Patents
Literature
74 results about "Anatomic Location" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
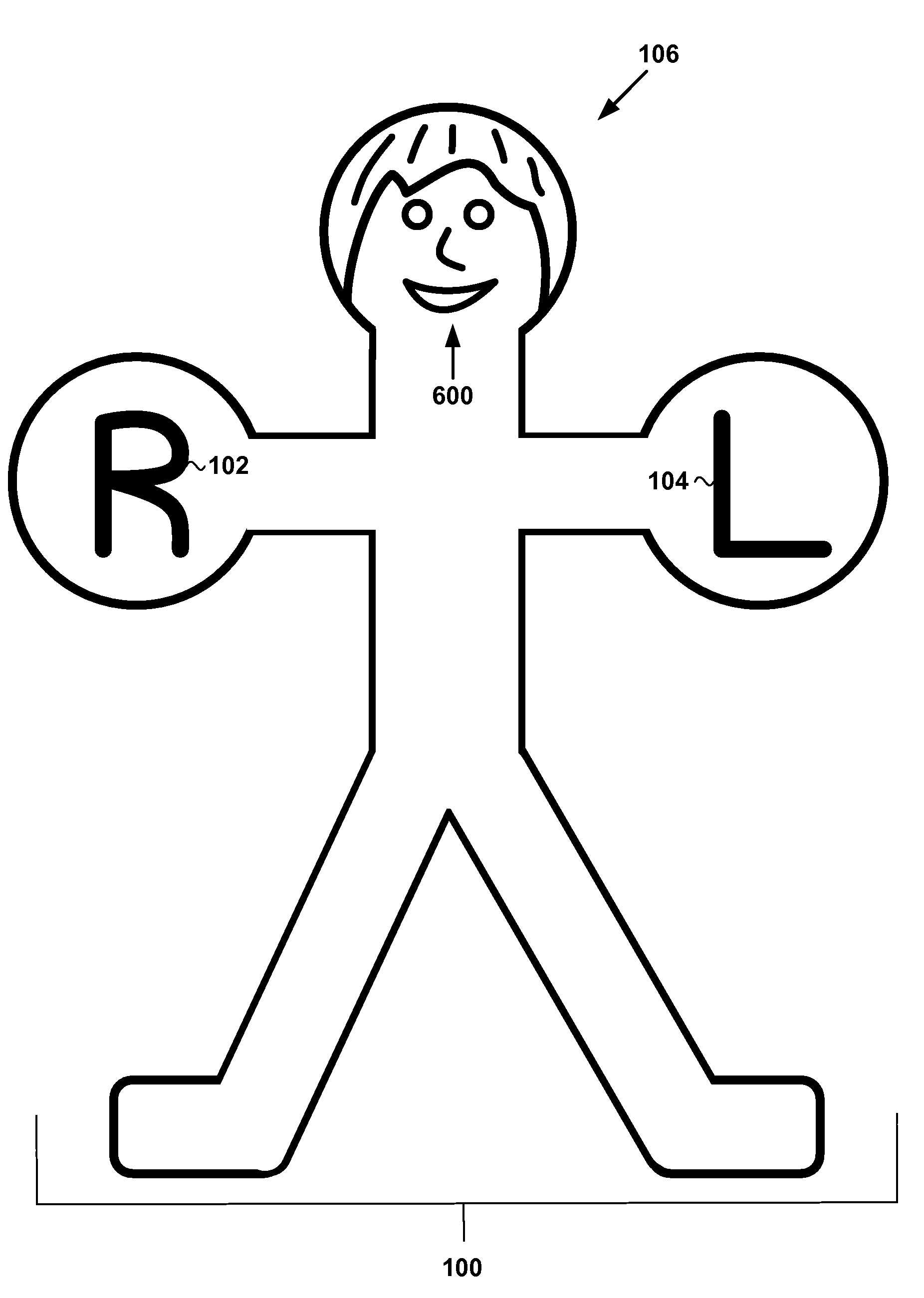
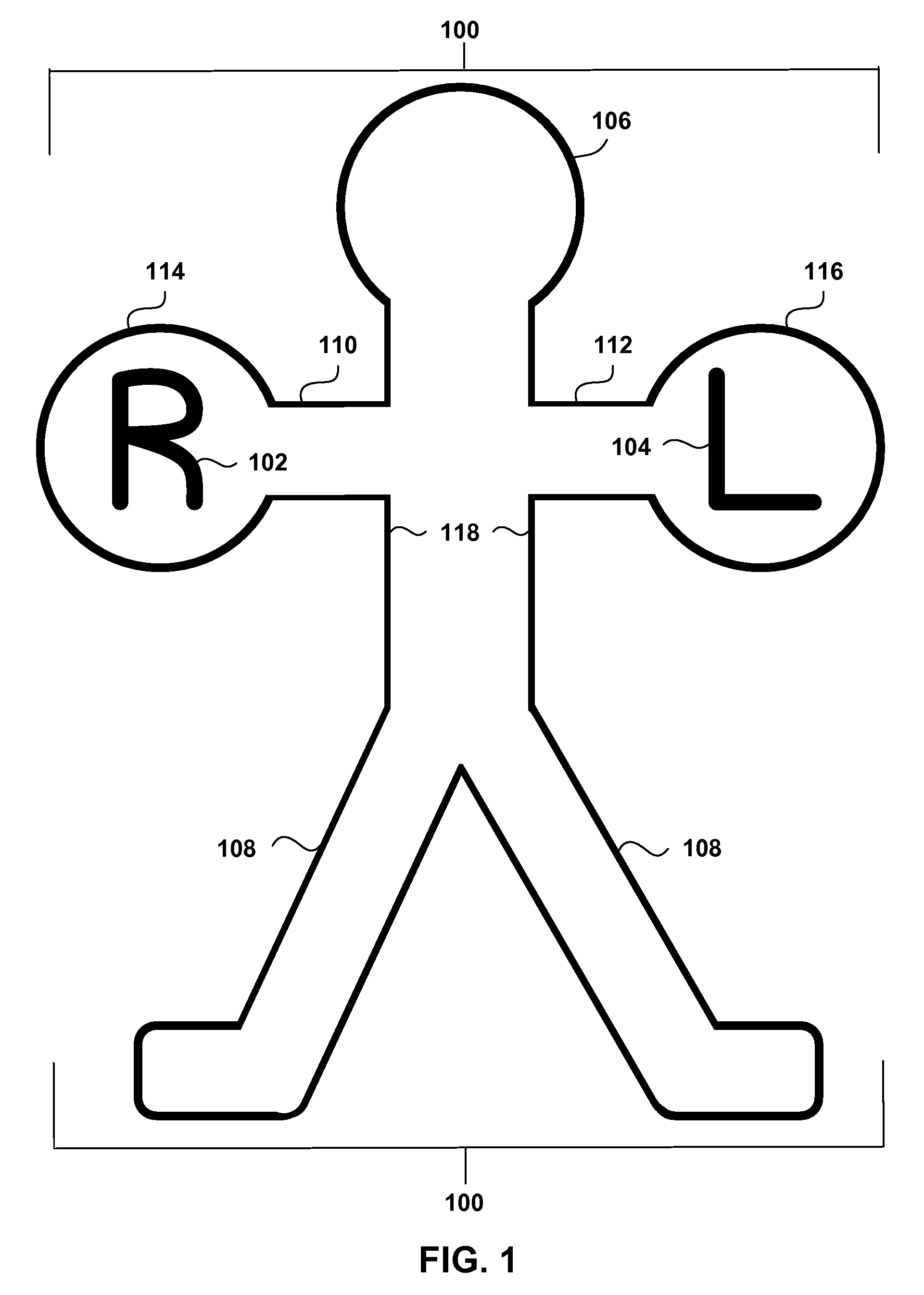
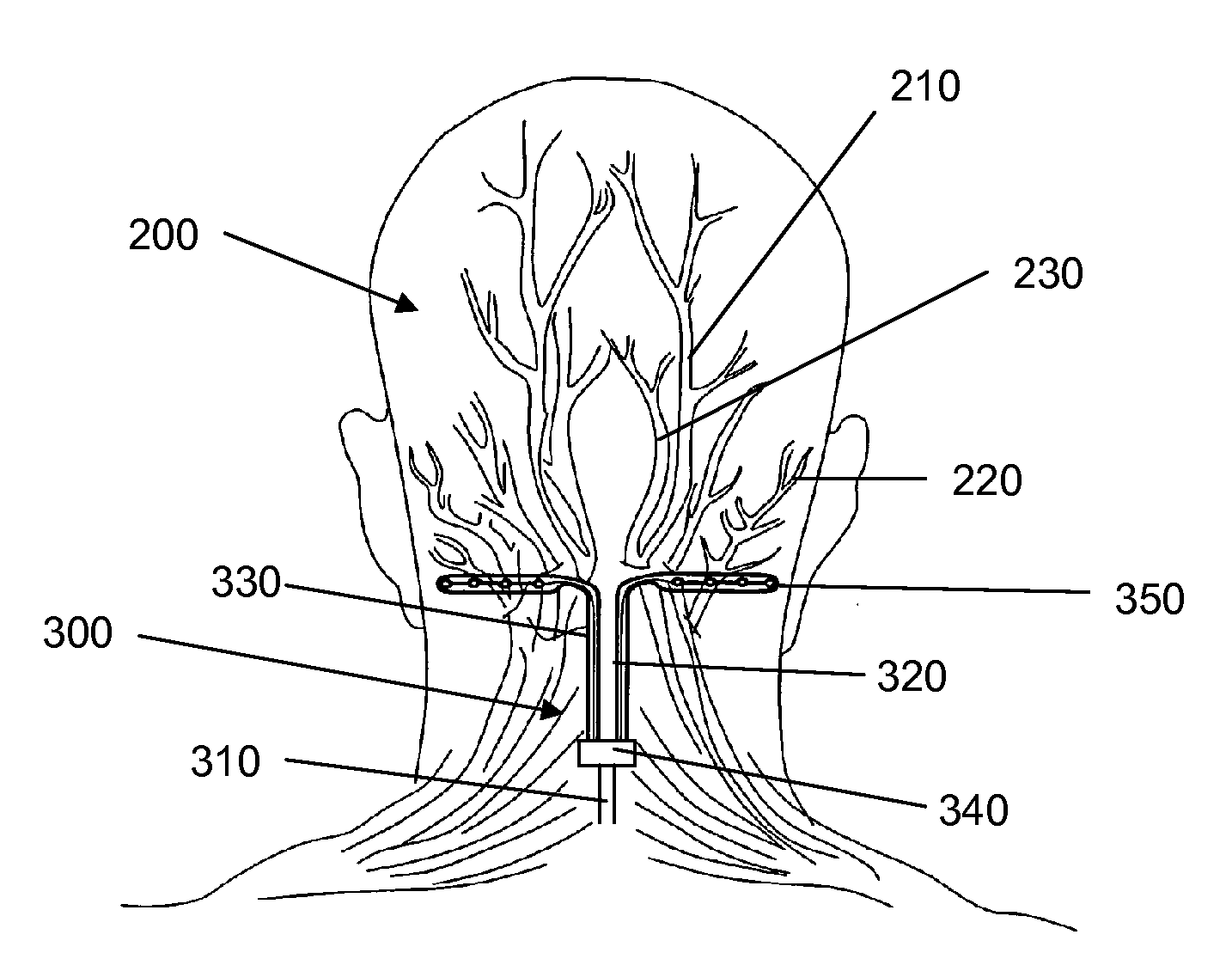
Anatomical terms used to describe location are based on a body positioned in what is called the standard anatomical position. This position is one in which a person is standing, feet apace, with palms forward and thumbs facing outwards.
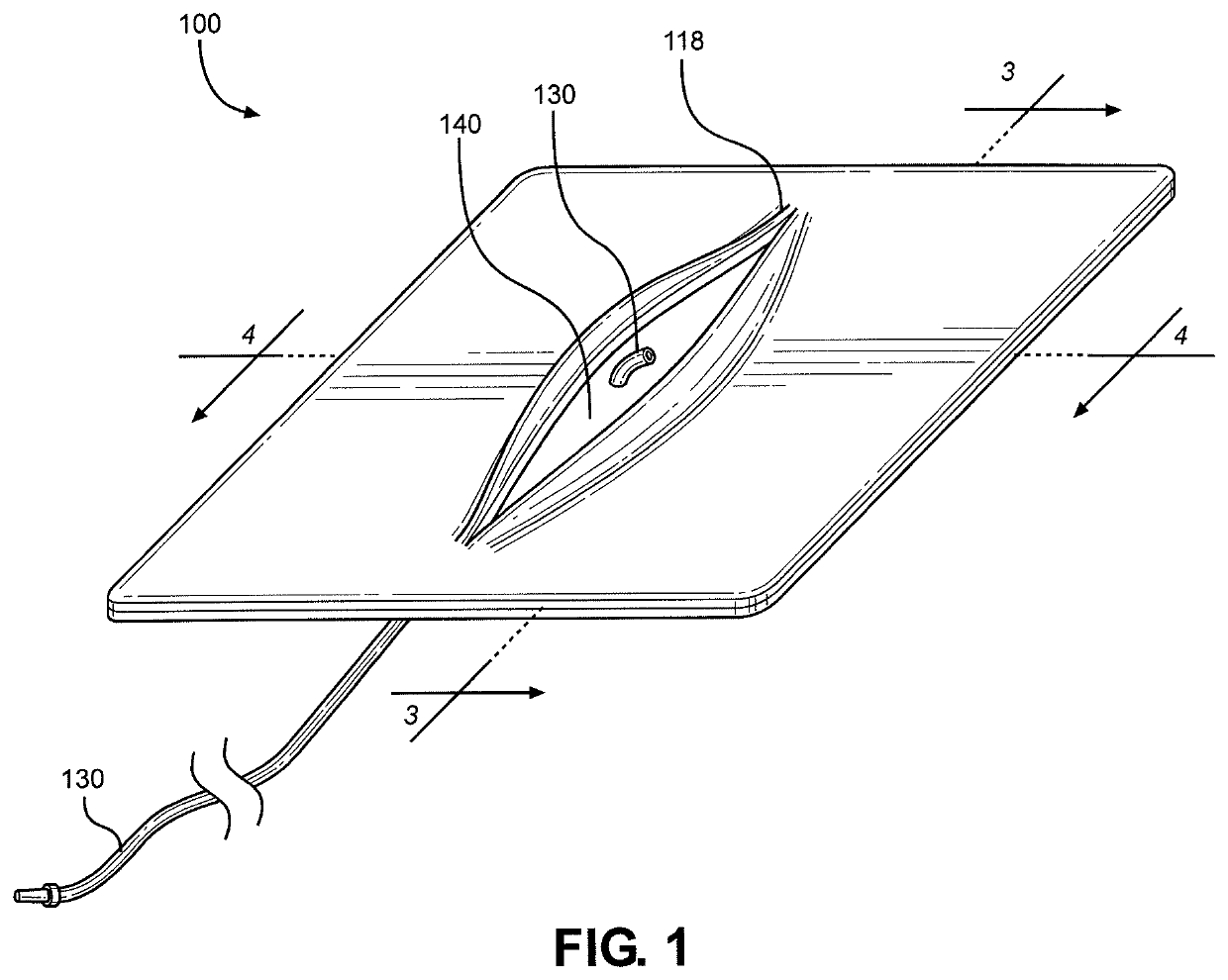
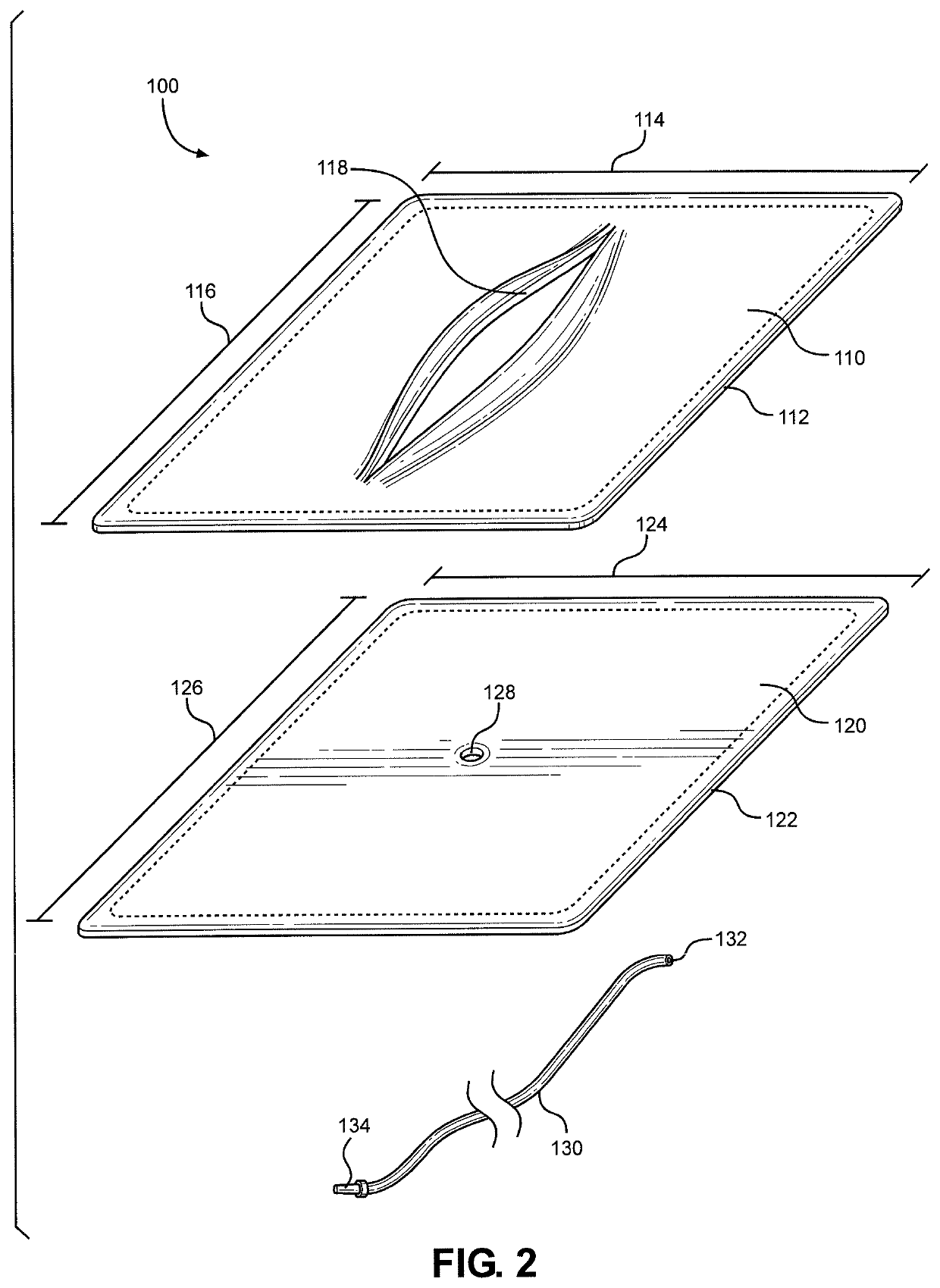
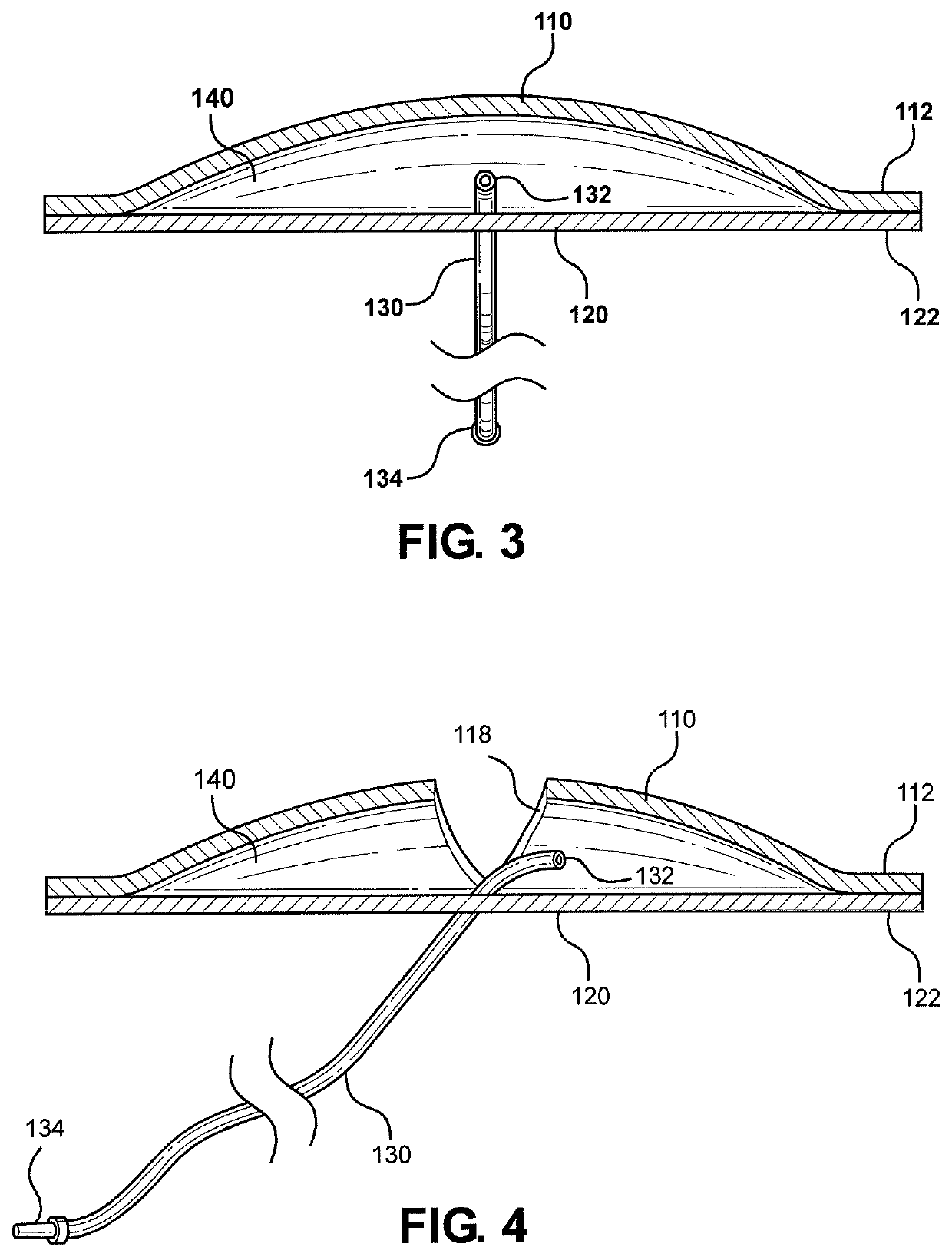
Dual drainage pathway shunt device and method for treating glaucoma
A shunt is provided for the flow of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber of the eye to Schlemm's canal and to other anatomical spaces of the eye. The shunt comprises at least one lumen and optionally has at least one anchor extending from a proximal portion of the shunt to assist in placement and anchoring of the device in the correct anatomic position.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
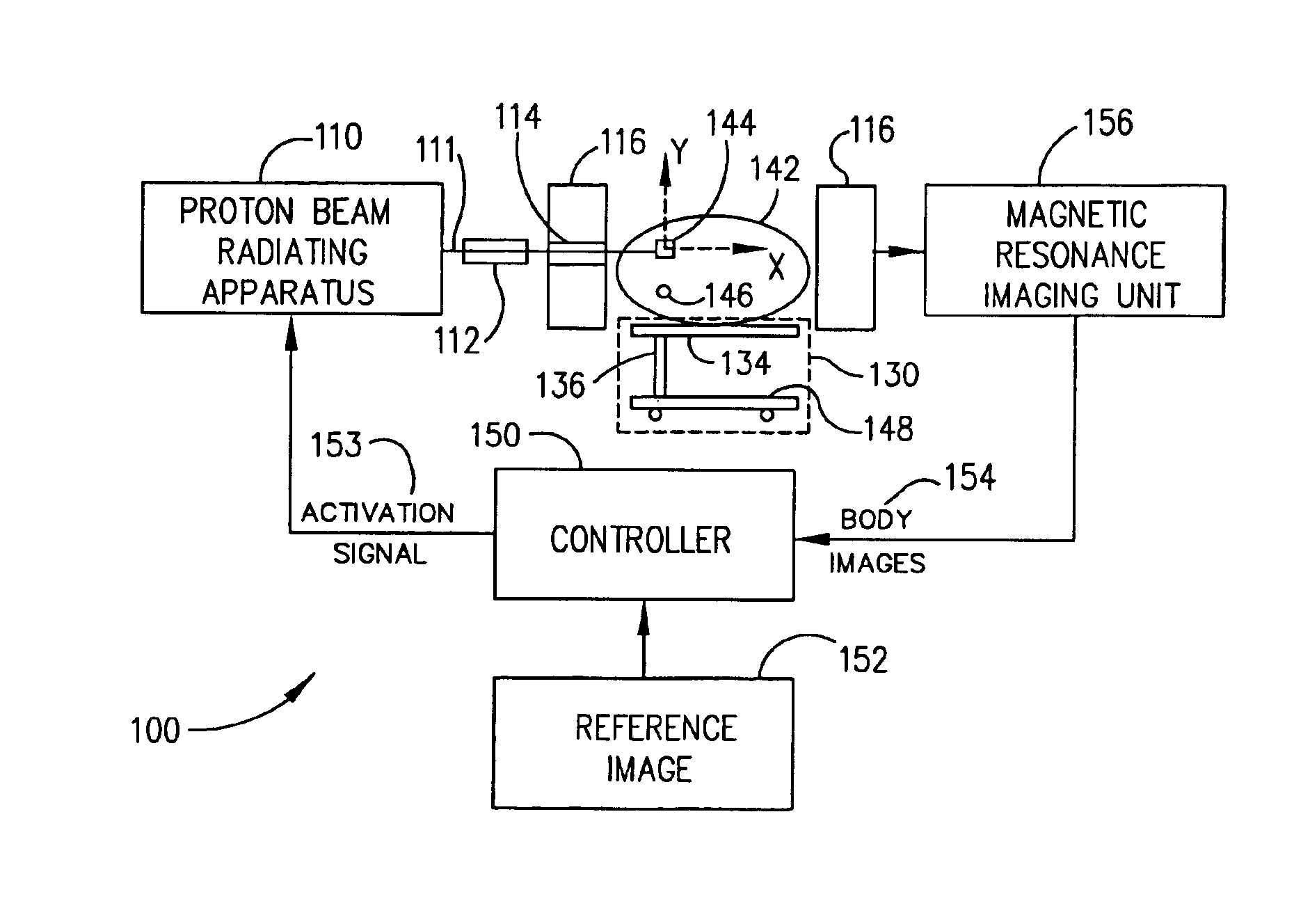
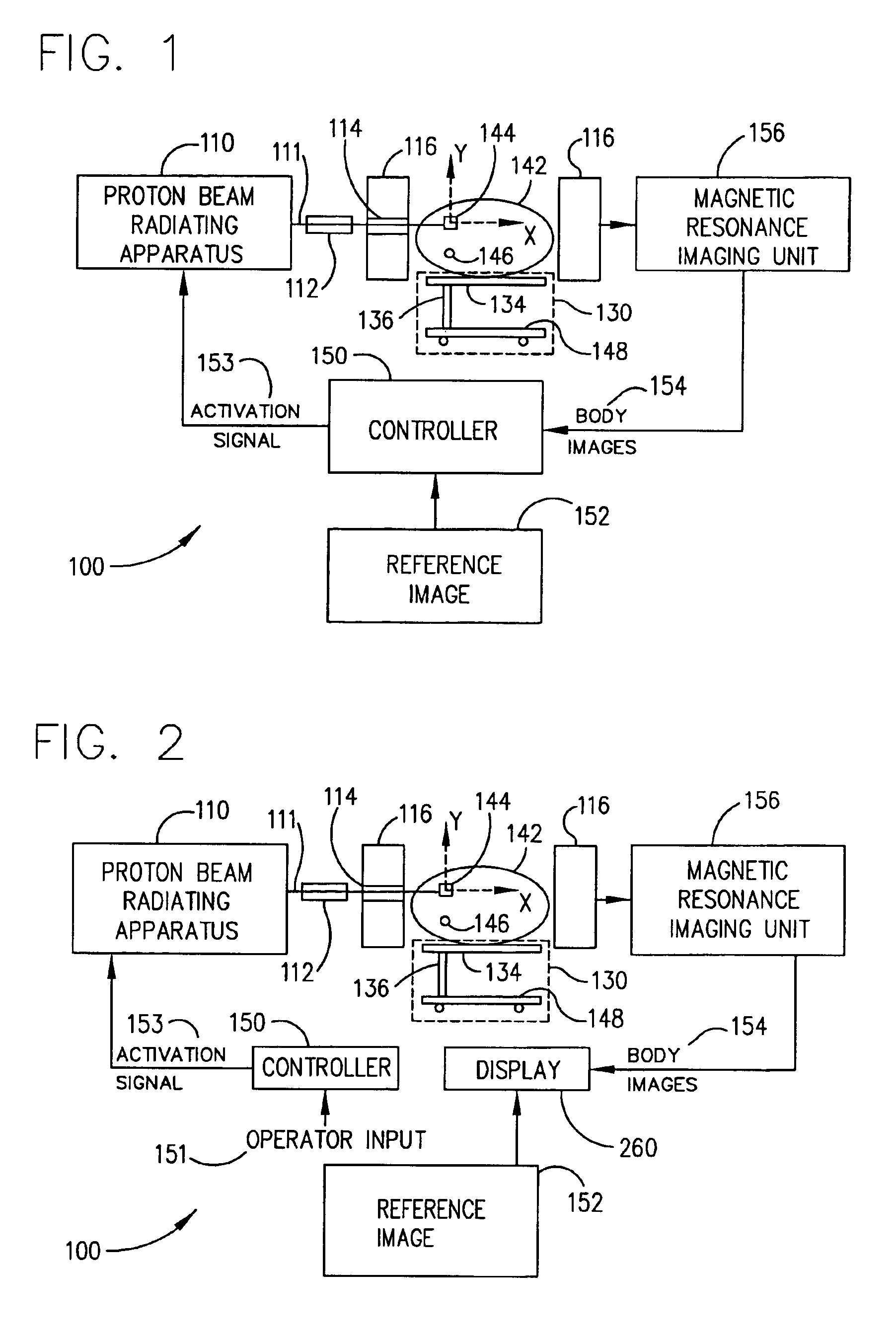
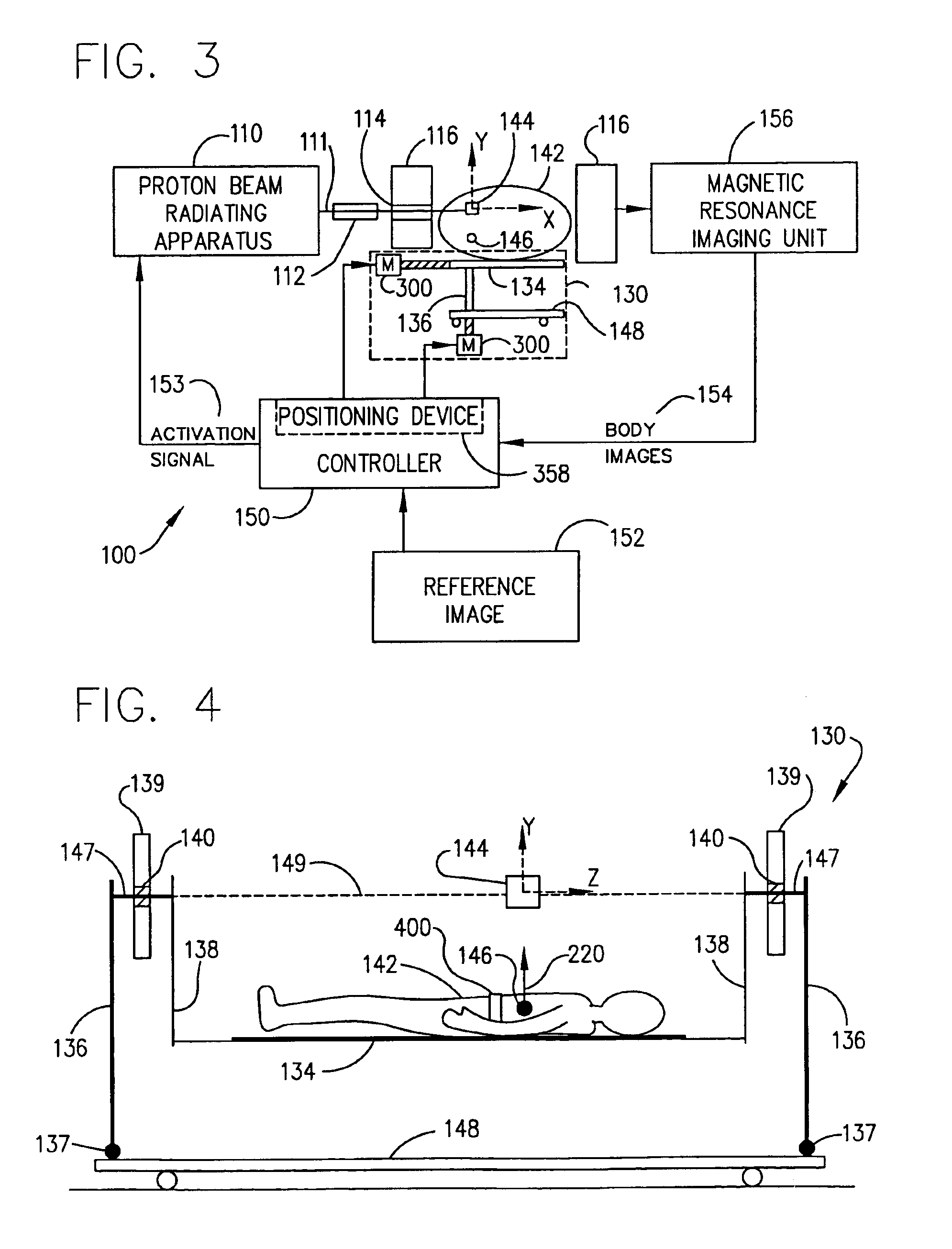
Method for combining proton beam irradiation and magnetic resonance imaging
A method which coordinates proton beam irradiation with an open magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) unit to achieve near-simultaneous, noninvasive localization and radiotherapy of various cell lines in various anatomic locations. A reference image of the target aids in determining a treatment plan and repositioning the patient within the MRI unit for later treatments. The patient is located within the MRI unit so that the target and the proton beam are coincident. MRI monitors the location of the target. Target irradiation occurs when the target and the proton beam are coincident as indicated by the MRI monitoring. The patient rotates relative to the radiation source. The target again undergoes monitoring and selective irradiation. The rotation and selective irradiation during MRI monitoring repeats according to the treatment plan.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
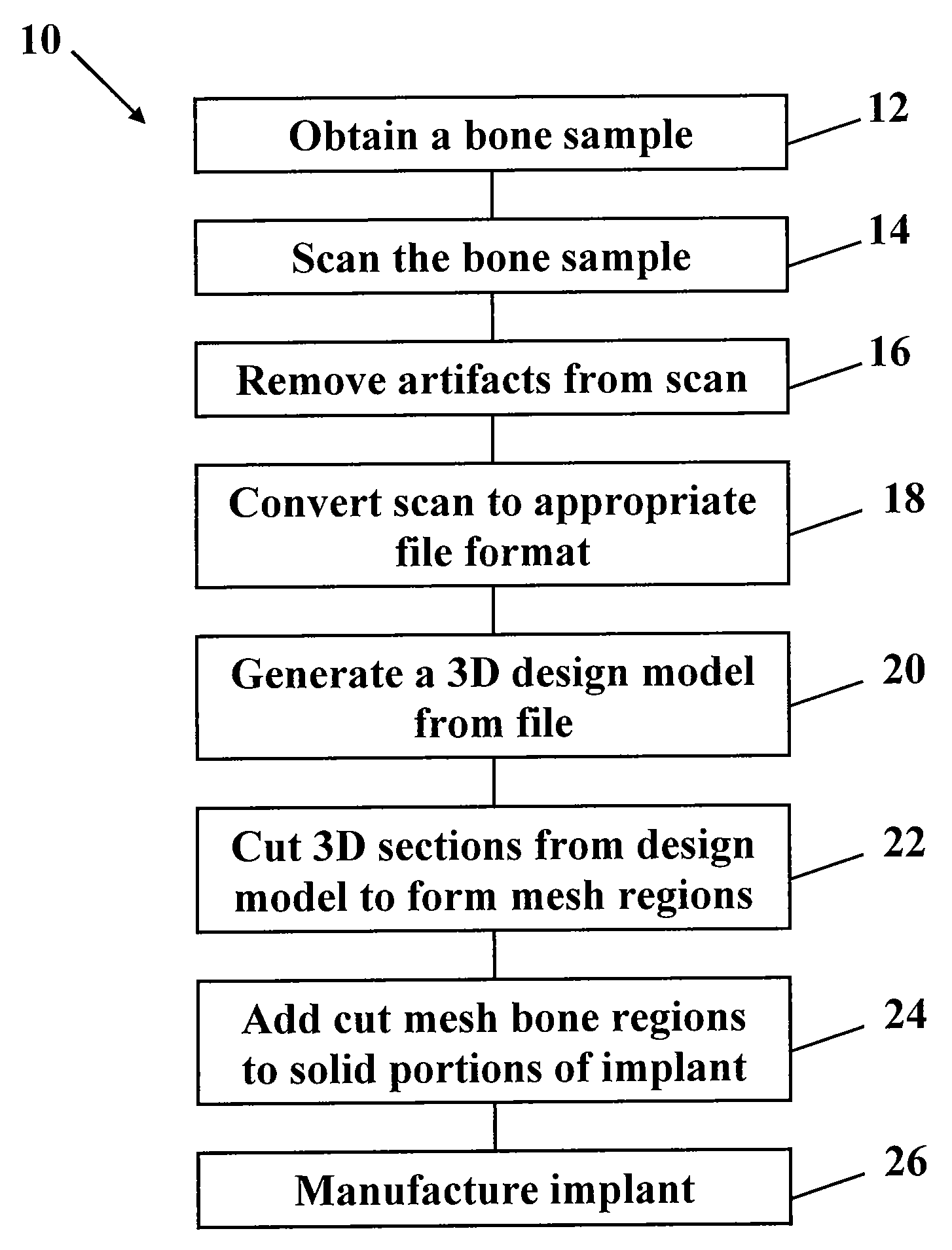
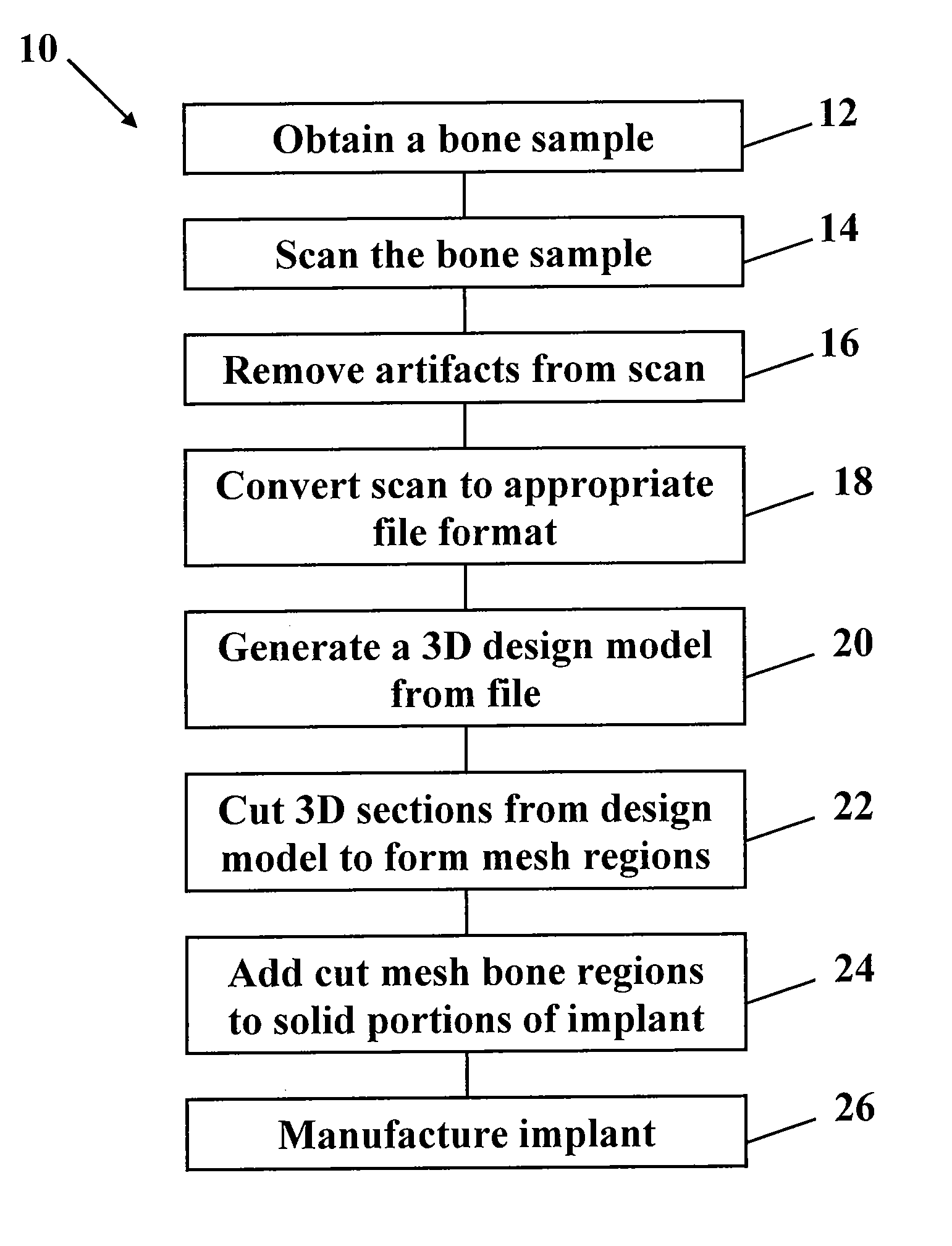
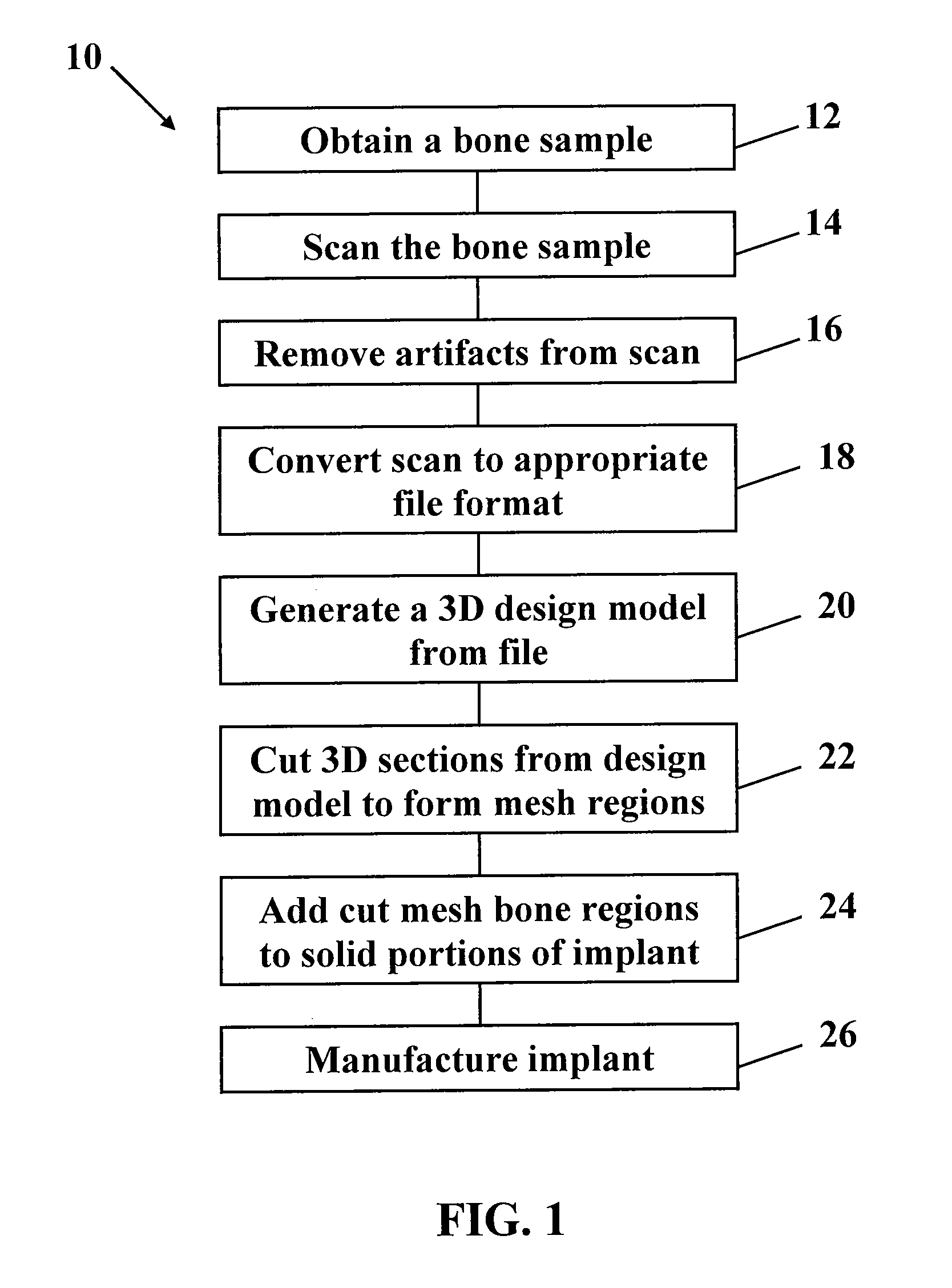
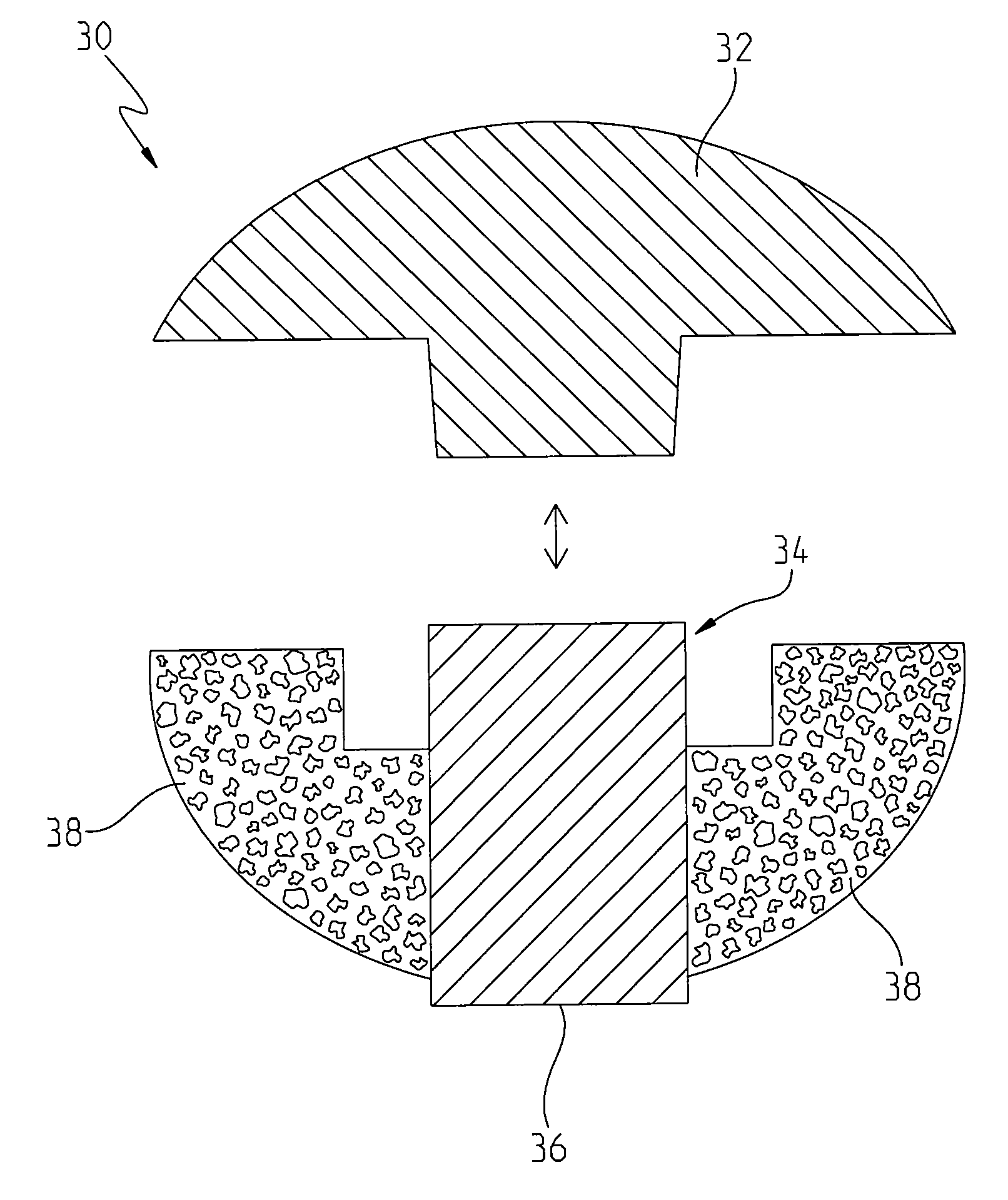
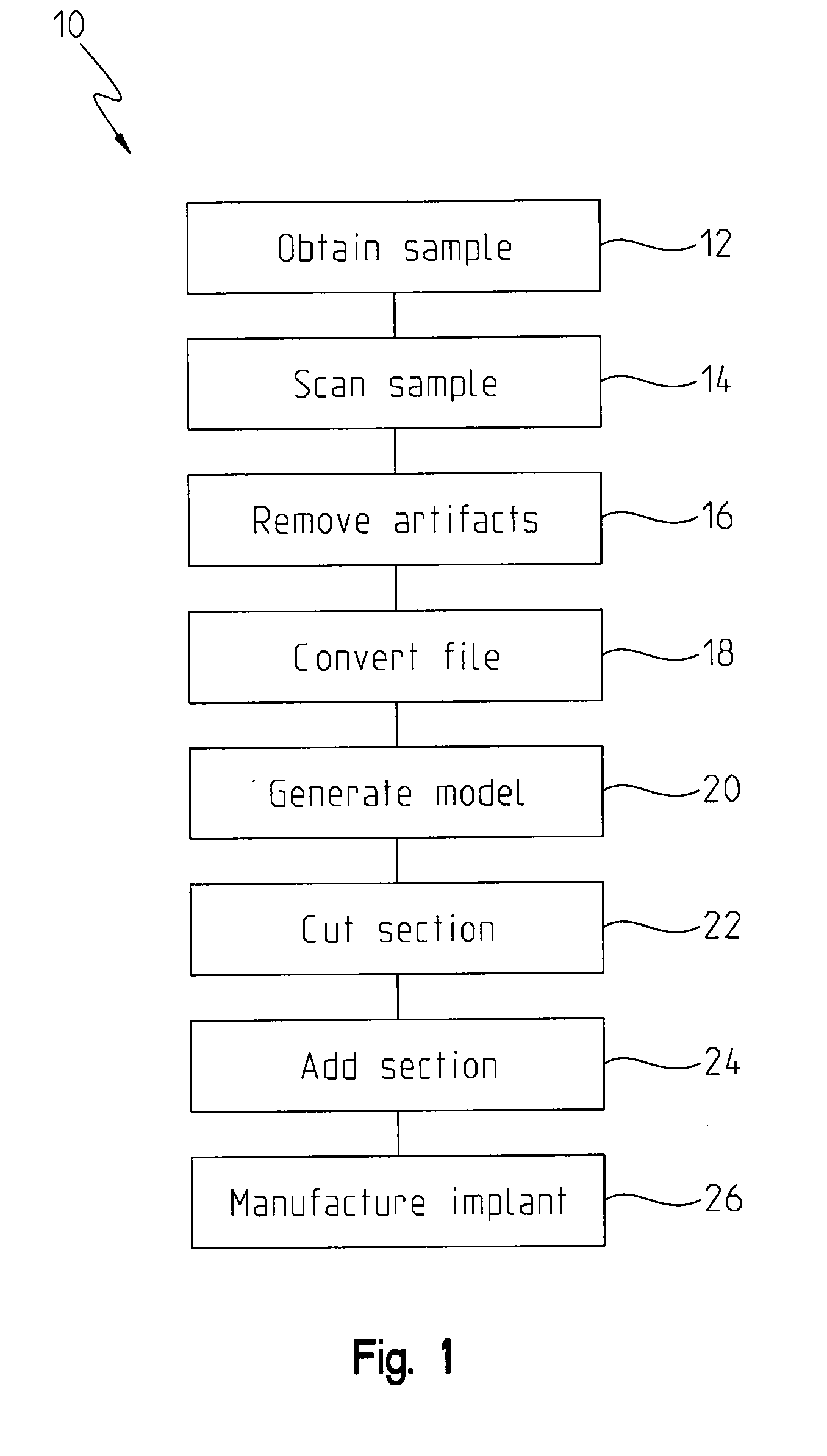
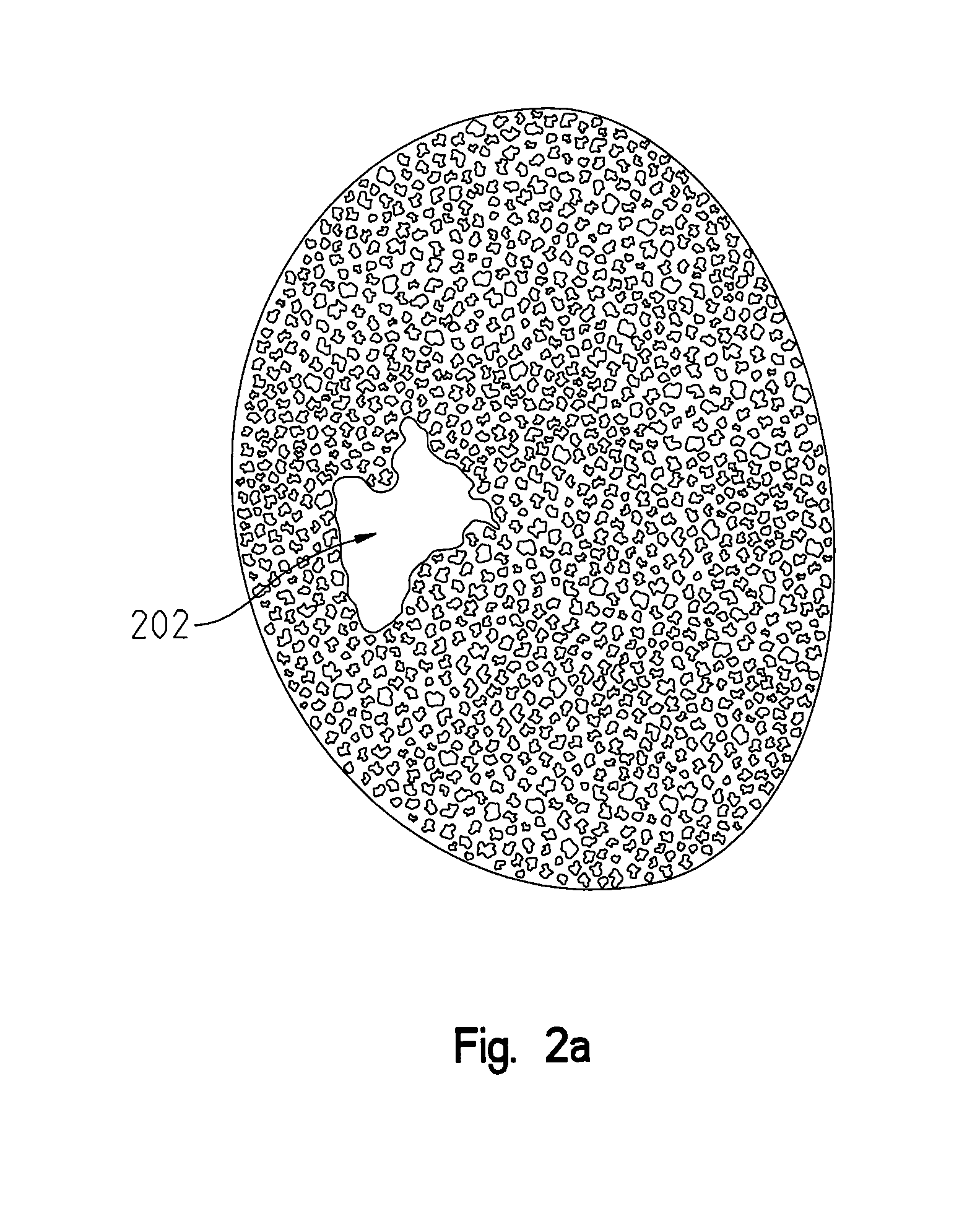
Metallic structures having porous regions from imaged bone at pre-defined anatomic locations
ActiveUS8843229B2Additive manufacturing apparatusBone implantBiomedical engineeringAdditive layer manufacturing
A method of forming an implant having a porous region replicated from scanned bone, the method comprising imaging bone with a high resolution digital scanner to generate a three-dimensional design model of the bone; removing a three-dimensional section from the design model; fabricating a porous region on a digital representation of the implant by replacing a solid portion of the digital implant with the section removed from the digital representation; and using an additive manufacturing technique to create a physical implant including the fabricated porous region.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Tracking cardiac forces and arterial blood pressure using accelerometers
ActiveUS20180020931A1Easy to detectSimplifies separationElectrocardiographyElectromyographyAccelerometerNon invasive
Modular, miniaturized cardiovascular sensors, systems, methods, and wearable devices for the non-obtrusive evaluation, monitoring, and high-fidelity mapping of cardiac mechanical and electromechanical forces and central arterial blood pressure are presented herein. The sensor manufacturing process is also presented. Using accelerometers, the sensors register body-surface (preferably torso-surface) movements and vibrations generated by cardiac forces. The sensors may contain single-use or reusable components, which may be exchanged to fit different body sizes, shapes, and anatomical locations; they may be incorporated into clothing, bands, straps, and other wearable arrangements. The invention presents a practical, noninvasive solution for electromechanical mapping of the heart, which is useful for a wide range of healthcare applications, including the remote monitoring of heart failure status and the guidance of cardiac resynchronization therapy. Exercise and cardiovascular fitness tracking applications are also presented.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
Metallic structures having porous regions from imaged bone at pre-defined anatomic locations
ActiveUS20140025181A1Additive manufacturing apparatusBone implantAdditive layer manufacturingBiomedical engineering
A method of forming an implant having a porous region replicated from scanned bone, the method comprising imaging bone with a high resolution digital scanner to generate a three-dimensional design model of the bone; removing a three-dimensional section from the design model; fabricating a porous region on a digital representation of the implant by replacing a solid portion of the digital implant with the section removed from the digital representation; and using an additive manufacturing technique to create a physical implant including the fabricated porous region.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Metallic structures having porous regions from imaged bone at pre-defined anatomic locations
ActiveUS20140371863A1Additive manufacturing apparatusBone implantParticulate debrisStructure of the Earth
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Noninvasive methods, apparatus, kits, and systems for intraoperative position and length determination
InactiveUS20070021644A1Simple and inexpensive and disposableImprove perceptionElectrotherapySurgeryAnatomic LocationSurgical patients
Methods, apparatus, kits and systems are presented for determining the intraoperative position of at least a first anatomic location of a surgical patient and optionally for measuring the distance between at least first and second anatomic locations of a surgical patient.
Owner:OSTEOMETRIX
Injection systems for delivery of fluids to joints
InactiveUS8002736B2Precise deliveryPatient benefitUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAutomatic syringesAnatomical structuresCatheter
Systems for injecting fluids and / or other materials into a targeted anatomical location, in particular, an intra-articular space, include a handpiece assembly having a proximal end and a distal end, a needle extending from the distal end of the handpiece assembly, a fluid delivery module comprising a cassette and a fluid transfer device. A conduit is generally configured to place the fluid delivery module in fluid communication with the handpiece assembly. Medications, formulations and / or other fluids or materials contained within vials that are secured to the fluid delivery module can be selectively delivered into an anatomy through a needle located at the distal end of the handpiece assembly. In some embodiments, ultrasound or other imaging technologies can be used to locate a joint or other targeted anatomical location.
Owner:CARTICEPT MEDICAL
Two-step/dual-diameter balloon angioplasty catheter for bifurcation and side-branch vascular anatomy
The present invention tackles the challenging anatomic characteristics of the coronary artery disease in the bifurcation point and the origin of side-branch. The invention has a specifically designed angioplasty balloon catheter, particularly the balloon shape and profile, to be used in the diseased vessels at these difficult anatomic locations. In stent implanting into a coronary artery, a balloon catheter application is an inseparable requirement. A stent is a passive device that cannot be deployed in a diseased or stenosed artery without a pre-stent, with-stent and / or post-stent balloon dilatation. In majority (more than 95%) of available coronary stents, a stent is deployed by balloon expandable mode, meaning that the stent is delivered and expanded inside a vessel lumen by expanding a delivery balloon. This is done by crimping a stent over a folded balloon for delivery into a coronary artery. When expanded by balloon inflation, a stent is expanded and shaped passively by the inflated balloon shape and profile. The balloon catheter is designed to do angioplasty in the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy of coronary arteries, while minimizing the side effect. This specially designed balloon catheter is not only for balloon angioplasty dilatation of the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy, but is also for delivering and deploying specially designed bifurcation or side-branch stents into these difficult anatomic locations, as a stent delivery system.
Owner:JANG G DAVID
Concentrated Protein Preparations of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Methods of Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100144631A1Efficient preparationHigh recovery rateSenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseWhole body
Disclosed herein are heretofore undescribed preparations of highly concentrated, solubilized proteins, such as but not limited to, Bone Morphogenetic Proteins. Such protein preparations can be formulated in an aqueous carrier at protein concentrations in excess of 10 mg / ml when using the methods of manufacture taught herein. Such methods yield stable protein preparations in either solubilized or lyophilized form. The protein preparations of the present invention are particularly beneficial when administered either locally or systemically, in part, because low administration volumes can be accomplished. This is especially important for local treatment of certain anatomic locations such as, for example, the synovial fluid of a joint when treating osteoarthritis with BMP-7 or the intradiscal space when treating degenerative disc disease with BMP-7.
Owner:MARIEL THERAPEUTICS
Two-step/dual-diameter balloon angioplasty catheter for bifurcation and side-branch vascular anatomy
The present invention tackles the challenging anatomic characteristics of the coronary artery disease in the bifurcation point and the origin of side-branch. The invention has a specifically designed angioplasty balloon catheter, particularly the balloon shape and profile, to be used in the diseased vessels at these difficult anatomic locations. In stent implanting into a coronary artery, a balloon catheter application is an inseparable requirement. A stent is a passive device that cannot be deployed in a diseased or stenosed artery without a pre-stent, with-stent and / or post-stent balloon dilatation. In majority (more than 95%) of available coronary stents, a stent is deployed by balloon expandable mode, meaning that the stent is delivered and expanded inside a vessel lumen by expanding a delivery balloon. This is done by crimping a stent over a folded balloon for delivery into a coronary artery. When expanded by balloon inflation, a stent is expanded and shaped passively by the inflated balloon shape and profile. The balloon catheter is designed to do angioplasty in the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy of coronary arteries, while minimizing the side effect. This specially designed balloon catheter is not only for balloon angioplasty dilatation of the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy, but is also for delivering and deploying specially designed bifurcation or side-branch stents into these difficult anatomic locations, as a stent delivery system.
Owner:JANG G DAVID
Patient-specific intraluminal implants
ActiveUS20140088698A1Increase chanceIncrease opportunitiesStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisPatient specific
Methods are provided for generating intraluminal prosthetic implants designed to fit onto specific anatomical locations within regions which are stable in terms of their motion in time.
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
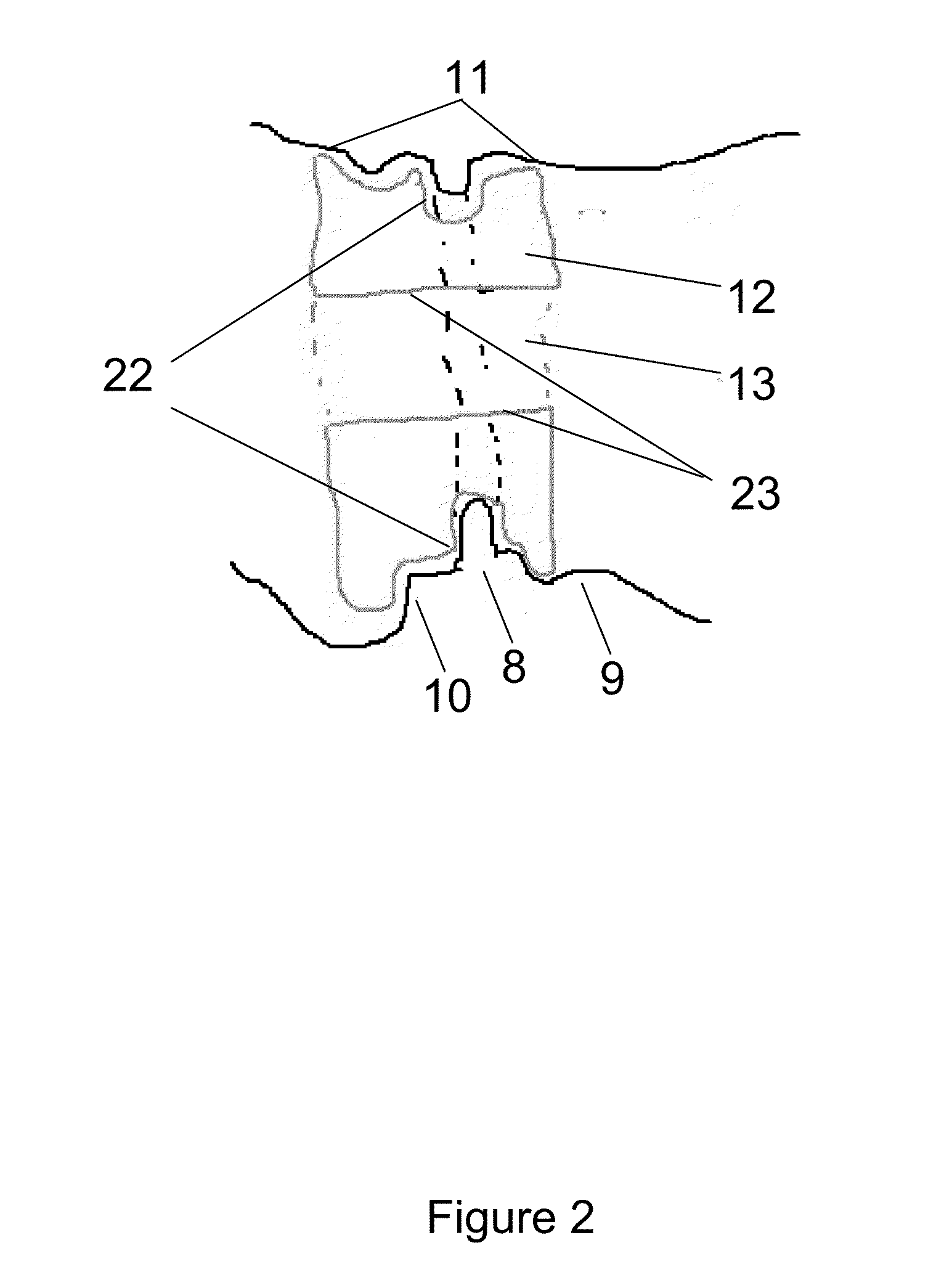
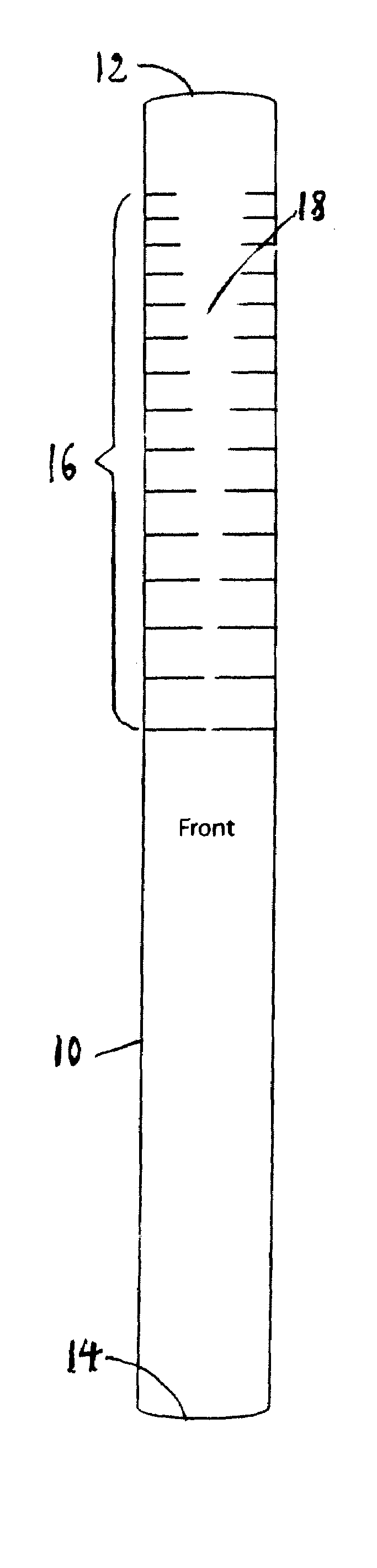
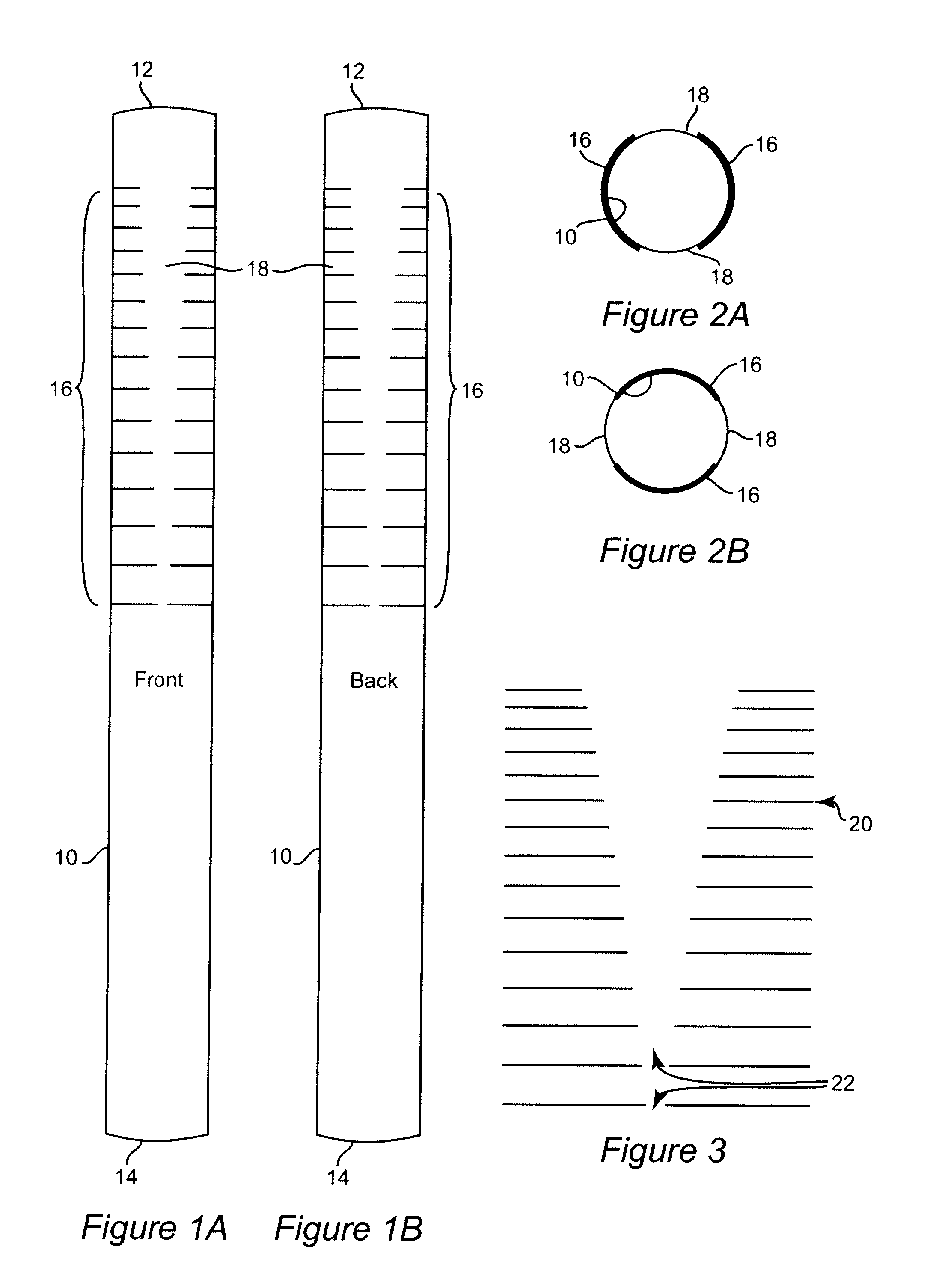
Catheter for Enhanced Image Location Detection
InactiveUS20090054760A1Enhance image location detectionEasy to distinguishSurgeryDiagnostic markersLocation detectionCatheter device
A catheter is used to assist in imaging, e.g., 3D imaging, an anatomical location in a human or veterinary subject. The catheter includes a plurality of horizontal markings which extend in the longitudinal direction between the distal and proximal ends. The horizontal markings can be made throughout the entire length of the catheter, or at one or more locations. At each location, the horizontal markings will appear as successive sets of markings. Each horizontal marking is made of two markings that are the same length. The two markings are arranged such that identically sized gaps between the ends of the markings are positioned on the front and back side of the catheter. In one embodiment, an image where the source and catheter are precisely aligned will show gaps of succeeding larger or smaller sizes. However, when the source is off center the gap lengths will be smaller or not exist. Particular marking locations can be highlighted by using relatively thinner or thicker markings and / or by spacing the markings progressively closer together or further apart.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS TECH
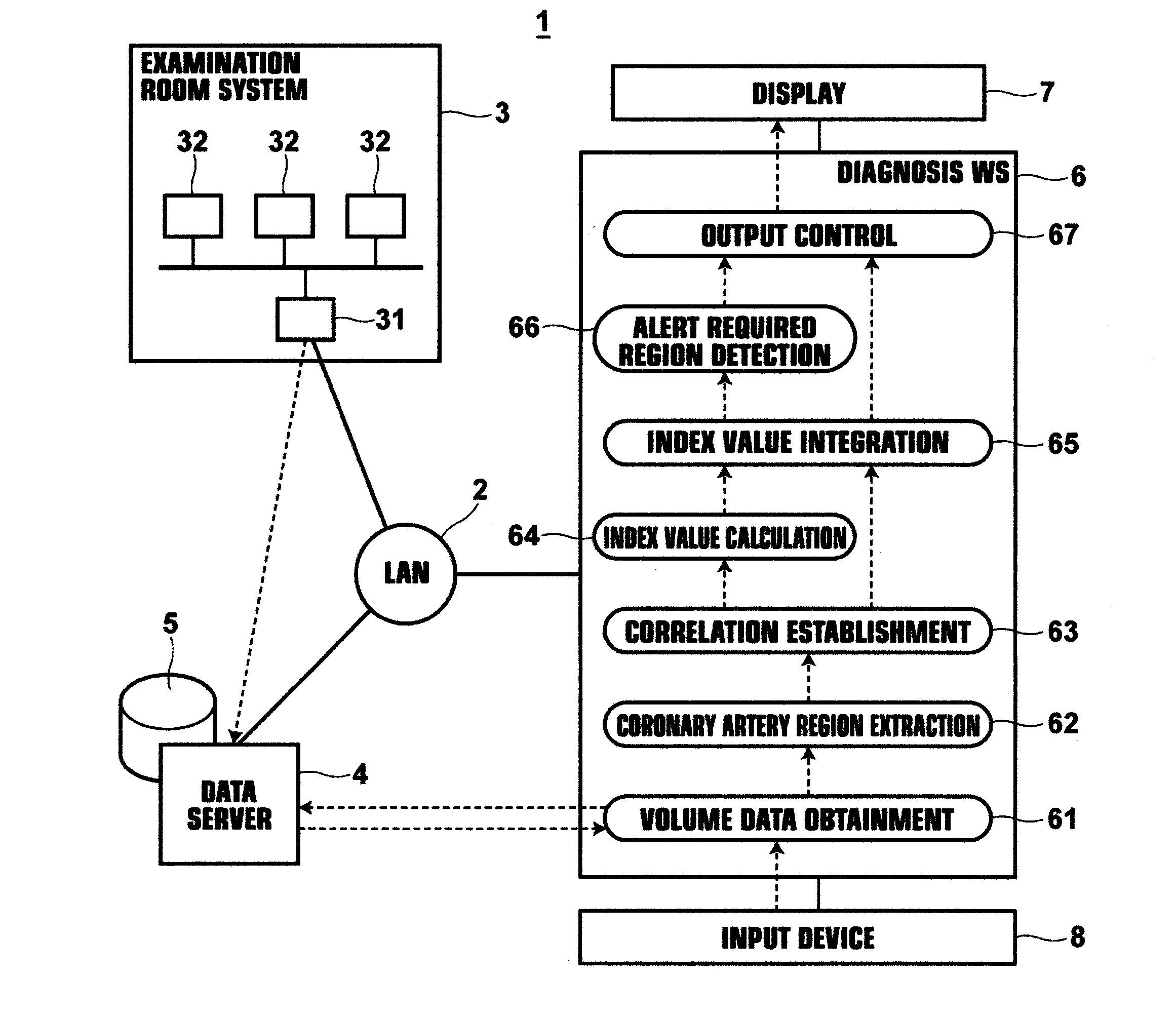
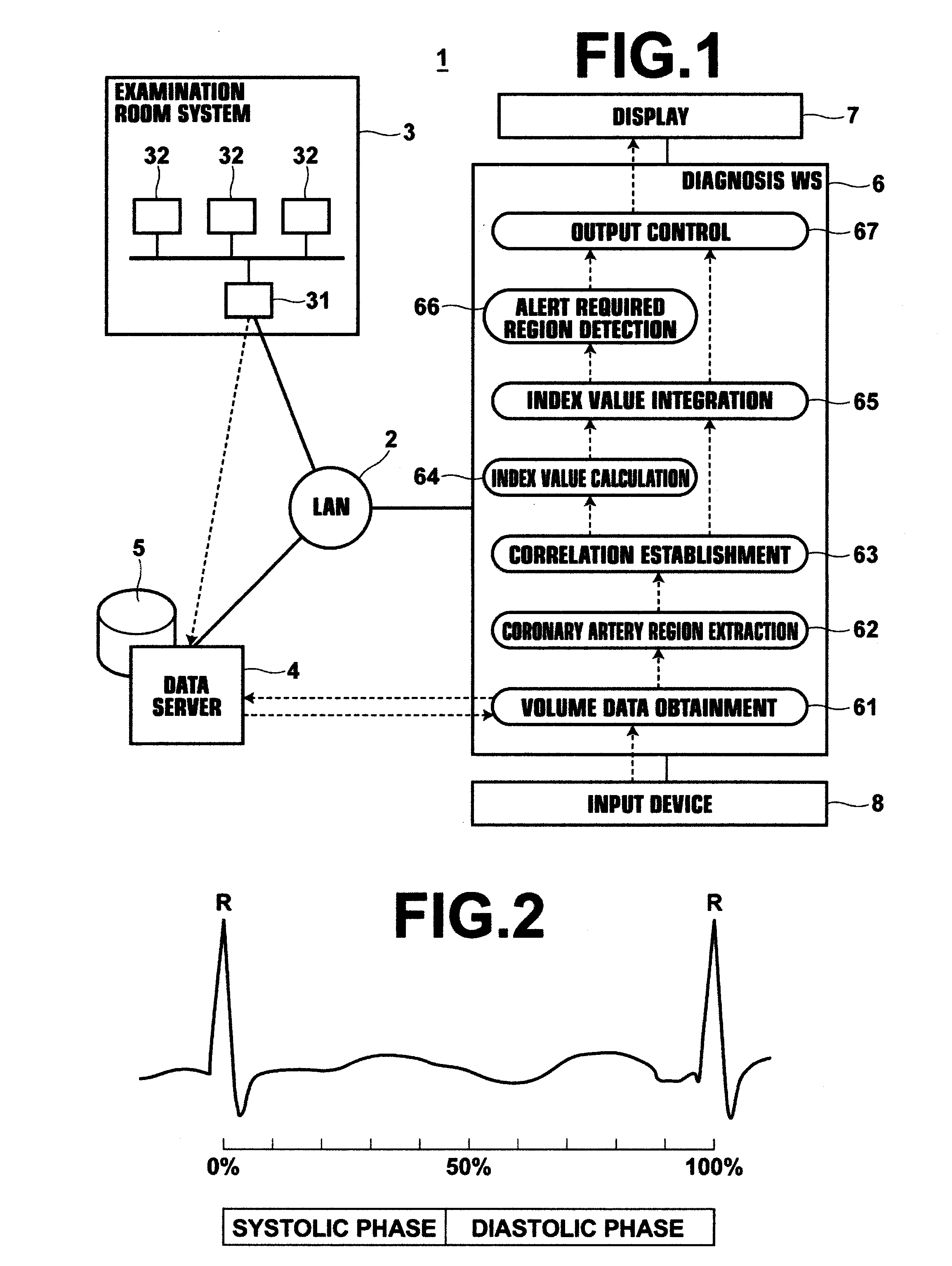
Diagnosis assisting apparatus, coronary artery analyzing method and recording medium having a coronary artery analyzing program stored therein
ActiveUS20110218427A1Reduce impactImprove assessment accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesCoronary arterial zone
A plurality of sets of volume data, each of which represent the state of a beating heart in different phases, are obtained. Coronary artery regions are extracted from at least two sets of volume data from among the obtained sets of volume data. A plurality of analysis points are set in each extracted coronary artery region. Correlations are established among analysis points set at the same anatomical positions within the coronary artery regions. Index values that indicate the character of plaque are calculated at each analysis point within all of the coronary artery regions. The character of plaque is evaluated at positions within the coronary artery regions, by integrating the index values calculated at the analysis points corresponding to each of the positions. The evaluation results regarding the character of plaque at each of the positions within the coronary artery regions are output, correlated with information regarding the positions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Anatomical marker for x-ray orientation
InactiveUS20100091951A1Reduce errorsThe process is fast and efficientX-ray apparatusPhotographyX-rayBody positions
A radiopaque marker for more effectively orienting a fluoroscopy image to a patient's body position is disclosed. A method for orienting a radiological image with a patient's anatomical position comprises the step of forming a marker with a first side indicator and a second side indicator formed substantially opposite the first side indicator. A device in accordance with the present invention comprises a radiopaque marker comprising a first side indicator, a second side indicator, and a humanoid shape.
Owner:MDX LAB
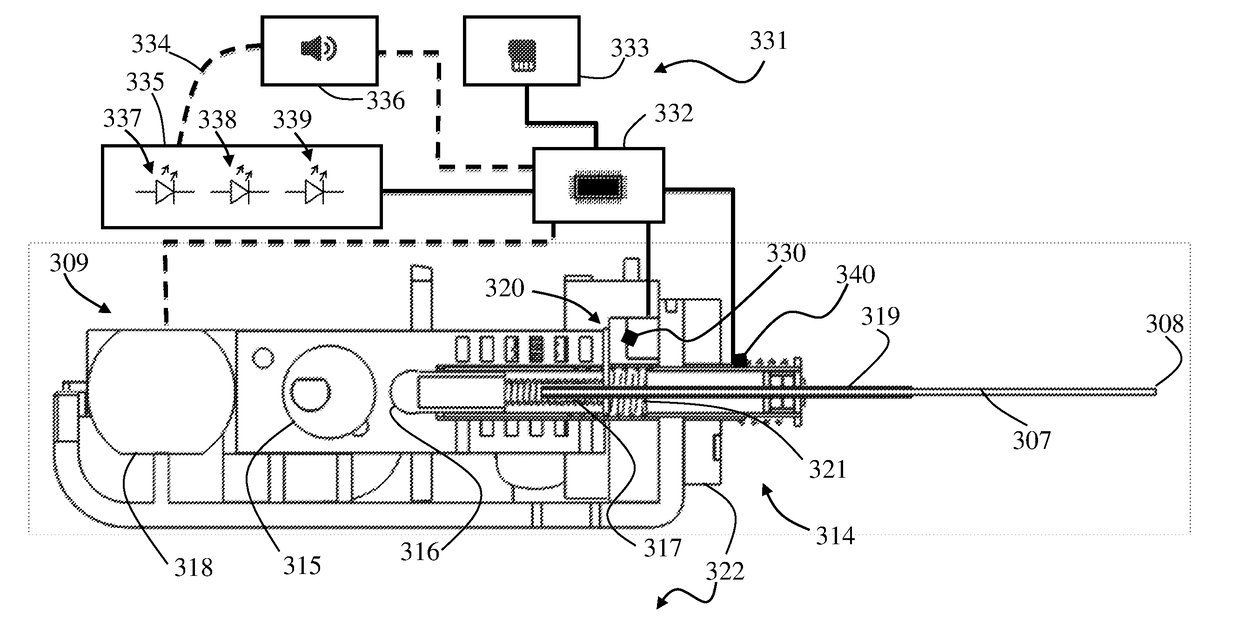
Bifurcated lead system and apparatus
InactiveUS20110071606A1Reduce surgery time and invasivenessReduce invasivenessSpinal electrodesHead electrodesOccipital nerveAnatomical location
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Orthopedic fixation system and method of use thereof
ActiveUS20200000464A1Easy to integrateInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsOrthopedic departmentHead bones
An orthopedic fixation system fuses bone, bones, or bone pieces in a predetermined anatomical position. The orthopedic fixation system includes an implant that transitions between an unconstrained shape and a constrained insertion shape, a drill guide, first and second K-wires, and a cannulated drill bit. The drill guide and the first and second K-wires retain the bone, bones, or bone pieces in an anatomical position corresponding with the predetermined anatomical position. The cannulated drill bit fits over the first and second K-wires and drills, respectively, first and second drilled holes into the bone, bones, or bone pieces. After insertion of the implant into the first and second drilled holes, the implant attempts to transition from its constrained insertion shape to its unconstrained shape such that the implant continuously compresses the bone, bones, or bone pieces thereby holding the bone, bones, or bone pieces in the predetermined anatomical position.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Multi-junctional bleeding simulator
ActiveUS20180190155A1Safely simulateControlling hemorrhagePharmaceutical delivery mechanismAdhesive dressingsAnatomical locationHemostat
The present invention, when used by a live actor, allows users to safely simulate hemorrhaging in some of the most challenging blood vessels in the most challenging anatomical locations such as the carotid artery, the axillary artery, and the inguinal artery. The present invention further provides the ability for users to safely perform hemorrhage control procedures, such as compression and ligation. The simulated wound of the present invention may be compressed to control hemorrhage. The simulated wound receptacle of the present invention may be packed with hemostatic or simple gauze to control hemorrhage. The simulated blood vessel of the device may be ligated with hemostats or other ligating instruments or material and bandaged with pressure dressings to control hemorrhage.
Owner:STRATEGIC OPERATIONS INC
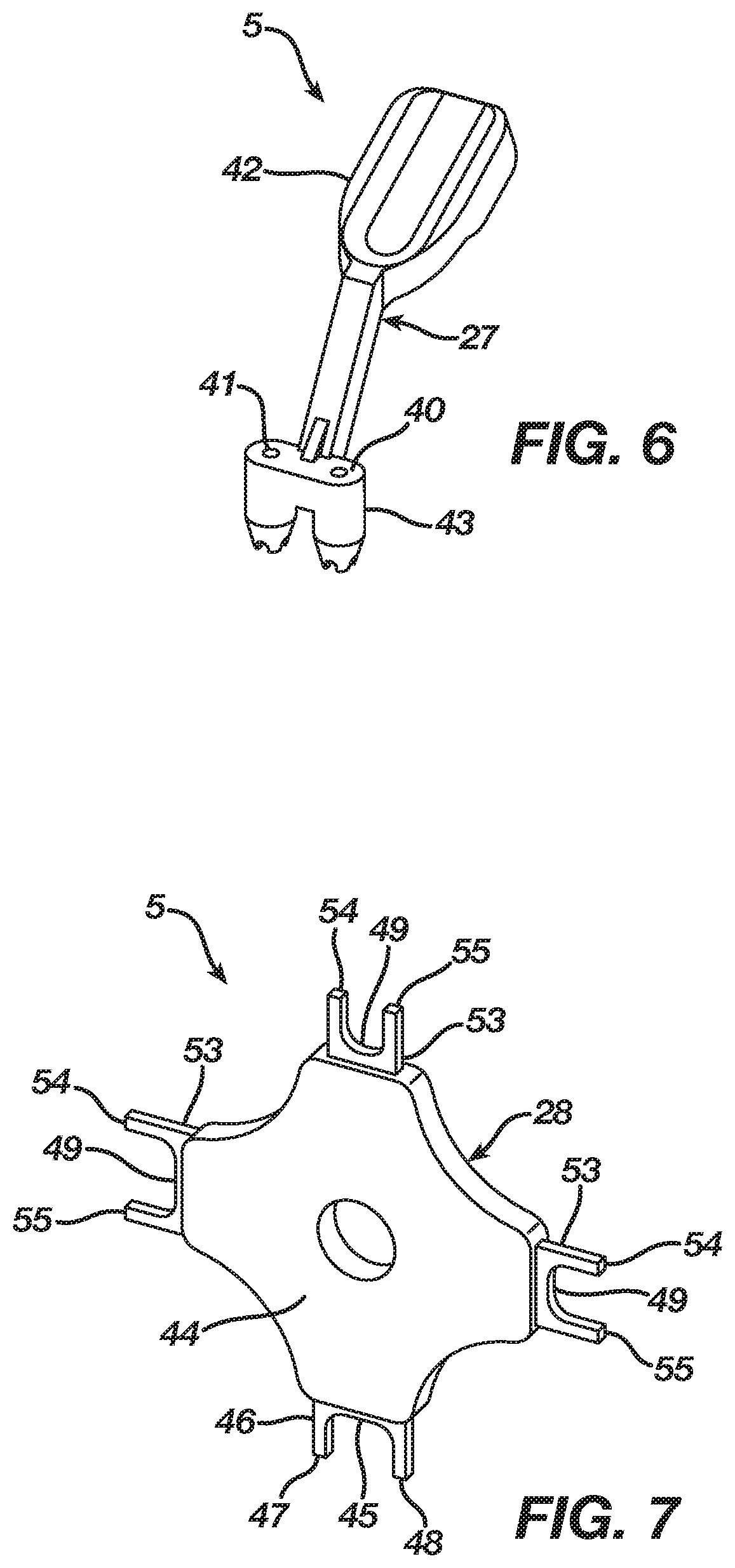
Deep fascia anchors
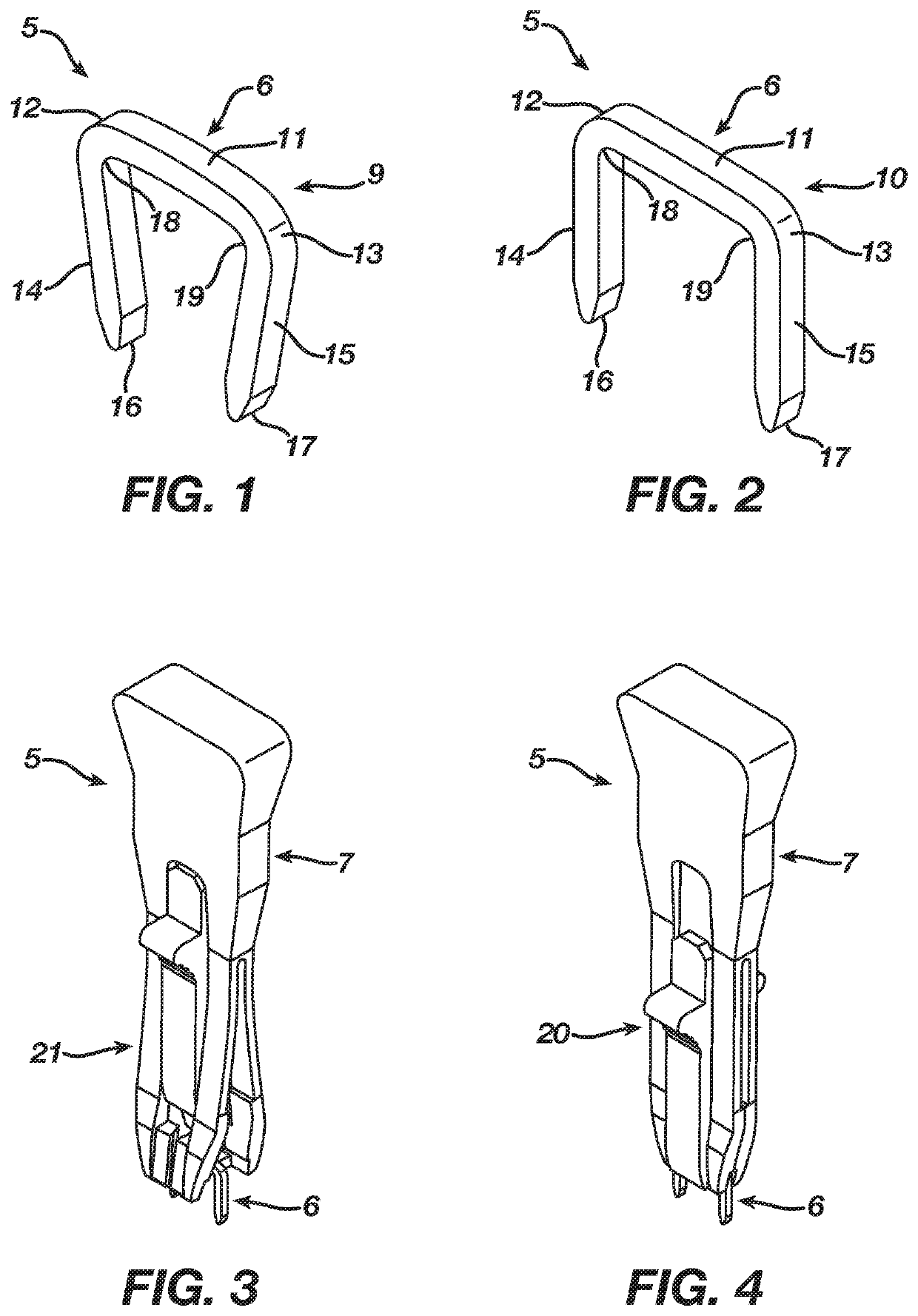
Deep fascia anchors provide a convenient way to bring fascia back to its anatomic location, thereby avoiding many of the problems and complications with current approaches. In the preferred embodiment, the anchors are made of a silastic or biodegradable material utilizing a design which mimics the spinous process. The anchors may attach to any suitable form of instrumentation, including rods, plates, and so forth. The anchors are adjustable to suit different mechanical structures. Anchors according to the invention include two opposing flexible arms which wrap around and lock on to the instrumentation, with a center tip portion preferably including attachment points or holes to which the deep fascia may be attached, much like the natural spinous process. Multiple anchors may be used according to the invention as dictated by the length of the instrumentation, and varying sizes and shapes may be provided to mimic anatomic differences in location (i.e., cervical, thoracic, lumbar) and patient (i.e., child, adolescent, adult, male / female).
Owner:FALAHEE MARK H
Experimental animal fixing device
The invention discloses an experimental animal fixing device, comprising a platform with a supporting leg. A through hole is arranged on the platform. The front of the platform is provided with a detachable rod, while the back of the platform is provided with a fixer. The position of the fixer corresponds to the hole. The experimental animal fixing device of the invention is multifunctional and very helpful for some specialist surgical experiments. Additionally, the experimental animal fixing device can effectively fix a specific anatomic location, and realize the function of an ordinary fixed table on limbs fixation.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Insertion device positioning guidance system and method
ActiveUS20190328620A1Minimizing sensitivityEasy to determineSurgical navigation systemsMedical devicesGuidance systemEngineering
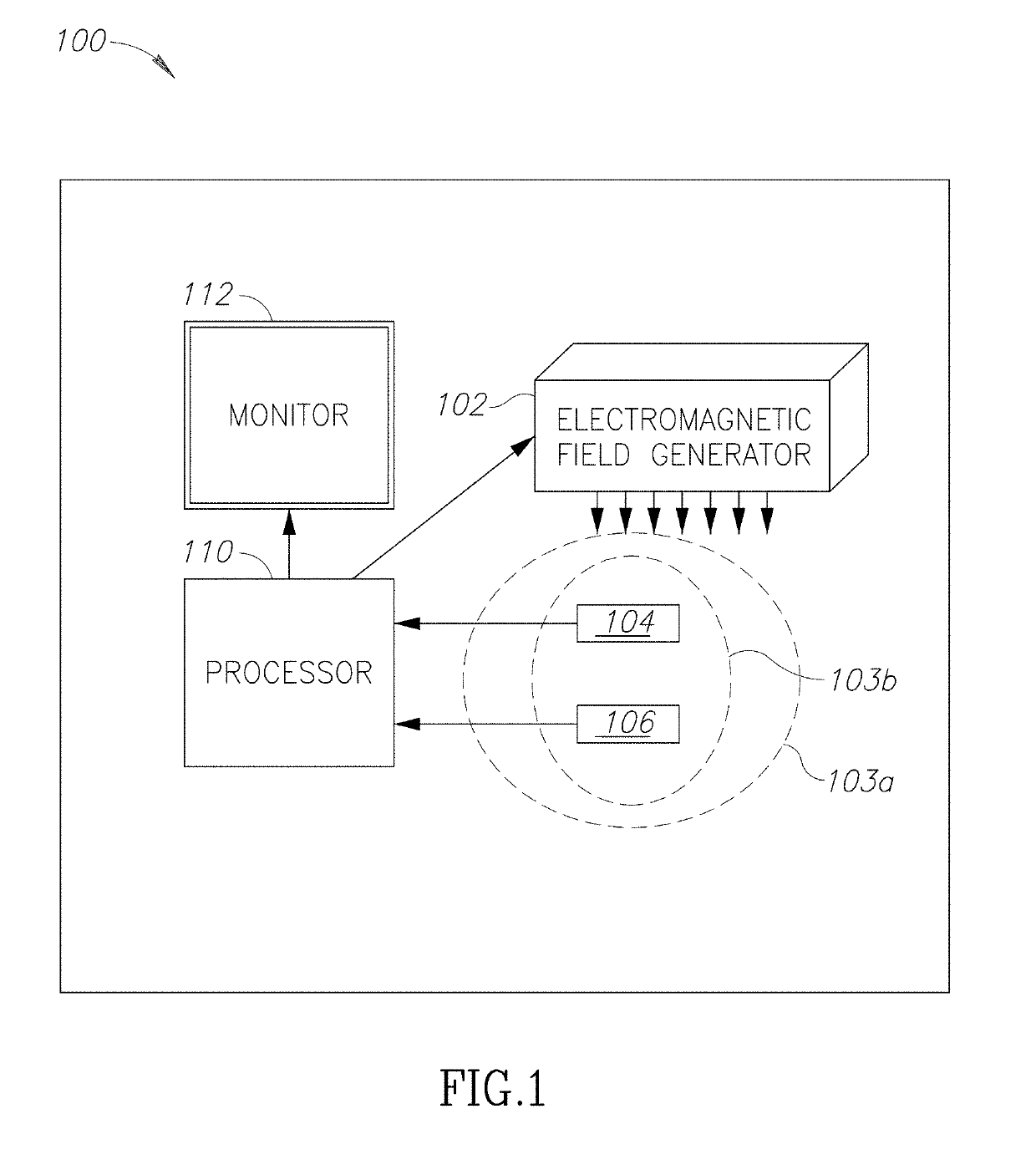
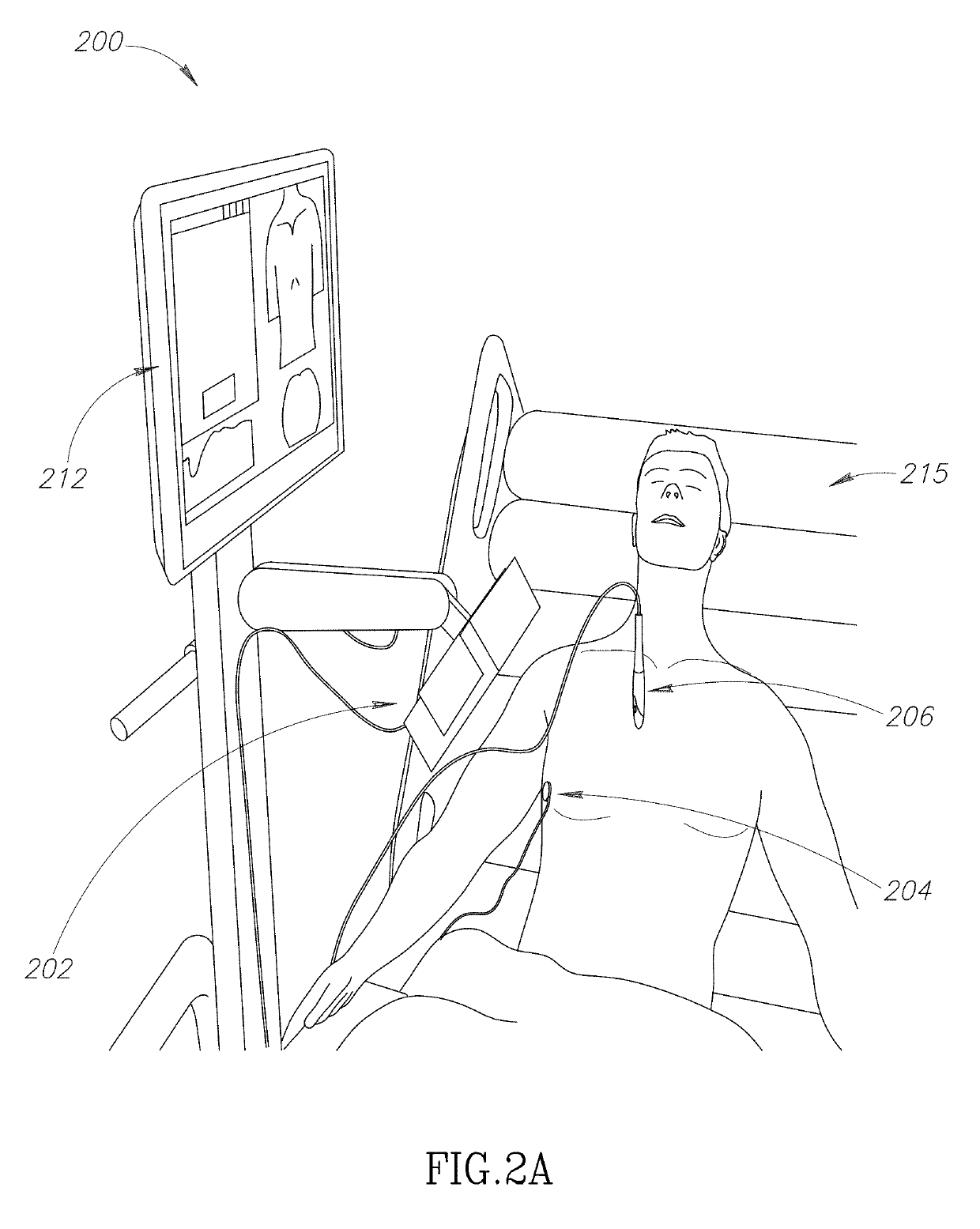
There is provided herein a system and a method for guiding insertion of a gastroenteral tube including: an electromagnetic field generator configured to generate an electromagnetic field covering a treatment area; wherein said electromagnetic field generator is external to the patient; a registration sensor configured to mark anatomic locations on the patient's torso; a gastroenteral tube comprising a tip sensor configured to sense its position and / or orientation relative to the electromagnetic field generator; and a processing circuitry configured to: calculate an orientation of the subject relative to the field generator based on the anatomic locations marked by the registration sensor, load a predefined anatomic map representing a torso; aligning the map based on the anatomic locations marked by the registration sensor, and showing on the map a path of the gastroenteral tube insertion; wherein the path is generated according to changes in the strength of the electromagnetic field sensed by the tip sensor's during the insertion of the gastroenteral tube, independent of the subject's movement and independent of deviations in the position and / or orientation of said field generator.
Owner:ENVIZION MEDICAL LTD
Emergency cardiac and electrocardiogram electrode placement system
ActiveUS9986929B1Diagnosis be limitedTreatment be limitedElectrocardiographySensorsElectrode placementMedical emergency
An emergency cardiac and electrocardiogram (ECG) electrode placement device is disclosed herein. The emergency cardiac and electrocardiogram (ECG) electrode placement device incorporates electrical conducting materials and elastic material into a pad that is applied to a chest wall of a patient, which places multiple electrodes in the appropriate anatomic locations on the patient to quickly obtain an ECG in a pre-hospital setting.
Owner:CB INNOVATIONS LLC
Identifying a target anatomic location in a subject's body, and delivering a medicinal substance thereto
ActiveUS20170231563A1Facilitates unhindered transtissual progressionGuide needlesDiagnostics using pressureAnesthetic AgentData information
Identifying target anatomic locations in a subject's body, and delivering medicinal substances thereto, following transtissual progression (penetrating, cutting through body tissue) and reaching body tissue with medical device distal tip. Involves acquiring mechanical properties of body tissue. Exemplary medicinal substance is, or includes, a drug (anesthetic agent), and exemplary target anatomic location is epidural space in subject's body. Exemplary system includes: cannular member enclosing cannula lumen; pusher-probe having distal end in cannula lumen and positionable from retracted to protruding positions, wherein pusher-probe distal end protrudes out of cannula distal end; and extending mechanism including cam member, a follower shiftable from first to second stations on cam member, and plunger selectively traveling in cannula lumen while forcing relative motion between cam member and follower, wherein pusher-probe distal end repositions between retracted and protruding positions. Optionally, includes data-information analyzing device having triggering mechanism via a winged hub member and associated components.
Owner:OMEQ MEDICAL
Tunneling needle design having an on-demand removable hub
InactiveUS20080065028A1Easy to installReduce riskEar treatmentSurgical needlesSubarachnoid spaceSpinal cord
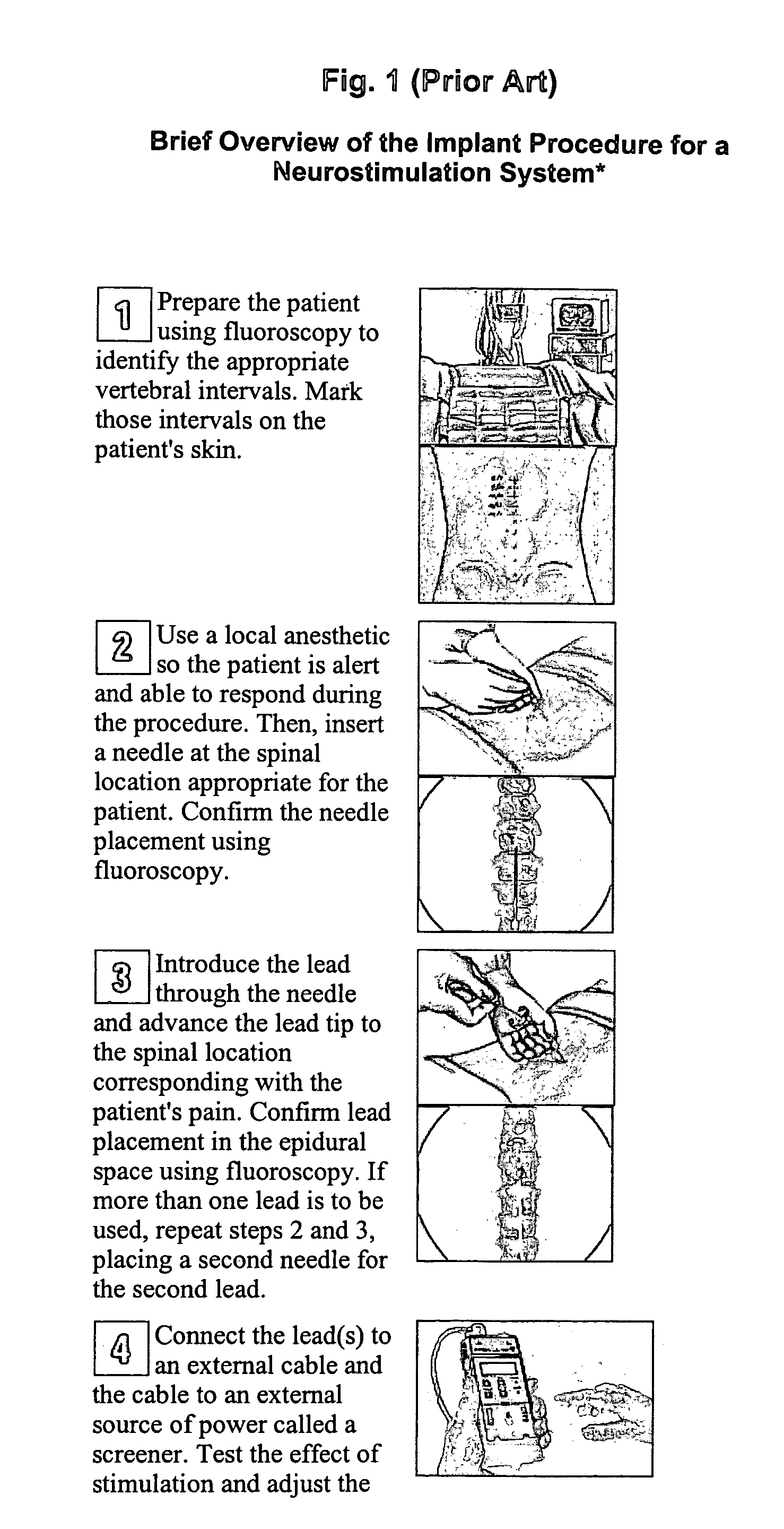
The present invention provides a medical needle assembly which has a removable at will needle hub for a spinal needle, which can be used to access the epidural or subarachnoid space of the spinal cord. This improvement in spinal needle design allows and facilitates the use of the medical needle for the purposeful creation of a subcutaneous tunnel and the placement of a catheter, or drain, or electrical wire lead which extends to an anatomic location remote from the original surgical incision site.The medical needle assembly has unique features and capabilities: a removable at will needle hub, which not only allows the surgeon to use the epidural / spinal needle initially to access the epidural or subarachnoid space of the spinal cord; but also permits the surgeon to use the same medical needle assembly again as a tunneling instrument. This allows the surgeon to perform the process of subcutaneous tunneling safely and in a manner previously considered to be surgically improbable.
Owner:VAISMAN JULIEN +1
Multi-junctional bleeding simulator
ActiveUS10726743B2Safely simulatePerformed safelyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAdhesive dressingsInguinal arteryPhysical therapy
Owner:STRATEGIC OPERATIONS INC
Skull guiding formwork for calvarium reconstruction surgery and manufacturing method of skull guiding formwork
InactiveCN102525608AImprove accuracyCircumvention of anatomySurgeryReconstruction surgerySurgical department
Disclosed is a manufacturing method of a skull guiding formwork for calvarium reconstruction surgery. The manufacturing method includes building a three-dimensional outline model of a skull of a patient; predicting a surgical objective model; determining a cutting path of craniotomy and the quantity and the shapes of bone flaps required to be cut and cutting and obtaining the bone flaps according to the cutting path; building a three-dimensional cutting guiding formwork model; designing splicing structures among the bone flaps and building a three-dimensional splicing guiding formwork model; and manufacturing a cutting guiding formwork and a splicing guiding formwork according to the cutting guiding formwork model and the splicing guiding formwork model. The skull guiding formwork for calvarium reconstruction surgery comprises the cutting guiding formwork and the splicing guiding formwork, and an outline of an edge of a cutting guiding formwork body shows the cutting path during surgery; and a mortise connecting structure which is spliced with the adjacent splicing guiding formwork or a skull base is arranged at the outer edge of a splicing guiding formwork body. The manufacturing method has the advantages that important anatomy position can be protected during surgery, excessive cutting to the bone flaps is avoided, and the manufacturing method is favorable for postoperation recovery and healing.
Owner:徐州冠珂工程科技有限公司
Catheter anchor system and method thereof
ActiveUS20200297976A1Readily attached to patientQuickly securedAdditive manufacturing apparatusCatheterSurgical operationCatheter
A method and system of and for securing a lumen or catheter, after placement in a patient, to prevent unwanted removal or dislodgement of the lumen or catheter caused by patient movement and / or further medical interventions such as cardiopulmonary chest compressions, electrical defibrillation, surgical procedures, and the like. The method and system comprising simple and sterile materials that preclude the use of excessive suturing and ineffective ad-hoc methods with tape and gauze. The catheter is secured by a rubber on plastic frictional force and will resist external forces while preventing the tube structure from bending and subsequent occlusion. The device can be comfortably attached to the patient in all of the anatomical locations typically targeted for large catheter installment. The method of securement is rapid and requires only a single personnel to handle the device and the catheter tube simultaneously.
Owner:TENSION SQUARE LLC
Interchangeable orthopedic blade
ActiveUS9050137B2Free from damageStable anatomic restorationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisStable fixationMalunion
An interchangeable orthopedic blade that includes an internal portion and an external portion. The internal portion threads onto either a pre-installed K-wire or a pre-installed screw so as to more accurately place the interchangeable orthopedic blade in, without excessive damage to, the bone when repairing a fracture in the bone, and ultimately providing absolute stable fixation by the interchangeable orthopedic blade holding the fracture in its anatomic position and resisting applied forces while healing, to thereby provide a stable anatomic restoration and eliminate a need for revision surgery due to failure of fixation or malunion. The internal portion is received in the external portion, and rotates relative to the external portion, but has the external portion move non-rotatably axially with the internal portion into the bone as the internal portion threads onto either the pre-installed K-wire or the pre-installed screw.
Owner:VIRAK ORTHOPEDIC RES
Tracking cardiac forces and arterial blood pressure using accelerometers
ActiveUS11253159B2Facilitates development and testing and productionInertial sensorsEvaluation of blood vesselsAccelerometerEngineering
Modular, miniaturized cardiovascular sensors, systems, methods, and wearable devices for the non-obtrusive evaluation, monitoring, and high-fidelity mapping of cardiac mechanical and electromechanical forces and central arterial blood pressure are presented herein. The sensor manufacturing process is also presented. Using accelerometers, the sensors register body-surface (preferably torso-surface) movements and vibrations generated by cardiac forces. The sensors may contain single-use or reusable components, which may be exchanged to fit different body sizes, shapes, and anatomical locations; they may be incorporated into clothing, bands, straps, and other wearable arrangements. The invention presents a practical, noninvasive solution for electromechanical mapping of the heart, which is useful for a wide range of healthcare applications, including the remote monitoring of heart failure status and the guidance of cardiac resynchronization therapy. Exercise and cardiovascular fitness tracking applications are also presented.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
Tunneling needle design having an on-demand removable hub
InactiveUS7549996B2Easy to installReduce riskEar treatmentSurgical needlesSubarachnoid spaceSurgical incision
The present invention provides a medical needle assembly which has a removable at will needle hub for a spinal needle, which can be used to access the epidural or subarachnoid space of the spinal cord. This improvement in spinal needle design allows and facilitates the use of the medical needle for the purposeful creation of a subcutaneous tunnel and the placement of a catheter, or drain, or electrical wire lead which extends to an anatomic location remote from the original surgical incision site.The medical needle assembly has unique features and capabilities: a removable at will needle hub, which not only allows the surgeon to use the epidural / spinal needle initially to access the epidural or subarachnoid space of the spinal cord; but also permits the surgeon to use the same medical needle assembly again as a tunneling instrument. This allows the surgeon to perform the process of subcutaneous tunneling safely and in a manner previously considered to be surgically improbable.
Owner:VAISMAN JULIEN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com