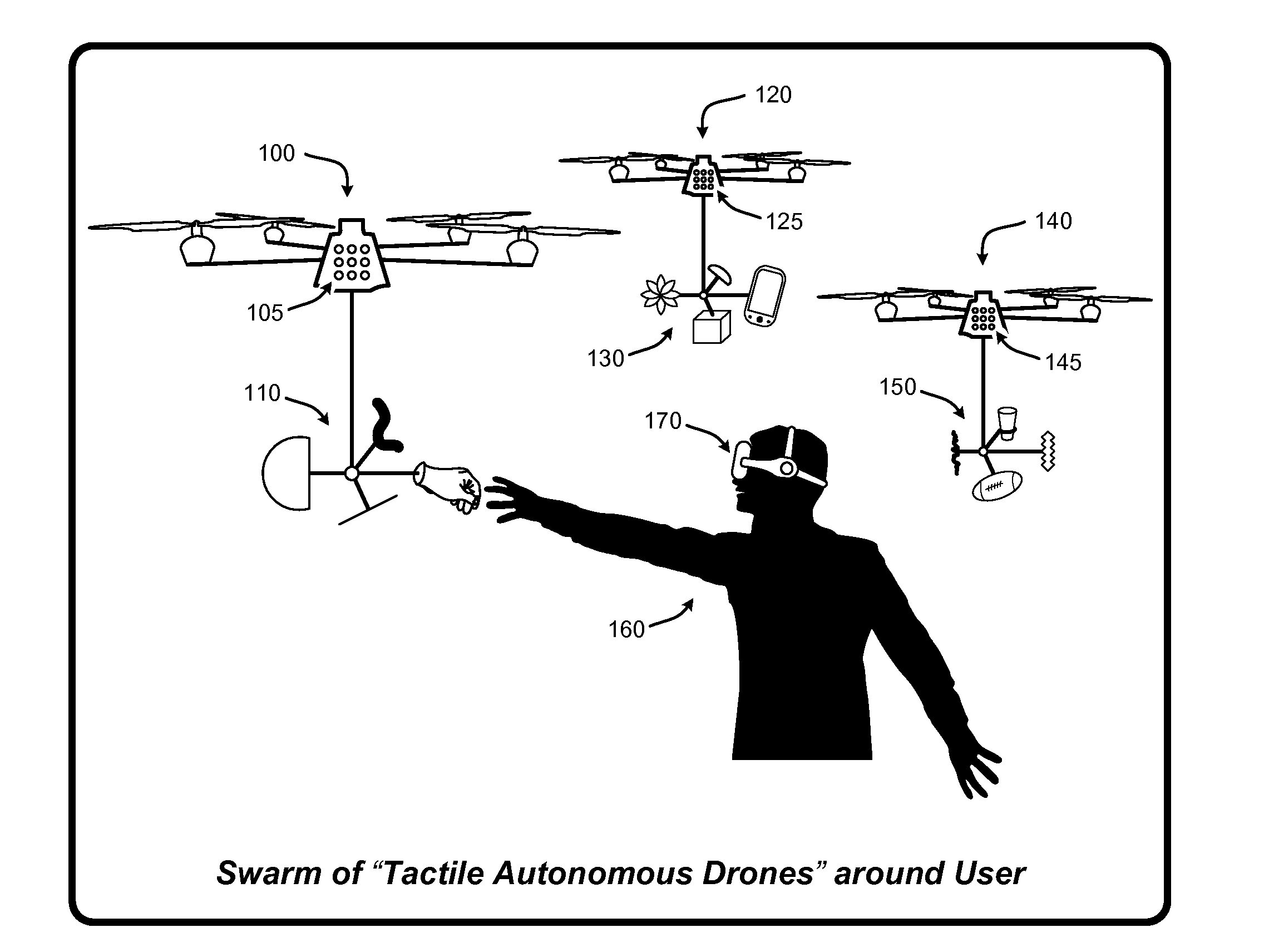
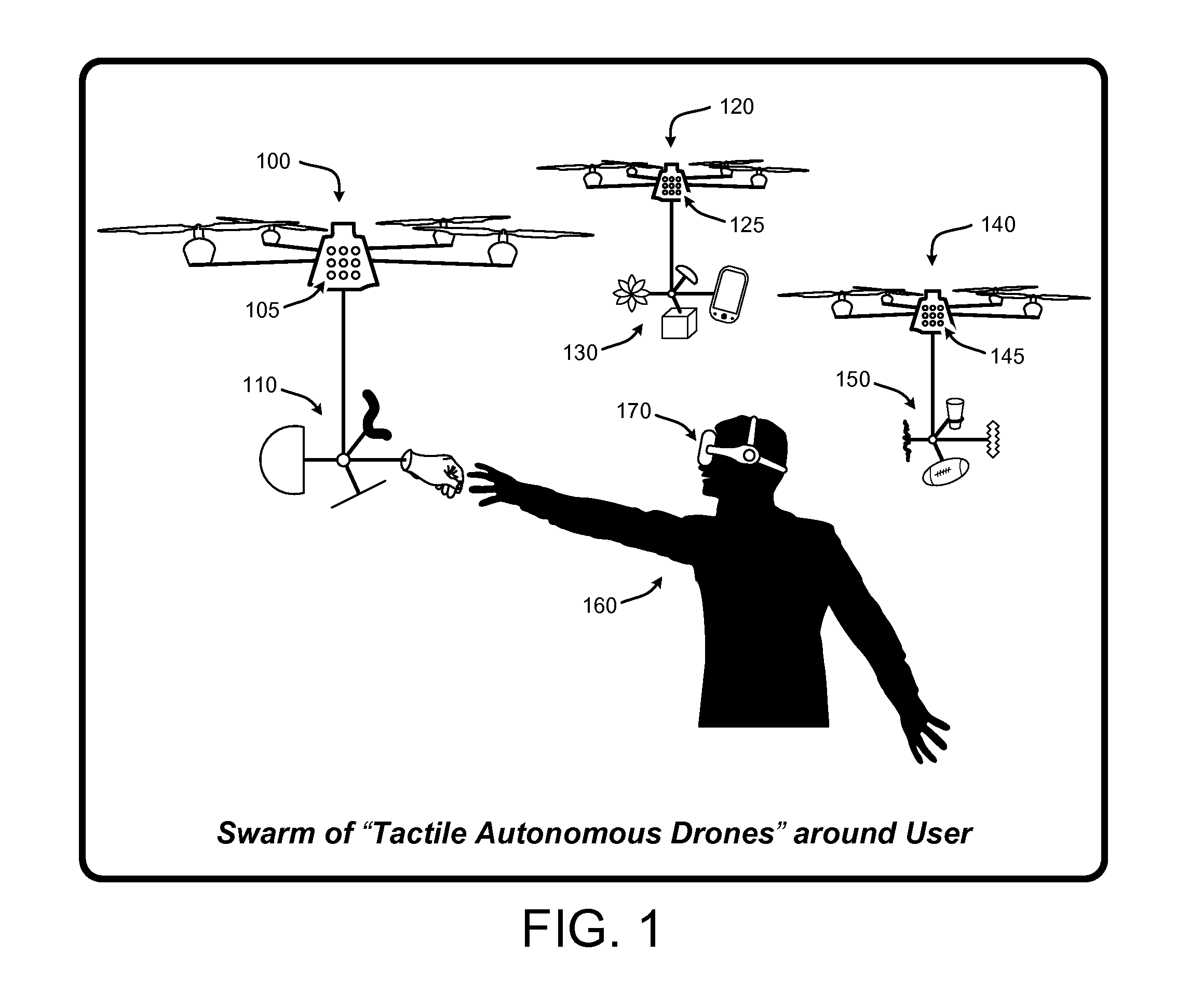
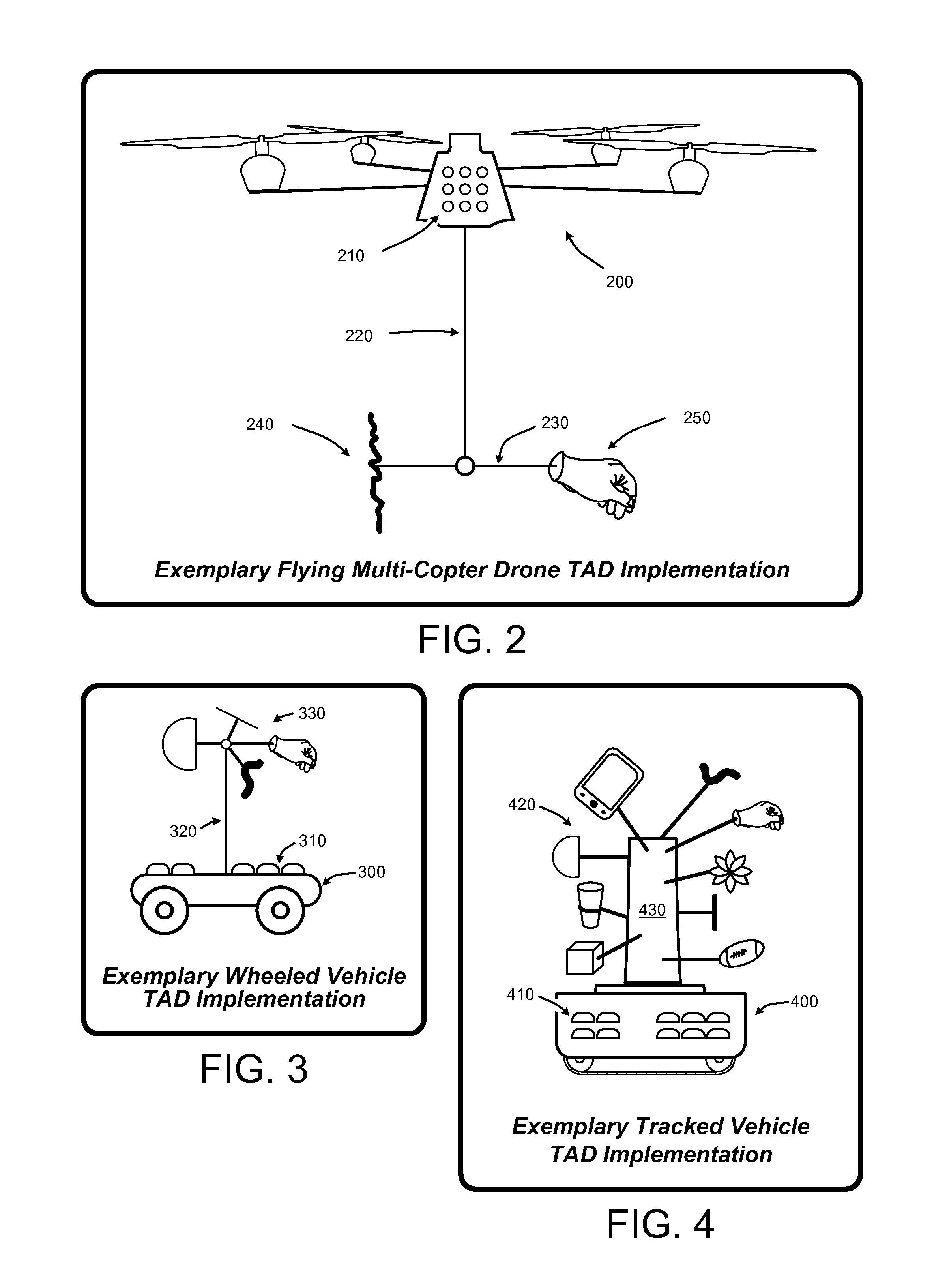
Autonomous drones for tactile feedback in immersive virtual reality
ActiveUS20160349835A1Enhancing user experience and sense of realityEnhances user experience and sense of realityInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorTouch PerceptionVirtual reality
A “Tactile Autonomous Drone” (TAD) (e.g., flying drones, mobile robots, etc.) supplies real-time tactile feedback to users immersed in virtual reality (VR) environments. TADs are not rendered into the VR environment, and are therefore not visible to users immersed in the VR environment. In various implementations, one or more TADs track users as they move through a real-world space while immersed in the VR environment. One or more TADs apply tracking information to autonomously position themselves, or one or more physical surfaces or objects carried by the TADs, in a way that enables physical contact between those surfaces or objects and one or more portions of the user's body. Further, this positioning of surfaces or objects corresponds to some real-time virtual event, virtual object, virtual character, virtual avatar of another user, etc., in the VR environment to provide real-time tactile feedback to users immersed in the VR environment.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
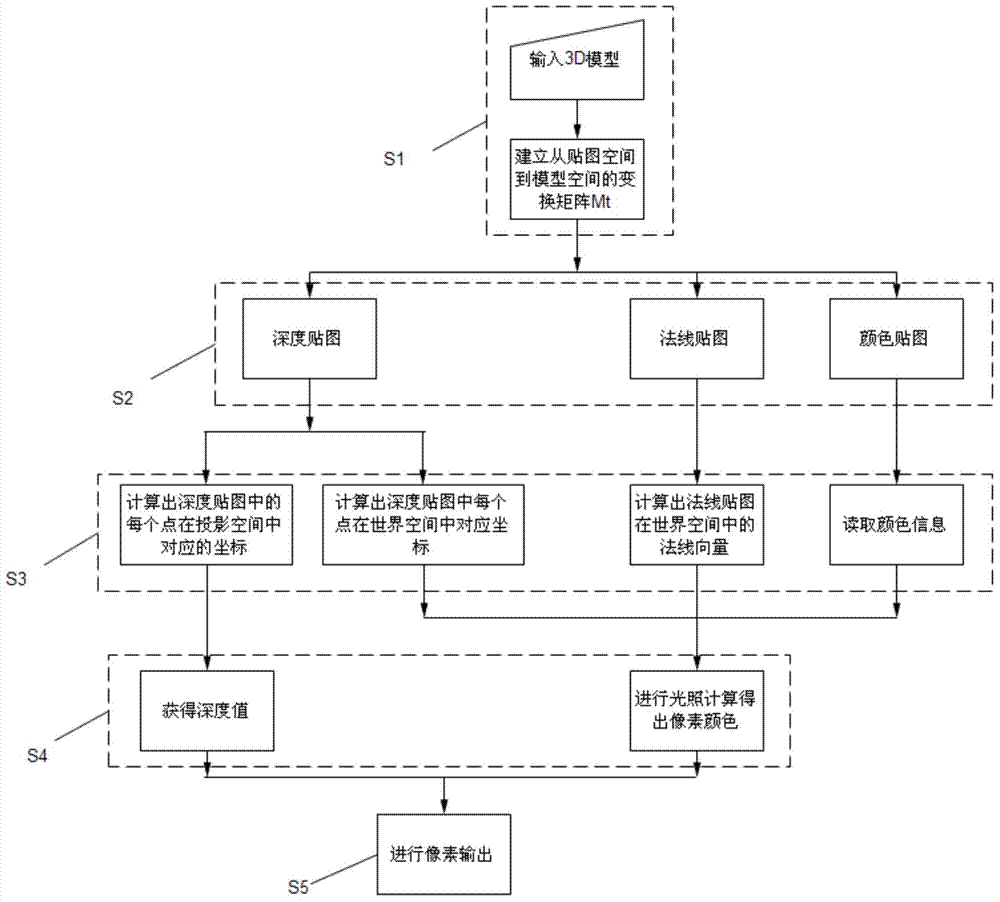
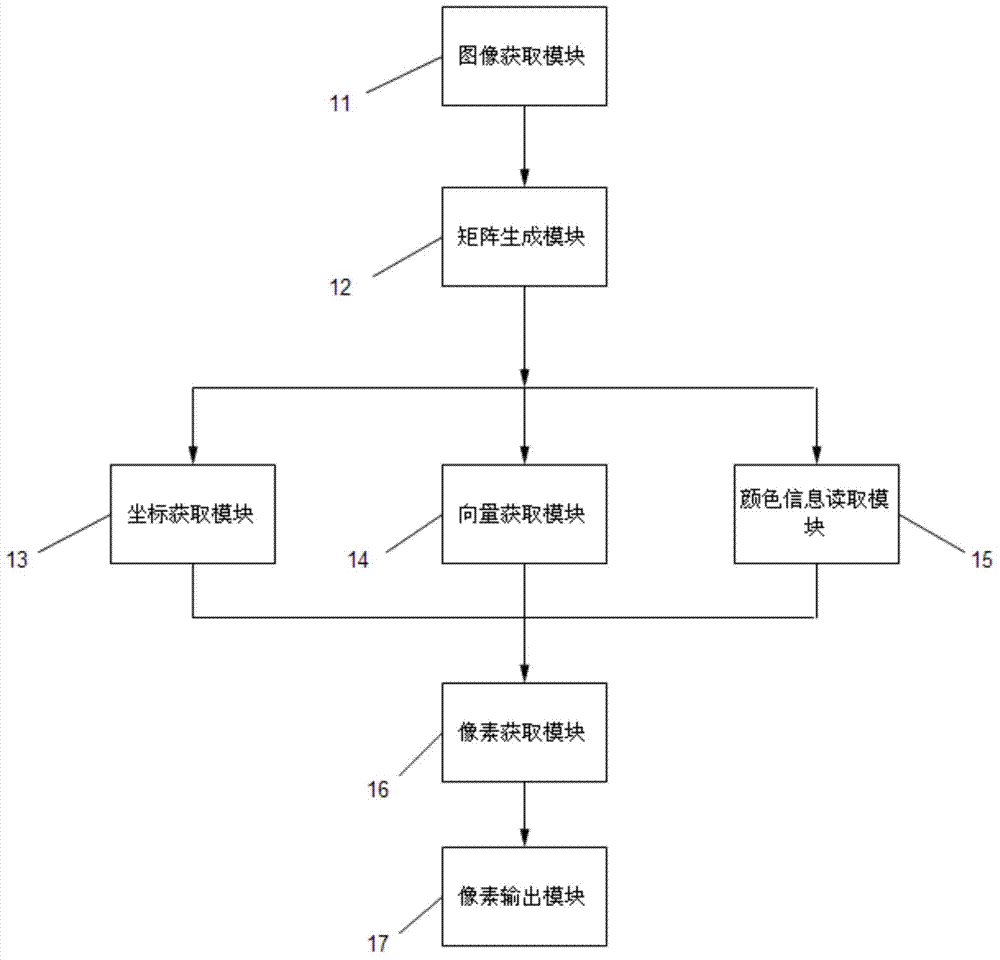
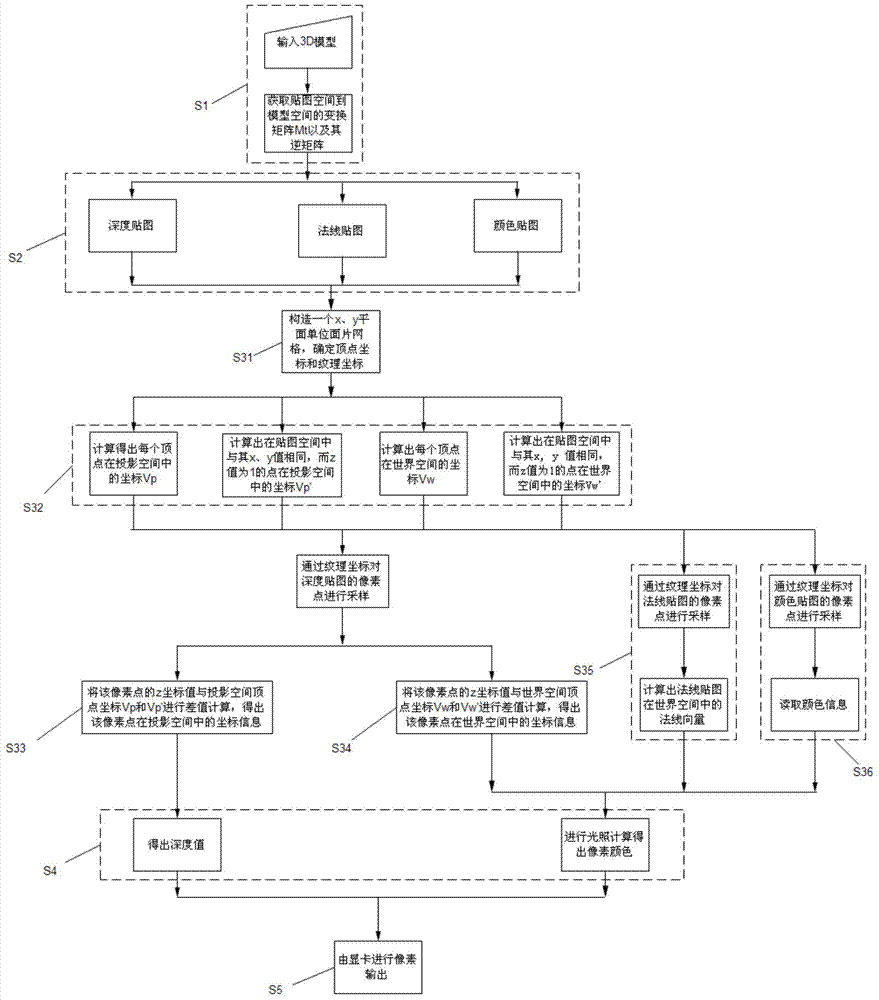
Image rendering method and device
ActiveCN104268922ARendering speed achievedAchieve rendering speed3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Normal mapping
The invention relates to an image rendering method. The image rendering method includes the following steps that a depth map, a normal map and a color map of an image needing to be rendered are obtained; the coordinates and the depth values in the projection space and the coordinates and the normal vectors in the world space of all points in the image needing to be rendered are obtained; according to the color map, color information of all the points in the image needing to be rendered is obtained; illumination calculation is carried out to obtain pixel colors of all the points in the image needing to be rendered; pixels are output to obtain the rendered image. The invention further relates to an image rendering device used for achieving the method. Compared with the prior art, the two-dimensional rendering speed and the three-dimensional rendering effect are combined to achieve the effects that 2D face pictures are adopted for displaying appearances of objects, and 3D shielding and lighting effects are adopted for scenes, and therefore the two-dimensional rendering speed and the three-dimensional rendering effect can be achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BOGUAN TELECOMM TECH LTD
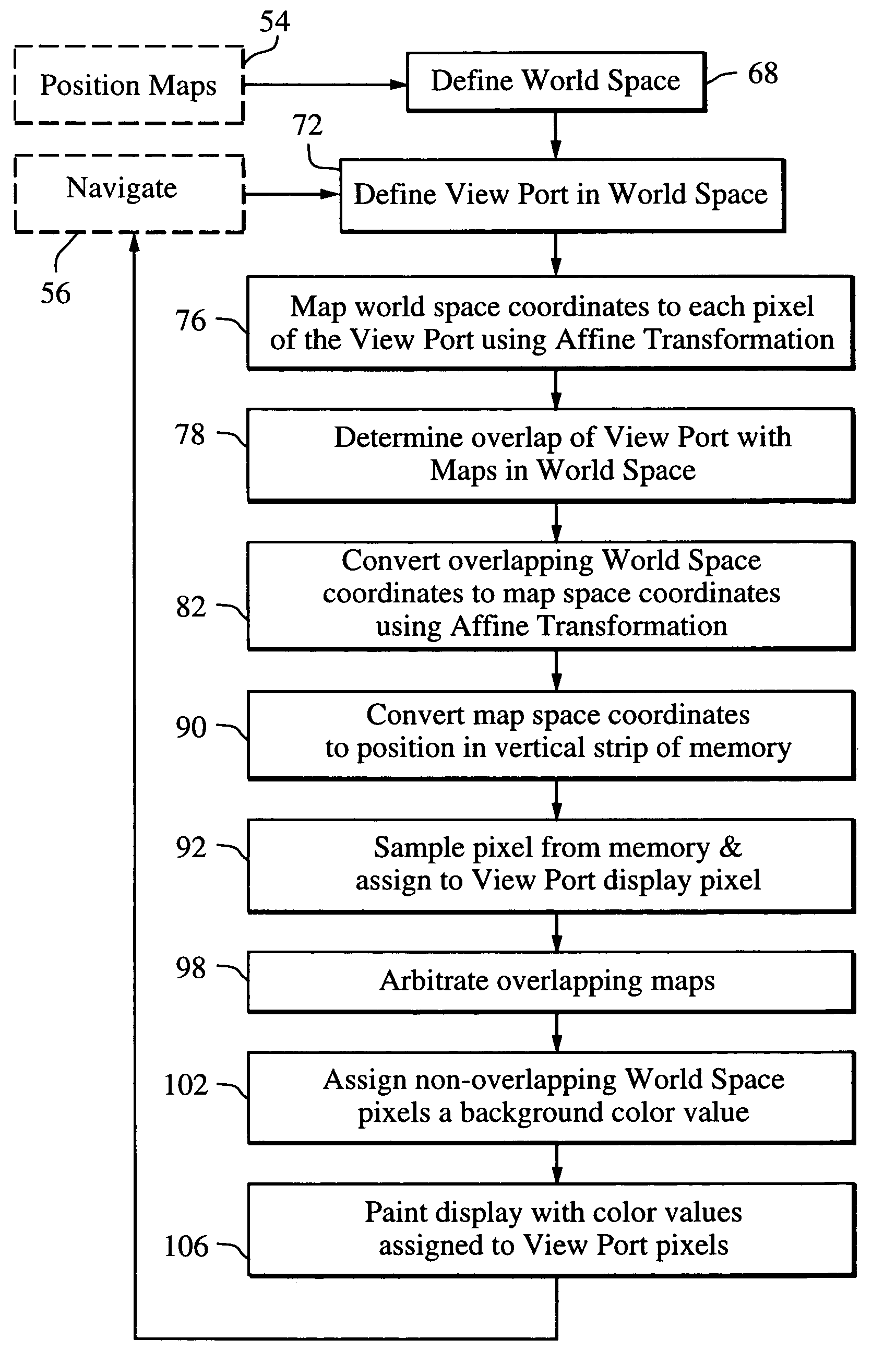
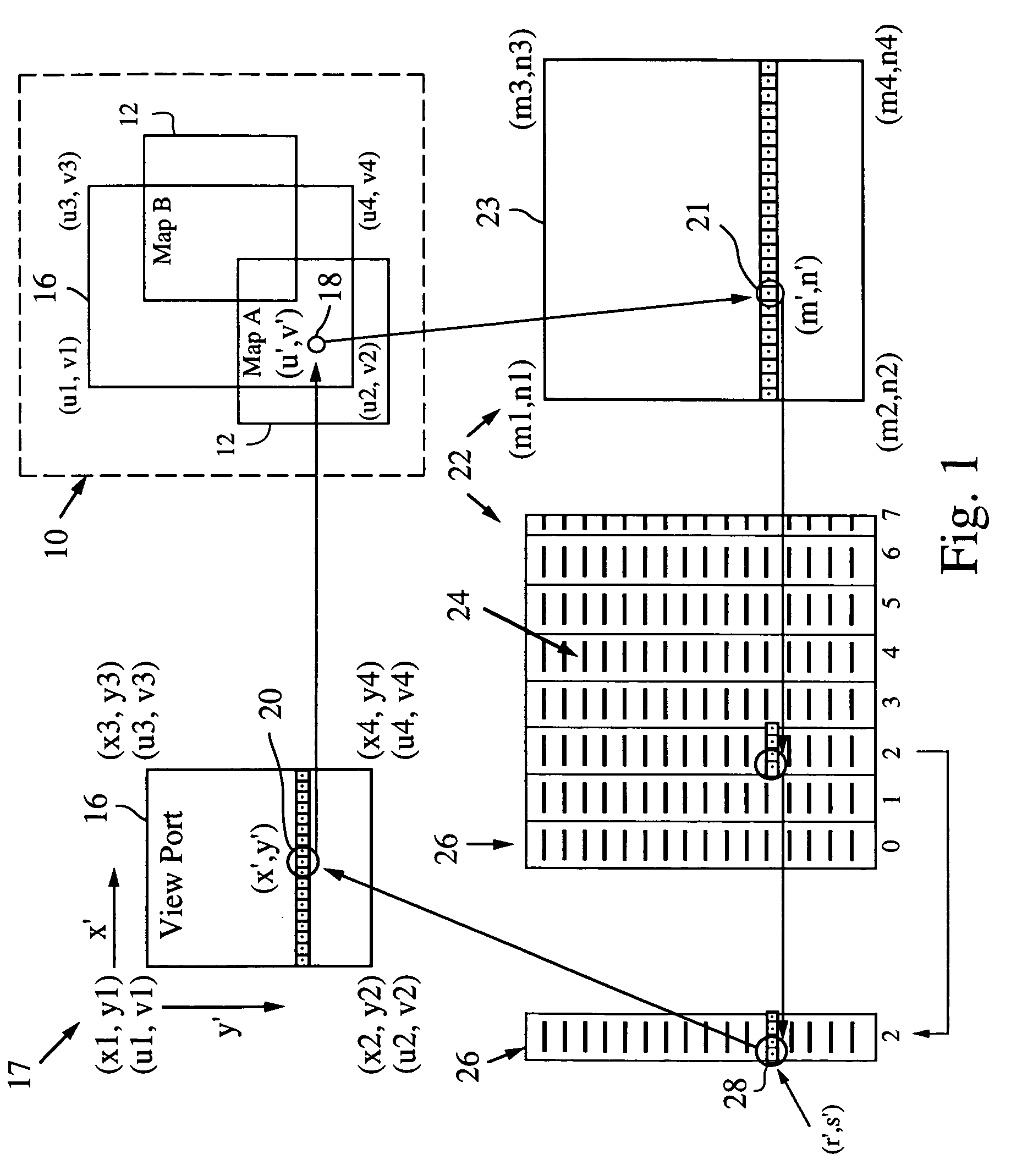
Mapping application for rendering pixel imagery
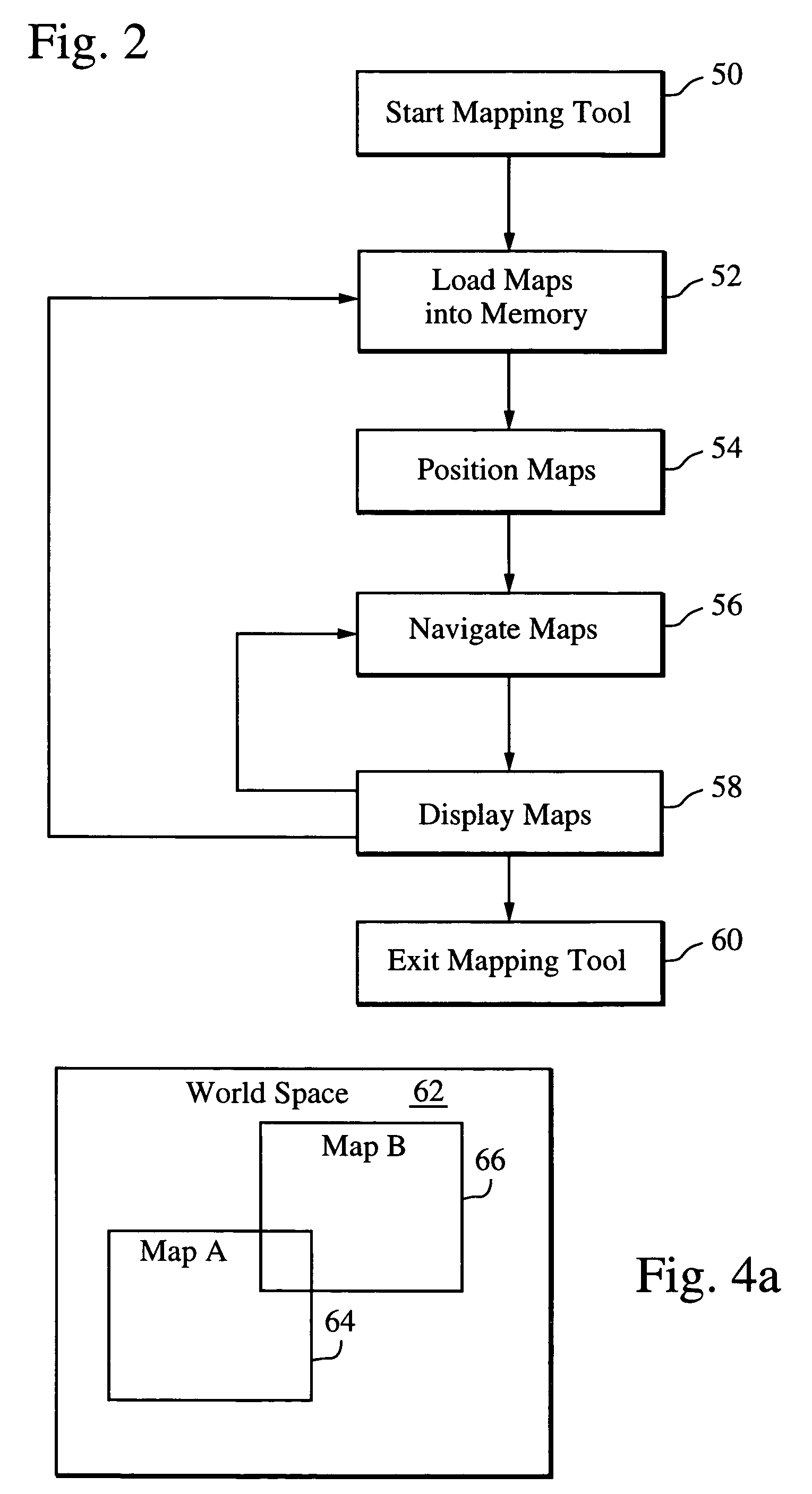
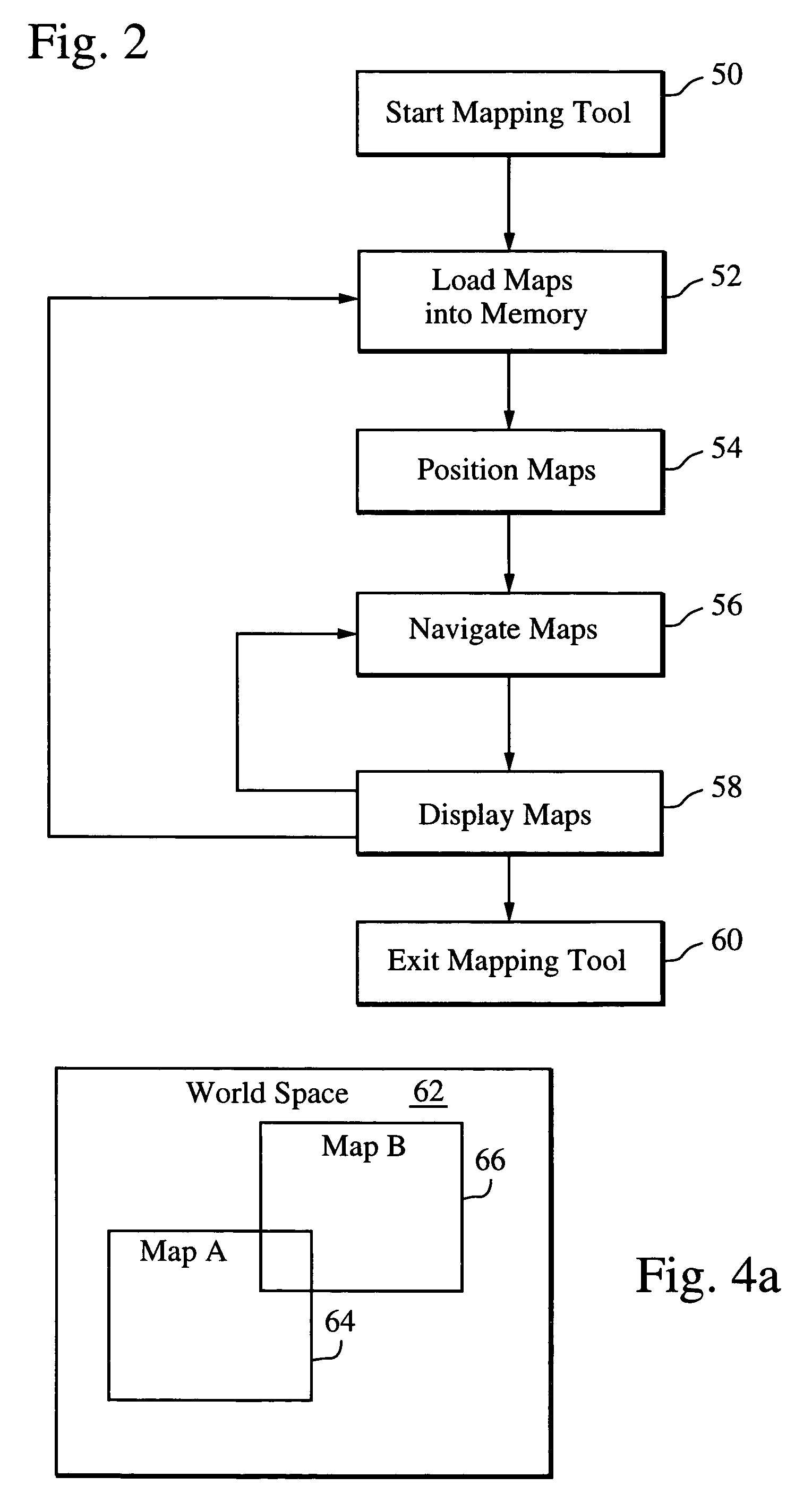
ActiveUS20060022978A1Reduce the possibilityExtension of timeGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsReal time navigationTransformation algorithm
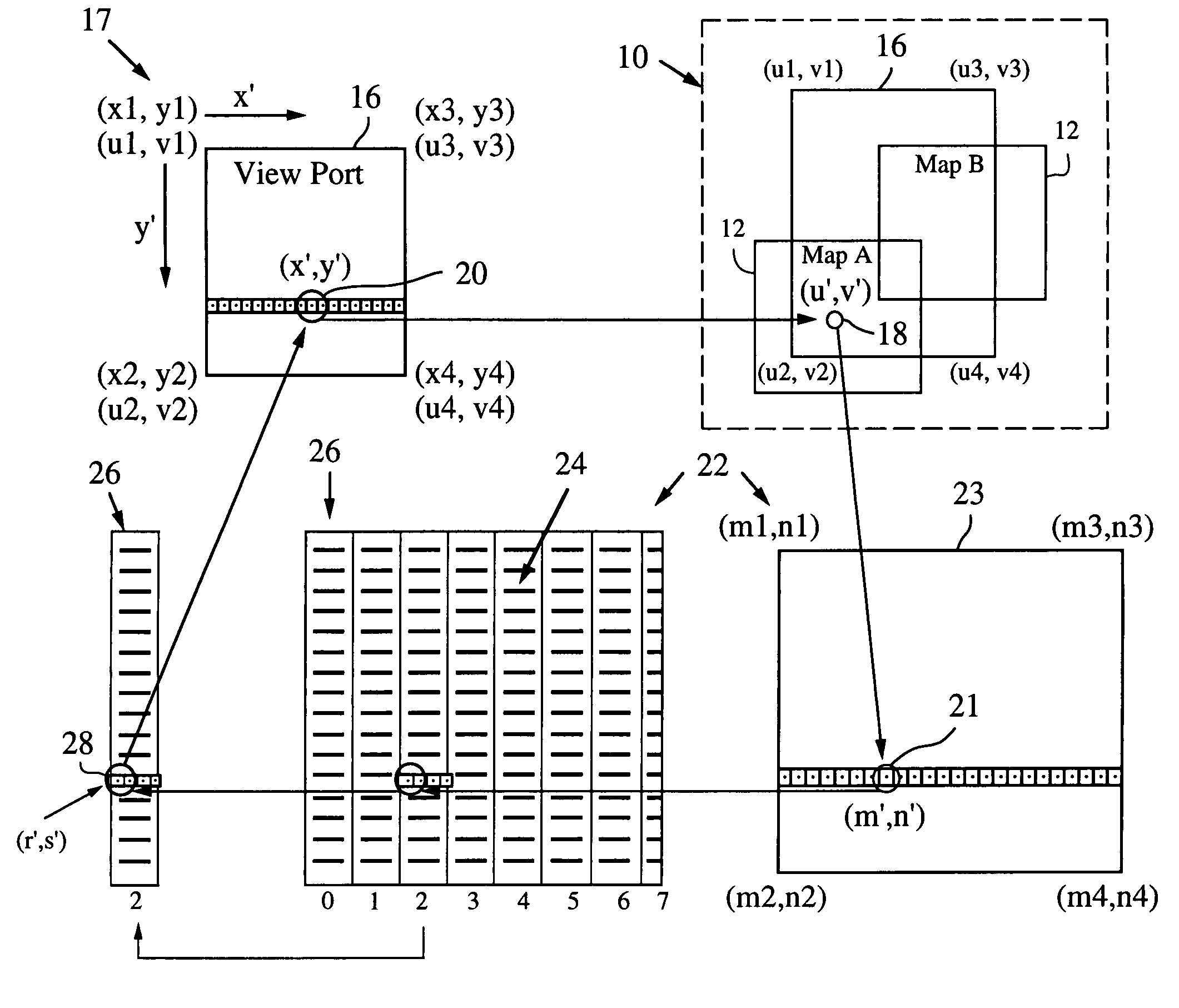
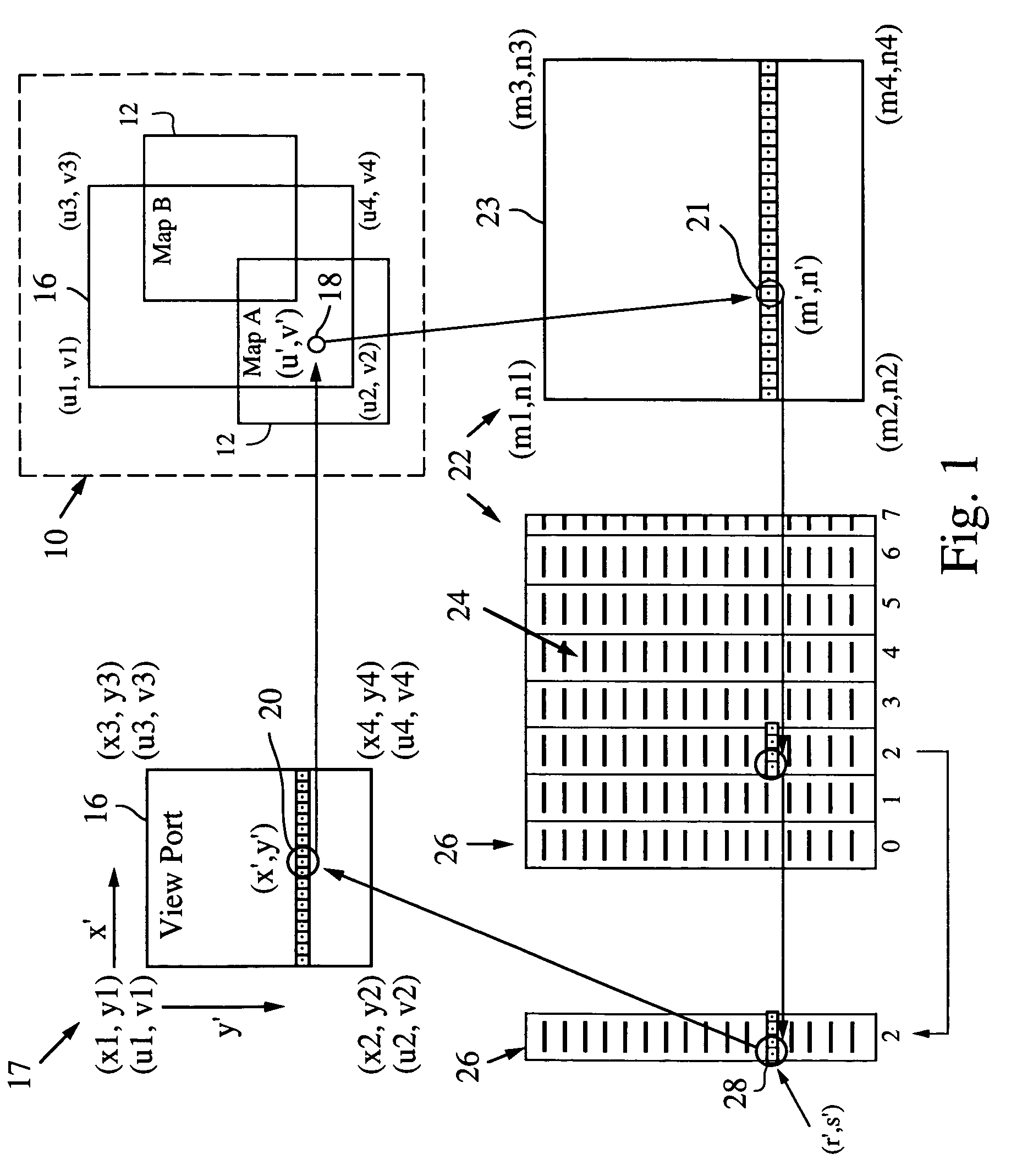
A mapping application relies on a modified affine transformation algorithm to provide near real-time navigation of imagery, track-up capability and integration of segment and picture data. The affine transformation is modified to map a “world space” comprised of a plurality of pixel maps onto a view port. The pixel data for the maps is preferably stored in vertical strips of memory to reduce the likelihood of cache misses. The mapping application is most useful for rendering pixel imagery on a platform with limited processing power, limited memory and small display sizes, e.g., “hand held devices” such as a GPS handset, or Pocket PC.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Primitive re-ordering between world-space and screen-space pipelines with buffer limited processing
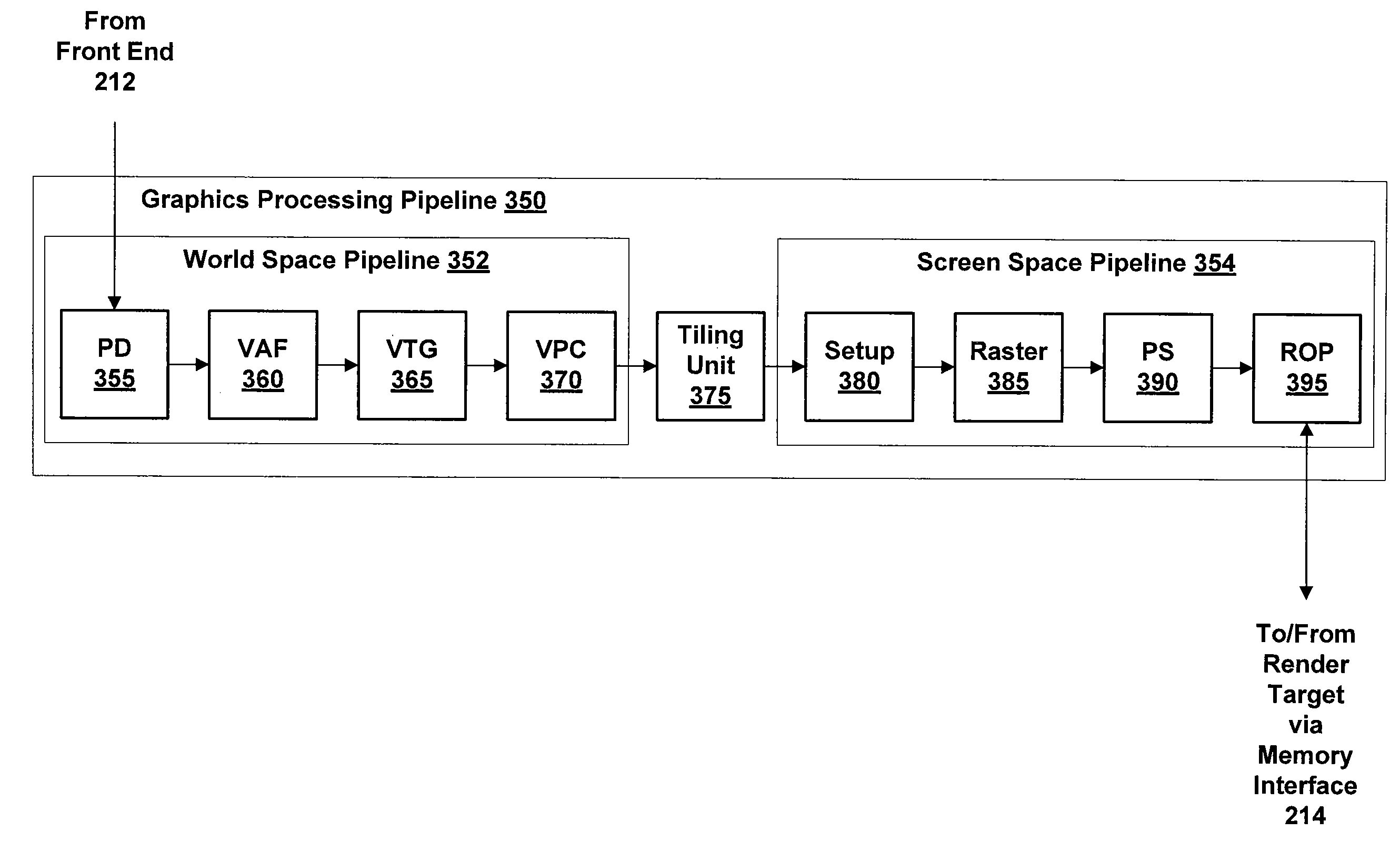
ActiveUS8704826B1Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTTiled renderingRender Target
One embodiment of the present invention includes approaches for processing graphics primitives associated with cache tiles when rendering an image. A set of graphics primitives associated with a first render target configuration is received from a first portion of a graphics processing pipeline, and the set of graphics primitives is stored in a memory. A condition is detected indicating that the set of graphics primitives is ready for processing, and a cache tile is selected that intersects at least one graphics primitive in the set of graphics primitives. At least one graphics primitive in the set of graphics primitives that intersects the cache tile is transmitted to a second portion of the graphics processing pipeline for processing. One advantage of the disclosed embodiments is that graphics primitives and associated data are more likely to remain stored on-chip during cache tile rendering, thereby reducing power consumption and improving rendering performance.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
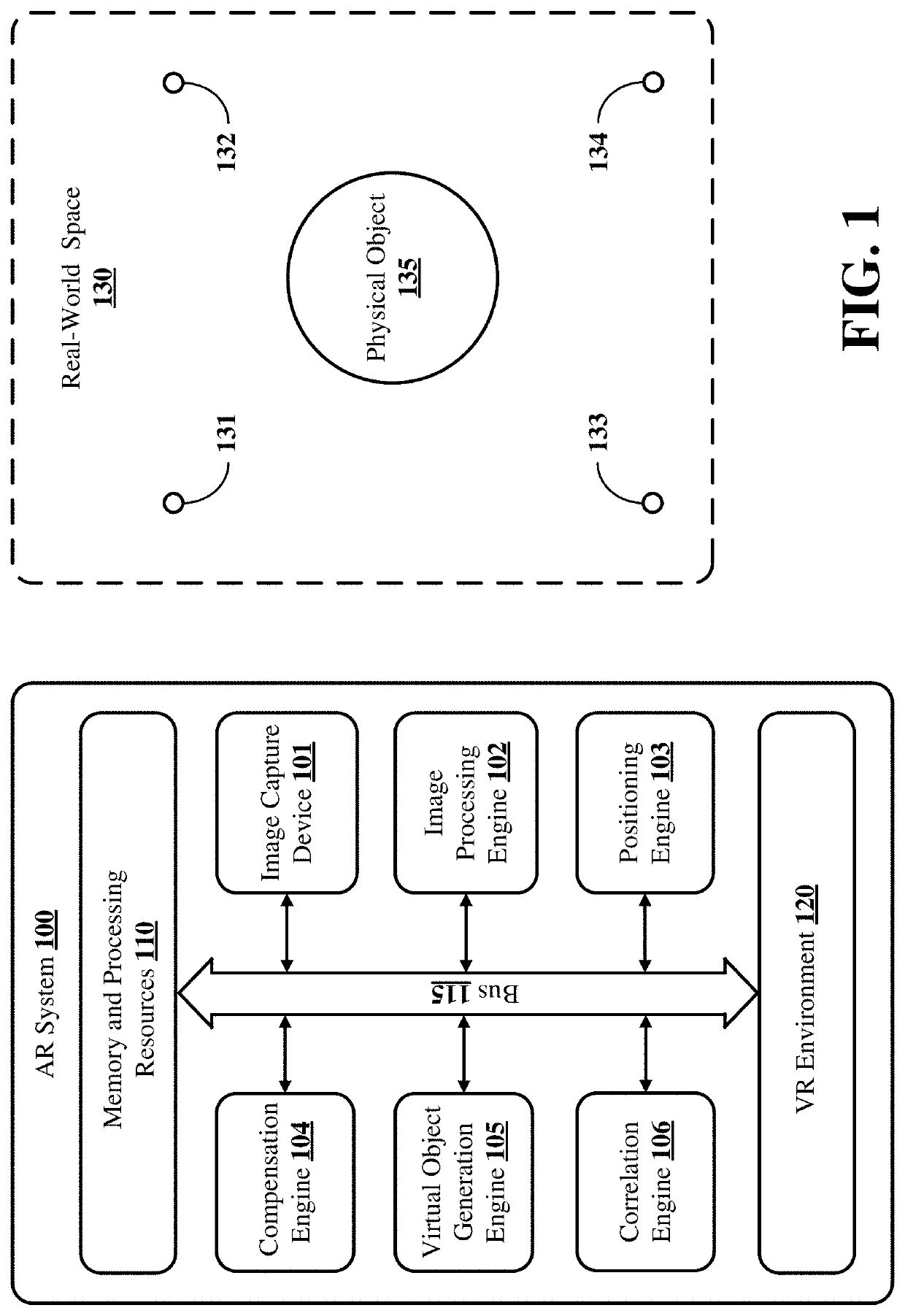
Methods and systems to create a controller in an augmented reality (AR) environment using any physical object
PendingUS20210201581A1Image data processingInput/output processes for data processingControl signalComputer graphics (images)
This disclosure provides systems, methods and apparatus for manipulating virtual objects in a virtual reality (VR) environment. In some implementations, an augmented reality (AR) system determines an orientation of a physical object in the real-world space based at least in part on images or video of the physical object captured by an image capture device, and generates a virtual object representative of the physical object based at least in part on the orientation and the at least one detected feature. The AR system detects movement of the physical object in the real-world space based at least in part on the captured images or video, and manipulates the virtual object based at least in part on the detected movements of the physical object. In some aspects, the AR system can determine the orientation and detect movement of the physical object without receiving control signals or communications from the physical object.
Owner:INTUIT INC
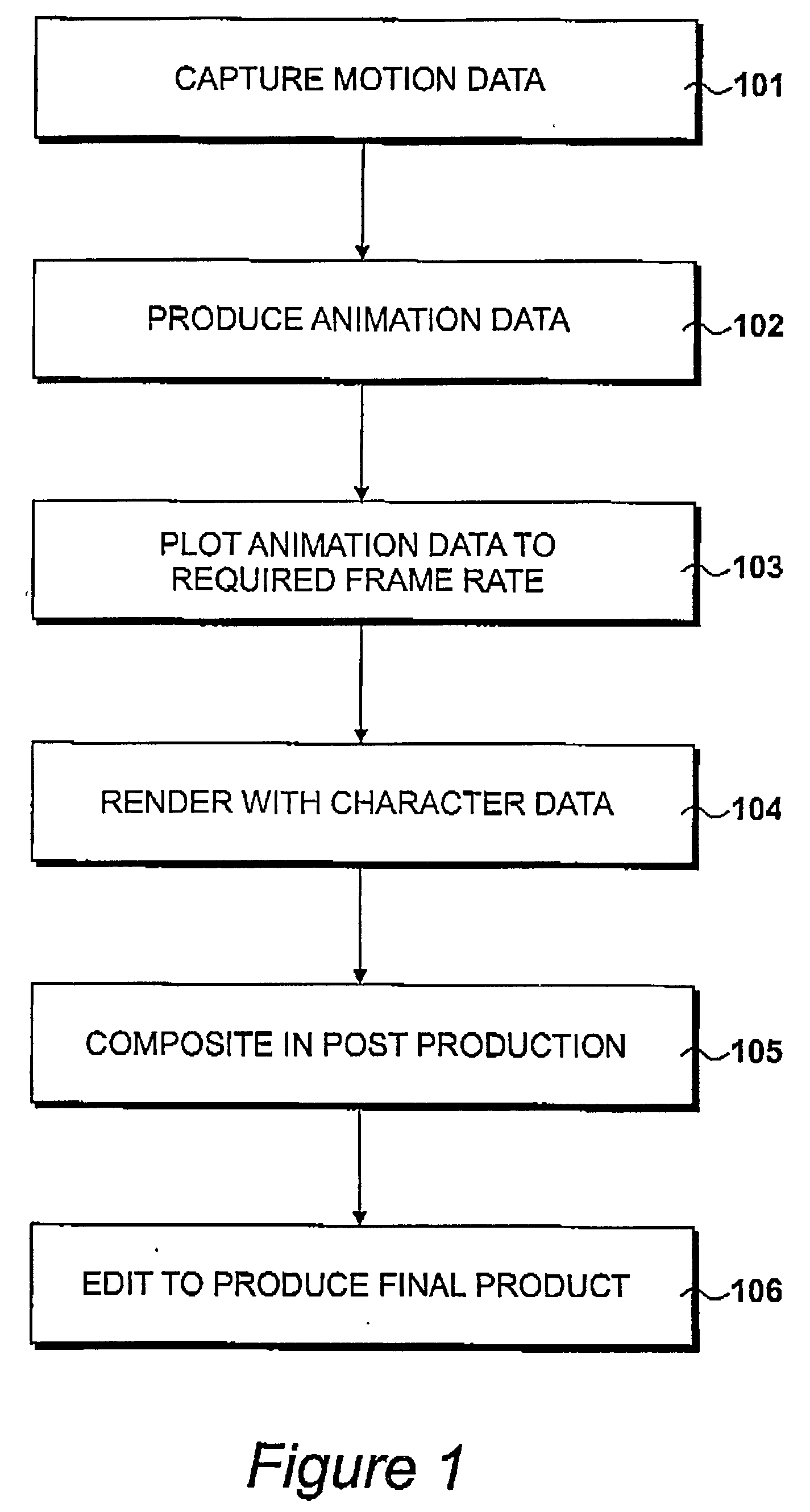
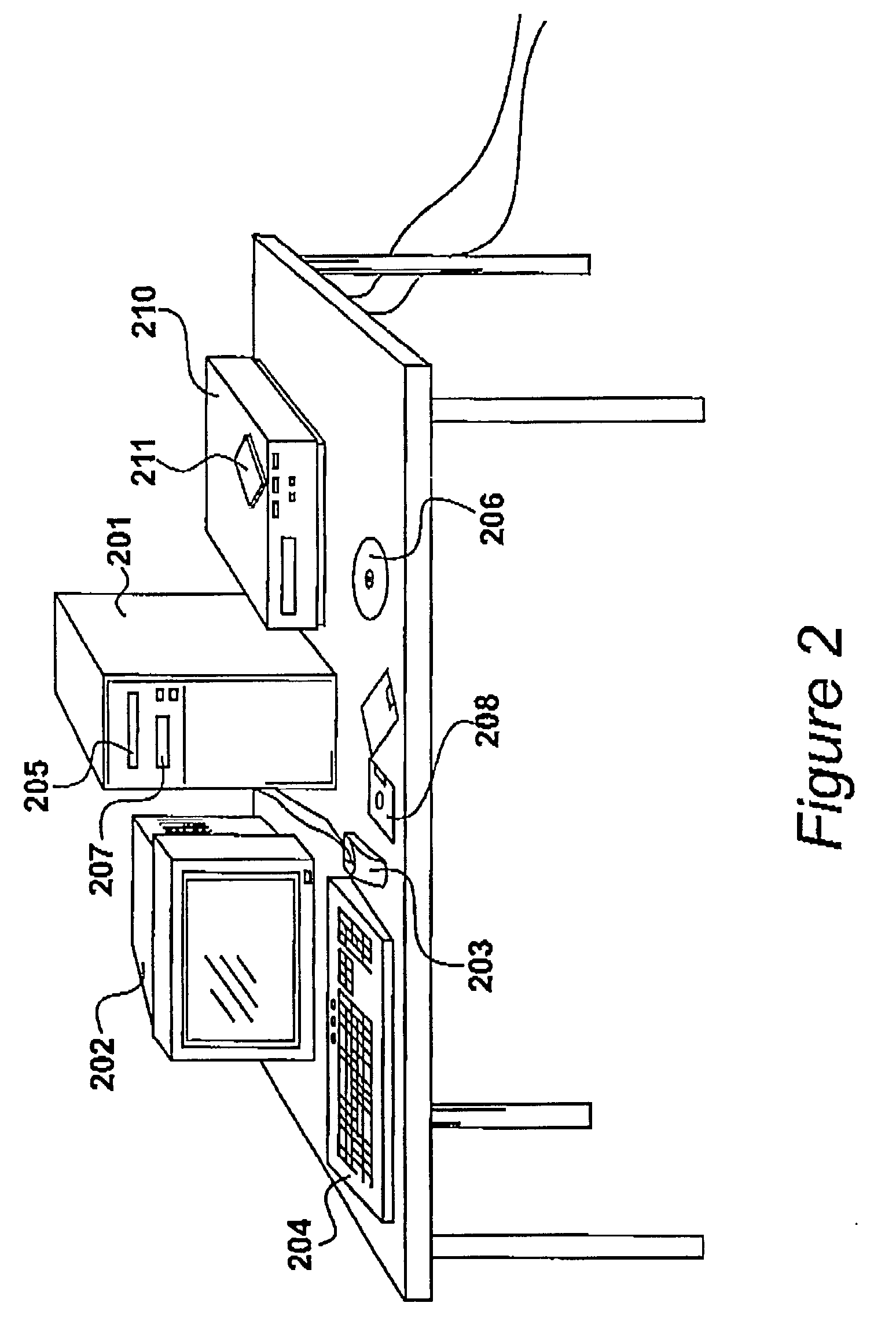
Generating animation data with constrained parameters
Animation data is produced in a data processing system having storage, a processing unit, a visual display unit (202) and input devices (203, 204). A simulated three-dimensional world-space is displayed to a user and an animatable actor is displayed in the world-space. Specifying input data is received from a user specifying desired locations and desired orientations of the actor in the world-space at selected positions along the time-line. First animation data is generated, preferably by a process of inverse kinematics. Animation of the actor is displayed in response to the generated first animation data. Parametric constraining data is received that selects an animation parametric constraint, such as the extent to which an actor's feet may slip. Defining data is received defining different values of parametric constrain at different identified positions along the time-line. The processor generates new constrained animation data in response to the defined values.
Owner:KAYDARA +1
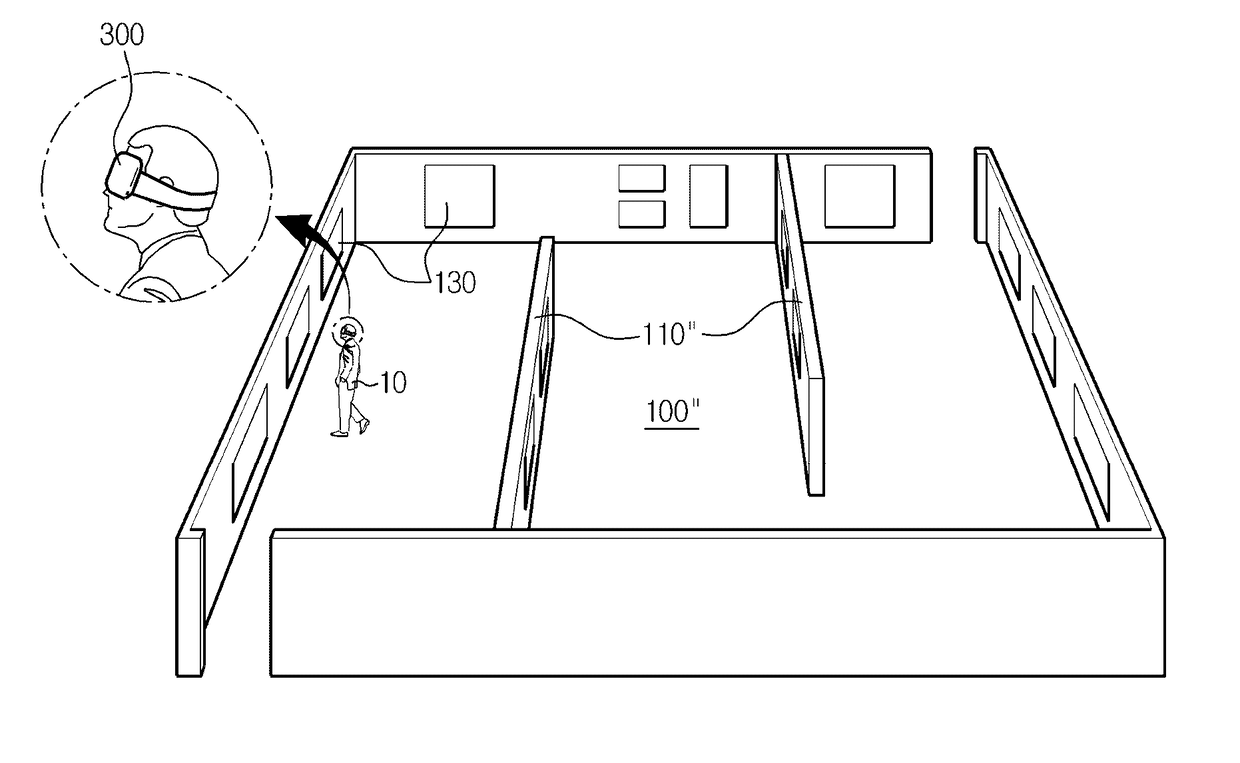
Virtual reality system allowing immersion in virtual space to consist with actual movement in actual space
A virtual reality system includes a playground defined within a real world space to have a predetermined area in which a user is movable, a head mounted device surrounds both eyes displaying an image of a virtual space formed corresponding to real objects in the playground, a sensor attached to a predetermined location in the playground, the head mounted device or body of the user sensing an actual location or motion of the user in the playground. A control unit calculates a location and direction of the user in the playground according to a signal from the sensor, and displays an image on the head mounted device of the virtual space, observed at the location and in the facing direction of the user. When the user wearing the head mounted device actually moves in the playground, a feeling of moving in the virtual space is given to the user.
Owner:VAN CUREN GREG +2
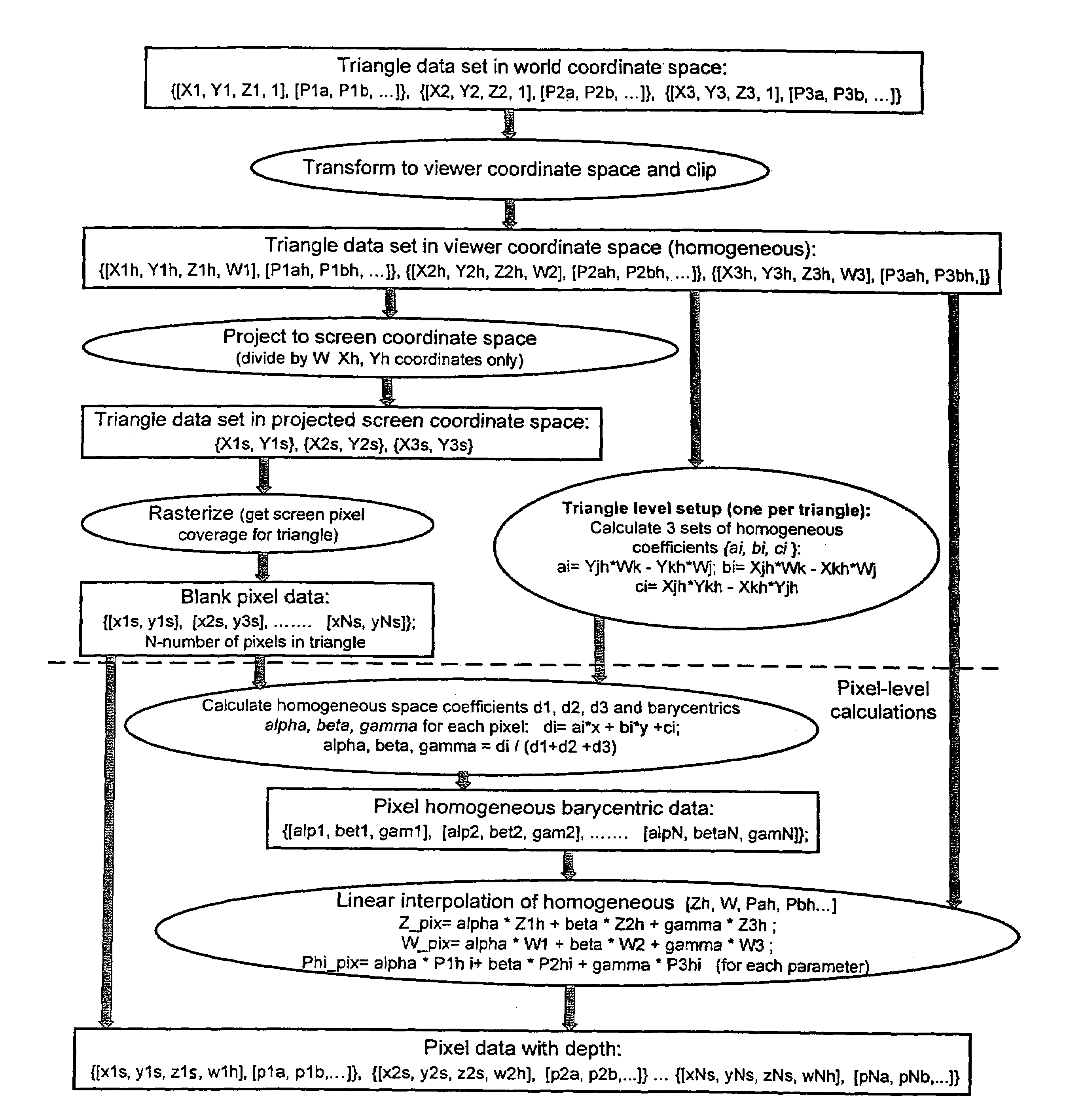
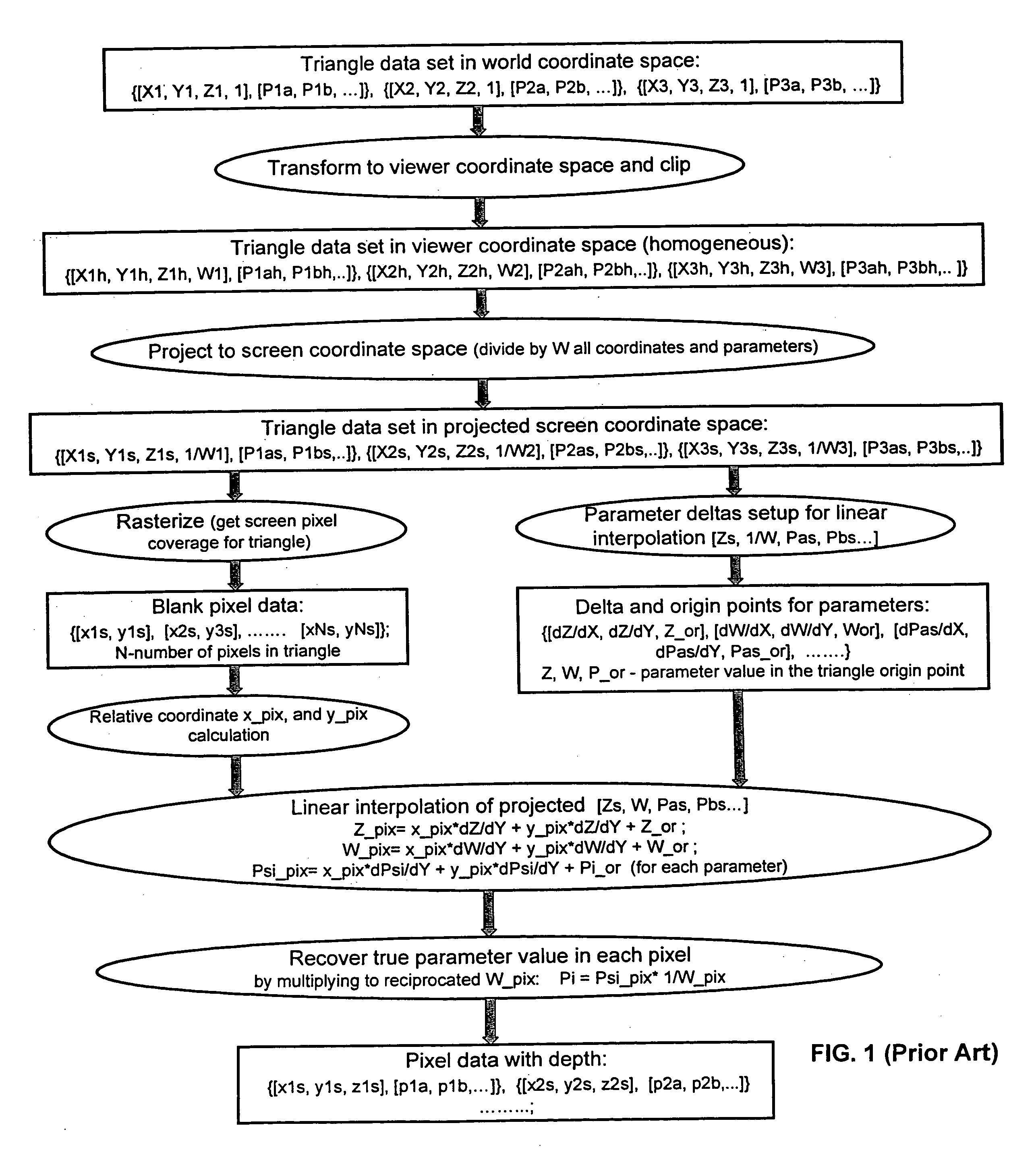
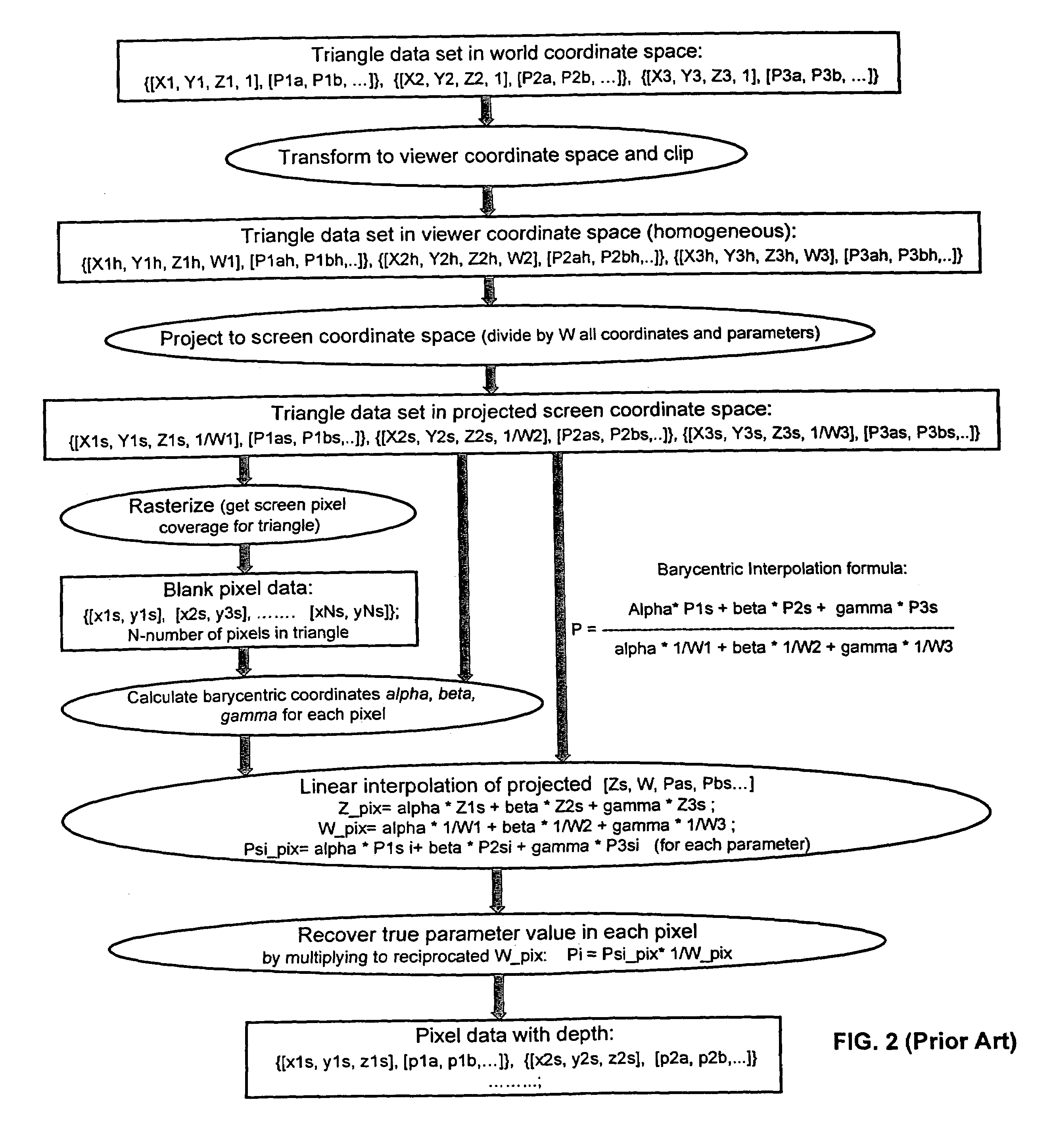
Method and programmable device for triangle interpolation in homogeneous space
ActiveUS7098924B2Improve performanceFew arithmetic operationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionObserver basedScreen space
A method and apparatus for obtaining an attribute in homogenous space. After obtaining the vertices of a triangle, the world space coordinates and the attribute of each vertex are transformed to homogeneous coordinates and an attribute in viewer space. Then a set of homogenous coefficients of the triangle is computed based on the viewer space vertex homogeneous coordinates, and the viewer space coordinates of each vertex are projected to coordinates in screen space. Pixels in the screen space that are affected by the projected triangle are determined. For each pixel affected by the triangle, a set of barycentric coefficients in viewer space is computed, based on the homogenous triangle coefficients, and a linear interpolation is performed based on the set of viewer space barycentric coefficients and the viewer space attributes of the triangle vertices to obtain the attribute of the pixel affected by the triangle.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
System for creating and modifying curves and surfaces
A system that has a flexible tape input device with bend and twist sensors spaced along the tape and a curve generation system producing a virtual B-spline tape curve using the bend and twist information. A shape of the tape can be physically constrained to assist a user in obtaining and holding a desired shape. A world position sensor senses the real world position and orientation for the tape in world space and the virtual curve is placed in a scene responsive to the position and orientation. The curve at a desired location can be input into a virtual scene. The virtual curve can be used to create, control and edit 3D curves, surfaces and objects in real time. The tape can also act as a shape scanning device as well as a command input device.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Selective interactive mapping of real-world objects to create interactive virtual-world objects
A method for interactively defining a virtual-world space based on real-world objects in a real-world space is disclosed. In one operation, one or more real-world objects in the real-world space is captured to define the virtual-world space. In another operation, one of the real-world objects is identified, the identified object is to be characterized into a virtual-world object. In yet another operation, a user is prompted for user identification of one or more object locations to enable extraction of parameters for real-world object, and the object locations are identified relative to an identifiable reference plane in the real-world space. In another operation, the extracted parameters of the real-world object may be stored in memory. The virtual-world object can then be generated in the virtual world space from the stored extracted parameters of the real-world object.
Owner:SONY COMP ENTERTAINMENT EURO +1
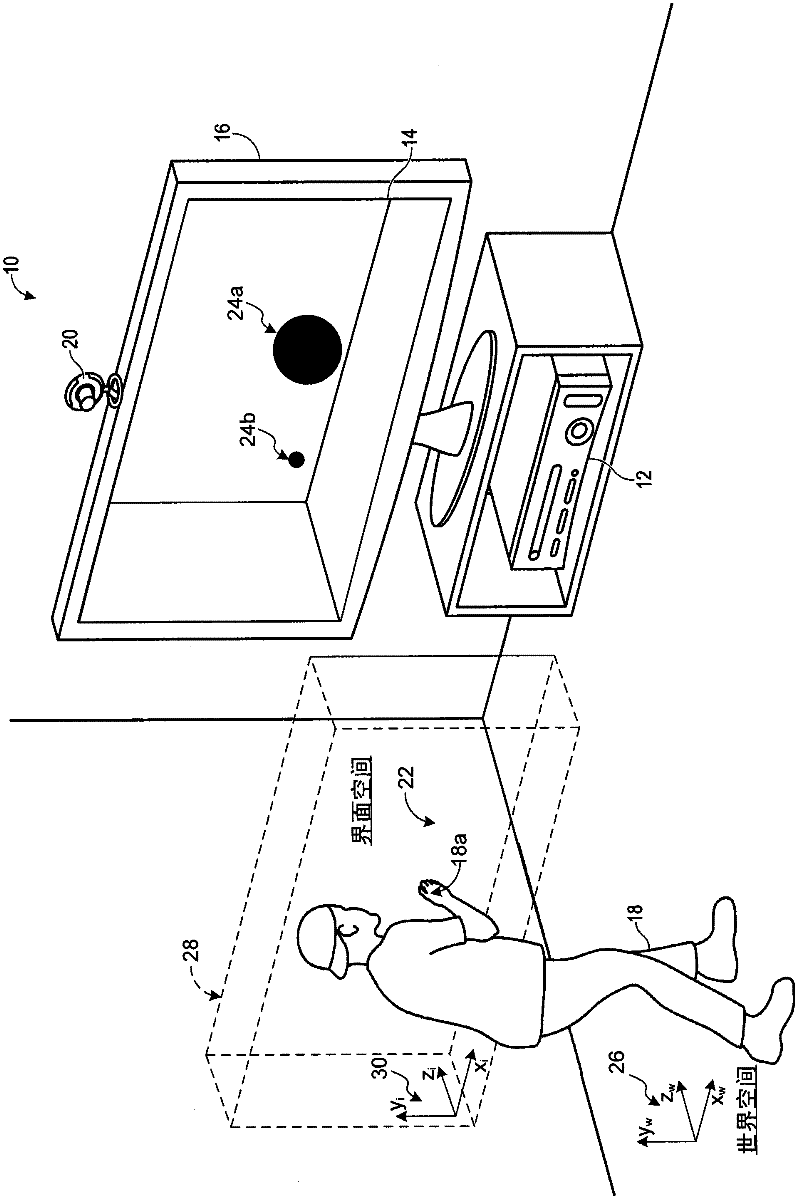
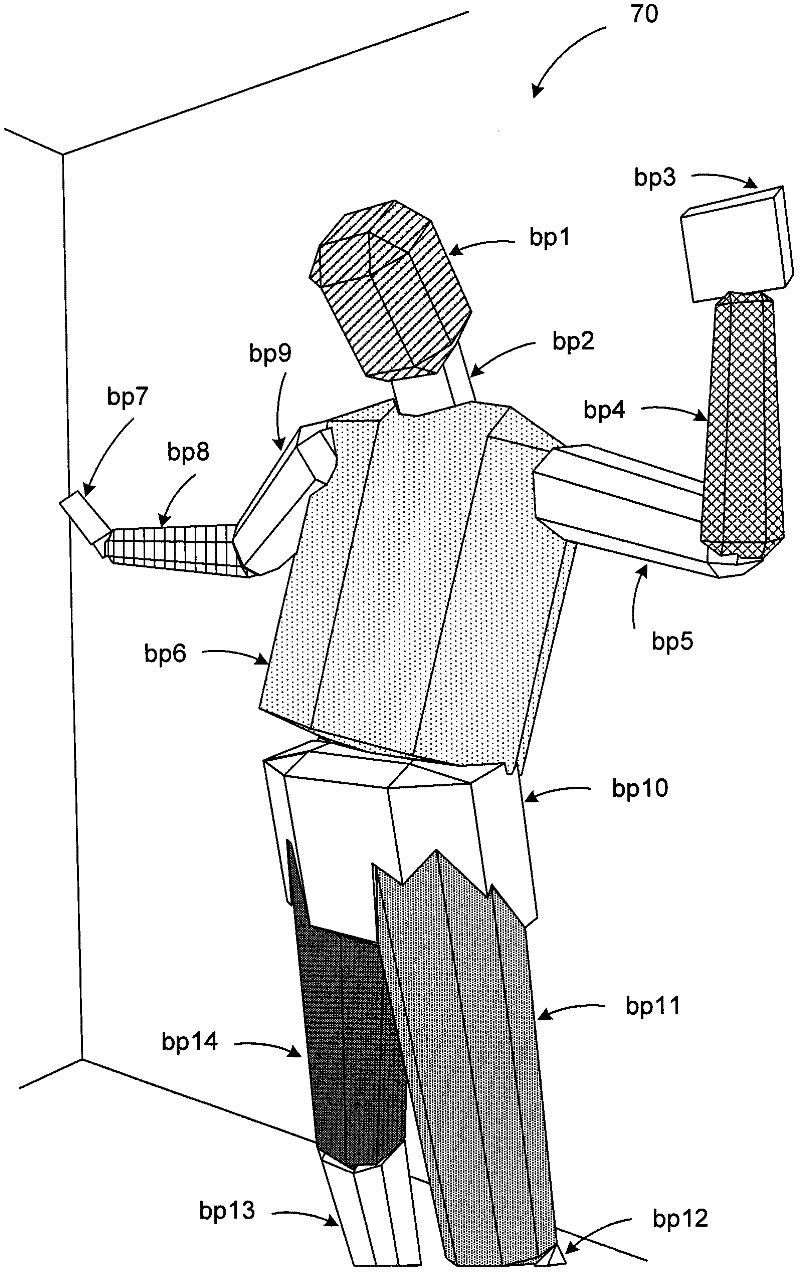
Virtual desktop coordinate transformation
ActiveCN102449577AInput/output for user-computer interactionVideo gamesImaging analysisComputing systems
A computing system includes a depth image analysis module to track a world-space pose of a human in a fixed, world-space coordinate system. The computing system further includes an interaction module to establish a virtual interaction zone with a movable, interface-space coordinate system that tracks the human and moves relative to the fixed, world-space coordinate system. The computing system also includes a transformation module to transform a position defined in the fixed, world-space coordinate system to a position defined in the movable, interface-space coordinate system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Object rendering method and device, storage medium and electronic device
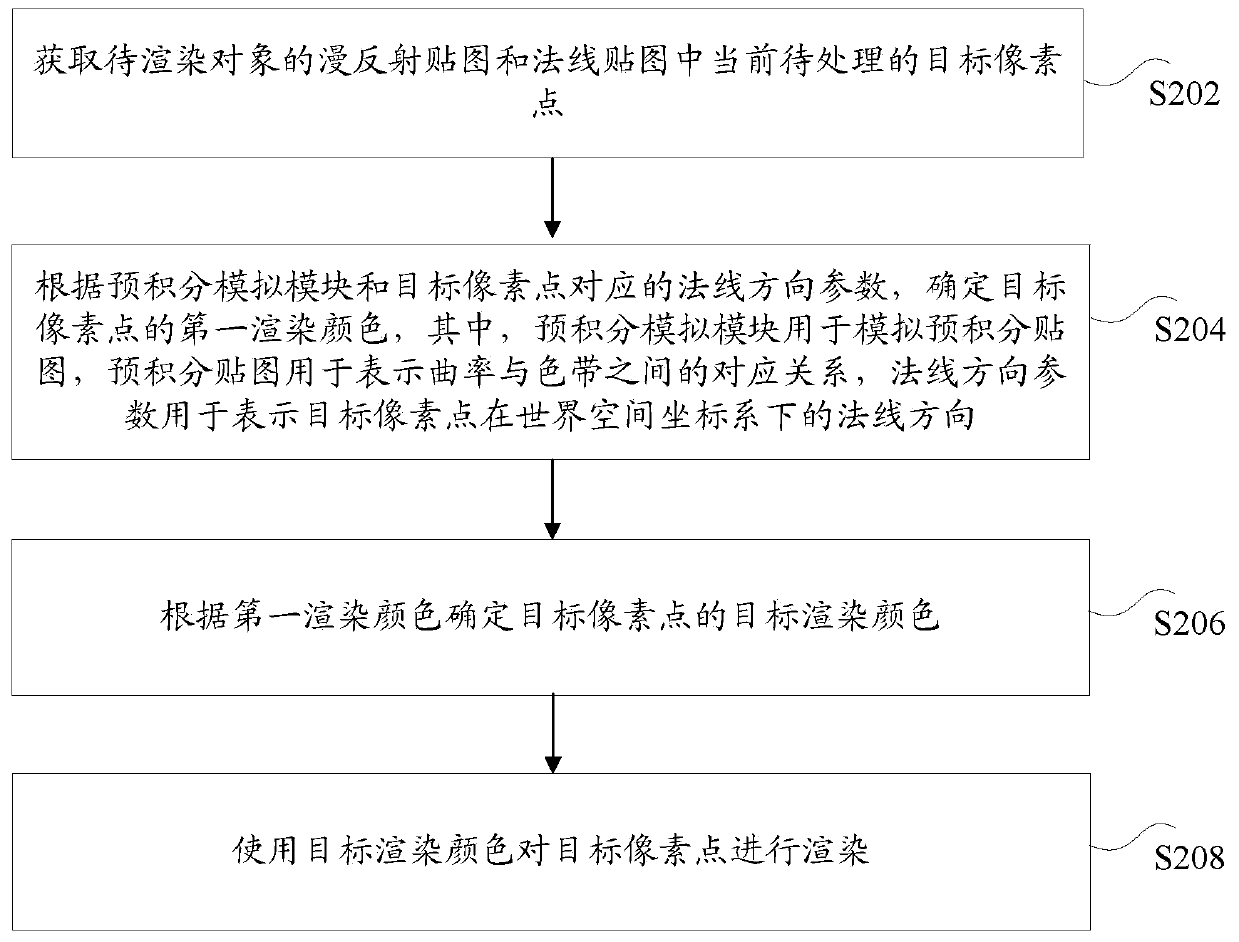
ActiveCN111009026AImprove efficiencyAvoid calculationVideo gamesImage generationPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an object rendering method and device, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a target pixel point to be processed currently ina diffuse reflection map and a normal map of a to-be-rendered object; according to normal direction parameters corresponding to a pre-integration simulation module and the target pixel point, determining the first rendering color of the target pixel point, the pre-integration simulation module being used for simulating a pre-integration map, the pre-integration map being used for representing a corresponding relationship between curvature and a color band, and the normal direction parameter being used for representing a normal direction of the target pixel point in a world space coordinate system; and rendering the target pixel point by using the target rendering color. By the adoption of the technical scheme, the problem that in the prior art, expenditure is large in the role rendering process is solved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
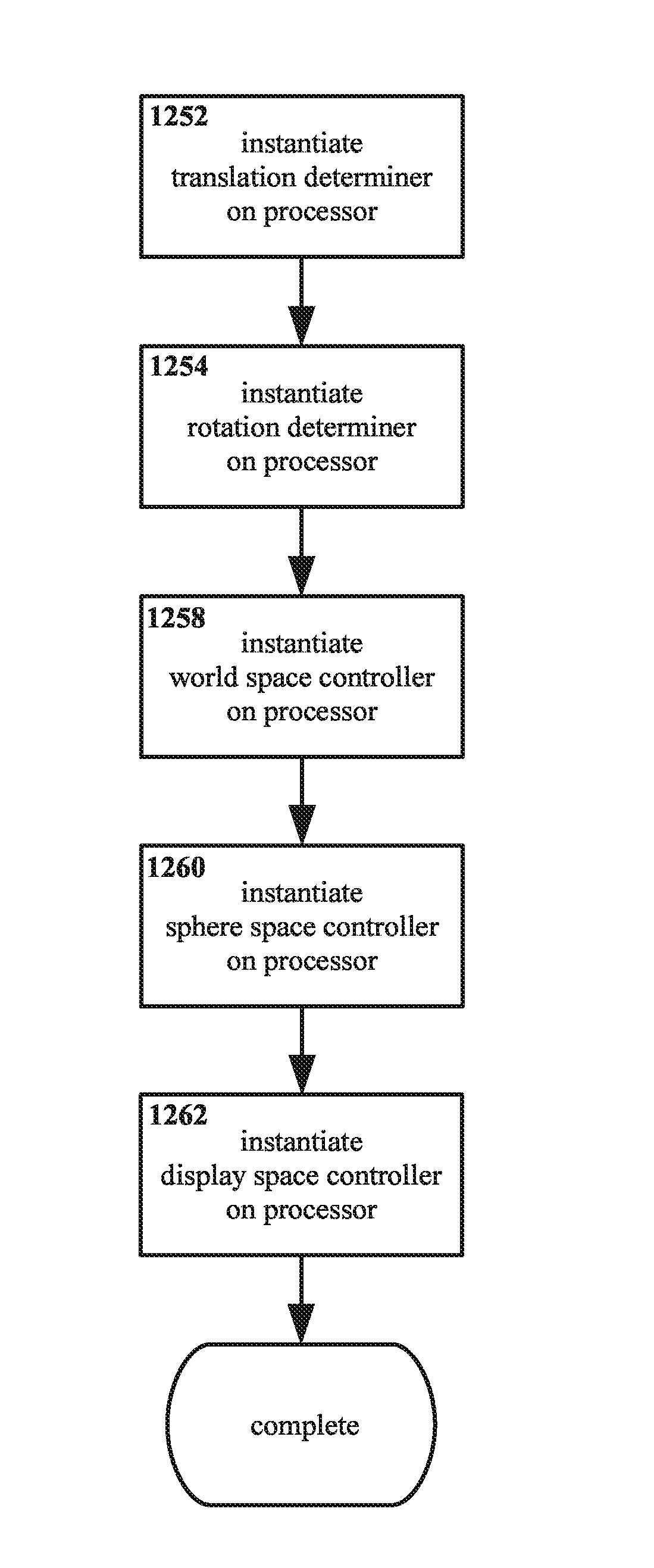
Method and apparatus for multiple mode interface
ActiveUS20150206351A1Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsVirtual realityWorld space
Each of a world space, a sphere space, and a display space are adapted to accept at least one entity therein, the entity being a virtual reality entity or an augmented reality entity. For world space, translation by a viewer substantially corresponds with translation with respect to world space, and rotation by the viewer substantially corresponds with rotation with respect to world space. For sphere space, translation by the viewer corresponds with substantially zero translation with respect to sphere space, and rotation by the viewer substantially corresponds with rotation with respect to sphere space. For display space, translation by the viewer corresponds with substantially zero translation with respect to display space, and rotation by the viewer corresponds with substantially zero rotation with respect to display space. Exceptions for translating, rotating, and / or resizing any of world space, sphere space, and display space may be invoked.
Owner:WEST TEXAS TECH PARTNERS LLC
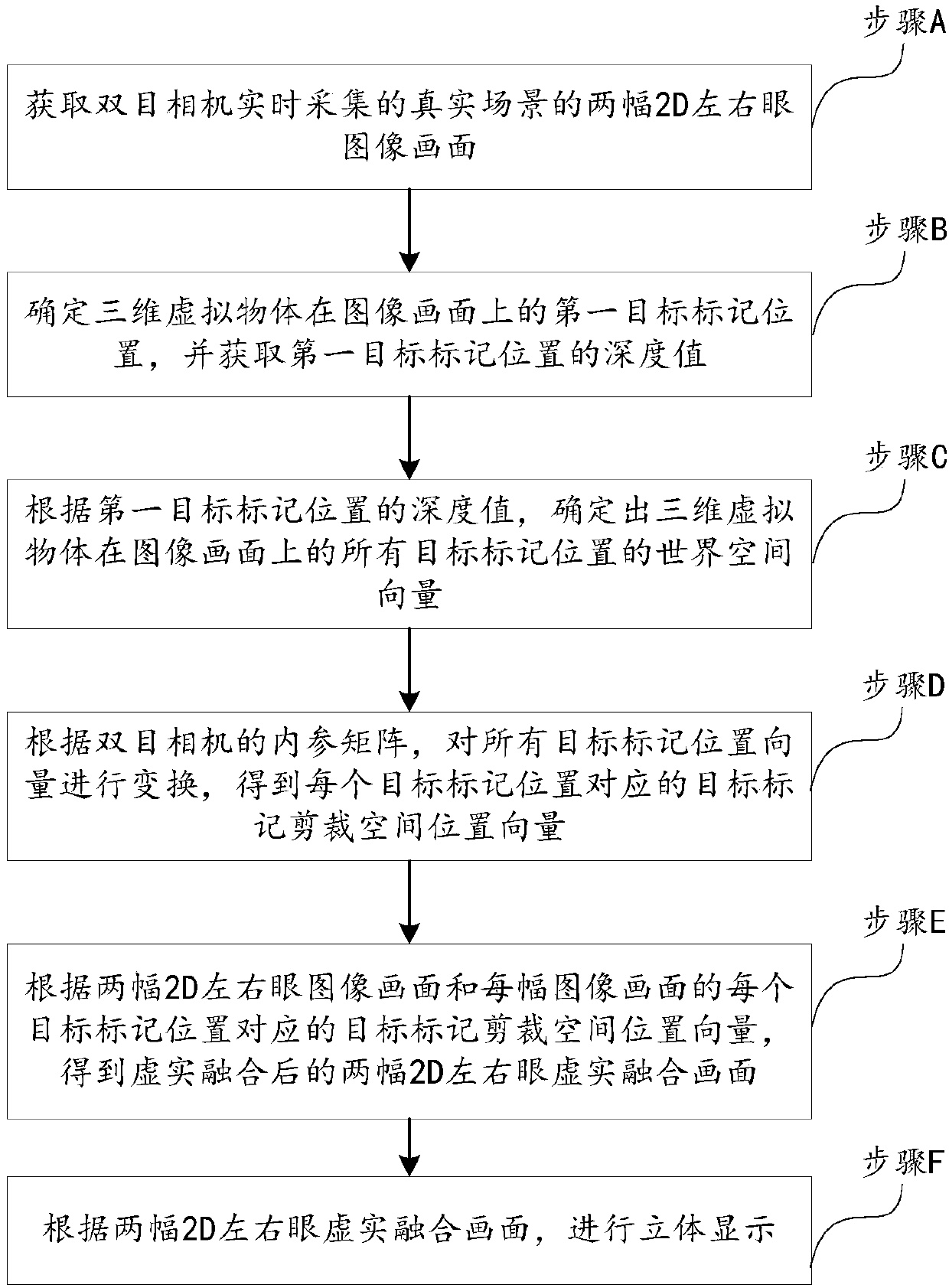
A method and a device for performing 3D fusion display on a real scene and a virtual object
InactiveCN109598796AImprove experienceEasy to integrateInput/output for user-computer interactionImage data processingReal time acquisitionWorld space
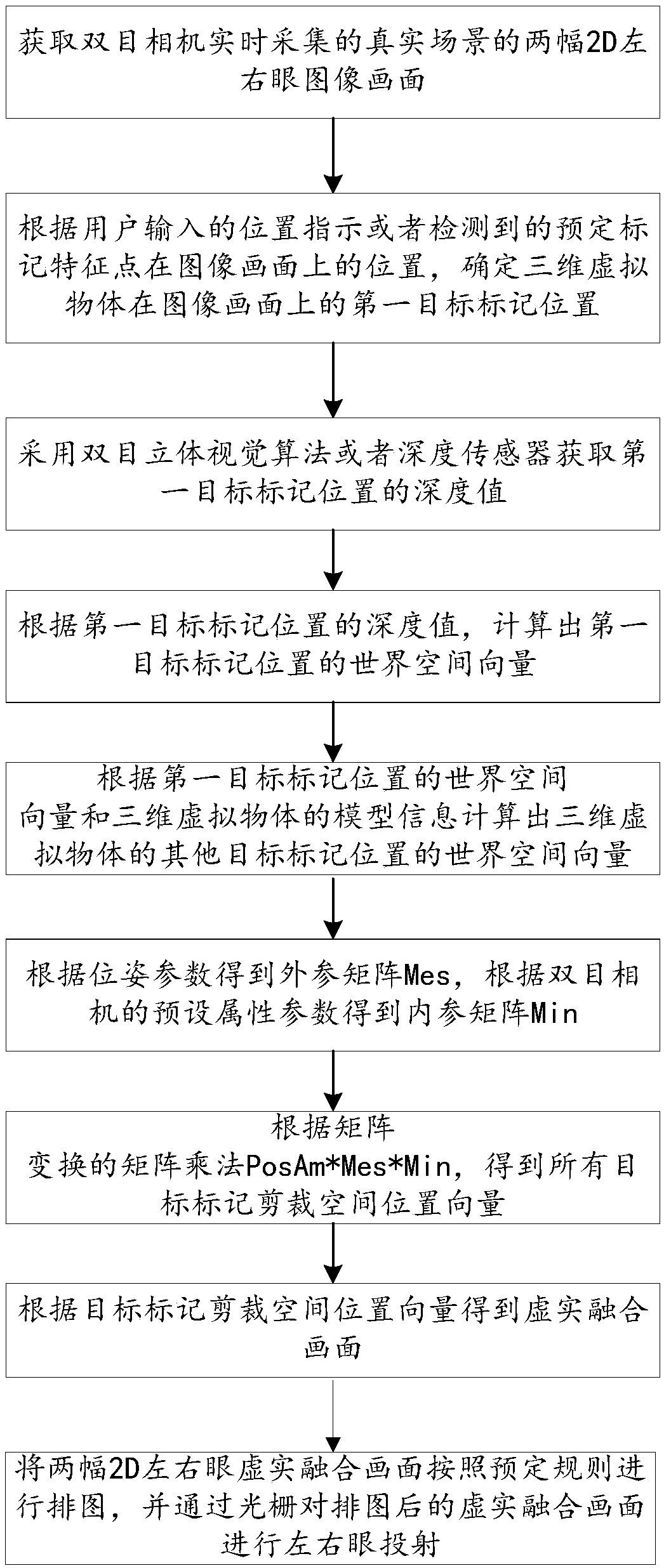
The invention discloses a method and a device for carrying out 3D fusion display on a real scene and a virtual object. The method comprises the steps: obtaining two 2D left-eye and right-eye image images, collected by a binocular camera in real time, of a real scene; Determining a first target mark position of the three-dimensional virtual object on the image picture, and obtaining a depth value of the first target mark position; Determining world space vectors of all the target mark positions of the three-dimensional virtual object on the image according to the depth value of the first targetmark position; Transforming the world space vectors of all the target mark positions according to the internal parameter matrix and the external parameter matrix of the binocular camera to obtain a target mark clipping space position vector corresponding to each target mark position; Cutting a space position vector according to the two 2D left-right eye image images and the target mark corresponding to each target mark position to obtain two 2D left-right eye virtual-real fusion images after virtual-real fusion; And performing three-dimensional display according to the two 2D left-right eye virtual-real fusion images.
Owner:SUPERD CO LTD
Mapping application for rendering pixel imagery
ActiveUS7379063B2Reduce the possibilityExtension of timeGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsReal time navigationTransformation algorithm
A mapping application relies on a modified affine transformation algorithm to provide near real-time navigation of imagery, track-up capability and integration of segment and picture data. The affine transformation is modified to map a “world space” comprised of a plurality of pixel maps onto a view port. The pixel data for the maps is preferably stored in vertical strips of memory to reduce the likelihood of cache misses. The mapping application is most useful for rendering pixel imagery on a platform with limited processing power, limited memory and small display sizes, e.g., “hand held devices” such as a GPS handset, or Pocket PC.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Model-based recognition of objects using a calibrated image system
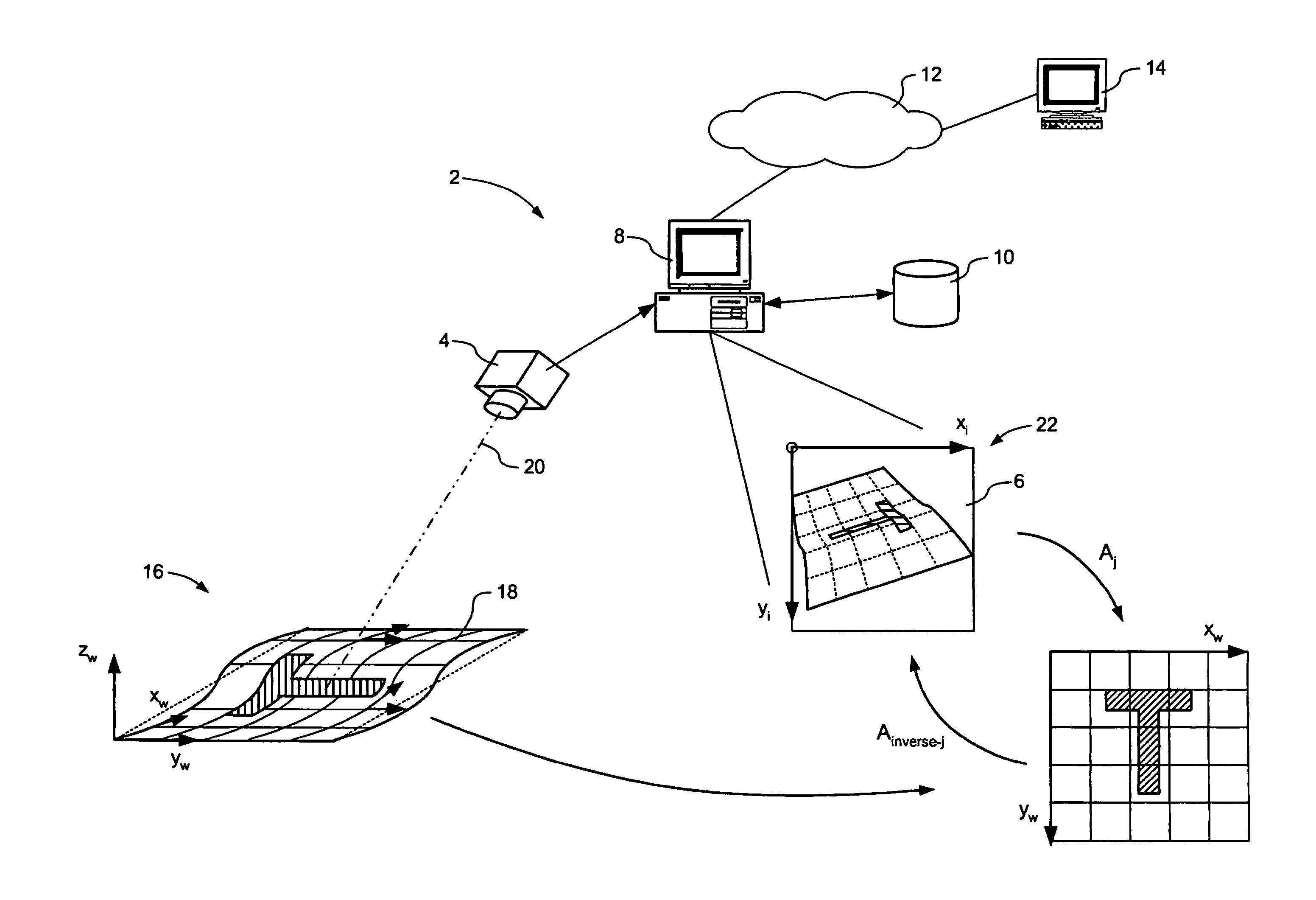
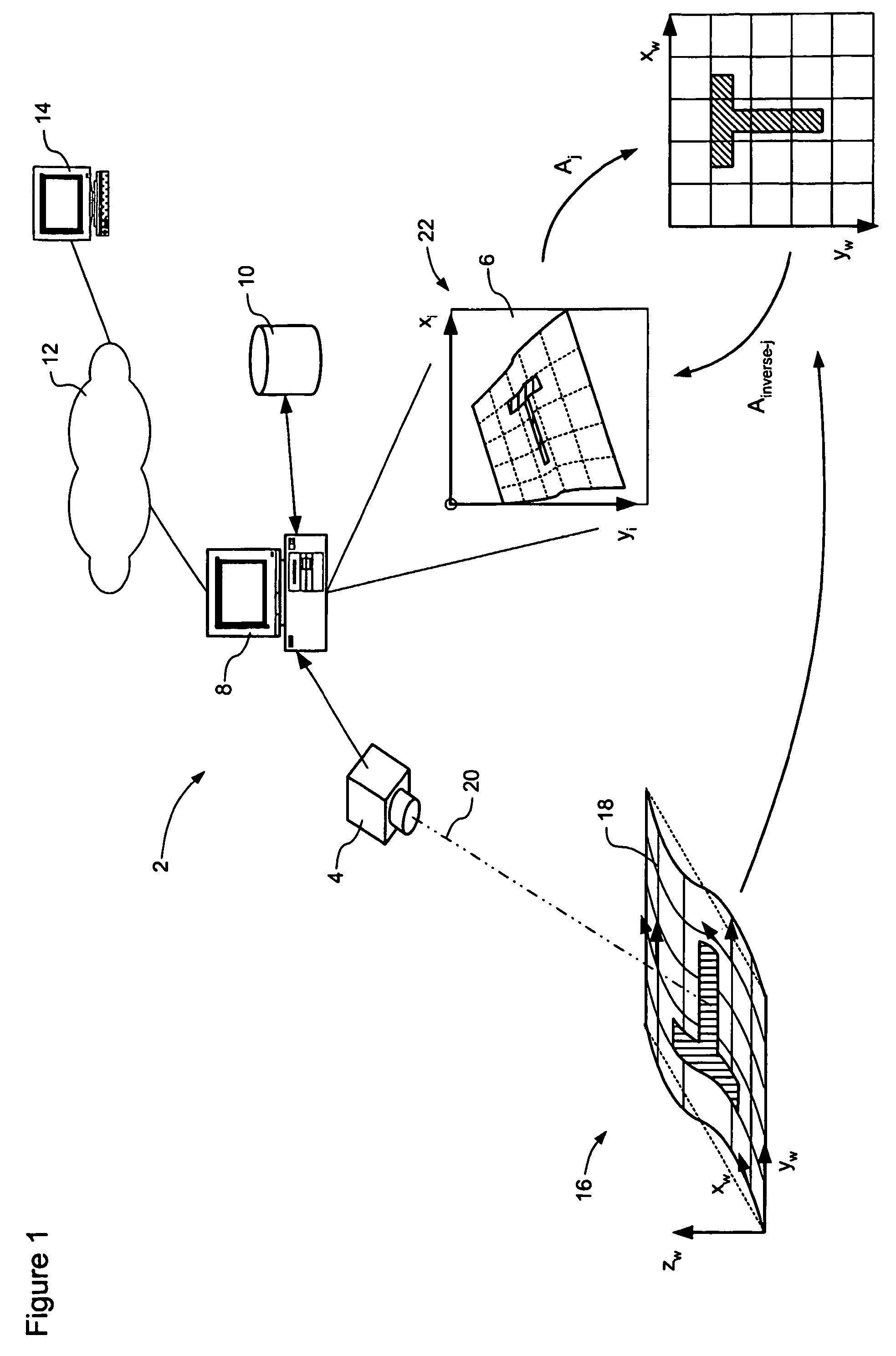
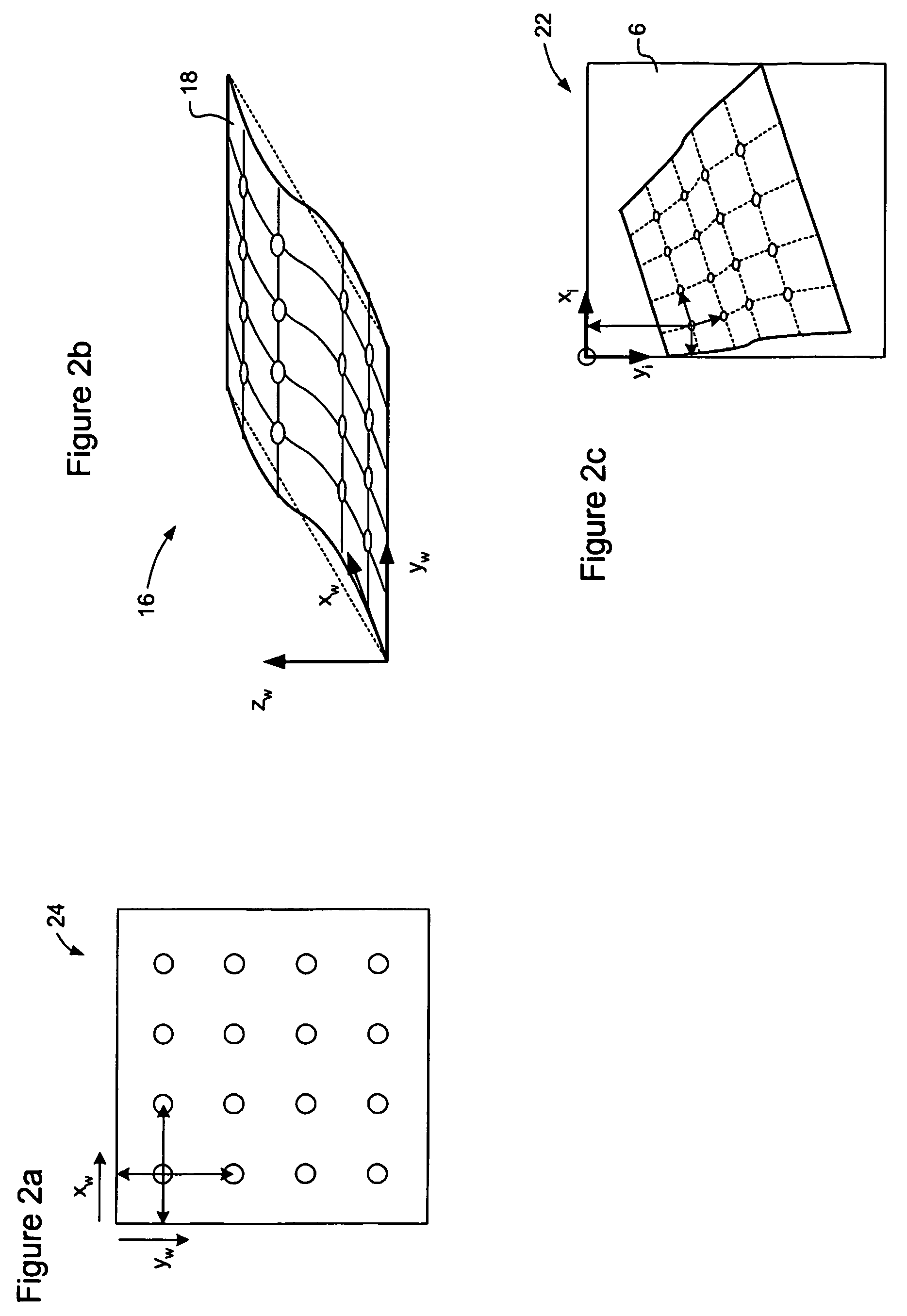
A model-based object recognition system operates to recognize an object on a predetermined world surface within a world space. An image of the object is acquired. This image is a distorted projection of the world space. The acquired image is processed to locate one or more local features of the image, with respect to an image coordinate system of the image. These local features are mapped a world coordinate system of the world surface, and matched to a model defined in the world coordinate system. Annotations can be arranged as desired relative to the object in the world coordinate system, and then inverse-mapped into the image coordinate system for display on a monitor in conjunction with the acquired image. Because models are defined in world coordinates, and pattern matching is also performed in world coordinates, one model definition can be used by multiple independent object recognition systems.
Owner:MATROX
Automatic bacterial colony screening method based on bacterial colony morphological characteristics
InactiveCN105420107AGuaranteed screening accuracyProof of accuracyMicroorganismsScreening methodComputer science
The invention discloses an automatic bacterial colony screening method based on bacterial colony morphological characteristics. The method includes the steps that firstly, a bacterial colony image is input; secondly, a conversion model of a bacterial colony image pixel coordinate system and a world space coordinate system is established; thirdly, the acquired bacterial colony image is preprocessed, and the preprocessed bacterial colony image is acquired; fourthly, the preprocessed bacterial colony image is subjected to binarization processing, a binary bacterial colony image is obtained and is segmented according to the communication principle, and a binary bacterial colony area is obtained after segmentation; fifthly, the morphological characteristics of the binary bacterial colony area are calculated; sixthly, bacterial colonies obtained in the fifth step are screened. According to the method, the bacterial colonies are screened according to the morphological characteristics of the individual bacterial colonies and are compared with a morphological characteristic sample base of excellent bacterial colonies so that the screening accuracy of the bacterial colonies can be guaranteed, universality is high, and meanwhile, bacterial colony screening accuracy and precision of the method are proved through a large number of bacterial colony screening experiments performed on a bacterial colony selector.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
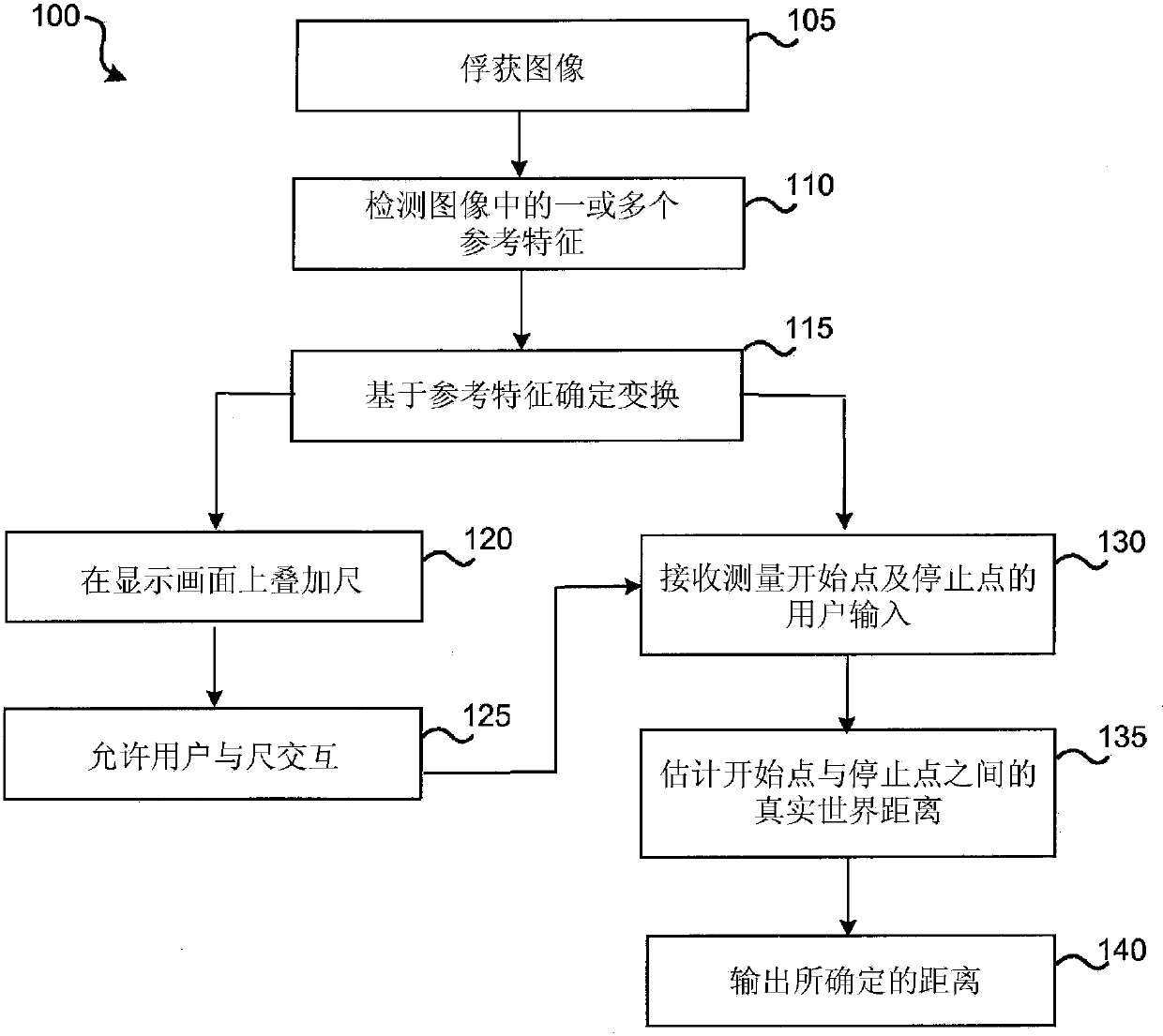
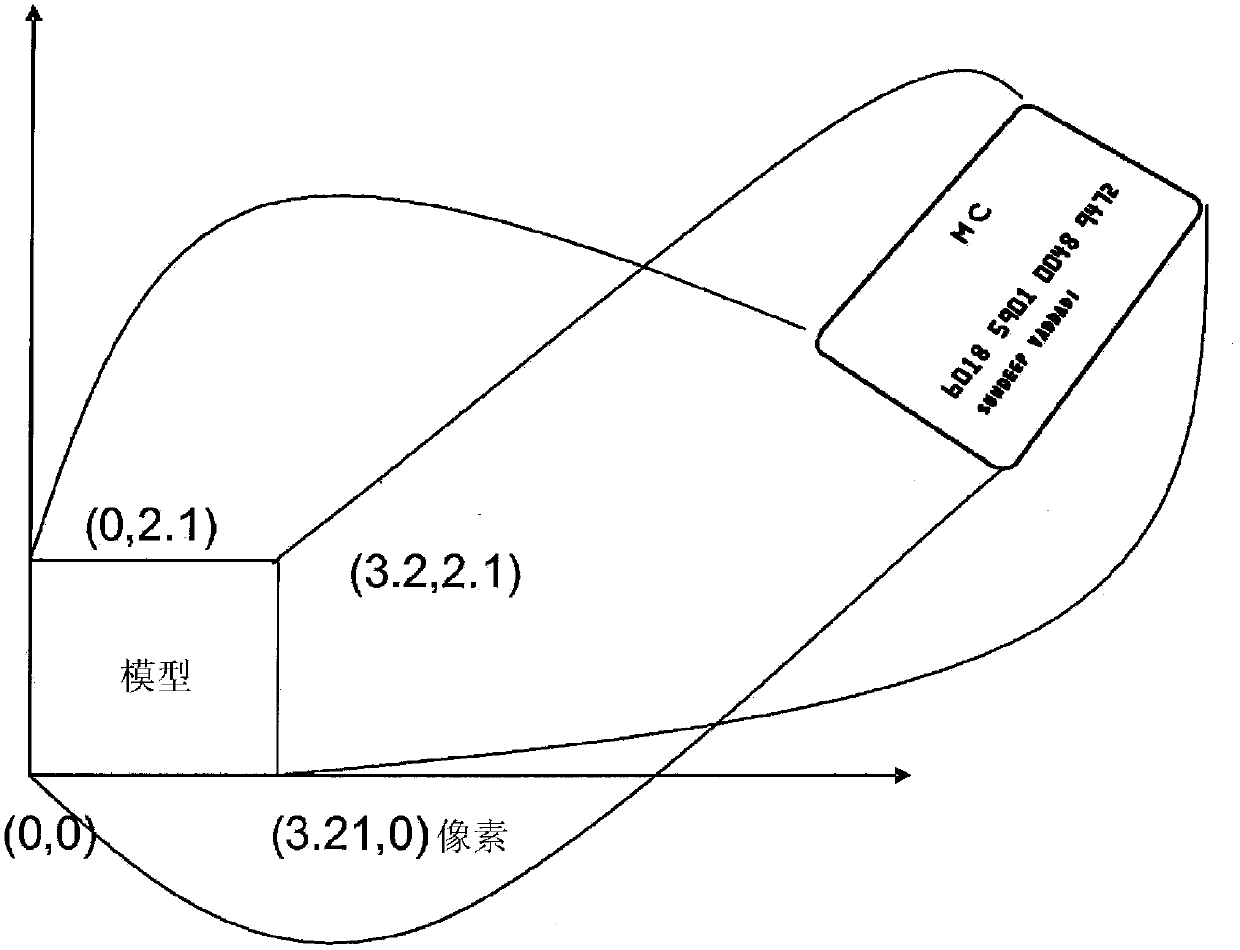
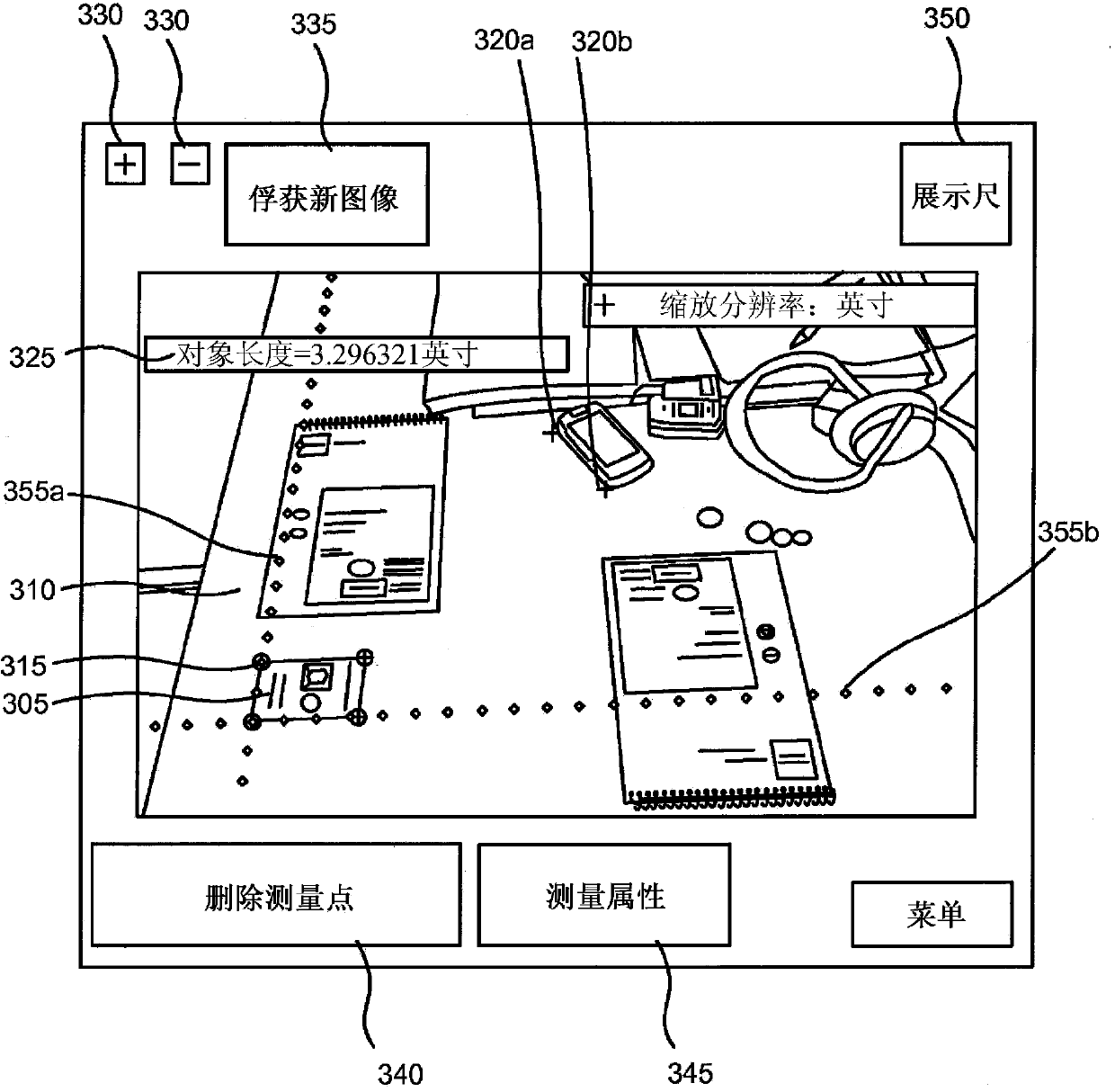
Virtual ruler
In some embodiments, first information indicative of an image of a scene is accessed. One or more reference features are detected, with the reference features being associated with a reference object in the image. A transformation between an image space and a real-world space is determined based on the first information. Second information indicative of input from a user is accessed, and identifies an image-space distance in the image space corresponding to a real-world distance of interest in the real-world space. The real-world distance of interest is then estimated based on the second information and the determined transformation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
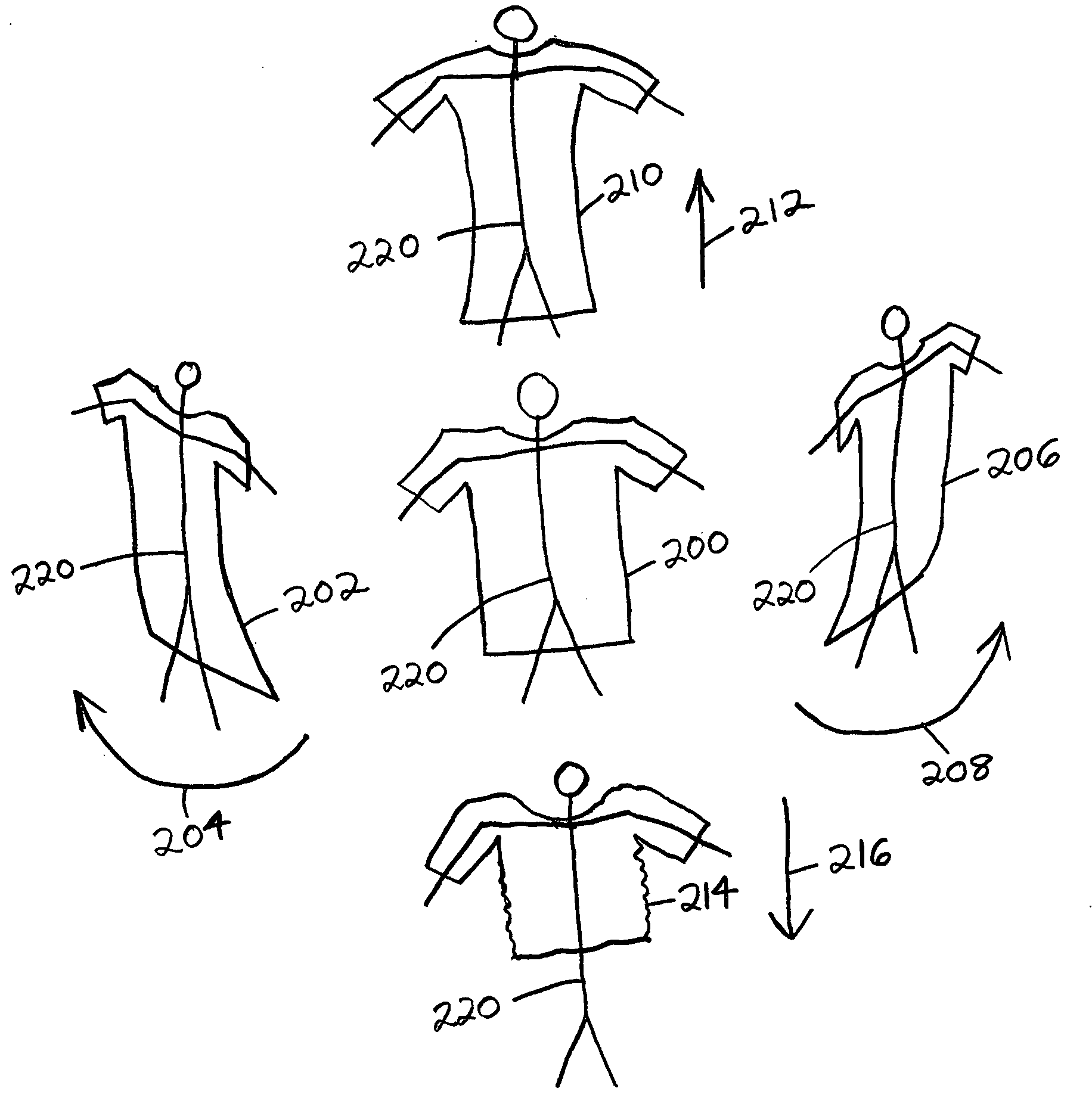
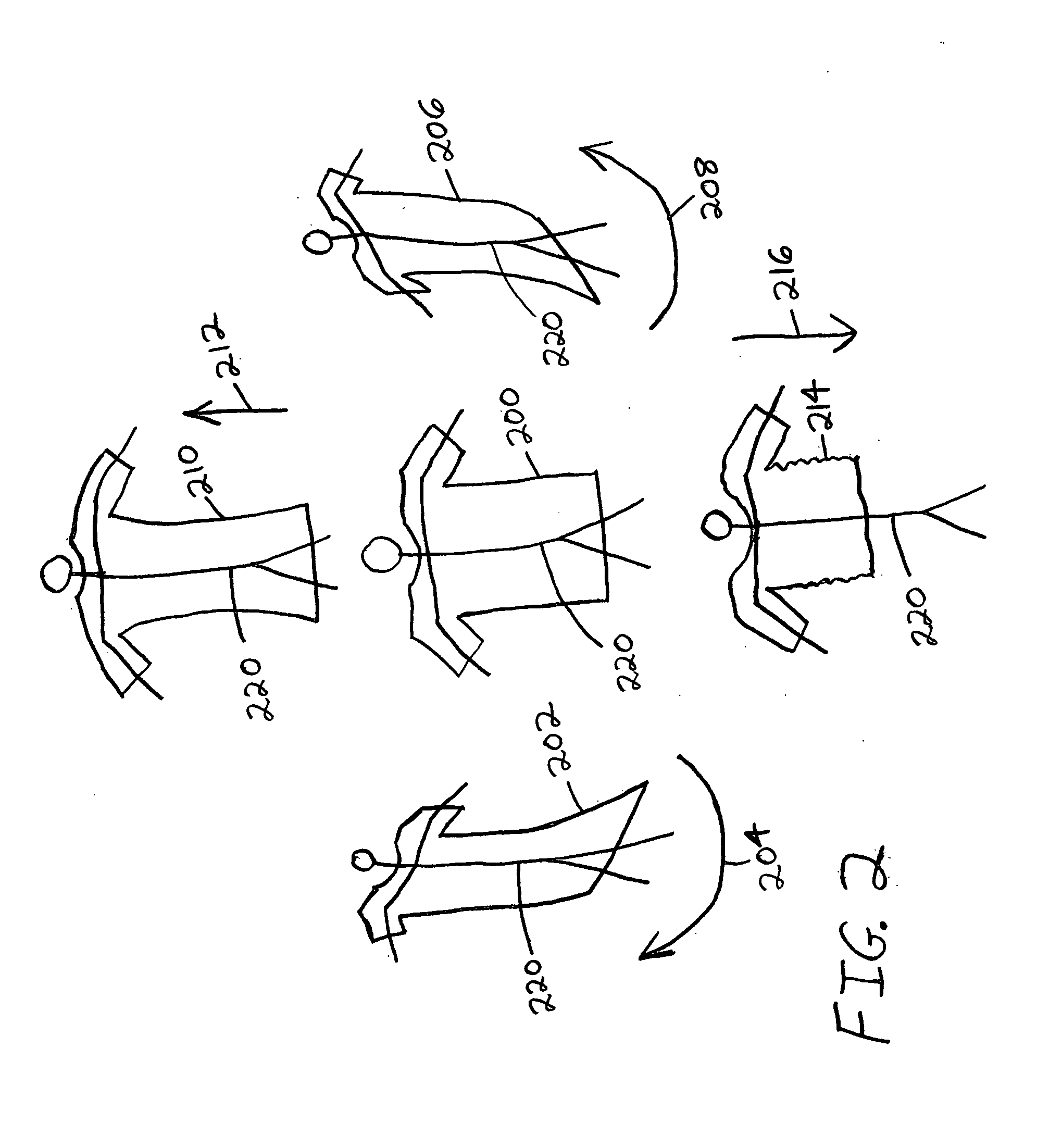
Polynomial encoding of vertex data for use in computer animation of cloth and other materials
An alternative to cloth simulation in which a plurality of different poses for a material are established, and then each component of each vertex position of the material is encoded into a polynomial by using corresponding vertices in the plurality of different poses for the material. The vertices are encoded relative to a neutral bind pose. The polynomial coefficients are calculated offline and then stored. At runtime, the poses are interpolated by using key variables which are input into the polynomials as different states, for example the turning speed of the player wearing the material, which may comprise a cloth jersey. The bind pose vertices are transformed into world space using the character skeleton. A smooth interpolation is achieved, and the polynomials can encode a large number of pose-meshes in a few constants, which reduces the amount of data that must be stored.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
Efficient model-based recognition of objects using a calibrated image system
InactiveUS20090268967A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern matchingModel matching
A model-based object recognition system operates to recognize an object on a predetermined world surface within a world space. An image of the object is acquired. This image is a distorted projection of the world space. The acquired image is processed to locate one or more local features of the image, with respect to an image coordinate system of the image. These local features are mapped a world coordinate system of the world surface, and matched to a model defined in the world coordinate system. Annotations can be arranged as desired relative to the object in the world coordinate system, and then inverse-mapped into the image coordinate system for display on a monitor in conjunction with the acquired image. Because models are defined in world coordinates, and pattern matching is also performed in world coordinates, one model definition can be used by multiple independent object recognition systems.
Owner:MATROX ELECTRONICS SYST LTD
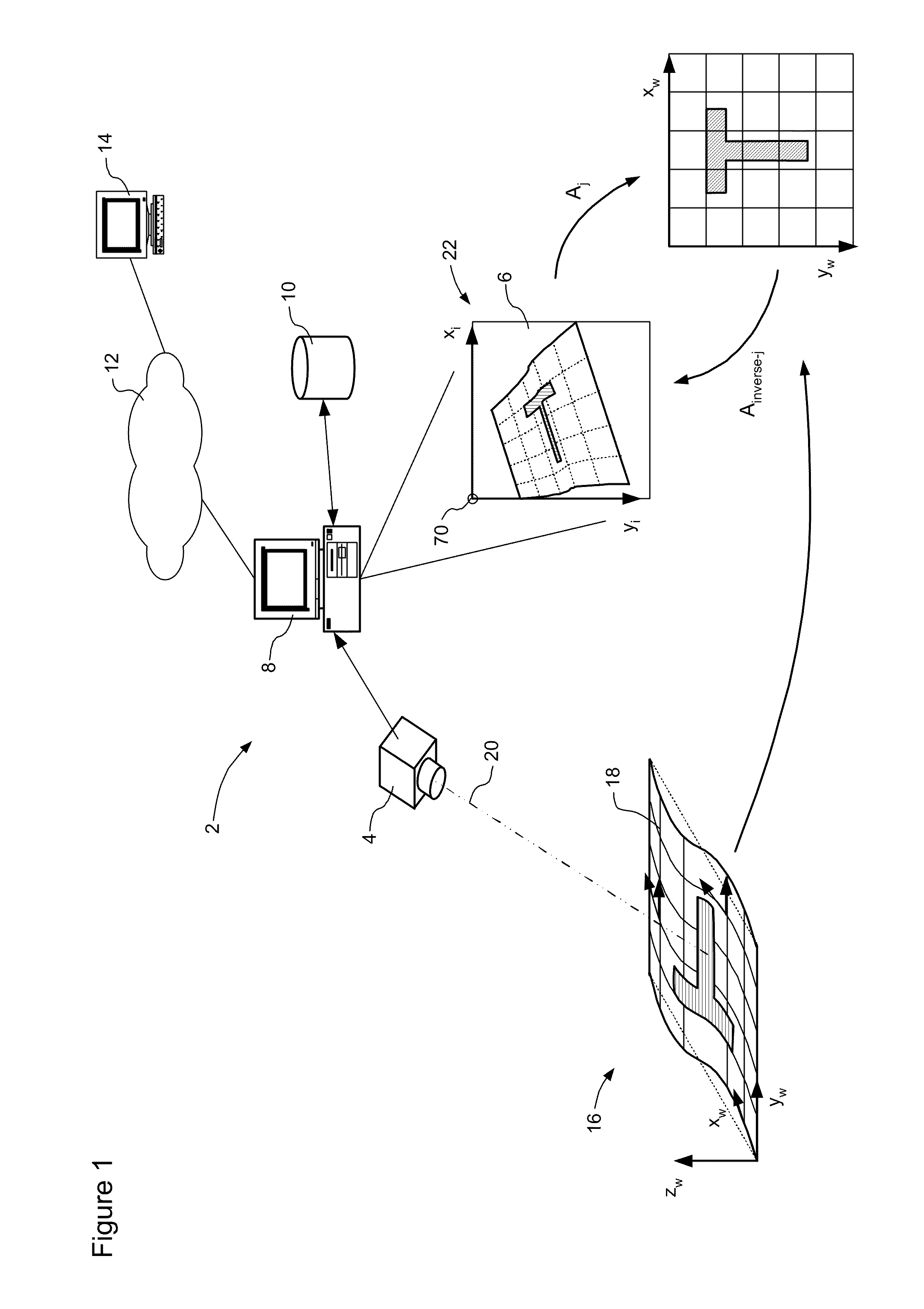
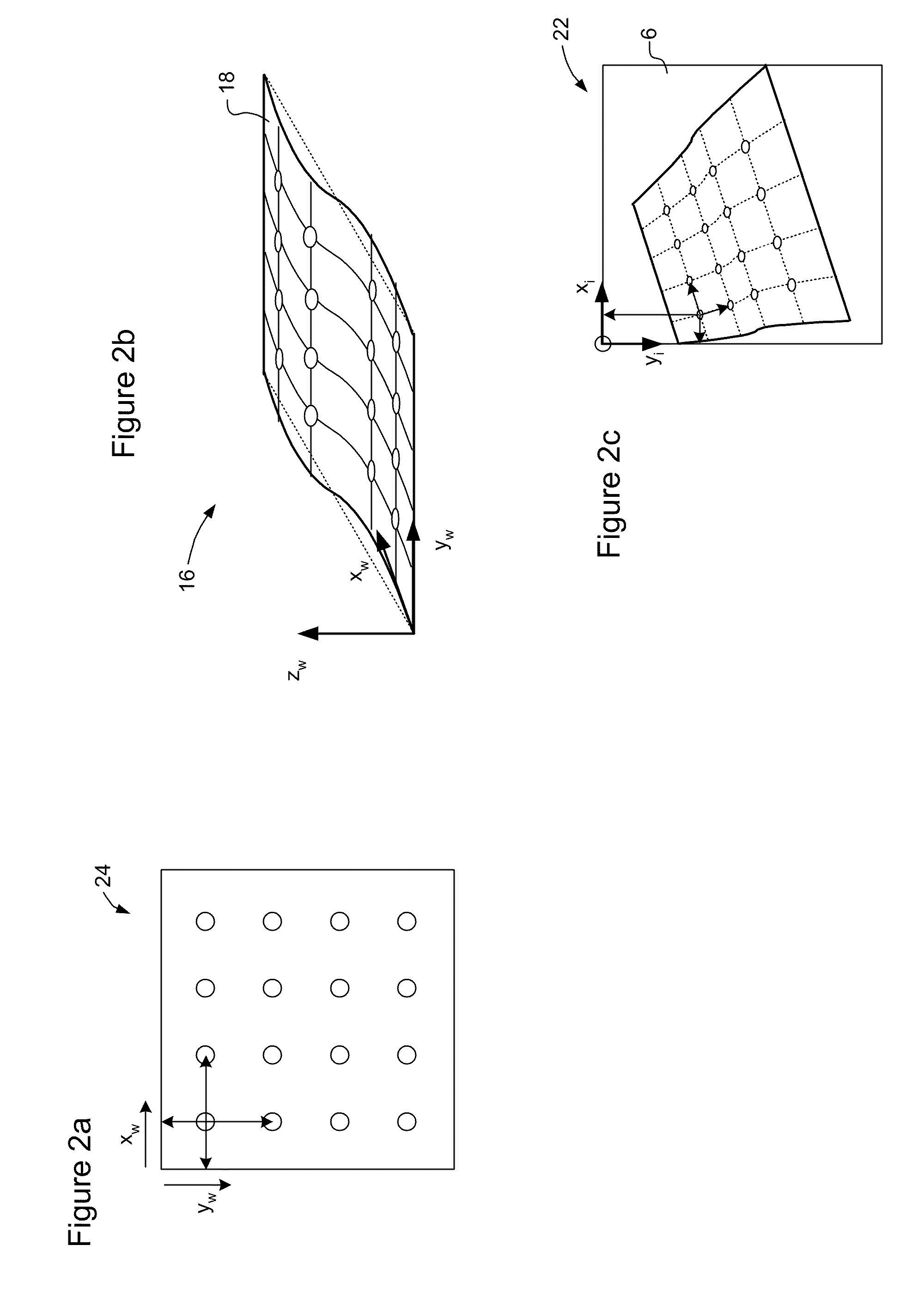
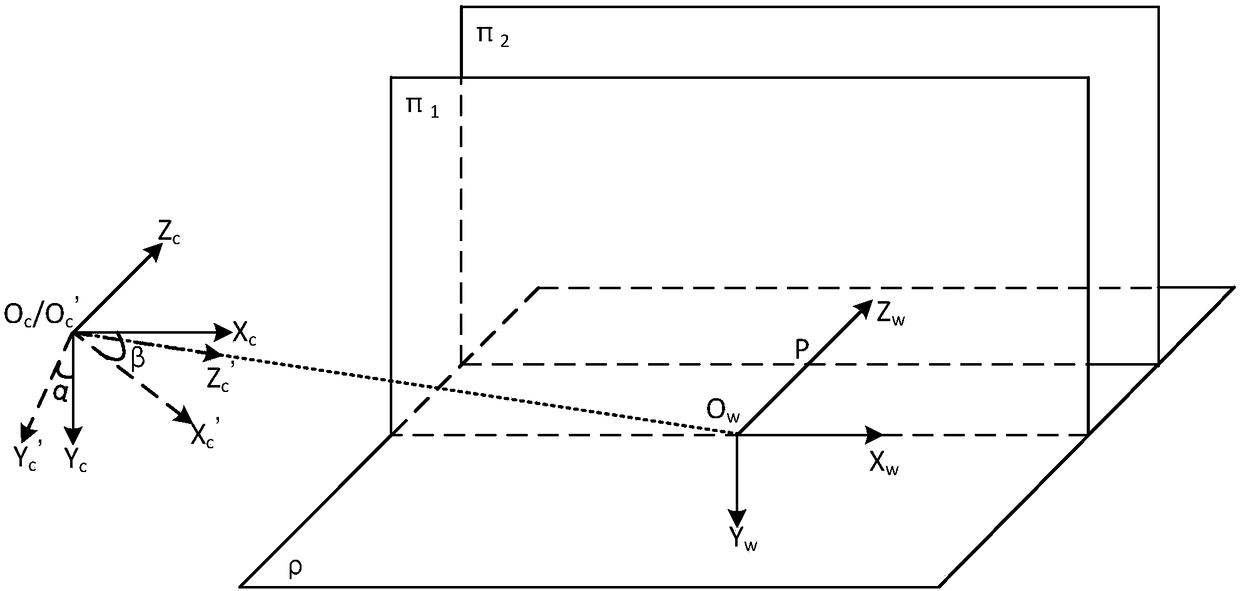
Image measurement method and system
ActiveCN108548485ARemove Transform Distortion EffectsQuick calibrationImage analysisPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryTest objectLaser beams
Owner:JINQIANMAO TECH CO LTD
3D asset inspection
InactiveUS20160249021A1Facilitating subsequent abilityTelevision system detailsColor television details3d sensorOdometry
Systems and methods for physical asset inspection are provided. According to one embodiment, a probe is positioned to multiple data capture positions with reference to a physical asset. For each position: odometry data is obtained from an encoder and / or an IMU; a 2D image is captured by a camera; a 3D sensor data frame is captured by a 3D sensor, having a view plane overlapping that of the camera; the odometry data, the 2D image and the 3D sensor data frame are linked and associated with a physical point in real-world space based on the odometry data; and switching between 2D and 3D views within the collected data is facilitated by forming a set of points containing both 2D and 3D data by performing UV mapping based on a known positioning of the camera relative to the 3D sensor.
Owner:CHARLES MACHINE WORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com