Method for testing conductivity of medium material
A technology for dielectric material, charge and discharge testing, applied in the field of testing, can solve the problems of different research purposes, different numbers of electrodes, regardless of storage time and quantity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
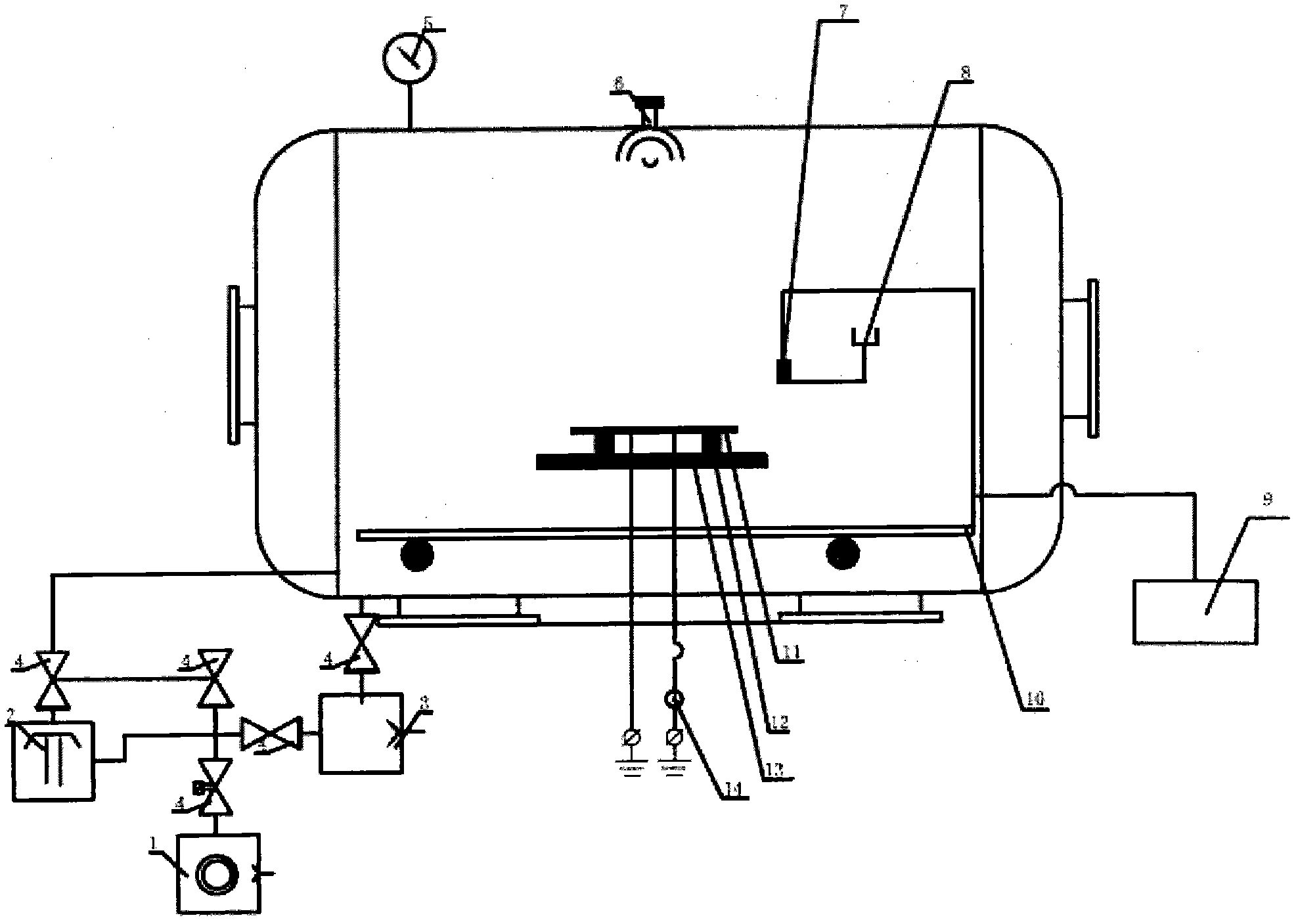
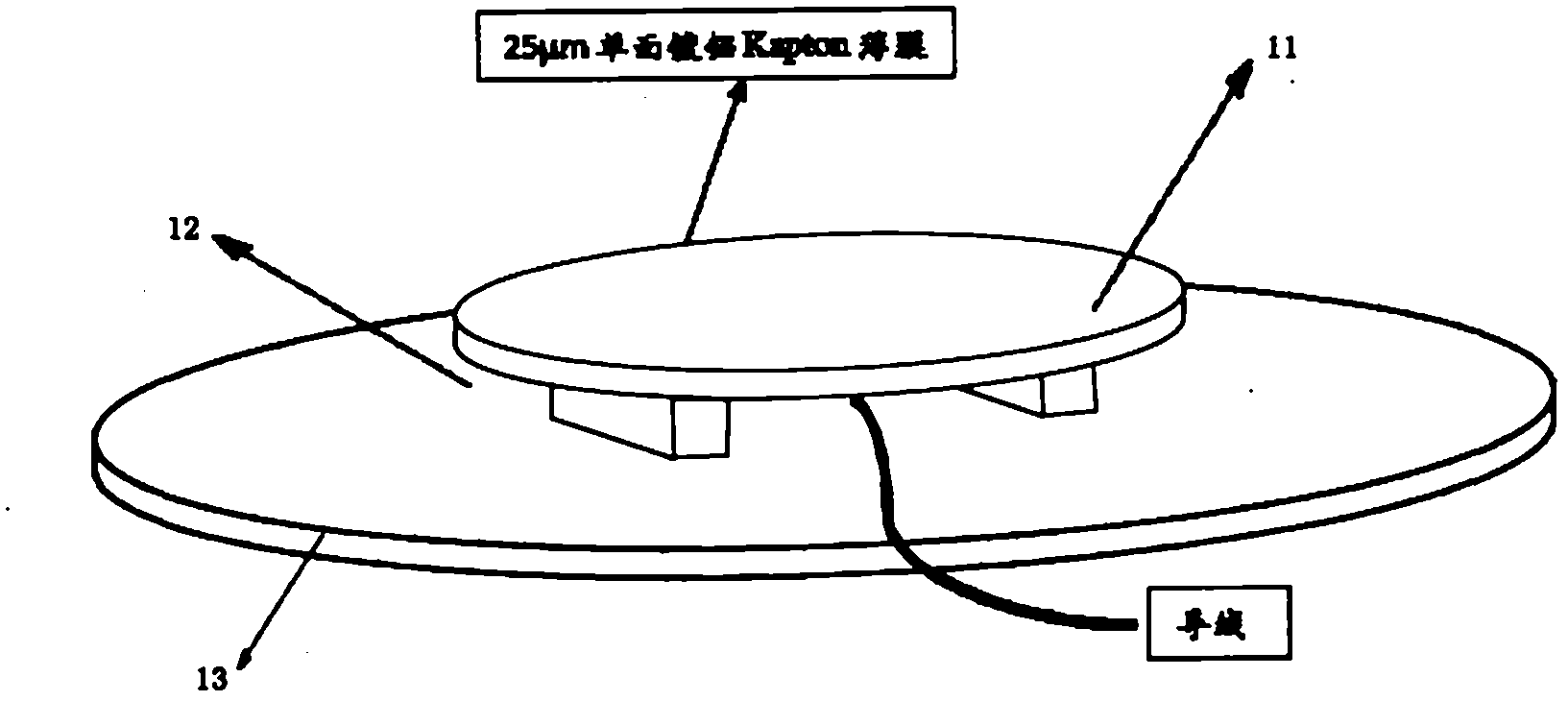
[0025] The testing equipment in the present invention includes a vacuum system, a charging and discharging system, and a potential testing system. The vacuum system includes a vacuum tank, a mechanical pump 3, a diffusion pump 2, a multistage rotary vane pump 1, valves, sealed pipelines and a workbench; the charging and discharging system consists of an electron gun 6 and a sample 11 installation system; the potential testing system includes a potentiometer 9 and microcurrent meter 14, vacuum valve 4 and vacuum gauge 5 are placed in the vacuum tank.
[0026] The connection relationship of this system is: the vacuum tank is placed on the workbench, connected to the mechanical pump through one sealed pipeline through the baffle valve A15, connected to the diffusion pump 2 through the other sealed pipeline through the baffle valve B16, and mechanical pump 3 , multi-stage rotary vane pump 1, and diffusion pump 2 form the pumping unit in the vacuum system; the electron gun 6 is loc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com