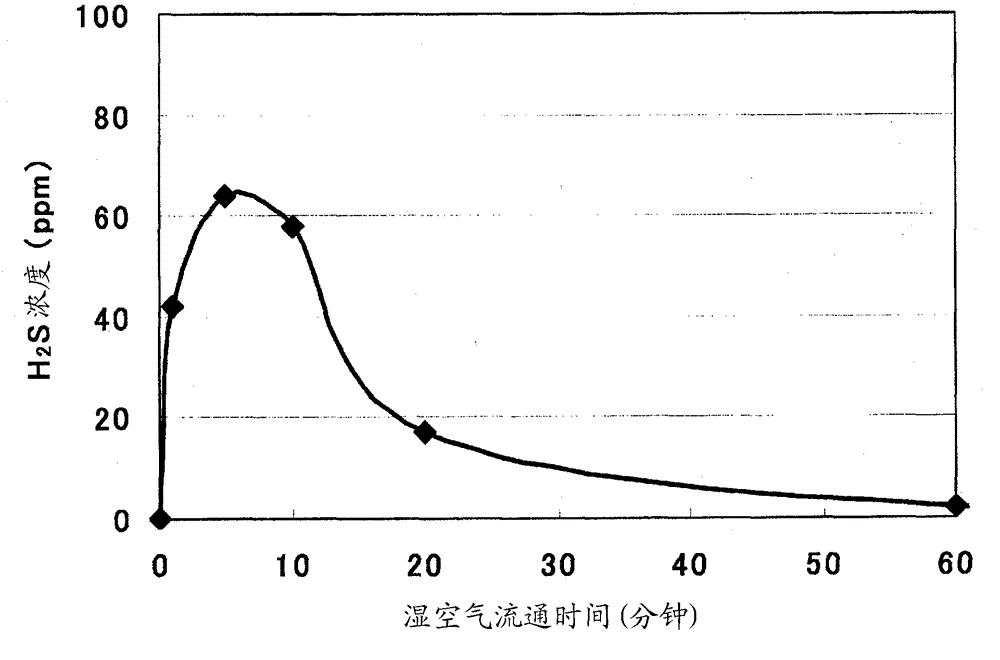
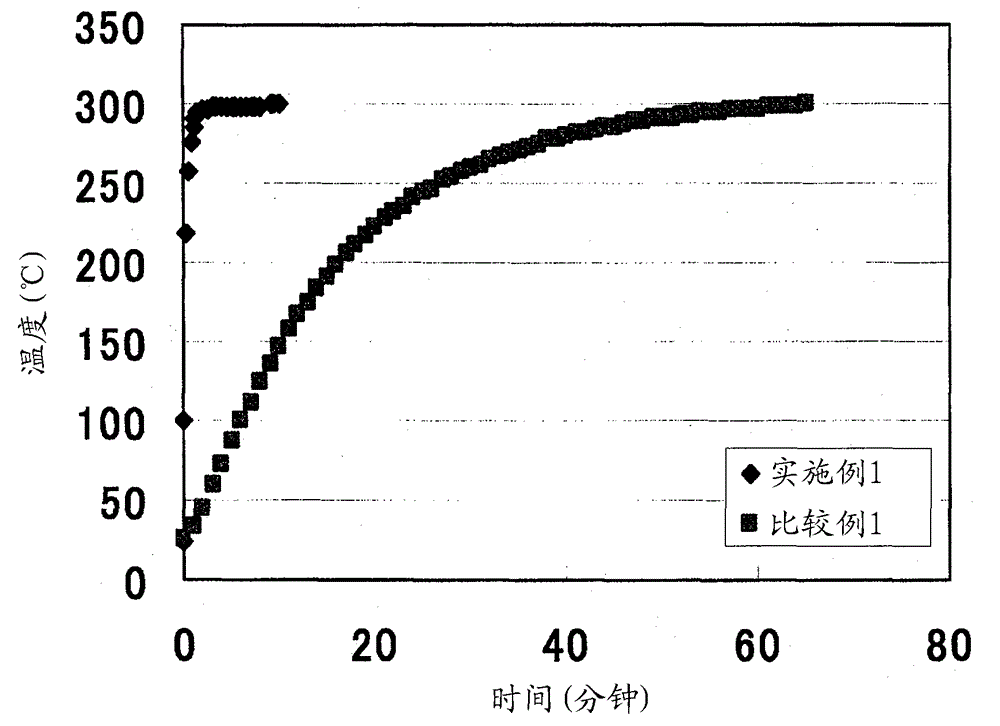
Solid electrolyte
A technology of solid electrolyte and electrolyte layer, applied in electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as reduced ionic conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
manufacture example 1
[0230] Production example 1 [lithium sulfide (Li 2 S) Manufacture, purification]
[0231] Lithium sulfide was produced and purified in the same manner as the method described in the Examples of International Publication No. 2005 / 040039 pamphlet.
[0232] Specifically, it performed as follows.
[0233] (1) Lithium sulfide (Li 2 S) Manufacture
[0234] Lithium sulfide is produced according to the method of the first embodiment (two-step method) of JP-A-7-330312. Specifically, 3326.4 g (33.6 moles) of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) and 287.4 g (12 moles) of lithium hydroxide were added to a 10-liter autoclave with a stirring paddle, and the temperature was raised to 130 ° C at 300 rpm . After the temperature was raised, hydrogen sulfide was blown into the liquid at a supply rate of 3 liters / minute for 2 hours.
[0235] Next, the temperature of the reaction solution was raised under nitrogen flow (200 cc / min), and a part of the reacted hydrogen sulfide was dehydrogenated. As ...
manufacture example 2
[0239] Production Example 2 [Sulfide-based solid electrolyte glass (Li 2 S / P 2 S 5 (Molar ratio) = 75 / 25) Manufacture - Mechanical ball milling method -]
[0240] Using the lithium sulfide produced in Production Example 1, a sulfide-based glass was produced by the method in accordance with Example 1 of WO 07 / 066539 pamphlet.
[0241] Specifically, it was performed as follows.
[0242] 0.383 g (0.00833 mol) of lithium sulfide produced in Production Example 1 and 0.618 g (0.00278 mol) of phosphorus pentasulfide (manufactured by Aldrich) were thoroughly mixed. Then, put this mixed powder together with 10 zirconia balls with a diameter of 10 mm into a planetary ball mill (manufactured by Fritsch Japan Co., Ltd.: model P-7) into an alumina tank and completely seal it. The alumina tank was filled with nitrogen to form a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0243] Then, the planetary ball mill was rotated at a low speed (85 rpm) for the first few minutes to thoroughly mix lithium sulfide and ...
manufacture example 3
[0248] Production Example 3 [Sulfide-based solid electrolyte glass (Li 2 S / P 2 S 5 (Molar ratio) = 75 / 25) production - slurry method -]
[0249] Using the lithium sulfide produced in Production Example 1, a sulfide-based glass was produced by the same method as in Example 1 of JP-A-2010-140893.
[0250] Specifically, it performed as follows.
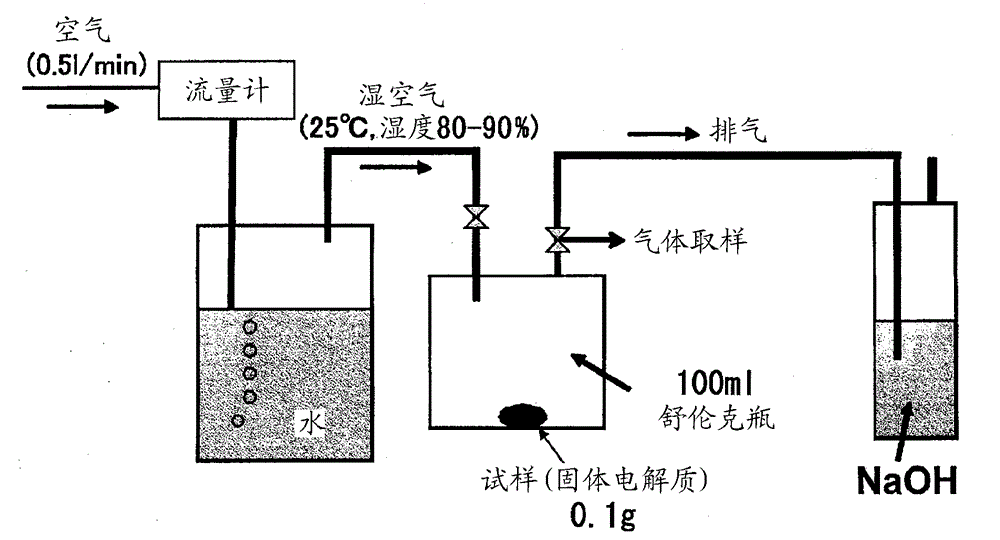
[0251] use figure 1 The shown apparatus 1 produces sulfide-based glass ceramics. As the mixer 10, Star mill mini Tse A (0.15 L) (bead mill) manufactured by Ashizawa Finetech Ltd. was used, and 450 g of 0.5 mmφ zirconia balls were charged. As the reaction tank 20, a 1.5 L glass reactor equipped with a stirrer was used.
[0252] A mixture obtained by adding 1080 g of dehydrated toluene (moisture content 8 ppm) produced by Hiroshima Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. to 45.90 g (75 mol%) of lithium sulfide produced in Production Example 1 and 74.10 g (25 mol %) of phosphorus pentasulfide produced by Aldrich Co., Ltd. In the reaction t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com