Patents
Literature
36 results about "Acoustic microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acoustic microscopy is microscopy that employs very high or ultra high frequency ultrasound. Acoustic microscopes operate non-destructively and penetrate most solid materials to make visible images of internal features, including defects such as cracks, delaminations and voids.
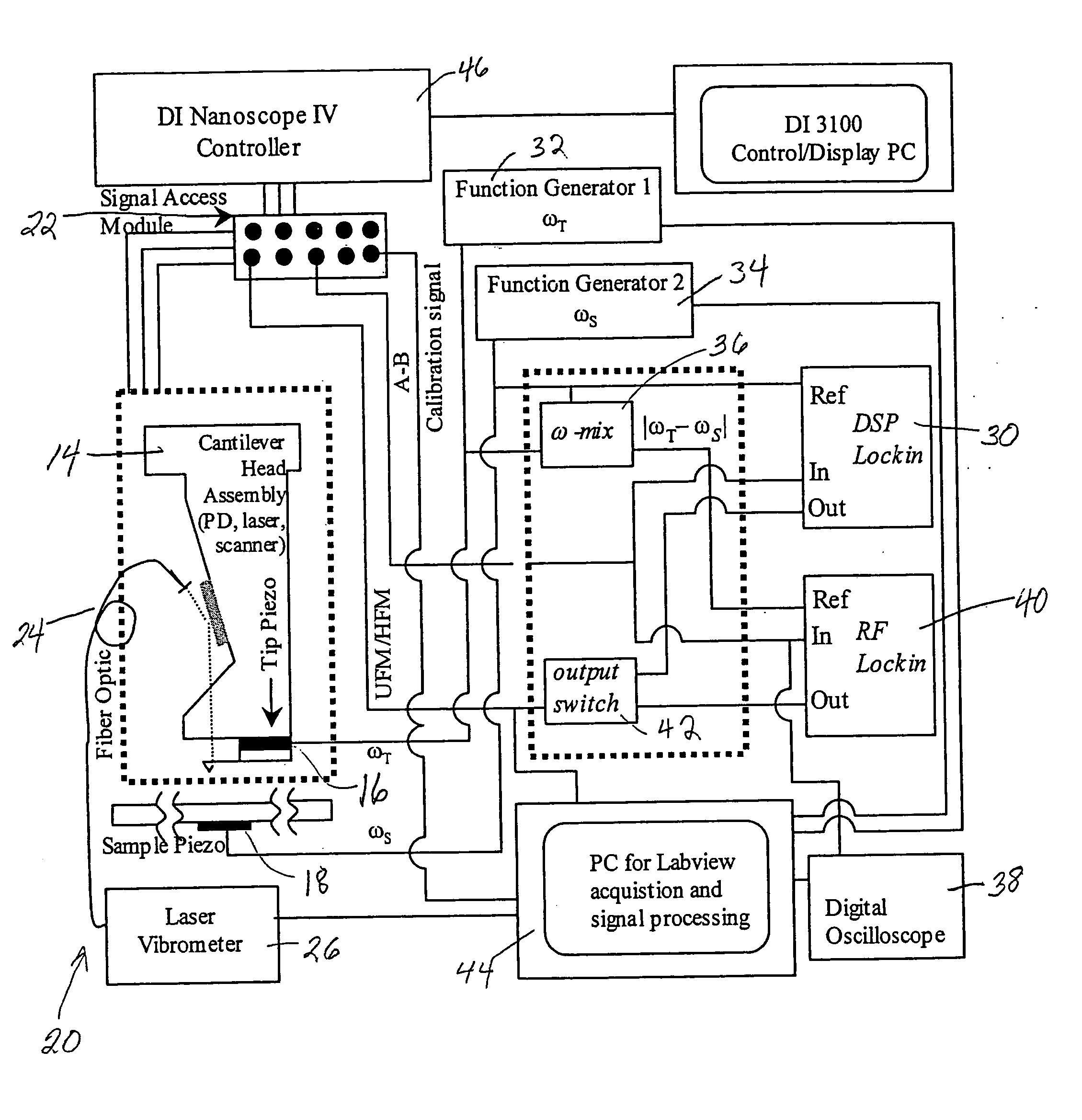
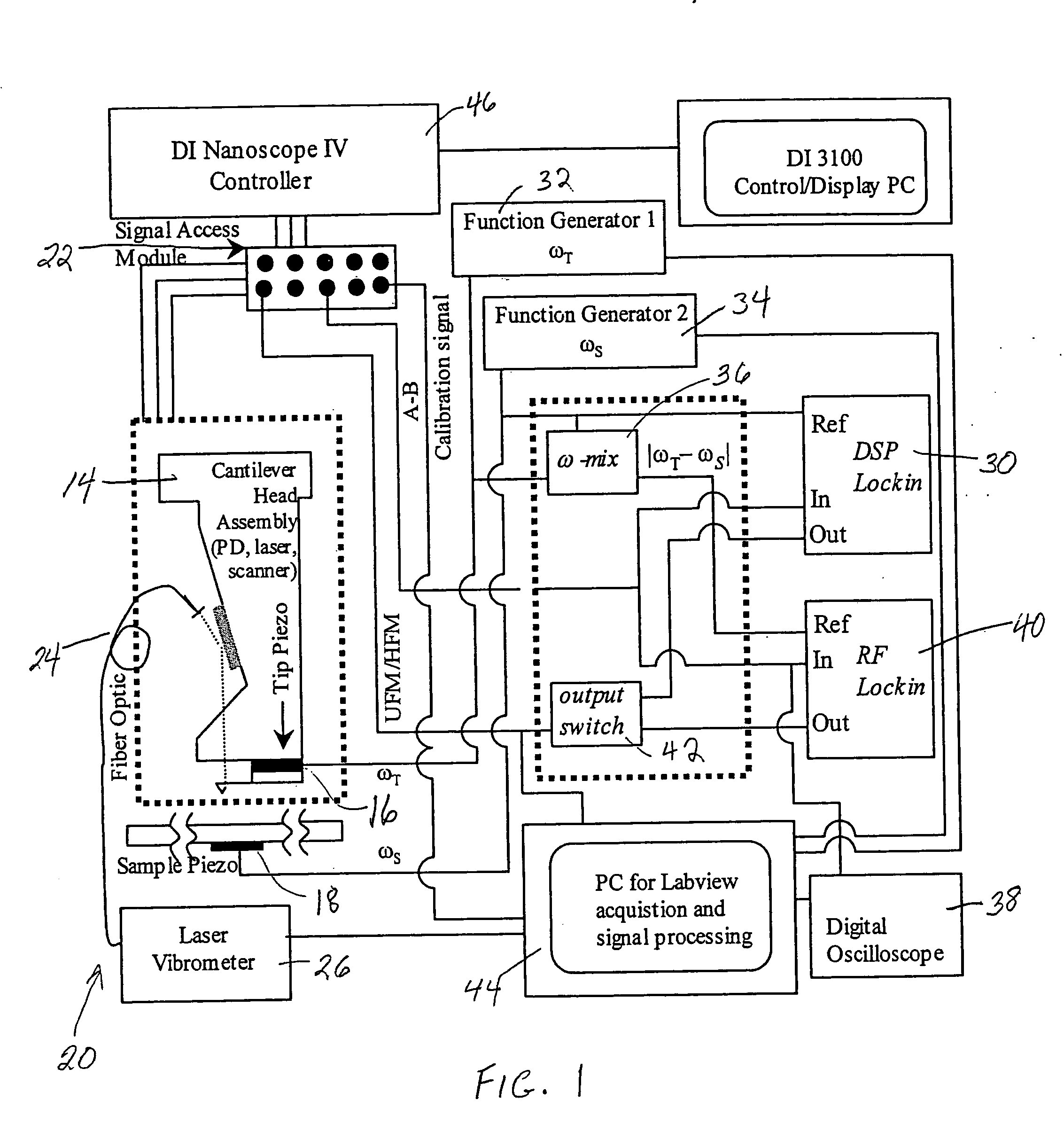
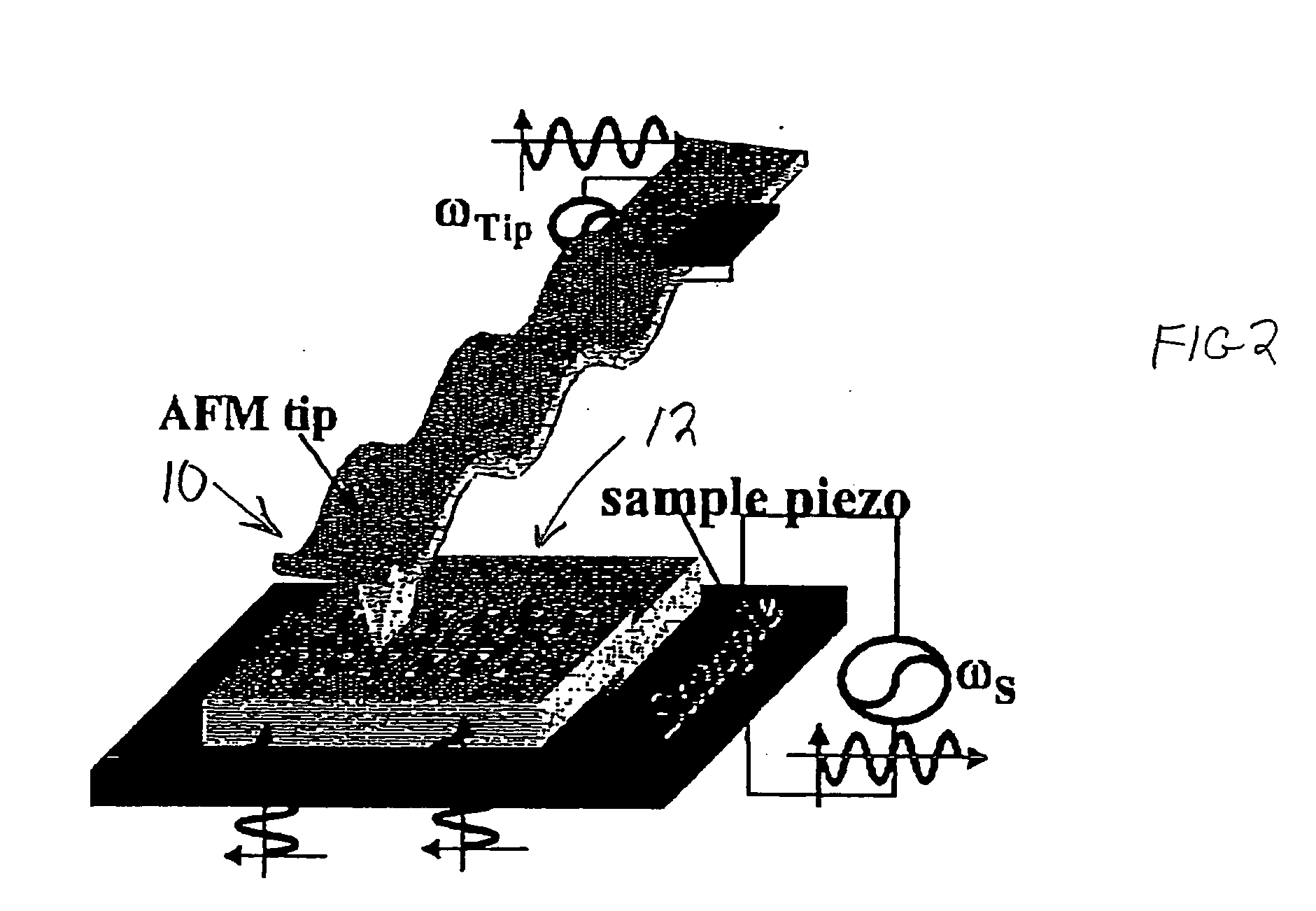
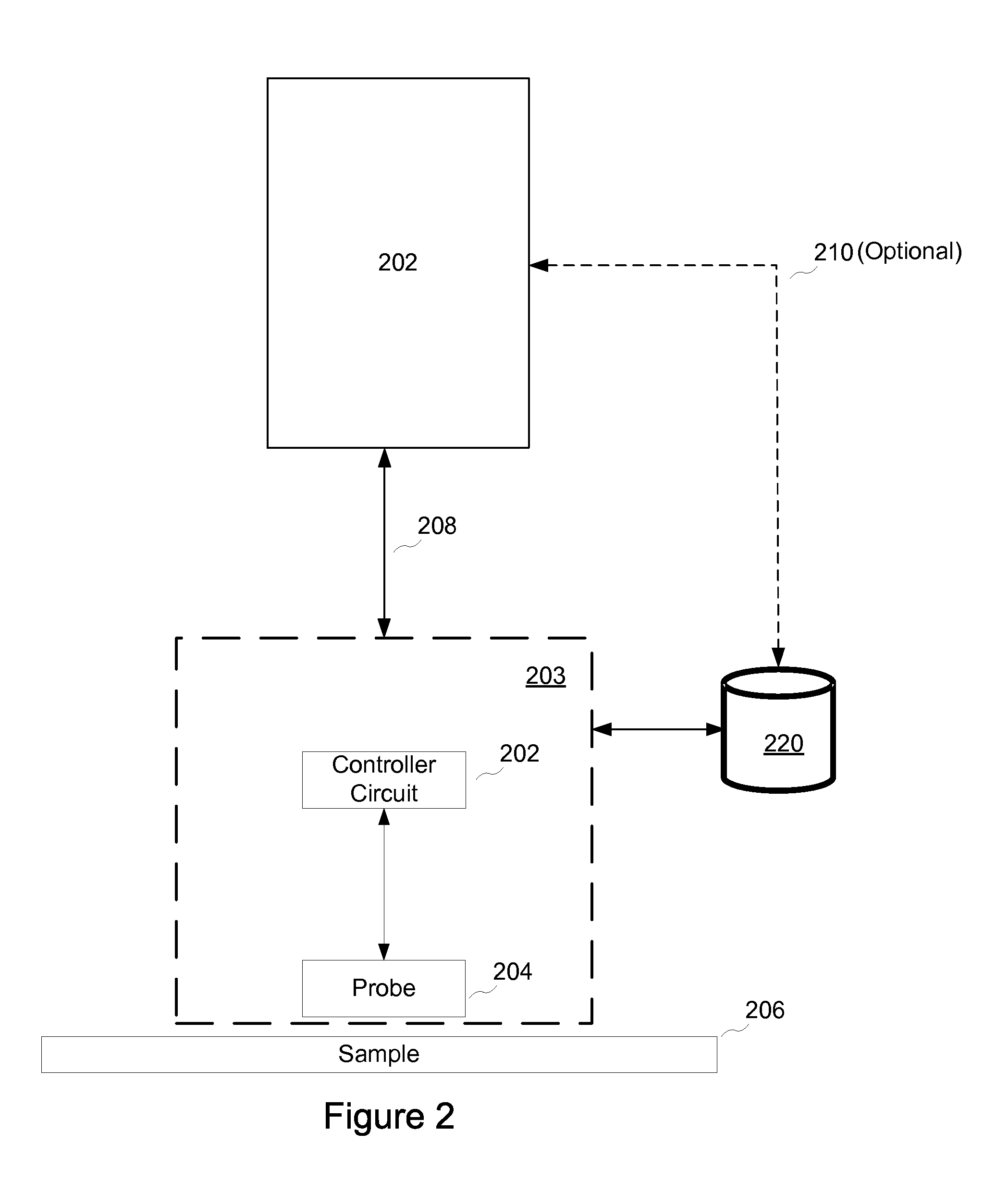
Methods, arrangements and systems for obtaining information associated with a sample using optical microscopy
ActiveUS20090323056A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryAcoustic waveConfocal microscopy
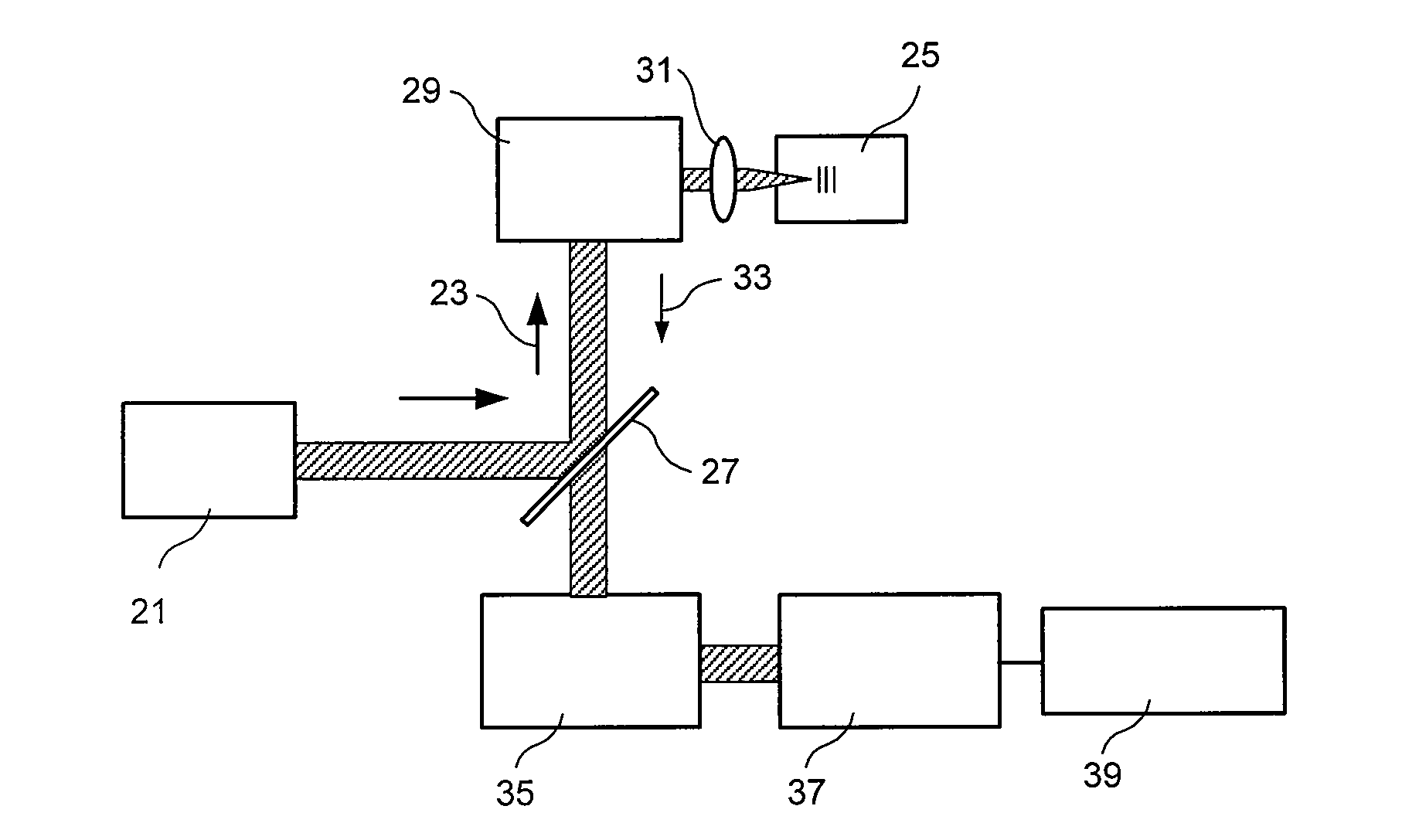
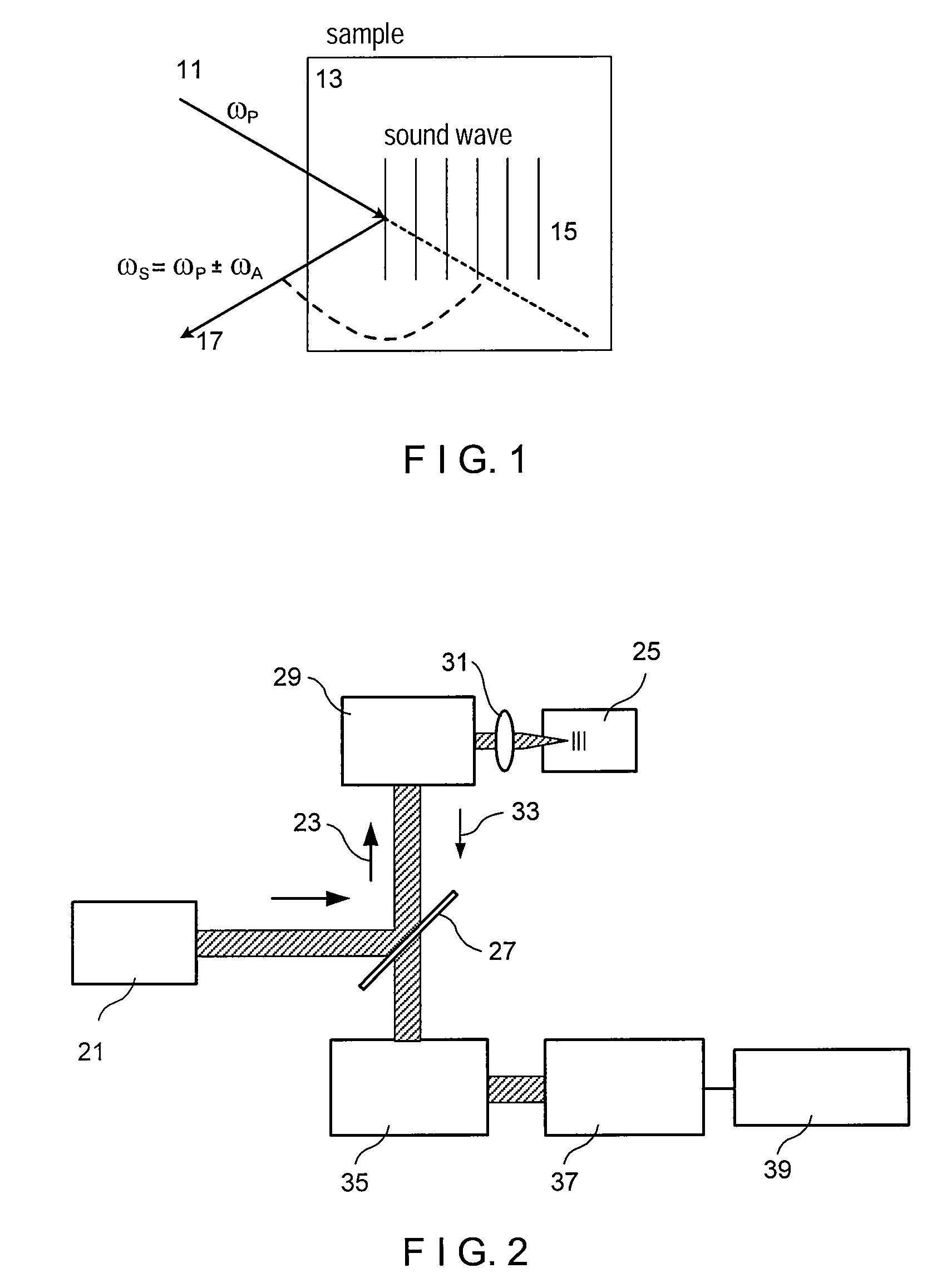
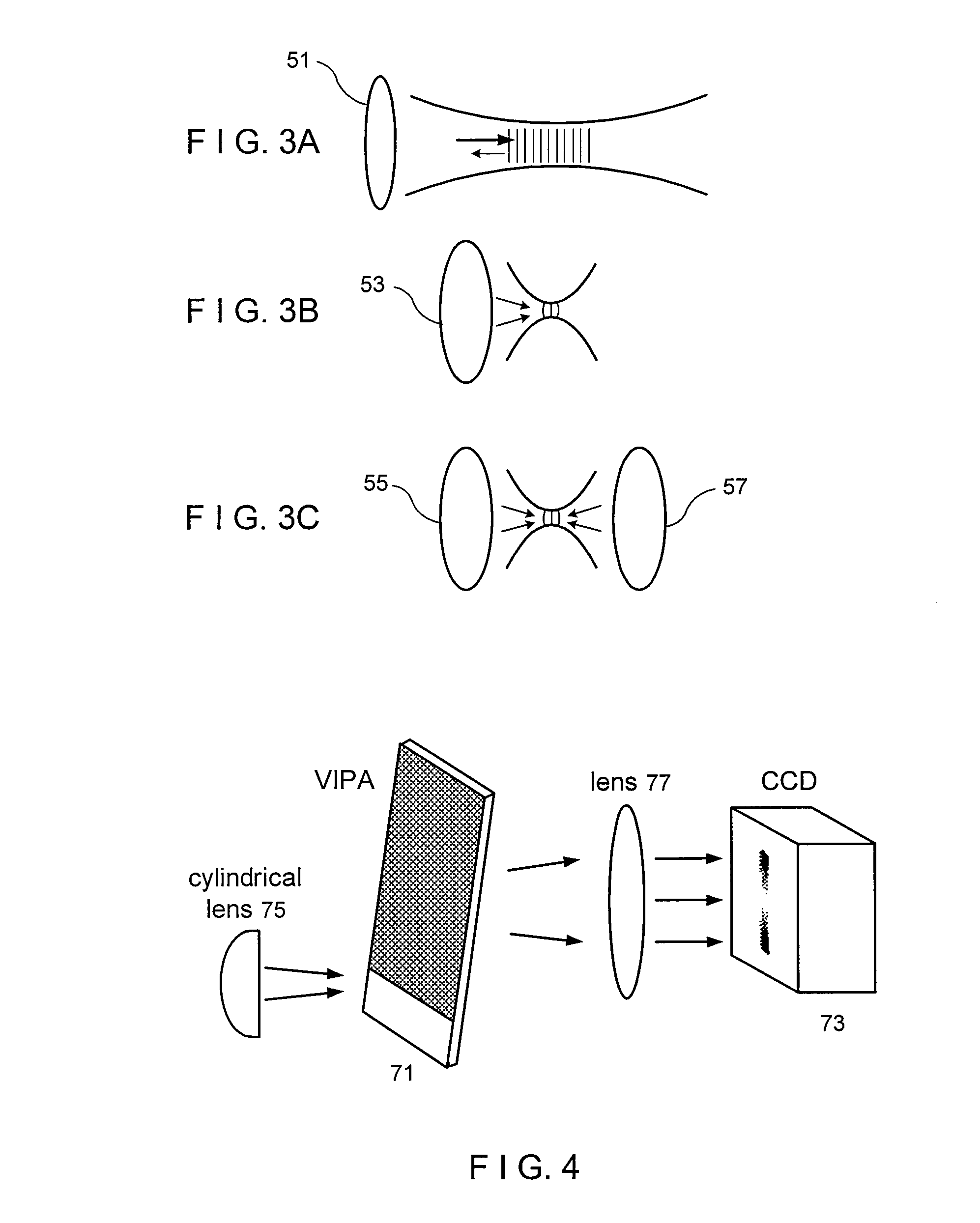
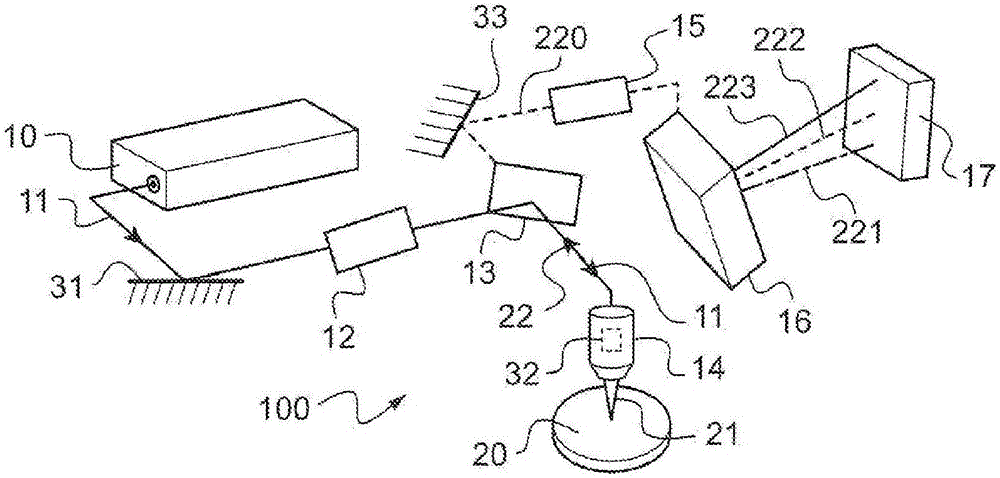
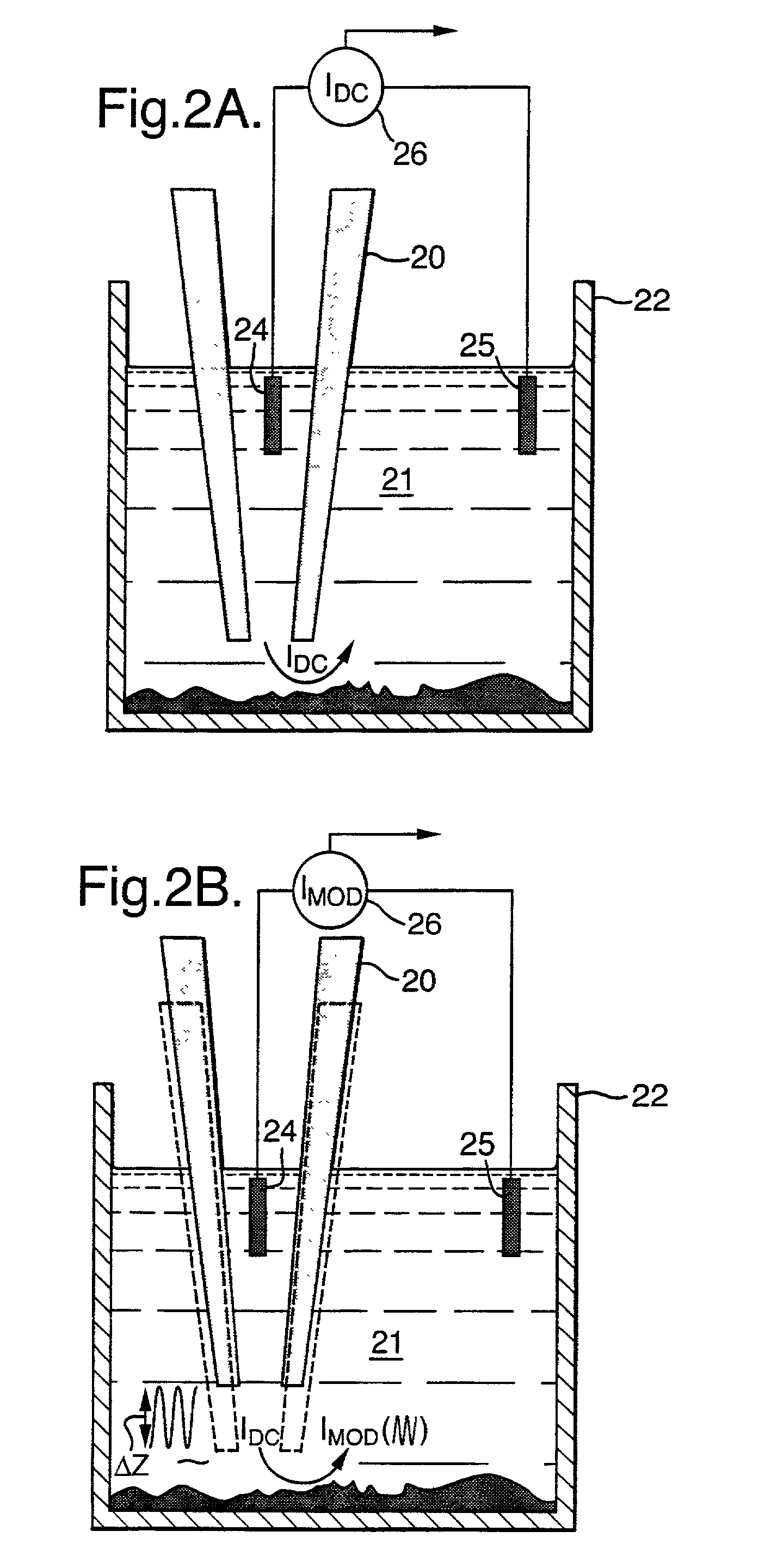
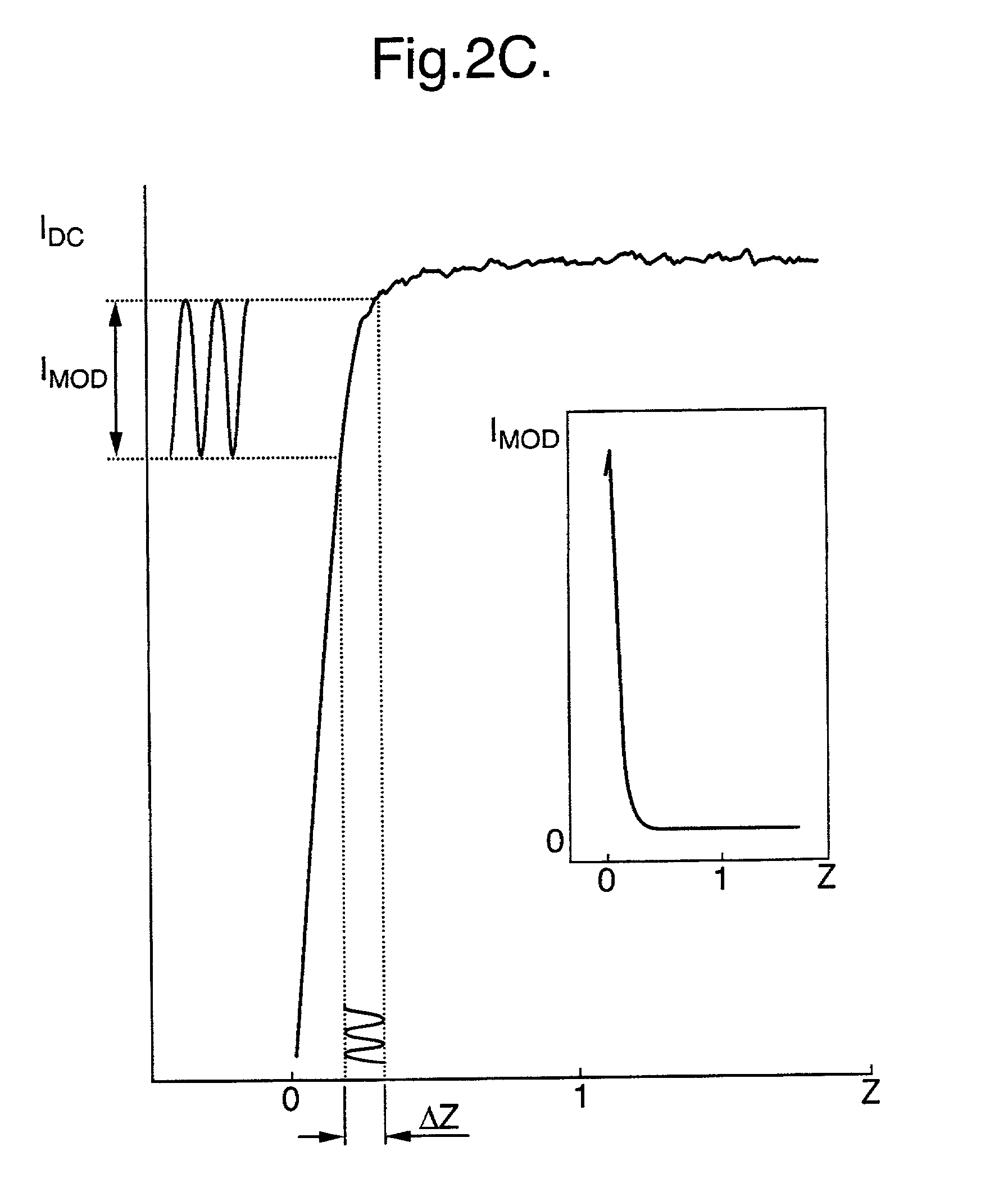
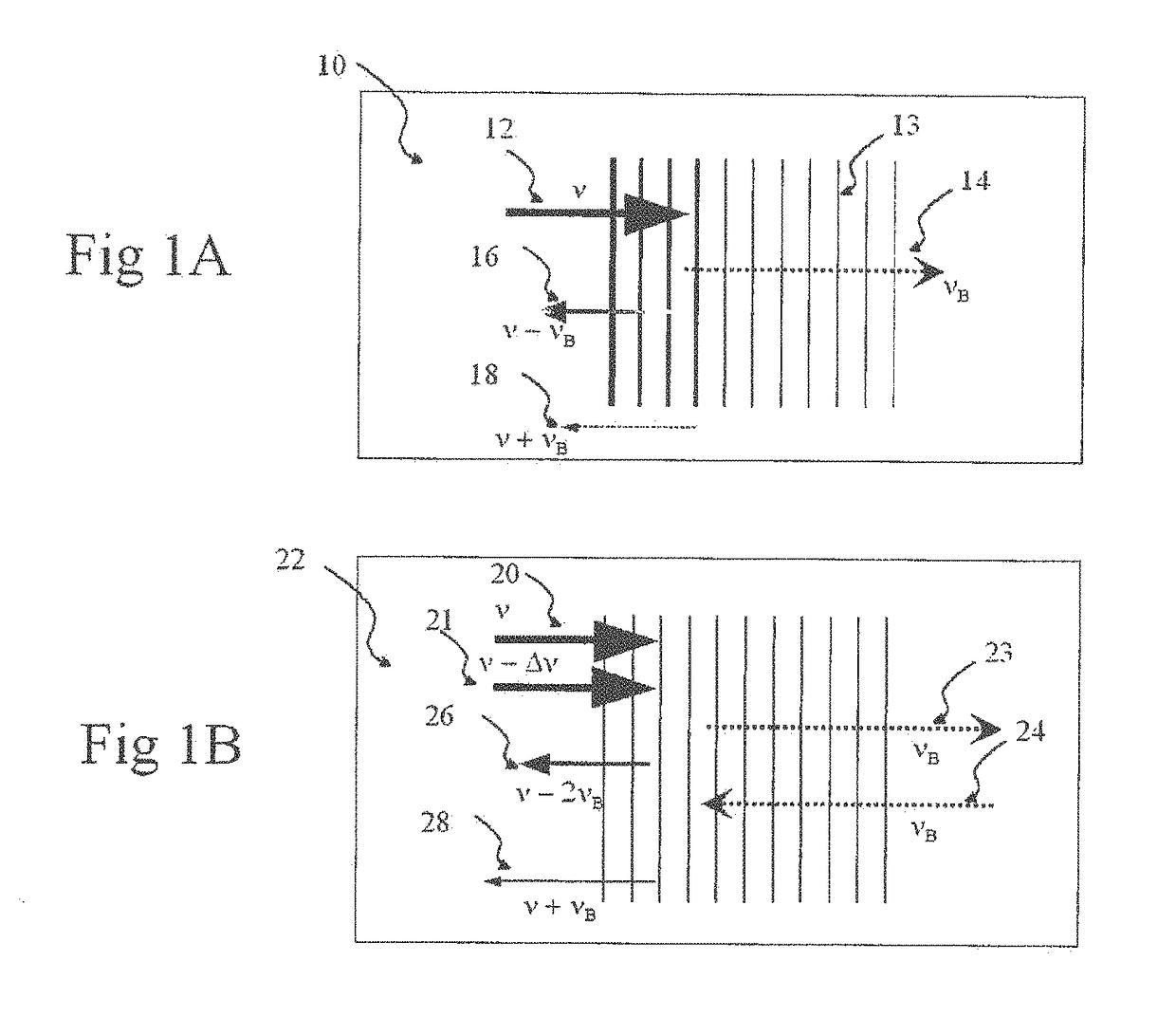
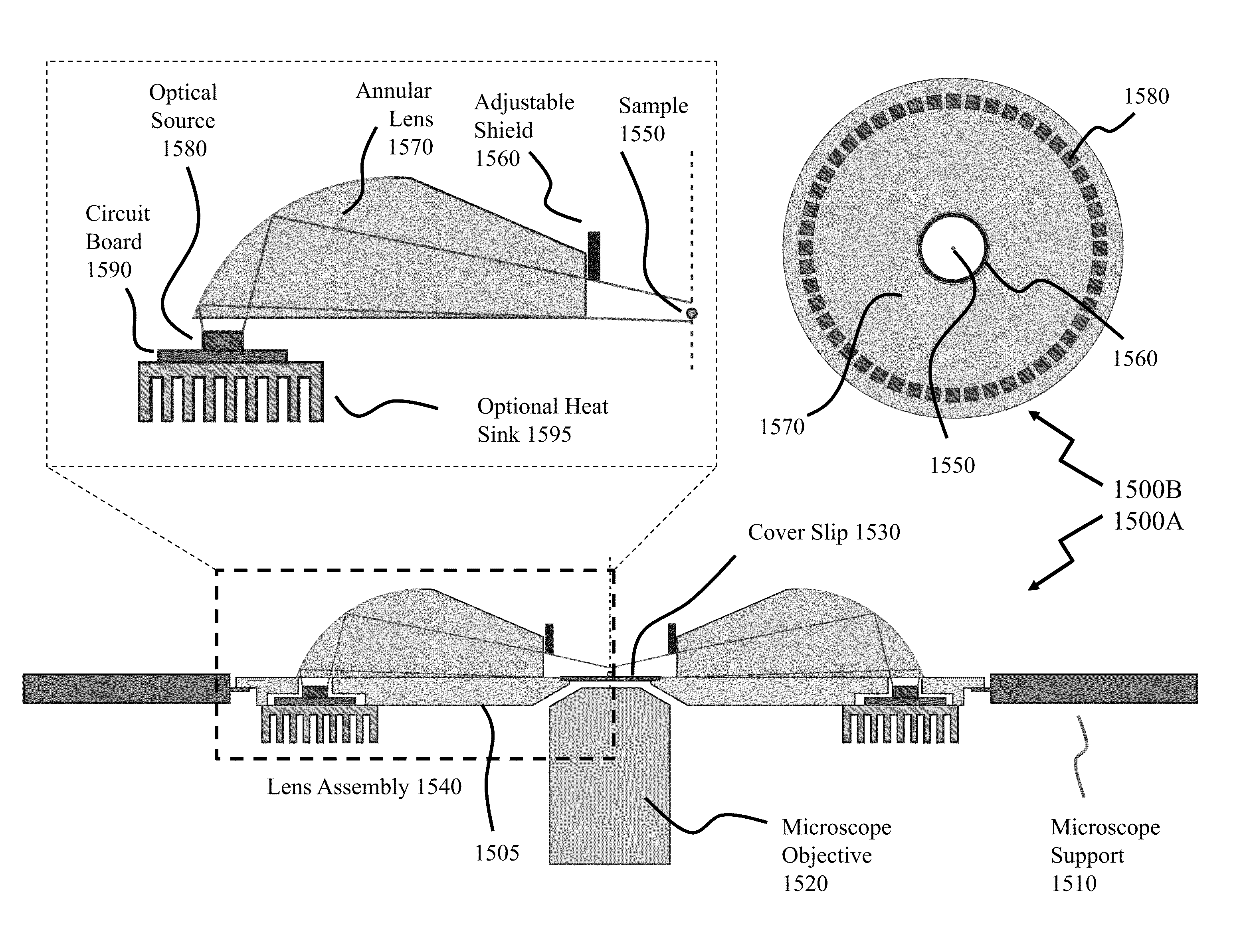
Exemplary embodiments of methods, arrangements and systems for obtaining information about a sample can be provided. For example, in one exemplary embodiment, it is possible to receive a first electro-magnetic radiation from a sample which is based on a second electro-magnetic radiation forwarded to the sample. The first electro-magnetic radiation may have a first frequency and the second electro-magnetic radiation may have a second frequency which is different from the first frequency. The difference between the first and second frequencies can be based on an acoustic wave inside the sample related to at least one characteristic of the sample. Further, it is possible to receive at least a portion of the first electromagnetic radiation and separate it into a particular finite number (N) of frequency component radiations. In addition, it is possible to receive a particular energy of more than 1 / N of energy of the third electro-magnetic radiation, and generate information associated with the sample. Certain exemplary embodiments of the present invention are capable of obtaining information associated with a sample, particularly its mechanical properties, non-contact using electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
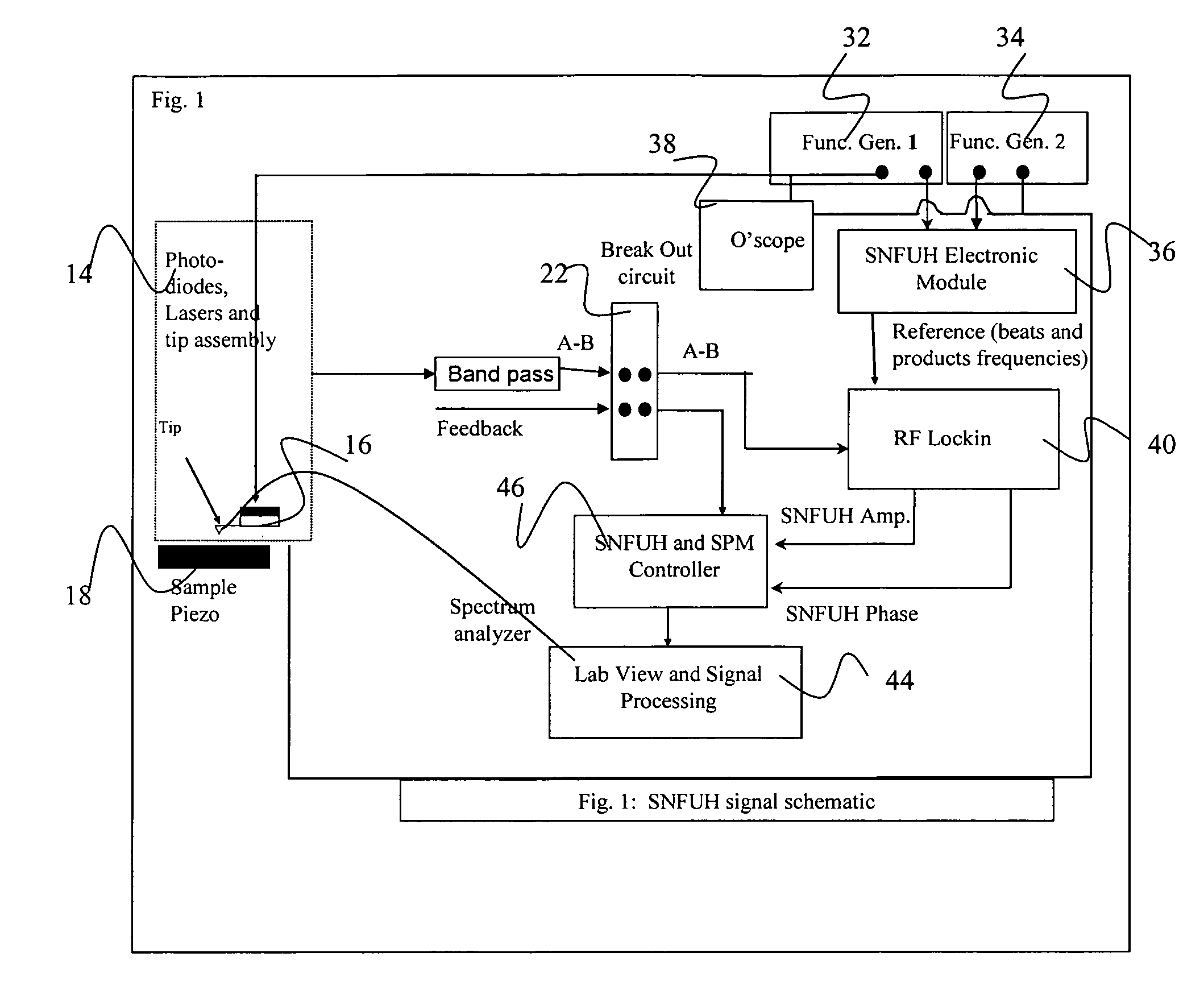
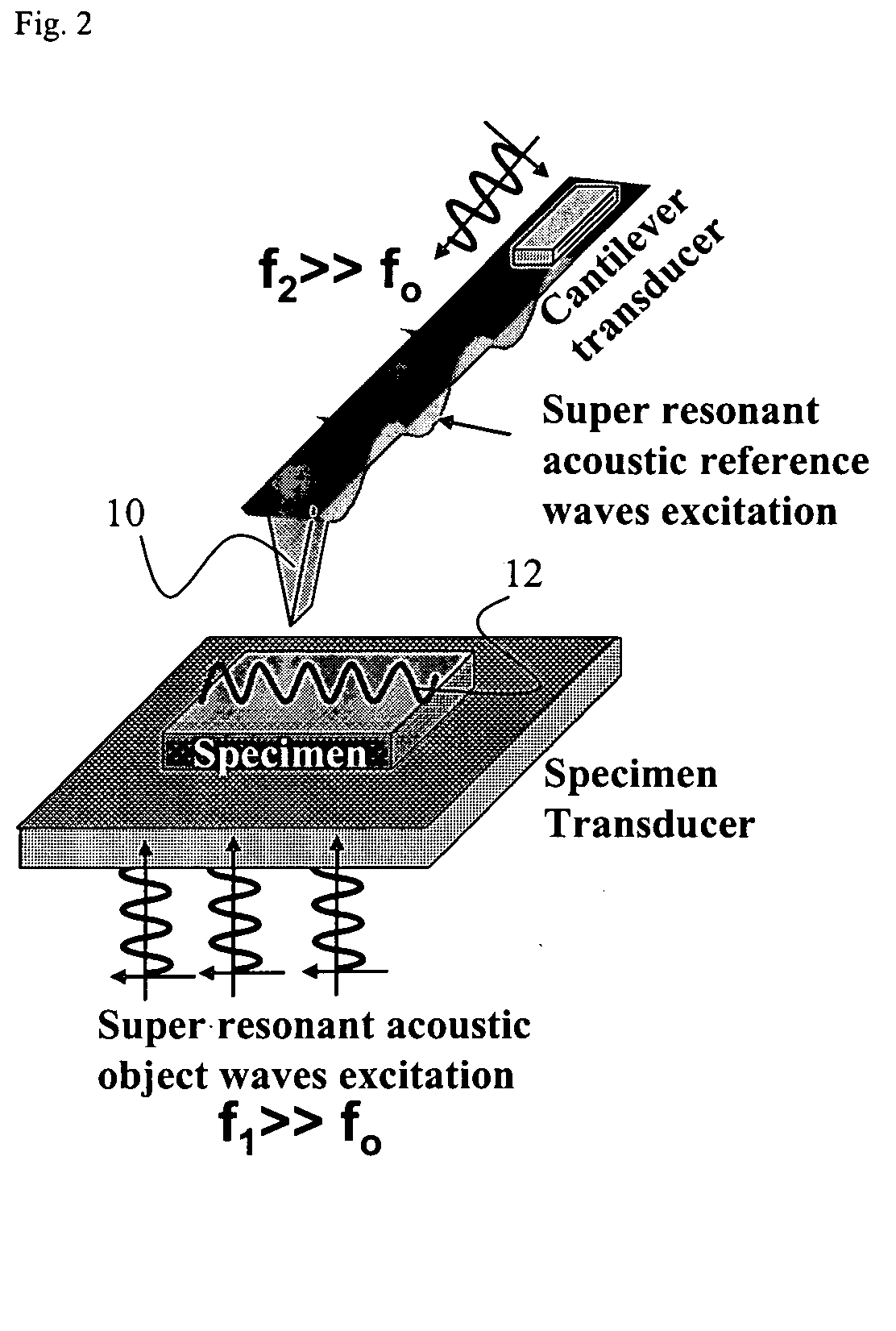
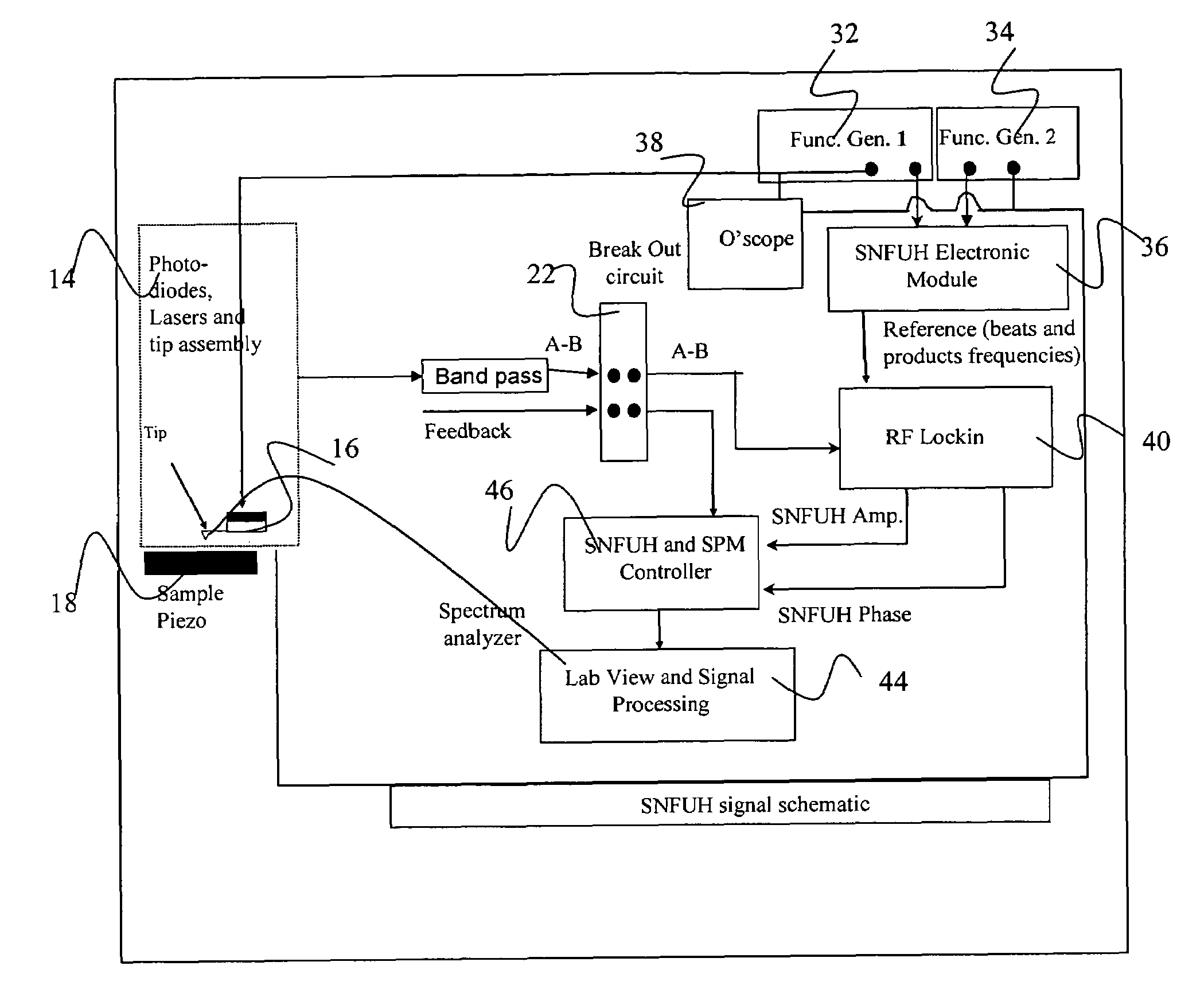
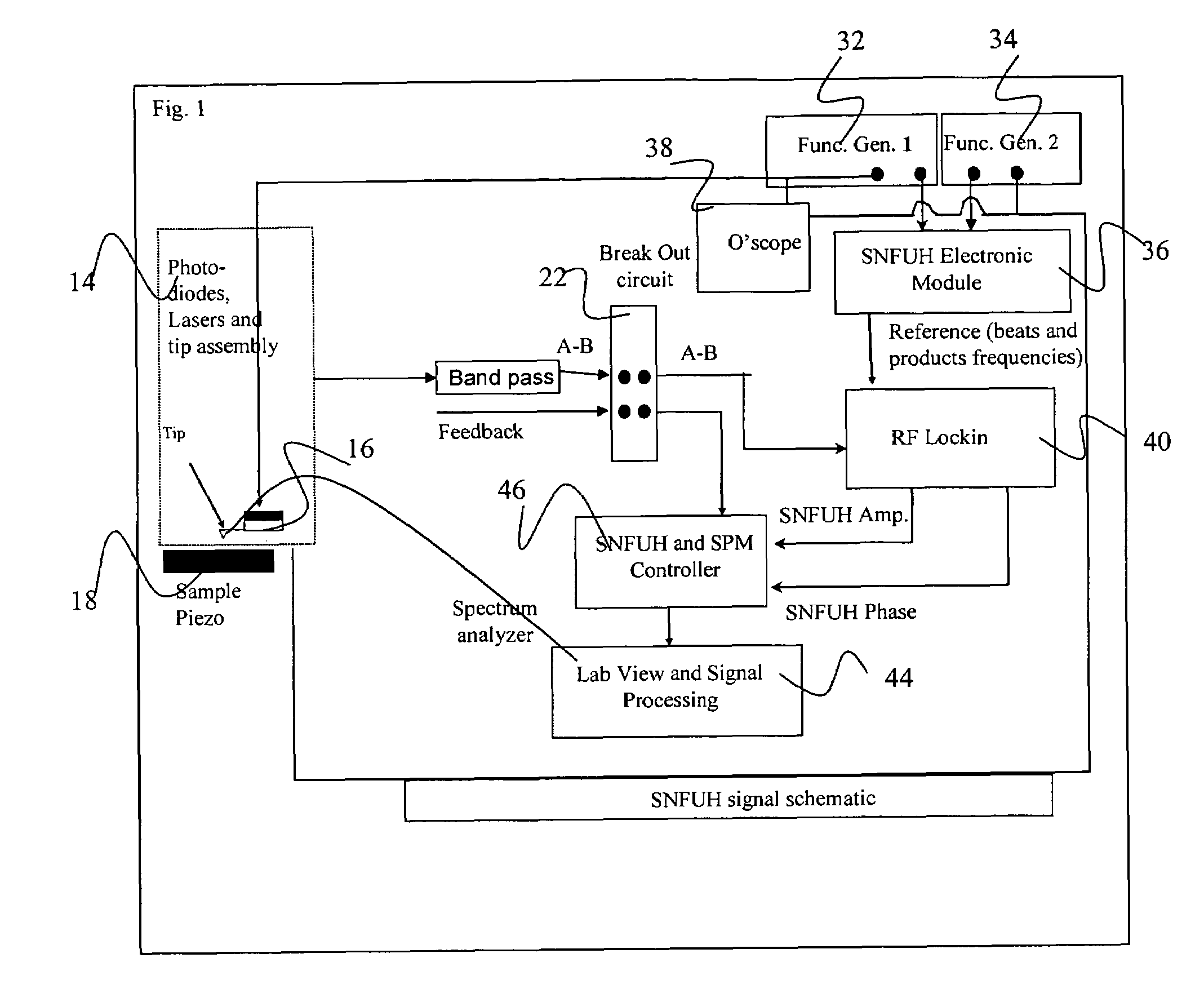
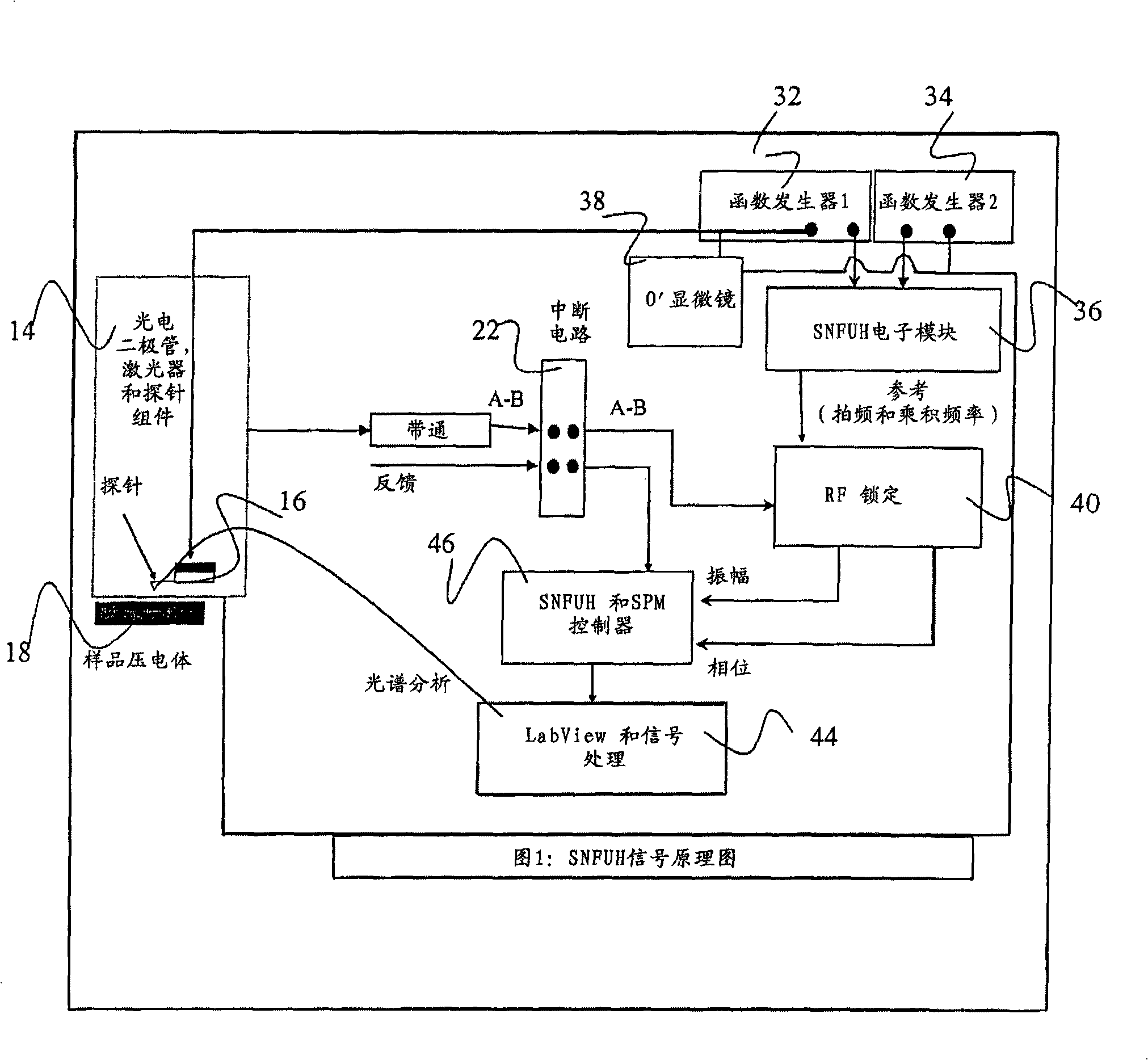
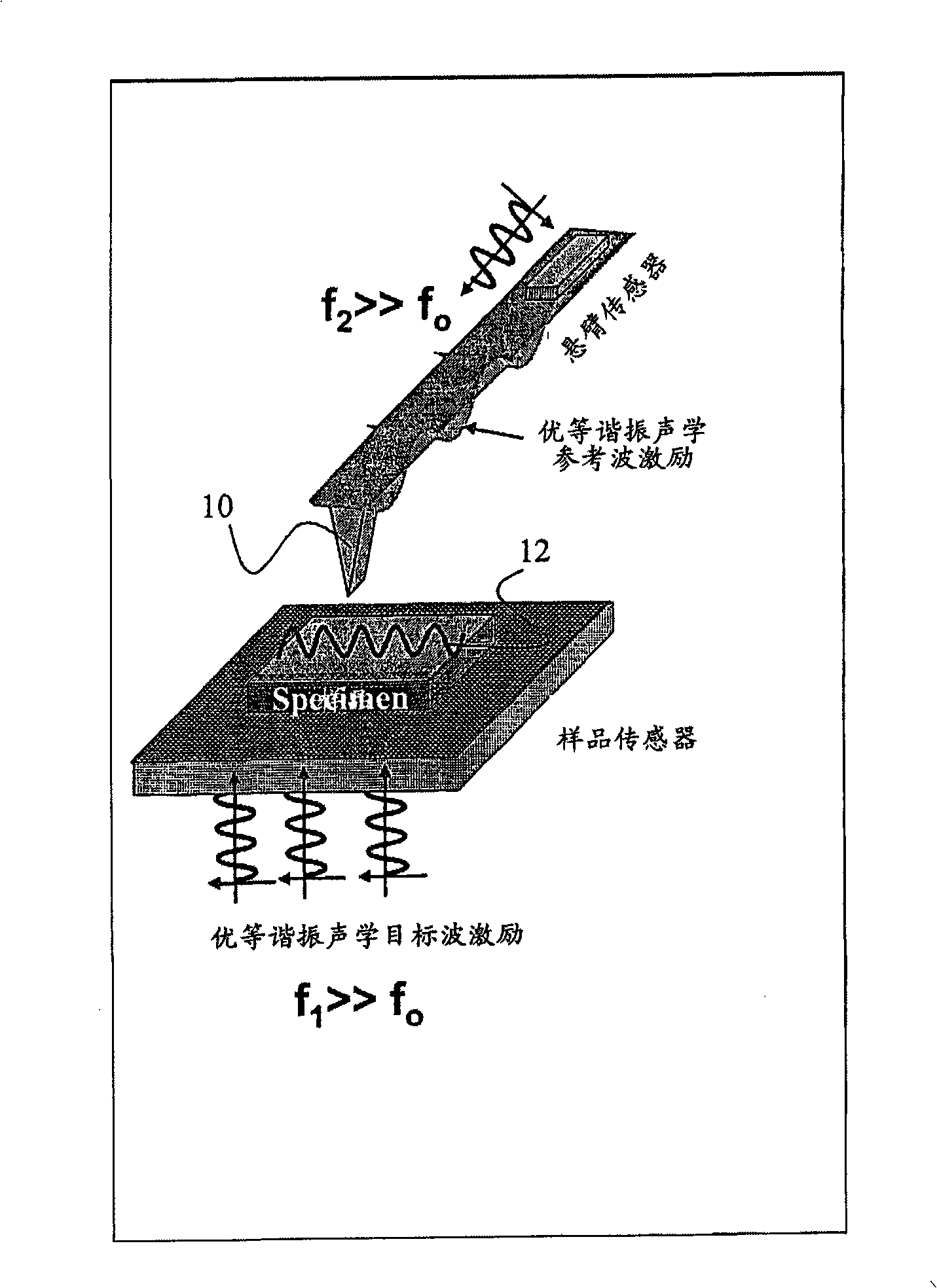
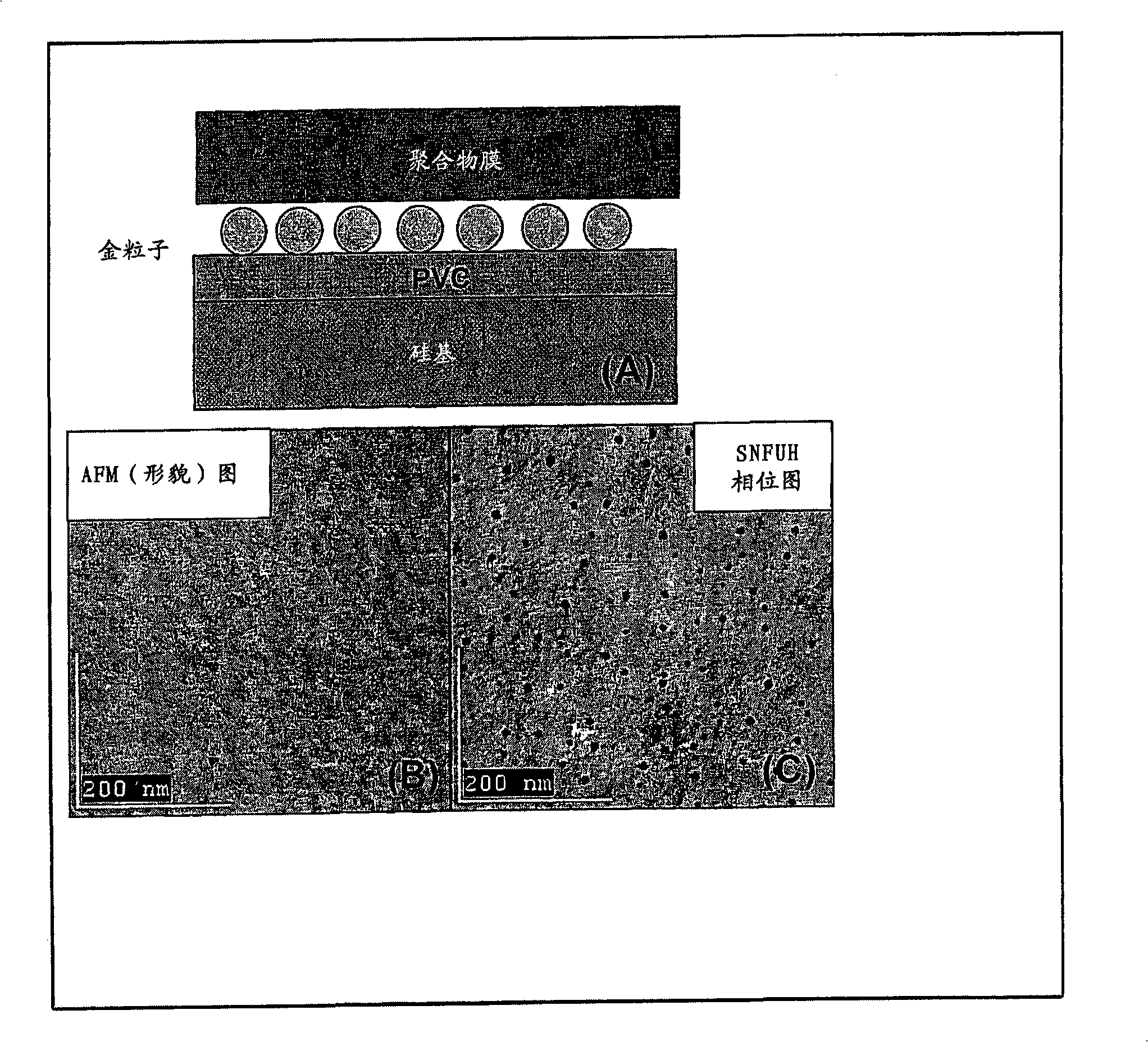
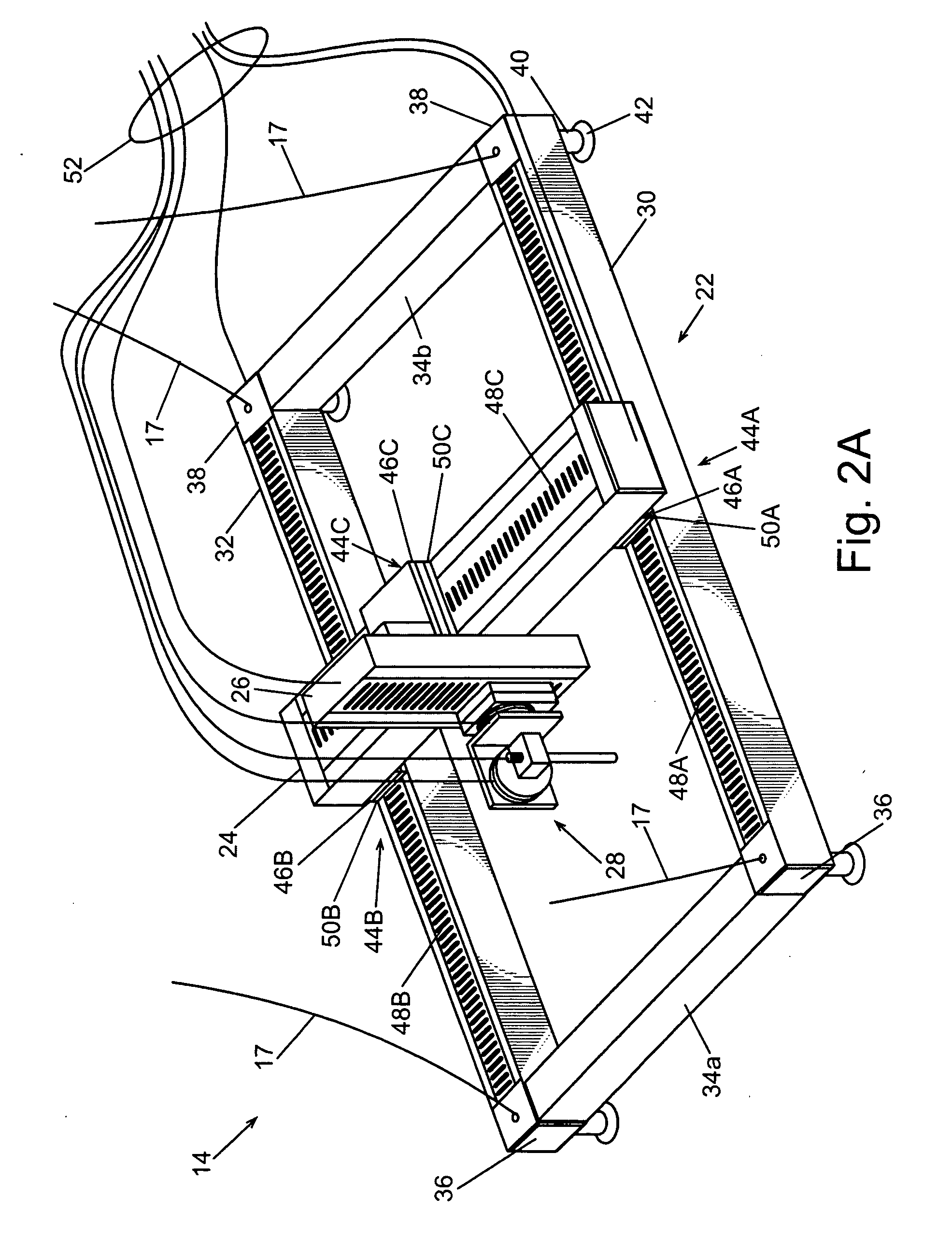
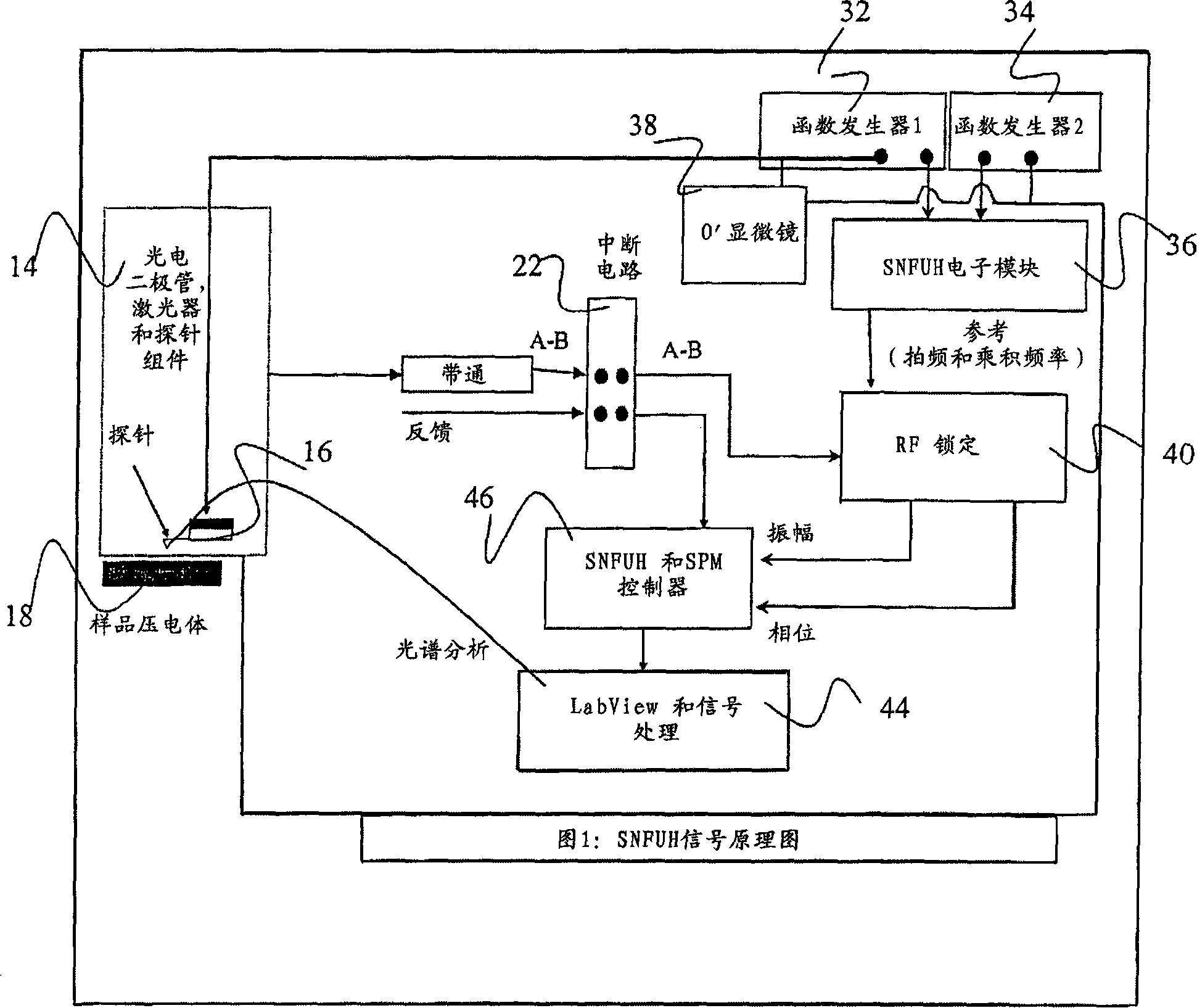
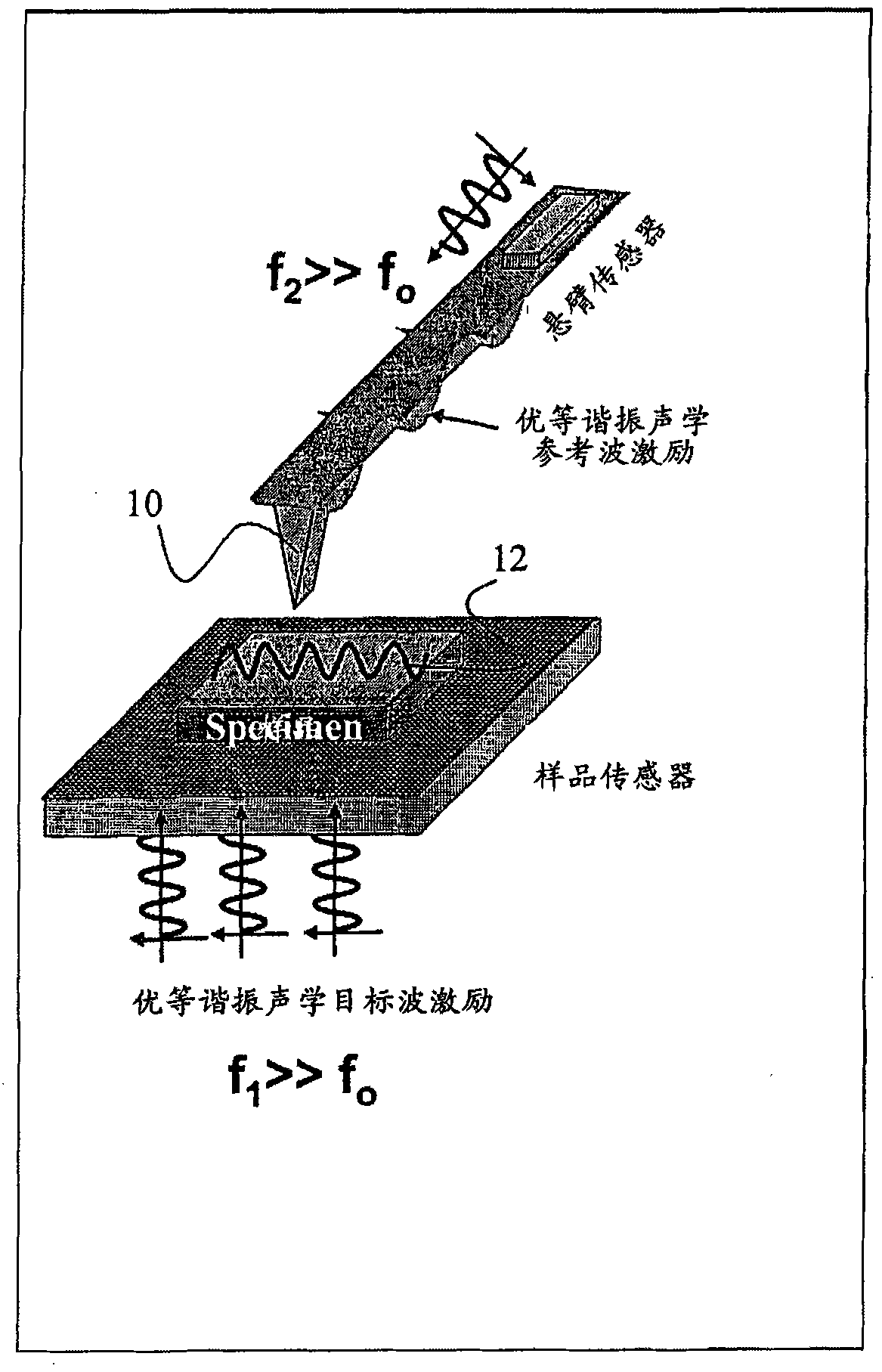
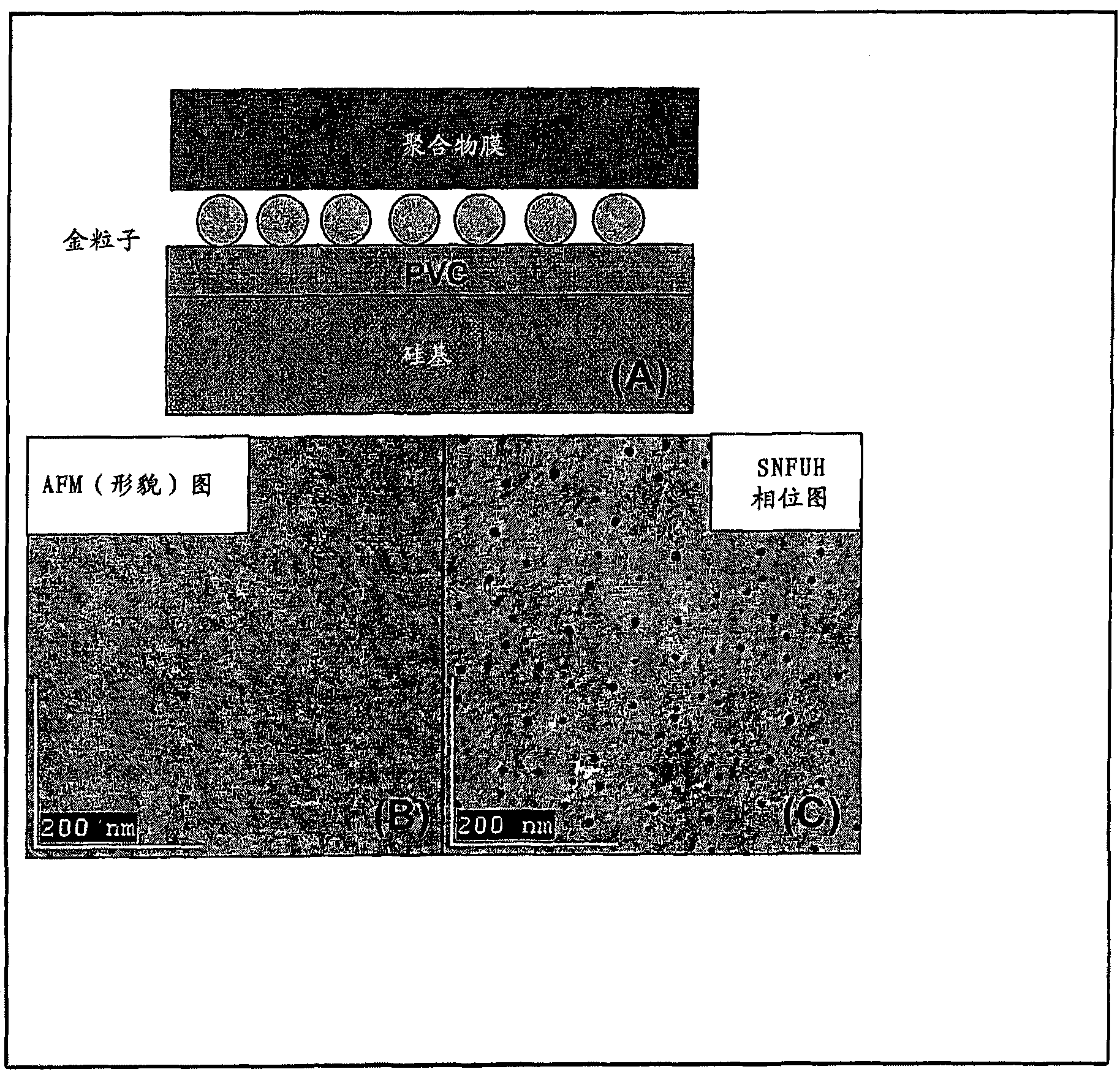
Scanning near field ultrasound holography
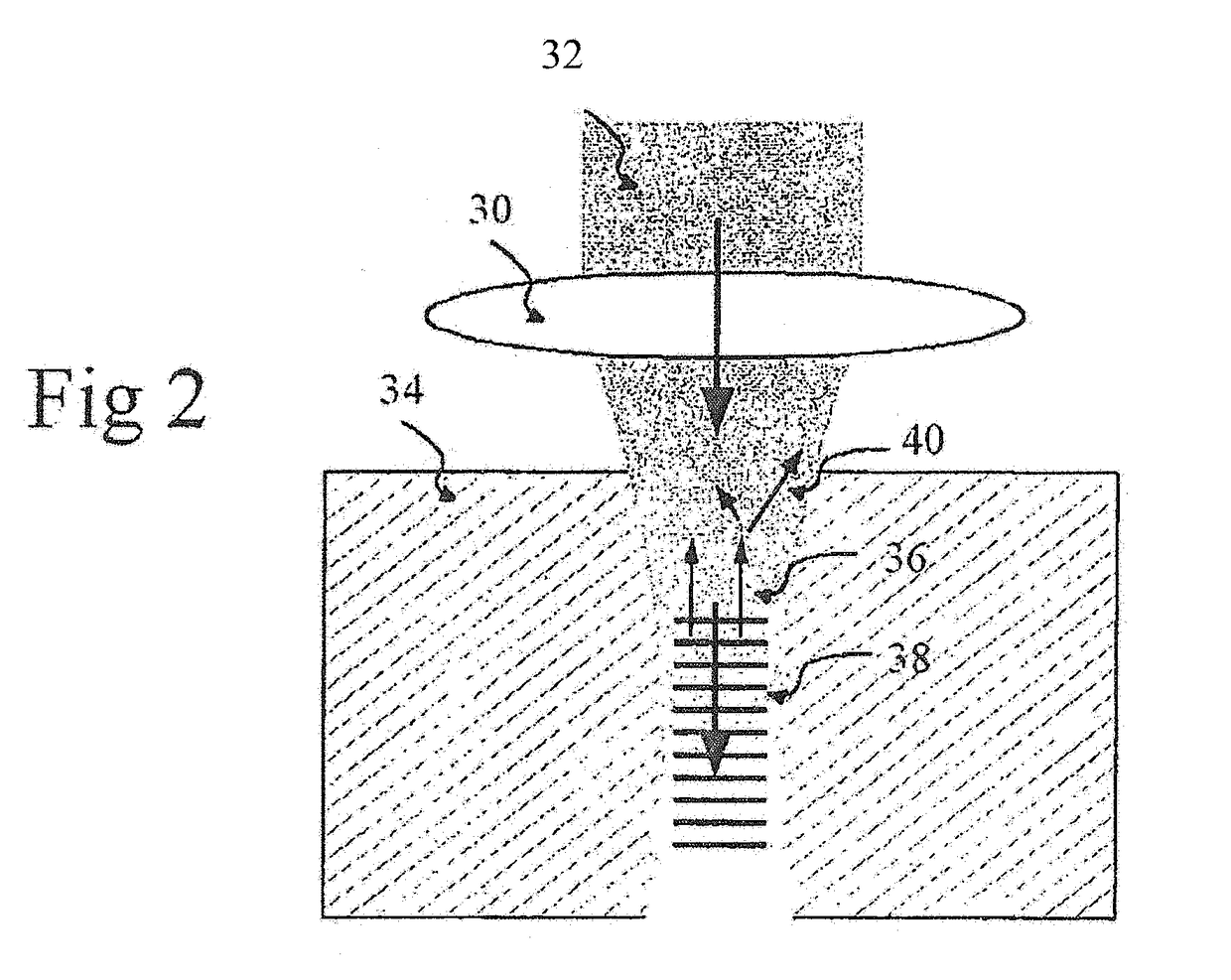
InactiveUS20060037401A1Improve spatial resolutionEliminate needAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurface/boundary effectSonificationHigh spatial resolution
A high spatial resolution phase-sensitive technique employs a scanning near field ultrasound holography (SNFUH) methodology for imaging elastic as well as viscoelastic variations across a sample surface. SNFUH uses a near-field approach to measure time-resolved variations in ultrasonic oscillations at a sample surface. As such, it overcomes the spatial resolution limitations of conventional phase-resolved acoustic microscopy (i.e. holography) by eliminating the need for far-field acoustic lenses.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
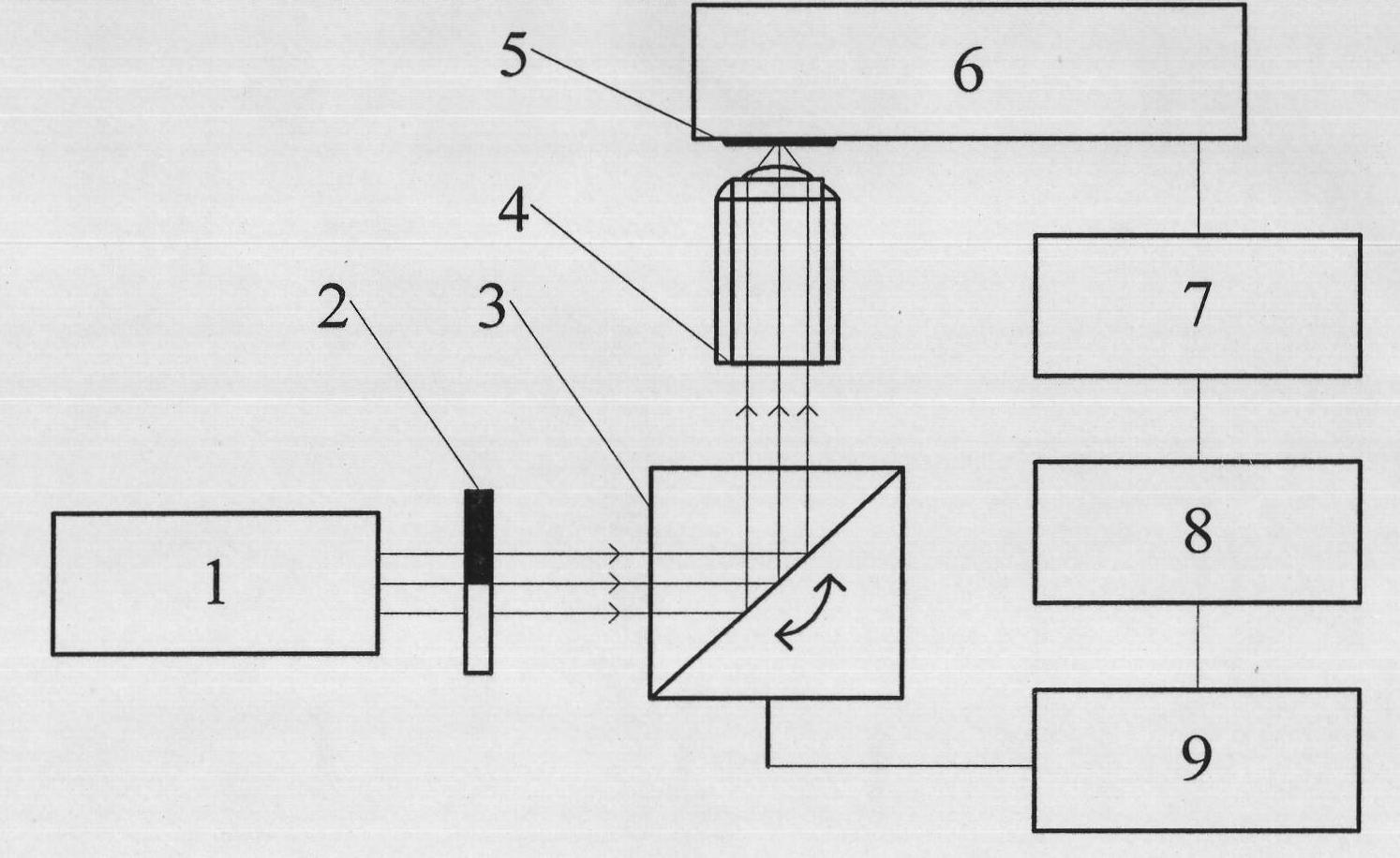
Integrated portable confocal opto-acoustic microscopy imaging device and method
ActiveCN102579080APromote reconstructionHigh sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImage resolutionGalvanometer
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopy imaging, and discloses an integrated portable confocal opto-acoustic microscopy imaging device and a method. The imaging device comprises an opto-acoustic excitation light source, an acousto-optical confocal opto-acoustic detector, a photodiode, a miniature X-Y two-dimensional galvanometer, a spectroscope, a lens, a sample table, a double-channel parallel acquisition card and a computer with acquisition control software and two-dimensional galvanometer control software. The method includes steps that after the direction of laser light emitted from the opto-acoustic excitation light source is changed via the miniature X-Y two-dimensional galvanometer, the laser light is focused by the balsaming lens and irradiates on samples to excite opto-acoustic signals, the opto-acoustic signals are received by the acousto-optical confocal opto-acoustic detector, the incident angle of a light beam is continuously changed by the two-dimensional galvanometer so that the samples are scanned, and finally, an opto-acoustic image is rebuilt by maximum projection algorithm. A micro-chip laser device and the miniature X-Y two-dimensional galvanometer are integrated to form the portable confocal opto-acoustic microscopy imaging device, mobility is good, imaging speed is fast, and resolution ratio and contrast ratio are high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
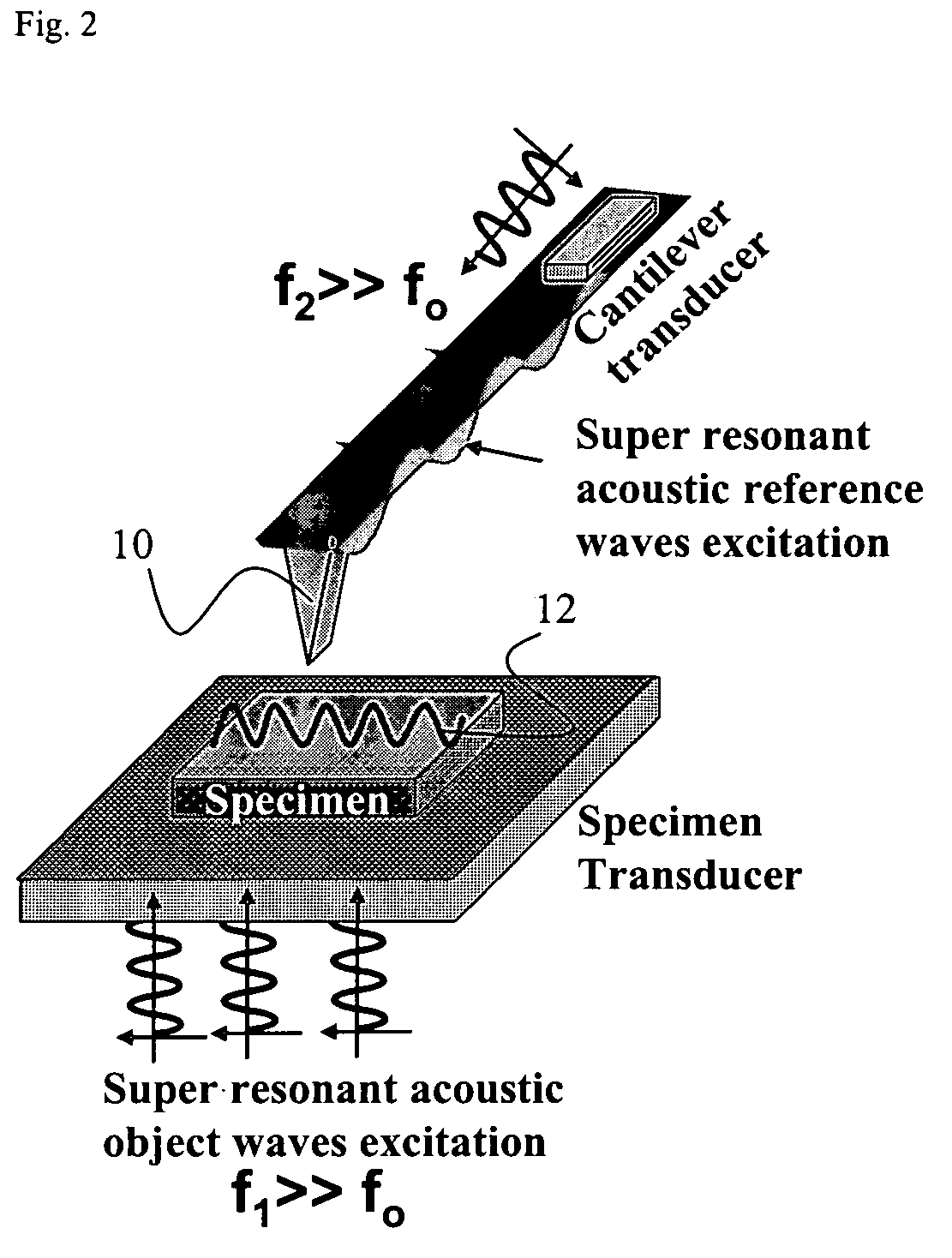
Near field acoustic holography with scanning probe microscope (SPM)
InactiveUS20050056782A1Improve spatial resolutionEliminate needMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationImage resolution
A high spatial resolution phase-sensitive technique employs a near field ultrasonic holography methodology for imaging elastic as well as viscoelastic variations across a sample surface. Near field ultrasonic holography (NFUH) uses a near-field approach to measure time-resolved variations in ultrasonic oscillations at a sample surface. As such, it overcomes the spatial resolution limitations of conventional phase-resolved acoustic microscopy (i.e. holography) by eliminating the need for far-field acoustic lenses.
Owner:SHEKHAWAT GAJENDRA +1
Scanning near field ultrasound holography
InactiveUS7448269B2Improve spatial resolutionEliminate needMultiple-port networksAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationImage resolution
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
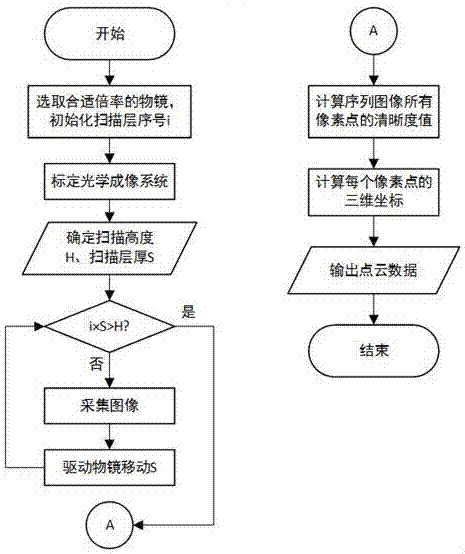
Three-dimensional surface topography measurement method and system based on optical microscopy
The invention discloses a three-dimensional surface topography measurement method and system based on optical microscopy, which relate to the field of micro nano object measurement. The method comprises steps: a measured surface is placed in an observation range of an optical microscope, an appropriate objective lens and a lighting system are selected, an objective lens driving system is used to drive the objective lens and the measured surface to perform longitudinal relative motion, and during a serial layer scanning process, an image acquisition module is used to acquire a sequence image, and the depth position information when each image is acquired is recorded at the same time; a focusing evaluation algorithm is used to calculate the definition value of each pixel point in the sequence image; and according to the change condition of the focusing degree of the pixel point in the image sequence, a depth calculation algorithm is used to calculate the depth information of each pixel point, and thus, three-dimensional coordinates of the pixel point are thus acquired. The method and the system are applicable to the micro nano object measurement field, the surface waviness and the roughness can be measured, the three-dimensional surface topography data are rebuilt, the material surface texture information can be acquired, and the method and the system can be used for measuring a complex surface.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Optical microscopy-atomic force microscopy double-probe imaging method and device
InactiveCN102095898ASimple structureTechnical conditions are easy to achieveMaterial analysis by optical meansScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyNanostructure
The invention discloses an optical microscopy-atomic force microscopy double-probe imaging method and an optical microscopy-atomic force microscopy double-probe imaging device. The device is provided with a scanner, an atomic force microscopy probe, an optical microscopy probe, a charge coupled device (CCD) detection probe, a data image acquisition system, a Z direction moving mechanism, an XY stepping moving mechanism and an open type large sample platform, wherein the scanner consists of a laser, a micro lens, single-pipe piezoelectric ceramics and a micro cantilever probe; the atomic force microscopy probe comprises a position sensitive detection unit, a photoelectric detection and feedback measurement control system and the like; and the optical microscopy probe consists of a micro objective group and a micro ocular group. An optical microscopy-atomic force microscopy double-probe system provided by the invention can simultaneously solve the problems of the observation of real-time optical microscopy in a wide range and the observation and the measurement of local high-resolution nano structures and performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical microscopy system and method for raman scattering with adapative optics
ActiveCN106461925AImprove spatial resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringConfocal microscopyOptic system
The present invention relates to a Raman scattering optical microscopy apparatus comprising a laser source (10) adapted to emit a laser beam (11) at an excitation wavelength [Lambda], a microscopy objective (14) adapted to receive the laser beam (11) and to focus the laser beam in an image plane of the microscope objective (14), the focused laser beam (21) being intended to illuminate a sample (20), an optical system adapted to collect an optical Raman scattering beam (22) and detection means (16, 17) adapted for detecting the Raman scattering beam (22) collected. More particularly, there is proposed according to the invention, a Raman scattering microscopy apparatus furthermore comprising an adaptive optics system (31, 32, 33) disposed on an optical path of the excitation laser beam (11), on an optical path of the Raman scattering beam (22) or on a common optical path of the excitation laser beam (11) and of the Raman scattering beam (22).
Owner:HORIBA JOBIN YVON
Optical microscopy and its use in the study of cells
InactiveUS6929934B1Minimize damageExposure of light can be limitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIon currentLive cell imaging
The present invention pertains to an apparatus for imaging an object, comprising a probe via which an assay component may be delivered; a sensor to detect ion current; and means for controlling the position of the probe relative to the object in response to the ion current. Such apparatus can be used to image live cells, without affecting them, in solution, e.g., using light, wherein the distance between probe and cell is less than the wavelength of light.
Owner:IONSCOPE
Systems and methods for obtaining information associated with an anatomical sample using optical microscopy
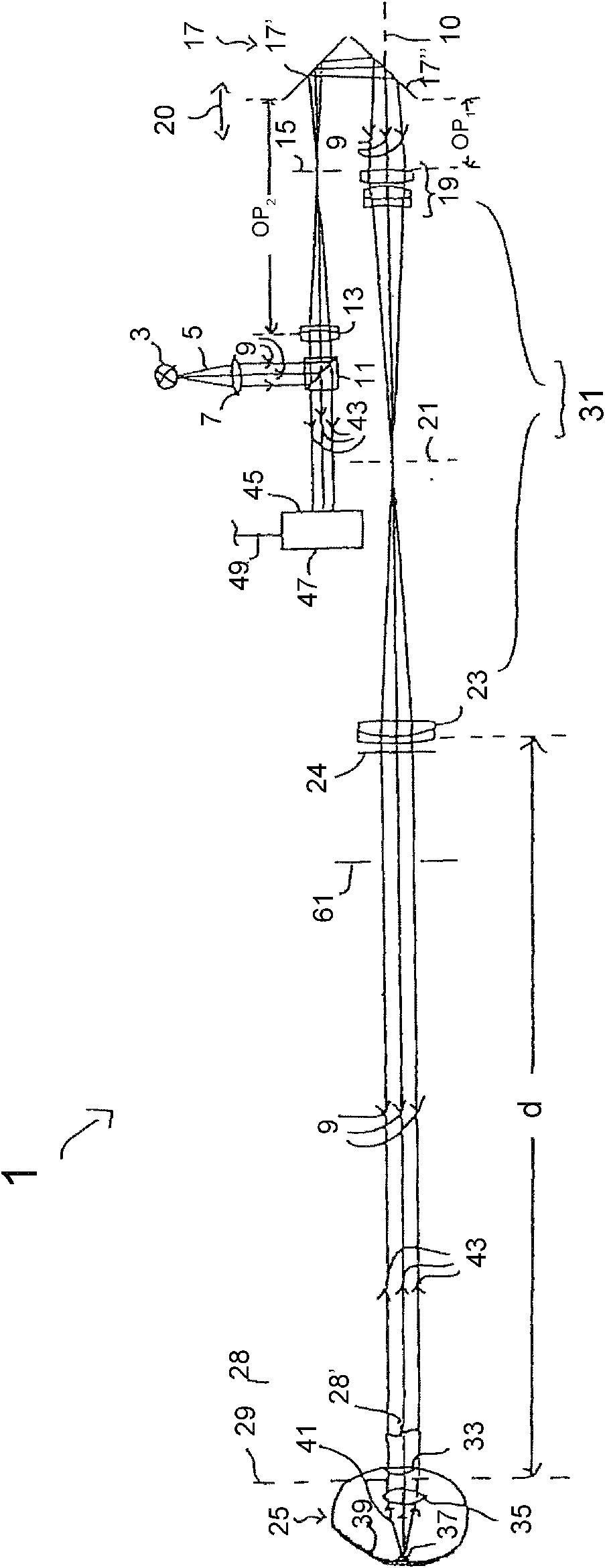
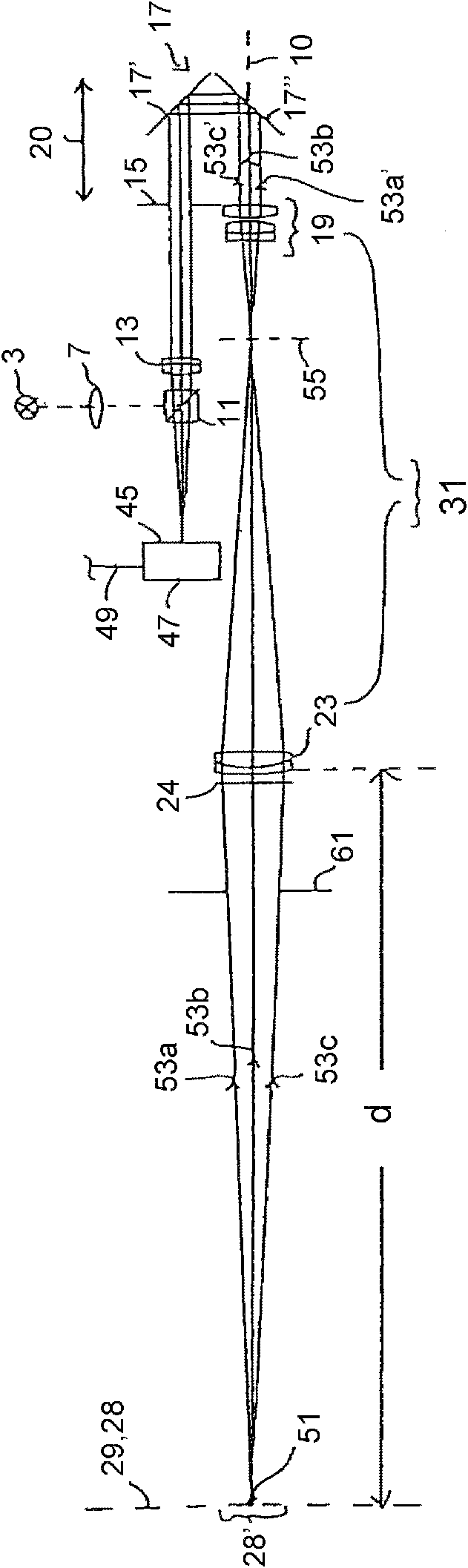
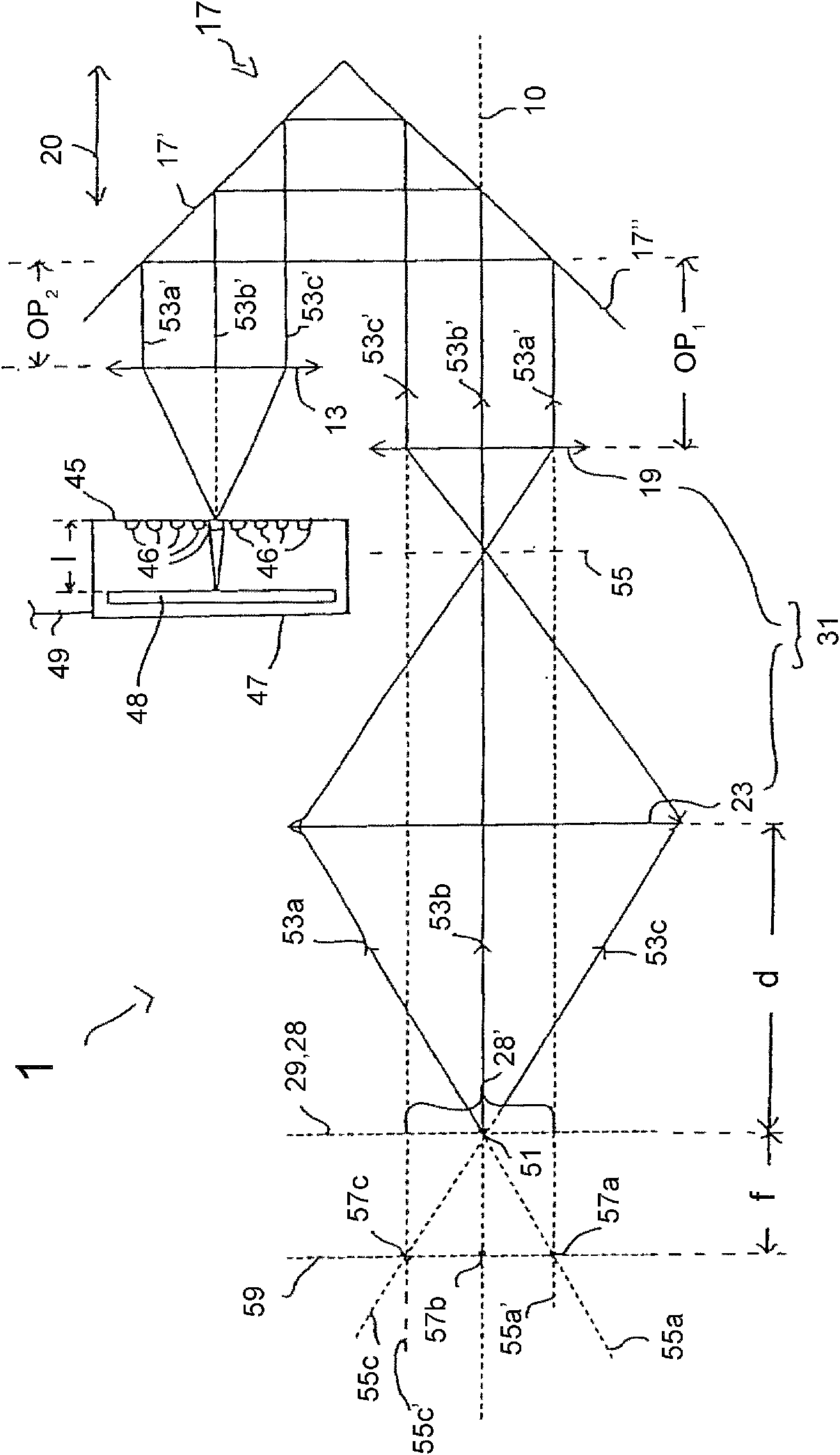
ActiveUS20170254749A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityLight beam
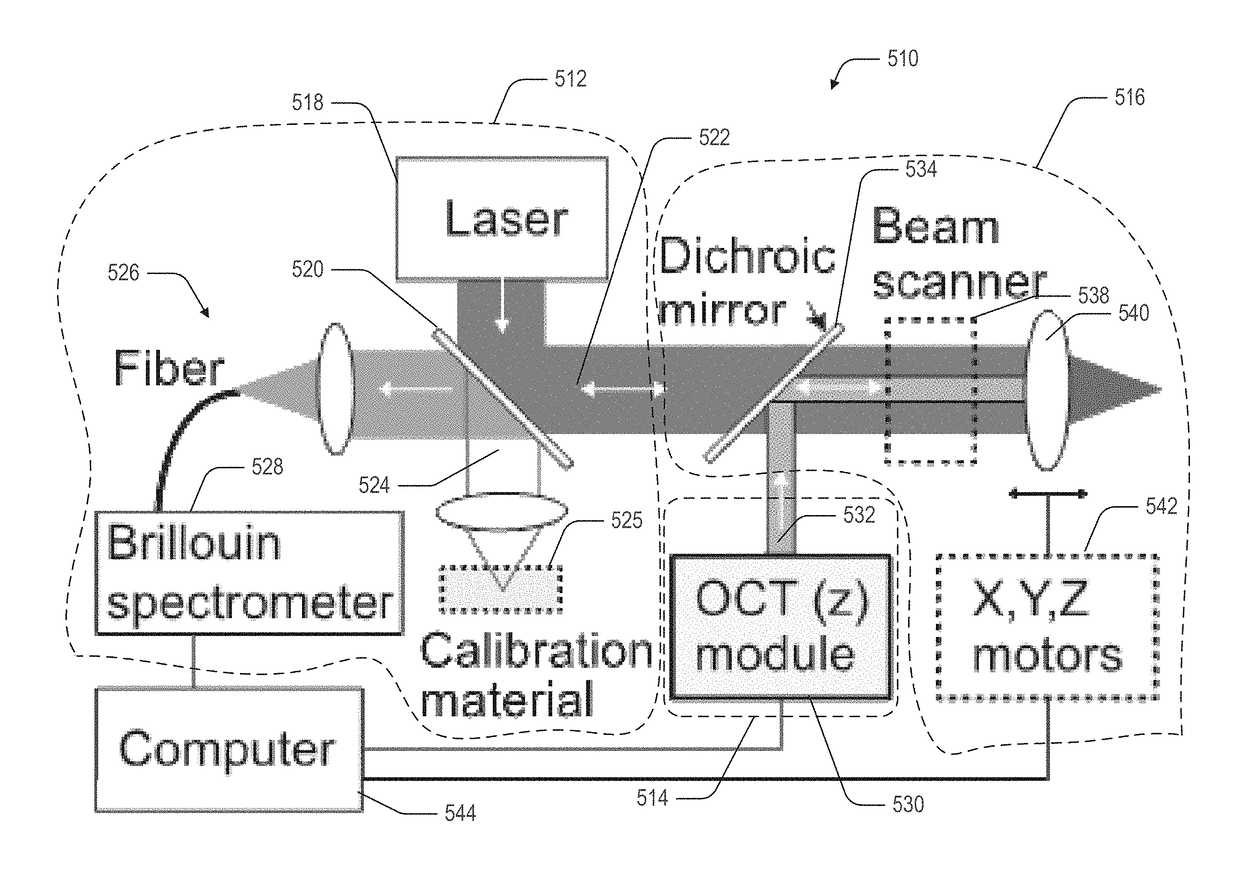
This disclosure provides systems and methods for mapping and / or measuring a mechanical property of a medium. The mechanical property can be measured by Brillouin spectroscopy. The systems and methods can include a three-dimensional imaging modality that is co-registered with a Brillouin probe beam of a Brillouin spectrometer. The three-dimensional imaging modality can be optical coherence tomography or Scheimpflug camera imaging.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
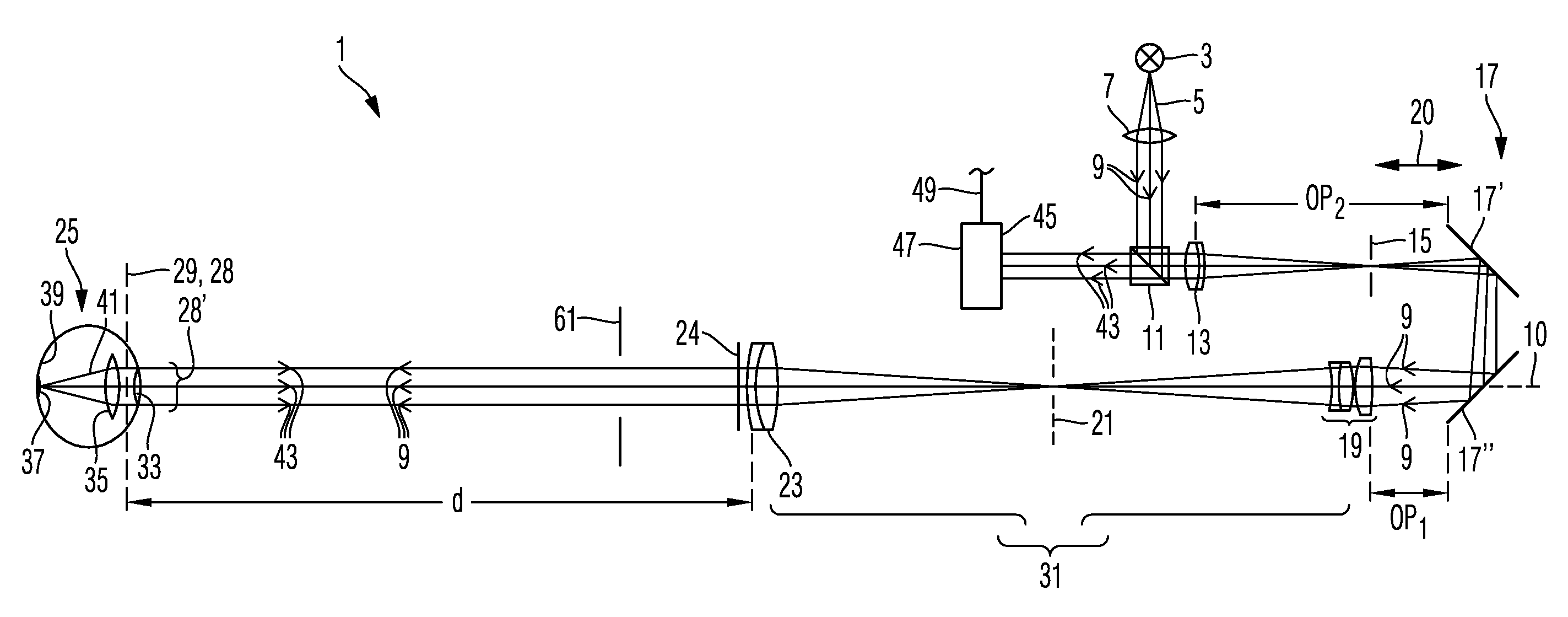
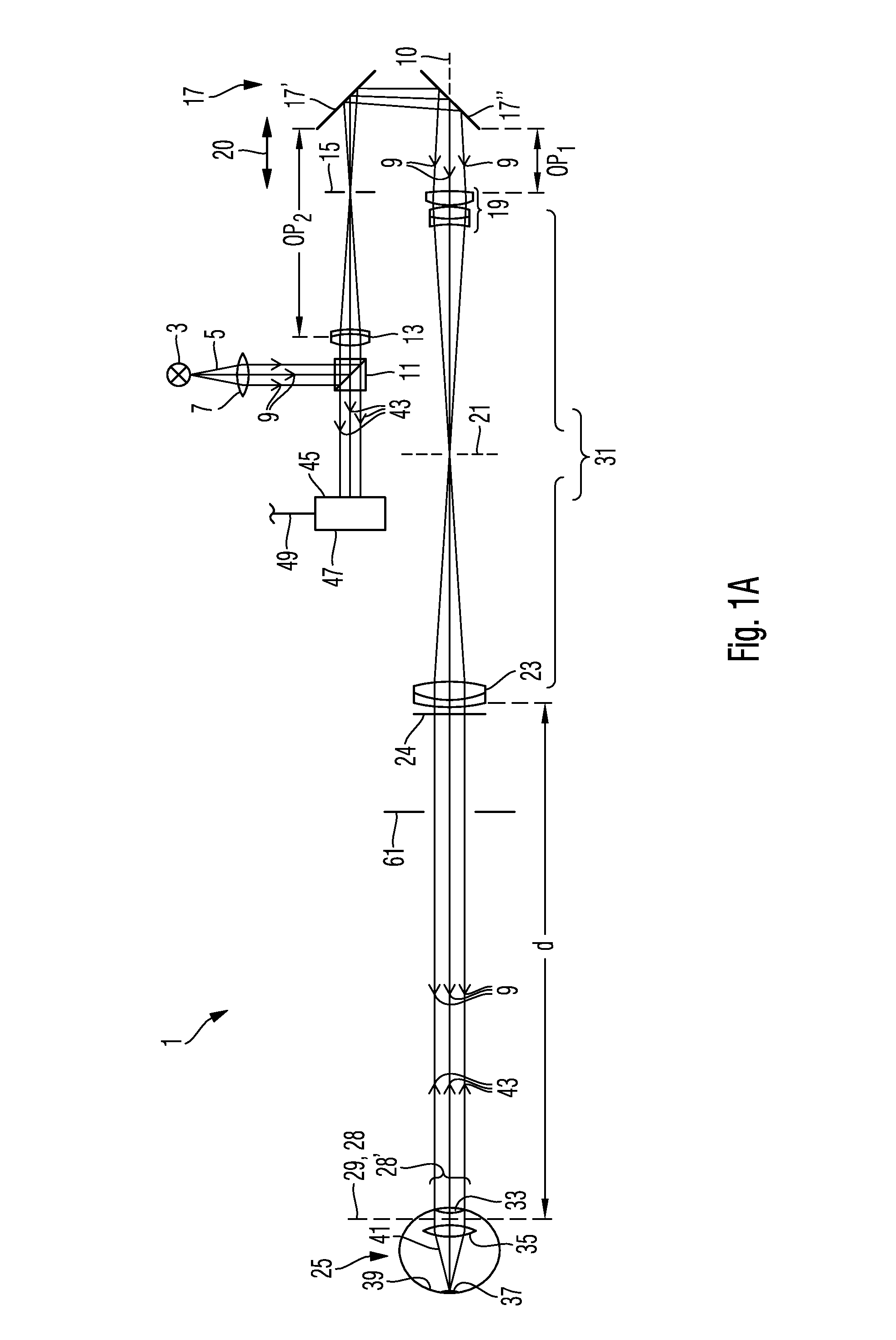
Measuring system for ophthalmic surgery
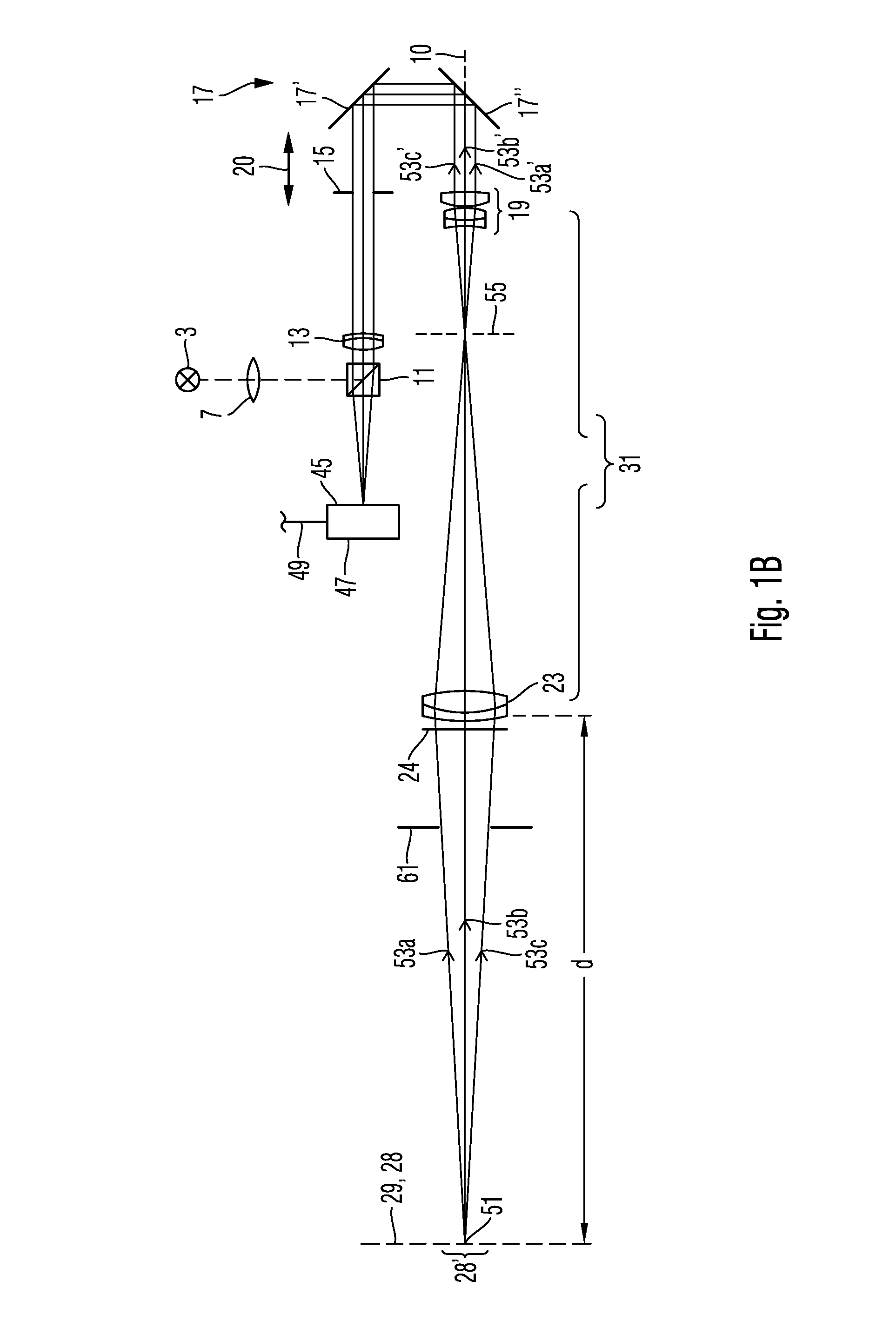
The invention relates to an optical measuring system comprising a wave front sensor for characterizing a shape of a wave front of measuring light and an imaging lens, wherein the imaging lens comprises a first optical assembly and a second optical assembly for imaging an object region in an entrance region of the wave front sensor. A distance between the object region and the first optical assembly is larger that a focal length of the first optical assembly. Furthermore, the optical measuring system can comprise an optical microscopy system and optionally an OCT system for carrying out different optical examination methods at the same time.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Image processing apparatus, computer program product and image processing process
InactiveCN101317138AMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanoinformaticsImaging processingHigh spatial resolution
A high spatial resolution phase-sensitive technique employs a scanning near field ultrasound holography methodology (47) for imaging elastic as well as viscoelastic variations across a sample surface. Scanning near field ultrasound holography (47) uses a near-field approach to measure time-resolved variations in ultrasonic oscillations at a sample surface (12). As such, it overcomes the spatial resolution limitations of conventional phase-resolved acoustic microscopy (i.e. holography) by eliminating the need for far-field acoustic lenses.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Cell opto-acoustic microscopic imaging method and device thereof
InactiveCN101782518AHigh resolutionImprove spatial resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationAnalysis by material excitationMicroscopic imageLaser scanning
The invention relates to a cell opto-acoustic microscopic imaging method, which comprises the following steps: placing a cell on the concave surface of microscopic glass, irradiating the cell with laser light permeating the microscopic glass, producing opto-acoustic effect after the cell absorbs the light, transferring acoustic pressure variation produced by the opto-acoustic effect to an opto-acoustic sensor, and detecting the opto-acoustic variation and outputting an opto-acoustic signal by using the opto-acoustic sensor to realize opto-acoustic detection of the single cell; and performing two-dimensional scanning on the cell by using light beam scanning and a micro objective with high resolution to realize the opto-acoustic microscopic imaging of the single cell. The invention also relates to a cell opto-acoustic microscopic imaging device, which comprises a laser light scanning imaging mechanism, the opto-acoustic sensor and a signal processor. In the method and the device, light beam scanning technology without mechanical noise is combined with the micro objective with the high resolution to generate the opto-acoustic signal with high spatial resolution and then the opto-acoustic sensor is adopted for the opto-acoustic detection to perform the opto-acoustic microscopic imaging on the cell, wherein the solution is less than 1 micron.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Measuring system for ophthalmic surgery
ActiveUS8459795B2Solve the lack of spaceSmall sizeEye diagnosticsWavefront sensorOptical measurements
The invention relates to an optical measuring system comprising a wave front sensor for characterizing a shape of a wave front of measuring light and an imaging lens, wherein the imaging lens comprises a first optical assembly and a second optical assembly for imaging an object region in an entrance region of the wave front sensor. A distance between the object region and the first optical assembly is larger than a focal length of the first optical assembly. Furthermore, the optical measuring system can comprise an optical microscopy system and optionally an OCT system for carrying out different optical examination methods at the same time.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
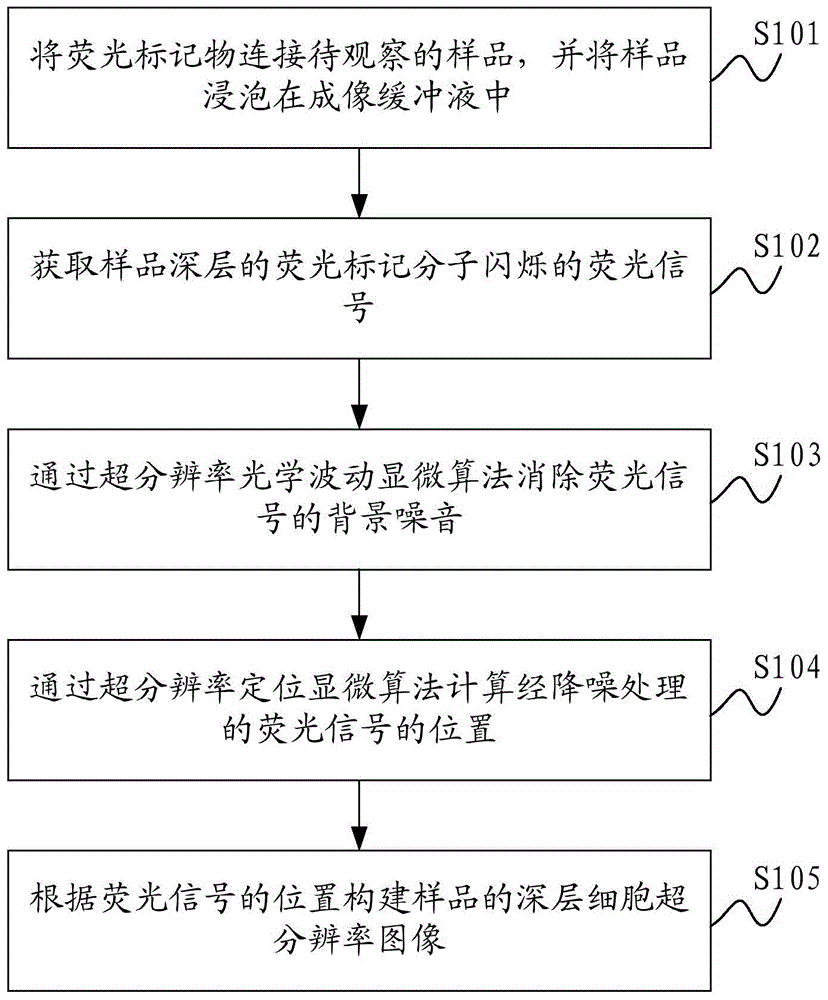
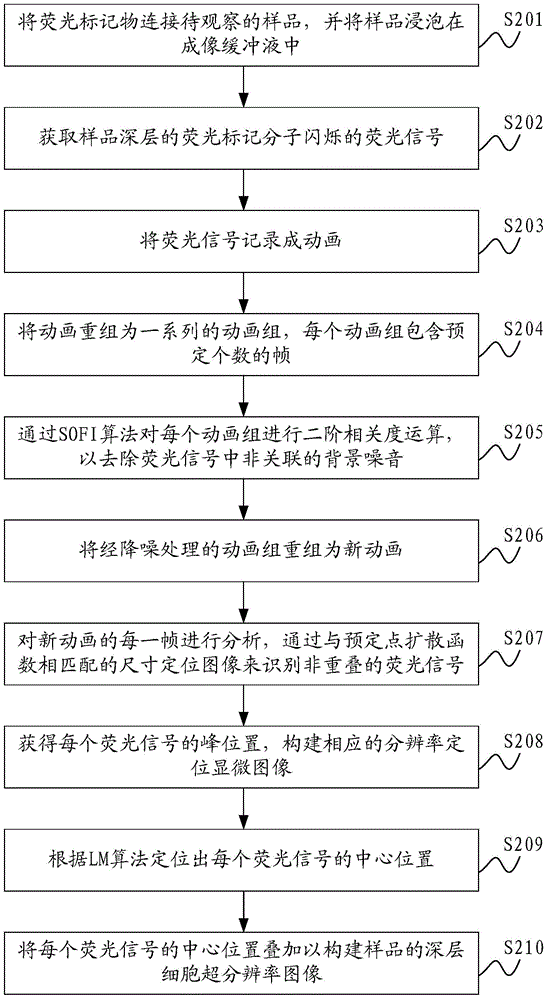
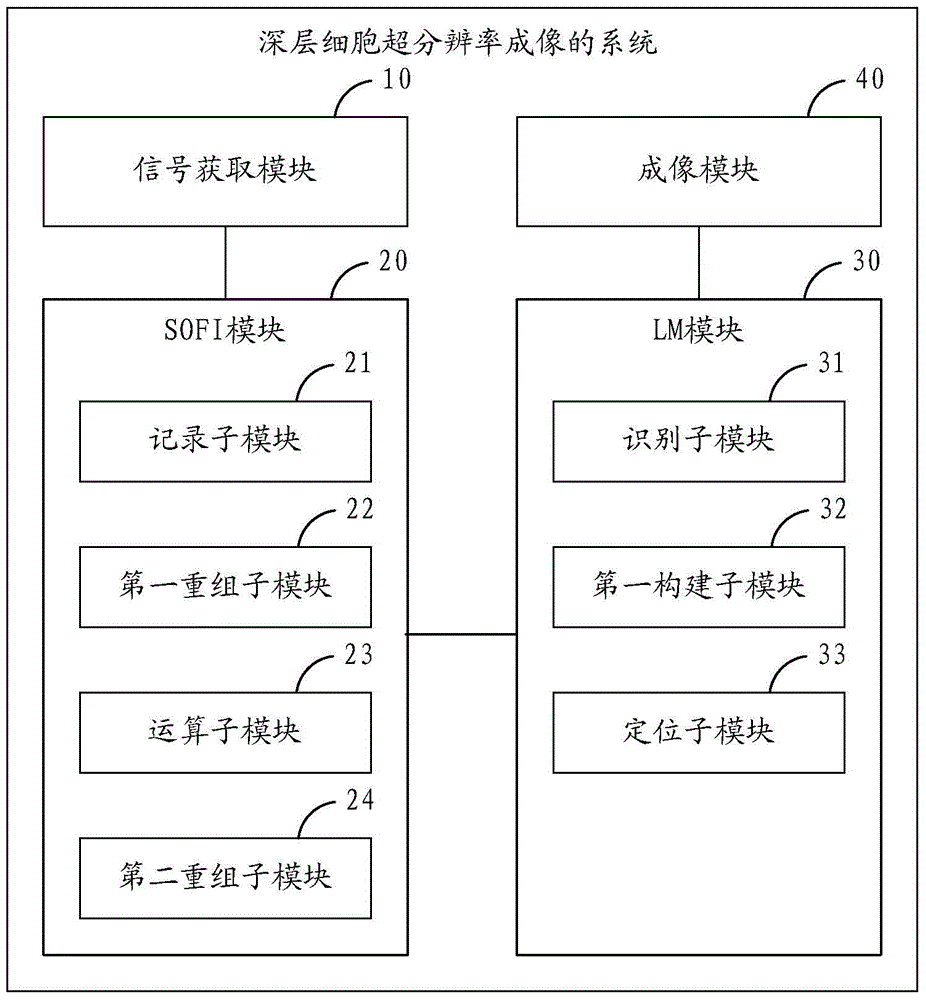
Deep cell super-resolution imaging methods, deep cell super-resolution imaging optical system and prism sheet device
ActiveCN104458683AReduce background noiseMicroscopesIndividual particle analysisBiological cellPrism
The present invention is applicable to optical microscopy and biological cell imaging technology, and provides a deeper cell super-resolution imaging methods, a deep cell super-resolution imaging systems and a prism light sheet device. The first technology program combines the super-resolution optical microscopy fluctuations (SOFI) and super-resolution localization microscopy (IM), so that the cells deep super-resolution image can be used to eliminate non-related background noise coming through the computer operation Get. The first aspect can be directly used in ordinary fluorescent microscope without modifying its original optical structure. A second aspect of light using a prism sheet unit loaded with the inverted microscope, to reduce the background noise by physical means and by positioning microscopy to obtain cells deep super-resolution images to the second aspect can be loaded directly to the traditional inverted fluorescence microscope.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Non-fluid acoustic coupling
InactiveUS6940212B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCouplingTransducer
An apparatus examines the internal structure of an object disposed substantially in a medium such as air, which essentially totally reflects acoustic signals in the 1-200 MHz frequency range. The apparatus has an acoustic transducer that emits and receives acoustic signals in the 1-200 MHz frequency range and an acoustic coupler that acoustically couples the acoustic transducer to the object. The acoustic coupler has a first end adapted to couple to the acoustic transducer and a second end adapted to make contact with a section of a surface of the object. The acoustic coupler carries acoustic signals in the 1-200 MHz frequency range between the acoustic transducer and the contacted section of the surface of the object. In operation, the apparatus examines the internal structure of the object using reflection mode acoustic microscopy, wherein emitted and reflected signals are carried between the acoustic transducer and the object by acoustic coupler.
Owner:METABCAN TECH
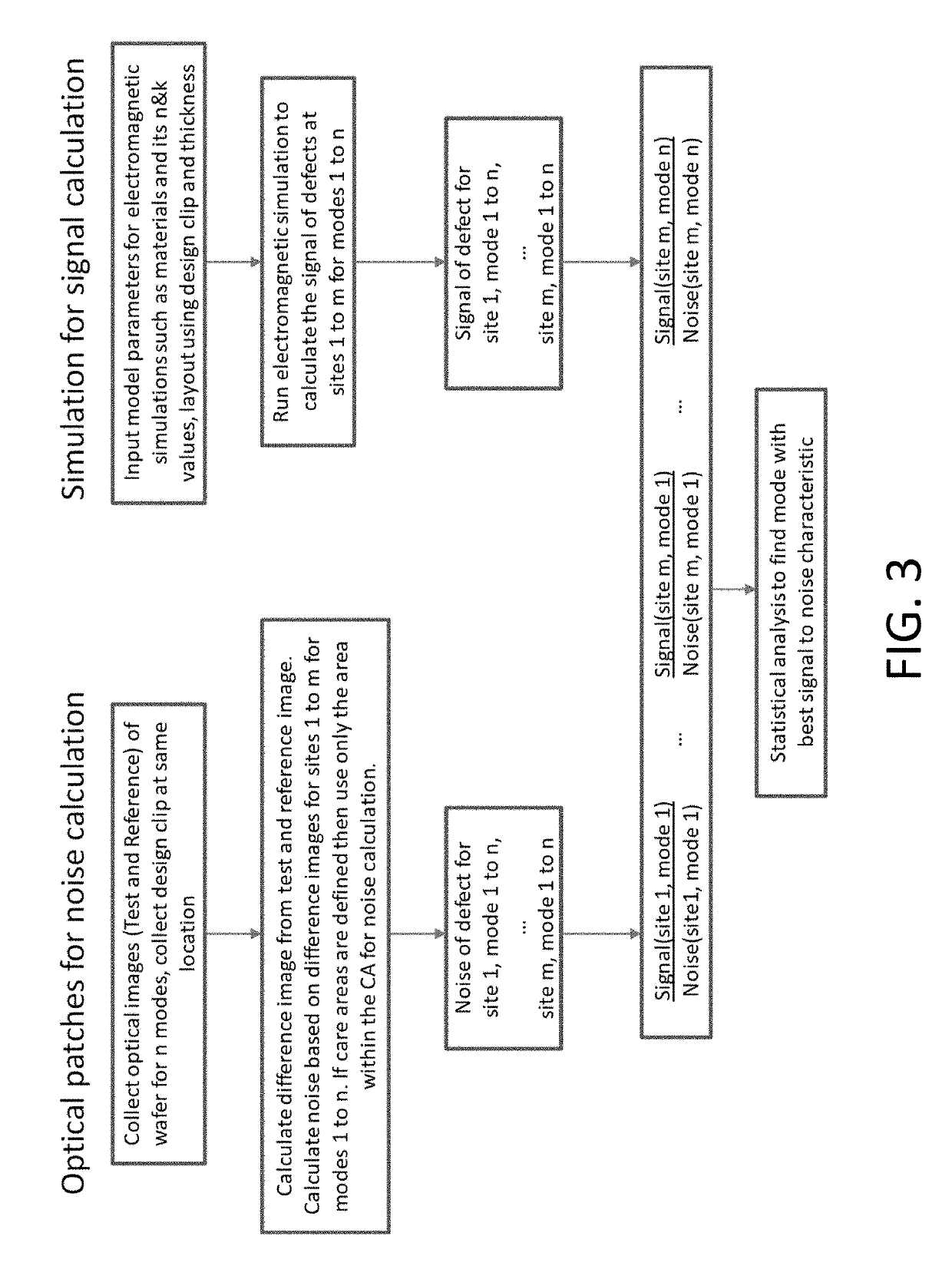
Combining simulation and optical microscopy to determine inspection mode
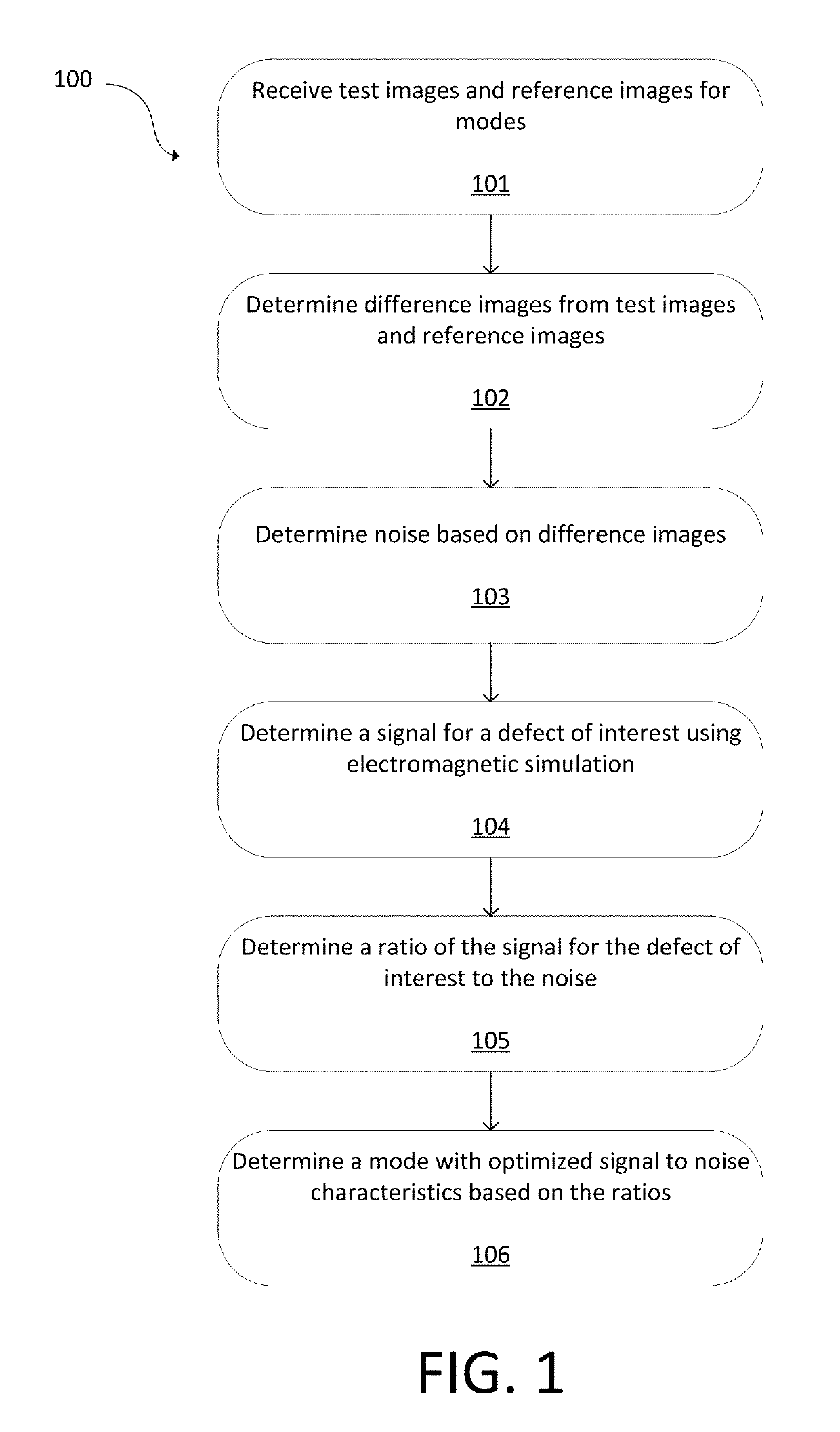
ActiveUS20190287232A1Improved signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
A best optical inspection mode to detect defects can be determined when no defect examples or only a limited number of defect examples are available. A signal for a defect of interest at the plurality of sites and for the plurality of modes can be determined using electromagnetic simulation. A ratio of the signal for the defect of interest to the noise at each combination of the plurality of sites and the plurality of modes can be determined. A mode with optimized signal-to-noise characteristics can be determined based on the ratios.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
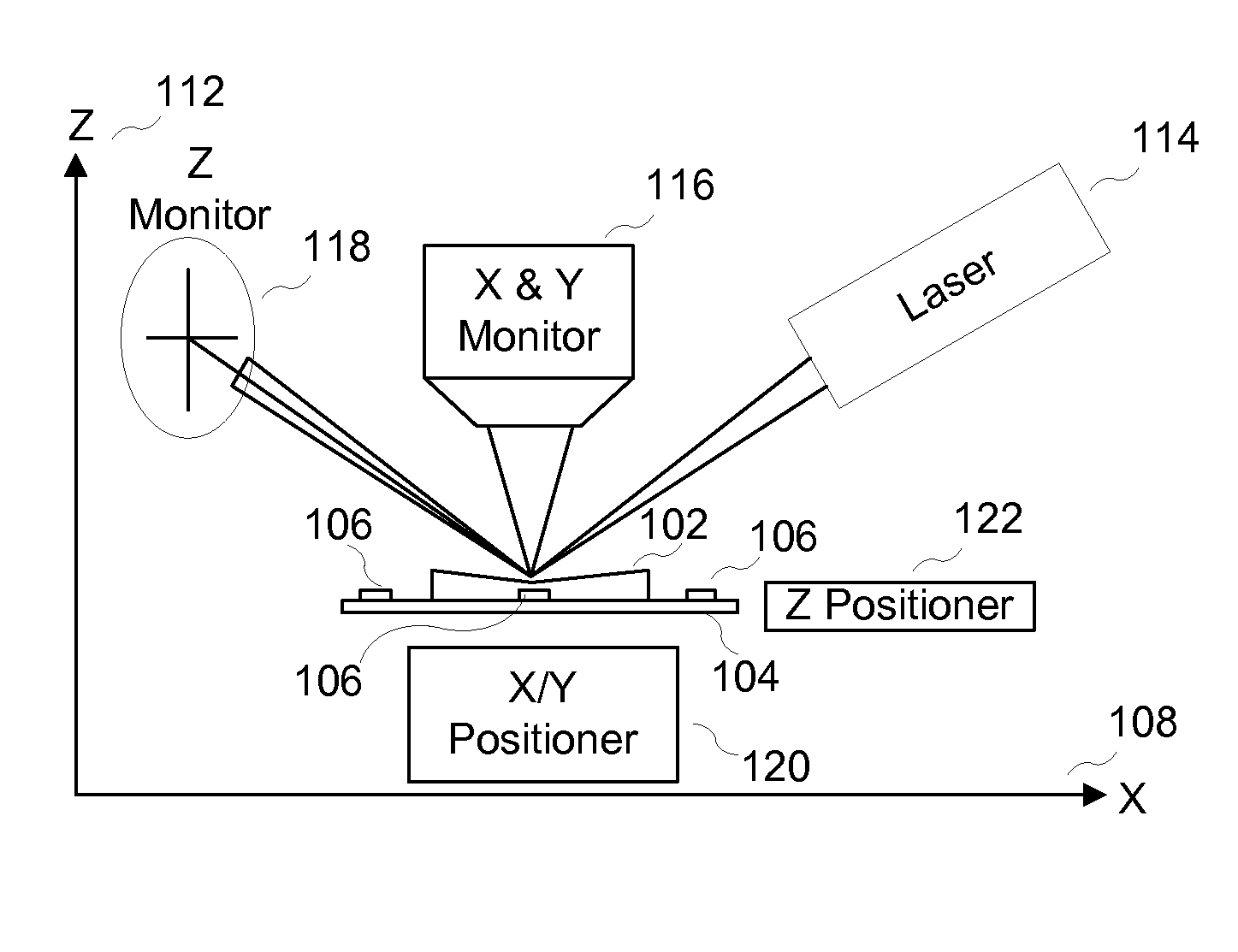
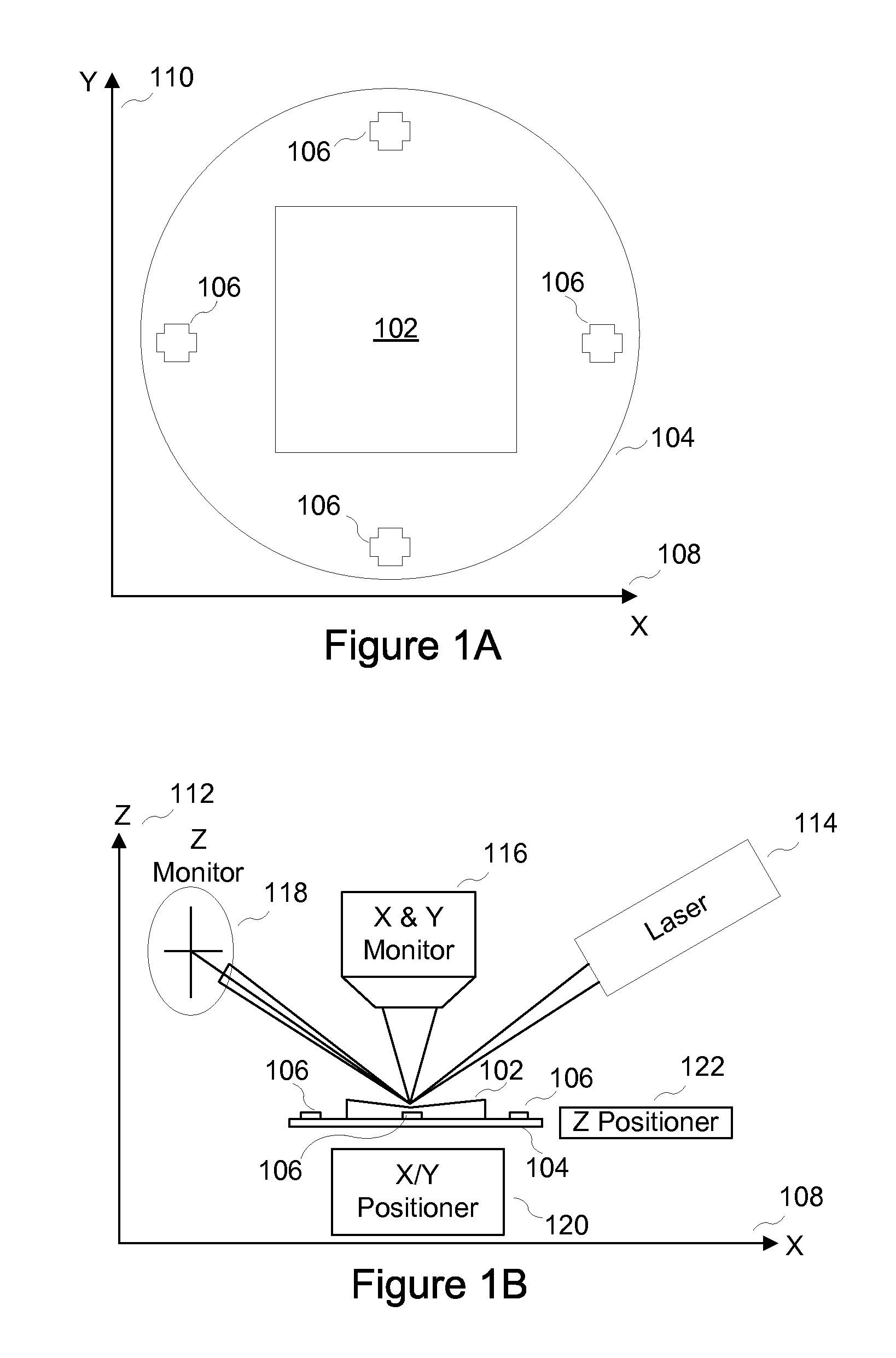
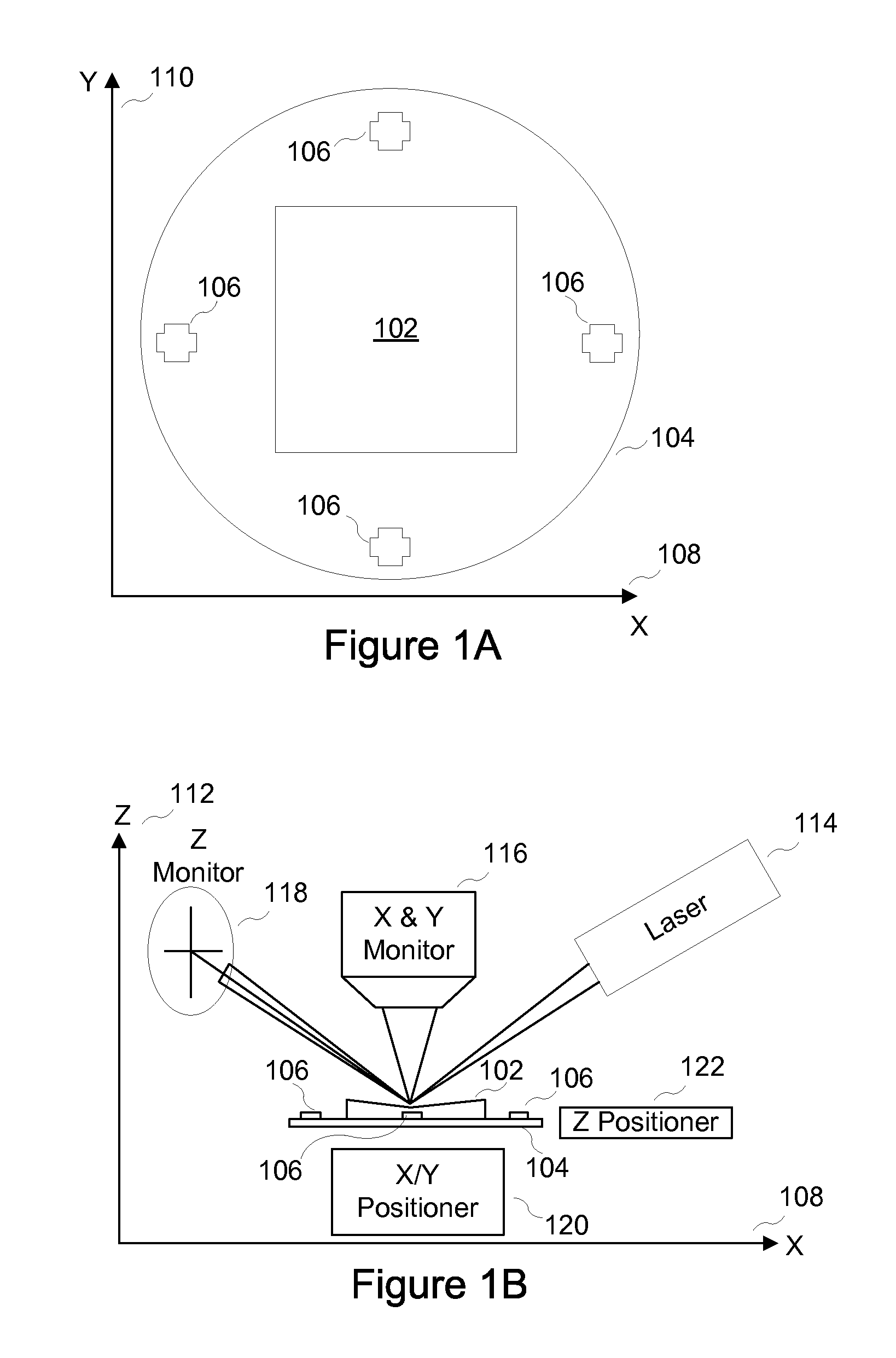
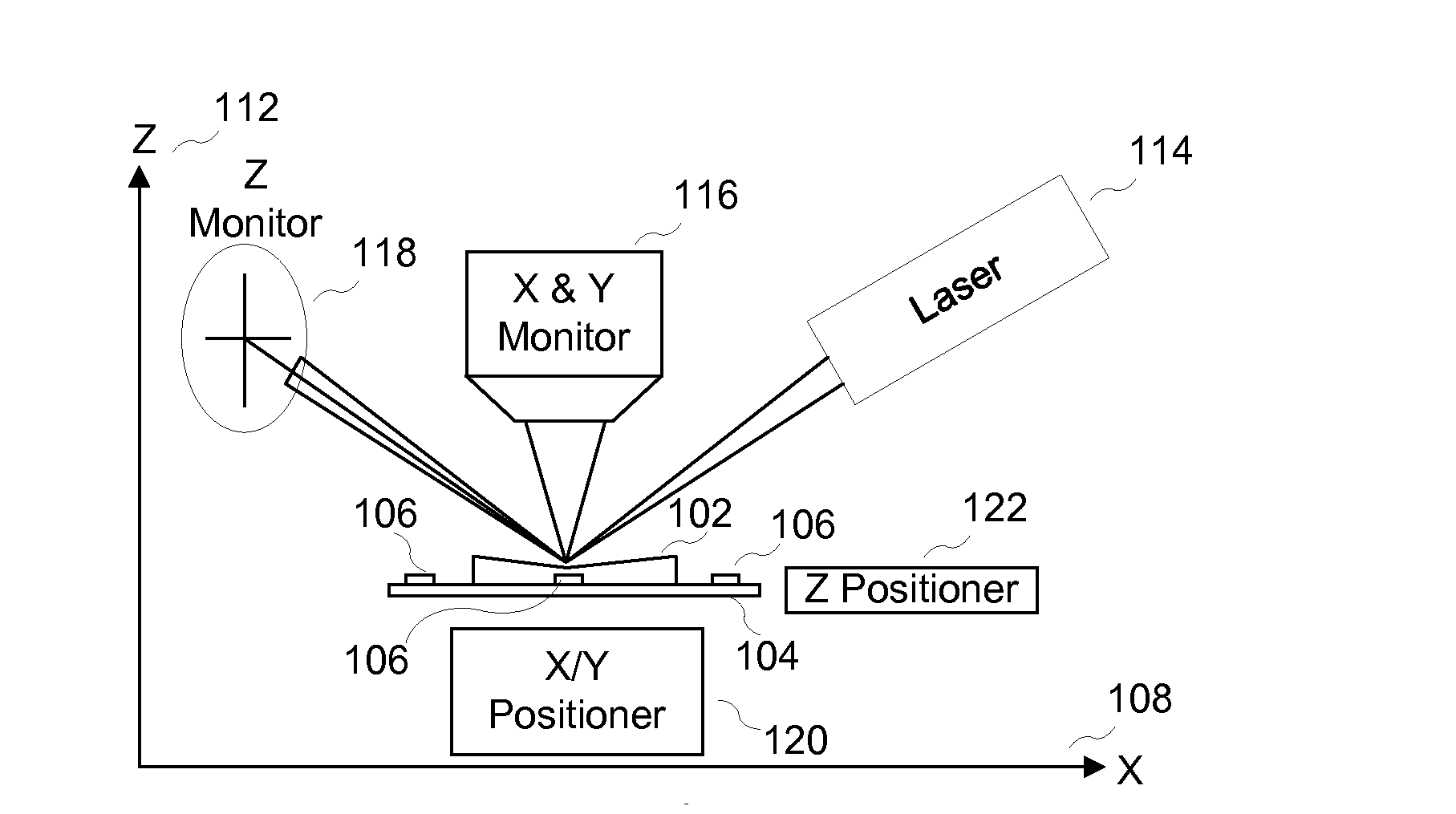
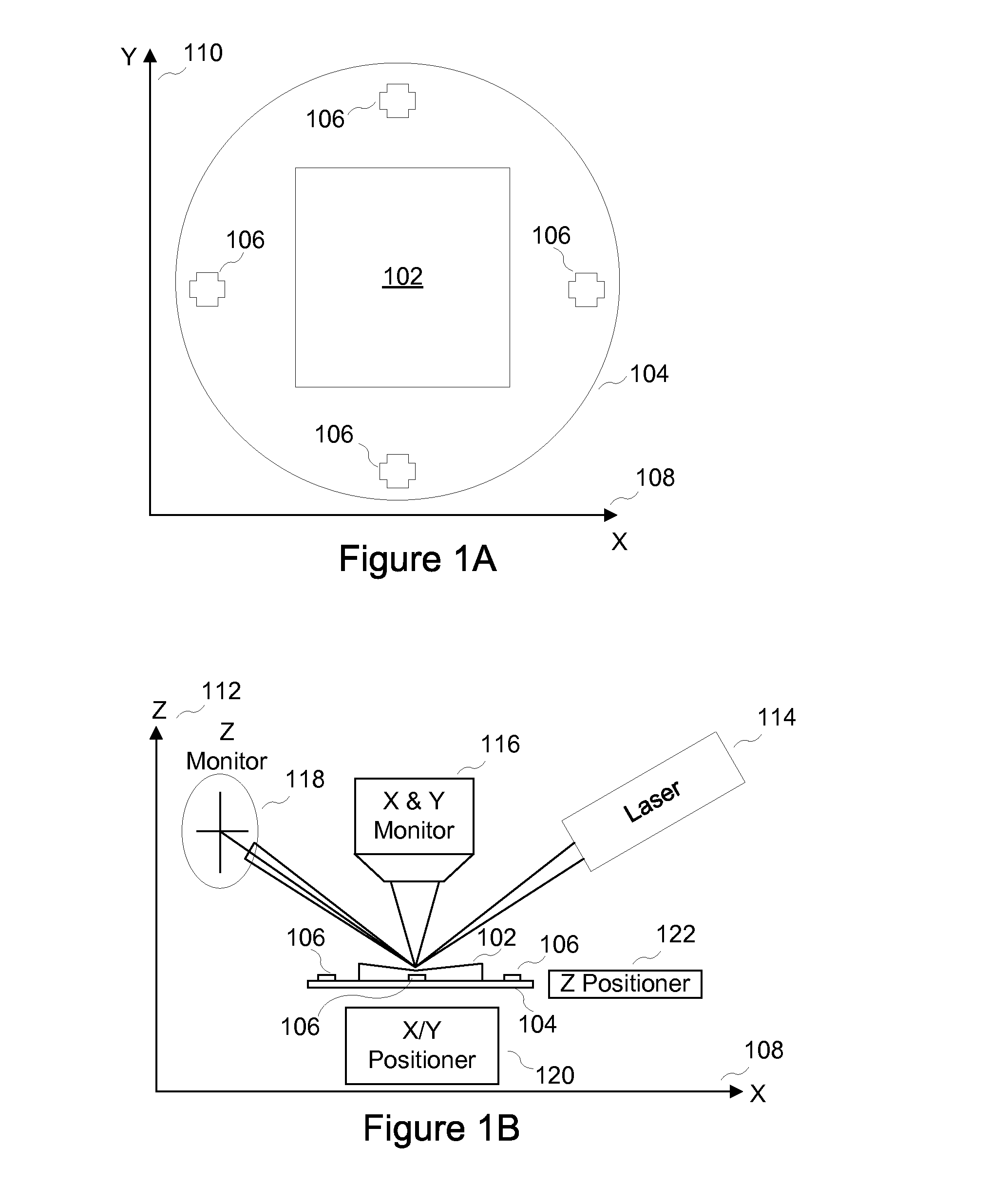
System and method for non-contact microscopy for three-dimensional pre-characterization of a sample for fast and non-destructive on sample navigation during nanoprobing
A system for performing sample probing. The system including an topography microscope configured to receive three-dimensional coordinates for a sample based on at least three fiducial marks; receive the sample mounted in a holder; and navigate to at least a location on the sample based on the at least three fiducial marks and the three-dimensional coordinates.
Owner:DCG SYST
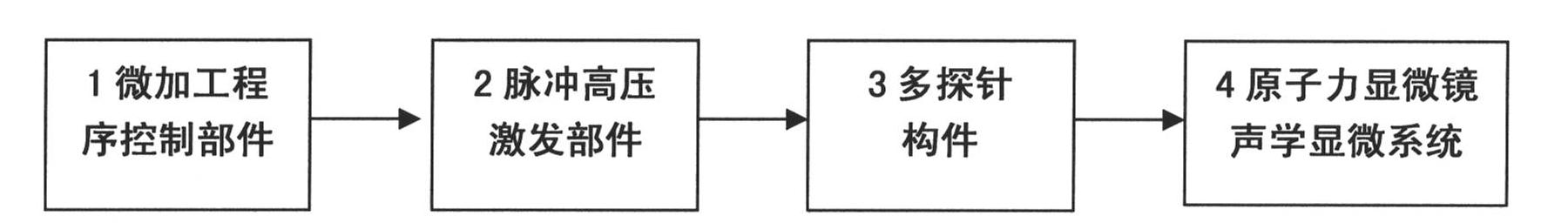
Etching device of micro-nano ferroelectric domain structure based on atomic force microscope acoustic microscopy system
ActiveCN102107853AEfficient and high-speed micromachiningAssess Structural IntegrityNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsMicro nanoHigh pressure
The invention relates to an etching device of a micro-nano ferroelectric domain structure based on an atomic force microscope acoustic microscopy system and belongs to the field of instrument development. The etching device comprises a microprocessing program control component, a pulse high-pressure excitation component, a multi-probe component and the atomic force microscope acoustic microscopy system. The etching device has the unique characteristics of nano-grade microprocessing, high pulse processing voltage, high-speed response, large-area microprocessing, high-resolution acoustic imaging of a microstructure and the like and is different from the microprocessing of the conventional commercial atomic force microscopes.
Owner:中科西卡思(苏州)科技发展有限公司
Specimen holder having alignment marks
ActiveUS8304745B2Increase opportunitiesSimpler retrievabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesParticle beamConfocal microscopy
For the microscopy of an object or a specimen with a combination of optical microscopy and particle beam microscopy, an electrically conducting specimen carrier (1) is used which is configured for use in a particle beam microscope as well as in an optical microscope and has at least one alignment mark (2). The alignment mark is configured as a pass-through structure and is detectable from the top and from the bottom of the specimen carrier.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
System and method for non-contact microscopy for three-dimensional pre-characterization of a sample for fast and non-destructive on sample navigation during nanoprobing
A system for performing sample probing. The system including an topography microscope configured to receive three-dimensional coordinates for a sample based on at least three fiducial marks; receive the sample mounted in a holder; and navigate to at least a location on the sample based on the at least three fiducial marks and the three-dimensional coordinates.
Owner:DCG SYST
Devices applicable to tissue(s) which facilitates confocal microscopy, optical microscopy, spectroscopy and/or imaging
ActiveUS20150233798A1Easy to optimizeEasy to analyzeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConfocal scanning microscopyConfocal microscopy
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
System and method for non-contact microscopy for three-dimensional pre-characterization of a sample for fast and non-destructive on sample navigation during nanoprobing
A system for performing sample probing. The system including an topography microscope configured to receive three-dimensional coordinates for a sample based on at least three fiducial marks; receive the sample mounted in a holder; and navigate to at least a location on the sample based on the at least three fiducial marks and the three-dimensional coordinates.
Owner:DCG SYST
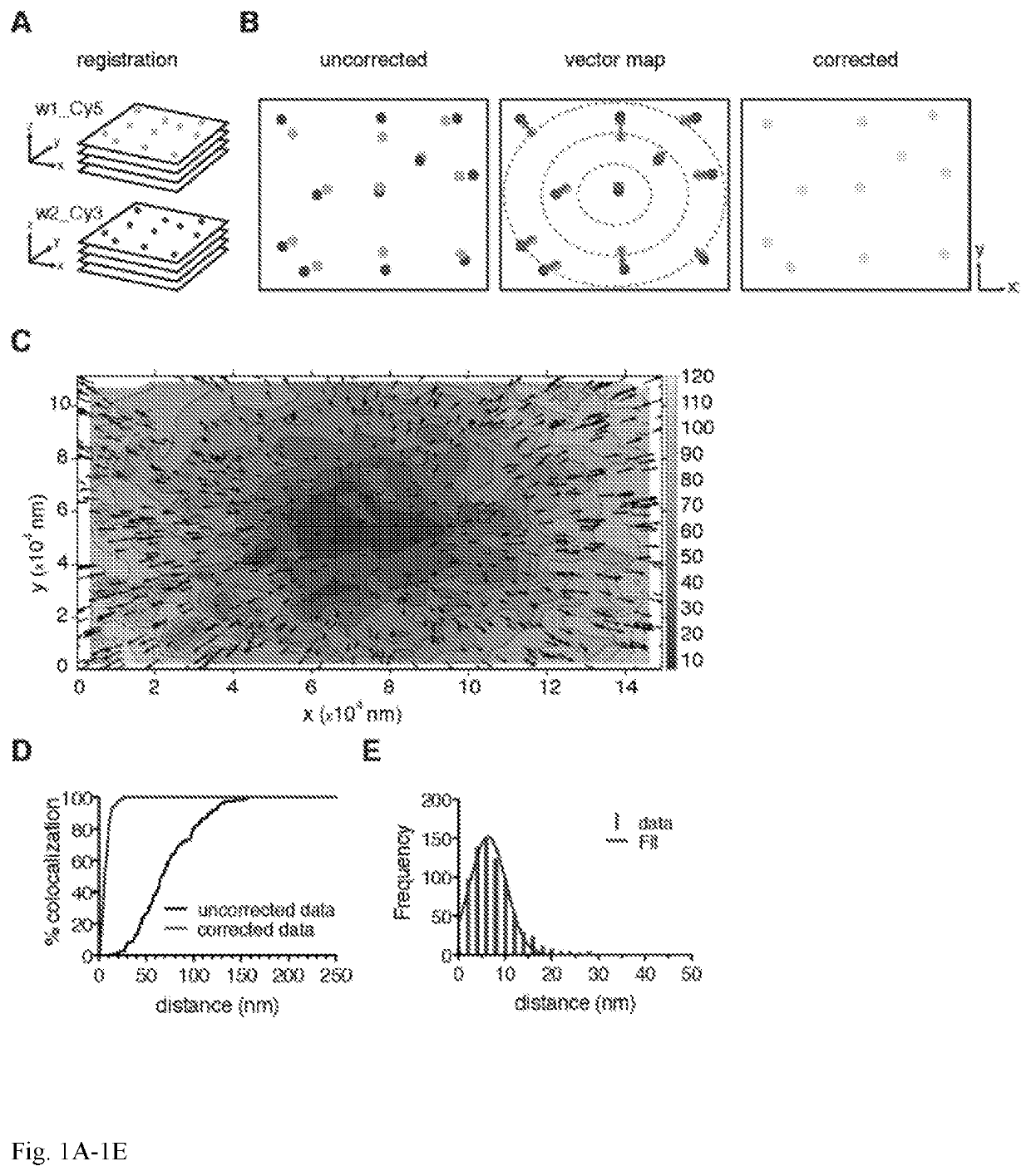
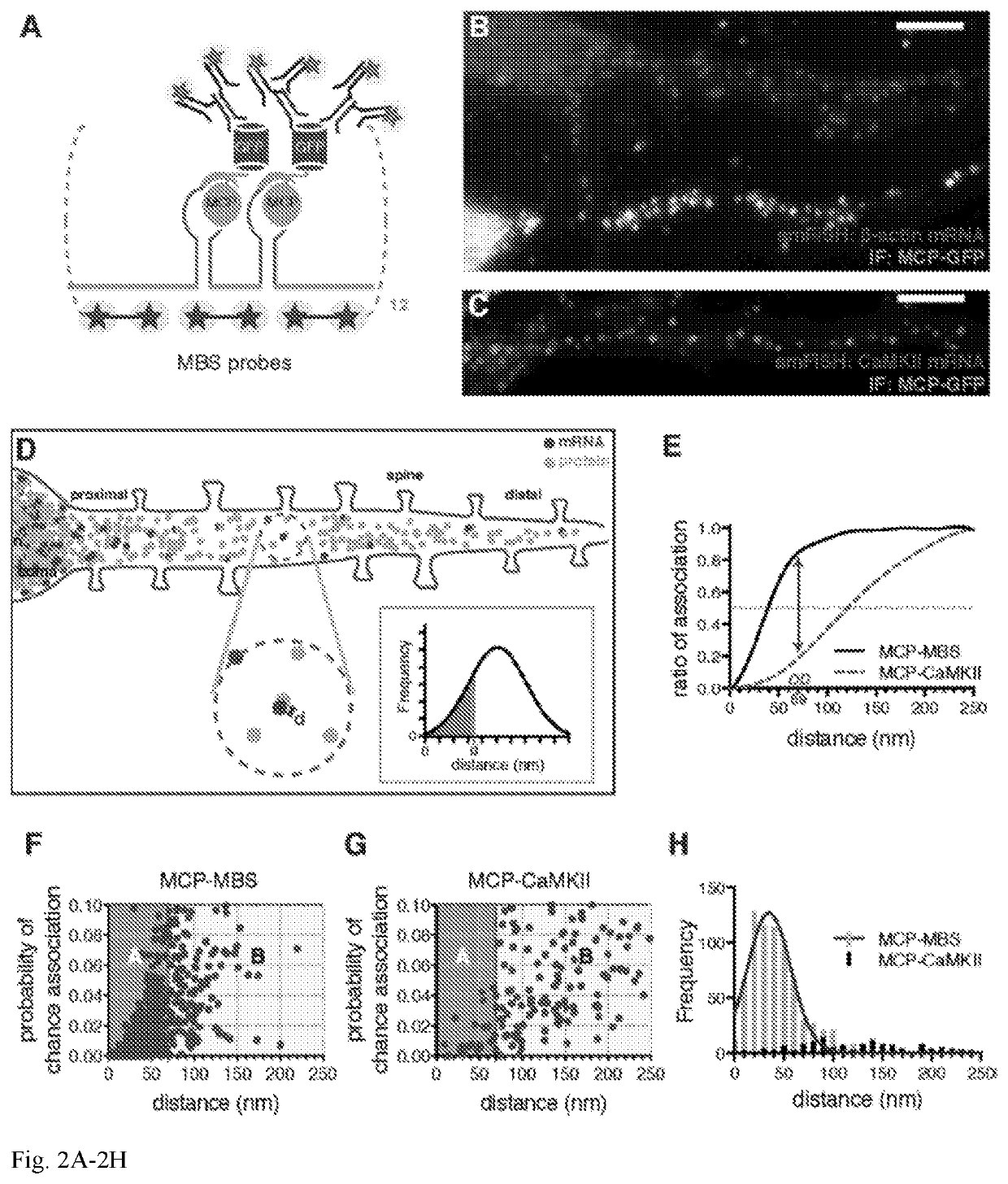
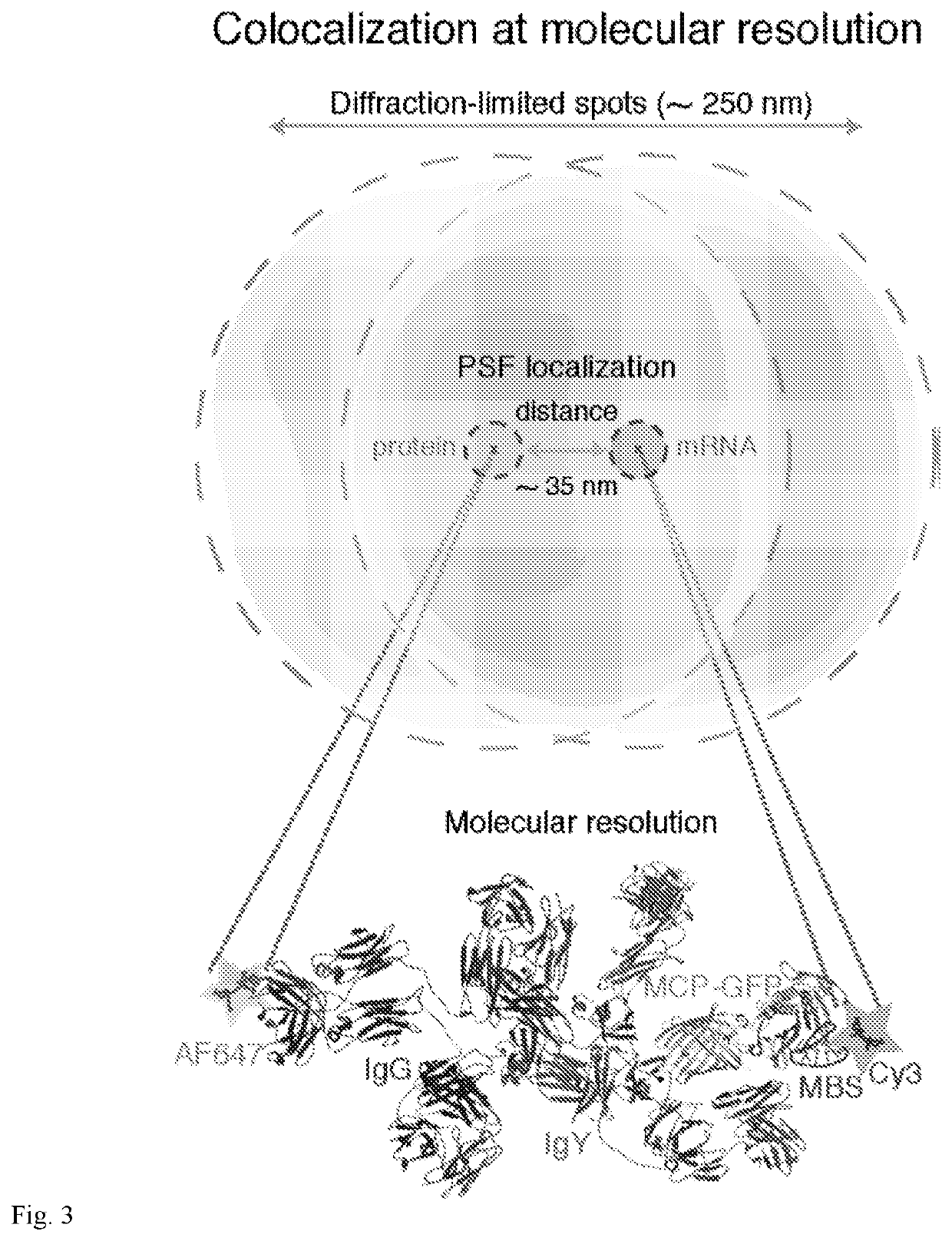
Co-localization at molecular resolution of multiple fluorescence channels acquired using optical microscopy
InactiveUS20190339204A1Aberration correctionExcellent fluorescence performanceMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceImage resolutionFluorescence
A method for improving the performance of a fluorescence microscopy imaging system and for correcting chromatic aberration of an optical objective in a fluorescence microscopy system.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Non-fluid acoustic coupling
InactiveUS20050162041A9Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCouplingTransducer
An apparatus examines the internal structure of an object disposed substantially in a medium such as air, which essentially totally reflects acoustic signals in the 1-200 MHz frequency range. The apparatus has an acoustic transducer that emits and receives acoustic signals in the 1-200 MHz frequency range and an acoustic coupler that acoustically couples the acoustic transducer to the object. The acoustic coupler has a first end adapted to couple to the acoustic transducer and a second end adapted to make contact with a section of a surface of the object. The acoustic coupler carries acoustic signals in the 1-200 MHz frequency range between the acoustic transducer and the contacted section of the surface of the object. In operation, the apparatus examines the internal structure of the object using reflection mode acoustic microscopy, wherein emitted and reflected signals are carried between the acoustic transducer and the object by acoustic coupler.
Owner:METABCAN TECH
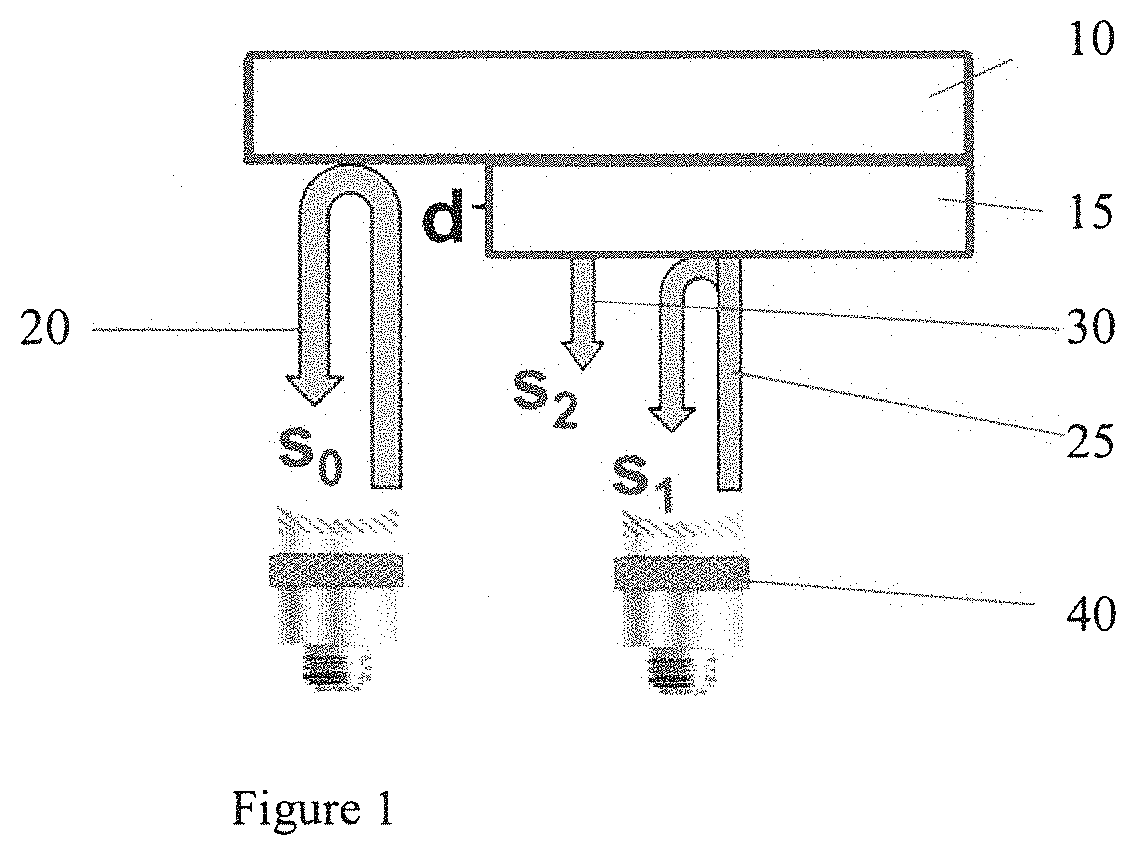
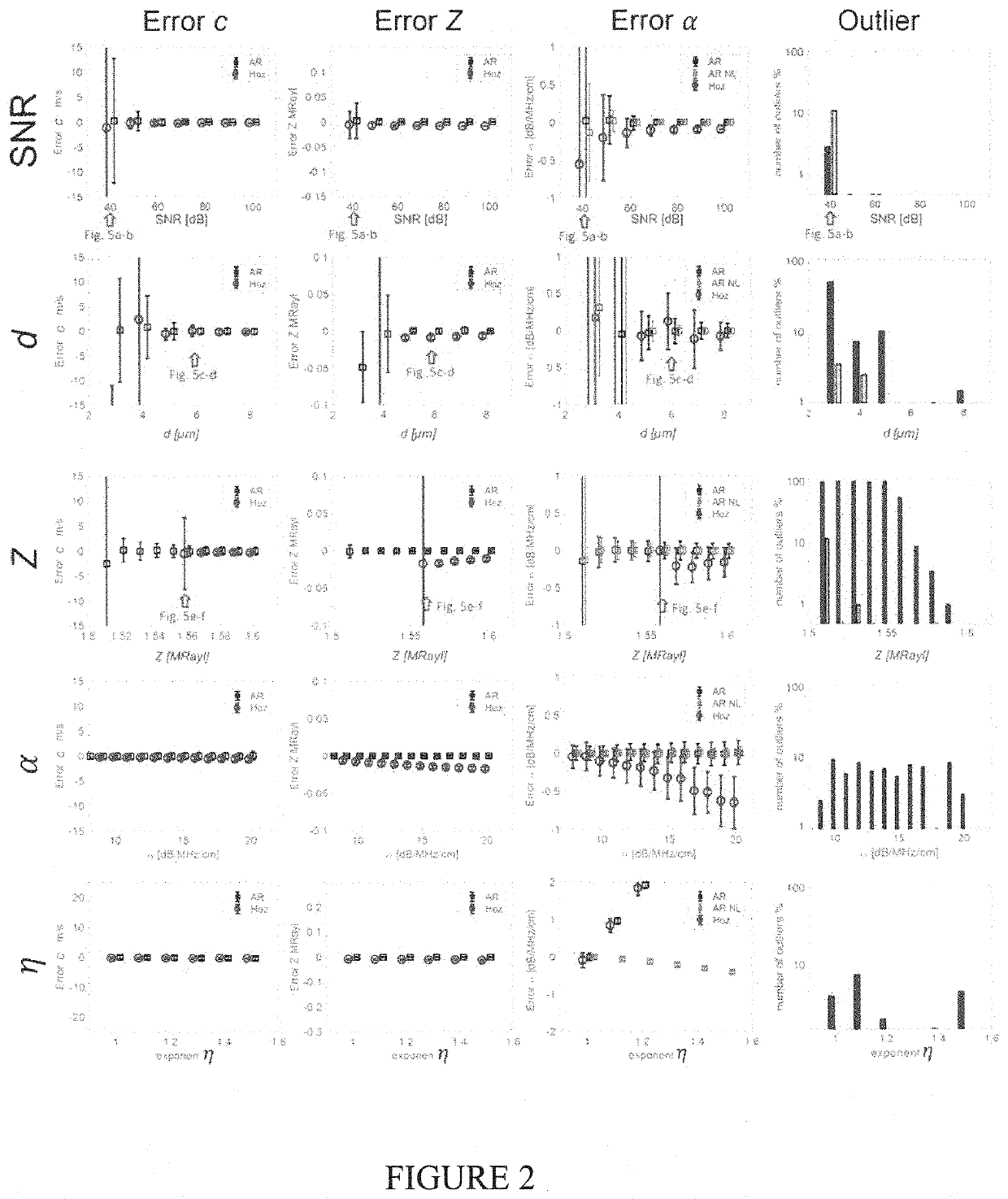
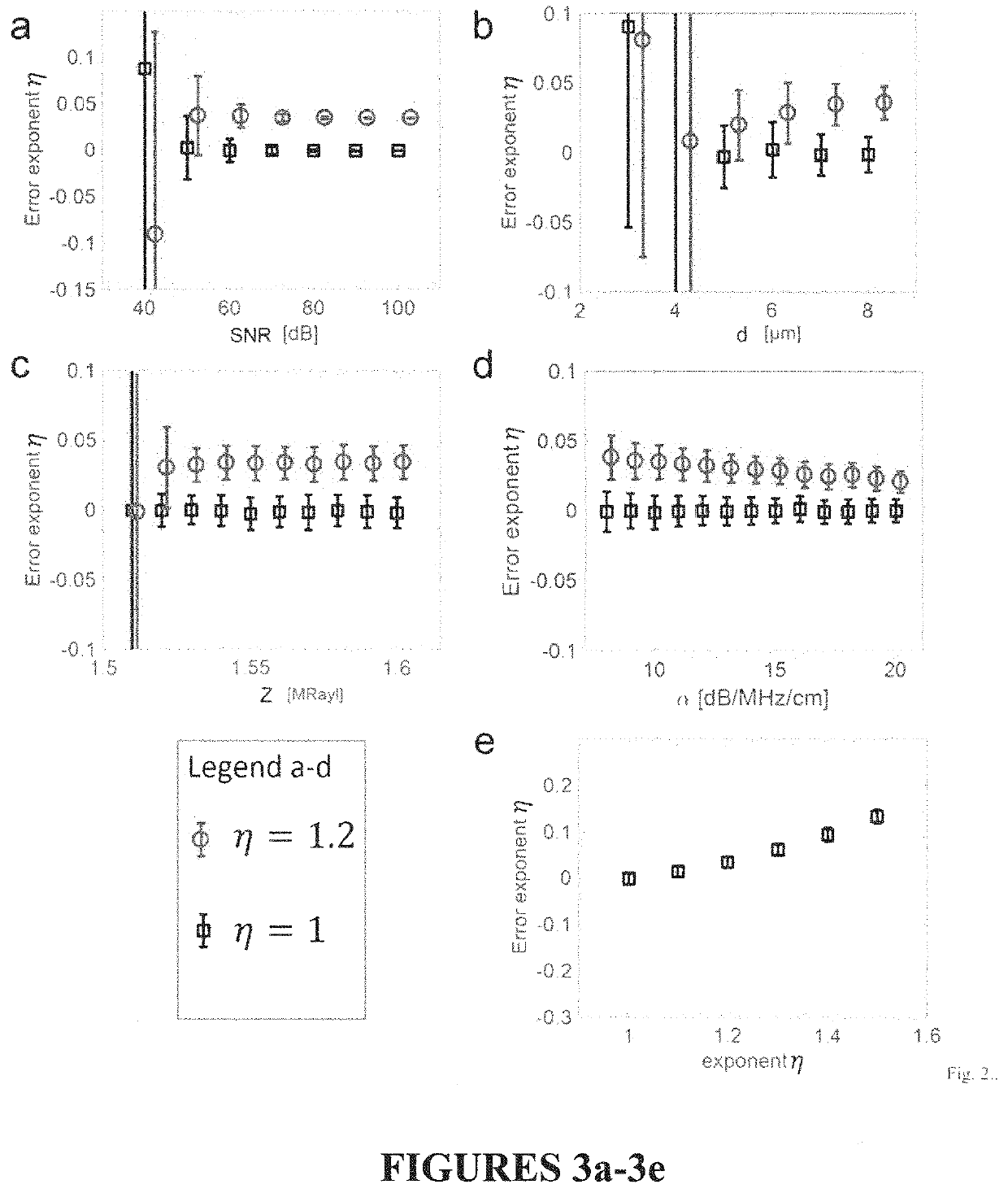
Autoregressive signal processing applied to high-frequency acoustic microscopy of soft tissues
InactiveUS20200088687A1Improve signal processingImprove parameter estimationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalUltrasound attenuationUltrasonic attenuation
A method to create a parameter map depicting acoustical and mechanical properties of biological tissue at microscopic resolutions to identify potential health related issues. The method including mounting the biological tissue on a substrate, raster scanning the biological tissue with an RF frequency, recovering RF echo signals from said substrate and from a plurality of locations on said biological tissue, wherein each of the plurality of locations corresponds to a specific pixel comprising the parameter map, the recovered RF echo signals including a reference signal recovered from the substrate at a point devoid of tissue, a first sample signal recovered from an interface between the biological tissue and water, and a second sample signal recovered from an interface between said biological tissue and said substrate, repeatedly applying a plurality of computer-generated calculation steps based on the reference signal, the first sample signal and the second sample signal to generate estimated values for a plurality of parameters associated with each of the specific pixels in the parameter map. The plurality of computer-generated calculation steps includes a denoising step, and using the generated estimated values to create said parameter map depicting parameters including, but not limited, to acoustic impedance, speed of sound, ultrasound attenuation, mass density, bulk modulus and nonlinear attenuation.
Owner:RIVERSIDE RES INST
Method and system for optical microscopy
Optical microscopy of biological specimens, particularly live cells, is difficult as they generally lack sufficient contrast to be studied successfully as typically the internal structures of the cell are colorless and transparent. Commonly, contrast is increased by staining the different structures with selective dyes, but this involves killing and fixing the sample. Staining may also introduce artifacts, apparent structural details caused by the processing of the specimen and are thus not a legitimate feature of the specimen. Further, microscopy of different elements of these biological specimens typically requires multiple microscopy techniques on multiple specimens. According to embodiments of the invention simultaneous imaging techniques are applied to a biological specimen such as fluorescent imaging and dark field imaging by designing an experimental evaluation system and associated illumination system addressing the conflicting demands of these approaches.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Sparse reconstruction method for micro-defect high-frequency ultrasonic microscopic imaging based on blind estimation
InactiveCN111340702AImprove detection accuracyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisMicro imagingMicro devices
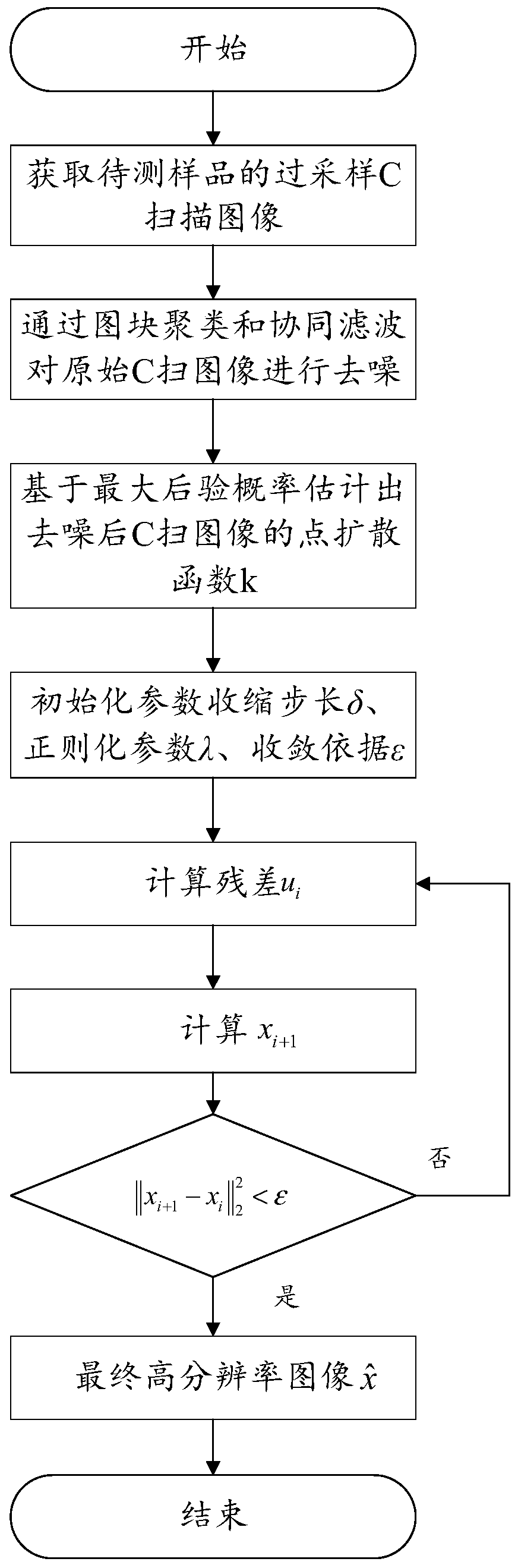
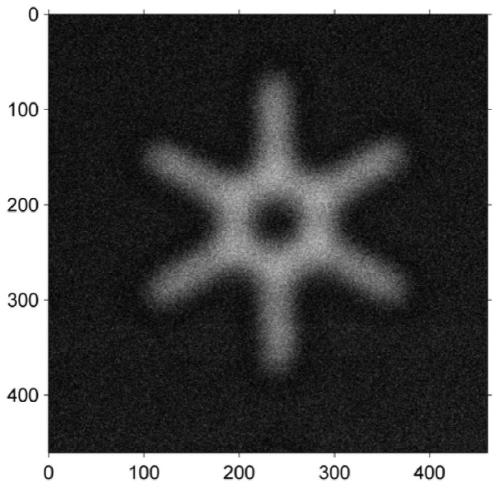
The invention discloses a sparse reconstruction method for micro defect high-frequency ultrasonic microscopic imaging based on blind estimation and relates to the technical field of image processing,the method comprises the following steps: 1, ; acquiring a C scanning image of the sample to be detected by using a high-frequency ultrasonic microscopic probe; and denoising the C-scan image throughblock clustering and collaborative filtering, estimating a point spread function from the denoised C-scan image according to the maximum posteriori probability, and finally performing sparse reconstruction on the ideal C-scan image based on l1 regularization to obtain a final high-resolution image. According to the method, the signal-to-noise ratio and the resolution of the image are enhanced, thedetection accuracy of acoustic microscopy imaging on tiny defects is improved, the practicability of the two-dimensional ultrasonic image sparse reconstruction method is expanded. Meanwhile, the method has very important significance on detection of microdefects, and the development of the reliability of micro devices can be effectively promoted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Non-fluid acoustic coupling
InactiveUS20050132810A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansCouplingTransducer
An apparatus examines the internal structure of an object disposed substantially in a medium such as air.. The apparatus has an acoustic transducer assembly that emits and receives acoustic signals and an acoustic coupler that acoustically couples the acoustic transducer assembly to the object. The acoustic coupler has a first end adapted to couple to the acoustic transducer assembly and a second end adapted to make contact with a section of a surface of the object. The acoustic coupler carries acoustic signals between the acoustic transducer assembly and the contacted section of the surface of the object. In operation, the apparatus examines the internal structure of the object using reflection mode acoustic microscopy, wherein emitted and reflected signals are carried between the acoustic transducer and the object by acoustic coupler.
Owner:METABCAN TECH
Scanning near field ultrasonic holography method and system
InactiveCN101317138BMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanoinformaticsHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
A high spatial resolution phase-sensitive technique employs a scanning near field ultrasound holography methodology (47) for imaging elastic as well as viscoelastic variations across a sample surface. Scanning near field ultrasound holography (47) uses a near-field approach to measure time-resolved variations in ultrasonic oscillations at a sample surface (12). As such, it overcomes the spatial resolution limitations of conventional phase-resolved acoustic microscopy (i.e. holography) by eliminating the need for far-field acoustic lenses.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com