Patents
Literature
146 results about "Arch form" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In music, arch form is a sectional structure for a piece of music based on repetition, in reverse order, of all or most musical sections such that the overall form is symmetric, most often around a central movement. The sections need not be repeated verbatim but must at least share thematic material.
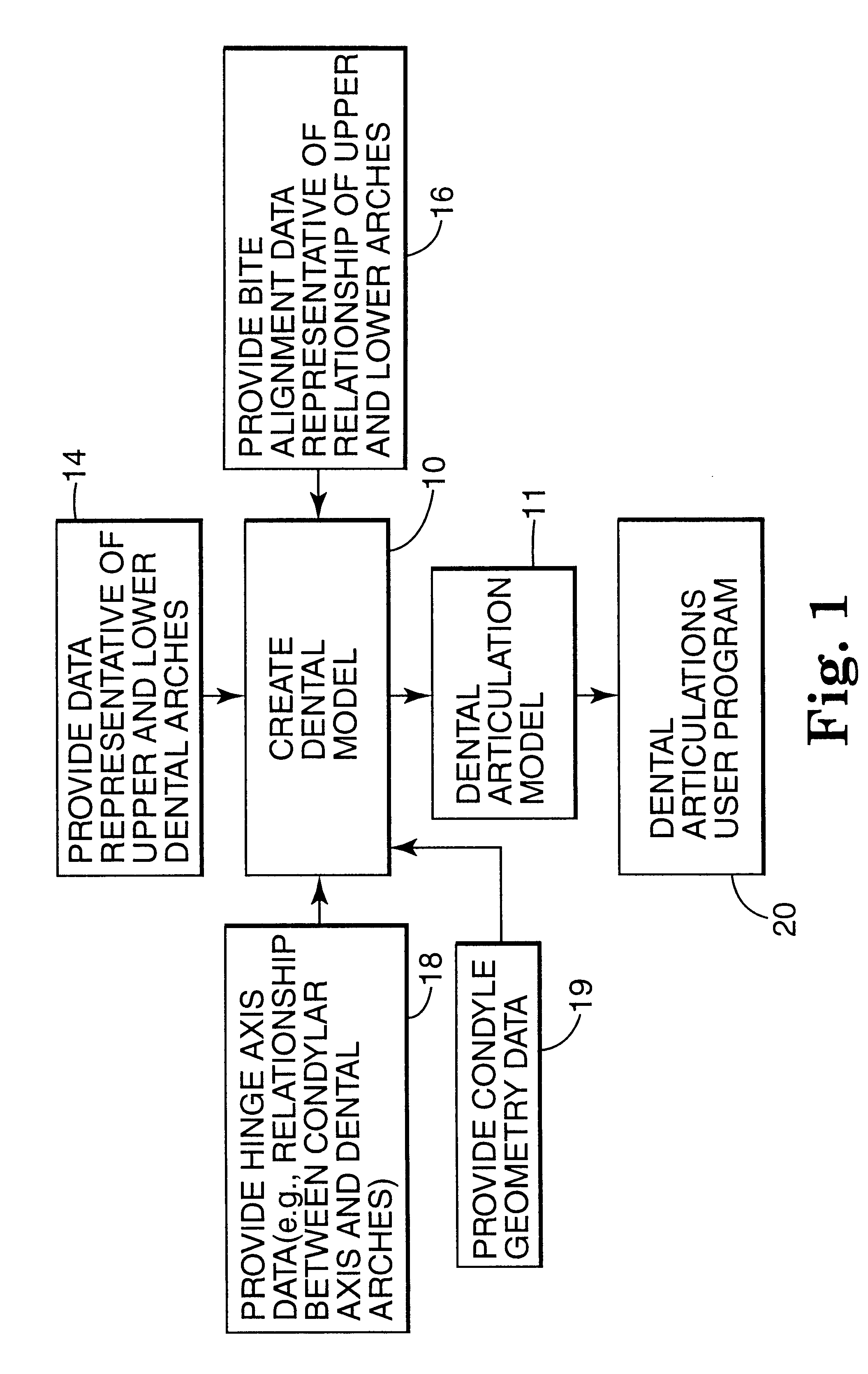
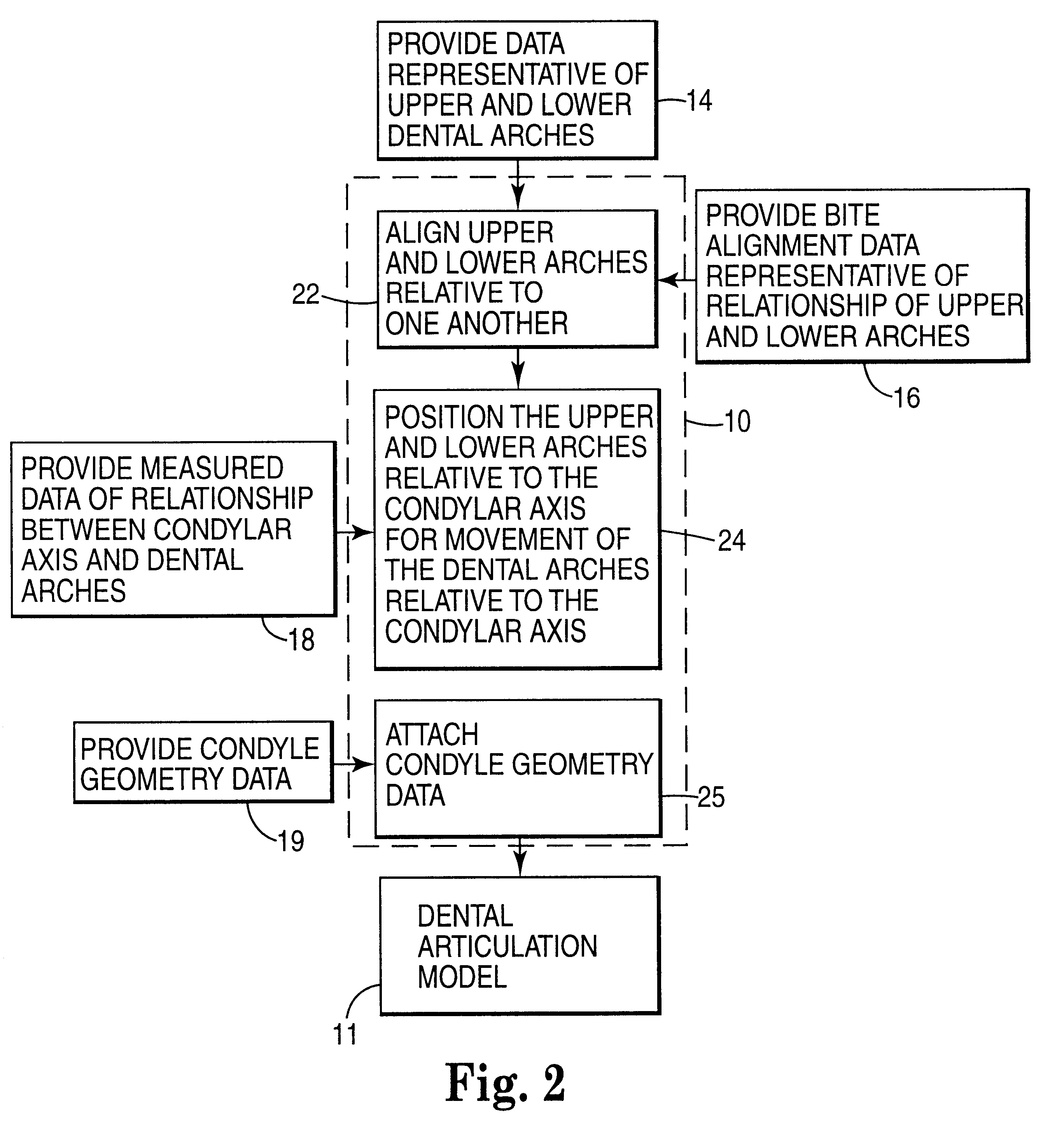
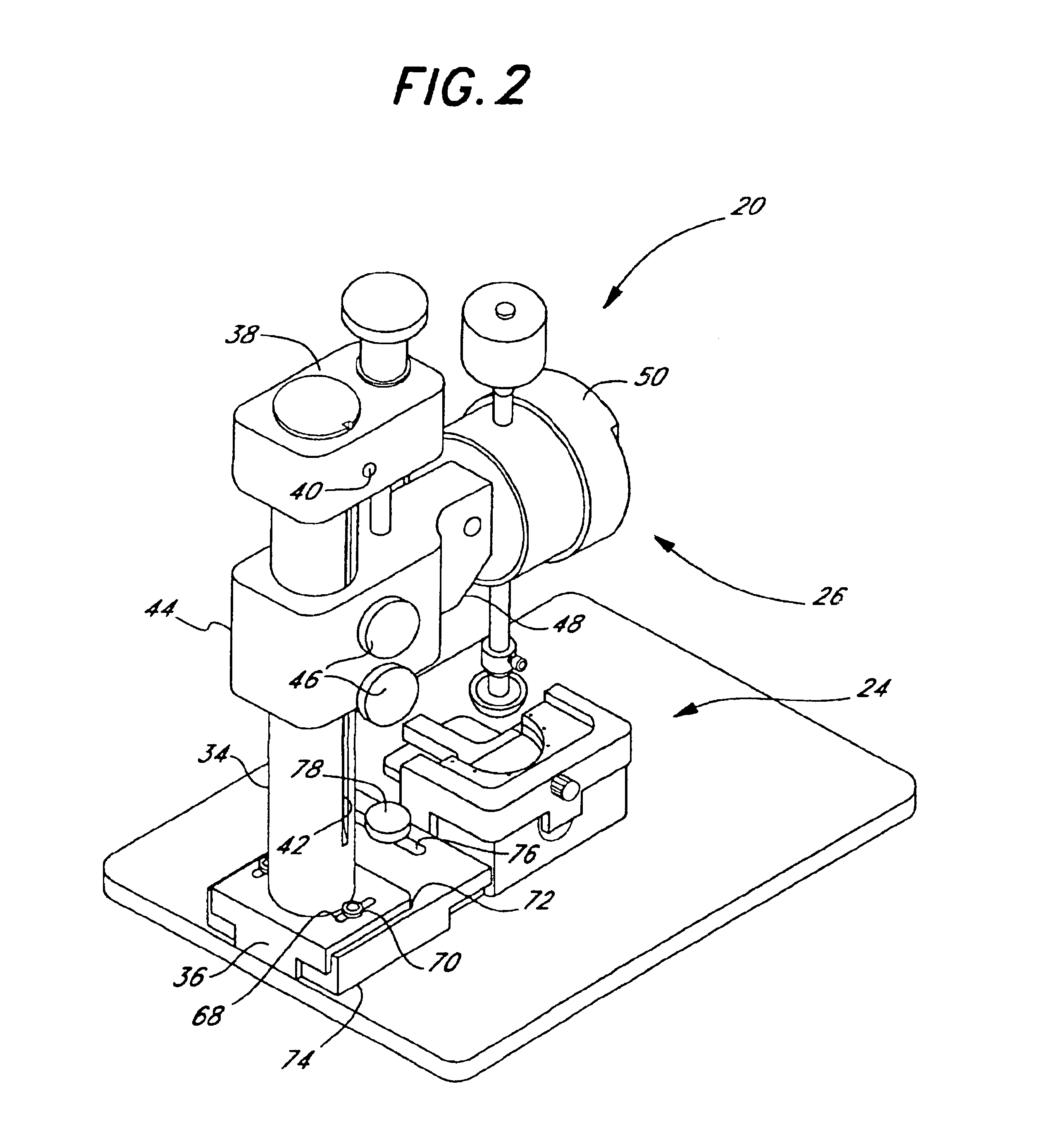
Methods for use in dental articulation
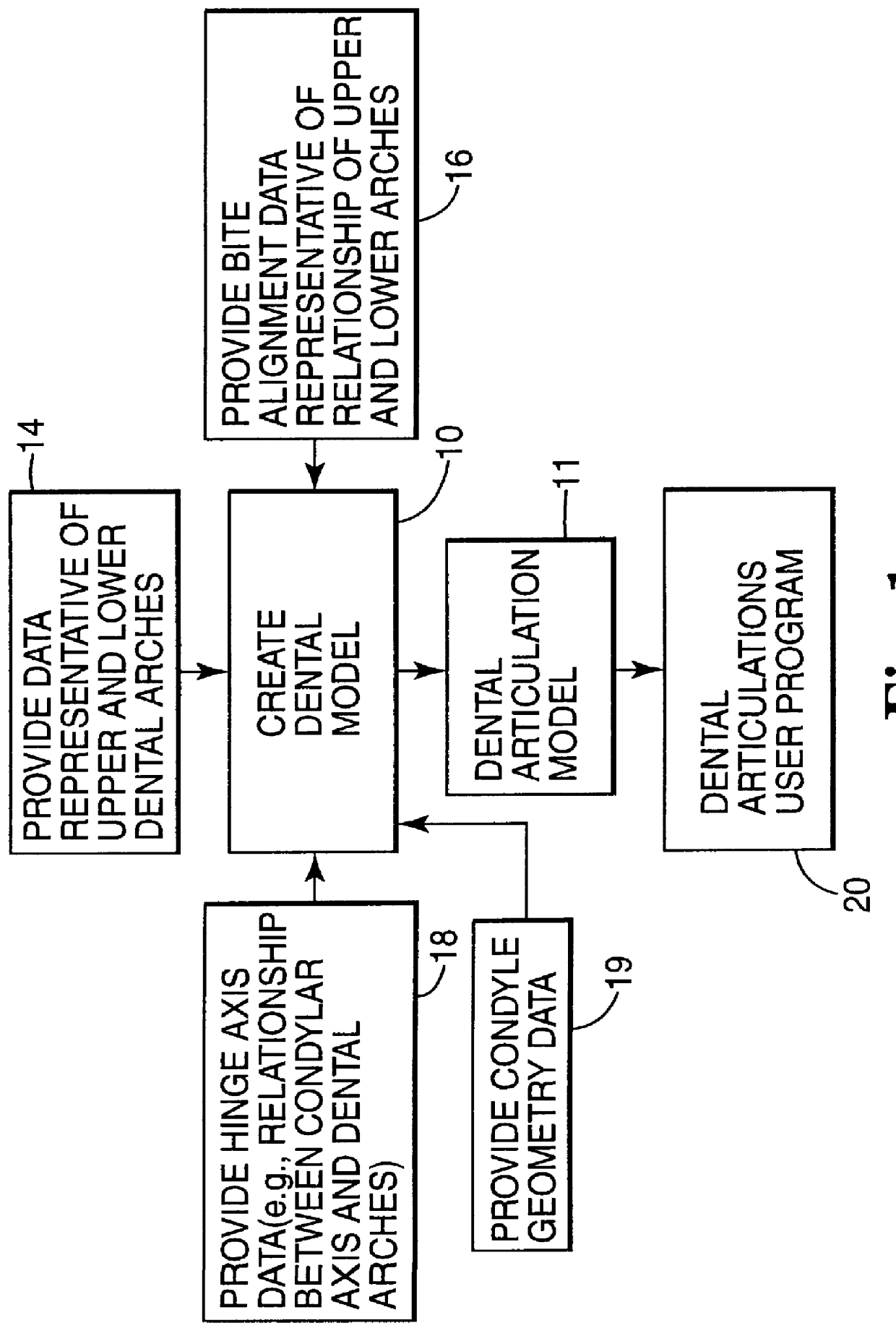
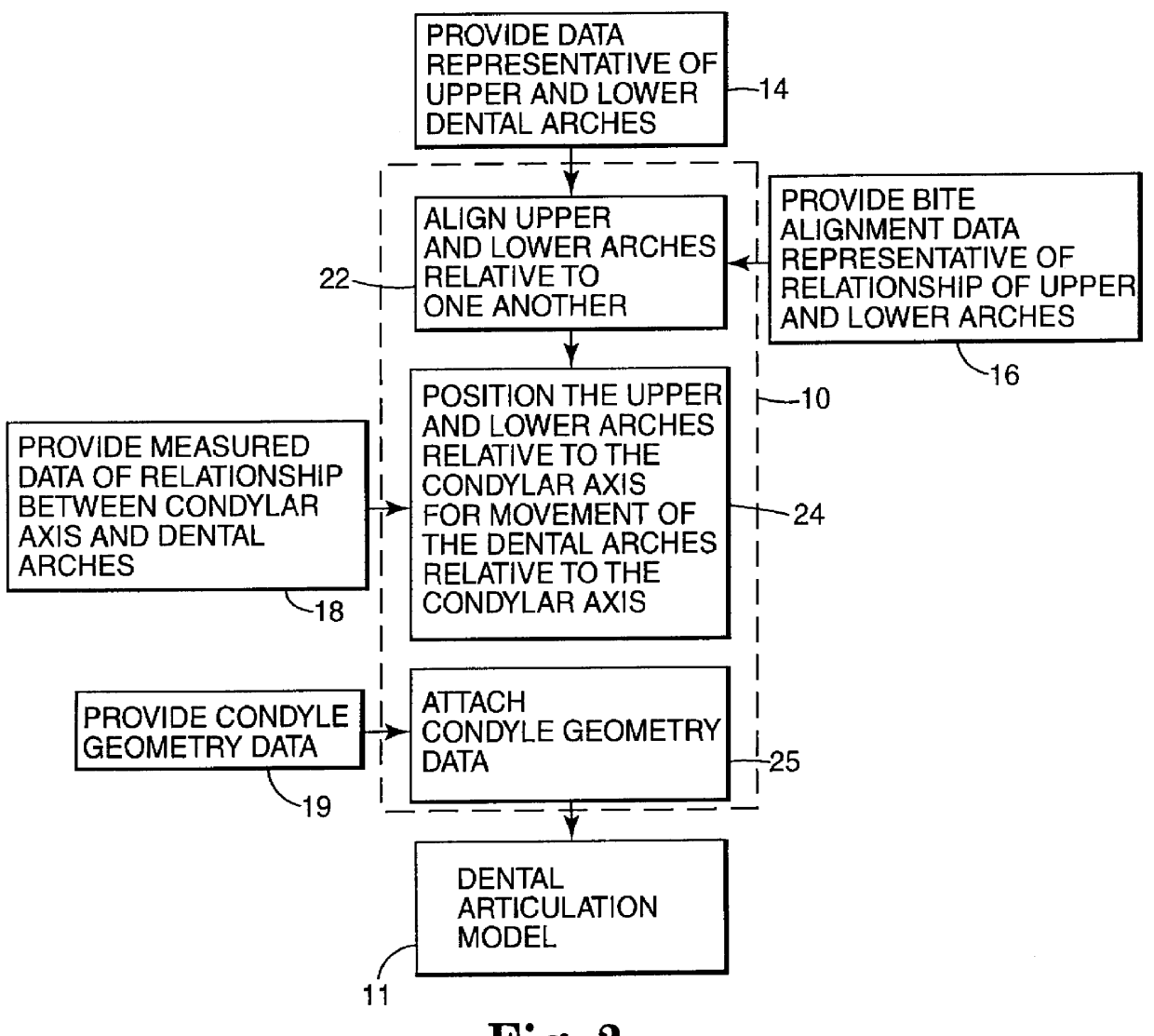
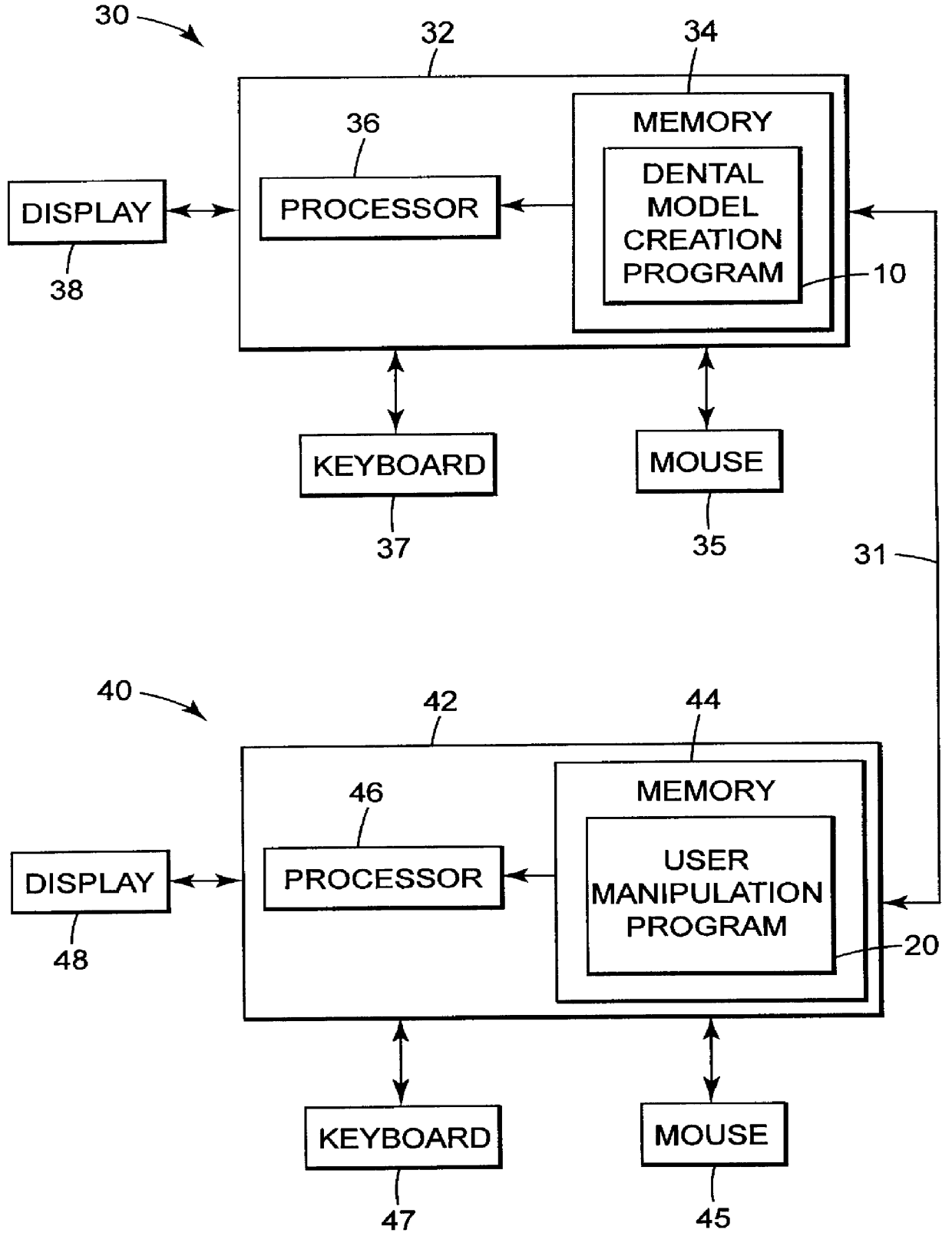
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO +1
Methods for use in dental articulation
A computer implemented method of creating a dental model for use in dental articulation includes providing a first set of digital data corresponding to an upper arch image of at least a portion of an upper dental arch of a patient, providing a second set of digital data corresponding to a lower arch image of at least a portion of a lower dental arch of the patient, and providing hinge axis data representative of the spatial orientation of at least one of the upper and lower dental arches relative to a condylar axis of the patient. A reference hinge axis is created relative to the upper and lower arch images based on the hinge axis data. Further, the method may include bite alignment data for use in aligning the lower and upper arch images. Yet further, the method may include providing data associated with condyle geometry of the patient, so as to provide limitations on the movement of at least the lower arch image when the arch images are displayed. Further, a wobbling technique may be used to determine an occlusal position of the lower and upper dental arches. Various computer implemented methods of dental articulation are also described. For example, such dental articulation methods may include moving at least one of the upper and lower arch images to simulate relative movement of one of the upper and lower dental arches of the patient, may include displaying another image with the upper and lower dental arches of the dental articulation model, and / or may include playing back recorded motion of a patient's mandible using the dental articulation model.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
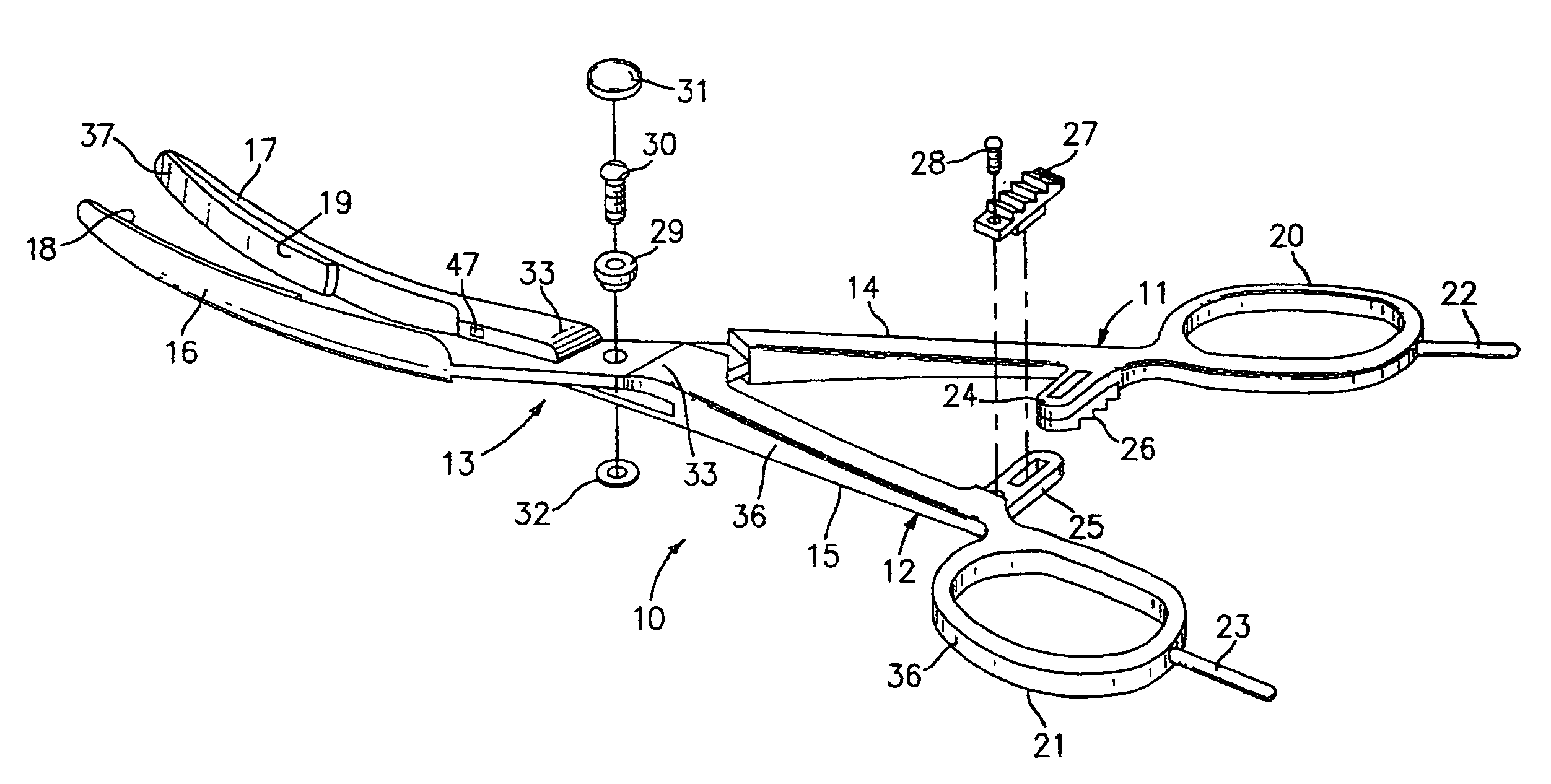
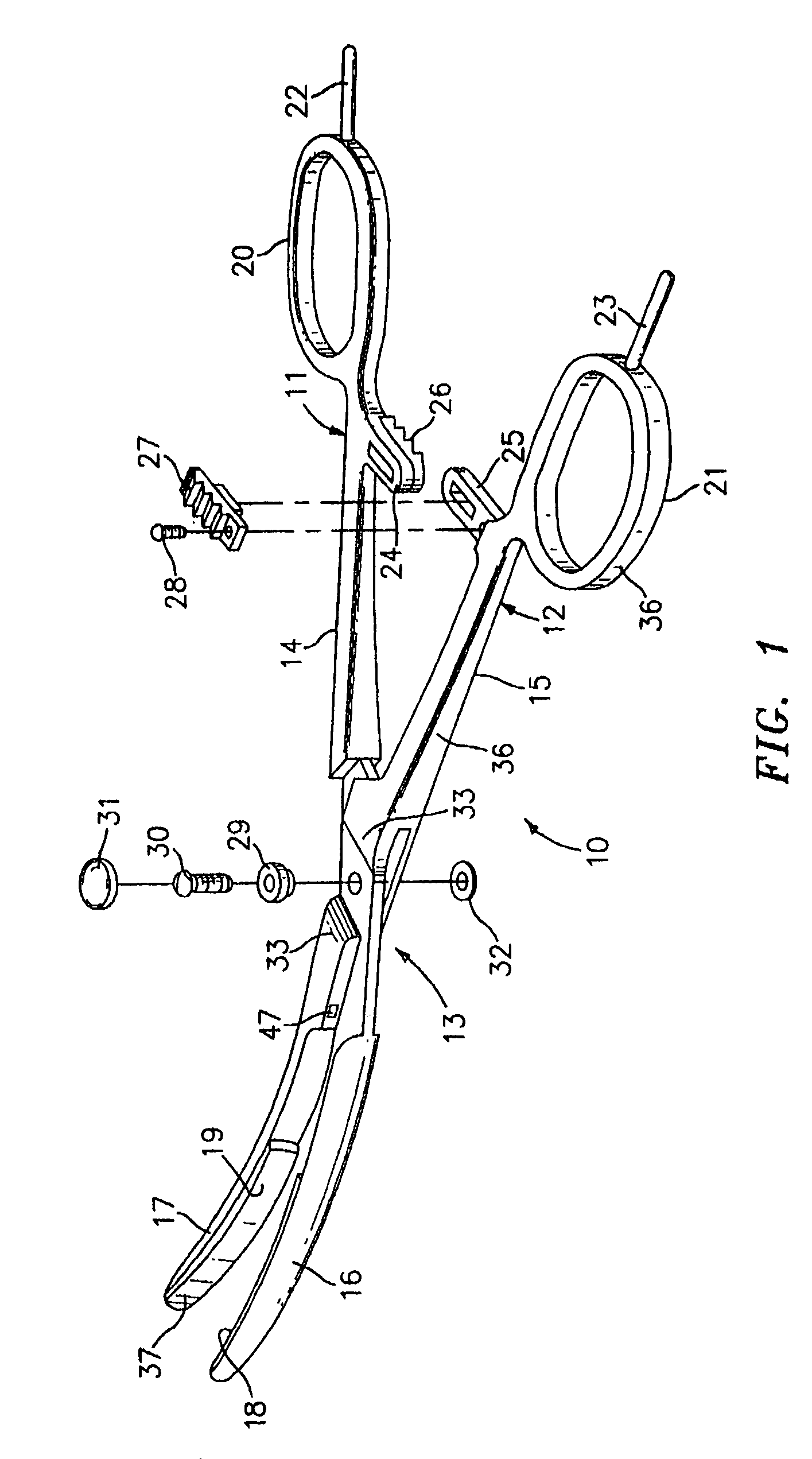
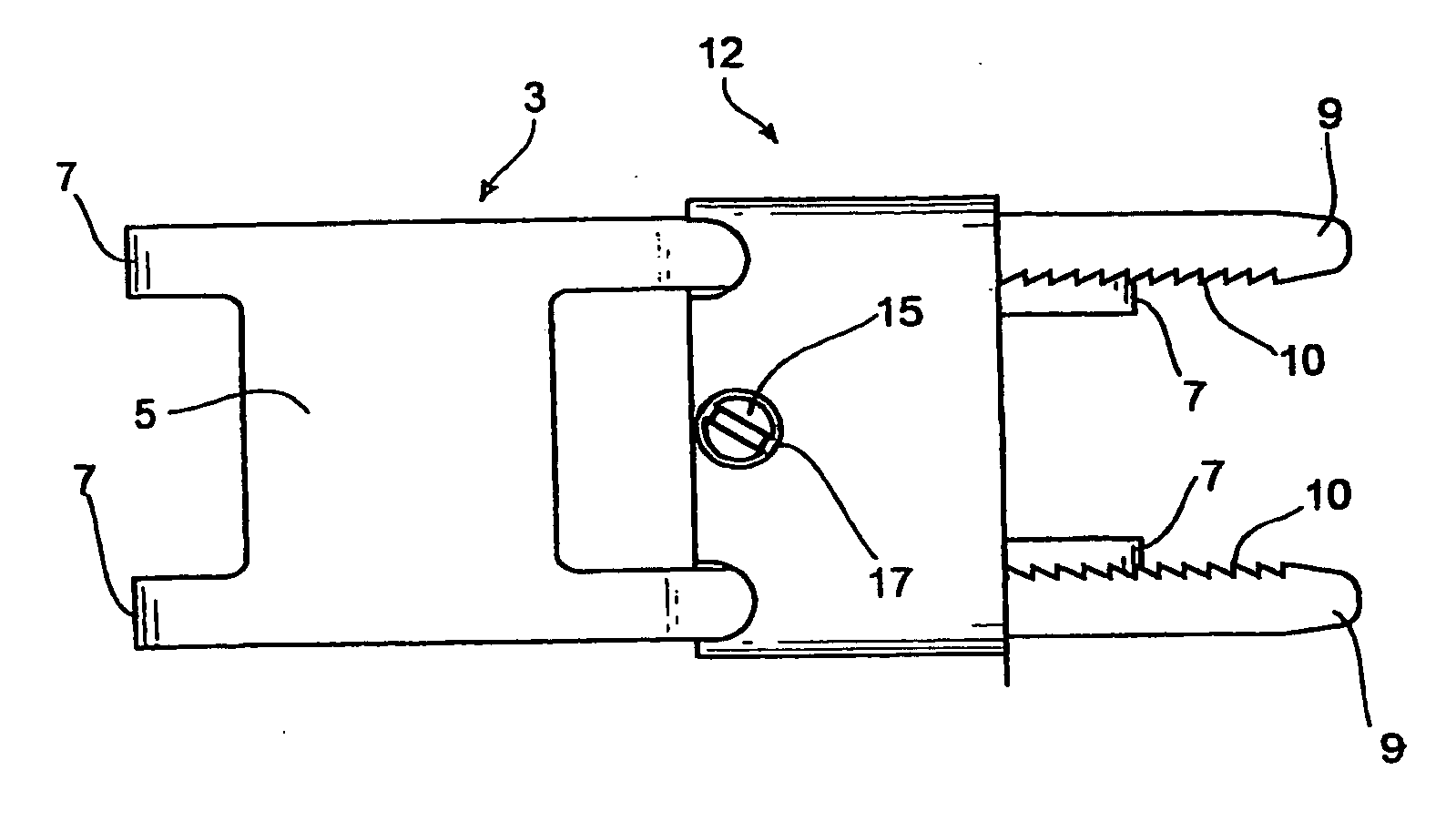
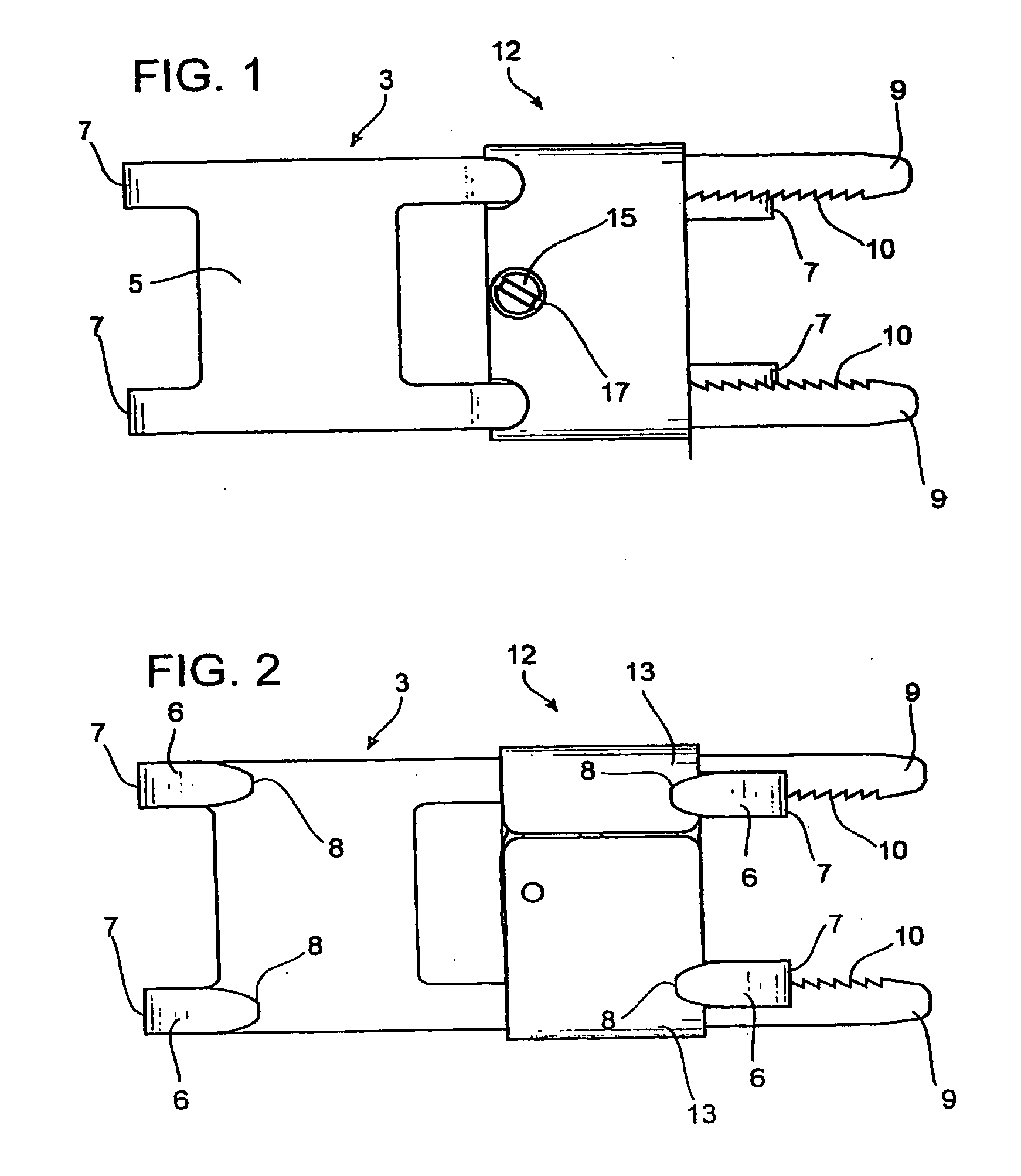
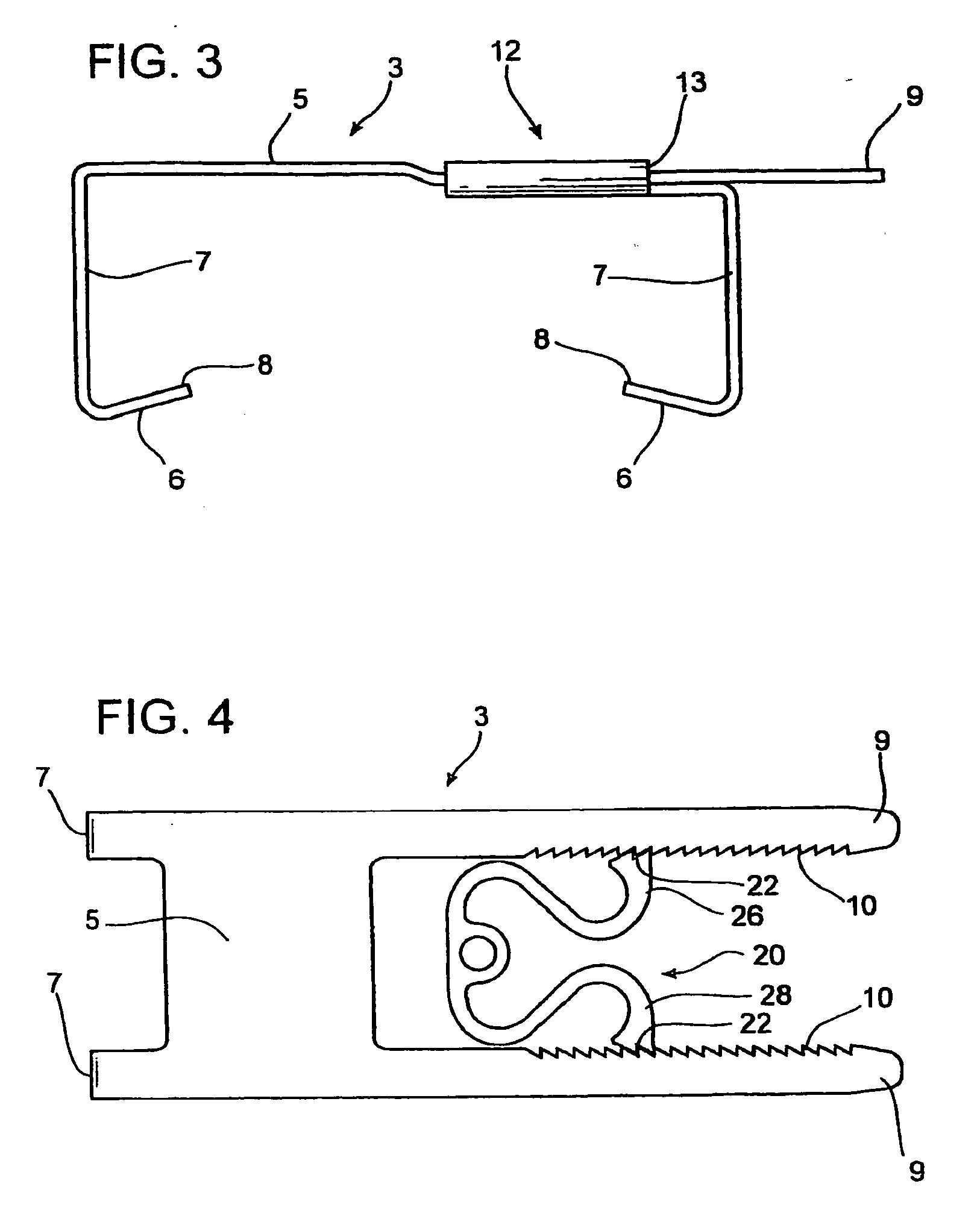
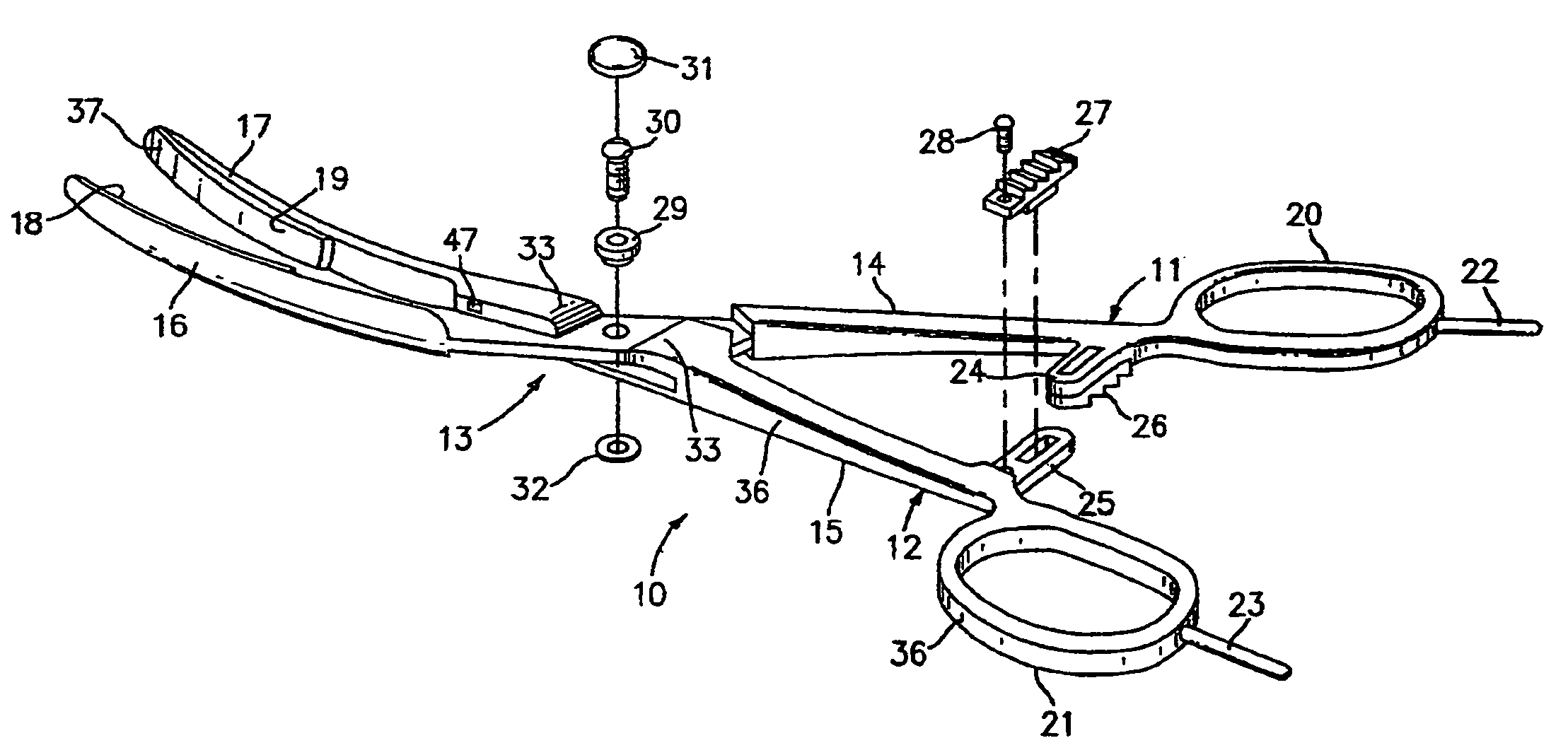
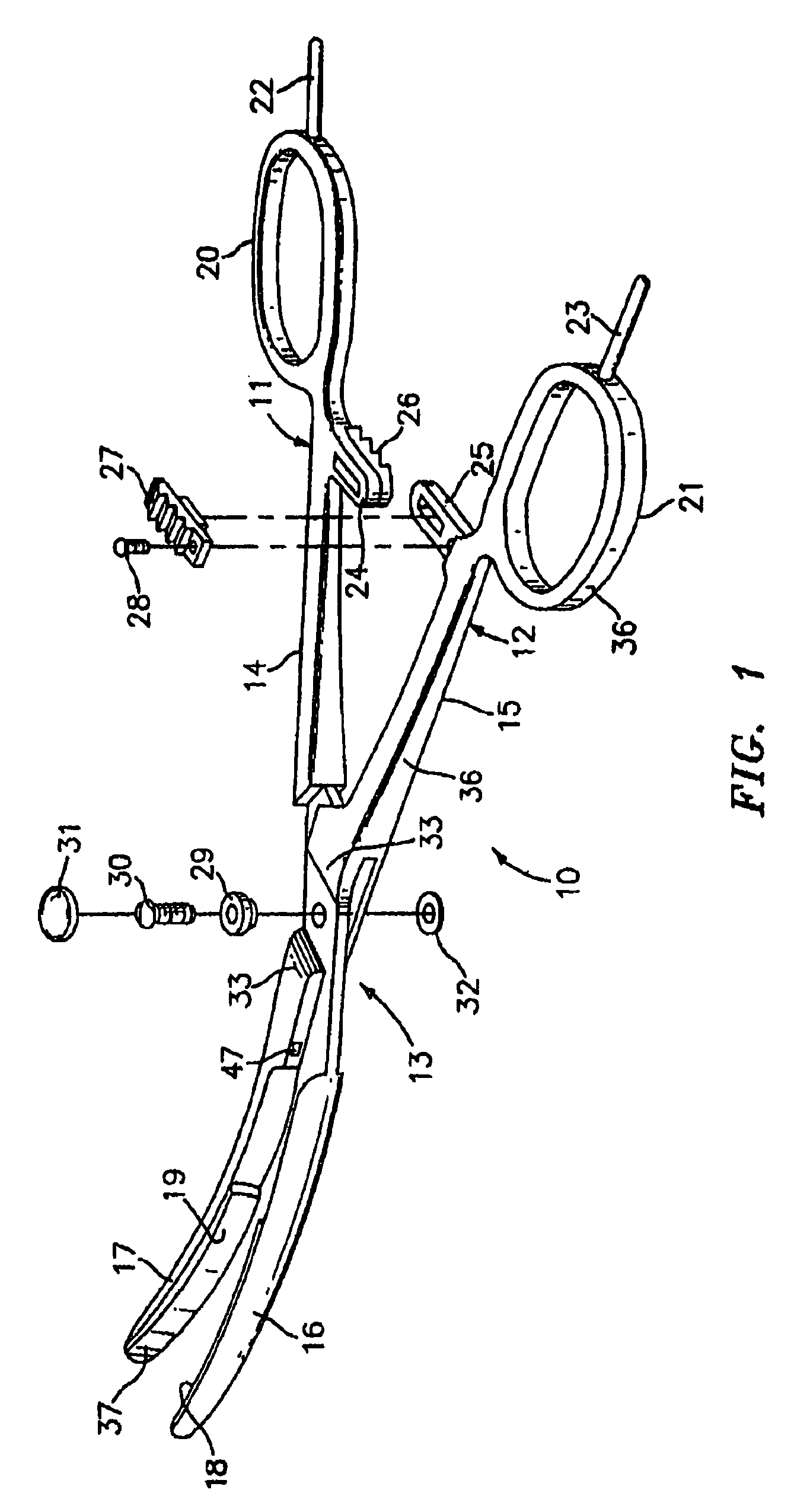
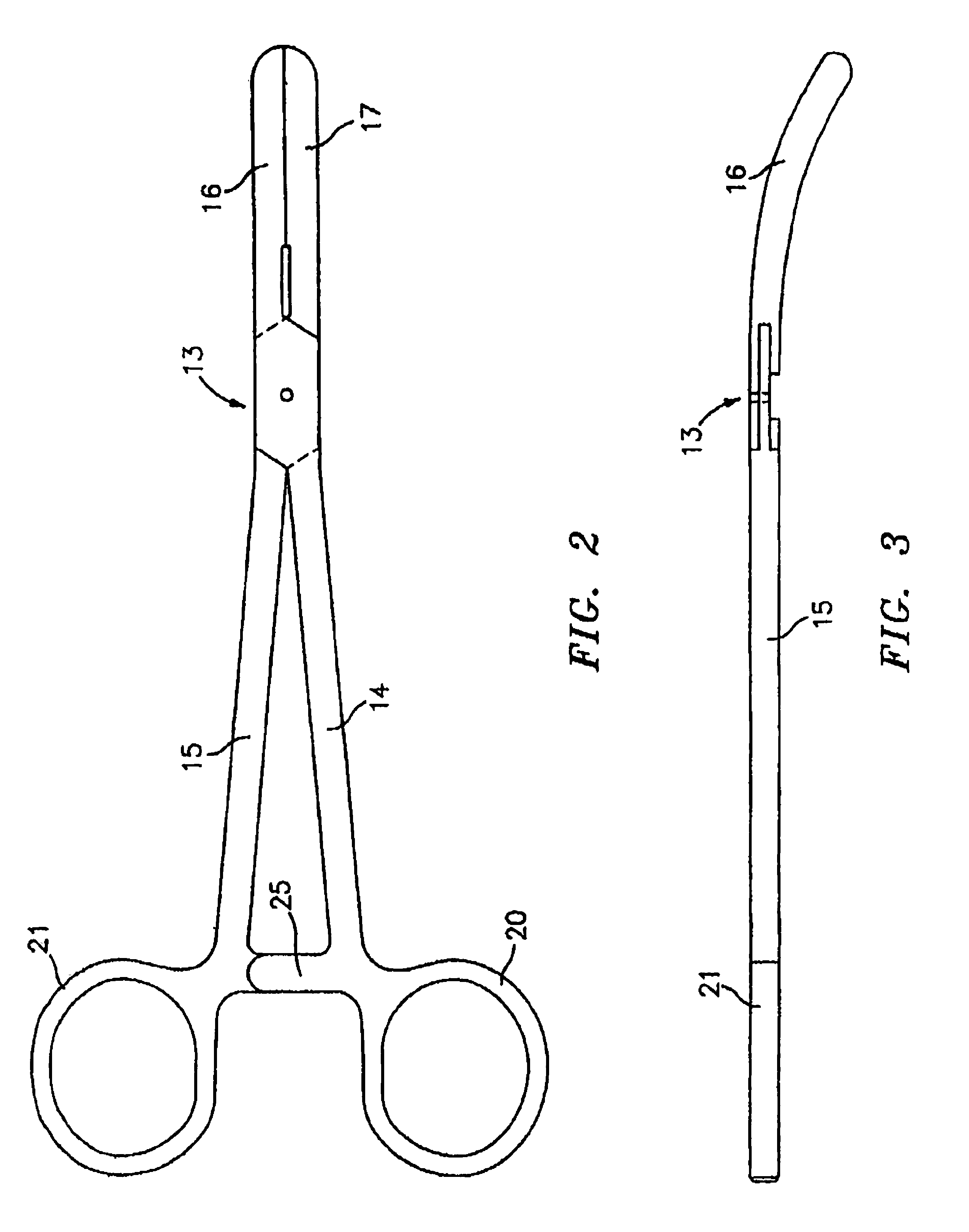
Bipolar electrosurgical instrument for sealing vessels
InactiveUS7241296B2Fast fusionShorten the timeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsPower flowBipolar electrosurgery
A bipolar electrosurgical instrument has opposable seal surfaces on its jaws for grasping and sealing vessels and vascular tissue. Inner and outer instrument members allow arcuate motion of the seal surfaces. An open lockbox provides a pivot with lateral support to maintain alignment of the lateral surfaces. Ratchets on the instrument members hold a constant closure force on the tissue during the seal process. A shank portion on each member is tuned to provide an appropriate spring force to hold the seal surfaces together. During surgery, the instrument can be used to grasp and clamp vascular tissue and apply bipolar electrosurgical current through the clamped tissue. In one embodiment, the seal surfaces are partially insulated to prevent a short circuit when the instrument jaws are closed together. In another embodiment, the seal surfaces are removably mounted on the jaws.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Catheter with variable arcuate distal section
ActiveUS20130006238A1Enhanced surface contactGood and more controlled distribution of loadElectrocardiographyCatheterCircular segmentHelix
A catheter includes an elongated body, a distal assembly with a shape-memory member defining a generally circular form, and a control handle adapted to actuate a deflection puller wire for deflecting a portion of the elongated body, and a contraction wire for contracting the generally circular form. The generally circular form which carries at least one ring electrode has an off-edge configuration relative to the elongated body such that a longitudinal axis of the elongated body does not intersect the circumference of the circular form and the generally circular form spirals about the longitudinal axis of the elongated body. Moreover, the circular form can have an on-axis configuration such that the longitudinal axis of the elongated body is axially aligned with a central longitudinal axis of the circular form, or an off-axis configuration such that these axes are axially offset from each other. In a more detailed embodiment, the catheter has a distal assembly with a helical form or a crescent form carrying a plurality of irrigated ablation ring electrodes and a plurality of smaller ring electrodes adapted for impedance recording or PV potential recording. A support member with shape memory extends through the distal assembly to provide the helical or crescent form. The support member has a varying stiffness along its length, for example, a decreasing stiffness toward a distal end of the support member. The support member can also be hollow so that it can receive a mandrel whose stiffness is greater than that of the support member.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Sternum closure device having locking member
Owner:STEVENS LEONARD
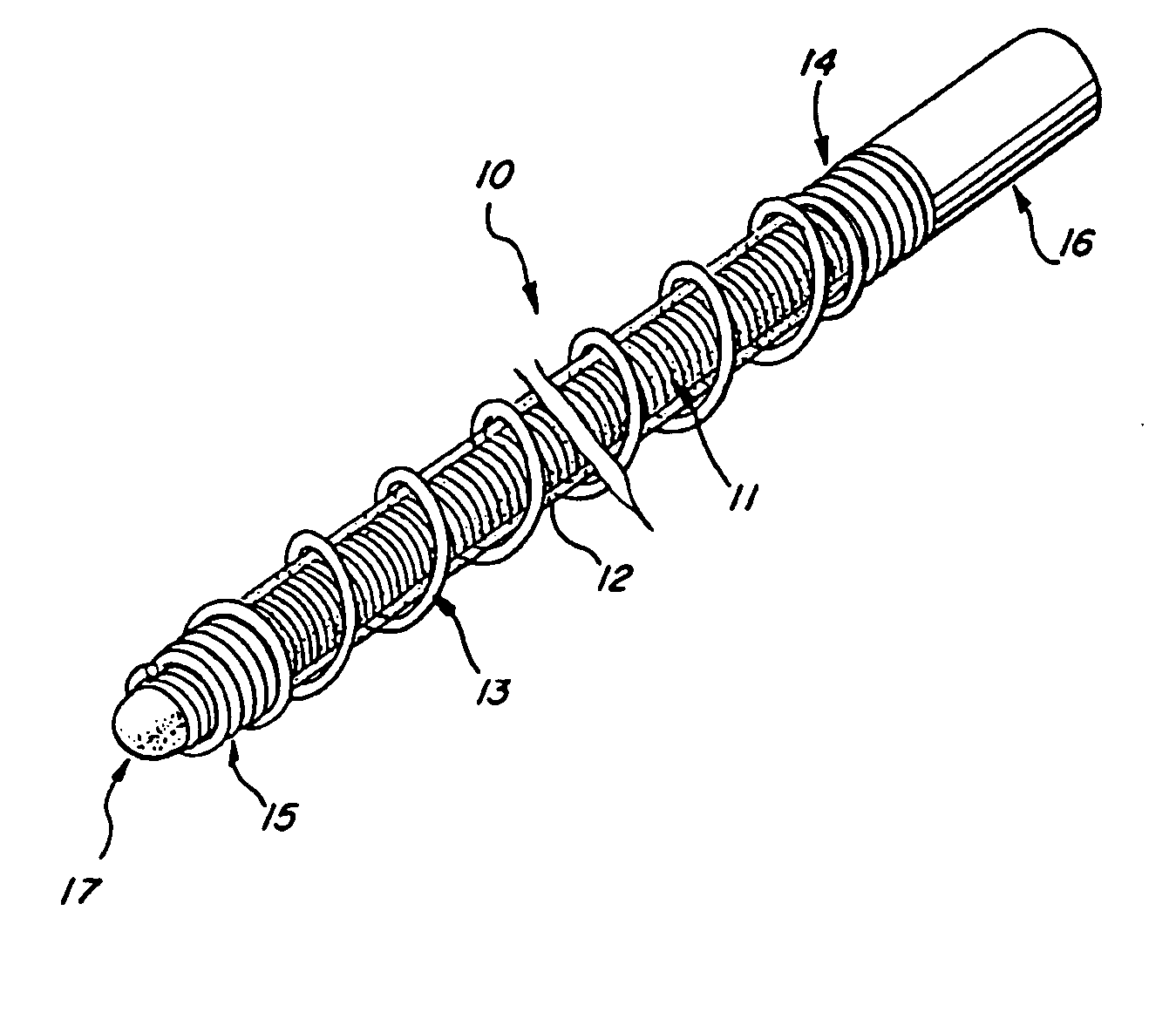
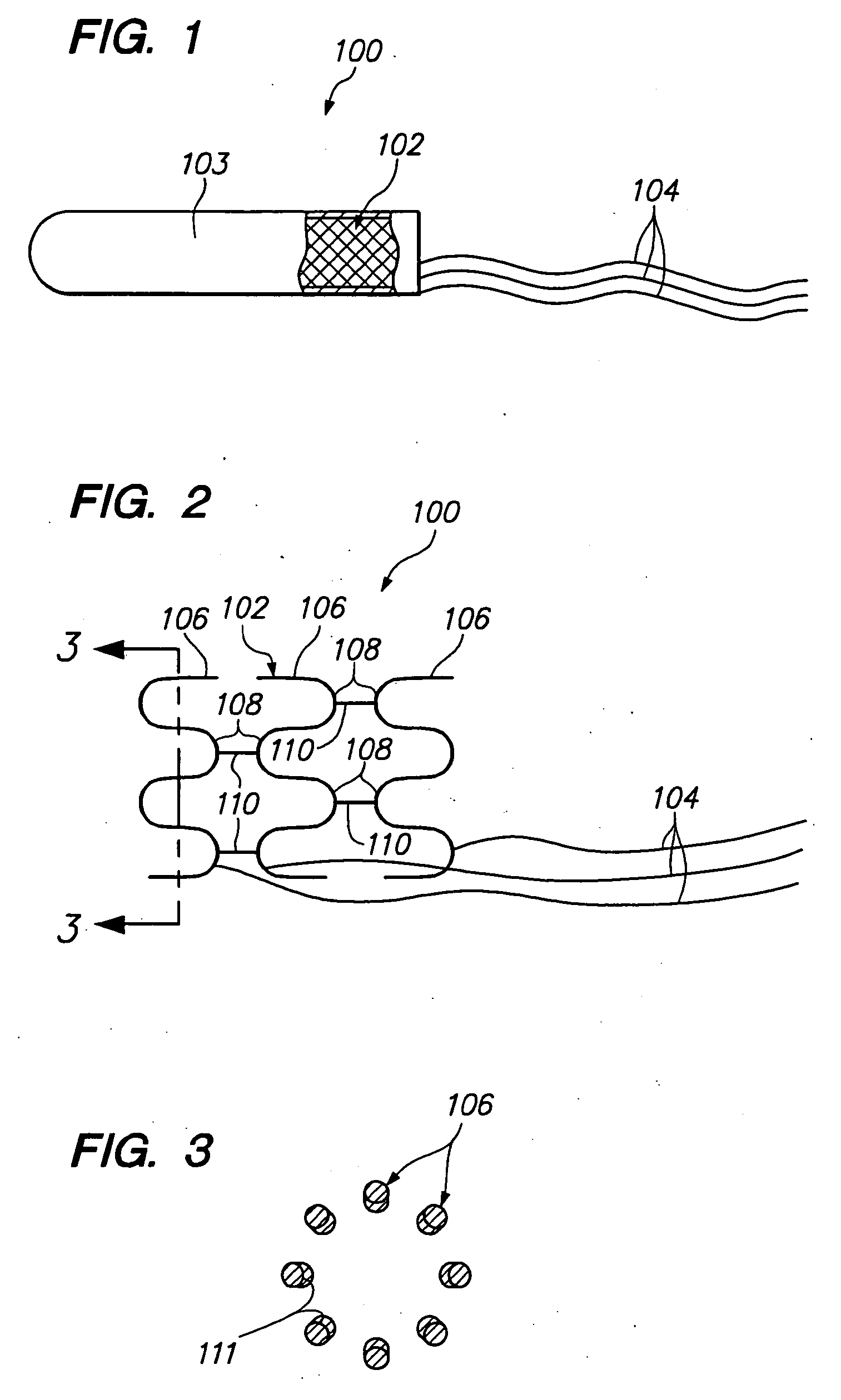
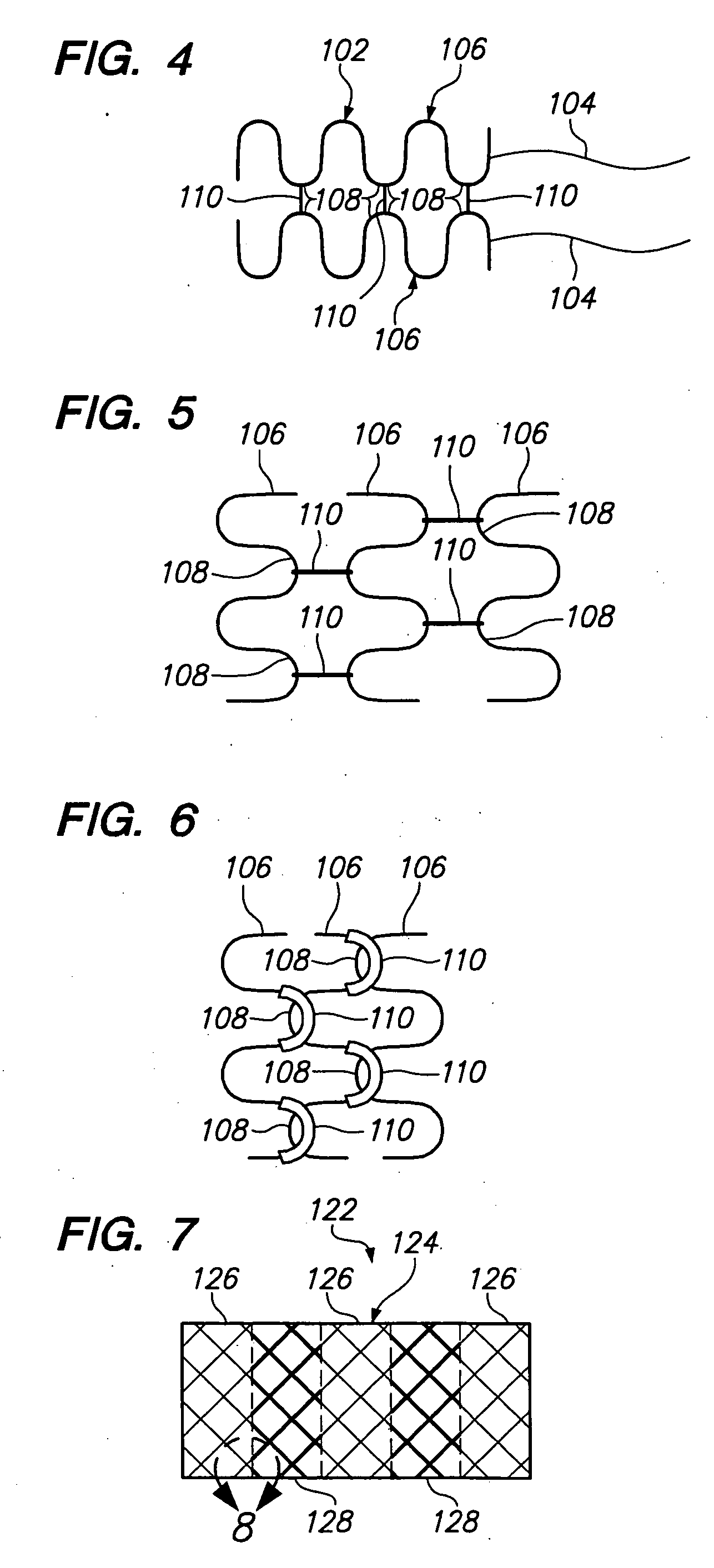
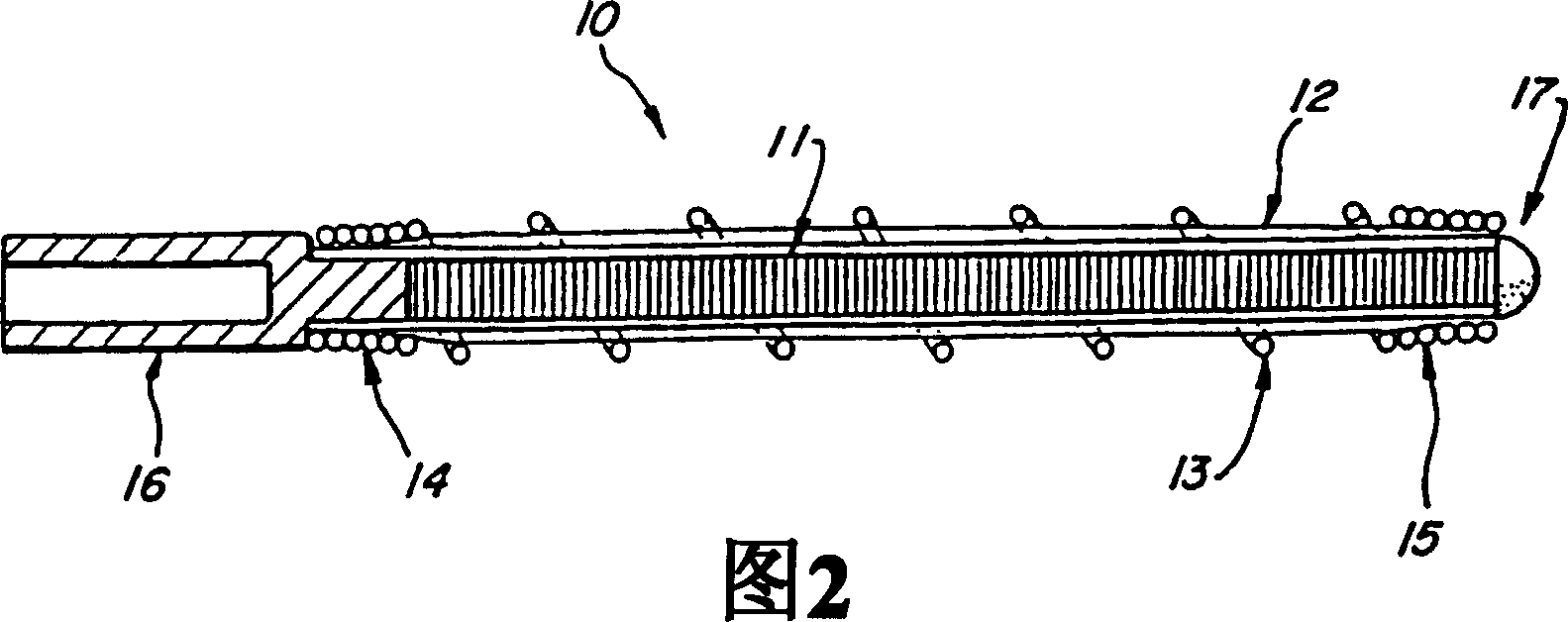
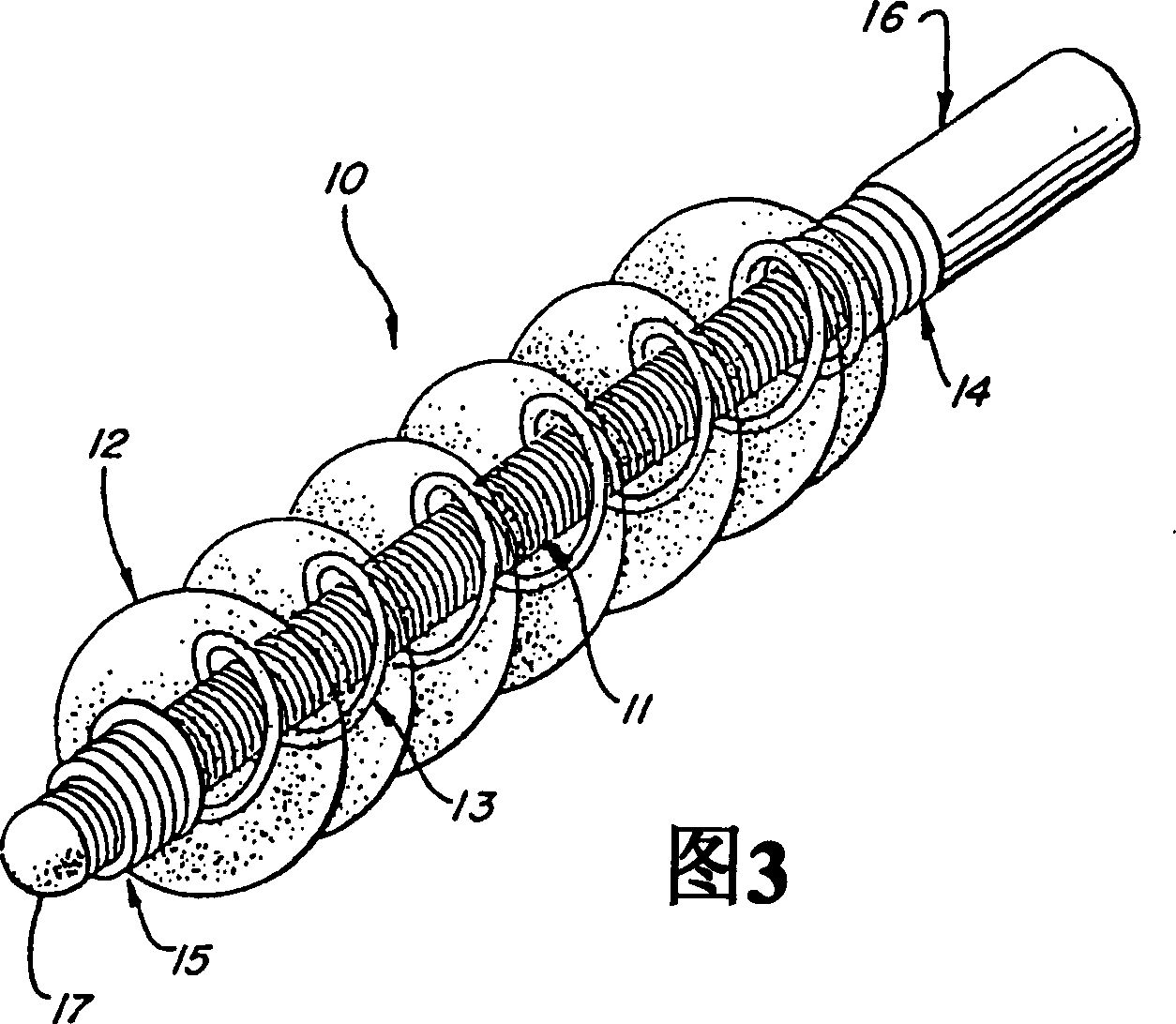
Multi-layer coaxial vaso-occlusive device
InactiveUS20050171572A1Reduces aggregate frictionDecreasing resistance to manipulationDilatorsCharacter and pattern recognitionMetallic materialsPliability
A vaso-occlusive device includes inner, intermediate, and outer elements arranged coaxially. The inner element is a filamentous element, preferably a microcoil. The intermediate element is made of a non-metallic material, preferably an expansile polymer. The outer element is substantially non-expansile and defines at least one gap or opening through which the intermediate element is exposed. In a preferred embodiment, when the intermediate element is expanded, it protrudes through the at least one gap or opening in the outer element and assumes a configuration with an undulating, convexly-curved outer surface defining a chain of arcuate segments, each having a diameter significantly greater than the diameter of the outer element. The expanded configuration of the intermediate element minimizes friction when the device is deployed through a microcatheter, thereby reducing the likelihood of buckling while maintaining excellent flexibility. The result is a device with enhanced pushability and trackability when deployed through a microcatheter.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Methods of making bioprosthetic heart valves with strain matched leaflets
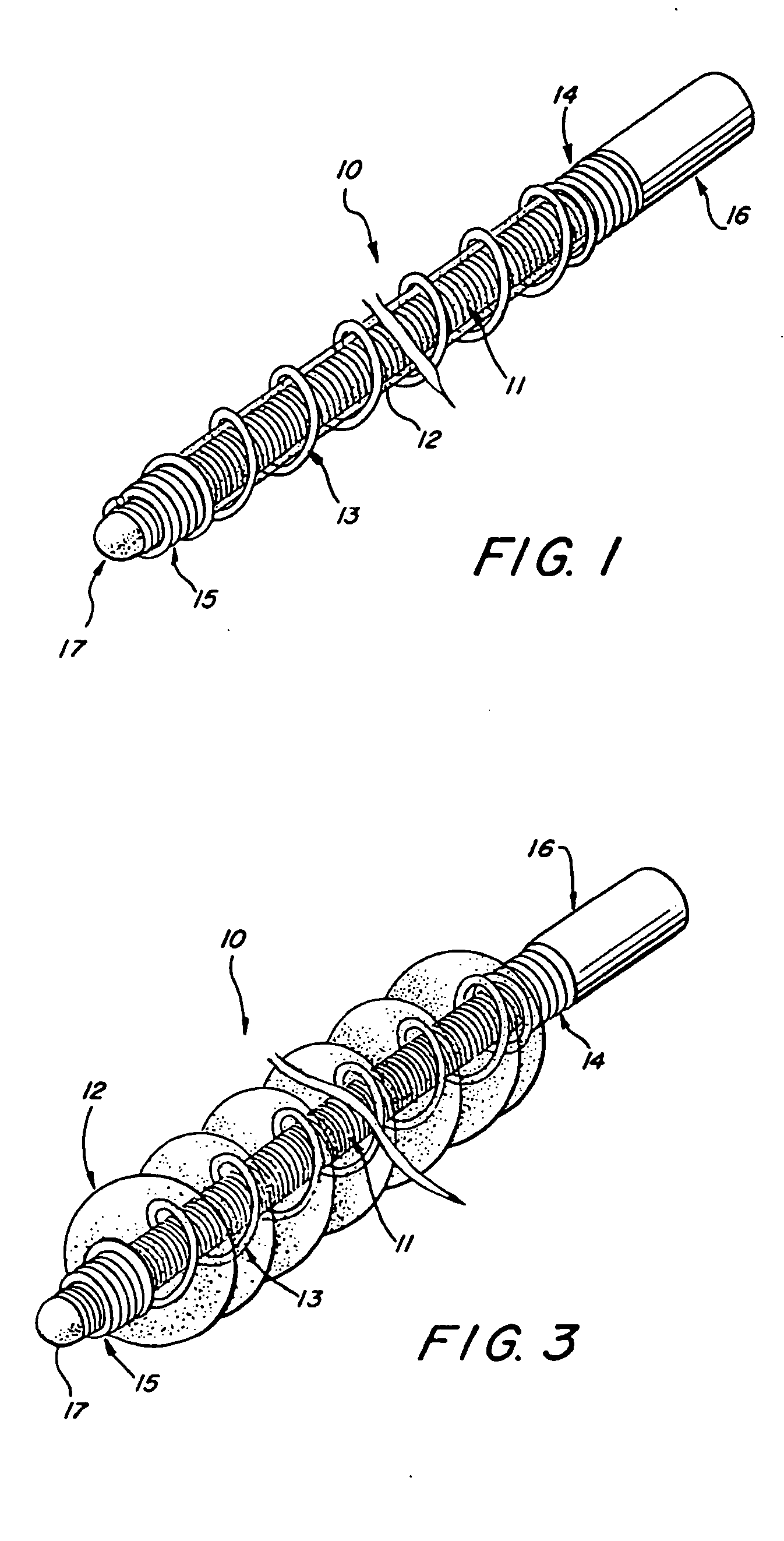
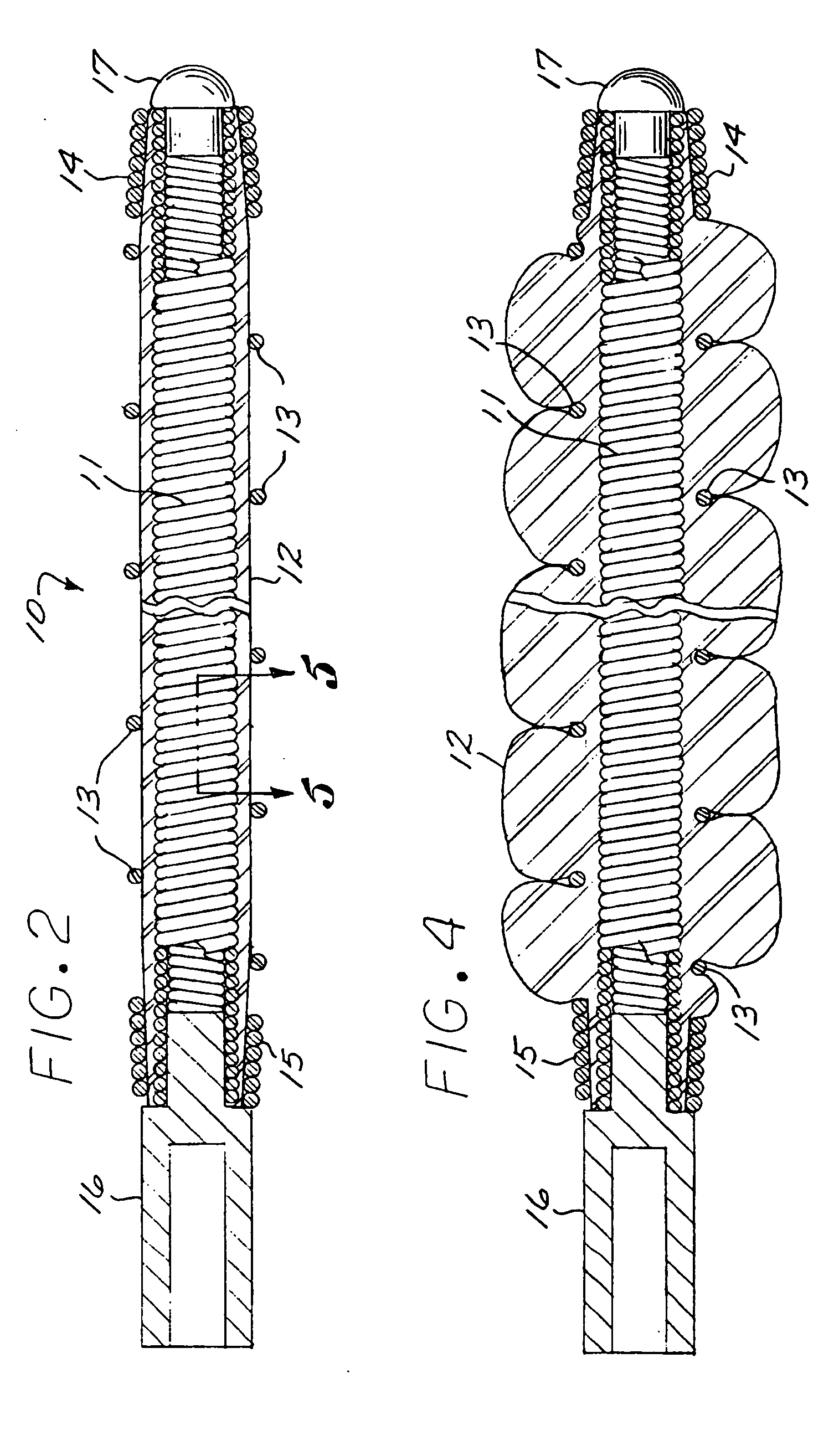
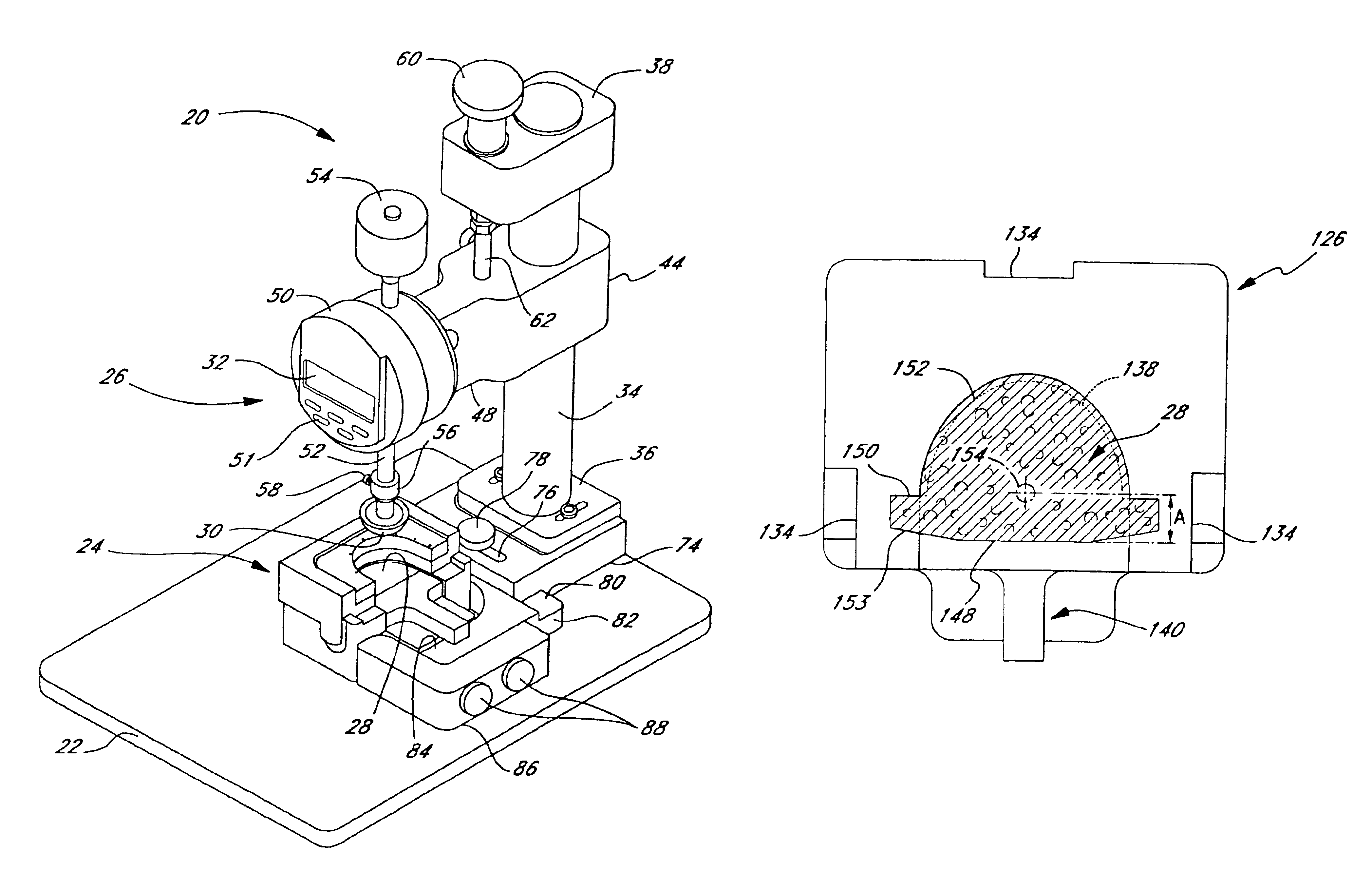
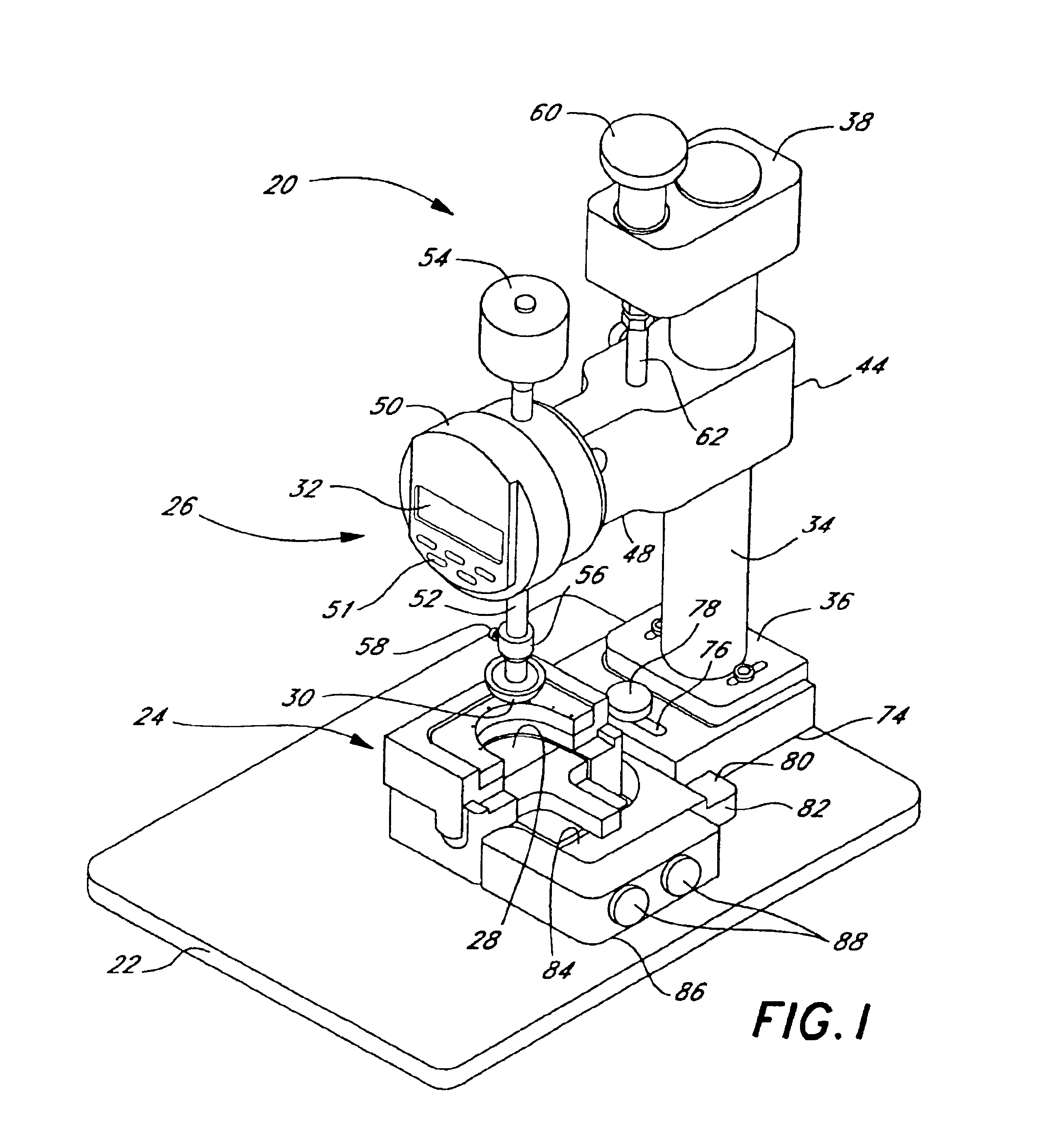
Heart valve leaflet selection methods and apparatuses which subject individual leaflets to loads and measure the resulting deflection to more reliably group leaflets of similar physical characteristics for later assembly in prosthetic heart valves. The deflection testing may be accomplished using a variety of test set ups which are designed to impart a load on the leaflet which simulates the actual loading within a heart valve. The results from a number of deflection tests are used to categorize individual leaflets, which data can be combined with other data regarding the characteristics of the leaflet to better select leaflets for assembly into a multi-leaflet heart valve. In one embodiment, the deflection test is combined with an intrinsic load test, and leaflets having similar deflection and intrinsic load values used in the same heart valve. One apparatus for testing the leaflets includes a frame for securing the arcuate cusp of the leaflet while the straight coapting edge remains free, to simulate the actual leaflet mounting configuration within the heart valve prosthesis. The frame may include a lower portion having a recess for the leaflet and plurality of receptor holes around the peripheral edge of the recess, and an upper portion having a plurality of needles which extend downward through the leaflet and into the receptor holes and secure the edges of the leaflet.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Intravascular self-anchoring electrode body with springs loops or arms
InactiveUS20050251239A1Guaranteed normal transmissionMinimize occlusionStentsTransvascular endocardial electrodesMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
An expandable intravascular medical device is provided. The medical device comprises an arcuate spring configured to be expanded into firm contact with the inner surface of a blood vessel. The medical device further comprises at least one electrode associated with the arcuate spring. For example, the electrode(s) can be discrete elements that are bonded to the arcuate spring, electrically conductive layers disposed on the arcuate spring, or the arcuate spring, itself, can form the electrode(s). The inner surface of the arcuate spring may optionally be electrically insulative. An intravascular medical device is provided. In one embodiment, the medical device comprises an electrode support structure, e.g., a non-tubular arcuate structure or a cylindrical member, and a plurality of resilient spring loops laterally extending from the support structure. The contact created between the loops and a blood vessel are sufficient to anchor the medical device within the blood vessel. In another embodiment, the medical device comprises an elongated member and two resilient spring arms extending distally from the elongated member. The arms are configured to be laterally moved towards each other to place the medical device in a collapsed geometry, and configured to be laterally moved away from each into contact with an inner surface of a blood vessel to place the medical device an expanded geometry. The contact created between the respective arms and the blood vessel are sufficient to anchor the medical device within the blood vessel. In either embodiment, the medical device further comprises an electrode associated with the electrode support structure or the spring arms.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
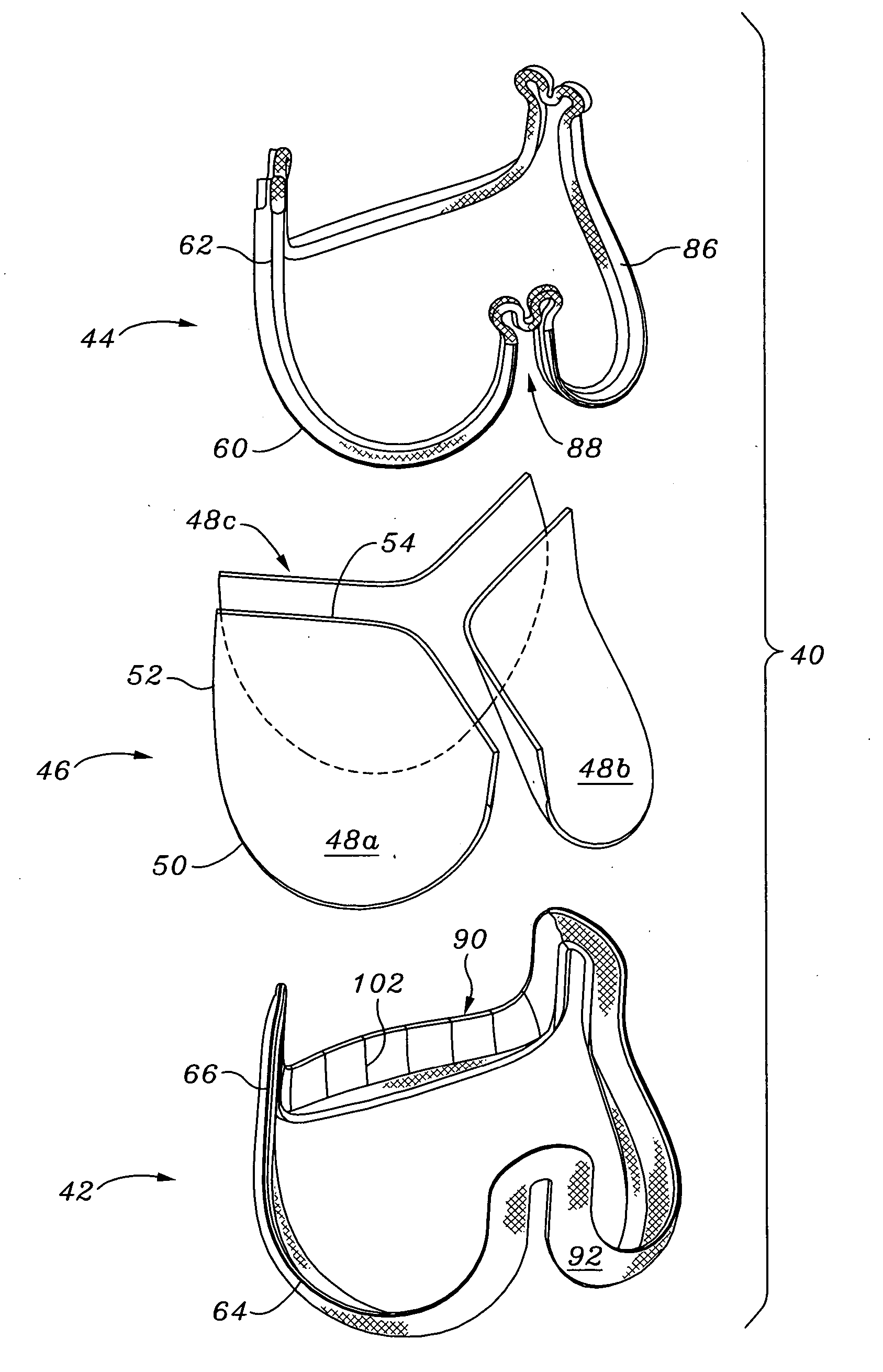
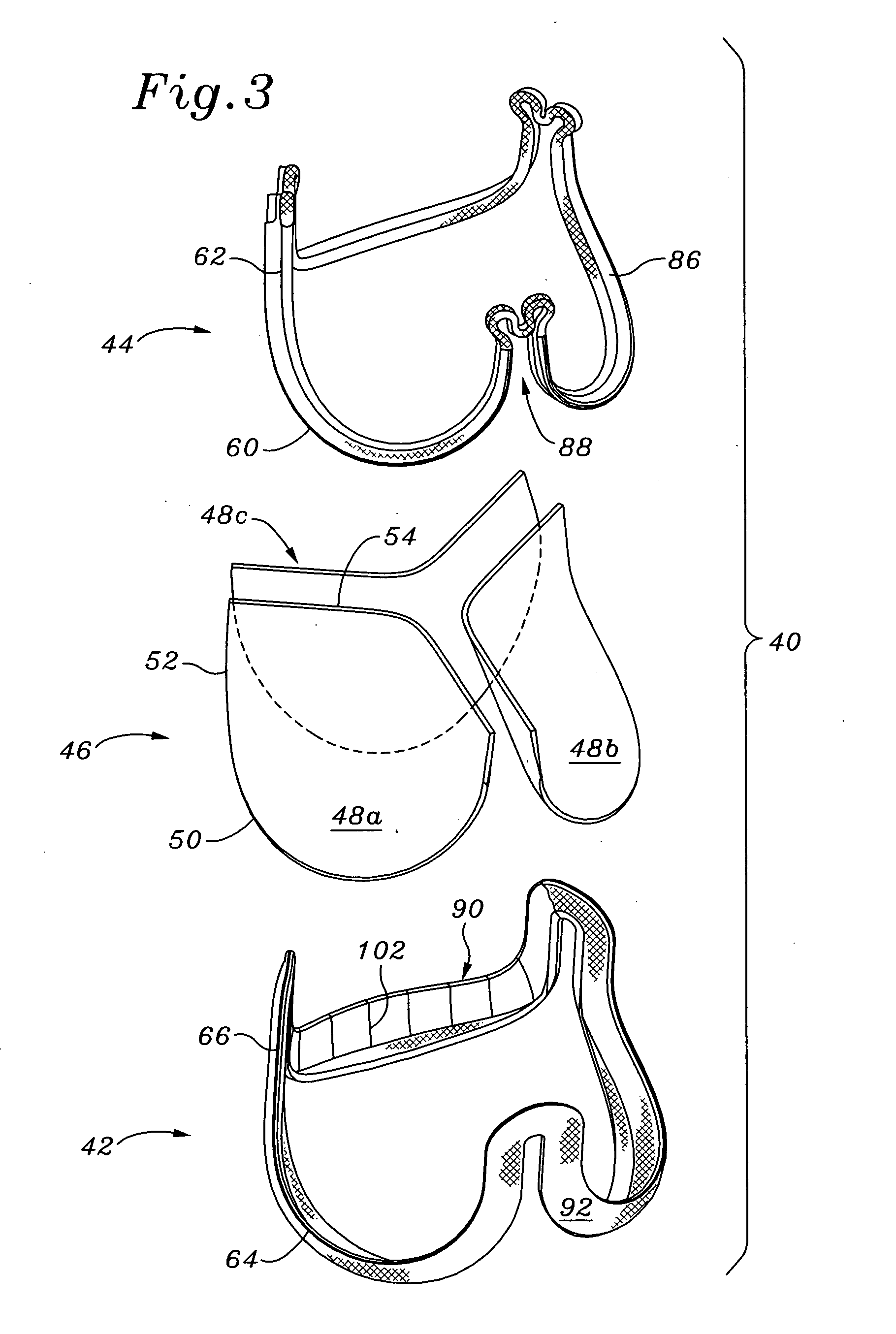
Stress absorbing flexible heart valve frame
ActiveUS20060229718A1Facilitates supra-annular attachmentIncrease flexibilityHeart valvesMedicineProsthetic heart
A flexible support frame for a prosthetic heart valve having commissure tips that are shaped to even out stresses imposed during use. The support frame is an elongated wire-like element formed by a plurality, typically three, of arcuate cusp regions on an inflow end alternating with the same number of commissures terminating in tips on an outflow end. The commissure tips are elongated relative to more simple shapes. The commissure tips may be shaped with a complex curve having two enlarged convex flexure portions separated by a concave bridge portion at the midpoint of the commissure tip. The support frame may be fabricated by separating a two-dimensional blank from a sheet and then converting the blank into a three-dimensional support frame shape. The cross-sectional thickness of the support frame may be variable, such as by adjusting the thickness of the pattern of the two-dimensional blank in the sheet. Desirably, the radial thickness remains constant while the circumferential dimension varies with a maximum located at the commissure tips.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Automatic surgical device for cutting a cornea and a cutting blade assembly and control assembly
A surgical device for cutting substantially across a cornea of an eye of a patient, the device including a positioning ring structured to be temporarily attached to a portion of the eye surrounding the cornea to be cut, and defining an aperture sized to receive and expose the cornea to be cut. The surgical device further includes a cutting head assembly structured to be guided and driven over an upper surface of the positioning ring in a generally arcuate path, and having a cutting element positioned therein and structured to oscillate laterally to facilitate smooth and effective cutting of the cornea. The cutting head assembly is structured to be detachably coupled to the positioning ring by a coupling member which permits movement of the cutting head assembly relative to the positioning ring along the generally arcuate path, but maintains sufficient engagement therebetween to ensure that smooth, steady, driven movement is maintained.
Owner:HELLENKAMP JOHANN F
System and method for automatic construction of orthodontic reference objects
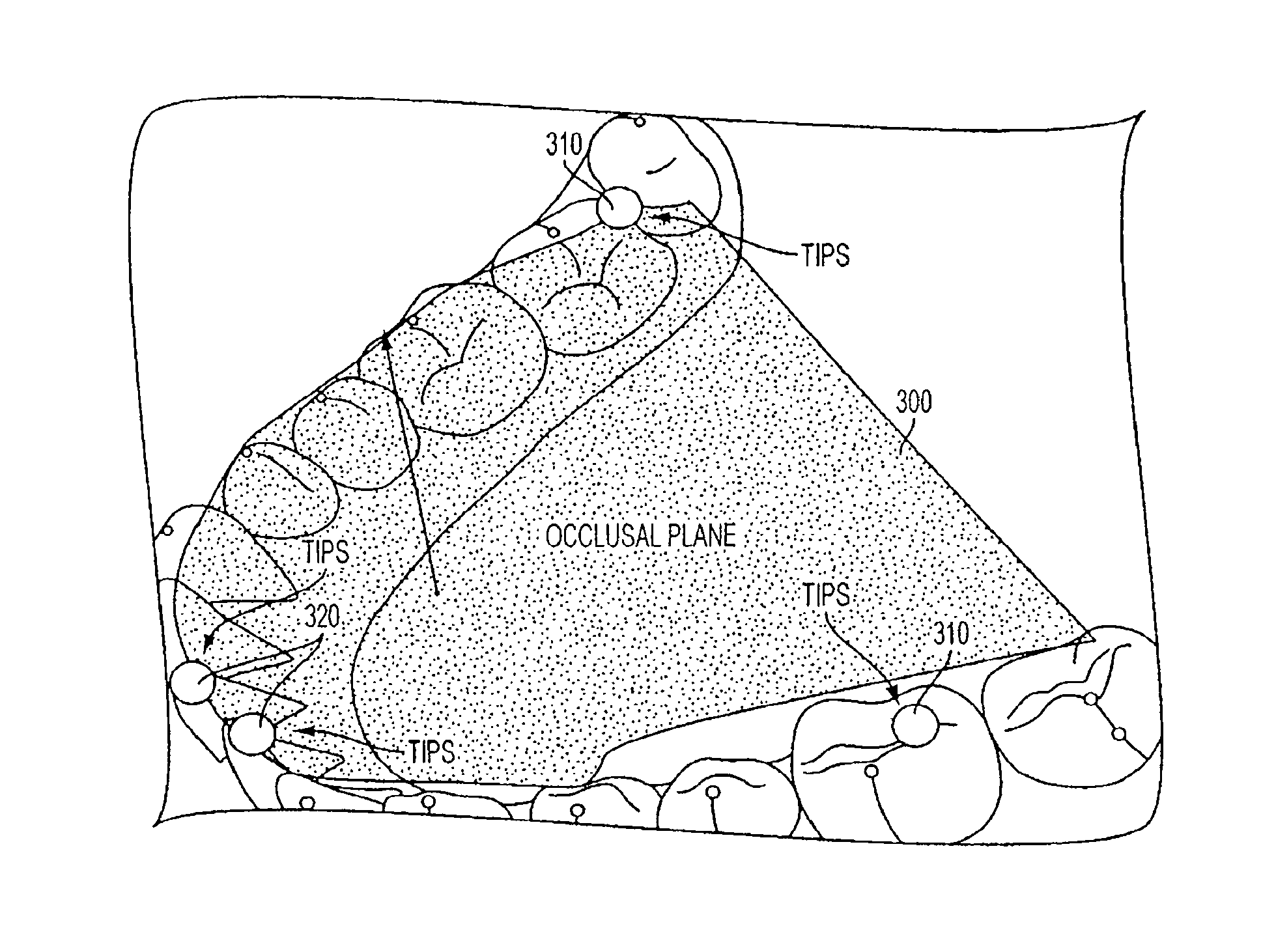
System and method for automatic construction of orthodontic reference objects, such as the occlusal plane, arch form, and the local occlusal plane for a patient's teeth are disclosed. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment, a computer-implemented system and method for automatic construction of orthodontic reference objects comprises receiving three dimensional data for the teeth, setting an initial direction for a normal of the occlusal plane, determining tips for selected teeth, calculating a plane that matches the determined tip, and determining a new normal for the calculated plane.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Deployable segmented TLIF device
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Bipolar electrosurgical instrument for sealing vessels
InactiveUS7963965B2Fast fusionShorten the timeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsPower flowBipolar electrosurgery
A bipolar electrosurgical instrument has opposable seal surfaces on its jaws for grasping and sealing vessels and vascular tissue. Inner and outer instrument members allow arcuate motion of the seal surfaces. An open lockbox provides a pivot with lateral support to maintain alignment of the lateral surfaces. Ratchets on the instrument members hold a constant closure force on the tissue during the seal process. A shank portion on each member is tuned to provide an appropriate spring force to hold the seal surfaces together. During surgery, the instrument can be used to grasp and clamp vascular tissue and apply bipolar electrosurgical current through the clamped tissue. In one embodiment, the seal surfaces are partially insulated to prevent a short circuit when the instrument jaws are closed together. In another embodiment, the seal surfaces are removably mounted on the jaws.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
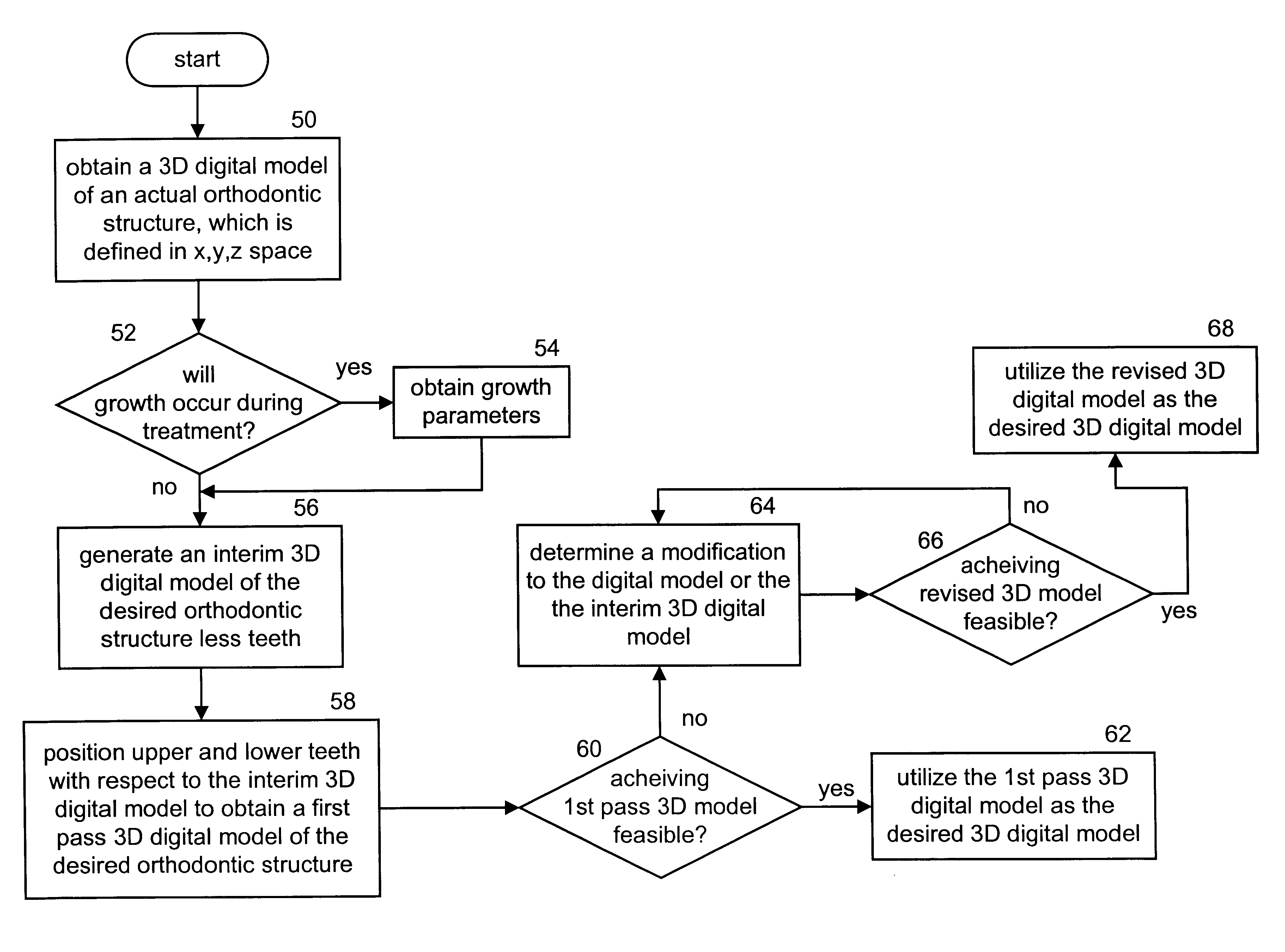
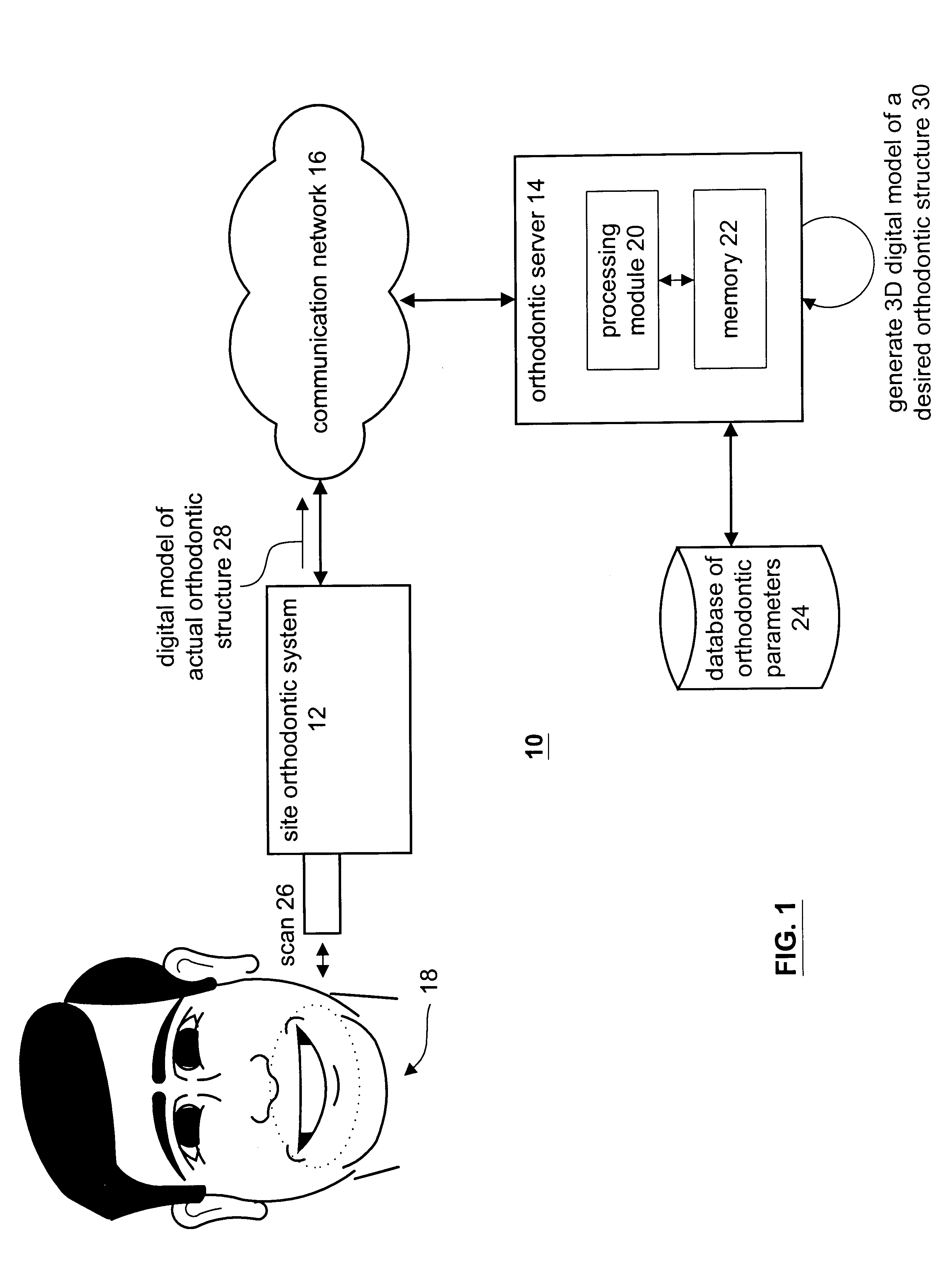
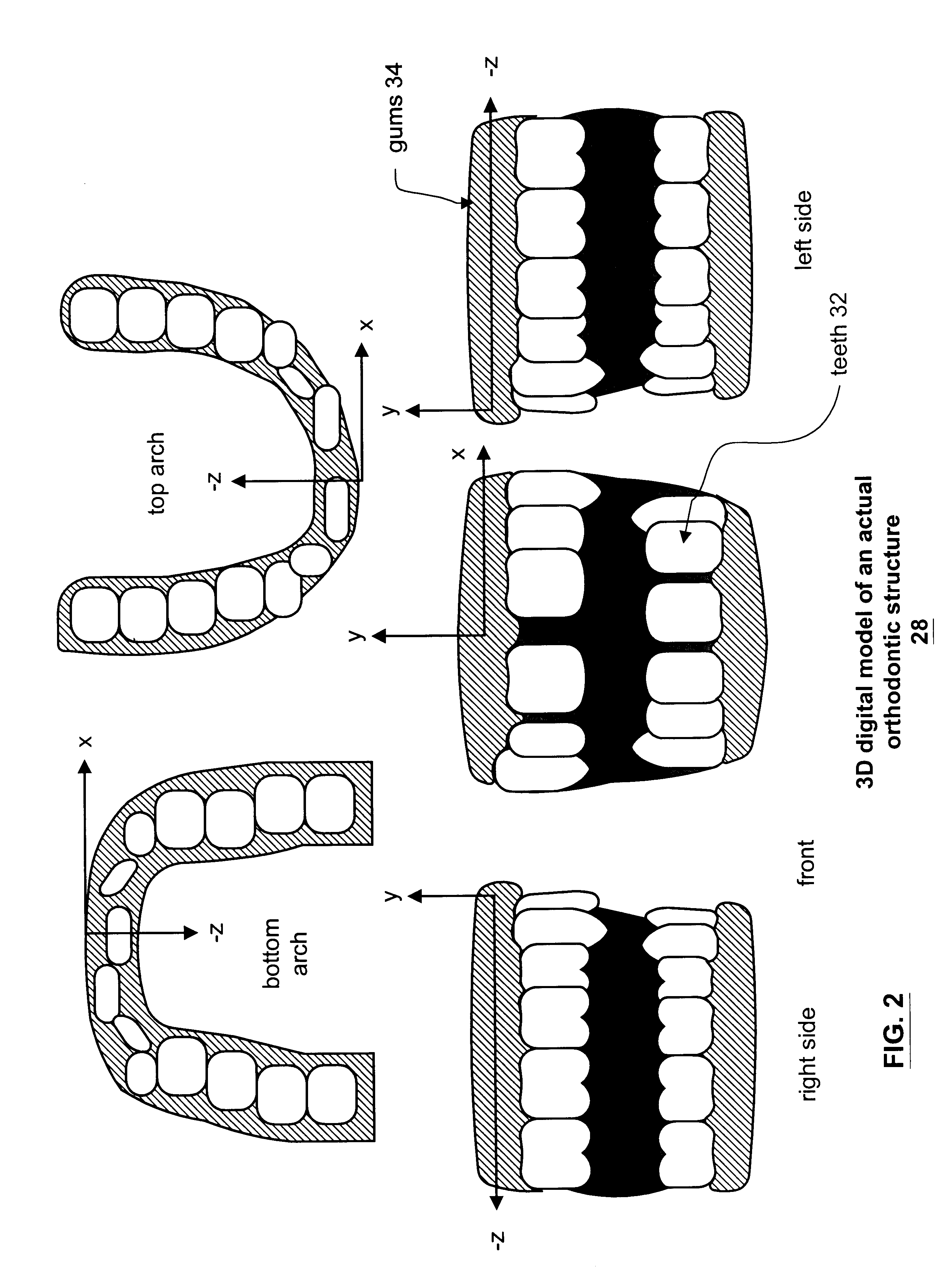
Method and apparatus for generating a desired three-dimensional digital model of an orthodontic structure
A method and apparatus for generating a three-dimensional digital model of a desired orthodontic structure include processing that begins by obtaining a three-dimensional model of an actual orthodontic structure, wherein the three-dimensional digital model is defined in x, y, z space. The processing then continues by generating an interim three-dimensional model of the desired orthodontic structure less teeth. The interim three-dimensional model is designed in x, y, z space and includes the desired placement of an occlusal plane, an upper-arch form, a lower-arch form, an upper-arch midline, and a lower-arch midline. The processing then continues by positioning the upper and lower teeth with respect to the interim digital model and the defined x, y, z space to obtain a first pass three-dimensional digital model of the desired orthodontic structure. The processing continues by determining whether achieving the first pass three-dimensional model is feasible. When achieving the first pass three-dimensional image is feasible, the processing continues by utilizing the first pass three-dimensional model as the desired three-dimensional digital model.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
Transport and positioning system for use in hospital operating rooms
A system for transporting and positioning a patient onto an operating room table from a movable transportation device, e.g., a stretcher, to be located immediately laterally of the operating room table and transporting back onto the movable transportation device after the surgery. The system basically comprises a first and second inflatable assemblies to effect the pivoting of the patient about a longitudinal axis extending between the table and stretcher from a supine position on the stretcher to a horizontal prone position on the table. A third inflatable assembly causes the patient's spine to be in an arcuate orientation suitable for spinal surgery.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Head support device for use when lying in the prone position
InactiveUS20050177946A1Comfortable facial supportHighly stablePillowsOperating tablesLeft frontal sinusProne position
A head support device which enables a user to comfortably rest in the prone position. The head support device includes a padded member having a generally horse-shoe shape with a top, arcuate sides spaced apart ends, a first inner side wall and a second inner side wall, a first region for supporting the user's face in the frontal sinus area, a second region adjacent to the eye socket and cheek area for supporting the user's face area, and a third region for support along the sides of the user's mandible. The support device also includes a substantially rigid support member for supporting the padded member. The support member has a pair of upstanding splayed outwardly walls which define an air channel for the free exchange of air when the user inhales or exhales. The support member has a plurality of opposing, substantially parallel zones which provide support for the above described support regions of the padded member when the user is lying in the prone position. The padded member is secured to the support member using an attachment method that does not interfere with said padded member conforming to the facial configuration of the user.
Owner:RILEY ENTERPRISES
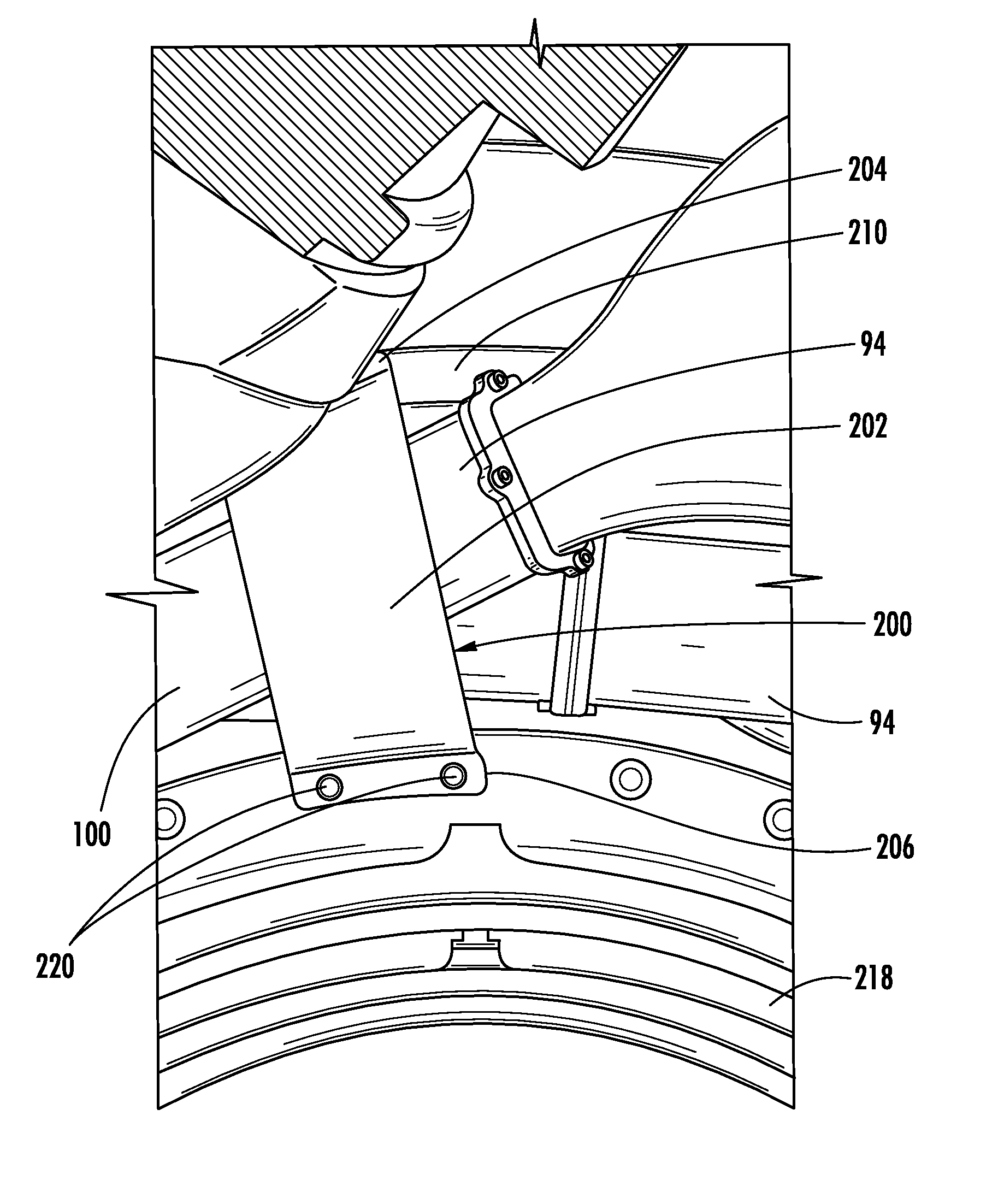
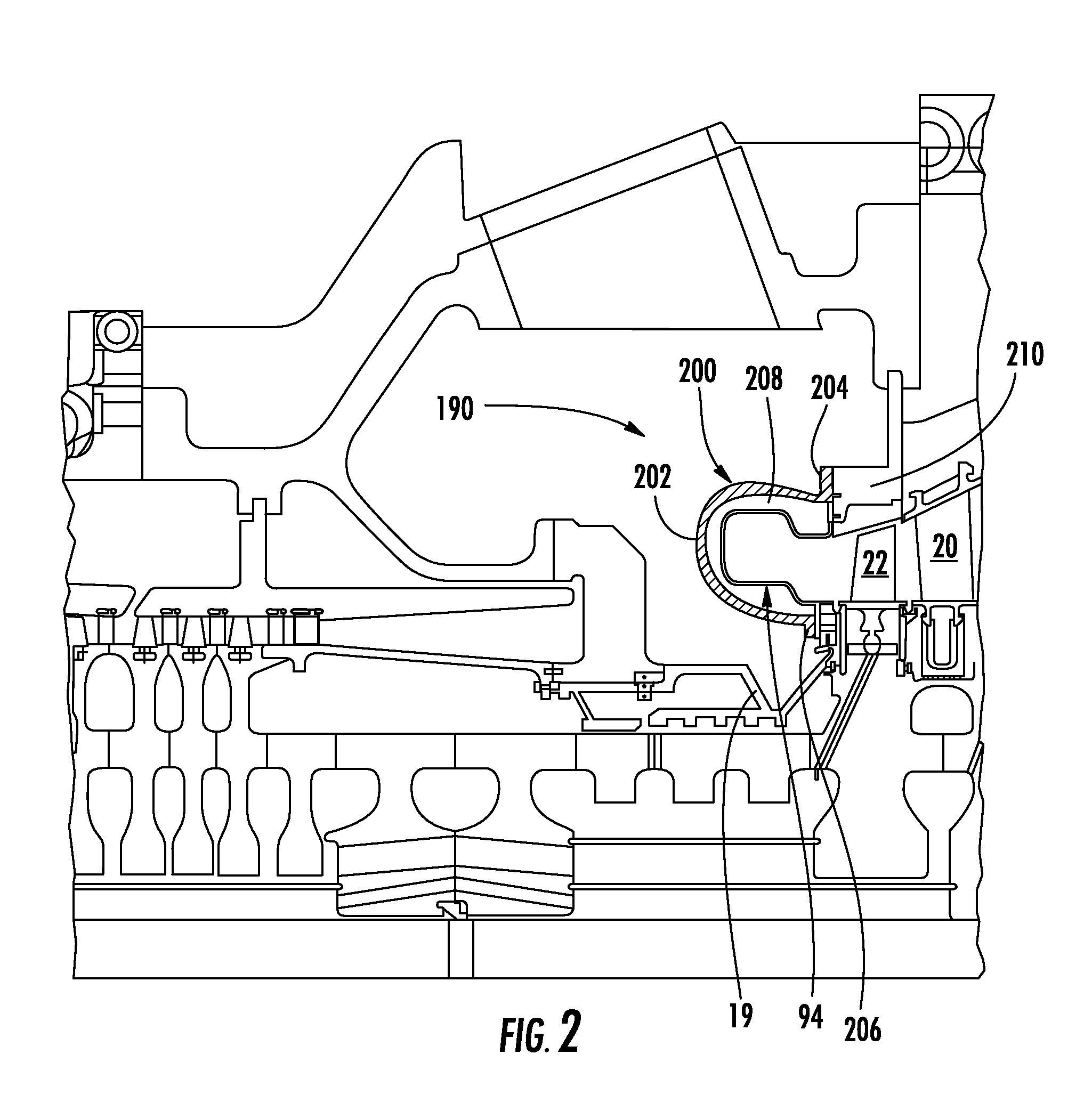
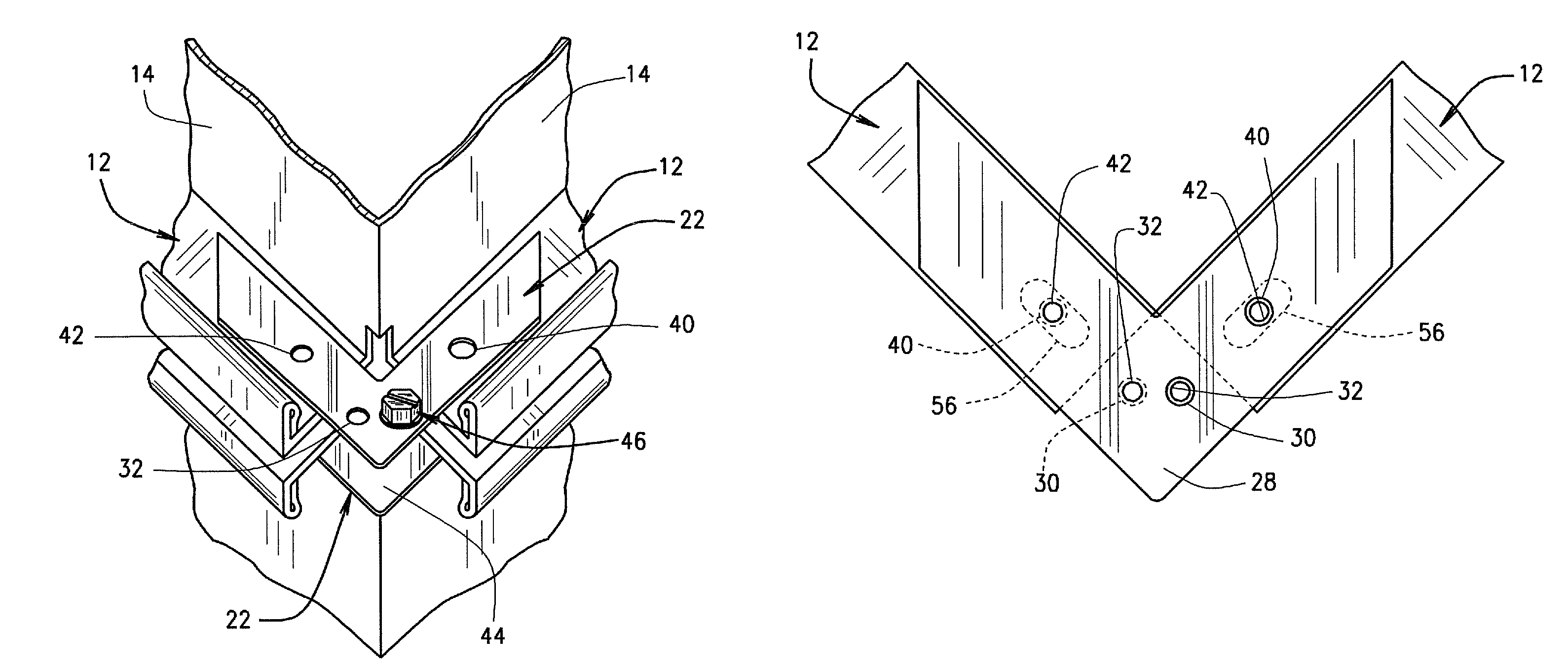
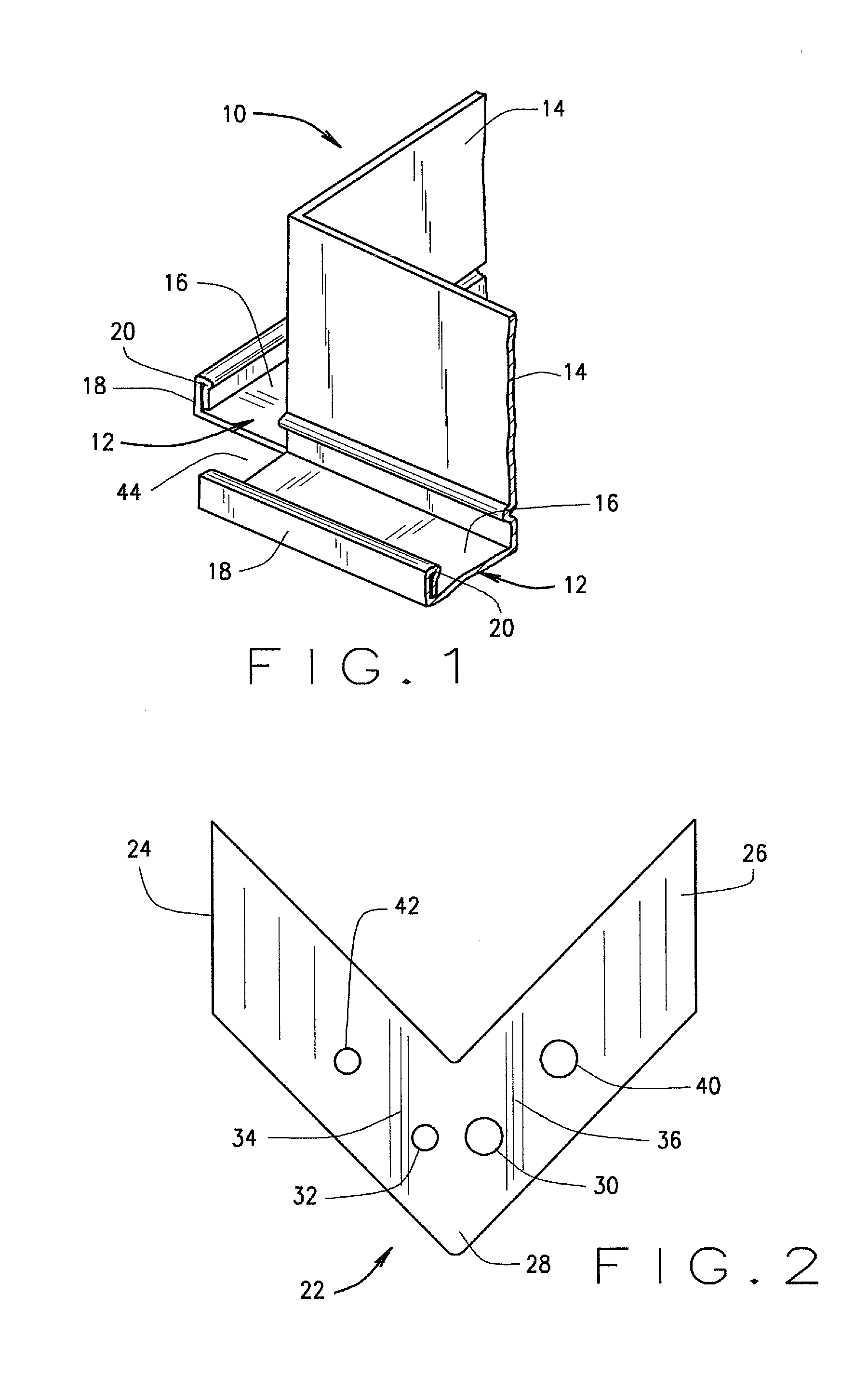
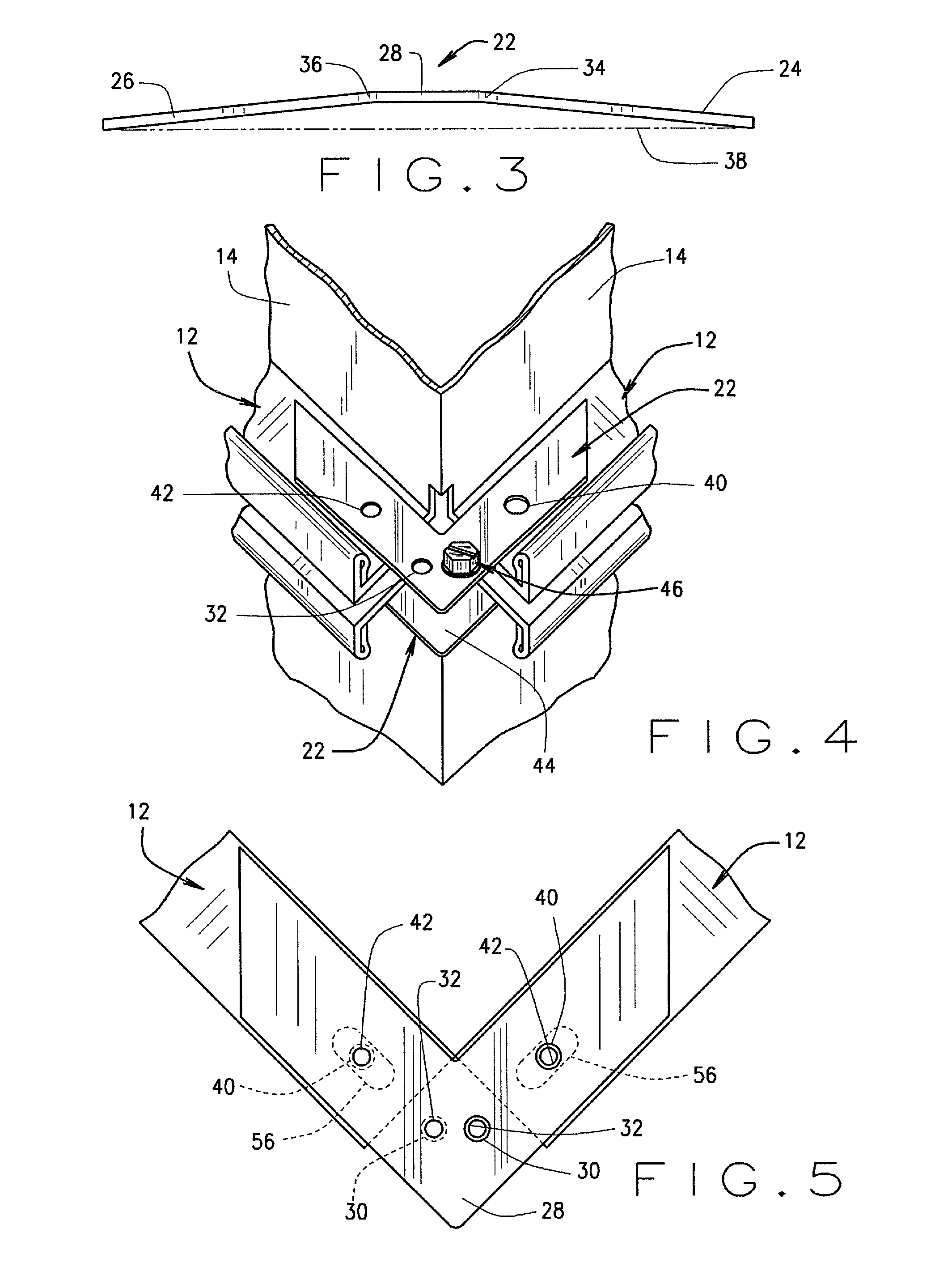
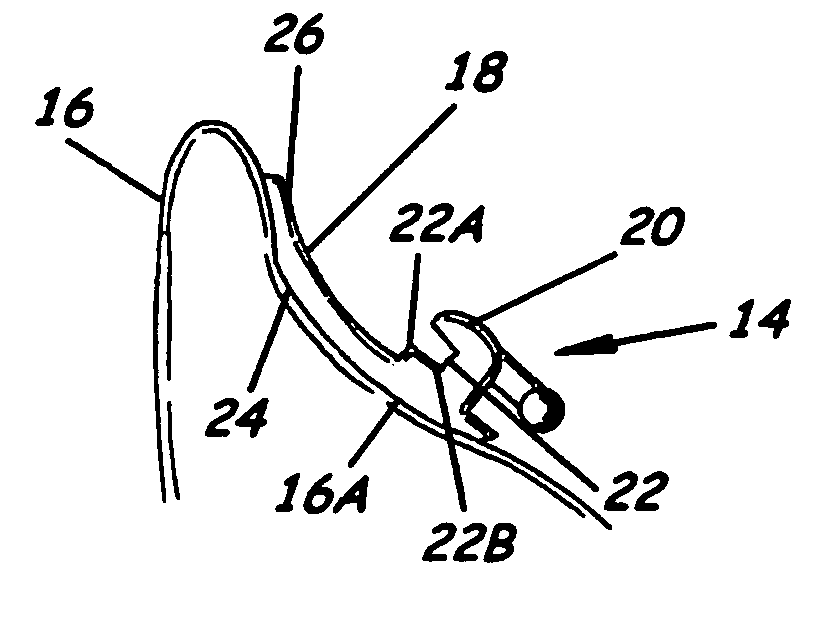
Structural Attachment System for Transition Duct Outlet
A structural attachment system for the outlet of a transition duct includes a structural attachment member that has a step over portion with an outer flange at one end thereof and an inner flange at the other end thereof. The step over portion can project away from the inner and outer flanges and can define an open area. The step over portion can have a cross-section that is generally u-shaped, v-shaped, c-shaped, semi-circular, semi-oval, parabolic, or bowed. A portion of the outlet of a transition duct is received within the step over portion of the structural attachment member. Because of such arrangement, the structural attachment member is not constrained circumferentially to fitting in between two neighboring transition ducts. The structural attachment member can manage the thermal displacements that can occur between the transitions, rotor shaft cover and first row of blades during transient engine operation.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
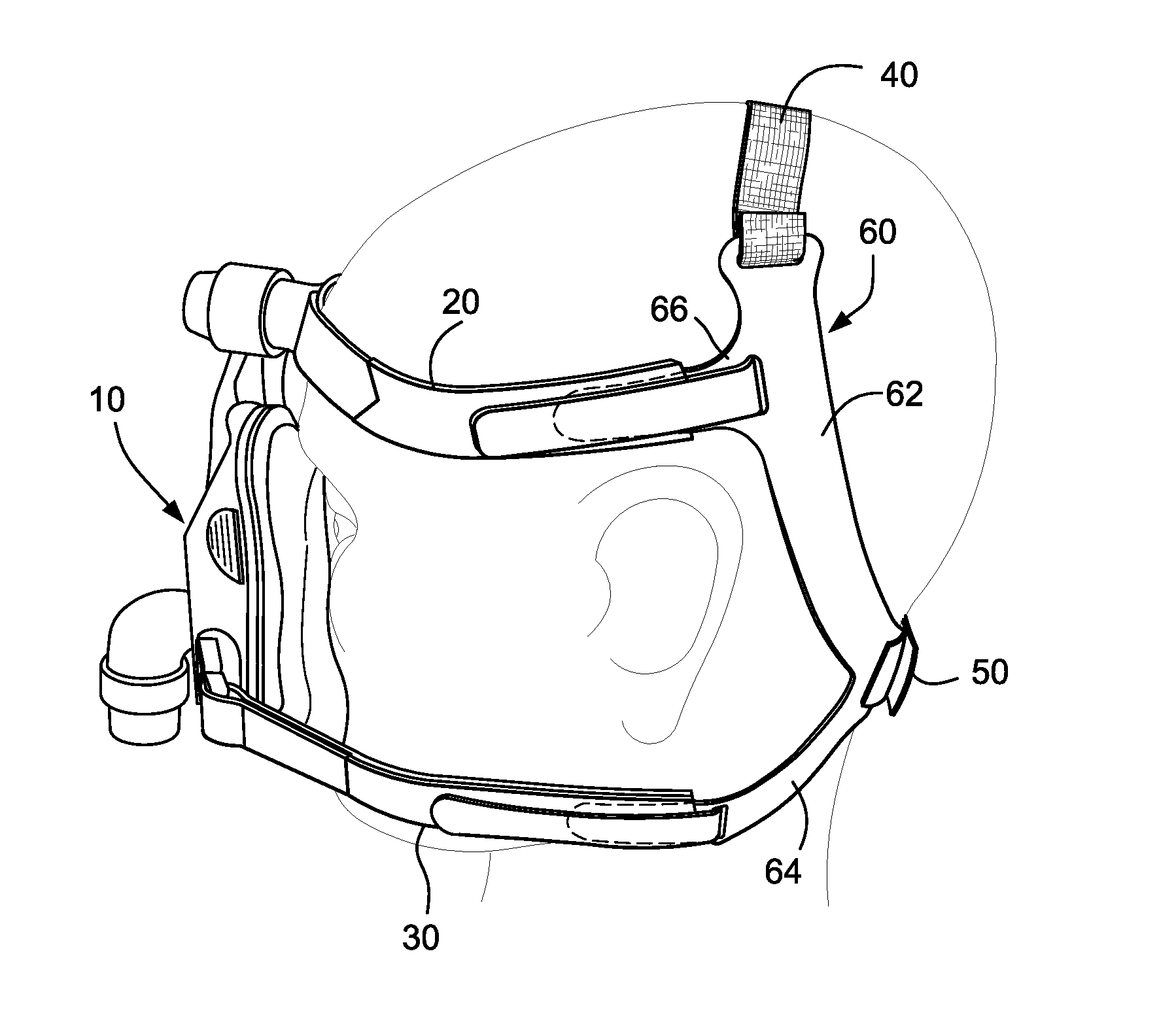
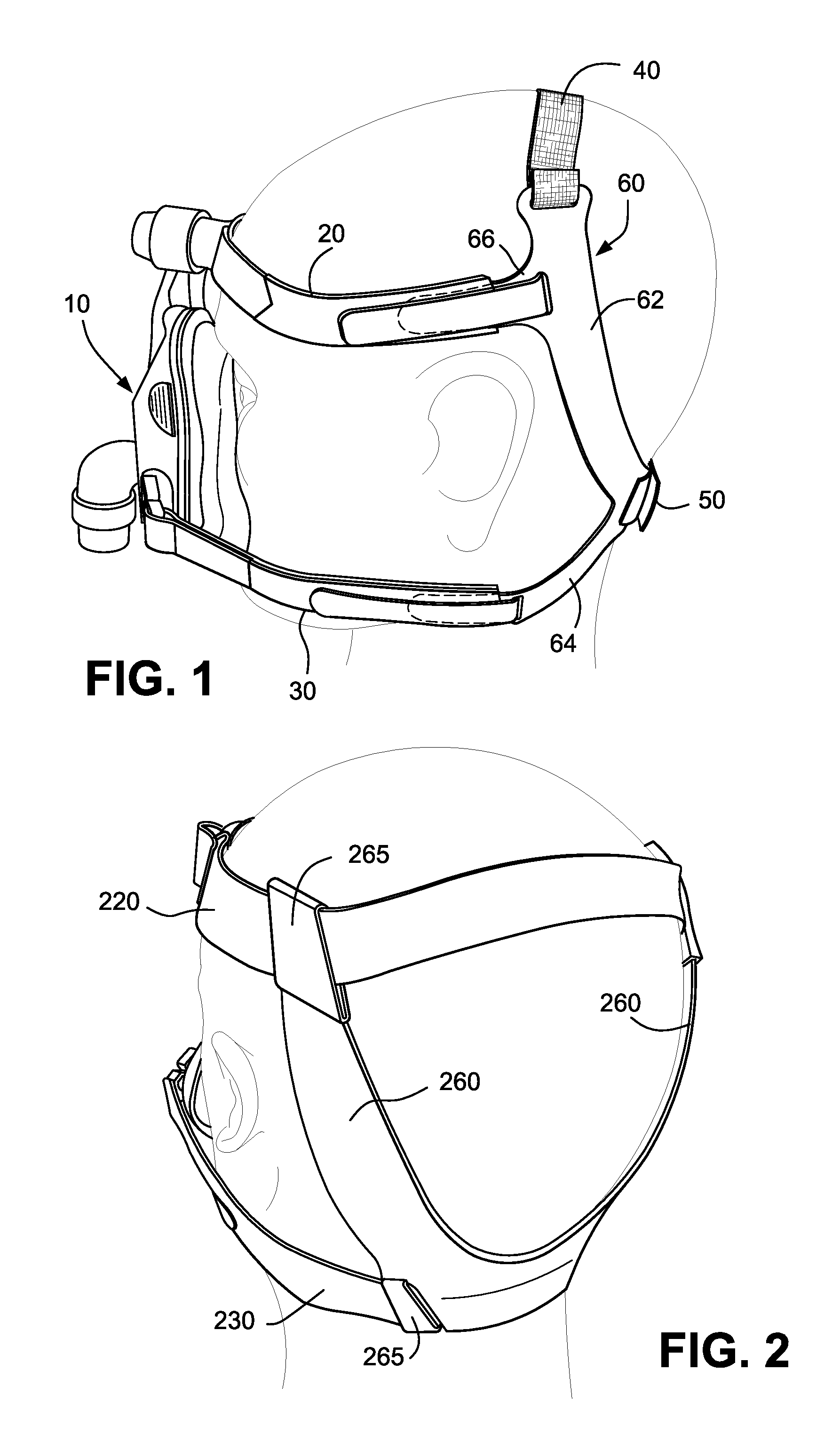
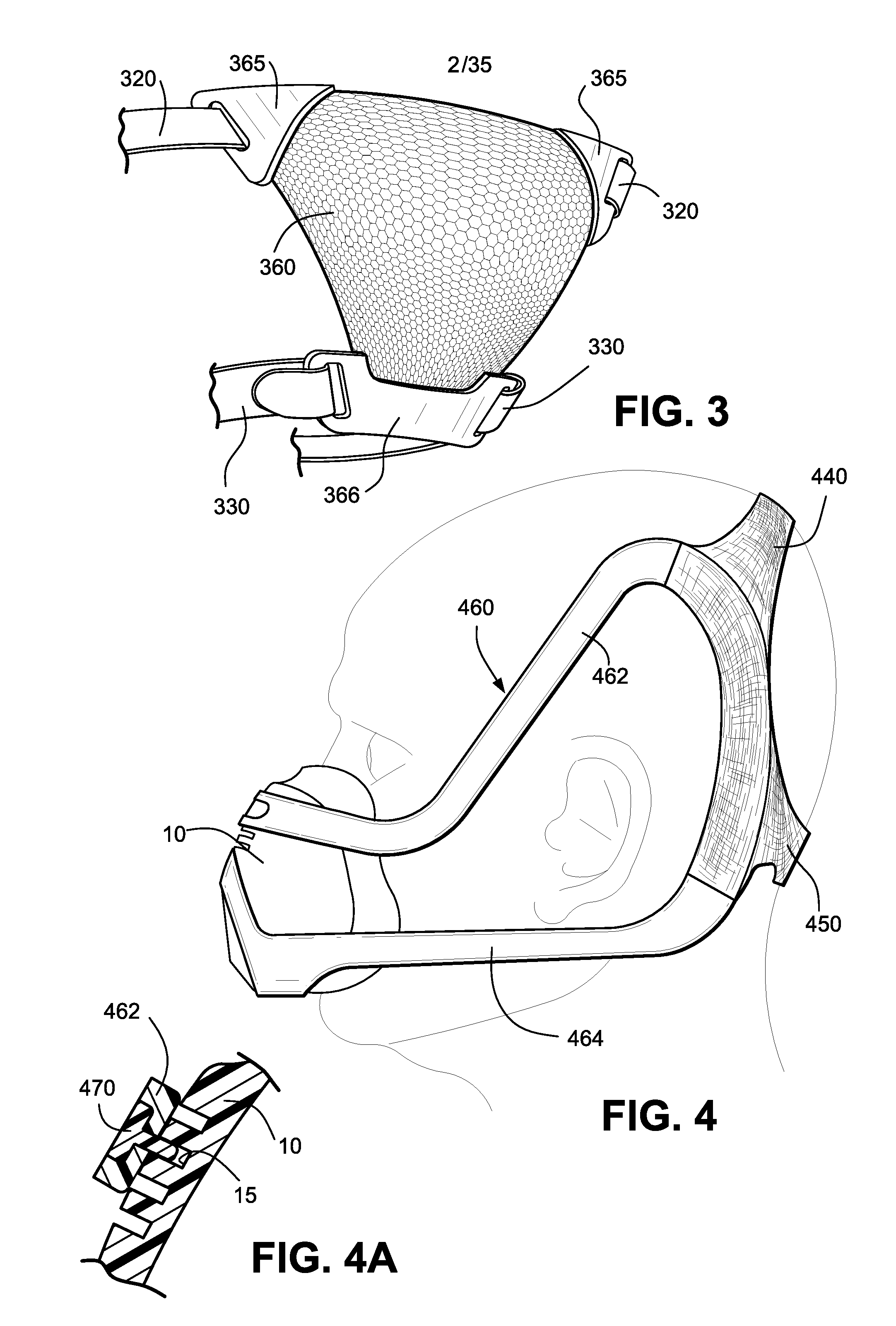
Headgear for masks
ActiveUS20150128953A1Low costEasy to useProtective equipmentBreathing masksMedicineThree dimensional shape
A headgear for use with a mask includes a first strap being configured to engage a back of a patient's head and extend on either side of the patient's parietal bone behind the patient's ears and assume, in use, a substantially circular or oval shape. At least a portion of the first strap is substantially inextensible. The headgear also includes at least one second strap configured to removably connect the first strap to the mask. The second strap may be more extensible than the first strap. At least a portion of the first strap is self-supporting such that the headgear maintains a three dimensional shape when not in use. The substantially inextensible portion of the first strap is constructed to resiliently return to a predetermined shape when not in use. The arcuate region includes a first portion that may be arranged to align substantially parallel with a top of the patient's head and a second portion being arranged to align substantially to a rear surface of the patient's head.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Surgical head holder and surgical accessories for use with same
A surgical head holder and accessories for use with the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, a horseshoe shaped head support includes two wings pivotally coupled that adjust the angle therebetween. Arcuate base members are coupled to the wings to accept a plurality of placement subassemblies, which are circumferentially adjustably positioned and secured within the channels. Each placement subassembly is configured to receive a skull pin and provide adjustable horizontal, vertical, and angular positioning of the skull pin with respect to the arcuate base. A table attachment supports the horseshoe shaped head support and is adapted to be selectively and rigidly coupled to an operating table. The table attachment includes a vertical body, a horizontal generally u-shaped bar adjustably intersecting therewith, and an attachment member extending therefrom for coupling to the operating table. Various neurosurgical accessories may be rigidly coupled to the table attachment.
Owner:SKLAR FREDERICK H
Prosthetic joint component having multiple arcuate bending portions
InactiveUS6869449B2Relieve pressureEasy to failFinger jointsAnkle jointsProsthetic joint componentEngineering
A joint prosthetic component that includes first and second arms, and a joint member interposed therebetween. The joint member is configured to permit flexion motion between the first and second arms, and includes a first concave surface and a second concave surface. The first concave surface has a plurality of arcuate portions defined therein. The first and second concave surfaces are located on opposing sides of the joint member.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
Methods and apparatus for improved cutting tools for resection
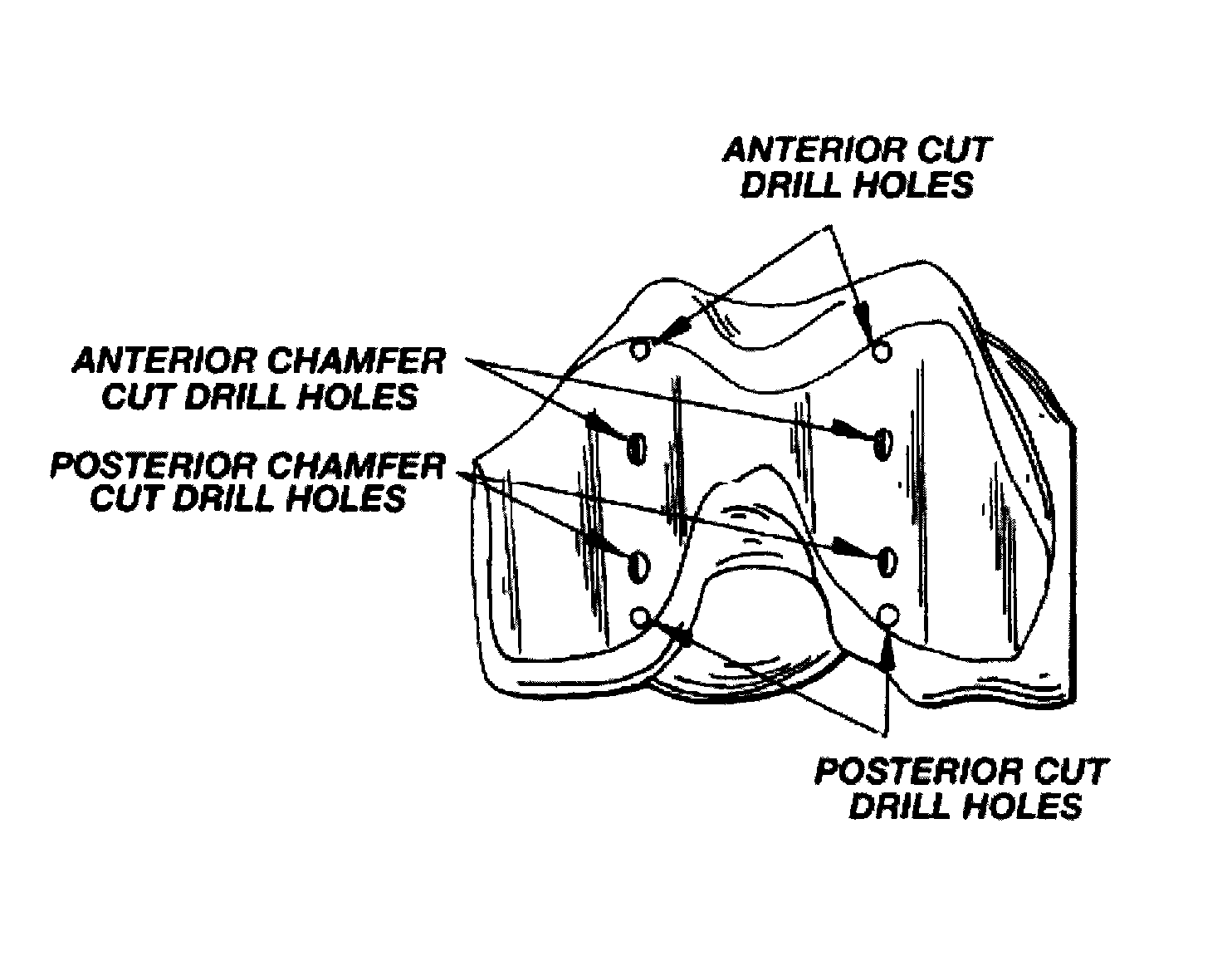
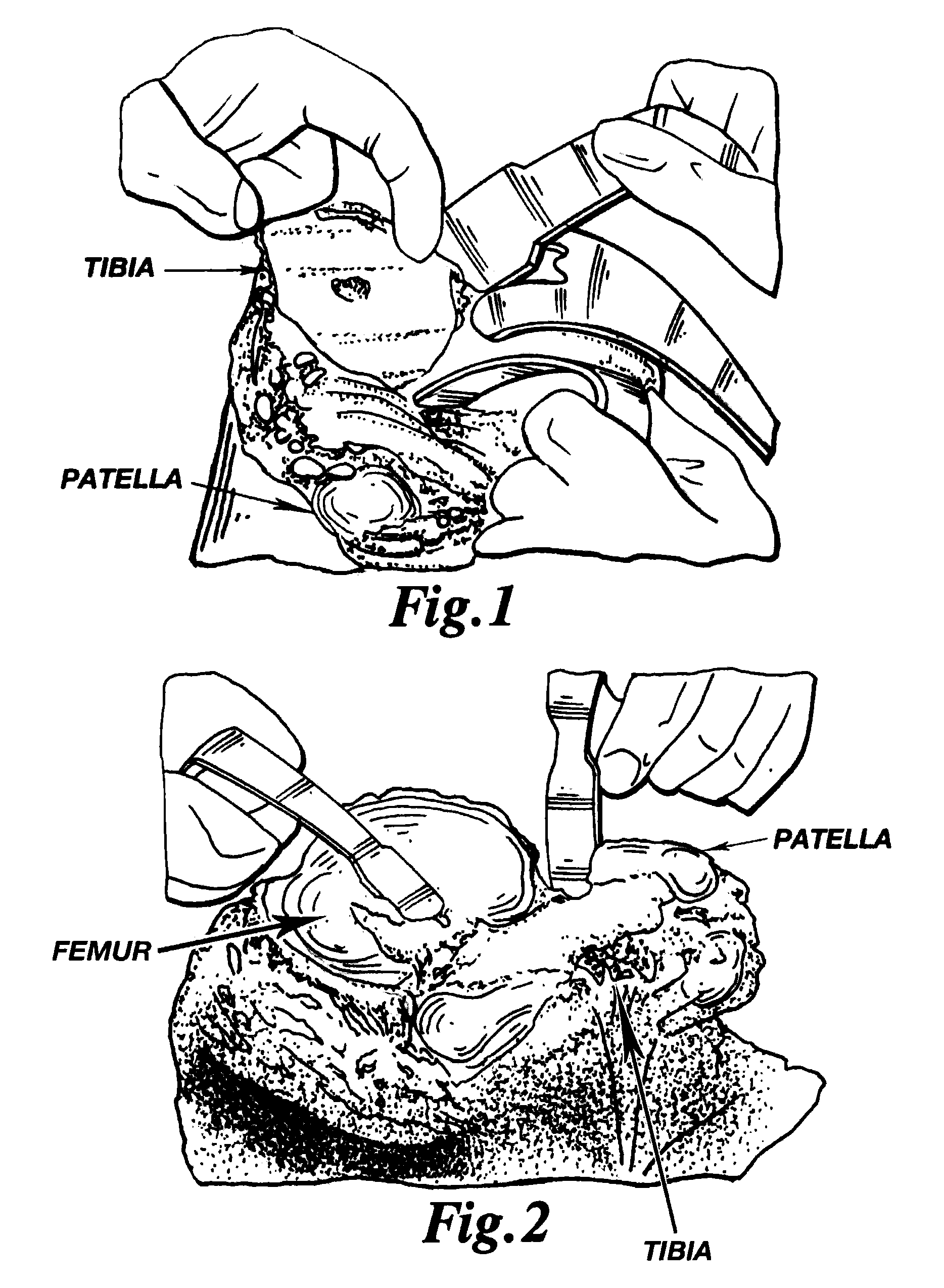
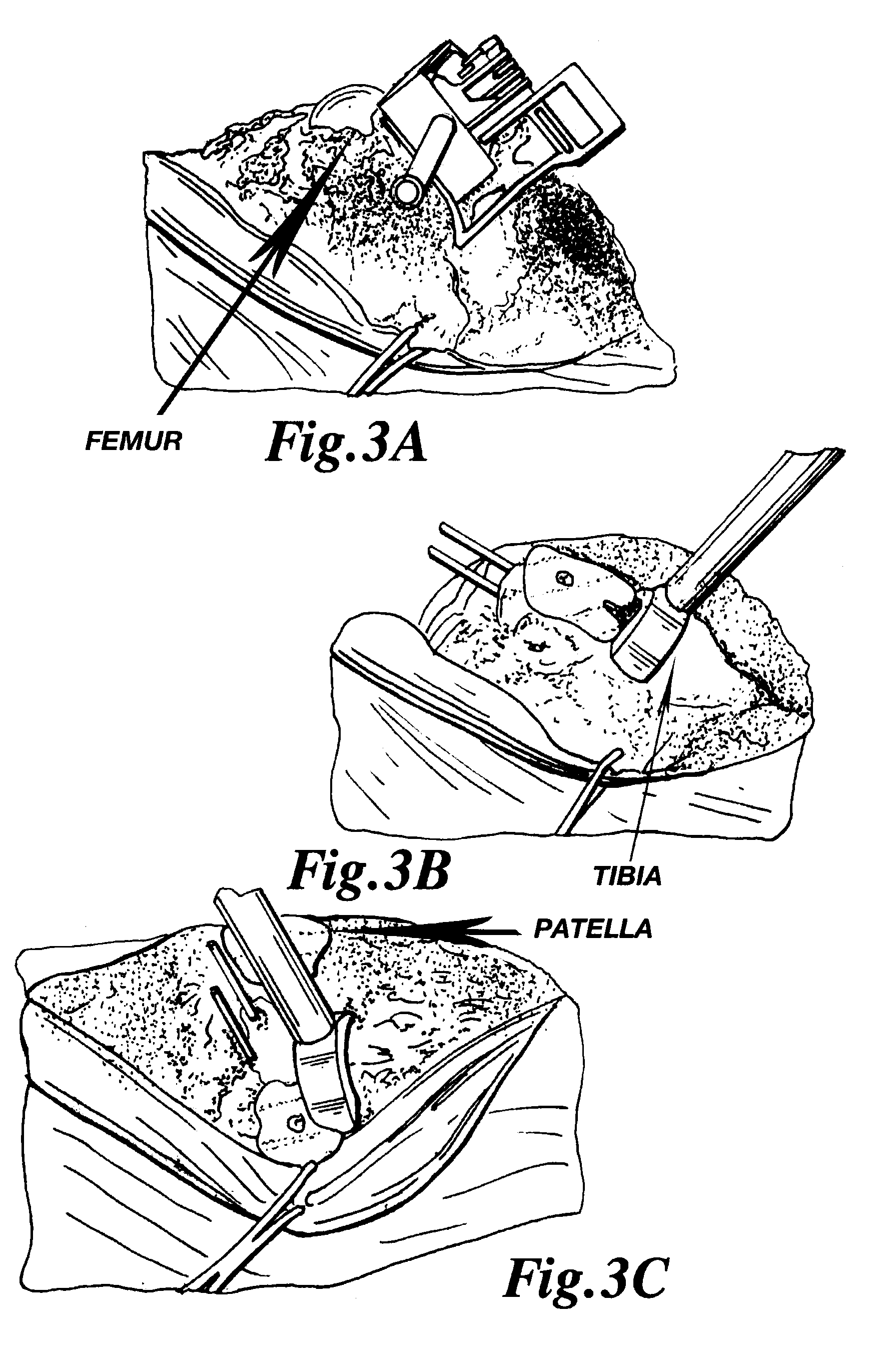
InactiveUS8021368B2Preventing the tool from accidentally harming soft tissuePrecise and accurate cut(s)Joint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaProximate
A cutting tool is provided with an arcuate cutting blade that preferably engages a guide tool to create a curved resected surface during an arthorplasty procedure. In one embodiment, a depth of the cutting blade is sufficient to permit the simultaneous creation of resected surfaces on two bones that articulate, such as both the femor and the tibia for a given condyle, without the need to reposition the guide or the leg. In another embodiment, a cutting member has a generally rectangular cross-section along a longitudinal axis with a first and second surface having cutting teeth defined thereon and a third and fourth surface adapted to interface with a cutting guide positioned proximate the bone. In this embodiment, the cutting tool can resect the bone in two different directions without reorienting the cutting member.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
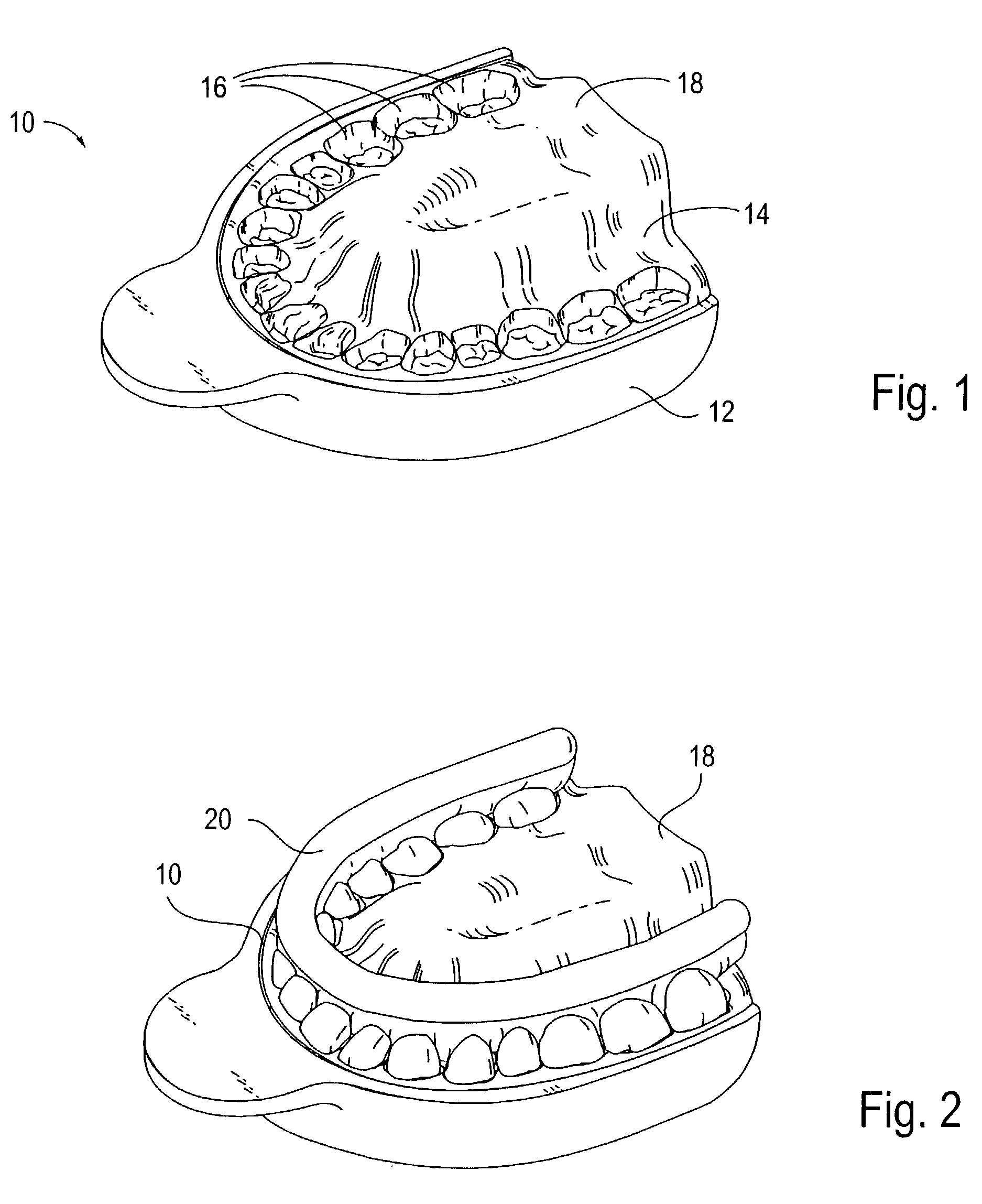
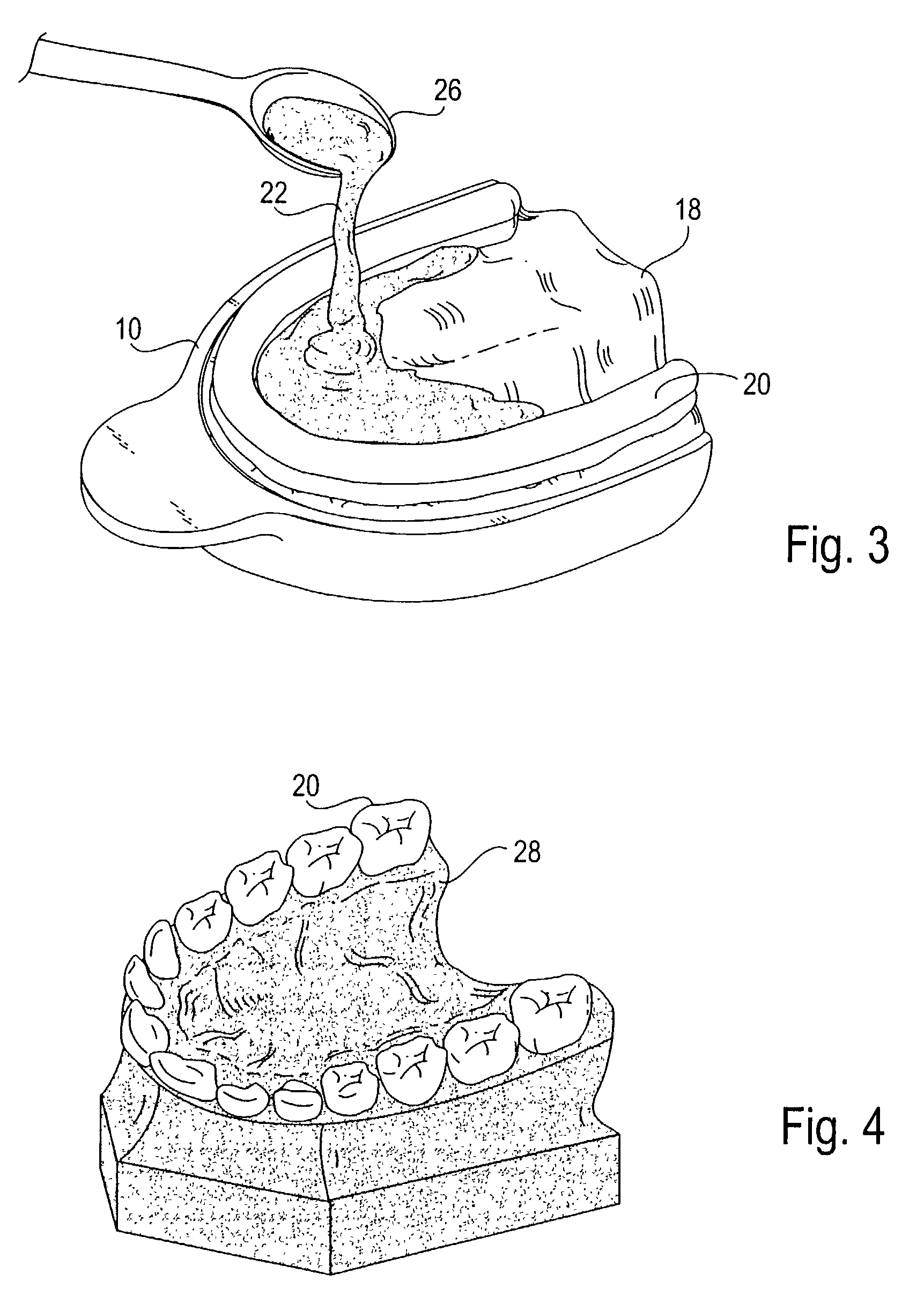
Modified tooth positioning appliances and methods and systems for their manufacture
InactiveUS7037111B2Eliminate timeFree laborImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusGingival tissueRapid prototyping
The present invention provides improved devices, systems and methods for producing dental molds, each having portions representing a patient's oral soft tissue and a desired tooth configuration. These molds are designed for use in the fabrication of appliances used in orthodontic treatment, particularly, elastic repositioning appliances. However, they may also be used in the fabrication of traditional appliances, such as retainers and positioners, used, for example in the final or finishing stages of an otherwise conventional treatment. The dental molds are comprised of a mold or relief of the patient's soft tissue, such as a palate, facial gingival tissue and / or lingual gingival tissue, and a separate or separable mold or relief of the patient's dental arch having teeth in a desired tooth configuration. Since, the tooth configuration will change as a patient progresses through orthodontic treatment, the relief of the dental arch will be fabricated separately from the relief of the oral soft tissue. Typically, the dental arch relief will be fabricated using rapid prototyping methods. The soft tissue relief may also be fabricated using rapid prototyping, however it may also be fabricated using traditional mold making methods, i.e., casting with plaster or other mold making materials. In either case, the resulting dental mold with be comprised of a “split-mold” having fixedly or removably joined arch and soft tissue reliefs.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
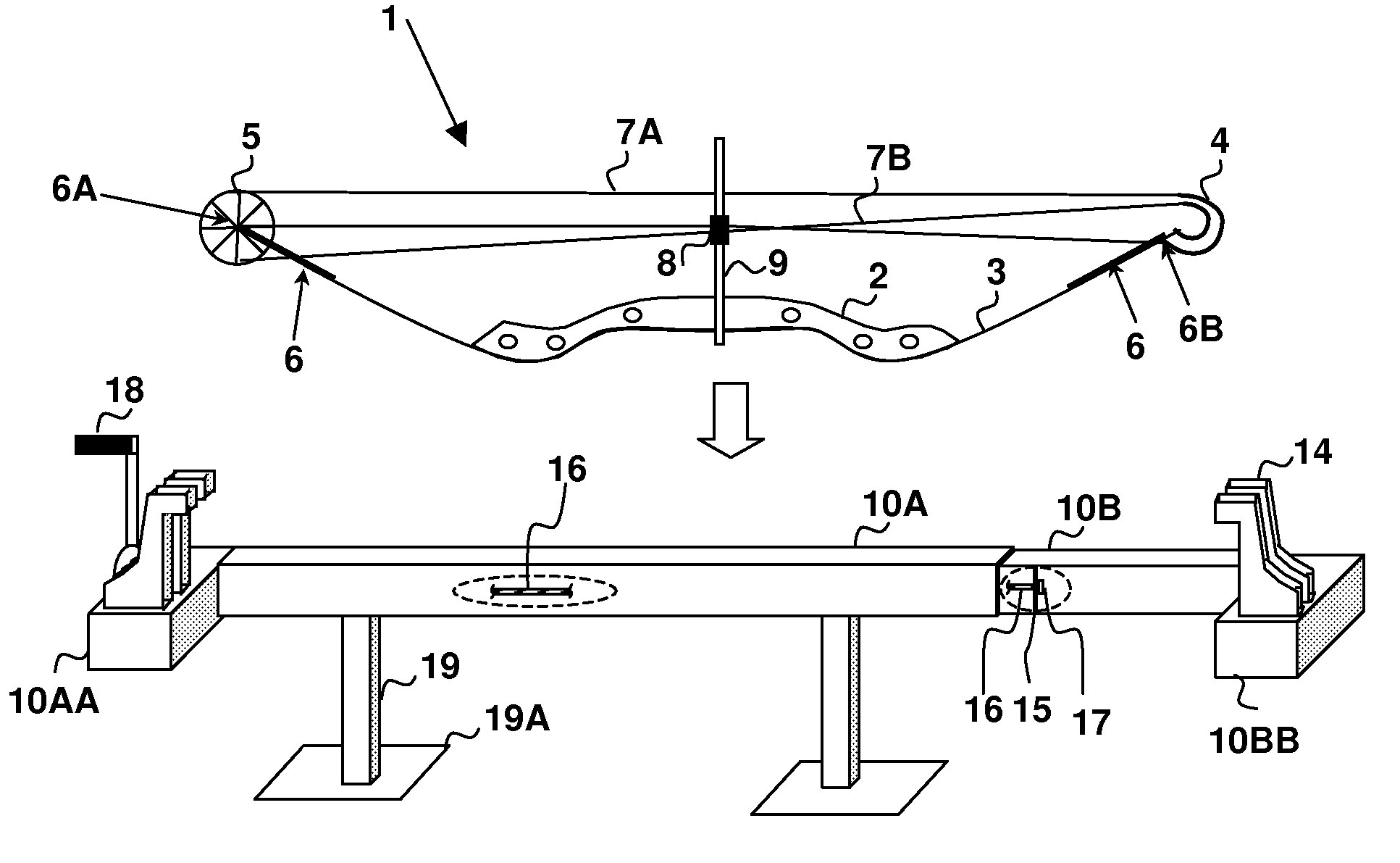
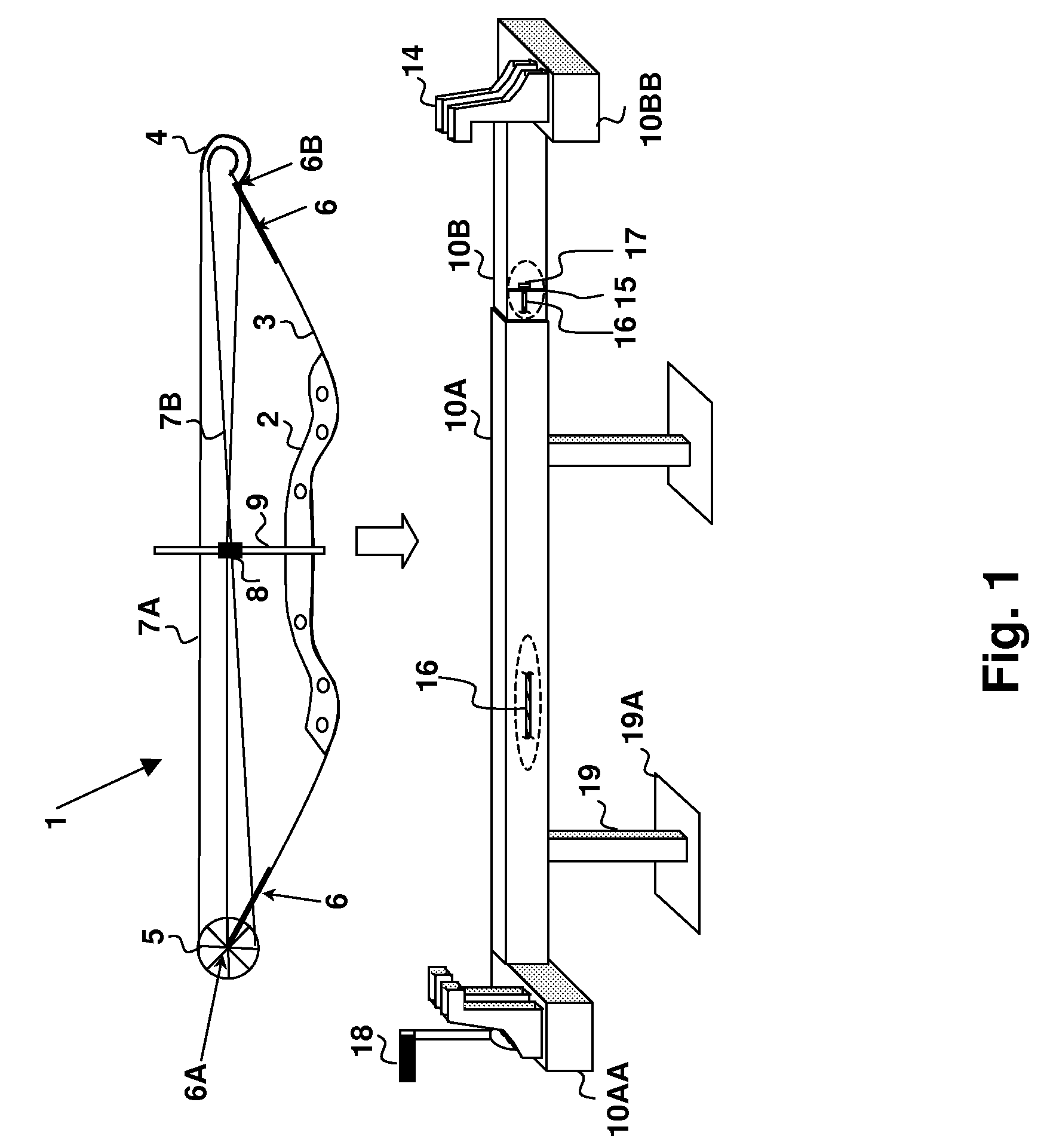
Compound bow maintenance press and method for compressing a compound bow from the bow limb ends
A compound bow maintenance press and method for compressing a compound bow from the bow limb ends provides a shop-installable bow press that prevents damage to the bow riser and limbs during service. The press contacts the bow only at the ends of the bow limbs and compresses the bow from outside of the curvature of the bow, providing clear access to the bow strings and a press that can be secured or stood on a workbench or a floor stand. The bow press can be operated by an electric motor or a hand crank and may include a worm gear drive system that provides for adjusting a telescoping member having arms extending to compress the bow limb ends. A limb end fixture is attached to or integrated with each arm, and provides a slot that accepts the bow limb end pulleys.
Owner:PITTMAN LEON MONROE
Arch support reinforcement device
Owner:KIM KIYONG
Sheet metal corner for duct flanges
ActiveUS20090224538A1Easy to slideStrengthen the joinder therebetweenSleeve/socket jointsFlanged jointsScrew threadMetal
The present invention relates to various embodiments of an improved high-speed corner flange connection member which is specifically shaped and designed to increase the clamping force applied to adjacent duct flanges when adjacent duct sections are connected together. In some embodiments, the corner connection members include creases or bends which allows the leg portions to be bent or angularly deflected away from such creases downwardly so as to form a bowed configuration; some embodiments include clearance holes and tap holes which are strategically positioned on the corner element such that when a pair of duct sections are positioned in end-to-end relationship for joinder, the opposed corner elements are arranged such that a clearance hole is positioned in registration with a tap hole; other embodiments include similarly shaped openings which are associated with the respective opposed corner elements; and in still other embodiments a substantially flat corner element is constructed utilizing the strategically placed clearance and tap holes so as to achieve a faster and stronger connection including the use of standard carriage type bolts. Still further, the present invention includes the use of a plurality of differently configured high-speed fastener members which are specifically designed to substantially eliminate misalignment and cross-threading issues commonly associated when using the conventional bolt / washer / nut arrangement for fastening adjacent duct sections.
Owner:H J FISCHER
Modular system for customized orthodontic appliances
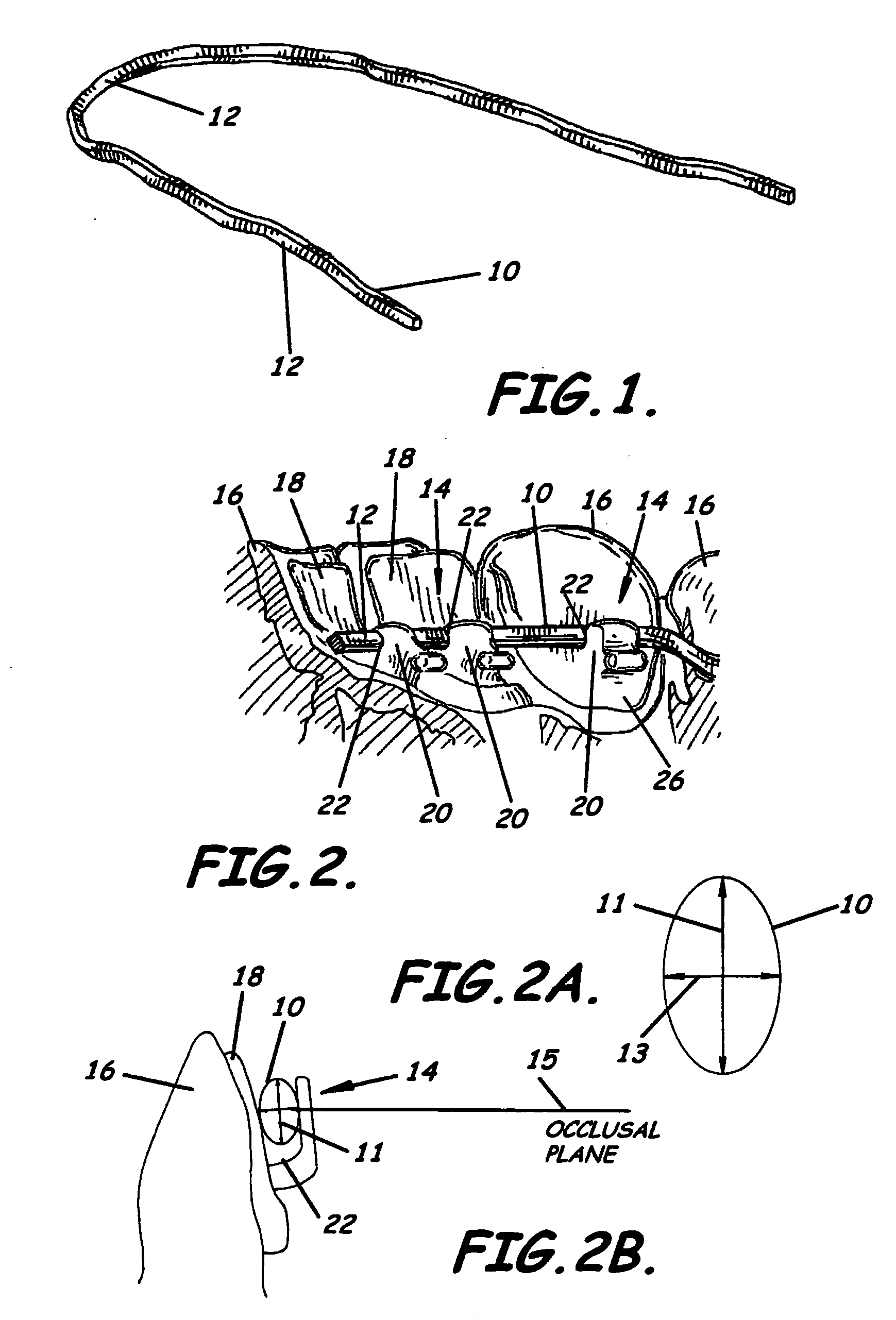
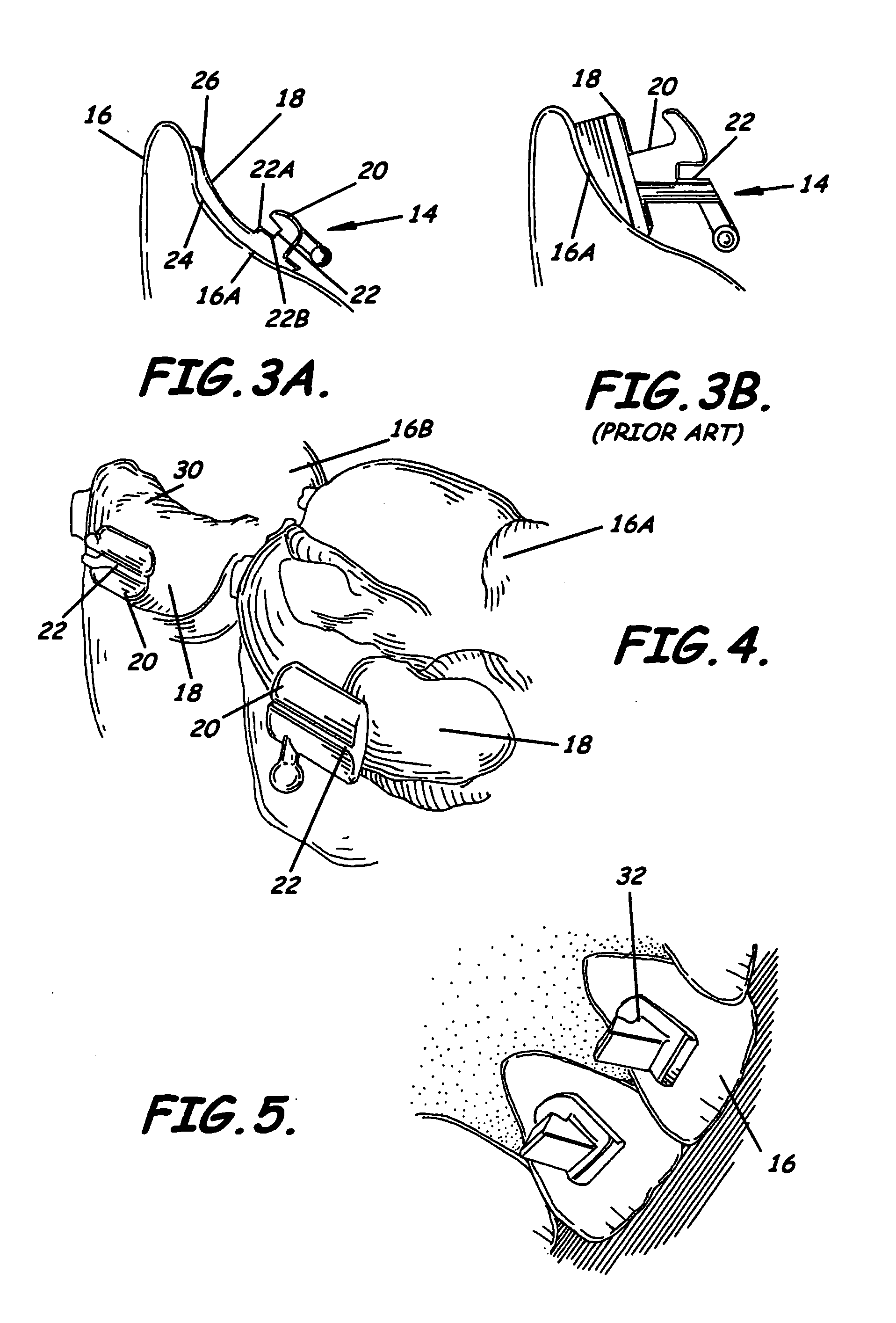
InactiveUS20050158686A1Reduce thicknessGuaranteed smooth progressArch wiresBracketsOcclusal planeModularity
A set of customized orthodontic brackets are provided with slots that are arranged substantially parallel to the tooth surface. The archwire, in an as-manufactured condition, has a portion of substantial arcuate extent, which is canted relative to the occlusal plane. The brackets are designed on a computer as a combination of three-dimensional virtual objects comprising the virtual bracket bonding pad and a separate virtual bracket body retrieved from a library of virtual bracket bodies. The virtual brackets can be represented as a file containing digital shape data and exported to a rapid prototype fabrication device for fabrication of the bracket in wax or other material and casting the wax prototype in a suitable alloy. Other manufacturing techniques are also contemplated, including milling and laser sintering.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
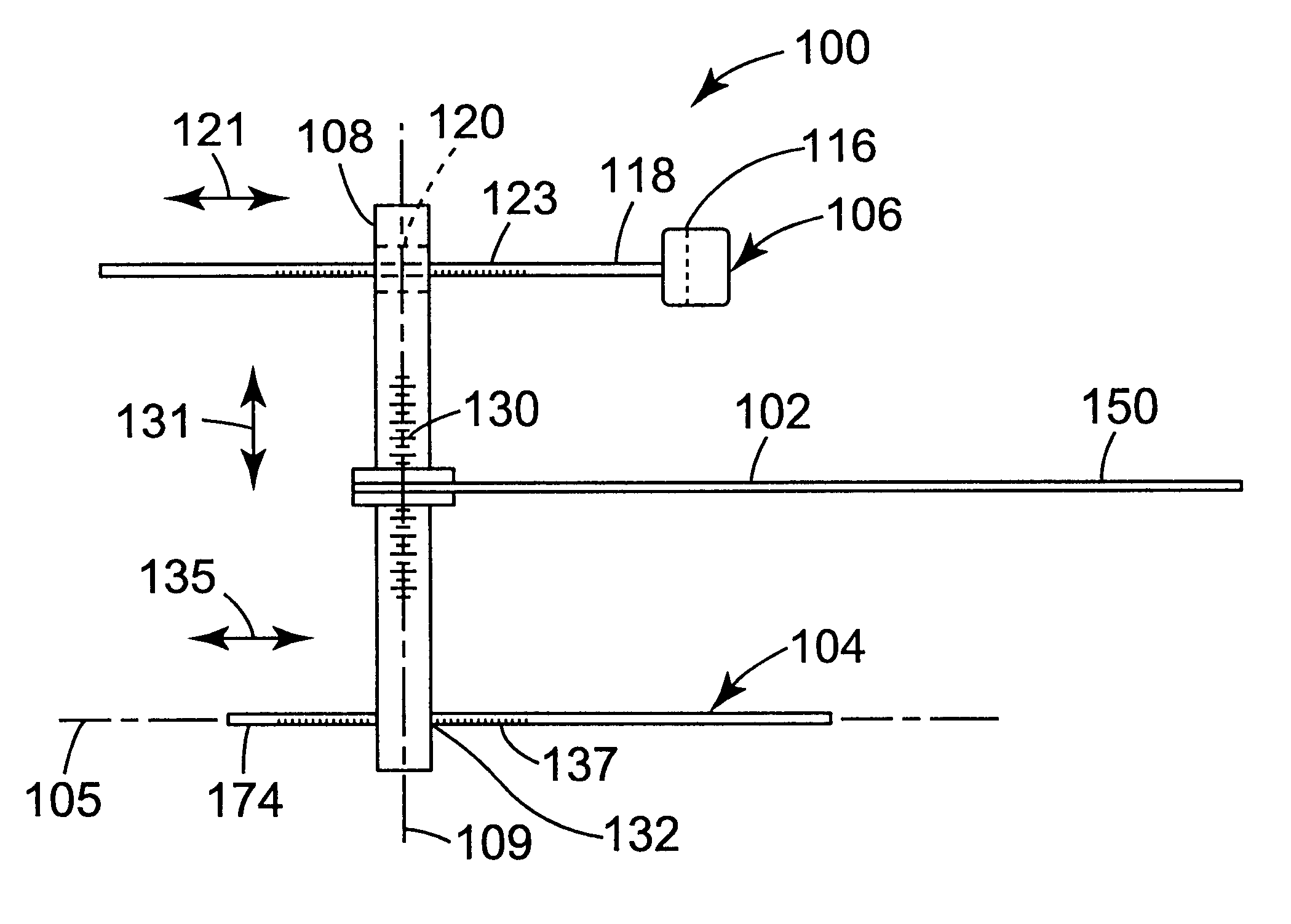
Determination Of A Three Dimensional Relation Between Upper and Lower Jaws With Reference To A Temporomandibular Joint
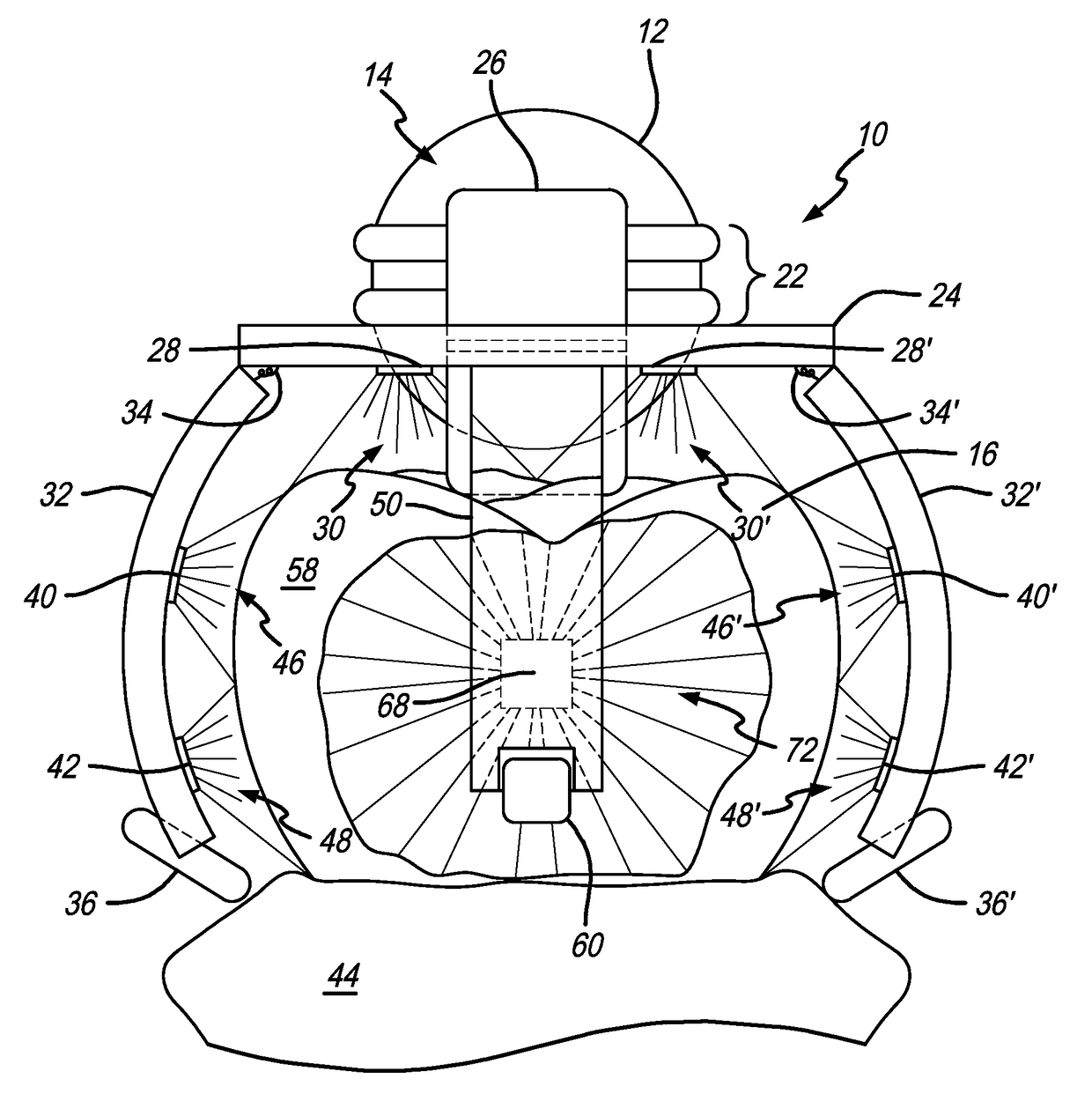
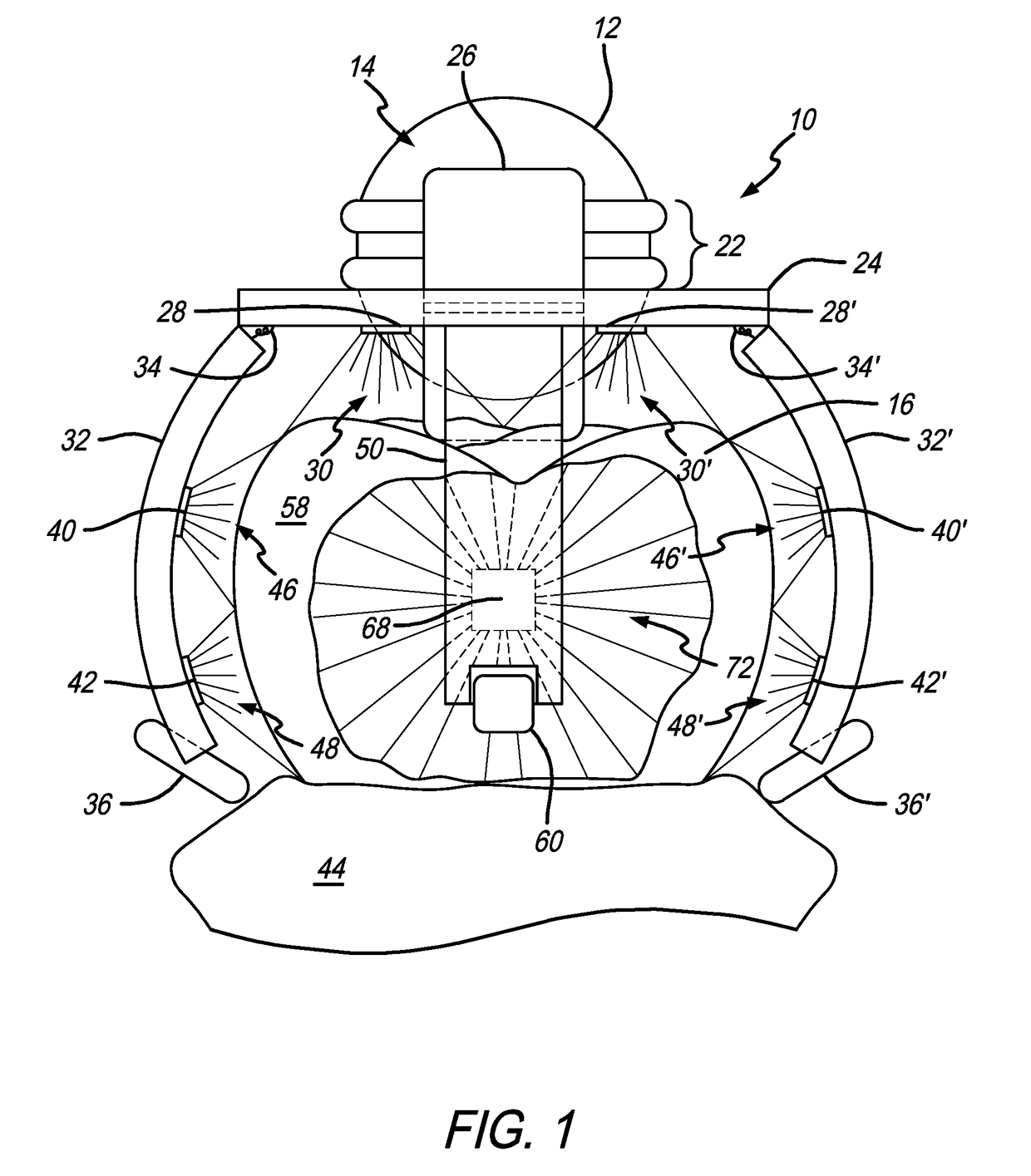
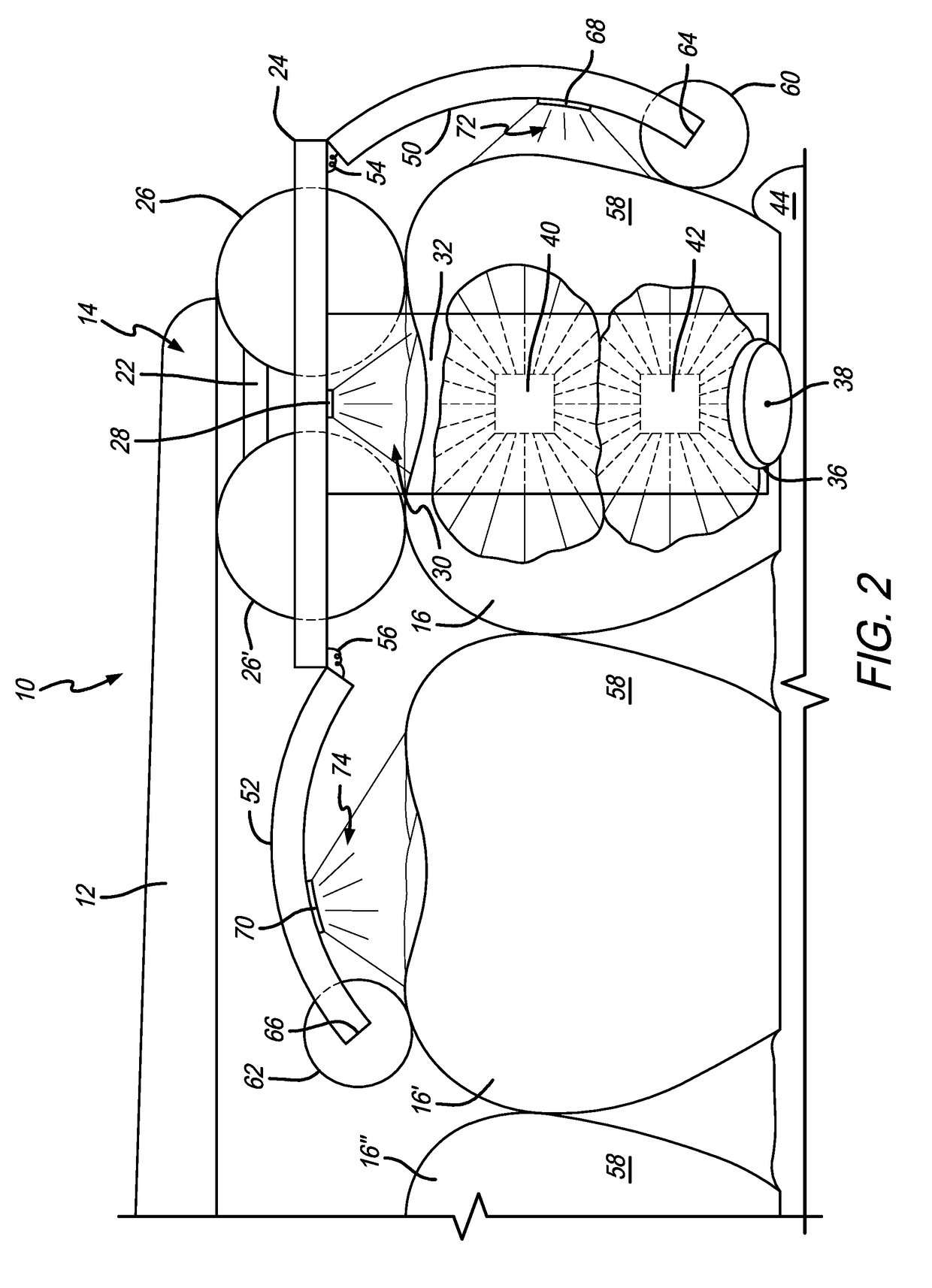
An apparatus including a bite frame and a bite shaped member is provided. The bite frame includes one or more arcuate frame elements defining an opening for accommodating a mesh element or the bite shaped member that receives a bite registration material for registering a bite impression. The bite shaped member has a geometrical body structure, upper and lower channels of configurable shapes, and upper and lower windows. The upper and lower windows are separated by a space for receiving and allowing flow of the bite registration material to register a vertical distance between the upper and lower jaws. An image processing system operably connected to the apparatus determines the three-dimensional relation between the upper and lower jaws with reference to temporomandibular joints using panoramic images of the upper and lower jaws, reference points provided by radio-opaque markers, three-dimensional scanned images of the bite impression, and three-dimensional head surface images.
Owner:HANKOOKIN
Devices, systems, and methods for dental arch expansion
Methods and systems are provided for generating a treatment plan for arch expansion where a polymeric shell appliance is utilized to generate one or more activation forces that facilitate tooth movement. The polymeric shell appliances may comprise one or more tooth receiving cavities, in which each of the plurality of tooth receiving cavities is shaped and arranged to provide a counter moment of each of the plurality of teeth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Dental imager and method for recording photographic impressions
ActiveUS20170215997A1Improve image qualityReduce errorsMusculoskeletal system evaluationImpression capsEngineering3d printer
A dental imager includes an elongated handle with a rotatable head coupled to a distal end thereof and having a central platform with a plurality of arcuate scanning arms pivotally coupled thereto by a hinge. The arcuate scanning arms are of a shape and size for general deployment around a tooth and each include at least one scanner and a roller guide that comfortably rolls along the surface of the tooth or gums to bias the scanners a desired distance from the surface of the tooth, conducive for imaging thereof. In this respect, such a dental imager may be used in a process to scan and record the contours of an intraoral surface, the data of which may be used to create a digital three-dimensional surface impression printable by a 3D printer or the like.
Owner:MARTIN MARCO
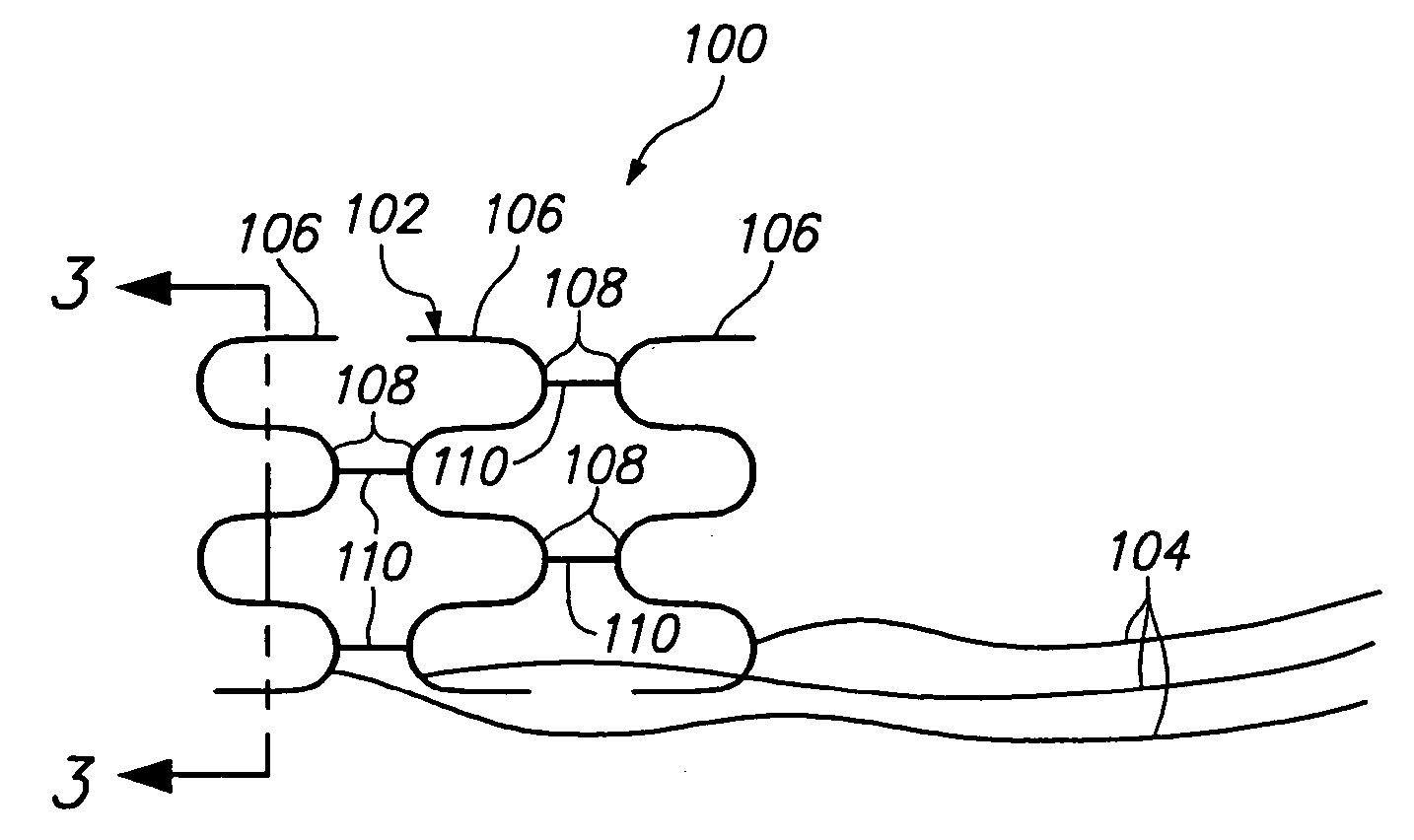
Three-part coaxial vaso-occlusive device
InactiveCN1671330AOcclusion is effectiveImprove convenienceCharacter and pattern recognitionOcculdersMetallic materialsMechanical engineering
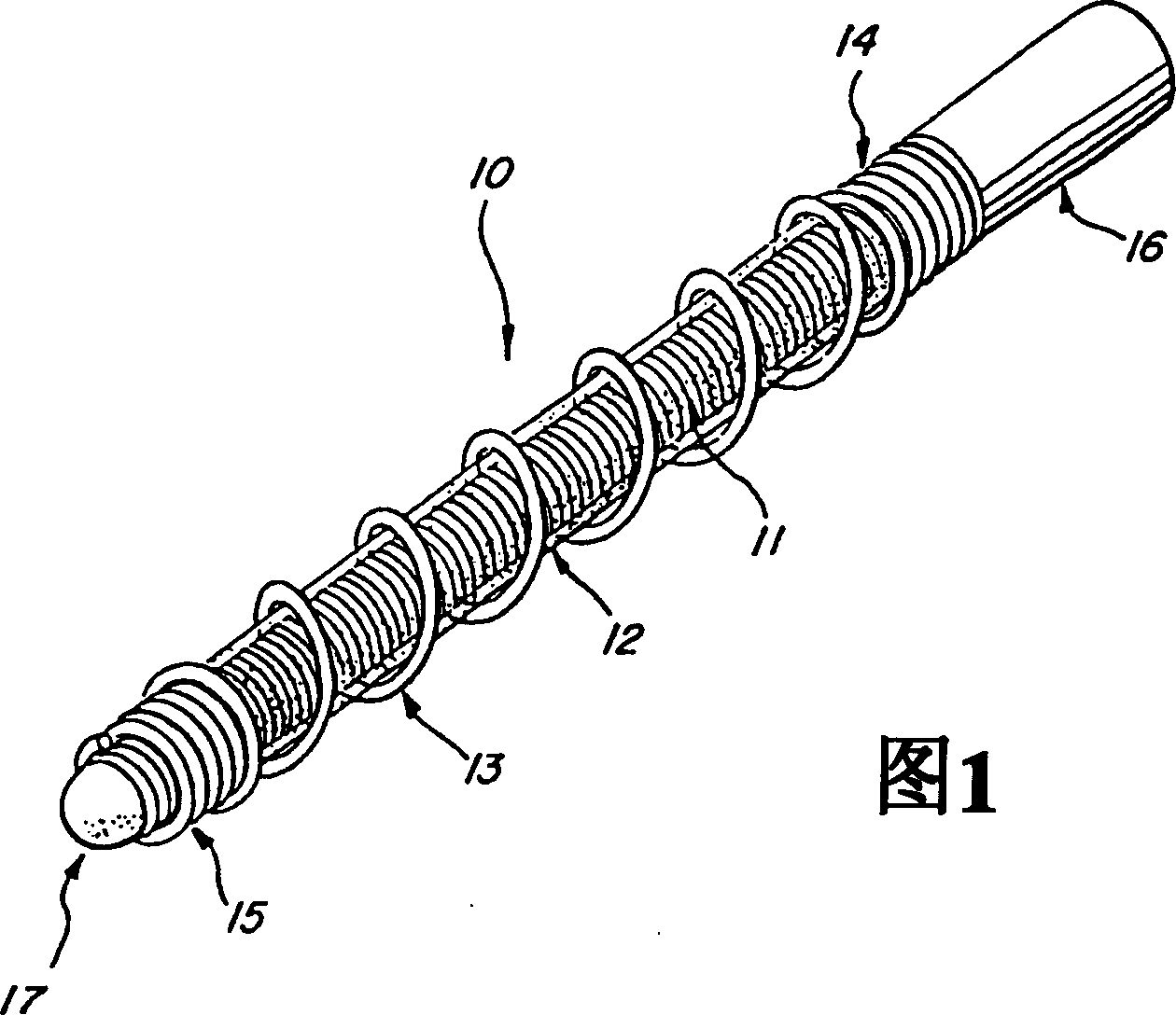
A vaso-occlusive device includes inner, intermediate, and outer elements arranged coaxially. The inner element is a filamentous element, preferably a microcoil. The intermediate element is made of a non-metallic material, preferably an expansile polymer. The outer element is substantially non-expansile and defines at least one gap or opening through which the intermediate element is exposed. In apreferred embodiment, when the intermediate element is expanded, it protrudes through the at least one gap or opening in the outer element and assumes a configuration with an undulating, convexly-curved outer surface defining a chain of arcuate segments, each having a diameter significantly greater than the diameter of the outer element. The expanded configuration of the intermediate element minimizes friction when the device is deployed through a microcatheter, thereby reducing the likelihood of buckling while maintaining excellent flexibility. The result is a device with enhanced pushabilityand trackability when deployed through a microcatheter.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com