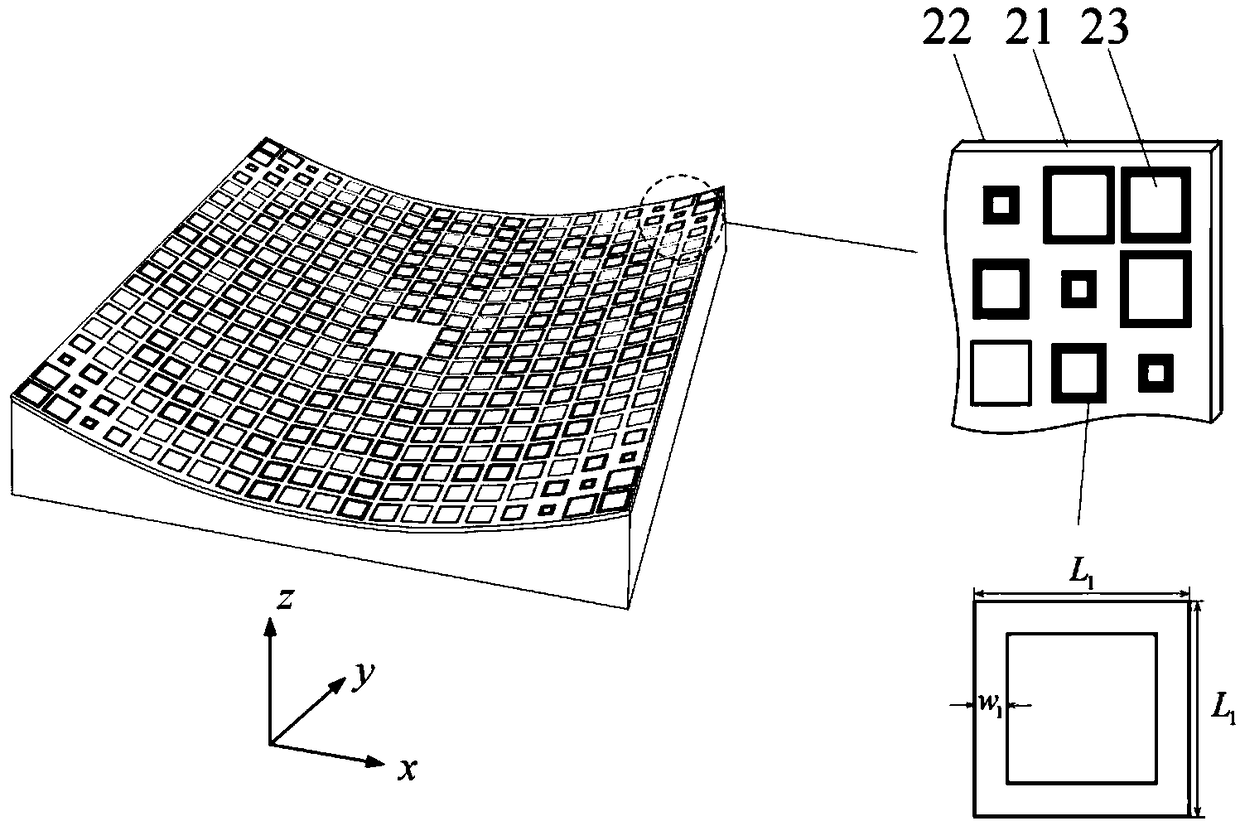
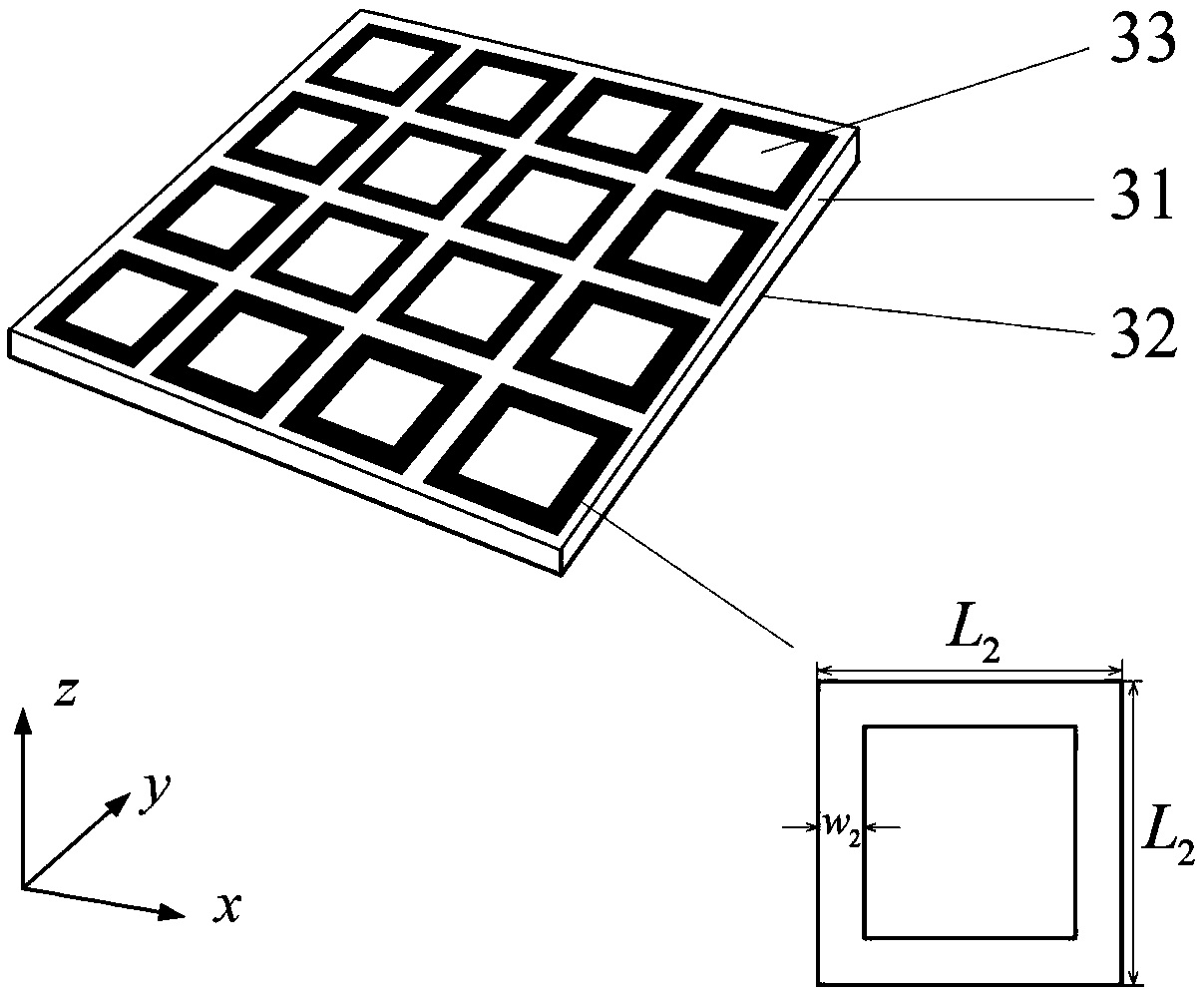
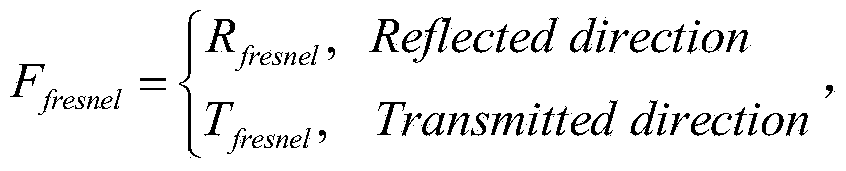
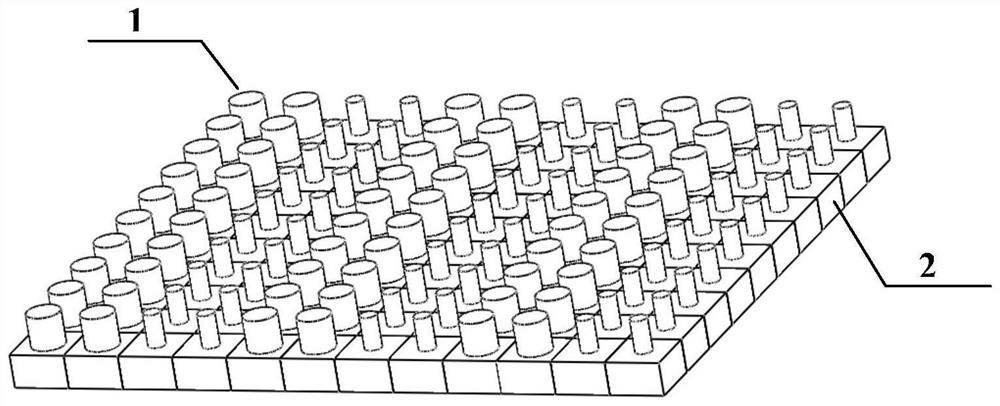
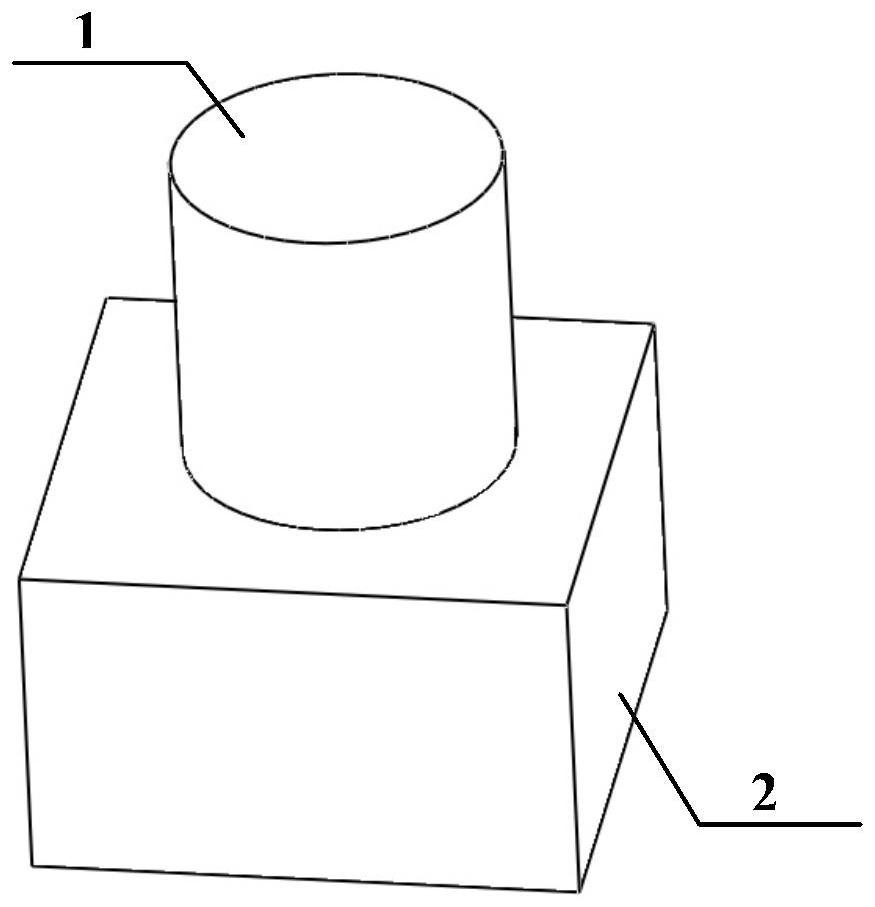
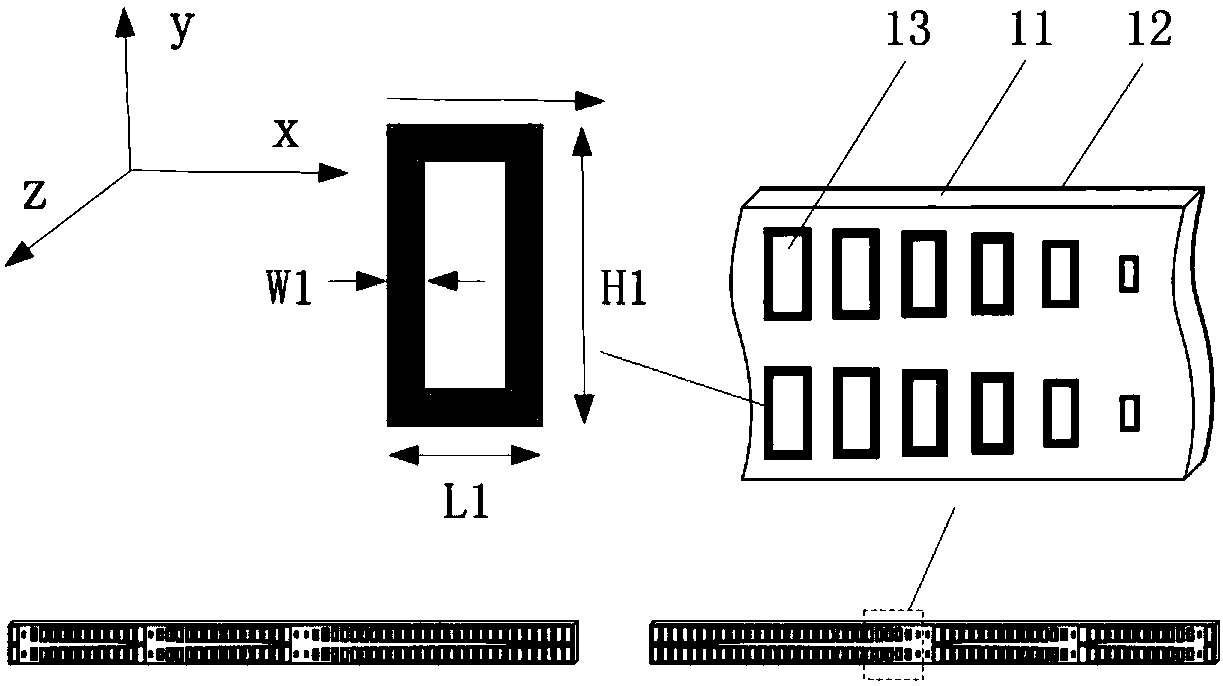
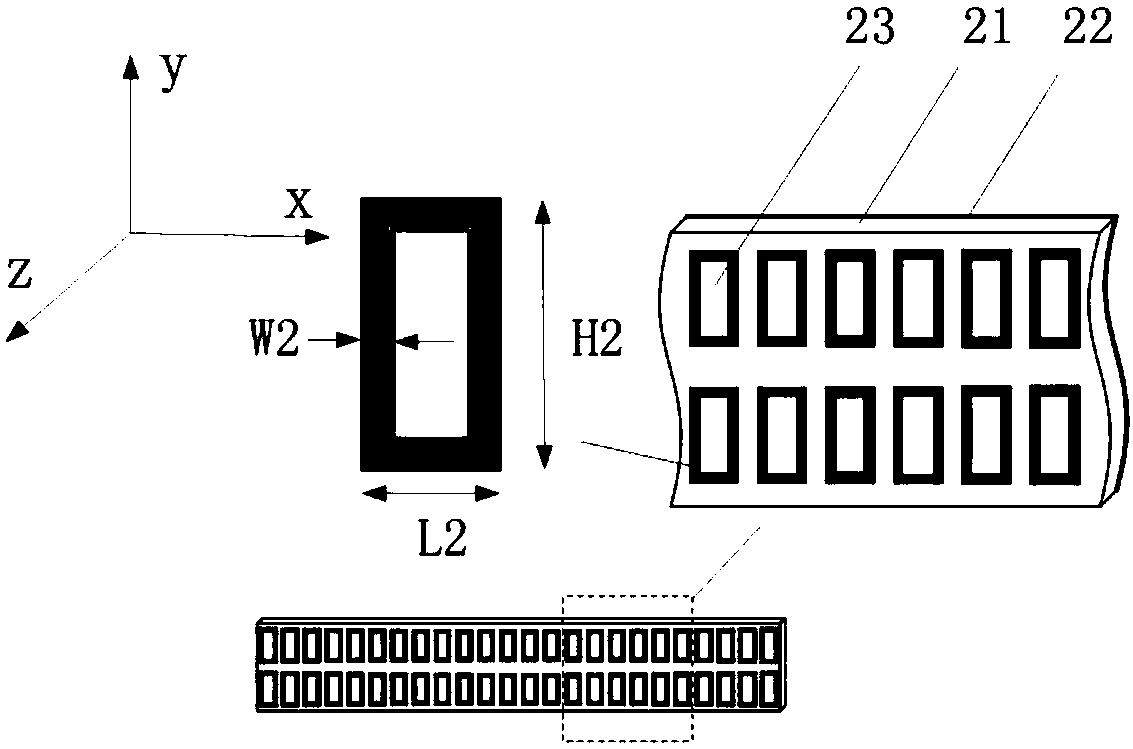
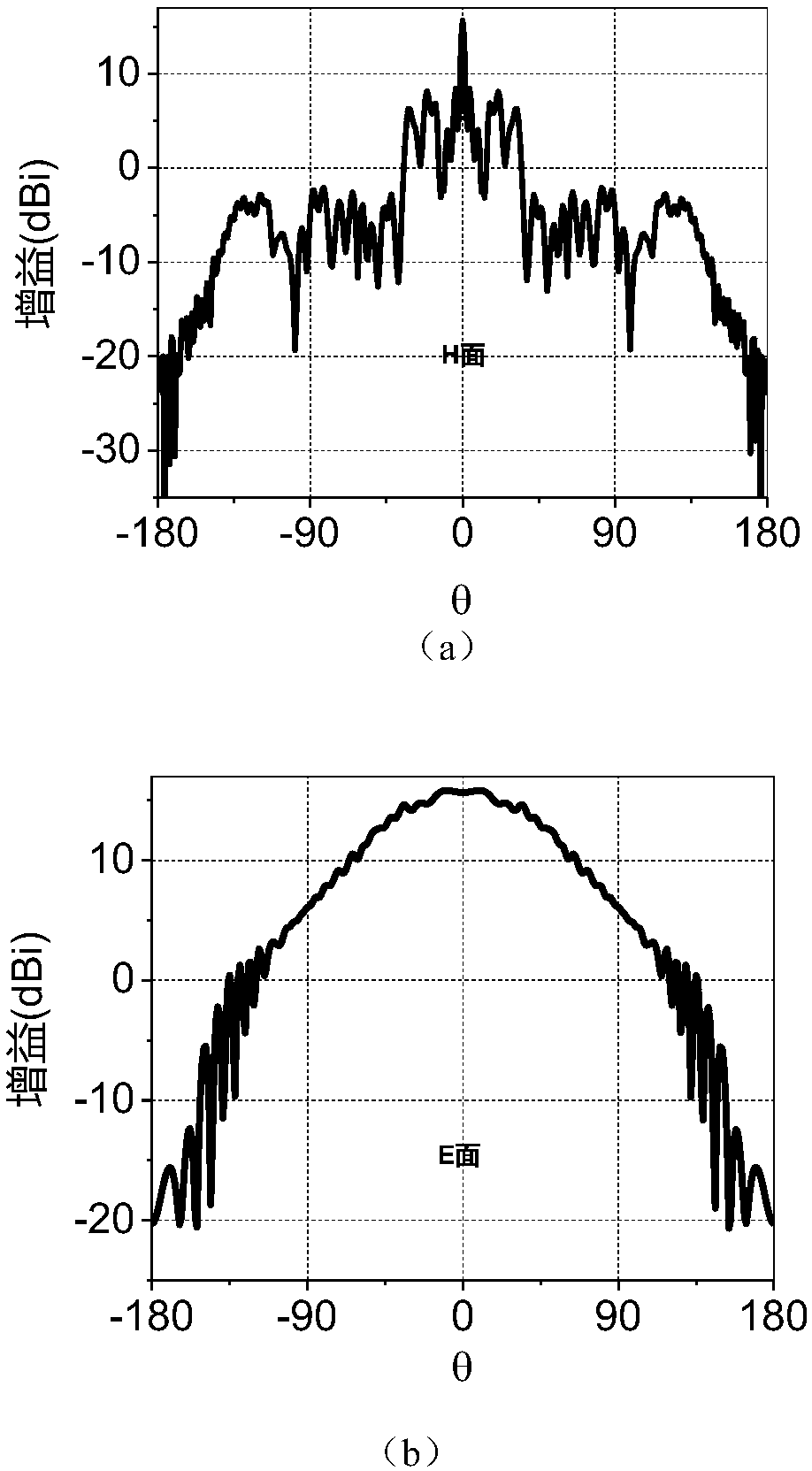
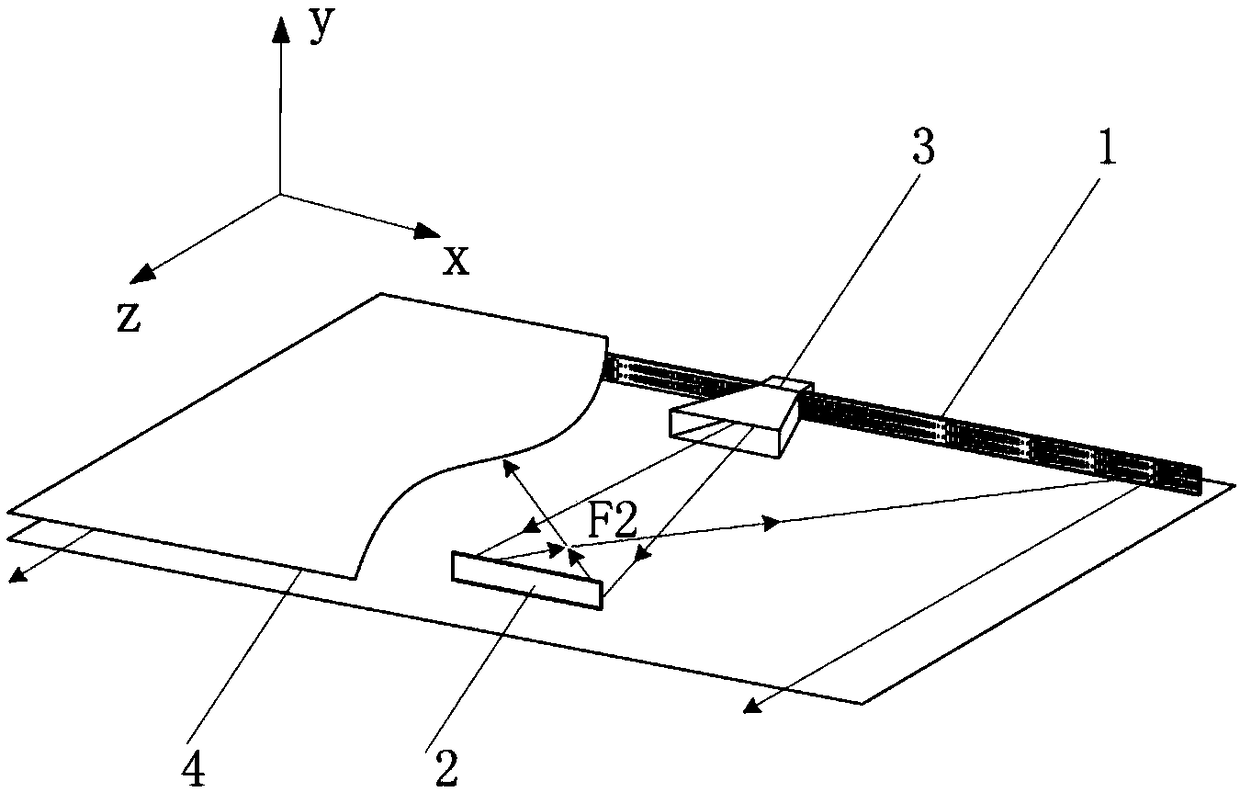
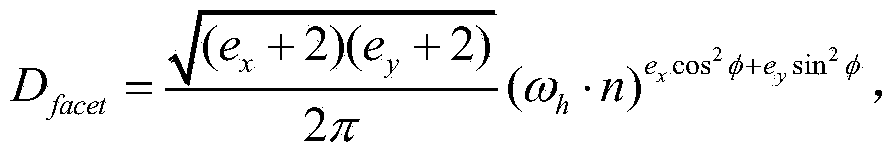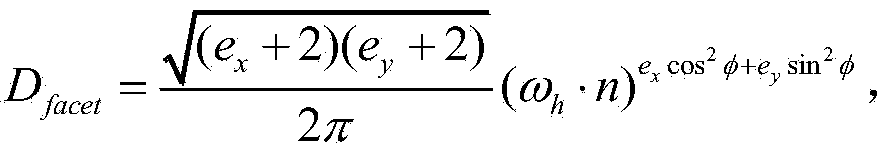Patents
Literature
68 results about "Snell's law" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
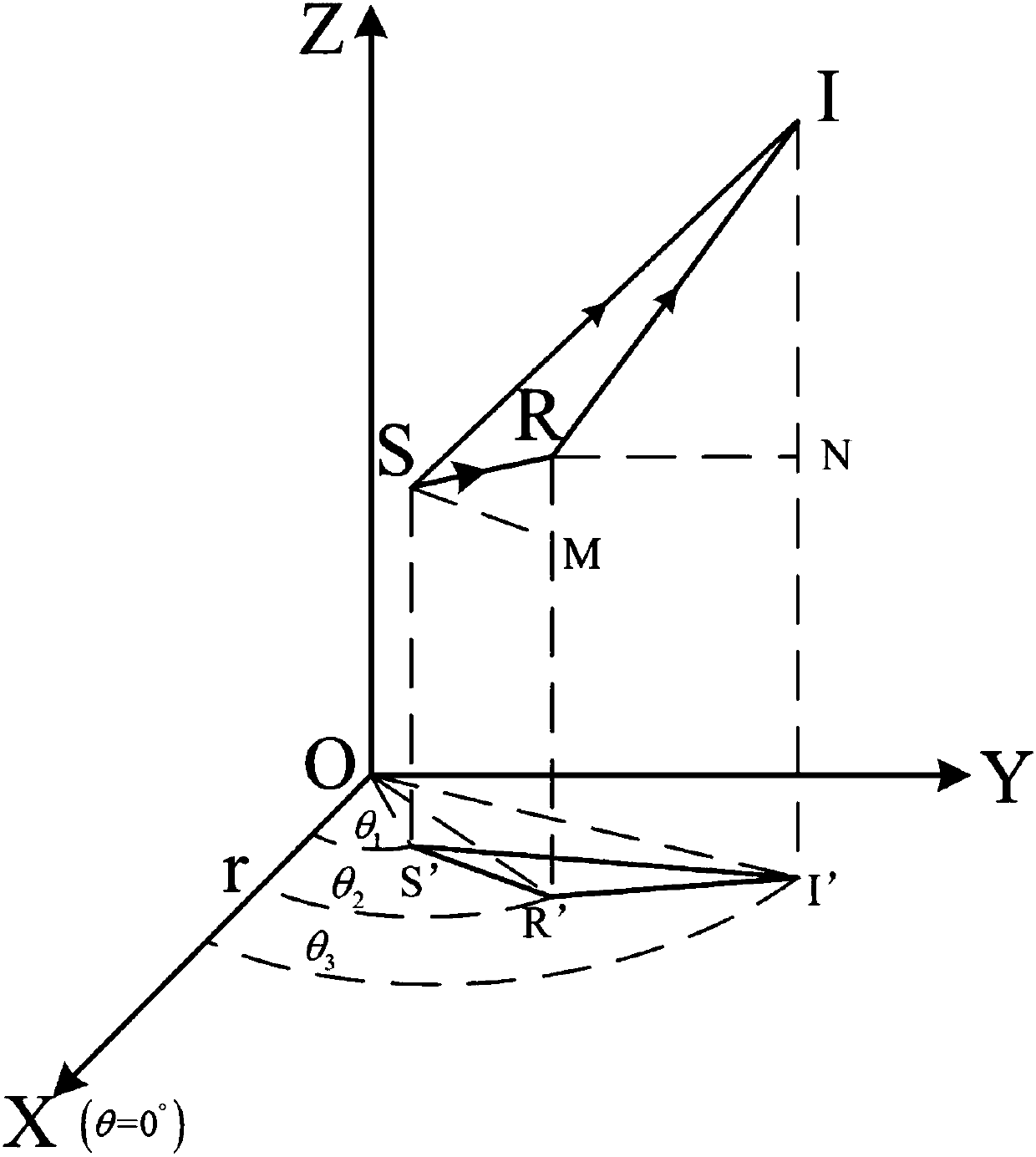
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material.
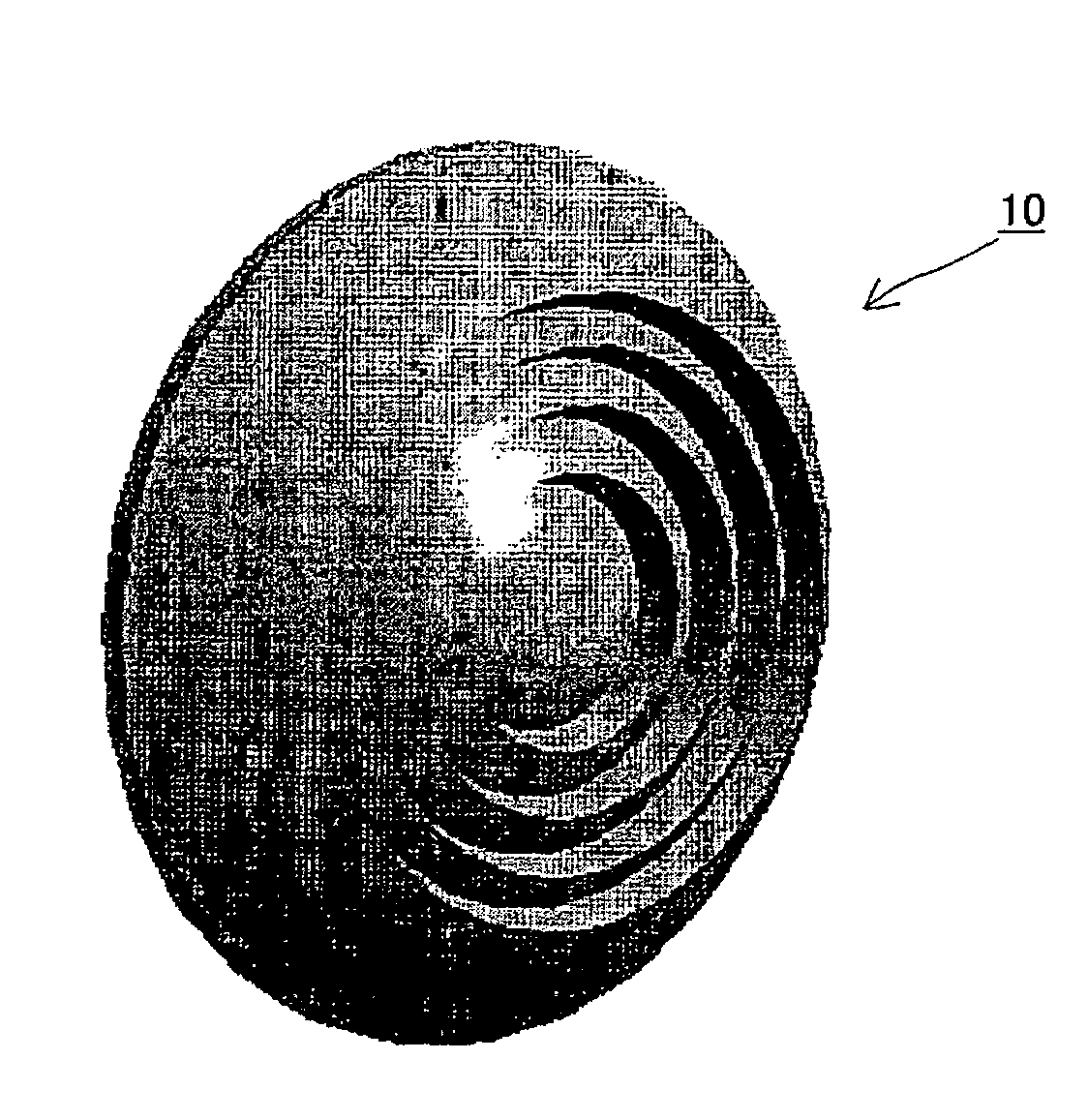
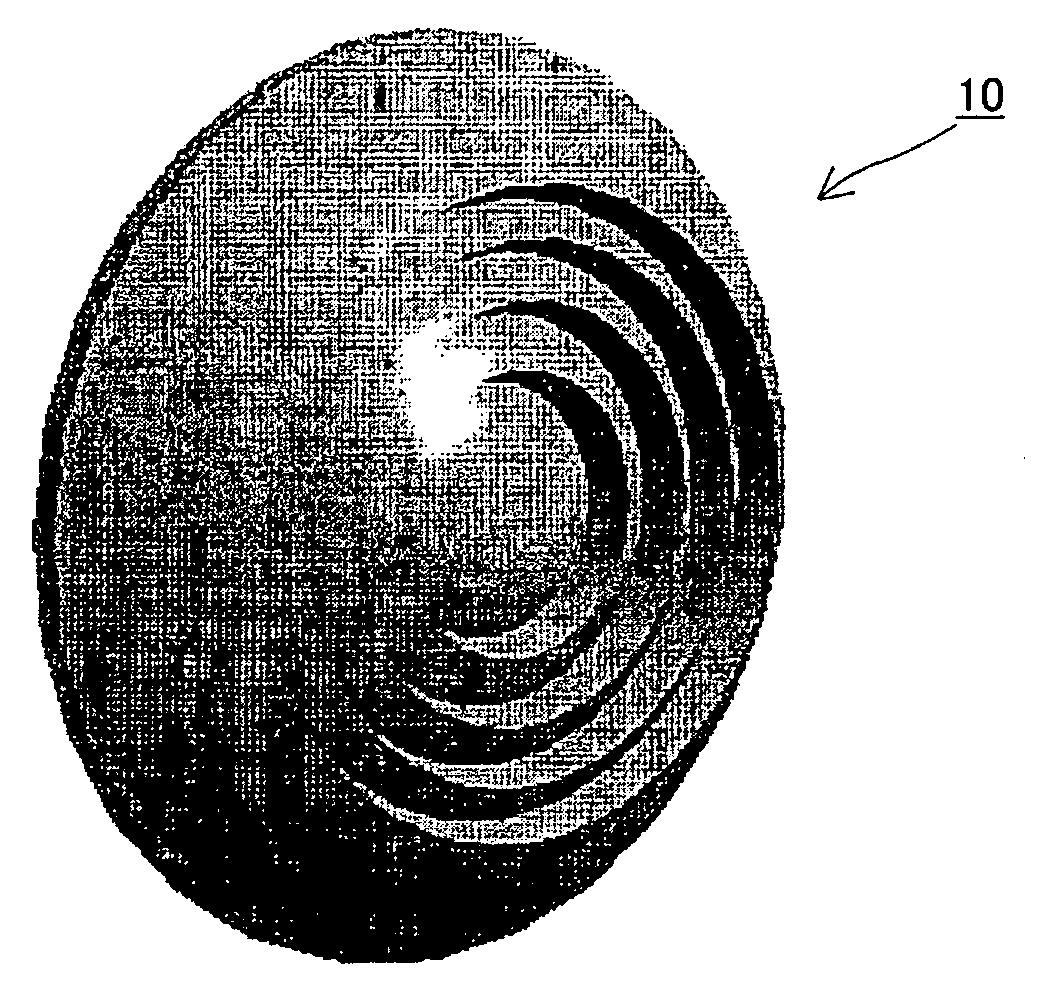
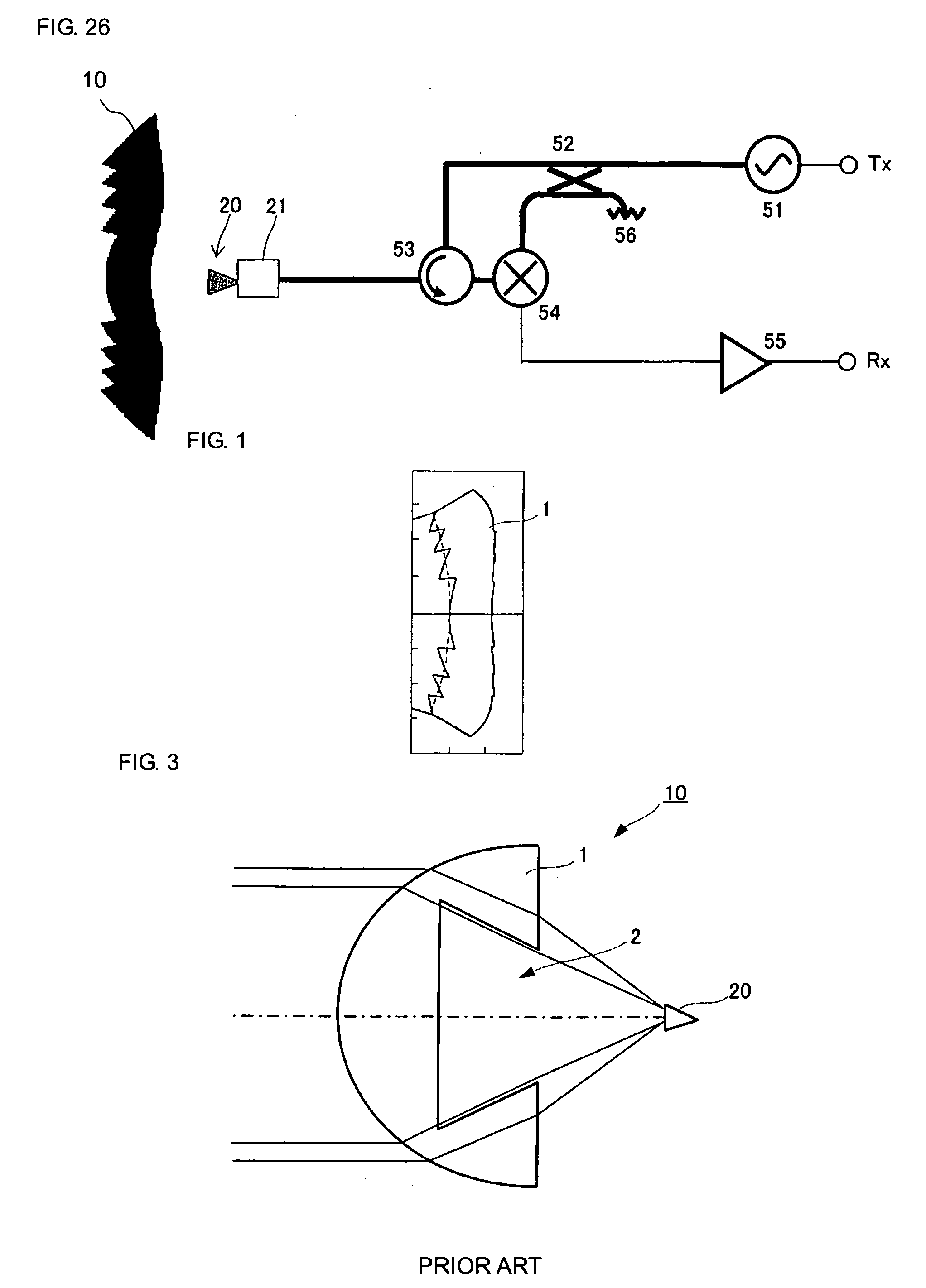
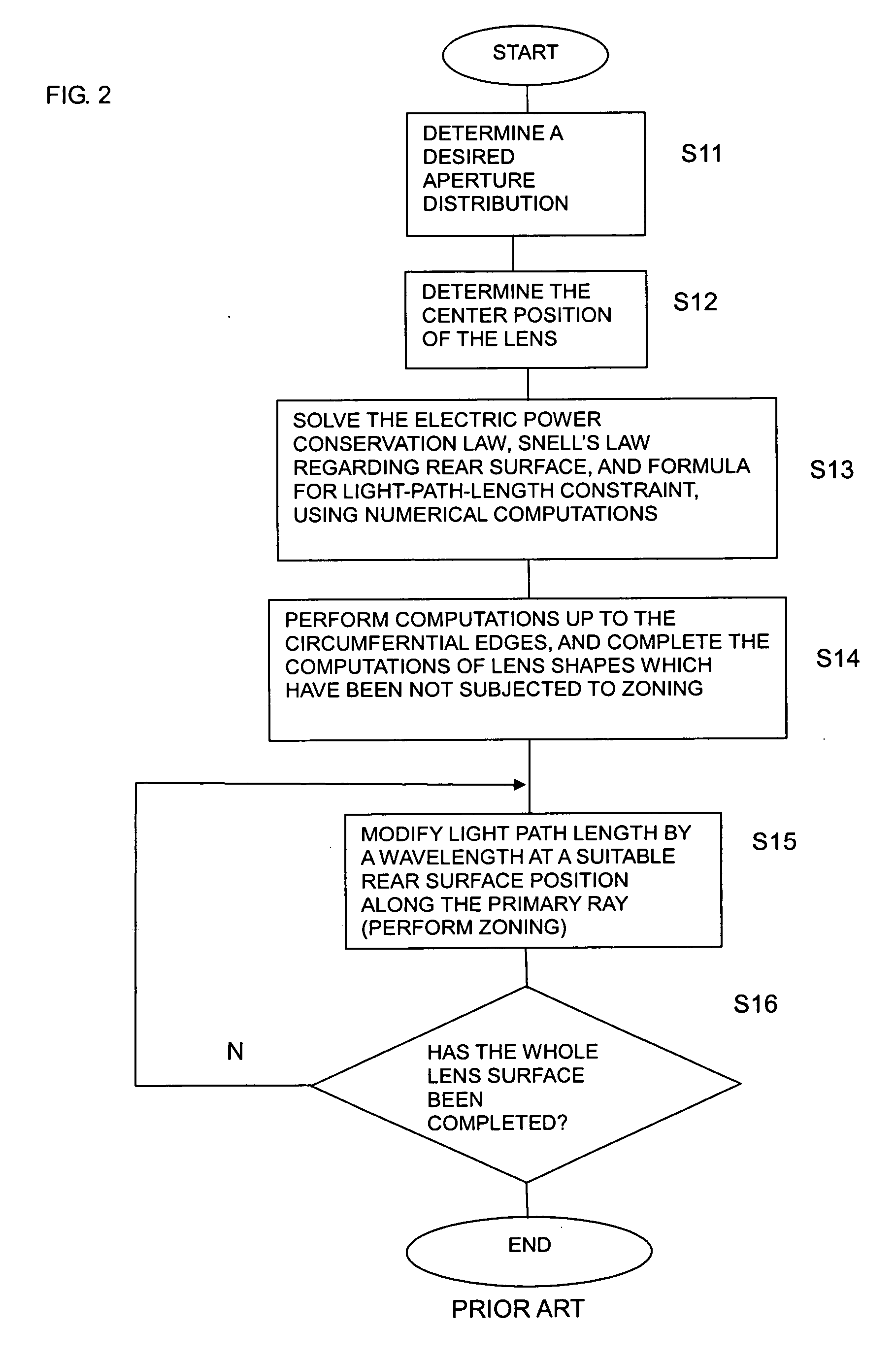
Dielectric lens, dielectric lens device, design method of dielectric lens, manufacturing method and transceiving equipment of dielectric lens
InactiveUS7355560B2Reduce weight and sizeEliminate the problemAntennasPath lengthSimultaneous equations
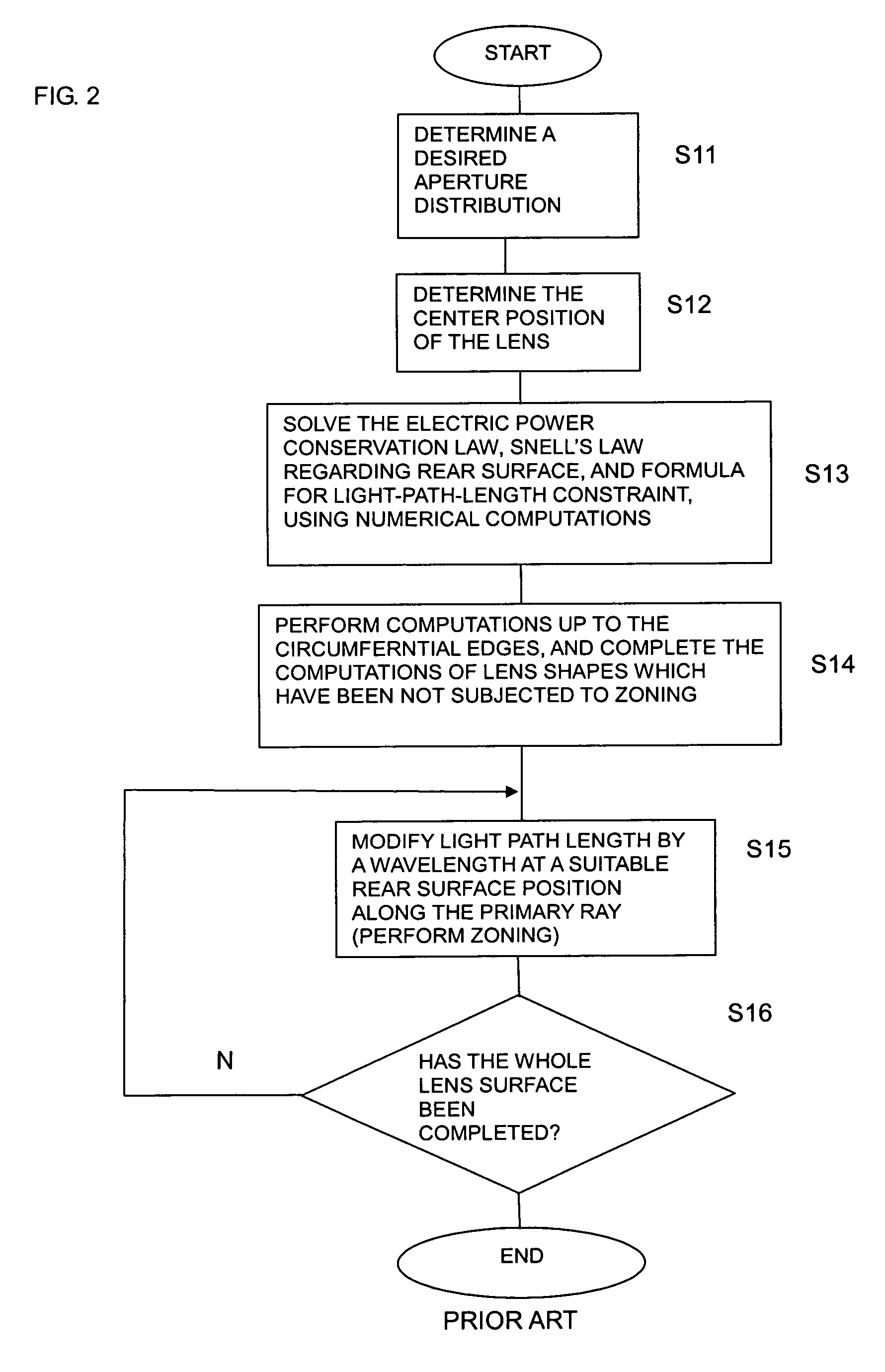
A design process first determines a desired aperture distribution, then converts the electric power conservation law, Snell's law on the rear face side of a dielectric lens, and the formula representing light-path-length constraint, into simultaneous equations, and computes the shapes of the surface and rear face of the dielectric lens depending on the azimuthal angle θ of a primary ray from the focal point of the dielectric lens to the rear face of the dielectric lens, and then reduces the light path length in the formula showing light-path-length constraint by an integral multiple of the wavelength when the coordinates on the surface of the dielectric lens reach a predetermined restriction thickness position. A dielectric lens is designed by sequentially changing the lazimuthal angle θ from its initial value, and also repeating the second and third steps. Thus, downsizing and quantification is realized by zoning while keeping antenna properties at the time of constituting a dielectric lens antenna in a good condition.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dielectric lens, dielectric lens device, design method of dielectric lens, manufacturing method and transceiving equipment of dielectric lens
InactiveUS20060202909A1Preventing antenna propertyAvoiding characteristicAntennasPath lengthSimultaneous equations
A design process first determines a desired aperture distribution, then converts the electric power conservation law, Snell's law on the rear face side of a dielectric lens, and the formula representing light-path-length constraint, into simultaneous equations, and computes the shapes of the surface and rear face of the dielectric lens depending on the azimuthal angle θ of a primary ray from the focal point of the dielectric lens to the rear face of the dielectric lens, and then reduces the light path length in the formula showing light-path-length constraint by an integral multiple of the wavelength when the coordinates on the surface of the dielectric lens reach a predetermined restriction thickness position. A dielectric lens is designed by sequentially changing the lazimuthal angle θ from its initial value, and also repeating the second and third steps. Thus, downsizing and quantification is realized by zoning while keeping antenna properties at the time of constituting a dielectric lens antenna in a good condition.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
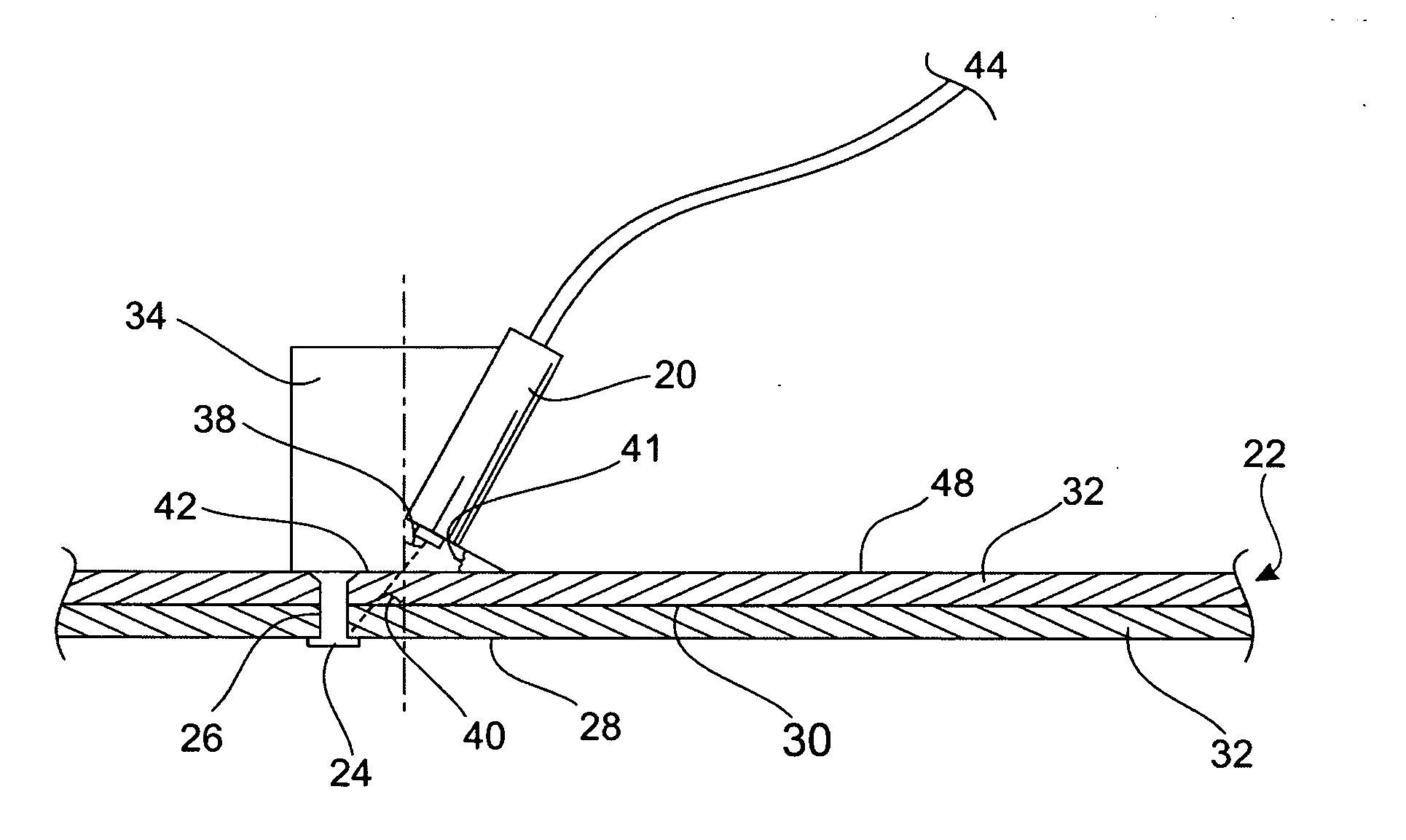
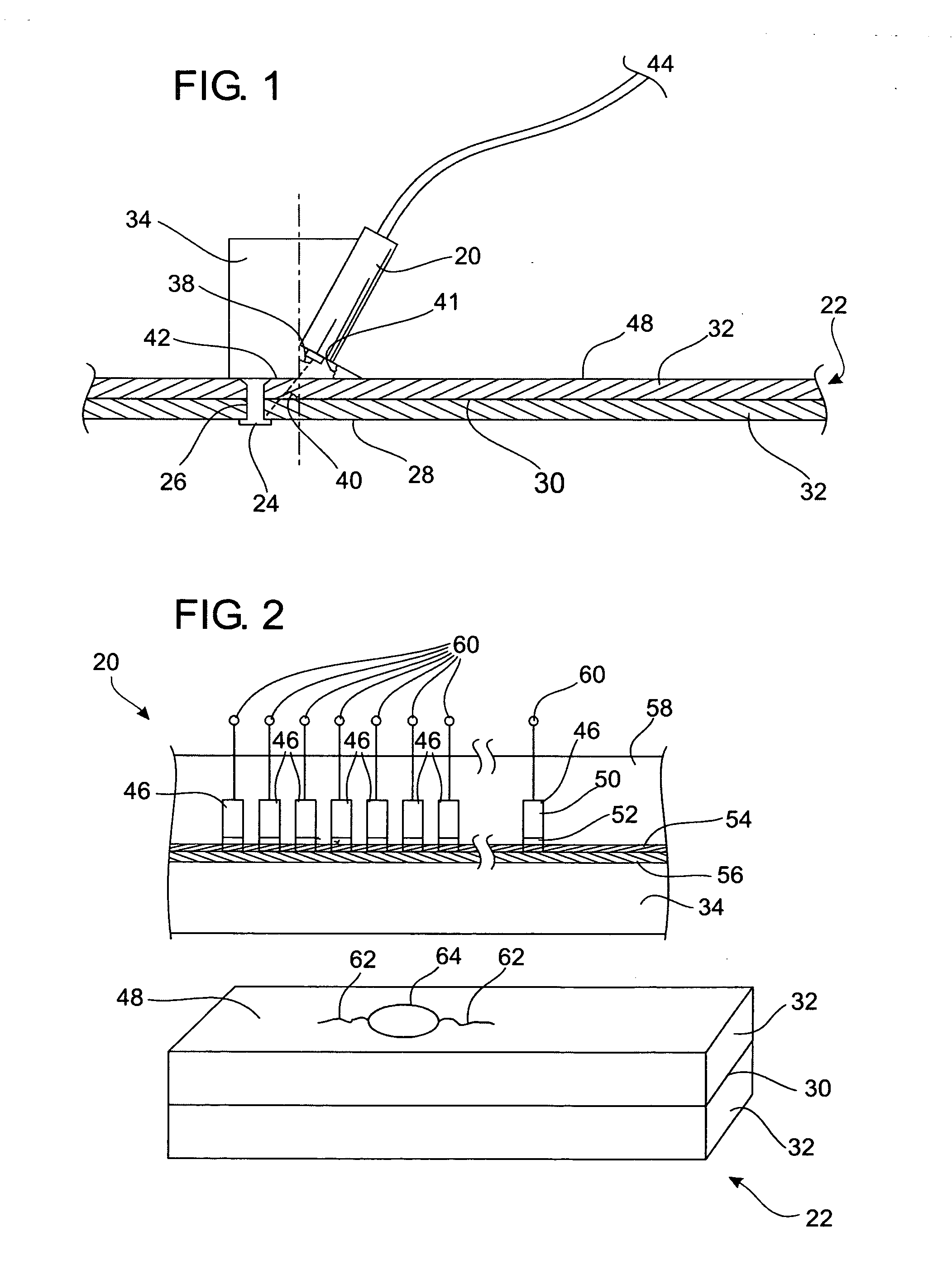
Rotary scanning laser head with coaxial refractive optics
ActiveUS7009141B1Expand accessMinimized cross sectionLaser beam welding apparatusCamera lensMotor speed
A rotary refractive laser scanner head uses two sets of lenses and prisms aligned along a common optical axis. Each prism is paired with one of the lenses. The lens-prism pairs are separately mounted rotatable on a common axis coaxial with the optical axis. A motor drives two gear sets. Each gear set is separately coupled to one of the two lens-prism pairs and rotates them at selected, typically different speeds. An input laser beam is directed along the optical axis at one of the lens-prism pairs. The first pair collimates and refracts the input beam into an intermediate deflected beam according to Snell's law and the characteristics of the laser beam and optics. The second pair receives the intermediate beam and further deflects it to form an output beam. By selecting the motor speed, gear ratios, optics spacing, characteristics and prism wedge (deflection) angle, the scanner head effectively can scan an output laser beam over a desired pattern area.
Owner:GEN LASERTRONICS
Multichip light emitting diode package
InactiveUS7989827B2Increase brightnessImprove cooling effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesHueSnell's law
A multichip light emitting diode package is provided. The multichip light emitting diode (LED) package includes a substrate having a non-plane surface including a plurality of sectioned-surfaces, a plurality of light emitting diode chips and a transparent molding material. Each of the light emitting diode chips is disposed on one of the sectioned-surfaces of the substrate. The transparent molding material is formed on the substrate for encapsulating the light emitting diode chips. By way of the configurations of the non-plane surface of the substrate and the transparent molding material, the multichip light emitting diode package emits converging light in accordance with the Snell's law. The purposes of evenly mixing emitting lights and improving brightness are achieved. The present invention can provide a single color, multi-color or full-color multichip LED package with uniform brightness and hues.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONIC TECH INC
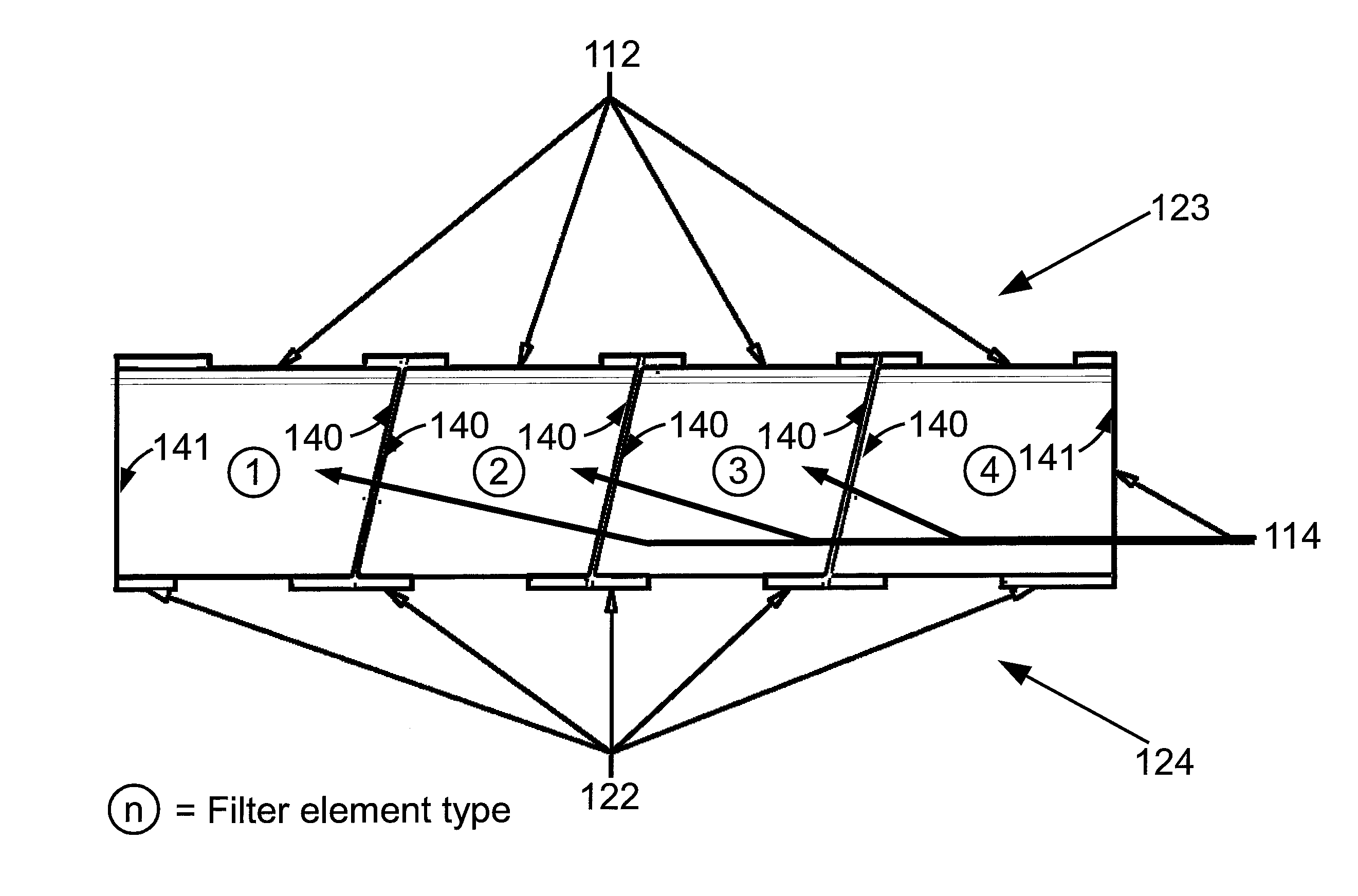
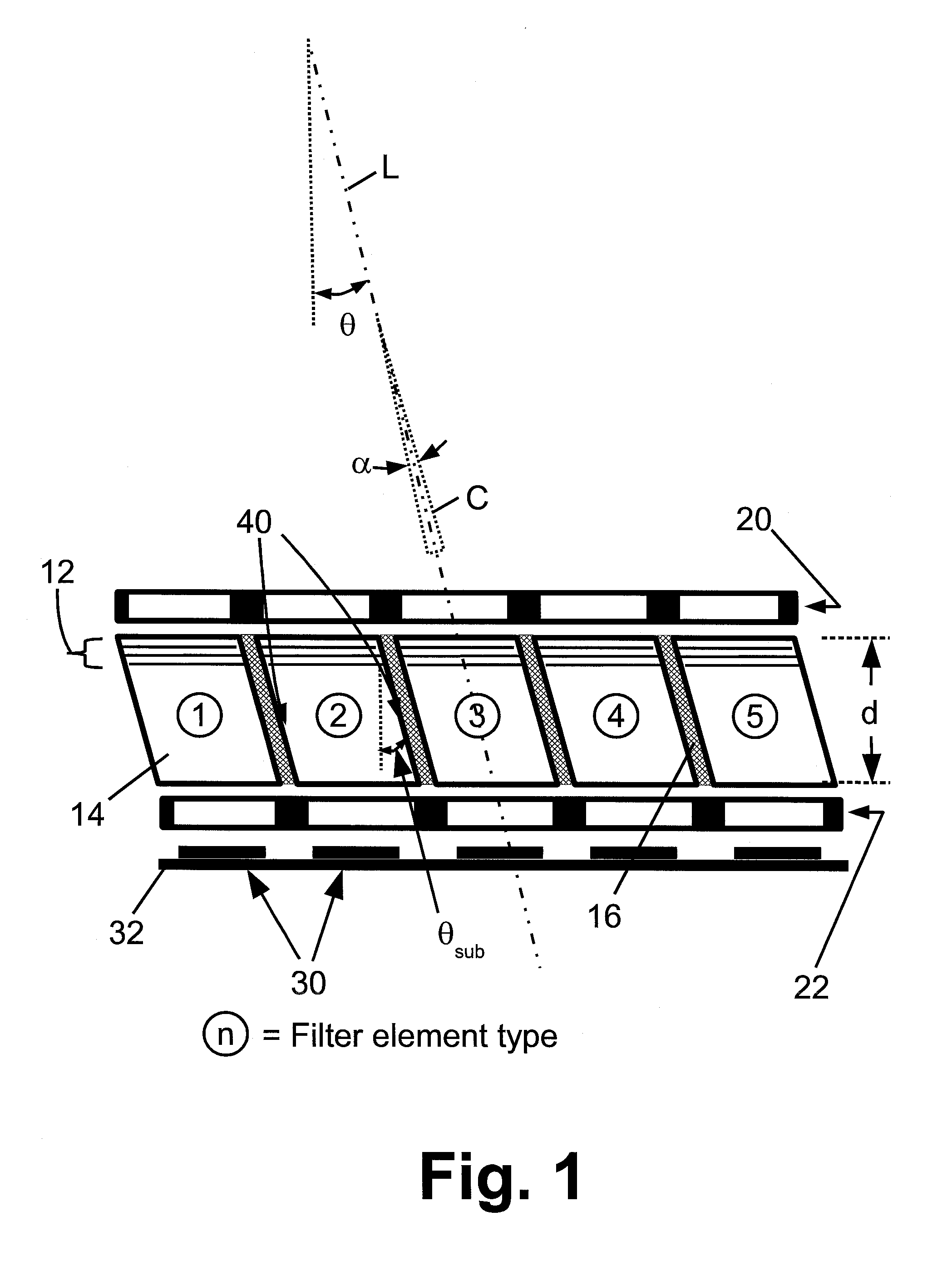
Filter array with reduced stray light
Optical filter elements each include a parallelogram-shaped substrate with parallel light entrance and light exit surfaces and parallel slanted sidewalls slanted at an angle, and an interference filter disposed on one or both of the light entrance surface and the light exit surface. The optical filter elements are bonded together at the slanted sidewalls to form the optical filter array. Light is filtered by illuminating the optical filter array at an angle θ equal to or corresponding to the angle of the slanted sidewalls. In some embodiments the angle of the slanted sidewalls corresponds to the angle-of-incidence θ by Snell's law.
Owner:MATERION
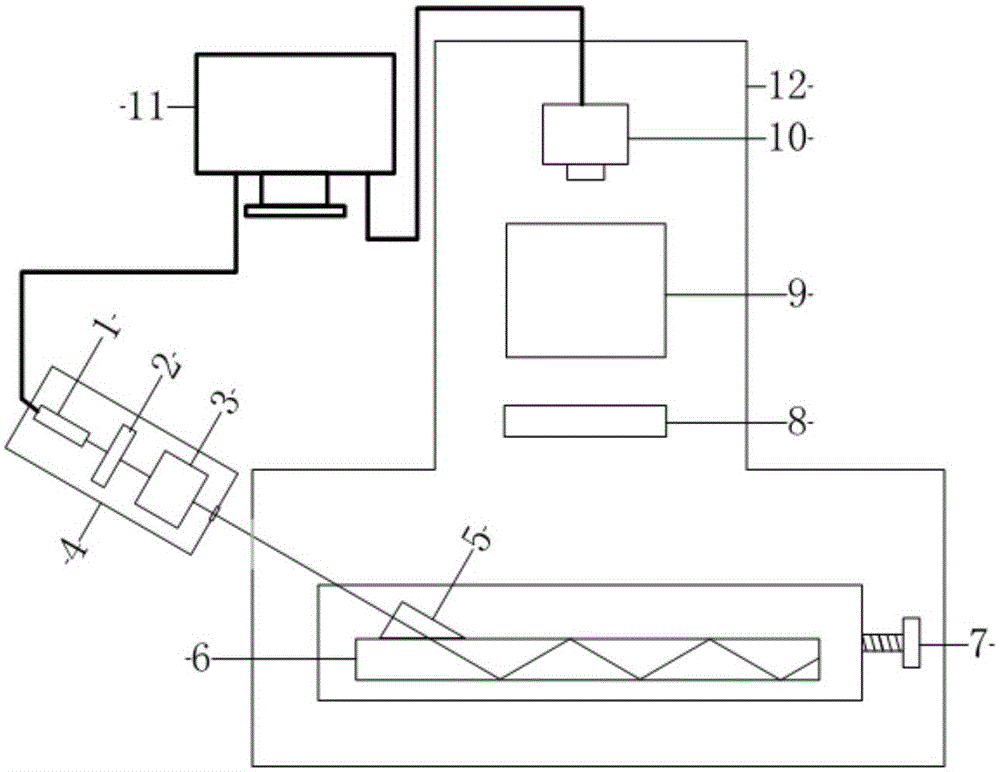
Large-diameter plane optical element defect three-dimensional fast dark field detection device and method
ActiveCN105158269ASolve the problem that the defect depth information of component materials cannot be obtainedImprove detection efficiencyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSupporting systemComputational physics
The invention provides a large-diameter plane optical element defect three-dimensional fast dark field detection device and method. The detection device comprises an illuminating light source, a polarizer, a collimating lens system, a one-dimensional electronic control light source adjusting support supporting system, a prism, a to-be-detected large-diameter plane optical element, a one-dimensional electronic control horizontal movement object support, a polarization analyzer, an imaging lens, a CCD, a computer and a box. Coordinate transformation is achieved through the Snell law, defect (or damage) position detection in the z axis direction can be achieved, and the problem that in the prior art, deep detection of the defect (or damage) in the optical element cannot be performed; detection speed is greatly increased, the device and method can be more effective for the large-diameter optical element, and the problem that in the prior art, time consumed during detection of the large-diameter optical element is long is effectively solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Panoramic refracting optic
An optical device having a semi-spherical or hemispherical field-of-view is provided. A conically-shaped piece of optical material has an annular surface satisfying Snell's Law for total internal reflection with respect to light passing through the piece and incident on the annular surface from within the piece.
Owner:NASA
Multichip light emitting diode package
InactiveUS20060261365A1Improved brightness and hueImprove cooling effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMonochromatic colorHue
A multichip light emitting diode package is provided. The multichip light emitting diode (LED) package includes a substrate having a non-plane surface including a plurality of sectioned-surfaces, a plurality of light emitting diode chips and a transparent molding material. Each of the light emitting diode chips is disposed on one of the sectioned-surfaces of the substrate. The transparent molding material is formed on the substrate for encapsulating the light emitting diode chips. By way of the configurations of the non-plane surface of the substrate and the transparent molding material, the multichip light emitting diode package emits converging light in accordance with the Snell's law. The purposes of evenly mixing emitting lights and improving brightness are achieved. The present invention can provide a single color, multi-color or full-color multichip LED package with uniform brightness and hues.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Thin film thickness measurement method and system
InactiveCN106441125AAvoid Streak CountsAvoid Positioning EffectsUsing optical meansShaped beamLight beam
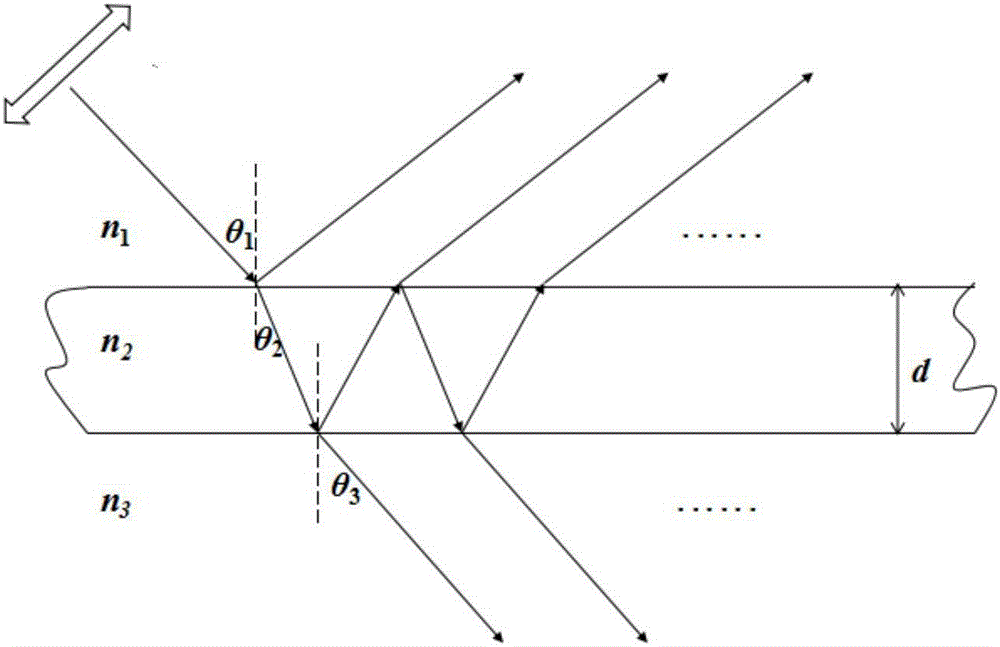
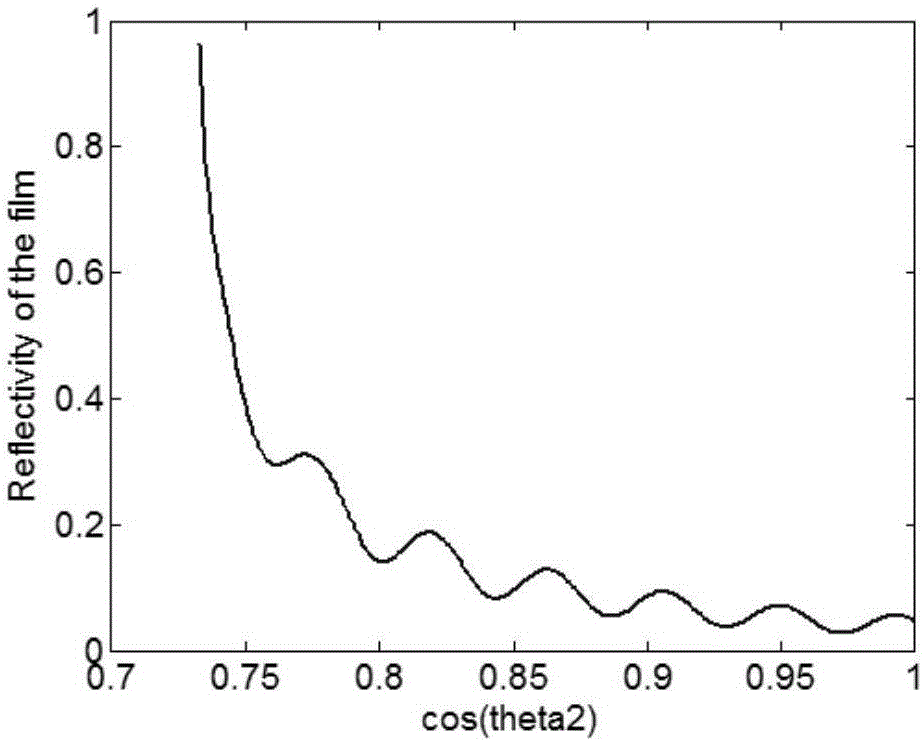
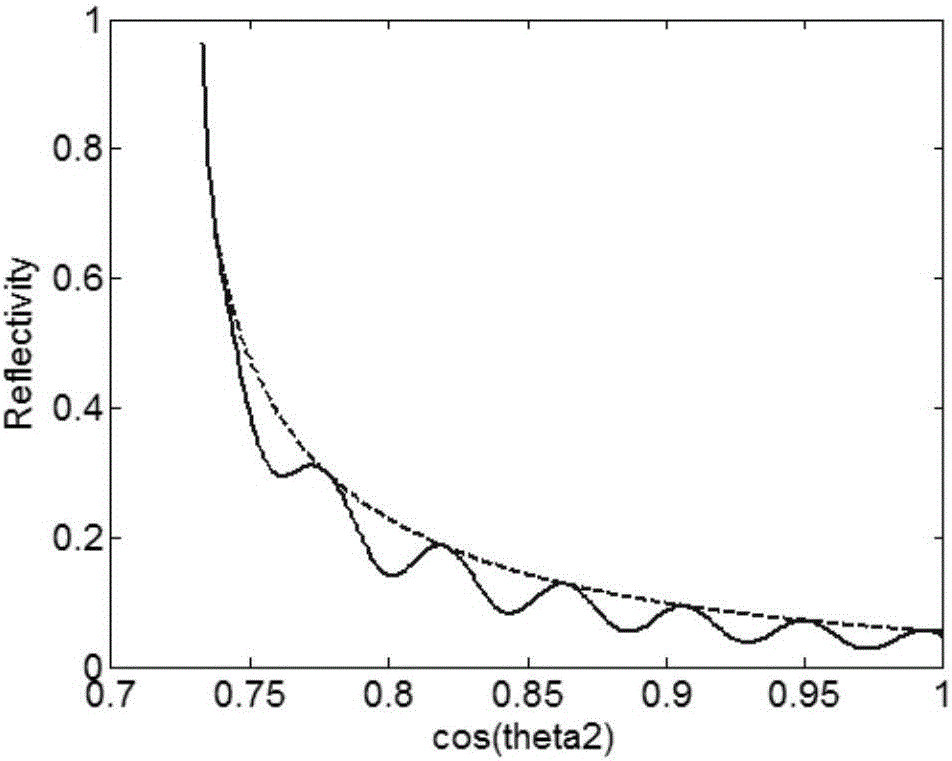
The invention discloses a thin film thickness measurement method and system. The thin film thickness measurement system comprises a lighting optical device, an imaging optical device and a thin film thickness analyzing device, and is characterized in that the lighting optical device is used for generating a cone-shaped beam and projecting the cone-shaped beam to a point on the thin film surface of a sample; the imaging optical device comprises a focusing lens and an image acquisition module; the focusing lens projects light reflected from the surface of the sample to the image acquisition module according to the sequence of an incidence angle from small to large, the image acquisition module detects to acquire reflection intensity information of the beam at the surface of the sample and builds a relation curve between the reflectivity and the incidence angle according to the reflection intensity information; and the thin film thickness analyzing device builds a function of the reflectivity and a refraction angle cosine value by utilizing the relation curve between the reflectivity and the incidence angle and a Snell's law, and acquires the thin film thickness of the sample through performing Fourier transform and analysis on the function. The thin film thickness measurement system is not only high in measurement accuracy, but also simple, compact and stable in light path, low in cost and easy to realize online measurement.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
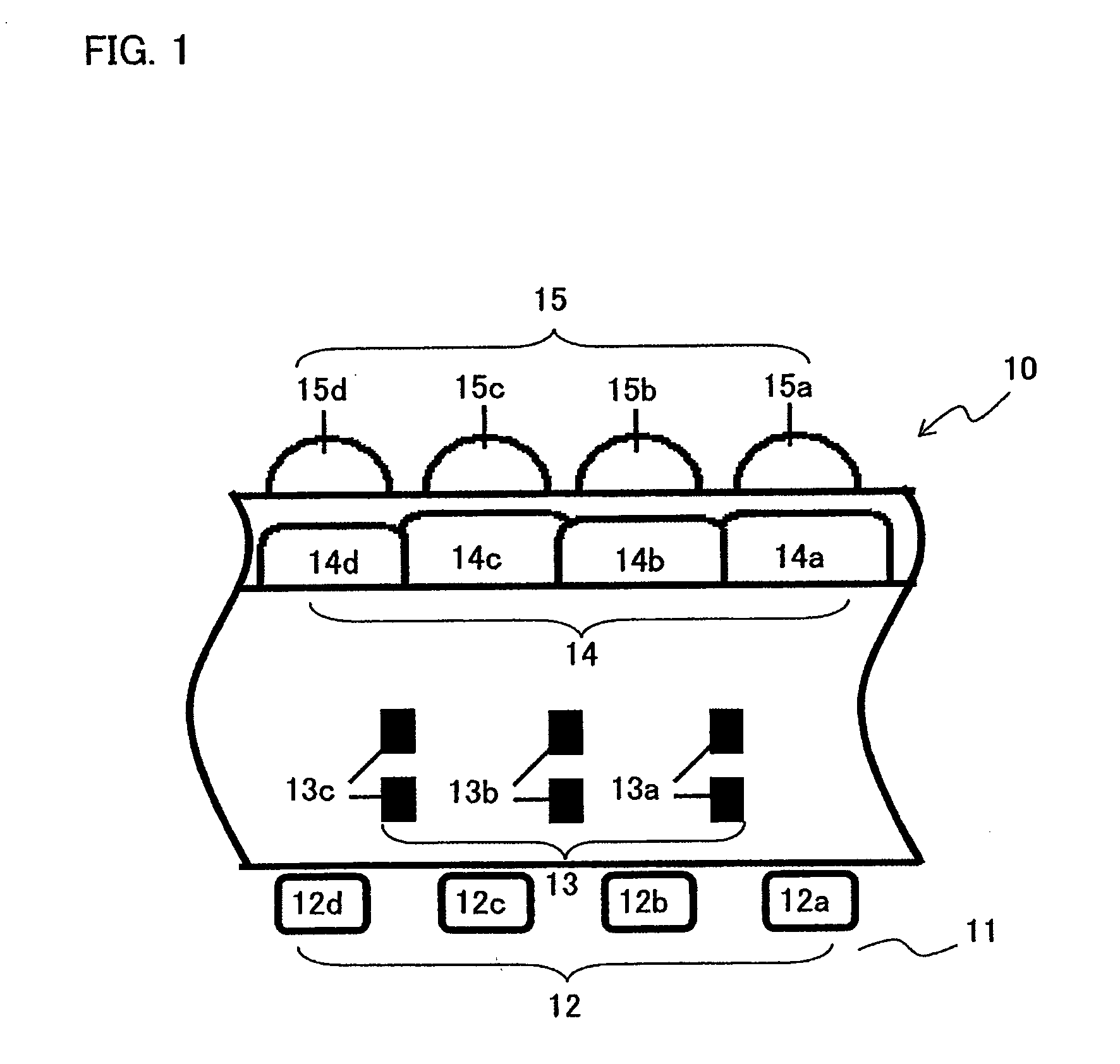
Solid-state image capturing device, solid-state image capturing apparatus, and electronic information device
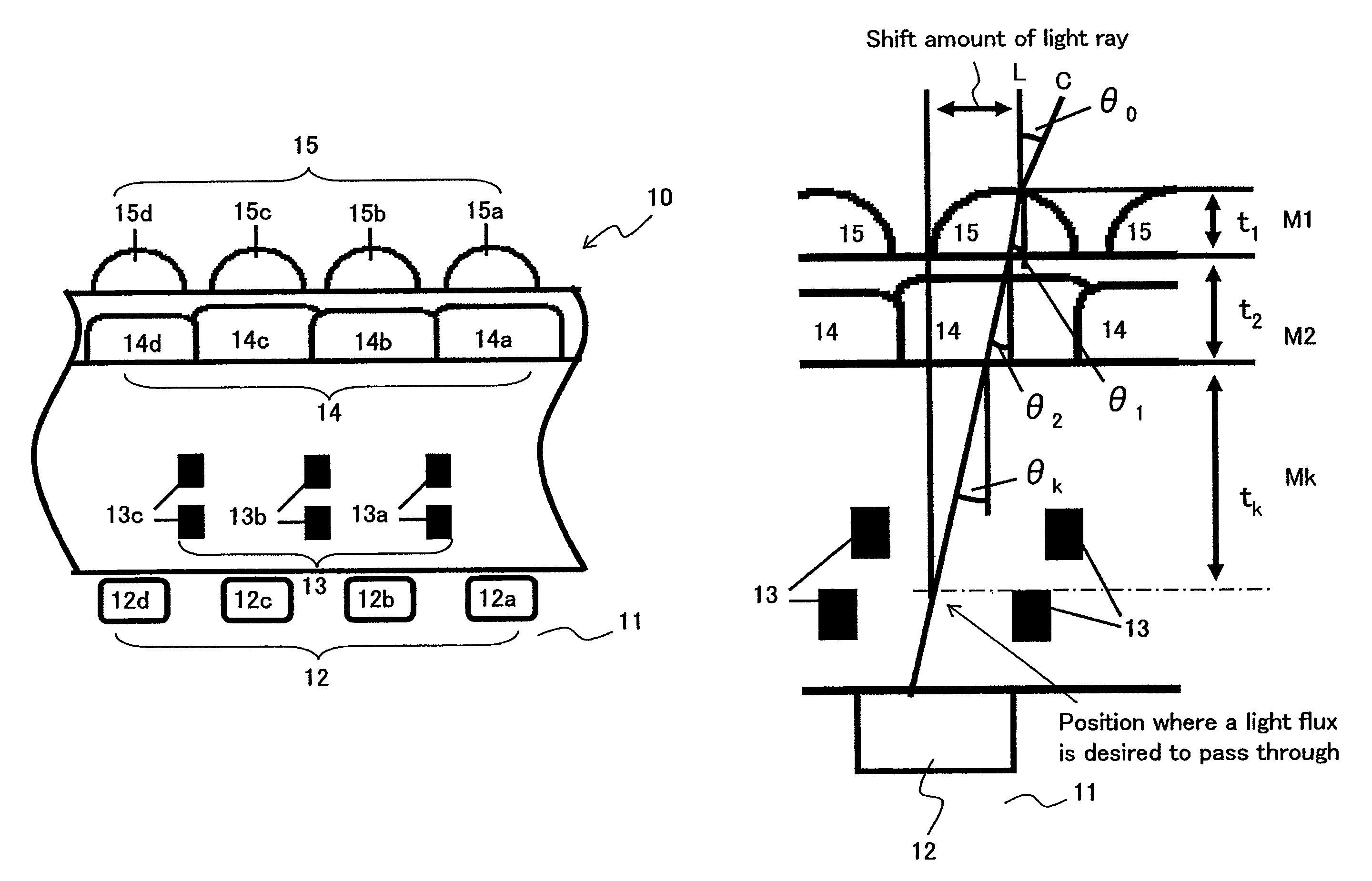
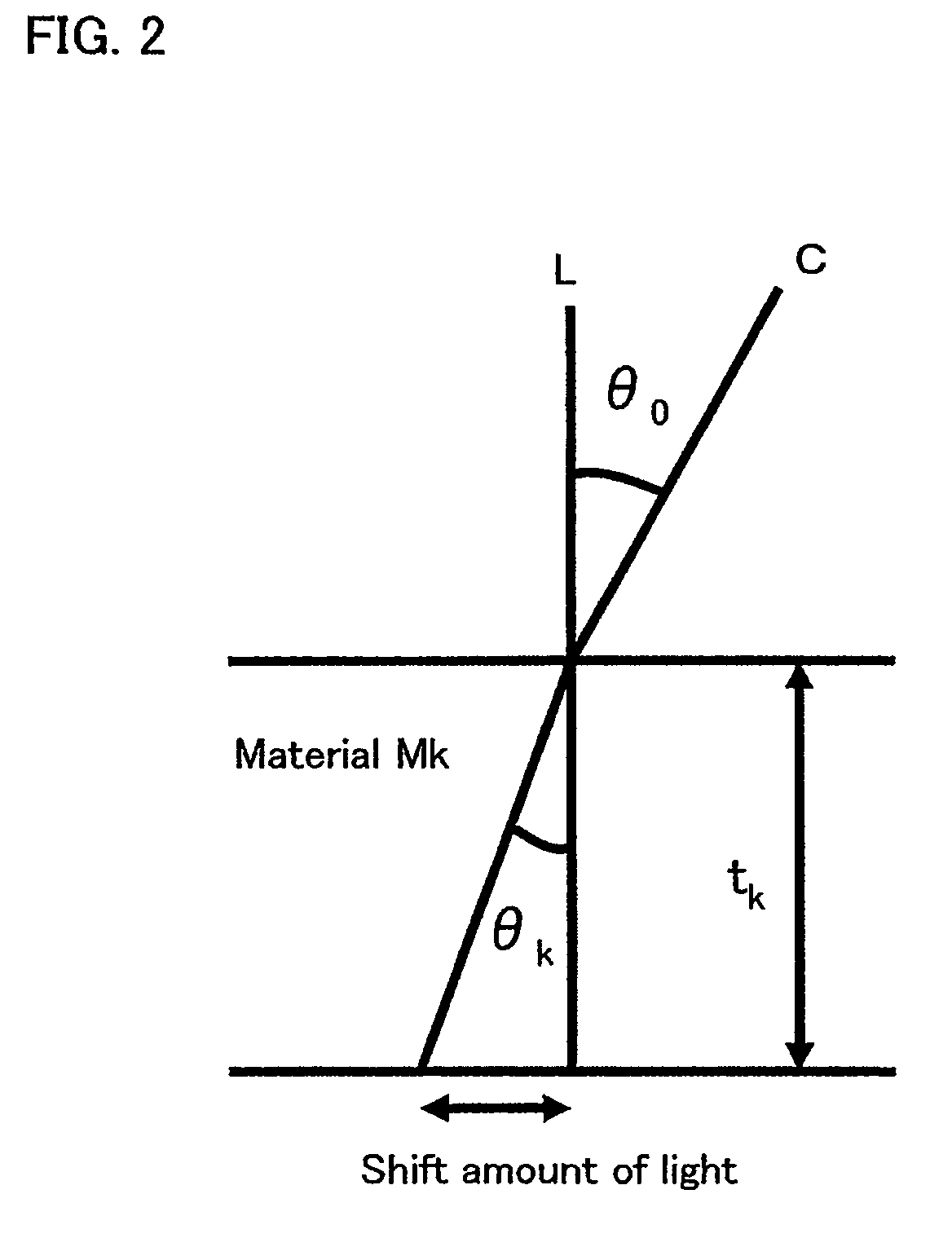
ActiveUS20090079019A1Shorten the design cycleReduce design costTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesLight fluxLight beam
A solid-state image capturing device is provided. In the solid-state image capturing device, at least any of openings of electrode wiring layers, color filters and microlenses are provided on a light incident side above light receiving elements as a light receiving region in which the plurality of light receiving elements are disposed on a semiconductor substrate or a semiconductor region provided on a substrate, wherein a shift amount of at least any of the openings of the electrode wiring layers, the color filters and the microlenses in relation to the light receiving elements or in relation to a standard position where a light flux is desired to pass through is calculated by Snell's law based on an incident angle θ0 of a light flux entering the light receiving region to a surface of the solid-state image capturing device.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for designing off-axial optical system with freeform surface
ActiveUS20160232257A1Simple system structureReduce aberrationComputer aided designComplex mathematical operationsComputer architectureOff-axis optical system
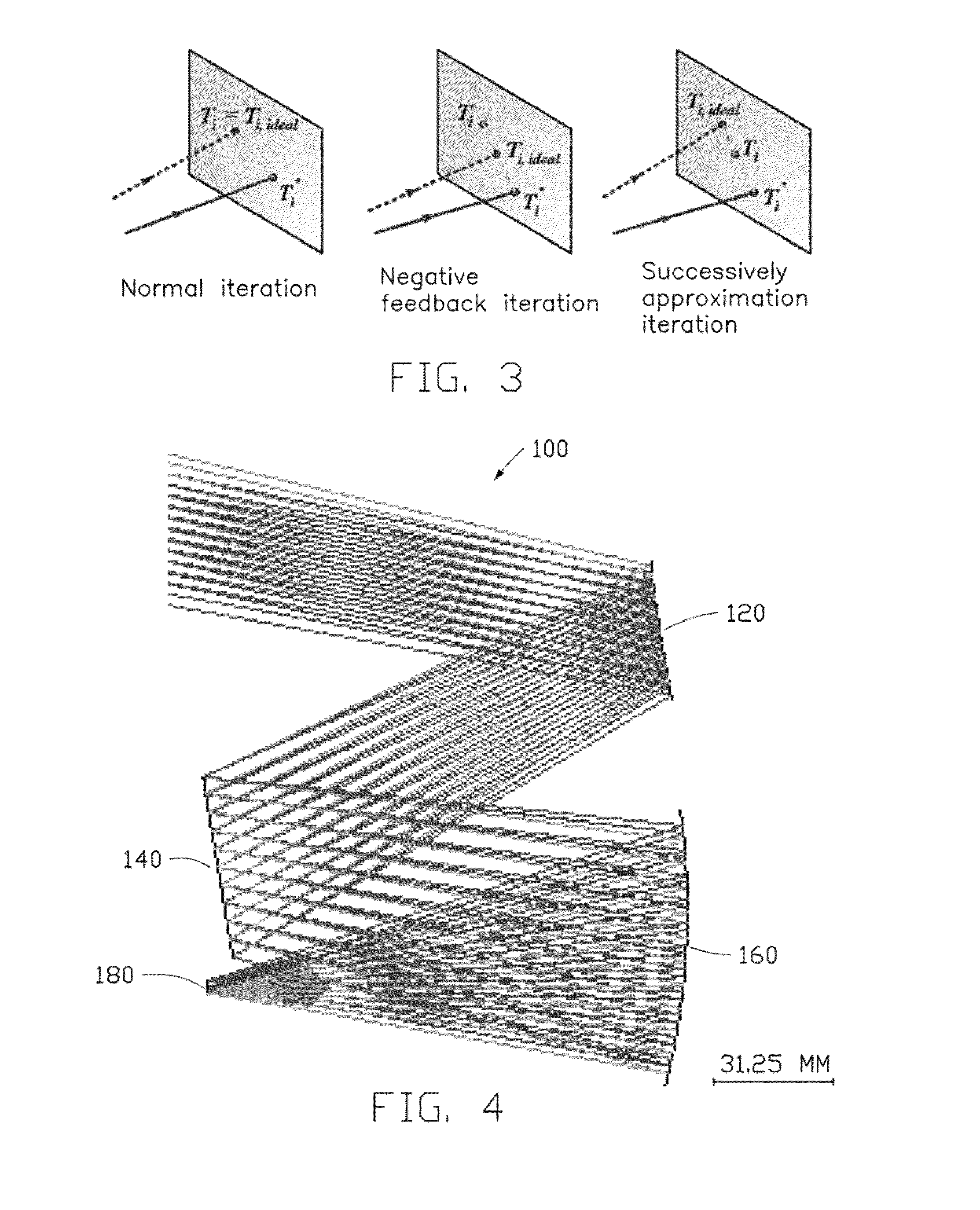
A method for designing off-axial optical system with freeform surfaces is provided. An initial system is established. A freeform surface of the off-axial optical system that needs to be solved is defined as a freeform surface. A number of feature rays are selected. A number of intersections of the feature rays with the freeform surface are calculated point by point based on a given object-image relationship and a vector form of Snell's law. A number of first feature data points are obtained from the intersections and surface fitted to obtain the freeform surface. All the freeform surfaces of the off-axial optical system that need to be solved are obtained by the method above to form a before-iteration off-axial optical system. The before-iteration off-axial optical system is used as the initial system for multiple iterations to obtain an after-iteration off-axial optical system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for detecting thickness reduction of heated surface tube of boiler
ActiveCN107632068AImprove reliabilityOvercome chanceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansFrequency dispersionAcoustics
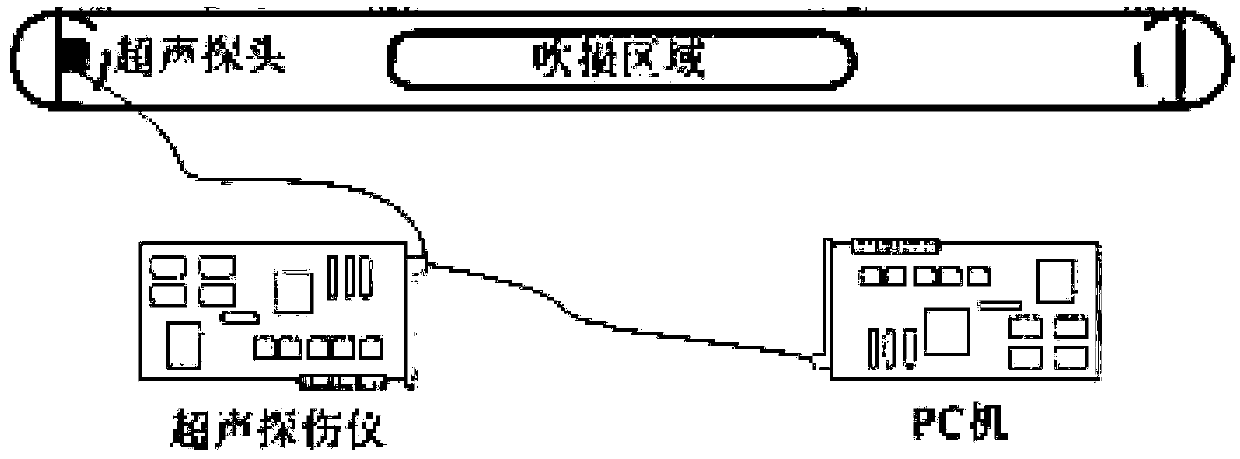
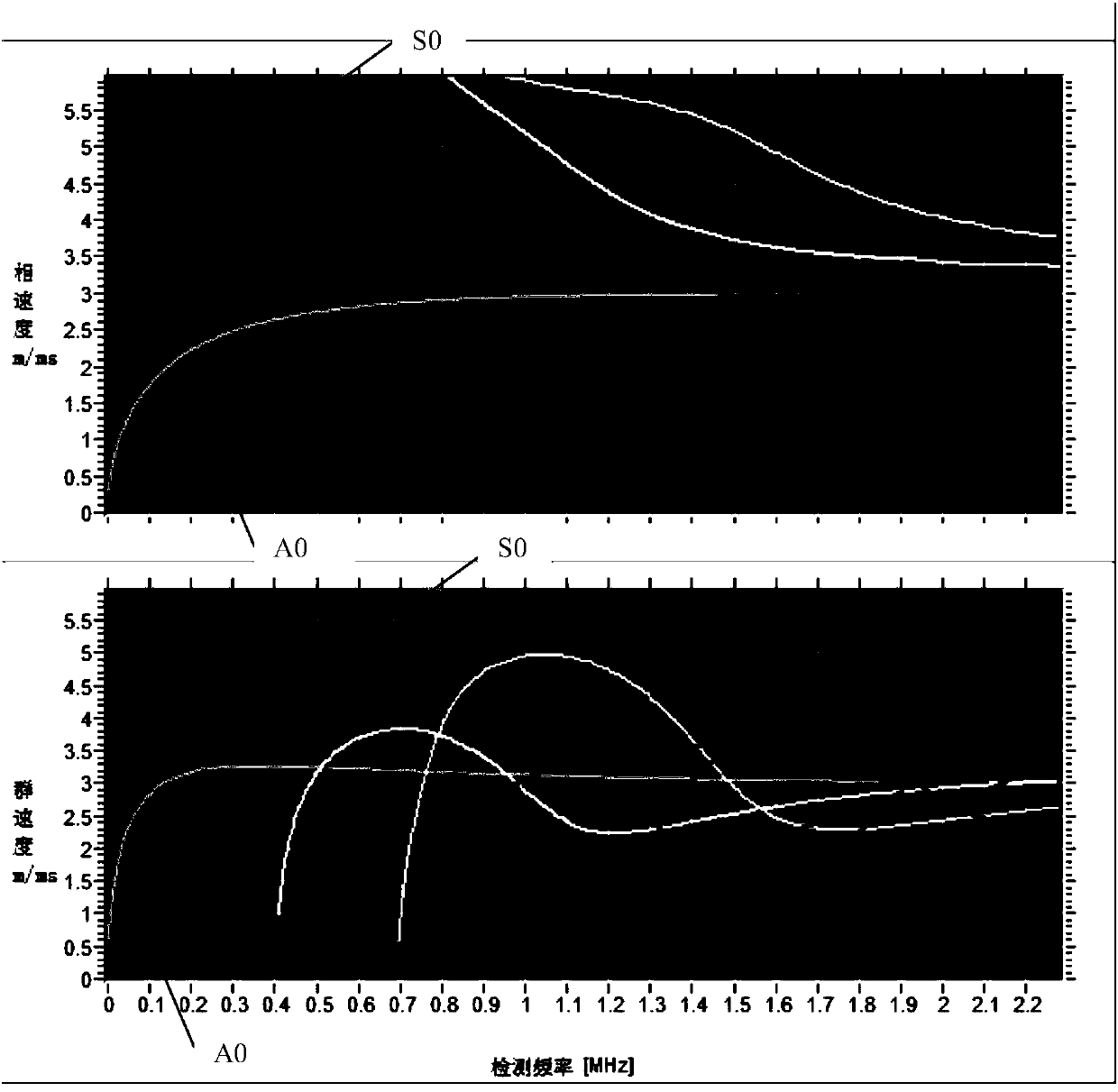
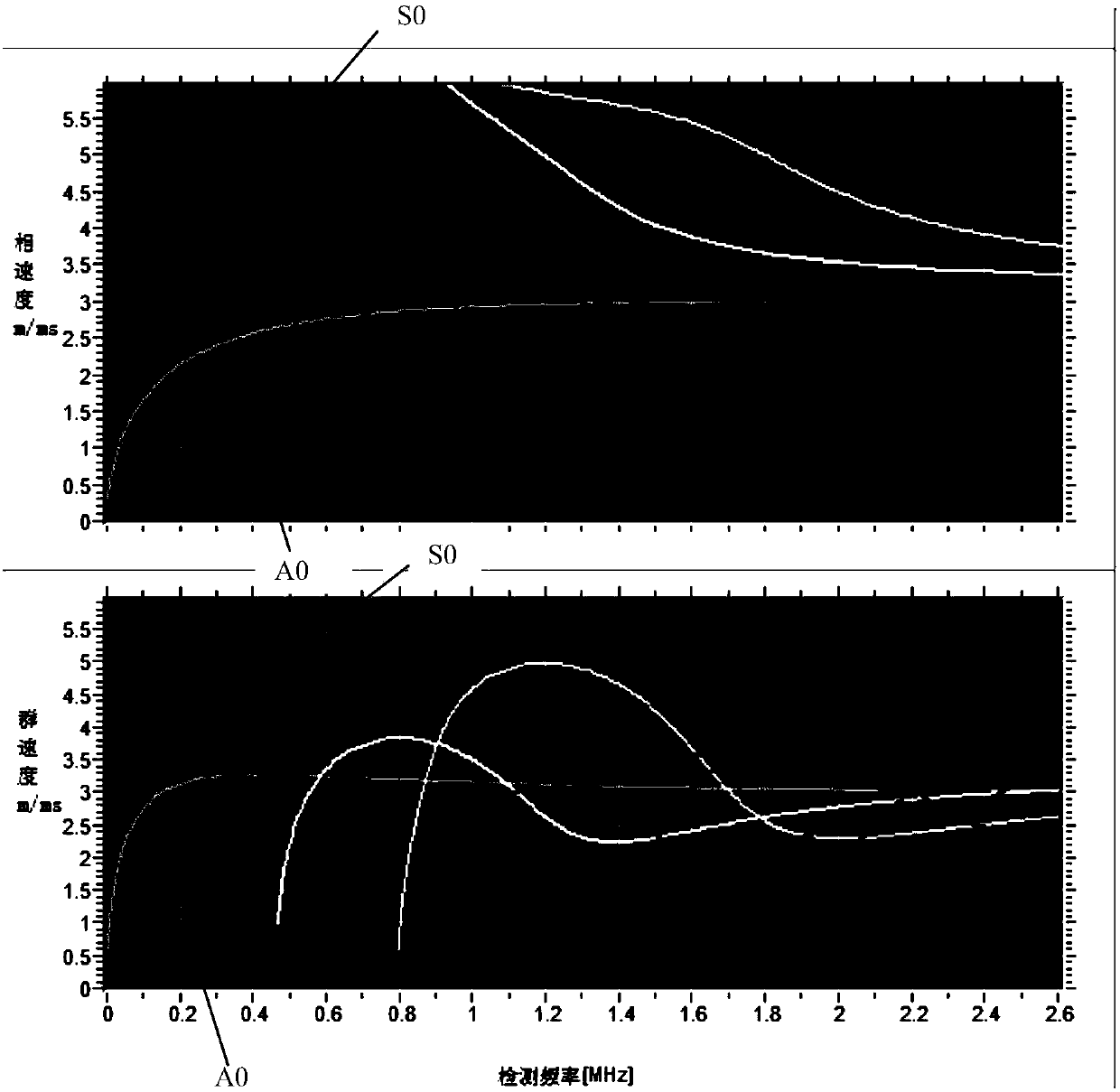
The invention discloses a method for detecting the thickness reduction of the heated surface tube of a boiler. The method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining the frequency dispersion curve ofLamb waves under the standard wall thickness d1 of the heated surface tube in the boiler to be detected; 2, obtaining an optimal detection frequency f1 according to a group velocity frequency dispersion curve in the frequency dispersion curve; 3, obtaining the phase velocity cp of the Lamb waves in a phase velocity frequency dispersion curve, corresponding to the optimal detection frequency f1 instep 2, and determining the incidence angle alpha of an acoustic beam according to the Snell's law; 4, allowing a variable angle probe to connect with an ultrasonic flaw detector and detect at the optimal detection frequency f1 according to the incidence angle alpha of the acoustic beam in step 3, and acquiring echo signals in an S0 mode and an A0 mode; and 5, obtaining the transit time differencebetween S0 mode echo and A0 mode end face echo waves according to the echo signals, and calculating the thickness reduction of the heated surface tube according to the transit time difference. The method has the advantages of convenience and fastness in completing of detection, and increase of the reliability of a detection result.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER +2
Panoramic refracting conical optic
An optical device having a semi-spherical or hemispherical field-of-view is provided. A conically-shaped piece of optical material has an annular surface satisfying Snell's Law for total internal reflection with respect to light passing through the piece and incident on the annular surface from within the piece.
Owner:NASA
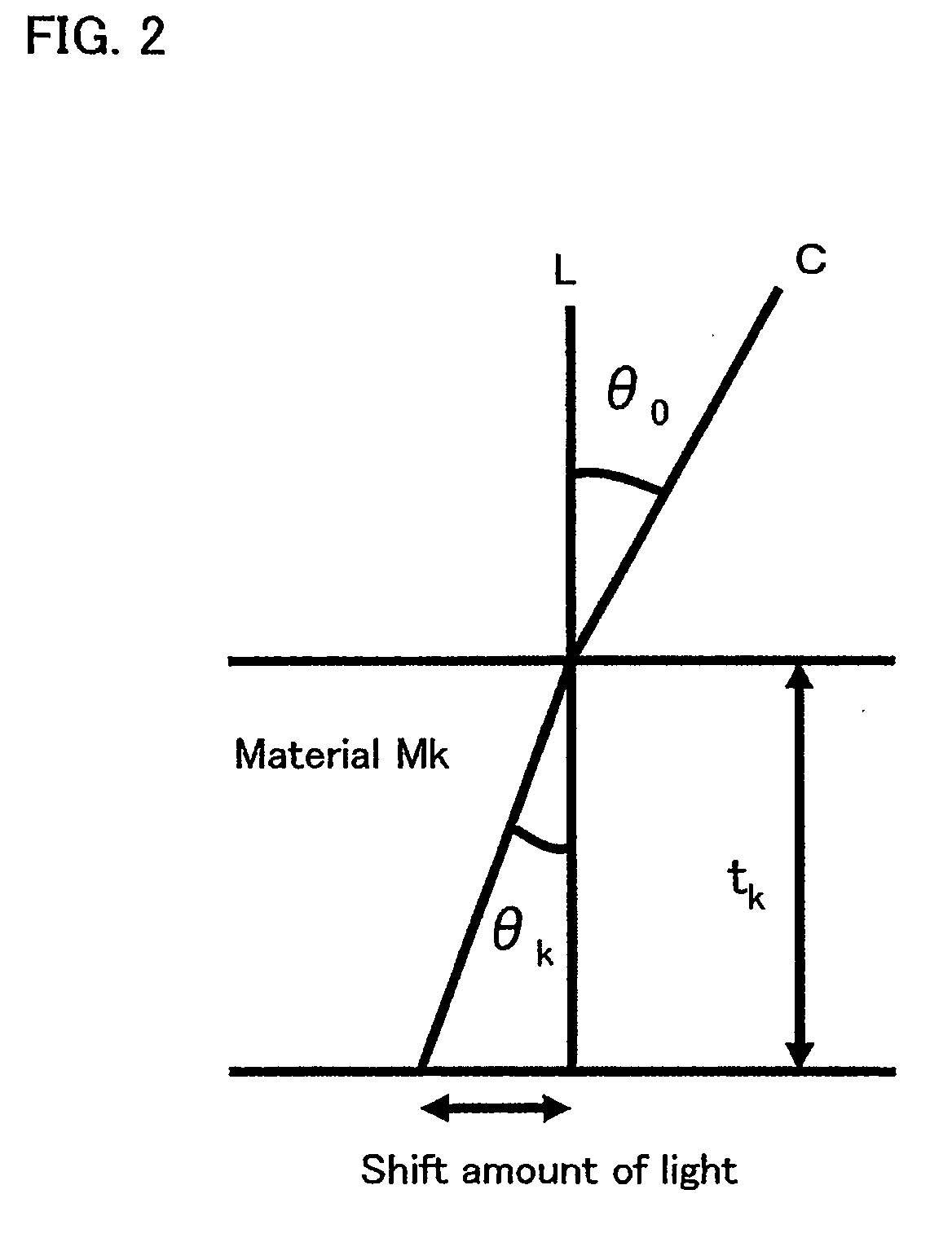
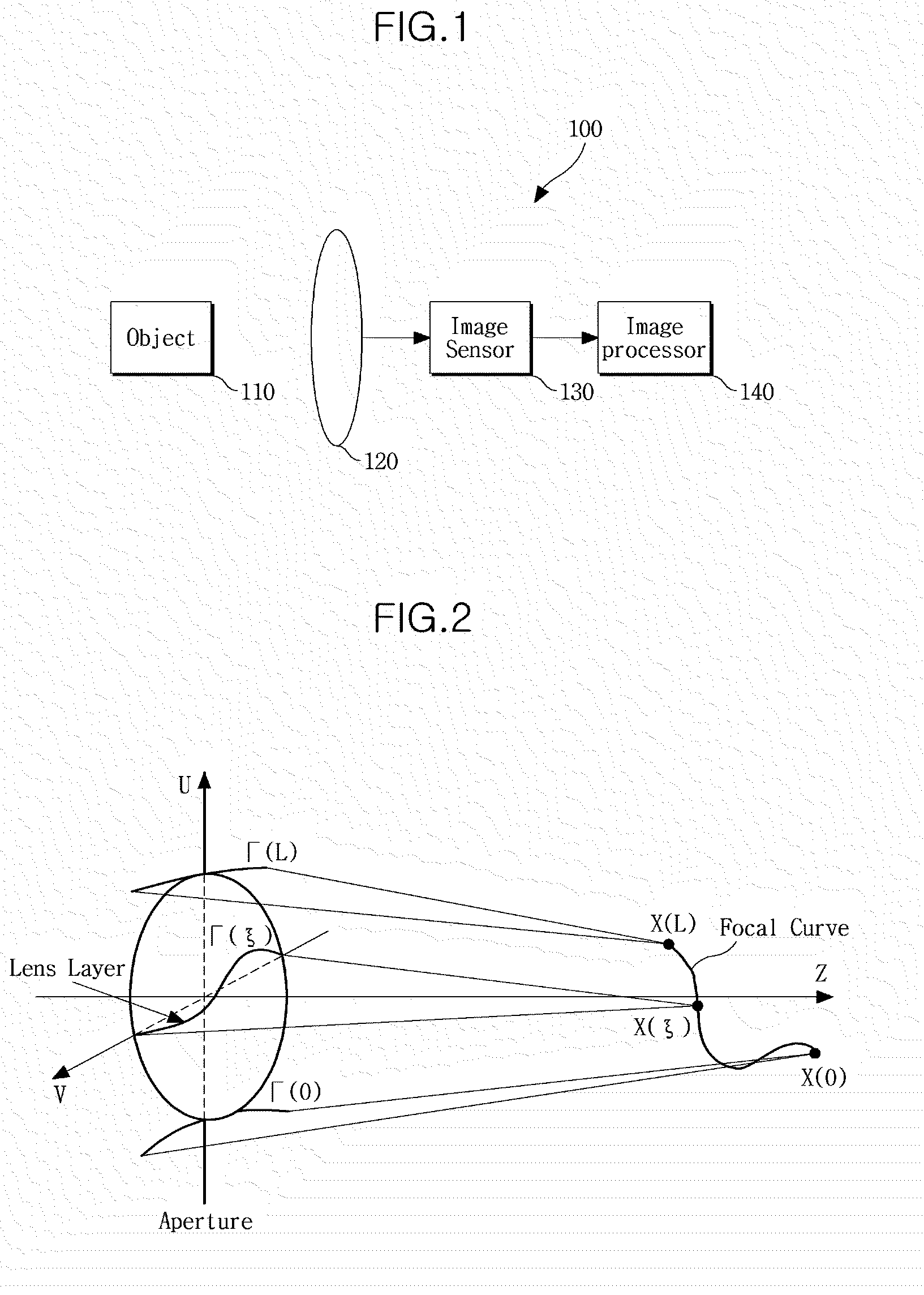
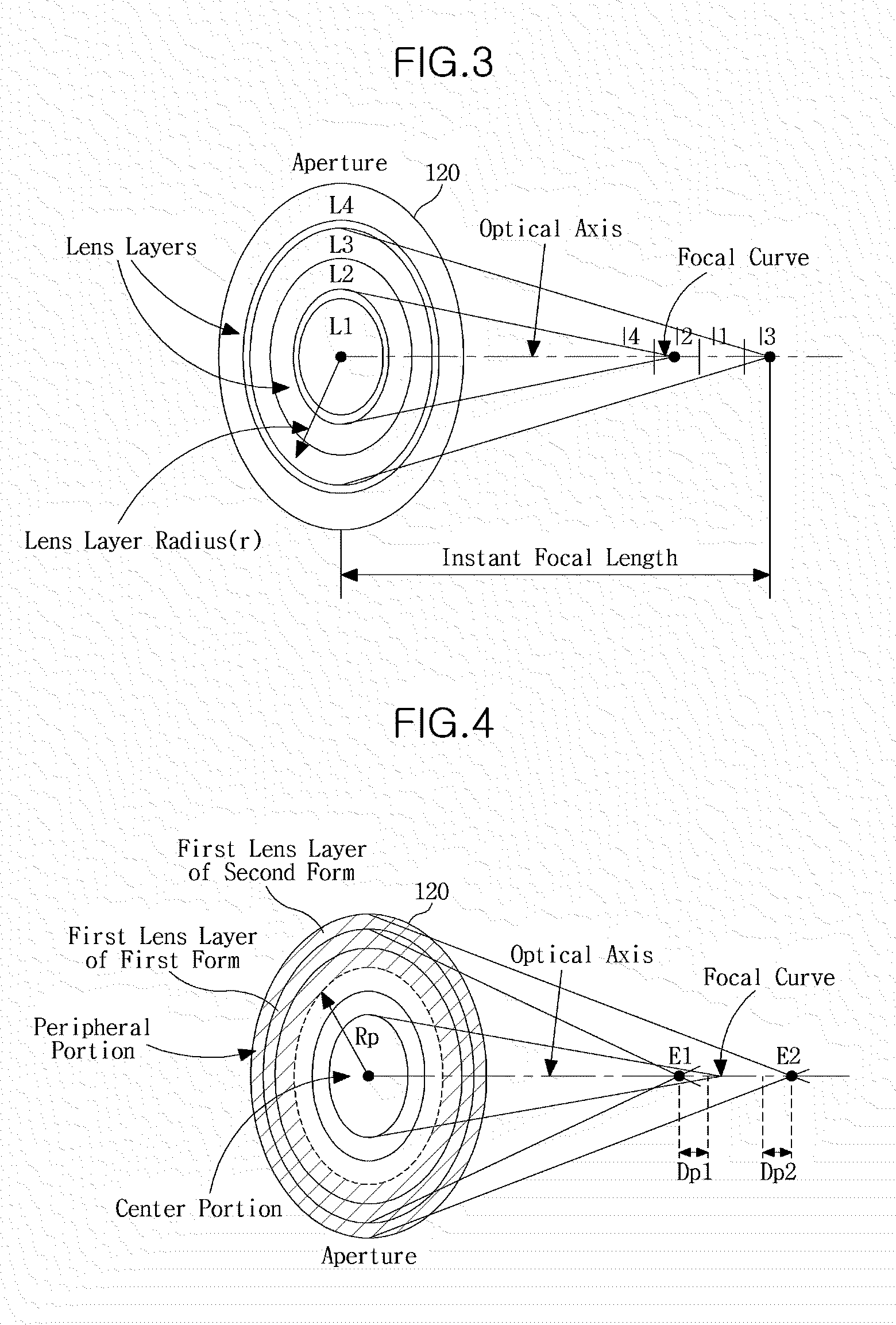
Method of constructing physical lens based on depth-of-focus characteristics, and lens with extended depth of focus constructed by the method
A method of constructing a physical lens based on depth of focus characteristics and an axially symmetric lens with an extended depth of focus constructed by the method are provided. An expression is deduced by substituting a depth of focus characteristic and a relation between vectors of arbitrary points on a lens surface into Snell's law, and partial differentiation is performed on the expression to yield a differential equation satisfied with arbitrary points on the lens surface. The differential equation is solved by, for example, numerical analysis to obtain a curve of an axially symmetric physical lens surface.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
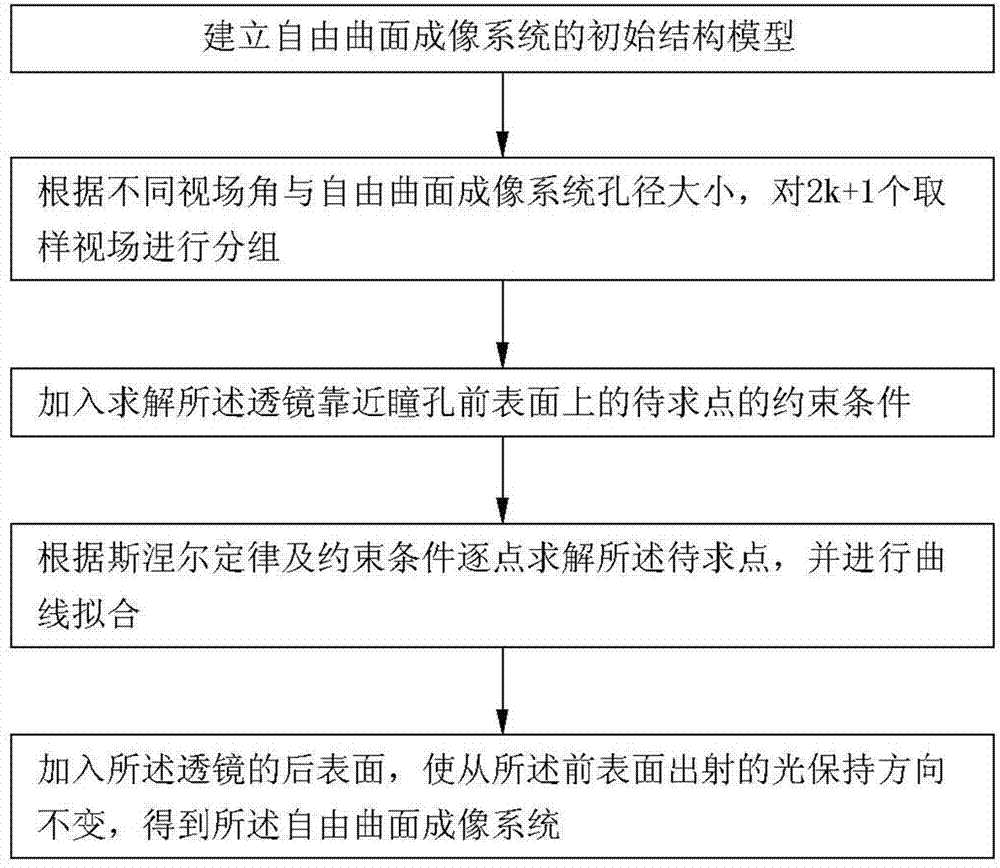
Design method for free curved surface imaging system
ActiveCN104516108AImprove fitting accuracyBroad application prospectsConstraint-based CADSpecial data processing applicationsLight beamCurve fitting
A design method of freeform imaging lens with a wide linear field-of-view (FOV) is provided. A initial freeform imaging lens is developed, and the initial freeform imaging lens includes a first lens surface and an entrance pupil spaced from each other, wherein the FOV of the system 2ω (±ω) is divided into 2k+1 sampling fields with equal interval Δω between each two adjacent sampling fields. Each two adjacent sampling fields are taken as one group. Two constraints are employed to calculate the plurality of data points of the first lens surface to obtain a front surface of the freeform imaging lens. The data points are calculated based on Snell's law, and a curve is obtained through the data points. A back surface is added to approximately keep the previous outgoing direction of rays from the front surface.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
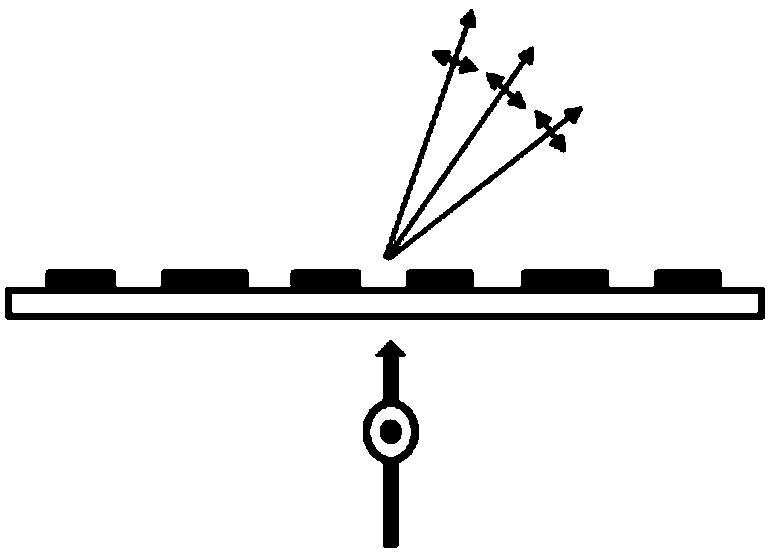
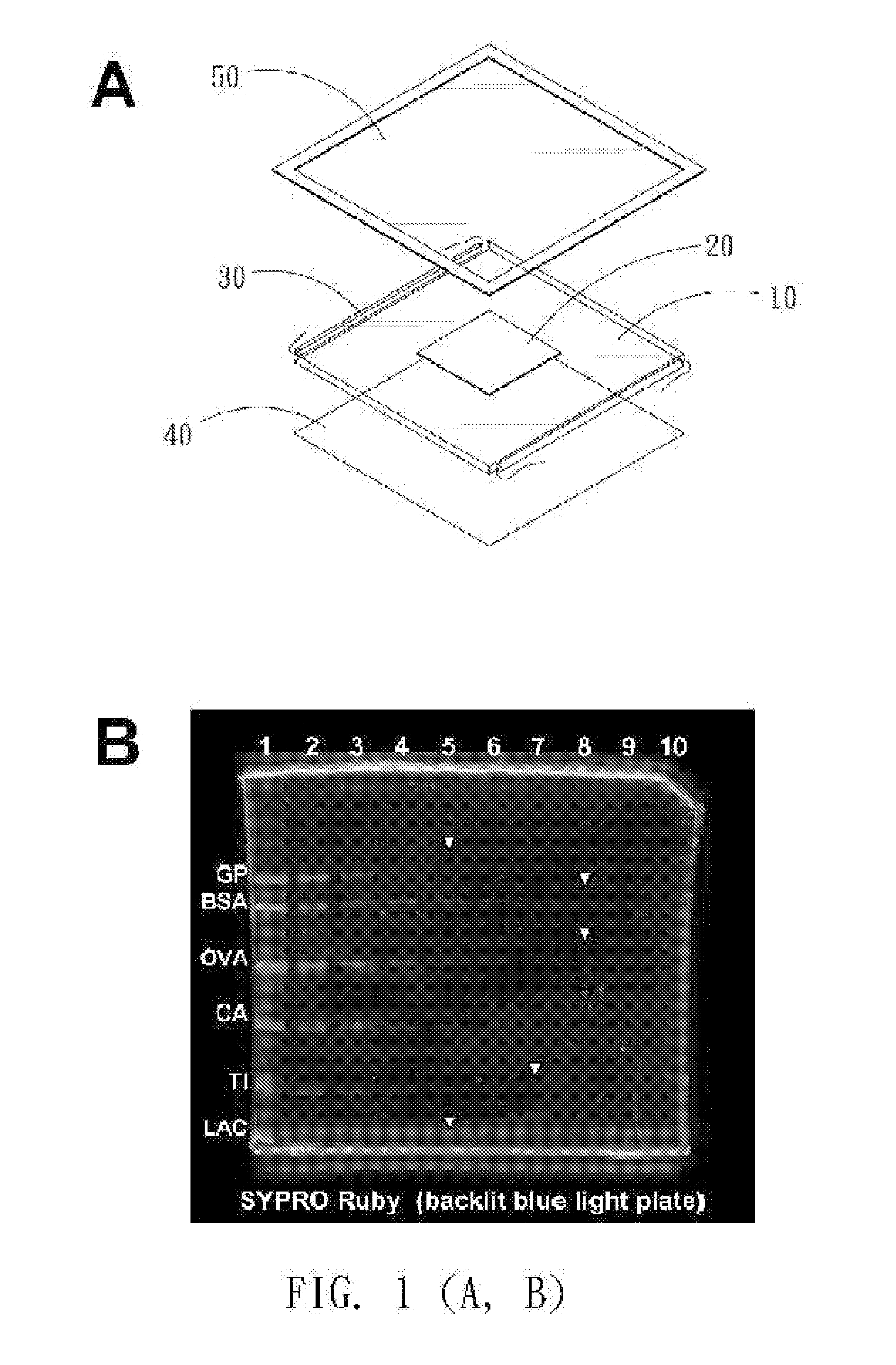
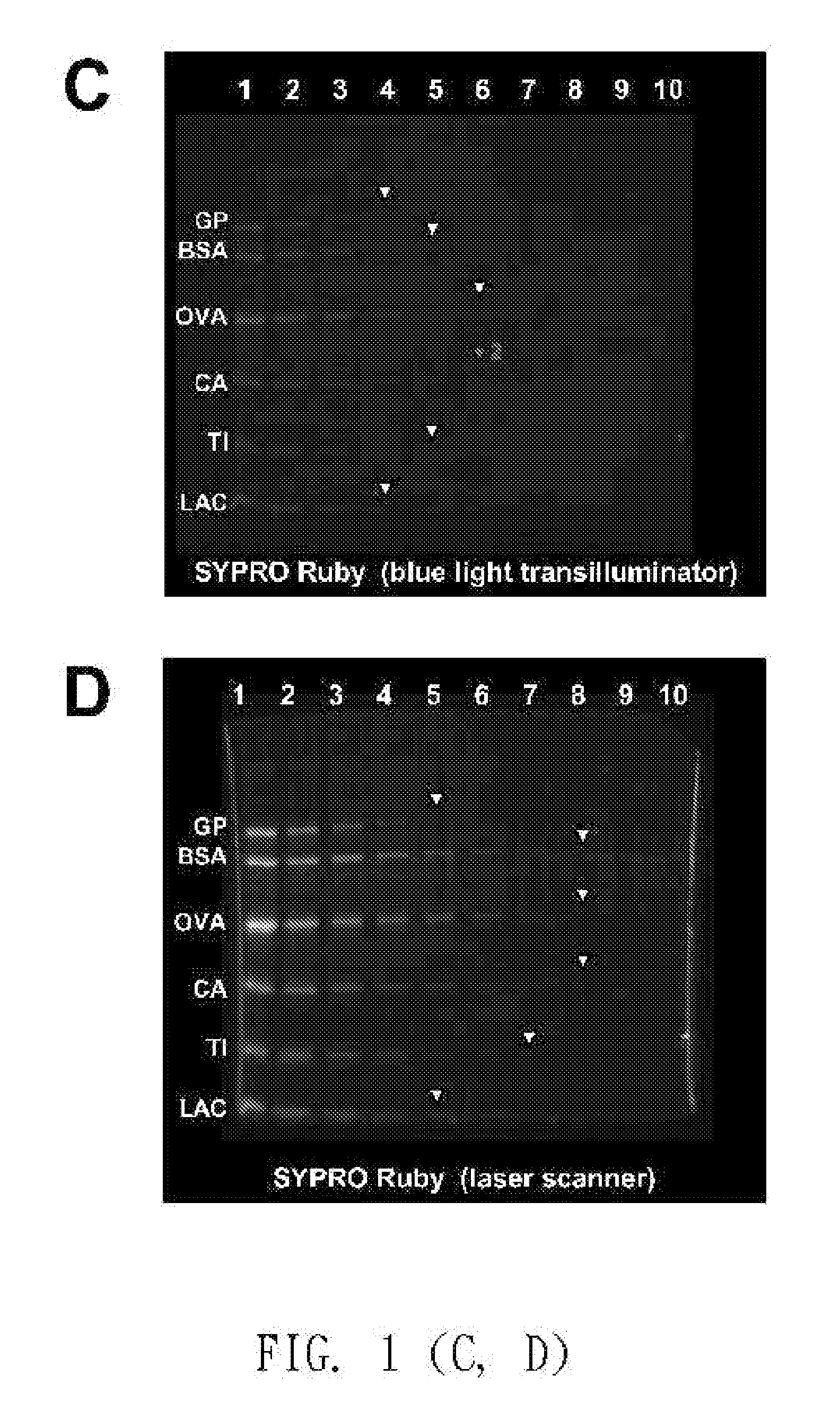
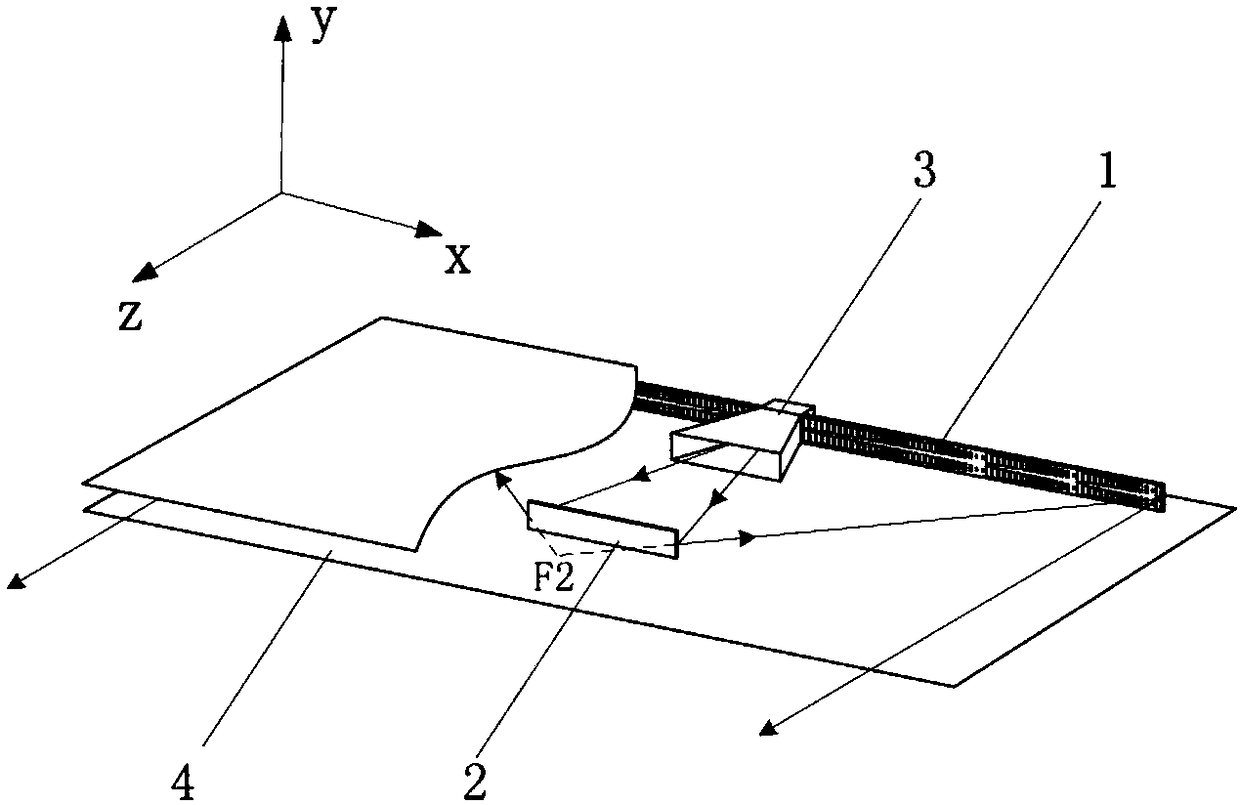
Device for exciting fluorescent sample by utilizing visible light
The invention relates to a device for exciting a fluorescent sample by utilizing visible light, in particular to a device for lightening a fluorescent signal of polyacrylamide protein gel or other similar objects by a backlight-type blue light plate so as to improve a signal-to-noise ratio in the exciting process. The embodiment of the invention shows that the device is suitable for observing a plurality of protein gels dyed by fluorescer, and can ensure that certain weak fluorescent signals can be inspected by naked eyes and a filter lens is not needed. The device for straightly observing the fluorescent signal of the protein gel by utilizing the backlight-type blue light plate comprises a transparent plate for guiding light and at least one light source, wherein the at least one light source is arranged beside the transparent plate so that the fluorescent sample placed on the transparent plate of the device can be excited by light refracted or reflected by the transparent plate according to the Snell's law; and the signal-to-noise ratio in the exciting process is improved through the light refraction effect of the device.
Owner:陈翰民 +1
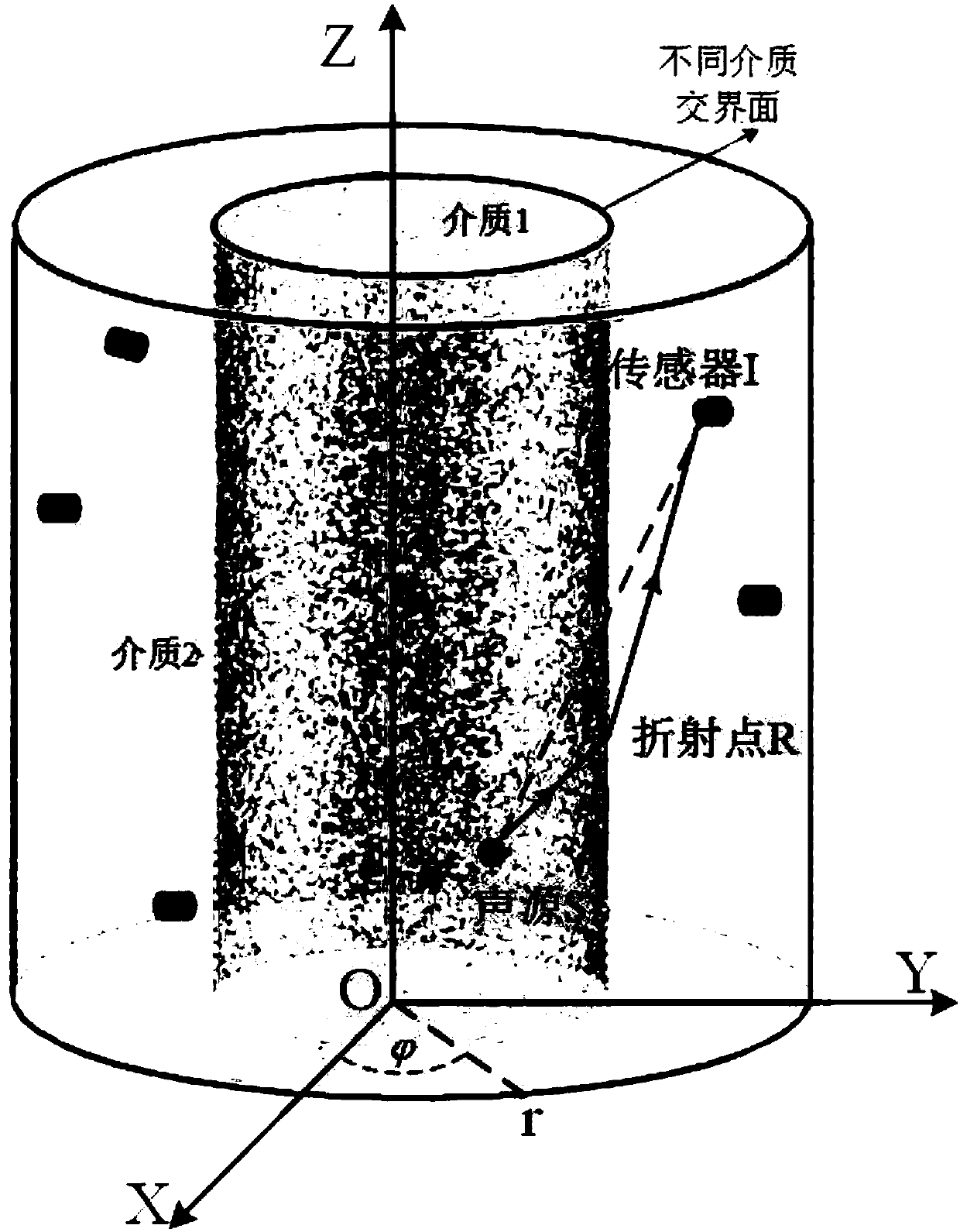
Acoustic emission source locating method and system used for rock mechanics triaxial test
InactiveCN107727744AAvoid errorsMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesProcessing detected response signalTriaxial shear testAcoustic emission
The invention discloses an acoustic emission source locating method and system used for a rock mechanics triaxial test. A reflection effect of acoustic emission in an interface of a triaxial loading oil cylinder and an internal sample is considered, a path equation of acoustic wave propagation is established according to a Snell's law, the time for sound to be transmitted from an acoustic emissionsource to a sensor is calculated, and by calculating the difference value between an arrival time difference matrix and an arrival time difference matrix which is measured actually, position coordinates of an acoustic source are obtained. A new method is provided for accurately locating acoustic emission of the rock mechanics triaxial test, and the situation is considered that when a test piece is pressurized during the triaxial test, acoustic waves are generated by internal cracks, and the paths of the test piece are changed in different medium contact surfaces. In the meanwhile, the acoustic emission source locating method and system can also be used for other conditions that acoustic emission sensors and the acoustic source are in different mediums, and the mediums are hook-face mediums.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Acoustic wave measuring system and method of generating image data thereof
InactiveUS20110182136A1Reduce the impactReduce impactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightTime domainElectricity
When correcting the acoustic wave refraction occurring on the interface between mediums having different sound speeds by Snell's law, an applicable back-projection method is limited to a time domain method. An image data generating method performed to receive and convert an acoustic wave generated by irradiating a subject with light into a first electrical signal with an acoustic wave receiver via a medium having a sound speed different from that of the subject, and to generate image data based on the first electrical signal is provided, wherein a second electrical signal obtained when the acoustic wave is received at each virtual reception point is generated based on the first electrical signal through an integral calculation performed by using an advanced Green's function, and image data is generated based on the second electrical signal.
Owner:CANON KK
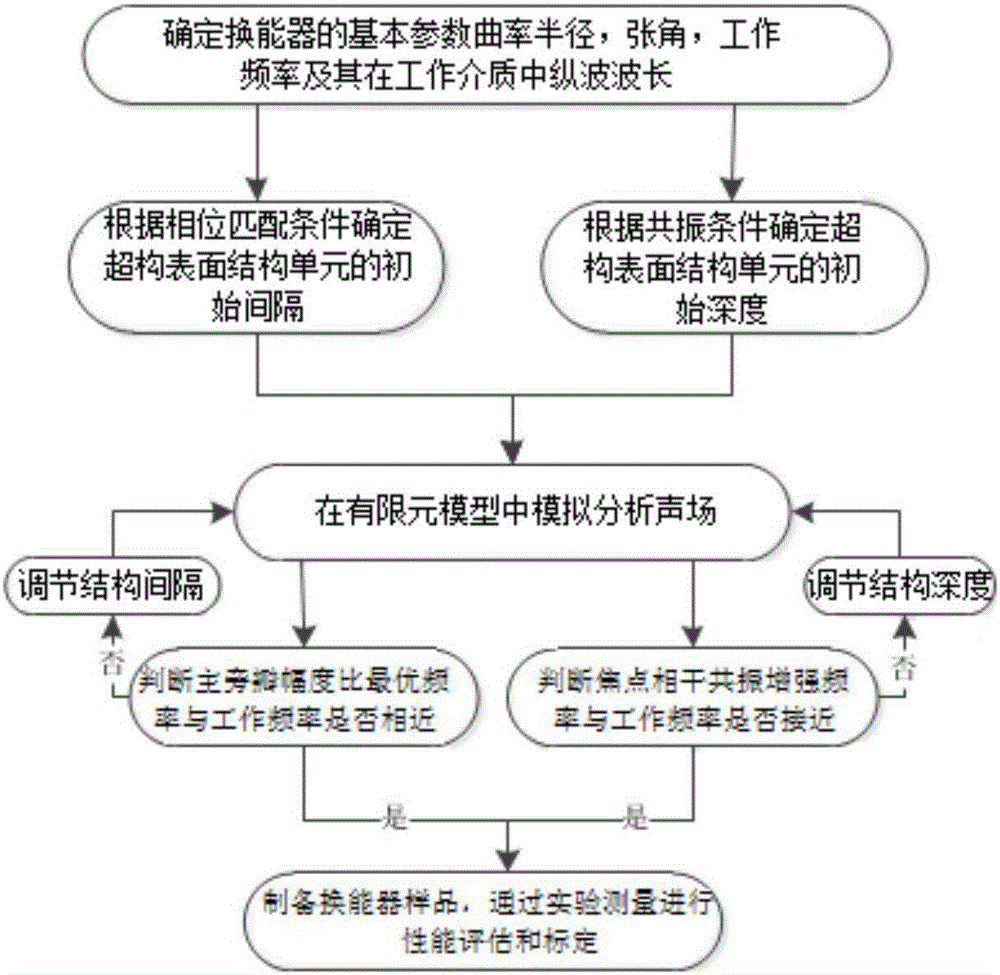
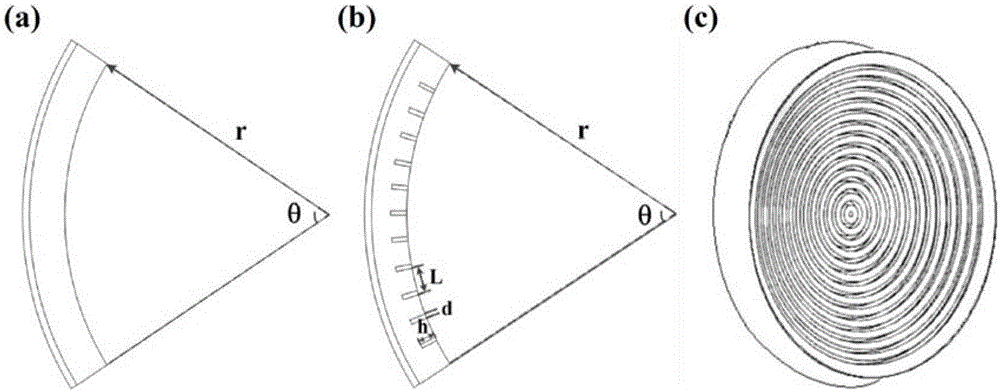
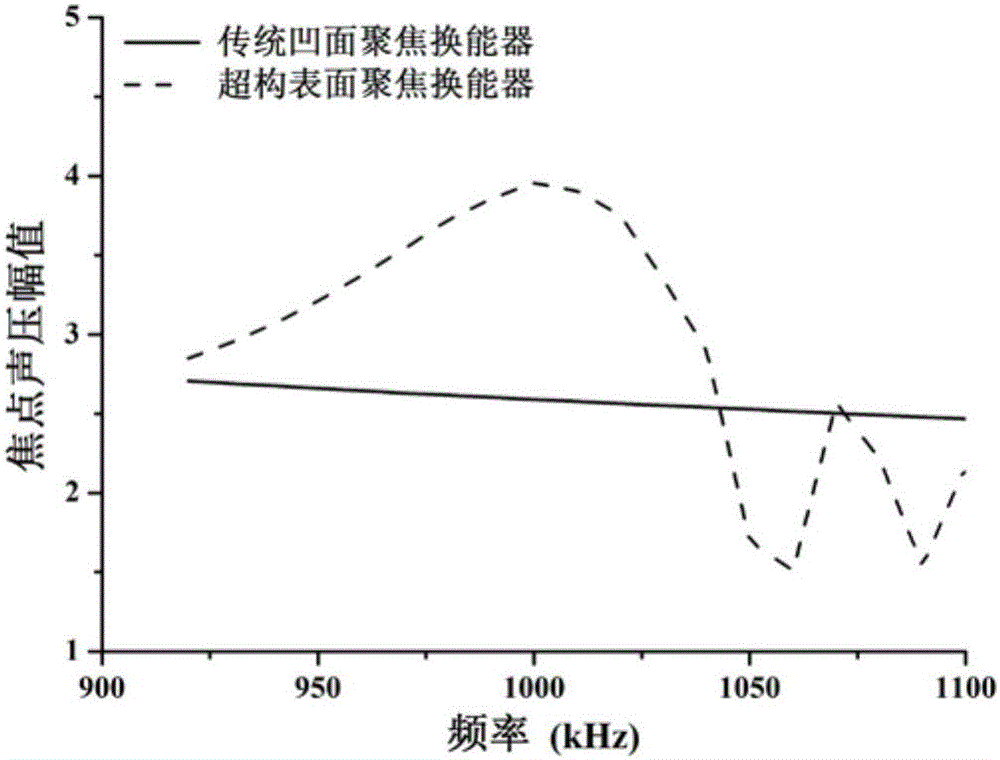
Design method for concave-focusing transducer with super formation surface
The invention discloses a design method for a concave-focusing transducer with a super formation surface and belongs to the technical of ultrasonic focusing. By virtue of constructing a super formation surface structure on the surface of a traditional concave focusing transducer and utilizing a cavity resonance mode of the super formation surface structure, the radiation efficiency of the focusing transducer is enhanced. When surface acoustic evanescent waves supported by the super formation surface structure spatially meets a phase matching condition, a coherent diffraction enhancement effect is caused, and improvement on the focusing property is realized; the concave-focusing transducer belongs to innovation of the ultrasonic focusing field; the super formation surface meets the generalized reflection and refraction Snell's law and is capable of realizing discontinuous modulation on phases; by virtue of modulating the super formation surface through a periodic wavy structure, the super formation surface of the concave focusing transducer is capable of regulating and controlling the sound field distribution within a specific frequency range and thus improving the main sidelobe ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUKEAN PHARM CO LTD
Method and apparatus for inspecting parts with high frequency linear array
InactiveUS20060009948A1Easy to viewAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationUltrasonic sensorEngineering
An apparatus and method for a nondestructive examination of an aircraft or other metal or composite object. The apparatus for a nondestructive examination includes a linear array of ultrasound transducer, a wedge used to provide an interface between the linear array and the object being examined wherein the angle of the wedge is determined by use of Snell's law wherein the signals from the linear array are manipulated by a micro computer which then presents a visual display of the object being examined and any flaws found in the object.
Owner:WULF DANNIS +1
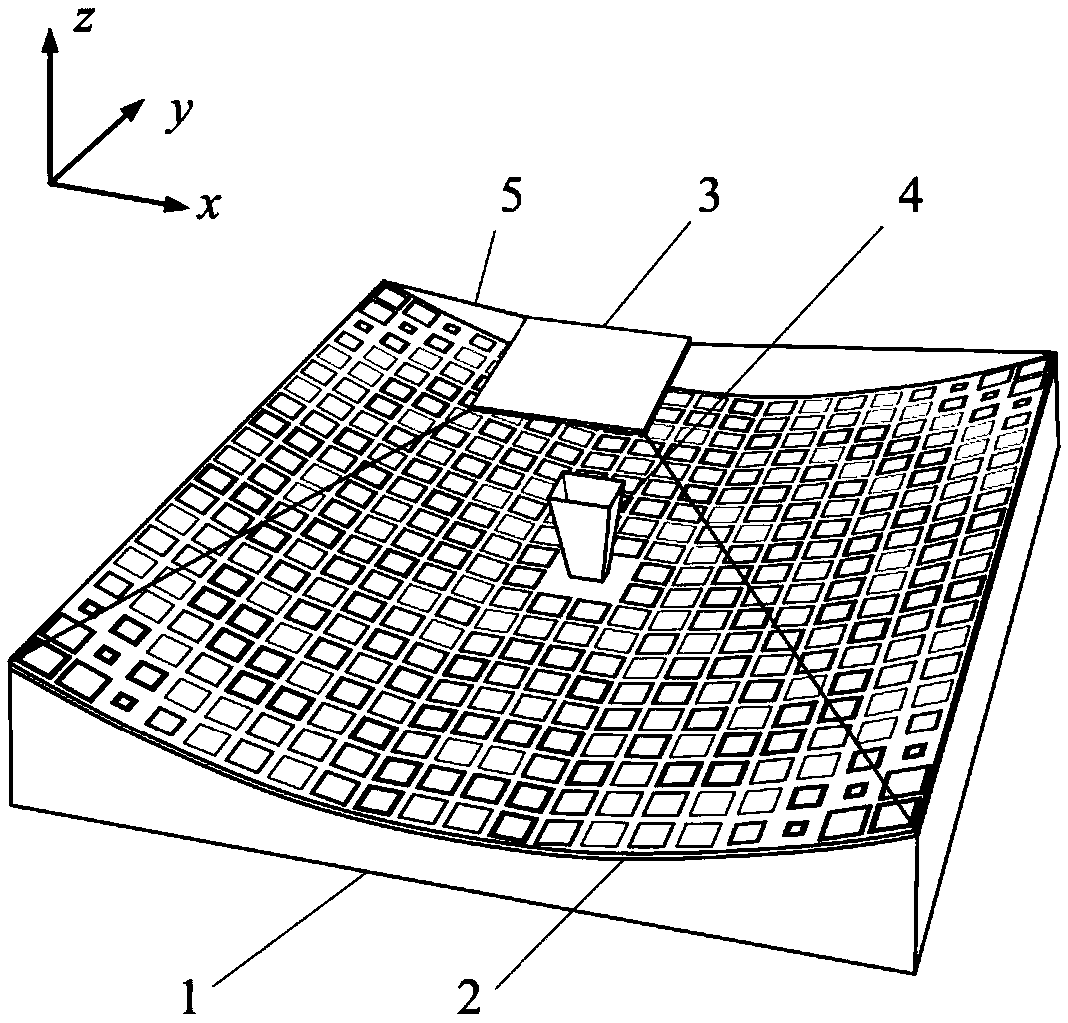
Metasurface-based cassegrain antenna
ActiveCN108808251AShorten focal lengthAchieving Phase CompensationWaveguide hornsConvex structureRadar
The invention discloses a metasurface-based cassegrain antenna, and mainly aims to solve the problems that the existing cassegrain antenna is high in phase error, complex in structure, and long in focal length. The metasurface-based cassegrain antenna comprises a carrier (1), a main reflecting mirror (2), an auxiliary reflecting mirror (3), a feed source (4) and a supporting structure (5); the carrier adopts a convex structure; the main reflecting mirror is conformal with the carrier; each of the main reflecting mirror and the auxiliary reflecting mirror adopts a phase change metasurface structure established based on generalized Snell law, wherein the auxiliary reflecting mirror is located below the focal point of the main reflecting mirror and has a hyperbolic characteristic phase, and is used for dispersing the electromagnetic waves emitted by the feed source into spherical waves; the main reflecting mirror and the auxiliary reflecting mirror are connected through the supporting structure; and the virtual focal point of the auxiliary reflecting mirror coincides with the focal point of the main reflecting mirror, and the solid focal point coincides with the phase center of the feed source. By virtue of the metasurface-based cassegrain antenna, the focal length of the cassegrain antenna can be shortened, wave beam calibration can be realized; and meanwhile, the antenna phase compensation error is lowered, the structure is simple, and the antenna can be used for communication and radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Thin film interference effect drawing method based on ray tracer
ActiveCN104183007AImproved ability to draw wave effectsGood drawing effect3D-image rendering3D modellingPhysical opticsRefraction angle
The invention discloses a thin film interference effect drawing method based on a ray tracer. The thin film interference effect drawing method based on the ray tracer comprises the following steps: obtaining multi-layer thin film mixed reflectivity and transmittance by applying a multi-beam interference equation, wherein single-layer film surface reflection coefficient and transmission coefficient can be determined by a Fresnel formula, and a refraction angle in the thin film obeys a Snell law; introducing in a rough surface scattering coefficient by considering that certain thin films generate the irregularity of reflection or transmission light distribution due to roughness to correct the thin film reflectivity and transmittance and simulate complex optical effects, such as colorful highlight, anisotropy and the like; and on the basis of a ray tracer imaging mechanism, constructing a link between physical optics and geometrical optics, and generating a whole scattering formula. The capability of the traditional ray tracer on drawing fluctuation effect is effectively improved, the invention can be continuously integrated into classical 3D modeling software Maya in a plugin way, so that a user obtains required colorful fluctuation effect directly through the modeling software to further improve the drawing capability of the modeling software which takes Maya as a representative, and the invention exhibits high application value.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
All-dielectric transmission type efficient ultrathin beam splitter and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112558218AExcellent beam splitting performanceImprove transmission efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideBeam splitterNanopillar
The invention discloses an all-dielectric transmission type efficient ultrathin beam splitter and a preparation method and application thereof. A beam splitter comprises a plurality of structural unitarrays, wherein each structural unit comprises: a substrate made of a transparent dielectric material; a dielectric functional layer which is made of a high-refractive-index transparent dielectric material, is arranged on the substrate and comprises a periodic nano-pillar array structure that comprises a limited number of pillars which are periodically and alternately arranged and have differentdiameters, wherein the arrangement rule of the limited number of cylinders with relatively large diameters and the limited number of cylinders with relatively small diameters conforms to the generalized Snell's Law. The beam splitter has excellent beam splitting performance, can split normally incident visible light into two beams of emergent light, and has the advantages of being high in transmission efficiency, wide in wave band, ultrathin, light, easy to integrate, low in power consumption, low in cost and relatively easy to manufacture. The beam splitter has application prospects in the fields such as an optical sensing system, a nanometer photonic device and an integrated optical system.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Solid-state image capturing device, solid-state image capturing apparatus, and electronic information device
ActiveUS7880252B2Inhibit coloringPrevent luminanceTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesLight fluxLight beam
A solid-state image capturing device is provided. In the solid-state image capturing device, at least any of openings of electrode wiring layers, color filters and microlenses are provided on a light incident side above light receiving elements as a light receiving region in which the plurality of light receiving elements are disposed on a semiconductor substrate or a semiconductor region provided on a substrate, wherein a shift amount of at least any of the openings of the electrode wiring layers, the color filters and the microlenses in relation to the light receiving elements or in relation to a standard position where a light flux is desired to pass through is calculated by Snell's law based on an incident angle θ0 of a light flux entering the light receiving region to a surface of the solid-state image capturing device.
Owner:SHARP KK
Demultiplexing device based on metasurface of V-shaped optical antenna and working method of demultiplexing device
InactiveCN109597160AImplement demultiplexingFlexible modulationOptical waveguide light guideMicro nanoPhase shifted
The invention relates to a demultiplexing device based on the metasurface of a V-shaped optical antenna and a working method of the demultiplexing device. The device comprises a substrate and a plurality of periodically-arranged V-shaped antenna unit groups arranged on the substrate; the plurality of the V-shaped antenna unit groups are arranged in sequence along an X axis and are arranged in parallel along a Y axis; each V-shaped antenna unit group comprises six V-shaped antennas; a phase difference between every two adjacent V-shaped antennas is pi / 3; and phase coverage of 0 to 2 pi is achieved. The demultiplexing device can realize different angle deflection for multi-wavelength light of a specific waveband. Based on a generalized Snell law, in a working waveband of 1,450-1,650nm, the arm length and an included angle of the V-shaped antennas are modulated to introduce a phase sudden change gradient at an interface, so that abnormal refraction is achieved. Through the interaction between incident light and a micro-nano antenna array at the interface, linear polarization conversion transmission phase shift in the range of 0-2 pi can be flexibly modulated, and chromatic dispersionat different angles can be performed for light with different wavelengths.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Device for exciting fluorescent samples using visible light or ultraviolet light
InactiveUS20110278476A1Increase contrastImprove visualizationPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersFluorescenceWaveguide
This invention proposes a device for exciting fluorescent samples using visible light or ultraviolet light, the device comprising, a transparent plate or strip as waveguide for guiding light; at least one lighting source placed alongside the transparent plate or strip; a transparent matrix;such that the fluorescent samples in the transparent matrix placed on waveguide of the device is excited by the light refracted from the waveguide to the transparent matrix according the Snell's Law; thus the exciting S / N ratio can be improved by the light refraction of the device; wherein the light emitted from the light source with a primary incident angle larger than the critical angle of transparent plate or strip:air, but smaller than the critical angle of transparent plate or strip:matrix.
Owner:CHEN HAN MIN +1
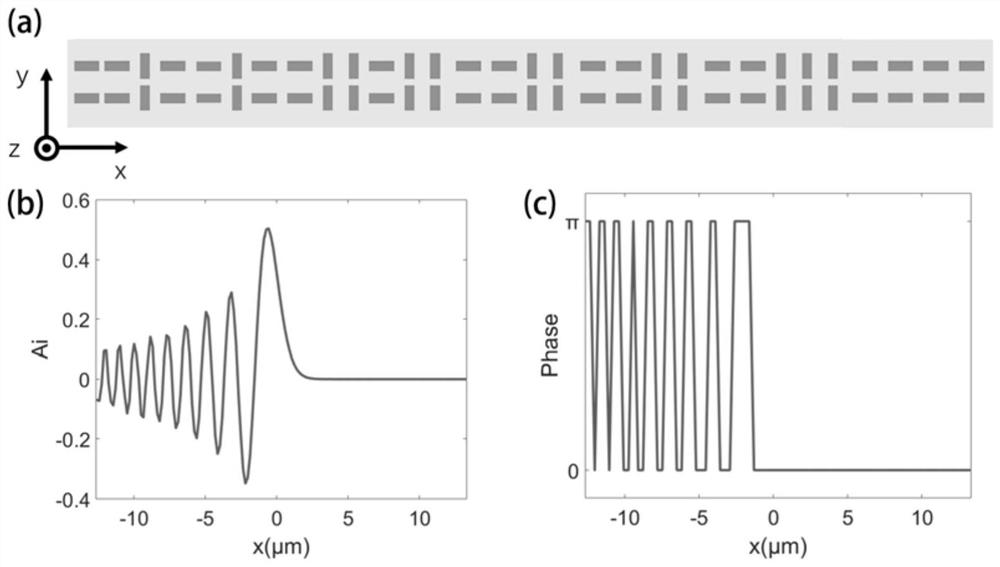
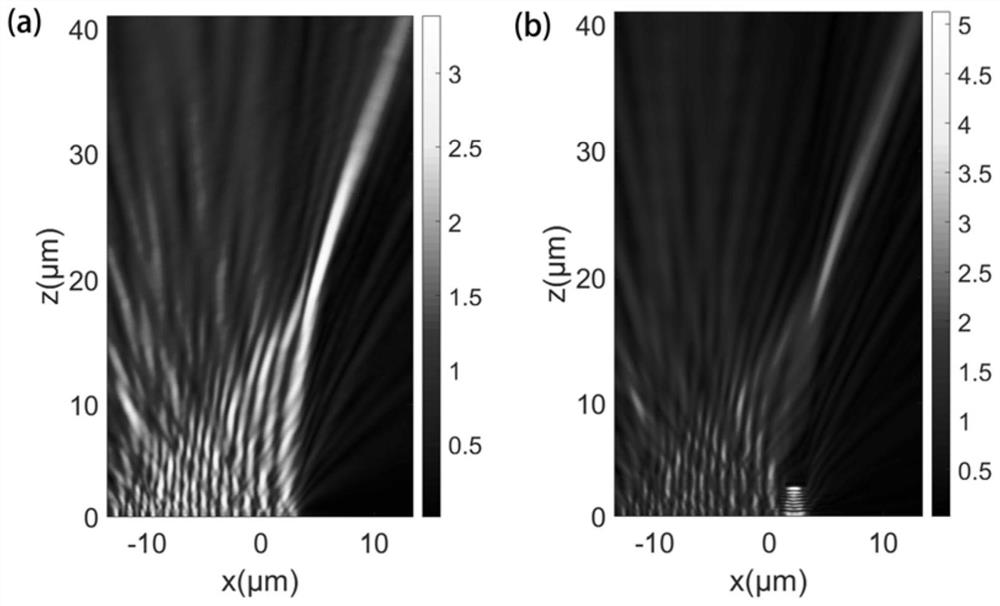
Geometric phase type super lens for generating Airy beams
The invention discloses a geometric phase type super lens for generating Airy beams, which is mainly based on generalized Snell's law and geometric phase, and designs a planar ultra-thin super lens for generating Airy beams. The super lens comprises glass serving as a lens substrate, and a micro-nano titanium dioxide cubic structure layer arranged on the upper surface of the glass and used for modulating an incident light beam. According to the super lens based on the single-layer micro-nano titanium dioxide cuboid array type distribution structure of different rotation angles, the problems that a device is heavy and the structure is complex in a traditional Airy beam generation method are solved; and the micro-nano structure is adopted to improve the traditional mode of generating one-dimensional, two-dimensional and array Airy beams, the size and weight of the lens are reduced as much as possible, and the miniaturization and integration trend of modern optical devices or photoelectric devices is met.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cassegrain antenna based on super surface
ActiveCN108306112AGood radiation characteristicsPrecise Phase CompensationAntennas earthing switches associationSnell's lawWaveguide
The invention provides a Cassegrain antenna based on a super surface, and aims to reduce the phase compensation error of the antenna and simplify the antenna structure at the same time. The Cassegrainantenna comprises a slab waveguide, a main reflector, an auxiliary reflector and a feed source, wherein the main reflector, the auxiliary reflector and the feed source are clamped between two metal plates of the slab waveguide, both the main reflector and the auxiliary reflector adopt a phase sudden change super surface structure constructed based on a generalized Snell's law, the size of a metalring microstructure on a phase control layer of the main reflector is decided by the electromagnetic wave incident angle and the scattering parameter phase at the location so as to realize an electromagnetic wave phase compensation characteristic similar to that of a paraboloid, the size of a metal ring microstructure on a phase control layer on the auxiliary reflector is decided by the electromagnetic wave incident angle and the scattering parameter phase at the location so as to realize an electromagnetic wave phase compensation characteristic similar to that of a hyperboloid; and the feedsource is located at the midpoint of the main reflector which is opposite to the phase control layer of the auxiliary reflector, a virtual focus of the auxiliary reflector is overlapped with a focus of the main reflector, and a real focus of the auxiliary reflector is overlapped with a phase center of the feed source.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Gregorian antenna based on super surface
ActiveCN108306111AGood radiation characteristicsPrecise Phase CompensationAntennas earthing switches associationSnell's lawWaveguide
The invention provides a Gregorian antenna based on a super surface, and aims to reduce the phase compensation error of the antenna and simplify the antenna structure at the same time. The Gregorian antenna comprises a slab waveguide, a main reflector, an auxiliary reflector and a feed source, wherein the main reflector, the auxiliary reflector and the feed source are clamped between two metal plates of the slab waveguide, both the main reflector and the auxiliary reflector adopt a phase sudden change super surface structure constructed based on a generalized Snell's law, the size of a metal ring microstructure on a phase control layer of the main reflector is decided by the electromagnetic wave incident angle and the scattering parameter phase at the location so as to realize an electromagnetic wave phase compensation characteristic similar to that of a paraboloid, the size of a metal ring microstructure on a phase control layer of the auxiliary reflector is decided by the electromagnetic wave incident angle and the scattering parameter phase at the location so as to realize an electromagnetic wave phase compensation characteristic similar to that of an ellipsoid; and the feed source is located at the midpoint of the main reflector which is opposite to the phase control layer of the auxiliary reflector, a near focus of the auxiliary reflector is overlapped with a focus of themain reflector, and a far focus of the auxiliary reflector is overlapped with a phase center of the feed source.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
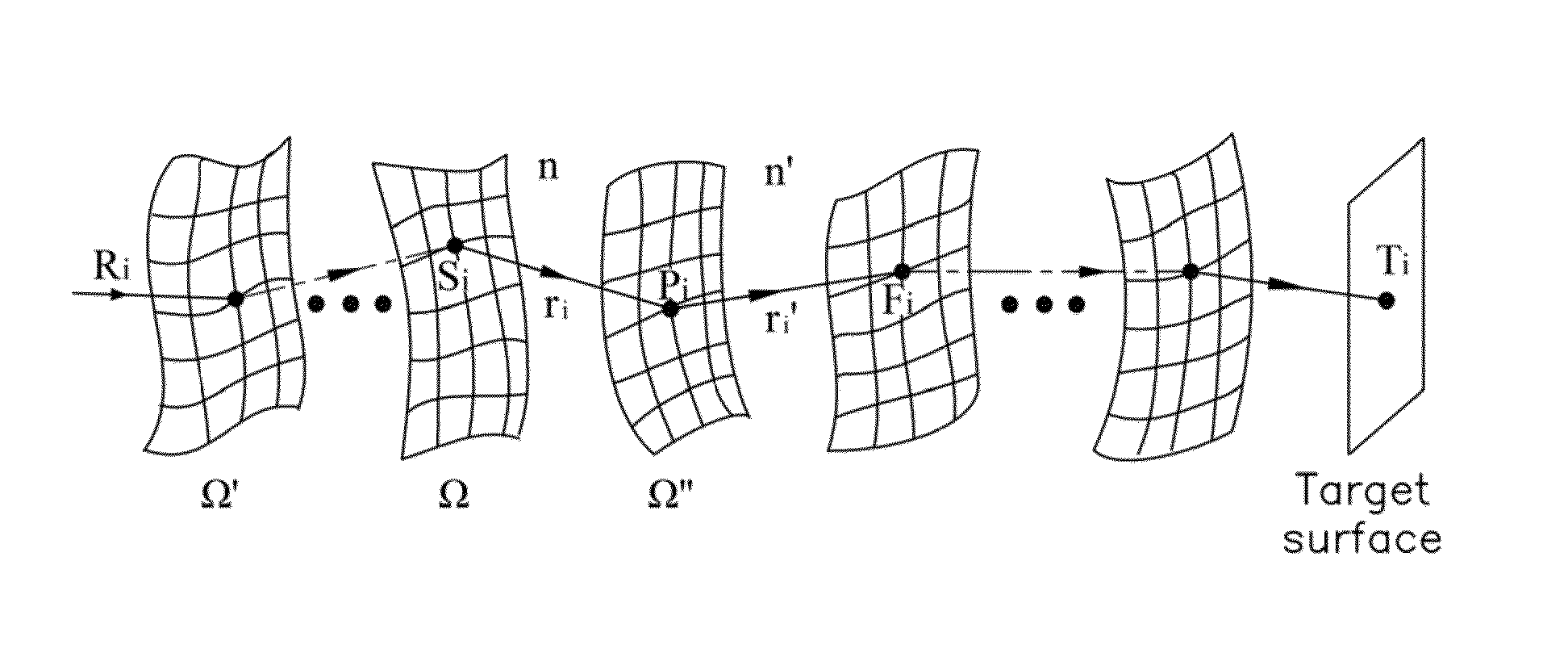
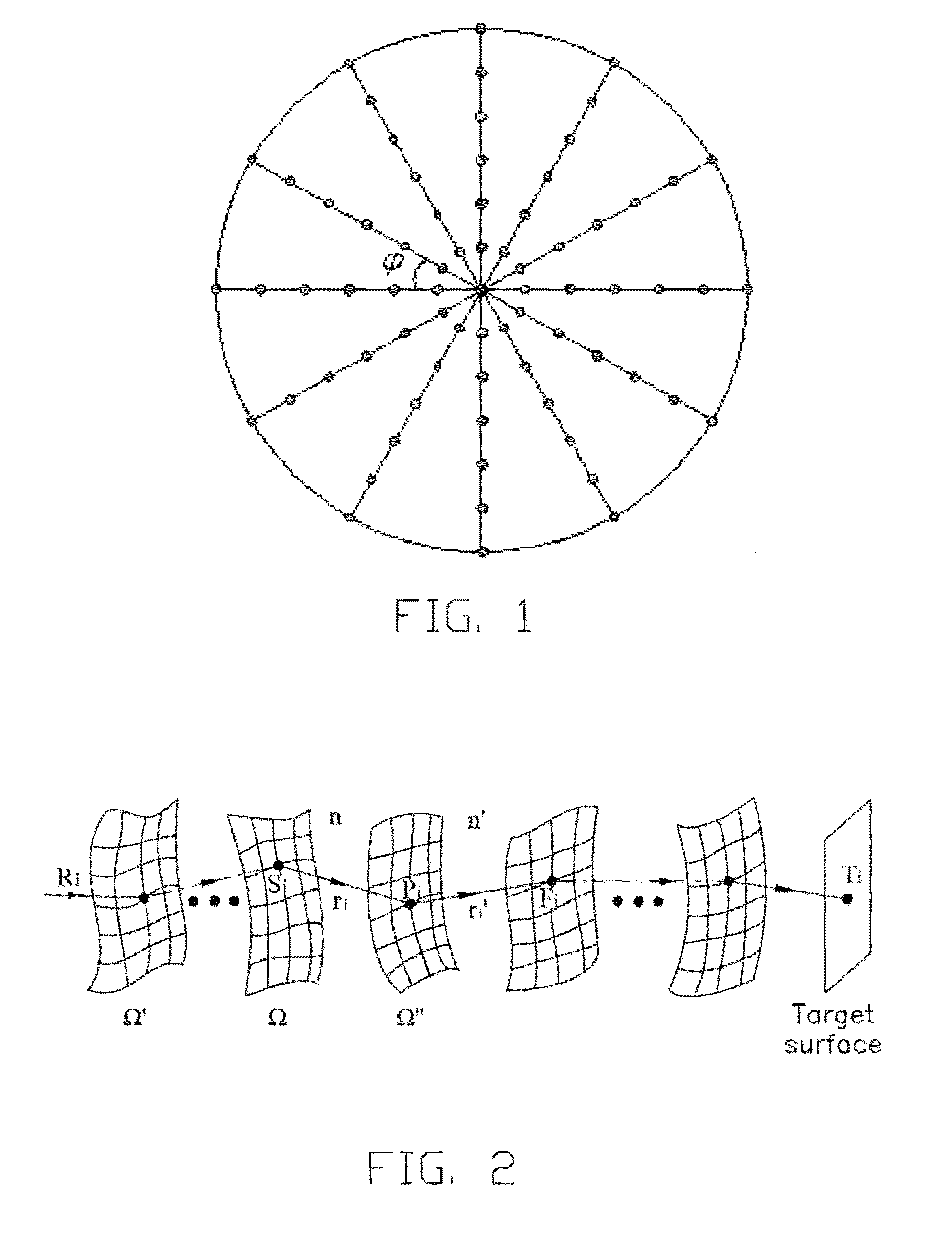
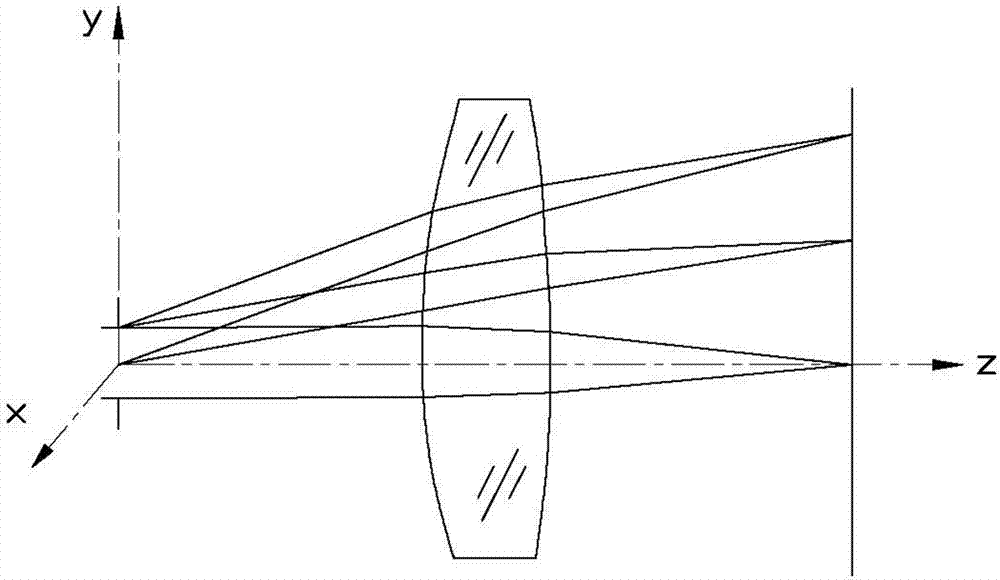
Method for designing freeform surface
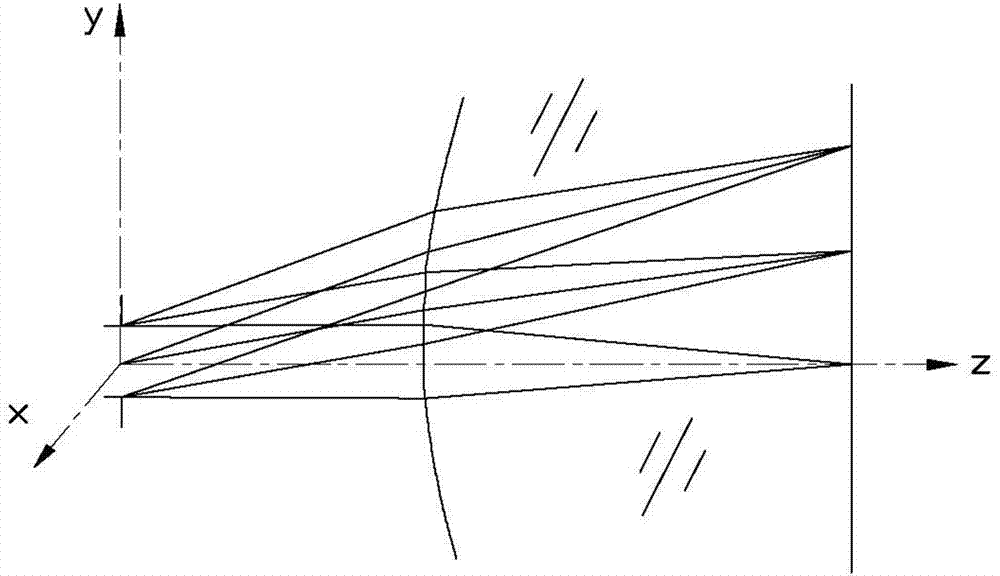
A method for designing freeform surface is provided. An initial surface is established. A plurality of feature rays are selected. A plurality of intersections of the plurality of feature rays with an unknown freeform surface are calculated based on a given object-image relationship and a vector form of the Snell's law. The plurality of intersections are a plurality of feature data points. An unknown freeform surface equation is obtained by surface fitting the plurality of feature data points.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com