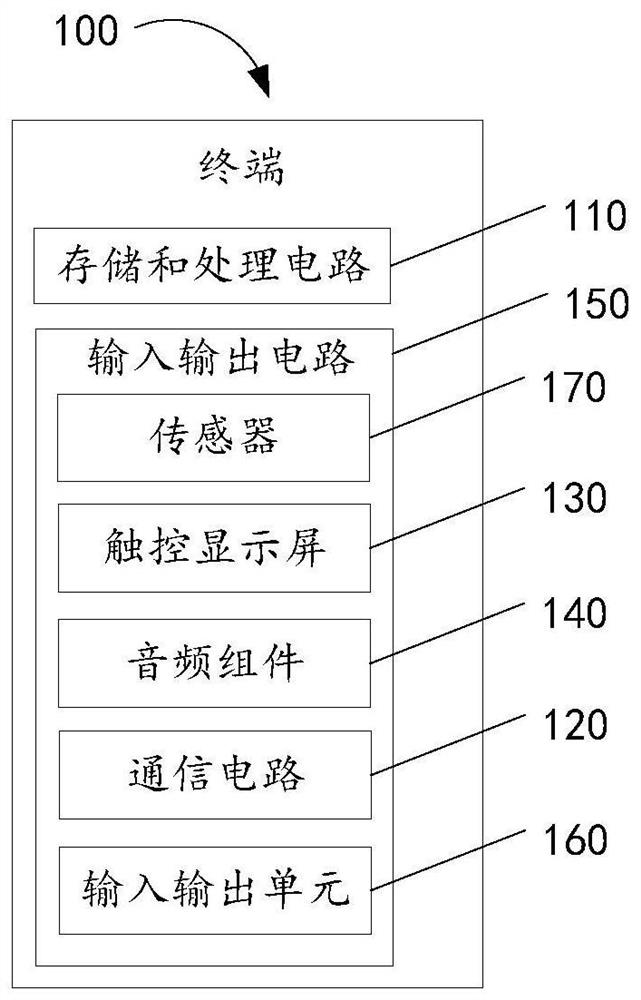
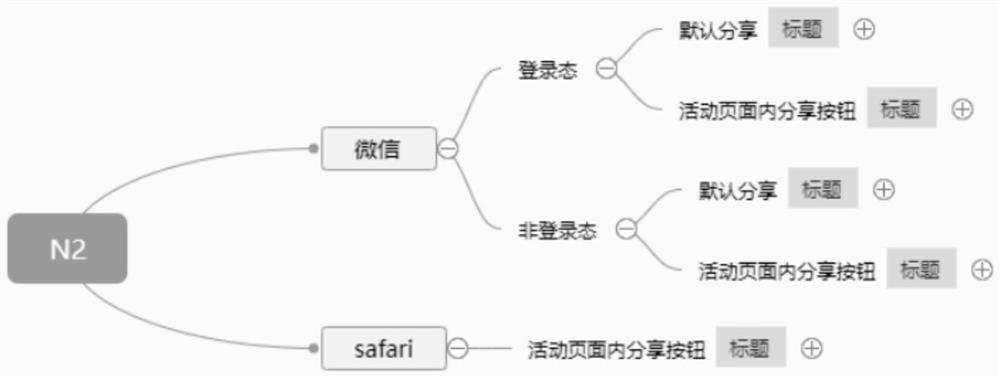
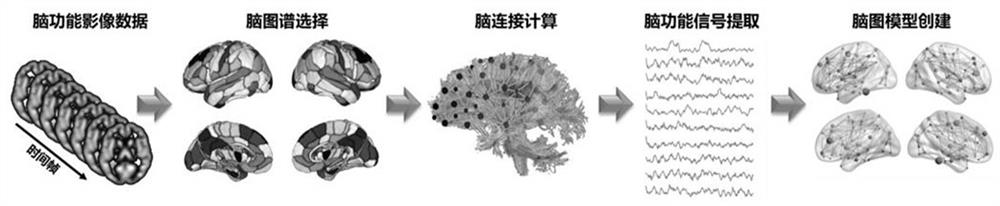
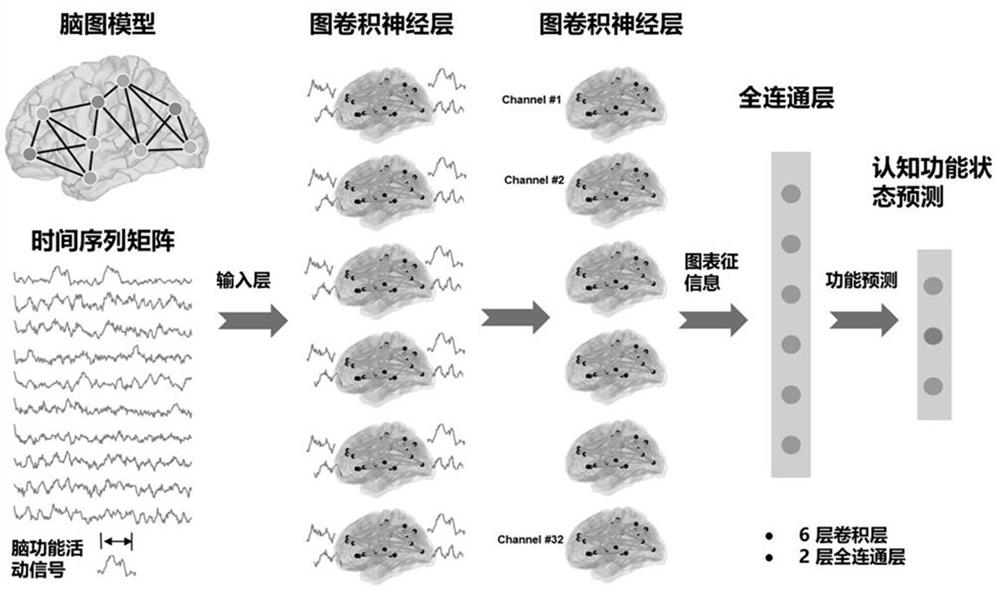
Patents
Literature
35 results about "BrainMaps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
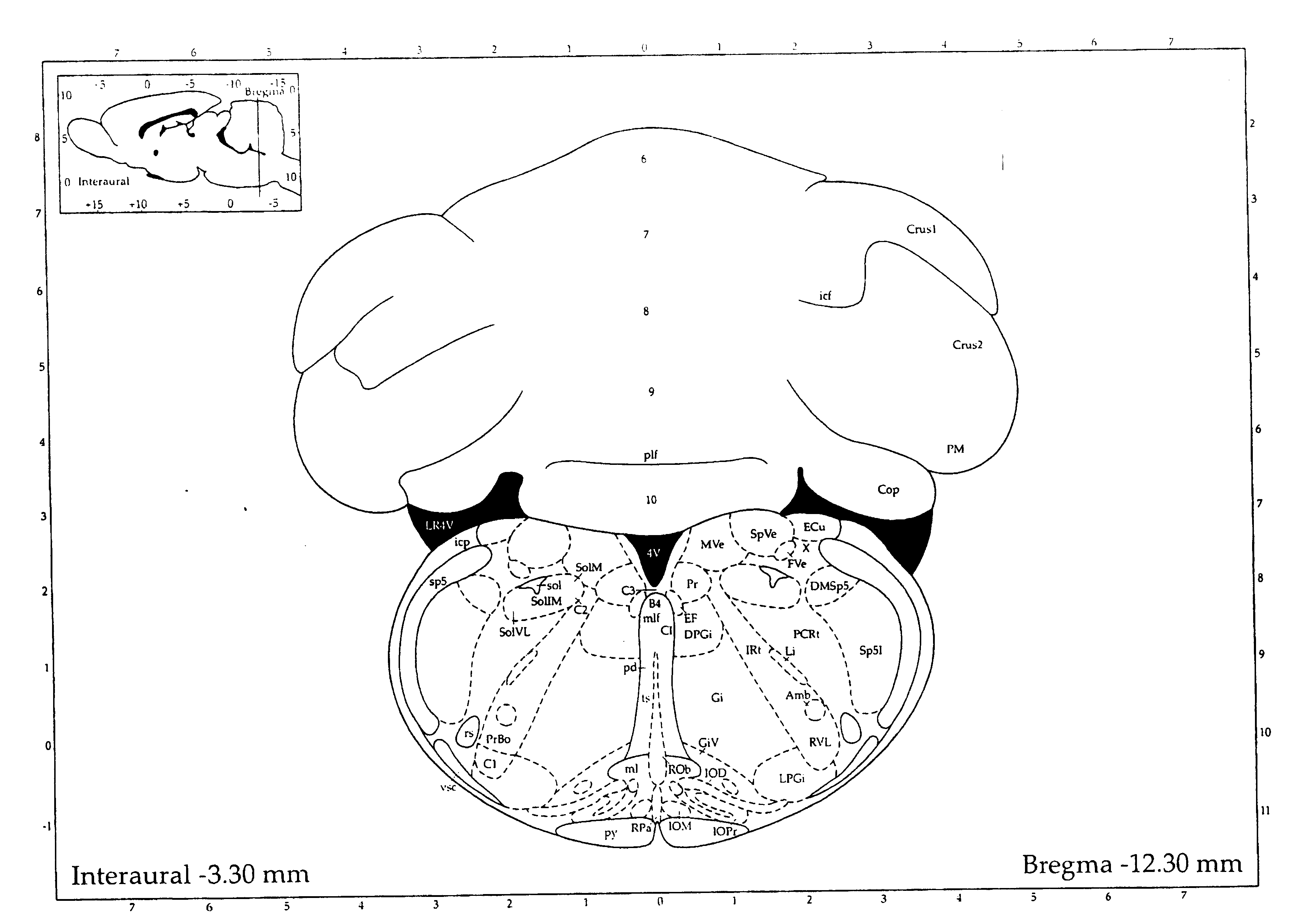
BrainMaps is an NIH-funded interactive zoomable high-resolution digital brain atlas and virtual microscope that is based on more than 140 million megapixels (140 terabytes) of scanned images of serial sections of both primate and non-primate brains and that is integrated with a high-speed database for querying and retrieving data about brain structure and function over the internet.
Systems and methods for detecting deception by measuring brain activity
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
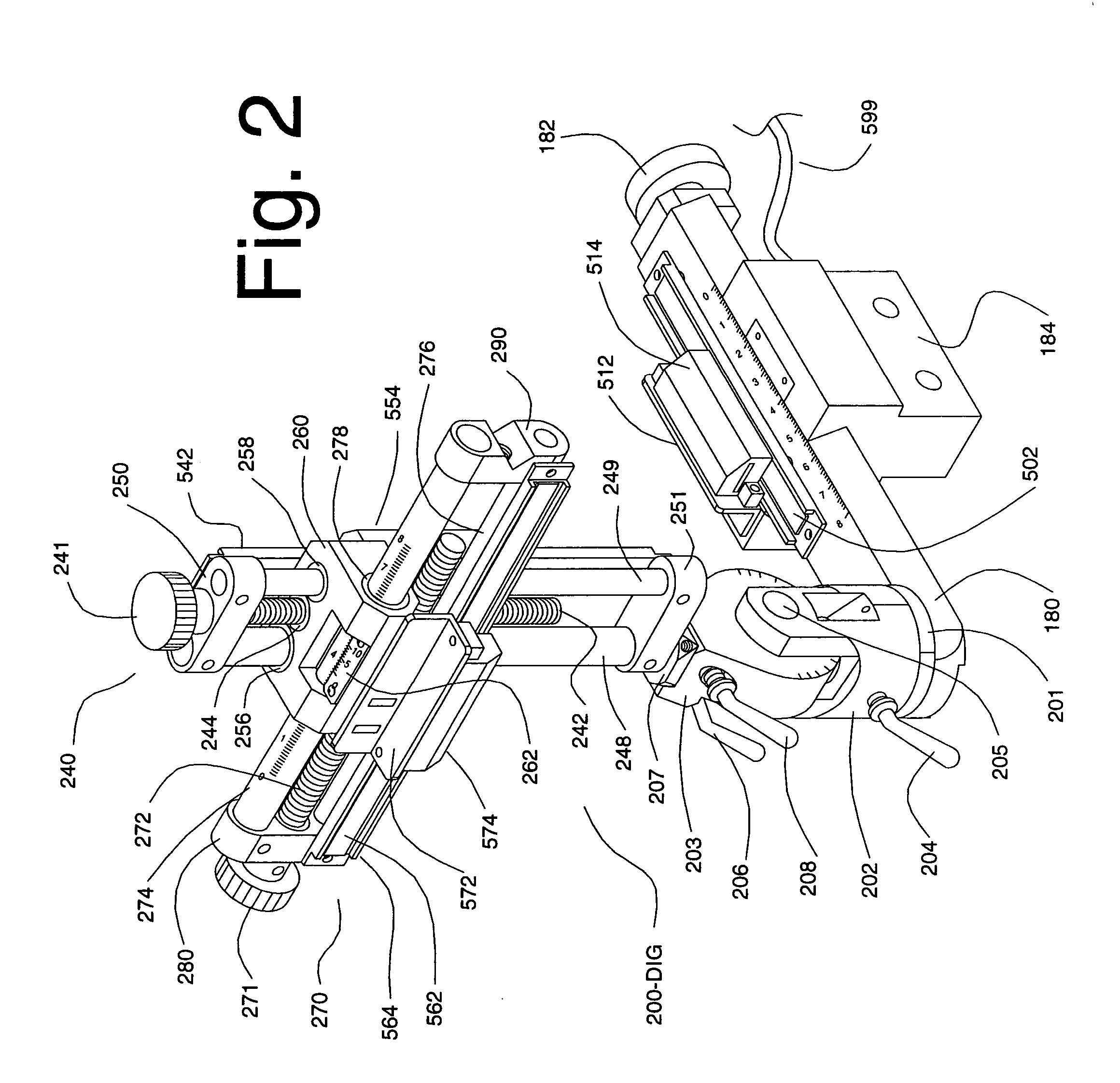
Digital stereotaxic manipulator with interfaces for use with computerized brain atlases
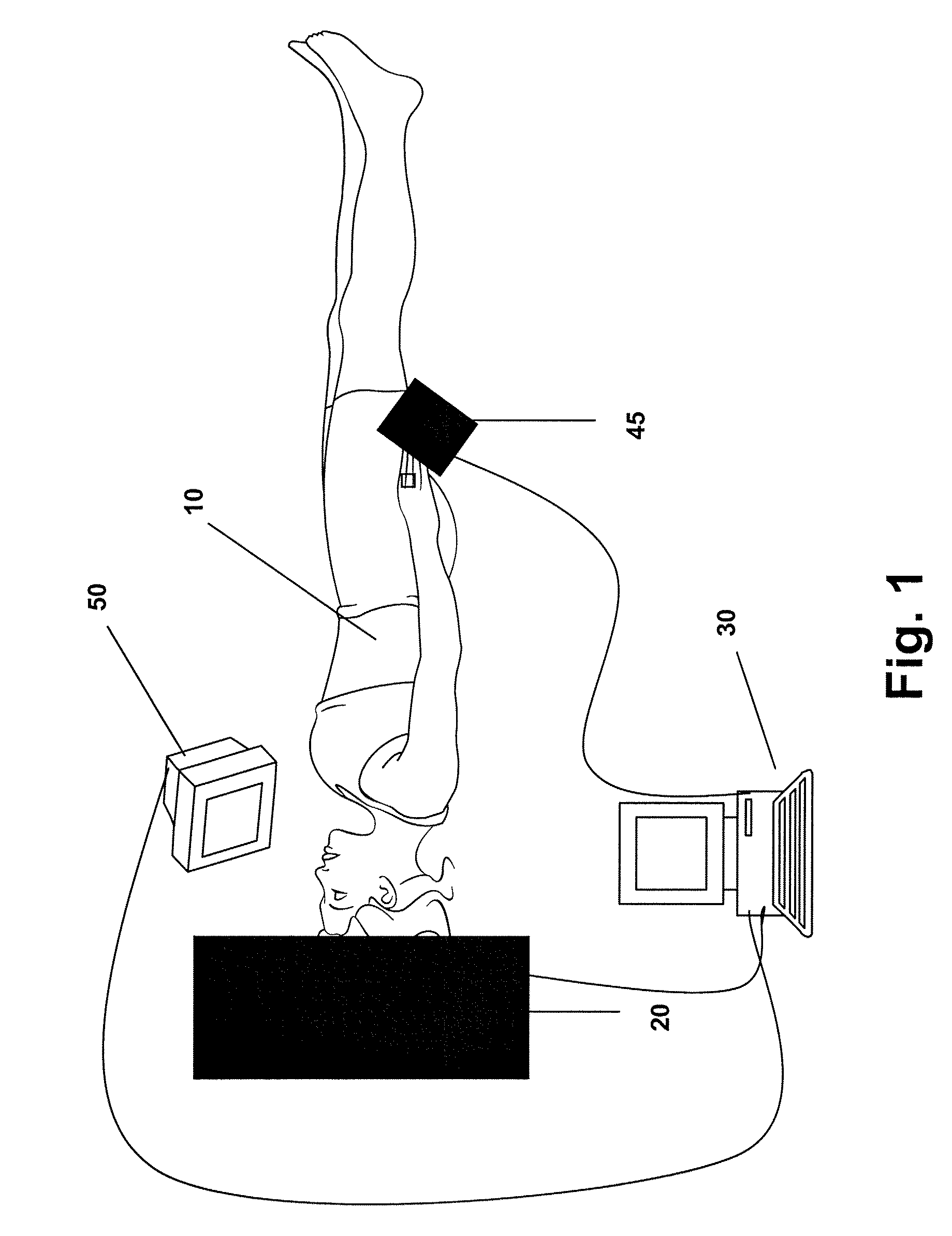
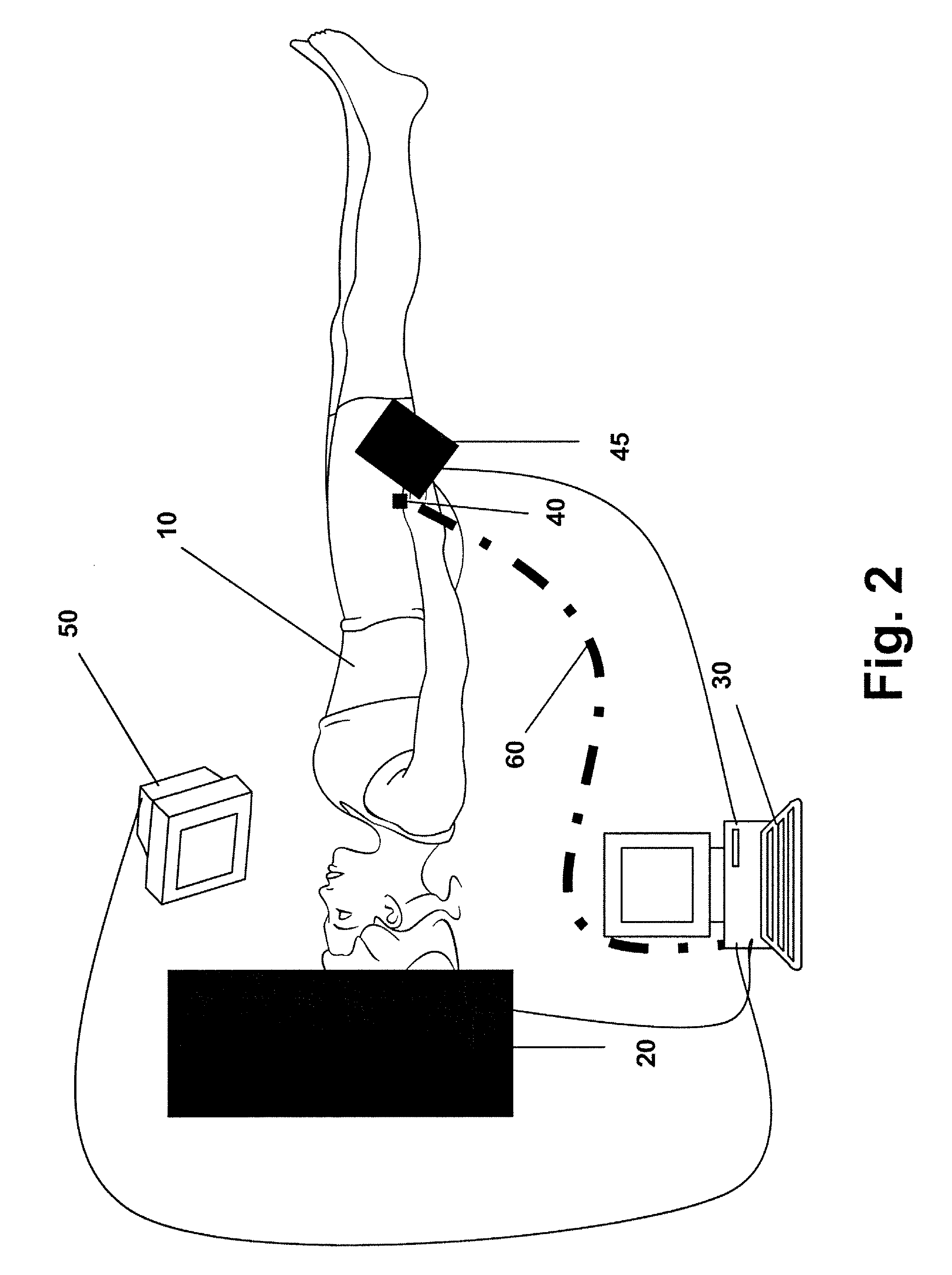
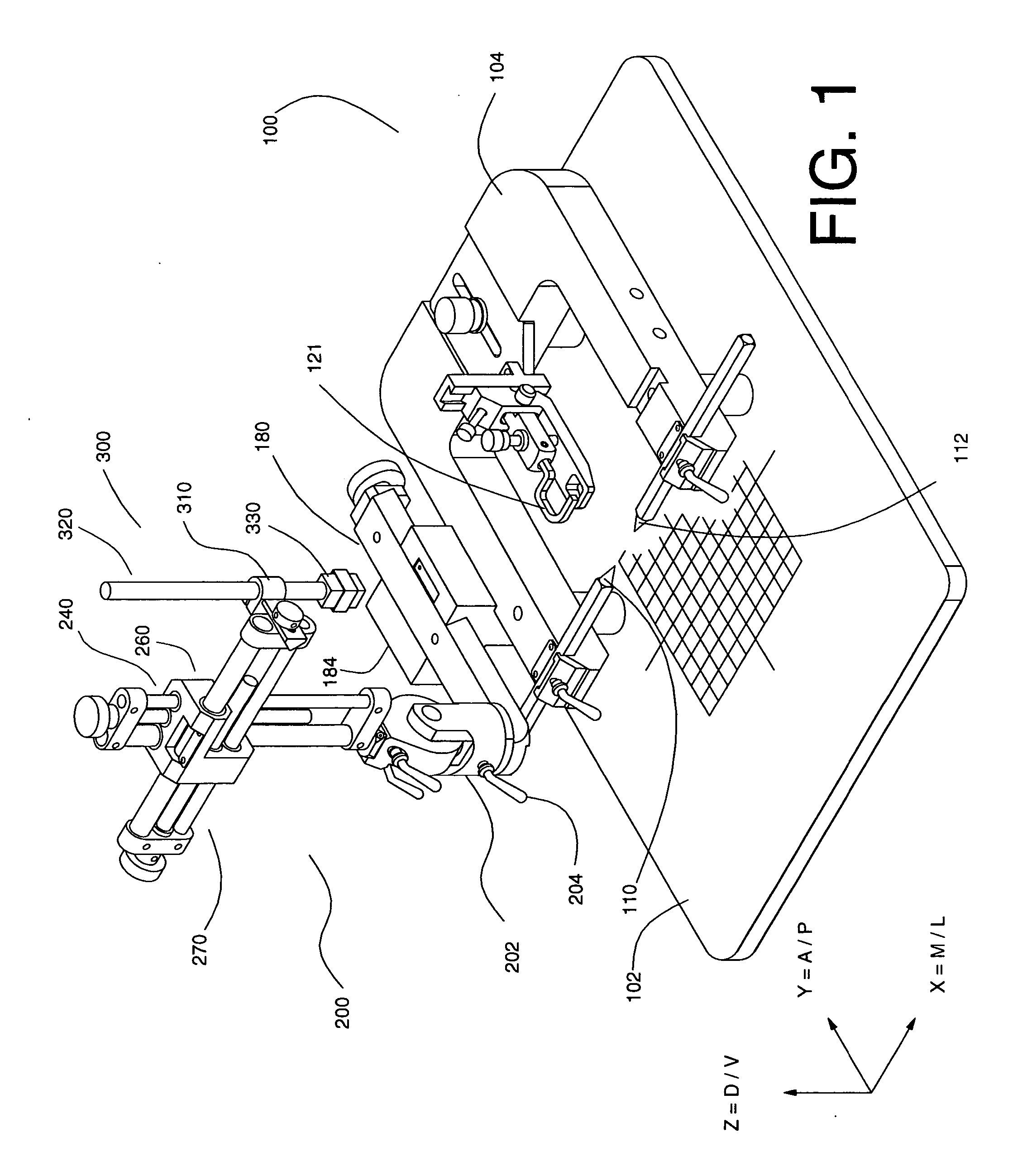
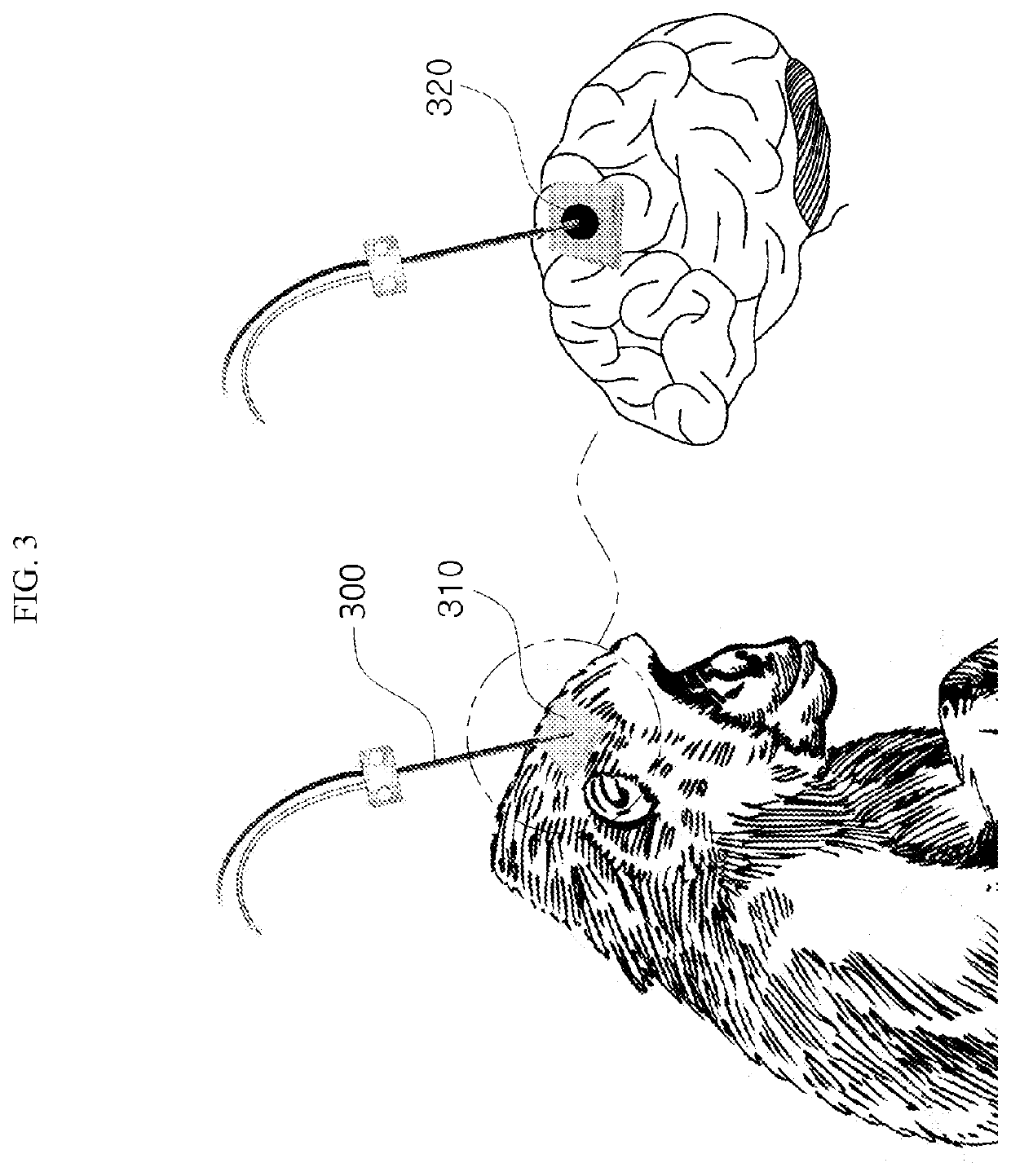
InactiveUS20060052689A1Least possible damageClear locationSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer monitorImage resolution
A system is disclosed that allows stereotaxic procedures being performed on lab animals to interact, on a “live” or “real-time” basis, with information that has been compiled in stereotaxic brain atlases. For example, during an invasive procedure, a researcher can see, on a cross-sectional brain map displayed on a full-sized computer monitor, the location and travel of an instrument tip, indicated by means such as a bright blinking cursor or icon. If desired, important brain structures (such as major nerve bundles) can been prominently labeled and / or colored, to clearly indicate their locations, and help the researcher ensure that they are avoided. This system can be provided by coupling a digital stereotaxic manipulator to a dedicated controller with touch-screen capability, and coupling the PLC processor to a computer having a monitor screen that is large enough to display a brain map with good resolution. Alternately, the digital stereotaxic manipulator can be coupled directly to a computer, via an interface card or other device.
Owner:SCOUTEN CHARLES W +2
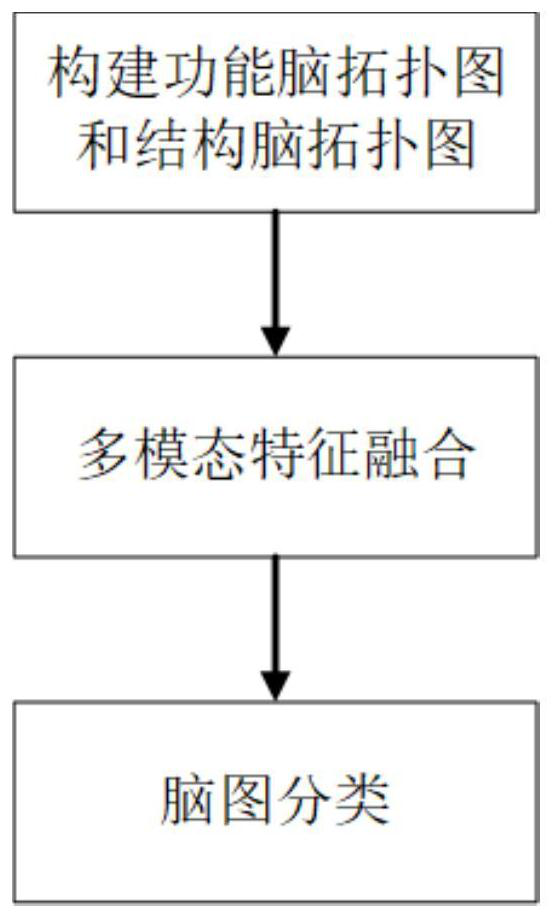
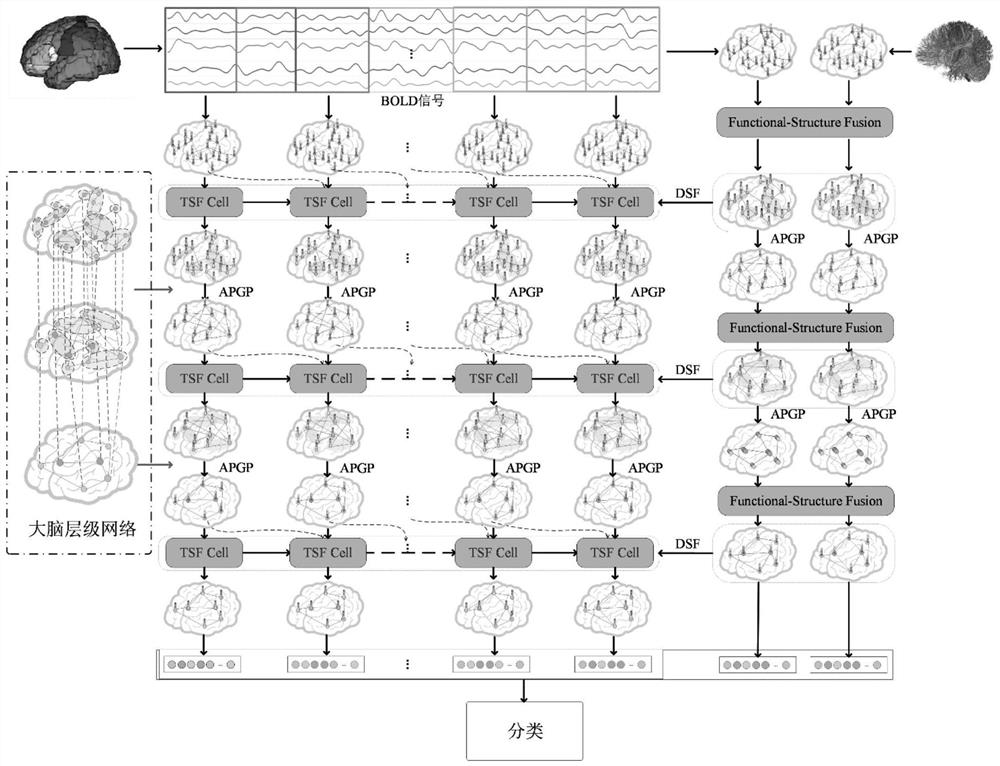
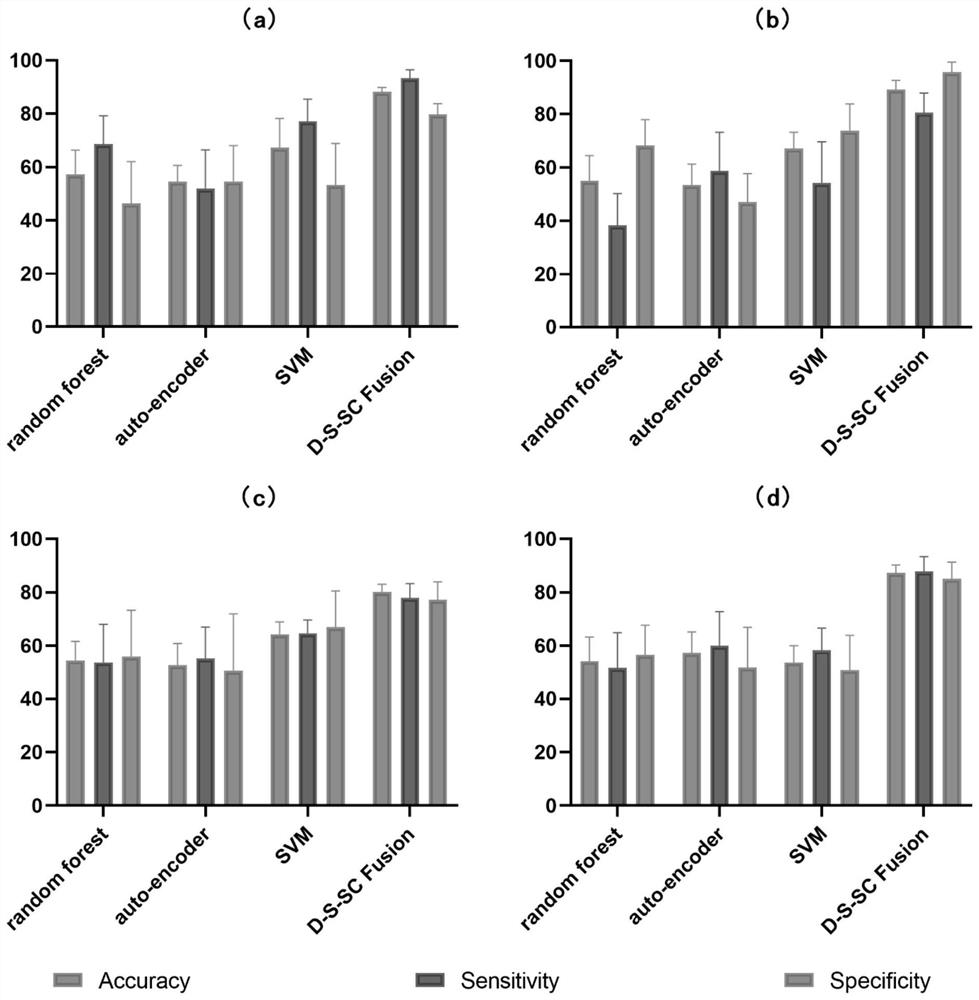
Brain map classification method based on deep multi-modal graph convolution
ActiveCN113592836AThe classification result is accurateTake advantage of similaritiesImage enhancementImage analysisTopological graphComputer vision
The invention provides a brain image classification method based on deep multi-modal image convolution. The purpose of brain image classification is achieved by fusing brain images of different modals. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing a multi-modal brain topological graph, and constructing the brain topological graph by using resting state functional magnetic resonance data and diffusion tensor magnetic resonance data according to biological meanings of the resting state functional magnetic resonance data and the diffusion tensor magnetic resonance data; and then, carrying out multi-modal fusion, wherein the multi-modal fusion comprises a function-structure fusion part and a dynamic-static fusion part. According to the invention, multiple modal features are used and fused, and the similarity and complementarity among the features can be fully utilized, so that a brain map classification result is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
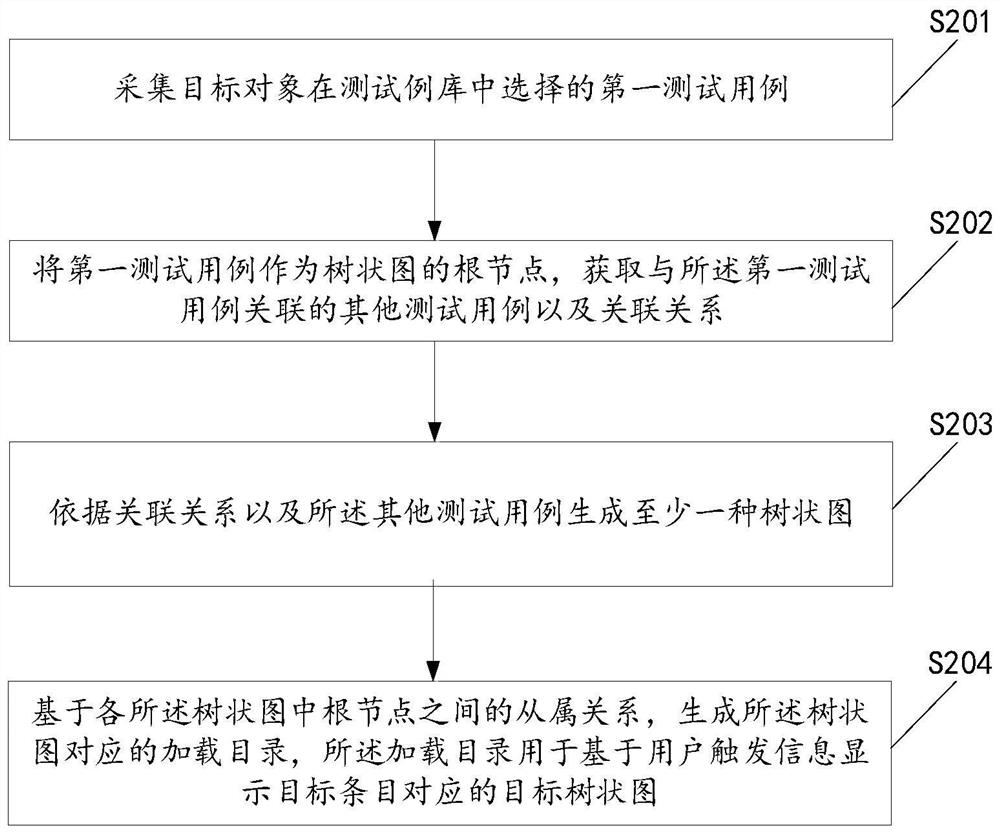
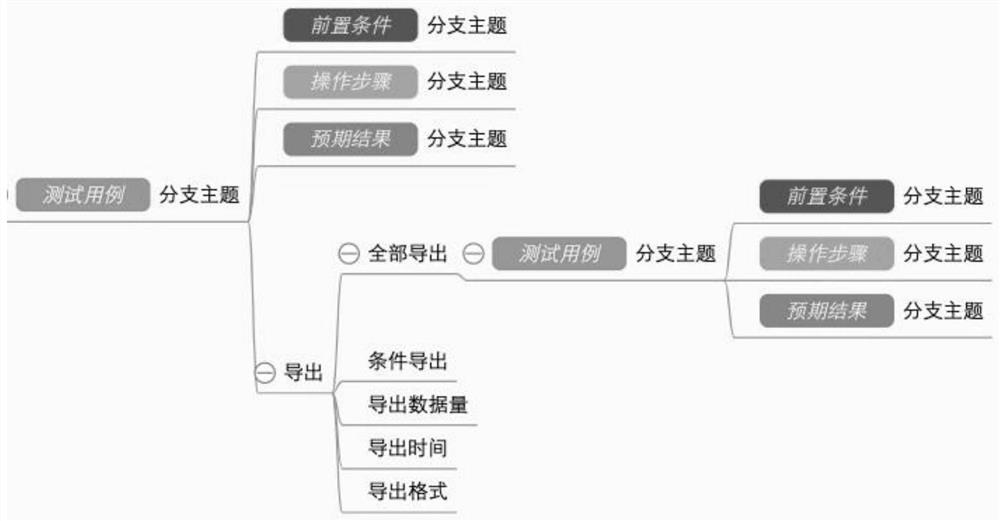
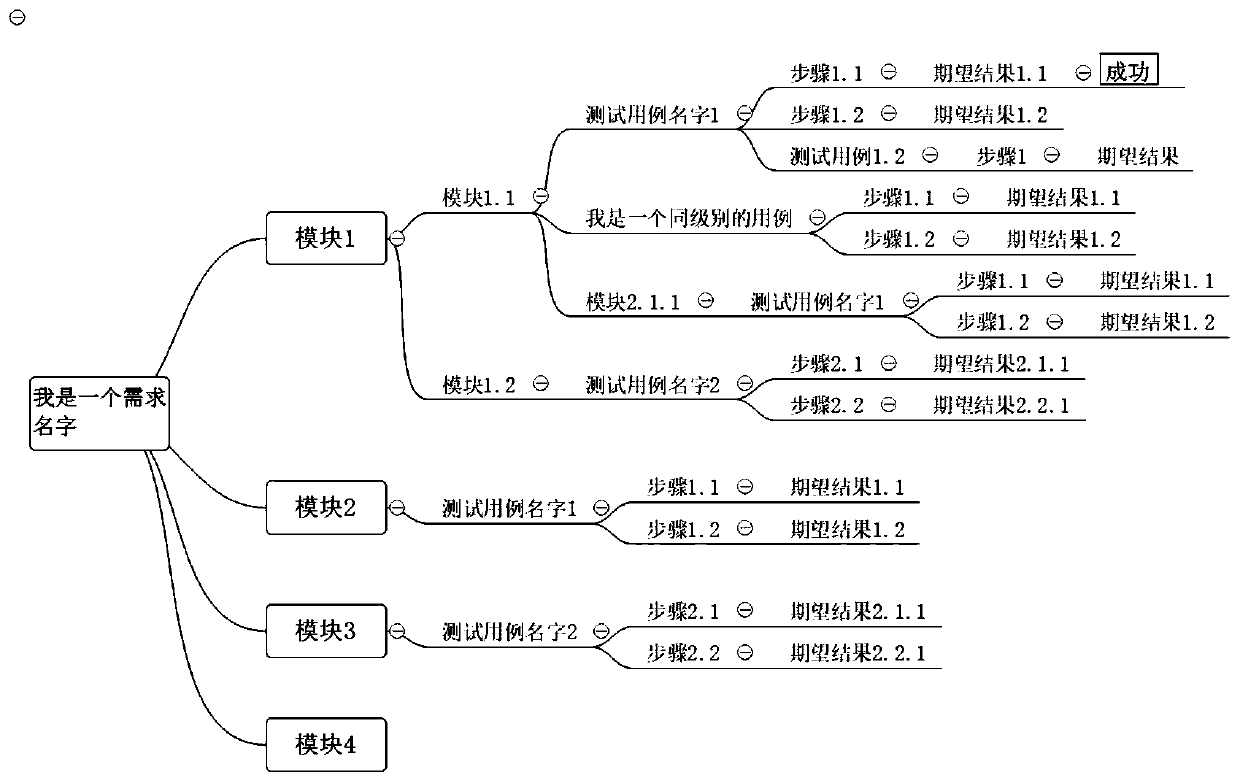
Test case application method and related product
PendingCN113312265AImprove experienceImprove display efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingOther databases indexingData displayAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a test case application method and a related product. The method comprises the steps of collecting a first test case selected by a target object in a test case library, taking the first test case as a root node of the tree diagram, and obtaining other test cases associated with the first test case and an association relationship, generating at least one tree diagram according to the incidence relation and other test cases, and generating a loading directory corresponding to the tree diagrams based on the subordination relationship among the root nodes in each tree diagram, so as to display a target tree diagram corresponding to the target entry based on the user triggering information. According to the technical scheme, when any test case is selected by the target object, the tree diagram with the first test case as the root node can be automatically generated, the tree diagram is displayed, then the relationship between the case libraries is determined through display, test case brain diagram display of any granularity is completed, the data display efficiency can be improved, and large-capacity test cases are managed in a unified manner.
Owner:FUTU NETWORK TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
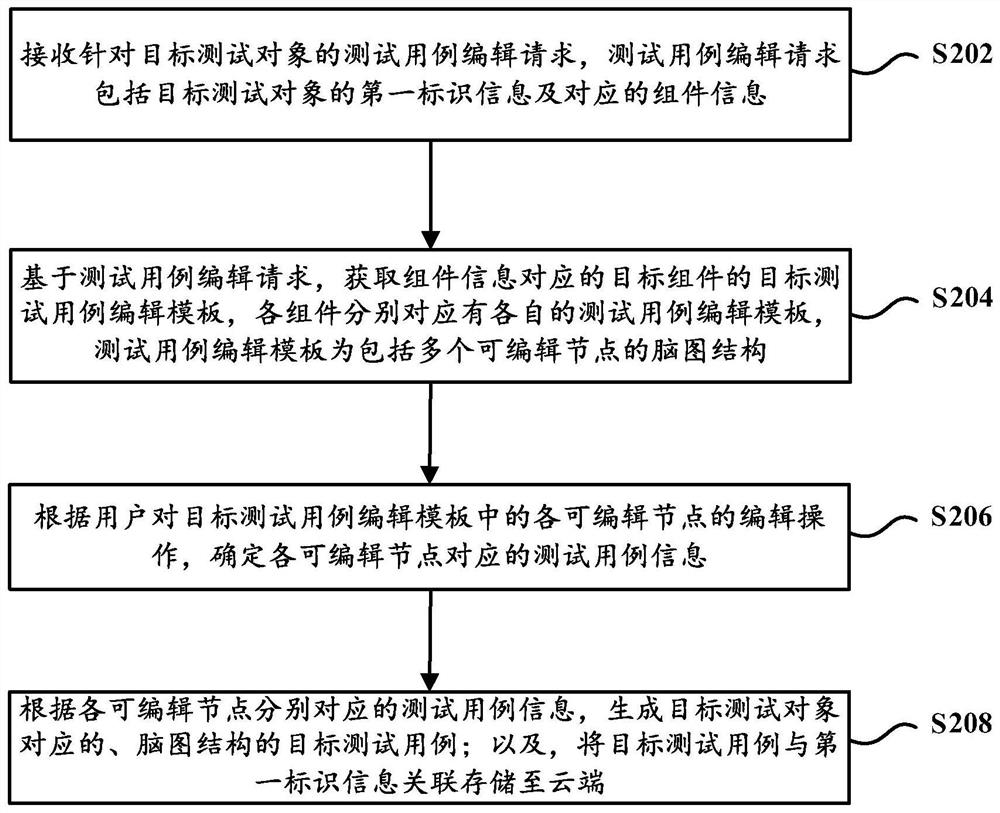
Test case management method, device and equipment
PendingCN112148593AImprove editing efficiencySave human resourcesSoftware testing/debuggingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a test case management method, device and equipment. The method, the device and the equipment are used for solving the problems of low test case editing efficiency and inconvenience in systematic management in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of receiving a test case editing request for a target test object; based on the test case editing request, obtaining a target test case editing template of a target component corresponding to the component information, wherein the test case editing template is of a brain graph structure comprises a plurality of editable nodes; determining test case information corresponding to each editable node according to an editing operation of a user on each editable node in the target test case editing template; generating a target test case of a brain graph structure corresponding to the target test object according to the test case information corresponding to each editable node; and associatively storing the target test case and the first identification information to the cloud. According to the technical scheme, the editing efficiency of the test cases is improved, and the systematic management effect of the test cases is achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DASOUCHE AUTO SERVICE CO LTD
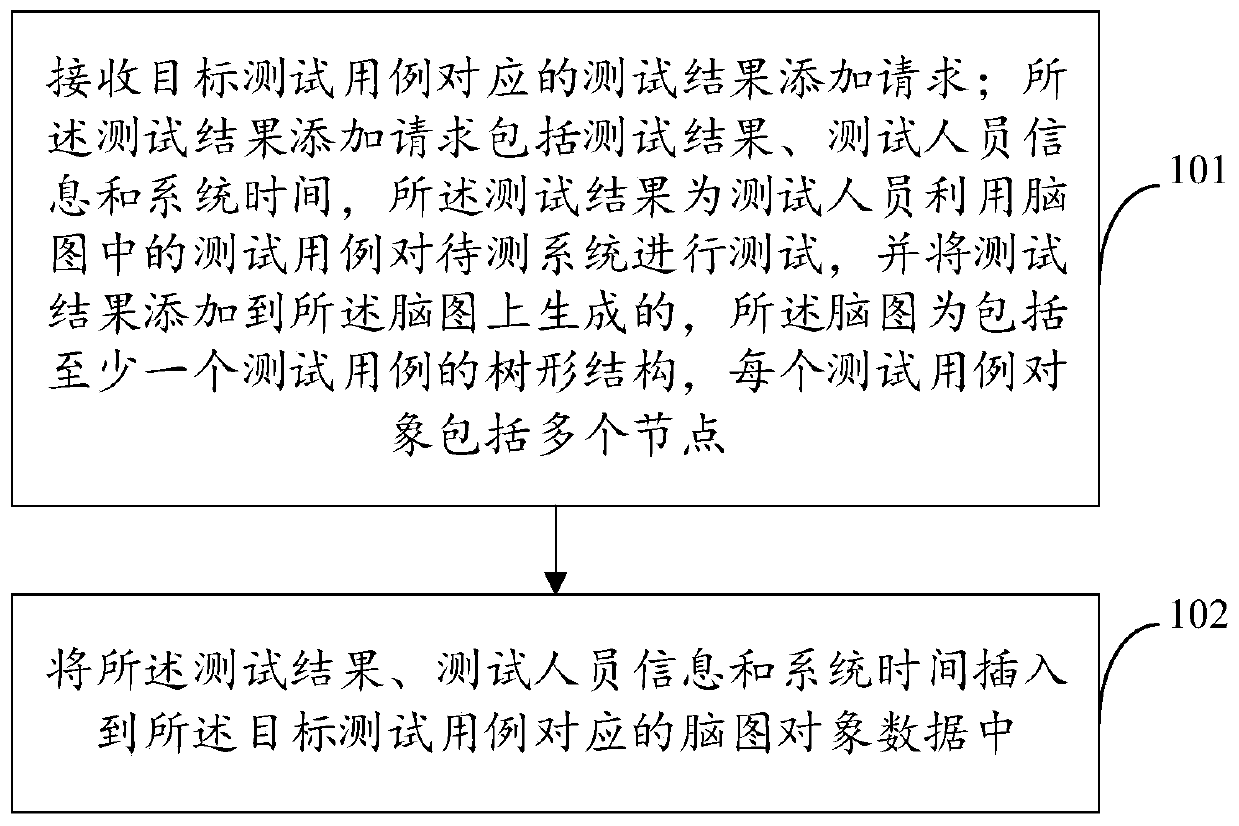
Brain graph-based test method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111290956AAchieve recordConvenient querySoftware testing/debuggingEnergy efficient computingTheoretical computer scienceBrainMaps
The invention provides a brain graph-based test method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of receiving a test result adding request corresponding toa target test case, wherein the test result adding request comprises a test result, test personnel information and system time, the test result is generated when a tester tests a to-be-tested system by using test cases in a brain graph; adding the test result to the brain graph, wherein the brain graph is of a tree structure comprising at least one test case, and each test case object comprises aplurality of nodes; and inserting a test result, test personnel information and system time into the brain map object data corresponding to the target test case. According to the embodiment of the invention, the recording of related data during user operation is realized, and then the test data of each test case in the brain diagram can be traced and counted.
Owner:贵阳货车帮科技有限公司
Stability calculation method for brain dynamic function mode
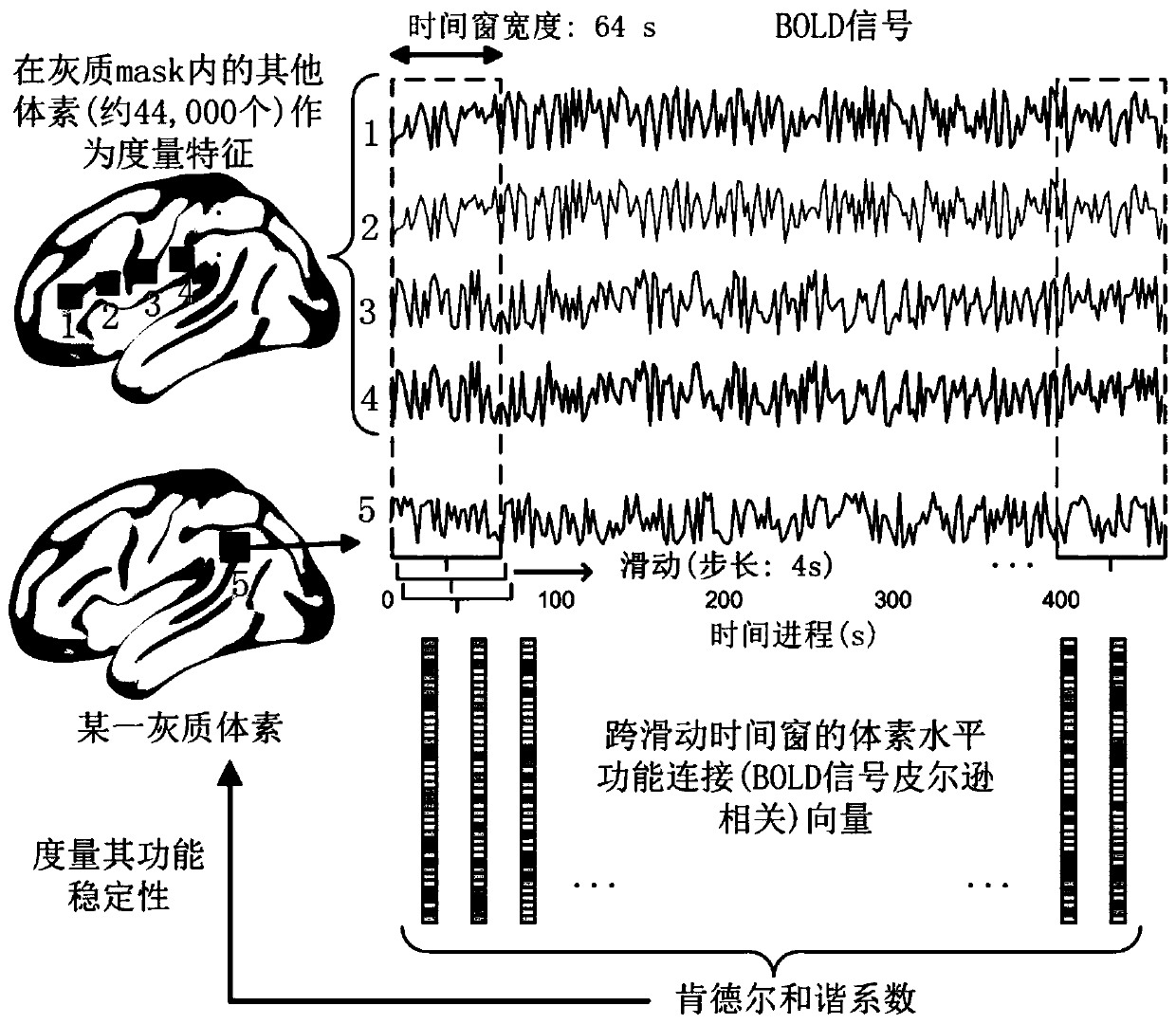
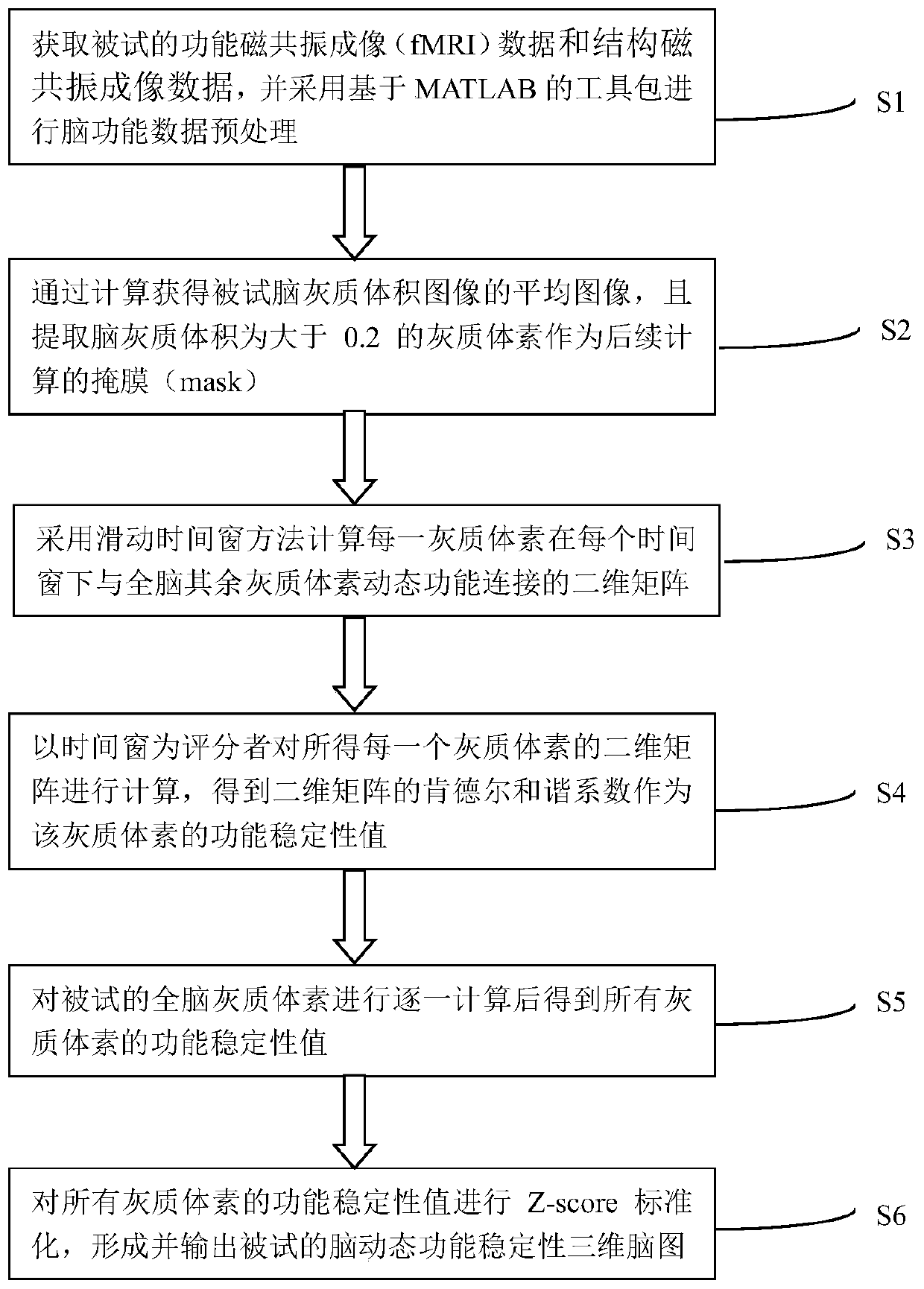
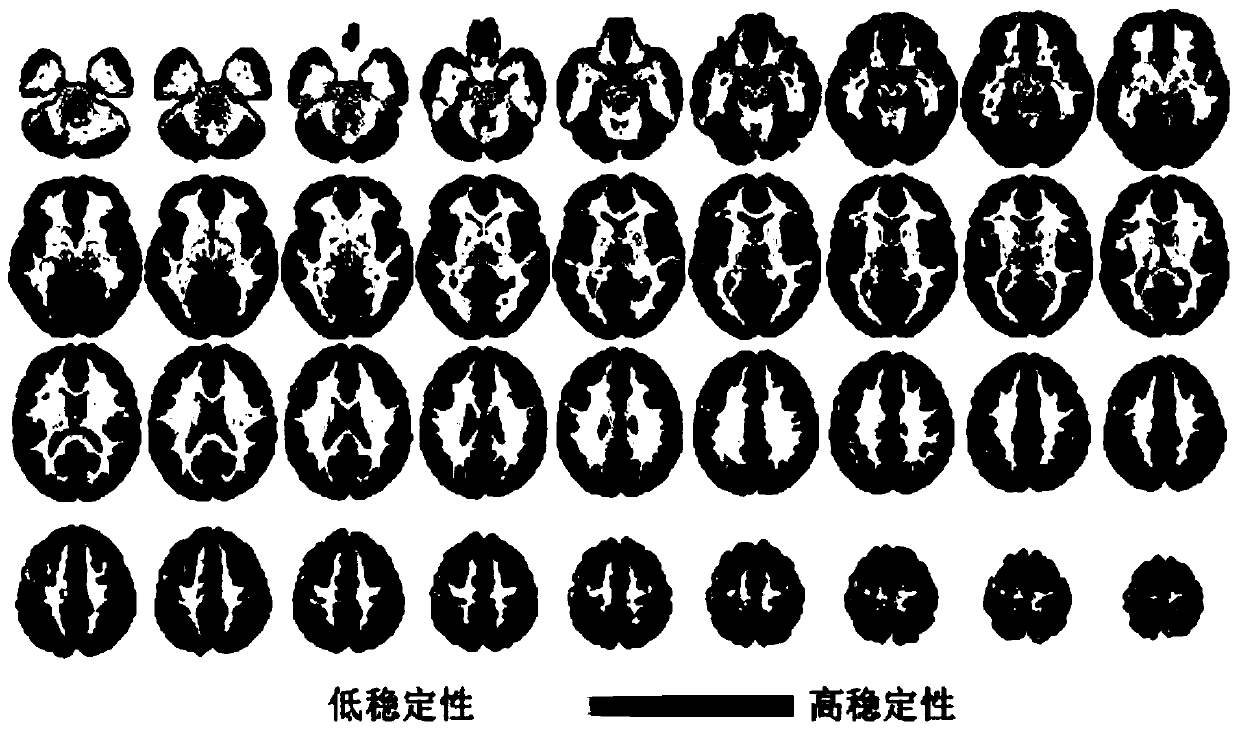
ActiveCN110322554AAvoid lossComprehensive description of dynamic characteristicsImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelBrain Gray Matter
The invention discloses a stability calculation method for a brain dynamic function mode. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring and preprocessing functional magnetic resonance imagingdata and structural magnetic resonance imaging data of a subject; extracting grey matter voxel with volume of brain grey matter being greater than 0.2 as a mask for subsequent calculation; calculatinga two-dimensional matrix of dynamic function connection between each gray voxel and other gray voxels of the whole brain under each time window by adopting a sliding time window method; calculating the obtained two-dimensional matrix of each gray voxel by taking a time window as a scorer to obtain a Kendall harmony coefficient of the two-dimensional matrix as a functional stability value of the gray voxel; calculating the tested whole-brain gray voxels one by one to obtain functional stability values of all the gray voxels; performing Z-score standardization of functional stability values ofall gray matter voxels and forming and outputting the brain dynamic function stability of the subject. . Calculation based on gray voxels is adopted. Brain activity signals are utilized to the maximumextent, and dynamic characteristics of brain functional activities can be accurately and comprehensively described.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Test case processing method and device and storage medium
PendingCN112433937AImprove management efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisData miningData science
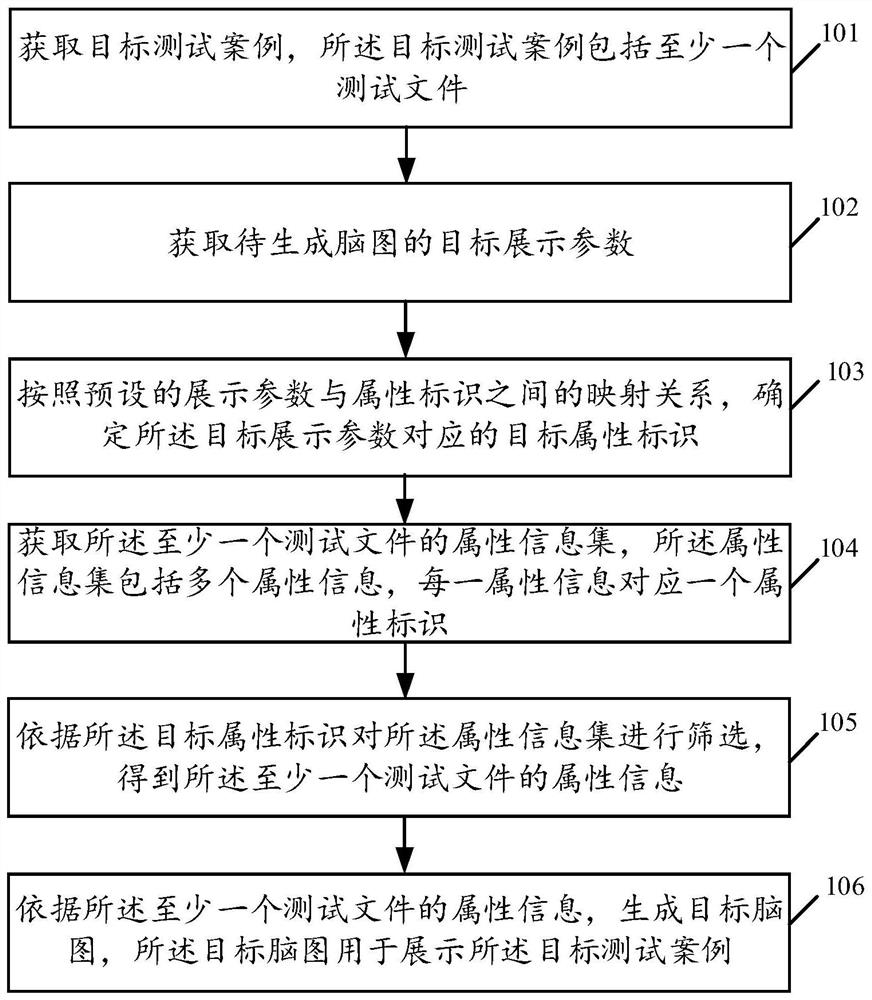
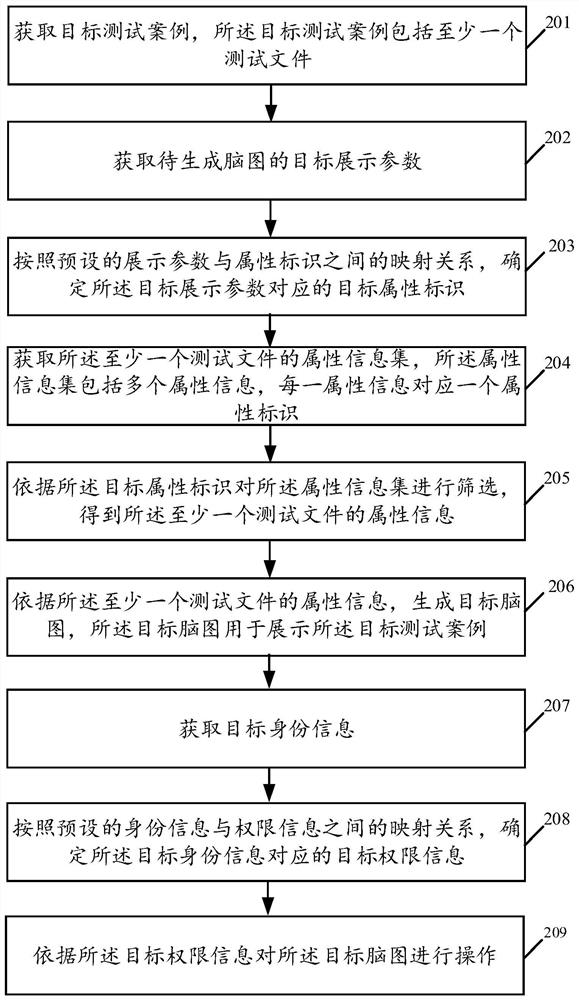
The invention relates to a data processing technology, in particular to a test case processing method and device and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a target test casewhich comprises at least one test file; obtaining a target display parameter of the to-be-generated brain graph; determining a target attribute identifier corresponding to the target display parameteraccording to a preset mapping relationship between the display parameter and the attribute identifier; obtaining an attribute information set of the at least one test file, the attribute informationset comprising a plurality of pieces of attribute information, and each piece of attribute information corresponding to one attribute identifier; screening the attribute information set according to the target attribute identifier to obtain attribute information of the at least one test file; and generating a target brain graph according to the attribute information of the at least one test file,the target brain graph being used for displaying the target test case. By adopting the embodiment of the invention, the management efficiency of the test case is improved.
Owner:平安消费金融有限公司
Document atlas extraction method and device based on machine learning and storage medium
InactiveCN112445915ASave time readingImprove read qualitySpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationShardKnowledge graph
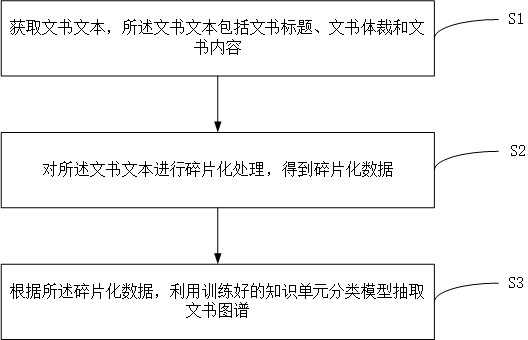
The invention discloses a document atlas extraction method and device based on machine learning and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a document text, wherein the documenttext comprises a document title, a document body and document content; carrying out fragmentization processing on the document text to obtain fragmentized data; and according to the fragmented data, extracting a document map by using a trained knowledge unit classification model. According to the method, the trained knowledge unit classification model is used for extracting the document text to obtain structured document atlas data, the document atlas of the brain graph structure can be automatically formed, the document content is clear at a glance, the reading time can be greatly shortened,and the reading quality is improved. The method can be widely applied to the technical field of knowledge maps.
Owner:京华信息科技股份有限公司
Graph model-based brain function registration method
ActiveCN113539435AReduce feature dimensionEnsure consistencyMedical imagingImage analysisAlgorithmGraph model
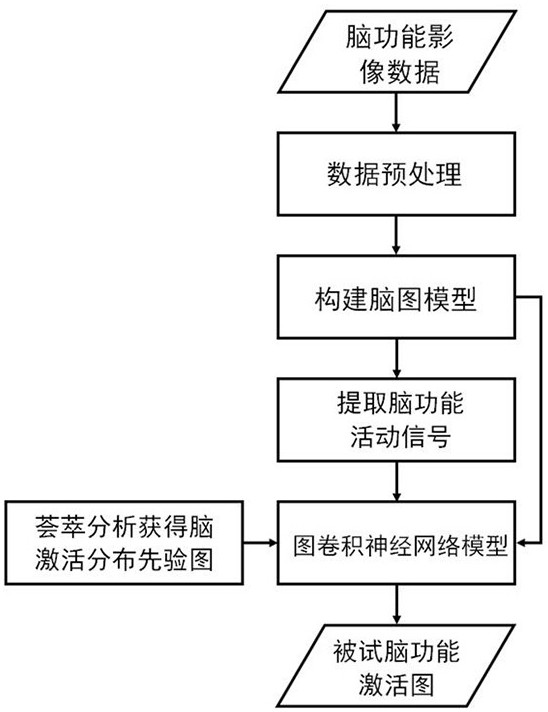
The invention discloses a brain function registration method based on a graph model, and the method comprises the following steps: mapping high-dimensional brain function image data to a two-dimensional time sequence matrix by taking a brain function activity signal of a subject in a specific cognitive function state as input and taking a brain graph model as a basis; constructing a graph convolutional neural network model to distinguish different cognitive function states, and utilizing a meta analysis method to generate a brain activation distribution prior graph to assist in predicting a brain function activation mode of each subject specificity; combining the two sides to map brain function image data of each subject to a shared representation space suitable for a large-scale group, and finally achieving the accurate brain function alignment between individuals. According to the method, the effect dose of statistical test on a group can be enhanced, the number of tested samples required in brain cognitive function research is reduced, the clinical research cost is saved, and meanwhile, the graph representation information generated in the shared representation space can also be used for accurately predicting the tested brain function state and behavioral indexes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
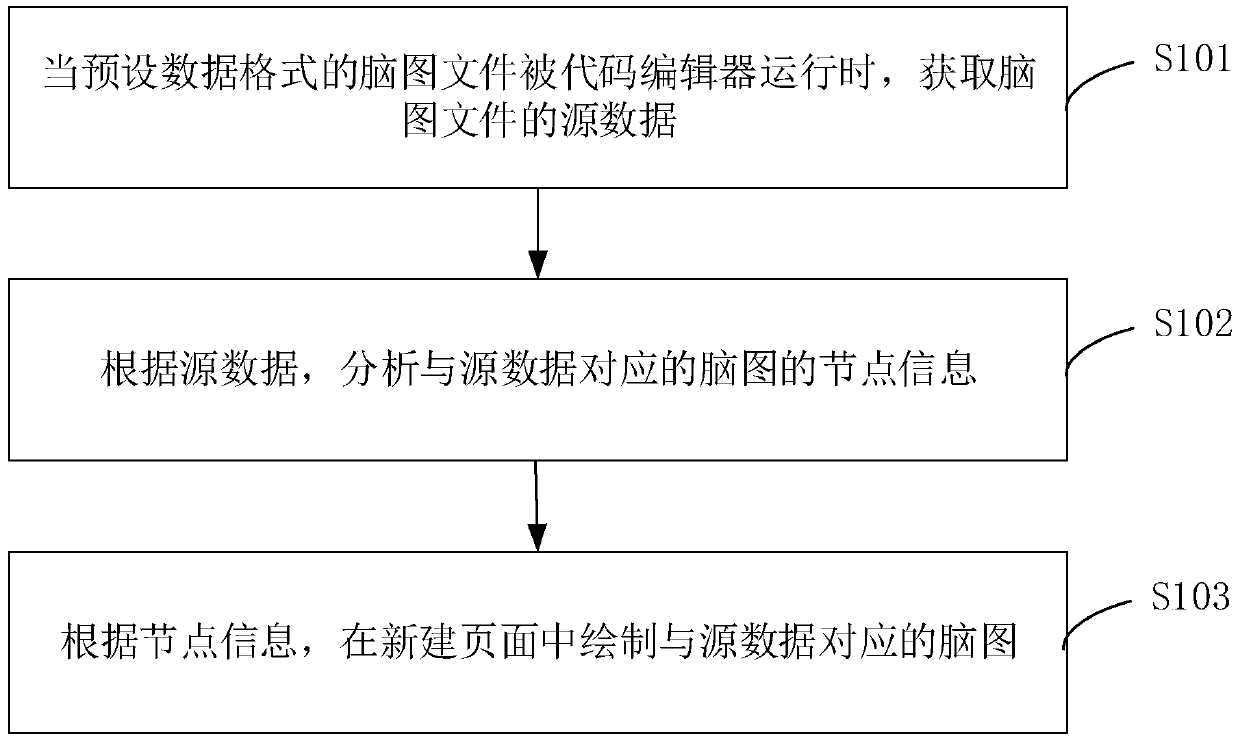
Brain map generation method and device and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN111078217AImprove user experienceAchieve normal operationSoftware engineeringSoftware testing/debuggingCode editorAlgorithm
The invention relates to a brain graph generation method and device and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises: obtaining source data of a brain graph file when the brain graph filein a preset data format is operated by a code editor; analyzing node information of the brain graph corresponding to the source data according to the source data; and drawing a brain graph corresponding to the source data in the new page according to the node information. The problem that the code editor in the related technology cannot run the brain graph file is solved, the brain graph file is run in the code editor, and the use experience of the brain graph in the code editing and testing process is improved.
Owner:浙江大搜车软件技术有限公司
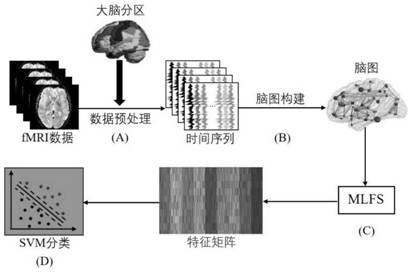
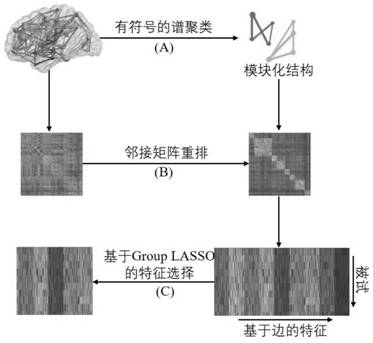
Modular feature selection method for brain disease classification
PendingCN113516186AImprove accuracySensitiveImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral clustering algorithmMedicine
The invention discloses a modular feature selection method (MLFS for short) for brain disease classification, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the preprocessing of a functional magnetic resonance image, and dividing a brain into a pre-designated brain region; extracting an average time sequence corresponding to all brain regions and constructing a functional brain map; searching modular structure information by using a signed spectral clustering algorithm; and selecting a discriminative feature through a group LASSO method based on modularization, wherein a support vector machine (SVM) is used for classification. According to the embodiment of the invention, the discriminative features in the brain map can be clearly identified by using modular information, and the method is used for brain disease classification, and has a certain reference value for studying cognitive impairment of the brain.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
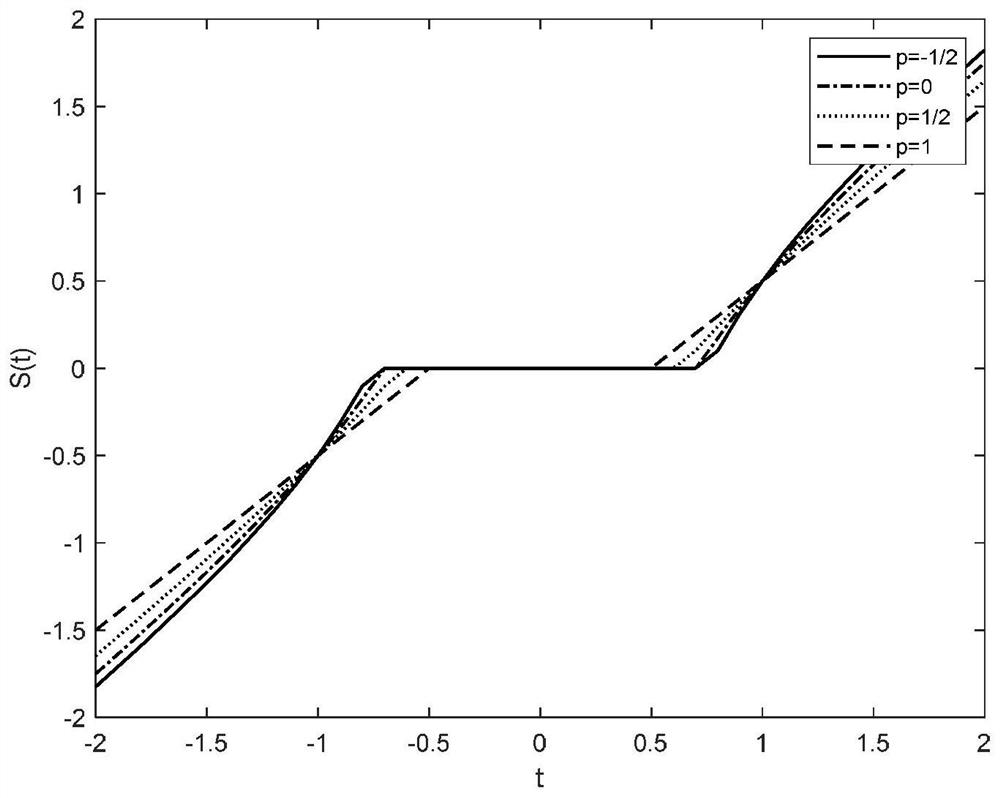
Compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method based on iterative p-threshold projection algorithm
ActiveCN112150570AImprove imaging speedImproving Imaging AccuracyReconstruction from projectionWater resource assessmentK-spaceT2 weighted
The invention discloses a compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging method based on an iterative p-threshold projection algorithm, and belongs to the field of magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: performing Fourier transform on a T2 weighted brain graph, transforming the T2 weighted brain graph subjected to Fourier transform into a K space to obtain K spacedata of the T2 weighted brain graph, and adopting the K space data of the T2 weighted brain graph according to a nonlinear sampling template to obtain T2 weighted brain graph under-sampling K space data; carrying out redundancy transformation on the T2 weighted brain graph undersampling k space data, and carrying out sparse representation on the T2 weighted brain graph undersampling k space data;and carrying out image reconstruction on the sparsely represented T2 weighted brain map undersampling k space data based on an iterative p-threshold projection algorithm or a fast iterative p-threshold projection algorithm, designing a new sparse target function by flexibly changing a p value, and achieving a better reconstruction effect .
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
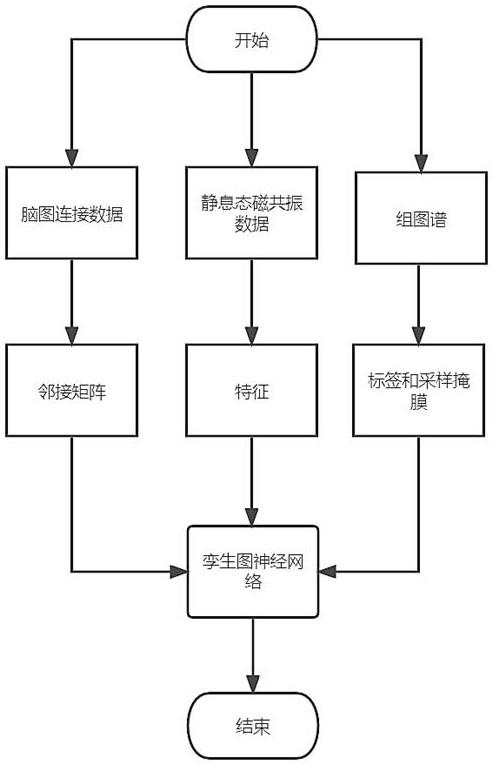
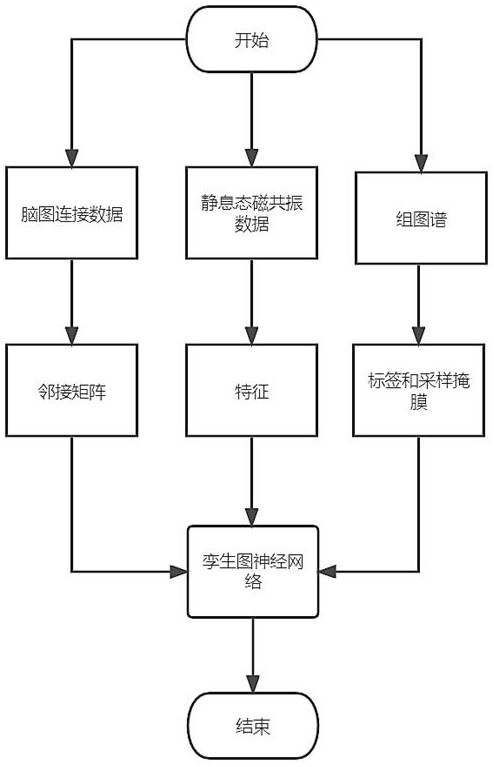
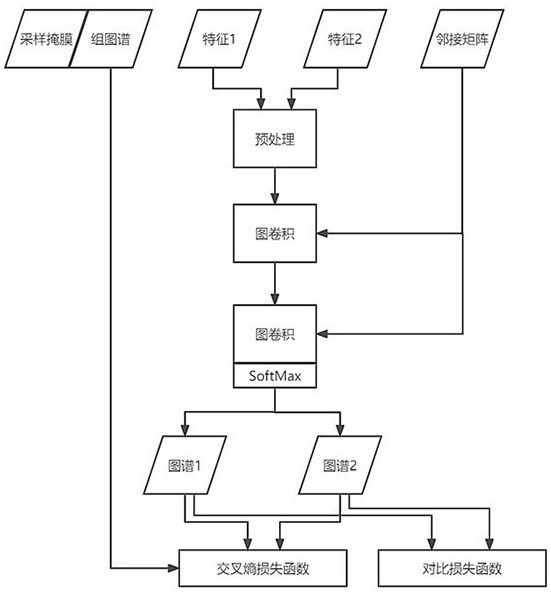
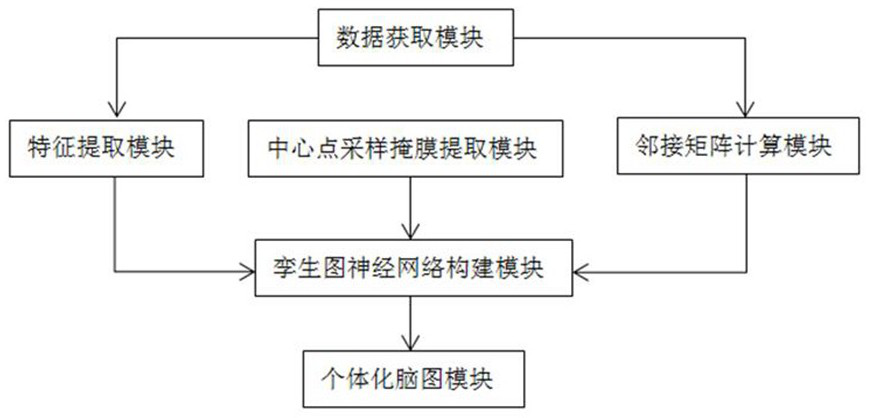
Brain map individualization method and system based on magnetic resonance and twin map neural network
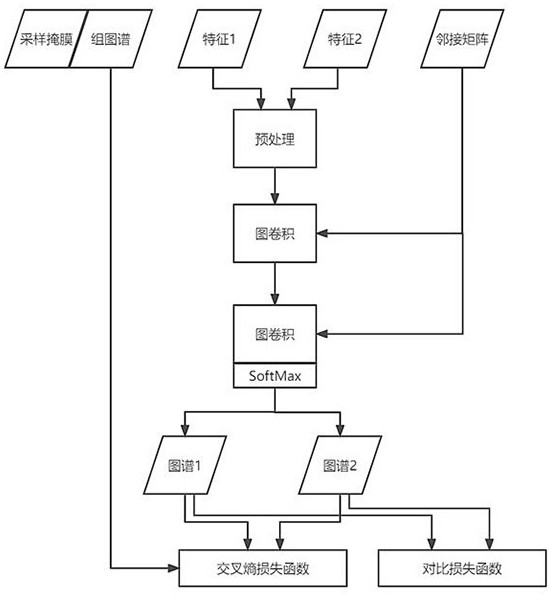
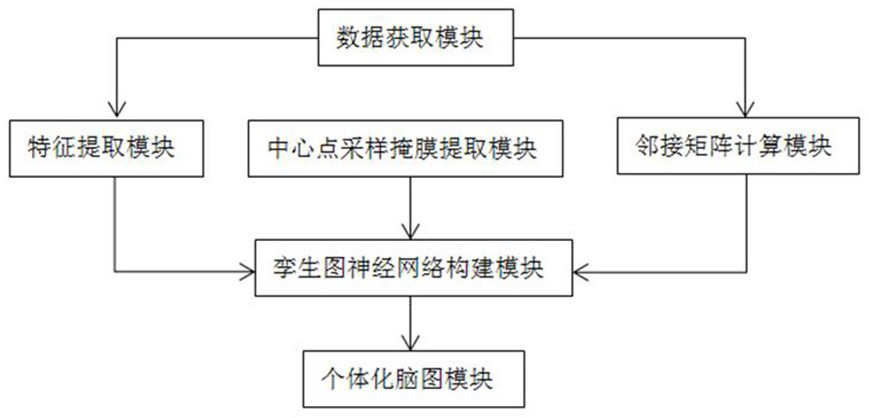
ActiveCN114376558AEnsure consistencyIncrease differentiationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPattern recognitionFunctional connectivity
The invention discloses a brain map individualization method and system based on magnetic resonance and a twin map neural network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting features from resting state functional magnetic resonance data (rs-fMRI) by using functional connection based on a region of interest, and meanwhile, carrying out Fisher transform and exponential transform on the features; secondly, extracting a corresponding adjacent matrix from the T1 weighted magnetic resonance data in the data set; and then, taking the transformed features and the adjacent matrix as input, taking a group map label and a sampling mask as output, and designing a twin map neural network for training and testing. Compared with other rs-fMRI individualized map schemes, the activation distribution of the individualized brain map reconstructed by a twin network architecture and a center sampling mode designed by utilizing the data characteristics of rs-fMRI and a group map is more uniform on the task state magnetic resonance data, and the reconstruction time is shorter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
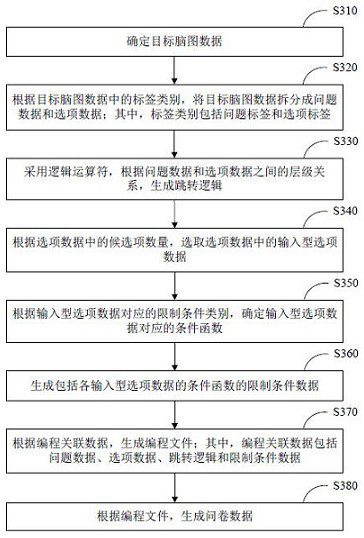
Brain map data processing method and device, equipment and storage medium
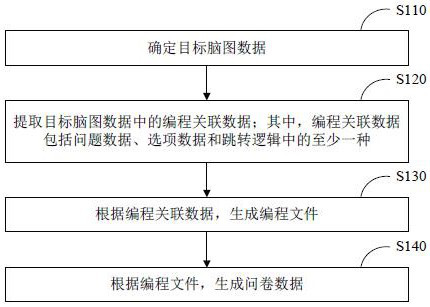
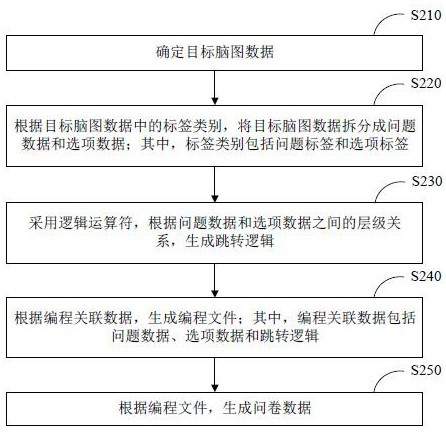
ActiveCN113050933AGenerate smart and efficientRealize automatic generationVisual/graphical programmingData ingestionData pack
The embodiment of the invention discloses a brain map data processing method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of determining target brain map data; extracting programming associated data in the target brain map data; wherein the programming associated data comprises at least one of problem data, option data and jump logic; generating a programming file according to the programming associated data; generating questionnaire data according to the programming file. Through the technical scheme, automatic generation of the questionnaire data is realized, and the questionnaire generation efficiency and the accuracy of the generated questionnaire are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TMI ROBOTICS TECH CO LTD
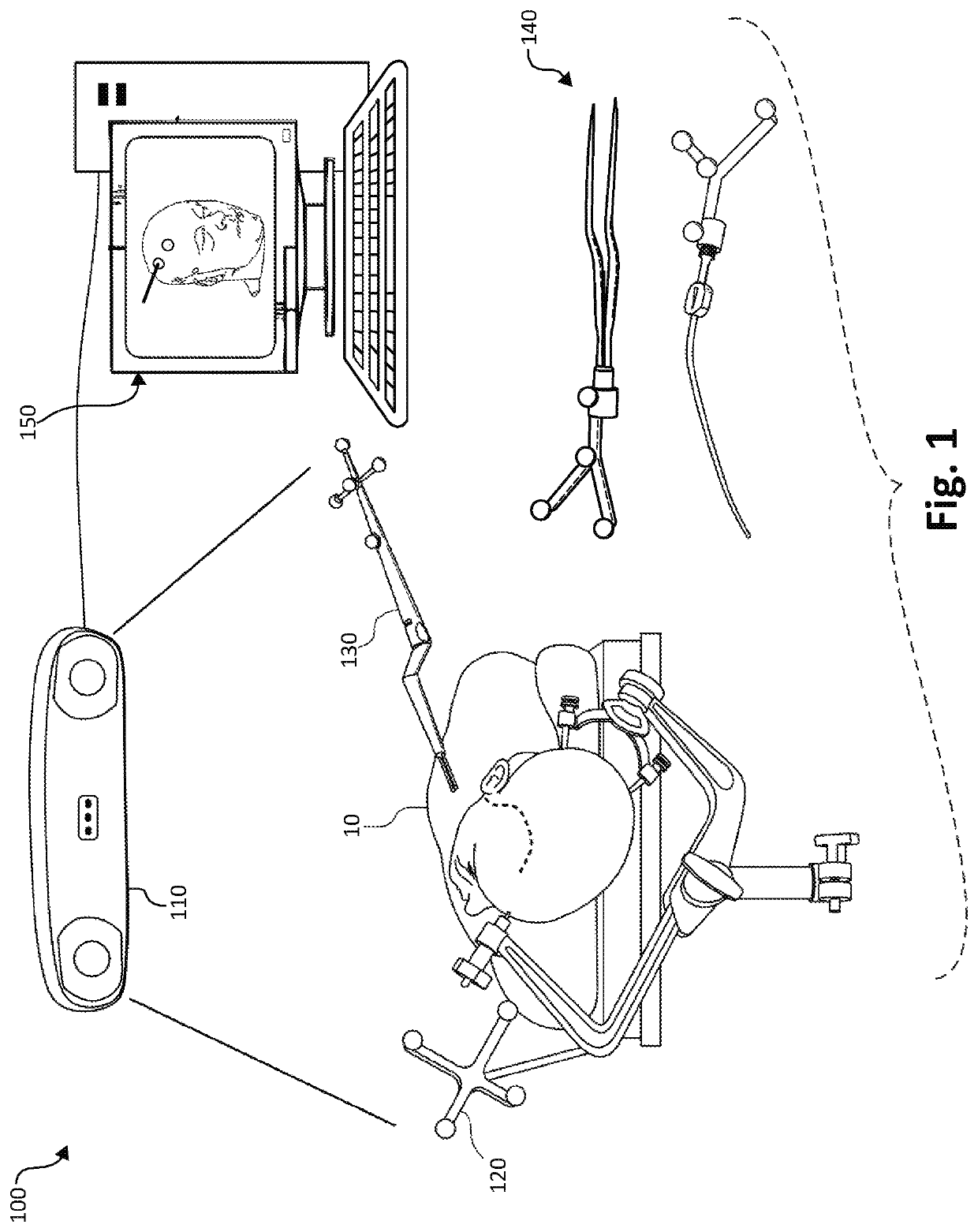
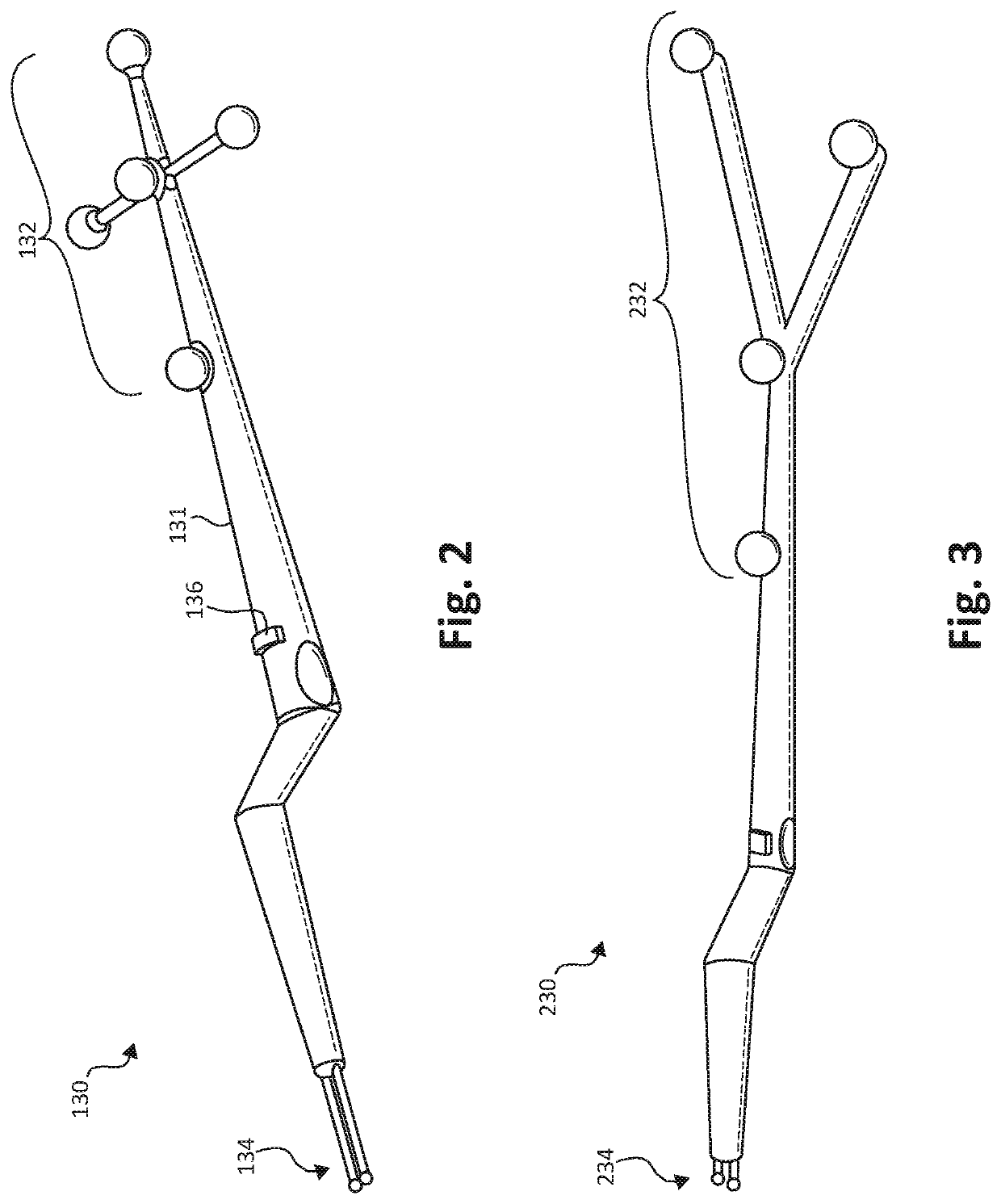
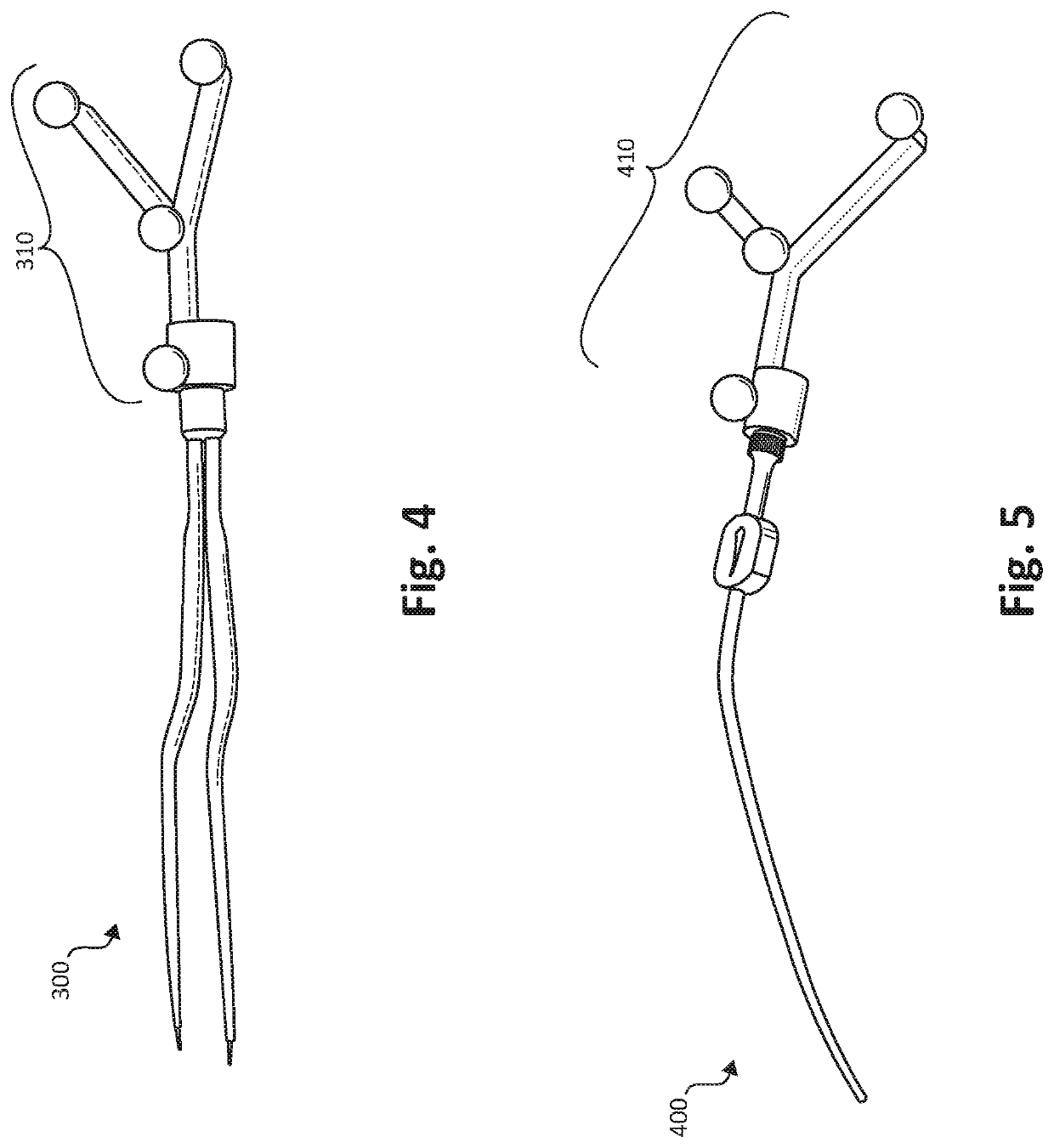
3D tracking-assisted functional brain region mapping
ActiveUS20200093547A1Maintaining awarenessIncrease stimulationHead electrodesElectromyography3d trackingEngineering
Systems and methods are described for functional brain mapping using neuronavigational equipment and additional features. For example, some implementations described combine novel cortical stimulator tools with stereotactic navigation for three-dimensional position tracking of the cortical stimulator tools. In some implementations, the systems and methods described herein can be used on an awake patient. In some implementations, the systems and methods described herein can be used on a patient that is asleep, via motor evoked potentials (MEPs), phase reversal, or electromyography (EMG) monitoring. Accordingly, in some cases sensory and language regions of the brain can be identified in addition to motor regions.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method and system for suicide risk assessment and intervention
A brain mapping system and methods that allow to predict and monitor the risk of suicide and provide personalized therapy. The brain mapping system and methods detect if brain dysfunctions (injuries) are located in suicidal hubs that trigger increased suicidal ideation and high risk of suicide. The brain mapping technology is suited for different technologies and allows to monitor the effects of therapy, provide precise therapy to decrease the risk of suicide.
Owner:ADDBRAIN INC
Brain atlas individualization method and system based on magnetic resonance and twin graph neural network
ActiveCN114376558BEnsure consistencyIncrease differentiationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFunctional connectivity
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
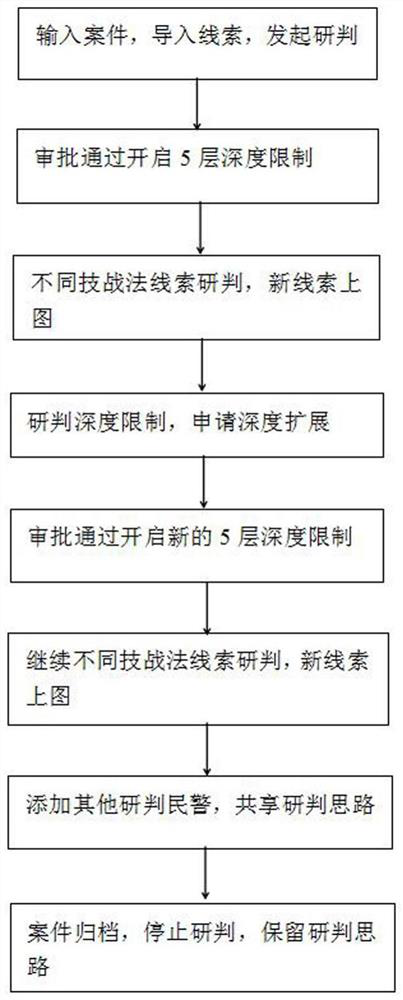
Smart brain graph investigation method
PendingCN112256788AImprove investigation efficiencySolving Dispersion ProblemsData processing applicationsVisual data miningPhysical medicine and rehabilitationInvestigation methods
Owner:ZHUHAI XINDEHUI INFORMATION TECH
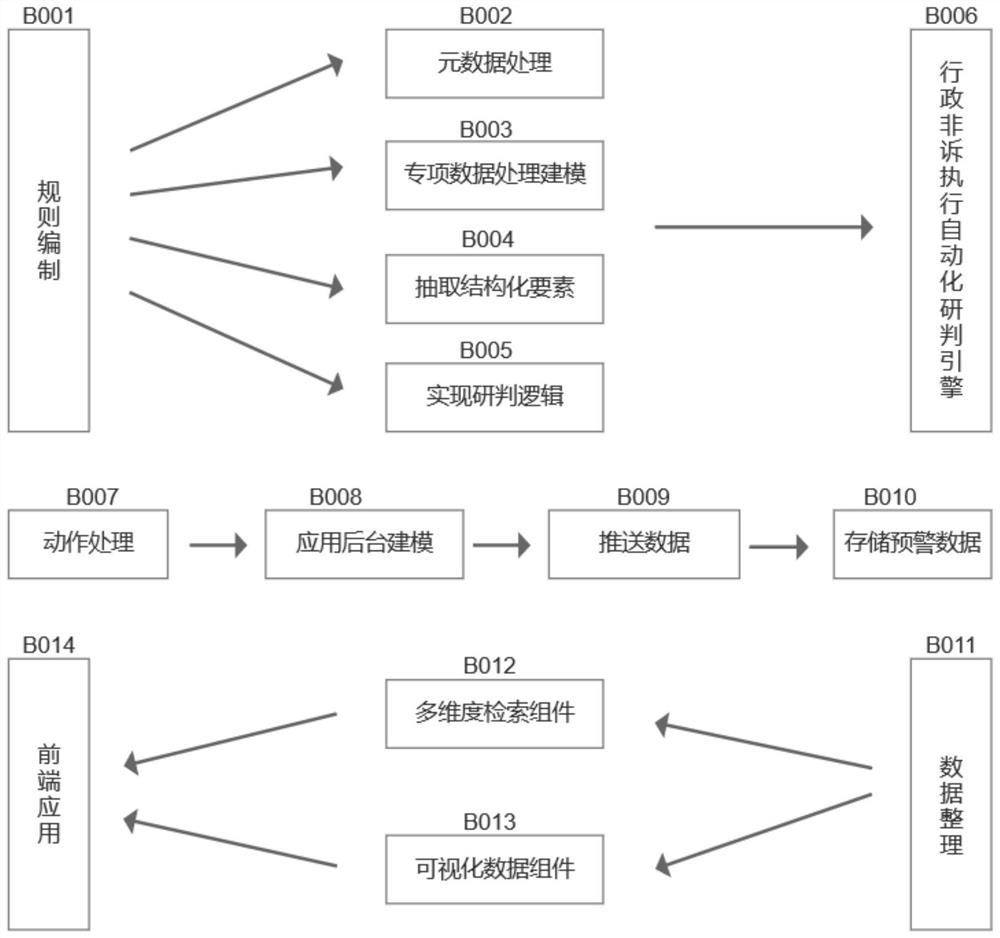
Method for automatically identifying administrative non-complaint execution case source
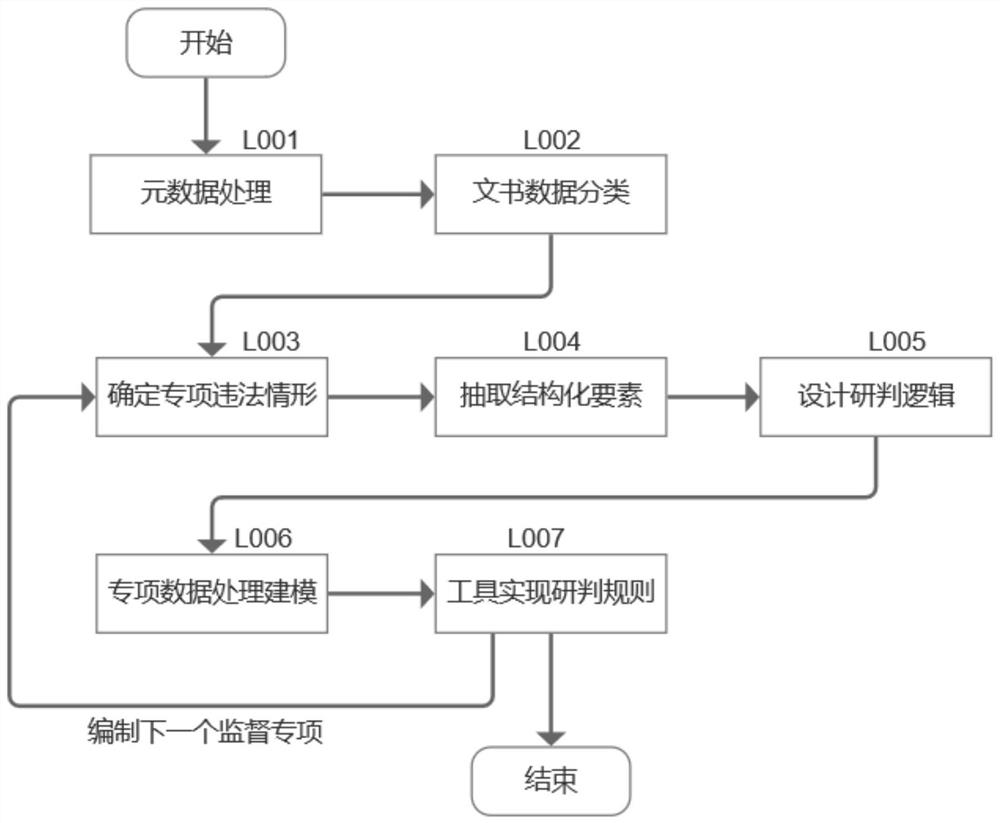
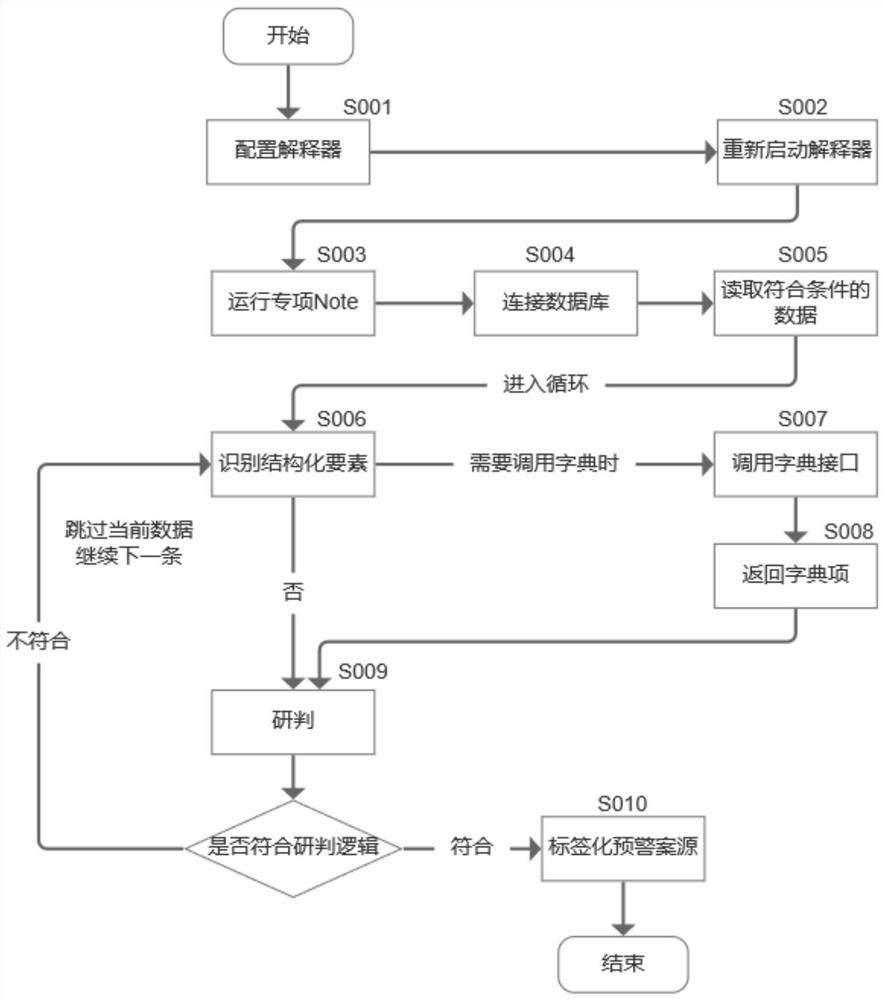
PendingCN113901034AImprove case handling efficiencySolve technical problems foundMetadata text retrievalData processing applicationsEngineeringData mining
The invention discloses a method for automatically identifying an administrative non-complaint execution case source. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, compiling a rule; 2, performing automatic study and judgment; step 3, performing action processing; and step 4, performing front-end application. The invention specifically comprises researching and judging administrative inspection case source data including judgment documents and administrative punishment decisions through an administrative non-complaint execution automation engine; marking an early warning case source in a tagging mode; carrying out the links of model processing, case source pushing and the like; presenting administrative non-complaint execution early warning case source data, legal basis, supervision key points, brain maps, case handling guidance and other data visually to case handling procurators. The method can be applied to the field of administrative inspection and supervision, assists a procurator in case handling decision making, improves case handling efficiency, improves the ability of administrative inspection case source discovery, and improves judicial authority and judicial credibility while saving judicial resources and maintaining normal judicial order.
Owner:CHANGCHUN JIACHENG NETWORK ENG
Brain map generation method and device based on picture input, equipment and storage medium
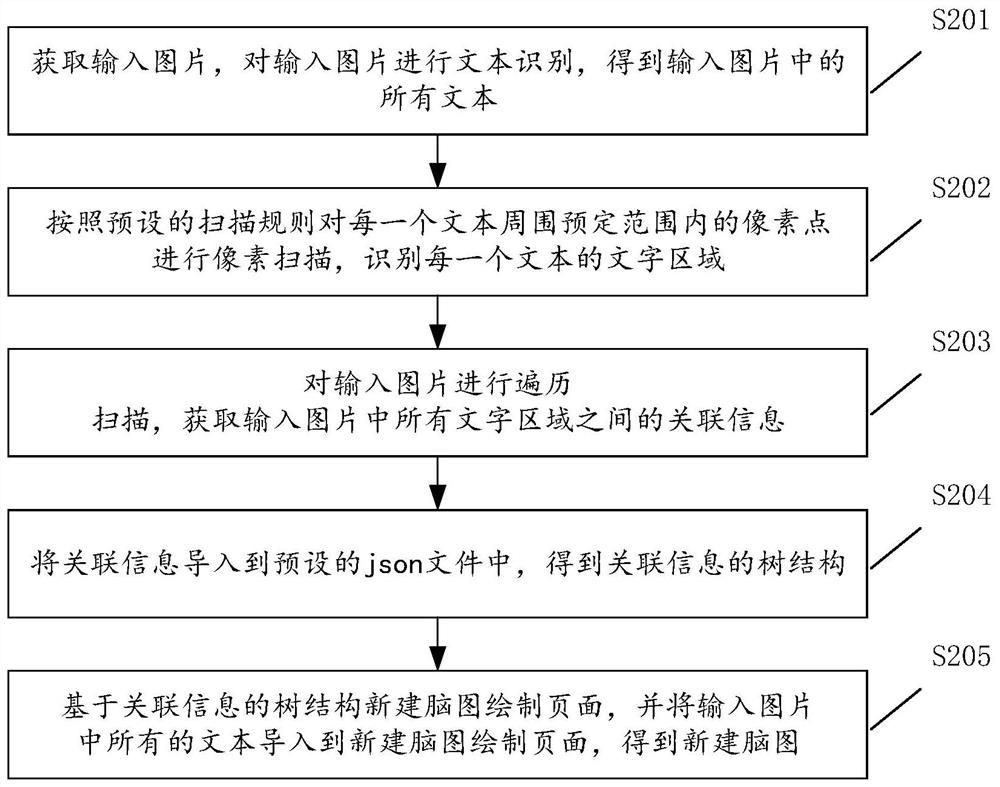
PendingCN112395834AAchieve conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingText recognitionMedicine
The invention discloses a brain graph generation method and device based on picture input, equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence. The method comprises the steps of performing text recognition on an input picture to obtain all texts in the input picture; scanning pixels in a predetermined range around each text, and identifying a text area ofeach text; carrying out traversal scanning on the input picture to obtain associated information between the character areas; importing the associated information into a preset json file to obtain a tree structure of the associated information; and newly establishing a brain map drawing page based on the tree structure of the associated information, and importing all texts in the input picture into the newly built brain map drawing page to obtain a newly built brain map. In addition, the invention also relates to a blockchain technology, and the relation object can be stored in the blockchain.According to the method and the device, the file imported from the picture style can be converted into the file in the brain graph format, so that a user can conveniently check and edit the file imported from the picture style on a brain graph tool.
Owner:PINGAN PUHUI ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT CO LTD
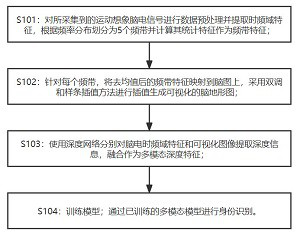
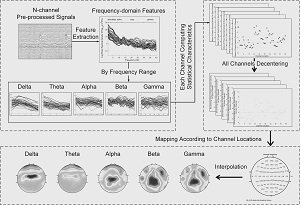
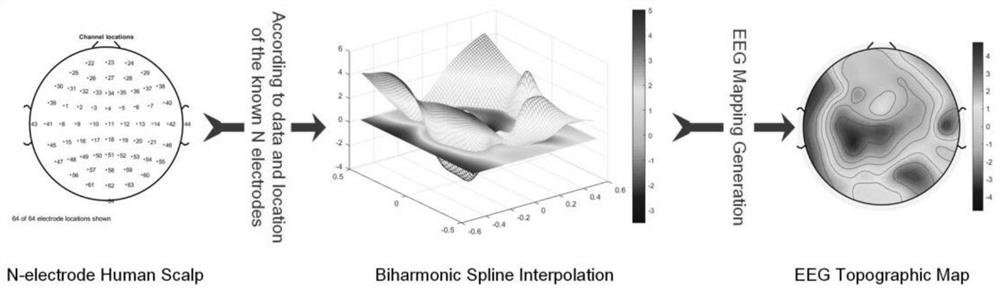
Electroencephalogram identity recognition method based on feature visualization and multi-modal fusion
PendingCN114578963AImprove accuracyEffects of biometric performance on effective discriminationInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionIdentity recognitionTopographical mapping
The invention discloses an electroencephalogram identity recognition method based on feature visualization and multi-modal fusion. The electroencephalogram identity recognition method comprises the following steps that firstly, data preprocessing is conducted on motor imagery electroencephalogram signals; secondly, aiming at each frequency band, mapping frequency band characteristics after mean value removal to a brain map according to electrode positioning of a human cerebral cortex, and performing interpolation by adopting a biharmonic spline interpolation method to generate a visual brain topographic map; then, depth information is extracted from the electroencephalogram time-frequency domain features and the electroencephalogram visualized image features through a deep network, and the electroencephalogram time-frequency domain features and the electroencephalogram visualized image features are fused on the same dimension to serve as multi-modal depth features; for each frequency band, an effective depth feature extractor and a multi-modal classifier are obtained through training, and a frequency band model with the highest performance is used as an identity recognition model of the system. The electroencephalogram visualization feature representation can reflect channel position information, meanwhile, potential electroencephalogram information of an uncollected electrode can be mined, and the complementary relation between image features and traditional vector features is deeply mined.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Panoramic brain map rapidly familiar with open platform merchant system docking
PendingCN110647633AIntuitive panoramic cognitionConvenient docking workFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsOpen platform
The invention relates to a panoramic brain graph capable of being quickly familiar with open platform merchant system docking. The panoramic brain graph comprises an information acquisition module, agraph generation module, a graph processing module and a graph display module, wherein the generated panoramic brain graph comprises four hierarchical structures; the first level is provided with service subsystems in butt joint with the platform system. The second level is provided with a butt joint mode selection module; the third level is provided with a distribution mode selection module; andthe fourth level is provided with an interface name, and the platform displays the corresponding merchant docking panoramic brain map on the first-focus page according to different BU type merchants,so that the merchants have more intuitive panoramic cognition on system docking, and the docking work is more convenient, comprehensive and efficient.
Owner:达疆网络科技(上海)有限公司
Deep neural network model reinforcing method based on distributed brain-like graph
PendingCN114048837APreserve integrityClose connectionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
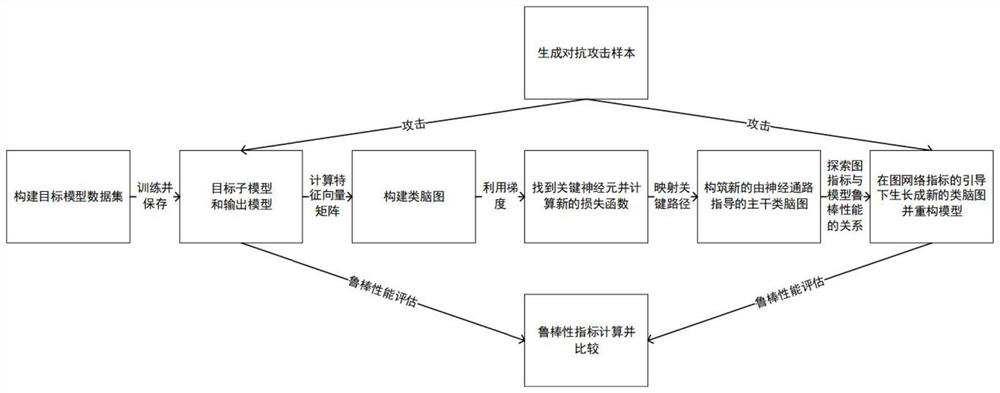
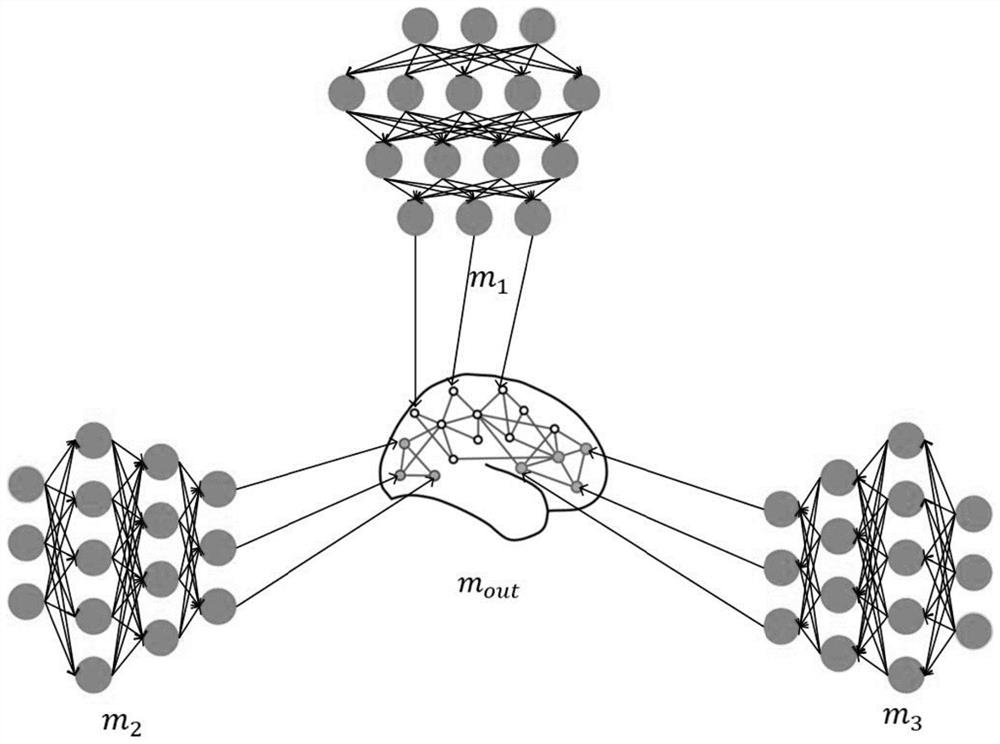
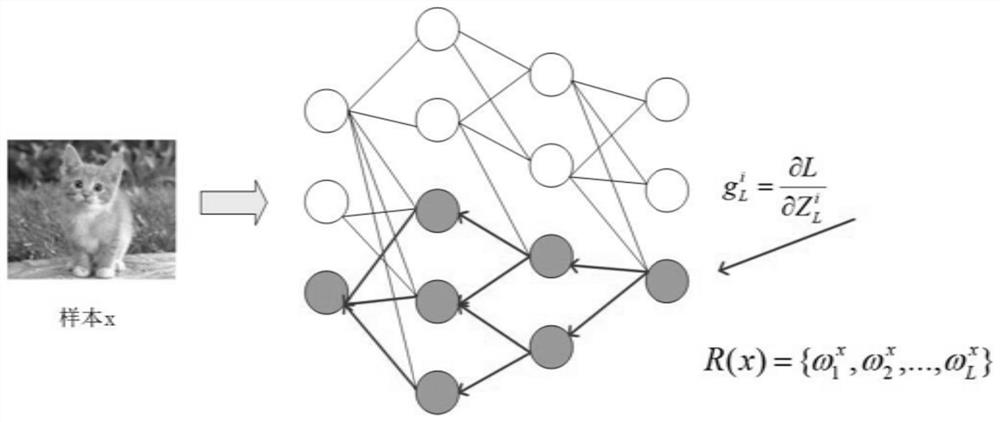
The invention discloses a deep neural network model reinforcing method based on a distributed brain-like graph. According to the method, a key path is applied to a distributed brain-like graph to generate a trunk brain-like graph to carry out more effective constraint on a propagation process and node behaviors on the path, for example, a new gradient loss function is constructed to weaken propagation of noise, so that a new robust brain-like graph structure is grown on the trunk brain-like graph guided by the key path by utilizing graph network indexes such as a length of the feature path and participation coefficients and is reconstructed back to a model, the robustness of the model is improved, and the model is reinforced. According to the method provided by the invention, a brain-like graph is used for showing closer contact with a biological neural network, only some key neurons in the neural network are operated, and the integrity of the neural network is greatly reserved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for suicide risk assessment and intervention
A brain mapping system and methods that allow to predict and monitor the risk of suicide and provide personalized therapy. The brain mapping system and methods detect if brain dysfunctions (injuries) are located in suicidal hubs that trigger increased suicidal ideation and high risk of suicide. The brain mapping technology is suited for different technologies and allows to monitor the effects of therapy, provide precise therapy to decrease the risk of suicide.
Owner:ADDBRAIN INC
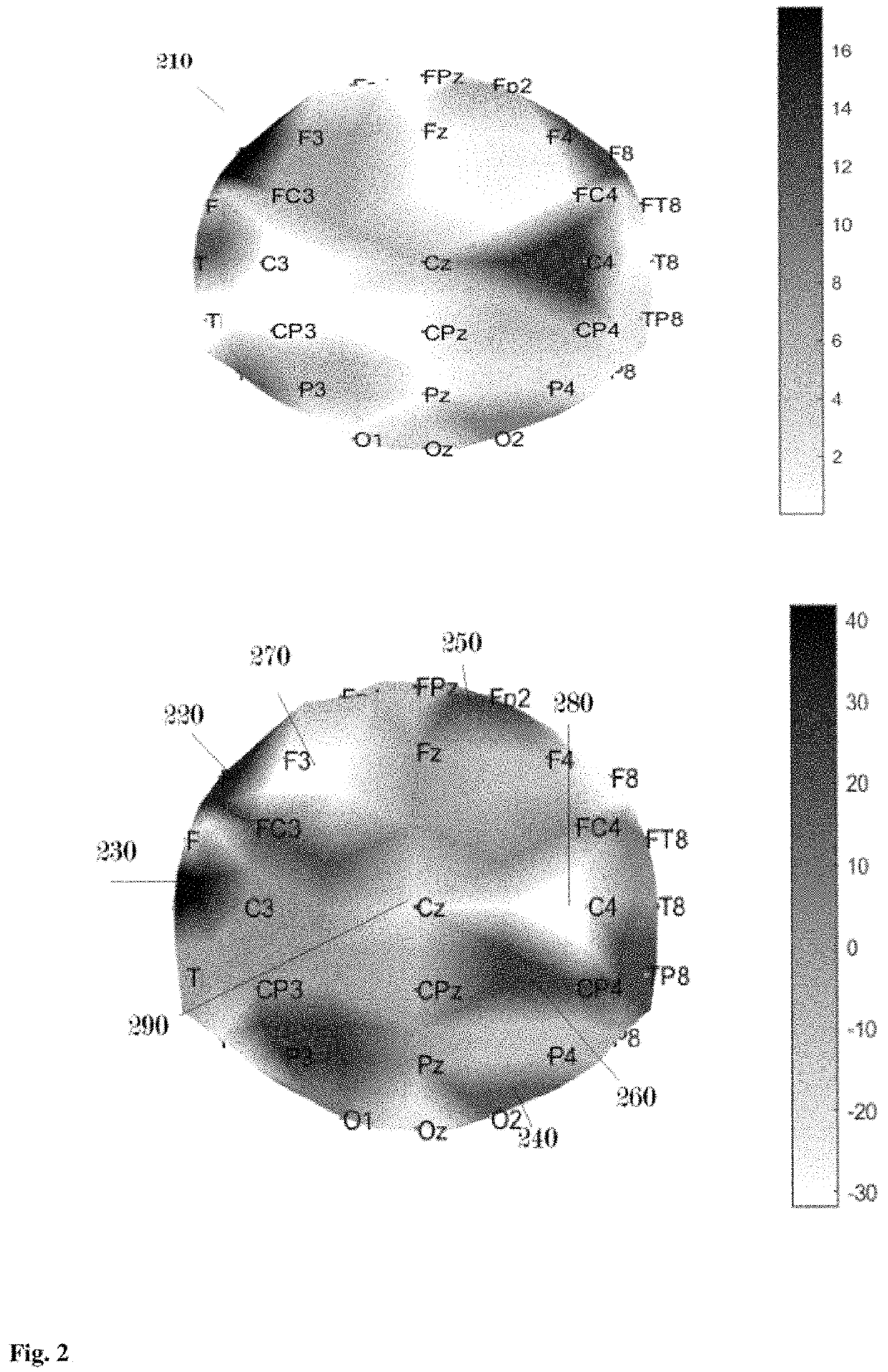
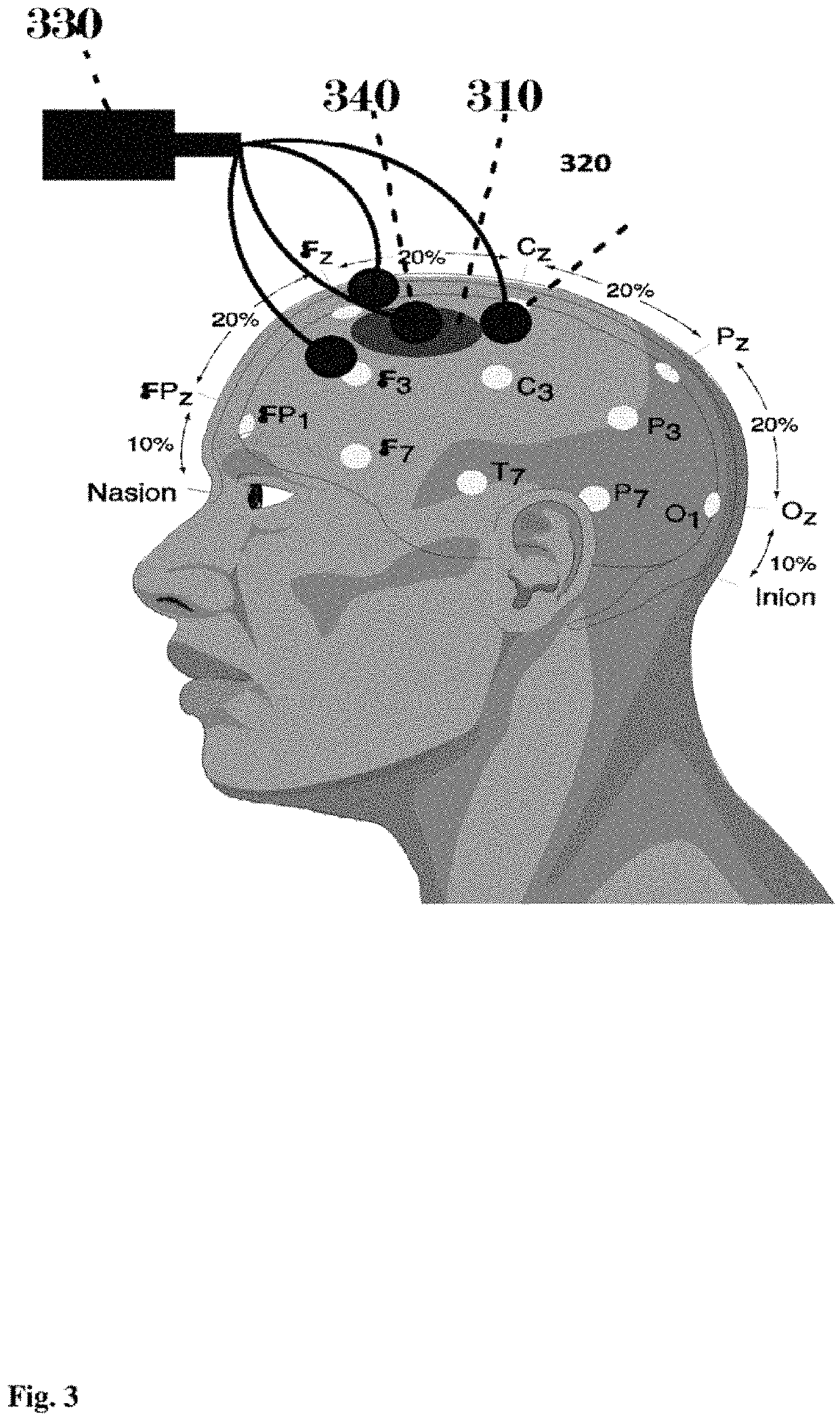
Neurotransmitter-based brain mapping method and use of brain map
PendingUS20220113288A1Eliminate the effects ofUnderstand clearlyComponent separationMass spectrometric analysisSerotoninMetabolite
An embodiment pertains to a method for evaluating efficacy of a drug which increases or decreases the secretion of a particular neurotransmitter, by measuring a concentration change of the particular neurotransmitter in a specific intracerebral site with reference to a brain map, the method comprising the steps of: selecting as a microdialysis target region in the brain map a first site of an animal, which corresponds to a site that the brain map represents as being the highest in the concentration of a first neurotransmitter of which the secretion is increased or decreased by the drug; and injecting the drug to the animal and monitoring a concentration change of the first neurotransmitter in the first site between pre- and post-injection of the drug. The brain map is constructed by acquiring a concentration distribution of 11 or more multiple neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, GABA, glutamate, and metabolites thereof, obtained by mass analysis of samples acquired from multiple sites in the human brain—hereinafter referred to as first concentration distribution—and a concentration distribution of 11 or more multiple neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, GABA, glutamate, and metabolites thereof, obtained by mass analysis of samples acquired from multiple sites in a monkey brain—hereinafter referred to as second concentration distribution—, and utilizing first correlation including at least 11 correlation data resulting from matching the multiple sites of the human brain to the multiple sites of the monkey brain on the basis of similarity in the concentration distribution of the individual neurotransmitters between the first concentration distribution acquired and the second concentration distribution acquired, and the second concentration distribution, wherein the first site corresponds to a second site in the second concentration distribution when the first neurotransmitter is the most abundant at the second site in the first concentration distribution.
Owner:NEUROVIS CO
Case management method and device based on brain map and storage medium
PendingCN114461518AImprove editing efficiencyRealize managementSoftware testing/debuggingExecution for user interfacesComputer graphics (images)Theoretical computer science
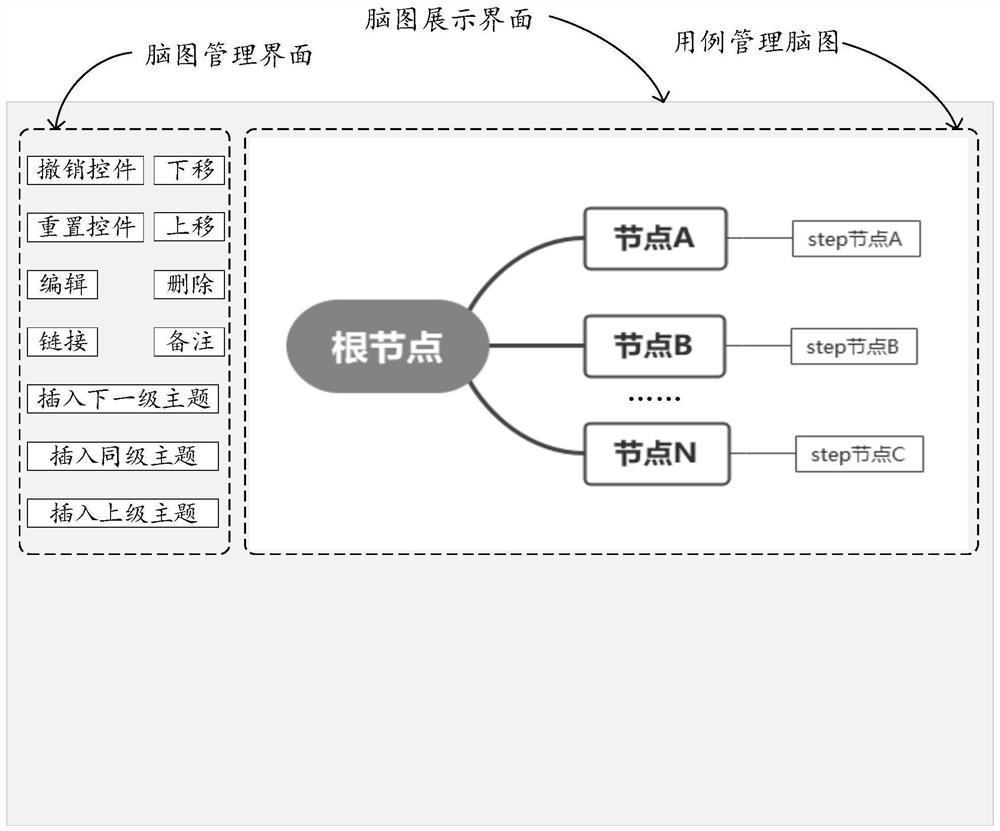
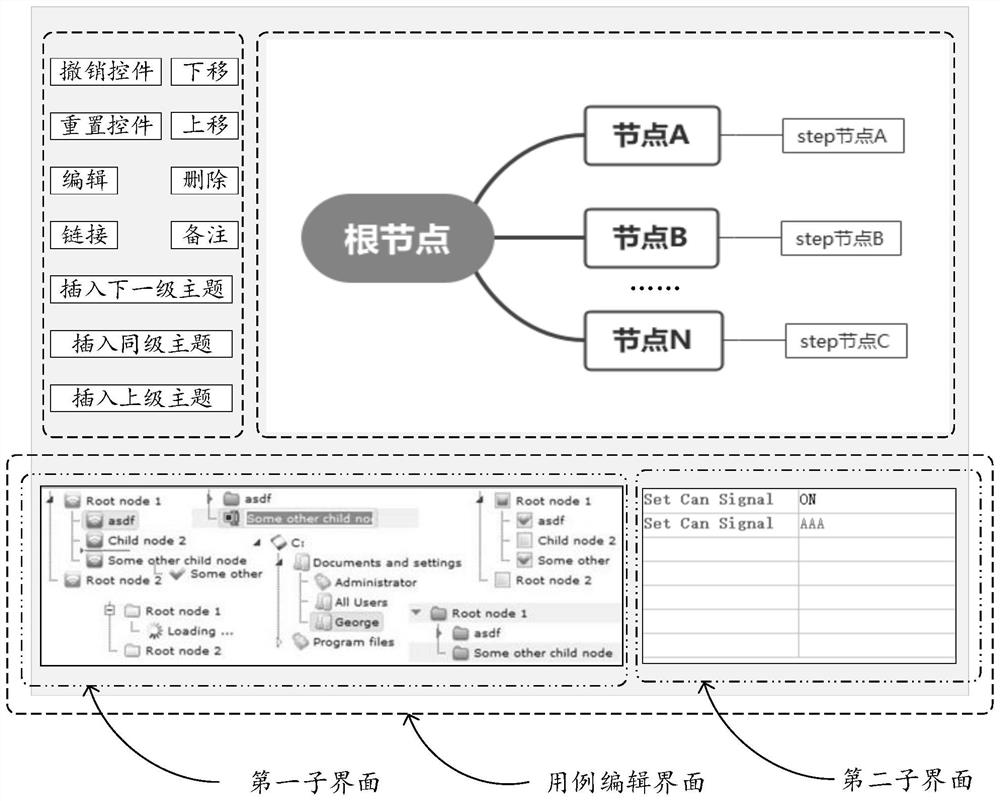
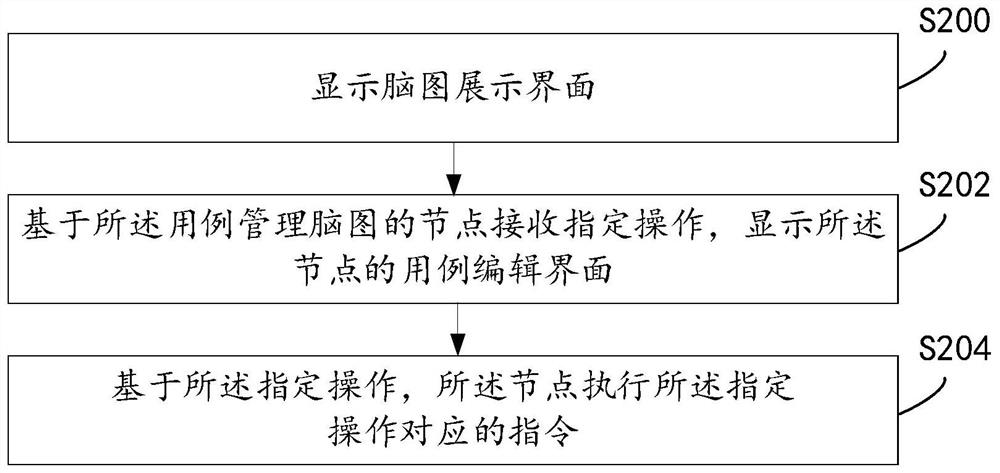
The invention discloses a use case management method and device based on a brain graph and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: displaying a brain graph display interface; wherein a useful case management brain map is displayed in the brain map display interface; receiving a specified operation based on a node of the use case management brain graph, and displaying a use case editing interface of the node; wherein the use case editing interface is used for editing information of use cases corresponding to the nodes, and a plurality of pieces of associated information capable of serving as the information of the use cases are displayed in the use case editing interface; based on the specified operation, the node executes an instruction corresponding to the specified operation, and the specified operation comprises at least one of use case editing, testing and classification tree orthogonal testing. According to the method in the specification, editing of the use case does not depend on a large amount of manual operation any more, so that human resources are saved, and the editing efficiency of the use case is greatly improved.
Owner:上海集度汽车有限公司
Global brain map construction method and system based on system thinking
PendingCN113495930ARealize entryImprove efficiencyRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsSystems thinkingGeneration process
The invention discloses a global brain map construction method and system based on system thinking, and belongs to the field of brain working mechanism simulation. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a global brain map based on system thinking for thinking emergence; firstly, building a unified thought knowledge base; forming a thinking map by newly creating thinking elements, and constructing a global brain map; then, performing correlation analysis, searching a closed loop, and realizing brain thinking emerging; meanwhile, developing a parallel brain software system, simulating the thinking mode of the brain to record and integrate knowledge, information and thoughts, performing deep mining, and simulating and reproducing the new thought generation process of the human brain. The method and system designed by the invention can help people to realize efficient knowledge management, improve the efficiency of cognizing things, assist people in forming new ideas, boost personal inspiration burst, accelerate information sharing among teams and effectively promote team cooperation.
Owner:牟善军
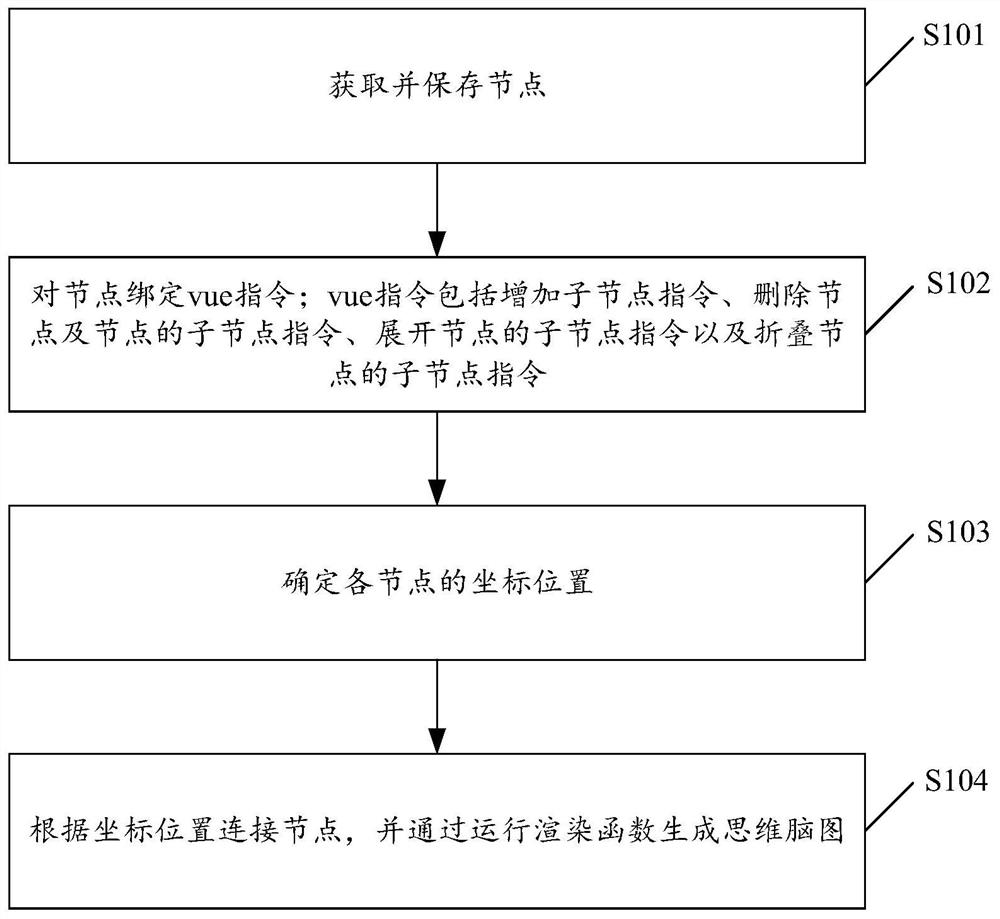
Vue-based thinking brain map drawing method and related device
PendingCN113628301AImprove interactivityMeet needsDrawing from basic elementsInput/output processes for data processingUser needsPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:HANGZHOU ANHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Brain map case set generation method and device
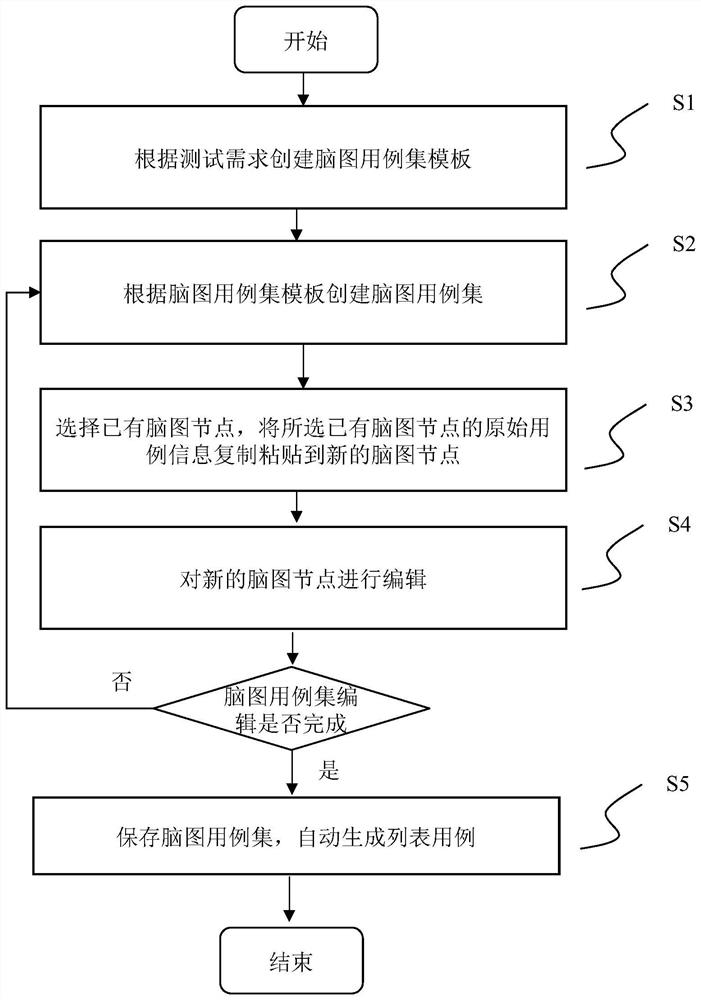
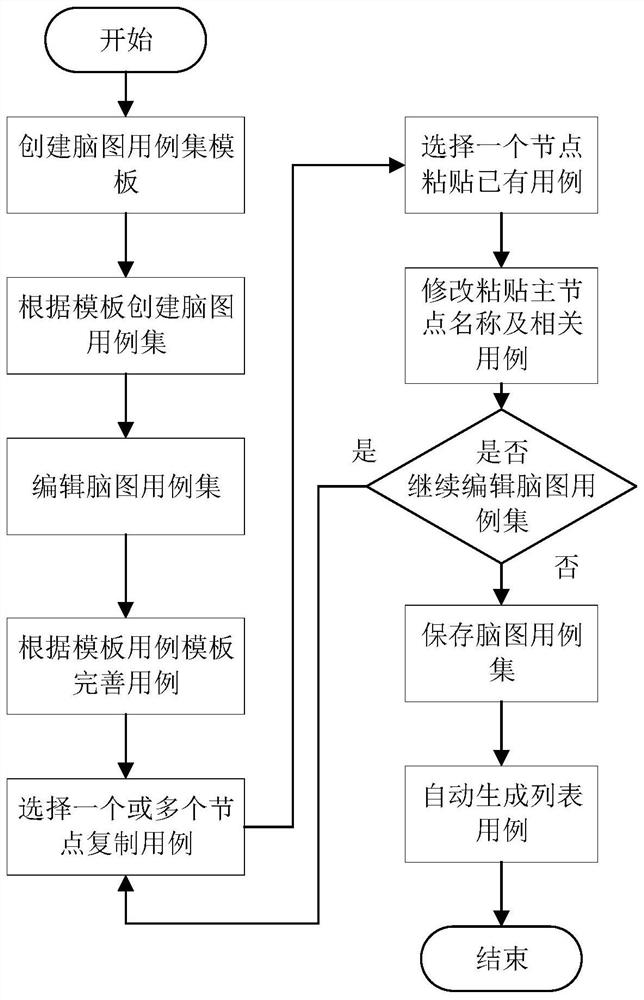
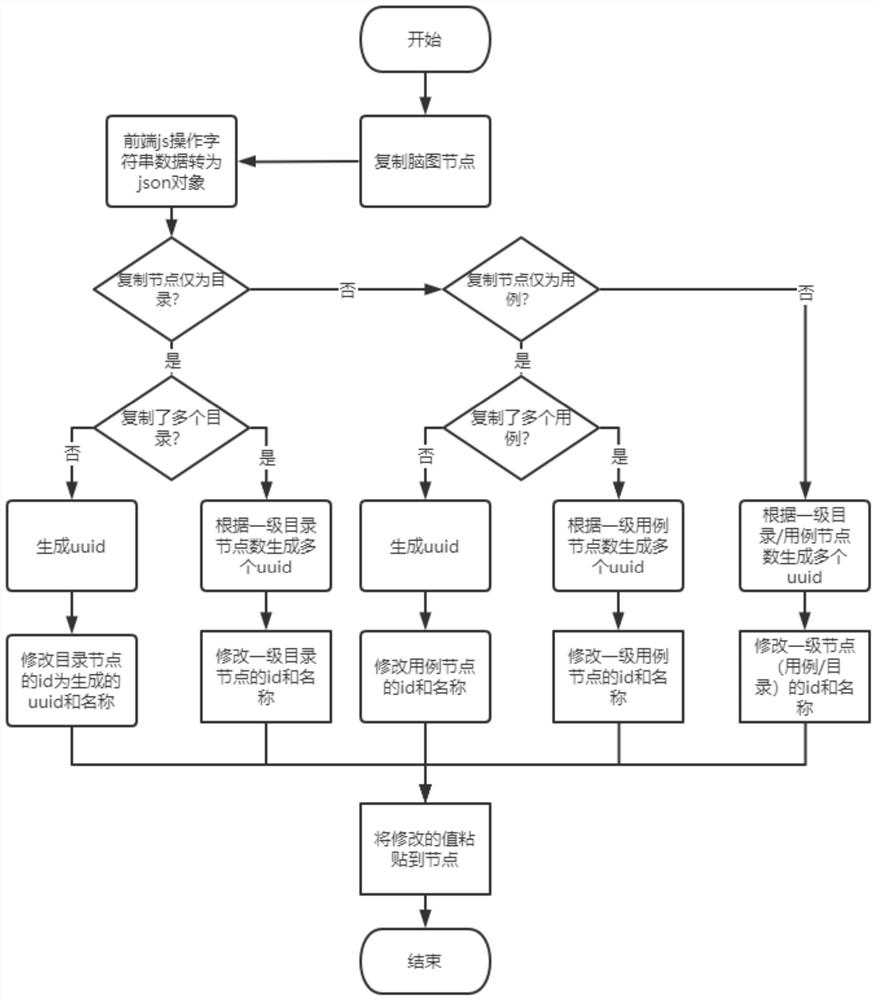
PendingCN113886241AImprove experienceAccurate and automatic generationInterprogram communicationSoftware testing/debuggingTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
The invention relates to the field of computer program testing, in particular to a brain map case set generation method and device. The invention provides a brain map case set generation method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, creating a brain map case set template according to a test requirement; s2, creating a brain map case set according to the brain map case set template; s3, selecting existing brain map nodes, copying and pasting original use case information of the selected existing brain map nodes to new brain map nodes, and modifying identity identification codes and node names of first-level nodes in the new brain map nodes; step S4, editing the new brain map nodes; and S5, repeating the steps S2-S4 until the brain map use case set is edited, storing the brain map use case set, and automatically generating a list use case. According to the invention, through rapid pasting and copying of the new brain map catalog and the use case node, only the first-level node is processed, the front-end performance is optimized, and the user experience when the brain map is accessed and edited is improved.
Owner:上海汇付支付有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com